- 1School of Engineering Science, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2Institute of Porous Flow and Fluid Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Langfang, China
- 3Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, PetroChina, Beijing, China
- 4PetroChina Hangzhou Research Institute of Geology, Hangzhou, China
- 5China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China
Compared with marine shale formations, marine-terrestrial transitional shales exhibit rapid lithofacies changes. This poses significant challenges for the classification of shale lithofacies and the study of their characteristics. The Permian Longtan Formation (LTF) coal-measure shale in marine-terrestrial transitional facies in the central-southern Sichuan Basin is expected to be a new gas-rich formation with development value in China. Based on core observation and thin-section identification, and using techniques such as XRD, TOC analysis, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, low-temperature gas adsorption, and high-pressure mercury intrusion, this study systematically analyzed the lithofacies types, geochemical characteristics, and pore features of the LTF coal-measure shale in the deep area (4,220–4,400 m) of the central Sichuan Basin. The study shows that the shale in the studied interval mainly developed four lithofacies: organic-rich clay shale (CS-H), medium-organic mixed shale (MS-M), medium-organic siliceous shale, and low-organic calcareous shale (CAS-L). The four lithofacies are interbedded with each other, and their characteristics differ significantly. Clay content and TOC content are the main factors affecting their quality. Through multiparameter analysis, it is determined that the CS-H lithofacies has a good hydrocarbon generation basis, well-developed pores, and good preservation conditions, making it a high-quality lithofacies. The research conclusions provide important insights into the study of marine-terrestrial transitional shale formations and offer a basis for further advancing the development and utilization of transitional shales.
1 Introduction
After more than a decade of exploration, the unconventional energy industry, including shale gas, has developed rapidly (Selley, 2012; Clarkson et al., 2013; Zou et al., 2016). In southern China, marine shale gas from the Longmaxi Formation (LMXF) of the Silurian System in the Sichuan Basin has achieved commercial development (Mohaghegh, 2013; He J. et al., 2020; Han et al., 2023), and breakthroughs have been made in the Qiongzhusi Formation (QZSF) of the Cambrian System and the Wujiaping Formation (WJPF) of the Permian System (Wei et al., 2015; Tang et al., 2024; Zou et al., 2024). However, compared with the numerous commercially developed shales in the United States, China’s proven shale gas reserves are still relatively limited (Kulga and Ertekin, 2018; Zhao et al., 2021; McMahon et al., 2024). Previous studies have demonstrated that, organic-rich shales can develop in marine, terrestrial, and marine-terrestrial transitional sedimentary systems (Moreira et al., 2024). Transitional coal-bearing shales are widely distributed in multiple basins (Ma and Guo, 2020; Qiu et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023), Rich in shale gas resources (Wang et al., 2024). Subsequently, coal-measure shale formations deposited in transitional environments have become an important subject in Earth science research.
Currently, the study of marine-terrestrial transitional shale gas in China is still in its early stages (Wang et al., 2021; Zhang B. et al., 2023; Wang L. et al., 2025). Recent studies have reported on the transitional shale in the Ordos Basin (Liu et al., 2018; Wei et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2021; He et al., 2022; Zhuang et al., 2025). In contrast, research on the transitional shales in the Sichuan Basin is relatively limited. The Upper Permian Longtan Formation (LTF) marine-terrestrial transitional shale is characterized by its considerable thickness and extensive distribution (Luo et al., 2019; Wang E. et al., 2022; Zhang M. et al., 2023). It comprises multiple lithofacies with great resource potential and has now become a key formation with the potential for shale gas development. For the southern part of the basin with relatively shallow burial depth (less than 3,500 m), some scholars have carried out partial research. Based on geochemical analysis ofLTZ samples from a depth of 2,500–2,600 m, (Yang et al., 2022) identified the shale as typical high - over mature organic - rich shale. Wang E. et al. (2022) conducted lithofacies classification for LTF shales at a depth of 3,000 m in the southeastern margin of the basin, identifying four lithofacies types: organic-poor calcareous shale, organic-poor mixed shale, organic-poor clay shale, and organic-rich clay shale. They also identified the organic-rich clay shale as the most favorable lithofacies in the study area. Chen Y. N. et al. (2023) analyzed LTZ samples from four representative shale gas wells in southern Sichuan to identify the dominant lithofacies types in their study area and investigated the pore structure characteristics of each lithofacies. Jizhen Zhang et al. (Zhang et al., 2017) characterized the pore structure of LTF shale samples from the southern Sichuan Basin and found that the organic pores are poorly developed. These studies have enriched the research on LTF in the basin. However, studies on the influence of the lithofacies types, geochemistry and pore structure characteristics of the LTF shale in the deep layer (with current burial depth >3500 m) in the deep layer (with current burial depth >3500 m) in the Sichuan Basin on the quality of the lithofacies are lacking.
This study focuses on the deep Permian LTF shales in the Suining area of the central Sichuan Basin (CSCB). It aims to establish a lithofacies classification scheme for transitional deep mud shales and identify the developed lithofacies types. To clarify the geochemical characteristics of each lithofacies and reveal the heterogeneity of each lithofacies. Conduct multi-scale systematic characterization of pore structures for different lithofacies, perform qualitative and quantitative analyses, and identify their pore structure characteristics. Finally, analyze the effects of geochemical characteristics and pore structures on lithofacies quality, and in combination with the analysis of preservation conditions, identify high-quality lithofacies. To lay a foundation for the characterization and quality assessment of this type of shale reservoir.
2 Geological overview
The Sichuan Basin is located in the central-western part of China, with an area of approximately 180,000 square kilometers. It is the most important oil and gas-bearing basin in China (Chen et al., 2019), with abundant natural gas resources and great exploration potential. The Sichuan Basin can be divided into six tectonic units (Lin et al., 2018) (Figure 1a). During the Late Permian, the basin was influenced by the Dongwu Movement, resulting in a paleotopography that gradually deepened from the southwest to the northeast. (Jiang et al., 2016; Ge and Bond, 2022). Due to the differences in paleotopographic patterns, the sedimentary systems during the same period varied significantly from the southwest to the northeast, with the development of sedimentary facies ranging from fluvial-deltaic to deep-water shelf facies. In particular, the southeastern and central parts widely developed swamp and lagoon sedimentary environments. Accompanied by large-scale sedimentation, a suite of coal-bearing transitional shale formations was formed., namely, the Permian LTF. The main lithology consists of interbedded black shales with thin siltstone and coal layers (Figure 1b). The LTF is divided into three third-order sequences, from bottom to top: Tan 1, Tan 2, and Tan 3 (Deng et al., 2023).
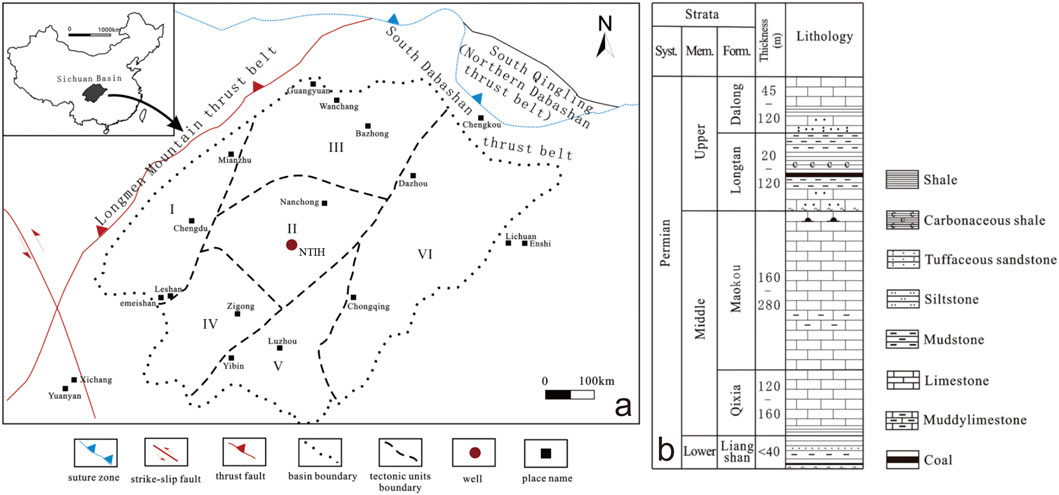
Figure 1. (a) Location of sampling wells (Lin et al., 2018); (b) Composite stratigraphic column of the Permian System (Yang et al., 2021; Chen Y. et al., 2023).
3 Materials and methods
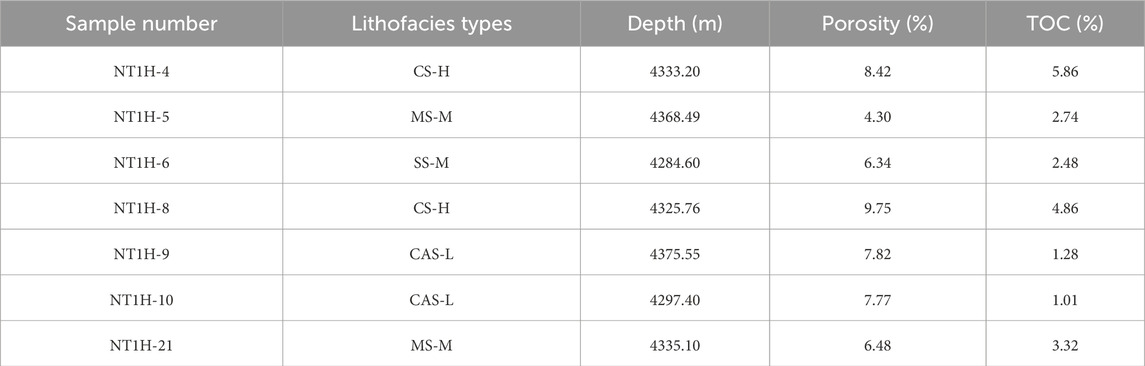
This study selected 33 drilled core shale samples from the LTF of well NT-1H. With depths ranging from 4284.60 to 4380.47 m, widely distributed in the vertical direction, as shown in Figure 1a. The testing methods and standards for XRD whole-rock mineral experiments, total organic carbon (TOC) analysis, rock pyrolysis, stable carbon isotope analysis of kerogen, and thermal maturity (Ro) analysis refer to Chen Y. et al. (2023). The testing methods and standards for FE-SEM testing, gas (CO2,N2) isothermal adsorption, and high-pressure mercury intrusion refer to Wang J. et al. (2025). It is particularly noted that the N2 isothermal adsorption was conducted under the conditions of approximately 77K and 0.15–0.2MPa, using particles with a mesh size of 60–80.
4 Results
4.1 Principles of lithofacies classification
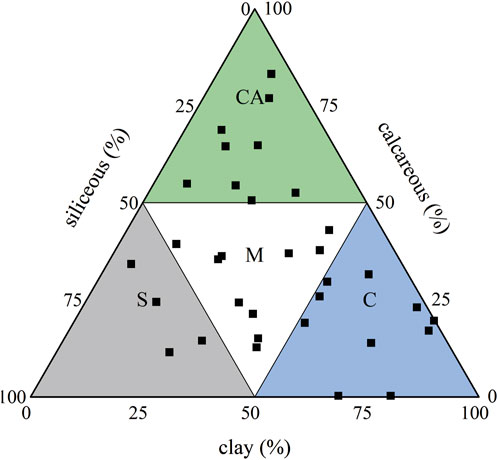
Each lithofacies often reflects the genesis of the rock and its comprehensive characteristics in different aspects. Currently, there are diverse lithofacies classification schemes in the academic community (Shi et al., 2020; Zhan et al., 2023), with redundant indicator information and no unified shale lithofacies classification standard. The percentage of minerals is a direct indicator of the lithofacies-forming environment, while the total organic carbon (TOC) content indicates the material basis for hydrocarbon generation in sedimentary rocks. Both play a significant role in the classification of mud shale types and the determination of their quality (Baudin et al., 2015). This study draws on previous lithofacies classification methods (Wu et al., 2021; Wang E. et al., 2022), and on the basis of the mineralogical ternary classification method, TOC is selected as a secondary parameter for lithofacies classification. Accurate quantitative mineral composition is obtained through whole-rock X-ray diffraction analysis as the first element for lithofacies classification. Mineral content is divided at the 50% threshold, and a ternary diagram of mineral percentage content is plotted (Figure 2). Using the TOC content as the secondary indicator, considering the poor quality of organic matter (OM), a TOC value of 2% is taken as the threshold between organic-poor and organic-moderate shales, and a TOC value of 4% is taken as the threshold between organic-moderate and organic-rich shales.
4.2 Lithofacies types
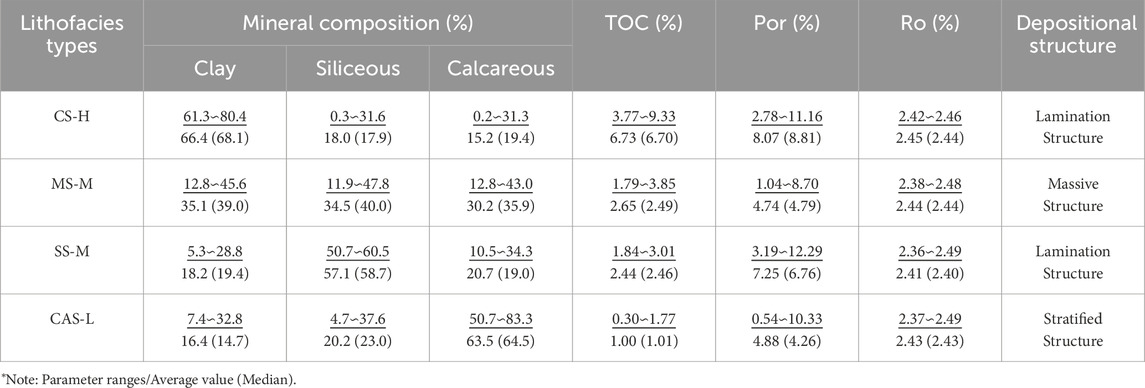
The TOC distribution of the Permian LTF transitional coal-bearing shales from well NT1H in the central Sichuan Basin ranges from 0.23% to 9.33%, with an average of 3.41% (n = 33), exhibiting typical characteristics of organic-rich shales. The Ro values range from 2.36% to 2.49%, with an average of 2.43% (n = 18), indicating that the OM is in the over-mature stage. The results of whole-rock X-ray diffraction analysis show that the mineral composition of LTF coal-bearing shales is complex, including clay minerals, quartz, feldspar, calcite, and dolomite, as well as minor amounts of pyrite and siderite, with clay minerals and siliceous minerals being dominant, The content of clay minerals varies widely, ranging from 5.3% to 80.4%, with an average of 37.4% (n = 33). The clay minerals are mainly composed of chlorite and kaolinite, with the content of illite/smectite mixed layers and illite minerals generally below 10%, except for one sample with a high illite content of 22.04%. The siliceous minerals are mainly quartz, with a content ranging from 0.2% to 60.5%, averaging 27.5% (n = 33). The calcareous minerals are more diverse (including gypsum, calcite, dolomite, etc.), with a content ranging from 0.3% to 83.30%, averaging 34.4% (n = 33). Compared with Chinese marine shales, they have higher clay mineral content and lower siliceous mineral content. Integrating mineral percentage content and TOC data, the deep LTF shales in CSCD mainly develop four lithofacies types.: high-organic clay shale facies (CS-H) (Figure 3a), medium-organic mixed shale facies (MS-M) (Figure 3b), medium-organic siliceous shale facies (SS-M) (Figure 3c), and low-organic calcareous shale facies (CAS-L) (Figure 3d). Parameters are shown in Table 1.

Figure 3. Typical core photos of Permian LTF shale lithofacies in the CSCB: (a) 4371.48–4371.62 m, CS-H, black shale with irregular pyrite development; (b) 429.82–4330.13 m, MS-M, dark gray shale; (c) 4333.69–4333.81 m, SS-M, grayish-black shale with clear bedding planes on the fracture surface; (d) 4376.06–4376.32 m, CAS-L, gray shale with dispersed spot-like py.
4.3 Geochemical characteristics
4.3.1 Mineralogical characteristics
The four types of shale lithofacies exhibit different mineralogical characteristics under the microscope. The CS-H lithofacies shows a laminated structure, with well-developed bedding planes observed under the microscope. With oriented recrystallization, and minor amounts of sandy debris, mainly fine silt of quartz and feldspar, distributed sporadically. Carbonaceous material is well-developed in the rock, often appearing in bands, with some in the form of carbonaceous fragments (Figure 4a). The bedding fractures are well-developed and unfilled (Figure 4b). The MS-M lithofacies shows a massive structure, with local bedding visible, and the rock composition is diverse (Figure 4c). Sandy debris mainly consists of fine silt of quartz, feldspar, and argillaceous fine debris, distributed sporadically. Siderite is uniformly distributed as mud crystals, with minor calcite nodules and carbonaceous fragments, and local occurrences of argillaceous-powdery dolomite (Figure 4d). Pores are well-developed, with the highest average porosity among the four lithofacies types. The SS-M lithofacies shows distinct laminated structure with well-developed bedding fractures (Figure 4e). The rock composition is mainly siliceous minerals, with slightly oriented recrystallization (Figure 4f). Sandy debris, mainly fine silt of quartz, feldspar, and argillaceous fine debris, is evenly distributed. The CAS-L lithofacies shows a stratified structure with interbedded sand and mud, and the long axes of debris are oriented (Figure 4g). The rock is deeply altered, with sandy debris mostly altered into argillaceous particles, followed by mica, completely altered and argillized, with a few quartz and feldspar grains. Some fine debris is enriched in layers, with carbonate development in the clayey layers. Siderite and dolomite powder crystals aggregate into patchy distributions, with evidence of replacement of debris (Figure 4h). Mineral percentage content is shown in Table 1.

Figure 4. Microscopic characteristics of lithofacies under the microscope: (a) CS-H lithofacies, 4320.27 m, ×50 (−); (b) CS-H lithofacies, 4328.88 m, ×50 (−); (c) MS-M lithofacies, local bedding visible, at 4332.6 m, ×25 (+); (d) MS-M lithofacies, 4332.6 m, ×100 (+); (e) SS-M lithofacies, 4333.81 m, ×50 (−); (f) SS-M lithofacies, ×100 (+); (g) CAS-L lithofacies, 4368.58 m, ×25 (+); (h) CAS-L lithofacies, 4368.58 m, ×100 (+).
4.3.2 Organic matter abundance
TOC content is the most universal parameter for characterizing OM abundance (Lai et al., 2024), nd it plays an indispensable role in lithofacies quality analysis. As shown in Table 1, the comparison reveals that the CS-H lithofacies of the LTF in CSCB has the best hydrocarbon generation potential, while the MS-M and SS-M lithofacies also have good hydrocarbon generation potential. In contrast, the CAS-L lithofacies has the poorest hydrocarbon generation potential. The subject of this study is at a higher level compared to the LTF shales from other wells in southern Sichuan reported by Chen Y. et al. (2023) and in southeastern Sichuan reported by Cao et al. (2022).
4.3.3 Organic matter type
Kerogen type is an indicator for evaluating the quality of OM (Niu et al., 2023), and it is divided into sapropel-type (Type I), mixed-type (Type II), and humic-type (Type III). There are many methods for evaluating kerogen type, and selecting appropriate methods is conducive to accurate determination. Multiple methods are usually applied to corroborate each other. As shown in Figure 5, most shale samples have low hydrogen indices (HI) and high peak temperatures for thermal decomposition, generally between 580°C and 600°C, which does not clearly indicate the OM type of the Upper Permian LTF shale. A plot with TOC as the x-axis and pyrolysis hydrocarbon yield (S2) as the y-axis is also used to indicate the type of kerogen in source rocks (Tao et al., 2013). As shown in Figure 6, the OM in all four lithofacies types is of Type III. The carbon isotope content of kerogen does not change significantly during the thermal degradation process. (Liang et al., 2020; Ogbesejana et al., 2021). Therefore, this parameter can also be used to effectively determine the type of OM. (Liang et al., 2009). According to previous experience (Zhang et al., 2015), taking δ13C equal to −29‰ and −26‰ as the two thresholds for distinguishing types I, II and III kerogen. Shows the OM type of the Upper Permian LTF shale identified by kerogen stable isotope data. The δ13C values of kerogen in the deep LTF shales of CSCB range from −26.2‰ to −23.8‰ (Figure 7). This range partially overlaps with that of the Shanxi Formation (SXF) (−25.5‰ to −22.6‰), but overall, the δ13C values of the SXF samples are relatively lighter. They are significantly lighter than those of the marine Wojiaping Formation (−28.0‰ to −26.0‰) and LMXF (−30.9‰ to −26.9‰). In summary, the OM of the four lithofacies is mainly Type III, with only the CAS-L lithofacies containing a small amount of Type II.
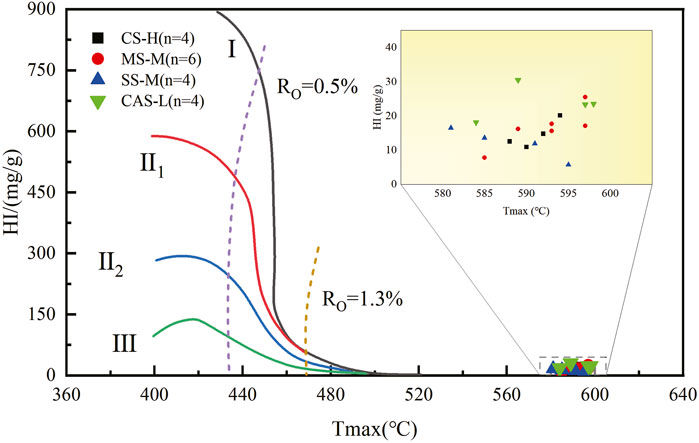
Figure 5. Figure of Hl and Tmax (peak temperature of thermal decomposition) and kerogen types of shale lithofacies.
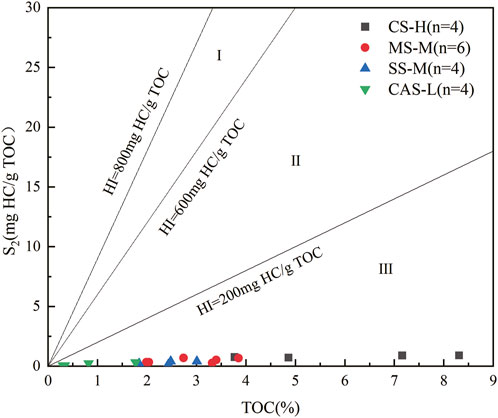
Figure 6. Figure of TOC and S2 for lithofacies. (Modified from (Tao et al., 2013)).
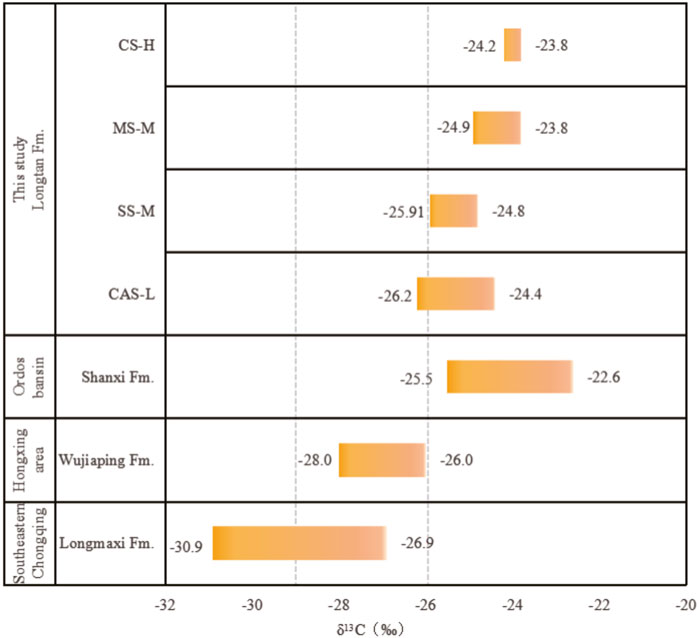
Figure 7. Distribution characteristics of kerogen δ13C(CS-H:n = 4; MS-M:n = 6; SS-M:n = 4; CAS-L:n = 6). (SXF from (Sun et al., 2017), WJPF from (Wang P. et al., 2022), LMXF from (Shengxiu et al., 2021)).
4.3.4 Organic matter maturity
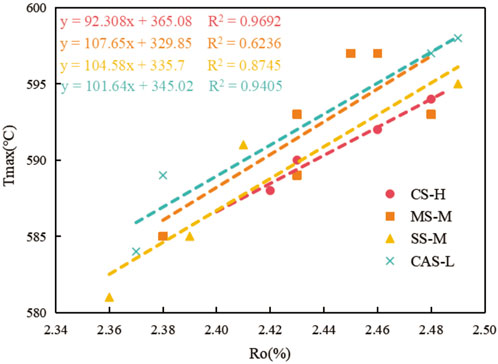
The maturity of OM is a key factor in determining whether the OM in a lithofacies has undergone the hydrocarbon generation process (Tessin et al., 2017; Adeyilola et al., 2022). The application of determining maturity (Ro) based on vitrinite reflectance is the most common in the petroleum industry (Xia et al., 2013; Liu et al., 2023). The maturity of the four types of LTF shales in CSCB shows minor differences, with each lithofacies experiencing a slight increase with increasing burial depth (Figure 8). The OM is primarily in the overmature stage. The maturity of the CS-H lithofacies is the highest among the four lithofacies types, the SS-M lithofacies is the lowest, while the MS-M and CAS-L lithofacies are intermediate between the two.
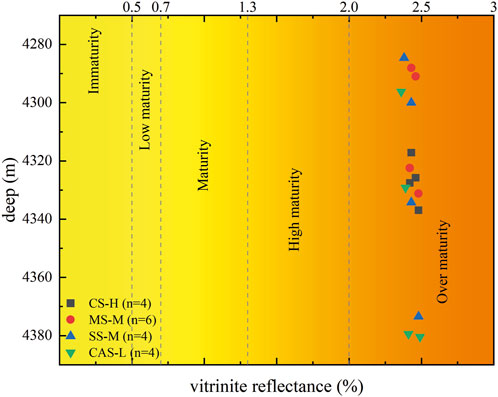
Figure 8. Distribution characteristics of vitrinite reflectance (Ro) for the four shale lithofacies types.
4.4 Porosity type and structural characteristics
Similar to conventional reservoirs, rock pores are the primary space for shale gas occurrence, and porosity is the most fundamental indicator for evaluating the storage capacity of lithofacies. The CS-H lithofacies has well-developed pores, with the highest average porosity among the four lithofacies types. The CAS-L lithofacies has the second-highest average porosity, followed by the SS-M lithofacies, with the MS-M lithofacies having the lowest average porosity. However, for shales, porosity measurement alone is not sufficient for evaluation. This study further characterizes the pore structures of typical samples using field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), CO2 gas adsorption (CO2GA), low-temperature N2 adsorption (LTN2A), and mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP). Typical sample test numbers are shown in Table 2.
4.4.1 Porosity type
To elucidate the characteristics of pores and microfractures (Wei et al., 2021; Guan et al., 2024), Field emission-scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) observations and analyses of pore types and morphologies were conducted on different lithofacies of the deep LTF shales in CSCD. Loucks et al. (2012), while studying the siliceous Barnett shales in the Fort Worth Basin in North America, proposed that matrix pores could be categorized into organic pores, intragranular pores, and intergranular pores based on their spatial relationship with grains, but this classification scheme did not include microfractures. Building on their research, the pores in the LTF shales of the study area can be classified into mineral framework pores, OM pores, and microfractures.
CS-H lithofacies: The interlayer pores in clay (Figure 9a) are well-developed and have a curved shape. The intergranular pores in clay (Figure 9b) are well-developed, with relatively irregular pore shapes and significant variations in pore size. OM appears as irregular clumps (Figure 9c), with poorly developed OM pores that are dispersed and relatively isolated (Figures 9d,e). OM shrinkage microfractures are developed at the edges (Figure 9c), and hydrocarbon generation-induced microfractures are developed internally (Figure 9e). In this study, OM internal fractures and OM-mineral interfacial fractures are collectively referred to as OM-related fractures, with the former termed A-OM-related fractures and the latter B-OM-related fractures. MS-M lithofacies: Local intergranular pores are developed to a certain extent (Figure 9f), appearing as pits and irregular shapes. Microfractures are developed (Figure 9g), with a single direction and relatively straight shape. OM appears irregular (Figure 9h), with underdeveloped OM pores. SS-M lithofacies: Abundant authigenic quartz is developed (Figure 9i), with well-developed intergranular pores in minerals. OM is distributed in filamentous form (Figure 9j). Microfractures are developed within OM (Figure 9k), with a high density. Fractures are visible at the edges of OM (Figure 9l), with the scale of OM edge fractures being slightly larger than that of internal OM fractures. CAS-L lithofacies: The pore types in this lithofacies are relatively simple, with limited development of inorganic pores. The OM in this lithofacies is basically distributed in a dispersed manner (Figure 9m). Some OM encloses pyrite grains (Figures 9n,o), with relatively abundant intergranular pores in pyrite.
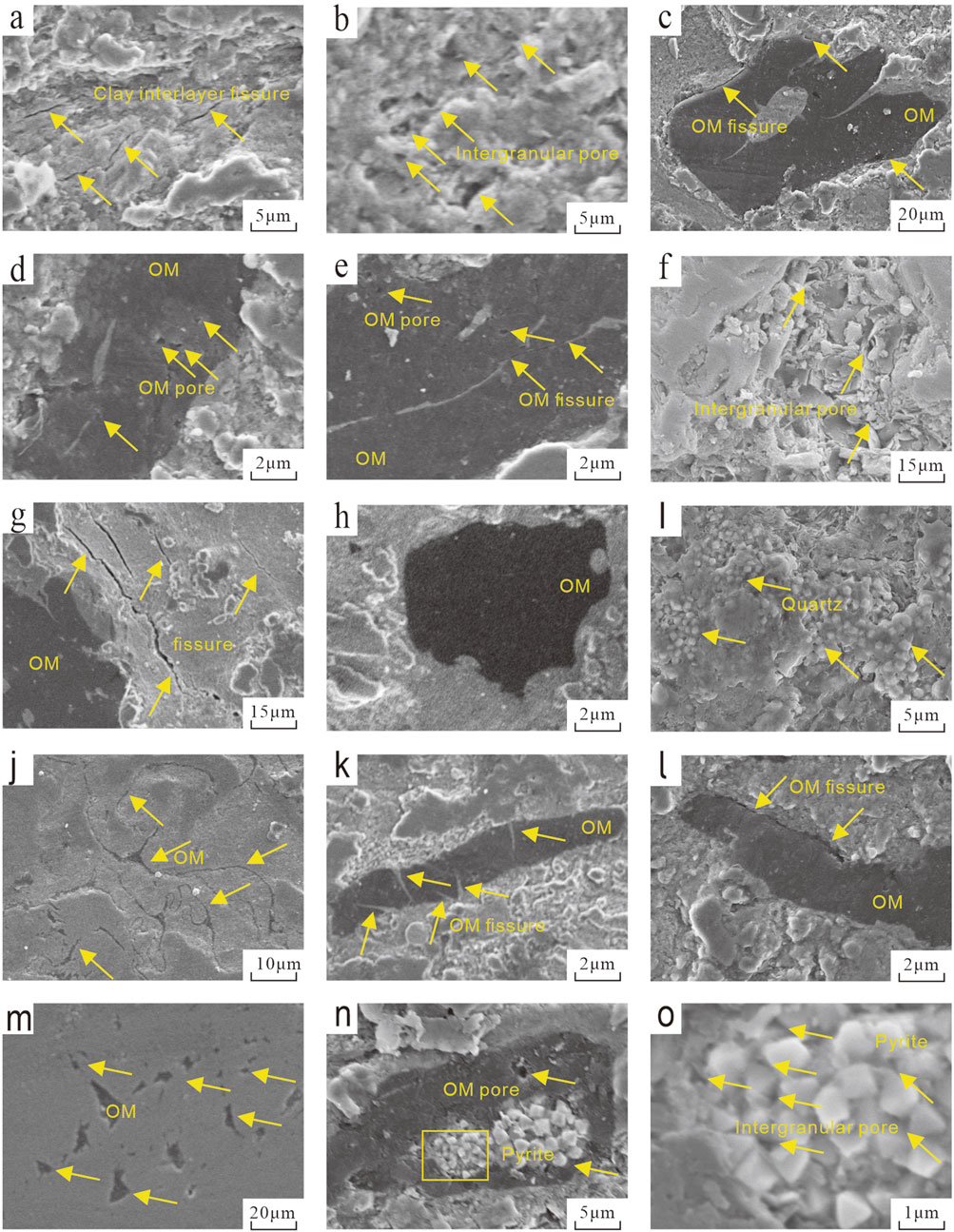
Figure 9. SEM Images of the Four Lithofacies Types: (a) CS-H lithofacies, interlayer pores in clay; (b) CS-H lithofacies, interlayer pores in clay; (c) CS-H lithofacies, irregular OM, shrinkage fractures; (d) CS-H lithofacies, minor organic pores developed; (e) CS-H lithofacies, isolated organic pores, microfractures; (f) MS-M lithofacies, intergranular pores; (g) MS-M lithofacies, microfractures; (h) MS-M lithofacies, organic pores underdeveloped; (i) SS-M lithofacies, abundant authigenic quartz, well-developed intergranular pores; (j) SS-M lithofacies, filamentous distribution of OM; (k) SS-M lithofacies, internal fractures in OM; (l) SS-M lithofacies, marginal fractures in OM; (m) CAS-L lithofacies, dispersed distribution of OM; (n) CAS-L lithofacies, OM in clumps enclosing pyrite grains, minor isolated organic pores developed; (o) Yellow-boxed area in Figure n, intergranular pores in pyrite.
4.4.2 Pore structure characteristics of different shale lithofacies
This study is based on the experimental methods of CO2GA, LTN2A, and MIP (Wang J. et al., 2025), and systematically characterized the pore morphology of different lithofacies of the Permian LTF coal-bearing shales in the CSCB. According to the classification criteria of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) (Rouquerol et al., 1994), hysteresis loops are divided into four types (H1-H4), adsorption isotherms are divided into five types (I-VI), and the pore structure is divided into micropores (<2 nm), mesopores (2–50 nm), and macropores (>50 nm) based on pore size.
Figures 10a,d,g,j shows the CO2 adsorption curve characteristics of different lithofacies shales in the study area. The experimental show that the adsorption volume of all samples increases with the increase in relative pressure. However, when the relative pressure is below 0.015, the adsorption volume of all four lithofacies samples increases rapidly. After the relative pressure exceeds 0.015, the rate of change in adsorption volume gradually becomes more gradual. All adsorption curves show a typical “convex upward” shape, which corresponds to Type I in the IUPAC classification of physical adsorption isotherms, indicating the presence of a certain number of irregular microporous structures in all four lithofacies. In terms of the final adsorption volume, the CS-H lithofacies shows the largest adsorption volume, the SS-H and CAS-L lithofacies have similar adsorption volumes, and the MS-M lithofacies has the smallest adsorption volume. This result reveals the pore development characteristics of different lithofacies: the CS-H lithofacies has the most developed micropores, which are likely mainly composed of irregular intergranular pores; the MS-M lithofacies has the least developed micropores, mainly characterized by intercrystalline pores; the SS-H and CAS-L lithofacies have similar micropore development, both characterized by the development of irregular intergranular pores.
Figures 10b,e,h,k shows the low-pressure N2 adsorption and desorption curves of different lithofacies shales in the study area. All four lithofacies samples of LTF show desorption hysteresis loops, thus forming hysteresis loops with the desorption branch and the adsorption branch. The structural characteristics of shale pores can be determined based on the shape of the hysteresis loops on the nitrogen adsorption-desorption curves. The N2 adsorption isotherms of the four lithofacies samples are of Type II, with hysteresis loops similar to H3 loops and some characteristics of H2 and H4 loops (Chen et al., 2016). CS-H and CAS-L mainly exhibit slit-like pore shapes produced by ink-bottle and plate-like particles (Figures 10b,k). The hysteresis of adsorption-desorption isotherms indicates pore connectivity and complex shapes. N2 adsorption experiments indicate that the MS-M lithofacies has a limited number of mesopores, with pore shapes predominantly ink-bottle and slit-like. The characteristics of the hysteresis loop suggest poor connectivity of these pores (Wang J. et al., 2025). The SS-M lithofacies exhibits more pronounced H4-type characteristics, indicating that the pores are primarily slit-like.
Figures 10c,f,i,l shows the mercury intrusion and extrusion curves of different lithofacies shales in the study area. All four lithofacies curves exhibit a significant hysteresis phenomenon similar to that observed in low-temperature N2 adsorption. This hysteresis indicates that a considerable amount of mercury remains in the matrix pores of the samples after extrusion. The phenomenon is typically associated with the ink-bottle effect, indicating the presence of ink-bottle pores in the matrix of the LTF shale samples in the study area, which further corroborates the results of low-temperature N2 adsorption experiments. When the intrusion pressure is between 1 and 10 MPa, the mercury saturation of MS-M and SS-M hardly increases, while CS-H and CAS-L show a significant increase. When the intrusion pressure exceeds 10 MPa, the mercury saturation increases in all four lithofacies. This indicates that CS-H and CAS-L have well-developed macropores and microfractures. The development of macropores and microfractures in MS-M and SS-M is very limited, especially in MS-M, which restricts its storage capacity.
4.4.3 Pore size distribution characteristics of different lithofacies
Integrating high-pressure mercury intrusion and low-temperature gas adsorption tests, the volumes of mesopores and micropores were determined using the Barrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) model and the Density Functional Theory (DFT) model, respectively (Thommes et al., 2015), to systematically analyze the pore size distribution characteristics of different lithofacies of LTF in the study area. For CS-H, the test shows that mesopores account for the largest proportion (Figures 11a,b), with pore size peaks ranging from 20 to 50 nm. Macropores account for 11.1% of the total pore volume, mesopores for 85.2%, and micropores for 3.7%. Micropores, mesopores, and macropores all contribute to the storage space of this lithofacies to varying degrees. The mesopore volume of MS-M clearly dominates (Figures 11c,d), with a bimodal pore size distribution, the main peak ranging from 20 to 100 nm and the secondary peak from 2 to 10 nm. Macropores account for a very small proportion, only 0.2% of the total pore volume, mesopores for 91.0%, and micropores for 8.8%. Mesopores are the main storage space for this lithofacies. The pore volume of SS-M is dominated by mesopores (Figures 11e,f), with pore sizes mainly distributed between 20 and 50 nm. Macropores account for 2.3% of the total pore volume, mesopores for 86.6%, and micropores for 11.1%. Micropores and mesopores constitute the main storage space for this lithofacies. The proportion of mesopores in CAS-L is lower than in other lithofacies (Figures 11g,h), at 85.7%. Micropores and macropores account for 4.0% and 10.3%, respectively. Mesopores remain the main contributor to the storage space of this lithofacies.
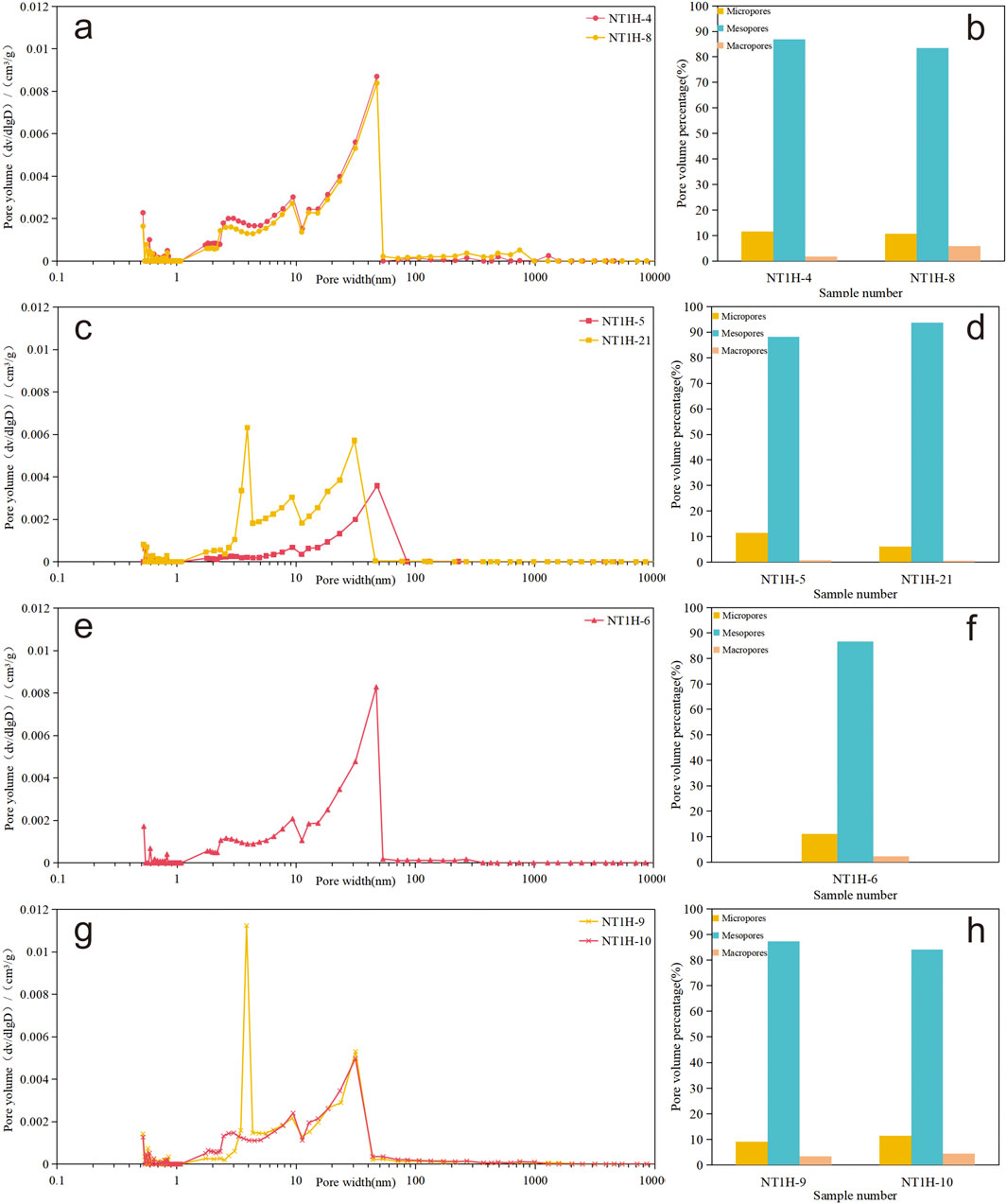
Figure 11. Pore size distribution curves and pore volume fraction histograms for different lithofacies of LTF shale: (a,b) CS-H; (c,d) MS-M; (e,f) SS-M; (g,h) CAS-L.
5 Discussion
5.1 The influence of geochemical characteristics on the quality of lithofacies
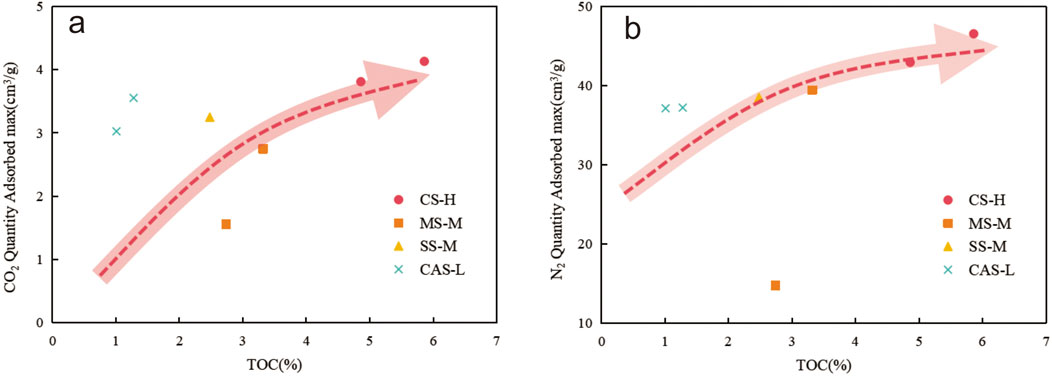
TOC is the material basis for shale gas generation (Ghanizadeh et al., 2015a; b), and is also one of the key factors affecting methane adsorption capacity. OM not only provides a carbon source for shale gas generation, but its microporous structure also makes it an important carrier for adsorbing gases, thereby significantly affecting the amount of adsorbed gases (Jarvie et al., 2007). It is noteworthy in this study that the CS-H samples exhibit non-closing hysteresis loops at low relative pressures. This may be due to the expansion of the rock or OM during the adsorption process, leading to incomplete desorption of nitrogen, or it may be due to irreversible adsorption occurring in pores with diameters similar to that of nitrogen molecules (Cao et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2018). This study shows that for the same lithofacies, gas adsorption is greater when TOC is relatively high (Figure 12). The adsorption capacity of the samples increases with increasing TOC, but the rate of increase gradually decreases as TOC increases. This indicates that higher TOC is associated with stronger adsorption properties (Jarvie et al., 2007), but the dominant degree of adsorption decreases. Previous studies have also shown (Zou et al., 2010) that under the same temperature and pressure conditions, organic-rich shales typically have larger micropore spaces and higher specific surface areas than organic-poor shales, and thus can adsorb more natural gas. Therefore, the high organic carbon content of LTF shale indicates a strong potential for hydrocarbon generation and adsorption performance.
For the transitional-phase deposited LTF shales, terrestrial biomass contributes a high proportion of its OM supply, making a significant contribution to the TOC content (He Q. et al., 2020). This study further clarifies that the LTF kerogen type is predominantly Type III, with relatively weaker hydrocarbon generation potential compared to the other two types of kerogen (Niu et al., 2023). The four lithofacies of LTF in the central Sichuan region (CAS-L, SS-M, MS-M, CS-H) are essentially consistent in OM type, but show certain differences in quality. Specifically, the kerogen isotope values of the CAS-L and SS-M lithofacies are slightly lower than those of the MS-M and CS-H lithofacies (Figure 7), while the light index is slightly higher (Figure 5), indicating that the OM quality of the former is slightly better than that of the latter. Compared with other typical shales, the OM quality of LTF shales shows certain regional characteristics (Figure 7). Compared with the transitional-phase SXF shales in the Ordos Basin, LTF shales have a relative advantage in OM quality. However, compared with the commercially developed marine LMXF shales in the southeastern Chongqing area and the contemporaneously deposited marine WJPF shales within the basin, the OM quality of LTF shales is at a distinct disadvantage. This difference mainly stems from the different sedimentary environments; marine shales typically have better kerogen types (I or II kerogen), thus having stronger hydrocarbon generation potential (Ji et al., 2020). In contrast, transitional-phase shales, influenced by terrigenous input, are predominantly Type III in kerogen type, with relatively limited hydrocarbon generation potential (Dang et al., 2016).
During the diagenetic evolution of organic-rich shales, OM undergoes a thermal maturation process associated with burial (Lin et al., 2018; Deng et al., 2023). The thermal maturation of OM is the primary cause for the formation of organic pores and organic fractures in transitional-phase shales. The OM in the four lithofacies of LTF is mainly in the over-mature stage. Meanwhile, Ro and Tmax exhibit a strong positive correlation (Figure 13). This indicates that all four shale lithofacies have experienced the peak hydrocarbon generation phase in geological history. Among them, CS-H and CAS-L show the best correlation, with R2 > 0.9, indicating a more gradual thermal evolution process of OM (Mango, 1987; 1991), which is conducive to the generation and expulsion of hydrocarbons. Compared with the Shanxi and Taiyuan formations in the Ordos Basin, which are also transitional-phase shales, it can be found that although LTF was deposited later, it has a higher degree of evolution (Qiu et al., 2021; Yu et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2024). Although excessively high organic matter maturity may not be conducive to finely characterizing the complete OM hydrocarbon generation process, pore evolution characteristics, and natural gas accumulation patterns in shale studies, the high maturity of the LTF shales in CSCD remains a favorable factor for lithofacies quality definition (Zhang et al., 2020).
5.2 The impact of pore characteristics on lithofacies quality
The results of this study indicate that the pore characteristics of transitional shales are similar to those of marine shales, mainly manifested as open pore structures. These pores have favorable morphological characteristics, providing favorable conditions for the migration and development of natural gas (Chen et al., 2016). Based on the correlation analysis between porosity tested by the saturated liquid method and shale composition, shale porosity is positively correlated with the percentage of clay minerals (Figure 14a) and TOC (Figure 14d), with fitting coefficients of 0.178 and 0.236, respectively. It is negatively correlated with calcareous minerals (Figure 13b), with a fitting coefficient of 0.234. There is no significant correlation with siliceous minerals (Figure 14c). This may be the reason why different lithofacies were not distinguished.
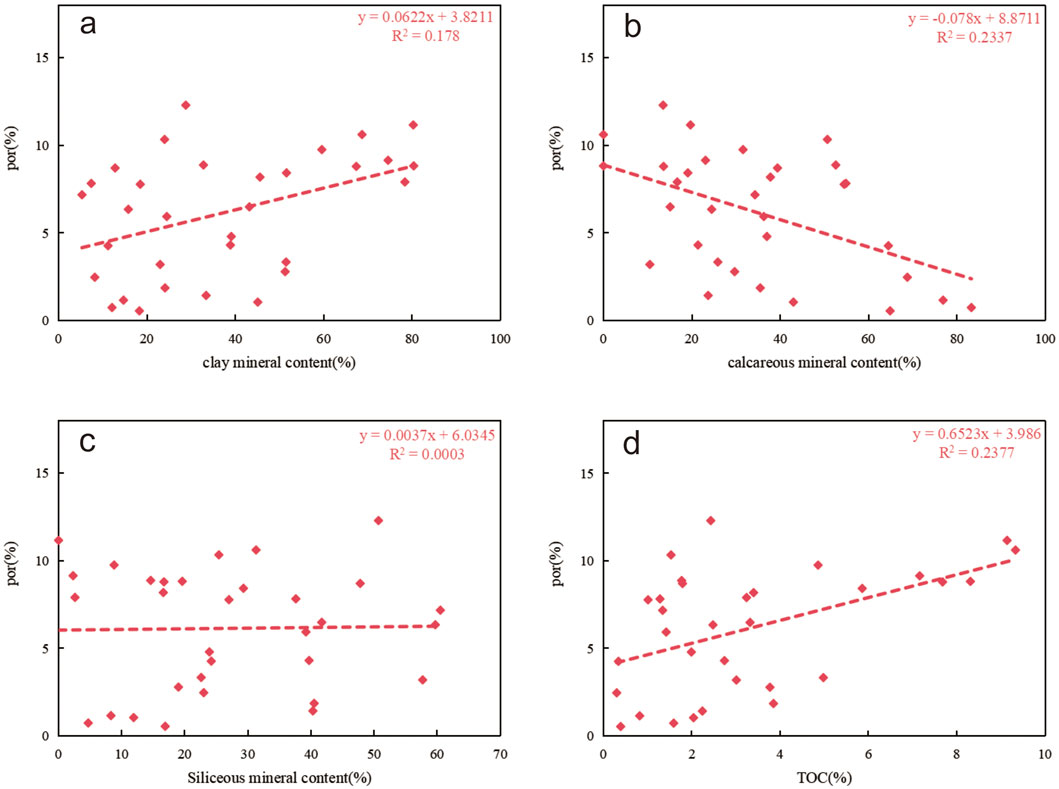
Figure 14. Figure showing the correlation analysis between porosity of LTF shale and different compositional components of shale. (a) por-clay mineral content; (b) por-calcareous mineral content; (c) por-Siliceous mineral content; (d) por-TOC.
Based on lithofacies classification, the sensitivity of porosity to different compositional components varies among each lithofacies. The porosity of CS-H shows a good positive correlation with clay and TOC content, indicating that the increase in clay (Figure 15a) and TOC (Figure 15d) content has a positive effect on pore formation. It has a weaker correlation with siliceous content (Figure 15c). It has a negative correlation with calcareous content (Figure 15b), reflecting that the increase in calcareous minerals is not conducive to pore formation. The porosity of MS-M has poor correlation with the content of the four types of shale components (Figures 15a–d), showing low sensitivity. For SS-M (Figures 15a,b), in addition to a significant negative correlation with the siliceous component (Figure 15c), the correlation with other components is not obvious (Figures 15a,b,d). The porosity of CAS-L has a clear positive correlation with clay minerals, siliceous minerals, and TOC content (Figures 15a–c), and a negative correlation with calcareous content (Figure 15b).

Figure 15. Figure showing the correlation analysis between porosity of different lithofacies and various compositional components of shale. (a) por-clay mineral content; (b) por-calcareous mineral content; (c) por-Siliceous mineral content; (d) por-TOC.
Given the overall underdevelopment of organic pores in LTF, the porosity of CS-H and CAS-L shows a good correlation with OM content, partly because these two lithofacies have a certain amount of organic pore development, and more likely because the OM-related fractures in these lithofacies are well-developed. By comparing Figure 16 with Figure 9, it can be seen that the number of organic pores in LTF is less than that in the SXF (Figures 16a–c), the contemporaneous marine Wojiaping Formation (Figure 16f), and the commercially developed LMXF (Figures 16d,e) (Chen Y. N. et al., 2023). However, compared with the Shanxi and Wojiaping formations, there are more OM-related fractures. Both have abundant B-OM-related fractures compared with LMXF shale. This may be due to the rapid thermal evolution rate of OM in LTF as described in Section 5.2. OM undergoes deformation (Zolfaghari et al., 2017), the formation of abundant OM-related fractures provides reservoir conditions for natural gas. Through SEM observation, full pore size testing, and correlation analysis between porosity and shale composition, for CS-H, the mesopore-level clay interlayer gaps, OM pores, OM-related fractures, and macropore-range intergranular pores provide abundant storage space for natural gas. Among them, the contribution of OM-related fractures cannot be ignored (Rexer et al., 2014; 2020). The pore size is mainly distributed in the mesopore range, with some reaching macropores (Pommer and Milliken, 2015; Shi et al., 2018). MS-M has various types of mesopores as the main storage space, possibly because the uniform distribution of components makes the rock more compact. The porosity of SS-M lithofacies shows poor correlation with TOC, possibly because the concentrated distribution of TOC results in a relatively fixed absolute value of the contribution of visible OM-related fractures to the storage space under the microscope. At the same time, Due to the presence of a significant amount of quartz, the intergranular pores are well-developed, leading to good storage conditions for this lithofacies. The porosity of CAS-L lithofacies is low, and the analysis identifies two reasons: first, the development of calcareous minerals and the underdevelopment of intergranular pores. Meanwhile, dissolution pores are underdeveloped and almost not observed under the microscope (Cao et al., 2022). On the other hand, the low TOC of this lithofacies limits the contribution of OM-related storage space.
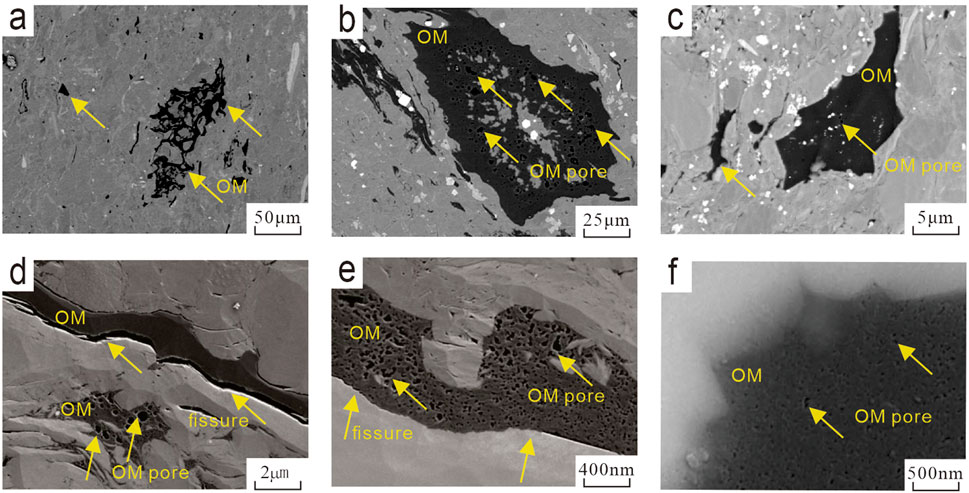
Figure 16. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Images of Typical Shales from Other Formations: (a–c) SXF, modified from (He et al., 2022); (d,e) LMXF, modified from (Chen et al., 2019); (f) Wojiaping Formation, modified from (Zhang et al., 2024).
5.3 Favorable lithofacies types and their distribution
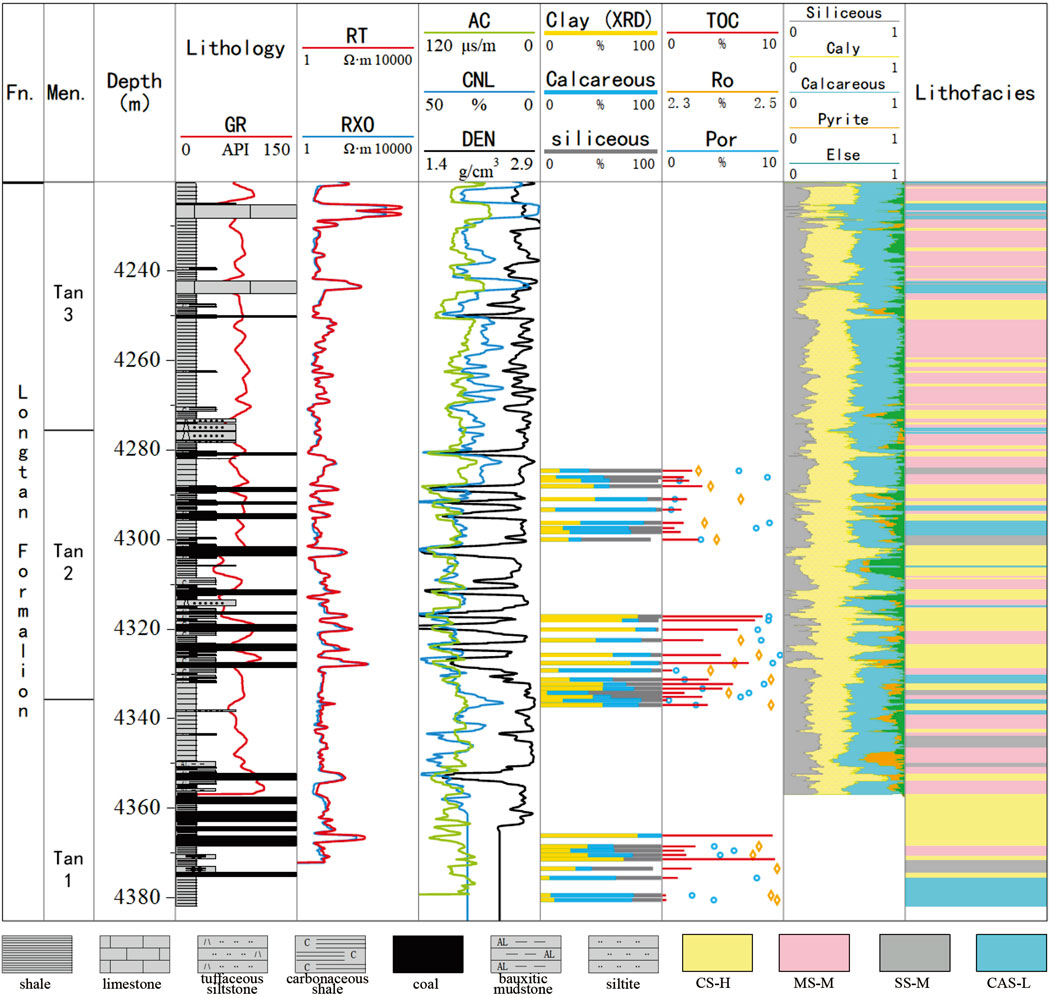
By comprehensively considering the hydrocarbon generation potential, pore development conditions, and preservation conditions, the CS-H lithofacies type can be identified as a high-quality lithofacies type. It is mainly sporadically distributed in the Tan 2 section and relatively continuously distributed in the upper middle part of the Tan 1 section (Figure 17). On one hand, it is characterized by high TOC and high Ro compared to other lithofacies. On the other hand, it features well-developed clay intergranular fractures and intergranular pores, providing ample storage space. Although its OM quality is not superior among the four lithofacies, its higher OM content and maturity result in well-developed organic pores and OM-related fractures. In terms of pore size, micropores are relatively well-developed compared to other lithofacies, while mesopores and macropores are even more developed. Under the background of favorable hydrocarbon generation conditions matched with high-quality storage spaces, natural gas accumulation has superiority (Hazra et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2023). In terms of depth, it has an appropriate burial depth (4200–4400 m). Regionally, the upper part of LTF has an effective cap rock and a stable tectonic setting (Liu et al., 2021). Spatially, the development locations of this lithofacies are often interbedded with coal seams, often interbedded with coal seams. According to the data from the NT1H well, including closed-core sampling and gas content testing (Wen et al., 2024), the distribution layer of this lithofacies exhibits overpressure and oversaturation, the formation pressure coefficient reaches 2.03, confirming the favorable quality of this lithofacies (Goulty et al., 2012; O'Neill et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2019).
6 Conclusion
On the premise of clarifying the lithofacies types of the Middle Permian LTF marine-continental transitional shales in the CSCB a detailed analysis of their organic geochemical and pore characteristics was conducted. Based on this, the impact of various factors on lithofacies quality was discussed, revealed high-quality lithological types. By comparing the favorable lithofacies with typical marine shales, the following conclusions were drawn:
(1) In the Suining area of CSCB, the Permian LTF marine-terrestrial transitional shales exhibit strong vertical heterogeneity. Four lithofacies types are mainly developed: organic-rich clay shale (CS-H), medium-organic mixed shale (MS-M), medium-organic siliceous shale (SS-M), and organic-poor calcareous shale (CAS-L). The mineral percentage content and organic matter (OM) abundance show clear differences among different lithofacies shales, while kerogen type and maturity (Ro) are essentially consistent.
(2) The Longtan shale has a diverse range of pore types and a complex pore structure. CS-H and CAS-L are primarily characterized by slit-like pore shapes produced by ink-bottle and plate-like particles. The pore shapes of the MS-M lithofacies are mainly ink-bottle and slit-like. The pores of the SS-M lithofacies are predominantly slit-like.
(3) The inorganic pores of CS-H and MS-M are mainly intergranular pores in clay, with CS-H not only having better-developed intergranular pores in clay but also exhibiting clay interlayer fractures. For SS-M and CAS-L, inorganic pores are predominantly intergranular pores. The development of OM pores is poor, typically appearing as isolated pores. There are significant differences in the development of OM-related fractures among different lithofacies, with CS-H and SS-M being superior to MS-M and CAS-L. Through full pore size characterization, mesopores and micropores are well-developed in LTF shales. Among them, mesopores dominate, accounting for over 85% of the pore volume, followed by micropores, which account for about 10%.
(4) Based on geochemical analysis and full-pore characterization, the organic-rich clay shale facies (CS-H) is identified as a high-quality lithofacies type by integrating its hydrocarbon generation potential, pore development, and preservation conditions. The study reveals the stratigraphic intervals where high-quality lithofacies are developed, providing important evidence for the development of this type of unconventional energy.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
LW: Conceptualization, Visualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XL: Supervision, Resources, Writing – review and editing. YaC: Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Supervision. HZ: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. XP: Visualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. YuC: Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Validation. NQ: Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Software. WH: Writing – review and editing, Investigation. WY: Writing – review and editing, Software. YL: Writing – review and editing. YZ: Writing – review and editing, Software.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by the “In-Depth Study on the Development Potential of the Permian Longtan Formation Coal-Shale System in the Sichuan Basin” (No. 2024-N/G-46602).
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the Sichuan Basin Research Center of the Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, China National Petroleum Corporation, for their invaluable support and guidance during the research and manuscript preparation process. We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the reviewers for their professional suggestions.
Conflict of interest
Authors LW, XL, YaC, HZ, XP, NQ, WH, WY, YL, YZ were employed by PetroChina.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2025.1650521/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
LTF, Longtan Formation; LMXF, Longmaxi Formation; QZSF, Qiongzhusi Formation; WJPF, Wujiaping Formation; SXF, Shanxi Formation; CS-H, high-organic clay shale facies; MS-M, medium-organic mixed shale facies; SS-M, medium-organic siliceous shale facies; CAS-L, low-organic calcareous shale facies; OM, Organic matter; TOC, total organic carbon; XRD, X-ray diffraction; FE-SEM, field-emission scanning electron microscopy; CO2GA, CO2 gas adsorption; LTN2A, low-temperature N2 adsorption; CSCB, central Sichuan Basin.
References
Adeyilola, A., Zakharova, N., Liu, K., Gentzis, T., Carvajal-Ortiz, H., Ocubalidet, S., et al. (2022). Hydrocarbon potential and organofacies of the Devonian Antrim shale, Michigan basin. Int. J. Coal Geol., 249. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2021.103905
Baudin, F., Disnar, J.-R., Aboussou, A., and Savignac, F. (2015). Guidelines for rock–eval analysis of recent marine sediments. Org. Geochem. 86, 71–80. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2015.06.009
Cao, Q., Qi, M., Li, X., Wang, D., Deng, Y., and Wu, C. (2022). Study on organic matter enrichment and reservoir characteristics of Permian longtan formation shale in southeast sichuan. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 895941. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.895941
Cao, T., Deng, M., Song, Z., Luo, H., and Hursthouse, A. S. (2018). Characteristics and controlling factors of pore structure of the Permian shale in southern Anhui province, east China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 60, 228–245. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2018.10.018
Chen, L., Jiang, Z., Liu, K., Wang, P., Ji, W., Gao, F., et al. (2016). Effect of lithofacies on gas storage capacity of marine and Continental shales in the sichuan basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 36, 773–785. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2016.11.024
Chen, Y., Pei, X., Zhang, J., Wang, N., Han, D., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Geochemical and gas bearing characteristics of the marine-continental transitional longtan shales in southern sichuan, China. Front. Earth Sci. 11, 1202005. doi:10.3389/feart.2023.1202005
Chen, Y., Qin, Y., Wei, C., Huang, L., Shi, Q., Wu, C., et al. (2018). Porosity changes in progressively pulverized anthracite subsamples: implications for the study of closed pore distribution in coals. Fuel 225, 612–622. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.164
Chen, Y. N., Yang, K., Wu, W., Yang, Y., Yang, X., and Ma, K. (2023). Favorable lithofacies and pore characteristics of the Permian longtan formation shale in the southern sichuan basin. Energy Geosci. 4 (3), 100193. doi:10.1016/j.engeos.2023.100193
Chen, Z., Song, Y., Jiang, Z., Liu, S., Li, Z., Shi, D., et al. (2019). Identification of organic matter components and organic pore characteristics of marine shale: a case study of wufeng-longmaxi shale in southern sichuan basin, China. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 109, 56–69. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.06.002
Clarkson, C. R., Solano, N., Bustin, R. M., Bustin, A. M. M., Chalmers, G. R. L., He, L., et al. (2013). Pore structure characterization of North American shale gas reservoirs using USANS/SANS, gas adsorption, and Mercury intrusion. Fuel 103, 606–616. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2012.06.119
Dang, W., Zhang, J., Tang, X., Chen, Q., Han, S., Li, Z., et al. (2016). Shale gas potential of Lower Permian marine-continental transitional Black shales in the southern north China basin, central China: characterization of organic geochemistry. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 28, 639–650. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2015.12.035
Deng, M., Zhao, G., Lin, X., Chen, C., Li, L., and Liang, Q. (2023). Sedimentary facies, paleogeography, and depositional models of the middle–late Permian in the sichuan basin, southwest China. Minerals 13 (11), 1406. doi:10.3390/min13111406
Ge, Y., and Bond, D. P. G. (2022). Two deep marine oxygenation events during the Permian-Triassic boundary interval in south China: relationship with ocean circulation and marine primary productivity. Earth-Science Rev. 234, 104220. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.104220
Ghanizadeh, A., Clarkson, C. R., Aquino, S., Ardakani, O. H., and Sanei, H. (2015a). Petrophysical and geomechanical characteristics of Canadian tight oil and liquid-rich gas reservoirs: I. pore network and permeability characterization. Fuel 153, 664–681. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2015.03.020
Ghanizadeh, A., Clarkson, C. R., Aquino, S., Ardakani, O. H., and Sanei, H. (2015b). Petrophysical and geomechanical characteristics of Canadian tight oil and liquid-rich gas reservoirs: II. Geomechanical property estimation. Fuel 153, 682–691. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2015.02.113
Goulty, N. R., Ramdhan, A. M., and Jones, S. J. (2012). Chemical compaction of mudrocks in the presence of overpressure. Pet. Geosci. 18 (4), 471–479. doi:10.1144/petgeo2012-018
Guan, W., Cai, W., Li, Z., and Lu, H. (2024). Microscopic characterization and fractal analysis of pore systems for unconventional reservoirs. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 12 (6), 908. doi:10.3390/jmse12060908
Han, L., Li, X., Liu, Z., Duan, G., Wan, Y., Guo, X., et al. (2023). Influencing factors and prevention measures of casing deformation in deep shale gas Wells in luzhou block, southern sichuan Basin, SW China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 50 (4), 979–988. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(23)60443-4
Hazra, B., Dutta, S., and Kumar, S. (2017). TOC calculation of organic matter rich sediments using rock-eval pyrolysis: critical consideration and insights. Int. J. Coal Geol. 169, 106–115. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2016.11.012
He, J., Deng, H., Ma, R., Wang, R., Wang, Y., and Li, A. (2020). Reservoir characteristics of the Lower Jurassic lacustrine shale in the eastern sichuan basin and its effect on gas properties: an integrated approach. Energies 13 (17), 4495. doi:10.3390/en13174495
He, Q., Chen, S., Li, S., Guo, B., Lu, J., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Organic geochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon generation mechanism of marine-continental transitional organic-rich shale: a case study from the Shanxi formation in the eastern margin of the ordos basin. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 219, 111116. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2022.111116
He, Q., Dong, T., He, S., Zhai, G., Guo, X., Hou, Y., et al. (2020). Sedimentological and geochemical characterization of the Upper Permian transitional facies of the longtan formation, northern Guizhou province, southwest China: insights into paleo-environmental conditions and organic matter accumulation mechanisms. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 118, 104446. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104446
Jarvie, D. M., Hill, R. J., Ruble, T. E., and Pollastro, R. M. (2007). Unconventional shale-gas systems: the Mississippian barnett shale of north-central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment. AAPG Bull. 91 (4), 475–499. doi:10.1306/12190606068
Ji, W., Hao, F., Song, Y., Tian, J., Meng, M., and Huang, H. (2020). Organic geochemical and mineralogical characterization of the Lower Silurian longmaxi shale in the southeastern chongqing area of China: implications for organic matter accumulation. Int. J. Coal Geol. 220, 103412. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2020.103412
Jiang, S., Xu, Z., Feng, Y., Zhang, J., Cai, D., Chen, L., et al. (2016). Geologic characteristics of hydrocarbon-bearing marine, transitional and lacustrine shales in China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 115, 404–418. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.10.016
Kulga, B., and Ertekin, T. (2018). Numerical representation of multi-component gas flow in stimulated shale reservoirs. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 56, 579–592. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2018.06.023
Lai, J., Zhao, F., Xia, Z., Su, Y., Zhang, C., Tian, Y., et al. (2024). Well log prediction of total organic carbon: a comprehensive review. Earth-Science Rev. 258, 104913. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2024.104913
Liang, D., Guo, T., Chen, J., Bian, L., and Zhao, Z. (2009). Geochemical characteristics of four suits of regional marine source rocks, southern China (part 2). Mar. Pet. Geol., 1–15.
Liang, T., Zou, Y.-R., Zhan, Z.-W., Lin, X.-H., Shi, J., and Peng, P. A. (2020). An evaluation of kerogen molecular structures during artificial maturation. Fuel 265, 116979. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116979
Lin, L., Yu, Y., Zhai, C., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, G., et al. (2018). Paleogeography and shale development characteristics of the late Permian longtan formation in southeastern sichuan basin, China. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 95, 67–81. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.04.016
Liu, B., Mohammadi, M.-R., Ma, Z., Bai, L., Wang, L., Wen, Z., et al. (2023). Experimental investigation and intelligent modeling of pore structure changes in type III kerogen-rich shale artificially matured by hydrous and anhydrous pyrolysis. Energy 282, 128799. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.128799
Liu, S., Yang, Y., Deng, B., Zhong, Y., Wen, L., Sun, W., et al. (2021). Tectonic evolution of the sichuan basin, southwest China. Earth-Science Rev. 213, 103470. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103470
Liu, Y., Tang, X., Zhang, J., Mo, X., Huang, H., and Liu, Z. (2018). Geochemical characteristics of the extremely high thermal maturity transitional shale gas in the southern north china basin (SNCB) and its differences with marine shale gas. Int. J. Coal Geol. 194, 33–44. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2018.05.005
Loucks, R. G., Reed, R. M., Ruppel, S. C., and Hammes, U. (2012). Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores. AAPG Bull. 96 (6), 1071–1098. doi:10.1306/08171111061
Luo, Q., Xiao, Z., Dong, C., Ye, X., Li, H., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). The geochemical characteristics and gas potential of the longtan formation in the eastern sichuan basin, China. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 179, 1102–1113. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2019.04.101
Ma, X., and Guo, S. (2020). Study on pore evolution and diagenesis division of a Permian longtan transitional shale in southwest Guizhou, China. Energy Sci. and Eng. 9 (1), 58–79. doi:10.1002/ese3.813
Mango, F. D. (1987). An invariance in the isoheptanes of petroleum. Science 237 (4814), 514–517. doi:10.1126/science.237.4814.514
Mango, F. D. (1991). The stability of hydrocarbons, under the time-temperature,conditions of petroleum genesis. Nature 352 (6331), 146–148. doi:10.1038/352146a0
Mcmahon, T. P., Larson, T. E., Zhang, T., and Shuster, M. (2024). Geologic characteristics, exploration and production progress of shale oil and gas in the United States: an overview. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 51 (4), 925–948. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(24)60516-1
Mohaghegh, S. D. (2013). Reservoir modeling of shale formations. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 12, 22–33. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2013.01.003
Moreira, V. B., Lämmle, L., Torres, B. A., Donadio, C., and Perez Filho, A. (2024). Geomorphological evolution in transitional environments on the eastern Coast of Brazil. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 49 (14), 4679–4693. doi:10.1002/esp.5989
Niu, D., Sun, P., Bai, Y., Lei, X., Wang, Z., Tao, L., et al. (2023). An FR–IR model method for restoring the original organic geochemical parameters of high over-mature source rocks with types I and II kerogen in China. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 228, 211971. doi:10.1016/j.geoen.2023.211971
Ogbesejana, A. B., Liu, B., and Ostadhassan, M. (2021). Stable isotope geochemistry of the organic elements within shales and crude oils: a comprehensive review. Molecules 27 (1), 34. doi:10.3390/molecules27010034
O'neill, S. R., Jones, S. J., Kamp, P. J. J., Swarbrick, R. E., and Gluyas, J. G. (2018). Pore pressure and reservoir quality evolution in the deep Taranaki basin, New Zealand. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 98, 815–835. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.08.038
Pommer, M., and Milliken, K. (2015). Pore types and pore-size distributions across thermal maturity, eagle ford formation, southern Texas. AAPG Bull. 99 (09), 1713–1744. doi:10.1306/03051514151
Qiu, Z., Song, D., Zhang, L., Zhang, Q., Zhao, Q., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). The geochemical and pore characteristics of a typical marine–continental transitional gas shale: a case study of the Permian Shanxi Formation on the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin. Energy Rep. 7, 3726–3736. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2021.06.056
Rexer, T. F., Mathia, E. J., Aplin, A. C., and Thomas, K. M. (2014). High-pressure methane adsorption and characterization of pores in posidonia shales and isolated kerogens. Energy and Fuels 28 (5), 2886–2901. doi:10.1021/ef402466m
Rexer, T. F., Mathia, E. J., Aplin, A. C., and Thomas, K. M. (2020). Supercritical methane adsorption and storage in pores in shales and isolated kerogens. SN Appl. Sci. 2 (4), 780. doi:10.1007/s42452-020-2517-6
Rouquerol, J., Avnir, D., Fairbridge, C. W., Everett, D. H., Haynes, J. H., Pernicone, N., et al. (1994). Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 66 (8), 1739–1758. doi:10.1351/pac199466081739
Selley, R. C. (2012). UK shale gas: the story so far. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 31 (1), 100–109. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.08.017
Shengxiu, W., Jia, W., Yuelei, Z., Dahua, L., Weiwei, J., Jinxi, W., et al. (2021). Relationship between organic geochemistry and reservoir characteristics of the wufeng-longmaxi formation shale in southeastern chongqing, SW China. Energies 14 (20), 6716. doi:10.3390/en14206716
Shi, J., Jin, Z., Liu, Q., and Huang, Z. (2020). Lithofacies classification and origin of the Eocene lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary rocks in the jiyang depression, Bohai Bay basin, eastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 194, 104002. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104002
Shi, J., Shen, G., Zhao, H., Sun, N., Song, X., Guo, Y., et al. (2018). Porosity at the interface of organic matter and mineral components contribute significantly to gas adsorption on shales. J. CO2 Util. 28, 73–82. doi:10.1016/j.jcou.2018.09.013
Sun, Z., Wang, Y., Wei, Z., Zhang, M., Wang, G., Wang, Z., et al. (2017). Gas-containing properties and gas geochemical characteristics of sea-land transition phase shale-Take Shanxi formation shale in ordos basin as an example. J. China Univ. Min. Technol., 859–868. doi:10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000663
Tang, W., Tuo, C., Ma, S., Yao, Y., Liu, D., Yang, X., et al. (2024). Shale reservoir characterization and implications for the exploration and development of the Upper Permian wujiaping formation, longmen–wushankan area, eastern sichuan basin. Front. Earth Sci. 12, 1453098. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1453098
Tao, S., Tang, D., Xu, H., Liang, J., and Shi, X. (2013). Organic geochemistry and elements distribution in dahuangshan oil shale, southern junggar basin: origin of organic matter and depositional environment. Int. J. Coal Geol. 115, 41–51. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2013.05.004
Tessin, A., Bianchi, T. S., Sheldon, N. D., Hendy, I., Hutchings, J. A., and Arnold, T. E. (2017). Organic matter source and thermal maturity within the Late Cretaceous niobrara formation, U.S. Western interior. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 86, 812–822. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.06.041
Thommes, M., Kaneko, K., Neimark, A. V., Olivier, J. P., Rodriguez-Reinoso, F., Rouquerol, J., et al. (2015). Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 87 (9-10), 1051–1069. doi:10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Wang, E., Guo, T., Liu, B., Li, M., Xiong, L., Dong, X., et al. (2022). Lithofacies and pore features of marine-continental transitional shale and gas enrichment conditions of favorable lithofacies: a case study of Permian longtan formation in the lintanchang area, southeast of sichuan basin, SW China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 49 (6), 1310–1322. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(23)60351-9
Wang, G., Sun, M., Yi, Z., Zhou, L., Ye, J., and Tan, H. (2021). Geochemical and petrographic characterization of marine-continental transitional facies shale (qilian basin, China): origin of organic matter input, depositional environments and hydrocarbon generation potential. Front. Earth Sci. 9, 615208. doi:10.3389/feart.2021.615208
Wang, J., Shao, H., Zhang, Y., Jiang, Z., Gao, B., Li, L., et al. (2025). Multifractal characteristics of pore structure in the terrestrial shale reservoirs of the lianggaoshan formation in northeast sichuan basin and its geological significance. Front. Earth Sci. 13, 1505090. doi:10.3389/feart.2025.1505090
Wang, J., Zhang, J., Xiao, X., Chen, Y. N., and Han, D. (2024). Pore structure and fractal characteristics of inter-layer sandstone in marine–continental transitional shale: a case study of the Upper Permian longtan formation in southern sichuan basin, south China. Fractal Fract. 9 (1), 11. doi:10.3390/fractalfract9010011
Wang, L., Li, X., Chen, Y. N., Guo, W., Pei, X., Luo, C., et al. (2025). Identification and application of favorable lithofacies associations in the transitional facies of the Permian longtan formation in central and southern sichuan basin. Minerals 15 (3), 198. doi:10.3390/min15030198
Wang, P., Liu, Z., Li, X., Liu, H., Zhou, L., Xiao, X., et al. (2022). Development of the Upper Permian wujiaping shale in hongxing area, eastern sichuan basin, and its significance to shale gas enrichment. Oil Gas Geol., 1102–1114. doi:10.11743/ogg20220508
Wang, X., He, S., Jones, S. J., Yang, R., Wei, A., Liu, C., et al. (2019). Overpressure and its positive effect in deep sandstone reservoir quality of bozhong depression, offshore Bohai Bay basin, China. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng., 182. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106362
Wang, Y., Cheng, X., Fan, K., Huo, Z., and Wei, L. (2023). The paleoenvironment and mechanisms of organic matter enrichment of shale in the Permian taiyuan and Shanxi formations in the southern north China basin. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 11 (5), 992. doi:10.3390/jmse11050992
Wei, H., Yu, H., Wang, J., Qiu, Z., Xiang, L., and Shi, G. (2015). Carbon isotopic shift and its cause at the Wuchiapingian–Changhsingian boundary in the Upper Permian at the zhaojiaba section, south China: evidences from multiple geochemical proxies. J. Asian Earth Sci. 105, 270–285. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.011
Wei, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, J., and Shi, M. (2021). A study on the morphology of natural microfractures in marine and Continental transitional shale based on scanning electron microscopy image. Micron 148, 103105. doi:10.1016/j.micron.2021.103105
Wen, L., Luo, B., Sun, H., Zhang, B., Ming, Y., Chen, X., et al. (2024). Geological characteristics and resources potential of deep coal-rock gas reservoir in the Upper Permian longtan formation of the sichuan basin. Nat. Gas. Ind. 44 (10), 22–32. doi:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2024.10.002
Wu, J., Wang, H., Shi, Z., Wang, Q., Zhao, Q., Dong, D., et al. (2021). Favorable lithofacies types and genesis of marine-continental transitional Black shale: a case study of Permian Shanxi formation in the eastern margin of ordos basin, NW China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 48 (6), 1315–1328. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(21)60289-6
Xia, X., Chen, J., Braun, R., and Tang, Y. (2013). Isotopic reversals with respect to maturity trends due to mixing of primary and secondary products in source rocks. Chem. Geol. 339, 205–212. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.07.025
Yang, H., Lin, L., Chen, L., Yu, Y., Li, D., Tian, J., et al. (2021). Characteristics of mineralogy, lithofacies of fine-grained sediments and their relationship with sedimentary environment: example from the Upper Permian longtan formation in the sichuan basin. Energies 14 (12), 3662. doi:10.3390/en14123662
Yang, K., Zhang, B., Yao, Y., Yang, H., Zhang, H., Xiao, W., et al. (2022). Organic matter accumulation mechanism and characteristics in marine-continental transitional shale: a case study of the upper Permian Longtan Formation from the well F5 in Sichuan Basin, China. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 208, 109604. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109604
Yang, Y., Wen, L., Zhou, G., Zhan, W., Li, H., Song, Z., et al. (2023). New fields, new types and resource potentials of hydrocarbon exploration in sichuan basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 44 (12), 2045–2069. doi:10.7623/SYXB202312004
Yu, C., Zhang, B., Wu, S., and Hu, G. (2022). Impact of CO2 generated from coal-measure source rocks on physical properties of reservoirs — a case study of the sulige gas field in the ordos basin, northwest China. Interpretation 10 (3), SJ67–SJ76. doi:10.1190/int-2021-0224.1
Yu, Y., Deng, X., and Deng, Y. (2024). Diagenesis of marine-continental transitional shale from the Upper Permian longtan formation in southern sichuan basin, China. Open Geosci. 16 (1), 0696. doi:10.1515/geo-2022-0696
Zhan, Y., Lin, C., Ma, C., Han, W., Ma, P., and Li, G. (2023). Lithofacies characteristics and sweet spot distribution of lacustrine shale oil reservoirs: a case study of the second member of the kongdian formation in the cangdong sag, Bohai Bay basin. Minerals 13 (11), 1391. doi:10.3390/min13111391
Zhang, B., Wen, S., Yang, K., Ma, K., Wang, P., Xu, C., et al. (2023). Diagenetic evolution sequence and pore evolution characteristics: study on marine-continental transitional facies shale in southeastern sichuan basin. Minerals 13 (11), 1451. doi:10.3390/min13111451
Zhang, B., Yang, K., Cao, G., Deng, J., Xu, Z., Yao, Y., et al. (2024). The influence of different diagenesis on the elastic properties of different shale lithofacies: a case study of the Upper Permian wujiaping formation in east sichuan basin, China. Geomechanics Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resources 10 (1), 136. doi:10.1007/s40948-024-00858-7
Zhang, J., Li, X., Wang, Y., Fu, Q., Cai, Y., and Niu, H. (2015). Accumulation conditions and reservoir characteristics of marine-terrigenous facies coal measures shale gas from longtan formation in south sichuan basin. J. China Coal Soc. 40 (8), 1871–1878. doi:10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2015.0320
Zhang, J., Li, X., Wei, Q., Gao, W., Liang, W., Wang, Z., et al. (2017). Quantitative characterization of pore-fracture system of organic-rich marine-continental shale reservoirs: a case study of the Upper Permian longtan formation, southern sichuan basin, China. Fuel 200, 272–281. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2017.03.080
Zhang, M., Hu, M., Wei, S., Cai, Q., Fu, W., Shi, F., et al. (2023). Factors controlling the pore development of low-mature marine–continental transitional shale: a case study of the Upper Permian longtan shale, Western Guizhou, south China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 11 (10), 1862. doi:10.3390/jmse11101862
Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Guo, W., Li, Y., and Dang, H. (2020). Differential evolution and the influencing factors of low-maturity terrestrial shale with different types of kerogen: a case study of a Jurassic shale from the northern margin of qaidam Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 230, 103591. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2020.103591
Zhao, W., Zhang, B., Wang, X., Wu, S., Zhang, S., Liu, W., et al. (2021). Differences in source kitchens for lacustrine in-source and out-of-source hydrocarbon accumulations. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 48 (3), 541–554. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(21)60044-7
Zhuang, H., Jiang, Y., Li, X., Jiang, C., Li, S., and Wang, Z. (2025). Geochemical characteristics and organic matter accumulation mechanism of the Permian Shanxi formation transitional shale, eastern ordos basin: implications for paleo-weathering, provenance and tectonic setting. Front. Earth Sci. 12, 1384098. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1384098
Zolfaghari, A., Dehghanpour, H., and Holyk, J. (2017). Water sorption behaviour of gas shales: I. Role of clays. Int. J. Coal Geol. 179, 130–138. doi:10.1016/j.coal.2017.05.008
Zou, C., Dong, D., Wang, S., Li, J., Li, X., Wang, Y., et al. (2010). Geological characteristics and resource potential of shale gas in China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 37 (6), 641–653. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(11)60001-3
Zou, C., Dong, D., Wang, Y., Li, X., Huang, J., Wang, S., et al. (2016). Shale gas in China: characteristics, challenges and prospects (II). Petroleum Explor. Dev. Online 43 (2), 182–196. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(16)30022-2
Keywords: marine-continental transitional facies, longtan formation, shale lithofacies, pore features, lithofacies quality
Citation: Wang L, Li X, Chen Y, Zhan H, Pei X, Chen Y, Qi N, He W, Yu W, Lin Y and Zhou Y (2025) Reservoir heterogeneity in deep marine-continental transitional shales: the role of lithofacies and quality in the coal-bearing longtan formation, central Sichuan basin. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1650521. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1650521
Received: 20 June 2025; Accepted: 24 July 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Jianhua He, Chengdu University of Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Hongjian Zhu, Yanshan University, ChinaYongbin Niu, Henan Polytechnic University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Li, Chen, Zhan, Pei, Chen, Qi, He, Yu, Lin and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xizhe Li, bHh6NjlAcGV0cm9jaGluYS5jb20uY24=; Hongming Zhan, emhhbmhvbmdtaW5nMTdAbWFpbHMudWNhcy5lZHUuY24=
 Longyi Wang
Longyi Wang Xizhe Li1,2,3*
Xizhe Li1,2,3* Ya’na Chen
Ya’na Chen