- 1China Shenhua Group Zhungeer Energy Co., Ltd, Ordos, China
- 2State Key Laboratory for Geomechanics and Deep Underground Engineering, China University of Mining & Technology, Xuzhou, China
- 3School of Mechanics and Civil Engineering, China University of Mining & Technology, Xuzhou, China
To address the need for minimal permeability and adequate strength in the reconstructed aquiclude of open-pit coal mine waste dumps, we formulated a mudstone-slag-based waterproof composite (MSWC), incorporating mudstone, slag, waste rock, and an alkaline catalyst. Initial cyclic damage was emulated using uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading (UCLU), after which we conducted a series of tests on the MSWC, including penetration, uniaxial compression, SEM, and CT scans, to assess the impact of varying degrees of initial cyclic damage. We explored the MSWC’s mechanical attributes, stiffness, permeability, and pore structure across a range of UCLU cycles (N) and developed a damage constitutive model to interpret the damage parameters. Our findings indicate that as N cycles escalate, there is a marked exponential reduction in the MSWC’s uniaxial compressive strength, and stiffness. This is attributed to the progressive enlargement of microcracks and pores within the material, leading to a reduction in its overall strength. Specifically, the uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) dropped by 6.56%, 13.13%, and 16.49%, the stiffness by 9.46%, 12.43%, and 19.73%, and porosity rose from 1.62% to 2.31%, 2.56%, and 2.67%. Consequently, the MSWC is deemed suitable for use as an aquiclude and can be effectively implemented in such applications. These findings offer valuable insights for the ecological rehabilitation of open-pit coal mine waste dumps.
1 Introduction
With the increasing demand for energy in China, open-pit coal mining activities have had a significant impact on the surrounding environment (Jie et al., 2021; Guanghe et al., 2024). In particular, the mining activities have destroyed the original water barrier layer, coupled with the loose structure and strong permeability of the dumping materials, it is difficult to store water in the stratum, which leads to many challenges in the reclamation and greening of the dump site (Ma et al., 2021; Olena and Grygorii, 2024; Zine et al., 2024). In view of this, the reconstructed aquiclude of open-pit coal mine waste dump site may become a pivotal measure to solve the ecological restoration of the dump site.
In the aspect of the reconstructed aquiclude of the dump site, many scholars have conducted extensive research and discussion on this, and found that the reconstructed aquiclude can effectively solve the water storage problem faced by the open-pit coal mine dump site (Ma et al., 2021; Jun-Jie et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2018; Ding et al., 2019). Sun et al. (2021) proposed a new concept and method of using backfill mining technology to reconstruct key aquifers and analyzed the principle and reconstruction technology of reconstructing key aquifers in detail. However, the artificial construction of the water-resisting layer in the open-pit coal mine dump site requires a large number of raw materials, which is best to meet the characteristics of easy preparation and low cost. The mudstone is a natural aquifuge raw material (Huanyi et al., 2022; Iyare et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023), which is widely used in the preparation of aquifuge materials because of its wide existence in open-pit coal mines and its characteristics of fine mineral particles and low permeability. It has become a development trend for the reconstructed aquiclude with mudstone, slag (Chen et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2024), red mud (Zhou et al., 2020; Kumar et al., 2021), and fly ash (Chuah et al., 2016; Lan-Ping et al., 2020; Zeng et al., 2020). Zhou et al. (2020) used standard sand as aggregate, mudstone, slag, red mud, and other powder materials to prepare water barrier materials, and took the uniaxial loading level as the damage variable, focusing on the analysis of the permeability characteristics of mudstone-geopolymer material damage. Lei et al. (2024) combined the synergistic stabilization technology of microorganisms and geopolymers to use the best mixture of metakaolin and alkali activators to stabilize red-bed mudstone fillers. The compactness, pore characteristics, unconfined compressive strength, and disintegration of red-bed mudstone fillers were analyzed, and the mechanism of microorganisms-geopolymers was analyzed by SEM and EDS.
Due to the frequent dumping operations of mining trucks on the dump site, not only the ground dynamic load effect caused by the ground is significant (Wu et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2022), but also the cyclic load generated by the dump site causes a series of problems such as fatigue damage, permeability change, and strength reduction. In terms of the initial damage caused by cyclic loading, scholars pay more attention to coal specimens, rock specimens, concrete, and so on. Zhong et al. (2019) carried out cyclic load-unload tests of saturated coal specimens with different loading rates, amplitudes and numbers of uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading cycles (N).
This study reveals for the first time that the radial residual strain decreases gradually with the increase of N cycles. Based on the pore-scale mechanical analysis, the mechanism of pore water pressure affecting the macroscopic mechanical response by changing the microstructure integrity of coal samples is clarified. Zhang et al. (2023) addressed the coupled effects of cyclic loading and moisture content on sandstone by: studying cyclic stress-dependent changes in elastic modulus, Poisson’s ratio, and irreversible strain during loading phases; developing a Weibull distribution-based constitutive model integrating hydric and mechanical damage evolution pathways. Chen et al. (2021) proposed a Hoek-Brown-damage coupled constitutive model to characterize the residual strength evolution of fractured rocks. For rocks subjected to cyclic loading, Liu et al. (2016) formulated a damage model using energy dissipation thresholds; identified exponential growth of damage variable with strain accumulation.
In summary, there have been many achievements in mudstone-based aquiclude materials, but the evolution mechanism of strength and permeability characteristics of the reconstructed aquiclude under cyclic loading of equipment is still unclear. Therefore, in this study, MSWC was used to construct the aquiclude of an open-pit coal mine dump site, and UCLU tests were carried out on MSWC specimens to simulate the cyclic loading damage of artificial reconstructed aquiclude equipment. Penetration velocity test, uniaxial compression test, SEM test, and CT scanning test were carried out on the damaged MSWC specimens. In this way, the mechanical properties, elastic modulus (Yang et al., 2024), permeability characteristics, pore structure, and energy evolution characteristics of MSWC under initial damage of cyclic loading are studied, and the damage constitutive model of the MSWC is established. The findings offer operable guidance for the restoration of open-pit coal mine dump sites.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental materials
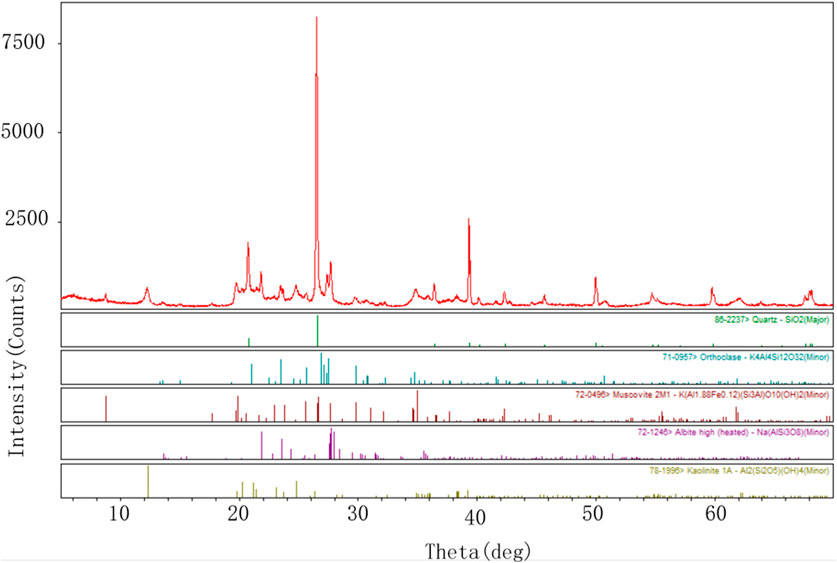
The MSWC specimens are primarily composed of mudstone, slag, waste rock aggregate, and an alkaline activator. An open-pit coal mine in Inner Mongolia provided the mudstone and waste rock aggregates used in this research. The mudstone is the byproduct of open-pit coal mining, while the waste rock aggregate consists of sandstone. For the slag component, we utilize S95 grade slag powder, which is mainly made up of CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3. Component analysis of the mudstone by performing XRD tests As shown in Figure 1, it can be seen that the mudstone, as a high-silicon aluminum material, has a composition of 77.10% and has a certain alkali-activated activity. Therefore, both mudstone and slag are employed as cementitious materials in this paper. The alkaline activator used is a sodium silicate solution with a modulus of 1.0, adjusted with NaOH, and the waste rock from the mining area serves as aggregate to prepare the MSWC.
2.2 Specimen preparation
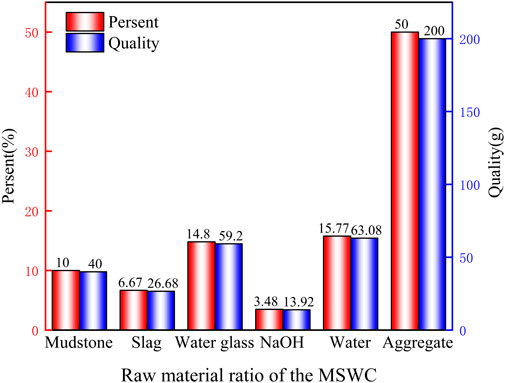
The average mass of MSWC specimens was 400 g, consisting of Mudstone, Slag, Water glass, NaOH, Water, Sandstone aggregate, and the content and mass of each component is shown in Figure 2, and the specimen preparation process is shown in Figure 3, after which the specimens were placed in a curing box with a humidity of 60% ± 2% and a temperature of 25 °C ± 2 °C for curing, and the curing ages (T) were 1 days, 3 days, 7 days, and 28 days. The specimens were taken out according to the curing age, and the specimens were processed into standard specimens of Φ50 × 100 mm according to the rock mechanical properties test standard.
2.3 Test scheme
1. HMTK600B mining truck has an approximate front and rear axle load distribution ratio of 0.33:0.67 when fully loaded, with each wheel bearing approximately 100.0 tons. The ground contact area is about 1.25 m × 0.42 m, resulting in a ground specific pressure of roughly 1.87 MPa. When unloaded, the front and rear axle load distribution ratio of HMTK600B mining truck is approximately 0.46:0.54. Each front wheel bears around 54.5 tons, with a ground contact area of 1.25 m × 0.35 m and a ground specific pressure of about 1.22 MPa. Each rear wheel carries approximately 32.0 tons, featuring a ground contact area of 1.25 m × 0.35 m and a ground specific pressure of roughly 0.72 MPa. The upper stress limit σmax in the single-axis cyclic loading and unloading test is determined to be 2 MPa, and the lower limit σmin is 0 MPa. According to the test requirements, the corresponding program is compiled. The uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading damage treatment of MSWC specimens is carried out by the TATW-2000 rock triaxial test system which is shown in Figure 4. The loading method is displacement loading, and the loading rate and unloading rate are 0.5 mm/min. The damage specimens of the MSWC under different numbers of N cycles are obtained. Uniaxial compression tests on damaged MSWC specimens to test their mechanical properties and energy evolution characteristics by the TATW-2000 rock triaxial test system.
2. The THMC multi-field coupled seepage test system is used to carry out gas injection permeability test on the damaged MSWC specimens, to obtain the permeability of MSWC under different damage conditions, and the confining pressure for the permeability test was set to 2 MPa, and the THMC multi-field coupled seepage test system is shown in Figure 5. To systematically study the influence of the number of damages on the permeability of the water barrier material, and to combine with the SEM test to analyze the characteristics of the different gelation products, to reveal the fine-scale mechanism for the permeability characteristics of the MSWC evolution.
3. The CT scanning test of the waterproof material is carried out by the Nano Voxel 3502E open tube transmission CT system which is shown in Figure 6. The damaged specimen was scanned using a CT scanning system to generate images, and AVIZO software was employed to reconstruct the CT scan images, resulting in a three-dimensional damage map of the specimen. This enables intuitive analysis of the pore structure and porosity variation of the MSWC specimen, as well as the permeability variation law of the MSWC specimen over N cycles. In this SEM test, the VEGA3 scanning electron microscope is used to determine the fine-scale characteristics of mudstone-slag-based water barrier materials with different mudstone occupancies and different numbers of uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading, and the instrumentation is shown in Figure 7.
4. The energy evolution, stress-strain curve, and elastic modulus of the MSWC under different N cycles are obtained by uniaxial compression test, and used to define the damage variables. The rock damage constitutive model is established by the characteristic that the microelement strength of the MSWC obeys the Weibull distribution.
3 Results and discussions
3.1 Analysis of mechanical properties of the MSWC under initial damage effect of cyclic loading
To study the influence of N cycles on the mechanical properties of the MSWC, the MSWC with a curing age of 7 days are analyzed and studied. According to the slope of the elastic deformation stage of stress-strain curve of MSWC specimens, the elastic modulus of the MSWC under different N cycles is calculated.
3.1.1 The variation of mechanical properties of the MSWC with N cycles
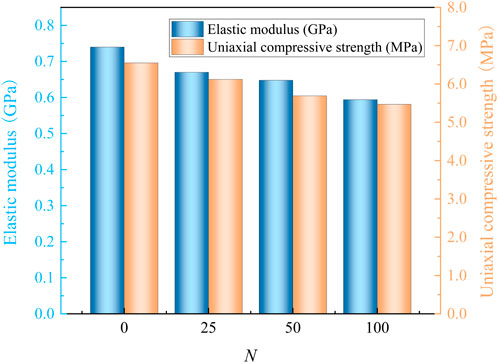
In order to study the variation law of mechanical properties of MSWC specimens under different N cycles, the variation curves of UCS and elastic modulus of the MSWC with N cycles are obtained, as shown in Figure 8.
From the diagram, it can be seen that the change rule of the elastic modulus of MSWC specimens is similar to that of UCS. When the number of N increases from 0 to 25, 50, and 100 times, both the UCS and elastic modulus of MSWC specimens decrease exponentially. The UCS is reduced by 6.56%, 13.13%, and 16.49%, and the elastic modulus is reduced by 9.46%, 12.43%, and 19.73%. During the initial phase of the UCLU experiment, the specimen undergoes cyclic loading that induces structural deterioration. This progressive damage mechanism facilitates pore nucleation within the material matrix, consequently diminishing its strain-resistance capacity. With the increase of N, new cracks and pores are generated inside, and its porosity increases. Its strength gradually decreases, and then the internal damage tends to be saturated, resulting in its UCS gradually approaching a threshold.
3.1.2 Energy evolution characteristics of the MSWC with N cycles
To accurately describe the energy evolution characteristics of MSWC specimens during loading, the energy evolution curves and stress-strain curves of each part are drawn as shown in Figure 9.
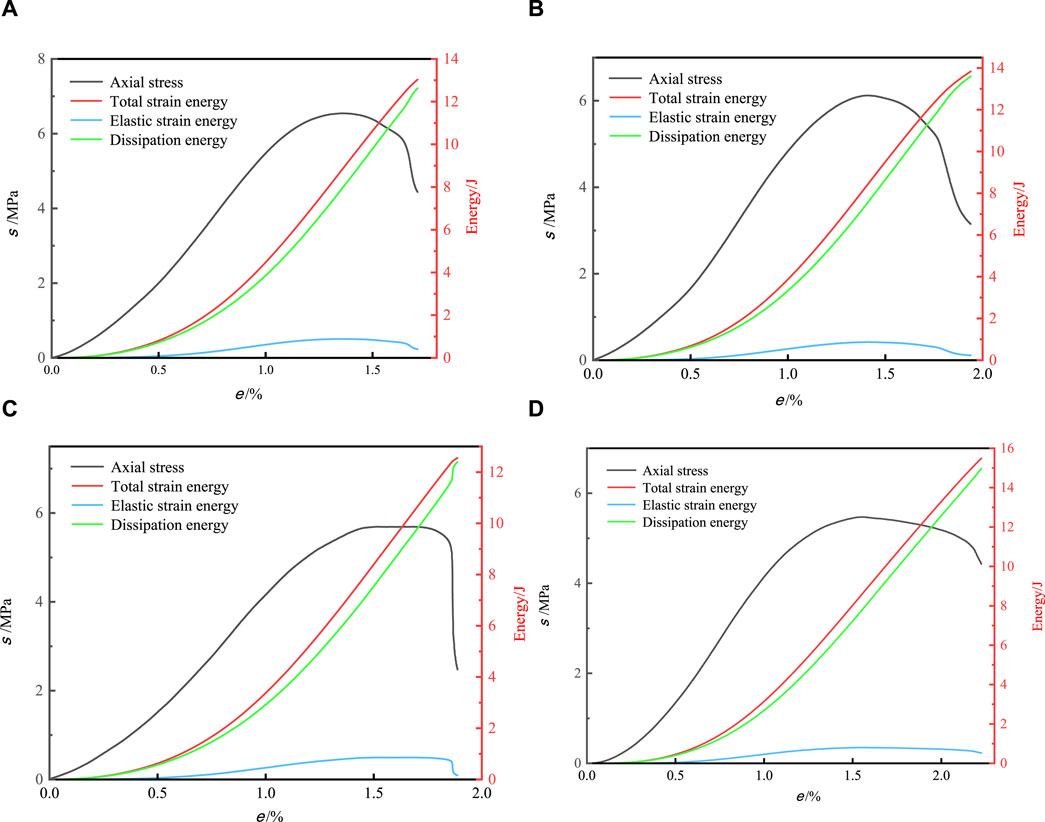
Figure 9. Energy evolution curve of the MSWC under different N. (a) N = 0. (b) N = 25. (c) N = 50. (d) N = 100.
It can be seen from Figure 9 that as N cycles increase, the energy of each part of MSWC specimens gradually decreases. Because the UCLU test causes damage to the interior of MSWC specimens, the energy storage limit of the MSWC specimen gradually decreases. Therefore, with the increase of N cycles, the energy storage limit of the MSWC specimen gradually decreases.
3.2 The permeability and internal structure characteristics of the MSWC under the initial damage effect of cyclic loading
3.2.1 The variation of the MSWC permeability with N cycles
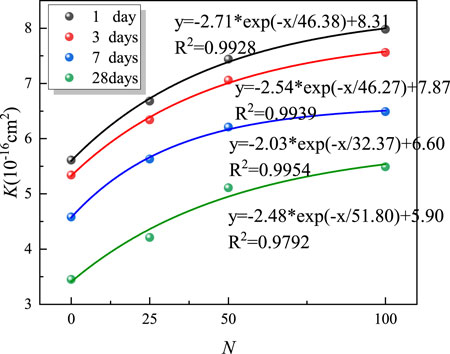
The permeability of the MSWC is a critical indicator for evaluating its effectiveness as a waterproofing layer material. Under different curing ages, the average permeability of the material varies with the number of damage cycles, and the corresponding variation pattern is illustrated in Figure 10.
It can be seen that under the curing age of 1 day, the permeability increased by 19.07%、32.62% and 42.25%, respectively, with the increase of N cycles from 0 to 25, 50, and 100 times. Under the 3-day curing age, the permeability increased by 18.73%、32.21% and 41.57%, respectively. Under the 7-day curing age, the permeability increased by 22.92%、35.59% and 41.70%, respectively. At the 28-day curing age, the permeability increased by 22.03%、48.12% and 59.13%, respectively. Under different curing ages, the variation law of the permeability of MSWC specimens is similar. With the increase of N cycles, the damage inside MSWC specimen gradually accumulates, the porosity of the specimen increases, and the permeability shows an exponential increase trend. With the increase of N cycles, the internal damage gradually tends to be stable, and finally, the permeability gradually tends to be gentle. When the permeability of rock materials is less than 1 × 10−15 cm2, they are considered low-permeability materials. In this study, the damaged MSWC all meet the permeability requirements for reconstructed water-resisting layers.
The primary influence of the number of uniaxial cyclic loading-unloading cycles on the permeability of MSWC can be summarized as follows: In the initial undamaged state, the material contains minimal inherent pores and microcracks formed during its structural formation. As the number of cyclic loading-unloading cycles increases, new pores and microcracks develop under cyclic stress. These internal fractures gradually interconnect, resulting in severe structural damage and a rapid increase in porosity, which consequently leads to a significant enhancement in material permeability. When the number of loading-unloading cycles exceeds 50, the cumulative damage caused by cyclic loading gradually approaches saturation. Concurrently, the porosity of the mudstone-slag-based water-resistant material stabilizes, and its permeability progressively converges toward a threshold value.
3.2.2 Analysis of pore structure of the MSWC under initial damage effect of cyclic loading
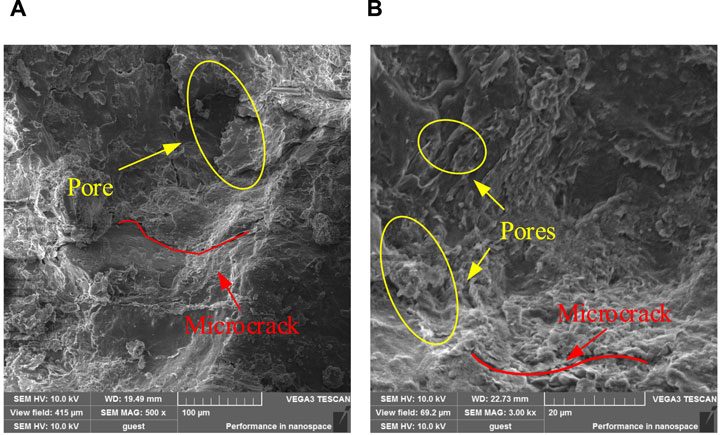
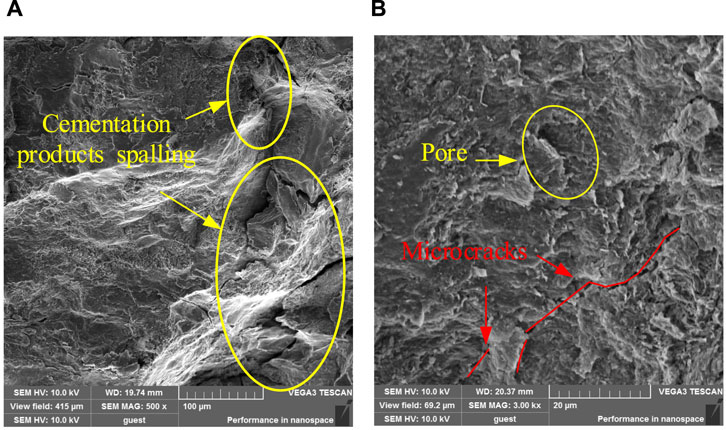
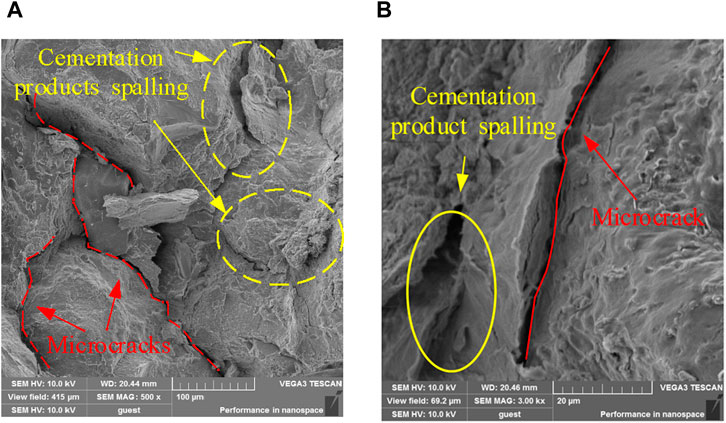
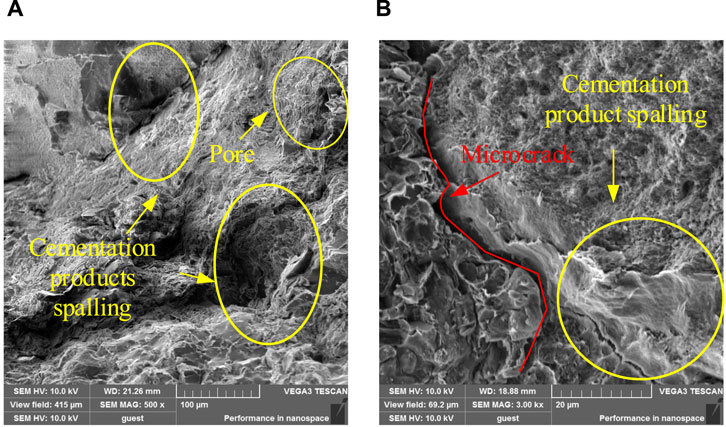
SEM tests with magnifications of 500 × and 3,000 × were carried out on the MSWC with N cycles of N = 0, 25, 50, and 100 to study the effects of different N cycles on the meso-structure of the MSWC, as shown in Figures 11–14. At 0th cycle, there are a small amount of pores and microcracks. Because there is no uniaxial cyclic damage, the MSWC specimen is the initial shape, the section is smooth, and the whole is smooth and relatively intact. At this time, the permeability of the MSWC is low. At 25th cycle, new pores and microcracks appear. Due to the application of cyclic load damage, the primary pores and cracks further develop under the influence of external load, and the section is relatively rough. At this time, the permeability of the MSWC is enhanced. At 50th cycle, the further application of uniaxial cyclic damage leads to the generation and penetration of new pores and microcracks, and the cross-section is rough. The permeability of the MSWC is enhanced, and the water-proof performance is decreased. At 100th cycle, under the continuous influence of external load, the internal damage of the MSWC specimen is serious due to the penetration of pores and cracks. The permeability of MSWC specimen is enhanced, and the water-resisting property is reduced.
3.2.3 Porosity analysis of the MSWC under initial damage effect of cyclic loading
CT scanning tests were carried out on MSWC specimens with N = 0, 25, 50, and 100 times. The variation law of internal pores and internal damage are observed intuitively by three-dimensional reconstruction technology, and the reconstructed specimen is shown in Figure 15. Through three-dimensional reconstruction technology, the internal pore structure and porosity of the MSWC under different N cycles can be obtained. When the number of N cycles increases from 0 to 25, 50, and 100 times, the porosity increases from 1.62% to 2.31%, 2.56%, and 2.67%, respectively. It can be seen that as N cycles increase, the porosity increases exponentially. The pores and crushed zones in MSWC specimens are predominantly located near the two ends of the specimen, indicating the presence of stress concentration phenomenon.
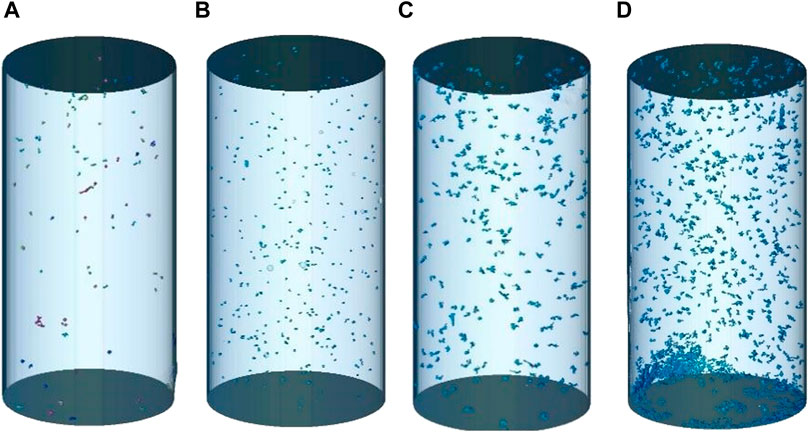
Figure 15. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the MSWC with d N cycles. (a) N = 0. (b) N = 25. (c) N = 50. (d) N = 100.
The permeability of MSWC specimens can be directly reflected by their porosity. As the number of cyclic loading-unloading increases, the internal porosity of MSWC specimens rises, leading to a corresponding gradual enhancement in permeability. With the generation of internal gelation products and the progressive development of pores within the specimens, as the gelation reactions gradually complete and the pores approach saturation during testing, the porosity of the specimens progressively stabilizes in an equilibrium state. Consequently, the permeability ultimately reaches a balanced threshold state.
3.3 Damage constitutive model of the MSWC
3.3.1 Damage changes in MSWC after uniaxial cyclic load-unload
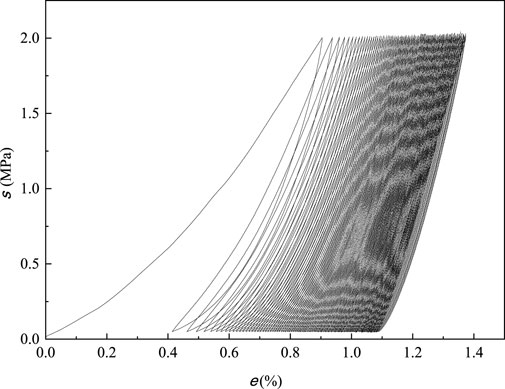
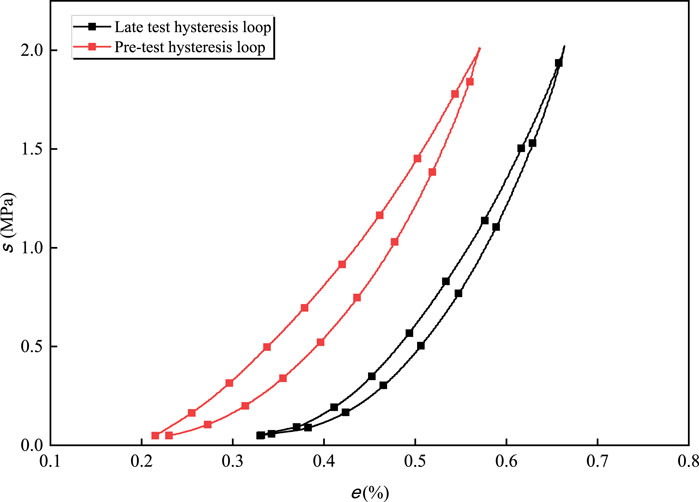
The cyclic load-unload curve of the specimen with a curing age of 7 days is selected for analysis. As shown in Figure 16, with the increase of N cycles, the total strain of the specimen gradually increases, and the resulting stress-strain hysteresis loop moves in the positive direction of strain. The hysteresis loop is relatively loose around the first 25 times, and then gradually becomes dense with the increase of N cycles. This is because the axial deformation of the specimen at the initial stage of the cycle is large, the specimen is gradually compacted, and the original void is sealed. As N cycles increases, the hysteresis loop becomes narrower To distinguish between the early hysteresis loop and the late hysteresis loop, two examples were selected for comparison, as shown in Figure 17.
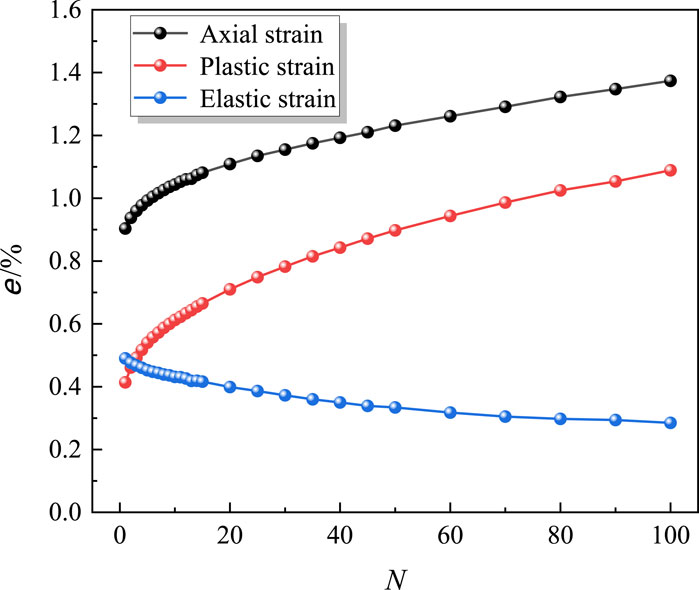
The plastic strain and elastic strain of the specimen under different N cycles are analyzed. As shown in the Figure 18 diagram, the plastic strain and axial strain change with N cycles are basically the same. Under the first cycle, due to the existence of the compaction stage, a large residual strain and axial strain will be generated, which will increase with the increase of N cycles, and finally become more and more gentle. The cumulative residual plastic strain of the 1st, 25th, 50th and 100th cycle are 0.0041, 0.0075, 0.0090 and 0.0109, respectively, accounting for 37.61%, 68.81% and 82.57% of the total residual plastic strain.
3.3.2 Establishment of the constitutive model of the MSWC
A large number of cracks and pores are generated inside the specimen under cyclic loading. Therefore, the damage variable (D)is defined as Equation 1:
Since the damaged area is difficult to measure, in order to be able to calculate its area indirectly, according to Lemaitre’s strain equivalence theory as Equation 2:
According to the Weibull distribution of the micro-unit strength, D can be expressed as (Zhi-Liang et al., 2007) (Equation 3):
The constitutive equation can be obtained as Equation 4:
In the formula, S′ is the area of the damaged part of the MSWC specimen, m2; S is the total cross-sectional area of the MSWC specimen, m2; ε is the strain tensor, is the effective stress tensor, MPa; E* is the effective elastic modulus, MPa; E is the elastic modulus of mudstone-slag-based water-resisting material, MPa; * is the nominal stress tensor, MPa; P(ε) is the micro-element strength distribution function; ε is a certain strain level; and ε0 are Weibull distribution parameters respectively.
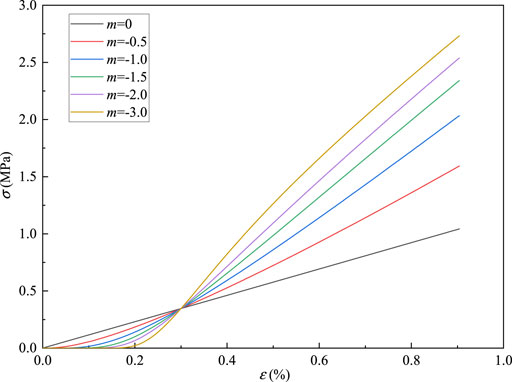
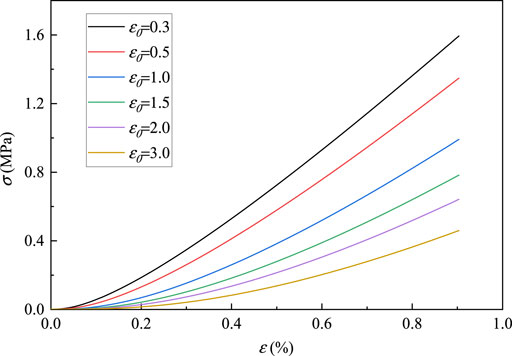
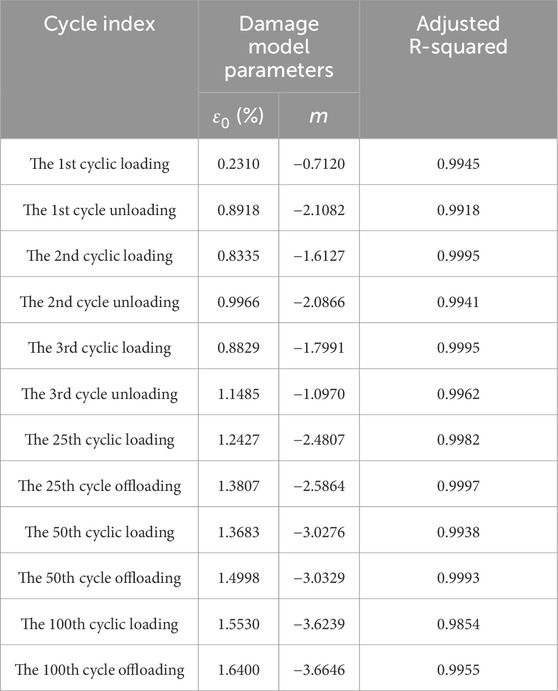
The sensitivity of the parameters ε0 and m of the cyclic load-unload damage constitutive model is analyzed. According to established damage constitutive model, when ε0 is unchanged, take m = 0, −0.5, −1, −1.5, −2, −3, the curve is shown in Figure 19. It can be found that the curves intersect at one point, and the stress value of the intersection is 0.35 MPa. When the stress is less than 0.35 MPa, the greater the absolute value of m, the slower the stress growth rate. When the stress is greater than 0.35 MPa, the greater the absolute value of m, the faster the stress growth rate. It shows that m is related to the concentration degree of the micro-unit strength distribution. The greater the absolute value of m, the higher the concentration degree, the more initial defects in the early stage, and the longer the compaction stage. When m is constant, take ε0 = 0.3, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0%, as shown in Figure 20 as ε0 increases, the smaller the stress growth rate, the lower the strength, the greater the ductility, the smaller the brittleness, the greater the degree of damage, indicating that the parameter ε0 is related to the macroscopic average strength of the material, the larger the parameter ε0, the lower the macroscopic average strength. Specific data are shown in table 1.
In order to verify the accuracy of the damage constitutive equation, the stress-strain curve of the UCLU test is used as the control group for parameter fitting and verification, and the curve of the specimen is obtained. The experimental value and the theoretical model calculation results are compared.
From Figure 21, it can be seen that the stress-strain curve obtained by the axial stress damage constitutive model of the specimen is similar to the experimental value, and the fitting degree of each cyclic loading and unloading curve is above 0.98. Therefore, the damage constitutive model of the MSWC proposed in this paper can effectively describe the whole process of damage of the MSWC under different N cycles, and accurately reflect the damage constitutive relationship of different N cycles.
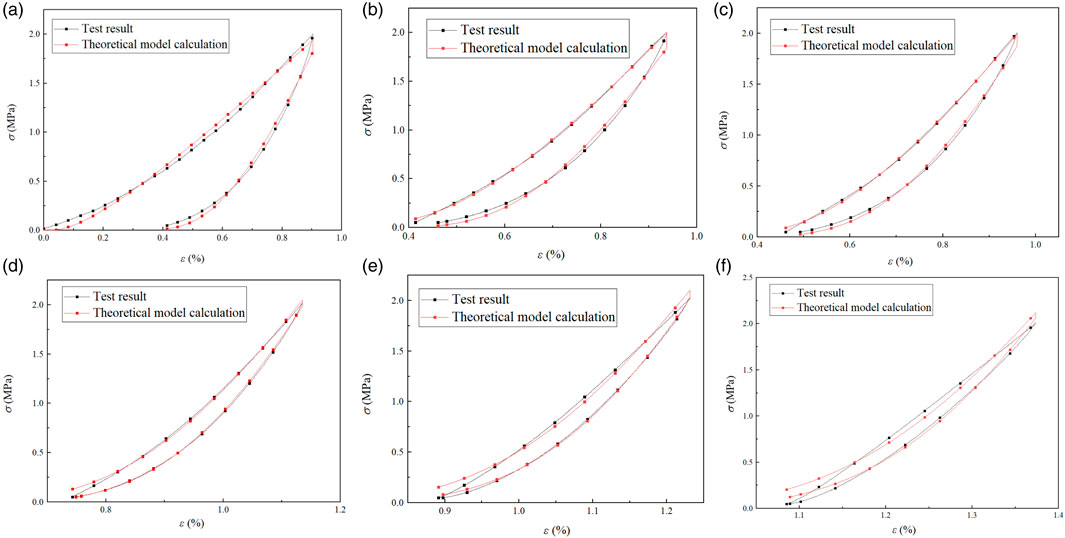
Figure 21. Hysteresis loop curves and theoretical model calculation curves under different cycle numbers. (a) The first cycle. (b) The second cycle. (c) The third cycle. (d) The 25th cycle. (e) The 50th cycle. (f) The 100th cycle.
4 Conclusion
A kind of low permeability high-strength geopolymer material, mudstone-slag-based waterproof material, was prepared, and the mechanical properties and permeability characteristics were tested by cyclic loading and unloading damage on MSWC specimens, and uniaxial compression test and permeability test were carried out on the damaged specimens to construct the mechanical model of damage loading and unloading damage.
1. At the beginning of the uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading test, the test is subjected to cyclic damage, and pores are generated inside, resulting in a decrease in its anti-deformation ability. With the increase of the number of uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading, the energy storage limit and bearing capacity of the MSWC gradually decrease, the porosity increases, the degree of cumulative damage increases, and the rate of decrease in elastic modulus gradually slows down, and gradually tends to a certain threshold.
2. It can be seen from the SEM test that the slag cementitious product has obvious brittleness and high strength, and the mudstone cementitious product has obvious plastic characteristics and low strength. With the increase of t N cycles, the micro-cracks and pores inside the specimen gradually increase, and the strength of the MSWC decreases, and the permeability increases.
3. The three-dimensional reconstruction of the CT test scan shows that under the condition of UCLU test damage, due to the obvious brittleness characteristics of the slag cementitious product, the plastic characteristics of the mudstone cementitious product are obvious. The permeability of the specimen progressively increases with the accumulation of cyclic loading-unloading cycles, ultimately converging toward a threshold value as internal damage intensifies.
4. According to the Weibull distribution and Lemaitre strain equivalence theory, the damage constitutive model of the MSWC is established. The fitting degree of each cyclic load-unload curve is above 98%, which can effectively describe the whole process of damage of the MSWC under different N cycles, and accurately reflect the damage constitutive relationship of different N cycles. The physical meaning of the damage model parameters is determined.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
GW: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YC: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XC: Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LK: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the Ordos major science and Technology program (select the best candidates to undertake key research projects) (JBGS-2023-003), the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Science and Technology Major Program (No. 2023A01002).
Conflict of interest
Author GW was employed by China Shenhua Group Zhungeer Energy Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Chen, Z., Jiang-Shan, L., Bao-Jian, Z., Sharma, U., and Poon, C. S. (2018). Compressive strength and microstructural properties of dry-mixed geopolymer pastes synthesized from GGBS and sewage sludge ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 182, 597–607. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.06.159
Chen, Y., Lin, H., Wang, Y., Xie, S., Zhao, Y., and Yong, W. (2021). Statistical damage constitutive model based on the Hoek–Brown criterion. Archives Civ. Mech. Eng. 21 (3), 117. doi:10.1007/s43452-021-00270-y
Chen, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., and Chen, T. (2024). Mechanical properties and penetration characteristics of mudstone slag-based waterproof composites under cyclic loading. Appl. Sci. 14, 198. doi:10.3390/app14010198
Chuah, S., Duan, W. H., Pan, Z., Hunter, E., Korayem, A., Zhao, X., et al. (2016). The properties of fly ash based geopolymer mortars made with dune sand. Mater. and Des. 92, 571–578. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2015.12.070
Ding, X., Shi, X., Zhou, W., and Luan, B. (2019). Experimental study on the permeability of a soil-rock mixture based on the threshold control method. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019 (1), 8987052. doi:10.1155/2019/8987052
Guanghe, L., Zihuan, H., Dong, W., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Zhao, L., et al. (2024). Instability mechanisms of slope in open-pit coal mines: from physical and numerical modeling. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 34, 1509–1528. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2024.10.003
Huanyi, Z., Fu, H., Chen, C., Yang, J., Wang, H., Zhu, X., et al. (2022). The use of eco-friendly lignin as a cementitious material to improve the engineering properties of disintegrated carbonaceous mudstone. Constr. Build. Mater. 359, 129456. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129456
Iyare, U. C., Blake, O. O., Frash, L. P., Carey, J. W., Jones, D., and Ramjarrie, K. (2023). Water-weakening effects on the failure behavior of mudstones. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 56 (12), 9171–9185. doi:10.1007/s00603-023-03544-4
Jie, D., Xu, X., and Guo, F. (2021). The future of coal supply in China based on non-fossil energy development and carbon price strategies. Energy 220, 119644. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2020.119644
Jun-Jie, W., Huang, S., Wen, Y., Yang, Y., and Liu, M. W. (2017). Experimental study on interaction between compressibility and permeability of a crushed sandstone–mudstone particle mixture. Mar. Georesources and Geotechnol. 35, 670–677. doi:10.1080/1064119x.2016.1216206
Kumar, A., Jothi, S. T., Kunal, B., and Kabeer, K. S. A. (2021). A review on the utilization of red mud for the production of geopolymer and alkali activated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 302, 124170. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124170
Lan-Ping, Q., Yan-Shuai, W., Yazan, A., and Dai, J. G. (2020). Experimental study on full-volume fly ash geopolymer mortars: sintered fly ash versus sand as fine aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 263, 121445. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121445
Lei, C., Huafeng, D., Jianlin, L., Xiong, Y., Xiao, Y., Zhu, W., et al. (2024). Synergistic stabilization of red-bedded mudstone with microbial-geopolymer: an experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 441, 137503. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.137503
Liu, X. S., Ning, J. G., Tan, Y. L., and Gu, Q. (2016). Damage constitutive model based on energy dissipation for intact rock subjected to cyclic loading. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 85, 27–32. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.03.003
Ma, L., Liu, C., Bi, Y., Peng, S., Jiang, K., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Experimental study on impermeability law of aquiclude reconstructed by mudstone of external dump in arid zone. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021 (1), 5561794. doi:10.1155/2021/5561794
Olena, H., and Grygorii, G. (2024). Coal mining and water resources: impacts, challenges, and strategies for sustainable environmental management. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1348 (1), 12017. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/1348/1/012017
Sun, Q., Zhang, J., Zhou, N., and Huang, Y. (2021). Key aquiclude strata reconstruction and fluid–solid coupled deformation mechanism study for backfill coal mining. Mine Water Environ. 40 (3), 793–802. doi:10.1007/s10230-021-00786-y
Wang, S., Zhu, W., Kang, F., Xu, C., and Zhang, N. (2018). Study on non-darcian flow sand-clay mixtures. Appl. Clay Sci. 151, 102–108. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2017.10.028
Wu, H., Bai, H., Chen, Y., Pu, H., and Zhang, K. (2020). Mechanical properties and damage in lignite under combined cyclic compression and shear loading. Sustainability 12, 8393–21. doi:10.3390/su12208393
Wu, H., Chen, Y., Lv, H., Xie, Q., and Gu, J. (2022). Stability analysis of rib pillars in highwall mining under dynamic and static loads in open-pit coal mine. Int. J. Coal Sci. and Technol. 9 (1), 38. doi:10.1007/s40789-022-00504-1
Yang, G., Chen, Y., Liu, X., Yang, R., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, J. (2023). Stability analysis of a slope containing water-sensitive mudstone considering different rainfall conditions at an open-pit mine. Int. J. Coal Sci. and Technol. 10 (1), 64. doi:10.1007/s40789-023-00619-z
Yang, G., Chen, Y., Xie, Q., Wu, P., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Physical and mechanical characteristics deterioration and crack evolution of sandy mudstone in an open-pit mine under multiple freeze–thaw cycles. Geomechanics Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resources 10 (1), 87. doi:10.1007/s40948-024-00808-3
Zeng, L., Hui-cong, Y., Qian-feng, G., and Bian, H. b. (2020). Mechanical behavior and microstructural mechanism of improved disintegrated carbonaceous mudstone. J. Central South Univ. 27 (7), 1992–2002. doi:10.1007/s11771-020-4425-8
Zhang, Z., Xiao-lou, C., Yang, K., Lyu, X., and Wang, Y. (2023). Studies on the deformation and macro–micro-damage characteristics of water-bearing sandstone under cyclic loading and unloading tests. ACS Omega 8 (22), 19843–19852. doi:10.1021/acsomega.3c01750
Zhi-Liang, W., Yong-Chi, L., and Wang, J. G. (2007). A damage-softening statistical constitutive model considering rock residual strength. Comput. and Geosciences 33 (1), 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2006.02.011
Zhong, C., Zhang, Z., Gamage, R. P., Lu, Y., and Choi, X. (2019). The role of pore water plays in coal under uniaxial cyclic loading. Eng. Geol. 257, 105125. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.05.002
Zhou, W., Shi, X., Xiang, L., Qi, C., Luan, B., and Liu, F. (2020). The mechanical and microstructural properties of refuse mudstone-GGBS-red mud based geopolymer composites made with sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 253, 119193. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119193
Keywords: uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading, permeability, constitutive equation, porosity, energy evolution
Citation: Wang G, Chen Y, Cao X, Kong L and Zhang Y (2025) Constitutive model and permeation evolution characteristics of mudstone-slag-based waterproofing composites considering cyclic damage. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1654026. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1654026
Received: 25 June 2025; Accepted: 09 September 2025;
Published: 21 October 2025.
Edited by:
Lidong Dai, Chinese Academy of Sciences, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Wang, Chen, Cao, Kong and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuanguang Chen, eXVhbmd1YW5nY2hlbkBjdW10LmVkdS5jbg==
 Guilin Wang1
Guilin Wang1 Yuanguang Chen
Yuanguang Chen