- 1School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China
- 2Fujian Institute of Geological Survey, Fuzhou, China
- 3State Key Laboratory of Deep Petroleum Intelligent Exploration and Development, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 4Information Center of Ministry of Natural Resources, Beijing, China
The Makeng-type Fe–polymetallic deposits in the southwestern Fujian constitute one of the most economically significant iron-polymetallic metallogenic belts of southeastern China. The Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit in Yongding County is an representative example of the Makeng-type iron–polymetallic deposits. With the progress in mining and exploration, the priority has transferred to deep and peripheral orebodies. However, the lack of high-precision ground magnetic survey, especially for the surrounding area of the Dapai deposit, constrains our understanding of its prospecting potential and further exploration orientation. Based on previous studies and an analysis of ore-controlling factors, in this study, we performed a high-precision magnetic ground survey in the Dapai deposit’s surrounding area. The reduction to the pole, upward continuation, total horizontal derivatives and magnetization vector inversion with an unstructured tetrahedral mesh were conducted on the magnetic anomaly results. The structure framework and favorable prospecting area were consequently inferred. Both of the resulting anomalies and three-dimensional inversion showed a trend extending northwards. The results were verified by borehole, revealing multi-layer ore bodies and ore-related intrusions with strong alteration below. The magnetic anomaly features, ore-controlling characteristics, and drilling results indicated that there is potential for prospecting in deeper and more peripheral positions. Based on geological and geophysical characteristics, we proposed a comprehensive prospecting model and summarized an exploration method for the Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit, which enables prospecting the deeper and surrounding areas of the Dapai deposit and provides a basis for investigations of similar Makeng-type iron–polymetallic deposits in this area.
1 Introduction
The Southwestern Fujian Depression Belt (SFDB), located in the southeastern part of the South China Block (SCB), straddles the superimposed part of the Tethyan tectonic domain and the Pacific tectonic domain (Wu et al., 2000). Owing to its unique position, the SFDB has experienced prolonged and complex tectonic evolution, therefore significant magmatism and mineralization have developed within it (Wu et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2021). Makeng-type iron deposits are located in the SFDB and include the Makeng, Dapai, Yangshan, Luoyang and Pantian deposits, which are some of the most economically important iron deposits in the southeastern coastal area of China (Figure 1; Zhang et al., 2021; Vatuva et al., 2023). It is known that orebodies generally occur within Lower Carboniferous–Middle Permian carbonate and clastic sequences with stratiform or stratoid patterns (Zhao et al., 1980; Wang et al., 1982; Liang et al., 1982).
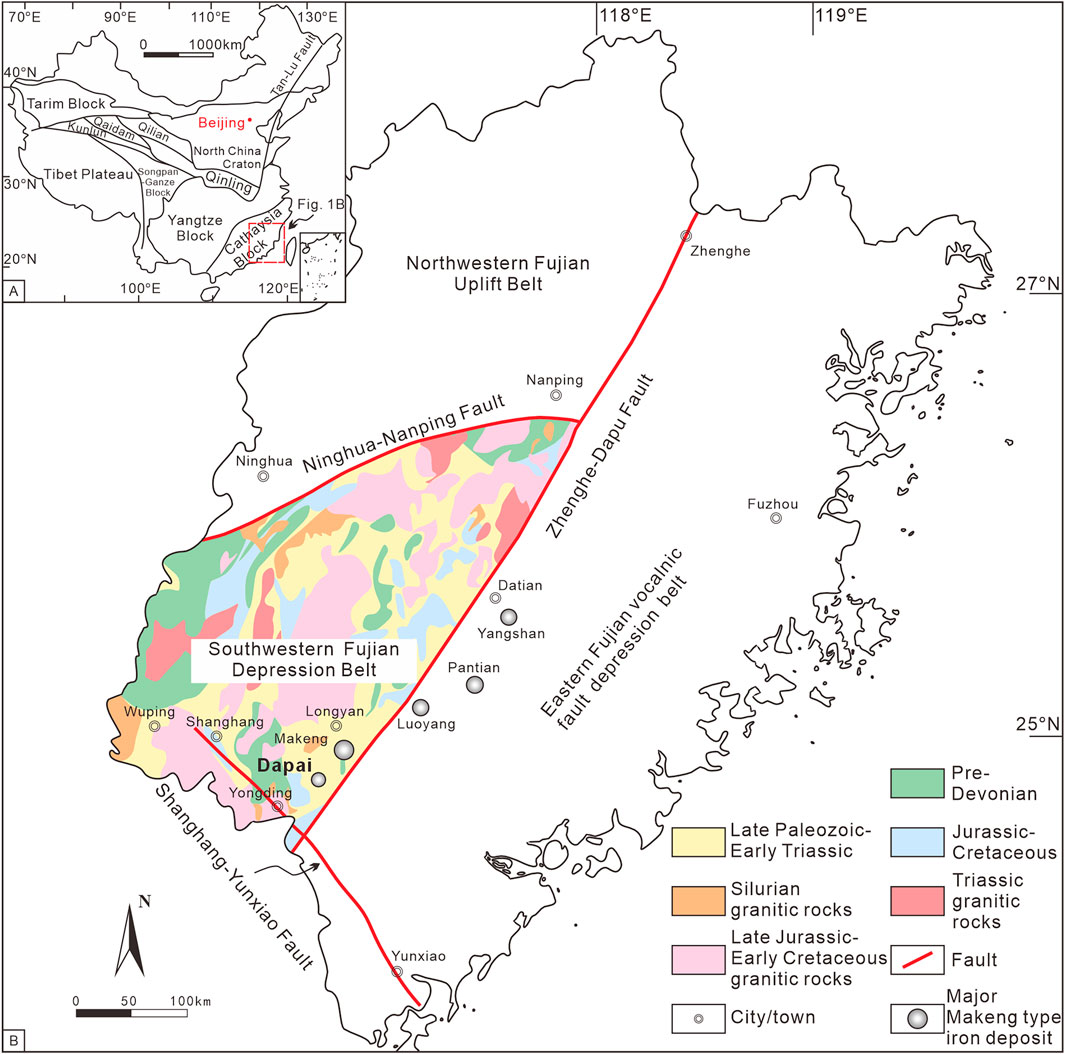
Figure 1. (A) Simplified tectonic map of China showing the location of the study area (modified after Li et al., 2016). (B) Simplified regional geological map of the Southwestern Fujian Depression Belt, showing the distribution of the major Makeng-type iron deposits (modified after FJIGS, 2016).
The Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit, as a typical Makeng-type iron deposit, has aroused widespread attention. Many researches on its ore-forming mechanism or ore-controlling factors have been carried out. The different viewpoints regarding on the ore genesis model of the Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit include: 1) or strata-bound skarn deposits (Xu et al., 2008; Yuan et al., 2014; Feng et al., 2015); 2) strata-bound–skarn-porphyry-type composite deposits (Zhao et al., 2016; Zhao et al., 2021); 3) deposits characterized by a marine volcanic sedimentary origin with hydrothermal reworking (Ni, 2012). Despite the disputes relating to the ore genesis, previous studies on the mineralization and diagenetic age of the Dapai deposit indicate that the Dapai deposit was formed during the Mesozoic (Zhao et al., 2016; Vatuva et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023). Besides, there is a general consensus that the ore bodies of the Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit are closely controlled by the thrusting structures and intrusions (Xu et al., 2008; Ni, 2012; Zhang et al., 2021).
With the progress in mining and exploration in recent years, there is increasing demand for an expanded prospecting techniques to discover concealed ore bodies all over the world (Kreuzer et al., 2020; Su et al., 2023; Xue et al., 2024a; Xue et al., 2024b; Xue et al., 2024c; Mahdi et al., 2025). Comprehensive geophysical exploration plays a crucial role in detecting the concealed ore bodies (Di et al., 2021; Xue et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2024). As a consequence, several geophysical methods have been applied in the Dapai deposit, including aeromagnetic surveys, 2D seismic reflection and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric (CSAMT) method, to analyze the deep structure characteristics, potential intrusions and ore bodies (Liu et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2018; Wang and Meng, 2019; Meng et al., 2021). Among these methods, magnetic prospecting has been widely used in metallic deposit exploration and to detect concealed structures because of its efficiency and convenience (Yan et al., 2016; Lv et al., 2023; Hamdi Nasr et al., 2025; Madrid et al., 2025; Ye et al., 2025; Zhang et al., 2025). Given that the ore bodies of the Dapai deposit are closely controlled by thrust structures, magnetic prospecting is essential to ascertain the structure characteristics and potential ore bodies in the area. However, high precision ground magnetic survey has rarely been conducted due to the large areas of vegetation and rugged topography in the Dapai deposit. And previous studies have mostly focused on the Dapai deposit and deep prospecting, less attention has been given to its surrounding area, which limits our knowledge concerning the potential for iron-polymetallic resources in the surrounding of the deposit.
In this study, a high-precision magnetic ground survey was carried out in the surrounding area north of the Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit. On the acquired magnetic anomaly results, reduction to the pole, upward continuation, total horizontal derivatives and magnetization vector inversion with an unstructured tetrahedral mesh are applied. Maps of these transformed data are plotted revealing the magnetic features in the surrounding area of the Dapai deposit. The structure characteristics and favorable ore-forming regions in the study area are inferred, and then, the favorable ore-forming locations were verified using borehole data, which revealed multi-layer iron-polymetallic ore bodies. Combining our findings with those of previous studies on the Dapai deposit, we propose a prospecting model for Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit in southwest Fujian. This study provides not only an example for the exploration of other similar concealed deposits in the adjacent area in the future but also gives insights on the mineralization distribution of the Makeng-type iron–polymetallic deposits in the SFDB, southwestern China.
2 Geological background
2.1 Regional geology
The SCB was formed by the amalgamation of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks in the early Neoproterozoic and subsequently underwent intracontinental rifting (Charvet et al., 1996; Li et al., 2009; Zhao and Cawood, 2012; Mao et al., 2014; Faure et al., 2017). The SFDB, located on the southeast part of the Cathaysia block, has developed crystalline basement by late Neoproterozoic Jinning movement (Figure 1A). In the early Paleozoic, Caledonian Orogeny generated deformation and low-grade metamorphism and formed folded basement in the SFDB (Zhang, 2000; Zhang et al., 2015). Afterward, the SFDB was dominated by crustal uplifting and depression with a neritic–bathyal sedimentary environment, forming thick marine sedimentation from the Late Devonian to Early Triassic (Zhang, 2000). In the early Mesozoic, the Indosinian movement lead to the closure of the Late Paleozoic basin in the SFDB and the transition from regional extension to compression. East China then turned into an active continental margin attributed to the subduction of the paleo-Pacific plate (Shu et al., 2021; Hu et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2023; Wang H. et al., 2024). Intense structural deformation and magmatism–mineralization activity occurred in the SFDB during this period (Mao et al., 2001; Vatuva et al., 2023).
The sedimentary sequence of the SFDB and its adjacent areas comprise a pre-Devonian basement, overlaid with Late Paleozoic–Middle Triassic cover rocks and Mesozoic–Cenozoic terrestrial clastic–volcanic rocks (Figure 2; Zhang, 2000; Mao et al., 2001). Different types of structures, such as regional faults and folds, thrust nappes, and detachment structures, were well developed in the SFDB (Lv, 2014; Zhang et al., 2021). The NEE-trending Nanping–Ninghua fault, NE-trending Zhenghe–Dapu fault and NW-trending Shanghang–Yunxiao fault roughly delineate the boundaries of the SFDB on the north, southeast and southwest, respectively (Figure 1B). The fold structures in the SFDB are dominated by a series of NE–NNE-trending composite folds, mainly including, from west to east, the Ninghua–Wuping synclinorium, Xuanhe anticlinorium and Datian–Longyan synclinorium (Mao et al., 2001). In addition, the nappe structures were formed in the Mesozoic and are characterized by older allochthonous pre-Devonian and Early Carboniferous rocks thrusting over the younger Late Carboniferous and Permian autochthonous rocks (Chen, 1999; Wang et al., 2017; Vatuva et al., 2023). Detachment faults are common in the SFDB arising from the Early Mesozoic compression deformation and Late Mesozoic extension (Zhang et al., 2021). Intrusive rocks mainly outcropped in the SFDB consist of Silurian, Carboniferous–Triassic, and Middle Jurassic–Early Cretaceous granitoids with a few Carboniferous and Cretaceous mafic dikes and sills, resulting from different tectonic events (Zhang et al., 2015; Vatuva et al., 2023). The distribution of these intrusions is generally controlled by the NE-trending structure (Zhang, 2006; Wang et al., 2017).
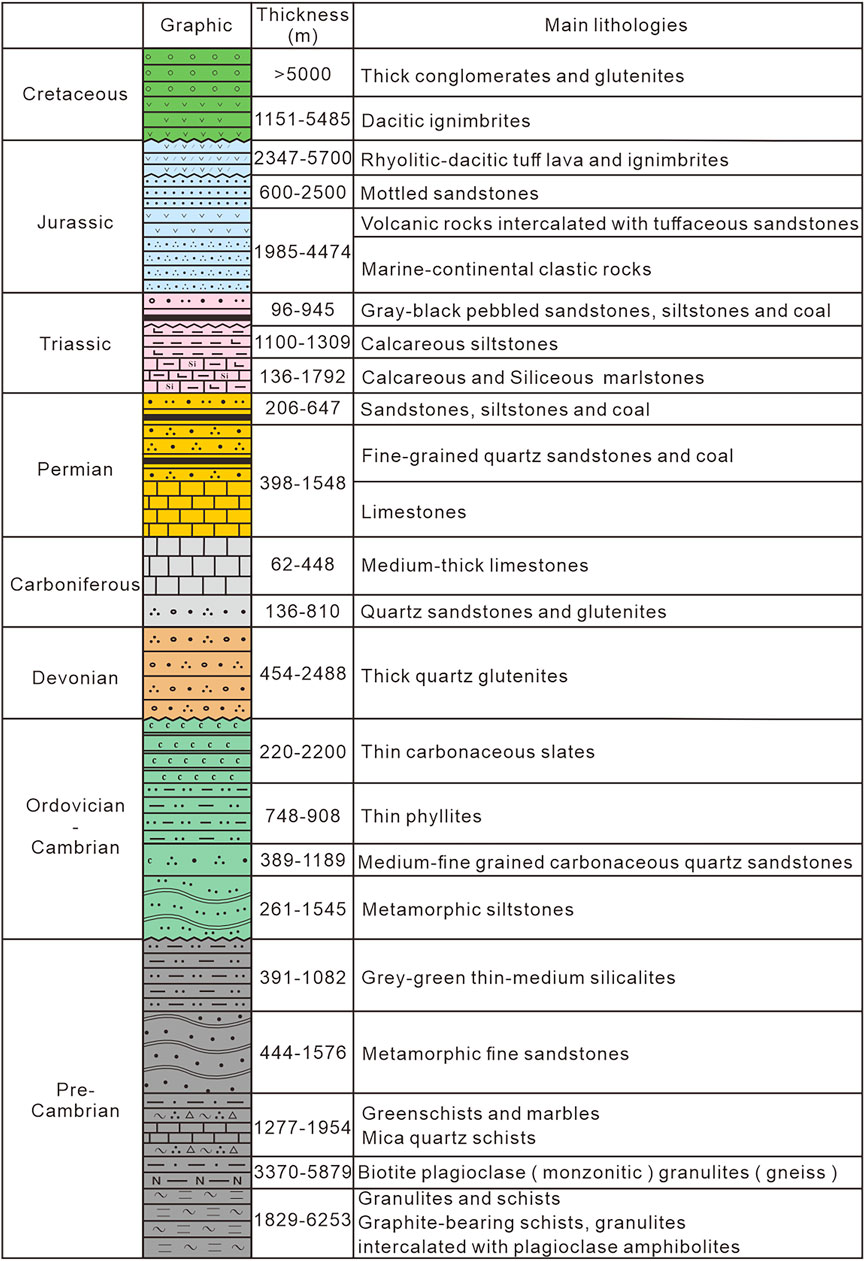
Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Southwestern Fujian Depression Belt and its adjacent area (modified after Yuan, 2020).
2.2 Geology of the Dapai deposit and its surrounding area
The Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit, Yongding County, is located on the southeastern margin of the SFDB. The study area is located on the northern surrounding part of Dapai deposit (Figure 3).
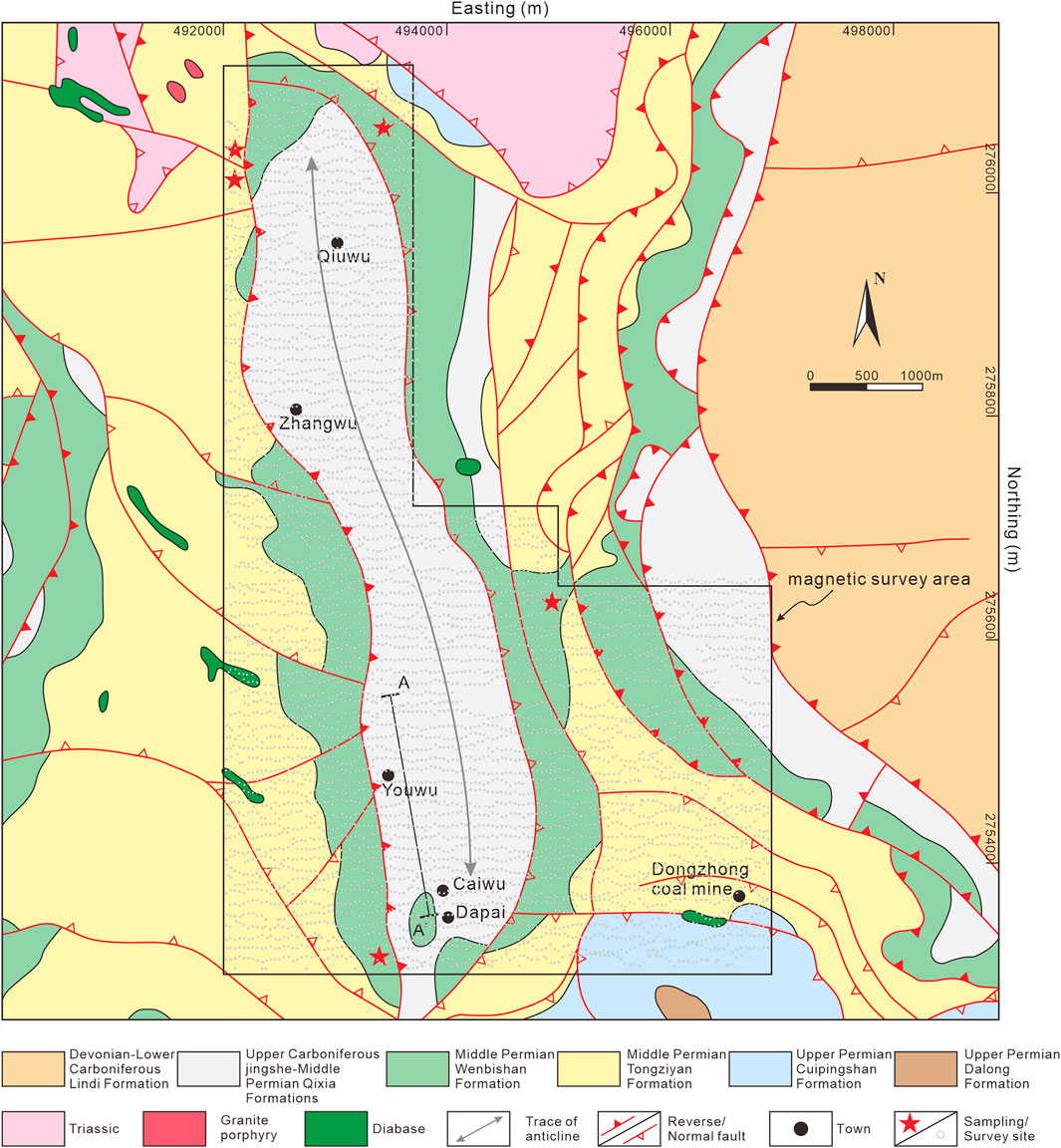
Figure 3. Geological map of the Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit and surrounding area. The black polygon and hollow dots represent the ground magnetic survey area and survey sites, respectively.
The main stratigraphic sequence in the study area consists of carbonate rocks of the Upper Carboniferous Jingshe, Lower Permian Chuanshan, and Middle Permian Qixia Formations and clastic rocks of the Lower Carboniferous Lindi, Middle Permian Wenbishan and Tongziyan, Upper Permian Cuipingshan and Dalong Formations and minor Upper Devonian and Lower Triassic. The Carboniferous Jingshe Formation and Permian Chuanshan, Qixia Formations are closely associated with mineralization. The mineralization is affected by a series of NNW-SSE-trending thrust faults and NNW-SSE-trending detachment faults. The fold structures in the study area are dominated by the nearly N–S-trending anticlinorium which generally plunges northwards and is cored by the limestone of the Jingshe, Chuanshan and Qixia Formations with limbs composed of the Permian Wenbishan and Tongziyan Formations. Magmatic rocks, which are rarely exposed in the study area, include stocks or dikes of granodiorite, granodiorite porphyry, monzogranite, and quartz monzonite. Granodiorite porphyry is the main magmatic rock closely related to the iron mineralization. The iron ore bodies are stratabound in the skarn and generally occur along the contact zone between the intrusions and the carbonate sequence (Vatuva et al., 2023).
The Dapai deposit dominantly features Fe-Pb-Zn-Cu-Mo mineralization, exhibiting vertical zonation from shallow Pb-Zn, middle Cu-Pb-Zn, Fe-Pb-Zn to deep Fe-Mo. Horizontally, the magnetite mainly developed in the northwestern and southeastern part of the Dapai deposit, while the Pb-Zn mineralization is common in the middle and transitioned into Fe-dominant mineralization at depth. The ore minerals in the Dapai deposit include magnetite, galena, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, and molybdenite. A total of 65 Fe-Pb-Zn polymetallic ore bodies have been identified in the Dapai deposit, generally striking NNW and dipping towards NEE at angles of 5°–25° (Ni et al., 2012). The ore bodies occur within the fault-related fractures and around the contact zone between the granite porphyry intrusions and carbonate surrounding rocks. Notably, the ore bodies are primarily hosted in the carbonate of Jingshe-Qixia strata, which constitutes the core of the Dapai anticlinorium. Alteration including silicification, marbleization, argillization and skarn alteration are well developed in the study area.
3 Methods
3.1 High-precision magnetic ground survey—data acquisition
Depending on the geological characteristics of the Dapai deposit, a magnetic ground survey was carried out on the northern area of Dapai deposit, covering ∼25 km2. To obtain the underground high-magnetic bodies and deduce potential ore bodies, total field measurement was employed. Besides, the study area features complex topography with residential areas distributed, which limits gradiometer or vector measurements. Therefore, total field data are used in this study.
The magnetic survey data were collected using Overhauser proton-precession magnetometers (GSM-19T) ∼2 m above the ground. Total magnetic field intensity was measured with a sensitivity of 0.15 nT/Hz and 0.2 nT absolute accuracy. The measurement was conducted at intervals of 40 m along west–east oriented survey lines with 90°azimuth spaced 100 m apart, and a total of 6,467 points were recorded. Portable GARMIN 72 GPS receivers were used to determine the measuring point position, with horizontal positioning accuracy <3 m (using the root mean square (RMS) method) and elevation accuracy <10 m. The diurnal observation ground station used an Overhauser proton-precession magnetometer (GSM-19T). The measurement accuracy of the magnetic anomalies is 1.51 nT. The total magnetic field was corrected for diurnal variations depending on the data recorded at the diurnal observation station. Normal field correction, height correction, and calculation of the magnetic anomalies were performed on the acquired data. Then, the data was processed with gridding spacing of 50 m × 50 m.
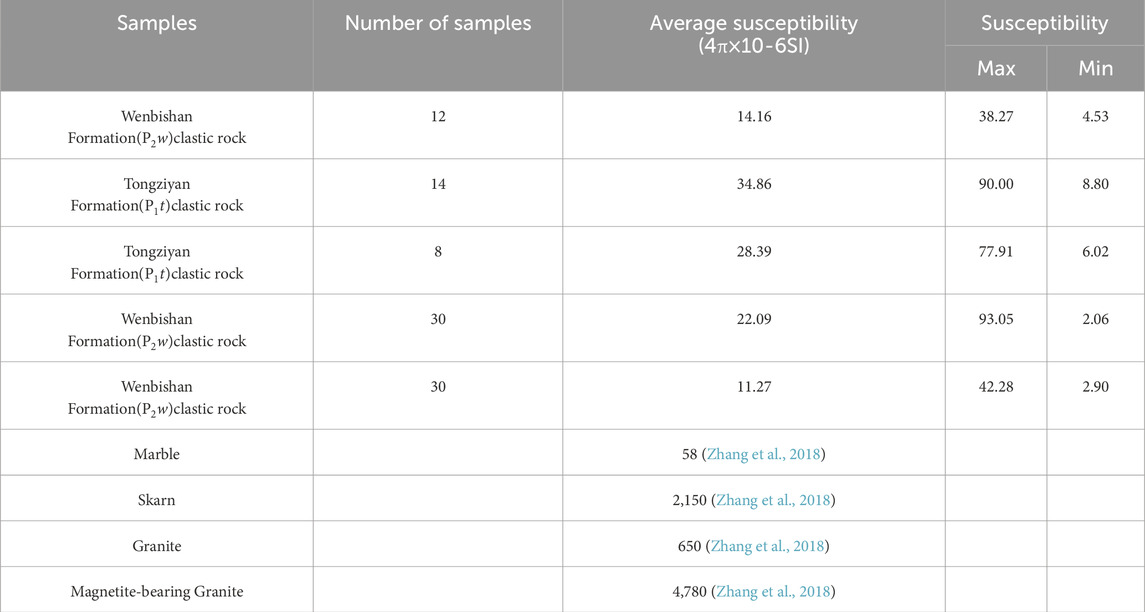
The magnetic susceptibility of 94 rock samples from the study area was collected and measured to determine their physical properties. The results are listed in Table 1.
According to the table, the magnetic susceptibility of the Wenbishan and Tongziyan Formations exposed in this area are weak; the magnetic susceptibility of the rocks is mainly between 10 and 50 (4π·10−6SI). As a reference, a previous study analyzed the anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) data from the Makeng iron deposit, indicating that the mean susceptibility (Km) of the Jingshe-Qixia Formation varies from 7.54 to 8.89 (4π·10−6SI) (Wang, 2016). It can be concluded that the sedimentary rocks in Dapai’s surrounding area generally exhibit weak magnetic or non-magnetic properties. In contrast, the susceptibility of skarn, granite, and magnetite-bearing granite is high, and the marble displays moderate magnetic properties. Generally, the susceptibility of granite and altered rocks is clearly stronger than that of sedimentary rocks. With the change in mineral composition, the susceptibility of the magmatic rocks in the study area gradually increases from the acidic rock to the ultrabasic rock. And the remanent magnetization in the study area is much smaller than the induced magnetization. Thus, only the induced magnetization was taken into account in this study (Wang and Meng, 2019).
3.2 Reduction to the pole
The magnetic anomaly corresponds well to the causative body under vertical magnetization, which only naturally exist at the north and south geomagnetic pole. However, elsewhere on earth, due to the effect of the oblique magnetization of geomagnetic fields, the shape of the anomaly is often complicated and its extreme value is often offset from the causative body. To eliminate the effect of oblique magnetization and achieve a better interpretation, the observed magnetic anomaly needs to be calculated and transformed into the anomaly under the vertical magnetization, that is to say, to the geomagnetic pole. The non-rectangular survey area was interpolated to a 50 m × 50 m grid using minimum curvature interpolation (Wang Y. et al., 2024). The scheme of cosine decreasing to zero was applied to extend edge, which provides a foundation for subsequent data processing. Therefore, we processed reduction to the pole (RTP) with an inclination of 38°45′ and a declination of −3°35′ in the study area.
3.3 Potential field separation
Upward continuation is a useful approach of data processing to reduce the shallow and local anomaly interference and highlight the signature of deep magnetic sources (Xiong, 1992). Peters (1949) first introduced the continuation by which the signals with different frequencies can be separated. In this study, upward continuation was utilized to reduce the effect of shallow and small ore bodies and enhance the deep causative bodies. In addition, to highlight the anomaly caused by magnetic bodies, the residual magnetic map was calculated by removing the regional field through high pass filtering method in this study.
3.4 Boundary identification
Calculation of derivatives is an instrumental method to suppress interference from the regional field and separate the superposition effects of different anomalies. Evjen (1936) first introduced boundary identification by using the zero value of the vertical derivative on gravity anomalies. The maximum of the total horizontal derivates (THD) of the gravity anomaly was then applied to distinguish the boundary of geological bodies (Cordell, 1979). Shortly after, Cordell and Grauch (1985) employed THD in the magnetic anomaly interpretation. For the identification of the structures and potential ore bodies in the study area, the total horizontal derivates were calculated in this work. The maximum of the THD is considered to represent the potential source boundaries. Thus, the THD of the RTP and upward continuation results were calculated to determine the structural framework of the study area.
3.5 Magnetization vector inversion with an unstructured tetrahedral mesh
The anomaly data obtained in the magnetic ground survey is the result of integrated anomaly response of subsurface geological bodies. The inversion of the magnetic data can visually illustrate the patterns of field sources and locate potential mineralization position. In this study, the inversion method introduced by Meng et al. (2023), Meng et al. (2024) was employed. It divides the subsurface into tetrahedral unstructured grid, which is more suitable for the undulating surface, irregular geological bodies and remanent magnetization. The volume weighting function is used to improve the convergence of inversion. To improve the computational efficiency, the calculation terms are combined depending on the equivalent surface characteristic between elements of the kernel matrix and Gaussian quadrature with a nonuniform fast Fourier transform method is used to calculate the function of a triangular facet in the kernel matrix.
4 Results and discussion
The following sections describe and discuss the results of the processing, interpretation and inversion of the magnetic anomaly data acquired.
4.1 High-precision magnetic maps of the study area
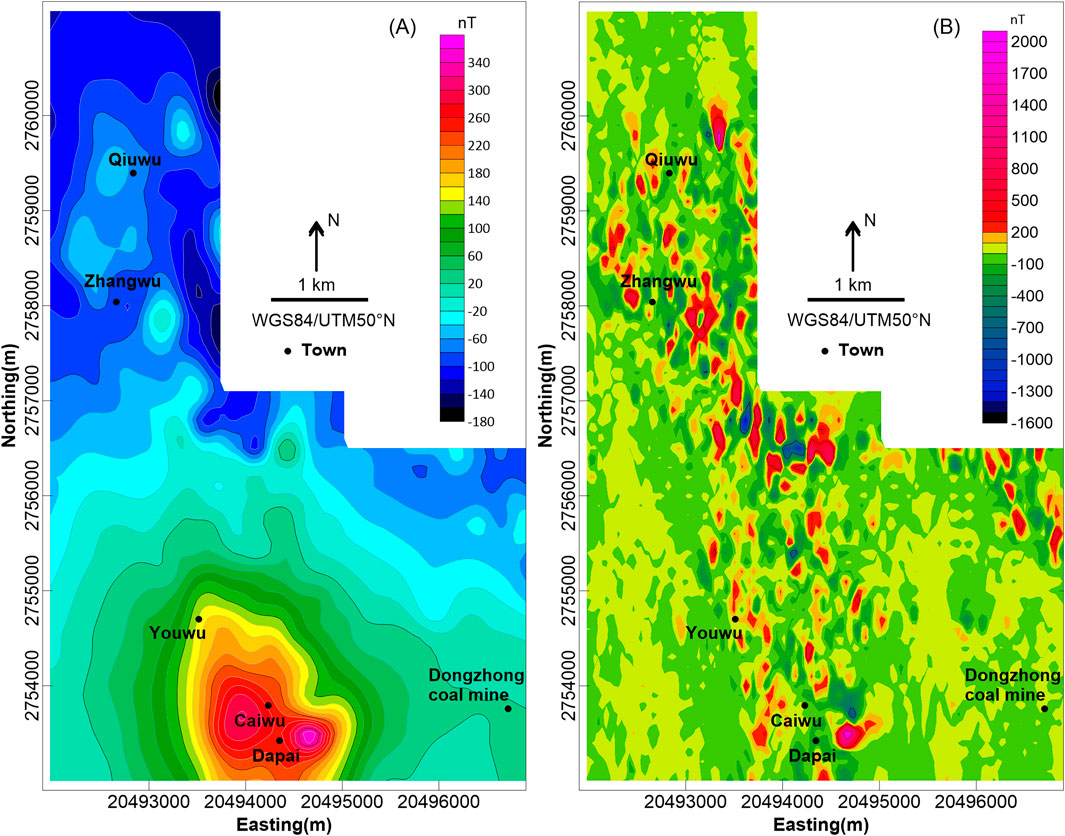
As illustrated on the total magnetic intensity (TMI) map in Figure 4A, the relative total magnetic intensity ranges from −1,384 nT to 1,369 nT.
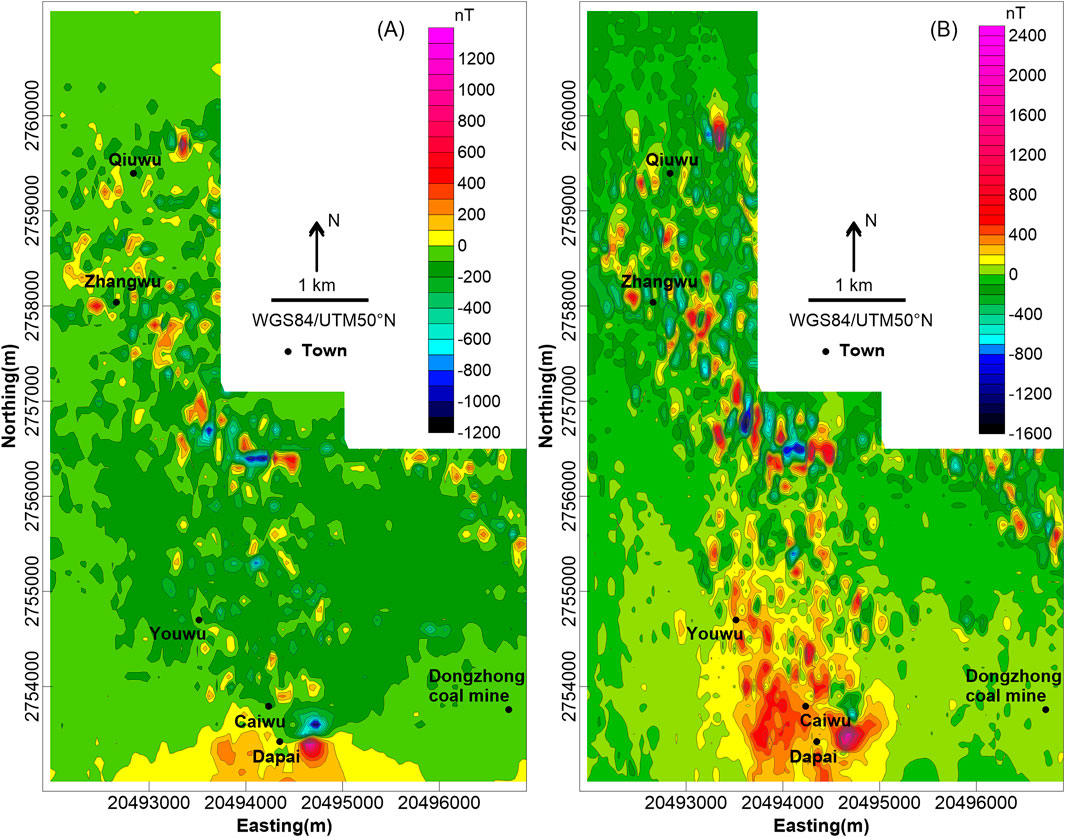
Figure 4. (A) Total magnetic intensity (TMI) map and (B) reduced-to-pole (RTP) magnetic map of the study area.
The magnetic field of the northern, southwestern, and southeastern part of the study area is flat with little fluctuation. The magnetic intensity is roughly −50 nT in the north and varies from −100 nT to 0 nT in the southwest, which can be regarded as the background field value of the study area. The weakly magnetic Permian Tongziyan, Qixia, and Wenbishan Formations are exposed from west to east in the north, while in the southwest, the strata of the Permian Tongziyan and Wenbishan Formations with weak susceptibility are mainly exposed. There are only sporadic and localized anomalies distributed in the NW-direction magnetic field in the north of the Dongzhong coal mine, which is probably related to the concealed thrust fault in the southeastern part of the study area.
The central of the study area is generally in the strong NW-trending anomaly field, consisting of several local magnetic anomalies randomly distributed with amplitudes ranging from −1,384 nT to 1,369 nT. The anomaly distribution characteristics in the central part are slightly different in the north and south. The northern part is a beaded strong magnetic anomaly zone with a pronounced oriented arrangement whereas the southern part exhibits relatively clustered features that correspond to the Dapai deposit in exploitation.
In order to reduce the effect of the oblique magnetization of the geomagnetic field and simplify the anomaly morphology and data processing, the RTP method was utilized, the results are shown in Figure 4B. Compared with the TMI map, it can be seen that the amplitudes of the magnetic anomalies after RTP are increased. In addition, the overall positive anomalies have moved slightly northward. The positive anomaly in the southern part and the NNW-oriented characteristics have become more conspicuous. The general magnetic anomaly intensity demonstrates an NNW-trending linear configuration, which is probably a result of the distribution pattern of the northward plunging anticlinorium.
To highlight the anomaly caused by the deep magnetic sources and reduce the effect of near-surface and small geological bodies, in this work, the upward continuation at a 200 m height was calculated on the basis of the RTP results. As is shown in Figure 5A, the southern part of the study area displays strong anomalies, whereas the northern part exhibits extensive weak anomalies. The anomaly amplitude in the central part is small, as a result of the weak susceptibility of the Permian Tongziyan, Qixia and Wenbishan Formations. Notably, the anomaly demarcation is obvious along Qiuwu–Zhangwu–Youwu, which implies that there may be concealed faults favorable to the magma emplacement on the two sides. This strong anomaly is probably related to magmatic rocks or the magnetic ore bodies. In addition, it can be seen that the anomaly around the Caiwu–Dongzhong warps, obvious on the upward continuation of the reduced-to-pole magnetic map, suggests the existence of deep faults in the subsurface. These faults intersect with the NNW-trending faults, contributing to magma emplacement and mineralization enrichment. A residual magnetic map was also calculated. It is helpful to reflect causative bodies in relatively shallow position. As is illustrated in Figure 5B, the NNW-oriented pattern of the positive anomaly generally remains unchanged. There is a wide range of positive anomalies around the Dapai deposit, extending northward in several local positive anomalies. These local strong anomalies might imply potential ore bodies.
4.2 Structure characteristics of the study area
The THD maps were used to determine the potential boundaries of the magnetic body and structures in the study area. As portrayed in Figure 6A, the study area is dominated by NNW-trending structures. In order to suppress shallow noise and understand the deep characteristics more clearly, the THD on the upward continuation at 200 m height map was calculated and is shown in Figure 6B. It can be seen that the general structural features are similar to those shown in Figure 6A. There are three NNW-trending faults and two nearly E–W-trending faults, namely, F1, F2, F3, F4, and F5, respectively (Figure 7). Notably, the F4 fault crosscuts the F1 and F2 faults. According to the susceptibility of the collected samples, the Permian Tongziyan and Wenbishan Formations demonstrate weak magnetic properties and, thus, do not result in an obvious anomaly. However, moderate anomalies were detected between F1 and F2 and northeast of F3, which correspond with the distribution of the Qixia Formation. The susceptibility of the Qixia Formation or alteration within Qixia Formation may be one factor accounting for this anomaly.
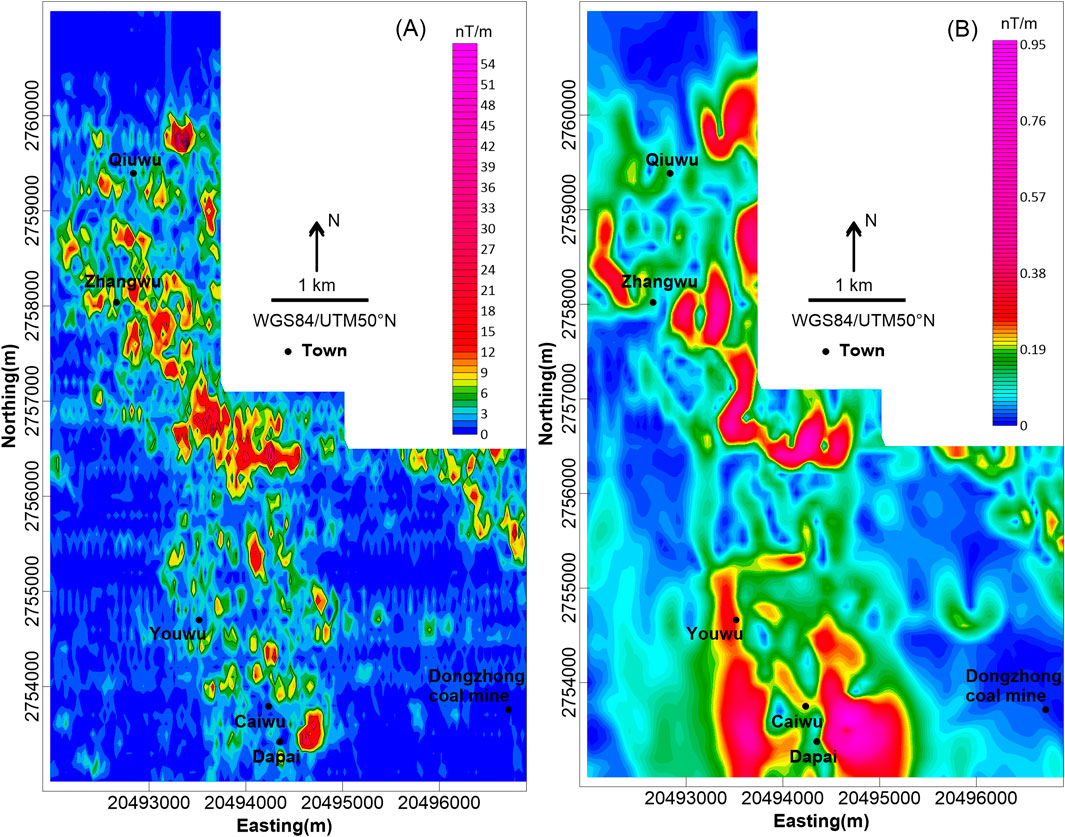
Figure 6. (A) Total horizontal derivates (THD) map and (B) the THD on the upward continuation at 200 m height map of the study area.
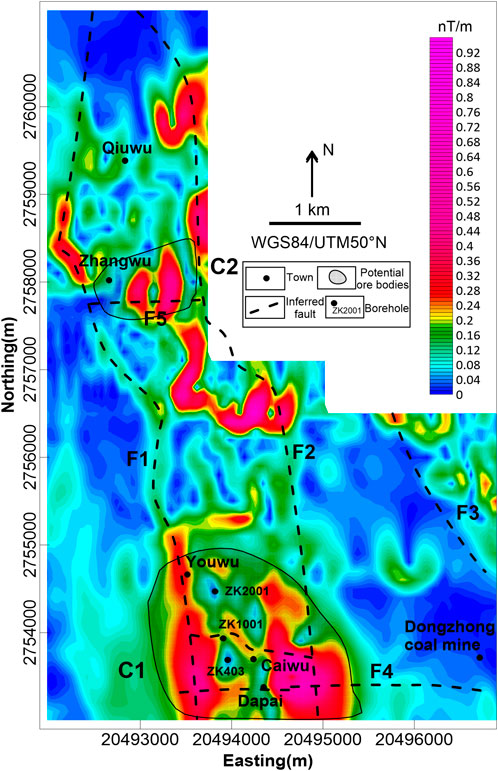
Figure 7. Inferred tectonic framework map and prospecting target of the study area. The crosshatch part represents potential ore body.
As is noted above, the faults in the study area were favorable to magma emplacement and mineralization enrichment. In addition, the geological characteristics of the Dapai deposit indicate that the ore bodies are controlled by thrust structures. Therefore, any potential ore bodies are more likely to be spatially close to the faults, especially at the intersection of different faults. Depending on the inferred structures in the study area, the variation zone between the positive and negative anomalies on the TMI map, the maximum value of the RTP map and residual map, the gradient zone of the upward continuation, and the maximum of total horizontal derivates, two regions characterized by greater ore formation potential were inferred, namely, C1and C2, as shown in Figure 7.
Region C1 is located near the Dapai deposit, which is at the boundary of the thrust nappe. The main exposed strata in region C1 are the Permian Tongziyan, Wenbishan and Qixia Formations. According to the inferred structure in the study area, region C1 is situated in a position where the F4 intersects with F1 and F2, covering about 3 km2 with an anomaly amplitude ranging from −1,384 to 1,370 nT. Compared with the southeastern anomaly, the anomaly on the southwest side is larger spatially and has a smaller amplitude, implying that the southeastern causative body is shallower and smaller, while the southwestern magnetic source is deeper. In addition, these two anomalies merge together along with an increase in the heights of the upward continuation, suggesting that there is a common magnetic source in the deep position. Therefore, it is deduced that the anomaly around Caiwu is caused by magnetic bodies and region C1 is a more favorable area for mineralization.
Region C2, between F1 and F2, is on the eastern part of Zhangwu. The anomaly of region C2 has smaller scale covers about 0.8 km2, with a medium amplitude ranging from −692 to 626 nT. The region C2 anomaly disappeared in the upward continuation map, indicating that its magnetic source is shallow. Besides, there is an inferred E–W striking fault, F5, in region C2, depending on the THD and structure map (Figures 6, 7) The C2 moderate anomaly is probably related to the magmatic rocks distributed along the faults, or the Permian Qixia Formation, which is the main exposed stratum in region C2. Moreover, the influence of the dense residential area in region C2 should not be neglected. Thus, there is relatively less mineralization potential on region C2.
4.3 Inversion results
To further define the underground structure characteristics and locate potential ore bodies, the inversion of the magnetic anomalies of region C1 around the Dapai deposit was carried out (Figure 7). The underground space from the surface to an elevation of −1000 m of the study area was divided into an unstructured tetrahedral mesh with 10,073 cells. The iteration termination condition is the relative root mean square error between the modeled magnetic anomalies derived from the inversion results and the measured magnetic anomalies less than 10−2. The computer used in the inversion is equipped with 2.4 GHz CPU and 64 GB RAM and the computation time of inversion is 6,963 s.
The three-dimensional magnetization inversion result is shown in Figure 8A. Depending on the magnetic parameter of the rock samples in the study area, the high-magnetization bodies mainly represent integration of the granite, skarn and magnetite-bearing granite. The slice along the core of anticline intuitively demonstrates the subsurface distribution of the high magnetization intensity bodies. The normalized sensitivity analysis data of magnetic weighted kernel matrix in Figure 8B is for uncertainty appraisal. It shows where the three-dimensional inversion model is reliable. The position with large normalized sensitivity data has more accurate and reliable physical properties (Meng et al., 2024).
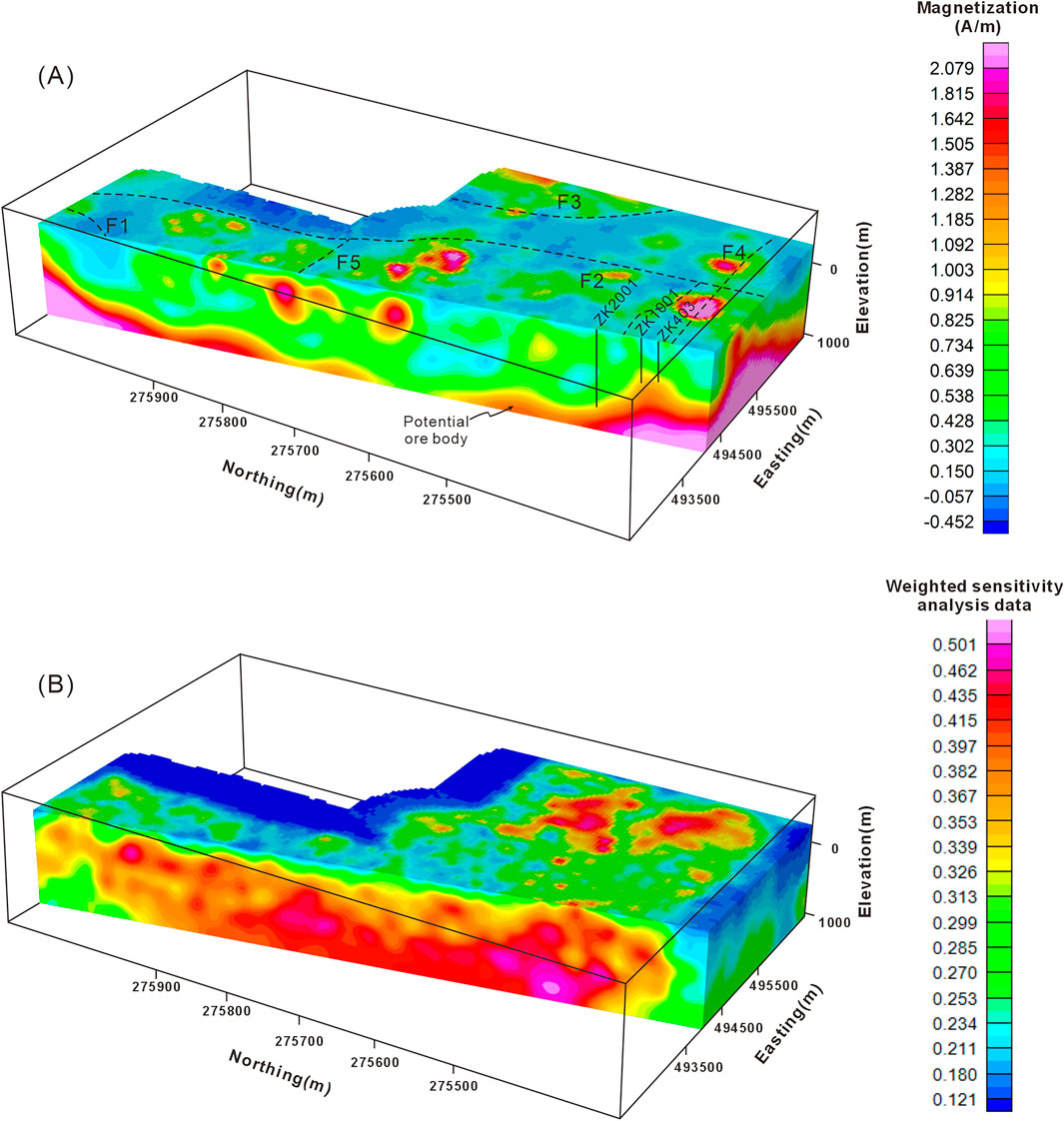
Figure 8. (A) Three-dimensional magnetic inversion result of the study area. The inferred faults are marked with black dotted lines and the location of boreholes are shown in the model. (B) Normalized sensitivity analysis data of magnetic weighted kernel matrix.
It can be seen that the high-magnetic body generally demonstrate a deepening trend towards the NNW direction, which is consistent with the plunging orientation of the fold. The top of high-magnetic body in region C1, as revealed by the inversion result, is about −100 m elevation and corresponds well with the geological information from existing borehole ZK403 and ZK1001. There are also some isolated high magnetic bodies at approximately −100 m elevation, which may be attributed to the isolated ore bodies or to local skarn caused by the hydrothermal alteration.
4.4 Drilling verification
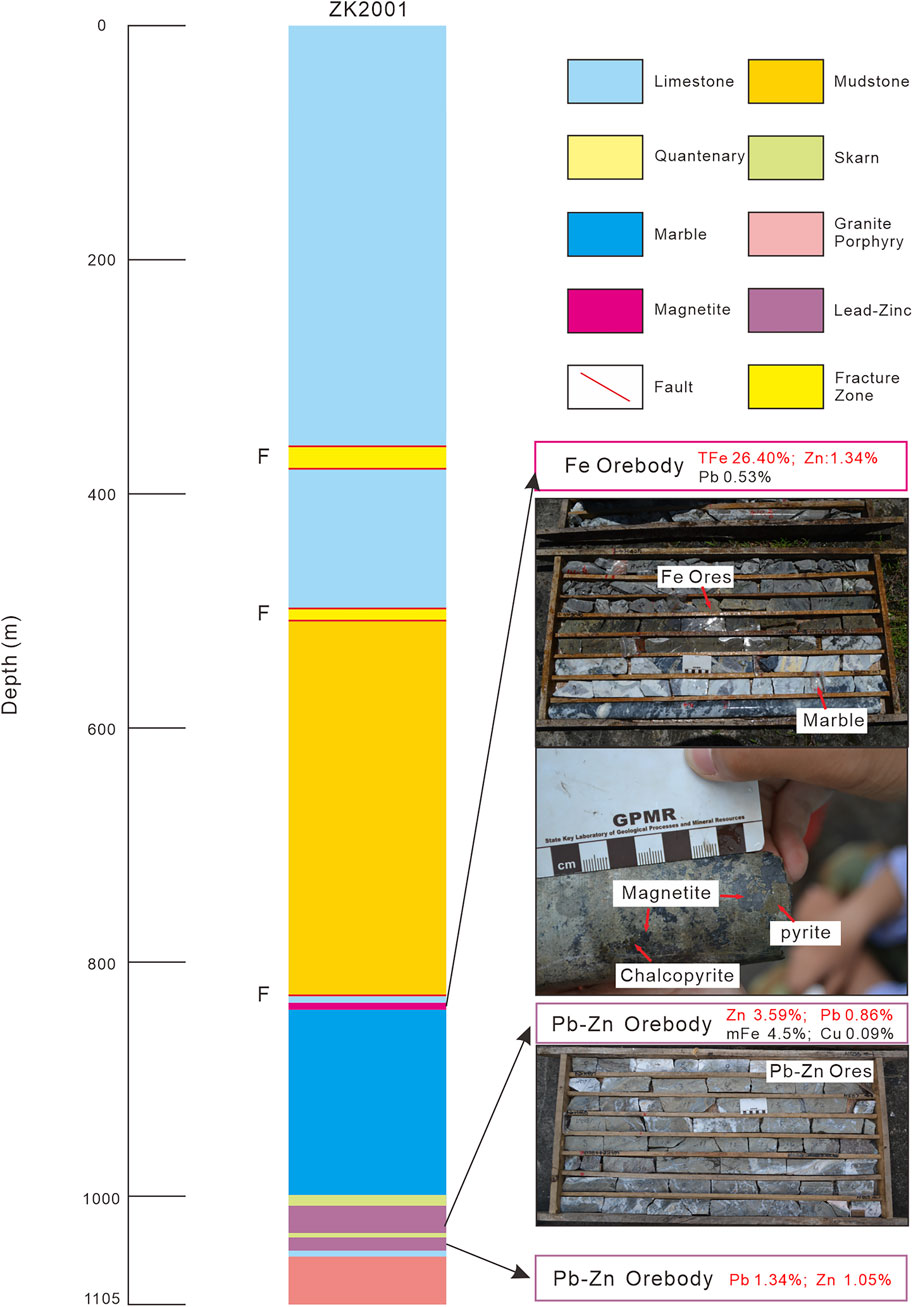
The Dapai deposit shows a strong positive magnetic anomaly and extends northward in both plan magnetic anomaly maps and three-dimensional inversion result. According to the regional geological background, geological characteristics of the deposit and magnetic anomaly characteristics, drill hole validation was carried out in the northern part of the Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit in the locally strong anomaly area (ZK2001 in Figure 7).
As is shown in Figure 9, the drilling results reveal thrust nappe structures between the Qixia and Wenbishan Formations at a depth of around 550 m. The decollement fault between the Wenbishan formation and Qixia formation is about 850 m deep, developing magnetite ore body within its fracture zone with a total Fe grade of 26.40%. The 850–1,014 m limestone stratum exhibits strong marbleization, with a local multi-layer skarn. Between 1,014 m and 1,054 m there is two-layers of lead-zinc mineralization, accompanied by magnetite and chalcopyrite mineralization (mFe 4.5%, Cu 0.09%).
The maximum depth of the drill hole is 1,105.64 m. Compared with drill holes ZK1001 and ZK403, the geological unit in ZK2001 is discontinuous with the southern ZK1001 and ZK403 drill holes and is much deeper than its counterparts. Therefore, it is inferred that there is a nearly E–W-trending concealed fault that has caused the northern geological unit in ZK2001 to be deeper, which is consistent with the fault on the north of Caiwu represented in Figure 7 and proves the reliability of our anomaly interpretation and explanation.
Drill hole ZK2001 revealed at least three-layers of Fe-Pb-Zn ore bodies. It also disclosed relatively strong alteration at depth and the existence of an intrusion associated with the mineralization. As is described above, the Dapai deposit is closely controlled by structures and strata. Based on the geological characteristics of the study area, it can be concluded that the increasing depth of the ore bodies and the NNW-oriented magnetic anomaly are affected by the faults and NNW-plunging fold. As a consequence, there is still great potential for the deeper and more peripheral prospecting to the north of the Dapai deposit.
4.5 Geological-geophysical model
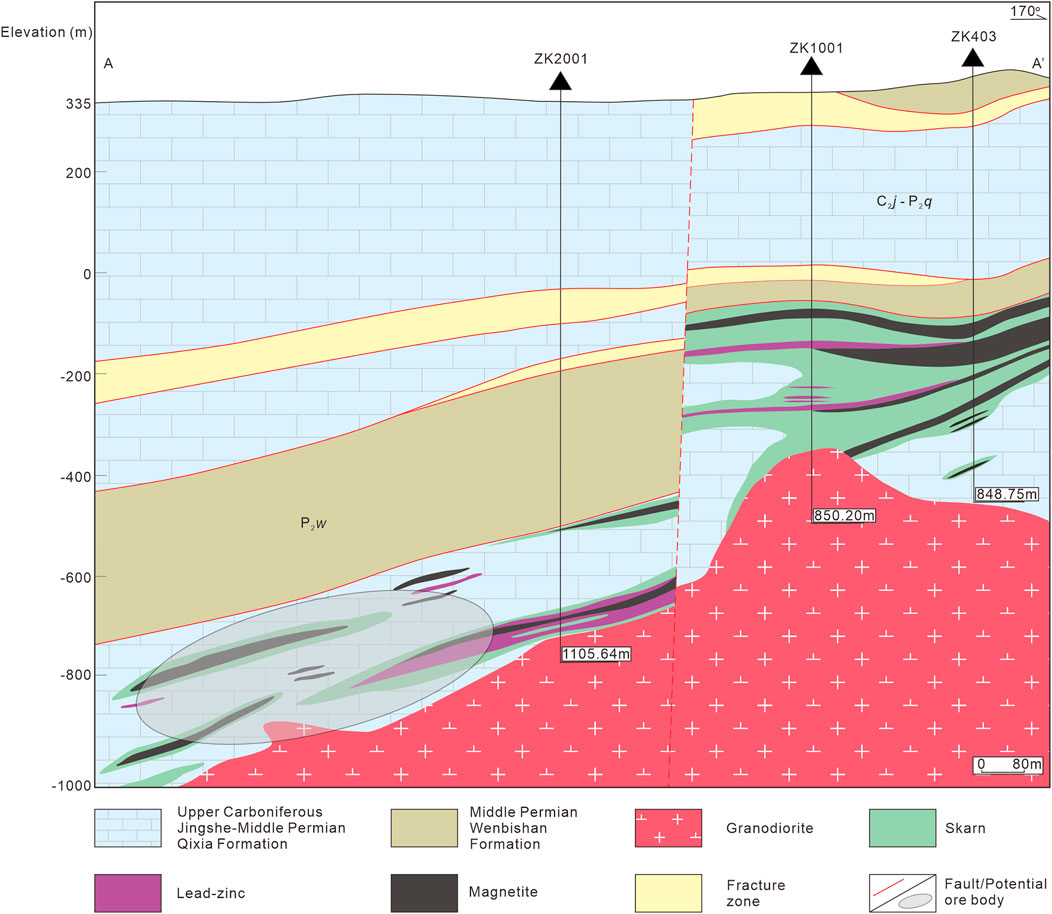
Zhang et al. (2012) proposed an ore-control model for the thrust structures in the SFDB, believing there to be great potential for mineralization where the thrust nappe structures developed and the ore-bearing strata, including the Upper Carboniferous to Middle Permian strata, were overlapped by the older strata and intruded by granite.
The ore-bearing strata of the Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit are similar to those of the Makeng iron deposit, including the Upper Carboniferous Jingshe to Middle Permian Qixia Formations. Ore bodies occur within these strata especially at the interface between the carbonate and clastic sequences. In addition, the ore bodies are obviously controlled spatially by thrust faults, fracture zones, and the core of folds. There are also some ore bodies reformed or crosscut by later faults. Furthermore, the Dapai deposit mineralization is closely associated with Mesozoic granitic rocks. This favorable mineralization position could be preliminarily deduced through a geological survey focusing on all of these factors. Afterward, geophysical methods could be employed to probe the potential ore bodies. The potential shallow ore bodies often demonstrate strong magnetic anomalies and deep ore bodies exhibit weak or moderate anomalies in magnetic surveys. Therefore, it would be more accurate to determine the prospecting target coupled with the geological characteristics.
On the basis of the geological characteristics of the Dapai deposit, combined with the interpretation and inversion of the high-precision magnetic survey data and the verified borehole results presented in this study, a prospecting model for the surrounding of the Dapai iron–polymetallic deposit is summarized in the Figure 10.
5 Conclusion
In this work, high-precision magnetic maps were obtained and a structural framework and potential locations of ore bodies in the area surrounding the Dapai deposit were delineated preliminarily through processing, interpreting and inversion of the high-precision magnetic ground data. Then these results were verified by drill holes.
The borehole drilling uncovered thrust nappe structures among the Qixia and Wenbishan Formations, magnetite and Pb–Zn ore bodies, ore-related alteration, and intrusions. The drilling results revealed at least three-layers of ore bodies and indicated great exploration potential within this deeper location. The verification result proves the effectiveness of the high precision ground magnetic survey in prospecting of iron–polymetallic ore bodies in the surrounding area of the Dapai deposit.
Combined with the regional geology, the ore deposit geology characteristics, the magnetic anomalies, and the distribution of ore bodies and intrusions revealed by the drilling results, we propose a prospecting model for the Dapai iron-polymetallic deposit in this study. According to this model, the structural interface between the carbonate and clastic rocks of the Upper Carboniferous–Middle Permian strata is a major ore-controlling feature. The Makeng-type ore bodies in the SFDB mainly occur at these interfaces or within these strata. In addition, the ore-controlling structures such as the thrust faults and cores of the folds need to be taken into account. Furthermore, the Mesozoic intrusions and alteration related to the mineralization are also important prospecting indicators. The high-precision magnetic ground survey anomalies can guide the exploration for iron–polymetallic ore bodies in the SFDB through proper processing and interpretation. The prospecting model, together with the magnetic survey utilized in the surrounding area of the Dapai deposit, provides reference and feasible solution for the future exploration of similar Makeng-type deposits in this region. Given that the precision of the interpretation results is usually affected by the ambiguity of one single geophysical method, the implementation of comprehensive methods, together with a geological survey, is essential and beneficial for further exploration.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JH: Methodology, Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Visualization. YY: Conceptualization, Supervision, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. SW: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Supervision. XZ: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. BH: Writing – review and editing, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was jointly supported by National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (grant No. 42025403), research funding by Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the project of China Geological Survey (Grant Nos. 1212011085472).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge associate professor Yuwen Zhang for the help in the processing and interpretation of the anomaly data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Charvet, J., Shu, L., Shi, Y., Guo, L., and Faure, M. (1996). The building of south China: collision of Yangzi and Cathaysia blocks, problems and tentative answers. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 13, 223–235. doi:10.1016/0743-9547(96)00029-3
Chen, A. (1999). Mirror-image thrusting in the south China orogenic belt: tectonic evidence from Western Fujian, southeastern China. Tectonophysics 305, 497–519. doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00036-0
Cordell, L. (1979). Gravimetric expression of graben faulting in Santa Fe country and the espanola basin, New Mexico. New Mex. Geol. Soc. doi:10.1126/science.192.4234.43-a
Cordell, L., and Grauch, V. J. S. (1985). “Mapping basement magnetization zones from aeromagnetic data in the San Juan Basin, New Mexico,” in The utility of regional gravity and magnetic anomaly maps: soc. Explor. Geophys. Editor W. J. Hinze, 181–197. doi:10.1190/1.0931830346.ch16
Di, Q. Y., Xue, G. Q., Lei, D., Zeng, Q. D., Fu, C. M., and An, Z. G. (2021). Summary of technology for a comprehensive geophysical exploration of gold mine in north China craton. Sci. China Earth Sci. 64 (9), 1524–1536. doi:10.1007/s11430-020-9818-2
Evjen, H. M. (1936). The place of the vertical gradient in gravitational interpretations. Geophysics 1, 127–136. doi:10.1190/1.1437067
Faure, M., Chen, Y., Feng, Z., Shu, L., and Xu, Z. (2017). Tectonics and geodynamics of south China: an introductory note. J. Asian Earth Sci. 141, 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.11.031
Feng, H., Zhang, D., Di, Y., Yuan, Y., and Vatuva, A. (2015). Oxygen, sulfur and lead isotopic compositions of the dapai iron-lead-zinc polymetallic deposit in Southwestern Fujian Province and their ore-formation significance. Geol. Bull. China. 34, 930–943. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.05.013
FJIGS (Fujian Institute of Geological Survey) (2016). Regional geology of China·Fujian volume. Beijing. Geological Publishing House.
Hamdi Nasr, I., Adama, Y. K., Wajdi, B., Adnen, A., Aboubacar, D., Souleymane, S., et al. (2025). Structural controls of gold mineralisation in birrimian structures, Western Mali: insights from magnetic data analysis. All Earth 37, 1–13. doi:10.1080/27669645.2025.2479992
Hu, J. X., Xiao, C. H., Wei, C. S., Shen, Y. K., Chen, Z. L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Polyphase deformation of the Youjiang fold-and-thrust belt during the Mesozoic: implications for the tectonic transition of the south China block. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 1033541–14. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.1033541
Kreuzer, O. P., Yousefi, M., and Nykänen, V. (2020). Introduction to the special issue on spatial modelling and analysis of ore-forming processes in mineral exploration targeting. Ore Geol. Rev. 119, 103391. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103391
Li, X. H., Li, W. X., Li, Z. X., Lo, C. H., Wang, J., Ye, M. F., et al. (2009). Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks in south China: constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks. Precambrian Res. 174, 117–128. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2009.07.004
Li, J. H., Dong, S. W., Zhang, Y. Q., Zhao, G. C., Johnston, S. T., Cui, J. J., et al. (2016). New insights into Phanerozoic tectonics of south China: part 1, polyphase deformation in the jiuling and lianyunshan domains of the central Jiangnan orogen. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 121, 3048–3080. doi:10.1002/2015JB012778
Liang, S., Qin, Y., and Xue, H. (1982). Geological setting and mechanics of ore bounding structure of Makeng type iron ore, Southwest Fujian. Bull. Nanjing Inst. Geol. Min. Res. Acta Geol. Sci. 3, 15–29.
Liu, G., Meng, X., Ni, J., Chen, Z., and Zhang, D. (2018). Evaluation of the 2D reflection seismic method toward the exploration of thrust-controlled mineral deposits in Southwestern Fujian Province, China. Geophysics 83, B209–B220. doi:10.1190/geo2017-0289.1
Lv, L. (2014). Discussions on features of Mesozoic thrust-fault belts and relationship between thrust-fault belts and magmatism in Southwestern Fujian and adjacent regions. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. PhD thesis.
Lv, P. F., Xue, G. Q., and Wu, X. (2023). Multi-source geophysical image fusion method to identify physical anomaly: a case study of airborne electromagnetic and magnetic data. Chin. J. Geophys. 66 (6), 2658–2669. doi:10.6038/cjg2022Q0166
Madrid, F. G., Fries, M., Luz dos Santos, B. M., and Luiz, H. dos R. (2025). Exploration and assessment of iron occurrences - a case study applying airborne geophysics and GIS allied to field magnetic susceptibility measurements. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 153, 105351. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2025.105351
Mahdi, A. M., Youssef, A. M., Gabr, S. S., Diab, H. I., Alarifi, S. S., Andráš, P., et al. (2025). Exploring potential mineral deposits: integrating airborne magnetic and remote sensing data in north-eastern desert, Egypt. Adv. Sp. Res. 75, 4472–4489. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2024.12.043
Mao, J., Tao, K., Xie, G., Xu, N., and Chen, S. (2001). Rock-forming and ore-forming processes and tectonic environments in southwest Fujian. Acta Petrol. Mineral., 329–336. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2001.03.016
Mao, J., Li, Z., and Ye, H. (2014). Mesozoic tectono-magmatic activities in south China: retrospect and prospect. Sci. China Earth Sci. 57, 2853–2877. doi:10.1007/s11430-014-5006-1
Meng, X., Wang, J., Liu, G., Chen, Z., Ni, J., Zhang, D., et al. (2021). Geophysical response characteristics of the dapai polymetallic mining area in Southwestern Fujian Province and its prospecting implications. Chin. J. Geophys. 64, 949–964. doi:10.6038/cjg2021O0502
Meng, Q., Ma, G., Li, L., Wang, T., Li, Z., Wang, N., et al. (2023). Joint inversion of gravity and magnetic data with tetrahedral unstructured grid and its application to mineral exploration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 61, 1–14. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2023.3302925
Meng, Q., Ma, G., Li, L., Wang, T., Li, Z., and Li, J. (2024). The ES-GNF method of unstructured tetrahedral mesh for fast inversion of gravity and magnetic data with undulating terrain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 62, 1–15. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2024.3484473
Ni, J. (2012). Geological characteristics and prospecting model of dapai iron-lead-zinc polymetallic deposit. Geol. Fujian 31, 206–214. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2012.03.002
Peters, L. (1949). The direct approach to magnetic interpretation and its practical application. Geophysics 14, 290–320. doi:10.1190/1.1437537
Shu, L., Yao, J., Wang, B., Faure, M., Charvet, J., and Chen, Y. (2021). Neoproterozoic plate tectonic process and Phanerozoic geodynamic evolution of the South China block. Earth-Science Rev. 216, 103596. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103596
Su, B. X., Qin, K. Z., Jiang, S. Y., Cao, M. J., Zhang, Z. C., Zhang, H. L., et al. (2023). Mineralization regularity, scientific issues, prospecting technology and research prospect of Co-Ni deposits in China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 39 (4), 968–980. doi:10.18654/1000-0569/2023.04.02
Vatuva, A., He, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, D., Feng, H., Yuan, Y., et al. (2023). Genesis of makeng-type Fe-Polymetallic deposits in SE China: new constraints by geochronological and isotopic data from the Dapai–Makeng metallogenic system. Geosci. Front. 14, 101614. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101614
Wang, S. (2016). Ore-forming factors and metallogenic prediction of makeng iron ore, Southwestern Fujian Province. Beijing: China University of Geoscience. PhD thesis.
Wang, J., and Meng, X. (2019). An aeromagnetic investigation of the dapai deposit in Fujian Province, south China: structural and mining implications. Ore Geol. Rev. 112, 103061. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103061
Wang, D., Shang, J., Cai, W., Li, S., and Liu, Z. (1982). Paleogeographic and paleotectonic control of iron ore sedimentation in Makeng. Fujian. J. Chang. Coll. Geol., 43–58.
Wang, S., Zhang, D., Wu, G., Vatuva, A., Di, Y., Yan, P., et al. (2017). Late Paleozoic to Mesozoic extension in Southwestern Fujian Province, south China: geochemical, geochronological and Hf isotopic constraints from basic-intermediate dykes. Geosci. Front. 8, 529–540. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2016.05.005
Wang, S., Cao, K., Zhang, D., Yi, J. J., Hu, B. J., Yang, J., et al. (2023). Mineralization age and genesis of the makeng-style iron deposits in the paleo-pacific tectonic domain of south China: in situ LA-ICPMS garnet U-Pb chronological and geochemical constraints. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 1027620. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.1027620
Wang H., H., Xiong, S., Li, F., Wang, W., Feng, B., Zhang, J., et al. (2024). Noise suppression of airborne transient electromagnetic data with minimum curvature. Geophysics 89, V291–V305. doi:10.1190/geo2022-0107.1
Wang Y., Y., Qian, X., Cawood, P. A., Gan, C., Zhang, Y., Zhang, F., et al. (2024). Temporal-spatial patterns of Mesozoic paleo-pacific and tethyan supra-subduction systems in SE Asia: key observations and controversies in borneo and its surroundings. Earth-Science Rev. 252, 104762. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2024.104762
Wu, G., Zhang, D., Chen, B., and Wu, J. (2000). Post-mesozoic transformation of TectonicDomain in southeastern chinaand its geodynamic mechanism. J. China Univ. Geosci., 94–98. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2000.04.011
Xiong, G. (1992). Some problems concerning the transformation of gravity and magnetic anomalies in progress of ore resources Ⅱ. The Effect and Peoblems of ppward Contiuuationc Geophys. Geochem. Explor, 358–364.
Xu, N., Mao, J., Ye, H., Shen, M., Liu, Y., and Chen, L. (2008). Geological characteristics and new ore-finding progress in the dapai lead and zinc deposit of yongding county, Fujian Province. Geol. Explor, 20–23.
Xue, G. Q., Zhou, N. N., and Tang, D. M. (2023). Geophysical technology for exploration of magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposits:case study in Kalatongke deposit. Acta Petrol. Sin. 39 (4), 1117–1124. doi:10.18654/1000-0569/2023.04.11
Xue, G. Q., Zhou, N. N., Su, B. X., Zhang, A. K., Yang, Y. C., Mo, J. P., et al. (2024a). Geophysical exploration strategy for cu-ni-co deposits in China: a review. Geophysics 89 (1), WB25–WB34. doi:10.1190/geo2023-0034.1
Xue, G. Q., Yin, C. C., Macnae, J., and Hu, X. Y. (2024b). Geophysics for critical minerals — introduction. Geophysics 89 (1), 1–2. doi:10.1190/geo2023-1117-spseintro.1
Xue, G. Q., Lv, P. F., Chen, W. Y., Li, X. C., Xu, Y., Wu, X. W., et al. (2024c). Determining the location of the Bayan Obo rare Earth elements mineralization body by the transfer learning method. Geophysics 89 (1), WB57–WB66. doi:10.1190/geo2023-0212.1
Yan, S., Xue, G. Q., and Chen, M. S. (2016). Response of CSAMT electromagnetic component in the magnetized layered earth. Chin. J. Geophys. 59 (12), 4457–4463. doi:10.6038/cjg20161208
Ye, Z., Gao, L., Li, Y., Chen, C., Xia, F., Li, S., et al. (2025). Prospecting model and deep mineralization predictions for the Lamasu-Saibo copper deposit based on combined geological and geophysical exploration information. Ore Geol. Rev. 176, 106443. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2025.106443
Yuan, Y. (2020). Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous granitoids and Fe–Mo polymetallic mineralization in yongding-dehua area, Southwestern Fujian Province. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. PhD thesis.
Yuan, Y., Zhang, D., Feng, H. B., Di, Y. J., Wang, C. M., and Ni, J. H. (2014). The Re-Os isotope geochronology of dapai iron polymetallic ore deposit in yongding county, fujian province and its genetic significance. Acta Geol. Sin. - Engl. Ed. 88, 1025–1026. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12378_30
Zhang, D. (2000). Tectonic evolution and tin polymetal regional metallogenesis in Southwestern Fujian Province. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. PhD thesis.
Zhang, D. (2006). Metallogenesis, deep process and potential assessment of resources in the Wuyishan-Taiwan geological corridor area. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
Zhang, X., Zhang, D., Tan, H., Lin, Q., Di, Y., Lv, L., et al. (2012). Geological and geophysical model of thrust controlling on iron ore deposits in the Southwestern Fujian Province. Earth Sci. 37, 1243–1251. doi:10.3799/dqkx.2012.132
Zhang, Z., Zuo, R., and Cheng, Q. (2015). The mineralization Age of the Makeng Fe deposit, south China: implications from U–Pb and Sm–Nd geochronology. Int. J. Earth Sci. 104, 663–682. doi:10.1007/s00531-014-1096-4
Zhang, X., Meng, X., Chen, Z., Wang, J., and Xiu, C. (2018). Comprehensive study of the geological and geophysical characteristics of the metallogenic belt in southwest Fujian——A case study in the yongding-dapai polymetallic ore deposit. Chin. J. Geophys. 61, 1588–1595. doi:10.6038/cjg2018L0666
Zhang, D., Li, F., He, X., Hu, B., Zhang, X., Bi, M., et al. (2021). Mesozoic tectonic deformation and its Rock/ore-control mechanism in the important metallogenic belts in south China. J. Geomech. 27, 497–528. doi:10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.04.045
Zhang, Z., Dong, Y., Du, X., Qi, K., Xia, Y., Sun, F., et al. (2025). Application of high-precision magnetic measurement in the exploration of deep fluorite deposits in ore concentrations. Minerals 15, 351. doi:10.3390/min15040351
Zhao, G., and Cawood, P. A. (2012). Precambrian geology of China. Precambrian Res. 222–223, 13–54. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.017
Zhao, Y., Tan, H., Xu, Z., Yuan, R., Zheng, R., and Lin, F. (1980). “Geological conditions of the formation of calcic-skarn iron deposits in Southwestern Fujian and characteristics of their alteration and mineralization,” in Proceedings of the proceedings of institute of mineral deposits geology, Chinese academy of geological sciences (Beijing: Geological Publishing House), 25–52.
Zhao, X., Yu, S., Yu, M., Jiang, Y., Liu, K., and Mao, J. (2016). Geological characteristics and metallogenic epochs of the Dapai fe-pb-zn polymetallic deposit in yongding county, Fujian Province. Geol. China 43, 174–187. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.013
Zhao, X., Li, L., Xu, M., Liu, H., Zhu, Q., Jin, G., et al. (2021). Control of basement on Paleozoic mineralizations in the wuyi metallogenic belt. Ore Geol. Rev. 131, 104037. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104037
Zhou, Y., Carter, A., Wu, J., Yao, Y., Zhu, R., Liu, H., et al. (2023). Nature of the paleo-pacific subduction along the East Asian Continental margin in the Mesozoic: insights from the sedimentary record of West Sarawak, borneo. Geophys. Res. Lett. 50, e2022GL102370. doi:10.1029/2022GL102370
Keywords: Southwestern Fujian Depression Belt, Makeng-type iron–polymetallic deposit, high-precision magnetic ground survey, prospecting model, periphery exploration
Citation: Hu J, Yuan Y, Wu S, Zhang X and Hu B (2025) Integrated geophysical and geological analysis for peripheral exploration of Makeng-type Fe-polymetallic deposits: a case study from the Dapai Fe-polymetallic deposit, SE China. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1682097. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1682097
Received: 08 August 2025; Accepted: 06 October 2025;
Published: 07 November 2025.
Edited by:
Xiuyan Ren, Jilin University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zhenwei Guo, Central South University, ChinaGuoqing Ma, Jilin University, China
Baoliang Lu, Chang’an University, China
Copyright © 2025 Hu, Yuan, Wu, Zhang and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuan Yuan, eV95dWFuMDczMUAxNjMuY29t; Shaojiang Wu, d3VzaGFvamlhbmdAbWFpbC5pZ2djYXMuYWMuY24=
 Jiaxiu Hu
Jiaxiu Hu Yuan Yuan2*
Yuan Yuan2* Shaojiang Wu
Shaojiang Wu Bojie Hu
Bojie Hu