Abstract
Recycled sand from construction waste presents a promising substitute for natural sand. However, such sand typically exhibits low strength, high crushing index, and poor grading, which collectively compromise its performance in subgrade applications subjected to cyclic shear stresses caused by wave, seismic, and traffic loads. This study investigates the application of Soybean Urease-Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation (SICP) method to enhance the engineering properties of recycled sands. Firstly, several factors influencing the precipitation process are examined, including soybean powder concentration, cementation solution concentration and the ratio between urea and calcium chloride. Subsequently, unconfined compressive tests are conducted on sands reinforced under various conditions. Results indicate that the sample strength increases significantly with higher cementation solution concentration and grouting frequency; however, excessively high concentrations lead to a decline in sample strength, likely due to the reduced calcium carbonate precipitation efficiency under supersaturated conditions. Scanning electron microscopy reveals that the reinforcing effect can be attributed to calcium carbonate crystals formed between particles, which function as binding agents for the recycled sands.
1 Introduction
With the continuous advancement of global urbanization and infrastructure development, construction and demolition waste (C&D waste) has become one of the largest sources of solid waste worldwide. Statistics indicate that approximately 9 × 108 tons of C&D waste are generated annually in Europe (Bernardo et al., 2016; López Ruiz et al., 2020), 5.5 × 108 tons in the United States (Zhang et al., 2019; Zou et al., 2020), and 7.7 × 107 tons in Japan (Evangelista et al., 2015). In China, the annual production reaches 23.5 × 108 tons (Zheng et al., 2017; Ghis et al., 2018), exceeding the combined total of the above three regions by 15.27 × 108 tons. Efficient recycling and resource utilization of this vast amount of C&D waste could not only mitigate the shortage of natural aggregates but also significantly reduce the environmental burden associated with construction activities. Among various recycling strategies, crushing and sieving C&D waste to produce recycled sand for use in road subbases, ground improvement, and backfilling has emerged as a sustainable and economical approach. However, recycled sand generally exhibits irregular particle shapes, rough surfaces, high porosity, and weak interparticle bonding, leading to low compactness, poor shear resistance, and inadequate mechanical strength—limiting its direct use in load-bearing engineering structures (Berredjem et al., 2020). Therefore, developing an environmentally friendly, efficient, and sustainable solidification technique to enhance the strength and stability of recycled sand is of great engineering and environmental importance.
Traditional soil solidification methods primarily rely on cement, lime, or chemical binders. Although these approaches effectively improve mechanical performance, they are associated with high energy consumption, considerable CO2 emissions, and potential chemical pollution, making them inconsistent with modern concepts of low-carbon and sustainable construction (Khaiyum et al., 2023; Cheng et al., 2023; Chaudhury et al., 2023). In recent years, biocementation technologies based on biomineralization principles have attracted increasing attention. This technology, first introduced by Whiffin (2004), utilizes biological metabolism or enzyme-catalyzed reactions to induce the precipitation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) within soil pores or on particle surfaces, forming mineral bonds that significantly enhance strength and stability. Compared with traditional binders, biocementation offers advantages such as low carbon emissions, and cost-effectiveness and is regarded as a promising alternative for green soil improvement and aggregate stabilization.
The Enzyme-Induced Carbonate Precipitation (EICP) technique employs urease to catalyze the hydrolysis of urea, generating ammonium (NH4+) and carbonate (CO3−) ions. The latter combine with calcium ions (Ca2+) in the cementation solution to form CaCO3 crystals that bond adjacent soil particles (Cui et al., 2023). Unlike the Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation (MICP), the EICP process eliminates challenges associated with microbial cultivation, viability, and environmental adaptability, offering higher biosafety; moreover, the small molecular size of the enzyme enables better penetration into fine-grained soils (Kavazanjian and Hamdan, 2015; Almajed et al., 2020), thereby extending its applicability to a wider range of geotechnical materials. Consequently, EICP is considered a more practical and scalable biocementation technique for civil and geotechnical engineering applications.
While EICP offers significant advantages in terms of simplicity and applicability, its reaction efficiency and product morphology are strongly influenced by environmental conditions. The performance of the EICP reaction is highly sensitive to environmental parameters such as pH and temperature. Urease exhibits maximum catalytic activity under near-neutral conditions (pH 6.5–8.0) and moderate temperatures (20 °C–30 °C) (Park and Choi, 2022; Xie et al., 2023), whereas extreme acidity or alkalinity can cause enzyme denaturation and reduce carbonate formation efficiency. Similarly, elevated temperatures may accelerate urea hydrolysis but lead to unstable crystal growth and irregular CaCO3 morphology (Zhang et al., 2023a). Therefore, maintaining an optimal reaction environment is essential for ensuring efficient precipitation and achieving desirable mechanical performance in EICP-treated materials. Recent studies have successfully applied EICP and its plant-derived variant, Soybean Urease-Induced Carbonate Precipitation (SICP), to sand and soil stabilization. For instance, Almajed et al. (2020) extracted urease from jack bean meal and achieved an unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of approximately 2300 kPa in natural sand—comparable to specimens stabilized with 10%–12% cement. Yuan et al. (2024) used soybean-derived urease to treat standard sand, achieving a UCS of about 1500 kPa, while Wu et al. (2024) applied soybean urease to stabilize desert aeolian sand, observing the formation of a dense CaCO3 crust that improved surface bonding and effectively reduced wind erosion. These findings confirm the significant potential of EICP in enhancing the strength and microstructural integrity of granular materials.
Nevertheless, studies on the application of EICP to recycled construction waste sand remain limited. Due to its distinct surface morphology and pore structure, recycled sand exhibits complex interfacial behaviors that may influence the spatial distribution and bonding efficiency of CaCO3. For example, Bai et al. (2023) reported that residual cement paste on recycled sand surfaces contains abundant micropores, which can increase water consumption and weaken the interfacial transition zone (ITZ), leading to reduced mechanical performance. Conversely, other studies suggest that the rough surface morphology of recycled sand can enhance mechanical interlocking, thereby improving tensile and flexural properties (Dang et al., 2022; Ding et al., 2021; Ma et al., 2024). Therefore, given the unique characteristics of recycled sand, it is of great scientific importance to systematically investigate the solidification effects and underlying mechanisms of EICP, thereby promoting its engineering application in the resource utilization of C&D waste.
Based on this, the present study employed the SICP technique to solidify construction waste recycled sand. The effects of soybean powder concentration, the urea-to-CaCl2 ratio, and the cementation solution concentration on calcium carbonate precipitation characteristics and reactant utilization efficiency were systematically investigated, and the optimal reaction conditions were determined. Furthermore, the influences of cementation solution concentration, grouting frequency, and particle size on the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) were examined. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis was conducted to elucidate the microstructural cementation mechanisms of SICP-treated recycled sand. The findings provide a theoretical foundation and technical reference for the engineering application of SICP in recycled aggregate utilization and green ground improvement.
2 Materials and sample preparation
2.1 Recycled sand
The recycled aggregate utilized in this study was sourced from a waste material stockpile at a sand-making factory in the city of Lishui, China. It primarily consisted of discarded fine-grained aggregates with particle sizes smaller than 2 mm. Figure 1 shows the storage location of the recycled sand, and Figure 2 shows a picture of the recycled construction waste sand and the basic physical properties of the sample. The mineralogical composition of the recycled sand was analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), with the results presented in Figure 3. This analysis revealed predominant content of SiO2, along with components such as CaCO3 and NaAlSi3O8.
FIGURE 1

Sampling location.
FIGURE 2

(a) A picture of recycled constructed waste sand; (b) basic physical parameters of the sample.
FIGURE 3

X-ray diffraction pattern of recycled construction waste aggregates.
2.2 Soybean urease
The urease used in the study was extracted from dried soybeans powder (protein content 20.8%, carbohydrate content 59.3%) shown in Figure 4. The extraction procedure was as follows: 1) A predetermined mass of soybean powder was weighed using an electronic balance and placed in a beaker, followed by the addition of a measured amount of deionized water; 2) The mixture was initially stirred manually with a glass rod and then magnetically stirred to ensure sufficient dispersion of the soybean powder; 3) Transferred homogenized mixture into 50 mL centrifuge tubes and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min; 4) Supernatant was collected as the urease solution for use in SICP reactions.
FIGURE 4

Extraction process of urease solution.
Fresh urease solutions were prepared daily to ensure enzymatic activity. The extraction process was performed under neutral conditions (pH ≈ 7) at room temperature (Park and Choi, 2022; Xie et al., 2023), and all enzyme solutions employed in this study were derived from the same batch of soybean powder to ensure consistency and reproducibility. To investigate the relationship between soybean powder concentration and urease activity, seven soybean powder suspensions were prepared with concentrations ranging from 2 g/100 mL to 20 g/100 mL. The details are outlined in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Soybean powder solution | Concentration (g/100 mL) | ||||||
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 20 | |
Test details for the investigation on the effects of soybean powder concentration.
2.3 Cementation solution
The cementation solution used in this study was prepared by mixing urea and calcium chloride (CaCl2) solution of equal volumes. According to the test requirement aiming to investigate the effect of raw solutions concentration on the utilization of urea and CaCl2, four representative concentrations were selected, as summarized in Table 2. For clarity, “U” denotes urea, “C” denotes calcium chloride, and the subsequent numbers indicate the corresponding solution concentrations. For instance, U1C1 represents a mixture of 5 mL of 1 mol/L urea solution and 5 mL of 1 mol/L CaCl2 solution.
TABLE 2
| Samples | Urea concentration (mol/L) | Calcium chloride concentration (mol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| U0.5C0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| U0.5C1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| U0.5C1.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| U0.5C2 | 0.5 | 2 |
| U1C0.5 | 1 | 0.5 |
| U1C1 | 1 | 1 |
| U1C1.5 | 1 | 1.5 |
| U1C2 | 1 | 2 |
| U1.5C0.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| U1.5C1 | 1.5 | 1 |
| U1.5C1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| U1.5C2 | 1.5 | 2 |
| U2C0.5 | 2 | 0.5 |
| U2C1 | 2 | 1 |
| U2C1.5 | 2 | 1.5 |
| U2C2 | 2 | 2 |
Test details for the investigation on the effects of cementation solution ratios.
2.4 Preparation of cylinder samples
In previous studies, two main methods have been used for preparing biocemented soil specimens: the pre-mixing method and the immersion method. In the pre-mixing method, the urease solution and cementation solution are directly mixed with the soil, which is more suitable for fine-grained soils (Shu et al., 2022a). However, since multiple treatments cannot be performed, the strength of specimens prepared by this method is often unsatisfactory. The immersion method (Liu et al., 2019), in which the specimens are soaked in the reaction solution, requires a large volume of reagent and is therefore not practical for field applications. Hence, it is necessary to improve the solidification method to achieve more efficient and feasible treatment.
In this study, a grouting method was employed to prepare cemented sand specimens for UCS testing. The preparation procedure consisted of three main stages: sand filling, grouting, and curing.
2.4.1 Mold preparation and sand filling
Cylindrical specimens with a diameter of 39.1 mm and a height of 80 mm were designed, and custom-made acrylic molds with a height of 90 mm were used. Prior to sand filling, the inner wall of each mold was coated with a thin layer of petroleum jelly and lined with a plastic release film to facilitate demolding. According to the Test Methods of Soils for Highway Engineering (GTJ 3430–2020, T 0123) (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, 2020; Zhang et al., 2023b), the mass of recycled sand required for specimen preparation was calculated based on the target relative density which was maintained at 0.6 throughout this study. The measured sand was then placed into a cylindrical mold in three layers. After each layer was added, the mold was vibrated along its outer wall using a vibration device at a frequency of 150–200 cycles per minute, while the specimen surface was lightly tapped with a hammer at 30–60 cycles per minute until the sand surface slightly exceeded one-third of the mold height. This procedure was repeated for the subsequent two layers until the final target height was reached and weighted as m1. To prevent interlayer separation, the surface of each compacted layer was slightly roughened before adding the next layer.
2.4.2 Grouting process
The grouting process is illustrated in Figure 5. To maintain specimen stability during grouting, cotton fabric and porous stones were placed at both ends of the sand column. The mold was then sealed with a threaded cap equipped with a centrally mounted injection tube, while the overall system remained semi-closed. Grouting was performed from the top using a peristaltic pump, allowing the reaction solution to flow freely from the bottom outlet. This setup ensured a uniform injection rate and minimized the risk of uneven cementation caused by repeated infiltration. All grouting operations were conducted at a room temperature of 20 °C. The cementation solutions were stored in an ice bath during injection to prevent premature urease deactivation. Initially, 50 mL of urease solution (approximately 1.1 times the pore volume which calculated from the soil three-phase parameters via index conversion) was injected at a constant flow rate of 2 mL/min. After that, the specimen was left undisturbed for 2 h, followed by the injection of an equal volume of cementation solution. The specimen was then left to react for 24 h, completing one grouting cycle. Thereafter, repeat the above steps for the prescribed number of grouting cycles until all cycles were completed.
FIGURE 5
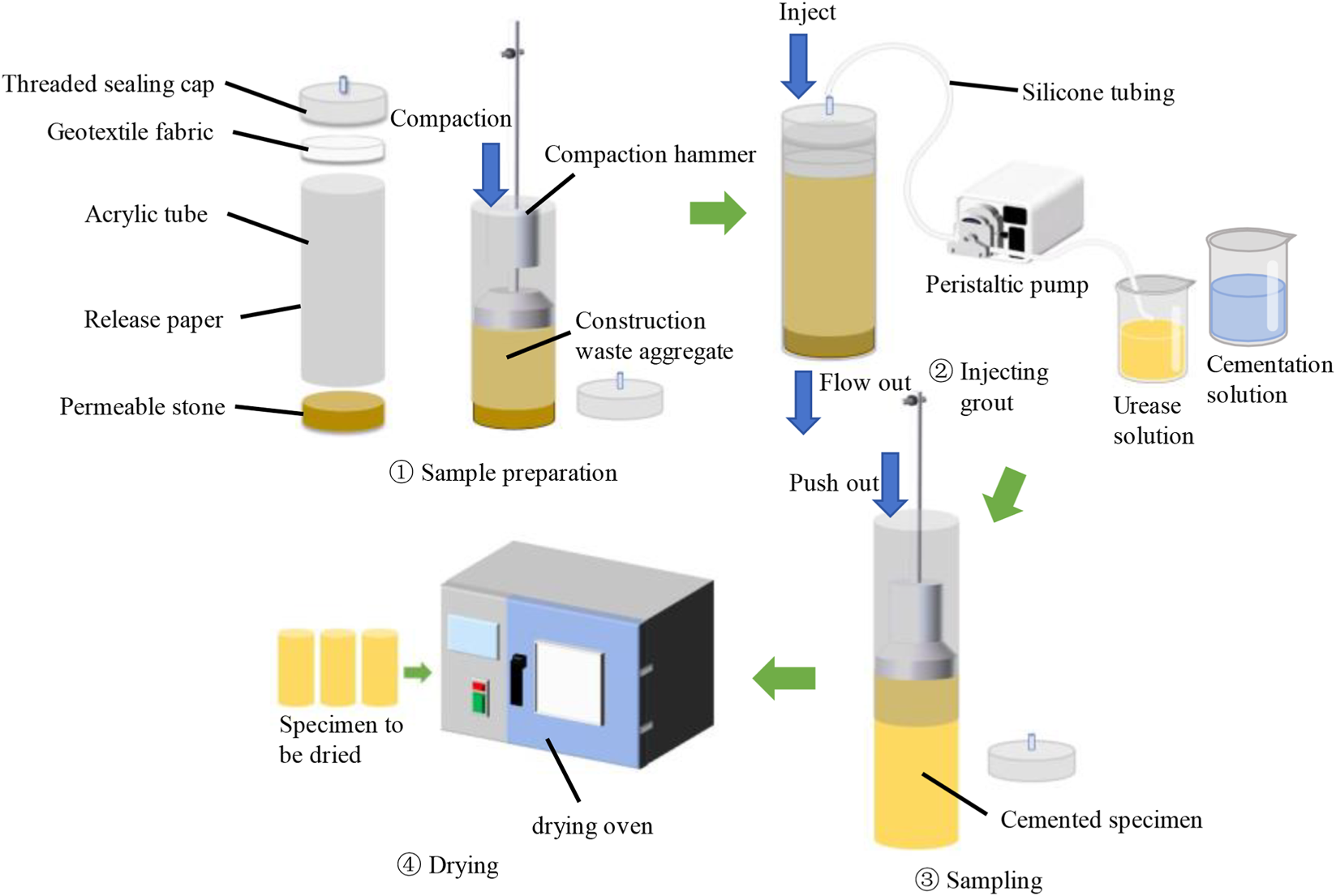
Grouting process.
2.4.3 Curing and post-treatment
After the final grouting cycle, the specimen was sealed with plastic wrap to prevent moisture evaporation and cured in a constant temperature curing chamber at 20 °C for 72 h. Subsequently, ultrapure water was injected to remove unreacted residues (Shu et al., 2022b). The specimens were carefully demolded and oven-dried at 50 °C until a constant weight was reached, which was recorded as m2. The complete sample preparation procedure is illustrated in Figure 5.
3 Methods
3.1 Urease activity test
Urease acts as a biocatalyst that hydrolyzes urea into ammonium and carbonate ions, thereby increasing the ionic concentration of the solution and consequently its electrical conductivity (EC). Variations in EC can thus be used to characterize the hydrolytic capacity of urease. According to Whiffin’s empirical relationship a conductivity change rate of 1 m/(cm·min) corresponds to the hydrolysis of 11.11 mmol of urea per minute (Whiffin, 2004). The urea hydrolysis rate (Ru) can therefore be expressed as Equation 1:
Where:
= urea hydrolysis rate (mmol·min-1); k = 11.11 (mmol·min-1)/(mS·cm-1·min-1) is the empirical conversion coefficient from Whiffin;
= average rate of conductivity change (mS/(cm·min));
During the urease activity test, 3 mL of urease solution was mixed with 27 mL of 1.11 mol/L urea solution, and the mixture was incubated in a 25 °C water bath. The electrical conductivity of the solution was recorded using a conductivity meter at 5-min intervals, with a total of four measurements taken to determine the rate of conductivity change.
3.2 Utilization rate test of CaCl2 and urea
The utilization rate test involved mixing 10 mL of enzyme solution with 10 mL of cementation solution, which was then allowed to react for 24 h in a 25 °C water bath. Following the reaction, the titration method was used to measure the calcium ion concentration in the filtered solution according to the Water quality–Determination of calcium–EDTA titrimetric method (ISO 6058–1984) (International Organization for Standardization, 1984). Finally, the utilization rate of CaCl2 and the utilization rate of urea were calculated as Equations 2, 3.
Where:
= utilization rate of CaCl2 (%);
= utilization rate of urea (%);
= initial moles of CaCl2 added;
= moles of unreacted calcium ions measured after reaction;
= initial moles of urea added;
= moles of unreacted urea remaining after reaction.
3.3 Calcium carbonate precipitation rate test
Since XRD analysis confirmed that the recycled sand inherently contains a certain amount of CaCO3, the mass of newly precipitated CaCO3 could not be accurately determined using the conventional acid-washing method. To address this issue, based on the previous studies conducted by scholars (Zhang et al., 2023b; Xu and Yan, 2024), we estimated the rate of calcium carbonate precipitation by analyzing the changes in the sample’s mass before and after SICP treatment.
Specifically, the dry mass of each specimen was recorded as m1 prior to SICP process and as m2 after completion of SICP treatment process and oven-drying to a constant weight. The difference in mass was attributed to the CaCO3 precipitated within the pore spaces during the reaction. The precipitation rate (RCaCO3) was then calculated using Equation 4:
Where:
m1= dry mass of each specimen before SICP treatment process (g);
m2= dry mass of each specimen after SICP treatment process (g).
This indirect gravimetric approach allows quantitative evaluation of CaCO3 formation in recycled sand while avoiding interference from its inherent carbonate content.
3.4 Unconfined compressive strength (UCS) test
The UCS test was performed using a computer-controlled electronic universal testing machine with an axial load applied at a rate of 1 mm/min until specimen failure. According to the ASTM 2166 (ASTM 2166 and International, 2010), a thin and uniform layer of petroleum jelly was applied to the surfaces of the loading plates to minimize horizontal friction between the specimen ends and the plates, thereby reducing end restraint and ensuring uniform axial deformation during compression. The peak stress at failure was recorded as the UCS value in kilopascals (kPa). This investigation examined the effects of varying grout solution concentrations (c = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3 mol/L), grouting cycles (n = 4, 6, 8, 10), and particle size ranges (d = 2–1 mm, 1–0.5 mm, 0.5–0.25 mm) on the resulting strength of the recycled construction waste sand. For each testing condition, three replicate specimens were prepared, as detailed in Table 3.
TABLE 3
| Sample | Cementation solution concentration (c) (mol/L) | Grouting times (n) | Particle size range (d) (mm) | Maximum dry density (g/cm3) | Minimum dry density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 6 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 2 | 1 | 6 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 6 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 4 | 2 | 6 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 5 | 2.5 | 6 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 6 | 3 | 6 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 7 | 1 | 4 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 8 | 1 | 8 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 9 | 1 | 10 | 0–2 | 1.42 | 1.03 |
| 10 | 1 | 6 | 2–1 | 1.32 | 1.06 |
| 11 | 1 | 6 | 1–0.5 | 1.38 | 1.04 |
| 12 | 1 | 6 | 0.5–0.25 | 1.41 | 1.07 |
Details for the UCS tests on recycled construction waste sand.
3.5 Microstructural analysis
Following the UCS test, crushed specimen fragments were collected for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. The samples were fixed to a tray using conductive adhesive and then subjected to ion sputtering. Images of the inter-particle CaCO3 precipitation patterns were captured at different magnifications to reveal the stabilization mechanism associated with the SICP method. Multiple images were taken for each condition.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Effect of soybean powder concentration on urease activity
Figure 6 shows the relationship between the urease activity and soybean powder concentrations. It is seen that the urease activity demonstrated an approximately linear growth pattern with the increasing soybean powder concentration. However, the unit mass urease activity (urease activity/soybean powder mass) exhibited a gradual decline as soybean powder concentration increased, especially for the low concentrations. This decreasing trend plateaued after reaching a concentration of 10 g/100 mL, suggesting a limitation in the solution’s urease extraction efficiency. While low-concentration solutions displayed higher unit mass urease activity, indicating enhanced extraction efficiency, the absolute urease activity under high-concentration solutions significantly exceeded that of low-concentration conditions. Based on these findings and considering both urease activity and extraction efficiency, a concentration of 10 g/100 mL was selected as the optimal soybean powder concentration for subsequent experimentation.
FIGURE 6

The relationship between urease activity and unit mass urease activity at different soybean powder concentrations.
4.2 Effect of cementation solution ratio on calcium chloride and urease utilization
The experimental results, as shown in Figure 7, indicate a significant correlation between the ratio of urea to CaCl2 in the cementation solution and the utilization rates of both components. In the figure, samples with a urea to CaCl2 concentration ratio of 1:1 (i.e., U0.5C0.5, U1C1, U1.5C1.5, and U2C2) are highlighted with circles.
FIGURE 7

The effect of cementation solution ratio on CaCl2 and urea utilization: (a) CaCl2 utilization efficiency at different urea concentrations; (b) Urea utilization efficiency at different CaCl2 concentrations.
Figure 7a demonstrates the relationship between the urea to CaCl2 ratio (U:C) and CaCl2 utilization. As shown, the utilization rate of CaCl2 generally increases with the increase in urea concentration. For example, in a 1 mol/L CaCl2 solution, increasing the urea concentration from 0.5 mol/L to 1 mol/L results in a 60% increase in CaCl2 utilization. This suggests that a higher ion concentration facilitates a more complete precipitation reaction. However, this enhancement reaches a plateau when the U:C ratio exceeds 1. In cases where U:C ratio exceeds 1, further increases in urea concentration have a negligible effect on improving CaCl2 utilization. For instance, in a 1 mol/L CaCl2 solution, increasing the urea concentration from 1 mol/L to 1.5 mol/L only increases CaCl2 utilization by approximately 5%, which may be due to insufficient Ca2+ in the cementation solution to continue the precipitation reaction.
Figure 7b shows that the highest urea utilization is also observed when the U:C ratio is 1:1, with a maximum utilization rate exceeding 90%. However, when the U:C ratio exceeds 1:1, increasing CaCl2 concentration has a negative impact on urea utilization. This suggests that both excessive and insufficient CaCl2 concentrations can inhibit urease hydrolysis, ultimately affecting calcium carbonate deposition.
Bases on these findings, a constant concentration ratio of 1:1 between urea and CaCl2 was selected for subsequent experimentation.
4.3 Effect of cementation solution concentration on calcium carbonate precipitation rate
This subsection discusses the effect of varying cementation solution concentration on the precipitation rate of CaCO3. The ratio of urea to CaCl2 in the solution was fixed at 1:1, as aforementioned.
Figure 8 illustrates the pattern of CaCO3 precipitation across different solution concentrations. The results demonstrate a linear growth in the amount of CaCO3 with increasing concentration until 1.5 mol/L, after which the growth rate decreases. The maximum amount of CaCO3 reaches 1.72 g at a concentration of 2.5 mol/L. Beyond which point, further increasing concentration leads to decreased precipitation.
FIGURE 8

Effect of cementation solution concentration on CaCO3 precipitation rate.
On the other hand, the CaCO3 precipitation rate maintains a high value (86%∼92%) at lower solution concentrations, and drops sharply after 1.5 mol/L. This phenomenon is likely associated with the ion saturation effect. At lower concentrations of cementation solution, increasing the concentration facilitates the combination of Ca2+ and CO32- ions to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3). However, as the concentration of the cementation solution increases, the ion concentration resulting from hydrolysis reaches saturation, thereby inhibiting further hydrolysis (Xu et al., 2023). Consequently, there are insufficient free Ca2+ and CO32- ions available for reaction, which limits the formation of CaCO3. Based on these findings regarding both quantity and rate of CaCO3 generation, maintaining the cementation solution concentration between 1–1.5 mol/L appears optimal.
4.4 Unconfined compressive strength test result
Figure 9 illustrates the relationship between UCS of SICP-cemented samples and varying cementation solution concentrations (c). The number of grouting cycles is n = 6. It is shown that the specimen’s UCS increases as the concentration rises from 0.5 mol/L to 2.5 mol/L. The strength of the 1 mol/L sample increased by 685.06 kPa compared to the 0.5 mol/L sample, and that of the 1.5 mol/L sample increased by 922.06 kPa compared to the 1 mol/L sample. The compressive strength of the 2 mol/L grout solution sample increased by 1,018.34 kPa relative to the 1.5 mol/L sample, indicating a more substantial increase in strength. For a solution concentration of 2.5 mol/L, the sample achieved a peak compressive strength of 3,375.14 kPa.
FIGURE 9

Variation curve of unconfined compressive strength for samples with different cementation solution concentrations.
However, with further increases in solution concentration, compressive strength began to decrease. At a concentration of 3 mol/L, the compressive strength was 1,735.32 kPa, representing a reduction of 1,639.81 kPa relative to the 2.5 mol/L concentration case. The relationship between solution concentration and UCS largely mirrors the trend observed for CaCO3 precipitation, discussed in the previous section. At a solution concentration of 3 mol/L, both the amount of generated CaCO3 and the UCS of the samples began to decline. Excessively high cementation solution concentrations reduce the precipitation of CaCO3, an unfavorable situation for preparing high-strength samples. Results in Figure 9 indicate that a solution concentration higher than 3 mol/L creates a high-salinity environment that hinders hydrolysis of urea. These findings underscore the importance of evaluating the effect of solution concentration on CaCO3 generation before implementing the SICP method.
In addition, to elucidate the performance disparity between natural and recycled sand, a review of relevant literature was conducted, and the comparative results are summarized in Table 4. It was found that the mix design and sample preparation methods for these two materials differ significantly, yet both can ultimately achieve unconfined compressive strength (UCS) within the range of 250 kPa–4000 kPa. The strength values of 500–3375 kPa were achieved after six grouting cycles in this study and are closely aligned with the range reported in existing research, thereby validating the reliability of the proposed technique.
TABLE 4
| Author | Raw material | Mix method | Urease concentration | Cementation concentration | Injection number | Volume of each injection cycle | UCS (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Almajed et al. (2020) | Natural sand | Pre-mixing | 6 g/L urease solution | 2 mol/L urea +1.34 mol/L CaCl2 | — | one pore volume | 2300 |
| Zhang et al. (2023b) | Natural sand | Grouting | 20 g/L | 0.75 mol/L urea +0.75 mol/L CaCl2 | 6 | 50 mL + 50 mL | 700 |
| 10 | 1600 | ||||||
| 60 g/L | 6 | 250 | |||||
| 10 | 800 | ||||||
| Yasuhara et al. (2012) | Natural sand | Grouting | 0.5 g urease mixed with 300 g sand | 1 mol/L urea +0.5 mol/L CaCl2 | 8 | 100 mL cementation solution | 466 |
| Shu et al. (2022b) | Natural sand | Grouting | 80 g/L | 1 mol/L urea +1 mol/L CaCl2 | 8 | 36 mL + 36 mL | 4000 |
| 6 | 2900 | ||||||
| 4 | 2000 | ||||||
| 2 | 1000 | ||||||
| 40 g/L | 8 | 3200 | |||||
| 6 | 2000 | ||||||
| 4 | 1500 | ||||||
| 2 | 500 | ||||||
| Current study | Recycled sand | Grouting | 10 g/L | 2.5 mol/L urea +0.5∼3 mol/L CaCl2 | 6 | 1.1 times pore volume | 500∼3375 |
UCS result summary.
The relationship between grouting cycles (n) and UCS is shown in Figure 10, using a cementation solution concentration of c = 1 mol/L. It is shown that the UCS demonstrates significant enhancement with increasing grouting cycles. Specifically, the strength of the 6-cycle sample increased by 676.99 kPa compared to the 4-cycle sample, the 8-cycle sample showed a 1,471.71 kPa increase compared to the 6-cycle sample, and the 10-cycle sample exhibited a 1,978.66 kPa increase relative to the 8-cycle sample. Therefore, as the cementation degree increased, the enhancing effect in compressive strength became larger. The UCS reaches 4,610.85 kPa at 10 grouting cycles. The solidification effect of further injection beyond 10 cycles was limited, as the pressure of the peristaltic pump was insufficient to inject slurry into the interior of the specimen. Additionally, excessive pressure induced excessive deformation of the specimen, since CaCO3 had occupied the inter-particle spaces and inhibited further infiltration of the solution. Therefore, only up to 10 cycles were considered in the present work.
FIGURE 10

Variation curve of compressive strength for samples with different cementation degrees.
Figure 11 shows the UCS of SICP-cemented samples with different particle sizes. To facilitate comparison with the original grading, a cementation solution concentration of c = 1 mol/L and grouting cycles of n = 6 was used, the relative density of the samples was also maintained at 0.6. The UCS of the 1–0.5 mm and 0.5–0.25 mm particle size samples were 1,805.95 kPa and 1,586.59 kPa, respectively, which are both higher than that of the original grading case (1,160.47 kPa). The strength of the 2–1 mm sample was only 344.59 kPa, significantly lower than the original grading case, indicating a strong variation in strength across different particle sizes. Based on previous studies of calcite-cemented porous materials (Ismail et al., 2002), the number of contact points and total particle surface area are both inversely proportional to particle diameter, which means smaller-particle specimen has more particle contacts and higher total particle surface area. In addition, according to Cheng et al. (2013), less CaCO3 is needed at contacts to bind particles as particle size decreases. Therefore, under otherwise the same condition, smaller-particle specimen can establish higher number of effective bindings between its particles and resulting in higher strength. As pointed out by Nafisi et al. (2020), a change in the particle size results in changes in the number of particle contacts, the amount of contact-precipitated CaCO3, and the amount of CaCO3 required to bind particles, leading to a change in the reinforcing effect of bio-cemented soil.
FIGURE 11

Unconfined compressive strength of samples with varying particle sizes.
illustrates the stress-strain relationship in UCS tests for specimens with varying reinforcing levels. All the specimens in this study reached their peak stresses at approximately 1% strain deformation and maintained some residual strength after peak. Furthermore, the stress-strain relationship of the specimens during the UCS test can be characterized into four stages:
Compaction Stage: occurring initially, where the stress-strain curves display positive curvature with gradual stress increase.
Elastic Stage: marked by linear stress-strain increase, with some fluctuations due to ununiform carbonation precipitation, causing localized failures within the specimen before global failure occurs.
Plastic Stage: characterized by nonlinear stress-strain behavior until peak stress.
Failure Stage: post-peak stage, marked by visible crack formation in the specimens, resulting in significant strength reduction.
FIGURE 12

Stress-strain relationships for different grouting cycles.
Figure 13 illustrates the failure modes of specimens under different conditions. The predominant failure type was concentrated shear failure near the upper portion of the specimen, accompanied by localized spalling. This pattern is consistent with the findings reported by Zhang et al. (2023b), who attributed such behavior to the uneven distribution of calcium carbonate precipitation. It should be noted that the distribution of calcium carbonate precipitation is affected by the synergistic effect of multiple factors, such as injection pressure, solution concentration, and raw material gradation, and the specific influencing mechanisms thereof still need to be further explored through in-depth research in the future.
FIGURE 13

Failure modes of SICP-cemented samples from recycled construction aggregate. (a)c= 0.5 mol/L (b)c= 2.5 mol/L (c)c= 3 mol/L (d) d = 2-1 mm (e) d = 1-0.5 mm (f) d = 0.5–0.25 mm. (g) n = 4 (h) n = 6 (i) n = 10.
For low-strength samples, such as those with a cementation solution concentration of c = 0.5 mol/L, particle size distribution d = 2–1 mm, and grouting cycles n = 4, large spalling failure areas appeared during failure, indicating a relatively weak bonding effect within the specimens. For high-strength samples, such as those with a cementation solution concentration of c = 2.5 mol/L, particle size distribution d = 1–0.5 mm, and grouting cycles n = 10, the samples maintained good integrity during failure. Distinct shear slip appeared at the sample tops and progressively developed as loading continued, indicating a relatively strong bonding effect within the specimens.
4.5 Calcium carbonate content
The correlation between CaCO3 content and compressive strength is examined and illustrated in Figure 14. The strength of SICP-cemented samples shows an approximate relationship of exponential growth with respect to CaCO3 content. As CaCO3 content increases, the sample strength improves accordingly. This observation is reasonable as CaCO3 acts as the primary cementing agent, filling the voids between sand particles and enhancing the overall stability. With further filling, the internal structure of the sample becomes denser, and interactions between particles become stronger, leading to significantly enhanced compressive strength.
FIGURE 14

The relationship between calcium carbonate content and compressive strength.
4.6 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis
The UCS-tested samples were collected for observation with a field-emission scanning electron microscope, to study their mineralized morphology and CaCO3 crystal characteristics. The accelerating voltage was set at 5000V.
Figure 15a,b show the microstructures of samples after 10 grouting cycles, magnified 500 times. Spherical CaCO3 crystals visibly coat the sand particle surfaces, rendering the particle contours indistinct. In some areas, cluster of spherical crystals are observed, which correlates to the earlier CaCO3 content tests results. Higher grouting frequency corresponds to increased CaCO3 generation, leading to enhanced crystalline bounding and higher strength. Figure 15c,d display the microstructures of samples after 4 grouting cycles, also magnified 500 times. Spherical CaCO3 crystals are also observed on the particle surfaces, albeit with reduced density and sparse distribution, allowing clear visibility of the sand particle surface. Less CaCO3 crystals results in weak bonding between sand particles and thereby relatively lower strength of the sample.
FIGURE 15

SEM images of SICP-cemented samples. (a)n = 10 (b)n = 10. (c) n = 4 (d) n = 4. (e) d = 2-1 mm (f) d = 2-1 mm. (g) Calcium carbonate crystal clusters (h) Bridge-like bonding. (i) Intergranular calcium carbonate deposition (j) Crescent-shaped bonding.
Figure 15e shows the SEM images of cemented samples with particles sizes ranging between 2–1 mm and Figure 15f is a 4000 times localized magnification of Figure 15e. It can be seen that tightly arranged rhombohedral crystals deposit on the particle surfaces. These deposits alter the surface morphology and may contribute to an increased internal friction angle of the cemented samples.
Figure 15g illustrates how CaCO3 crystal clusters form tight connections between surfaces and voids of recycled aggregates. This filling of inter-particle voids densifies the sample and enhances the sample strength. Figures 15h–j depict two modes of CaCO3 precipitation, namely particle surface precipitation and inter-particle precipitation. The surface-precipitated CaCO3 crystal are in general considered ineffective in creating bonding connections between particles. The image in Figure 15h displays “bridge-shaped” bonds that connect adjacent particles. During non-saturated grouting, slurry accumulates in inter-particle contact zones, forming tensioned regions that promote substantial spherical crystal deposition. Figure 15i,j illustrate this with crescent-shaped bonds that bind particles and restrict relative movement. Despite some voids still existing between particles, which act to retain sample permeability, these bonds enhance the compressive strength, as evidenced by the UCS test results.
5 Conclusion
A series of experiments were conducted to study the mechanical behavior of recycled construction waste sand strengthened through Soybean Urease-Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation (SICP) method. The investigation included analysis of urease activity, cementation solution ratio, cementation solution concentration, unconfined compressive strength (UCS), calcium carbonate content, and SEM analysis. The results form a preliminary reference for the engineering application of recycled construction waste sand. Based on these results, the following conclusions were established:
1. The enzymatic activity of urease increases approximately linearly with soybean powder concentration. The extraction efficiency of urease is significantly higher in low-concentration soybean powder solutions than in high-concentration solutions, reaching a maximum threshold at a soybean powder solution concentration of 10 g/100 mL.
2. To optimize curing effectiveness and economic efficiency, considering CaCO3 precipitation factors, a cementation solution ratio of 1:1 between urea and CaCl2 is recommended. In addition, with a given 10 g/100 mL concentration of enzyme solution, the cementation solution concentration of 1–1.5 mol/L appears to be optimized choice for CaCO3 precipitation in this study. Further increase in cementation solution concentration results in declining trends for both CaCO3 precipitation amount and precipitation rates, leading to significant waste of unused calcium ions.
3. The SICP method significantly enhance the strength of recycled sand. This study revealed that the strength is influenced by the cementation solution concentration, the degree of reinforcement, and particle size distribution. The relationship between unconfined compressive strength and cementation solution concentration aligns with the pattern between concentration and CaCO3 precipitation. Notably, excessively high cementation solution concentration proves detrimental to achieving high-strength specimens, while increased grouting frequency substantially enhances specimen strength. Under otherwise the same condition, improving the particle size distribution effectively increases the specimen’s strength. Moreover, there is a positive linear relationship between CaCO3 content and specimen strength, with higher CaCO3 content corresponding to greater unconfined compressive strength.
4. Finally, inter-particle precipitation of CaCO3 establishes cohesive bonds, significantly enhancing the shear strength of the specimen. Surface precipitation of CaCO3 alters the surface properties, leading to a small increase in the material’s frictional resistance. Overall, the increase in cohesive strength is the primary factor contributing to improvements in shear strength of the recycled sand.
It is worth noting that while this study offers practical guidance for recycled sand solidification via the EICP technique, further in-depth exploration of environmental impacts is needed (Alotaibi et al., 2022; Lee and Gomez, 2024; Yan et al., 2022). Specifically, focus should be on the generation law, migration path, and potential ecological risks of ammonium ions (NH4+/NH3), as well as the systematic verification of contaminant removal efficiency and applicable conditions through processes like water washing. Ultimately, this will provide a multi-dimensional comprehensive evaluation for the technology’s engineering application.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JH: Methodology, Software, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. DW: Writing – review and editing, Supervision. ZW: Supervision, Methodology, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. NL: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis. SL: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. PZ: Software, Writing – review and editing, Data curation.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52408369) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. LY23E080004 and No. LQN25A020008).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Almajed A. Abbas H. Arab M. Alsabhan A. Hamid W. Al-Salloum Y. (2020). Enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation (EICP)-based methods for ecofriendly stabilization of different types of natural sands. J. Clean. Prod.274, 122627. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122627
2
Alotaibi E. Arab M. G. Abdallah M. Nassif N. Omar M. (2022). Life cycle assessment of biocemented sands using enzyme induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) for soil stabilization applications. Sci. Rep.12, 6032. 10.1038/s41598-022-09723-7
3
ASTM 2166, International, Standard test method for unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soil, (2010).
4
Bai M. Xiao J. Gao Y. Ding T. (2023). Pore structure characteristics and mechanical property of engineered cementitious composites (ECC) incorporating recycled sand. Constr. Build. Mater.408, 133721. 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133721
5
Bernardo M. Gomes M. C. De Brito J. (2016). Demolition waste generation for development of a regional management chain model. Waste Manag.49, 156–169. 10.1016/j.wasman.2015.12.027
6
Berredjem L. Arabi N. Molez L. (2020). Mechanical and durability properties of concrete based on recycled coarse and fine aggregates produced from demolished concrete. Constr. Build. Mater.246, 118421. 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118421
7
Chaudhury R. Sharma U. Thapliyal P. C. Singh L. P. (2023). Low-CO2 emission strategies to achieve net zero target in cement sector. J. Clean. Prod.417, 137466. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137466
8
Cheng L. Cord-Ruwisch R. Shahin M. A. (2013). Cementation of sand soil by microbially induced calcite precipitation at various degrees of saturation. Can. Geotech. J.50, 81–90. 10.1139/cgj-2012-0023
9
Cheng D. Reiner D. M. Yang F. Cui C. Meng J. Shan Y. et al (2023). Projecting future carbon emissions from cement production in developing countries. Nat. Commun.14, 8213. 10.1038/s41467-023-43660-x
10
Cui M. Xiong H. Zheng J. Lv S. Cui M. Fu X. et al (2023). Variable research on engineering characteristics of soybean urease reinforced sand. KSCE J. Civ. Eng.27, 3313–3322. 10.1007/s12205-023-1959-y
11
Dang J. Xiao J. Duan Z. (2022). Effect of pore structure and morphological characteristics of recycled fine aggregates from clay bricks on mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater.358, 129455. 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129455
12
Ding T. Xiao J. Zou S. Yu J. (2021). Flexural properties of 3D printed fibre-reinforced concrete with recycled sand. Constr. Build. Mater.288, 123077. 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123077
13
Evangelista L. Guedes M. De Brito J. Ferro A. C. Pereira M. F. (2015). Physical, chemical and mineralogical properties of fine recycled aggregates made from concrete waste. Constr. Build. Mater.86, 178–188. 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.03.112
14
Ghisellini P. Ji X. Liu G. Ulgiati S. (2018). Evaluating the transition towards cleaner production in the construction and demolition sector of China: a review. J. Clean. Prod.195, 418–434. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.084
15
International Organization for Standardization (1984). Water quality — determination of calcium — EDTA titrimetric method.
16
Ismail M. A. Joer H. A. Randolph M. F. Meritt A. (2002). Cementation of porous materials using calcite. Géotechnique52, 313–324. 10.1680/geot.2002.52.5.313
17
Kavazanjian E. Hamdan N. (2015). “Enzyme induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) columns for ground improvement,” in IFCEE 2015 (San Antonio, Texas: American Society of Civil Engineers), 2252–2261. 10.1061/9780784479087.209
18
Khaiyum M. Z. Sarker S. Kabir G. (2023). Evaluation of carbon emission factors in the cement industry: an emerging economy context. Sustainability15, 15407. 10.3390/su152115407
19
Lee M. Gomez M. G. (2024). Removal of ammonium by‐products produced during biocementation soil improvement using rinse injection strategies. Soil Use Manag.40, e12984. 10.1111/sum.12984
20
Liu S. Wen K. Armwood C. Bu C. Li C. Amini F. et al (2019). Enhancement of MICP-treated sandy soils against environmental deterioration. J. Mater. Civ. Eng.31, 04019294. 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002959
21
López Ruiz L. A. Roca Ramón X. Gassó Domingo S. (2020). The circular economy in the construction and demolition waste sector – a review and an integrative model approach. J. Clean. Prod.248, 119238. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119238
22
Ma J. Wang Y. Zhang L. Zeng L. Wang X. Dang J. (2024). Influence of geometric shape, pore structure and surface modification of recycled fine aggregate on the rheology behaviour and strength development of mortar. J. Build. Eng.91, 109604. 10.1016/j.jobe.2024.109604
23
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China (2020). Test methods of soils for highway engineering, (GTJ 3430-2020, T 0123).
24
Nafisi A. Montoya B. M. Evans T. M. (2020). Shear strength envelopes of biocemented sands with varying particle size and cementation level. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng.146, 04020002. 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002201
25
Park J. Choi B.-Y. (2022). Feasibility study of enzyme-induced calcium carbonate precipitation (EICP) for CO2 leakage prevention. Geosci. J.26, 279–288. 10.1007/s12303-021-0033-3
26
Shu S. Yan B. Meng H. Bian X. (2022a). Comparative study of EICP treatment methods on the mechanical properties of sandy soil. Soils Found.62, 101246. 10.1016/j.sandf.2022.101246
27
Shu S. Yan B. Ge B. Li S. Meng H. (2022b). Factors affecting soybean crude urease extraction and biocementation via enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) for soil improvement. Energies15, 5566. 10.3390/en15155566
28
Whiffin V. S. (2004). Microbial CaCO3 precipitation for the production of biocement.
29
Wu L. Miao L. Sun X. Wang H. (2024). Effect of calcium sources on enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation to solidify desert aeolian sand. J. Environ. Manag.366, 121687. 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121687
30
Xie D. Zhang R. Wang J. (2023). The influence of environmental factors and precipitation precursors on enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) process and its application on modification of recycled concrete aggregates. J. Clean. Prod.395, 136444. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136444
31
Xu X. Yan X. (2024). Experiment on MICP-solidified calcareous sand with different rubber particle contents and sizes. Front. Mater.11, 1425653. 10.3389/fmats.2024.1425653
32
Xu K. Huang M. Cui M. Li S. (2023). Retarding effect of cementation solution concentration on cementation ability of calcium carbonate crystal induced using crude soybean enzyme. Acta Geotech.18, 6235–6251. 10.1007/s11440-023-01987-1
33
Yan Z. Gowthaman S. Nakashima K. Kawasaki S. (2022). Polymer-assisted enzyme induced carbonate precipitation for non-ammonia emission soil stabilization. Sci. Rep.12, 8821. 10.1038/s41598-022-12773-6
34
Yasuhara H. Neupane D. Hayashi K. Okamura M. (2012). Experiments and predictions of physical properties of sand cemented by enzymatically-induced carbonate precipitation. Soils Found.52, 539–549. 10.1016/j.sandf.2012.05.011
35
Yuan L. Li G. Liu J. Wang P. Liu C. Zhang J. (2024). Study on mechanical properties of sandy soil solidified by enzyme-induced calcium carbonate precipitation (EICP). Buildings14, 1977. 10.3390/buildings14071977
36
Zhang J. Gu F. Zhang Y. (2019). Use of building-related construction and demolition wastes in highway embankment: laboratory and field evaluations. J. Clean. Prod.230, 1051–1060. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.182
37
Zhang J. Yin Y. Shi W. Song D. Yu L. Shi L. et al (2023a). Experimental study on the calcium carbonate production rates and crystal size of EICP under multi-factor coupling. Case Stud. Constr. Mater.18, e01802. 10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01802
38
Zhang J. Yin Y. Shi W. Bian H. Shi L. Wu L. et al (2023b). Strength and uniformity of EICP-treated sand under multi-factor coupling effects. Biogeotechnics1, 100007. 10.1016/j.bgtech.2023.100007
39
Zheng L. Wu H. Zhang H. Duan H. Wang J. Jiang W. et al (2017). Characterizing the generation and flows of construction and demolition waste in China. Constr. Build. Mater.136, 405–413. 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.01.055
40
Zou G. Zhang J. Liu X. Lin Y. Yu H. (2020). Design and performance of emulsified asphalt mixtures containing construction and demolition waste. Constr. Build. Mater.239, 117846. 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117846
Summary
Keywords
construction waste recycled sand, soybean urease, calcium carbonate precipitation, cementation solution concentration, unconfined compressive strength
Citation
Huang J, Wu D, Wang Z, Lu N, Liu S and Zhou P (2025) Experimental investigation on the construction waste recycled sand reinforced by soybean urease-induced calcium carbonate precipitation. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1687298. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1687298
Received
17 August 2025
Revised
17 October 2025
Accepted
03 November 2025
Published
28 November 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Giovanni Martinelli, National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Italy
Reviewed by
Arvind Kumar Jha, Indian Institute of Technology Patna, India
Hadi Mohamadzade, Buein Zahra Technical University, Iran
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Huang, Wu, Wang, Lu, Liu and Zhou.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhe Wang, wangzhe@lsu.edu.cn; Nan Lu, nan.n.lu@outlook.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.