- 1Exploration Division, PetroChina Xinjiang Oilfield Company, Karamay, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
The resource potential of shale in Fengcheng formation in Mabei is huge, but it must rely on efficient hydraulic fracturing technology to obtain reservoir stimulation and achieve economic development. The propagation of hydraulic fractures in shale oil reservoir is significantly affected by natural fractures, and the interaction mechanism between hydraulic fractures and natural fractures is the key of realizing the optimal fracturing design. In particular, shale oil reservoir has complex conditions, such as interlayer blocking effect, differentiation of natural fracture development and variation of formation dip angle. In that case, the influence law of natural fracture on hydraulic fracture propagation is not clear, which restricts efficient development of shale oil. Therefore, based on the mechanical properties of shale in the Fengcheng formation, numerical model of the intersection of natural fractures and hydraulic fracture has been built. This intersection behaviors with different approach angle, interlayer stress and strength, natural fracture development degree and formation inclination have been fully analyzed. The results indicate that the hydraulic fracture is more favorable to penetrate the natural fracture with the increasing of the approaching angle. The barrier layer is conducive to the hydraulic fracture penetrating the natural fracture, restricting activation of the natural fracture. Also, the stress barrier effect is greater than the strength barrier effect. With the increase of the development degree of natural fractures, a large number of fractures weaken the overall strength of the formation, which is more conducive to the propagation of hydraulic fractures. When formation dip is large and propagation from weak strength to strong strength formation, hydraulic fracture is more susceptible to the influence of natural fractures and show the characteristics of turning along natural fractures. Outcomes deepen the understanding of the interaction mechanism between natural fracture and hydraulic fracture, which is beneficial for the optimal fracturing design and providing theoretical support for shale oil exploitation.
1 Introduction
The Permian Fengcheng formation in the northern Tarim Basin has been the hotspot of nearly three decades of oil and gas exploration, which has confirmed its role as the primary hydrocarbon source rock and a major reservoir in the region (Wang et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2017; Wang, 2013; Chen et al., 2016; Du et al., 2019; Xu and Yang, 2019). Notably, the Ma Ye 1 well yielded high-production industrial oil flows, marking a breakthrough in shale oil exploration within the Junggar Basin. Subsequently, eight additional exploratory wells had been drilled and also demonstrated favorable production, further highlighting the significant exploration and development potential of this shale oil (Yang et al., 2022; Zou et al., 2022). Experience from the Mahu shale oil field has demonstrated that hydraulic fracturing is essential for achieving efficient resource development. Geological investigations indicate that the shale is characterized by well-developed natural fractures (Figure 1 (Jin et al., 2022)). Oilfield engineering practices reveal that hydraulic fractures in the Fengcheng formation are generally simple in geometry and not form effective fracture network. It also means that these induced artificial fractures have not yet activated natural fractures, generating a major single artificial fracture. As a result, the reservoir stimulation effectiveness is low and can not have a good oil production. Therefore, enhancing the activation of natural fractures and increasing fracture-network complexity remain critical for improving hydraulic fracturing performance and production efficiency of shale oil (Zhou et al., 2020).

Figure 1. Natural fracture in Fengcheng Formation of Maye 1 well, Mabei Block (Jin et al., 2022).
When hydraulic fractures intersect natural fractures, their interaction induces a complex redistribution of stresses, significantly altering the propagation behavior of the hydraulic fractures. This interaction may manifest as propagation along natural fractures, interception and obstruction by natural fractures, or direct penetration through them. Extensive researches have been conducted to elucidate the interaction mechanisms between hydraulic fractures and natural fractures. Blanton (1986) reported that hydraulic fractures tend to penetrate natural fractures when both the stress difference and intersection angle are large, and also proposed a criterion for assessing fracture interaction. Building on this work, Warpinski and Teufel (1987) incorporated the combined effects of in-situ stress and pore pressure into the classical Mohr–Coulomb strength theory, developing a more comprehensive intersection criterion. Based on fracture mechanics, Renshaw and Pollard (1995) established a stress analysis model of natural fractures by superimposing the crack-tip stress field with the in-situ stress field. This model indicated that hydraulic fractures interacting with natural fractures may result only in two outcomes, which are penetration or slippage. Gu and Weng (2010) applied R&P criterion to arbitrary intersection angles and proposed corresponding evaluation criteria. Although these criteria addressed some limitations of the original R&P criterion, it neglected the role of intermediate principal stress and was valid only for 2D interactions between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures. These theoretical criteria can predict whether hydraulic fracture penetrate natural fracture, but can not describe hydraulic–natural fracture crossing behaviors in detail (Taleghani, 2009; Taleghani and Olson, 2009; Tale and ghani, 2011). Thus, Olson et al. (2012) conducted pioneering physical simulations by substituting glass plates for natural fractures. Their study systematically showed deflection and penetration behaviors when hydraulic fracture interacts with natural fracture. Zhao et al. (2014) applied elastic mechanics theory, developed a stress field model for hydraulic fractures approaching natural fractures and investigated the influence of induced stresses on natural fracture stability. Zhang et al. (2014) proposed a penetration criterion and introduced a method for calculating penetration angles. Hou et al. (2014), Li et al. (2024) performed fracturing experiments using rock cores, demonstrating that interaction behavior depends on fracture aperture, cementation strength, and approach angle. Higher cementation strength and larger approach angles promote more simple hydraulic fracture propagation. On the basis of such physical experiments, Cheng et al. (2014) formulated a penetration criterion for hydraulic fractures crossing natural fractures by analyzing three-dimensional stress distributions at fracture tips and along natural fracture surfaces. They identified horizontal stress difference as the primary control factor and established a critical threshold. Except for these theoretical and experimental studies, lots of scholars (Dahi and Olson, 2011; Li et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2021) applied finite element, boundary element, and discrete element methods to build numerical models of hydraulic fracture propagation in naturally fractured reservoirs. Their findings showed that lower rock strength, smaller stress differences, and higher injection rates enhance the likelihood of hydraulic fracture penetration. Furthermore, Zhou et al. (2022) investigated the effects of interlayers on fracture interaction mechanisms. Their results indicated that greater interlayer strength and stress promote hydraulic fracture propagation while reducing the likelihood of its capture by natural fractures.
Although extensive researches have been conducted on the interaction between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures, both numerical simulations and physical experiments have been conducted under relatively simple geological conditions. However, in the shale oil reservoir of Fengcheng formation, when hydraulic fractures intersect with natural fractures, complex conditions such as interlayer interference, varying degrees of natural fracture development, and differing formation dip inevitably affect the interaction between hydraulic fractures and natural fractures. Therefore, this study employs the cohesion unit method and finite element simulation techniques to establish a model for the interaction between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures. This model clarifies the influence of natural fractures on the propagation of hydraulic fractures, providing a theoretical foundation for the efficient development of the shale oil reservoir of the Fengcheng formation.
2 Model development for hydraulic–natural fracture intersections
2.1 Numerical simulation methods
In this study, the finite element method was employed to simulate hydraulic fracture propagation by incorporating cohesive element theory and the traction-separation law, together with a damage model, which has been widely used in describing fracture evolution and rock structure damage (Teng et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2025; Sun et al., 2025). The damage or failure was determined according to fracture mechanics criteria. Once complete failure occurred, a fracture was generated. For each cohesive element, the damage evolution process was characterized using the traction-separation law. Prior to damage initiation, the stress–strain response satisfied the following relationship:
In the above equations, σ denotes the stress vector, MPa. ε represents the strain matrix, %. σn is the normal stress, MPa. σs and σt correspond to the first and second shear stresses, MPa. K is the stiffness matrix. εn, εs, and εt are the normal, first shear, and second shear strains, %. The corresponding strains can be expressed as follows:
In this expression, dn, ds and dt denote the displacements in the normal, first tangential, and second tangential directions of the cohesive element, m. do represents the constitutive thickness, m.
Based on Equations 1, 2, the damage criterion is applied to determine the damage state of the element. Damage initiates when the tensile force reaches the maximum value of rock. In this study, the maximum nominal stress criterion is adopted, which is defined as Equation 3:
In the above equation, f = 1 indicates the onset of damage. σno, σso, and σto represent the peak tensile stresses perpendicular to the interface and along the first and second tangential directions, MPa. The notation ⟨σn⟩ indicates that pure compressive deformation under normal stress does not induce damage.
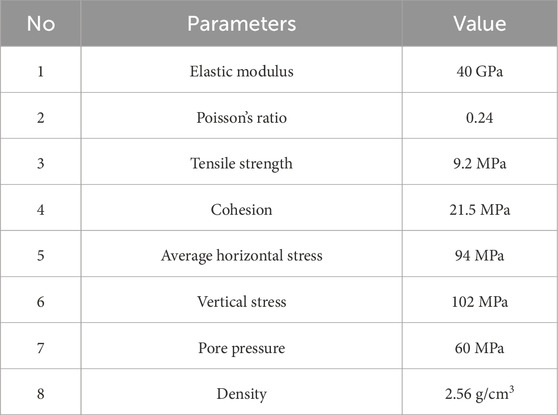
2.2 Numerical model
In the modeling process, geomechanical parameters were acquired from rock mechanical tests and geomechanical logging profile of the Fengcheng formation in the Mabei area (Table 1). Based on that, a numerical model was established to investigate the intersection behavior of natural fractures and hydraulic fractures under different approach angles (Figure 2a). The simulation was set to a size of 40 m × 100 m. To better reflect the actual geological conditions of the Fengcheng formation, numerical models including interlayer strength and stress, multiple natural fractures and formation dip were further developed, shown as Figures 2b−d.
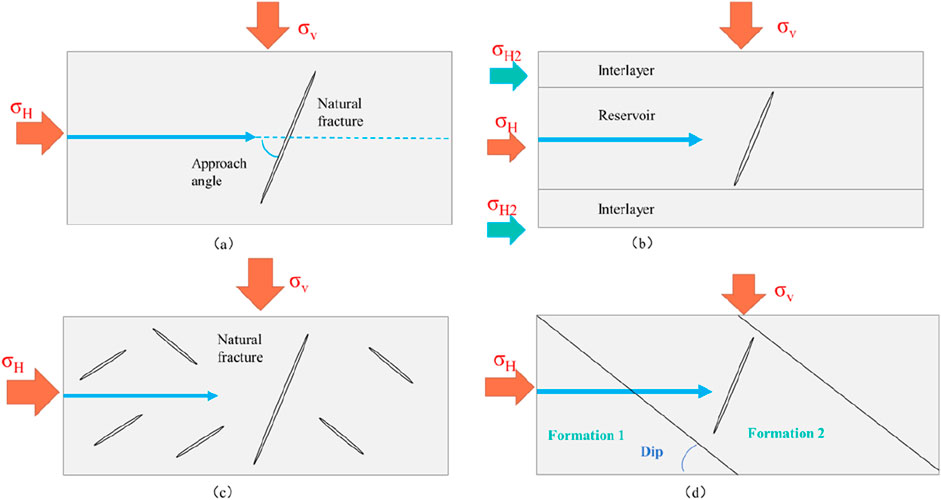
Figure 2. Models of intersection relationships between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures. (a) Homogeneous formation. (b) Interlayer (stress strength shieding). (c) Fractured formation. (d) Dip formation.
3 Simulation results and analysis
3.1 Effect of approach angle on hydraulic–natural fracture intersections
Figure 3 presents the simulation results of intersections between hydraulic fracture and natural fracture under varying approach angle conditions. In this study, four distinct approach angles were selected for simulation: 90°, 60°, 30° and 0°. As depicted in the figure, when the approach angle is large (90°), hydraulic fracture can directly penetrate natural fracture without significant deviation in their propagation path (Figure 3a). At a moderate approach angle (60 and 30°), natural fracture exhibits the capability to capture hydraulic fracture, which implies that the propagation direction of hydraulic fracture is diverted toward the natural fracture (Figures 3b,c). When the approach angle is small (i.e., natural fractures is parallel to the propagation direction of hydraulic fracture), the impact of natural fracture on hydraulic fracture propagation is negligible (Figure 3d).
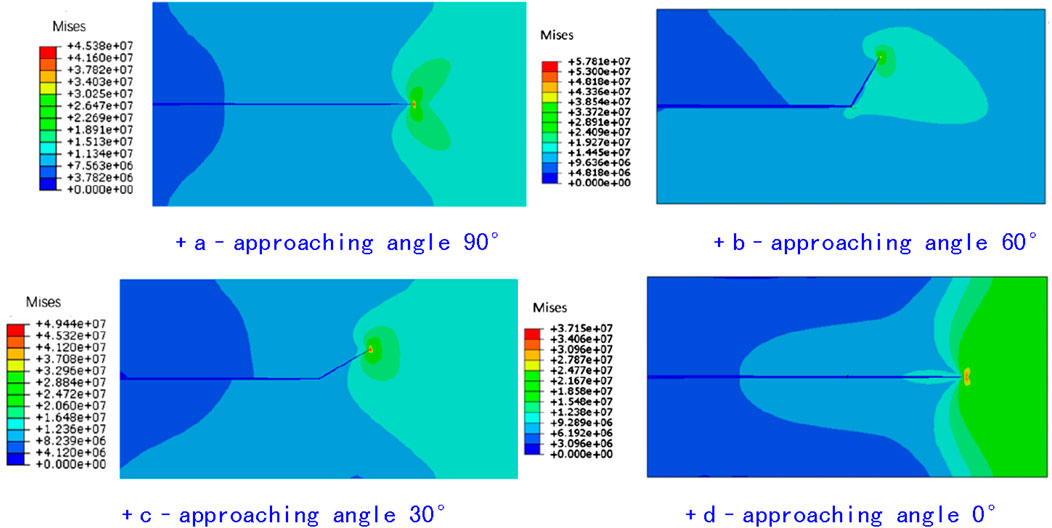
Figure 3. Intersection between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures under different approaching angles. (a) Approaching angle 90° (b) Approaching angle 60°. (c) Approaching angle 30° (d) Approaching angle 0°.
3.2 Effect of interlayers on hydraulic–natural fracture intersections
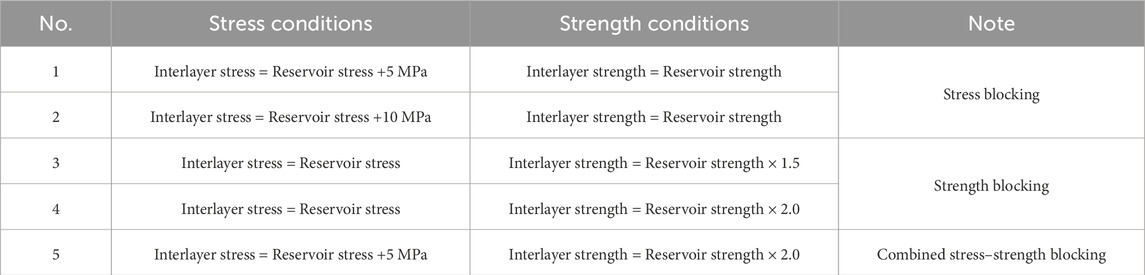
The shale oil reservoirs of the Fengcheng formation in the Mahu area exhibit pronounced interlayer blocking effects. Interlayers generally possess relatively high stress and strength, which exert a significant influence on fracture propagation. Accordingly, interlayer blocking is classified into three categories: stress blocking, strength blocking, and combined stress–strength blocking (Table 2). Strength blocking primarily refers to the simultaneous increase in rock strength parameters, such as tensile strength and cohesion.
Based on the parameter in Table 2, the interaction behaviors between hydraulic fractures and natural fractures under various interlayer blocking scenarios were systematically investigated, with the corresponding results presented in Figure 4. As depicted in this figure, under the stress blocking scenario, the propagation of hydraulic fracture within the reservoir formation is subjected to effective confinement. This confinement not only restricts the lateral deviation of hydraulic fracture, but also compels them to propagate along a relatively fixed trajectory, thereby maintaining a high degree of propagation directionality. In the contrast, under the pure strength blocking scenario, hydraulic fracture remains susceptible to the perturbation of natural fracture. As clearly illustrated in Figures 4c,d, hydraulic fracture exhibits a distinct deflection tendency. This observation explicitly demonstrates that the constraining effect of strength blocking on hydraulic fracture propagation is substantially weaker than that of stress blocking.
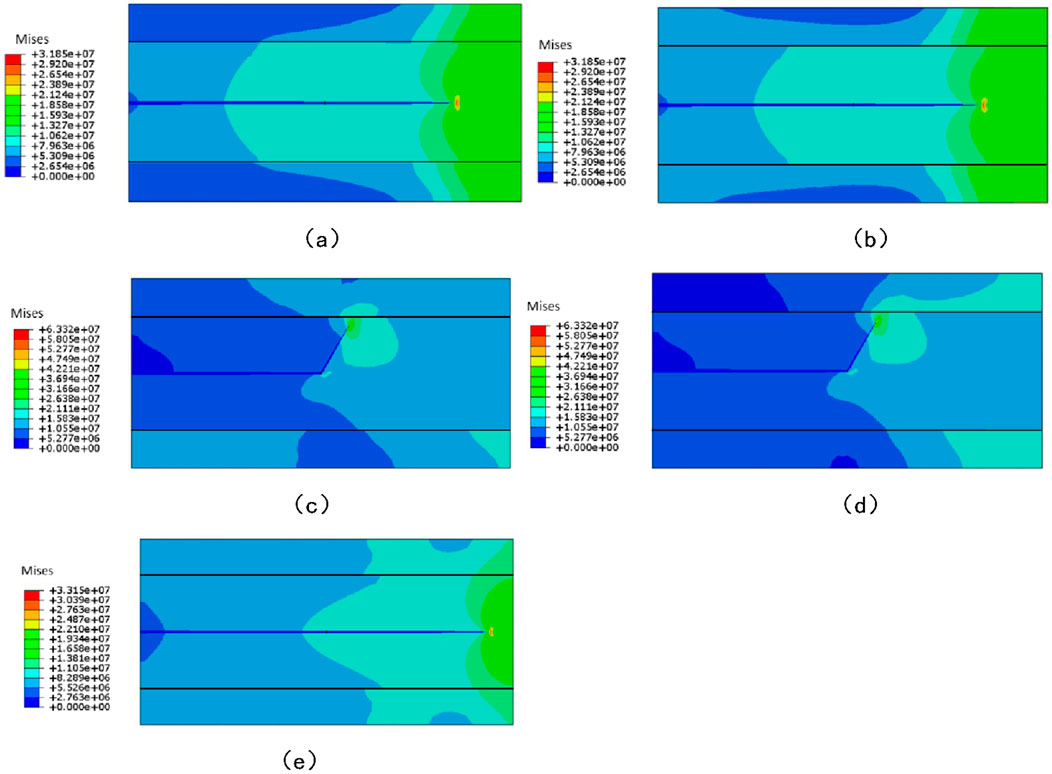
Figure 4. Intersection relationships between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures under different interlayer characteristics. (a) Group 1. (b) Group 2. (c) Group 3. (d) Group 4. (e) Group 5.
Furthermore, when stress blocking and strength blocking act in synergy (i.e., the combined blocking scenario), the propagation of hydraulic fracture is no longer disrupted by the presence of natural fracture. Instead, hydraulic fracture directly penetrates through the natural fracture and continue its propagation, as shown in Figure 4e.
3.3 Influence of natural fracture development on intersection behavior
Natural fractures in the Fengcheng formation of Mabei exhibit varying degrees of development, ranging from well-developed to poorly developed. During the interaction between hydraulic fractures and natural fractures, not only the intersecting natural fracture can affect hydraulic fracture propagation, but also the surrounding natural fractures can put impact on propagation. To investigate this effect, three scenarios were established: absence of additional natural fractures, moderately developed natural fractures, and highly developed natural fractures. The simulated interactions between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures under these conditions are shown in Figure 5.
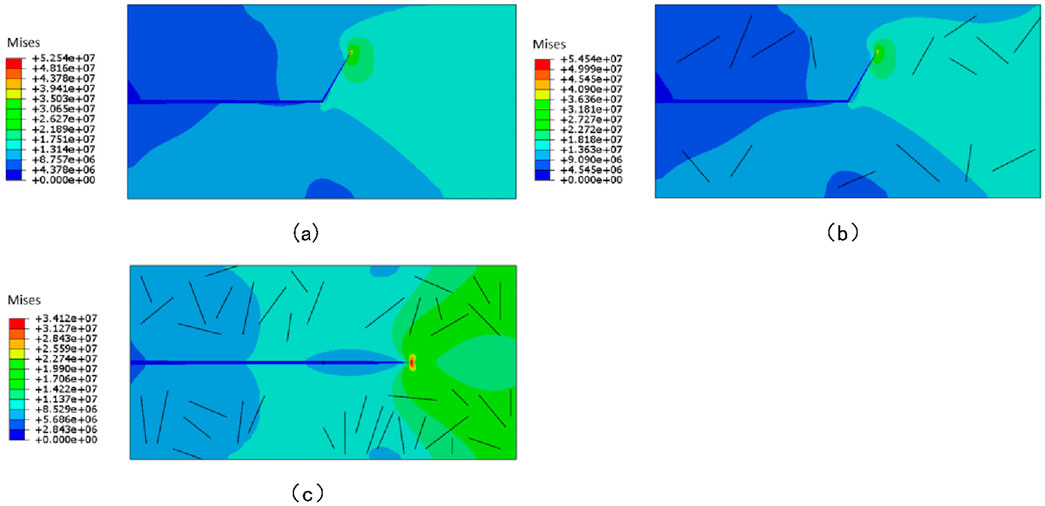
Figure 5. Interaction between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures under varying degrees of natural fracture development. (a) No additional natural fractures. (b) Moderately developed. (c) Extremely developed.
The results reveal that with an increasing degree of natural fracture development, distinct patterns of hydraulic fracture propagation emerge. Specifically, under the condition of moderately developed natural fractures, natural fracture retains the capability of capturing hydraulic fracture. In contrast, when natural fractures are highly developed, the interaction mechanism between hydraulic fracture and natural fracture undergoes a fundamental shift. Hydraulic fracture directly penetrates natural fracture without significant deflection. This phenomenon can be attributed to the fact that a high density of natural fractures weakens the overall mechanical strength of the formation. The reducing strength not only lowers the resistance to hydraulic propagation, but also facilitates more efficient pressure transmission within the formation. These combined effects collectively promote the penetration of hydraulic fracture through natural fracture, as illustrated in Figure 5c.
It is important to note that the above analysis is constrained to investigating the influence of natural fracture development degree on the interaction between a single natural fracture and a single hydraulic fracture. Normally, an increase in the number of natural fractures inevitably leads to multiple intersections between hydraulic fractures and natural fractures. Such multiple intersections introduce greater complexity into the propagation path of hydraulic fractures (Kolawole and Ispas, 2020). This kind phenomenon can not be analyzed in this simulation. This limitation highlights the need for further studies to explore hydraulic fracture behavior in reservoirs with complex and multi-fracture networks.
3.4 Influence of formation dip angle on intersection behavior
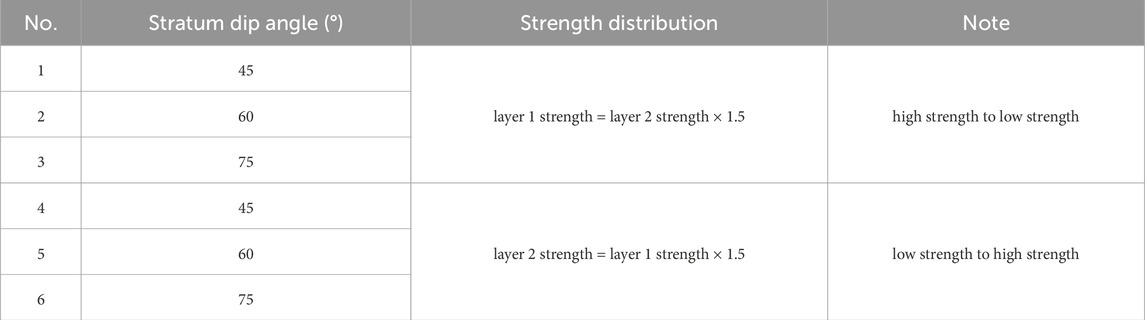
In the Fengcheng formation of the Mabei area, highly deviated well is widely employed for hydraulic fracturing operations. Under this operational condition, hydraulic fractures typically penetrate formation interfaces and subsequently intersect with natural fractures. This process significantly affects fracture network complexity and reservoir stimulation efficiency. To systematically investigate the influence of formation dip angle on the hydraulic fracture and natural fracture intersection relationship, three dip angles (45°, 60° and 75°) were selected. Additionally, two critical interface transition scenarios were incorporated into the study: (1) hydraulic fracture propagating from high-strength formations into low-strength formations. (2) hydraulic fracture propagating from low-strength formations into high-strength formations. Based on these variables and scenarios, six distinct formation dip angle cases were established. Detailed parameters are summarized in Table 3.
Numerical simulations were performed to analyze the hydraulic fracture and natural fracture intersection characteristics under the six formation dip scenarios, and results are visualized in Figure 6. For the scenario where hydraulic fracture propagates from high-strength to low-strength formations, hydraulic fracture exhibits a higher tendency to penetrate natural fracture within the low-strength formation. With increasing formation dip angle, hydraulic fracture gradually deviates from their original propagation direction and tends to propagate along the plane of natural fracture, as evident in Figures 6a–c. In contrast, when hydraulic fracture propagates from low-strength to high-strength formations, the enhanced mechanical strength of the target formation increases the resistance to hydraulic penetration through natural fracture. As a result, hydraulic fracture is more prone to divert along pre-existing weak structural planes (i.e., natural fracture) rather than penetrating them, leading to significant propagation deviation along natural fracture, as illustrated in Figures 6d–f.
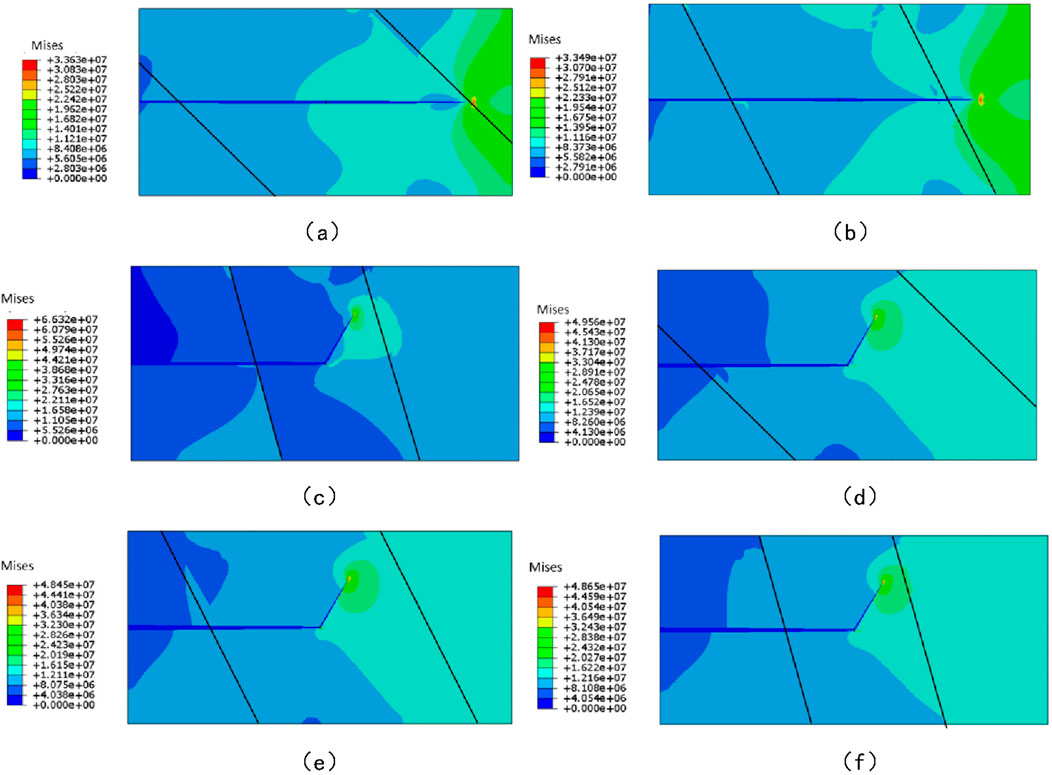
Figure 6. Intersection between natural fractures and hydraulic fractures under different formation dip angles. (a) Group 1. (b) Group 2. (c) Group 3. (d) Group 4. (e) Group 5. (f) Group 6.
4 Engineering analysis
To further validate the accuracy and reliability of the numerical simulations presented in this study, four fracturing stages in the Mabei Fengcheng formation were selected, all of which had identical operational parameters, including injection rate, cluster spacing, perforation phase, and perforation density. Under these consistent engineering conditions, the correlations between influencing factors (approach angle, stress contrast between interlayers and the reservoir, strength ratio between interlayers and the reservoir, formation dip angle) and the resulting fracture length were analyzed, shown in Table 4. The approach angle was determined based on the wellbore trajectory relative to the dominant orientation of natural fractures. The interlayer-reservoir stress contrast and strength ratio were calculated from logging data. As shown in Table 4, larger approach angles and smaller formation dip angles, combined with higher interlayer stress and strength, correspond to longer fracture lengths. Specifically, the single-wing fracture lengths of Section 1 and Section 2 are significantly greater than those of Section 3 and Section 4. These findings confirm the validity of the numerical simulations and further demonstrate that the interaction mechanism between hydraulic and natural fractures exerts a substantial influence on the morphology of hydraulic fracture network.
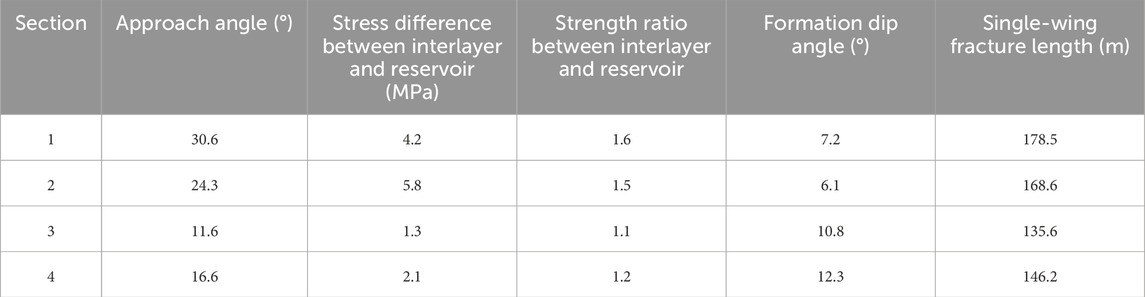
Table 4. Geological-engineering parameters and microseismic detection results of different fracturing stages.
5 Conclusion
Based on the geological and engineering characteristics of the shale oil reservoir in the Fengcheng formation, finite element simulation techniques were employed to establish numerical model for the intersection between natural fractures and hydraulic fracture, encompassing interlayer blocking effect, varying degrees of natural fracture development and formation dip. These simulations systematically clarified the regulatory role of natural fracture in the propagation behavior of hydraulic fracture.
The results indicate that as the approach angle decreases, the influencing effect of natural fracture on hydraulic fracture propagation becomes more prominent. This enhanced influence increases the propensity of hydraulic fracture to divert from their original trajectory and extend along the plane of natural fracture. Additionally, the interlayer exerts a significant control on the natural and hydraulic fracture interaction mechanism. Specifically, under the interlayer stress shielding effect, hydraulic fracture exhibits minimal tendency to divert. Instead it tends to directly penetrate natural fracture, maintaining a relatively stable propagation direction. In contrast, the interlayer strength shielding effect is less impactful than the interlayer stress shielding effect. Under the impact of strength shielding, hydraulic fracture remains susceptible to the perturbation of natural fracture, and diversion behavior may still occur during propagation.
For the scenario involving a fixed, single intersection between a single natural fracture and a single hydraulic fracture, the overall mechanical strength of the formation weakens with the increasing degree of natural fracture development. This reduction in matrix strength lowers the resistance to hydraulic fracture penetration, thereby facilitating the penetration of hydraulic fracture through natural fracture.
Furthermore, the formation dip angle exerts a strong influence on the intersection behavior between natural fracture and hydraulic fracture. As the dip angle increases, hydraulic fracture shows a higher likelihood of propagating along the plane of natural fracture. When hydraulic fracture propagates from low-strength formations to high-strength formations, the elevated mechanical strength of the high-strength formation inhibits hydraulic fracture penetration through natural fracture, rendering hydraulic fracture more prone to extending along the pre-existing natural fracture plane.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
GR: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. FL: Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Project administration. RD: Writing – original draft. WY: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. HS: Software, Investigation, Writing – review and editing. DY: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Investigation. LX: Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors GR, FL, RD, WY, and HS were employed by PetroChina Xinjiang Oilfield Company.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Blanton, T. L. (1986). “Propagation of hydraulically and dynamically induced fractures in naturally fractured reservoirs,” in SPE-15261-MS, presented at SPE Unconventional Gas Technology Symposium, Louisville, Kentucky. doi:10.2118/15261-ms
Chen, J. P., Wang, X. L., and Deng, C. P. (2016). Petroleum source, distribution and system in Junggar Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 90 (3), 421–450. doi:10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60041-9
Cheng, W., Yan, J., Mian, C., Xu, T., Zhang, Y., and Diao, C. (2014). A criterion for identifying hydraulic fractures crossing natural fractures in 3D space. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 41 (3), 371–376. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(14)60042-2
Dahi, T. A., and Olson, J. E. (2011). Numerical modeling of multi-stranded hydraulic fracture propagation: accounting for the interaction between induced and natural fractures. SPE J. 16 (3), 575–581. doi:10.2118/124884-pa
Du, J. H., Zhi, D. M., and Tang, Y. (2019). Prospects in Upper Permian and strategic discovery in Shawan sag, Junggar Basin. China Pet. Explor. 24 (1), 24–35. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.01.004
Gu, H., and Weng, X. (2010). “Criterion for fractures crossing frictional interfaces at non-orthogonal angles,” in 44th US Rock Mechanics Symposium and 5th US-Canada Rock Mechanics Symposium (Salt Lake City, Utah: OnePetro).
Hou, B., Cheng, W., and Chen, M. (2014). Experiments on the non-planar extension of hydraulic fractures in fractured shale gas reservoirs. Nat. Gas. Ind. 34 (12), 81–86. doi:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.12.011
Jin, Z. J., Liang, X. P., and Wang, X. J. (2022). Shale Oil Enrichment Mechanism and Sweet Spot Selection of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 43 (6), 631–639.
Kolawole, O., and Ispas, I. (2020). Interaction between hydraulic fractures and natural fractures: current status and prospective directions. J. Petroleum Explor. Prod. Technol. 10, 1613–1634. doi:10.1007/s13202-019-00778-3
Li, R., Yi, X. B., and Wang, T. Y. (2022). Numerical simulation of hydraulic fracturing for low permeability reservoirs based on particle flow code-discrete element method. Petroleum Sci. Bull. 7 (4), 576–583. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2022.04.049
Li, Z. Y., Chen, J. B., and Zuo, H. L. (2024). Interaction laws of hydraulic fractures and natural fractures in shale reservoirs. Fault-Block Oil Gas. Field 31 (2), 232–240. doi:10.6056/dkyqt202402007
Olson, J. E., Bahorich, B., and Holder, J. (2012). “Examining hydraulic fracture–natural fracture interaction in hydrostone block experiments,” in SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference, The Woodlands, Texas, USA, February 6–8, 2012. doi:10.2118/152618-ms
Renshaw, C. E., and Pollard, D. D. (1995). An experimentally verified criterion for propagation across unbounded frictional interfaces in brittle, linear elastic materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 32 (3), 237–249. doi:10.1016/0148-9062(94)00037-4
Sun, C., Shi, C., Zhu, Z., Haixiao, L., Zhenhua, L., Feng, D., et al. (2025). Overburden failure characteristics and fracture evolution rule under repeated mining with multiple key strata control. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 28029. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-14068-y
Taleghani, A. D. (2011). Modeling simultaneous growth of multi-branch hydraulic fractures. San Francisco: ARMA.
Taleghani, A. D. (2009). “Analysis of hydraulic fracture propagation in fractured reservoir: an improved model for the interaction between induced and natural fractures,”. PhD Thesis (Austin, Texas: University of Texas at Austin).
Taleghani, A. D., and Olson, J. E. (2009). Numerical modeling of multistranded hydraulic fracture propagation: accounting for the interaction between induced and natural fractures. SPE J. 16 (03), 575–581. doi:10.2118/124884-PA
Teng, T., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., and Qiao, X. (2025). In situ nuclear magnetic resonance observation of pore fractures and permeability evolution in rock and coal under triaxial compression. J. Energy Eng. 151 (4), 04025036. doi:10.1061/jleed9.eyeng-6054
Wang, X. L. (2013). Hydrocarbon source rocks and petroleum geochemistry in the Junggar Basin. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press.
Wang, W., Fu, H., Xing, L. X., Chai, B., Liu, B., and Shi, X. (2021). Fracture propagation behavior of carbonate geothermal reservoirs based on XFEM. Earth Sci. – J. China Univ. Geosciences 46 (10), 3509–3519. doi:10.3799/dqkx.2021.005
Wang, J. T., Yang, S., and Zou, Y. (2022). Characteristics, genesis and distribution of high-quality reservoir of the first member of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mabei area, Junggar Basin. China Pet. Explor. 27 (3), 99–109. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2022.03.009
Wang, L., Zhu, L., Cao, Z., Liu, J., Xue, Y., Wang, P., et al. (2025). Thermo-mechanical degradation and fracture evolution in low-permeability coal subjected to cyclic heating–cryogenic cooling. Phys. Fluids 37 (8), 086617. doi:10.1063/5.0282266
Warpinski, N. R., and Teufel, L. W. (1987). Influence of geologic discontinuities on hydraulic fracture propagation (includes associated papers 17011 and 17074). J. Petroleum Technol. 39 (2), 209–220. doi:10.2118/13224-pa
Xu, P., and Yang, J. (2019). Review of China’s energy industry in 2018 and outlook for 2019. Petroleum Sci. Forum 38 (1), 8–19. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-302x.2019.01.002
Yang, F., Meng, X., and Wang, X. H. (2022). Micropore characteristics and influencing factors of Fengcheng Formation shale in well maye-1. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 43 (1), 1–10. doi:10.7657/XJPG20220101
Zhang, R., Li, G. S., and Zhao, Z. H. (2014). New criteria for hydraulic fracture crossing natural fractures. Chin. J. Geotechnical Eng. 36 (3), 585–588. doi:10.11779/CJGE201403024
Zhao, J. Z., Yang, H., and Li, Y. M. (2014). Stability of the natural fracture when the hydraulic fracture is approaching. Nat. Gas. Geosci. 25 (3), 402–408. doi:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.03.0402
Zhou, X. J., Yong, R., and Fan, Y. (2020). Influence of natural fractures on fracturing of horizontal shale gas wells and process adjustment. China Pet. Explor. 25 (6), 94–104. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.06.010
Zhou, X., Liu, X. J., and Ding, Y. (2022). Simulation of intersecting hydraulic fractures with natural fractures considering layer barrier effect. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 12 (3), 515–525. doi:10.13809/j.cnki.cn32-1825/te.2022.03.014
Zhu, S., Qin, Y., Liu, X., Wei, C., Zhu, X., and Zhang, W. (2017). Origin of dolomitic rocks in the lower permian Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin, China: evidence from petrology and geochemistry. Mineralogy Petrology 111 (2), 267–282. doi:10.1007/s00710-016-0467-x
Keywords: natural fracture, hydraulic fracture, fracture propagation, barrier layer, formation dip
Citation: Renzhong G, Lianming F, Dong R, Yue W, Sicheng H, Yi D and Xiangjun L (2025) The influence mechanism of natural fractures on hydraulic fracture propagation in Mabei shale reservoir. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1696774. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1696774
Received: 01 September 2025; Accepted: 23 September 2025;
Published: 13 October 2025.
Edited by:
Qingchao Li, Henan Polytechnic University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zhengzheng Cao, Henan Polytechnic University, ChinaYan Zhuang, Changzhou University, China
Copyright © 2025 Renzhong, Lianming, Dong, Yue, Sicheng, Yi and Xiangjun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ding Yi, ZGluZ3N3cHVAZm94bWFpbC5jb20=
 Gan Renzhong1
Gan Renzhong1 Ding Yi
Ding Yi