- 1School of Earth Science and Resources, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Environmental Geochemistry, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guiyang, China
Introduction: Lithium (Li) isotopes are powerful tracers of silicate weathering processes. However, the geochemical behavior of lithium isotopes in granite leachates remains unclear.
Methods: Here we report Li isotope compositions of leachates from a granite weathering profile in southeastern China. The parameter tau (τSi and τAl) and the Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA) were also used to characterize weathering intensity and related geochemical processes.
Results: The Li concentration in the leachate varied from 0.05 to 1.03 mg/kg, and the δ7Lileachate values were −15.0‰ to +6.0‰ (mean = −0.85‰, n = 28). Below 0.8 m depth, the leachate had similar Li isotopic composition (−0.80‰ to +6.0‰, mean = +2.5‰, n = 19) with parent granite (+3.7‰).
Discussion: The leachate δ7Li values exhibit distinct vertical variations, reflecting contrasting geochemical processes along the profile. Below 0.8 m, δ7Li values are comparable to those of the parent granite, indicating limited isotopic fractionation during early weathering process. In contrast, markedly lower δ7Li values above 0.8 m suggest the release of 6Li from the dissolution of secondary minerals. This interpretation is supported by increased τSi and τAl values and their negative correlations with δ7Lileachate, implying co-migration of 6Li, Si, and Al during mineral dissolution. A positive correlation between δ7Li and CIA in the upper profile further indicates enhanced secondary mineral dissolution under intensified weathering. Our results suggest that as weathering progressed, the Li isotopic composition of the leachate from the upper weathering profile became gradually heavier toward the top, positively correlating with weathering intensity and indicating the dissolution of surface secondary minerals under intense weathering conditions.
1 Introduction
Chemical weathering of silicate is an important process in atmospheric CO2 sequestration, and plays a role in regulating Earth’s climate over geological timescales (Berner et al., 1983; Kump et al., 2000). Silicate rock weathering is essential to continent-ocean systems. The rapid development of several non-traditional stable isotope geochemical proxies (such as Li, Si, Mg, K) has improved the information on past and present weathering environments (Huh et al., 1998; 2001; Georg et al., 2006; 2007; Huang et al., 2012; Pogge von Strandmann et al., 2013; 2019; Teng et al., 2020; Steinhoefel et al., 2021; Li et al., 2021; 2022). However, most non-traditional stable isotope proxies are directly affected by biological processes and redox conditions, and may therefore interfere with the information we obtain about silicate weathering processes (e.g., Pogge von Strandmann et al., 2012).
Li isotopes are considered as a proxy during silicate weathering (e.g., Rudnick et al., 2004; Huh et al., 2004; Kısakürek et al., 2005; Misra and Froelich, 2012; Liu et al., 2011; 2013; Ryu et al., 2014; Pogge von Strandmann et al., 2021). The weathering profiles of silicate rock may provide insights into the geochemical behavior and fractionation mechanisms of Li isotopes during weathering. Previous studies on Li isotopes in weathering profiles have discovered that δ7Li values in weathering products are generally lower than in parent rocks (Rudnick et al., 2004; Kısakürek et al., 2004; Négrel and Millot, 2019; Li et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021a; Zhu et al., 2023). The main mechanism causing this difference is that during the chemical weathering process, the lighter 6Li is preferentially incorporated into the newly formed secondary minerals (such as clay and Fe-Mn hydroxides) (Taylor and Urey, 1938; Pistiner and Henderson, 2003; Millot and Girard, 2007; Chan and Hein, 2007; Vigier et al., 2008; Wimpenny et al., 2010a; Wimpenny et al., 2015; Hindshaw et al., 2019). Therefore, dissolved Li in rivers is isotopically heavier than suspended Li (Huh et al., 2001; Kısakürek et al., 2005; Liu et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2015; Dellinger et al., 2015; Pogge von Strandmann et al., 2017; Murphy et al., 2019; Gou et al., 2019; Ma et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023).
Continental weathering is a fundamental process that supplies nutrients (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus, iron) to oceans, thereby enhancing marine primary production (Howarth, 1988; Filippelli, 2008; Lalonde et al., 2012). Granite consists of primary minerals (quartz, feldspar, biotite) with distinct Li concentrations and isotopic compositions, which makes it a critical archive for investigating weathering-related Li cycling. However, bulk Li isotope signals of granitic weathering products (e.g., saprolites) are inherently ambiguous. These signals integrate contributions from both residual primary minerals (e.g., weathering-resistant quartz that dominates weathering products; Zhang et al., 2021b) and secondary minerals. This leads to primary mineral interference that may mask the isotopic signatures specific to secondary mineral formation and dissolution. In contrast, dissolved Li isotopes (e.g., in pore water or leachates) offer a more direct tracer for weathering processes. Previous work on silicate weathering profiles has shown that dissolved Li isotopes are sensitive to weathering intensity, as they reflect the equilibrium between primary mineral dissolution and secondary mineral formation (Pogge von Strandmann et al., 2012). This partitioning is driven primarily by two processes: (1) preferential adsorption of 6Li onto clay mineral surfaces, and (2) incorporation of 6Li into the crystal structure of secondary minerals (Vigier et al., 2008; Dellinger et al., 2015). These processes enrich 7Li in dissolved phases (e.g., riverine loads) and link leachate Li isotopes directly to secondary mineral dynamics. This means δ7Li values in leachate can capture secondary mineral-related signals that bulk samples obscure.
Despite this advantage, a critical research gap persists. Studies explicitly investigating leachate Li isotopes during granite weathering remain extremely limited, with only one prior report (Lemarchand et al., 2010). This scarcity hinders a comprehensive understanding of how leached Li isotopic fractionation responds to granite weathering processes. It is particularly problematic for clarifying the link between leachate δ7Li, weathering intensity, and secondary mineral dynamics, which is essential for refining Li isotopes as a tracer of continental weathering.
To address this gap, the aim of this study is to advance our comprehension of leached Li isotopic fractionation during granite weathering. To achieve this, we conducted a multi-analytical approach: (1) analyzing major and trace element compositions of saprolites and the parent granite to characterize weathering intensity; (2) measuring Li concentrations and δ7Li values in leachates to capture dissolved Li isotopic signatures; and (3) exploring the relationship between δ7Li values in leachate, weathering intensity, and secondary mineral processes. This work seeks to clarify how weathering processes modulate leachate Li isotopes and validate δ7Li values in leachate as a robust proxy for granitic weathering.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sampling
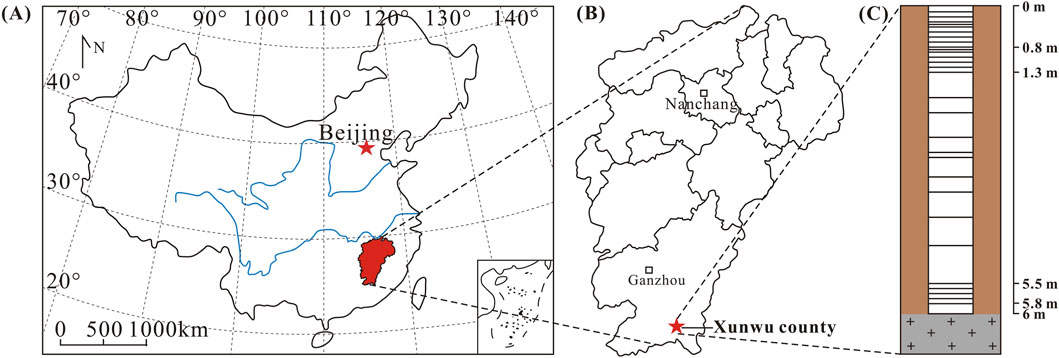
Geologically, the South China Block comprises the Yangtze Block to the northwest and the Cathaysia Block to the southeast (Li et al., 2012). These two crustal segments were welded together along the Jiangshan-Shaoxing Fault (JSF) during the early-middle Neoproterozoic (Li et al., 2008). The block underwent several major tectono-magmatic events during the Neoproterozoic, Early Paleozoic, and Mesozoic, as evidenced by its sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous records. The widespread occurrence of granitic rocks from these periods renders South China a globally significant granite province dominated by extensive Mesozoic (Triassic to Cretaceous) magmatism (Tao et al., 2018 and references therein). Granites in the Xunwu area are mainly products of magmatic activity that occurred during the Yanshanian. The granite lithology in the Xunwu County consists of monzogranite and syenogranite, with zircon U-Pb ages of 95.3 ± 0.3 Ma and 96.4 ± 0.3 Ma, respectively (Zhao et al., 2025).
The Xunwu region, characterized by a subtropical monsoon climate with the mean annual precipitation and temperature (1650 mm/yr and 18.9 °C, respectively), provides an ideal environment for chemical weathering. These conditions accelerate the weathering of granitic rocks, particularly enhancing the dissolution of Li-bearing primary minerals such as feldspar and biotite. As a result, clay minerals like kaolinite and illite are formed. These clay minerals exhibit a selective affinity for Li, facilitating isotope fractionation during weathering. The region’s climate thus amplifies this process, offering a natural setting to clearly identify the drivers of Li isotope fractionation. For this reason, a saprolite profile with relatively high weathering intensity developed on monzogranite was selected from Xunwu County (Figure 1).
Twenty-eight saprolite samples were taken from a 6 m high granite profile. Sampling intervals ranged from 0.1 to 1.3 m and 5.5–6.0 m (mostly 0.1 m), while intervals between 1.3 and 5.5 m were irregular (Figure 1C). The weathering intensity was highest at the top of the profile, which was covered by forest. After removing visible plant roots, the samples were air-dried, ground in an agate mill, sieved through 200-mesh screens, and homogenized. Our study is designed to explore the activation, migration, re-precipitation characteristics, and isotopic variation of Li during secondary processes like weathering and leaching in soils. As such, we focus on the lithium present in the adsorbed and carbonate phases, leaving the silicate phase intact, and directly dissolve the ground samples with acid. The leachate samples were obtained following these steps: (1) Weigh 2.0 g of finely ground sample into a centrifuge tube, add 40 mL of 0.5 mol/L HCl, seal the tube, and shake for 48 h. After shaking, centrifuge the mixture and collect the supernatant. (2) Add 40 mL of ultrapure water to the residue, seal, shake for 24 h, then centrifuge and collect the supernatant. (3) Add another 40 mL of 0.5 mol/L HCl to the residue, seal, shake for 48 h, centrifuge, and collect the supernatant. (4) Add 40 mL of ultrapure water to the residue again, seal, shake for 24 h, then centrifuge and collect the supernatant. (5) Repeat step 3 once. (6) Repeat step 4 once. (7) Combine all supernatants obtained from the above steps and filter through a 0.22 μm cellulose acetate filters. (8) the leachate was collected and prepared for analysis.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Analytical methods
An X-ray fluorescence quantified the major elemental content of the saprolite samples. The trace element concentrations in saprolite samples and leachate samples were determined using an inductively-coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). The measuring instruments for the major elemental analysis were precalibrated by two Chinese national standard samples: GBW07103 (granite) and GBW07105 (basalt). The accuracy of the trace elemental analyses was evaluated by the USGS rock standards GSP-2 and BCR-2. Both measurements had precision better than ±5% (2σ) and ±10% (2σ), respectively. The analyses were done at the State Key Laboratory of Environmental Geochemistry, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The Li isotopic analytical method follows the procedures outlined by Zhang et al. (2019). Leachate samples for analysis were prepared using Teflon beakers, dried at 120 °C on a thermostatic hot plate, and then re-dried at 120 °C after the addition of 1 mL of distilled HNO3. The dried samples were subsequently dissolved in 1 mL of 0.40 mol/L HCl for cation exchange column separation. For Li purification, Bio-Rad AG 50 W-X12 resin (200–400 mesh) was used, and Li was eluted with 0.40 mol/L HCl. This purification process was repeated to achieve a relatively pure Li solution. The eluted Li solution was collected, dried again at 120 °C, and then dissolved in 2% HNO3 to ensure nearly complete Li recovery before analysis by multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (MC-ICP-MS, Nu Plasma II, Wales, United Kingdom). We adopted the international standard SSB (standard-sample bracketing) method and used the international standard L-SVEC (NIST RM 8545) for isotopic calibration. The standard L-SVEC and the samples were prepared at similar Li concentrations, approximately 80 ng/mL. The external precision (2σ) of repeated dissolutions, purifications, seawater analyses, and rock standards was better than ±0.7‰. The measured δ7Li values for international rock standards and seawater samples, including GSP-2 and AGV-2, were −0.2‰ ± 0.5‰ (n = 3), 7.0‰ ± 0.7‰ (n = 3), and 31.4‰ ± 0.6‰ (n = 5), respectively, which are consistent with values reported in previous studies (e.g., Lin et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2019).
2.2.2 Calculation of CIA and τj values
The chemical index of alternation (CIA) is usually applied as an effective proxy to indicate weathering intensity. It is defined as the molar ratio of Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O + K2O)×100, where CaO* represents Ca that is absent in phosphate and carbonate forms (Nesbitt and Young, 1982). The current research corrected the part of Ca from apatite using measured P2O5 content. However, we found that the calculated Ca/Na ratio was <1 in the saprolites, indicating that little carbonate was present (McLennan, 1993; Rudnick et al., 2004).
The parameter tau (τj = [(Ci,p × Cj,w)/(Ci,w × Cj,p) - 1] × 100) is defined as the relative loss (τj < 0) or gain (τj > 0) of elements during weathering, where C represents the concentration of the relatively immobile (i) or mobile (j) elements in the parent (p) or weathered (w) materials (Chadwick et al., 1990). For the present profile, Zr was chosen as the most suitable immobile element compared with other immobile elements. When Zr is selected as the immobile reference element, the calculated τ values of Nb, Th, Ta, and Ti range from −98.6% to −57.8%, whereas τHf varies from −24.1% to −13.7%. All these τ values are negative, indicating significant depletion of these elements relative to the immobile Zr during the weathering process (more details can be seen in the Supplementary Material) (Supplementary Table SM3 and Supplementary Figure SM1).
3 Results
3.1 Major and trace elements
The major and trace elements in the saprolites and parent granite are presented in Supplementary Tables SM1, SM2. The calculated CIA values of the saprolite samples increased from 54 to 85 towards the profile surface from 5.8 to 0.1 m depth. Also, the CIA values of these samples were higher than that of parent granite (CIA = 50) (Figure 2A; Supplementary Table SM1).
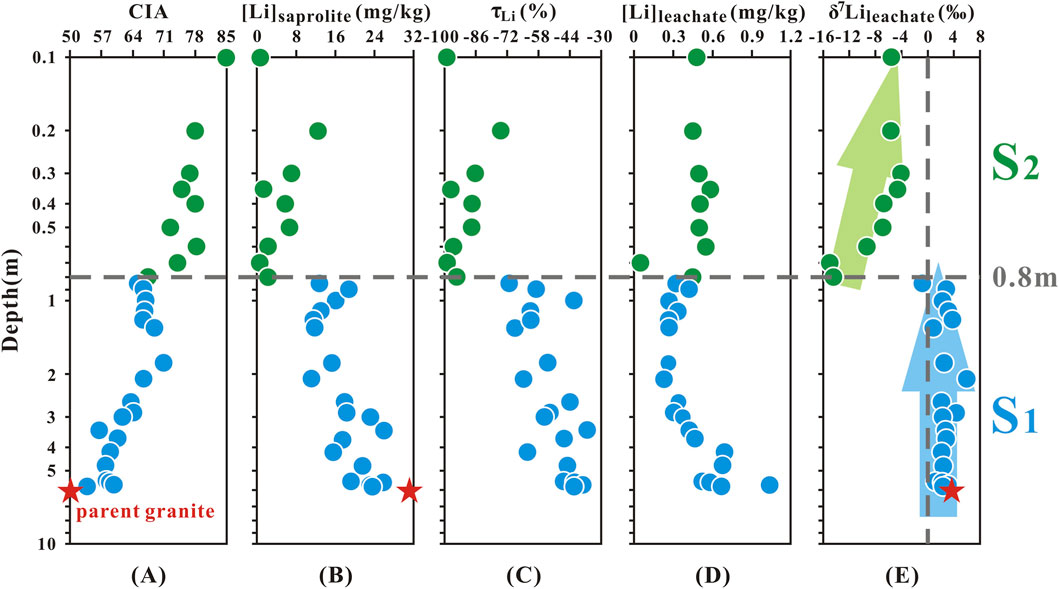
Figure 2. Depth profile of (A) CIA, (B) [Li]saprolite, (C) τLi, (D) [Li]leachate and (E) δ7Lileachate (Green points represent the sampling sites in the S2 layer; blue points represent the sampling sites in the S1 layer).
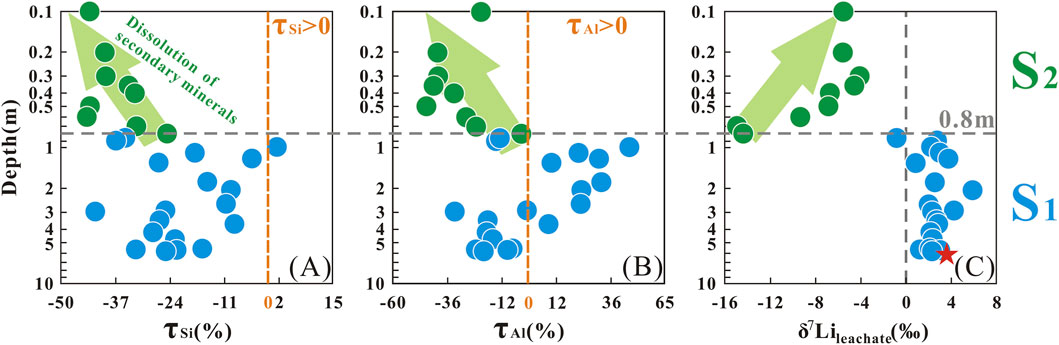
Previous studies have confirmed that taking advantage of relatively immobile elements (e.g., Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf, Th, and Ti) to normalize relatively mobile elements (e.g., Ca, Na, and K) can quantitatively evaluate the relative depletion or enrichment of the latter elements. The τSi and τAl values in the S2 layer were generally lower than those in the S1 layer, with the lowest values reaching −44% for τSi and −45% for τAl (Supplementary Table SM3). In the S1 layer, positive τSi and τAl values were observed (τSi > 0, n = 1; τAl > 0, n = 8), with the maximum τSi and τAl values occurring at a depth of 0.8 m, at 1.6% and 43.8%, respectively.
3.2 Li concentration and isotopic composition
The concentration of Li in saprolites varied between 0.6 and 25 mg/kg. The calculated τLi values were all less than 0 (−36.1% to −98.9%, mean = −64.8%) and showed a decreasing trend from the bottom of the profile to the surface (Figures 2B,C; Supplementary Tables SM2, SM3).
The concentration of Li in leachate showed a smaller range (from 0.05 to 1.03 mg/kg, mean = 0.45 mg/kg) (Supplementary Table SM2; Figure 2D). The δ7Lileachate values ranged from −15.0‰ to +6.0‰ (mean = −0.85‰), respectively (Supplementary Table SM2; Figure 2E). Most of δ7Lileachate values had a relatively small range of variations from 5.8 to 0.8 m depth (−0.80‰ to +6.0‰, mean = +2.5‰, n = 19), similar to the measured δ7Liparent granite (+3.7‰) (Figure 2E). However, above 0.8m, the δ7Lileachate values increased gradually towards the surface from 0.8 m depth (−15.0‰ to −4.1‰, mean = −8.0‰, n = 9) (Figure 2E). According to the variations of the δ7Lileachate values, the saprolite profile was divided into two layers: S2 (0.1–0.8 m) and S1 (0.8–5.8 m).
4 Discussion
4.1 Formation and dissolution of secondary minerals
The Li isotope fractionation result indicates that 6Li preferentially enters into secondary minerals, while 7Li is preferentially leached into the solution during the silicate weathering (Pistiner and Henderson, 2003; Vigier et al., 2008; Hindshaw et al., 2019). Furthermore, Li isotopic fractionation magnitudes vary across clay mineral types (Zhang et al., 1998; Pistiner and Henderson, 2003; Williams and Hervig, 2005; Millot and Girard, 2007; Vigier et al., 2008; Wimpenny et al., 2015; Li and Liu, 2020; 2022). For example, Zhang et al. (1998) reported significant fractionation during Li sorption onto kaolinite (α = 0.979) and vermiculite (α = 0.971) from seawater, consistent with observations of lower δ7Li in weathered products and higher δ7Li in soil solutions. This framework helps interpret the temporal evolution of our saprolite profile, which exhibits two distinct chemical weathering stages. The initial stage (Stage I, S1 layer) is dominated by primary mineral dissolution and secondary mineral formation, which is evidenced by the similarity between δ7Lileachate and δ7Liparent granite of S1 layer, which implies minimal isotopic fractionation during primary mineral discussion. The subsequent stage (Stage II, S2 layer) involves dissolution of secondary minerals in the surface, as supported by the upward-increasing δ7Lileachate trend in S2 layer. Collectively, these observations highlight that the transition from primary mineral weathering to secondary mineral dissolution modulates the Li isotopic signature of the profile.
4.1.1 The initial weathering stage of primary mineral dissolution and secondary mineral formation (stage Ӏ)
In the initial stage of granite weathering, the dissolution of primary minerals (e.g., K-feldspar, plagioclase) is the main process, which is manifested in the migration of soluble elements (e.g., K, Na and Ca). As shown in Supplementary Figure SM2, the τ values for K, Na, and Ca are all negative with depth. In the S2 layer, these values exhibit a decreasing trend from the bottom to the surface. Near the surface, the values approach −100%, possibly indicating near-complete dissolution of K-feldspar and plagioclase. During the dissolution of primary minerals, Li is concurrently released. However, Li isotopes do not fractionate during the decomposition of primary minerals (Verney-Carron et al., 2011; Wimpenny et al., 2015). As weathering progressed, some primary minerals were chemically modified to become secondary (clay) minerals. For example, biotite could be altered into illite and kaolinite during weathering process (Morad, 1990). Previous studies have shown that during the weathering process, the mechanism of Li isotope fractionation is 6Li being preferentially incorporated into the newly formed secondary minerals and absorbed onto the surface of secondary minerals. As a result, 6Li was incorporated into the structure of secondary minerals and retained in localized weathering products, leading to isotopically lighter Li in the weathering products compared to that in the pore water (Pistiner and Henderson, 2003; Vigier et al., 2008; Wimpenny et al., 2015; Hindshaw et al., 2019).
4.1.2 The later stage involving dissolution of secondary minerals near the surface layer of profile (stage II, S2 layer)
At stage II, the S2 layer experienced higher weathering intensity than stage Ӏ. It can be inferred that if secondary minerals within the S2 layer begin to dissolve, Li with δ7Li values lower than those of the parent granite would be released, thereby reducing the δ7Li values in the liquid phase. A previous investigation of a saprolite profile has demonstrated that secondary minerals may become unstable at low pH, leading to the release of 6Li into the dissolved phase and causing an increase in δ7Li values of pore water towards the surface (Pogge von Strandmann et al., 2012). Similarly, Lemarchand et al. (2010) attributed upward-increasing δ7Li values in pore water to secondary mineral dissolution, which consistent with the depth-dependent trend of our δ7Lileachate values (Section 3.2). This consistency supports the inference that secondary mineral dissolution is the key driver of δ7Lileachate variation in the S2 layer (Figure 3C). Potential evidence supporting this dissolution is presented below.
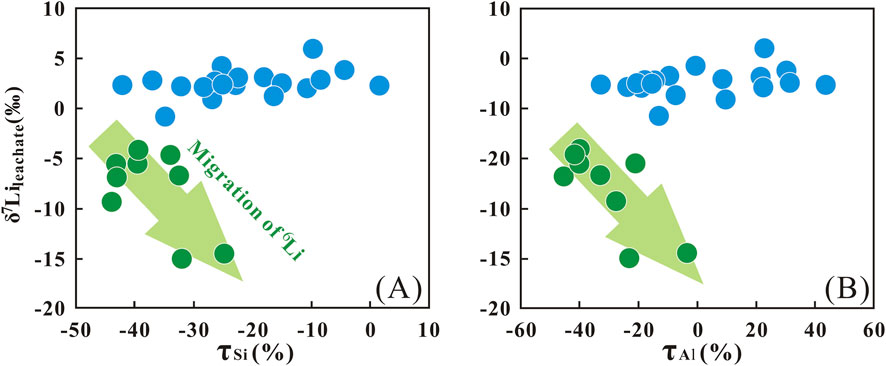
Compared with K, Na, and Ca, Si and Al are termed “relatively immobile elements” due to their weak mobility. During the granite weathering process, elemental ions are released due to the decomposition of primary minerals. Such as K+, Ca2+, and Na+ would migrate down with the soil solution, while Al3+ and Si4+ remain in-situ and participate as secondary minerals (clay minerals). When these situations happen, the τSi and τAl values in the S2 layer would theoretically result in near-zero negative τSi and τAl values, indicating minimal elemental loss. However, the depth-dependent trends in τSi and τAl (Section 3.1) provide critical insights into weathering processes across the profile. At the boundary near 0.8 m in the S1 layer, both τSi and τAl exhibit positive values, with τAl showing more frequent enrichment (Figures 3A,B). This enrichment of Si and Al likely reflects an accumulation associated with the downward migration of these elements from the upper S2 layer. Further, the more negative τSi and τAl values in the S2 layer, together with the negative correlation between δ7Lileachate and these elemental mobility proxies, suggest coupled migration of 6Li, Si, and Al (Figure 4). This co-migration is most plausibly attributed to the dissolution of secondary minerals, which releases Si and Al along with the 6Li preferentially incorporated in their structures. Such dissolution-driven release provides a coherent explanation for the observed elemental and isotopic patterns. This interpretation is in agreement with previous studies on silicate weathering profiles. For instance, Gong et al. (2019) and Xiong et al. (2022) both observed elevated τSi and τAl ratios in surface horizons, which they attributed to secondary mineral dissolution. This process, similar to our findings, appears to play a key role in governing the mobility of both Li isotopes and elements in the S2 layer.
To support this mechanism more accurately, two types of literature mineral data were selected for reference in this study. First, regarding the parent granite from the same Xunwu region as this study, Zhao et al. (2025) has reported that the parent monzogranite in the Xunwu area consists primarily of K-feldspar (60%), quartz (20%–25%), plagioclase (10%), and biotite (2%–3%), along with accessory minerals such as magnetite, ilmenite, rutile, zircon, muscovite, and minor amounts of cerianite and apatite. The rocks are relatively fresh, with little evidence of weathering, except for minor alteration of plagioclase to kaolinite (<1%). These compositions can be reasonably regarded as representative of the granite mineralogy in our studied profile. Second, for granite weathering profiles in South China that share the same climate (subtropical monsoon climate) and vegetation (evergreen broad-leaved forest) as the Xunwu area (China), such as the Guangdong saprolite profile studied by Zhang et al. (2021b), their mineral composition data show that the saprolites in this region are mainly composed of K-feldspar (5%–33%, average 20%), quartz (18%–59%, average 32%), kaolinite (28%–46%, average 37%), and illite (1%–18%, average 10%).
Notably, in the Guangdong profile of this study, the intensely weathered layer has a wide distribution, and the weathering intensity of the region above 1 m depth is comparable to that of the S2 layer in our study. Within this region above 1 m, kaolinite content decreases from the profile surface down to 1 m depth. This distribution may be related to secondary mineral dissolution in the surface layer: stronger weathering here may cause dissolution of secondary minerals like kaolinite, which is presumably the main reason for decreasing kaolinite content with shallower depth.
To summarize, the saprolite profile exhibits a two-stage evolutionary sequence of Li cycling during weathering (Figure 5). In Stage I, primary mineral dissolution releases Li with no isotopic fractionation. Newly formed secondary minerals preferentially incorporate 6Li, while 7Li remains in pore water and migrates downward (Figure 5A). Stage II is marked by intensified weathering in surface horizons (high CIA values), where secondary mineral dissolution becomes the dominant process. This releases the 6Li previously sequestered in secondary minerals into pore water, driving changes in the isotopic composition of the leachate. The observed increase in δ7Lileachate values from the bottom to the top of the S2 layer (Figure 5B) may suggest that isotopic fractionation occurred during Li transport, possibly associated with interactions between pore water and residual secondary minerals. Lastly, a stratigraphic column illustrating vertical variations of mineral characteristics, CIA and key geochemical proxies with depth is presented to explain the overall changes in the saprolite profile (Supplementary Figure SM3).
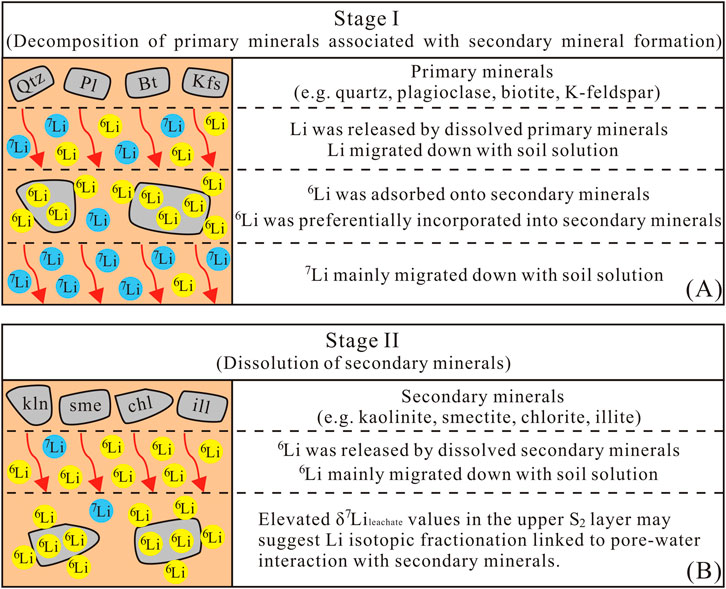
Figure 5. A simple cartoon illustrating two distinct stages in the saprolite profile during the weathering process. (A) Stage Ӏ: the initial weathering stage of primary mineral dissolution and secondary mineral formation; (B) Stage II: the later stage involving dissolution of secondary minerals near the surface layer of profile (the S2 layer).
4.2 Reasons for the minimum δ7Lileachate values
Several reasons could possibly account for the minimum δ7Li values in leachate (−15.0‰, sample: XW1-8; −14.5‰, sample: XW1-9). We discuss these potential reasons as follows: (1) the presence of a paleowater table (Kısakürek et al., 2004; Rudnick et al., 2004; Teng et al., 2010), (2) biological influence (Li et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2025) and (3) the dissolution of secondary minerals near the surface (Lemarchand et al., 2010; Pogge von Strandmann et al., 2012).
4.2.1 Presence of a paleo water table
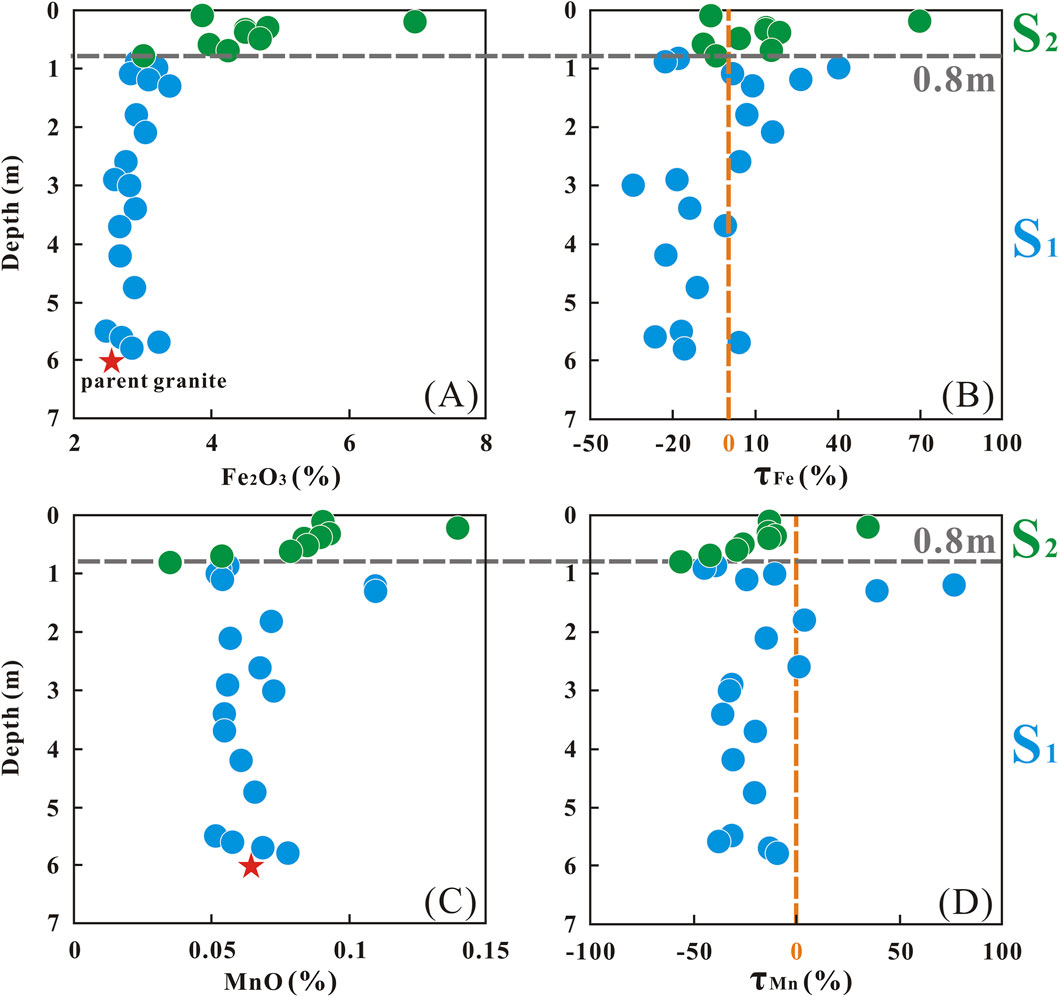
Paleo water table has been proved that it can affect the redox conditions of a weathering profile (Kısakürek et al., 2004; Rudnick et al., 2004; Teng et al., 2010). In this case, the paleo-water table may have facilitated the formation of secondary minerals, particularly Fe and Mn hydroxides. Previous studies have shown that Li is incorporated into the crystal lattice of Fe-Mn oxides-oxyhydroxides through inner-sphere complexation, with a preference for incorporating 6Li (Chan and Hein, 2007; Wimpenny et al., 2010b). According to a prior study, the concentration of Fe2O3 at the paleo-water table position was unusually high throughout the entire profile (Kısakürek et al., 2004). In line with Fe, Mn, which is likewise sensitive to redox conditions, is expected to manifest a parallel trend of variation.
However, paleo-water table effects are unlikely to drive secondary mineral-related Li fractionation in our profile. First, redox-sensitive elements (Fe, Mn) do not show the characteristic enrichment expected at paleo-water table horizons (Figure 6). Their concentrations and τ values at the 0.8 m depth (a potential redox boundary) lack the distinct anomalies observed in previous studies, instead aligning with adjacent layers. Second, the sampling location itself mitigates water table influence, as it is situated on a mountain top, above the regional water table. Collectively, these observations suggest that Fe-Mn hydroxide formation (and associated Li isotopic effects) is not a dominant process in our profile.
4.2.2 Biological influence
Although litterfall inputs have been proposed to influence the Li isotopic composition of soils (Li et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2025), direct quantification of their role in our study is not possible because Li concentrations and δ7Li values of the local vegetation were not analyzed. Nonetheless, recently published data indicate that roots, barks, and leaves generally possess positive δ7Li values, with the lowest value of −0.9‰ observed in roots (Liu et al., 2025). This minimum remains higher than the δ7Li values of all leachates in the profile, suggesting that plant litter is unlikely to dominate the isotopic signature of surficial leachates. Moreover, earlier study has shown that biological uptake and recycling do not significantly alter Li isotopes in the uppermost soil layer, due to the very low Li concentrations in vegetation relative to soils (Lemarchand et al., 2010). Considering also the low vegetation density in the surface of profile, the influence of plant-derived inputs on the Li isotope composition of leachates is likely to be minimal.
4.2.3 Dissolution of secondary minerals near the surface
Secondary mineral dissolution is a well-established driver of pore water δ7Li values profile evolution in weathering systems. Previous studies consistently document a downward trend in δ7Li values from the surface to a discrete depth, where a distinct minimum value emerges. This pattern is attributed to the release of 6Li during secondary mineral dissolution (Lemarchand et al., 2010; Pogge von Strandmann et al., 2012). For context, Lemarchand et al. (2010) observed δ7Li decreasing from near-surface values to a minimum at 0.3 m, while Pogge von Strandmann et al. (2012) reported a similar pattern. Their data showed the lowest δ7Li occurring at 1.13 m following precipitation correction. Our δ7Lileachate values align with this literature-derived pattern. They exhibit a decreasing trend from the surface to the bottom of the S2 layer and a clear minimum in the 0.8 m depth range. This consistency reinforces the role of secondary mineral dissolution in shaping our profile’s Li isotopic signature. This interpretation is further supported by the co-variation between τ values (τSi and τAl) and δ7Lileachate in the S2 layer (Section 4.1.2). Collectively, the alignment of our δ7Li trend with established literature patterns, paired with τ values evidence, confirms that secondary mineral dissolution is the primary driver of the minimum δ7Lileachate observed in the S2 layer.
4.3 Implications of the relationship between chemical weathering intensity and δ7Li values of granite weathering
The relationship between CIA and δ7Li values in this leachate study was compared with the results of some previous bulk-sample of granite studies (Rudnick et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2021a; Zhang et al., 2021b; Zhu et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023) (Figure 7B). These comparative studies have been carefully examined to ensure methodological consistency, thereby confirming that the cross-study comparisons presented in this work are valid and reliable. In the previous studies, the relationships between CIA and δ7Li values of bulk samples presented the three situations: (I) as CIA values increase within the profile, δ7Li values in the saprolite decrease in a monotonic trend (Rudnick et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2021a); (II) as CIA values increase within the profile, δ7Li values in the saprolite exhibit two distinct decreasing trends in the upper and lower parts of the profile (Zhang et al., 2023). (III) as the CIA values increase within the profile, the δ7Li values of saprolite initially decrease and then increase (Zhang et al., 2021b; Zhu et al., 2023); In situation (I), the alteration of δ7Li values in the saprolite was primarily attributed to the formation of secondary minerals. In situation (II), Zhang et al. (2023) proposed that the variation in δ7Li values in the upper profile was driven by the input of eolian dust, whereas the pattern observed in the lower profile aligned with the scenario described in situation (I). As for situation (III), Zhang et al. (2021b) considered that the increased δ7Li values in weathering products was caused by the increase in the Li-rich quartz content in the upper profile, while the situation in the lower profile was consistent with situation (I). Moreover, Zhu et al. (2023) believed that the variation in δ7Li values in weathering products was driven by the dissolution of secondary minerals in the upper profile and the formation of secondary minerals in the lower profile.
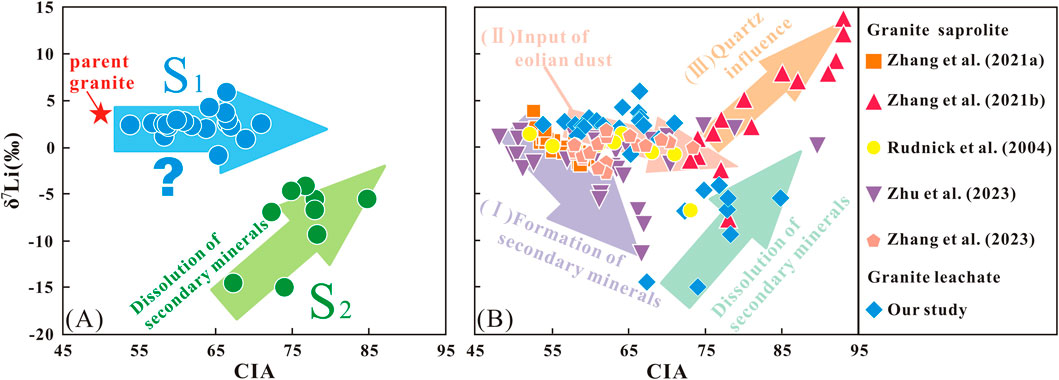
Figure 7. The relationship between δ7Li and CIA values. (A) δ7Lileachate as a function of CIA values in this study; (B) comparison of the relationship between δ7Li and CIA values in granite saprolite and leachate.
Compared with previous bulk-sample data, our leachate data in the upper layer of profile showed positive correlation between δ7Lileachate and CIA values, while there is no correlation between δ7Lileachate values and CIA values in the lower profile (S1 layer) (Figure 7A). The variations in δ7Lileachate values in the S2 layer were attributed to the dissolution of secondary minerals under high weathering intensity. This was consistent with previous river studies, which have shown that under intense weathering conditions, the dissolution of secondary minerals could result in lower δ7Li values in river water, closer to those of the parent rock or upper crust (Dellinger et al., 2015). For the variations of δ7Lileachate values in the S1 layer, we speculate two potential explanations: (1) the amount of secondary minerals formed in the S1 layer during the weathering process was limited, resulting in a smaller Li isotope fractionation; (2) the Li in pore water from the upper profile, with high δ7Lileachate values, was mixed with the Li from the lower profile, resulting in relatively high δ7Lileachate values (e.g., He et al., 2021). Regarding potential explanation (1), if the formation of secondary minerals was limited, a smaller amount of 6Li would retain in the profile. However, the extent of 6Li incorporation into secondary minerals and adsorption onto the surface of clay minerals would directly influence the degree of Li isotopic fractionation in the weathering products. An observation of the correlation between δ7Li in weathering products and the content of secondary minerals in a granite profile revealed that δ7Li values tended to decrease with increasing secondary mineral content, suggesting that Li isotope fractionation was linked to the formation of additional secondary minerals in the saprolites as weathering progressed (Zhang et al., 2021a). Therefore, small Li isotopic fractionation may be observed in weathering products due to the low abundance of secondary minerals.
He et al. (2021) discovered that the δ7Lileachate values in the lower loess profile were high, which they interpreted it as a result of the downward migration of more 7Li and adsorption by clay minerals. Therefore, for the potential explanation (2), as weathering progressed, 6Li was absorbed onto the surface of clay minerals, while more 7Li migrated downward with pore water and adsorbed onto the surface of clay minerals in the S1 layer, resulting in relatively high δ7Lileachate values which was close to the δ7Liparent granite value.
To sum up, the negative correlation between δ7Libulk-sample and CIA values can primarily be attributed to the preferential incorporation and adsorption of 6Li by secondary minerals. Additionally, the input of eolian dust may also contribute to this negative correlation. In contrast, the dissolution of secondary minerals results in a positive correlation between CIA values and both δ7Libulk-sample and δ7Lileachate values, while the presence of quartz in granite also could cause a positive correlation between CIA values and δ7Libulk-sample. In our study, however, the CIA values showed no correlation with δ7Lileachate values in the S1 layer, indicating that the intensity of weathering may not directly correspond to the information conveyed by the secondary minerals in the weathering products.
5 Conclusion
We investigated the Li isotopic composition in leachate in weathered saprolites developed on granite from Xunwu, southeastern China. The δ7Lileachate values were negative, increasing from the depth of 0.8 m to the surface layer and remaining lower than those of the parent rock. However, most of δ7Lileachate values were positive and similar to parent granite below 0.8 m depth. Above 0.8 m depth, the migration and accumulation of 6Li released by secondary mineral dissolution were the significant reasons for the significant variation in δ7Lileachate values. The correlation between δ7Lileachate and CIA values was positive above 0.8 m depth, albeit with no correlation below 0.8 m depth. Two potential explanations that have been discussed may be responsible for the similarity in the Li isotopic compositions among most leachate samples and parent granite below 0.8 m depth. Our results suggest that as weathering advanced, the Li isotopic composition of the leachate from the upper weathering profile exhibited a progressive increase in heaviness towards the surface, showing a positive correlation with weathering intensity, indicating the dissolution of surface secondary minerals under conditions of intense weathering. Further studies on the mechanism of Li isotope fractionation in leachate during silicate weathering are still required.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
QL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. J-WZ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. TG: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. Z-QZ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported jointly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 41930863 and 42373058), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CHD (grant number 300102274203).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the scientific editors and reviewers for their careful consideration and constructive feedback on our manuscript. Their thoughtful and valuable comments have greatly contributed to improving the quality of our work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2025.1710330/full#supplementary-material
References
Berner, R. A., Lasaga, A. C., and Garrels, R. M. (1983). The carbonate silicate geochemical cycle and its effect on atmospheric carbon-dioxide over the past 100 million years. Am. J. Sci. 283 (7), 641–683. doi:10.2475/ajs.283.7.641
Chadwick, O. A., Brimhall, G. H., and Hendricks, D. M. (1990). From a Black to a gray box-a mass balance interpretation of pedogenesis. Geomorphology 3 (3-4), 369–390. doi:10.1016/0169-555x(90)90012-f
Chan, L.-H., and Hein, J. R. (2007). Lithium contents and isotopic compositions of Ferromanganese deposits from the global ocean. Deep-Sea Res. Part II 54, 1147–1162. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.04.003
Dellinger, M., Gaillardet, J., Bouchez, J., Calmels, D., Louvat, P., Dosseto, A., et al. (2015). Riverine Li isotope fractionation in the Amazon River basin controlled by the weathering regimes. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 164, 71–93. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2015.04.042
Filippelli, G. M. (2008). The global phosphorus cycle: past, present, and future. Elements 4, 89–95. doi:10.2113/gselements.4.2.89
Georg, R. B., Reynolds, B. C., Frank, M., and Halliday, A. N. (2006). Mechanisms controlling the silicon isotopic compositions of river waters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 249, 290–306. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.07.006
Georg, R. B., Reynolds, B. C., West, A. J., Burton, K. W., and Halliday, A. N. (2007). Silicon isotope variations accompanying basalt weathering in Iceland. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 261, 476–490. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.07.004
Gong, Y. Z., Zeng, Z., Chen, Z., Nan, X. Y., Yu, H. M., Lu, Y., et al. (2019). Barium isotopic fractionation in latosol developed from strongly weathered basalt. Sci. Total Environ. 687, 1295–1304. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.427
Gou, L. F., Jin, Z. D., Pogge von Strandmann, P. A. E., Li, G., Qu, Y. X., Xiao, J., et al. (2019). Li isotopes in the middle Yellow River: seasonal variability, sources and fractionation. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 248, 88–108. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2019.01.007
He, M. Y., Dong, J. B., Jin, Z. D., Liu, C. Y., Xiao, J., Zhang, F., et al. (2021). Pedogenic processes in loess-paleosol sediments: clues from Li isotopes of leachate in Luochuan loess. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 299, 151–162. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2021.02.021
Hindshaw, R. S., Tosca, R., Goût, T. L., Farnan, I., Tosca, N. J., and Tipper, E. T. (2019). Experimental constraints on Li isotope fractionation during clay formation. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 250, 219–237. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2019.02.015
Howarth, R. W. (1988). Nutrient limitation of net primary production in marine ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 19 (1), 89–110. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.19.1.89
Huang, K. J., Teng, F. Z., Wei, G. J., Ma, J. L., and Bao, Z. Y. (2012). Adsorption- and desorption-controlled magnesium isotope fractionation during extreme weathering of basalt in Hainan Island, China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 359-360, 73–83. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.10.007
Huh, Y., Chan, L.-H., Zhang, L., and Edmond, J. M. (1998). Lithium and its isotopes in major world Rivers: implications for weathering and the Oceanic budget. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 62 (12), 2039–2051. doi:10.1016/s0016-7037(98)00126-4
Huh, Y., Chan, L.-H., and Edmond, J. M. (2001). Lithium isotopes as a probe of weathering processes: orinoco river. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 194 (1-2), 189–199. doi:10.1016/s0012-821x(01)00523-4
Huh, Y., Chan, L. H., and Chadwick, O. A. (2004). Behavior of lithium and its isotopes during weathering of Hawaiian basalt. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 5 (9), Q09002. doi:10.1029/2004gc000729
Kısakürek, B., Widdowson, M., and James, R. H. (2004). Behaviour of li isotopes during Continental weathering: the bidar laterite profile, India. Chem. Geol. 212, 27–44. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.08.027
Kısakürek, B., James, R. H., and Harris, N. B. (2005). Li and δ7Li in Himalayan rivers: proxies for silicate weathering. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 237 (3-4), 387–401. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.07.019
Kump, L. R., Brantley, S. L., and Arthur, M. A. (2000). Chemical weathering, atmospheric CO2, and climate. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 28, 611–667. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.611
Lalonde, K., Mucci, A., Ouellet, A., and Gelinas, Y. (2012). Preservation of organic matter in sediments promoted by iron. Nature 483, 198–200. doi:10.1038/nature10855
Lemarchand, E., Chabaux, F., Vigier, N., Millot, R., and Pierret, M. C. (2010). Lithium isotope systematics in a forested granitic catchment (Strengbach, Vosges Mountains, France). Acta 74, 4612–4628. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2010.04.057
Li, W. S., and Liu, X. M. (2020). Experimental investigation of lithium isotope fractionation during kaolinite adsorption: implications for chemical weathering. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 284, 156–172. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2020.06.025
Li, W. S., and Liu, X. M. (2022). Mineralogy and fluid chemistry controls on lithium isotope fractionation during clay adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 851, 158138. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158138
Li, X. H., Li, W. X., Li, Z. X., and Liu, Y. (2008). 850-790 Ma bimodal volcanic and intrusive rocks in northern Zhejiang, South China: a major episode of Continental rift magmatism during the breakup of rodinia. Lithos 102 (1-2), 341–357. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.04.007
Li, X. H., Li, Z. X., He, B., Li, W. X., Li, Q. L., Gao, Y. Y., et al. (2012). The early Permian active Continental margin and crustal growth of the cathaysia block: in situ U-Pb, Lu-Hf and O isotope analyses of detrital zircons. Chem. Geol. 328 (0), 195–207. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.10.027
Li, W. S., Liu, X. M., and Chadwick, O. A. (2020). Lithium isotope behavior in Hawaiian regoliths: soil-Atmosphere-Biosphere exchanges. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 285, 175–192. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2020.07.012
Li, W. S., Liu, X. M., Wang, K., and Koefoed, P. (2021). Lithium and potassium isotope fractionation during silicate rock dissolution: an experimental approach. Chem. Geol. 568, 120142. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2021.120142
Li, W. S., Liu, X. M., Hu, Y., Teng, F. Z., and Chadwick, O. A. (2022). Potassium isotope fractionation during chemical weathering in humid and arid Hawaiian regoliths. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 333, 39–55. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2022.07.001
Li, X. Q., Han, G. L., Zhang, Q., Liu, J. K., and Qu, R. (2023). Contrasting riverine K and li isotope signatures during silicate weathering in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 622, 118402. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2023.118402
Lin, J., Liu, Y., Hu, Z., Yang, L., Chen, K., Chen, H., et al. (2016). Accurate determination of lithium isotope ratios by MC-ICP-MS without strict matrixmatching by using a novel washing method. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 31 (2), 390–397. doi:10.1039/c5ja00231a
Liu, X. M., Rudnick, R. L., McDonough, W. F., Teng, F., and Cummings, M. L. (2011). Behavior of lithium and magnesium isotopes during extreme weathering of the columbia river basalt. AGU Fall Meet. Abstr.
Liu, X. M., Rudnick, R. L., McDonough, W. F., and Cummings, M. L. (2013). Influence of chemical weathering on the composition of the Continental crust: insights from li and Nd isotopes in bauxite profiles developed on columbia river basalts. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 115, 73–91. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2013.03.043
Liu, X. M., Wanner, C., Rudnick, R. L., and McDonough, W. F. (2015). Processes controlling δ7Li in Rivers illuminated by study of streams and groundwaters draining basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 409, 212–224. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2014.10.032
Liu, X. Y., Wilson, D. J., Burton, K. W., Sigurdsson, B. D., Bos, J. C., Fraser, W. T., et al. (2025). Rapid and significant lithium isotope response to afforestation in Icelandic topsoils. Catena 254, 108967. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2025.108967
Ma, T., Weynell, M., Li, S. L., Liu, Y., Chetelat, B., Zhong, J., et al. (2020). Lithium isotope compositions of the yangtze river headwaters: weathering in high relief catchments. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 280, 46–65. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2020.03.029
McLennan, S. M. (1993). Weathering and global denudation. J. Geol. 101 (2), 295–303. doi:10.1086/648222
Millot, R., and Girard, J. P. (2007). Lithium isotope fractionation during adsorption onto mineral surfaces. 3rd Int. Meet. Clays Nat. and Eng. Barriers Radioact. Waste Confinement, 307–308.
Misra, S., and Froelich, P. N. (2012). Lithium isotope history of Cenozoic seawater: changes in silicate weathering and reverse weathering. Science 335, 818–823. doi:10.1126/science.1214697
Morad, S. (1990). Mica alteration reactions in Jurassic reservoir sandstones from the haltenbanken area, offshore Norway. Clay Clay Min. 38, 584–590. doi:10.1346/ccmn.1990.0380603
Murphy, M. J., Porcelli, D., Pogge von Strandmann, P. A. E., Hirst, C. A., Kutscher, L., Katchinoff, J. A., et al. (2019). Tracing silicate weathering processes in the permafrost-dominated lena river watershed using lithium isotopes. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 245, 154–171. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2018.10.024
Négrel, P., and Millot, R. (2019). Behaviour of li isotopes during regolith formation on granite (massif central, France): controls on the dissolved load in water, saprolite, soil and sediment. Chem. Geol. 523, 121–132. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.05.037
Nesbitt, H., and Young, G. M. (1982). Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 299, 715–717. doi:10.1038/299715a0
Pistiner, J. S., and Henderson, G. M. (2003). Lithium-isotope fractionation during Continental weathering processes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 214 (1-2), 327–339. doi:10.1016/s0012-821x(03)00348-0
Pogge von Strandmann, P. A. E., Opfergelt, S., Lai, Y.-J., Sigfússon, B., Gislason, S. R., and Burton, K. W. (2012). Lithium, magnesium and silicon isotope behaviour accompanying weathering in a basaltic soil and pore water profile in Iceland. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 339-340, 11–23. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.05.035
Pogge von Strandmann, P. A. E., Jenkyns, H. C., and Woodfine, R. G. (2013). Lithium isotope evidence for enhanced weathering during Oceanic anoxic event 2. Nat. Geosci. 6, 668–672. doi:10.1038/ngeo1875
Pogge von Strandmann, P. A. E., Frings, P. J., and Murphy, M. J. (2017). Lithium isotope behaviour during weathering in the ganges alluvial plain. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 198, 17–31. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2016.11.017
Pogge von Strandmann, P. A. E., Fraser, W. T., Hammond, S. J., Tarbuck, G., Wood, I. G., Oelkers, E. H., et al. (2019). Experimental determination of li isotope behaviour during basalt weathering. Chem. Geol. 517, 34–43. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.04.020
Pogge von Strandmann, P. A. E., Burton, K. W., Opfergelt, S., Genson, B., Guicharnaud, R. A., and Gislason, S. R. (2021). The lithium isotope response to the variable weathering of soils in Iceland. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 313, 55–73. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2021.08.020
Rudnick, R. L., Tomascak, P. B., Njo, H. B., and Gardner, L. R. (2004). Extreme lithium isotopic fractionation during Continental weathering revealed in saprolites from South Carolina. Chem. Geol. 212, 45–57. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.08.008
Ryu, J.-S., Vigier, N., Lee, S.-W., Lee, K.-S., and Chadwick, O. A. (2014). Variation of lithium isotope geochemistry during basalt weathering and secondary mineral transformations in Hawaii. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 145, 103–115. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.08.030
Steinhoefel, G., Brantley, S. L., and Fantle, M. S. (2021). Lithium isotopic fractionation during weathering and erosion of shale. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 295, 155–177. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2020.12.006
Tao, J., Li, W., Wyman, D. A., Wang, A., and Xu, Z. (2018). Petrogenesis of Triassic granite from the jintan pluton in central Jiangxi province, south China: implication for uranium enrichment. Lithos 320-321, 62–74. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2018.09.003
Taylor, T. I., and Urey, H. C. (1938). Fractionation of the lithium and potassium isotopes by chemical exchange with zeolites. J. Chem. Phys. 6 (8), 429–438. doi:10.1063/1.1750288
Teng, F. Z., Li, W. Y., Rudnick, R. L., and Gardner, L. R. (2010). Contrasting lithium and magnesium isotope fractionation during Continental weathering. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 300, 63–71. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2010.09.036
Teng, F. Z., Hu, Y., Ma, J. L., Wei, G. J., and Rudnick, R. L. (2020). Potassium isotope fractionation during Continental weathering and implications for global K isotopic balance. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 278, 261–271. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2020.02.029
Verney-Carron, A., Vigier, N., and Millot, R. (2011). Experimental determination of the role of diffusion on li isotope fractionation during basaltic glass weathering. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 75, 3452–3468. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2011.03.019
Vigier, N., Decarreau, A., Millot, R., Carignan, J., Petit, S., and France-Lanord, C. (2008). Quantifying Li isotope fractionation during smectite formationand implications for the li cycle. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 72 (3), 780–792. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2007.11.011
Wang, Q. L., Chetelat, B., Zhao, Z. Q., Ding, H., Li, S. L., Wang, B. L., et al. (2015). Behavior of lithium isotopes in the changjiang river system: sources effects and response to weathering and erosion. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 151, 117–132. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.12.015
Williams, L. B., and Hervig, R. L. (2005). Lithium and boron isotopes in illite-smectite: the importance of crystal size. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 69, 5705–5716. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2005.08.005
Wimpenny, J., James, R. H., Burton, K. W., Gannoun, A., Mokadem, F., and Gíslason, S. R. (2010a). Glacial effects on weathering processes: new insights from the elemental and lithium isotopic composition of west Greenland Rivers. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 290, 427–437. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.12.042
Wimpenny, J., Gíslason, S. R., James, R. H., Gannoun, A., Pogge von Strandmann, P. A. E., and Burton, K. W. (2010b). The behaviour of li and Mg isotopes during primary phase dissolution and secondary mineral formation in basalt. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 74 (18), 5259–5279. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2010.06.028
Wimpenny, J., Colla, C. A., Yu, P., Yin, Q. Z., Rustad, J. R., and Casey, W. H. (2015). Lithium isotope fractionation during uptake by gibbsite. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 168, 133–150. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2015.07.011
Xiong, Y. W., Qi, H. W., Hu, R. Z., Xiao, Y. L., and Wei, L. Y. (2022). Lithium isotope behavior under extreme tropical weathering: a case study of basalts from the Hainan island, south China. Appl. Geochem. 140, 105295. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105295
Zhang, L. B., Chan, L.-H., and Gieskes, J. M. (1998). Lithium isotope geochemistry of pore waters from ocean drilling program sites 918 and 919, irminger basin. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 62, 2437–2450. doi:10.1016/s0016-7037(98)00178-1
Zhang, J. W., Meng, J. L., Zhao, Z. Q., and Liu, C. Q. (2019). Accurate determination of lithium isotopic compositions in geological samples by multi-collector inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 47 (3), 415–422. doi:10.1016/s1872-2040(19)61148-5
Zhang, J. W., Zhao, Z. Q., Yan, Y. N., Cui, L. F., Wang, Q. L., Meng, J. L., et al. (2021a). Lithium and its isotopes behavior during incipient weathering of granite in the eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Chem. Geol. 559, 119969. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119969
Zhang, J. W., Zhao, Z. Q., Li, X. D., Yan, Y. N., Lang, Y. C., Ding, H., et al. (2021b). Extremely enrichment of 7Li in highly weathered saprolites developed on granite from huizhou, southern China. Appl. Geochem. 125, 104825. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104825
Zhang, J. W., Yan, Y. N., Zhao, Z. Q., Liu, X. M., Li, X. D., Zhang, D., et al. (2022). Spatiotemporal variation of li isotopes in the yarlung tsangpo river basin (upper reaches of the brahmaputra river): source and process. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 600, 117875. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2022.117875
Zhang, J. W., Yan, Y. N., Meng, J. L., Zhang, Z. J., and Zhao, Z. Q. (2023). Lithium isotope geochemical behavior in the weathering process of granites in the greater khingan Mountain area, northeastern China. Bull. Mineralogy, Petrology Geochem. 42 (04), 873–881. doi:10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2023.42.079
Zhao, X., Li, N. B., Smith, M. P., Tan, S. C., Fu, R. X., Yang, Y. Y., et al. (2025). Progressive enrichment of rare earth elements (REE) between parent granites and weathering crust contributed to the generation of regolith-hosted REE deposits in south China. Geol. Soc. Am. 137, 4516–4532. doi:10.1130/b38051.1
Keywords: Li isotopes, granite weathering, leachate, secondary mineral, weathering intensity
Citation: Liu Q, Zhang J-W, Gao T and Zhao Z-Q (2025) Behaviour of Li isotopes in leachate during granite weathering: the Xunwu profile, southeastern China. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1710330. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1710330
Received: 22 September 2025; Accepted: 11 November 2025;
Published: 25 November 2025.
Edited by:
Ramanathan Alagappan, Independent Researcher, Tiruchirapalli, IndiaReviewed by:
Quanyou Liu, SINOPEC Petroleum Exploration and Production Research Institute, ChinaGilles Levresse, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Zhang, Gao and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun-Wen Zhang, emhhbmdqdW53ZW5AY2hkLmVkdS5jbg==; Zhi-Qi Zhao, emhhb3poaXFpQGNoZC5lZHUuY24=
 Qi Liu1,2
Qi Liu1,2 Jun-Wen Zhang
Jun-Wen Zhang