Abstract
Rockburst prevention poses a major challenge in coal mining, with thick and hard roof strata being the primary cause of rockbursts. To analyze the feasibility and effectiveness of using hydraulic fracturing as an alternative to blasting methods for treating thick and hard roof strata, this study takes the Kuangou Coal Mine as a case study. First, the energy sources of rockbursts were quantitatively analyzed, and rockburst prevention data from more than a decade at the Kuangou Coal Mine were compiled to summarize its prevention techniques. By examining blasting schemes for thick and hard roof strata under different mining conditions, the hydraulic pressure relief effects of “long-hole fracturing” and “roof axial cutting technology of abrasive jet and fracture” were compared and analyzed. Treatment methods for thick and hard roof strata under various mining conditions at the Kuangou Coal Mine were proposed, with the results holding significant implications for the prevention and control of rockbursts induced by thick and hard roof strata.
1 Introduction
China is the world’s largest energy producer and consumer. Coal, as China’s most important basic energy source, plays a fundamental role in supporting the national energy structure (Ge et al., 2024; Lyu et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023). According to the Chinese Academy of Engineering’s “Energy Development Strategy 2030–2050” report, by 2050, coal will account for 50% or less of the country’s total primary energy consumption, but the demand will still reach 2.5–3 billion tons of standard coal. Given China’s “coal-rich, oil-poor, and gas-poor” energy structure, the coal-dominated energy consumption pattern is difficult to change in the near future (Chong et al., 2023; Lin, 2018; Suo et al., 2024).
At present, many coal mines in China have entered the deep mining stage. Deep coal and rock masses are characterized by high geostress, high gas pressure, and low permeability, which intensify the risk of dynamic disasters in deep coal seams (Li et al., 2022; Qi et al., 2018; Xia et al., 2024a). Coal and rock dynamic disasters can be divided into three types based on their energy sources: coal and gas outburst disasters, rockburst disasters, and coal–rock composite dynamic disasters (Qi et al., 2020; Yuan et al., 2023).
A rockburst refers to the sudden and violent failure of coal or rock caused by the instantaneous release of stored elastic deformation energy under high stress in the surrounding rock mass. This phenomenon is often accompanied by the ejection of coal and rock, loud noise, and air waves, resulting in severe destruction (He et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2023). Rockburst disasters are primarily driven by geostress. As geostress increases with mining depth, rockburst hazards become more pronounced (Gao et al., 2024; Pan et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). The distribution of rockburst-prone mines in China is shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Province | Number of rockburst coalmines | Percentage/% |
|---|---|---|
| Shandong | 43 | 31 |
| Shaanxi | 22 | 16 |
| Nei Mongol Zizhiqu | 13 | 9 |
| Gansu | 13 | 9 |
| Heilongjiang | 12 | 9 |
| Jiangsu | 10 | 7 |
| Liaoning | 8 | 6 |
| Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu | 6 | 4 |
| Jilin | 4 | 3 |
| Henan | 3 | 2 |
| Shanxi | 2 | 1 |
| Hebei | 1 | 1 |
| Jiangxi | 1 | 1 |
Distribution of rockburst coalmines in China.
Rockburst prevention and control methods are generally classified into regional and local approaches (Pan et al., 2013). Regional methods primarily involve large-scale stress relief through engineering means, such as optimizing development layouts, applying layer-liberation mining, and adopting pillarless mining techniques. Local active relief methods include deep-hole roof blasting (Wu et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2024), coal seam unloading blasting, high-pressure water injection into coal seams (Yang et al., 2024), large-hole unloading, directional hydraulic fracturing (Kang et al., 2023), floor-breaking blasting, pre-excavation of unloading chambers, high-pressure hydraulic fracturing (Li et al., 2023; Qin and Chen, 2021), and floor-slot cutting.
China’s coal production distribution shows a clear pattern of “less in the east and more in the west, less in the south and more in the north” (Yang and Xu, 2021).
For a long time, blasting has been the primary method for treating thick and hard roof strata in coal mines. In recent years, research advances in hydraulic fracturing fracture propagation mechanisms (Han et al., 2023; Han and Zhou., 2025a; Han and Zhou, 2025b; Wang et al., 2018) and studies on the damage and seepage characteristics of water-bearing rocks (Han and Zhou, 2025c; Niu and Zhou, 2021; Shou and Zhou, 2021; Zhou et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2022) have provided a reliable theoretical foundation for applying hydraulic fracturing to manage such roof strata. Currently, hydraulic fracturing for roof control has been implemented in multiple mines, including the Hongqinghe, Muduchaideng, and Menkeqing Mines in Inner Mongolia; the Dahaize, Hujiahe, Wenjiapo, and Yadian Mines in Shaanxi; the Wudong, Tunbao, and Kuangou Mines in Xinjiang; and the Yushupo and Malan Mines in Shanxi. Increasingly, mines are transitioning from blasting to hydraulic fracturing.
The Kuangou Coal Mine began applying hydraulic fracturing technology in 2021, successfully replacing blasting and serving as a model for the transition to hydraulic pressure relief. The first rockburst with casualties occurred on 8 October 2010, in panel W1143, resulting in four deaths, one injury, severe equipment damage, and roadway deformation (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1

Rockburst site conditions. (a) Destruction of mechanical equipment and (b) coal body crushing.
The rockburst at the Kuangou Coal Mine exhibited two distinct characteristics: (1) shallow depth—the coal seam where the rockburst occurred was at 317 m, much shallower than most previously recorded rockburst events; and (2) occurrence at the working face—while most past rockbursts occurred in roadways, this one occurred at the working face and exhibited strong dynamic behavior. Post-accident analysis revealed that the geological cause of the “10.8” rockburst was a thick (more than 10 m) hard sandstone roof above the B4 coal seam, which had strong bursting potential. Due to the prolonged absence of roof pressure relief, a hanging roof formed behind the working face (Figure 2). Combined with the intrinsic bursting tendency of the coal body, a serious disaster occurred (Li, 2015).
FIGURE 2

Rockburst induced by a large, thick, and hard roof overhang.
The Kuangou Coal Mine was the first in Xinjiang to implement rockburst prevention and control measures for thick and hard roofs. The B4 coal seam uses comprehensive mechanized mining technology, while the B2 seam adopts both comprehensive mechanized and roof-retaining mining methods, covering most existing coal mining techniques (Lan, 2014; Li et al., 2013; Lu et al., 2024; Sun et al., 2024).
For many years, the Kuangou Coal Mine relied on blasting for thick, hard roof management, but the mine has successfully transitioned to hydraulic fracturing. As the coal industry increasingly emphasizes safety, efficiency, and environmentally friendly production, more mines are adopting hydraulic fracturing to replace traditional blasting. Summarizing Kuangou’s experience provides a valuable reference for other mines in Xinjiang. This article takes the Kuangou Coal Mine as the research object, using theoretical analysis to identify the main controlling factors of rockbursts, assess the feasibility and necessity of thick and hard roof management, compile post-2011 management plans, and analyze prevention and control measures across different mining periods. The results offer important insights for managing thick, hard roof rockbursts in Xinjiang.
2 Analysis of the main control factors of rockbursts in the Kuangou Coal Mine
The energy sources of rockbursts are quantitatively described, the underlying physical quantities are identified, and the main controlling factors are analyzed based on the geological conditions of the Kuangou Coal Mine.
2.1 Analysis of the mechanism of the rockburst in the Kuangou Coal Mine
Before mining, the coal seam is in a stable, three-dimensional stress state. After mining, stress redistribution occurs, particularly due to vertical stress concentration near the mined-out area, coal pillars, and hard roof overhangs. When the combined static and dynamic loads exceed the coal–rock strength limit, failure occurs. Part of the accumulated elastic energy is dissipated through plastic deformation, while the remainder transforms into kinetic energy, resulting in violent ejection and rockburst phenomena, as expressed in Equation 1.where Erc represents the elastic energy accumulated internally in the coal rock body; Em is the elastic energy generated by stress concentration caused by mining; Erf is the dynamic load energy generated by roof breakage; Es is the energy dissipated by its own plastic deformation and destruction.
The three-way stress state of the coal–rock body without the influence of mining is shown in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3

Three-way stress state of coal and rock.
Elastic energy accumulated internally in the coal rock body can be calculated according to the Equation 2.
Elastic energy generated by stress concentration caused by mining can be calculated according to the Equation 3.where Erfc is the coal body elastic energy accumulation caused by roof overhang bending; Ej is the coal body elastic energy accumulation of the coal body caused by the mining structure.
The accumulation of elastic energy in the coal body caused by mining is influenced by the distribution, relative position, and size of the mining structures and can be calculated using the stress concentration coefficient derived from in situ stress monitoring. The elastic energy accumulation caused by roof overhang bending can be calculated according to the Equation 4.where q is the converted load per unit length of the weight of the roof plate and the additional load of the overlying rock layer; L is the overhanging length of the roof slab; E is the modulus of elasticity of the coal body; J is the end face inertia distance of the roof.
The dynamic load energy generated by the roof breaking can be calculated according to the Equation 5.where Erf0 is the initial energy released by roof breakage, which can be obtained by monitoring; R is the distance between the location of roof breakage and the limit equilibrium zone of coal seam; η is the energy attenuation coefficient of elastic wave transmission in the coal–rock medium.
Therefore, the energy criterion of impact manifestation can be calculated according to the Equation 6.
According to this equation, rockburst factors can be divided into five categories: original rock stress (K1), roof overhang bending at the goaf (K2), mining structure (K3), overburden breakage (K4), and mechanical properties and support strength of coal and rock (K5). The mathematical principle of rockburst prevention is to reduce the contribution of these factors through engineering measures to maintain an adequate safety margin in the mining space.
2.2 Analysis of the main controlling factors for the occurrence of the rockburst in the Kuangou Coal Mine
2.2.1 Original rock stress
In the Kuangou Mine, the maximum principal stress ranges from 12.8 MPa to 13.9 MPa, the intermediate principal stress ranges from 6.5 MPa to 8.1 MPa, and the minimum principal stress ranges from 5.5 MPa to 7.37 MPa. The B4 coal seam lies at a relatively shallow depth with simple geological conditions, and the rockburst in panel W1143 occurred at only 317 m, indicating that original rock stress was not the main controlling factor.
2.2.2 Mining structure
The relative positional relationship of the panel is as shown in Figure 4. The B4 coal seam is the first seam to be mined in Kuangou. Except for panels W11423 and E11422, which mined the B4-2 seam, the remaining panels mined the B4-1 seam. Some panels were affected by the residual mining structures of B4-2, making mining structure a contributing—but not dominant—factor for rockbursts in the B4 seam. During B2 seam mining, however, the stress concentration and strong dynamic loads induced by overburden breakage under mining influence are major triggering factors.
FIGURE 4

Relative position relationship of the panel.
2.2.3 Thick and hard roof
A thick, hard sandstone roof (over 10 m) exists above both B4-1 and B4-2 seams. The roof of B4-1 shows bursting liability, while that of B4-2 has a strong bursting tendency. During panel mining, the hard roof tends to hang and is difficult to collapse, leading to large-area overhangs and stress concentrations ahead of the working face. This generates high static loads, while sudden roof breakage produces strong dynamic loads, jointly increasing rockburst risk.
3 Kuangou Coal Mine thick-hard roof blasting decompression methods
3.1 Thick-hard roof blasting decompression principle
Deep-hole pre-cracking blasting of the roof involves drilling and blasting deep holes to damage the roof with high-pressure shock waves. This creates fractures around the boreholes, disrupting roof continuity. After pre-cracking, the roof collapses more readily during mining, avoiding stress concentration and sudden dynamic loading caused by large hanging areas. This method effectively mitigates both static and dynamic loads, thus preventing rockbursts.
The parameters for deep-hole pre-cracking blasting are determined based on the required roof processing height and actual construction conditions, and the blasting height can be calculated according to the Equation 7.where Hx is the hypothetical blast treatment height; Hc is the panel mining height; Ha is the thickness of roof collapse; ξ is the rock fragmentation coefficient.
3.2 Blasting pressure relief method of the thick-hard roof in coalseam B4
For the prevention and control of rockbursts caused by the thick and hard roof of coal seam B4, the basic management approach is as follows. First, deep-hole pre-cracking blasting is used to destroy the continuity of the roof within a large range and reduce its mechanical parameters. The preferred diameter of blasting holes is 94 mm; when this is not feasible, 75 mm holes may be used. The spacing between holes is generally approximately 10 m, and the pre-cracking height of the roof deep holes is approximately 20 m above the roof. During the first weighting step, high-risk areas such as one-sided squares and double-sided squares require enhanced pre-cracking, with hole spacing reduced from 10 m to 5 m. Due to the instability of coal and rock conditions, using the same blasting parameters may not achieve effective pre-cracking across the entire face. In some areas, the pre-cracking effect may be insufficient, or overhanging roofs may be observed; in such cases, additional treatment is required. Blasting holes are then constructed to cut through the full cross-section of the working face roof, as shown in Figure 5. Through roof blasting, the thick and hard roof in the goaf can collapse in a timely manner, reducing high stress concentration in the panel, decreasing the dynamic load generated by roof breakage, and lowering the likelihood of rockbursts in the coal seam.
FIGURE 5
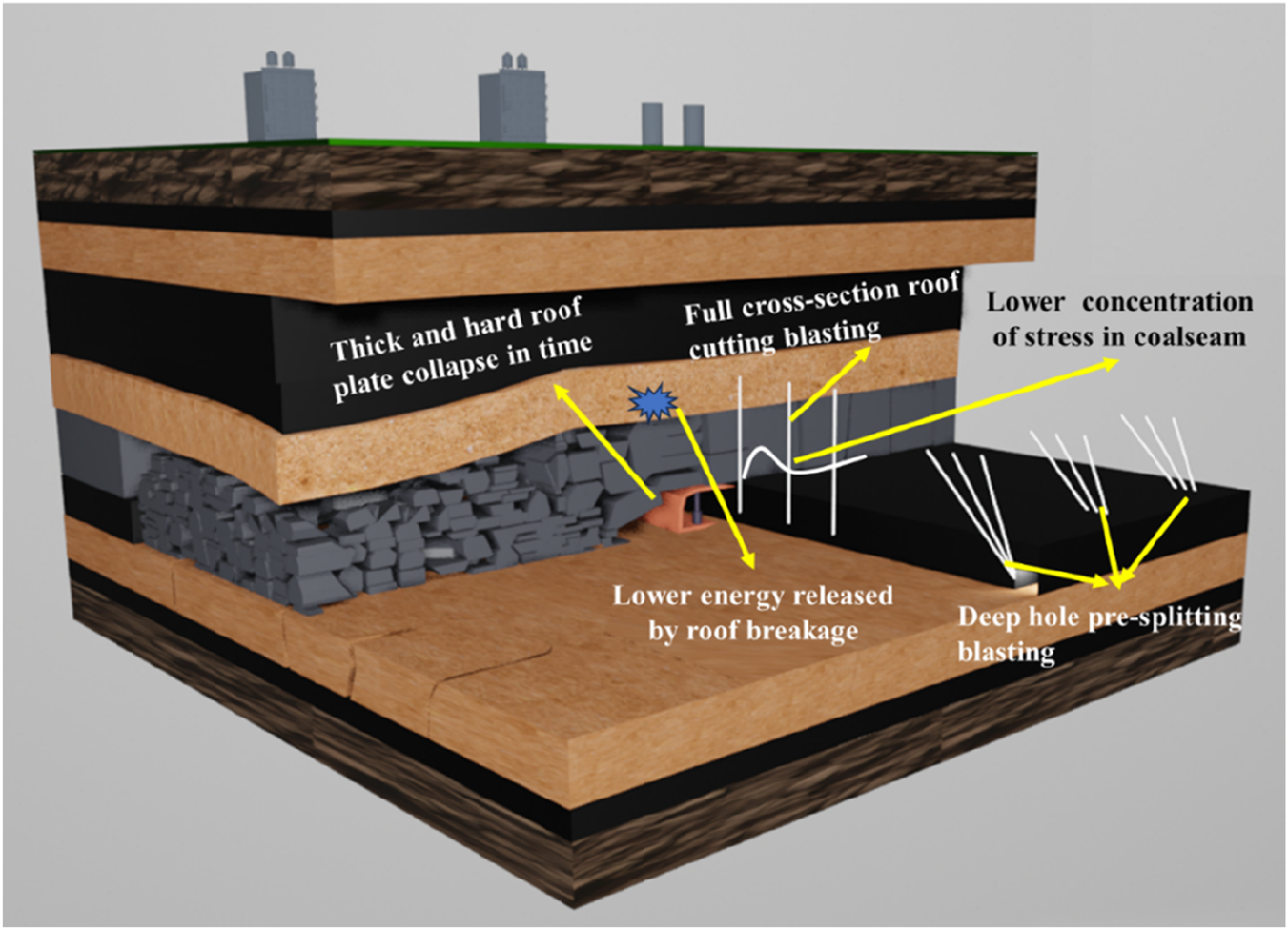
Blasting unloading method for the thick-hard roof in coalseam B4.
3.3 Blasting pressure-relief method for thick and hard roof in coalseam B2
The thick and hard roof remains the main controlling factor for rockbursts in coal seam B2. Because the B2 seam is mined by top-coal caving, blasting cannot be performed directly at the working face. During mining of panel 1,121, it was found that pre-cracking without full-section roof cutting could not ensure the timely collapse of the thick-hard roof. Therefore, a process roadway was designed to conduct full cross-section roof cutting blasting, enabling real-time treatment of the thick and hard roof, as shown in Figure 6.
FIGURE 6

Process roadway of panel 1,121.
Pre-cracking blasting conducted from the upper and lower roadways is limited by construction and loading conditions, resulting in ineffective coverage of the roof and leaving a pressure-relief blind zone in the middle of the panel. To address this, panels 1,122 and 1,123 were designed with a process lane specifically for blasting the thick and hard roof in the center of the face, as shown in Figure 7. This design significantly improved the coverage of pre-cracking blasting. Each process lane could be used to drill roof blasting holes across the panel, and the roof pressure-relief capacity of three lanes was equivalent to that of four upper or lower troughs. The roof treatment range of a single lane increased by more than 33%.
FIGURE 7
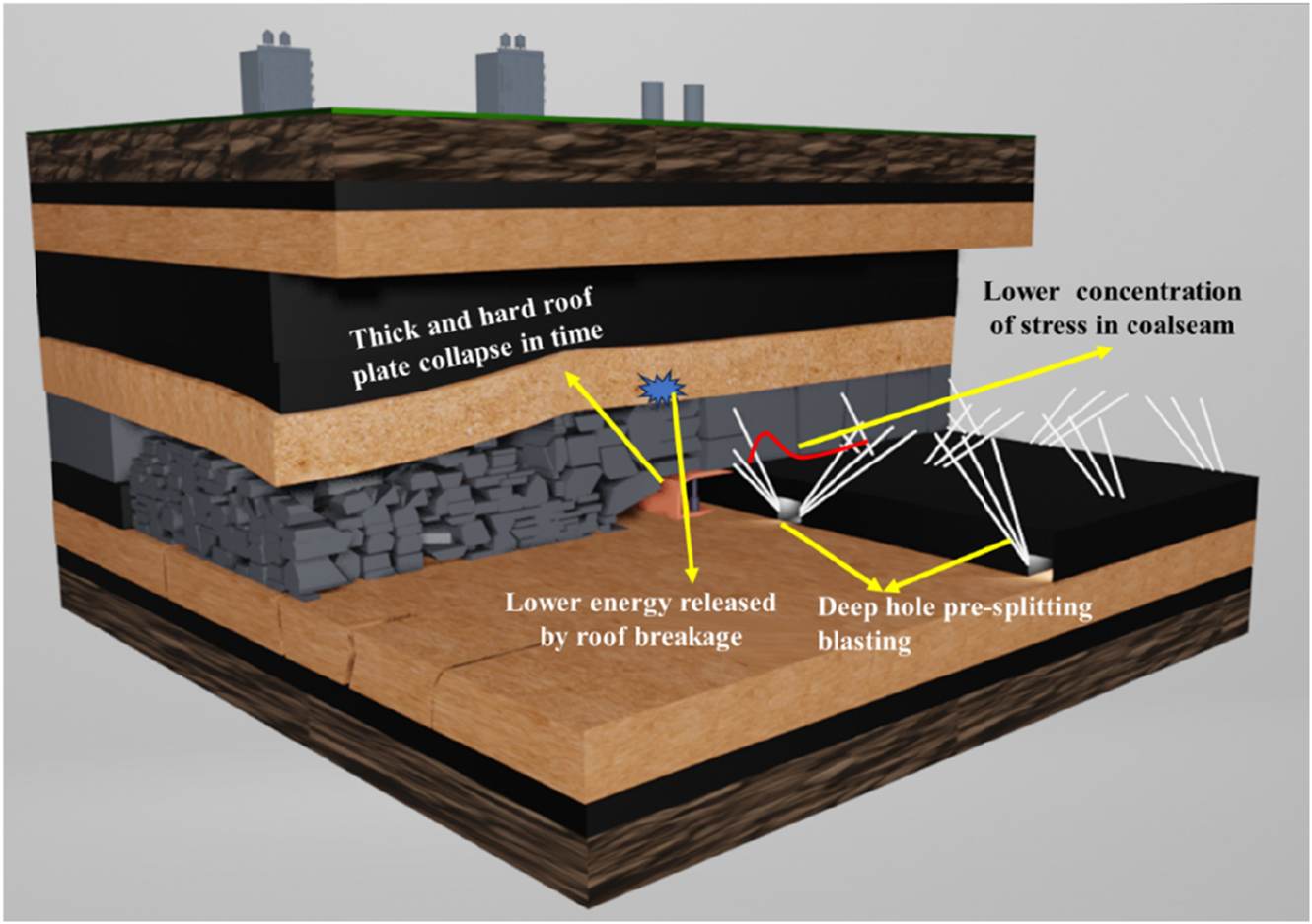
Blasting unloading method for the thick-hard roof in coalseam B2.
4 Roof axial cutting technology of abrasive jet and fracture
Roof blasting operations involve safety risks, particularly the potential for excessive CO concentrations during blasting. To mitigate these risks, the Kuangou Coal Mine introduced the thick and hard roof axial cutting technology using abrasive jet and hydraulic fracturing and successfully conducted an industrial trial in panel I010206. Transient electromagnetic detection and monitoring data analysis from the test area verified the effectiveness of this technology for hard roof treatment at the Kuangou Mine.
4.1 Pressure-relief principle
The roof axial cutting technology using abrasive jet and hydraulic fracturing can create initial fractures 300–500 mm deep along the borehole wall. During the fracturing process, these initial fractures guide the propagation of main fractures, forming a fracture network dominated by axial cracks within the hard roof. This facilitates timely roof caving. The construction process mainly consists of three stages: drilling, slotting, and fracturing, as shown in
Figure 8.
Drilling: Boreholes with specific azimuth and inclination angles are drilled into the roadway roof.
Slotting: The front-end operating assembly is advanced to the predetermined position in the borehole. The water-jet system is activated and switched to slotting mode. High-pressure water mixed with abrasive is ejected from nozzles on both sides of the slotting tool. The drill rig is operated to steadily advance or retract the drill pipe, forming pre-cut fractures on both sides along the borehole axis in a single pass.
Fracturing: The abrasive supply system is shut down, and the water-jet system is switched to packer mode. High-pressure water is injected into the packer to seal both ends of the fracture section. The system is then switched to fracturing mode, and high-pressure water is continuously injected through the front outlet holes of the slotting tool. The initial fractures propagate further along the pre-cut depth. Once significant water outflow is observed from adjacent boreholes or a sudden drop in pump pressure occurs, the high-pressure pump is shut down and the packer is depressurized, completing the fracturing process for that section.
FIGURE 8

Abrasive jet axial roof cutting equipment and process.
After axial roof cutting using the abrasive jet, a network of cracks forms near the goaf along the strike and dip directions of the roadway. The roof collapse becomes more complete, and both the static load and additional dynamic load caused by large roof overhangs are significantly reduced, thereby decreasing the occurrence of rockbursts (Figure 9) (Xia et al., 2024b).
FIGURE 9
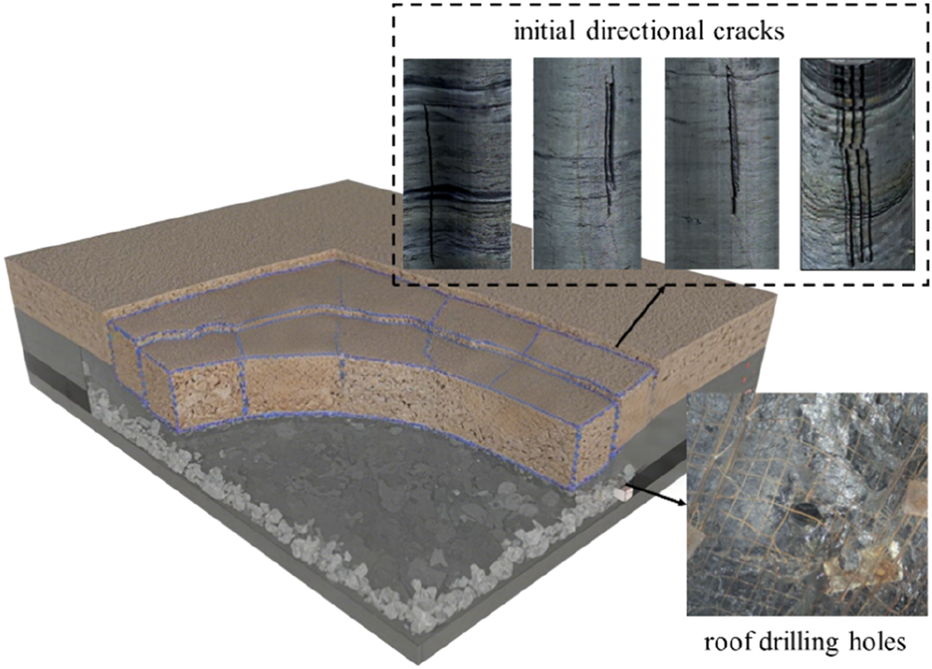
Pressure-relief method of roof axial cutting by abrasive jet and fracture.
4.2 Effect analysis
4.2.1 Analysis of transient electromagnetic detection of crack extension in the roof plate
A comparative analysis was conducted in the 620–430 m section of panel I010206 to evaluate the effectiveness of a combined pre-cracking technique that integrates roof axial cutting using abrasive jet and hydraulic fracturing with blasting pre-cracking. In the combined pre-cracking area, one abrasive jet axial roof cutting hole was placed between every two blasting holes, as shown in Figure 10.
FIGURE 10
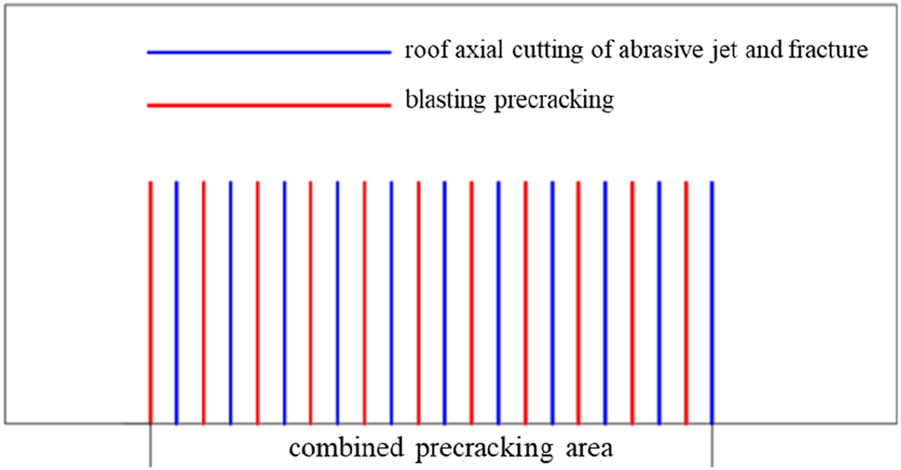
Drilling layout for the combined pre-cracking area.
To assess the pressure-relief effect, two transient electromagnetic detections were carried out. The apparent resistivity cloud results are shown in Figure 11, where the legend color represents resistivity decreasing from red to blue. Before fracturing, a low-resistance anomaly was observed within 0–20 m vertically at the 30–70 m detection position. After fracturing, low-resistance anomalies appeared within 0–40 m and 20–50 m vertically. The post-fracturing low-resistance anomaly range was significantly larger, reflecting increased water content in fractures after axial cutting. Thus, the abrasive jet axial cutting technology effectively achieved pre-cracking and pressure relief for roof sections up to 50 m in height in panel I010206.
FIGURE 11

Transient electromagnetic detection results: (a) Before the roof axial cutting using the abrasive jet and fracture and (b) after the roof axial cutting using the abrasive jet and fracture.
4.2.2 Characterization of the intensity of surrounding rock activity
Figure 12 shows the overall support pressure evolution of panel I010206. Comparing the support pressures in the blasting pre-cracking area and the combined pre-cracking area, the latter exhibited a significant increase in support pressure at the working face, with shortened periodic weighting intervals.
FIGURE 12

Cloud chart of bracket pressure.
The periodic weighting steps in the blasting area were 13.6 m, 12 m, 16 m, 18.4 m, and 19.2 m, with an average of 15.84 m. In the combined pre-cracking area, the steps were 12 m, 8.8 m, 8.8 m, 14.4 m, 8 m, and 12.8 m, averaging 10.8 m. The periodic weighting time in the combined area increased slightly compared with the blasting area, but the weighting step was reduced.
4.2.3 Characterization of energy release intensity
Figure 13 presents the distribution of microseismic events in the conventional blasting area and the combined pre-cracking area. A total of 459 microseismic events occurred in the combined pre-cracking area, releasing cumulative energy of 8.24 × 104 J, with an average energy of 2.52 × 102 J. In blasting area no. 1, 689 microseismic events occurred, releasing 9.62 × 104 J of cumulative energy and an average of 1.4 × 102 J. In blasting area no. 2, 667 events occurred, releasing 2.02 × 105 J of cumulative energy and an average of 3.03 × 102 J.
FIGURE 13

Comparison of microseismic events.
The distribution of microseismic events in the combined pre-cracking area is relatively sparse, mainly concentrated near the boundary area of the overlying coal seam I010408. The density of microseismic events near the upper downstream trough of the working face is significantly reduced, indicating that the combined pre-cracking effectively reduces the load of the roof on the coal seam.
5 Discussion
Thick-hard roof strata represent inherent geological conditions in coal mines and cannot be completely eliminated. Therefore, to ensure safe production in rockburst-prone mines, engineering measures must be applied to mitigate their impact as much as possible. Long-term engineering practice has shown that presplit blasting is an effective method for managing thick-hard roofs that has been widely used in many mines. However, blasting operations can easily cause gas concentrations (such as CO) to exceed safety limits and present additional hazards. With increasing demands for safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly production, presplit blasting can no longer meet operational requirements.
Hydraulic fracturing, originally developed for petroleum extraction, has recently been introduced for managing thick-hard roof strata. It has already been successfully applied in numerous mines across Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia, Shaanxi, and other regions, achieving notable results in controlling rockbursts and mining-induced seismicity. Compared with roof blasting, the advantages of roof axial cutting technology using abrasive jet and hydraulic fracturing are as follows:
Enhanced Safety and Controllability: Hydraulic fracturing is a non-explosive process using only high-pressure water and abrasives, fundamentally eliminating the risks associated with explosive materials. In contrast, blasting poses high risks such as misfires and accidental detonations.
Controlled Energy Input and Gradual Rock Disturbance: Hydraulic fracturing provides stable, controllable energy input, resulting in gradual disturbance of the surrounding rock. Blasting, by contrast, involves instantaneous and less controllable energy release.
Precise and Controllable Fracturing: Abrasive jet roof axial cutting creates highly precise and directed fractures, forming an ideal fracture network that effectively interrupts stress transmission within the roof. Blasting typically produces random, radially distributed fractures that are difficult to control.
Continuous Operation Capability: Hydraulic fracturing enables continuous operation without the need for blasting permits or explosive procurement. It does not interfere with other underground activities and can proceed concurrently with other production phases, improving efficiency.
Reduced Environmental Impact: Hydraulic fracturing avoids the strong vibrations, shock waves, and toxic fumes produced by blasting, significantly improving underground working conditions and promoting worker safety and equipment reliability.
Regarding hydraulic pressure relief, the Kuangou Mine has developed a combined pressure-relief model of “directional long-hole hydraulic fracturing for large-scale pressure relief + roof axial cutting technology using abrasive jet and hydraulic fracturing for localized treatment.” Directional long-hole hydraulic fracturing effectively pre-cracks the thick, hard roof over a wide area and reduces overhangs; however, its construction period is long and complex, making it unsuitable for localized treatment. Therefore, for local areas or during the final mining stages where roof plates are difficult to collapse, abrasive jet axial cutting is applied for targeted treatment.
Compared with mines relying solely on a single hydraulic fracturing method for pressure relief, this combined model has nearly eliminated dependence on explosives. The pressure-relief mode of “directional long-hole hydraulic fracturing for wide-area pressure relief + roof axial cutting using abrasive jet and hydraulic fracturing for local treatment” provides a valuable reference for disaster prevention and control in other rockburst-prone mines affected by thick-hard roof strata.
6 Conclusion
After more than 10 years of impact ground pressure prevention and control in the Kuangou Coal Mine, we have mastered the manifestation patterns and occurrence mechanism of impact ground pressure in the mine, formed a variety of effective prevention and control technologies for different mining environments, and obtained the following conclusions:
A thick, hard roof plate exists above each main mining seam in the Kuangou Coal Mine. The energy source of impact ground pressure was quantitatively analyzed, and five factors of impact ground pressure occurrence were proposed: original rock stress (K1), overhanging bending of the roof plate of the backing face (K2), mining structure (K3), overburden breakage (K4), and support capacity (K5). The analysis determines that the thick-hard roof impact ground pressure is the main controlling factor for the occurrence of impact ground pressure in the Kuangou Coal Mine.
When using blasting methods to treat the roof in the B4 coal seam, which allows blasting between racks at one mining height, the main approach is to effectively break and dissipate the energy of the thick, hard roof through “deep-hole pre-cracking of the roof plate beforehand and blasting between racks.”
The B2 coal seam adopts comprehensive mining with top-coal caving; therefore, blasting between frames cannot be performed. By constructing strike- or dip-oriented technology lanes, the effective blasting range can be improved. The dip-oriented technology lane is a one-end roadway; construction is more complex and less safe. In the B2 coal seam, the scheme of “upper and lower channels + strike-oriented technology lane” increases the single-channel roof processing range by more than 33%, can effectively comb the thick, hard roof with deep-hole pre-cracking, and can effectively achieve energy dissipation. The top slab treatment range of a single roadway adopted in the B2 coal seam has been increased by more than 33%, which can effectively comb out the thick and hard top slabs.
Through the introduction of new technology and equipment, the Kuangou Mine has realized complete hydraulic decompression of the roof slab and has formed the decompression mode of “directional long-drilling hydraulic fracturing to decompress a wide range of roof slabs + roof axial cutting technology of abrasive jet and fracture for local treatment.” First, the thick and hard roof of the working face is pre-fractured on a wide scale by directional long-drilling hydraulic fracturing to reduce overhang. Then, during the mining-back process, the roof axial cutting technology of abrasive jet and fracture is carried out to provide targeted treatment for the end and for local roof areas that are difficult to collapse.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
KL: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft. TD: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. YW: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. HpL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XY: Data curation, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JL: Formal Analysis, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. HbL: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. JW: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. “Tianchi Talents” Introduction Plan.
Conflict of interest
Author KL was employed by Xinjiang Energy and Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., CHN Energy.
Author TD was employed by CCTEG Coal Mining Research Institute and Tiandi Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
Authors YW, HpL, XY, JL, HbL, and JW were employed by Xinjiang Kuangou Mining Co., Ltd., CHN Energy.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Chong C. H. Zhou X. Y. Zhang Y. C. Ma L. W. Bhutta M. S. Li Z. et al (2023). LMDI decomposition of coal consumption in China based on the energy allocation diagram of coal flows: an update for 2005-2020 with improved sectoral resolutions. Energy285, 129266. 10.1016/j.energy.2023.129266
2
Gao F. Q. Lu Z. G. Peng X. Y. Lou J. F. Cao S. W. Wang X. Q. et al (2024). Coal pillar burst mechanism and prevention based on local mine stiffness (LMS) criterion. Coal Sci. Technol.52 (9), 125–136. 10.12438/cst.2024-0706
3
Ge S. R. Fan J. L. Liu S. Q. Song M. Xian Y. J. Wang B. et al (2024). Low carbon modern coal-based energy technology system and development strategy. J. China Coal Soc.49 (1), 203–223. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.1773
4
Han L. Y. Zhou X. P. (2025a). A coupled hydro-mechanical field-enriched finite element method for simulating the hydraulic fracture process of rocks subjected to in situ stresses. Acta Geotech.20 (3), 1315–1339. 10.1007/s11440-024-02518-2
5
Han L. Y. Zhou X. P. (2025b). Numerical simulations of the hydraulic fracture propagation in poroelastic media using the coupled hydro-mechanical field-enriched finite element method. Rock Mech. Rock Eng.58 (1), 245–274. 10.1007/s00603-024-04153-5
6
Han L. Y. Zhou X. P. (2025c). Thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling field-enriched finite element method for thermo-poroelastic fractured rock mass and its application. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci.195, 106276. 10.1016/J.IJRMMS.2025.106276
7
He S. Q. Song D. Z. He X. Q. Li Z. L. Chen T. Shen F. et al (2023). Numerical modelling of rockburst mechanism in a steeply dipping coal seam. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ.82 (7), 261. 10.1007/s10064-023-03248-7
8
Kang H. P. Feng Y. J. Zhang Z. Zhao K. K. Wang P. (2023). Hydraulic fracturing technology with directional boreholes for strata control in underground coal mines and its application. Coal Sci. Technol.51 (1), 31–44. 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2022-2004
9
Lan H. (2014). Prevention measures and types of mine strata pressure bump occurred in shallow depth seam. Coal Sci. Technol.42 (1), 9–13. 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2014.01.003
10
Li X. H. (2015). Case analysis and prevention technology of kuangou coalmine rock burst. Shenhua Sci. Technol.13 (3), 20–22. 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8492.2015.03.007
11
Li H. D. Lan H. Du T. T. Hou D. J. (2013). Micro-seismic characteristic and danger-relief method in rock-burst danger period of mining face under hard and thick roof of Kuangou mine. J. China Coal Soc.38 (S1), 6–11. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2013.s1.019
12
Li X. W. Wang C. J. Chen Y. J. Li H. N. (2022). Influence of temperature on gas desorption characterization in the whole process from coals and its application analysis on outburst risk prediction. Fuel321, 124021. 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124021
13
Li F. Liu H. W. Wang C. C. Sun R. C. Xiang G. Y. Ren B. R. et al (2023). Stress relief and permeability enhancement with hydraulic fracturing in overlying key strata of deep and soft coal seams. ACS Omega8 (13), 12183–12193. 10.1021/ACSOMEGA.2C08161
14
Lin A. M. (2018). New perspectives and explorations on coal resource integration: a review of research on the relationship between government and enterprises in coal resource integration. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. Soc. Sci.20 (3), 113. 10.3969/j.issn.1009-105X.2018.03.009
15
Liu G. J. Lei R. D. Huang L. Li M. L. Zhou J. K. (2024). Study on the mining response law and coal burst risk assessment of an isolated working face. Front. Earth Sci.12, 1487505. 10.3389/feart.2024.1487505
16
Lu A. L. Song D. Z. Li Z. L. He X. Q. Dou L. M. Xue Y. R. et al (2024). Numerical simulation study on pressure-relief effect of protective layer mining in coal seams prone to rockburst hazard. Rock Mech. Rock Eng.57 (8), 6421–6440. 10.1007/s00603-024-03826-5
17
Lyu X. Yang K. Fang J. J. (2022). Utilization of resources in abandoned coal mines for carbon neutrality. Sci. Total Environ.822, 153646. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153646
18
Niu Y. Zhou X. P. (2021). Forecast of time-of-instability in rocks under complex stress conditions using spatial precursory AE response rate. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci.147, 104908. 10.1016/J.IJRMMS.2021.104908
19
Pan J. F. Mao D. B. Lan H. Wang S. W. Qi Q. X. (2013). Study status and prospects of mine pressure bumping control technology in China. Coal Sci. Technol.41 (6), 21–25+41. 10.13199/j.cst.2013.06.27.panjf.012
20
Pan J. F. Xia Y. X. Wang S. W. Ma W. T. Zhang C. Y. Wang B. (2024). Technical difficulties and emerging development directions of deep rock burst prevention in China. J. China Coal Soc.49 (3), 1291–1302. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.1480
21
Qi Y. Liu B. G. Shi X. M. Wang Y. (2018). Stability study of inclined shield tunnels under deep mining. Chin. J. Rock. Mech. Eng.37 (S1), 3584–3592. 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1022
22
Qi Q. X. Pan Y. S. Li H. T. Jiang D. Y. Shu L. Y. Zhao S. K. et al (2020). Theoretical basis and key technology of prevention and control of coal-rock dynamic disasters in deep coal mining. J. China Coal Soc.45 (5), 1567–1584. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.DY20.0453
23
Qin J. T. Chen Y. T. (2021). Research and application of combined antireflection technology of high pressure hydraulic fracturing and punching in low permeability coal seam. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot.48 (6), 53–57. 10.19835/j.issn.1008-4495.2021.06.010
24
Shou Y. D. Zhou X. P. (2021). A coupled hydro-mechanical non-ordinary state-based peridynamics for the fissured porous rocks. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem.123, 133–146. 10.1016/j.enganabound.2020.12.001
25
Sun R. D. Zhao Z. P. Yang W. Li H. P. (2024). Research and application of hydraulic fracturing axial roof cutting technology for gently inclined hard roof based on abrasive jet. Front. Earth Sci.12, 1485210. 10.3389/feart.2024.1485210
26
Suo R. X. Wang Q. Han Q. T. (2024). Fixed-variable weight combination prediction of China’s energy consumption structure from the perspective of compositional data. China coal.50 (11), 21–29. 10.19880/j.cnki.ccm.2024.11.003
27
Wang Y. T. Zhou X. P. Wang Y. Shou Y. D. (2018). A 3-D conjugated bond-pair-based peridynamic formulation for initiation and propagation of cracks in brittle solids. Int. J. Solids Struct.134, 89–115. 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2017.10.022
28
Wang S. M. Shen Y. J. Song S. J. Liu L. Gu L. J. Wei J. B. (2023). Underground CO2 storage and technical problems in coal mining area under the “dual carbon” target. J. China Coal Soc.48 (7), 2599–2612. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.yg21.1872
29
Wang C. Jin Z. J. Liu X. F. Wang T. H. Liu Y. Zhang S. Y. et al (2024). A coal bursting liability evaluation model based on fuzzy set theory and analysis of three influencing factors. Front. Earth Sci.12, 1378956. 10.3389/feart.2024.1378956
30
Wu K. B. Zou J. P. Jiao Y. Y. He S. J. Wang G. M. (2023). Insight and effectiveness of working-face deep-hole blasting for prevention of strong seismicity induced by deep coal mining. Rock Mech. Rock Eng.56 (12), 8693–8709. 10.1007/s00603-023-03516-8
31
Xia T. Q. Li D. Li X. L. Yan X. Wang J. G. (2024a). A novel in-depth intelligent evaluation approach for the gas drainage effect from point monitoring to surface to volume. Appl. Energy353, 122147. 10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.122147
32
Xia Y. X. Zhang C. Y. Du T. T. Zhou J. L. Sun R. D. Lu C. et al (2024b). Process research and application of axial roof cutting technology of abrasive jet and fracture. J. China Coal Soc.49 (S1), 36–44. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0794
33
Yang F. L. Xu H. N. (2021). Analysis on the development path of ecological environment protection and resources comprehensive utilization in coal industry during the 14th five-year plan period. China coal.47 (5), 73–82. 10.19880/j.cnki.ccm.2021.05.012
34
Yang L. Q. Han Y. C. Chen B. L. Feng A. X. Rui Q. L. (2024). Study on the fracturing and penetration enhancement effect of high-pressure water injection in coal seams. Shanxi Coking Coal Sci. Technol.48 (3), 14–16+27. 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0652.2024.03.004
35
Yuan L. Wang E. Y. Ma Y. K. Liu Y. B. Li X. L. (2023). Research progress of coal and rock dynamic disasters and scientific and technological problems in China. J. China Coal Soc.48 (5), 1825–1845. 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.0264
36
Zhang Q. J. Liu C. J. Guo S. Wang W. T. Luo H. M. Jiang Y. H. (2023). Evaluation of the rock burst intensity of a cloud model based on the CRITIC method and the order relation analysis method. Min. Metall. Explor.40 (5), 1849–1863. 10.1007/S42461-023-00838-7
37
Zhao T. L. Hou G. Y. Shao Y. H. Zhang H. W. Xue J. S. (2024). Study on technology of deep-hole blasting combined cutting of hard thick roof in fully mechanized caving face of extra-thick coal seam. J. Min. Saf. Eng.41 (6), 1179–1189. 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2023.0569
38
Zhou X. P. Wang Y. T. Shou Y. D. (2020). Hydromechanical bond-based peridynamic model for pressurized and fluid-driven fracturing processes in fissured porous rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci.2020, 104383. 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104383
39
Zhou X. P. Du E. B. Wang Y. T. (2022). Thermo-hydro-chemo-mechanical coupling peridynamic model of fractured rock mass and its application in geothermal extraction. Comput. Geotech.148, 104837. 10.1016/J.COMPGEO.2022.104837
Summary
Keywords
rockburst, thick-hard roof, roof blasting decompression, roof hydraulic fracturing, coal mining
Citation
Liu K, Du T, Wu Y, Li H, Yang X, Liu J, Liang H and Wang J (2025) Evolution of roof treatment processes from blasting to hydraulic fracturing to prevent rockburst in thick-hard roof coal mines in Xinjiang, China. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1714727. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1714727
Received
28 September 2025
Revised
16 October 2025
Accepted
21 October 2025
Published
17 November 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Xiaoping Zhou, Chongqing University, China
Reviewed by
Yong Niu, Shaoxing University, China
Longfei Wang, Henan Polytechnic University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Liu, Du, Wu, Li, Yang, Liu, Liang and Wang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kunlun Liu, 1954535732@qq.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.