- 1Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training, Universitas Islam Negeri Sjech M.Djamil Djambek Bukittinggi, Bukittinggi, Indonesia
- 2BRAC Business School, BRAC University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
- 3Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Negeri Padang, Padang, Indonesia
The rapid evolution of digital technology has significantly influenced learning systems. Digital technology serves as a catalyst for transformative shifts in the manner in which individuals engage in many activities including educational pursuits. The widespread use of digital technology throughout all sectors, including education, has served as a catalyst for students to embrace and utilize new technology. However, challenges arise with the incorporation of digital technology into the classroom. This study investigated the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance, taking into account the role of digital informal learning, self-efficacy, and students’ digital competence as mediators. This study utilized a quantitative methodology employing a structured questionnaire for data collection and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) for hypothesis testing. This study found that improving students’ digital literacy skills can lead to thriving in academic pursuits. The empirical findings demonstrate that an increase in digital literacy improves digital competence, informal digital learning engagement, and digital self-efficacy. Additionally, possessing digital competence, engaging in digital informal learning, and having digital self-efficacy increases the likelihood of academic success. Therefore, digital competence, digital informal learning, and digital self-efficacy serve as partial mediators in the relationship between digital literacy and academic success. Hence, possessing digital competence, engaging in digital informal learning, and having digital self-efficacy contribute to enhancing the influence of digital literacy on academic achievement. These findings offer insightful implications for educators and policymakers.
1 Introduction
Accessibility of information has become limited. Accessing news from various areas of the globe in a fraction of a second is no longer regarded as miraculous, owing to technological advancements. Education has greatly benefited from the development of technology, making the dissemination of information simpler and less cumbersome. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has increased the significance of digital technologies in the education sector (Sesmiarni et al., 2024). Moreover, the proliferation of digital tools has inspired students to use them to boost their learning outcomes (Mehrvarz et al., 2021; Mehrvarz et al., 2023).
In the contemporary era, students often engage with online platforms as they interact with the digital systems provided by educational institutions. They navigate through a multitude of websites in their quest for materials relevant to their assignments, engage in file downloads, and participate in email correspondence, both for academic and personal purposes (Ng, 2012; Terrile, 2023). However, effective and efficient utilization of various features of digital technology requires a certain level of literacy. Digital literacy encompasses the ability to effectively utilize digital resources to generate and share new knowledge. This includes skills such as locating, organizing, managing, integrating, evaluating, analyzing, and synthesizing digital information (Ng, 2012; Degner et al., 2022). Digital literacy refers to students’ intellectual capacity to effectively and responsibly generate information using the internet (Ng, 2012). This has been found to have a positive impact on students’ academic performance and self-confidence (Jeon and Kim, 2022).
In educational institutions, students’ academic performance reflects their learning processes and ability to achieve institutional objectives. Engaging in homework, assignments, theory practice, class discussion, and exam preparation contributes to the final score or GPA of higher education students (Yu et al., 2010; Sakitri, 2020). This raises an important question: Does digital literacy have a significant impact on the academic performance of university students, considering their frequent use of the internet and technological devices? This study aims to address this research question by building upon previous studies such as Vrana (2014), Ukwoma et al. (2010), Khan et al. (2022), and Limniou et al. (2021). These studies have identified several challenges related to student proficiency in digital technology, the availability of technological infrastructure, competence in top-level management, and the effectiveness of the IT department in determining the success of digitalization (Bygstad et al., 2022). The present investigation focuses on the higher-education milieu in Indonesia. The primary objective of this study is to examine the potential mediation effects that may amplify the influence of digital literacy on academic skills and abilities.
In the context digital literacy, Spante et al. (2018) conducted a systematic review of digital literacy, specifically comparing it to digital competence. According to Calvani et al. (2008), digital competence is observed in the proficient utilization of technology, encompassing a wide range of competencies that extend beyond values and ethics. Digital competence refers to the ability to effectively utilize information and communication technology with the aim to actively participate and contribute to society (Terrile, 2023; Ferrari et al., 2013). Therefore, this study selected digital competence as a mediator in the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance. Additionally, empirical findings suggest that digital literacy in AI generative tools (i.e., ChatGPT) plays a significant role in influencing students’ self-efficacy, engagement, and revision strategies during academic writing tasks (Lo et al., 2025). As education increasingly utilizes AI technologies, the acquisition of digital literacy skills is vital. With the beginning of the AI era, students’ preparation for the skills to perform and use these tools effectively is essential for enhancing academic performance.
Given the widespread availability of knowledge through various platforms and social media channels such as YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram, it is now possible for students to supplement their formal education with informal learning opportunities. Students often seek additional educational resources from external course providers in order to enhance their academic performance. Informal learning occurs in a community or group of individuals who share similar ideas, interests, and goals (Dron and Anderson, 2022). Dron and Anderson (2022) emphasized that informal digital learning occurs in various contexts and at any time. Furthermore, a significant aspect of digital informal learning is its emphasis on self-direction and regulation. However, the availability of learning materials necessitates learner efficacy (Fu et al., 2020). Self-directed capabilities are necessary for success in informal digital learning. Without self-efficacy, one’s ability to succeed is limited. Self-efficacy helps individuals develop strategies to search for information (Tsai and Tsai, 2003), gain confidence in completing challenging assignments (Lee and Wu, 2012), and experience feelings of comfort and satisfaction (Meelissen and Drent, 2008).
Based on the above discussion and motivation, this study examines the potential mediating effects of digital competency, informal learning, and self-efficacy on the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance among university students. Specifically, this study aims to (i) examine the direct influence of digital literacy on competency, self-efficacy, and informal learning engagement and the direct impacts of informal learning, competency, and self-efficacy on performance; (ii) evaluate the mediating roles of digital competency and informal learning in the relationship between digital literacy and academic achievement; and (iii) assess whether self-efficacy mediates the influence of digital literacy and competency on performance. By examining these links, this study offers valuable insights into enhancing students’ digital skills in order to fully leverage the benefits of technology in higher education. This is particularly important because of the increasing popularity of online and blended-learning alternatives. This study intends to provide empirical evidence for enhancing learners’ academic achievement in a rapidly evolving digital learning setting.
2 Literature review and hypothesis development
2.1 Theoretical background
Digital literacy is a 21st century capability that everyone should possess. The ability to use digital media to explore digital-based information sources is essential because almost all of these sources are designed, managed, and disseminated using digital media.
2.1.1 Academic performance in online learning
Academic performance is the ability of an academic (student) to carry out his function as a student, such as the ability to attend lectures and the capacity to complete academic and non-academic tasks. The level of student academic performance is measured based on indicators, components, or desired patterns; however, student academic performance is commonly measured using students’ Grade Point Average (GPA) (Mehrvarz et al., 2021; Mehrvarz et al., 2023). Academic performance is also assessed by measuring students’ ability to study and administer academic activities and their academic success (Chang et al., 2019; Salendab, 2023). Academic performance can be improved by integrating digital media with learning. The integration of digital technology into learning to improve students’ academic performance is a challenge (Hutain and Michinov, 2022; Shafiee Rad et al., 2023) for lecturers, students, and institutions. Empirically, the use of several functions of digital technology has made a significant contribution to improving student academic performance, as students can focus on increasing their interest and curiosity and learning more to acquire the information needed openly and responsibly.
2.1.2 Digital literacy for ICT learning
The term digital literacy was first proposed by Gilster (1997). The initial concept explained under the term digital literacy refers to the extraordinary ability of accessing various sources of information on internet (Meyers et al., 2013), which exceeding the basic ability to read, write, speak or listen. Along with the development of digital technology, the term digital literacy has also developed, changed, and been used variably (Aabø, 2005). As Meyers et al. (2013) clarified, digital literacy is defined as technological competence in applying information literacy skills, such as the ability to find, use, manage, organize, present, and evaluate information digitally. Digital literacy is connected to the application of digital technologies, where digital technologies are a component of electronic technology that includes the application and use of different software for educational, social, and entertainment purposes at educational institutions and at home (Ng, 2012). Electronic equipment includes computers, tablets, and smartphones, which are integrated into the Internet. Mastery of digital literacy allows one to explore unlimited information resources, collaborate globally, and communicate anytime and anywhere.
Somebody with good digital literacy skills can access various information resources, collaborate and communicate effectively, and be competent in analyzing the period of using technology to support daily activities (Ng, 2012). According to Jeon and Kim (2022), digital literacy refers to the perception, attitude, identifying ability, access, accomplishment, evaluation, integration, analysis, and synthesis of digital resources in order to generate and express new knowledge. The context of the discussion of digital literacy focuses not only on a person’s ability to use digital technology to explore information in an effort to fulfill daily interests but also on its impact on human life (Meyers et al., 2013). This condition encourages the occurrence of “fear” of “blindness” to technological capabilities. That is to say, the responsibility for mastering technology for students is no longer limited to the responsibility of formal institutions but is also the responsibility of non-formal institutions.
Ng (2012) narrated the three dimensions of digital literacy as cognitive, technical, and social–emotional. The cognitive dimension of digital literacy is associated with critical thinking skills for finding, evaluating, and creating cycles for handling digital information. The cognitive dimension also enables the assessment and selection of appropriate software for these purposes. Digital literacy enables people to have the ethical, moral, and legal knowledge to use digital resources. The technical dimension requires adequate knowledge and skills in Information and Communication Technology (ICT) for learning and performing regular activities. Cognitive learning comprises an individual’s ability to use the Internet to communicate, socialize, and learn.
2.1.3 Digital informal learning
Learning can be executed, both formally and informally. Formal learning is organized in a structured, systematic education unit (Meyers et al., 2013), which has a clear and measurable planning, implementation, and evaluation system. Formal education is conducted by institutions that issue scientific certifications and diplomas (Czerkawski, 2016) as a legacy of the competencies possessed by students. In contrast, informal learning is conducted outside formal institutions, unstructured, and unorganized (Czerkawski, 2016). Digital technology (the Internet) is a major component of DIL, as students experience broad opportunities to find or obtain information to solve problems they face in learning (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023).
In the context of DIL, students are required to choose the right strategy and technology (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023) to support their learning. DIL enables students to find and determine learning strategies that suit their learning styles, making it easier to monitor learning progress, expand learning opportunities, and acquire more comprehensive knowledge according to their needs.
2.1.4 Self-efficacy for online learning
According to Bandura’s theory, self-efficacy is one of the determinants of learning behavior (Beldarrain, 2006). Bandura further stated that self-efficacy is the ability to perform and complete tasks in order to achieve goals. Self-efficacy is a key feature of online learning (Shen et al., 2013). This has a positive impact on in-person learning (McCleary-Jones, 2016). Additionally, it has a significant influence on achieving academic goals and communicating with instructors and classmates. Having high self-efficacy, a student can perceive online learning more accurately (Shen et al., 2013) and be more confident in completing their course (Chang et al., 2014; Jeon and Kim, 2022).
There are at least 5 (five) dimensions of self-efficacy in online learning: (a) self-efficacy to complete online lectures, (b) self-efficacy to interact socially among classmates, (c) self-efficacy to utilize appropriate tools and software for learning, (d) self-efficacy to properly interact with tutors, and (e) self-efficacy to communicate with classmates for academic purposes (Shen et al., 2013). Shen et al. (2013) also highlighted that three components must be considered regarding self-efficacy in online learning: technology, learning, and social interaction. Learning comprises academic accomplishments and social interactions between academics and classmates (Froehlich et al., 2023; Jeon and Kim, 2022; Shen et al., 2013).
2.1.5 Students’ digital competence
Students with better digital competence can accurately use digital media to find information that can be utilized for better outcomes. Students can also perform better by utilizing digital tools and systems in their communication processes (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023). The digital competency framework comprises of three dimensions: technical, cognitive, and ethical. This technical dimension suggests that users are more capable of finding and dealing with new problems accurately and flexibly. This dimension contains the concepts of visual literacy, problem solving, and technology understanding. The cognitive dimension indicates that users can read, select, interpret, and evaluate data and information, considering the appropriateness and consistency of the information. This dimension comprises data organization and visualization, data structuring, and information research. According to Lo (2024), digital competence in higher education should encompass not only functional skills, but also ethical and environmental responsibility. The ethical dimension denotes a person’s ability to interact fruitfully and correctly with others in a safe and respectful manner while using technology (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023). This ethical dimension distinguishes digital competence from literacy. Students possessing digital competence are able to use digital media in their learning. The digital competence possessed by a student can be used to (1) find information or for certain content for better presentation of information and understanding in learning, (2) as a communication and cooperation vehicle in the communication process among individuals and groups, and (3) control or regulate the learning process in which learning can be better managed (Degner et al., 2022).
2.2 Hypotheses development
2.2.1 Direct effects
Students who can utilize digital technology accurately will have a positive outcome in online learning. As Meyers et al. (2013) mentioned, a person with digital literacy skills can perform better in academia as they can utilize the materials properly and more accurately. Ng (2012) stated that a person with sound digital literacy skills can collect better information, communicate properly, and utilize that information to achieve success. Similarly, Mehrvarz et al. (2021) stated that students’ digital literacy has a positive impact on their academic performance. Thus, we propose the following hypotheses:
H1a: Digital literacy has a positive effect on students’ academic performance (AC) in online learning.
Digital competence has a positive influence on DIL (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023) and DIL plays a role in increasing students’ digital competence. The ability to master digital literacy will create worth integrates formal and informal education to create good learning (Meyers et al., 2013) and digital literacy skills used to support DIL (Schwan et al., 2018). Thus, we hypothesize the following:
H1b: Digital literacy has a positive effect on digital informal learning (DIL).
Digital literacy affects attitudes toward online learning and self-efficacy (Jeon and Kim, 2022). The development of computer technology and the polarization of technology itself has resulted in the need for self-efficacy toward technology, which in general, self-efficacy toward computers is a current demand (Kim and Jeon, 2020). Self-efficacy, along with sound digital literacy skills, helps students find and understand information through online learning. Self-efficacy also helps students understand and express numerous opinions and thoughts among instructors and classmates during online sessions (Froehlich et al., 2023; Kim and Jeon, 2020). Thus, we propose the following hypotheses:
H1c: Digital literacy has a positive effect on Self-efficacy for online learning (SE).
In the last decade, digital literacy and competence have often been discussed issues (Spante et al., 2018). Although these two terms have different meanings and descriptions, −as previously set out in the theoretical background section-, in fact they are often used as synonyms for one another (Lordache et al., 2017; Martin and Grudziecki, 2006). Spante et al. (2018) outline that digital literacy is being used earlier than the digital competence. Although both are used similarly in academia, digital literacy is extensively used in English-speaking countries such as the UK and the USA, and digital competence is commonly used by European countries rather than the UK.
In contrast, digital competence is considered one of the most important competencies for lifelong learning, as per the European Union (Ala-Mutka, 2011). Similarly, digital competence refers to self-confidence in using ICT to attain goals related to employment, employability, learning, reformation, and participation in community activities. Jin et al. (2020) stated that, according to scholars, the scope of digital competence is wider than that of digital literacy. Based on the above statements, the following hypothesis is proposed.
H1d: Digital literacy has a positive effect on students’ digital competence (DC).
Digital Informal Learning (DIL) has a positive influence on student learning outcomes, as outlined by Song and Lee (2014), who also conveyed a similar article by Sackey et al. (2015), where DIL helps improve student learning outcomes. Reciprocally, the results of research by Mehrvarz et al. (2021) suggest that DIL has a positive effect on student academic performance, since DIL allows students to improve academic performance. Therefore, the proposed hypotheses are as follows.
H2: Digital informal learning (DIL) has a positive effect on students’ academic performance (AC) in online learning.
Students’ digital capabilities positively influence informal digital learning, as stated by Mehrvarz et al. (2021, 2023). The higher the digital competency level of students, the better they are at achieving their learning goals in DIL (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023). As also previously discovered by He and Li (2019), students with a higher level of digital competence are likely to become rounded up in DIL, wherein He and Li (2019) divided DIL behavior into three dimensions: cognitive learning, meta-cognitive learning, and social and motivational learning. Accordingly, we propose the following hypotheses:
H3a: Students’ digital competence (DC) has a positive effect on Digital informal learning (DIL).
Students with digital competence possess multidimensional abilities such as competence in mastering ICT and high-level ethical awareness in using technology (Calvani et al., 2008). Therefore, DC had a positive effect on academic performance. When students’ digital competence increases, their academic performance also increases (Mehrvarz et al., 2021). However, Claro et al. (2012) disclosed that the use of ICT at school did not have an interconnection with students’ scores, especially in courses related to digital utilization. Thus, the associated hypotheses are as follows.
H3b: Students’ digital competence (DC) has a positive effect on students’ academic performance (AC) in online learning.
The key feature of learning activities is the presence of communication, that is, communication between students and their learning environment, with instructors, tutors, teachers, friends, learning hubs, and available resources. Belief that you have encouraged a person to try to get what he/she wants. Self-efficacy has a strong effect on DIL. Learning is not bound by place or time. Learning occurs in the family, environment, and media. Learning is conducted between parents, children, brothers, and sisters. Learning does not have a certain curriculum level that must be followed.
Self-efficacy is a determinant of learning success (Prior et al., 2016). The success of online learning is also determined by self-efficacy, where learning conditions are dissimilar to those learning conditions in ordinary classes, with obstacles in the form of minimal social interaction with colleagues, the possibility of the costs required to maintain and update learning systems and devices, and obstacles due to less flexibility of online tutorials (Wu et al., 2010). Unlike offline informal learning, which focuses on self-directed learning, digital informal learning requires good self-control to obtain new lessons that adapt to the interests of the learner and, hence, are not based on the curriculum and usually occur outside the formal classroom (He and Li, 2019; He et al., 2018). Thus, hypothesis H4a is proposed: Self-efficacy for online learning has a positive effect on digital informal learning (DIL). Thus, we propose the following hypotheses:
H4a: Self-efficacy for online learning has a positive effect on digital informal learning (DIL).
Scholes et al. (2022) studied students’self-efficacy in relation to their digital skills in the context of video gaming among elementary school students. Katsarou (2021) conducted research on computer anxiety and computer self-efficacy of L2 learners, which predicted their digital competence and satisfaction. Tramontano et al. (2021) conducted a study on employees’self-efficacy to assess their digital competencies in remote working during the COVID-19 situation, where self-efficacy was arranged as a tool to measure the digital resilience competency of employees working remotely. In addition, numerous studies have been conducted on how teachers’ computer self-efficacy affects their development of digital competence (Dai, 2023; Instefjord and Munthe, 2017; Amhag et al., 2019; Andreasen, 2022; Norden et al., 2017). Consequently, we propose the following hypotheses:
H4b: Self-efficacy for online learning has a positive effect on Student’s Digital Competence.
Academic self-efficacy is a predictor that is more significantly used to predict academic achievement than is academic self-concept. A person’s assessment of his/her academic ability, which includes the ability to attend lectures/lessons, the ability to achieve achievements in the field of academic activities, and activities on campus or in the classroom, is also related to perceptions, thoughts, feelings, and a person’s assessment of his/her academic ability. According to Bandura (1997a), self-efficacy can be obtained, studied, and developed from four sources of information that affect it. These four features are considered to be the experience of success and achievement, the experience of others, verbal persuasion, and physiological and psychological states. Thus, we propose the following hypotheses:
H4c: Self-efficacy for online learning has a positive effect on students’ academic performance (AC) in online learning.
2.2.2 Mediating effects
DIL, as a mediating variable, has a positive effect on the relationship between digital modules and student performance (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023). DIL can enable students to find and determine learning strategies that suit their learning styles, be more easily involved in learning progress, broaden learning opportunities, and gain integrated knowledge according to their abilities. The positive influence of DIL on literacy competence and academic achievement is that it can increase students’ motivation to learn, involve them in constructive activities, and teach them how to carry out lecture assignments successfully, which will increase their academic achievement (Kim and Jeon, 2020; Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023).
H5a: DIL played a mediating role in the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance.
Students with more opportunities for DIL and higher levels of digital competency will contribute more to their academic performance (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023; Zhou et al., 2023). Although DC has a direct effect on students’ academic performance, it plays a mediating role between DC and students’ academic performance (Mehrvarz et al., 2021). DIL contributes to the academic performance of students in two ways: it has a direct effect on students’ academic performance and enhances their digital competencies (Mehrvarz et al., 2021, 2023; Zhou et al., 2023).
H5b: DIL plays a mediating role in the relationship between DC and academic performance.
In terms of digital education for prospective teachers, various models and literacy developments are needed for teachers and educators to build the digital capabilities of their students so that they can take advantage of the latest digital technology to meet their future teaching needs. Previous models which focused on producing digitally “literate” prospective teachers were considered to have many drawbacks since they had a narrow focus and did not pay attention to socio-cultural aspects and other important aspects including ethics, health, welfare and security (Gruszczynska and Pountney, 2013). Falloon (2020) identified that the emphasis on literacy should be replaced with a broader competency model that summarizes more diverse knowledge and capabilities, and includes mindsets, as stated by Janssen et al. (2013). Based on the above explanation, the authors propose that DC play a mediating role in the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance.
H5c: DC plays a mediating role in the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance.
Alghamdi et al. (2020) researched academic performance which is influenced by multitasking behavior related to technology or the digital world such as using the internet together with listening to music through digital platforms. Most studies with similar variables have found that multitasking behavior has a negative impact on students’ academic performance. The self-efficacy variable for independent learning became a mediator in the study, making students who perform multiple tasks have low self-efficacy for independent learning, resulting in low grade point averages or GPA scores for these students. In a study by Zhu et al. (2011), self-efficacy mediated the relationship between searching for information via the Web and academic performance. The mediating effect of self-efficacy on academic performance differs from that of searching for information via the internet. Based on these studies, we hypothesize that SE plays a mediating role in the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance.
H5d: SE plays a mediating role in the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance.
Liu et al. (2020) investigated the mediating effect of student self-efficacy, with reference to Bandura (1997b) social cognitive career theory. A student’s self-efficacy is one of the cognitive variables that determines formative behavior, which helps students achieve work eligibility. Liu et al. (2020) used the teacher’s transformational leadership variable as the dependent variable, one of which was the teacher’s ability to encourage and guide their students to grow and develop (Bolkan and Goodboy, 2011), which affects students’ employability. Student work eligibility refers to the ability of students to place their competencies and adapt to changes in the labor market (Heijde and Heijden, 2006). As a result, teachers’ transformational leadership can influence students’ employability by influencing their academic self-efficacy. Thus, this study proposes the hypothesis that SE plays a mediating role in the relationship between DCs and academic performance.
H5e: SE plays a mediating role in the relationship between DC and academic performance.
2.3 Conceptual framework
This study constructed a conceptual framework to investigate the mediating roles of informal digital learning, self-efficacy, and students’ digital competence in relation to digital literacy and academic performance. The framework is based on the theoretical background and proposed hypotheses H1-H5. This framework demonstrates that Digital Literacy impacts Academic Performance both directly and indirectly through the mediators of DIL, Self-Efficacy, and Digital Competence. The hypotheses examined each connection within this comprehensive network, which dictates the relationships between the important variables in online learning environments (Figure 1).
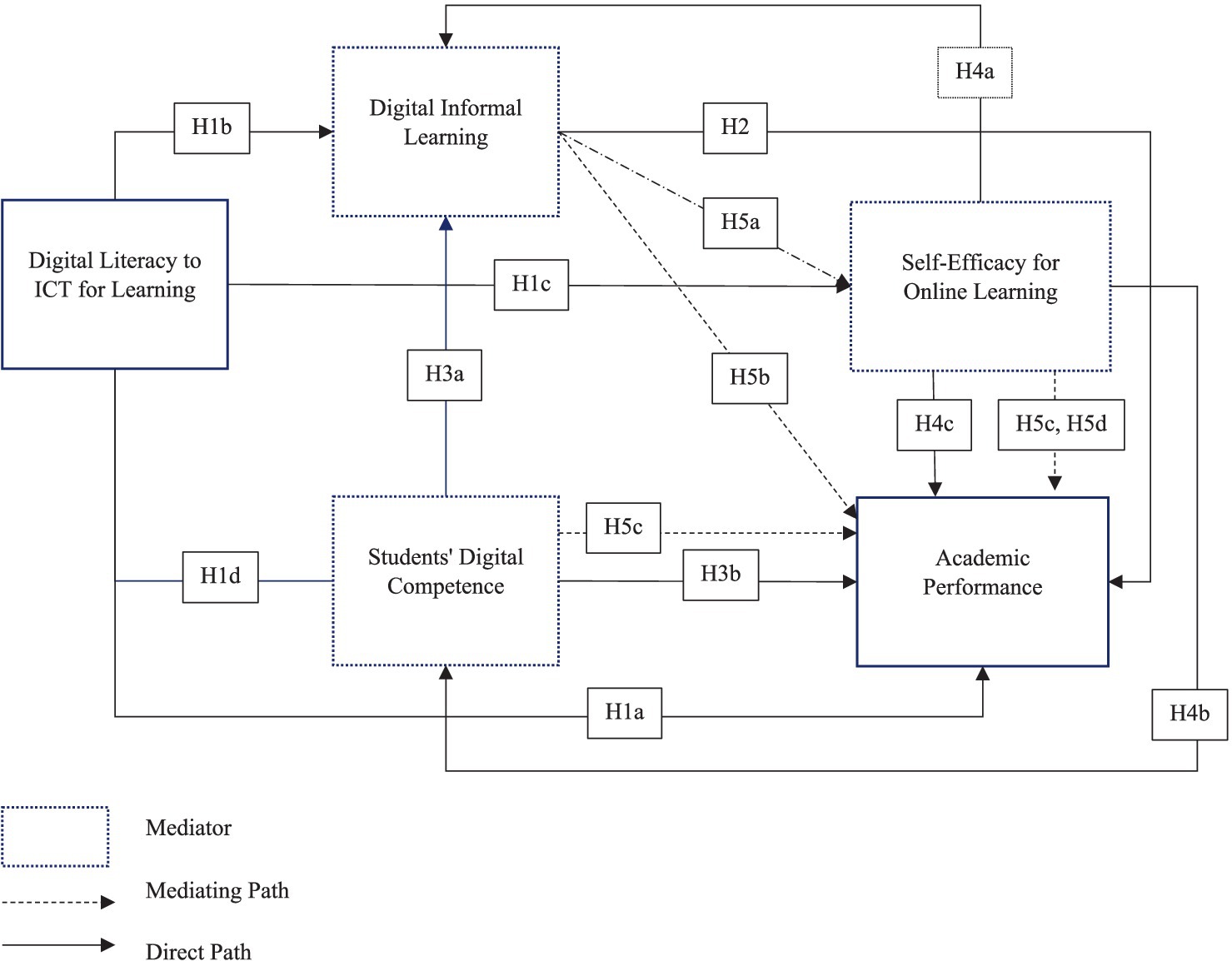
Figure 1. Conceptual framework for the mediating roles of digital informal learning, self-efficacy, and students’ digital competence between digital literacy and academic performance.
3 Methods
3.1 Study design
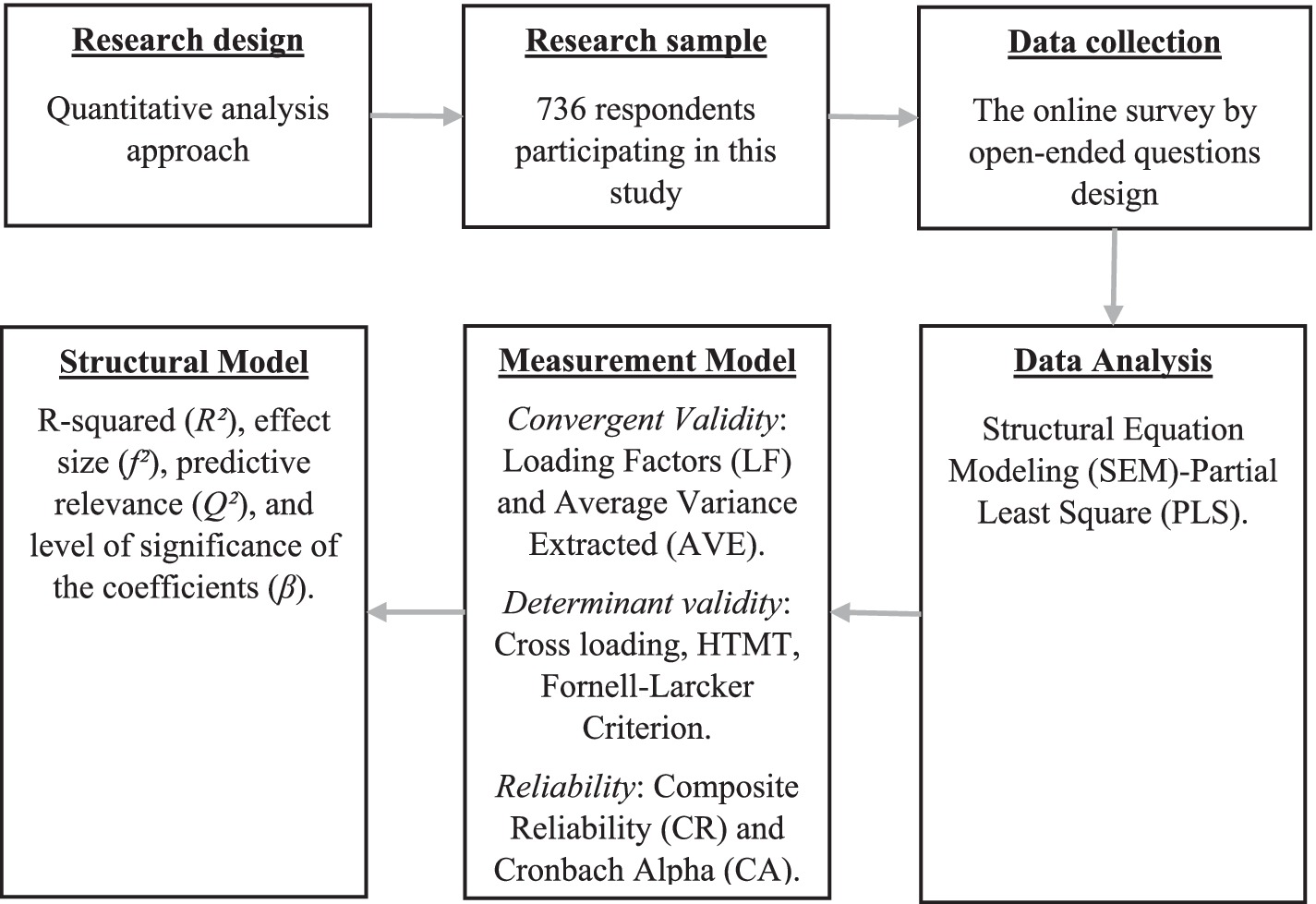
This study aimed to introduce quantitative concepts to digital learning using an approach different from previous experimental studies (Cohen et al., 2018). The development of materials was informed by constructivist philosophy, which seeks to improve the quality of research and the understanding of knowledge through theoretical frameworks that aid the interpretation of findings (Butler and Kern, 2016). The questionnaire included two sections: collection of respondents’ demographic information and measurement of model variables. A seven-point Likert scale ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree was used to assess the measurement variables. These scales have been adopted from previous studies. The research procedure is illustrated in Figure 2.
The demographic section gathered data on the respondent profiles. The students served as the survey participants. An online questionnaire was distributed and collected and 800 responses were returned. After the review, 36 questionnaires were excluded owing to incomplete or inconsistent answers, leaving 736 valid questionnaires. The research instrument comprised statements rated on a seven-point Likert scale, in line with this quantitative approach.
A total of 736 respondents participated in this study, comprising 72.01% females and 27.85% males. The majority of respondents belonged to the age groups of 18–20 years (46.88%) and 21–23 years (40.08%), with fewer percentages in the above 24 years. In terms of educational levels, most respondents had a bachelor’s degree of 91.03%, followed by master’s and doctoral students. Handphones were the most utilized devices (89.54%), followed by laptops (51.90%), desktops (10.46%), tablets/iPads (1.49%), and other devices (3.26%). These findings show that the study’s target population is young, academically active, and digitally engaged, which positions them as highly relevant and appropriate for examining concerns about digital behavior and educational technology.
In the measurement items section, we adopted construct and sub-construct measurements from previous studies, such as self-efficacy (adopted from Shen et al., 2013), digital competence (adopted from Mehrvarz et al., 2021), digital literacy of ICT for learning (adopted from Mehrvarz et al., 2021), digital informal learning (adopted from Mehrvarz et al., 2023), and academic performance (adopted from Mehrvarz et al., 2021). Further details are provided in Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
4 Results
4.1 Measurement model
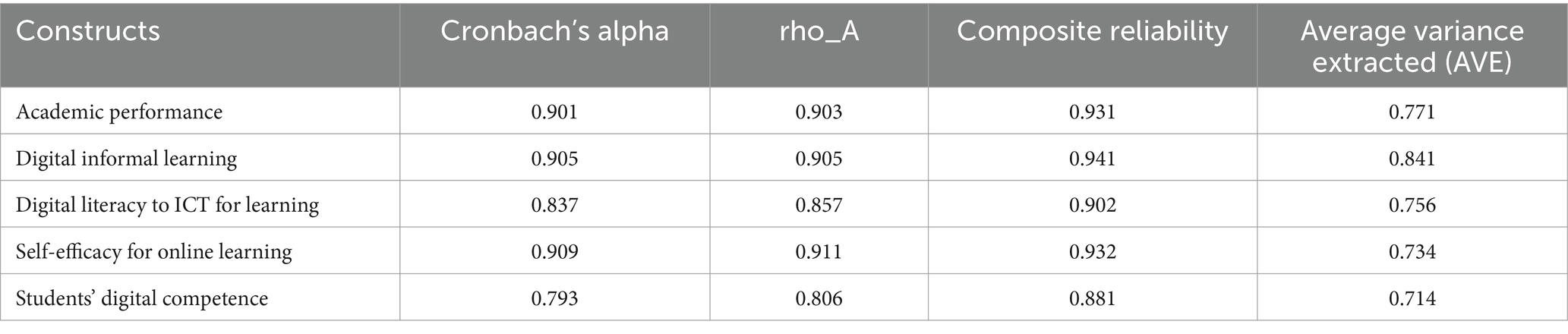
In the measurement model, we tested the constructs using Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability, and average variance extracted (AVE). This provides information on reliability and convergent validity, demonstrating that the first-and second-order measurement models are valid. Construct reliability was assessed using composite reliability (CR). Cronbach’s alpha and CR values were above the threshold of 0.70 (Fornell and Larcker, 1981). As shown in the table, the constructs of the variables (academic performance, digital informal learning, digital literacy for ICT learning, self-efficacy for online learning, and students’ digital competence) exceeded the suggested value of 0.70. They also presented higher composite reliability and AVE (over 0.86) above the suggested value of 0.70 (Hair, 2013) (Table 1).
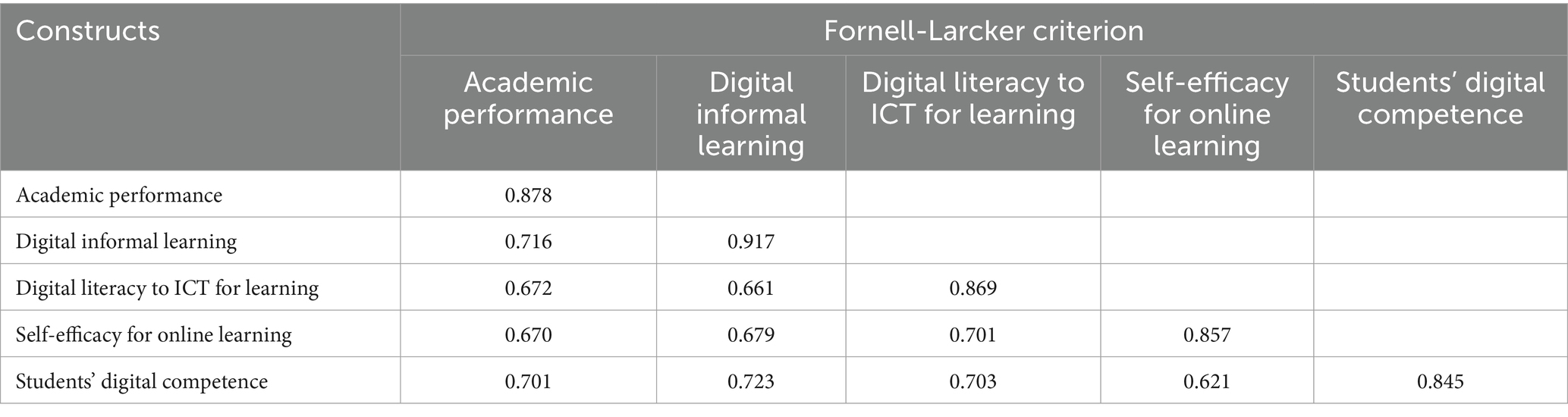
To assess discriminant validity, we examined the cross-loading factors that were useful in determining whether a construct demonstrated adequate discriminant validity. This was performed by comparing the loading value of an item on its intended construct with the loading values of the other constructs. The variables - academic performance, digital informal learning, digital literacy for ICT learning, self-efficacy for online learning, and students’ digital competence–have been accepted as demonstrating greater loading, where the correlation value of the association with their respective constructs is higher compared to other constructs. Therefore, it can be said that the model demonstrates good discriminant validity (Table 2).
4.2 Structural model
A structural model was constructed by continuing with the measurement model. In the structural model, we must consider collinearity (VIF), the coefficient of determination (R2), and predictive relevance – redundancy measurement (Q2), along with statistical significance and path coefficients (Hair et al., 2018). The inner VIF values of Digital Informal learning, Digital literacy to ICT learning, Self-efficacy for online learning and Student Digital Competence constructs, respectively, are 2,608, 2,601, 2,357, 2,599. These numbers meet the requirements because the ideal number is below three, meaning there is no collinearity problem in the predictor constructs (Hair et al., 2018).
Regarding the coefficient of determination (R2), which aimed to determine the accuracy of the predictions of the independent variable on the dependent variable, R2 academic performance was 0.628, Digital Informal Learning was 0.617, self-efficacy for online learning was 0.491, and students’ digital competence was 0.527. The R2 is between the strong and moderate levels (Henseler et al., 2009), indicating that the prediction accuracy of the independent variable on the academic performance variable was 62.8% (R2 = 0.628), Digital Informal Learning was 61.7%, self-efficacy for online learning was 49.1%, and students’ digital competence was 52.7%. To determine the Q2 value or predictive relevance, a cross-validated redundancy approach was applied by running blindfolds using SmartPLS. The Q2 value obtained from the endogenous variables is >0 (Academic Performance = 0.480, digital informal learning = 0.512, self-efficacy for online learning = 0.355, and students’ digital competence = 0.371), meaning that the exogenous variable (digital literacy) is predictive of the endogenous variables. Regarding path coefficients, with a significance level of 5%, p ≤ 0.05 are obtained. Details are presented in Table 3.
5 Discussion and implications
5.1 Direct effects
After testing the hypotheses, the effects of digital literacy on digital informal learning (β = 0.137), self-efficacy for online learning (β = 0.701), students’ digital competence (β = 0.527), and academic performance (β = 0.159) had p ≤ 0.05. That is, the greater the students’ digital literacy, the more frequently they were involved in informal digital learning, the better their self-efficacy in online learning, the higher their digital competence, and the better their academic performance. Thus, H1a, H1b, H1c, and H1d are accepted. Digital literacy was found to be key to the successful academic performance of students across Indonesia in online learning. This finding is in accordance with the research of Vrana (2014), who stated that skills appropriately used by digitally literate persons are vital for students’ personal and academic development, as they are required to build a successful informal learning environment to address the gaps between digital and non-digital learning methods (Mehrvarz et al., 2023; Mehrvarz et al., 2021). Youth in Indonesia who are digitally literate are more likely to be successful in managing their own digital informal learning, as they have flexibility not only with technology but also with people and environments. Similar to the findings of Jeon and Kim (2022) and Spante et al. (2018), digital literacy affected Indonesian students’ self-efficacy, as they are aware of their capabilities and thus confident in completing given tasks/projects or even curricula. This study found that digital literacy led to the development of digital competence. As Falloon (2020) explained, the terms and concepts of digital literacy are limited to technical skills without considering other factors such as sociocultural, ethical, security, and adaptability. Digital competence encompasses a complex context. This explains why students developing technical skills and mastering these skills strive to acquire technological competencies in the future (see Jin et al., 2020). Overall, this study presents empirical evidence supporting the positive effects of digital literacy on various aspects of student performance in Indonesia. This study highlights the crucial role of digital literacy in developing a comprehensive set of digital skills including technical proficiency and the ability to navigate sociocultural, ethical, and adaptive challenges. Hence, the findings confirm that investing in students’ digital literacy has a positive impact on various educational outcomes, and is crucial for their success in online learning environments. This study provides valuable insights into how Indonesian students can create digital opportunities and enhance their academic performance in the digital age.
Subsequently, Hypothesis H2 (β = 0.288, p-value 0.000 < 0.05) was confirmed, in which a student’s ability to engage in digital informal learning helped them achieve better academic performance. This is consistent with the studies by Mehrvarz et al. (2021) and Sackey et al. (2015), who concluded that the DIL environment helps students construct their own study strategies, see whether progress is on track, and gain an understanding of the course material, all of which lead to better academic performance. Hence, this study reinforces the importance of developing students’ digital skills, such as by implementing DIL, to enhance educational outcomes.
H3a (β = 0.432, p-value 0.000 < 0.05) and H3b (β = 0.253, p-value 0.000 < 0.05) were both accepted. Students’ digital competence was found to have significantly positive effects on their DIL and academic performance. These findings confirm H3a and H3b, and add to the body of evidence linking digital skill development to educational benefits. This confirms the study by He and Li (2019) on Chinese university students, where digital competence had a strong effect on DIL behavior. They explained that university students are the primary users of new technologies compared to other groups in the population. As such, students are expected to meet the standards of digital globalization by continually developing their digital skills. This condition may be similar for students in Indonesia, where digital skills are crucially needed, particularly in universities, where academic requirements are digitally based, and lectures require students to engage with technology. With regards to digital competence and academic performance, the results of this study reinforce studies by López-Belmonte et al. (2019) and Wang et al. (2021), among others.
H4a (β = 0.315, p-value 0 < 0.05), H4b (β = 0.251, p-value 0 < 0.05), and H4c (β = 0.253, p-value 0 < 0.05) are the hypotheses involving the self-efficacy variable. Students with high self-efficacy in using technology performed better in their DIL environment, gained greater digital competence, and ultimately attained better academic performance. The findings of Wu et al. (2010) were in line with the results of H4a, which explained students’ self-efficacy in using a blended e-learning system. It is understandable that students in Indonesia with high self-efficacy have the power to shape their beliefs about successfully completing DIL programs. An example of a prominent DIL programme in Indonesia is language learning. As studied by Nugroho (2021), the self-directed use of devices to learn and practice English is adequate to support learning success. On average, Indonesian learners believe that DIL help to broaden their language capacity. Concerning self-efficacy in online learning in the development of digital competence (H4b), this study confirms the study by Katsarou (2021), which found that computer self-efficacy is one of three variables, along with gender and computer anxiety, predicting L2 learners’ digital competence and satisfaction with online learning modules. With respect to H4c on self-efficacy and academic performance, this aligns with previous studies, such as Brady‐Amoon and Fuertes (2011), Shen et al. (2013), and De Clercq et al. (2013), Feldman and Kubota (2015) and Kassab et al. (2015) showed that students’self-efficacy leads them to attain satisfactory course grades. Our empirical findings support hypotheses H4a, H4b, and H4c, further establishing a connection between self-efficacy and digital learning outcomes. This study provides valuable cultural insights by focusing on the relationships between Indonesian students. They also provide evidence that self-efficacy has an impact on student engagement, competency gains, and academic performance.
5.2 Mediating effects
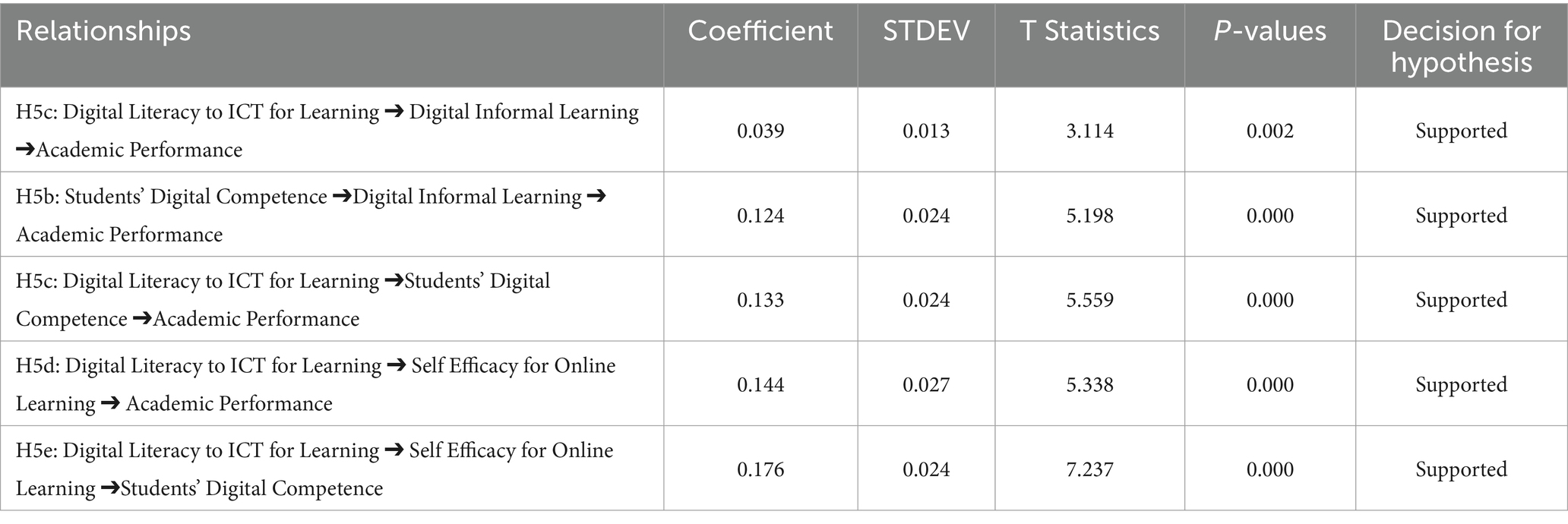
Examining the path coefficient table regarding indirect effects, H5a (β = 0.039, p-value 0.002 < 0.05), H5b (β = 0.124, p-value 0 < 0.05), H5c (β = 0.133 p-value 0 < 0.05), H5d (β = 0.144, p-value 0 < 0.05), and H5e (β = 0.176, p-value 0 < 0.05) all gained support. DIL is considered an effective mediator in achieving academic success, whether students have only digital literacy or have acquired digital competence. As Mehrvarz et al. (2021, 2023) stated, DIL significantly mediates the relationship between digital competence and academic performance. Since digital literacy comprises assembling digital skills to attain digital competence, it also significantly influences academic achievement mediated by DIL. For Indonesian students, DIL is crucial for improving their digital skills and competencies to help them master specific trajectories (Astuti and Setiawan, 2022) (Table 4).
Regarding Hypothesis H5c, the coefficient was 0.133 and the p-value was 0.000, demonstrating that digital competence significantly bridges the relationship between digital literacy and academic performance. Because digital literacy is insufficient, students must equip themselves with extensive capabilities and appropriate mindsets, as explained by Falloon (2020) and Janssen et al. (2013). Indonesian students require broad digital learning horizons and must possess ethical knowledge (a component of digital competence) to sufficiently develop their academic skills and abilities. Further, hypotheses H5d (β = 0.144, p-value 0 < 0.05) and H5e (β = 0.176, p-value 0 < 0.05), which apply student self-efficacy as a mediating variable, are significant. Self-efficacy in digital tasks assists in boosting digital literacy, competence, and academic performance. However, these variables have not yet been studied in detail. Alghamdi et al. (2020) previously found information searched through the web leads to low self-efficacy and low GPA, contradicting this study’s results.
In summary, the effects of digital skills and abilities on key student outcomes were effectively transmitted through DIL and self-efficacy, as hypothesized. DIL mediates the relationships between digital literacy, competence, and academic performance. Self-efficacy also plays a role in connecting digital literacy with both digital competence and academic performance. The results of this study strongly support the proposed indirect relationships through mediating variables, thus providing valuable insights into how digital literacy benefits can be achieved through education. Finally, our study extends the findings of Mehrvarz et al. (2021) and Mehrvarz et al. (2023) (Supplementary Data Sheet 1).
6 Conclusion and practical implications
This study examined the relationship between digital literacy, informal digital learning, self-efficacy, digital competence, and academic performance among Indonesian university students. The results provide strong empirical evidence that digital literacy positively affects these aspects of educational experience, both directly and indirectly, through mediating variables. In particular, enhanced digital literacy results in greater engagement in DIL, improved confidence in online learning, enhanced digital skills, and enhanced academic achievement. In addition, students who possess digital literacy skills are more capable of independently managing their learning using digital tools, acquiring the necessary abilities in digital environments, and achieving academic success. Additionally, participating in DIL assists students in developing effective study strategies and comprehension, while competence demonstrates their ability to navigate the technologies required by universities effectively. Furthermore, in terms of mediators, the findings indicated that DIL mediated the impact of digital literacy on academic performance and the impact of digital competence on academic performance. Digital competence has also been found to link digital literacy with achievement. Finally, self-efficacy was shown to act as a mediator between digital literacy and competence, as well as between digital literacy, competence, and academic performance.
These empirical results have practical implications. First, educational institutions should prioritize the development of pupils’ digital literacy skills via specific courses and training efforts (e.g., digital literacy modules, peer mentoring programs, or cross-disciplinary ICT integration), which could improve their success in online learning. Second, educational institutions should provide greater access to self-directed informal online learning opportunities. The availability of resources and platforms that allow people to actively engage in digital information literacy (DIL) has the potential to enhance overall performance. They may also incorporate educational practices to improve students’ self-efficacy in completing their online assignments. The level of confidence influences both the level of participation and competence.
There is an urgent need to broaden the scope of digital competence development to encompass not only technical skills, but also ethical, social, and other complex talents. The growth of internet capabilities has simplified the learning process. It is critical to evaluate students’ digital literacy abilities upon enrolment to establish the exact areas for targeted skill-building programs.
The fundamental goal of this project is to create a curriculum and educational activities that systematically combines the development of digital literacy, online learning habits, self-efficacy, and digital competence. Provide educators with professional development opportunities focused on improving their ability to successfully help students develop these skills and behaviors. To measure the success of programs and therapies, it is critical to track numerous indicators over time, including but not limited to participation in digital information literacy (DIL), levels of digital competence, and self-efficacy. Establish collaborative connections with businesses and community organizations to give students a great opportunity to gain hands-on experience, demonstrating practical applications of digital skills.
These findings are practical for Indonesian education leaders, as well as Southeast Asian nations’ leaders, as policy-driven references based on the Indonesian context. These findings highlight that digital literacy has concrete effects on curriculum design, teacher professional development, and resource allocation in this era of artificial intelligence. Educational technological advancement—more precisely, the advancement of AI tools such as ChatGPT— cannot be ignored, as these tools exert significant impacts on how education systems frame curricula, prepare instructors, and distribute resources.
The limitations of this study are that it must acknowledge some weaknesses in the scope of time, types of respondents, technique sampling, and model, which are considered moderating modes. This study has implications for future research on educational learning trends and policies. Therefore, the findings of this study suggest that the mediating roles of informal digital learning, self-efficacy, and students’ digital competence can significantly enhance digital literacy and academic performance.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
SZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. VN: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KA: Writing – review & editing. HK: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EM: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2025.1590274/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA SHEET 1 | Structural Model Analysis.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA SHEET 2 | Blindfolding Analysis.
References
Aabø, S. (2005). The role and value of public libraries in the age of digital technologies. J. Librariansh. Inf. Sci. 37, 205–211. doi: 10.1177/0961000605057855
Ala-Mutka, K. (2011). Mapping digital competence: Towards a conceptual understanding. Sevilla: Institute for Prospective Technological Studies, 7–60.
Alghamdi, A., Karpinski, A. C., Lepp, A., and Barkley, J. (2020). Online and face-to-face classroom multitasking and academic performance: moderated mediation with self-efficacy for self-regulated learning and gender. Comput. Hum. Behav. 102, 214–222. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2019.08.018
Amhag, L., Hellström, L., and Stigmar, M. (2019). Teacher educators’ use of digital tools and needs for digital competence in higher education. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 35, 203–220. doi: 10.1080/21532974.2019.1646169
Andreasen, J. K. (2022). Professional digital competence in initialteacher education: an examination of differences in two cohorts of pre-service teachers. Nordic J. Digital Liter. 17, 61–74. doi: 10.18261/njdl.17.1.5
Astuti, K. L., and Setiawan, A. I. (2022). Fostering teacher’ s digital competencies and innovative work behavior in facing Merdeka Belajar policy. Digital Inf. Learn. Mediator 4, 288–295. doi: 10.51601/ijersc.v4i2.619
Beldarrain, Y. (2006). Distance education trends: integrating new technologies to foster student interaction and collaboration. Distance Educ. 27, 139–153. doi: 10.1080/01587910600789498
Bolkan, S., and Goodboy, A. K. (2011). Behavioral indicators of transformational leadership in the college classroom. Q. Res. Rep. Commun. 12, 10–18. doi: 10.1080/17459435.2011.601520
Brady‐Amoon, P., and Fuertes, J. N. (2011). Self‐Efficacy, Self‐Rated abilities, adjustment, and academic performance. Journal of Counseling & Development, 89, 431–438.
Butler, J., and Kern, M. L. (2016). The PERMA-profiler: a brief multidimensional measure of flourishing. Int. J. Wellbeing 6, 1–48. doi: 10.5502/ijw.v6i3.526
Bygstad, B., Øvrelid, E., Ludvigsen, S., and Dæhlen, M. (2022). From dual digitalization to digital learning space: exploring the digital transformation of higher education. Comput. Educ. 182:104463. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104463
Calvani, A., Cartelli, A., Fini, A., and Ranieri, M. (2008). Models and instruments for assessing digital competence at school. J. E-Learn. Knowledge Soc. 4, 183–193. doi: 10.20368/1971-8829/288
Chang, C. T., Tu, C. S., and Hajiyev, J. (2019). Integrating academic type of social media activity with perceived academic performance: A role of task-related and non-task-related compulsive Internet use. Computers \u0026amp; Education, 139, 157–172.
Chang, C. S., Liu, E. Z. F., Sung, H. Y., Lin, C. H., Chen, N. S., and Cheng, S. S. (2014). Effects of online college student’s Internet self-efficacy on learning motivation and performance. Innovations in education and teaching international, 51, 366–377.
Claro, M., Preiss, D. D., San Martín, E., Jara, I., Hinostroza, J. E., Valenzuela, S., et al. (2012). Assessment of 21st century ICT skills in Chile: Test design and results from high school level students. Computers and education, 59, 1042–1053.
Czerkawski, B. C. (2016). Blending formal and informal learning networks for online. Learning 17:2344. doi: 10.19173/irrodl.v17i3.2344
Dai, W. (2023). An empirical study on English preservice teachers’ digital competence regarding ICT self-efficacy, collegial collaboration and infrastructural support. Heliyon 9:e19538. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19538
Degner, M., Moser, S., and Lewalter, D. (2022). Digital media in institutional informal learning places: a systematic literature review. Comput. Educ. Open 3:100068. doi: 10.1016/j.caeo.2021.100068
De Clercq, D., Honig, B., and Martin, B. (2013). The roles of learning orientation and passion for work in the formation of entrepreneurial intention. International small business journal, 31, 652–676.
Dron, J., and Anderson, T. (2022). “Informal learning in digital contexts” in Handbook of Open, Distance and Digital Education. eds. O. Zawacki-Richter and I. Jung (Singapore: Springer Singapore), 1–17.
Falloon, G. (2020). From digital literacy to digital competence: the teacher digital competency (TDC) framework. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 68, 2449–2472. doi: 10.1007/s11423-020-09767-4
Ferrari, A., Punie, Y., and Bre, B. N. (2013). DIGCOMP: A framework for developing and understanding digital competence in Europe. Available online: https://tinyurl.com/yc9at8t6 (Accessed on 5 October 2024).
Froehlich, L., Bick, N., Nikitin, J., and Martiny, S. E. (2023). Social identity threat is related to ethnic minority adolescents’ social approach motivation towards classmates via reduced sense of belonging. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 27, 751–776. doi: 10.1007/s11218-023-09800-3
Feldman, D. B., and Kubota, M. (2015). Hope, self-efficacy, optimism, and academic achievement: Distinguishing constructs and levels of specificity in predicting college grade-point average. Learning and Individual Differences, 37, 210–216.
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of marketing research, 18, 39–50.
Fu, S., Li, H., Liu, Y., Pirkkalainen, H., and Salo, M. (2020). Social media overload, exhaustion, and use discontinuance: examining the effects of information overload, system feature overload, and social overload. Inf. Process. Manag. 57:102307. doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102307
Gruszczynska, A., and Pountney, R. (2013). Developing the concept of digital literacy in the context of schools and teacher education. Enhancing Learn. Soc. Sci. 5, 25–36. doi: 10.11120/elss.2013.05010025
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., and Ringle, C. M. (2018). The results of PLS-SEM article information. Eur. Bus. Rev. 31, 2–24. doi: 10.1108/EBR-11-2018-0203
He, T., and Li, S. (2019). A comparative study of digital informal learning: the effects of digital competence and technology expectancy. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 50, 1744–1758. doi: 10.1111/bjet.12778
He, T., Zhu, C., and Questier, F. (2018). Predicting digital informal learning: an empirical study among Chinese university students. Asia Pac. Educ. Rev. 19, 79–90. doi: 10.1007/s12564-018-9517-x
Heijde, C. M., and Heijden, B. R. (2006). A competence-based and multidimensional operationalization and measurement of employability. Hum. Resour. Manag. 45, 449–476. doi: 10.1002/hrm.20119
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sinkovics, R. R. (2009). The use of partial least squares path modeling in international marketing. Adv. Int. Mark. 20, 277–319. doi: 10.1108/S1474-7979(2009)0000020014
Hutain, J., and Michinov, N. (2022). Improving student engagement during in-person classes by using functionalities of a digital learning environment. Comput. Educ. 183:104496. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104496
Instefjord, E. J., and Munthe, E. (2017). Educating digitally competent teachers: a study of integration of professional digital competence in teacher education. Teach. Teach. Educ. 67, 37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2017.05.016
Janssen, J., Stoyanov, S., Ferrari, A., Punie, Y., Pannekeet, K., and Sloep, P. (2013). Experts’ views on digital competence: commonalities and differences. Comput. Educ. 68, 473–481. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2013.06.008
Jeon, J., and Kim, S. (2022). Effects of digital literacy and self-efficacy on the relationship between learning attitudes and Ehealth literacy in nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ. Today 113:105378. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105378
Jin, F., Schjølberg, S., Wang, M. V., Eadie, P., Nes, R. B., Røysamb, E., et al. (2020). Predicting literacy skills at 8 years from preschool language trajectories: A population-based cohort study. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 63, 2752–2762.
Kassab, S. E., Al-Shafei, A. I., Salem, A. H., and Otoom, S. (2015). Relationships between the quality of blended learning experience, self-regulated learning, and academic achievement of medical students: a path analysis.
Katsarou, E. (2021). The effects of computer anxiety and self-efficacy on L2 learners’ self-perceived digital competence and satisfaction in higher education 2. Lit. Rev. 8, 158–172. doi: 10.20448/journal.509.2021.82.158.172
Khan, N., Sarwar, A., Chen, T. B., and Khan, S. (2022). Connecting digital literacy in higher education to the 21st century workforce. Knowledge Manage. E-Learn. 14, 46–61. doi: 10.34105/j.kmel.2022.14.004
Kim, S., and Jeon, J. (2020). Factors influencing eHealth literacy among Korean nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Nurs. Health Sci. 22, 667–674. doi: 10.1111/nhs.12711
Lee, Y. H., and Wu, J. Y. (2012). The effect of individual differences in the inner and outer states of ICT on engagement in online reading activities and PISA 2009 reading literacy: exploring the relationship between the old and new reading literacy. Learn. Individ. Differ. 22, 336–342. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2012.01.007
Limniou, M., Varga-Atkins, T., Hands, C., and Elshamaa, M. (2021). Learning, student digital capabilities and academic performance over the COVID-19 pandemic. Educ. Sci. 11:361. doi: 10.3390/educsci11070361
Liu, G., Cheng, G., Hu, J., Pan, Y., and Zhao, S. (2020). Academic self-efficacy and postgraduate procrastination: A moderated mediation model. Frontiers in psychology, 11:1752.
Lo, N. P. K. (2024). The confluence of digital literacy and eco-consciousness: harmonizing digital skills with sustainable practices in education. Platforms 2, 15–32. doi: 10.3390/platforms2010002
Lo, N., Wong, A., and Chan, S. (2025). The impact of generative AI on essay revisions and student engagement. Comput. Educ. Open 22:100249. doi: 10.1016/j.caeo.2025.100249
López-Belmonte, J., Pozo-Sánchez, S., Fuentes-Cabrera, A., and Trujillo-Torres, J. M. (2019). Analytical competences of teachers in big data in the era of digitalized learning Education Science. 9, 177.
Lordache, C., Mariën, I., and Baelden, D. (2017). Developing digital skills and competences: A quick-scan analysis of 13 digital literacy models. Italian Journal of Sociology of Education, 9, 6–30.
Martin, A., and Grudziecki, J. (2006). DigEuLit: Concepts and tools for digital literacy development. Innovation in teaching and learning in information and computer sciences, 5, 249–267.
McCleary-Jones, V. (2016). A systematic review of the literature on health literacy in nursing education. Nurse Educ. 41, 93–97. doi: 10.1097/NNE.0000000000000204
Meelissen, M. R. M., and Drent, M. (2008). Gender differences in computer attitudes: does the school matter? Comput. Hum. Behav. 24, 969–985. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2007.03.001
Mehrvarz, M., Heidari, E., Farrokhnia, M., and Noroozi, O. (2021). The mediating role of digital informal learning in the relationship between students’ digital competency and their academic performance. Comput. Educ. 167:104184. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2021.104184
Mehrvarz, M., Keshavarzi, F., Heidari, E., and McLaren, B. M. (2023). Improving computational thinking: the role of students’ networking skills and digital informal learning. Interact. Learn. Environ. 32, 6081–6095. doi: 10.1080/10494820.2023.2249049
Meyers, E. M., Erickson, I., and Small, R. V. (2013). Digital literacy and informal learning environments: an introduction. Learn. Media Technol. 38, 355–367. doi: 10.1080/17439884.2013.783597
Ng, W. (2012). Can we teach digital natives digital literacy? Comput. Educ. 59, 1065–1078. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2012.04.016
Norden, L.-A., Mannila, L., and Pears, A. (2017). Development of a self-efficacy scale for digital competences in schools. In 2017 IEEE Frontiers in education conference (FIE) IEEE.. 1–7.
Nugroho, A. (2021). EFL learners’ beliefs and practices on informal digital learning of English beyond classroom. IJEE 8, 198–212. doi: 10.15408/ijee.v8i2.19843
Prior, D. D., Mazanov, J., Meacheam, D., Heaslip, G., and Hanson, J. (2016). Attitude, digital literacy and self efficacy: flow-on effects for online learning behavior. Internet High. Educ. 29, 91–97. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2016.01.001
Sackey, D. J., Nguyen, M. T., and Grabill, J. T. (2015). Constructing learning spaces: What we can learn from studies of informal learning online. Computers and Composition, 35, 112–124.
Sakitri, G. (2020). The relationship among student stress, type a personality, and academic performance in a business school in Indonesia. J. Educ. Bus. 95, 169–179. doi: 10.1080/08832323.2019.1627994
Salendab, F. (2023). Proposed instructional scheme in new Normal education: the basis for pedagogical strategies/practices. Psychol. Educ. Multidisciplinary J. 6, 712–719.
Scholes, L., Rowe, L., Mills, K. A., Gutierrez, A., and Pink, E. (2022). Video gaming and digital competence among elementary school students students. Learn. Media Technol. 49, 200–215. doi: 10.1080/17439884.2022.2156537
Schwan, S., Dutz, S., and Dreger, F. (2018). Multimedia in the wild: Testing the validity of multimedia learning principles in an art exhibition. Learning and Instruction, 55, 148–157.
Sesmiarni, Z., Hoque, M. E., Susanto, P., Islam, M. A., and Hendrayati, H. (2024). Adoption of SPACE-learning management system in education era 4.0: an extended technology acceptance model with self-efficacy. Front. Educ. 9:1457188. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1457188
Shafiee Rad, H., Namaziandost, E., and Razmi, M. H. (2023). Integrating STAD and flipped learning in expository writing skills: impacts on students’ achievement and perceptions. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 55, 710–726. doi: 10.1080/15391523.2022.2030265
Shen, D., Cho, M. H., Tsai, C. L., and Marra, R. (2013). Unpacking online learning experiences: online learning self-efficacy and learning satisfaction. Internet High. Educ. 19, 10–17. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2013.04.001
Spante, M., Hashemi, S. S., Lundin, M., and Algers, A. (2018). Digital competence and digital literacy in higher education research: systematic review of concept use. Cogent Educ. 5, 1–21. doi: 10.1080/2331186X.2018.1519143
Song, D., and Lee, J. (2014). Has W eb 2.0 revitalized informal learning? The relationship between W eb 2.0 and informal learning. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 30, 511–533.
Terrile, V. C. (2023). Finding the answers: community college students’ non-academic information behaviors. Commun. College J. Res. Prac. 47, 165–182. doi: 10.1080/10668926.2021.1985014
Tramontano, C., Grant, C., and Clarke, C. (2021). Development and validation of the e-work self-efficacy scale to assess digital competencies in remote working. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 4:100129. doi: 10.1016/j.chbr.2021.100129
Tsai, M., and Tsai, C. (2003). Information searching strategies in web-based science learning: the role of internet self-efficacy. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 40, 43–50. doi: 10.1080/1355800032000038822
Ukwoma, S. C., Iwundu, N. E., and Ifeanyichukwu Emmanuel, I. (2010). Digital literacy skills possessed by students of UNN, implications for effective learning and performance: a study of the MTN universities connect library. Energies 6:7.
Vrana, R. (2014). Digital literacy as a prerequisite for achieving good academic performance. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 492, 160–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-14136-7_17
Wang, X., Zhang, R., Wang, Z. Y., and Li, T. (2021). How does digital competence preserve university students’ Psychological Well-Being. Front. Psychol. 12:652594. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.652594
Wu, J. H., Tennyson, R. D., and Hsia, T. L. (2010). A study of student satisfaction in a blended e-learning system environment. Comput. Educ. 55, 155–164. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2009.12.012
Yu, A. Y., Tian, S. W., Vogel, D., and Chi-Wai Kwok, R. (2010). Can learning be virtually boosted? An investigation of online social networking impacts. Comput. Educ. 55, 1494–1503. doi: 10.1016/J.COMPEDU.2010.06.015
Zhou, N., Wang, J., Liu, X., Yang, L., and Jin, X. (2023). The digital competence of Chinese higher education students and the linkage with their career adaptability. Educ. Train. 65, 939–954. doi: 10.1108/ET-08-2022-0315
Keywords: digital literacy, academic performance, digital informal learning, self-efficacy, student’s digital competence
Citation: Zakir S, Hoque ME, Susanto P, Nisaa V, Alam MK, Khatimah H and Mulyani E (2025) Digital literacy and academic performance: the mediating roles of digital informal learning, self-efficacy, and students’ digital competence. Front. Educ. 10:1590274. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1590274
Edited by:
Baojuan Ye, Jiangxi Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Cristina Mª García-Fernández, University of Cordoba, SpainNoble Lo, Lancaster University, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Zakir, Hoque, Susanto, Nisaa, Alam, Khatimah and Mulyani. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Perengki Susanto, cGVyZW5na2lAZmUudW5wLmFjLmlk
 Supratman Zakir1
Supratman Zakir1 Mohammad Enamul Hoque
Mohammad Enamul Hoque Perengki Susanto
Perengki Susanto Md. Kausar Alam
Md. Kausar Alam