- Department of Nephrology, Nanjing BenQ Medical Center, The Affiliated BenQ Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the Bridge-in, Objective, Pre-assessment, Participatory learning, Post-assessment, and Summary (BOPPPS) teaching model in improving educational outcomes within a blood purification nursing residency training program.
Background: BOPPPS model is a structured, and learner-centered instructional framework that fosters active participation and self-directed learning. Despite its growing application in general education, its utility in specialized clinical nursing education remains insufficiently studied.
Methods: A quasi-experimental design was used to facilitate sampling. A total of 118 undergraduate nursing students were included: 55 in the control group (2018–2019, traditional lecture-based teaching) and 63 in the intervention group (2020–2021, BOPPPS model). Data were collected using validated instruments, including the Academic Self-Efficacy Scale, the College Student Learning Engagement Scale, and the Learning Burnout Scale. In addition, final exam scores (scale of 0–100) and course satisfaction (17-item scale covering cognitive, skill-based, and emotional domains) were assessed. Statistical data analysis was conducted using SPSS 26.0, applying descriptive statistics, independent samples t-tests, and paired samples t-tests.
Results: Compared to the control group, students in the BOPPPS group reported significantly higher levels of academic self-efficacy and learning engagement, lower levels of learning burnout, improved examination performance, and greater course satisfaction (p < 0.05 or p < 0.01).
Conclusion: BOPPPS teaching model can significantly enhance cognitive, behavioral, and affective learning outcomes in the context of specialized clinical nursing education. This presents a promising pedagogical approach for residency training programs to optimize learner development while reduce academic burnout.
1 Introduction
In recent years, the growing burden of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) has posed a serious challenge to healthcare systems worldwide (Elder et al., 2023), especially in the domain of long-term renal replacement therapy. With the increasing prevalence of chronic kidney disease, it is estimated that the number of patients requiring maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) in China will reach 1.5 to 3 million by 2030 (Rovin et al., 2024). This rising demand calls for a well-trained nursing workforce equipped with specialized competencies in blood purification care (Gardner et al., 2007).
Blood purification nursing is a complex and rapidly evolving specialty that requires advanced clinical reasoning (Thomas-Hawkins and Flynn, 2015), technical proficiency (Bergjan and Schaepe, 2016), and critical decision-making (Lok et al., 2025). However, traditional undergraduate nursing education often struggles to keep pace with these demands (Hoekstra et al., 2021). Although clinical placements have been included in curricula, there is a persistent gap between theoretical instruction and the real-world competencies required in specialized clinical settings (Rowe et al., 2024). For many institutions, including those in Jiangsu Province, China, undergraduate nursing students typically follow a staged progression—from two years of campus-based theoretical study, to one year of hospital-based resident teaching, and finally, a year of clinical internship. Despite this structure, resident teaching often rely heavily on didactic lectures, offering limited opportunities for active learning or development of specialized practical skills.
Conventional lecture-based teaching is increasingly recognized as insufficient for cultivating clinical reasoning and long-term knowledge retention (Bergjan and Schaepe, 2016). Students frequently report low engagement, weak self-efficacy, and inadequate preparation for complex clinical tasks (Bulfone et al., 2022). These limitations point to the need for innovative and student-centered teaching models that can more effectively bridge the gap between theory and practice. BOPPPS model (Wen et al., 2023)—comprising Bridge-in, Objective, Pre-assessment, Participatory learning, Post-assessment, and Summary—offers a structured instructional framework designed to promote active participation, real-time feedback, and learner autonomy. Evidence from general medical education suggests that BOPPPS enhances student engagement, improves academic self-efficacy, and reduces learning burnout (Ma et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024b). However, its application in nursing education—particularly in specialized fields such as blood purification—remains limited and under-researched.
To address this gap, BOPPPS teaching model was adopted within a blood purification nursing residency program and its impact on multiple educational outcomes was evaluated, including academic self-efficacy, learning engagement, learning burnout, theoretical exam performance, and course satisfaction. By exploring the effectiveness of this structured, student-centered teaching strategy, this work aimed to inform the ongoing development of clinical nursing education and provide practical guidance for the optimization of residency teaching in specialized nursing domains.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design
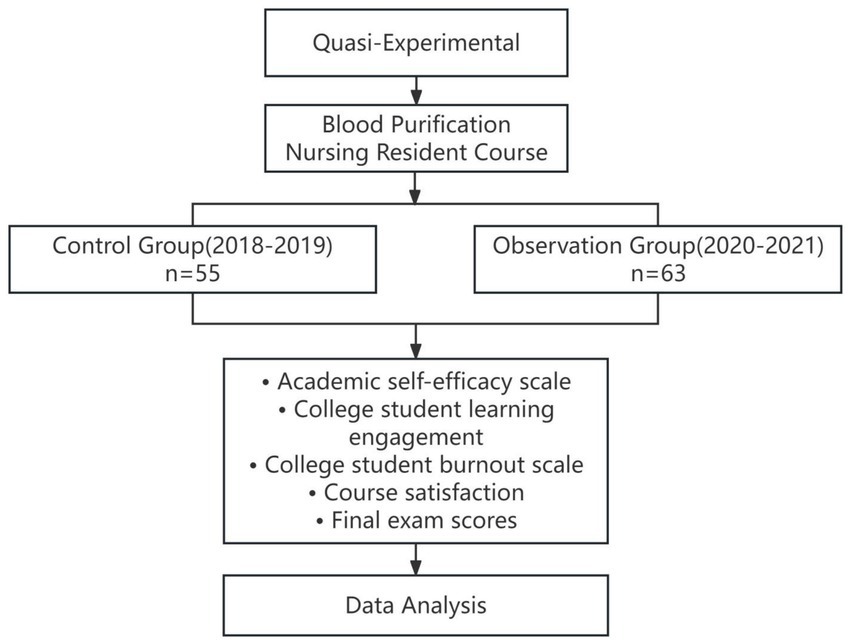
A quasi-experimental design with a non-randomized, nonequivalent control group structure used in this study. The purpose was to evaluate the effectiveness of the BOPPPS teaching model in the context of a blood purification nursing residency course. The technical roadmap of the study is presented in Figure 1, outlining the design, intervention, data collection, and analysis processes. Random assignment was not feasible due to the academic structure of the nursing program and institutional constraints. Therefore, existing class cohorts from two academic cycles were used as comparison groups. Although not fully randomized, the two groups shared the same educational context, curriculum framework, instructors, and clinical training base, which minimized variability.
2.2 Participants
A total of 118 third-year undergraduate nursing students from Kanda College of Nanjing Medical University in Jiangsu, China, were included. The control group consisted of 55 students from the 2018–2019 blood purification nursing resident cohort. The observation group consisted of 63 students from the 2020–2021 cohort.
These two specific cohorts were chosen based on the timeline of curriculum reform: the BOPPPS teaching model was introduced starting in the 2020 academic year as part of a broader instructional innovation initiative.
Sampling Technique: A convenience sampling method was used based on complete inclusion of students enrolled in the corresponding year and course. Non-random assignment is a limitation, but both groups were comparable in baseline curriculum exposure and clinical placement conditions.
2.3 The inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion Criteria: full-time undergraduate nursing students at Kanda College of Nanjing Medical University; enrolled in the third year of the residency program in “Blood Purification Nursing”; completion of both the theoretical and practical components of the program; and consent to participate in educational data collection for the purpose of the study.
Exclusion Criteria: Students who did not complete the course or withdrew mid-term; students with prior clinical work experience in blood purification before the course; and students who missed more than 20% of the course sessions.
2.4 Teaching intervention
A total of 118 third-year undergraduate nursing students from Kanda College of Nanjing Medical University participated in the “Blood Purification Nursing” course during their clinical rotation at the same affiliated teaching hospital. All students completed the course over the span of one academic year, with a total of 70 credit hours. To ensure teaching consistency, the same instructional team delivered the course for both the control and observation groups. Students were assigned to groups based on their academic cohort: the control group consisted of 55 students from the 2018–2019 academic year, and the observation group included 63 students from the 2020–2021 academic year. This grouping was determined by the timing of a university-level curriculum reform, which introduced the BOPPPS teaching model in 2020. A convenience sampling method was employed, and all eligible students were included.
2.5 Control group: traditional teaching model
The control group received instruction through a traditional teaching approach. The curriculum was divided into two semesters. In the first semester, students completed 30 credit hours of theoretical instruction and 6 credit hours of hospital-based practical training. In the second semester, they received 28 credit hours of theoretical instruction and another 6 credit hours of practical training.
Teaching methods in the control group primarily relied on PowerPoint-based lectures, instructor-led demonstrations, and group discussions. Practical training took place in the hospital’s blood purification center, where students observed clinical procedures and engaged in limited supervised practice. At the end of the practical rotation, students were required to submit a written training report summarizing their experience.
Assessment in the control group was composed of three parts: a final theoretical examination accounting for 70% of the grade, post-class assignments accounting for 20%, and classroom participation accounting for the remaining 10%.
2.6 Observation group: BOPPPS-based teaching model
In contrast, the observation group received instruction based on the BOPPPS model, which includes six stages: Bridge-in, Objective, Pre-assessment, Participatory Learning, Post-assessment, and Summary. Although the total credit hours remained the same (70), the internal structure of the course was reformed to align with student-centered pedagogical principles.
Specifically, the observation group completed 54 credit hours of theoretical instruction, 12 credit hours of practical training, and an additional 4 credit hours of extended learning modules—2 in each semester. These extended modules were designed to deepen clinical understanding and foster research awareness.
The curriculum reform process was led by a multidisciplinary team comprising academic administrators, clinical instructors, and department leaders. Prior to implementation, student needs were assessed using validated instruments measuring academic self-efficacy, learning engagement, and satisfaction. Based on these findings and expert consensus, a structured BOPPPS teaching plan was developed and piloted.
In terms of instructional process, students in the observation group were first provided with pre-class learning materials and guided learning objectives. They completed online pre-tests and engaged in discussion forums, which helped identify knowledge gaps and contributed to formative assessment.
During in-class sessions, instructors tailored teaching activities based on the diagnostic results of the pre-assessments. Teaching strategies included interactive case discussions, student-led presentations, group projects, and real-time Q&A, all designed to enhance critical thinking, clinical decision-making, and communication skills.
After class, students participated in extended learning modules focusing on symptom management and nursing techniques in various dialysis scenarios. These modules, co-developed with nephrology experts, incorporated role-playing, expert interviews, literature reviews, and patient-centered qualitative inquiries. The goal was to cultivate a deeper understanding of symptom heterogeneity, improve clinical empathy, and develop students’ reflective and research skills.
The assessment system for the observation group was adjusted accordingly: the final theoretical examination accounted for 60% of the total grade, extended module performance contributed 20%, practical training contributed 10%, and routine performance—including online learning and class participation—accounted for the remaining 10%.
2.7 Quality control and implementation oversight
To ensure the fidelity and quality of the instructional intervention, the curriculum leader was responsible for overseeing all stages of the teaching reform, including instructor training, monitoring classroom delivery, and co-teaching selected modules. The teaching team strictly adhered to the BOPPPS framework. Feedback was collected continuously from students and instructors to support iterative improvements in the curriculum.
2.8 Evaluation procedure
Upon course completion, all students were invited to complete a standardized post-course questionnaire administered by trained investigators. The survey was conducted on-site under supervised conditions, and all responses were immediately checked for completeness and accuracy.
2.9 Measurement tools
The academic self-efficacy scale (Tating et al., 2023) consisted of two dimensions, study behavior self-efficacy and study ability self-efficacy, including 22 items. Each item was scored 1–5 points, and higher score indicates higher academic self-efficacy (Hjeltnes et al., 2015). The scale showed a high reliability with an overall internal consistency coefficient of 0.88.
The college student learning engagement scale was developed by Schaufeli and Bakker (2023), including 17 items across three dimensions of motive, vigor, and absorption, with each scoring 1–7 points. The scale showed good stability and internal consistency, with Cronbach’s α coefficients of 0.857, 0.826, and 0.815 for motive, vigor, and absorption, respectively, and a total Cronbach’s α coefficient of 0.919.
The college student learning burnout scale (Tang et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2022), including three dimensions of low spirits, low sense of achievement, and improper conduct, with a total score of 100 points. The higher the score is, the more severe the learning burnout will be.
Final theoretical exam scores. After a theoretical course, an exam paper was formulated according to the teaching syllabus, and a theoretical assessment was conducted in a unified closed-book format, with a maximum score of 100 points.
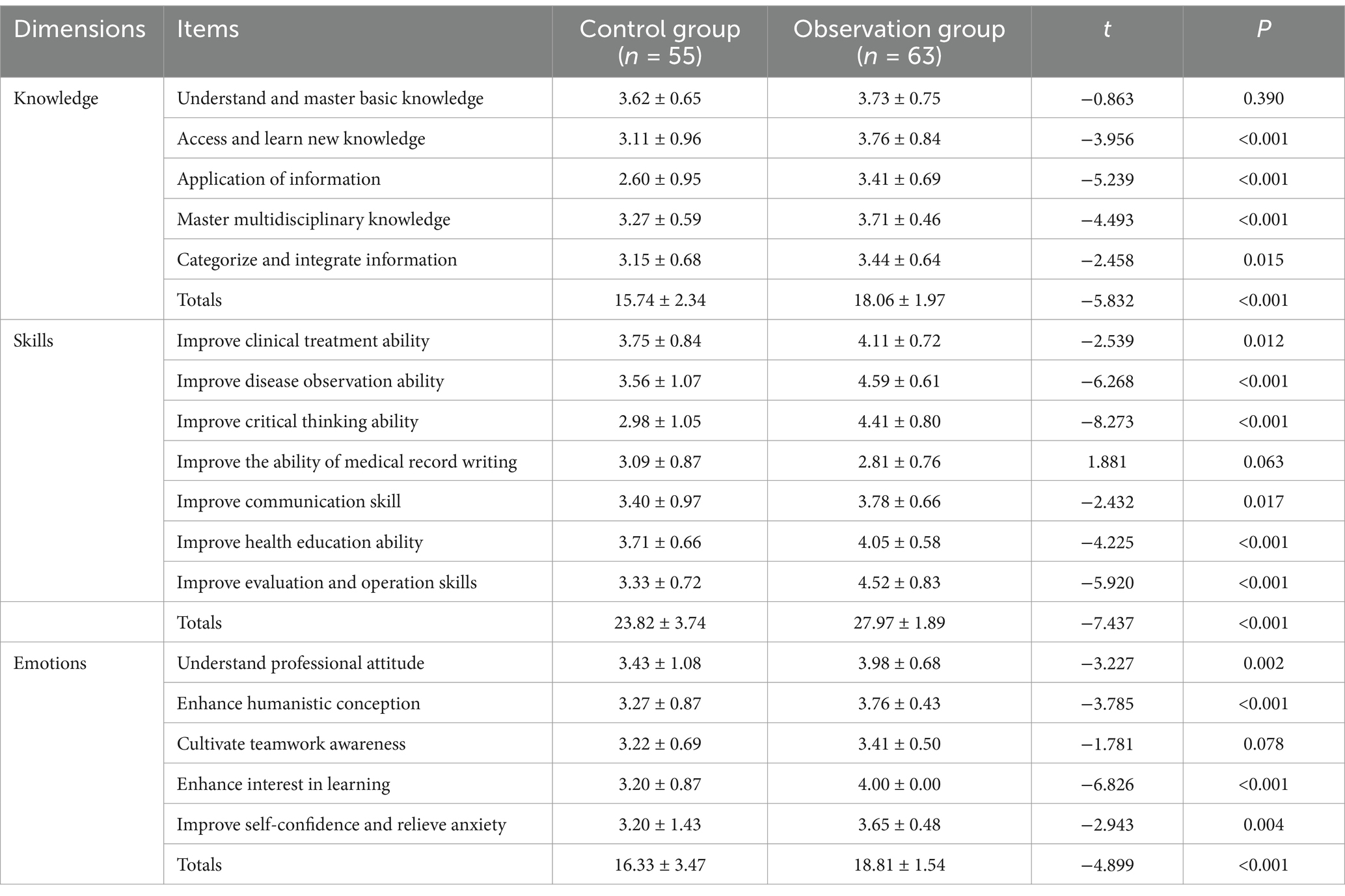
Course satisfaction (Xu et al., 2023) at the end of the course, a satisfaction scale was used for survey, covering three dimensions of knowledge, skills, and emotions, with a total of 17 items and the Cronbach’s α coefficient of 0.841. Each item was scored 1–5 points from “completely inconsistent” to “completely consistent.”
2.10 Data analysis
SPSS 26.0 was adopted for statistical analysis. Quantitative data following a normal distribution was expressed as mean ± standard deviation (x̅ ± s). T-test was used for component comparison. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
A total of 118 third-year undergraduate nursing students participated in the study, with 55 students in the control group and 63 in the observation group. Baseline characteristics, including age and cumulative GPA, showed no significant differences between the two groups (p > 0.05). This suggests the comparability in terms of academic foundation and demographic composition.
3.1 Academic self-efficacy
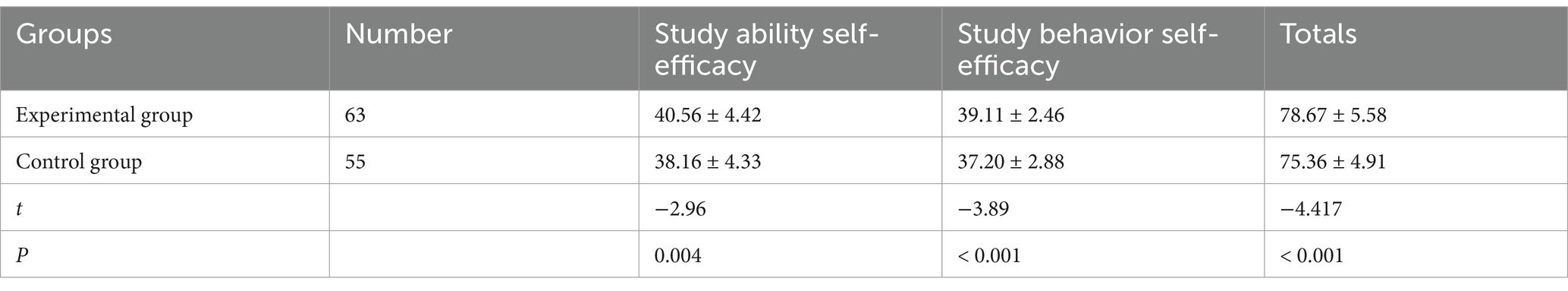
As shown in Table 1, students in the observation group reported significantly higher scores in both dimensions of academic self-efficacy: study ability self-efficacy and study behavior self-efficacy, compared to the control group (p < 0.01). Therefore, the BOPPPS-based instructional approach was more effective in enhancing students’ confidence in their academic capabilities.
3.2 Learning engagement
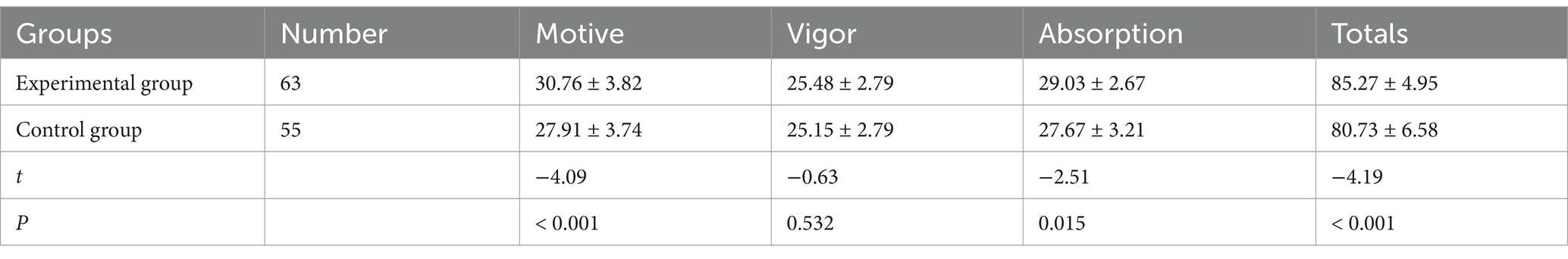
Differences in learning engagement were also significant between the two groups. According to Table 2, the observation group demonstrated higher levels of learning motivation and learning absorption, with statistical significance (p < 0.01). These findings indicate that the BOPPPS model fostered more active and sustained engagement in the learning process.
3.3 Learning burnout
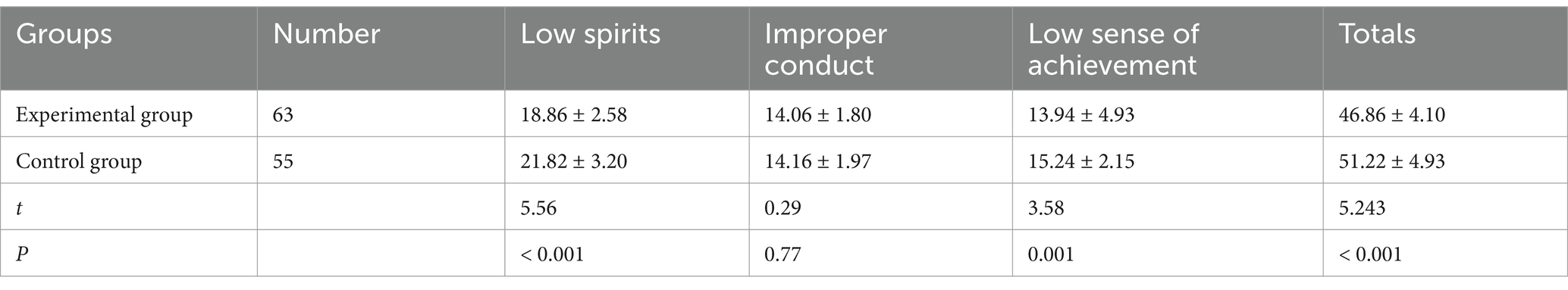
As indicated in Table 3, the observation group showed significantly lower scores in key dimensions of learning burnout, including low spirits and reduced sense of achievement (p < 0.01). The reformed teaching model contributed to a more positive academic experience and helped mitigate emotional exhaustion.
3.4 Theoretical performance
Final examination scores further reflected the effectiveness of the intervention. The observation group achieved a significantly higher mean score (79.83 ± 5.18) compared to the control group (75.16 ± 5.06), with the difference reaching statistical significance (t = −4.933, p < 0.001), indicating improved theoretical mastery.
3.5 Course satisfaction
As presented in Table 4, students in the observation group reported significantly higher satisfaction levels across all measured domains: knowledge acquisition, skills development, and emotional experience (p < 0.01). This demonstrates that students perceived the BOPPPS model to be more effective and engaging than traditional instruction.
Overall, these results support the effectiveness of the BOPPPS teaching model in improving academic outcomes, and motivational and emotional dimensions of learning within specialized nursing education.
4 Discussion
The scores for academic self-efficacy, learning behavior self-efficacy, and learning ability self-efficacy were significantly higher in the experimental group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). This suggests that the implementation of the BOPPPS-based teaching reform in the Blood Purification Nursing course under the resident teaching framework has a positive effect on enhancing students’ self-efficacy. These results are consistent with the findings of Li et al. (2023), who also reported improvements in students’ perceived academic control under structured, student-centered teaching models. By clarifying learning objectives and integrating guiding questions into instruction, the revised curriculum promotes self-directed learning and active exploration. Furthermore, the incorporation of diversified assessment strategies helps address individual learning needs and fosters autonomy and confidence in learning (Li et al., 2024a).
Importantly, the traditional teacher-centered approach was transformed into an inquiry-based learning model that emphasized student initiative and active participation. Students in the experimental group achieved significantly higher scores on the final theoretical examination and outperformed their peers in each dimension of the learning engagement scale (p < 0.05), aligning with the results reported by Hu et al. (2022). The curriculum reform expanded teaching content and integrated real clinical cases, enabling students to gain a more comprehensive understanding of hemodialysis patients’ needs. This in turn sparked their intrinsic interest in learning and shifted their motivation from task completion to professional value pursuit. This transformation fosters deeper engagement in knowledge acquisition and supports the transition from passive learning to active inquiry.
Additionally, the experimental group demonstrated significantly lower scores in the “low spirit” subdimension and total score of the learning burnout scale (p < 0.05), indicating that the reformed curriculum effectively mitigated student burnout. Unlike traditional didactic methods that emphasize rote memorization and passive reception of information (Chen et al., 2022), the BOPPPS model incorporates active learning elements, contextualized teaching, and emotional engagement. These strategies enhance the perceived value and relevance of knowledge (Gong et al., 2023), thereby improving student motivation and reducing psychological fatigue. Diversified learning approaches and flexible formats also contributed to this effect (Yu et al., 2023).
Moreover, the experimental group reported significantly higher scores in the “sense of achievement” subdimension. This can be attributed to students’ active involvement in the clinical case discussions, symptom recognition, and development of personalized care plans for patients undergoing blood purification. Their ability to translate theoretical knowledge into practice, which was acknowledged by both patients and healthcare teams, reinforced their self-identity and professional identity, ultimately contributing to an enhanced sense of achievement.
Finally, student satisfaction with the course was markedly higher in the experimental group across cognitive, skills-based, and affective dimensions. Specifically, participants reported improved abilities in information integration, clinical observation, critical thinking, communication, health education, and professional attitude. They also demonstrated heightened interest, self-confidence, and emotional resilience. These outcomes further validate the necessity and effectiveness of teaching reform in the Blood Purification Nursing curriculum.
5 Conclusion
Implementing the BOPPPS teaching model within a resident teaching framework for the Blood Purification Nursing curriculum significantly enhances nursing students’ academic self-efficacy, engagement, theoretical performance, and course satisfaction, while alleviating learning burnout. The structured, student-centered approach of BOPPPS facilitates more interactive and reflective learning, aligning effectively with the clinical training needs in the hospital setting. Given the promising outcomes, this approach presents a feasible pathway for educational innovation in nursing education. However, considering the limited sample size and single-institution scope, further research is warranted before widespread application.
6 Implications
The findings carry several important implications for nursing education practice and curriculum development:
Pedagogical Innovation: BOPPPS model serves as an effective pedagogical framework that fosters active learning, timely feedback, and learner autonomy. It can be integrated into clinical teaching settings to enhance both knowledge acquisition and practical readiness.
Curricular Reform: Nursing educators and program designers can utilize the BOPPPS model to promote outcome-based education, in line with national policies advocating for the integration of education and clinical training.
Professional Development: This model supports the development of critical soft skills such as self-efficacy and resilience, which are essential for professional identity formation and lifelong learning in nursing practice.
7 Limitations
This study has several limitations that must be considered when interpreting the results.
One notable limitation of this study is the non-simultaneous implementation of the control and experimental groups. The control group comprised students from the 2018–2019 blood purification nursing cohort, whereas the experimental group included students from the 2020–2021 cohort. This design was determined by the timeline of the curriculum reform at Nanjing Medical University, during which the BOPPPS teaching model was formally introduced in 2020 as part of a broader teaching innovation initiative. Therefore, it was not feasible to conduct both groups concurrently.
While baseline clinical placement conditions and curriculum content were largely comparable across the two cohorts, the time difference may have introduced uncontrolled confounding variables, such as variations in instructional staff, student characteristics, or institutional policies. Additionally, the use of a convenience sampling method without random assignment limits the ability to fully control for these factors. This may affect the internal validity of the findings. Future studies should aim to use parallel-group, randomized controlled designs to more rigorously assess the effectiveness of instructional models like BOPPPS.
Single-Institution Sample: Data were collected from one institution in Jiangsu, China, reducing the generalizability of findings to other regions or nursing programs.
8 Future directions
Building on the current findings, several avenues for future research are recommended:
Mixed-Methods Research: Combining quantitative analysis with qualitative data (e.g., focus groups, reflective journals) could offer deeper insights into learner experiences and perceived value.
Curricular Expansion: Exploring the adaptation of BOPPPS in other nursing specialties such as critical care, community health, or pediatric nursing may further validate its broader applicability.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
NNX: Project administration, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Validation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Software, Visualization. JL: Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Supervision, Software, Methodology, Resources, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Investigation, Visualization. HYW: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Scientific Research Projects: The “SPRING School-Hospital Integration 2.0” Talent Cultivation Project of School of Nursing, Nanjing Medical University and was supported by Teaching Reform Project of Nanjing Medical University (2023ZC050).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bergjan, M., and Schaepe, C. (2016). Educational strategies and challenges in peritoneal dialysis: a qualitative study of renal nurses' experiences. J. Clin. Nurs. 25, 1729–1739. doi: 10.1111/jocn.13191
Bulfone, G., Iovino, P., Mazzotta, R., Sebastian, M., Macale, L., Sili, A., et al. (2022). Self-efficacy, burnout and academic success in nursing students: a counterfactual mediation analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 78, 3217–3224. doi: 10.1111/jan.15231
Chen, L., Tang, X. J., Chen, X. K., Ke, N., and Liu, Q. (2022). Effect of the BOPPPS model combined with case-based learning versus lecture-based learning on ophthalmology education for five-year paediatric undergraduates in Southwest China. BMC Med. Educ. 22:437. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03514-4
Elder, M., Moonen, A., Crowther, S., Aleksova, J., Center, J., and Elder, G. J. (2023). Chronic kidney disease-related sarcopenia as a prognostic indicator in elderly haemodialysis patients. BMC Nephrol. 24:138. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03175-5
Gardner, J. K., Thomas-Hawkins, C., Fogg, L., and Latham, C. E. (2007). The relationships between nurses' perceptions of the hemodialysis unit work environment and nurse turnover, patient satisfaction, and hospitalizations. Nephrol. Nurs. J. 34, 271–281. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530320025008
Gong, Z., Wang, H., Zhong, M., and Shao, Y. (2023). College students' learning stress, psychological resilience and learning burnout: status quo and coping strategies. BMC Psychiatry 23:389. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-04783-z
Hjeltnes, A., Binder, P. E., Moltu, C., and Dundas, I. (2015). Facing the fear of failure: an explorative qualitative study of client experiences in a mindfulness-based stress reduction program for university students with academic evaluation anxiety. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well-being 10:27990. doi: 10.3402/qhw.v10.27990
Hoekstra, B., Amiri, F., van Beenen, S., Winkels, B., van Leeuwen, M., Hesseling, L., et al. (2021). Training and education, what has changed this last decade? J. Ren. Care 47, 250–254. doi: 10.1111/jorc.12376
Hu, K., Ma, R. J., Ma, C., Zheng, Q. K., and Sun, Z. G. (2022). Comparison of the BOPPPS model and traditional instructional approaches in thoracic surgery education. BMC Med. Educ. 22:447. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03526-0
Li, Z., Cai, X., Zhou, K., Qin, J., Zhang, J., Yang, Q., et al. (2023). Effects of BOPPPS combined with TBL in surgical nursing for nursing undergraduates: a mixed-method study. BMC Nurs. 22:133. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01281-1
Li, Y., Li, X., Liu, Y., and Li, Y. (2024b). Application effect of BOPPPS teaching model on fundamentals of nursing education: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 11:1319711. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1319711
Li, S., Wei, W., Li, X., Ma, L., Li, Q., Sun, X., et al. (2024a). Impacts of blended learning with BOPPPS model on Chinese medical undergraduate students: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of 44 studies. BMC Med. Educ. 24:914. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05917-x
Lok, C. E., Yuo, T., and Lee, T. (2025). Hemodialysis vascular access: core curriculum 2025. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 85, 236–252. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2024.05.021
Ma, X., Zeng, D., Wang, J., Xu, K., and Li, L. (2022). Effectiveness of bridge-in, objective, pre-assessment, participatory learning, post-assessment, and summary teaching strategy in Chinese medical education: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 9:975229. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.975229
Rovin, B. H., Ayoub, I. M., Chan, T. M., Liu, Z. H., Mejía-Vilet, J. M., Balk, E. M., et al. (2024). Executive summary of the KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the Management of Lupus Nephritis. Kidney Int. 105, 31–34. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.09.001
Rowe, D. G., Dalton, J. C., Ladowski, J. M., Soto, A. L., Rhodin, K. E., Migaly, J., et al. (2024). Prior teaching experience and barriers to effective resident teaching: a cross-sectional study. J. Surg. Res. 301, 371–377. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2024.06.008
Schaufeli, W. B., and Bakker, A. B. (2023). Utrecht work engagement scale: Preliminary manual. Utrecht: Occupational Health Psychology Unit, Utrecht University.
Tang, L., Zhang, F., Yin, R., and Fan, Z. (2021). Effect of interventions on learning burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 12:645662. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.645662
Tating, D., Tamayo, R. L. J., Melendres, J. C. N., Chin, I. K., Gilo, E. L. C., and Nassereddine, G. (2023). Effectiveness of interventions for academic burnout among nursing students: a systematic review. Worldviews Evid.-Based Nurs. 20, 153–161. doi: 10.1111/wvn.12628
Thomas-Hawkins, C., and Flynn, L. (2015). Patient Safety Culture and Nurse-Reported Adverse Events in Outpatient Hemodialysis Units[J]. Res. Theory Nurs. Pract. 29, 53–65. doi: 10.1891/1541-6577.29.1.53
Wen, H., Xu, W., Chen, F., Jiang, X., Zhang, R., Zeng, J., et al. (2023). Application of the BOPPPS-CBL model in electrocardiogram teaching for nursing students: a randomized comparison. BMC Med. Educ. 23:987. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04983-x
Xu, Z., Che, X., Yang, X., and Wang, X. (2023). Application of the hybrid BOPPPS teaching model in clinical internships in gynecology. BMC Med Educ. 23:465. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04455-2
Yu, S., Li, W., Yu, H., Ju, X., and Ling, C. (2023). The relationship between learning burnout, professional commitment, and psychological capital in undergraduate clinical medical students. Medicine 102:e35207. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000035207
Keywords: BOPPPS teaching model, blood purification nursing, resident teaching, nursing education, academic self-efficacy, learning burnout
Citation: Xia N, Liu J and Wang H (2025) Effectiveness of a BOPPPS teaching in blood purification nursing within the context of resident teaching. Front. Educ. 10:1609959. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1609959
Edited by:
Scott Schaffer, Western University, CanadaReviewed by:
John Mark R. Asio, Gordon College, PhilippinesYanquan Liu, Guangdong Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Xia, Liu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ningning Xia, NzgxOTAxODA5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Jing Liu, bGl1amluZzY2MzgyQDEyNi5jb20=
 Ningning Xia
Ningning Xia Jing Liu*
Jing Liu*