- 1School of Foreign Languages, Yibin University, Yibin, China
- 2School of Foreign Languages, Hunan University of Technology and Business, Changsha, China
In China, the conventional structure of classrooms frequently demotivates students’ vocabulary learning. To solve the dilemma, blended learning provides a more motivated, learner-centered, and engaged classroom. Taking the Community of Inquiry (CoI) framework and Self-Determination Theory (SDT) as the theoretical basis, this study examines the structural relationships between the three dimensions of CoI—Teaching Presence, Social Presence, and Cognitive Presence—and four types of Vocabulary Learning Motivation (VLM): Intrinsic Motivation, Identified Regulation, Introjected Regulation, and External Regulation among Chinese university students. A quantitative survey method was applied, and 12 hypotheses were tested with a sample of 400 undergraduates who have participated in a blended English course at a public university in Changsha, China. Utilizing Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) technique, results showed notable positive predictive effects of the three dimensions of CoI on the four aspects of VLM. Exceptionally, Teaching Presence did not predict significantly with Identified and Introjected Regulation. These findings highlight the potential of CoI-based blended learning to improve vocabulary acquisition by promoting diverse motivating factors. Consequently, this study enhances the theoretical application of the CoI and SDT in the EFL context. It also provides practical implications for improving blended learning environments to enhance student motivation and achievement in vocabulary learning.
Introduction
The importance of having a strong vocabulary is widely recognized as a fundamental and crucial aspect of learning English as a Foreign Language (EFL), since it forms the basis for all other language abilities (Ritonga et al., 2022). Studies have shown that motivation has a significant part in the process of acquiring EFL vocabulary (Li J. et al., 2022; Okkan and Aydın, 2020; Tanaka, 2017). Regrettably, within the Chinese educational system, vocabulary development is impeded by time constraints and restricted exposure in traditional classroom settings, resulting in heightened demotivation among EFL students; hence, there is a requirement to explore new approaches that can complement traditional classroom teaching and rekindle students’ motivation to acquire vocabulary (Zhang and Zhang, 2022).
Blended learning, a teaching approach that integrates the benefits of traditional classroom instruction and internet resources, has been shown to create a more motivated, learner-centered, and engaged classroom environment in recent decades (Chen, 2022). Globally, the COVID-19 epidemic has drastically changed how education is delivered, hastening the shift to blended learning paradigms (Lo and Wong, 2023). This strategy enhances the dynamism of educational experiences, including in the context of learning EFL vocabulary (Harrell and Wendt, 2019). The Community of Inquiry (CoI) framework, rooted in the “collaborative constructivist” approach to education, has become a significant model for designing and facilitating blended learning (Martin et al., 2022). The statement emphasizes the importance of participating in group activities that promote student collaboration and the use of critical thinking abilities to create knowledge (Akyol and Garrison, 2008). The emergence of meaningful learning experiences is generally attributed to the interaction of three key factors: Teaching Presence, Social Presence, and Cognitive Presence (Harrell and Wendt, 2019).
Over time, many scholars have undertaken surveys and empirical studies to comprehend the significance of the CoI framework in relation to motivation in blended and online EFL settings. Nevertheless, the majority of these studies have predominantly focused on analyzing the relationship between CoI framework and general learning motivation (Zhang, 2020; Zuo et al., 2022). In addition, research in academic motivation rarely touches the realm of vocabulary learning (Susanto et al., 2022). The current body of research indicates that the perception of the CoI learning experience and motivation are two closely interconnected notions in online and blended learning settings. Under this premise, this study aims to examine how the three components of the CoI framework (Teaching Presence, Social Presence, and Cognitive Presence) affect students’ Vocabulary Learning Motivation (VLM) (Intrinsic Motivation, Identified Regulation, Introjected Regulation, and External Regulation) in a blended learning environment within the Chinese EFL context.
Literature review
Community of Inquiry
The CoI framework has become prominent among the several frameworks used in blended learning (Yu and Li, 2022). Proposed by Garrison et al. (2000), this approach has been widely acknowledged for its significant capacity to facilitate advanced and profound learning by integrating teaching, social, and cognitive presences. Teaching Presence comprises three elements: instructional design and organization, facilitating discourse, and direct instruction (Akyol and Garrison, 2008). It is deemed as the most important construct influencing online learning contexts, indicating students’ perceptions of teaching behaviors and performances in online or blended pedagogical approaches (Garrison et al., 2010). Social Presence is also comprised of three elements: affectiveness, open communication, and group cohesion (Shea et al., 2014). It denotes online social activities such as emotional expression among peers, interactions and discussions, and group rapport as first-order constructs (Nasir and Ngah, 2022). Cognitive Presence refers to the extent to which students engage in reflective thinking and discussion to generate knowledge (Shea et al., 2014). It consists of four distinct stages: triggering event, exploration, integration, and solution (Garrison and Arbaugh, 2007). According to Hu et al. (2016), students who have stronger cognitive capacities can improve their own motivation to learn, as well as develop advanced skills like metacognition, critical thinking, and creativity.
Three presences of CoI framework and motivation
Teaching presence and motivation
Research has identified a noteworthy association between Teaching Presence and motivation (Cole et al., 2017; Suharno et al., 2023). This was achieved through instructors employing well-organized lesson structures, offering prompt feedback, and consistently displaying enthusiasm. In addition to pedagogical knowledge, effective teaching presence in blended learning environments necessitates sufficient institutional support for professional development and digital tools (Lo and Wong, 2023). Instructors who carefully design their courses, strive to create interactive sessions, and employ captivating teaching techniques can effectively maintain students’ motivation over the duration of the course (Martin et al., 2022; Adam et al., 2023). For example, Chan et al. (2024) found that AI-generated feedback using large language models significantly improved university students’ English writing proficiency, engagement, and motivation.
Social presence and motivation
Multiple research have discovered a substantial correlation between Social Presence and motivation (Weaver and Albion, 2005; Yilmaz et al., 2013; Zuo et al., 2022; Ebadi and Amini, 2024). Engaging social interactions and a sense of connectedness are crucial factors in motivating individuals in online and blended learning environments (García-Carrión et al., 2020). The presence of a robust community and the capacity to actively interact with fellow students can amplify both the self-determination and the innate drive of students. Students with strong motivation actively participate in group discussions and collaborative activities and boost their active engagement, idea sharing, and contributions to group unity (Smith et al., 2020).
Cognitive presence and motivation
A significant relationship was observed between students’ Cognitive Presence and motivation by a number of studies (Husni et al., 2022; Li J. et al., 2022; Chi, 2023). Motivation, whether it originates internally or externally, is vital in shaping students’ cognitive processes; hence, it improves their ability to learn and comprehend knowledge (Tokan and Imakulata, 2019). When students are motivated, they frequently demonstrate improved Cognitive Presence by persisting in difficult activities, employing critical thinking abilities, and actively engaging with course material. Engaging in critical thinking, reflection, and knowledge application enables students to recognize the worth and appeal of the learning tasks.
Self-determination theory
Self-determination theory (SDT) is a well-established framework for comprehending human motivation (Deci and Ryan, 2000). The primary objective is to assess the degree to which an individual’s motivation is driven by their own volition. It categorizes motivation into three main types: Intrinsic Motivation, extrinsic motivation, and amotivation (Deci and Ryan, 2000). Intrinsic Motivation is the internal drive to engage in a particular behavior due to the enjoyment it brings. Extrinsic motivation is the state of being motivated by external factors. Amotivation is defined as a deficiency in motivation. In addition, extrinsic motivation refers to doing something because it leads to a separable outcome and it can be divided into four subcategories: external regulation, integrated regulation, introjected regulation and identified regulation (Ryan and Deci, 2020). As per prior research, it is advisable to exclude the amotivation section since it may compromise the psychometric qualities due to the presence of negatively interpreted items (Kim et al., 2002). Howard et al. (2017) excluded integrated regulation from the analysis due to its overly high inter-factor correlations and overlapping confidence intervals with identified regulation and intrinsic motivation. Consequently, this study only involves intrinsic motivation, identified, introjected, and external regulation—all of which have been widely used in EFL research (Noels et al., 2000).
SDT offers a comprehensive framework for comprehending motivation in EFL learning (Karimi and Fallah, 2021) and EFL vocabulary acquisition (Deci and Ryan, 2000). Students who have Intrinsic Motivation are more inclined to actively participate in vocabulary activities, take responsibility for their learning tasks, and demonstrate better recall of the learned material (Chen and Jang, 2010). When they have a strong sense of Identified Regulation, they are more motivated to engage in vocabulary learning because they perceive it as crucial for achieving their life objectives (Tanaka, 2017). While not as effective as Intrinsic Motivation or Identified Regulation, Introjected Regulation can nonetheless motivate EFL students to practice vocabulary due to internal demands (Zhou, 2016). The issue is the preservation of one’s sense of value, which involves taking steps to prevent receiving negative assessments from their peers (Tanaka, 2017). However, depending exclusively on Introjected Regulation may result in emotional exhaustion and less enduring learning results (Assor et al., 2002). Thus, students are driven to learn English vocabulary in order to obtain course credits, achieve excellent grades, or attain high marks on assessments (Tanaka, 2017).
Factors affecting students’ vocabulary learning motivation
Vocabulary learning motivation is defined as “the driving force” of vocabulary learning (Dornyei and Ryan, 2015, p. 72), which directly impacts learning outcomes (Zhang et al., 2016). To enhance students’ vocabulary learning motivation, one of the main factors is listed as the function of the instructor (Fontecha and Gallego, 2012). Students’ motivated conduct is closely correlated with teachers’ motivational strategies (Papi and Abdollahzadeh, 2012). Additionally, collaborative efforts driven by the motivation generated by social contacts in order to collaborate and share goals in order to accomplish the mutually significant vocabulary objective are also crucial (Ritonga et al., 2022). Furthermore, recalling and retaining vocabulary is a cognitive process that is greatly influenced by the motivational conditions surrounding the initial encoding and subsequent processing of unfamiliar words through task performance. These conditions include motivation and cognitive style (Ajideh et al., 2013).
Method
Research design, model and hypotheses
This quantitative study presents a model that demonstrates the predictable connections between the three dimensions of the CoI framework (Teaching Presence, Social Presence, Cognitive Presence) and students’ VLM (Intrinsic Motivation, Identified Regulation, Introjected Regulation, External Regulation) in a blended learning environment (see Figure 1).
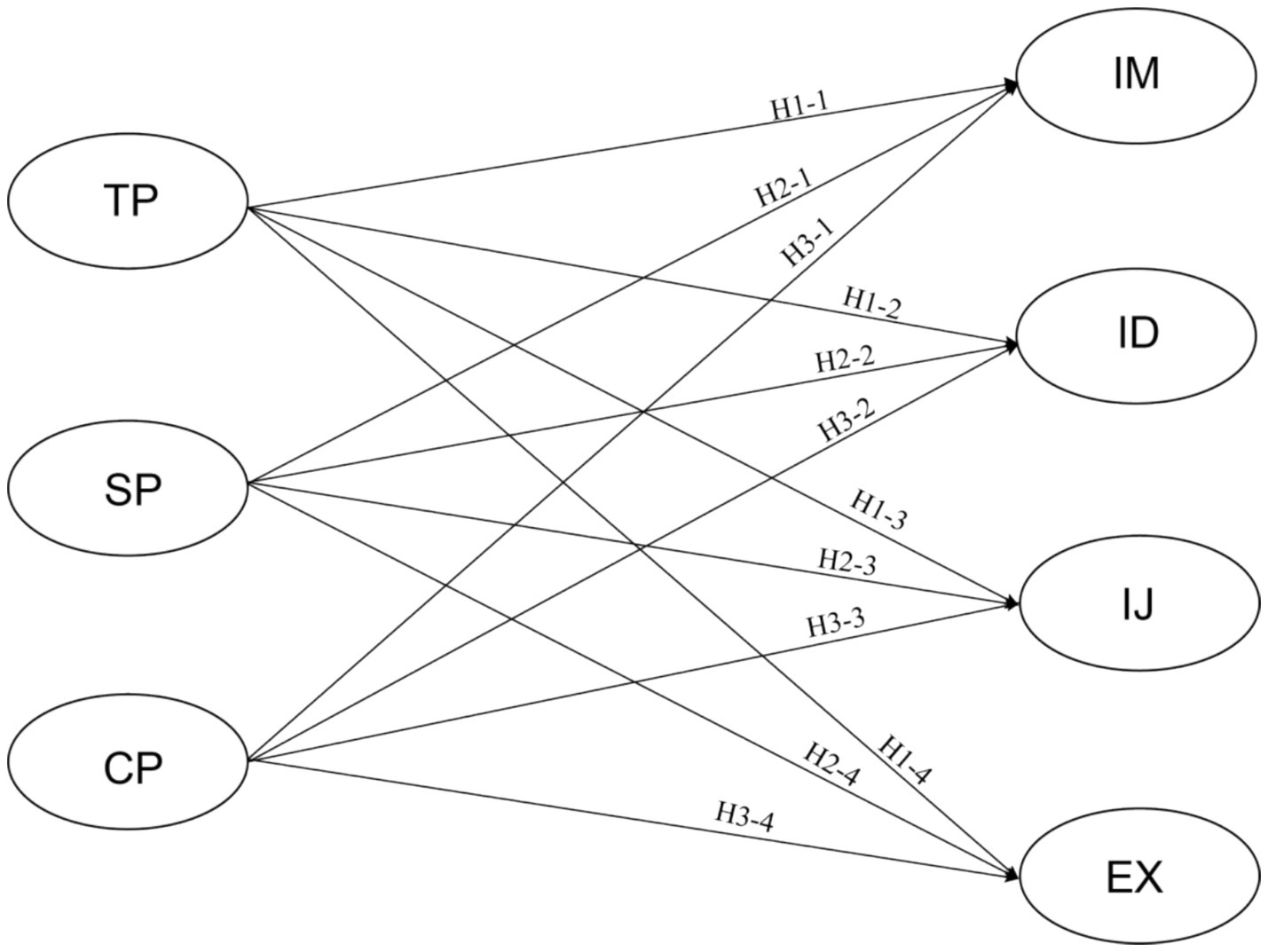
Figure 1. Constructing model of CoI framework predicting VLM. TP, Teaching Presence; SP, Social Presence; CP, Cognitive Presence; IM, Intrinsic Motivation; ID, Identified Regulation; IJ, Introjected Regulation; EX, External Regulation.
The hypotheses of the current study are as follows:
H1-1: Teaching Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Intrinsic Motivation.
H1-2: Teaching Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Identified Regulation.
H1-3: Teaching Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Introjected Regulation.
H1-4: Teaching Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary External Regulation.
H2-1: Social Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Intrinsic Motivation.
H2-2: Social Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Identified Regulation.
H2-3: Social Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Introjected Regulation.
H2-4: Social Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary External Regulation.
H3-1: Cognitive Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Intrinsic Motivation.
H3-2: Cognitive Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Identified Regulation.
H3-3: Cognitive Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary Introjected Regulation.
H3-4: Cognitive Presence has a positive effect on students’ Vocabulary External Regulation.
Data collection and participants
The participants for the current study were selected from a public university located in Changsha, China. Using a purposive sampling method, a total of 400 voluntary undergraduate students were involved. Referring to the objective of this study, the sample students were those who have experienced blended English courses for at least one semester. Data was collected through a survey conducted by Questionnaire Star, a renowned Chinese survey tool, during the end of the second semester of the academic year 2023–2024. Before initiating the study, participants were obligated to complete a consent form for ethical purposes. Out of the 400 participants examined, there were 221 male students and 179 female students with ages ranging from 18 to 22.
Instruments
The instruments utilized in this investigation consist of VLM and CoI scales. The VLM scale consists of two sections. The first section was to gather demographic data from the participants, including their gender, grade level, and age. The second part was on the VLM inquiries. This scale was adapted from Li G. et al. (2022), who validated it in the context of a Chinese high school. A total of 19 items (item 7 was excluded) and four dimensions was determined (Intrinsic Motivation, 5 items; Identified Regulation, 4 items; Introjected Regulation, 5 items; and External Regulation, 5 items) after being validated by experts. Additionally, to align with the CoI scale, this scale was adapted and modified from a 6-point Likert scale to a 5-point one. The CoI survey instrument was adapted from Zhang (2020) who had validated it in Chinese blended learning environment. It has 34 items initially; following expert validation, a total of 20 questions (item 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 10, 13, 14, 19, 21, 23, 27, 29, 32 were excluded) for the three dimensions were adapted. Specifically, there were 6 items for Teaching Presence, 6 items for Social Presence, and 8 items for Cognitive Presence.
The participants were required to answer all questions in both scales using a five-point Likert-type scale ranging from “strongly agree” (five points) to “strongly disagree” (one point). The items in the two scales were translated into Chinese using a forward-backward translation method (Brislin, 1986). This involved having an English teacher translate the items into Chinese, and then having another English teacher translate the Chinese version back into English. The inconsistencies were resolved through discussion and modification of wordings. The Chinese translations were confirmed to be accurate based on the high level of resemblance between the two versions. Furthermore, the content validity of the two scales was established by soliciting input from three TESL experts for verification.
Data analysis
The gathered data were analyzed using SPSS 26.0 and AMOS 26.0. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was employed to assess the construct validity of each scale, while Cronbach’s α coefficients were utilized to evaluate the reliability of the sub-scales. Descriptive statistics, including means (M) and standard deviations (SD), were calculated. Ultimately, the researchers conducted structural equation modeling (SEM) to investigate the structural association between students’ CoI and VLM.
Results
Descriptive statistics
The Mean and Standard Deviation of each construct of CoI and VLM scales were analyzed with all scored above 3. In terms of the surveys of VLM scale, the participants reported an overall mean score of 3.53 (SD = 0.56), 3.50 (SD = 0.80) for Intrinsic Motivation, 3.76 (SD = 0.77) for Identified Regulation, 3.11 (SD = 0.92) for Introjected Regulation, and 3.75 (SD = 0.85) for External Regulation. For the survey of CoI scale, the overall mean score is 3.79 (SD = 0.54), 4.00 (SD = 0.72) for Teaching Presence, 3.74 (SD = 0.75) for Social Presence, and 3.62 (SD = 0.71) for Cognitive Presence.
The measurement model
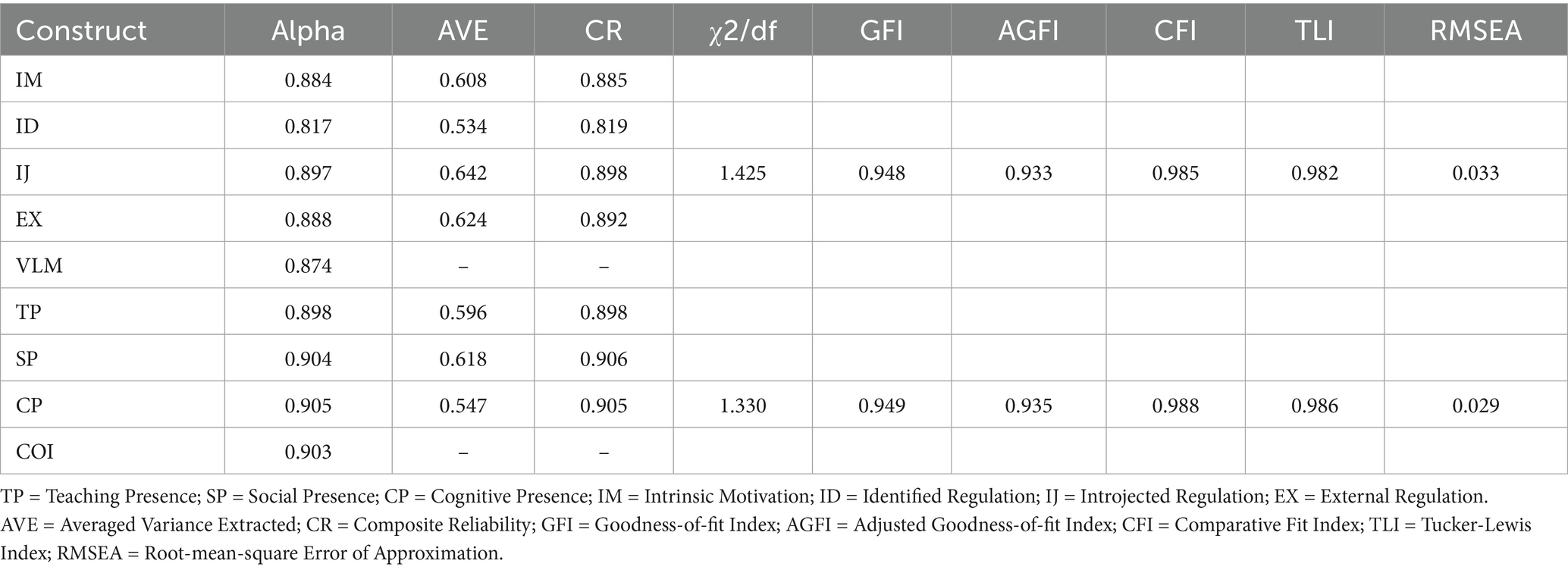
The CFA results for each scale indicated that both of the measurement models had good construct validity (Hair et al., 2014). The CFA results for the VLM scale revealed a good fit (χ2/df = 1.425, GFI = 0.948, AGFI = 0.933, CFI = 0.985, TLI = 0.982, RMSEA = 0.033). The fit indices of the CoI scale were also good (χ2/df = 1.330, GFI = 0.949, AGFI = 0.935, CFI = 0.988, TLI = 0.986, RMSEA = 0.029) (see Table 1).
The reliability of the VLM and CoI scales was assessed using measures of convergent validity and discriminant validity. The scale items were evaluated for convergent validity using three criteria: Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability (CR), and average variance-extracted (AVE). Table 1 shows that the Cronbach’s alpha values for all the constructs ranged from 0.817 to 0.905, which is higher than the minimum loading threshold of 0.60 (Hair et al., 2014). The overall alpha values of VLM and CoI scales were 0.874 and 0.903, indicating that the assessment items had sufficient internal consistency. Furthermore, all variables had CR values ranging from 0.819 to 0.906, which were higher than the threshold value of 0.80. Similarly, all constructs had AVE values ranging from 0.534 to 0.642, which were above the needed minimum of 0.50 as stated by Hair et al. (2014). Therefore, all three criteria for convergent validity were satisfied.
The formula of average variance-extracted is:
The formula of composite reliability is:
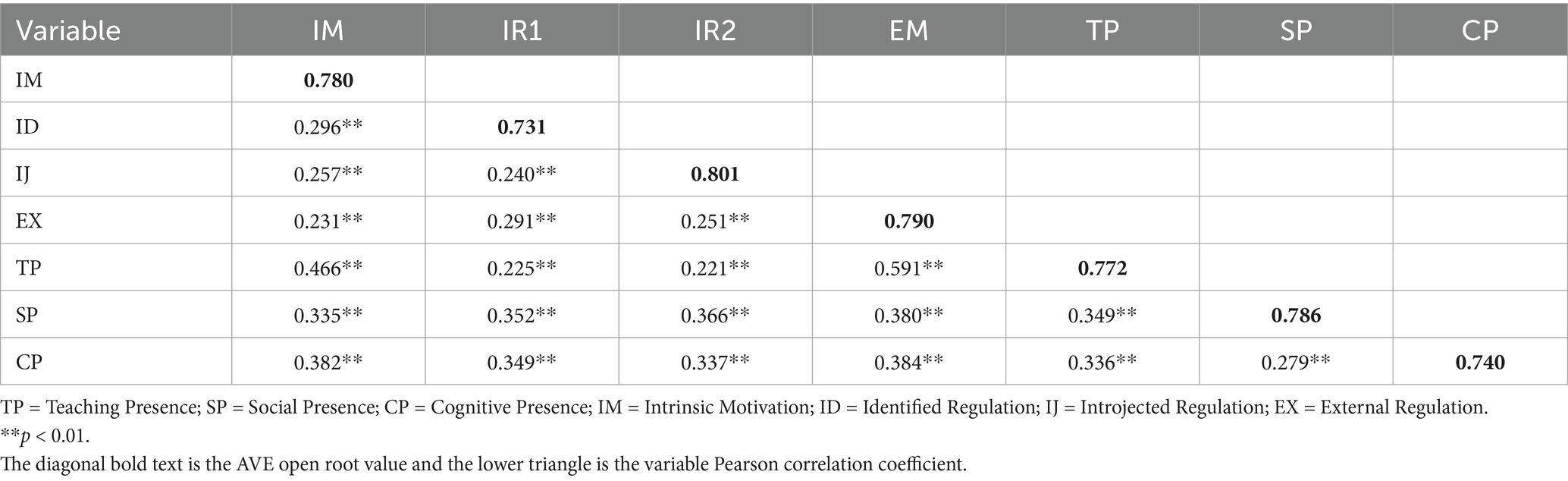
All correlations between the variables of VLM and the variables of CoI, as indicated in Table 2, were found to be statistically significant based on the correlation matrix findings. The correlation between Teaching Presence and External Regulation was determined to be the strongest (r = 0.591, p < 0.001). Conversely, the association between Teaching Presence and Introjected Regulation was determined to be the weakest (r = 0.221, p < 0.001). Construct discriminant validity refers to the extent to which the components of one construct differ from those of another construct. This metric was derived by comparing the Pearson correlation coefficients of each construct with the square root of the corresponding AVE estimates. According to the data shown in Table 2, it was concluded that the discriminant validity of each construct was considered sufficient because all of the square roots of AVE were determined to be larger than the absolute values of the correlation coefficients.
The structural model
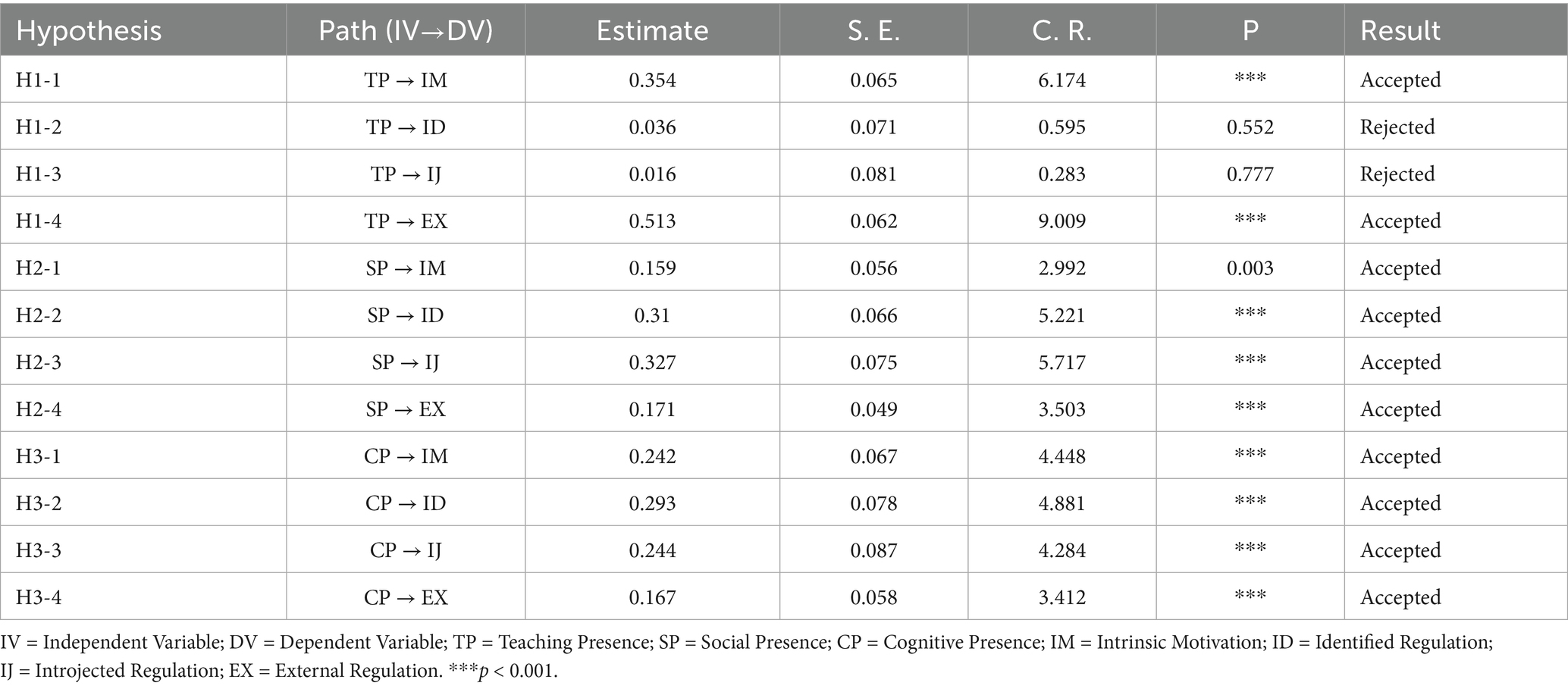
The structural model was assessed using the SEM technique with AMOS 26.0. The SEM results demonstrated that the fit indices were deemed satisfactory, with χ2/df = 1.261, GFI = 0.902, AGFI = 0.888, CFI = 0.980, TLI = 0.978, and RMSEA = 0.026 (Hair et al., 2014). The findings of the hypotheses in the study are outlined in Figure 2 and Table 3. The coefficient values obtained from the path analysis indicated that most of the factors in the CoI model had a substantial influence on students’ VLM. Teaching Presence had a positive effect on students’ vocabulary Intrinsic Motivation (β = 0.354, p < 0.001) and External Regulation (β = 0.513, p < 0.001). A positive effect of Social Presence on students’ vocabulary Intrinsic Motivation (β = 0.159, p < 0.05), Identified Regulation (β = 0.310, p < 0.001), Introjected Regulation (β = 0.327, p < 0.001), and External Regulation (β = 0.171, p < 0.001) was revealed. It was also found that Cognitive Presence had a significant positive effect on students’ vocabulary Intrinsic Motivation (β = 0.354, p < 0.001), as well as their Identified Regulation (β = 0.310, p < 0.001), Introjected Regulation (β = 0.327, p < 0.001), and External Regulation (β = 0.513, p < 0.001). Thus, the hypotheses H1-1, H1-4, H2-1, H2-2, H2-3, H2-4, H3-1, H3-2, H3-3, and H3-4 were accepted. Nevertheless, the study did not find any significant predictive effect of Teaching Presence on students’ vocabulary Identified Regulation (β = 0.036, p = 0.552) or Introjected Regulation (β = 0.016, p = 0.777), which means that hypotheses H1-2 and H1-3 were rejected.
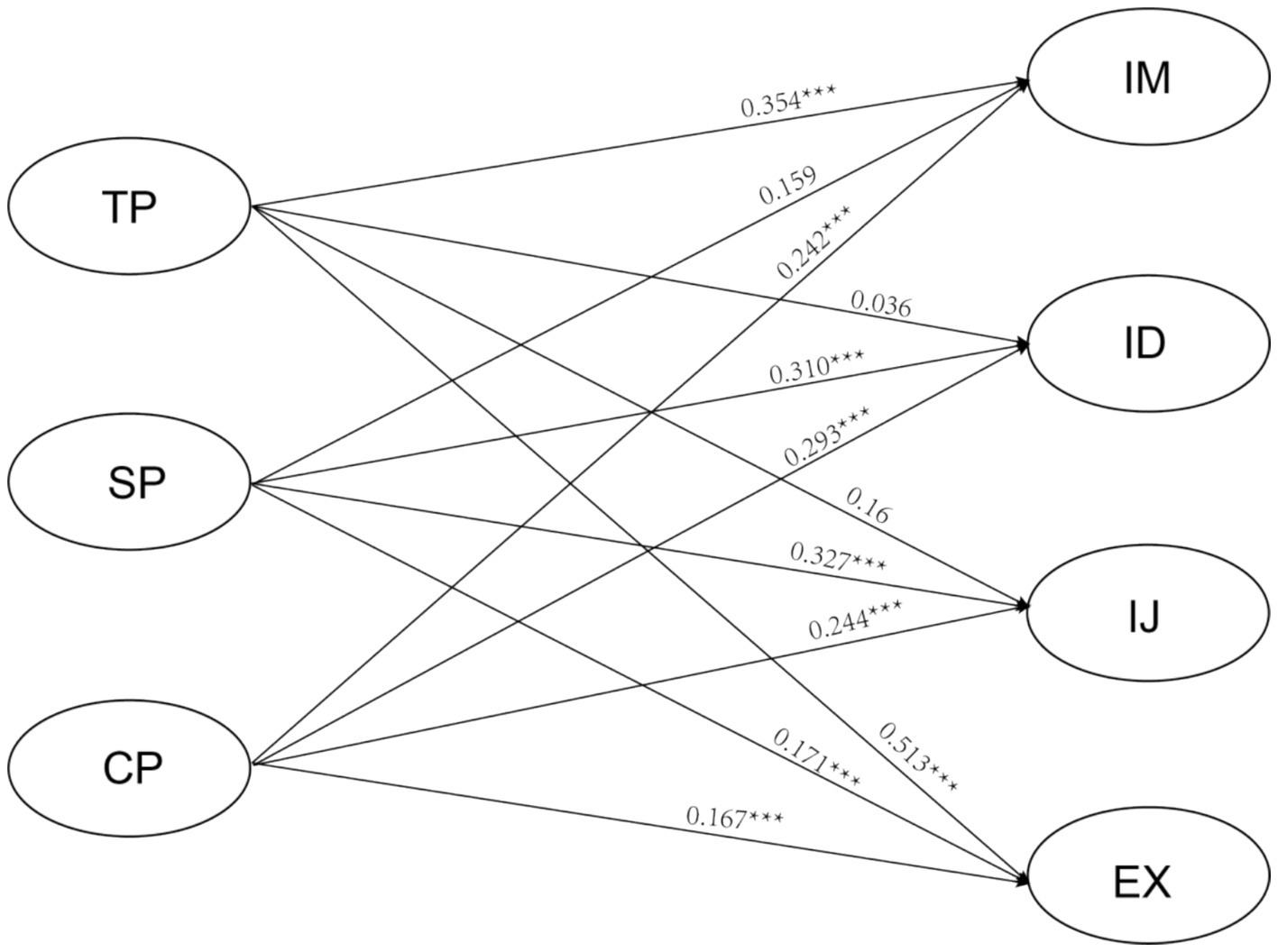
Figure 2. Verification of the structural model. TP, Teaching Presence; SP, Social Presence; CP, Cognitive Presence; IM, Intrinsic Motivation; ID, Identified Regulation; IJ, Introjected Regulation; EX, External Regulation.
Discussions
This research aimed to examine the effects of Teaching Presence, Social Presence, and Cognitive Presence within the CoI framework on different aspects of VLM—specifically Intrinsic Motivation, Identified Regulation, Introjected Regulation, and External Regulation—among Chinese EFL university students.
Teaching presence and vocabulary learning motivation
The observed impact of Teaching Presence on Intrinsic Motivation and External Regulation can be attributed to the organized and interactive characteristics of Teaching Presence. Effective teaching that is well-organized, encouraging, and captivating can cultivate a learning atmosphere that promotes students’ internal drive to learn. For instance, AI-generated feedback can enhance teaching presence in real-world teaching scenarios by providing prompt, tailored responses that mimic important elements of teacher assistance (Chan et al., 2024). Specifically, efficient pedagogical vocabulary learning techniques, such as dividing students into smaller, more manageable groups and facilitating discussions, can augment students’ External Regulation (Ryan and Deci, 2000). In line with Chen’s (2023) findings, the research also indicates that when teachers connect well with students, it leads to increased intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Possible contributing factors could include the findings of Cole et al. (2017) and Martin et al. (2022), which suggest that when students perceive their instructors as highly organized and supportive, they are more inclined to develop a genuine interest in the subject (Intrinsic Motivation) and respond positively to external incentives such as grades and praise (External Regulation). Nevertheless, Teaching Presence was found not to affect Identified Regulation or Introjected Regulation, possible reasons may be consistent with post-pandemic research that indicates teachers are often unprepared for the demands of technology, even while they acknowledge the importance of digital tools for student motivation (Lo and Wong, 2023). This implies that in order to fully achieve its motivational potential, Teaching Presence in blended environments needs to be backed by extensive training curricula and technology infrastructure. Additionally, Identified Regulation, characterized by the individual’s genuine endorsement of the learning activity, and Introjected Regulation, motivated by internal pressures, may require profound personal values and significance that surpass what structured Teaching Presence alone can provide (Deci and Ryan, 2000). Identified and Introjected Regulation are associated with deeper personal and moral obligations.
Social presence and vocabulary learning motivation
Social Presence was found to have a significant impact on all types of VLM. This phenomenon can be elucidated by the inherent characteristics of social relationships and interactions within the educational setting. Students were inspired to participate due to their sense of belonging to a supportive community. This is consistent with research conducted by García-Carrión et al. (2020) and Smith et al. (2020), which emphasizes that feeling connected and actively participating in group activities are important factors that drive intrinsic motivation. An extensive and strong Social Presence can help foster a feeling of belonging and alignment with the values and objectives of a group or community. For example, in Chan et al. (2024)‘s study, the Peer-AI Hybrid Tasks motivated students to discuss AI feedback in groups. Prompting AI to phrase feedback as questions can mimic collaborative discourse. In the current study, when individuals have a genuine sense of connection with others, they are more inclined to embrace and incorporate these values as their own, resulting in the development of identified regulation for learning vocabulary. When individuals are highly conscious of others’ expectations due to strong Social Presence, they adopt certain standards in a regulated and pressured way. This results in internal pressures such as feelings of guilt, personal investment in one’s ego, or self-esteem being dependent on reaching these standards. Furthermore, Social Presence amplifies the significance of social cues such as commendation, incentives, or penalties from others, as students assimilate the importance of acquiring vocabulary and participate in educational tasks to obtain social validation and avoid unfavorable evaluations (Weaver and Albion, 2005; Yilmaz et al., 2013; Ebadi and Amini, 2024). Creating a strong sense of community and meaningful social involvement in learning environments appears crucial for promoting motivating factors associated with responsibilities and external rewards (Ebadi and Amini, 2024).
Cognitive presence and vocabulary learning motivation
The study’s results demonstrate that Cognitive Presence significantly impacts all four types of VLM: Intrinsic Motivation, Identified Regulation, Introjected Regulation, and External Regulation. This underscores the vital importance of cognitive engagement in the learning process. These findings are consistent with previous research by Husni et al. (2022) and Roberts and Lee (2017), which emphasize the critical role of cognitive engagement and higher-order thinking in motivating students. Also in line with Chan et al. (2024), AI can elevate cognitive presence by motivating students to analyze, reflect, and iterate. Students evaluate AI versus instructor feedback, fostering critical thinking. Cognitive Presence promotes profound involvement, analytical reasoning, and ongoing contemplation, all of which are vital for students to construct meaningful knowledge and cultivate an inherent fascination with vocabulary acquisition. This facilitates students’ recognition of the personal significance of their learning (Identified Regulation), their response to internal pressures (Introjected Regulation), and their favorable response to external rewards (External Regulation). This implies that when students actively and profoundly engage with the subject matter, they are more inclined to develop enduring motivation across various contexts (Kintu et al., 2017; Brown and Jones, 2018). These findings align with research by Brown and Jones (2018), which demonstrated that learning environments that engage students cognitively enhance their ability to persist in challenging tasks. Therefore, the significance of creating an educational environment that promotes critical thinking, in-depth engagement with the subject matter, and reflective learning practices is clearly highlighted.
Conclusion
This study investigated the effects of Chinese university students’ CoI (Teaching Presence, Social Presence, and Cognitive Presence) on the four dimensions of VLM (Intrinsic Motivation, Identified Regulation, Introjected Regulation, and External Regulation) within the theoretical frameworks of the CoI and SDT. To summarize, the study highlights the capacity of CoI-based blended learning to improve students’ motivation to learn vocabulary. By improving these measures, educators can design more effective and engaging blended learning environments that enhance student motivation and vocabulary acquisition in EFL settings.
Recommendations
This study offers theoretical and practical recommendations with the goal of improving educational procedures and results, specifically in the Asia-Pacific educational region. In theory, this study provides empirical evidence for applying the CoI framework and SDT to vocabulary learning in EFL environments. To enhance VLM, several practical practices should be prioritized: First, teachers are suggested to offer purposeful and motivating tasks, supported by their supervision and prompt, valuable critique (Soffer and Cohen, 2019). Curriculum designers should employ explicit instructional design and captivating pedagogical techniques to captivate students’ attention and stimulate their intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Institutions should provide professional development programs that address both pedagogical and technological skills for blended teaching (Lo and Wong, 2023). Second, educational tools and online platforms should be employed to enable collaborative activities, peer conversations, and group cohesion. Generative AI tools should also be adopted for boosting student motivation and engagement in blended learning environments to facilitate peer comparison and collaborative learning through shared analytics (Chan et al., 2024). Customized course designs that incorporate interactive components foster collaboration, and providing incentives enhances students’ motivation (Veletsianos et al., 2015). Furthermore, educators should provide educational tasks that promote analytical thinking and deep involvement. Utilizing problem-based learning, introspective tasks, and chances for knowledge application can improve Cognitive Presence to foster more profound and motivated learning experiences when acquiring vocabulary.
Limitations
This study provides interesting insights, but it is important to consider its limitations. First, while SEM effectively models relationships among multidimensional variables, the cross-sectional design prevents the observation of dynamic interactions or the establishment of causal linkages between the CoI and VLM. The reliance on self-report data, which may be influenced by social desirability bias or inaccurate self-assessment, constrains the establishment of reciprocal relationships between CoI presence and motivation types. Future research should use longitudinal or experimental designs incorporating multimodal data like LMS analytics, teacher assessments, and behavioral traces to establish causal relationships and enhance validity. Second, due to the limited scope of this study’s sample, which was restricted to one university in Changsha, China, its findings may lack generalizability. Future research should include a variety of situations, larger groups of population, and a wider diversity of student backgrounds and academic fields to confirm and build upon these findings. Additionally, this study solely concentrates on VLM. It is suggested that future research explore other forms of motivation, such as amotivation, extrinsic motivation, achievement motivation, curiosity motivation, and competence motivation, using the CoI framework as a perspective. Lastly, future research is also suggested to investigate the specific effects of AI-driven feedback on the aforementioned types of motivational regulation through CoI framework and SDT.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Sultan Idris Education University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
QC: Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Software, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Validation, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. HX: Supervision, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adam, M. S., Abd Hamid, J., Khatibi, A., and Azam, S. F. (2023). Autonomous motivation in blended learning: effects of teaching presence and basic psychological need satisfaction. Learn. Motiv. 83:101908. doi: 10.1016/j.lmot.2023.101908
Ajideh, P., Rahimpour, M., Amini, D., and Farrokhi, F. (2013). Motivational strategies, task effectiveness and incidental acquisition of second language vocabulary. J. Lang. Teach. Res. 4:1044. doi: 10.4304/jltr.4.5.1044-1052
Akyol, Z., and Garrison, D. R. (2008). Understanding cognitive presence in an online and blended community of inquiry: assessing outcomes and processes for deep approaches to learning. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 39, 233–250. Available at: http://sloanconsortium.org/publications/jaln_main
Assor, A., Kaplan, H., and Roth, G. (2002). Choice is good, but relevance is excellent: autonomy-enhancing and suppressing teacher behaviours predicting students’ engagement in schoolwork. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 72, 261–278. doi: 10.1348/000709902158883
Brislin, R. W. (1986). “The wording and translation of research instruments” in Field methods in cross-cultural research. eds. W. J. Lonner and J. W. Berry (Sage), 137–164.
Brown, A., and Jones, M. (2018). The role of cognitive presence in a blended learning environment. J. Educ. Psychol. 15, 47–61.
Chan, S. T. S., Lo, N. P. K., and Wong, A. M. H. (2024). Enhancing university level English proficiency with generative AI: empirical insights into automated feedback and learning outcomes. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 16:ep541. doi: 10.30935/cedtech/15607
Chen, R. H. (2022). Effects of deliberate practice on blended learning sustainability: a community of inquiry perspective. Sustainability 14:1785. doi: 10.3390/su14031785
Chen, L. (2023). Transactional distance and college students’ learning engagement in online learning: the chain mediating role of social presence and autonomous motivation. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 16, 2085–2101. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S409294
Chen, K. T.-C., and Jang, S. J. (2010). Motivation in online learning: testing a model of self-determination theory. Comput. Human Behav. 26, 741–752. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2010.01.011
Chi, X. (2023). The influence of presence types on learning engagement in a MOOC: the role of autonomous motivation and grit. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 16, 5169–5181. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S442794
Cole, A., Anderson, C., Bunton, T., Cherney, M., Fisher, V. C., Featherston, M., et al. (2017). Student predisposition to instructor feedback and perceptions of teaching presence predict motivation toward online courses. Online Learning J. 21, 245–262. doi: 10.24059/olj.v21i4.966
Deci, E. L., and Ryan, R. M. (2000). The "what" and "why" of goal pursuits: human needs and the self-determination of behavior. Psychol. Inq. 11, 227–268. doi: 10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_01
Ebadi, S., and Amini, A. (2024). Examining the roles of social presence and human-likeness on Iranian EFL learners’ motivation using artificial intelligence technology: a case of CSIEC chatbot. Interact. Learn. Environ. 32, 655–673. doi: 10.1080/10494820.2022.2096638
Fontecha, A. F., and Gallego, M. T. (2012). The role of motivation and age in vocabulary knowledge. Vigo Int. J. Appl. Linguist. 9, 39–62.
García-Carrión, R., López de Aguileta, G., Padrós, M., and Ramis-Salas, M. (2020). Implications for social impact of dialogic teaching and learning. Front. Psychol. 11:500061. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00140
Garrison, D. R., Anderson, T., and Archer, W. (2000). Critical inquiry in a text-based environment: computer conferencing in higher education. Internet High. Educ. 2, 87–105.
Garrison, D. R., Anderson, T., and Archer, W. (2010). The first decade of the community of inquiry framework: a retrospective. Internet High. Educ. 13, 5–9. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2009.10.003
Garrison, D. R., and Arbaugh, J. B. (2007). Researching the community of inquiry framework: review, issues, and future directions. Internet High. Educ. 10, 157–172. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2007.04.001
Hair, J. F., Gabriel, M., and Patel, V. (2014). AMOS covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM): guidelines on its application as a marketing research tool. Braz. J. Mark. 13, 44–55. doi: 10.5585/remark.v13i2.2718
Harrell, K. B., and Wendt, J. L. (2019). The impact of blended learning on community of inquiry and perceived learning among high school learners enrolled in a public charter school. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 51, 259–272. doi: 10.1080/15391523.2019.1590167
Howard, J. L., Gagné, M., and Bureau, J. S. (2017). Testing a continuum structure of self-determined motivation: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 143, 1346–1377. doi: 10.1037/bul0000125
Hu, M., Wang, X., and Li, Z. (2016). Exploring student engagement in blended learning. J. Educ. Technol. Dev. Exch. 9, 83–99. doi: 10.33258/biolae.v6i2.1080
Husni, N. A., Jumaat, N., and Tasir, Z. (2022). Investigating student’s cognitive engagement, motivation and cognitive retention in learning management system. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learning (iJET) 17, 184–200. doi: 10.3991/ijet.v17i09.29727
Karimi, M. N., and Fallah, N. (2021). Academic burnout, shame, intrinsic motivation and teacher affective support among Iranian EFL learners: a structural equation modeling approach. Curr. Psychol. 40, 2026–2037. doi: 10.1007/s12144-019-0138-2
Kim, Y., Deci, E. L., and Zuckerman, M. (2002). The development of the self-regulation of withholding negative emotions questionnaire. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 62, 316–336. doi: 10.1177/0013164402062002008
Kintu, M. J., Zhu, C., and Kagambe, E. (2017). Blended learning effectiveness: the relationship between student characteristics, design features and outcomes. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 14:7.
Li, J., King, R. B., and Wang, C. (2022). Adaptation and validation of the vocabulary learning motivation questionnaire for Chinese learners: a construct validation approach. System 108:102853. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2022.102853
Li, G., Luo, H., Lei, J., Xu, S., and Chen, T. (2022). Effects of first-time experiences and self-regulation on college students’ online learning motivation: based on a national survey during COVID-19. Educ. Sci. 12:245. doi: 10.3390/educsci12040245
Lo, N. P. K., and Wong, A. M. H. (2023). Reimagining teaching and learning in higher education in the post-COVID-19 era: The use of recorded lessons from teachers’ perspectives. In critical reflections on ICT and education: Selected papers from the HKAECT 2023 international conference. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 215–230.
Martin, F., Wang, C., and Sadaf, A. (2022). Student perception of helpfulness of instructional strategies in online and blended learning environments. J. Cyber Learn. 46, 268–290.
Nasir, M. K. M., and Ngah, A. H. (2022). The sustainability of a community of inquiry in online course satisfaction in virtual learning environments in higher education. Sustainability 14:9633. doi: 10.3390/su14159633
Noels, K. A., Pelletier, L. G., Clément, R., and Vallerand, R. J. (2000). Why are you learning a second language? Motivational orientations and self-determination theory. Lang. Learn. 50, 57–85. doi: 10.1111/0023-8333.00111
Okkan, A., and Aydın, S. (2020). The effects of the use of Quizlet on vocabulary learning motivation. Lang. Technol. 2, 16–25.
Papi, M., and Abdollahzadeh, E. (2012). Teacher motivational practice, student motivation, and possible L2 selves: an examination in the Iranian EFL context. Lang. Learn. 62, 571–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9922.2011.00632.x
Ritonga, M., Tazik, K., Omar, A., and Saberi Dehkordi, E. (2022). The effect of peer assessment (PA) on reading comprehension, reading motivation, and vocabulary learning among EFL learners. Lang. Test. Asia 12:36. doi: 10.1186/s40468-022-00188-z
Roberts, P., and Lee, P. (2017). Cognitive presence in an online learning environment: strategies for establishing social and teaching presence. J. Online Learn. 10, 183–196.
Ryan, R. M., and Deci, E. L. (2000). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: classic definitions and new directions. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 25, 54–67. doi: 10.1006/ceps.1999.1020
Ryan, R. M., and Deci, E. L. (2020). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation from a self-determination theory perspective: definitions, theory, practices, and future directions. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 61:101860. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2020.101860
Shea, P., Hayes, S., Uzuner-Smith, S., Gozza-Cohen, M., Vickers, J., and Bidjerano, T. (2014). Reconceptualizing the community of inquiry framework: an exploratory analysis. Internet High. Educ. 23, 9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2014.05.002
Smith, T. E., Sheridan, S. M., Kim, E. M., Park, S., and Beretvas, S. N. (2020). The effects of family-school partnership interventions on academic and social-emotional functioning: a meta-analysis exploring what works for whom. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 32, 511–544. doi: 10.1007/s10648-019-09509-w
Soffer, T., and Cohen, A. (2019). Students’ engagement characteristics and motives in asynchronous online courses. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 22, 99–111.
Suharno, S., Suherdi, D., and Gunawan, W. (2023). The effects of teaching presence on students’ motivation and performance in a long-term online gamified EFL listening course. Int. J. Instr. 16, 1111–1134. doi: 10.29333/iji.2023.16259a
Susanto, A., Nuwrun, S., Tegor, T., Azhari, W., Megah, M., and Yuliani, S. (2022). Bussu as online learning platform on vocabulary learning motivation achievement among students. Jurnal Pendidikan Al-Ishlah 14, 249–260. Available at: https://repository.uir.ac.id/id/eprint/22980
Tanaka, M. (2017). Examining EFL vocabulary learning motivation in a demotivating learning environment. System 65, 130–138. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2017.01.010
Tokan, M. K., and Imakulata, M. M. (2019). The effect of motivation and learning behaviour on student achievement. S. Afr. J. Educ. 39, 1–8. doi: 10.15700/saje.v39n1a1510
Veletsianos, G., Kimmons, R., and French, J. N. (2015). Developing a community of inquiry in online environments. Tech Trends 54, 37–40.
Weaver, C. M., and Albion, P. (2005). Momentum in online discussions: The effect of social presence on motivation for participation. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference of the Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education (ASCILITE 2005). Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education.
Yilmaz, R. M., Topu, F. B., Goktas, Y., and Coban, M. (2013). Social presence and motivation in a three-dimensional virtual world: an explanatory study. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 29, 823–839. doi: 10.14742/ajet.425
Yu, Z., and Li, M. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of community of inquiry in online learning contexts over twenty-five years. Educ. Inf. Technol. 27, 11669–11688. doi: 10.1007/s10639-022-11081-w
Zhang, R. (2020). Exploring blended learning experiences through the community of inquiry framework. Lang. Learn. Technol. 24, 38–53.
Zhang, Y., Lin, C. H., Zhang, D., and Choi, Y. (2016). Motivation, strategy, and English as a foreign language vocabulary learning: A structural equation modelling study. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 87, 57–74.
Zhang, S., and Zhang, X. (2022). The relationship between vocabulary knowledge and L2 reading/listening comprehension: a meta-analysis. Lang. Teach. Res. 26, 696–725. doi: 10.1177/1362168820913998
Zhou, Y. (2016). Digital vocabulary competition as motivator for learning in CFL classrooms. J. Technol. Chin. Lang. Teach. 7, 1–22.
Keywords: community of inquiry framework, blended learning, vocabulary learning motivation, effects, SEM
Citation: Chuane Q and Xiangjun H (2025) Effects of Community of Inquiry on EFL students’ vocabulary learning motivation in a blended learning environment. Front. Educ. 10:1642267. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1642267
Edited by:
Abusufiyan Shaikh, Anjuman-I-Islam's Kalsekar Technical Campus, IndiaReviewed by:
Noble Lo, Lancaster University, United KingdomJianhua Wang, Renmin University of China, China
Copyright © 2025 Chuane and Xiangjun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: He Xiangjun, NjA1NDg4MDUwQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Qiu Chuane
Qiu Chuane He Xiangjun2*
He Xiangjun2*