- 1Department of Instrumentation and Electronics Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok, Bangkok, Thailand
- 2Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok, Bangkok, Thailand
The rising demand for electricity presents significant challenges to grid stability. Demand response programs address this issue by incentivizing consumers to adjust consumption during peak periods. Load aggregators facilitate these programs by coordinating load reductions across participants; however, they face challenges in maintaining profitability and minimizing operational costs, particularly in nascent demand response markets. In this study, we evaluate three participant selection strategies: duration based, price based, and forecast based, within the context of Thailand’s pilot demand response programs. We propose a dual forecasting methodology that combines short-term load profile forecasting using XGBoost and long-term load duration curve predictions using SARIMAX. This integrated approach improves forecast accuracy and enables more strategic participant selection. Simulation results demonstrate that the dual forecasting strategy consistently minimizes operational costs and reduces the number of participant calls, outperforming conventional strategies even under resource-constrained, high-risk scenarios. These findings suggest that the dual forecasting strategy offers a cost-effective and reliable solution for demand response management, particularly in environments with limited participant availability, making it well-suited for deployment in emerging markets.
1 Introduction
The rapid rise in global electricity demand is fueled by significant growth across various sectors. For example, the increasing heating and cooling needs due to climate change (Zhang et al., 2022), the increasing reliance on artificial intelligence and data centers (de Vries, 2023), and the substantial shift in the transportation sector driven by the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) are major contributors (Blumberg et al., 2022). Among these, EVs are expected to grow at an exponential rate, placing considerable pressure on electricity infrastructure, potentially causing supply imbalances during peak times. This surge in load demands new approaches to grid management, where balancing supply and demand becomes more critical than ever to maintain grid stability and avoid costly infrastructure expansions.
In response to these growing pressures, the demand response market has emerged as a key solution for grid operators worldwide (Behrangrad, 2015). Demand response programs allow for the dynamic adjustment of electricity consumption by incentivizing consumers to reduce or shift their usage during peak periods (Panda et al., 2023). As a result, demand response programs have gained significant traction globally, helping to balance grids more efficiently and reduce the need for costly investments in additional generation capacity. These programs also allow consumers to play a more active role in managing energy use, providing new economic incentives for participants (Nebey, 2024).
A pivotal player in the success of demand response initiatives is the load aggregator, who acts as an intermediary between the grid operator and individual consumers. The role of load aggregators is to combine the reduction capacities of multiple participants into a manageable resource, which can be called upon during demand response events (Stede et al., 2020). Nowadays, Thailand is currently piloting its own demand response programs, which present unique challenges in terms of market readiness and participant engagement (Sonsaard et al., 2023). With a relatively small pool of businesses and entrepreneurs familiar with demand response programs, there is a pressing need to optimize the utilization of available participants.
Since load aggregators face significant challenges in maintaining profitability while minimizing the operational costs of curtailing load. Therefore, they must develop effective strategies to select participants based on factors such as duration, price, and forecasted demand, ensuring both cost-effectiveness and reliability. Identifying effective participant selection strategies is crucial to ensure that the demand response initiative can achieve its objectives while fostering greater awareness and participation in the market. Developing tailored strategies that make the best use of limited resources will be essential to driving the success of Thailand’s demand response efforts, especially as the country looks to expand its clean energy and grid management capabilities.
In this paper, we explore strategies for optimizing participant selection in demand response programs, with a focus on maximizing the efficiency of the participant pool in Thailand’s pilot programs. By comparing different approaches, we aim to offer insights that can help load aggregators enhance their profitability while contributing to a more resilient and flexible power grid.
2 Related research work
2.1 Participant selection in demand response
Demand response programs are increasingly important for balancing electricity supply and demand, especially as renewable energy sources grow, and grids require more flexibility (Gils, 2016). Load aggregators play a key role in managing participants, typically industrial or commercial users, who agree to reduce electricity usage during peak times. The success of these programs depends on how well aggregators select participants to meet load reduction targets at the lowest cost while maintaining reliability (Mei et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2024).
One common method for selecting participants is the price-based strategy, where participants are ranked by the cost they charge per megawatt (MW) of load reduction, and the lowest-cost options are chosen first. This method is simple and cost-focused but has significant limitations. It often ignores other critical factors like how long participants can sustain reductions (callable duration) and their reliability in meeting commitments. This can result in participants failing to deliver promised reductions or struggling to sustain them, ultimately reducing the program’s effectiveness (Silva et al., 2023).
To address these gaps, forecasting-based strategies are being explored. Forecasting models predict when and where load reductions will be needed, helping aggregators choose participants who can best meet these demands. Machine learning models like XGBoost (Chen and Guestrin, 2016) have shown good results in forecasting short-term electricity demand (Abbasi et al., 2019; Liao et al., 2019). However, single forecasting models have limitations in accuracy, prompting research into combining multiple models to improve predictions (Semmelmann et al., 2022).
In addition, optimization algorithms offer advanced methods for participant selection. Techniques like genetic algorithms are used to balance cost, duration, and reliability, especially in large-scale programs with many participants. These algorithms help identify effective solutions without the heavy computation required for exhaustive analysis (dos Santos Junior et al., 2024; Mellouk et al., 2018; Mohanty et al., 2022).
In summary, while traditional cost-focused methods like the price-based strategy are simple, they often may not take account for key factors like duration and reliability. Advanced methods such as dual forecasting, optimization algorithms, and game theory (Goudarzi et al., 2021) now offer more effective ways to select participants, ensuring that demand response programs are both cost-efficient and reliable.
2.2 XGBoost short-term forecasting model
Short-term forecasting plays an important role in fields like energy management, finance, and supply chains, where quick and accurate predictions drive effective decision-making. These applications demand models capable of adapting to rapid changes and uncertainties in data. Popular methods include traditional statistical models like ARIMA and SARIMA (Musbah and El-Hawary, 2019; Tarmanini et al., 2023), as well as modern machine learning models like XGBoost, Random Forest, and neural networks (Dudek, 2022; He, 2017). Among these, XGBoost has emerged as a top choice for short-term forecasting, especially when dealing with dynamic and high-frequency data.
XGBoost, short for “Extreme Gradient Boosting,” is a powerful ensemble learning algorithm that combines multiple decision trees to create highly accurate predictions. Its strength lies in its ability to handle large, noisy, and high-dimensional datasets efficiently (Ahmetoglu and Das, 2022). This makes it particularly suitable for applications like energy forecasting, where data complexity and timeliness are critical.
One of XGBoost’s key advantages is its ability to manage real-world challenges like missing data, which is common in fields like energy load forecasting. The model can adaptively decide the best course of action in decision trees when data points are missing. Moreover, it incorporates regularization techniques (L1 and L2 penalties) to avoid overfitting, a common problem in short-term forecasting with noisy or high-frequency data (Belyadi and Haghighat, 2021).
From a broader perspective, XGBoost excels in short-term forecasting due to its robustness, scalability, and accuracy. It efficiently captures non-linear patterns, handles complex datasets, and integrates external variables, all while maintaining fast training speeds. Compared to other models like ARIMA, Random Forest, or neural networks, XGBoost offers a balanced combination of performance, ease of interpretation, and computational efficiency. For industries such as energy management, where timely and precise forecasts are essential, XGBoost stands out as a reliable and effective tool.
2.3 SARIMAX long-term forecasting model
Long-term forecasting is useful for strategic planning in industries like energy, retail, and finance, where accurate predictions over extended periods guide key decisions (Zhou et al., 2019). Models for long-term forecasting must capture trends, seasonality, and external factors to address the complexities of time series data. Among these models, SARIMAX (Seasonal AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average with eXogenous variables) is widely recognized for its effectiveness (Alharbi and Csala, 2022). By incorporating seasonal components and external influences, SARIMAX builds on the ARIMA model, making it ideal for data with cyclical patterns, such as energy demand or retail sales (Arunraj et al., 2016).
SARIMAX excels because it can simultaneously model seasonal patterns, trends, and external variables. For example, energy consumption often follows yearly cycles due to heating and cooling needs, while retail sales peak during holidays. SARIMAX captures these behaviors using its seasonal features. Unlike ARIMA, SARIMAX integrates external variables, allowing it to handle more complex datasets and provide accurate, long-term forecasts (Vagropoulos et al., 2016).
When compared to other models like Facebook’s Prophet, SARIMAX offers greater flexibility. Prophet is simple to use and effective for seasonality and trends but assumes an additive structure, which may not suit datasets with complex seasonality. In contrast, SARIMAX supports both additive and multiplicative components and allows the integration of external factors, making it more robust for intricate patterns (Žunić et al., 2020).
In summary, SARIMAX is a powerful tool for long-term forecasting. Its ability to model trends, seasonality, and external influences makes it a top choice for industries like energy and retail, where understanding long-term patterns is essential. Compared to alternatives, SARIMAX strikes a balance between flexibility, accuracy, and interpretability, ensuring reliable forecasts that inform strategic decisions.
3 Methodology
3.1 Participants calling strategies
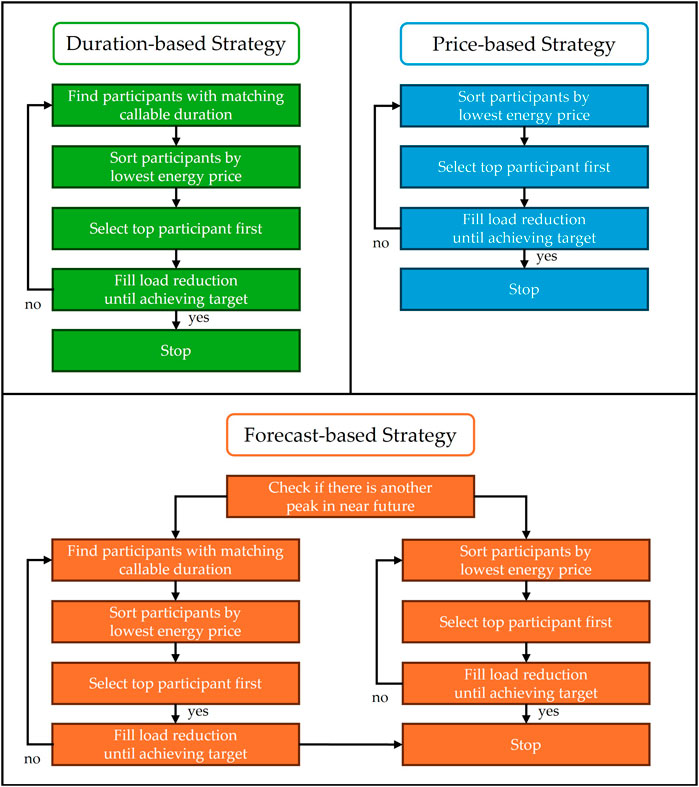
In the context of demand response programs, one of the key operational challenges faced by load aggregators is determining how to select participants who will reduce their energy consumption during critical events. The goal is to balance the need for cost efficiency with the need to meet load reduction targets while considering factors such as reliability and duration of load reduction. To address these challenges, we propose three distinct participants calling strategies that aim to optimize different aspects of demand response management: duration-based, price-based, and forecast-based strategies, the overview of which is summarized in Figure 1. Each strategy offers a different approach to selecting participants based on a set of criteria designed to maximize cost-effectiveness, ensure load reduction reliability, and improve decision-making through predictive insights.
• Duration-Based Strategy: This strategy prioritizes reducing the number of participants involved in each demand response event, thereby simplifying management and maximizing the number of spared participants available in the pool. While it offers operational advantages, it may fall short in terms of profitability compared to other strategies.
• Price-Based Strategy: This approach emphasizes minimizing the overall cost of energy reduction by selecting the least expensive participants. Although widely adopted, it can lead to inefficiencies in management. Participants who are frequently called upon may experience fatigue or disengagement, potentially diminishing their willingness to participate in future programs.
• Forecast-Based Strategy: Our proposed strategy harnesses the predictive capabilities of forecasting models to optimize the utilization of the participant pool. By reducing both costs and the number of participants required for each event, it proves to be a more effective and balanced solution. However, its success depends on the availability of reliable historical statistical data for accurate forecasting.
3.1.1 Duration-based strategy
The duration-based strategy is designed to align participant selection with the specific duration of a demand response event, ensuring that participants can sustain their load reduction commitments for the entirety of the event. In a typical demand response event, the length of time for which the grid requires load reduction can vary. Events might last for as little as an hour or extend up to several hours, depending on the grid’s requirements. The primary goal of this strategy is to ensure that the selected participants can provide continuous load reductions without the need for frequent switching or replacing participants mid-event, which can introduce operational inefficiencies.
To implement this strategy, each participant’s callable duration is compared against the event duration. The participants are ranked based on how closely their callable duration matches or exceeds the event’s length. For example, if the demand response event is scheduled to last for 4 h, participants with at least 4 h of callable duration will be prioritized. If a participant only has 2 h of callable duration, they may not be selected unless there are no other options, as the aggregator would have to replace them halfway through the event.
In cases where several participants have similar callable durations, additional criteria such as load reduction capacity and cost are factored in. For instance, if two participants can both provide 4 h of load reduction, but one offers a higher reduction capacity at a reasonable price, they would be prioritized. This ensures that not only is the duration matched, but the load reduction target is met with fewer participants, reducing complexity in managing the event.
An example of how this strategy might play out is during a long 6-h demand response event. The aggregator would first look for participants who can offer 6 continuous hours of load reduction. Once those participants are exhausted, the aggregator might then look at participants with 5 h of callable duration and then filling the gaps as needed. The goal is to minimize interruptions by choosing participants who can remain engaged throughout the event. This strategy may benefit the aggregator that has hard time upon calling multiple participants due to technical difficulties or management difficulties.
3.1.2 Price-based strategy
The price-based strategy focuses on cost efficiency by prioritizing participants based on the price they charge for reducing their load. Participants in demand response events typically offer different prices for the energy they are willing to curtail, often measured in terms of Thai baht (THB) per megawatt (MW). The goal of this strategy is to minimize the overall cost of the demand response event by selecting the lowest-cost participants first, ensuring that the target reduction is achieved at the most economical price.
In this strategy, participants are ranked solely based on their price per megawatt of load reduction, and the aggregator starts by selecting the lowest-priced participants. For example, if one participant offers to reduce their load for 500 THB per MW and another offers to reduce for 1,000 THB per MW, the first participant will be selected until their capacity is exhausted or the load reduction target is met. Once the lowest-priced participants are fully utilized, the aggregator moves on to the next-lowest-priced participant, continuing this process until the load reduction target is reached.
While this approach is straightforward and effective in minimizing costs, it presents potential limitations. Participants offering the lowest prices may not always possess the necessary callable duration or load reduction capacity to meet the event’s requirements. For instance, a participant may submit a low bid but only sustain load reduction for 2 h during a 6-h event. This mismatch could result in gaps in load reduction or necessitate the inclusion of additional, higher-cost participants to compensate for the shortfall, potentially increasing overall costs.
Additionally, price-based selection can sometimes lead to the selection of participants who may be less reliable, as their lower price may reflect a lower willingness or ability to commit to load reductions over the long term. Despite these potential issues, the price-based strategy remains a commonly used approach in markets where reducing costs is the primary objective, and where there is a surplus of participants willing to reduce their load at competitive prices.
3.1.3 Forecast-based strategy
The forecast-based strategy, which constitutes our proposed approach, is a more advanced methodology that utilizes predictive models to guide the participant selection process. The fundamental principle of this strategy is the use of load forecasts to anticipate the likelihood of additional demand peaks later in the month or quarter. By forecasting these future peaks, the load aggregator is able to make more informed and strategic decisions regarding participant selection for the current demand response event, addressing not only the immediate requirements but also accounting for potential future needs.
The operation of this strategy is as follows: upon the initiation of a demand response event, the aggregator employs load profile forecasts to assess the likelihood of additional demand peaks occurring later in the same month or quarter. Given the limited opportunities to call participants, if the forecast anticipates future demand peaks, the aggregator must strategically decide whether to reserve certain participants, particularly those offering longer callable durations and lower prices—for these forthcoming events. This consideration is especially critical when the pool of participants capable of sustaining long-duration reductions or offering competitive pricing is limited.
For example, given a scenario where a demand response event has just commenced, the aggregator is tasked with selecting participants to reduce load. Based on the forecast, the aggregator identifies a high likelihood of an even larger demand peak occurring later in the month. In such a case, the aggregator may choose to reserve the lowest-cost participants, particularly those with long callable durations, for the future event, as their contributions would be more valuable when the grid experiences greater strain. For the current event, the aggregator would instead select participants with shorter durations or those with slightly higher costs, ensuring that the target reduction is achieved without depleting the resources needed for future peaks.
Conversely, if the forecast does not predict any significant peaks later in the month or quarter, the aggregator can confidently utilize the lowest-cost participants without concern for resource conservation in subsequent events. In this scenario, the focus shifts solely to minimizing costs for the present event. The forecast-based strategy enables the aggregator to optimize the timing of participant selection and the allocation of resources across multiple demand response events, ensuring that the most valuable participants are preserved for periods of heightened demand.
An example of the forecast-based strategy in action might involve a scenario where the current event is relatively moderate, but a forecast indicates that a major demand peak is likely in 2 weeks. The aggregator could choose to use medium-cost participants with shorter callable durations for the current event, while holding back the most cost-effective, long-duration participants for the upcoming peak. This dynamic decision-making process ensures that the load reduction resources are managed efficiently across multiple events, reducing the risk of over-calling participants and avoiding unnecessary costs.
3.2 Short-term load profile forecast
In this work, we employed XGBoost for the short-term load profile forecast. The XGBoost works through a boosting technique where multiple decision trees are constructed sequentially. Each tree is trained to correct the errors made by the previous trees, resulting in a highly accurate prediction model. The model’s objective is to minimize the difference between the predicted load values and the actual load values by optimizing an objective function, which balances both the prediction error and the complexity of the model.
The objective function
where
The regularization term is defined in Equation 2:
where
λ = the penalty on the sum of the squared leaf weights
The final prediction for the load at time
where
Each tree is added with the aim of minimizing the residual errors from the previous trees, thereby enhancing the model’s overall accuracy as additional trees are constructed. This iterative process continues until the model’s prediction error is minimized or a stopping criterion is met, such as reaching a predefined number of trees or implementing early stopping when no further improvement in error is observed. In practical programming applications, particularly with Python, several hyperparameters can be tuned, including:
• Learning Rate: This factor controls the contribution of each tree to the final prediction. A lower learning rate requires more trees to reach optimal performance but can lead to better accuracy.
• Max Depth: This maximum depth determines the maximum depth of each decision tree, controlling how complex the model can become. A higher max depth allows the model to capture more intricate relationships but can increase the risk of overfitting.
• Number of Trees: This parameter specifies how many trees are built in the ensemble. More trees typically improve performance but increase computational cost.
• Subsample: The fraction of the training data is used to grow each tree. Lower values can prevent overfitting by introducing more randomness.
3.3 Long-term load duration curve prediction
To improve the load profile forecast, we use prediction of load duration curve to scale the forecasted load profile, resulting in improved accuracy. Since the load duration curve is typically formed on a yearly basis, the Seasonal AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average with eXogenous variables (SARIMAX) model was employed due to its ability to capture both the trend and seasonality in time series data while also incorporating external variables. The SARIMAX model extends the ARIMA framework by introducing seasonality (through seasonal differencing) and enabling the integration of external variables (exogenous factors) that can influence load demand over longer periods.
The objective of using SARIMAX is to predict the yearly load duration curve, which represents the relationship between load demand and the percentage of time the demand exceeds specific levels. SARIMAX is well-suited for modeling this curve as it captures both the temporal trends in load data and the impact of external factors that influence demand fluctuations.
The SARIMAX model builds on the ARIMA model by incorporating seasonal components and exogenous variables, as represented in Equation 4:
where
The SARIMAX model is represented in Equation 5:
where
After obtaining the load duration curve prediction results using the SARIMAX model, we integrated them with the previously forecasted load profile to adjust the maximum, minimum, and average values of the original forecast. While these adjustments caused the specific values to shift, the overall pattern of fluctuations, including the rise and fall in different periods, was preserved, ensuring that the original load dynamics remained intact.
4 Results
4.1 Load forecast results
In this work, load profile forecasting serves as the foundation for effective demand response planning, which involves selecting participants capable of adjusting their power usage in response to grid demands. The objective is to forecast load profiles with sufficient accuracy to support strategic decision-making in selecting participants for demand response programs. Two forecasting approaches were employed to achieve this objective. The first approach uses the XGBoost machine learning model, leveraging 10 years of historical data to predict load profiles month by month. The second approach, aimed at improving forecast accuracy, involves scaling the load profile forecasts using a load duration curve prediction generated through the SARIMAX statistical model. By incorporating the SARIMAX-based load duration curve scaling into the XGBoost predictions, we sought to refine the forecasted values and reduce prediction errors.
To conduct the study, data from The Dayton Power and Light Company for the years 2005–2017, obtained from the publicly available Kaggle repository, was used. Two test cases were designed for the experiments:
• Test Case 1 used data from 2005 to 2015 to forecast the load profile in 2016.
• Test Case 2 used data from 2006 to 2016 to forecast the load profile in 2017.
In the first test case, we applied the XGBoost model to predict the load profiles for each month of 2016, generating a total of 12 monthly forecasts. Over the course of the year, the mean absolute percentage error was found to be 13.78%. While certain periods exhibited larger deviations between the predicted and actual values, the overall trends of increasing and decreasing load levels were well captured. This consistency in predicting monthly trends is essential crucial for demand response planning, as it allows for reliable participant selection based on load variations.
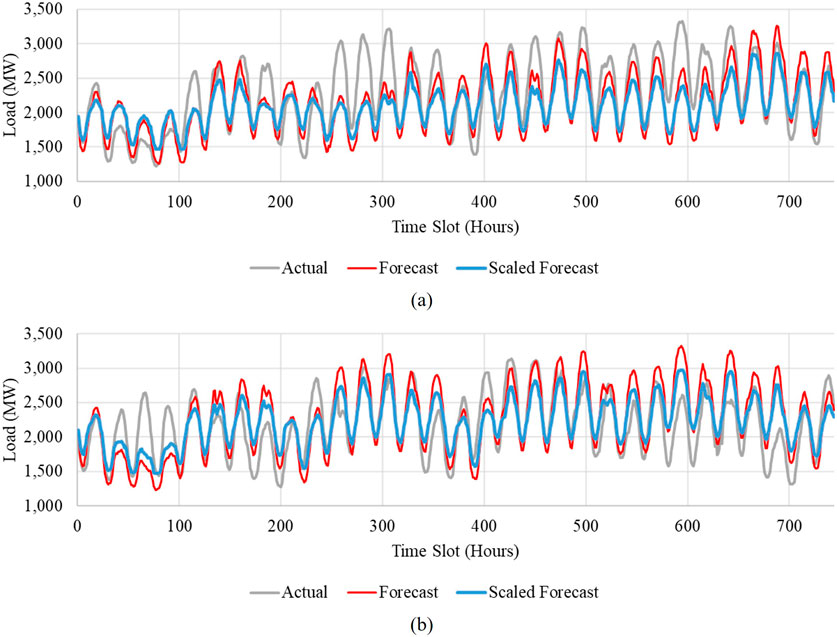
For example, Figure 2 illustrates the forecast for July 2016, the peak electricity consumption month of the year. In this figure, the grey line represents the actual load values, while the red line depicts the forecasted load produced by the XGBoost model. Despite some forecast deviations, the model’s ability to capture the general upward trend in load demand during peak periods makes the forecast effective for practical use in demand response planning.
Similarly, for the 2017 forecast, the XGBoost model performed satisfactorily, with a mean absolute percentage error of 13.07%. The overall consistency in monthly load trends ensured the model’s practical utility in planning for demand response participation in 2017, as demonstrated in Figure 2a, which shows the model’s forecast for July 2017.
To improve the accuracy of these forecasts, we incorporated the SARIMAX model to generate a long-term load duration curve prediction. This prediction, unlike the month-by-month XGBoost approach, provided a single, comprehensive prediction of the load duration curve for the entire year. The results of this load duration curve prediction showed a high level of alignment with the actual data, yielding a mean absolute percentage error of only 5.92% for the year 2016 and 6.97% for the year 2017. These highly accurate load duration curve predictions are illustrated in Figure 3, which show the load duration curve predictions for July of 2016 and 2017, respectively.
The precision of these predictions highlights the SARIMAX model’s effectiveness in capturing the overall distribution of load demand across different periods of the year. By scaling the XGBoost load profile forecasts based on the SARIMAX-predicted load duration curve, even though the pattern has still maintained, and the values were slightly changed, we were able to reduce the average forecast error even further. After scaling, the mean absolute percentage error for 2016 dropped to 12.75%, and for 2017, it decreased to 11.94%. These improvements can be observed in the blue lines in Figure 2b.
4.2 Calling strategies results
After obtaining the load profile forecasts, the next step is to apply these forecasts in the selection of participants for load reduction events to meet the demand response objectives. In this section, we focus on how these forecasts are utilized to choose the appropriate participants for each load reduction event, ensuring that the demand response goals are achieved. In this research, we consider the fact that demand response remains a relatively new business concept, with pilot programs still ongoing in many countries. As a result, we aligned our calling strategy with the global context, where demand response is being gradually adopted to delay infrastructure investments or to enhance grid stability. To reflect this early-stage adoption, the load reduction target is not overly ambitious, with the primary goal being to attract load aggregators and promote participation in the program. For our demand response strategy, we set a target load reduction of 50 MW per event. Additionally, each event is limited to a maximum duration of 6 consecutive hours, with no more than one event per day, and a maximum of 10 events per month.
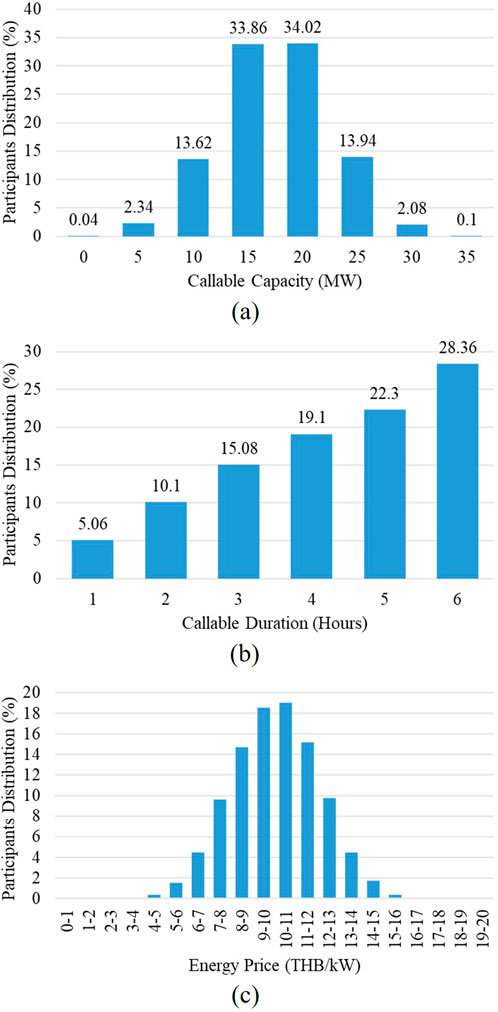
The participants in this demand response scenario are treated as resources aggregated by the load aggregator, each subject to various constraints related to callable duration, size, and the cost of load reduction per unit of energy. These participants have varying load reduction potentials, with callable durations ranging from 1 to 6 h per event. In Thailand’s demand response programs, the callable duration is typically limited to 3 h per session. However, our study broadens this concept to better reflect real-world conditions under a load aggregator model. Different businesses offer different levels of flexibility; for instance, factories may handle longer reductions by adjusting operations. In contrast, service-based businesses like supermarkets, which depend heavily on HVAC systems, may prefer shorter durations. To represent this diversity, we randomly assign callable durations across participants, with a slight preference toward longer durations, which are more advantageous from the aggregator’s perspective. We also assume high reliability from all participants, as their operational characteristics are considered during selection, ensuring a dependable demand response program.
Participants capable of sustaining reductions for the full 6-h duration are prioritized, forming a significant portion of the resource pool in this test case. The overall participant pool offers an average reduction capacity of around 15–20 MW, with a maximum capacity of up to 35 MW. The cost that the load aggregator must pay for load reductions also varies, with the average cost set at 1,000 THB per megawatt (1 THB/kW). This means that for every megawatt of reduced load, the aggregator pays 1,000 THB. To encourage participation, additional conditions were also added, limiting each participant to being called a maximum of three times per quarter. The constraints on callable duration, size, and cost distribution among participants are summarized in Figure 4, where the figures illustrate the range of capabilities across the participant pool.
To evaluate the effectiveness of participant selection strategies in demand response events, we conducted simulations to provide clear insights into how the load forecasts can be used in practice. We divided the simulations into two distinct scenarios to explore different approaches to calling participants for load reduction. The first scenario represents a case where the number of demand response events is relatively low compared to the number of available participants and their capacity. In contrast, the second scenario involves a higher frequency of demand response events relative to the total participants’ capacity, simulating a more intensive program. These two scenarios were designed to reflect different operational contexts, allowing us to assess the flexibility and robustness of the calling strategies in both low and high-intensity demand response situations.
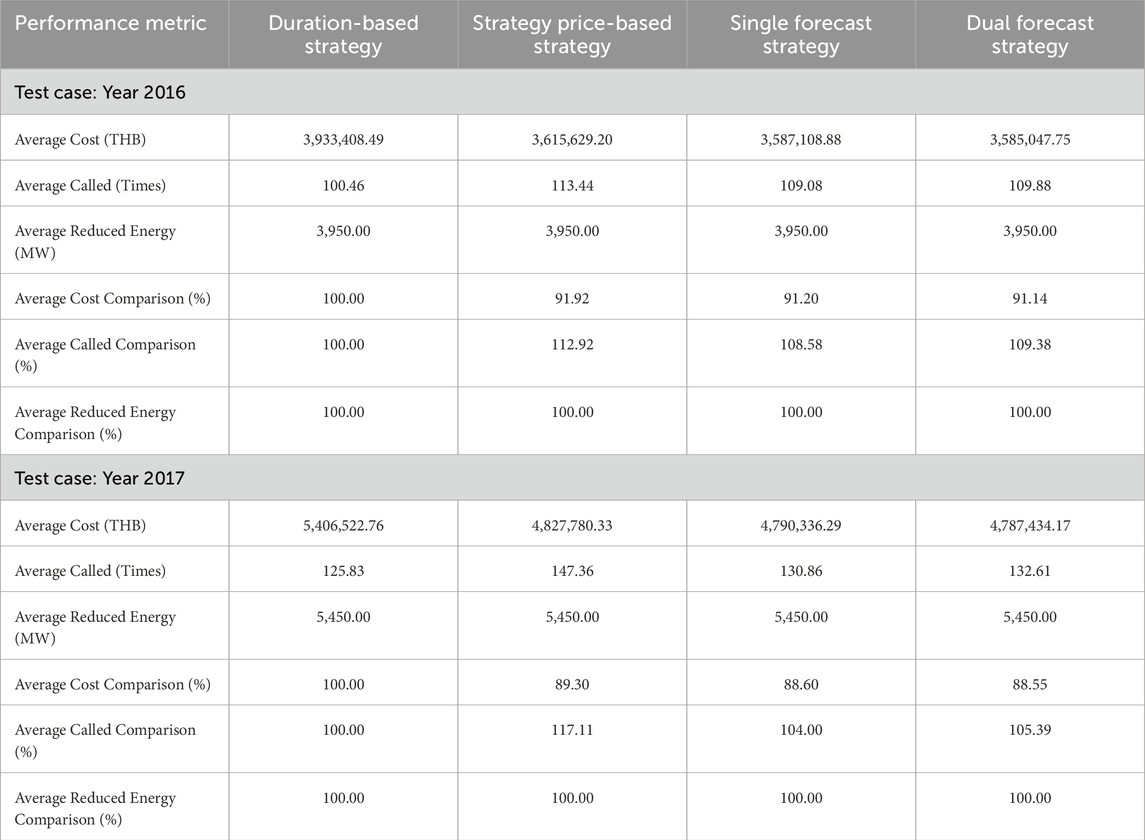
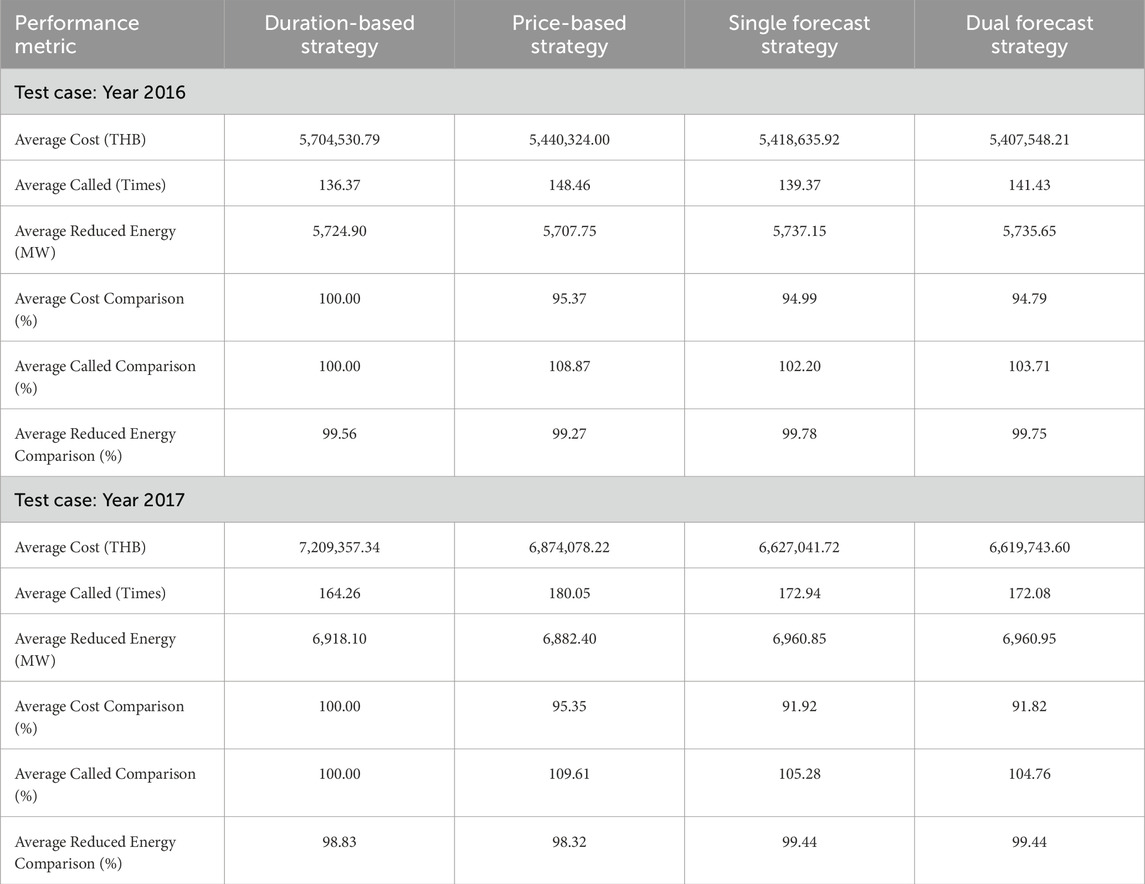
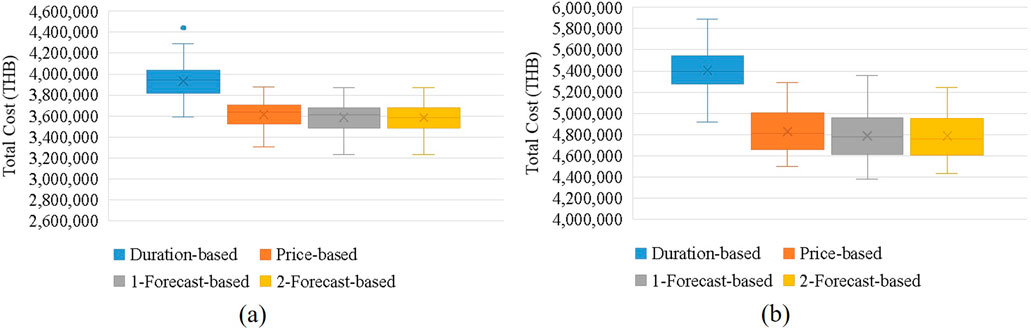
For the simulations, we assumed a penalty of 4,000 THB/MW for any missing load reduction compared to a target load reduction of 50 MW per event, while a pool of approximately 50 participants, with each participant having distinct characteristics and constraints, as described earlier. Each simulation was executed 100 times to calculate average results and provide a comprehensive assessment of the participant selection strategies. This repeated simulation approach allows us to capture the variability in outcomes and ensures that the results are not skewed by any single instance of random variation. The results of each strategy are summarized in Table 1, 2. For further visualization, the boxplots in Figures 5–8 represent a distribution of the cost and the number of calls in each simulation trial.
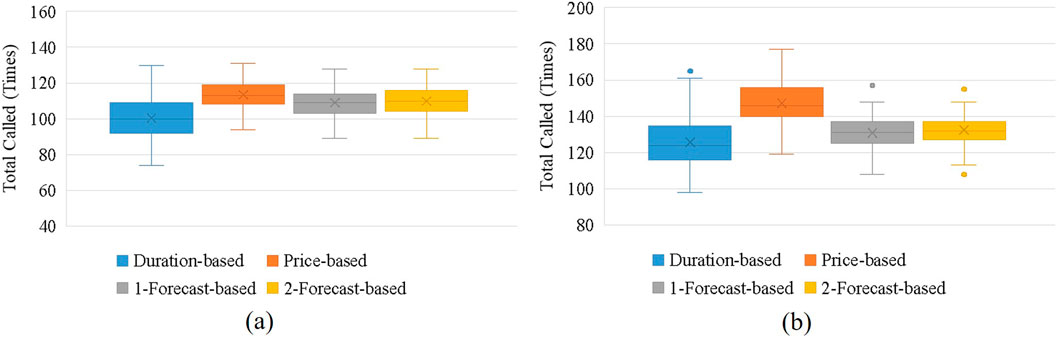
Figure 6. Boxplots of simulated total called in normal scenarios of (a) year 2016 and (b) year 2017.
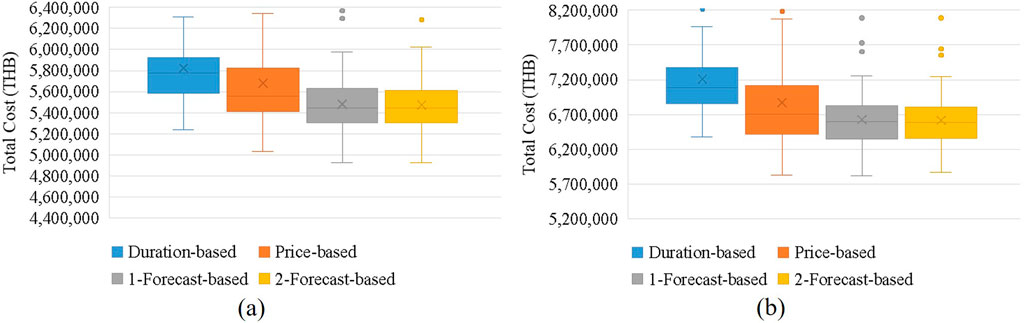
Figure 7. Boxplots of simulated total cost in high-risk scenarios of (a) year 2016 and (b) year 2017.

Figure 8. Boxplots of simulated total called in high-risk scenarios of (a) year 2016 and (b) year 2017.
Based on the results from the normal scenarios, the demand response targets for 2016 involved a total duration of 79 h or 3,950 MW, while for 2017, the targets amounted to 109 h or 5,450 MW. In the high-risk scenarios, the targets for 2016 required a total of 115 h or 5,750 MW, and for 2017, the targets remained at 140 h or 7,000 MW. From these outcomes, the following conclusions can be drawn:
• The duration-based strategy saw the fewest total participant calls, minimizing the number of times participants were called while still meeting the load reduction targets.
• The price-based strategy demonstrated a significant reduction in overall costs by prioritizing the selection of participants with the lowest cost per megawatt. However, this approach is vulnerable to high-risk scenarios, particularly during periods of resource scarcity, where it exhibits the least effective cost reduction compared to other strategies
• The single forecast strategy resulted in slightly better cost savings than the price-based strategy, requiring fewer participant calls overall.
• The dual forecast strategy consistently outperformed the single forecast strategy in all tested scenarios, providing the best results regarding both cost efficiency and minimizing the number of participant calls.
These findings suggest that in normal scenarios where the participant pool is sufficient, aggregators can reliably select participants to meet load reduction targets. In such cases, all strategies demonstrate perfect reliability, consistently fulfilling DRCC targets without issue. However, under high-risk scenarios with tighter resource availability, our forecast-based strategies continue to perform strongly, outperforming the standard price-based approach in both reliability and cost management. As financial penalties can impact overall profitability, especially in more demanding conditions, the forecast-based strategies highlighted in this study offer a more resilient and advantageous solution, ensuring both economic efficiency and dependable performance.
5 Discussion and conclusion
This research has explored various strategies for selecting demand response participants by integrating load forecasting models, aiming to optimize costs and ensure reliable load reductions. The strategies evaluated include the duration-based strategy, price-based strategy, and forecast-based strategies. Among the forecast-based strategies, the study employed XGBoost to predict short-term load profiles and SARIMAX to forecast long-term load duration curves. By combining these two models, the investigation aimed to improve both the accuracy of load forecasts and the efficiency of participant selection.
The duration-based strategy, which prioritized participants capable of sustaining longer load reductions, proved highly effective in reducing the frequency of participant calls. This strategy simplified operational complexity, making it particularly valuable in scenarios that required consistent and sustained load reductions. On the other hand, the price-based strategy was focused on selecting participants offering the lowest cost per megawatt of load reduction. While it demonstrated significant cost-saving potential in normal scenarios, it faced challenges in high-risk scenarios where limited participant availability led to fewer achieved load reductions and overall underperformance.
The single forecast strategy, which relied solely on XGBoost for load profile forecasting, offered a balanced solution by achieving notable cost savings and reducing the frequency of participant calls. Its ability to adapt to fluctuations in load demand reduction made it a more effective option compared to the price-based strategy. However, the dual forecast strategy, integrating XGBoost and SARIMAX, emerged as the most robust and efficient. By leveraging SARIMAX’s long-term load duration predictions to refine XGBoost’s short-term forecasts, this combined approach delivered the highest accuracy in load predictions, minimized costs, and reduced the participant calls. These advantages made the dual forecast strategy the optimal choice across both standard and high-risk scenarios.
In conclusion, this study underscores the critical role of integrating accurate load forecasting with thoughtful participant selection strategies to improve the performance of demand response programs. The dual forecast strategy proves to be the most effective approach, striking a balance between cost efficiency and operational reliability. Future research could focus on further enhancing forecast accuracy by incorporating advanced machine learning techniques, exploring hybrid models that combine the strengths of multiple algorithms, or integrating additional exogenous variables. Moreover, adopting AI-driven strategies, such as reinforcement learning or neural network-based participant selection, could enable real-time and adaptive decision-making, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness in demand response management. Expanding the scope of simulations to include diverse market conditions and participant characteristics would provide deeper insights into the robustness and scalability of these strategies, addressing the growing demands of modern energy systems while ensuring sustainable and efficient grid management.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/robikscube/hourly-energy-consumption/data.
Author contributions
PP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere thanks and high appreciation to King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok (KMUTNB) for research facilities.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbasi, R. A., Javaid, N., Ghuman, M. N. J., Khan, Z. A., Ur Rehman, S., and Amanullah, (2019). “Short term load forecasting using XGBoost,” in Advances in intelligent systems and computing (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1120–1131.
Ahmetoglu, H., and Das, R. (2022). A comprehensive review on detection of cyber-attacks: Data sets, methods, challenges, and future research directions. Internet Things 20, 100615. doi:10.1016/j.iot.2022.100615
Alharbi, F. R., and Csala, D. (2022). A seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average with exogenous factors (SARIMAX) forecasting model-based time series approach. Inventions 7, 94. doi:10.3390/inventions7040094
Arunraj, N. S., Ahrens, D., and Fernandes, M. (2016). Application of SARIMAX model to forecast daily sales in food retail industry. Int. J. operations Res. Inf. Syst. 7, 1–21. doi:10.4018/ijoris.2016040101
Behrangrad, M. (2015). A review of demand side management business models in the electricity market. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 47, 270–283. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.033
Belyadi, H., and Haghighat, A. (2021). “Supervised learning,” in Machine learning guide for oil and gas using Python (Elsevier), 169–295.
Blumberg, G., Broll, R., and Weber, C. (2022). The impact of electric vehicles on the future European electricity system – a scenario analysis. Energy Policy 161, 112751. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112751
Chen, T., and Guestrin, C. (2016). “XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system,” in Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (New York, NY, United States: ACM), 785–794.
de Vries, A. (2023). The growing energy footprint of artificial intelligence. Joule 7, 2191–2194. doi:10.1016/j.joule.2023.09.004
dos Santos Junior, L. C., Tabora, J. M., Reis, J., Andrade, V., Carvalho, C., Manito, A., et al. (2024). Demand-side management optimization using genetic algorithms: A case study. Energies 17, 1463. doi:10.3390/en17061463
Dudek, G. (2022). A comprehensive study of random forest for short-term load forecasting. Energies 15, 7547. doi:10.3390/en15207547
Gils, H. C. (2016). Economic potential for future demand response in Germany – Modeling approach and case study. Appl. Energy. 162, 401–415. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.083
Goudarzi, A., Li, Y., Fahad, S., and Xiang, J. (2021). A game theory-based interactive demand response for handling dynamic prices in security-constrained electricity markets. Sustain. cities Soc. 72, 103073. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2021.103073
He, W. (2017). Load forecasting via deep neural networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 122, 308–314. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2017.11.374
Liao, X., Cao, N., Li, M., and Kang, X. (2019). “Research on short-term load forecasting using XGBoost based on similar days,” in 2019 international conference on intelligent transportation, big data and smart city (ICITBS) (IEEE).
Mei, S., Tan, Q., Liu, Y., Trivedi, A., and Srinivasan, D. (2023). Optimal bidding strategy for virtual power plant participating in combined electricity and ancillary services market considering dynamic demand response price and integrated consumption satisfaction. Energy Oxford, Engl. 284, 128592. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.128592
Mellouk, L., Boulmalf, M., Aaroud, A., Zine-Dine, K., and Benhaddou, D. (2018). Genetic algorithm to solve demand side management and economic dispatch problem. Procedia Comput. Sci. 130, 611–618. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2018.04.111
Mohanty, S., Panda, S., Sahu, B. K., and Rout, P. K. (2022). “A genetic algorithm-based demand side management program for implementation of virtual power plant integrating distributed energy resources,” in Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering (Singapore: Springer Singapore), 469–481.
Musbah, H., and El-Hawary, M. (2019). “SARIMA model forecasting of short-term electrical load data augmented by fast Fourier transform seasonality detection,” in 2019 IEEE Canadian conference of electrical and computer engineering (CCECE) (IEEE).
Nebey, A. H. (2024). Recent advancement in demand side energy management system for optimal energy utilization. Energy Rep. 11, 5422–5435. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2024.05.028
Panda, S., Mohanty, S., Rout, P. K., Sahu, B. K., Parida, S. M., Samanta, I. S., et al. (2023). A comprehensive review on demand side management and market design for renewable energy support and integration. Energy Rep. 10, 2228–2250. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2023.09.049
Semmelmann, L., Henni, S., and Weinhardt, C. (2022). Load forecasting for energy communities: a novel LSTM-XGBoost hybrid model based on smart meter data. Energy Inf. 5. doi:10.1186/s42162-022-00212-9
Silva, C., Faria, P., and Vale, Z. (2023). Rating and remunerating the load shifting by consumers participating in demand response programs. IEEE Trans. industry Appl. 59, 2288–2295. doi:10.1109/tia.2022.3224414
Sonsaard, P., Ketjoy, N., and Mensin, Y. (2023). Market strategy options to implement Thailand demand response program policy. Energy policy 173, 113388. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113388
Stede, J., Arnold, K., Dufter, C., Holtz, G., von Roon, S., and Richstein, J. C. (2020). The role of aggregators in facilitating industrial demand response: evidence from Germany. Energy policy 147, 111893. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111893
Tarmanini, C., Sarma, N., Gezegin, C., and Ozgonenel, O. (2023). Short term load forecasting based on ARIMA and ANN approaches. Energy Rep. 9, 550–557. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2023.01.060
Vagropoulos, S. I., Chouliaras, G. I., Kardakos, E. G., Simoglou, C. K., and Bakirtzis, A. G. (2016). “Comparison of SARIMAX, SARIMA, modified SARIMA and ANN-based models for short-term PV generation forecasting,” in 2016 IEEE international energy conference (ENERGYCON) (IEEE), 1–6.
Xu, G., Song, S., Li, Y., Lu, Y., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2024). Application of deep reinforcement learning in electricity demand response market: demand response decision-making of load aggregator. MethodsX 12, 102735. doi:10.1016/j.mex.2024.102735
Zhang, H., Chen, B., Li, Y., Geng, J., and Zhao, W. (2022). Research on medium- and long-term electricity demand forecasting under climate change. Energy Rep. 8, 1585–1600. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2022.02.210
Zhou, F., Page, L., Perrons, R. K., Zheng, Z., and Washington, S. (2019). Long-term forecasts for energy commodities price: what the experts think. Energy Econ. 84, 104484. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2019.104484
Keywords: demand response, load aggregation management, load forecast, xgboost model, SARIMAX model
Citation: Prakobkaew P and Sirisumrannukul S (2025) Load aggregation management strategies for demand response: a dual forecasting approach for cost minimization. Front. Energy Res. 13:1511207. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2025.1511207
Received: 14 October 2024; Accepted: 25 April 2025;
Published: 15 May 2025.
Edited by:
Haifeng Qiu, Nanyang Technological University, SingaporeReviewed by:
Yunting Yao, Nanjing Normal University, ChinaLeo Raju, SSN College of Engineering, India
Copyright © 2025 Prakobkaew and Sirisumrannukul. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Somporn Sirisumrannukul, c29tcG9ybi5zQGVuZy5rbXV0bmIuYWMudGg=
 Pokpong Prakobkaew
Pokpong Prakobkaew Somporn Sirisumrannukul
Somporn Sirisumrannukul