- 1Institute of Land Engineering and Technology, Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd., Xi’an, China
- 2Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, Shaanxi, China
- 3Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd., Xi’an, China
Introduction: The gully erosion control and land construction project was a major land improvement project implemented by human beings to increase the cultivated land area and improve the quality of cultivated land, and the implementation of the project had a great intervention and influence on the carbon cycle.
Methods: The microcosm experiment was carried out to reveal carbon cycle process of maize photosynthetic carbon in reconstructed soils during gully reclamation using a14C continuous labeling technique. The experimental soil came from Nanniwan Town, Yan’an City.
Results: The distribution ratios of photosynthetic carbon in plants, roots and reconstructed soils were 83.96%–85.19%, 9.47–10.55% and 5.49–5.62%, respectively. It was revealed that the renewal rates of the dissolved organic carbon (DOC), microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and soil organic carbon (SOC) in reconstructed soils were 6.72%–14.64%, 1.70%–7.67% and 0.73%–1.99%, respectively.
Discussion: The distribution and transformation of maize photosynthetic carbon had a greater impact on the changes in the DOC and MBC that SOC. It was found that the mineralization rate of maize photosynthetic carbon in reconstructed soils was higher than 0.6 μg/g·d after construction, but with the extension of cultivation time, it slowed down, the decreasing rate increased, and finally stabilized at about 0.15 μg/g·d.
Introduction
Photosynthetic carbon was an important part of the carbon cycle in the atmosphere–plant–soil system and is the main source of soil organic matter (SOM). This was closely related to changes in the atmospheric environment and soil quality (Zhao et al., 2020). Its photosynthesis was the driving force to promote and support the entire ecosystem, driving the matter and energy cycle of the entire biosphere (Hu et al., 2021). Approximately 10%–40% of the photosynthetic products generated during plant growth were distributed underground for root growth, and carbon was released into the soil environment in the form of rhizodeposition, and was used by rhizosphere microorganisms as part of Microbial biomass carbon (MBC), or stored in the soil pools in the form of soil organic carbon (SOC) (Byeon et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2021). In addition, some plant-assimilated carbon was returned to the atmosphere via plant and rhizosphere microbial respiration (Li et al., 2016; Li et al., 2021). Different plant species had an impact on the input of photosynthetic carbon (Song, 2020a).
In 2012, with the support of the China Ministry of Land and Resources, the gully erosion control and land construction project began to be implemented in Yan’an, Which was typical area of loess hilly and gully region (Yu et al., 2020). This project focuses on the construction of dam systems, restoration of old dams, and transformation of saline-alkali land and idle land in barren gullies (Jin, 2014). It was a new mode of gully management that integrates development and ecological construction. Through main measures such as damming and repairing canals, padding ditches, and covering the soil, the soil of the surrounding slope was cut off and filled into the gully, which then becomes relatively flat through mechanical action (Jin et al., 2012). Subsequently, the surface layer of gully after regulation was covered with 30–50 cm of fertile soil. The project reconstructed degraded and inefficient soil, transformed the soil in poor condition into soil suitable for life to survive and multiply, and improved the quantity and quality of cultivated land (Liu et al., 2013). The reconstructed high-quality land was used for crop-growing, which effectively maintained water and soil resources, ensured regional food security, improved agricultural production conditions and ecological environment, and had a great intervention and influence on the carbon cycle (Li et al., 2019). It can be seen that the development of gully reclamation project is of great significance for local food security and ecological environment protection. In the process of promoting urbanization in China, the construction land needed for urban construction continues to increase, and the red line of ensuring 1.8 billion mu of arable land cannot be broken through (Qiao et al., 2023). Carrying out “land renovation project” was obviously an innovative way to solve this contradiction. In 2022, the scale of land renovation funds increased to 81.03 billion yuan in China. It covers an area of 1,913,900 hm2 (Zhang et al., 2019).
As the main crop for reconstructed soils in the Loess Plateau, maize’s photosynthetic products enter the soil through root deposition, and the slight change in its underground distribution will affect the input of photosynthetic carbon in the reconstructed soils. Therefore, in this study, soil before and after construction was selected as a comparison, carbon isotope (14C-CO2) continuous labeling was applied to explore the input of maize photosynthetic carbon and its distribution in different carbon pools, and the distribution, transformation and underground input rule of maize photosynthetic carbon were quantified. This will provide data support for the reconstruction soil maize ecosystem underground carbon cycle process research. With the development of land regulation projects, the amount of reconstructed soils will also increase. Clarifying the carbon cycle rule of reconstructed soils is of great significance for a comprehensive understanding of plant-soil-microbial interaction, regional carbon cycle and sustainable land use.
Materials and methods
Collection and treatment of test soil
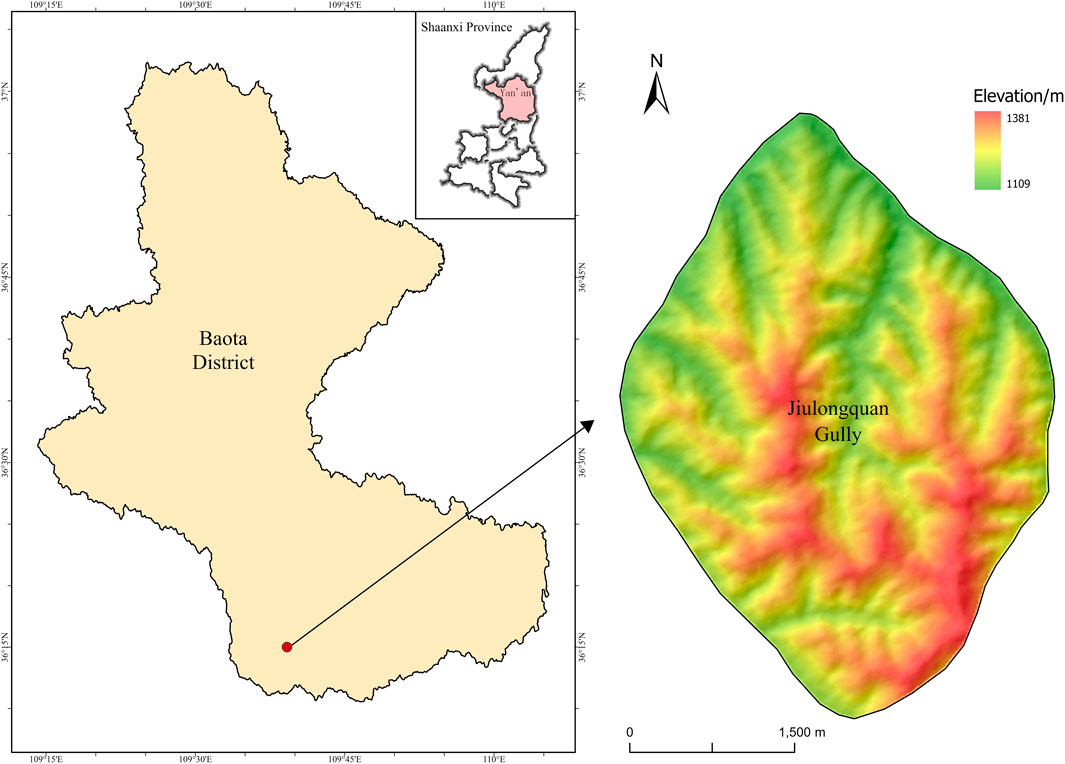
The soil tested in this experimental study was collected from the Jiulongquan gully reclamation area of Nanniwan Town, Baota District, Yan’an City in Loess Plateau (Figure 1). The average temperature in the gully watershed is 8.1°C, the annual rainfall is 530–600mm, and the frost-free period is 120–140 days. The thickness of the soil layer is 0.4–5.0 m in gully. The soil is developed on the loess and shale parent material, with obvious profile layers. The soil upper part (0–60 cm) is dense and the lower part (60–80 cm) has obvious viscosification (Ma et al., 2020a). The mean soil grain size distribution from 18 samples were described as follows: jiulongquan gully: clay (<0.002 mm; 6.3%), silt (0.002–0.05 mm; 66.3%) and sand (>0.05 mm; 27.4%), mengjia gully: clay (<0.002 mm; 5.7%), silt (0.002–0.05 mm; 59.1%) and sand (>0.05 mm; 35.2%) (Ma et al., 2020b). Both are silty loam soil. The two gullies belong to Nanniwan watershed. The main crops are maize, there are abandoned land, barren grass land and damaged forest land in Mengjia gully. Jiulongquan gully is the main gully, which is 9.8 km long, and the valley width is generally between 250 and 500 m. The gully erosion control and land construction project has been implemented in stages. The total construction scale was 662.96 hm2. The completion time was 2014 at the earliest and 2020 at the latest. Mengjia gully is a branch gully, which is 8.3 km long and 120–150 m wide (Lei et al., 2024). The project has not been implemented. The both gully approximately 1 km apart have similar climates, channel shapes, and soil conditions.
The sampling times were April 2023. Using the method of spatial replaced time, the control soil that was collected in Mengjia gully (N36°15′48″∼36°19′13″, E109°40′22″–109°42′41″). The soil in the tilled layer (0–20 cm) was collected 3 years after construction (completed in 2020), and 9 years after construction (completed in 2014) in Jiulongquan gully (N36°14′40″∼36°19′25″, E109°35′50″∼109°39′50″). All samples were transported back to the laboratory placed in incubators. Ice plates and ice cubes sealed with ziplock bags are placed at the bottom, around and top of the incubator. Part of the sample (1 kg) was immediately passed through a nylon screen with a aperture of 2 mm, mixed, sealed and stored in a refrigerator at 0°C–4°C away from light for DOC and MBC, the other part was naturally air-dried for SOC and other soil physicochemical properties determination, and the rest of the soil sample was used for the layout of cultivate test.
Labelling and culture experiments
The experiment was conducted at the Fuping pilot base of Shaanxi Institute of Land Construction and Land Engineering Technology. The size of the cultivation pots was 10 cm × 20 cm of PVC material pipe. Five kilograms of soil were placed in each cultivation pot. Thirty days after planting in the maize field, maize plants showing the same growth pattern were selected and transplanted into cultivation pots. Nine pots were planted, three of which were the control group (soil collected from Mengjia gully), three pots were from the 3-year construction group and three pots were from the 9-year construction group (soil collected from jiulongquan guly). After the maize was transplanted, all treatments were watered 500 mL every 3 days. The cultivation pots were placed in an artificial climate room in order to label the cultures in a closed system with a labelling test time of 100 days. Light was provided for 12 h per day (8:00–20:00), and the plants were maintained at a relative humidity of 80%–90%. Continuous labelling of carbon isotopes (14C-CO2) was self-generated by a reaction of NaHCO3 (1 mol•L-1) and HCL (1 mol•L-1). The CO2 concentration in the greenhouse was maintained at about 300–350 μmol·L-1 by controlling the addition amount (Ge et al., 2012).
Research methods
After 100 days of marked culture, destructive sampling was performed, the maizewas cut along the base, and shoots and roots were collected. The soil attached to the root system was put into a CaCl2 (0.01 mol•L-1) solution, shaken gently, and then washed with distilled water. After the crowns and roots greened, they were dried to a constant weight. SOC and DOC were determined using a German TOC/TN analyser (MultiC/N 3100). Soil microbial carbon was determined using the chloroform fumigation-K2SO4 extraction method, and 14C in the soil was determined using the method proposed by Wu et al. (Wu and O'Donnell, 1997).
Microsoft Excel software was used for data processing, and SPSS 22 software was used for statistical analysis. The significance of differences among different treatments was tested by one-way ANOVA.
Results and analysis
Distribution of maize photosynthetic carbon in plants, roots and soil
Distribution of 14C in plants and roots
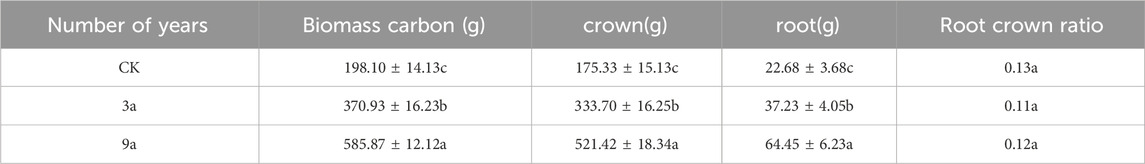
The 14C contents of the aerial parts, roots, and soil after 80 d of labelling and culturing were shown in Table 1. Before gully reclamation, the total biomass carbon of maize was 198.10 g/plant, the carbon content of crown was 175.33 g/plant, and the carbon content of root was 22.68 g/plant. After 3 years of reclamation, the total biomass carbon content, crown carbon content, and root carbon content of maize were 370.93, 333.70 t and 37.23 g/plant, respectively. After 9 years of reclamation, they were 585.87, 521.42 and t 64.45 g/plant respectively. When compared with the control experiment, the total biomass carbon, crown carbon content, and root carbon content of maize increased by 87.24%, 90.33%, and 64.15% after 3 years of reclamation. After 9 years of reclamation, they were seen to have increased by 57.95%, 56.25%, and 73.11%, respectively. However, the root-shoot ratios of maize before and after the project were very similar, indicating that the implementation of the project had a negative impact on maize roots.
By calculating the proportion of photosynthetic carbon in maize crowns and roots, The experiments indicated that about 83.96%–85.19% of maize photosynthetic carbon was used for the synthesis of assimilation products, such as stems, leaves and other tissues, 9.47%–10.55% still remained in the root system, and about 5.49%–5.62% was stored in the soil in the form of SOM.
Distribution of 14C in SOC and root deposition rates
By measuring and analysing the content of photosynthetic carbon distributed underground, 14C-SOC was 114.34, 209.04 and 348.22 mg·kg-1 before, 3 years after reclamation, and 9 years after reclamation, respectively. Compared with the control, 14C-SOC increased by 82.82% and 66.58% after 3 and 9 years of reclamation, respectively. The efficiency of maize in converting assimilated carbon to SOC through rhizosphere deposition was expressed as the ratio of soil 14C-SOC to maize carbon content. The conversion of SOC differed before and after construction, but the rhizosphere deposition rate was very similar, with ratios ranging from 5.35:1 to 5.62:1.
Distribution and renew maize photosynthetic carbon in active SOC
Distribution of 14C in active SOC pools
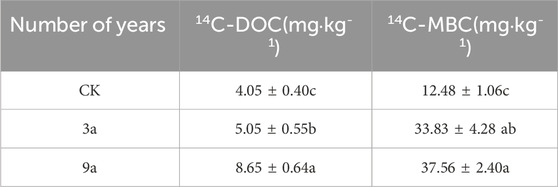
The 14C-DOC was 4.05, 5.05, and 8.65 mg·kg-1 before, 3 years after, and 9 years after reclamation, respectively. Compared with the control, the content of 14C-DOC increased by 24.69% after 3 years of gully reclamation and 71.29% after 9 years. Through a correlation analysis of 14C-SOC and 14C-DOC, we found a significant positive correlation between the both (R2 = 0.91, P < 0.01). The 14C-MBC were 12.48, 37.56, and 33.83 mg·kg-1 before, 3 years after, and 9 years after gully reclamation, respectively. Compared with the control, the 14C-MBC increased by 171.03% after 3 years of reclamation and 11.02% after9 years (Table 2).
Renew of 14C in active SOC
The 14C-DOC/DOC ratios were 6.72%, 7.73%, and 14.64% before, 3 years after, and 9 years after reclamation, respectively. Compared with the control, 14C-DOC/DOC increased by 15.03% and 89.39% after 3 and 9 years of reclamation, respectively. Before, 3 years after, and 9 years after gully reclamation, the 14C-MBC/MBC ratios were 1.70%, 7.19%, and 7.67%, respectively. 14C-MBC/MBC increased by 322.94% and 14C-MBC/MBC by 6.67% at 3 and 9 years following gully reclamation. The soil microbial content increased significantly after gully reclamation, and the rate of increase showed a decreasing trend. After 9 years of project implementation, maize root input contributed the most to soil soluble organic carbon. In the evaluated period, the values of 14C-DOC/DOC of maize were all greater than 14C-MBC/MBC (Table 3).
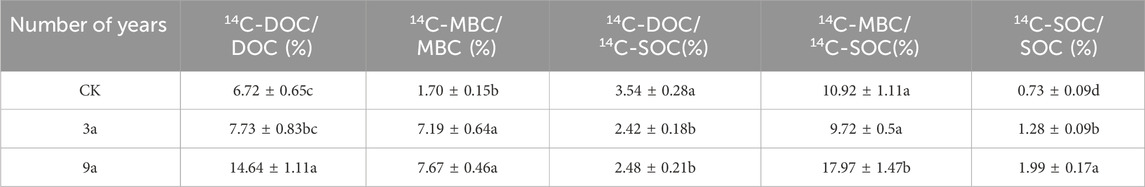
Table 3. The distribution ratio of photoassitable carbon in reconstructed soils organic carbon pool.
The ratios of 14C-DOC/14C-SOC were 3.54%, 2.42%, and 2.48% before, 3 years after, and 9 years after gully reclamation, respectively. 14C-MBC/14C-SOC were 10.92%, 9.72%, and 17.97% after 3 and 9 years of gully reclamation. The proportions of 14C-DOC/14C-SOC and 14C-MBC/14C-SOC in the soil decreased after 3 years but began to increase again after 9 years.
14C-SOC/SOC represents the renewal rate of SOC, and the 14C-SOC/SOC ratios were 0.73%, 1.28%, and 1.99% before, 3 years after, and 9 years after gully reclamation. Compared with the control, the 14C-SOC/SOC increased by 75.34% after 3 years and 55.49% after 9 years, respectively. As the project implementation time increased, the renewal rate of organic carbon increased, but the renewal rate slowed.
Mineralization dynamic characteristics of the maize photosynthetic carbon
Dynamic analysis of 14C mineralisation
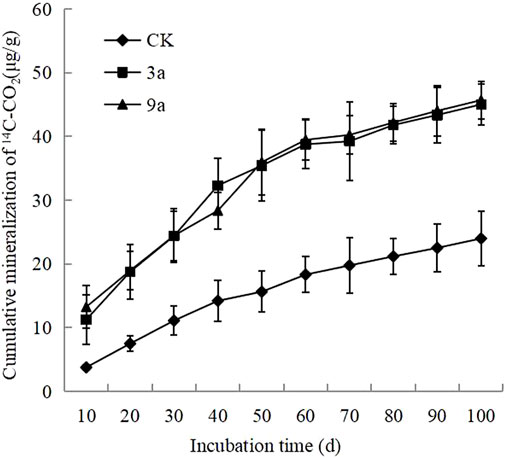
During the experimental period, the accumulated mineralised carbon of maize photosynthetic carbon in the soil was the highest 7 years after gully reclamation (45.69 μg/g). Photosynthetic carbon was the lowest at 23.98 μg/g before gully reclamation. There was no significant difference in the cumulative mineralisation after three and 7 years of gully reclamation, but the cumulative mineralisation three and 7 years after gully reclamation was nearly double the level before construction (Figure 2).
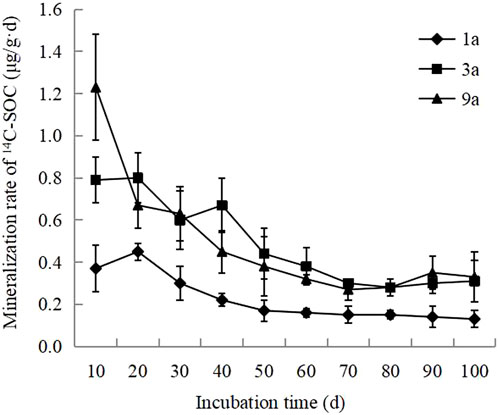
During the early stages of cultivation (0–20 days), the mineralisation rate of 14C-SOC was faster after 3 and 7 years of reclamation. The levels gradually stabilised after 60 d of culture. In the early stage of cultivation, the mineralisation rate was faster after 3 and 9 years of gully management, with both greater than 0.6 μg/g·d, gradually decreased in the middle stage, and the decreasing rate increased and stabilised at about 0.3 μg/g·d after 60 days. The mineralisation rate of photosynthetic carbon in the soil before reclamation was relatively slow, below 0.4 μg/g·d. After a brief increase, it continued to decrease, and finally stabilized at about 0.15 μg/g·d (Figure 3). Regardless of how long after the project was implemented, the mineralisation rate of Photosynthetic carbon in the reconstituted soil was fast during the early stage of cultivation, continued to rise, and gradually stabilised during the middle stage of cultivation. However, this difference was not significant during the later stages of cultivation.
The cumulative mineralisation of the original SOC in the soil and the cumulative mineralisation of 14C-SOC are shown in Figure 4. The cumulative mineralisation of SOC was not very different before construction and after 3 years, but both were significantly different after 9 years of construction.

Figure 4. Cumulative mineralisation of original SOC and photosynthetic carbon input into reconstructed soils.
Dynamic changes of 14C in the active SOC pool
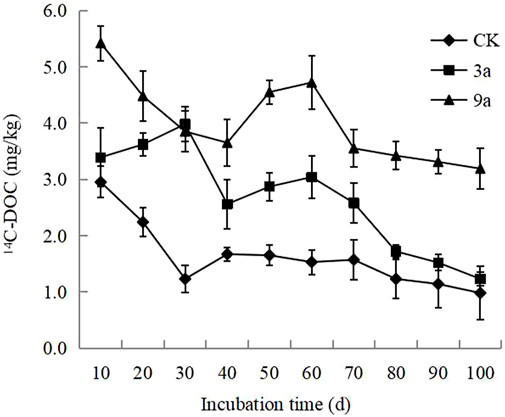
During the culture period, the dynamic changes in 14C-DOC were relatively large and did not follow a particular trend. Different construction years showed significant differences in the mid-cultivation period, and the reconstructed soils 7 years after construction in the later period of cultivation were significantly different from those without construction and after 3 years. In general, the content of 14C-DOC was relatively low, only 0.98–5.42 mg·kg-1. (Figure 5).
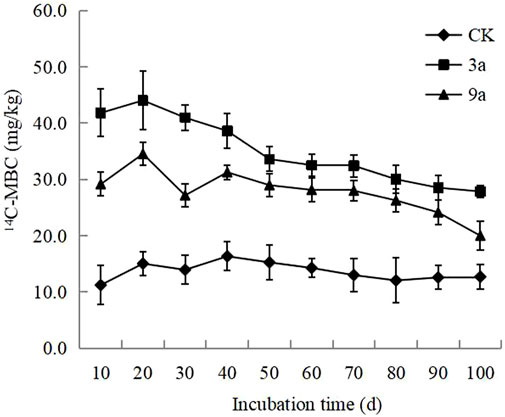
During the experimental period, 14C- MBC in the different construction years tended to be stable. In the early stages of cultivation, the range of change was large and then decreased until it stabilised. With a decrease in the available carbon sources in the soil, 14C-MBC showed a slow decreasing trend. The content of 14C-MBC during the culture period without construction was 11.21–16.32 mg·kg-1, that of the culture period 3 years after construction was 30.01–44.02 mg·kg-1, and that of 7 years after construction was 19.98–34.52 mg·kg-1, and the difference between different construction years was significant (Figure 6).
Discussion
Effects of different construction years on the distribution of photosynthetic carbon in plants, roots and reconstructed soils
In this study, the proportion of photosynthetic carbon fixed in the plants, roots and soil after the end of the growing period of maize is similar to that of previous studies on rice, ryegrass, wheat and forage (Lu et al., 2004; Kuzyakov and Schneckenberger, 2004; Lu et al., 2005; Hütsch et al., 2002; He et al., 2008). The photosynthetic production capacity of maize was not the same in different construction years, but the root-shoot ratio was very close (0.11–0.13), and the rhizosphere deposition efficiency was similar. This may be because during the process of carbon input from maize photosynthetic carbon into the ground, a part of carbon was returned to the atmosphere through plant respiration and rhizosphere microbial respiration, and the construction mainly affected this part of carbon, while the effect on root-shoot ratio was negligible. After a certain number of years of construction, with the increase of planting years, the soil gradually ripened (organic matter content>10 g·kg-1, soil salt content<1 g·kg-1, soil erosion<1,000 t·(km.a)−1), creating a good condition and foundation for the conversion of photosynthetic carbon. The distribution of photosynthetic carbon in the SOC pools in the reconstructed soils increased, but the increase amplitude decreased with the soil ripening. In the long run, Compared to barren gullies, soils under gully management had higher levels of photosynthetic carbon. This may be due to the implementation of organic land reconstruction and irrigation and drainage projects to regulate farmland groundwater level, ensured reasonable water content of farmland layer, prevented natural disasters such as drought and flood and soil erosion, improved soil quality, provided high-quality microenvironmental conditions for maize plant growth and root respiration, and enhanced the photosynthetic production capacity of maize. These changes conducived to the accumulation of SOC (Feng et al., 2022). In the loess Plateau, the mixing of sand and soft rock can be reconstructed to form a “soil” with good water and fertility preservation, which can reduce soil erosion and improve the soil carbon sequestration capacity of sandy land (Guo et al., 2023). In the area of bare rock and gravel land, soil reconstruction can be carried out with sand, shale and other materials, which can solve the problems of barren land, water leakage and fertilizer leakage in the region, and was conducive to soil carbon sequestration (Lei et al., 2022). All these proved that soil reconstruction to improved soil quality and ecological environment was conducive to soil carbon sequestration. The gully erosion control and land construction project reduced the sediment transport of the basin by about 10%, and increase the soil layer thickness and soil fertility of the cultivated land (Song, 2020b). In addition, various fertilization measures also increased the biomass of maize to varying degrees, thus increasing the input of SOC (Wan et al., 2021).
Distribution of maize photosynthetic carbon in soil active organic carbon pool
DOC and MBC were the main destinations for new carbon in the soil activated carbon pool and were closely related to the release of CO2 and CH4 via soil respiration. This also explained that DOC and MBC were often used as indicators to characterize soil active organic carbon, and were also considered to be sensitive indicators to evaluate the response of land use type change to SOC (Kuzyakov and Jones, 2006). MBC only accounts for 1%–5% of SOC, but the size of MBC reflects the activity of microorganisms and the rate of turnover of SOM and nutrients. MBC can control the accumulation and loss of SOC through the decomposition and transformation of input SOM (Gil-Sotres et al., 2005). During the growth period of maize, the renewal rates of DOC and MBC were 14.64% and 7.67% respectively, while SOC was 1.9%, indicating that the input of photosynthetic carbon into maize rhizosphere had a greater impact on the change of DOC and MBC contents than SOC, which was basically consistent with previous studies (Wang et al., 2004). This may be because the rhizosphere secretion was an important source of DOC during the growth of maize, and it was also a raw material for the growth of soil microorganisms, thus affecting the dynamic changes of DOC and MBC. The 14C-DOC/DOC of maize were all greater than 14C-MBC/MBC, indicating that the effect of construction on DOC was greater than that of MBC. This may be due to the fact that water resources were controlled mainly through irrigation and drainage in gully erosion control and land construction project, soil water content changed greatly before and after reconstruction, and DOC was more affected by water content than MBC. In addition, it was found that maize growth would significantly affect 14C-DOC and 14C-MBC, which may be due to the higher photosynthetic productivity and root biomass of maizein the reconstructed soils system, and the increase of available carbon sources to soil microorganisms, thus changing the content of rhizosphere deposited carbon as well as the population and quantity of soil microorganisms (He et al., 2008).
Mineralisation and dynamic changes of maize photosynthetic carbon in the SOC pool
It was generally believed that the depolymerisation and dissolution of SOC are prerequisites for its mineralisation. Some studies indicate that the mineralisation of SOC was carried out by microorganisms and was affected by many factors, such as temperature, water, soil properties and plant communities (Karhu et al., 2022). Previous studies have shown that increases in atmospheric CO2 concentration and temperature do not increase the accumulation of SOC, but accelerated the turnover rate of SOC (Fang et al., 2022). Soil carbon mineralization rate was negatively correlated with soil clay content. Due to different litter and root exudates of different plant communities, the SOC in soil also change (Yang et al., 2022). During the incubation period of this study, the cumulative mineralization amount of 14C-CO2 continued to increase, and the mineralization rate gradually decreased and stabilized. This was because the engineering disturbance in the early stage of construction was large. With the increase of construction years, the physical and chemical properties of soil changed, the soil quality gradually improved, and the mineralization rate gradually stabilized. In the early stage of experiment, the mineralization rate of the soil tested was relatively fast, mainly because the SOC and DOC in the soil in the early stage were decomposed rapidly, and a large amount of nutrients were released rapidly, which promoted the microbial activity. However, with the extension of cultivate time, the easily decomposed components in the soil began to turn to the components that were difficult to decompose after being used up by microorganisms, and the mineralization rate slowed down. This was similar to the research conclusion of Zhang P. et al. (Zhang et al., 2011).
During the experimental period, the variation of 14C-DOC fluctuated frequently, with no apparent pattern. The difference of 14C-DOC was obvious among different construction years. This may be due to the low content of 14C-DOC and the instability of the detected data, or it may be related to the soil structure and soil water content, which was one of the main environmental factors affecting the decomposition, transformation and accumulation of SOM (Schurer et al., 2022). At the initial stage of cultivation, the mineralized amount of 14C-MBC in soil of different construction years was relatively large, and with the progress of cultivation time, it tended to stabilize after 40 days of culture. This was because, water, O2 and nutrients were abundant, and the transformation process was active during the early stages of cultivation. Later, these substances were gradually consumed and reduced, and the transformation process slowed or even stopped. Another reason was that the microbial substrate was gradually utilised in the later stage, the nutrients in the cultivation system were limited, microbial activity was stabilised, and the transformation process tended to be stable (Six et al., 2006).
Conclusion
The results showed that the land reclamation project was beneficial to SOM accumulation and had a strong effect on active organic carbon. In the implementation of land construction projects, some ecological and green technologies such as topsoil stripping, reasonable irrigation and drainage, and organic soil reconstruction should be adopted to form project implementation standards, reduce the impact of engineering measures on soil, increase the accumulation of carbon, and protect the ecological environment while improving soil quality.
In addition, in our experiment, limited to sampling methods, only DOC and MBC represented soil active organic substances were determined, while active organic substances on rhizosphere and root surface, such as root exudates and root exfoliations were ignored. Therefore, we believe that it is also an important direction for our future research to explore the microbial mechanism of mineralization difference between newly imported photosynthetic carbon and original organic carbon.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
NL: Writing – original draft. JZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZS: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. XM: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Scientific Research Item of the Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group (DJNY 2024-38 and DJTD-2023-1); Xi’an Science and Technology Plan Project (22NYGG0001); Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi, China (2023-ZDLNY-52 and 2022ZDLNY02-01).
Conflict of interest
Authors NL, JZ, and ZS were employed by Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Byeon, S., Song, W., Park, M., Kim, S., Kim, S., Lee, H., et al. (2022). Canopy height affects the allocation of photosynthetic carbon and nitrogen in two deciduous tree species under elevated CO2. J. Plant Physiol. 268, 153584. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2021.153584
Fang, R., Li, Y., Yu, Z., Xie, Z., Wang, G., Liu, X., et al. (2022). Warming offsets the beneficial effect of elevated CO2 on maize plant-carbon accumulation in particulate organic carbon pools in a Mollisol. Catena 213, 106219. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2022.106219
Feng, G., Li, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., Xi, B., et al. (2022). Variation of SOC and bulk density during afforestation regulates soil hydraulic properties. Journal of Mountain Science 19(9), 2322–2332.
Ge, T., Yuan, H., Zhu, H., Wu, X., Nie, S., Liu, C., et al. (2012). Biological carbon assimilation and dynamics in a flooded rice-soil system. Soil Biol. Biochem. 48, 39–46. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.01.009
Gil-Sotres, F., Trasar-Cepeda, C., Leirós, M., and Seoane, S. (2005). Different approaches to evaluating soil quality using biochemical properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 37, 877–887.
Guo, Z., Han, J., Zhang, Y., and Wang, H. (2023). Mineralization mechanism of organic carbon in maize rhizosphere soil of soft rock and sand mixed soil under different fertilization modes. Front. Plant Sci. 14, 1278122. doi:10.3389/fpls.2023.1278122
He, M., Meng, F., Shi, Y., and Wu, W. (2008). Estimating photosynthesized carbon distribution and inputs into belowground in a maize soil following 13 C pulse-labeling. Environ. Sci. 29, 446–453.
Hu, J., Tang, Y., Qu, Y., and Zhou, Z. (2021). Global vegetation photosynthetic phenology products based on modis vegetation greenness and temperature: modeling and evaluation. Remote Sens. 13, 5080. doi:10.3390/rs13245080
Hütsch, B., Augustin, J., and Merbach, W. (2002). Plant rhizodeposition-animportant source for carbon turnover in soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sc. 165, 397–407. doi:10.1002/1522-2624(200208)165:4<397::aid-jpln397>3.0.co;2-c
Jin, Z. (2014). The creation of farmland by gully filling on the Loess Plateau: a double-edged sword. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 883–884. doi:10.1021/es405392c
Jin, Z., Cui, B., Song, Y., Shi, W., Wang, K., Wang, Y., et al. (2012). How many check dams do we need to build on the Loess Plateau? Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 8527–8528. doi:10.1021/es302835r
Karhu, K., Alaei, S., Li, J., Merilä, P., Ostonen, I., and Bengtson, P. (2022). Microbial carbon use efficiency and priming of soil organic matter mineralization by glucose additions in boreal forest soils with different C: N ratios. Soil Biol. Biochem. 167, 108615. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108615
Kuzyakov, Y., and Jones, D. (2006). Glucose uptake by maize roots and its transformation in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 38, 851–860. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.07.012
Kuzyakov, Y., and Schneckenberger, K. (2004). Review of estimation of plant rhizodeposition and their contribution to soil organic matter formation. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 50, 115–132. doi:10.1080/03650340310001627658
Lei, N., Han, J., Zhang, Y., Sun, Z., Li, Y., and Xia, L. (2024). The formation mechanism of soil interflow in loess hill gully. Water 16, 2371. doi:10.3390/w16172371
Lei, N., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., and Chen, T. (2022). Components of respiration and their temperature sensitivity in four reconstructed soils. Sci. Rep-Uk 12, 6107. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-09918-y
Li, L., Dong, J., Xu, L., and Zhang, J. (2019). Spatial variation of land use carbon budget and carbon compensation zoning in functional areas: a case study of wuhan urban agglomeration. J. Nat. Res. 34, 1003–1107. doi:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190508
Li, Y., Zhou, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, M., Zhou, B., Chen, H., et al. (2021). The bloom-forming dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi adopts different growth modes when exposed to short or long period of seawater acidification. Toxins 13 (9), 629. doi:10.3390/toxins13090629
Li, Z., Zhao, B., and Zhang, J. (2016). Effects of maize variety on rhizospheric microbe utilizing photosynthetic carbon. Acta Pedol. Sin. 53, 1286–1295.
Liu, Q., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., and Chen, Y. (2013). Filling gullies to create farmland on the loess plateau. Environ Sci & Technol. 47, 7589–7590. doi:10.1021/es402460r
Lu, Y., Tanabe, A., and Kimura, M. (2004). Contribution of plant photosynthates to dissolved organic carbon in a flooded rice soil. Biogeochemistry 71, 1–15. doi:10.1007/s10533-004-3258-0
Lu, Y., Watanabe, A., and Kimura, M. (2005). Contribution of plant photosynthates to dissolved organic carbon in a flooded rice soil. Biogeochemistry 71, 1–15. doi:10.1007/s10533-005-3258-8
Ma, J., Chen, Y., Wang, H., Wang, H., Wu, J., Su, C., et al. (2020a). Newly created farmland should be artificially ameliorated to sustain agricultural production on the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 31, 2565–2576. doi:10.1002/ldr.3618
Ma, J., Han, J., Zhang, Y., Dong, Q., Lei, N., Liu, Z., et al. (2020b). Temporal stability of soil water content on slope during the rainy season in gully regulation watershed. Environ. Earth Sci. 79, 173–186. doi:10.1007/s12665-020-08921-8
Ma, Z., Bork, E. W., Li, J., Chen, G., and Chang, S. X. (2021). Photosynthetic carbon allocation to live roots increases the year following high intensity defoliation across two ecosites in a temperate mixed grassland. Agr Ecosyst. Environ. 316, 107450. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2021.107450
Qiao, Q., Zhen, Z., Liu, L., and Luo, P. (2023). The construction of ecological security pattern under rapid urbanization in the loess plateau: a case study of taiyuan city. Remote Sens. 15, 1523. doi:10.3390/rs15061523
Schurer, R., Hijnen, W., and Wal, A. (2022). The significance of the biomass subfraction of high-MW organic carbon for the microbial growth and maintenance potential of disinfectant-free drinking water produced from surface water. Water Res. 209, 117898. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2021.117898
Six, J., Frey, S., Thiet, R., and Batten, M. (2006). Bacterial and fungalcontributions to carbon sequestration in agroecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 70, 555–569. doi:10.2136/sssaj2004.0347
Song, M. (2020a). Effect of nitrogen addition with different chemical forms on dynamics of photosynthate using 13CO2 tracing in an alpine grassland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 40, 145–154.
Song, M. (2020b). Effect of nitrogen addition with different chemical forms on dynamics of photosynthate using 13CO2 tracing in an alpine grassland. Acta Ecol. sin. 40, 145–154.
Wan, H., Wen, S., Wang, X., Li, Y., Zhang, H., Gao, M., et al. (2021). Effects of long-term straw return on SOC fractions and enzyme activities in a double-cropped rice paddy in South China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 20(1), 236–247. doi:10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63347-0
Wang, G., Zhou, L., Zhan, X., and Wang, H. (2004). Dynamics of dissolved organic matter and its effect on metal availability in paddy soil: field micro-plot trials. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 24, 858–864.
Wu, J., and O'Donnell, A. (1997). Procedure for the simultaneous analysis of total and radioactive carbon in soil and plant materials. Soil Biol. Biochem. 29, 199–202. doi:10.1016/s0038-0717(96)00300-8
Yang, S., Jansen, B., Absalah, S., Kalbitz, K., Chunga Castro, F. O., and Cammeraat, E. L. (2022). Soil organic carbon content and mineralization controlled by the composition, origin and molecular diversity of organic matter: a study in tropical alpine grasslands. Soil Till Res. 215, 105203. doi:10.1016/j.still.2021.105203
Yu, Y., Jin, Z., Chu, G., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Effects of valley reshaping and damming on surface and groundwater nitrate on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Hydrol. 584, 124702. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124702
Zhang, B., Sun, P., Jiang, G., Zhang, R., and Gao, J. (2019). Rural land use transition of mountainous areas and policy implications for land consolidation in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 29, 1713–1730. doi:10.1007/s11442-019-1687-x
Zhang, P., Wei, T., Jia, Z., Han, Q., and Ren, X. (2011). Effects of straw returning on SOC and carbon mineralization in semi-arid areas of southern Ningxia, China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(12), 2518–2525.
Keywords: photosynthetic carbon, reconstructed soils, gully erosion control and land construction project, soil labile organic carbon, 14C continuous labeling
Citation: Lei N, Zhang J, Sun Z and Mu X (2025) Transformation of maize photosynthetic carbon in reconstructed soils. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1498089. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1498089
Received: 18 September 2024; Accepted: 07 April 2025;
Published: 29 April 2025.
Edited by:
Martin Siegert, University of Exeter, United KingdomReviewed by:
Xiaoyan Song, Northwest A & F University, ChinaHuijun Li, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2025 Lei, Zhang, Sun and Mu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Na Lei, bGlueWUyMzIzQDEyNi5jb20=
 Na Lei
Na Lei Jing Zhang1,3
Jing Zhang1,3