- 1Pingdingshan Vocational and Technical College, Pingdingshan, China
- 2Pingdingshan University, Pingdingshan, China
The rapid development of digital economy provides necessary technical support for green and low-carbon transformation, and it is of great significance to explore the impact of digital economy on green and low-carbon development for the sustainable development of the economy and society. Balanced panel data of 30 provinces and cities from 2005 to 2021 are used to construct a dual machine learning model for empirical analysis. It is found that digital economic development can reduce the regional carbon emission intensity and promote green and low-carbon development. The mechanism test shows that digital economic development significantly promotes regional green low-carbon development through the knowledge spillover dimension. The heterogeneity analysis shows that the level of green low-carbon development in the central region is significant at the 1% level, while the levels in the eastern and western regions are not significant. A government with less fiscal pressure has a more significant effect on green low-carbon development.
1 Introduction
The low-carbon effect of the digital economy is an area of focus for scholars. As an important engine of economic development in today’s world, the rapid development and application of the digital economy have profoundly changed the operation mode and industrial pattern of various industries and also played an important role in boosting employment and investment and stimulating consumption (Guo et al., 2023; Tang et al., 2022). In the era of information technology, the digital economy has become an important driving force for high-quality economic development (Yeo and Jung, 2024). National Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zones are China’s opportunity to follow the digital era (Wang and Shao, 2024), implement special regional economic policies with Chinese characteristics, and provide an experience that can be learned, replicated, and scaled up to promote the development of the digital economy, among other things. Because they give full play to the policy benefits of national-level comprehensive big data pilot zones and promote the radiation-driven and demonstration-led role of the pilot zones in the regional digital economy, the digital economy has been developing steadily and rapidly. Driven by the dual-wheel drive of the mega-market and new technology R&D and innovation (Dian et al., 2024), the development momentum of China’s digital economy is getting stronger and stronger.
Green low-carbon development must realize the transformation of industries from high carbon to low carbon (Busch et al., 2018). The Chinese government attaches great importance to green low-carbon development and sustainable development and clearly proposes to accelerate the construction of a green low-carbon and recycling development economic system, establish and improve the mechanism of green low-carbon development, accelerate the comprehensive green transformation of economic and social development, and promote the development mode of ecological priority, conservation, and intensification through a sound ecological and environmental governance system (Wang and Chang, 2014). With the booming development of the digital economy, digital means are fully utilized to promote low-carbon transformation in all fields of the economy and society. In recent years, the international community has gradually increased its attention to green and low-carbon development. Among them, 40% of the carbon dioxide emissions in the United States come from power plants. In order to reduce carbon emissions, the United States issued the US Clean Power Plan in 2015. Since then, the carbon dioxide emissions of various states in the United States have significantly decreased (Davis et al., 2016), but there are significant differences in emissions between states (Gurney et al., 2016). Compared to physical laws, the digital economy has a structural advantage of data-driven systematic emission reduction, which helps reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
It should be noted that the industries related to the digital economy are mostly low-carbon industries (Zhang et al., 2022), which themselves are characterized by low-carbon emissions, and by replacing high-carbon industries in the process of their rapid development, they can not only promote regional industrial upgrading but also greatly reduce the level of regional carbon dioxide emissions (Bai et al., 2023). In this regard, some scholars have constructed a regional digital economy development index using a series of indicators, such as the number of regional Internet users and the value added of the information industry, and used spatial econometric modeling to study and discuss how the development of the digital economy can reduce the level of regional carbon emissions (Abban et al., 2025). In the long run, increased digital economy infrastructure investment can bring the effect of regional carbon emission level reduction. However, some scholars believe that the rapid development of the digital economy represented by the information industry can lead to a surge in electricity consumption, increasing the level of regional carbon emissions (Salahuddin and Alam, 2015).
By combining through the existing research, it can be found that some literature has paid attention to the impact of the digital economy on the environment. At present, there are not many studies on the relationship between the development of the digital economy and carbon emissions, and the research methods are relatively simple. The existing research primarily focuses on measurement methods and results of the scale of the digital economy, which require further improvement. Therefore, the possible innovations in this article are as follows: First, the research object will focus on the National Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zone and explore its unique role in promoting green and low-carbon transformation. This study deeply analyzes how the economic policy of this special region promotes the development of green and low-carbon industries and the effect of regional carbon emission reduction, which makes up for the lack of the combination of digital economy and policy effect in the existing literature and enriches the theoretical understanding of the interaction between digital economy and regional low-carbon development. Second, the dual machine learning model provides a more accurate and dynamic policy evaluation tool. This article analyzes the long-term dynamic effects of the digital economy development on the low-carbon transition and provides a new perspective on the long-term low-carbon contribution of the digital economy.
The follow-up arrangements are as follows: The second part focuses on the theory of the impact of the National Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zone on the provincial green and low-carbon development; The third part introduces the model design, variable selection, and data source of dual machine learning. The fourth part analyzes and discusses the empirical results and discusses the relevant mechanism analysis and heterogeneity analysis. The research conclusions and policy suggestions are given in the conclusion.
2 Theoretical mechanisms
The National Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zone is an area designated by the Chinese government to promote the digital economy and promote the innovation and application of big data technology. Its goal is to promote the digital transformation of the regional economy and society through policy support and technological innovation. Green and low-carbon development is intended to achieve the coordinated development of the economy and the ecological environment by improving energy efficiency, reducing carbon emissions, and promoting the transformation of industrial structures (Busch et al., 2018).
Through the implementation of pilot policies, the National Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zone not only promotes the development of the digital economy but also provides policy experience for green and low-carbon development. Policy innovations in the pilot zone, such as green data centers, smart energy management systems, and low-carbon transportation, can provide examples for other provinces to learn from and promote. Through cross-regional policy cooperation, experience sharing, and demonstration effects, the government will accelerate the implementation of successful policies in the pilot zones at the provincial level. The big data-driven carbon emission monitoring and management system implemented in the pilot zone can be promoted at the provincial level, thereby promoting the implementation of low-carbon policies in the region. The development of big data technologies and green and low-carbon technologies has the potential for cross-regional cooperation (De Gennaro et al., 2016). Provincial-level regions can carry out in-depth cooperation with national-level big data comprehensive pilot zones, share low-carbon technology research and development results, and optimize the efficiency of energy and resource utilization through big data platforms to promote green and low-carbon cooperation between regions.
The increased application of digital technology in all aspects of society promotes the digitalization and greening of infrastructure (Feng et al., 2024) and reduces carbon emission intensity. On the one hand, the digital economy, based on its platform and sharing characteristics, optimizes the industrial structure and releases structural dividends by promoting the reasonable flow and allocation of production factors, upgrading the level of low-carbonization of traditional industries, and fostering new low-carbon industries through the use of big data technology (Peng and Dan, 2023), which improves the quality and efficiency of economic development and helps low-carbon transformation of the economy (Ren et al., 2022). The development of the digital economy uses new media to disseminate low-carbon concepts, which helps promote the formation of green and low-carbon consumption concepts and lifestyles of residents (Xiang et al., 2022). The development of the sharing economy profoundly affects the low-carbon values and behaviors of the general public and pushes for the formation of a green and low-carbon social atmosphere. The popularization of digital fiber optics, mobile Internet, and smartphones allows the public to access various information conveniently and efficiently, which in turn makes network public opinion become an informal means of environmental regulation (Wu et al., 2021), urging the government and relevant enterprises to reduce pollution and carbon emissions. At the same time, it reduces information asymmetry and transaction costs, improves energy utilization efficiency (Giraudet, 2020), reduces the carbon emission intensity of production and life, and promotes the optimization and transformation of the energy system. Therefore, the rapid development of the digital economy provides important technical means and value concept support for regional low-carbon economic transformation and is an important driving force to promote regional low-carbon transformation.
Hypothesis 1. The digital economy can significantly promote the transition to a low-carbon economy in the region.
Knowledge spillover effects of the digital economy. The theory of biased technological progress holds that technological innovation and progress are the internal energy of economic growth, and new technologies can utilize resources more efficiently and reduce the consumption of carbon energy (Zhen et al., 2021). Knowledge spillover can stimulate the formation and development of innovative ecological industrial systems, promote cross-border knowledge exchange and cooperation among different industries, facilitate the flow of talent elements and cross-learning, and break down industry barriers. Technology spillover effects enhance the efficiency of energy utilization (Zhang et al., 2021). On the one hand, the rapid development of the digital economy has brought rich opportunities and resources for green technology innovation, releasing new dividends of green technology innovation (Zhang et al., 2023), reducing pollution from the source, improving the ability of governance and restoration, and strengthening the environmental supervision, which is an important scientific and technological support to promote the transformation of the regional low-carbon economy. On the other hand, digital technology has the advantage of energy saving and environmental protection in the three aspects of production, life, and ecology and helps low-carbon economic transformation in many ways. In the field of production, digital intelligent manufacturing can improve the efficiency of resource utilization; in the field of life, the rise of new modes of telecommuting and other modes reduce transportation energy consumption (Roberto et al., 2023). In the ecological field, big data and artificial intelligence make the “innovation compensation” exceed the “compliance cost,” which effectively helps environmental governance.
Hypothesis 2. The digital economy can significantly promote regional green and low-carbon development through knowledge spillover.
3 Methodology
3.1 Model building
Traditional causal inference models for policy effect assessment, such as the double difference model (DID), require more demanding sample data as well as a sufficiently large amount of data to satisfy fixed-effect and parallel trend tests. Then, the synthetic control method (SCM), although it can construct a virtual control group that meets the parallel trend, only applies to univariate disposition groups, not to the multivariate disposition group situation. Therefore, this article employs dual machine learning and shifts the research approach to the application of machine learning in the field of causal inference (Chernozhukov et al., 2018; Knittel and Stolper, 2021) as a way to improve the limitations of traditional models.
Compared with traditional causal inference models, dual machine learning has unique advantages in variable selection and model estimation and is also more applicable to the research questions in this article. First, green and low carbon is a comprehensive indicator to measure the sustainable development of the region, which is affected by many factors in the economy and society. To ensure the accuracy of the estimation of the policy effect, the interference of other factors on green and low-carbon development should be controlled as much as possible. Dual machine learning uses machine learning and its regularization algorithms to automatically screen among the pre-selected sets of high-dimensional control variables to obtain an effective set of control variables with high prediction accuracy. Furthermore, in the process of digital economic development, nonlinear relationships between variables are the norm, and conventional linear regression may bring about bias in a model setting. In addition, the estimation is not robust enough, while dual machine learning can effectively avoid the problem of model misspecification by virtue of the advantages of machine learning algorithms in dealing with nonlinear data (Farbmacher et al., 2022). The partially linear dual machine learning model used in this study is constructed as follows:
where i is the province; t is the year; Yit is the explained variable, which is green low-carbon development; Event is the explanatory variable, which is the establishment of the Big Data Pilot Zone, which is 1 after the policy implementation; otherwise, it is 0;
Considering that the data volume is a small sample, we continue to construct an auxiliary regression so that the estimated value of the disposal coefficient meets the unbiased assumption:
where m(Xit) is the regression function of the treatment variable on the high-dimensional variable, and the estimated value m(Xit) is also obtained through machine learning; Vit is the error term, and the conditional mean is 0. Based on Equations 1–4, the unbiased estimated coefficient 0 is obtained through the three-step method.
3.2 Variable setting
3.2.1 Dependent variable: green low-carbon development
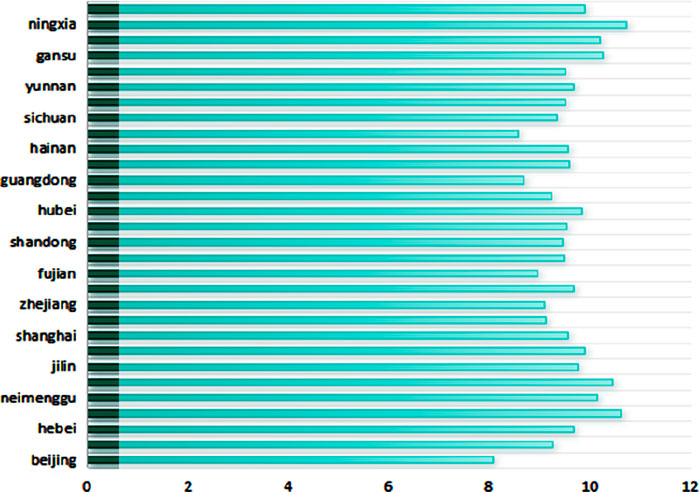
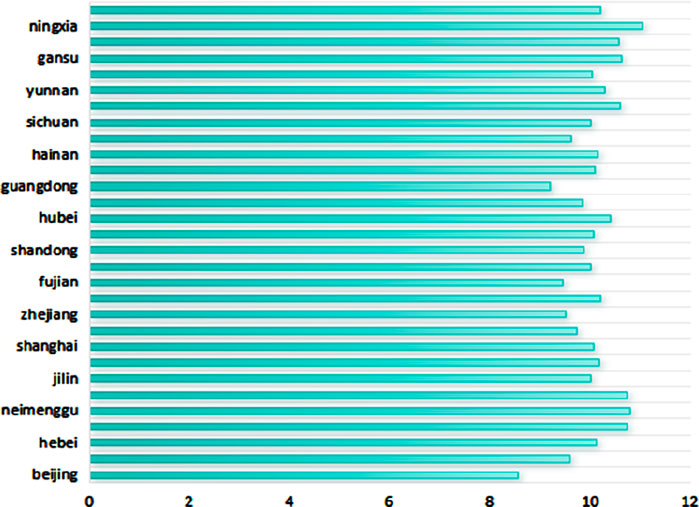
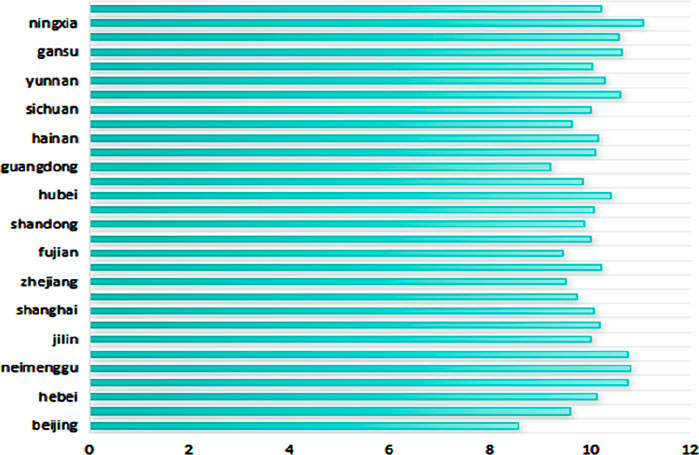
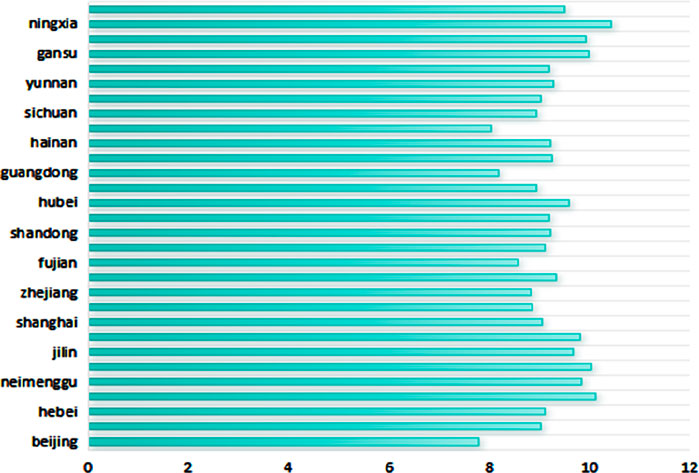
Considering that the development of the provincial digital economy may have some impact on carbon dioxide emissions, this article uses the proportion of total carbon dioxide emissions to provincial GDP to express the level of carbon emissions; that is, carbon intensity is used as a proxy variable for low-carbon green development (GCD). The low-carbon green development situation is shown in Figures 1 to 4.
3.2.2 Explanatory variable: establishment of big data pilot zones
This article assigns a value to the dummy variable (BDZ) based on the time when each province became a pilot zone. Taking into account the approval time of the construction of big data pilot zones and the actual process, the relevant documents in August 2015 put forward “to carry out regional pilots to promote the construction of comprehensive pilot zones of big data in Guizhou and other provinces,” and the construction of comprehensive pilot zones of big data in Guizhou was officially launched in September of the same year. The second group of pilot zone provinces was announced in October 2016. Therefore, this article assigns a value of 1 to the first batch of pilot zones from 2015 and a value of 1 to the second batch of pilot zones from 2016.
3.2.3 Control variables
Economic level (economy). The level of regional economic development reflects, to a certain extent, the level of regional infrastructure services and the development potential of the digital economy, which is one of the elements that constrain the development of the regional digital economy. This study argues that the larger the logarithmic value of the regional GDP per capita is, the more conducive it is to the development of the regional digital economy.
Industrial structure (ind). The main industries for the development of the digital economy often belong to the knowledge-intensive and technology-intensive industries in the tertiary industry, while the primary and secondary industries often belong to the labor-intensive and capital-intensive industries. The industrial structure has an important impact on the digital economy, which is manifested in the upgrading and transformation of the traditional industries and reshaping of the regional industrial structure. The ratio of tertiary industry output to GDP is used to reflect the level of industrial structure in the region. The ratio of tertiary industry output to GDP is used to reflect the level of regional industrial structure.
Social consumption (spending). The digital economy provides consumers with more convenience and choices, and consumers can easily obtain various goods and services through e-commerce platforms, which improves the quality and efficiency of consumption. Therefore, the amount of social consumer goods as a percentage of GDP is used to indicate the level of social consumption in the region.
Fiscal expenditure (policy). The pilot zone is established with the promotion of the local government and the support of the higher level government, so the central government and local governments at all levels will be actively involved in the construction process of the pilot zone, and the government will make its due contribution to the construction of the pilot zone through the exercise of its management functions and coordination rights to better promote the construction of the pilot zone in terms of taxation, procurement, and financial subsidies, etc. However, because the government’s support is not easily quantified, the proportion of total fiscal expenditures to GDP is used to indicate the level of social consumption of the government. Total fiscal expenditure as a proportion of GDP indicates the government’s regulatory behavior: the larger the logarithmic value, the greater the government’s regulatory efforts.
Degree of marketization (md). The digital economy is another form of economy influenced by technology after the development of the monetary economy to a certain extent. The degree of its acceptance and development are closely related to the development and popularization of technology in society, while the technology market turnover can show the active degree of regional technology and the degree of transformation of scientific and technological fruits to a large extent. Therefore, the logarithm of technology market turnover is used to indicate the degree of technology acceptance and application by the market.
Scientific research level (srl). The digital economy is inseparable from the information network technology represented by big data and cloud computing, and to a certain extent, the more advanced and mature these information technologies are, the better the digital economy develops. The R&D of a series of technologies cannot be separated from the support of scientific research, so scientific research expenditures can, to a large extent, indicate a certain region’s support for science and technology and thus reflect the region’s scientific research capability through the proportion of regional scientific research expenditures to GDP × 100, which in turn reflects the region’s support for scientific research. Therefore, the proportion of regional scientific research expenditure to GDP × 100 reflects the region’s scientific research capability, which in turn reflects the degree of regional R&D investment in developing the digital economy.
3.2.4 Mechanism variable
This article intends to reveal the mechanism effect of digital economy development affecting green and low-carbon development from the path of knowledge spillover level. The number of invention patents granted usually reflects the innovation vitality and scientific and technological development level of a region. Patents can ensure that the rights and interests of innovators are effectively protected, which in turn improves the enthusiasm for innovation and the possibility of transformation of achievements. The use of mobile Internet access traffic reflects, to a certain extent, the convenience of information exchange and access to knowledge and information, breaking the previous limitations of relying on traditional media to obtain knowledge and information and improving the efficiency of knowledge overflow. Among them, two proxies, regional invention patent authorization (ipa) after natural logarithm and mobile Internet access traffic (itra) after natural logarithm, are used to measure knowledge spillover (KSO).
3.3 Data sources and descriptive statistics
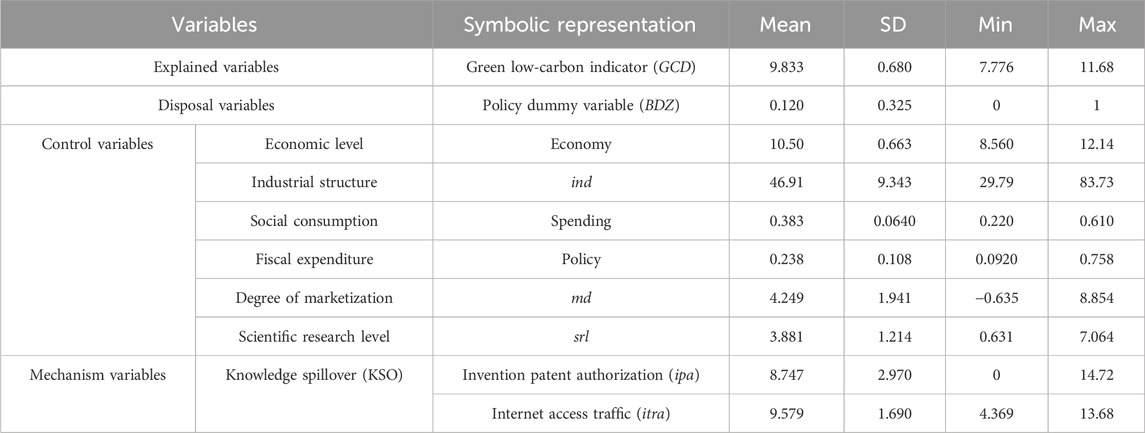
Limited to the conditions of data collection, the sample does not include Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan, or Tibet. Except for the collations and calculations specified, the remaining data used in this article come from the China Statistical Yearbook, the China Regional Statistical Yearbook, and the State Intellectual Property Office. A small amount of missing data is interpolated using the interpolation method. The descriptive statistics of the variables are as shown in Table 1.
4 Results
4.1 Baseline regression
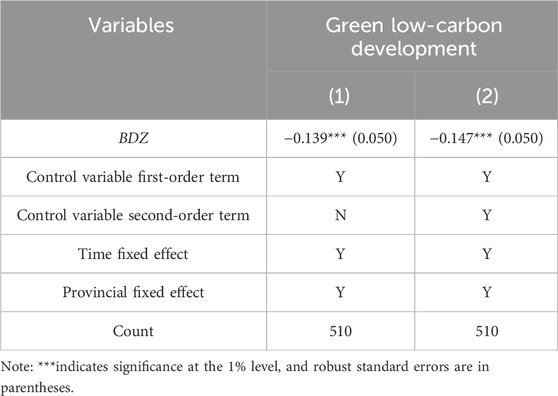
A dual machine learning model is used to estimate the policy effects of establishing a big data pilot zone on green and low-carbon development. Among them, the sample is split using a ratio of 1:4, using the random forest algorithm for the main regression and auxiliary regression prediction solution. The regression results shown in Table 2 column (1) are, in the full sample interval, controlling for individual fixed effects, time fixed effects, and the primary term of the control variable. The regression coefficient of its opening on the green and low-carbon development is negative, and all are significant at the level of 1%, indicating that the Big Data Pilot Zone establishment significantly reduces carbon emissions. On the basis of Table 2 (1), column (2) further adds the quadratic terms of the control variables. The regression results show that the coefficients are still significantly negative, and all of them are still significant at the 1% level. Therefore, establishing the Big Data Pilot Zone can significantly reduce carbon emissions and provide a power guarantee for green low-carbon development. H1 is verified.
4.2 Robustness test
4.2.1 Adjust the sample interval
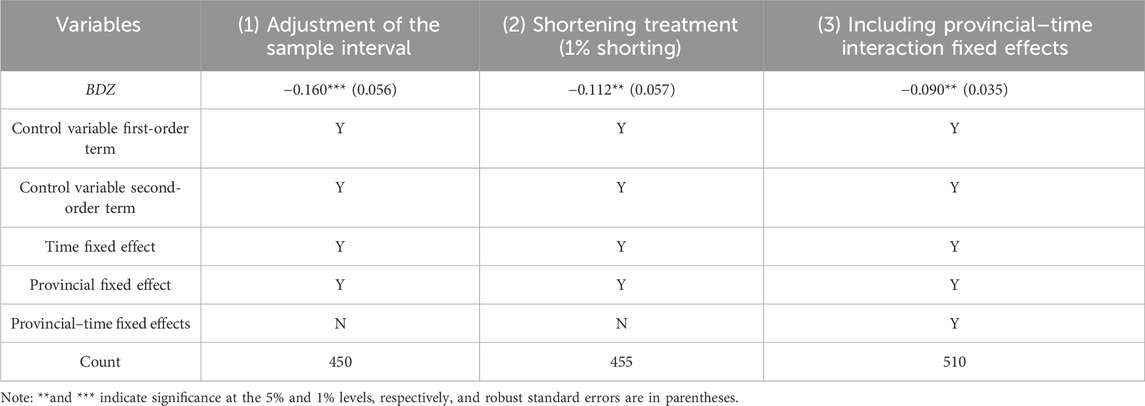
In order to exclude the influence of time-point samples that are far away from the time point of the establishment of the Big Data Pilot Zone, this article restricts the study interval to 2007–2021 to ensure the symmetry of the time zones before and after the establishment of the Big Data Pilot Zone. The results are shown in column (1) of Table 3. The BDZ coefficients are all significantly negative and still significant at the 1% level, indicating that establishing the Big Data Pilot Zone can still significantly reduce carbon emissions and promote green and low-carbon development, which suggests that the results are still robust after adjusting the sample research interval.
4.2.2 Eliminate the influence of outliers
Because outliers in the regression sample may lead to biased estimation results, this article shrinks all variables in the baseline regression, except the disposition variable at the 1% and 99% quantiles, replaces the values above the highest and below the lowest quantiles, and conducts the regression analysis in this way. The specific regression results are shown in column (2) of Table 3, where the BDZ is significant at the 5% level, and the coefficient is negative. The regression results are still robust after removing outliers.
4.2.3 Including province–time interaction fixed effects
On the one hand, there may be some common features among different provinces. On the other hand, based on the geographic location and other relevant factors, different provinces may be influenced by similar political and administrative management systems as well as cultural traditions and social customs, and there are some similarities in policy-making, resource allocation, and urban development. Therefore, this article adds province–time interaction fixed effects on the basis of the baseline regression to control the influence of different provinces over time to improve the explanatory power and predictive ability of the model. The specific regression results are shown in column (3) of Table 3. The regression coefficient of BDZ is negative and significant at the 5% level, indicating that the results of the benchmark regression still hold.
4.2.4 Resetting dual machine learning models
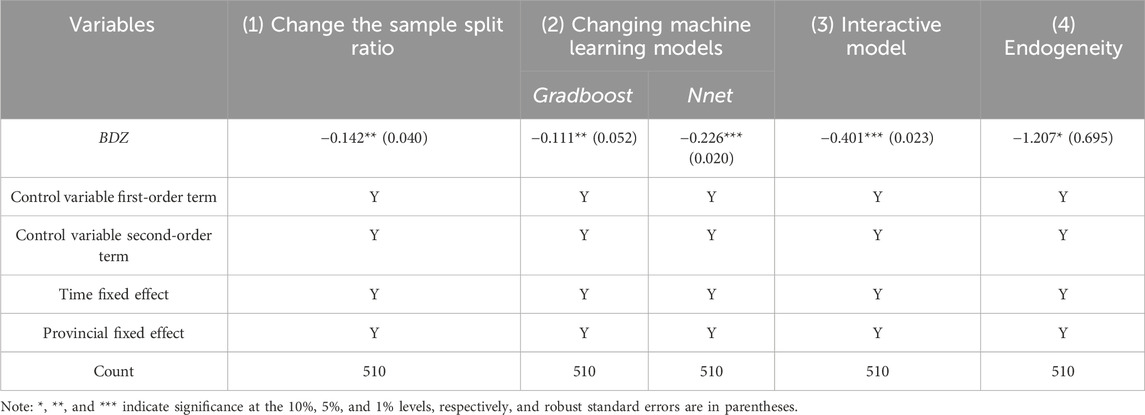
In order to avoid the impact of the dual machine learning model setting bias on the conclusions, this article starts from the following aspects to verify the robustness of the conclusions. First, the sample partition ratio of the dual machine learning model is changed from the previous 1:4 to 1:7 to explore the possible impact of the sample partition ratio on the conclusions of this article; second, the machine learning algorithm is replaced, and the random forest algorithm previously used as a prediction is replaced with gradient boosting tree and Nnet to explore the possible interference of the validation algorithm on the conclusions of this article; lastly, the benchmark regression constructed based on dual machine learning in a partial linear model is analyzed, and there is some subjectivity in the model form setting. Next, this article adopts dual machine learning to construct a more general interactive model to explore the influence of the model setting on the conclusions of this article, and the main regression and auxiliary regression used for analysis are changed as follows.
4.2.5 Dealing with endogeneity issues
Although this article adjusts the research sample interval in the robustness test and considers the factors affecting green and low-carbon development in the control variables as much as possible, it is difficult to avoid the existence of legacy variables due to the different levels of socioeconomic development in various regions and the limitations of data selection, which in turn results in the establishment of a big data pilot zone facing potential endogeneity problems in the process of promoting green and low-carbon development. Therefore, in order to deal with the potential endogeneity problem, the partial linear instrumental variable model of dual machine learning (Chernozhukov et al., 2018) is constructed, and the specific model is set as follows:
where IVit is the instrumental variable of Eventit, and the instrumental variable for the establishment of big data pilot zones is set as the degree of topographic relief of provinces. First, topographic relief is closely related to the construction of transportation facilities. Topographic relief affects the efficiency and cost of transportation, as well as the economic development and resource utilization of the region, so topographic relief is a factor that must be taken into full consideration for establishing the big data pilot area. Furthermore, topographic relief meets the condition of exogeneity for the selection of instrumental variables; that is, as a natural geographic variable, it has a complete exogeneity and is not related to carbon emissions. Moreover, as topographic relief is relatively stable and does not change over time, the interaction term between topographic relief and the time trend term is constructed as a panel instrumental variable to control the change of topographic relief in the time dimension (Nunn and Qian, 2014).
Through column (4) of Table 4, it can be found that the BDZ is still significant and has a negative coefficient at the 1% level when dealing with the endogeneity problem distress. The results indicate that it does not affect the conclusion that establishing the BDZ promotes green and low-carbon development, thus indicating the robustness of the benchmark regression results.
5 Further analysis
5.1 Mechanism test
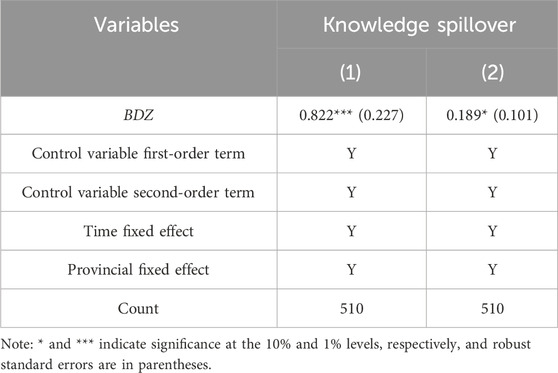
The above results have proved that establishing big data pilot zones can significantly promote green low-carbon development. This article needs to pay more attention to how it is the operational path to promote green low-carbon development. After analyzing the related literature, it is found that establishing big data pilot zones based on the knowledge spillover level is a possible path to explain green low-carbon development. To this end, this section carries out the causal mediation effect analysis of double machine learning, based on machine learning algorithms, to test the conduction mechanism of the establishment of big data pilot zones on green low-carbon development. The specific test results are shown in Table 4. It can be seen that the regression results of different mediation paths are significant at the level of 1% as well as 10% and do not change the conclusions obtained from the benchmark regression.
Establishing the Big Data Pilot Zone not only accelerates the development of China’s digital economy but also compels real enterprises to enhance technological innovation, realizing the effective penetration of innovation and green technology and the deep integration of enterprises. The development of the digital economy brought about by technological innovation and resource-sharing platforms to give enterprises innovative resources and power, green technology innovation, and upgrading of industrial-level interactions are conducive to the development of open innovation among relevant enterprises and promote industry innovation-driven connotative upgrading. The number of invention patents authorized usually reflects the innovation vitality and scientific and technological development level of the region. Patents can ensure that the rights and interests of innovators are effectively protected, thereby increasing the enthusiasm for innovation and the possibility of transformation of results, to a certain extent, responding to the convenience of information exchange and access to knowledge information and improving the efficiency of knowledge spillover, which to a certain extent promotes the upgrading of enterprise sewage technology and reduces carbon emissions.
Table 5 shows the regression results of knowledge spillover. It can be seen that the regression results of the two proxy variables are significantly positive at the 1% level as well as at 10%. It indicates that the development of the digital economy promotes the improvement of technological innovation and effectively reduces the level of carbon emissions. Digital economic development accelerates the transformation of scientific research and innovation results, while production technology innovation can break through the original boundaries of resource allocation, improve the efficiency of raw material use, and promote the effective recycling of resources, thus further controlling and reducing carbon emissions. H2 is verified.
5.2 Heterogeneous analysis
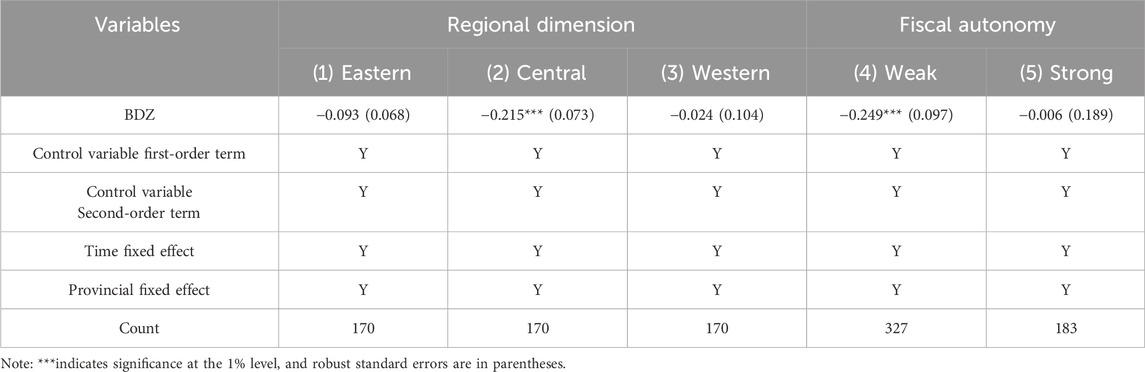
The imbalance and insufficiency of China’s regional development are particularly obvious based on location differences such as geographic location, transportation base, and resource endowment. Based on the research needs of policy and economy, the sample regions are divided into three groups, eastern, central, and western, to test the locational differences in the impact of establishing big data pilot zones on green and low-carbon development.
As can be seen from Table 6, there are obvious differences in the policy effects of establishing national-level big data comprehensive pilot zones on the regional digital economy, with the most significant green and low-carbon effects in the central part of the country and insignificant green and low-carbon effects in the eastern and western parts of the country. There are obvious differences in the policy effects of establishing a comprehensive big data pilot zone on regional green low-carbon development; the most affected Ministry can significantly reduce the level of carbon emissions. The carbon emission reduction effect of the policy effect on the east and west is not significant. The national-level Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zone has achieved significant results in the central region due to the deep integration of high energy-consuming industrial structure and big data technology in its industrialization stage, which can quickly release the potential for energy efficiency improvement. However, in the East, the effects are limited due to the priority of low-carbon industries and limited emission reduction space, while in the West, the policy effects are diluted due to the contradiction between lagging digital infrastructure and industrial absorption.
Fiscal autonomy (also known as fiscal pressure) is an important factor affecting local government development strategy decisions. This study defines fiscal autonomy as the ratio of local government general budget revenue to local government general budget expenditure, divided into two levels: 0%–50% and 50%–100%. Higher fiscal autonomy indicates that the provincial government has greater flexibility in terms of economic development.
The heterogeneity analysis results of the differences in fiscal autonomy are shown in Table 6. For provincial governments with higher fiscal autonomy, their green and low-carbon effects are not significant. This can be attributed to local governments’ excessive pursuit of fiscal revenue and neglect of ecological development, resulting in ineffective carbon emission reduction effects. In contrast, provincial governments with lower fiscal autonomy have shifted their development goals toward pursuing social welfare, paying attention to ecological environment quality, and promoting green and low-carbon development.
6 Conclusion and implications
The conclusion that the development of the digital economy has a significant contribution to regional green and low-carbon development still holds after a series of robustness tests. The development of the digital economy promotes regional reduction of carbon emission intensity and promotes green low-carbon development through knowledge spillovers. Heterogeneity analysis shows that the central provinces have a significant effect on green and low-carbon development, while the eastern and western provinces are not affected by establishing the Big Data Pilot Zone and do not realize green and low-carbon development.
The conclusion leads to the following suggestions: Comprehensively push forward the construction of the digital economy and promote the in-depth integration of the digital economy and regional low-carbon economic transformation. Further increase investment in the construction of digital infrastructure such as 5G networks, edge computing, and big data centers fully support the research and development of the application of blockchain, artificial intelligence, and other digital technologies in improving energy efficiency, emission reduction monitoring, and green manufacturing; focus on the layout of a number of demonstration parks for the in-depth fusion of digital technologies and low-carbon industries so as to lead the digital upgrading of relevant low-carbon industries; explore in-depth the path and mode of the transformation of a regional low-carbon economy empowered by digital technologies.
First, strengthen the connection of regional policies. The eastern region can deploy zero-carbon data centers with conditions, the central region can strengthen the establishment of industrial digital emission reduction funds, and the western region can gradually implement tiered electricity subsidies. Second, establish a verifiable technology promotion mechanism. Establish a carbon emission monitoring platform, requiring parks with an annual energy consumption of over 10,000 tons of standard coal to connect to the national platform for supervision. Finally, design a sustainable path for resident participation. Promote and guide residents to adopt various green digital technologies and services and cultivate a green and low-carbon digital lifestyle. Promote digital means of government affairs, convert travel points such as buses and subways into corresponding shopping vouchers, and achieve more green travel.
As the world’s largest carbon emitter, the success or failure of China’s green transformation has a profound impact on global climate change. The Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zone provides a platform for China to explore new models of environmental governance, promoting more efficient resource utilization and environmental protection. Especially in optimizing energy structure and improving energy efficiency, it will provide important inspiration for other countries, which can help more developing countries achieve sustainable development goals while pursuing economic development. In the future, the international community should strengthen cooperation and share experiences to achieve a broader green and low-carbon transformation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YY: formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing – original draft. ZW: methodology, software, supervision, and writing – original draft. SC: data curation, software, and writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abban, O. J., Rajaguru, G., and Acheampong, A. O. (2025). The spillover effect of economic institutions on the environment: a global evidence from spatial econometric analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 373, 123645. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.123645
Bai, T., Qi, Y., Li, Z., and Xu, D. (2023). Digital economy, industrial transformation and upgrading, and spatial transfer of carbon emissions: the paths for low-carbon transformation of Chinese cities. J. Environ. Manag. 344, 118528. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118528
Busch, J., Foxon, T. J., and Taylor, P. G. (2018). Designing industrial strategy for a low carbon transformation. Environ. Innovation Soc. Transitions 29, 114–125. doi:10.1016/j.eist.2018.07.005
Chernozhukov, V., Chetverikov, D., Demirer, M., Duflo, E., Hansen, C., Newey, W., et al. (2018). Double/debiased machine learning for treatment and structural parameters. Econ. J. 21 (1), C1–C68. doi:10.1111/ectj.12097
Davis, C. B., Bollinger, L. A., and Dijkema, G. P. J. (2016). The state of the states: data-driven analysis of the US clean power plan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 60, 631–652. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2016.01.097
De Gennaro, M., Paffumi, E., and Martini, G. (2016). Big data for supporting low-carbon road transport policies in Europe: applications, challenges and opportunities. Big Data Res. 6, 11–25. doi:10.1016/j.bdr.2016.04.003
Dian, J., Song, T., and Li, S. (2024). Facilitating or inhibiting? Spatial effects of the digital economy affecting urban green technology innovation. Energy Econ. 129, 107223. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107223
Farbmacher, H., Huber, M., Lafférs, L., Langen, H., and Spindler, M. (2022). Causal mediation analysis with double machine learning. Econ. J. 25 (2), 277–300. doi:10.1093/ectj/utac003
Feng, Y., Gao, Y., Hu, S., Sun, M., and Zhang, C. (2024). How does digitalization affect the green transformation of enterprises registered in China’s resource-based cities? Further analysis on the mechanism and heterogeneity. J. Environ. Manag. 365, 121560. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121560
Giraudet, L.-G. (2020). Energy efficiency as a credence good: a review of informational barriers to energy savings in the building sector. Energy Econ. 87, 104698. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104698
Guo, B., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Liang, C., Feng, Y., and Hu, F. (2023). Impact of the digital economy on high-quality urban economic development: evidence from Chinese cities. Econ. Model. 120, 106194. doi:10.1016/j.econmod.2023.106194
Gurney, K. R., Huang, J., and Coltin, K. (2016). Bias present in US federal agency power plant CO2 emissions data and implications for the US clean power plan. Environ. Res. Lett. 11 (6), 064005. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/11/6/064005
Knittel, C. R., and Stolper, S. (2021). Machine learning about treatment effect heterogeneity: the case of household energy use. AEA Pap. Proc. 111, 440–444. doi:10.1257/pandp.20211090
Nunn, N., and Qian, N. (2014). US food aid and civil conflict. Am. Econ. Rev. 104(6), 1630–1666. doi:10.1257/aer.104.6.1630
Peng, Z., and Dan, T. (2023). Digital dividend or digital divide? Digital economy and urban-rural income inequality in China. Telecommun. Policy 47 (9), 102616. doi:10.1016/j.telpol.2023.102616
Ren, S., Li, L., Han, Y., Hao, Y., and Wu, H. (2022). The emerging driving force of inclusive green growth: does digital economy agglomeration work? Bus. Strategy Environ. 31, 1656–1678. doi:10.1002/bse.2975
Roberto, R., Zini, A., Felici, B., Rao, M., and Noussan, M. (2023). Potential benefits of remote working on urban mobility and related environmental impacts: results from a case study in Italy. Appl. Sci. 13 (1), 607. doi:10.3390/app13010607
Salahuddin, M., and Alam, K. (2015). Internet usage, electricity consumption and economic growth in Australia: a time series evidence. Telematics Inf. 32(4), 862–878. doi:10.1016/j.tele.2015.04.011
Tang, G. N., Ren, F., and Zhou, J. (2022). Does the digital economy promote “innovation and entrepreneurship” in rural tourism in China? Front. Psychol. 13, 979027. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.979027
Wang, L., and Shao, J. (2024). Digital economy and urban green development: a quasi-natural experiment based on national big data comprehensive pilot zone. Energy Environ. doi:10.1177/0958305X241238348
Wang, N., and Chang, Y.-C. (2014). The evolution of low-carbon development strategies in China. Energy 68, 61–70. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2014.01.060
Wu, W., Wang, W., Zhang, L., Wang, Q., Wang, L., and Zhang, M. (2021). Does the public haze pollution concern expressed on online platforms promoted pollution control? – Evidence from Chinese online platforms. J. Clean. Prod. 318, 128477. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128477
Xiang, X., Yang, G., and Sun, H. (2022). The impact of the digital economy on low-carbon, inclusive growth: promoting or restraining. Sustainability 14 (12), 7187. doi:10.3390/su14127187
Yeo, Y., and Jung, S. (2024). Assessing the economy-wide impacts of digital transformation in the Korean economy: a social accounting matrix multiplier approach. Telecommun. Policy 48 (10), 102871. doi:10.1016/j.telpol.2024.102871
Zhang, J., Lyu, Y., Li, Y., and Geng, Y. (2022). Digital economy: an innovation driving factor for low-carbon development. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 96, 106821. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106821
Zhang, W., Hong, M., Li, J., and Li, F. (2021). An examination of green credit promoting carbon dioxide emissions reduction: a provincial panel analysis of China. Sustainability 13 (13), 7148. doi:10.3390/su13137148
Zhang, Y., Hong, X., and Wang, Y. (2023). Study on the coupled and coordinated development and evolution of digital economy and green technology innovation. Sustainability 15 (10), 8063. doi:10.3390/su15108063
Keywords: digital economy, green low-carbon, dual machine learning, knowledge spillover, big data
Citation: Yao Y, Wang Z and Cao S (2025) Can establishing the National Big Data Comprehensive Experimental Zone promote green low-carbon development? Evidence from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1520715. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1520715
Received: 31 October 2024; Accepted: 09 May 2025;
Published: 10 July 2025.
Edited by:
Jinyu Chen, Central South University, ChinaReviewed by:
Magdalena Klimczuk-Kochańska, University of Warsaw, PolandFeng Hu, Zhejiang Gongshang University, China
Copyright © 2025 Yao, Wang and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhe Wang, d2FuZ3owOTIxQDEyNi5jb20=
 Yushan Yao1
Yushan Yao1 Zhe Wang
Zhe Wang