- School of Economics and Management, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
The historic convergence of the world situation and China’s development has set the stage for changes in the international environment that have not been seen in a century. In this context, the economic, political, cultural, and social crises are intertwined, and the traditional development that uses ecology and resources as consumables is unsustainable, and the resulting ecological crisis further amplifies the anxiety for social change. With the introduction of China’s comprehensive deepening reform strategy, green governance, as a critical platform to carry the transformation of the shaping of the governance system and the modernization of governance capacity, is in line with and integrated with the construction of the sustainable pattern, and has become a key initiative in response to various crises. While the enthusiasm and enthusiasm for green governance have surged dramatically in the process of its formation and extension, the homogenization of recent years has further widened the differences in development within regions. The convergence of green governance, which rejects the objective directives of the laws of development, has led to an increase in the scale of resource redundancy and a significant decrease in the green effectiveness of many local governments. This paper examines the formation mechanism of the peer effect of green governance in local governments and clarifies the continuity of green governance by sorting out the origins, main contents, and connotations of green governance in local governments. In this study, a scientific definition of green governance is distilled based on the core changes in green governance in the broader historical context. In addition, the study examines the peer effect of local governments in past administrative decisions, and through the analysis of its origins and connotations, clarifies the potential possibilities and environmental influences on local governments’ convergent decisions. On this basis, the study summarizes the senses, external manifestations, and characteristics of the green governance peer effect through the overlap of the green governance + administrative decision-making peer effect at the historical level and the potential correlation and interoperability mechanisms within the two. The study found that green governance is a comprehensive organizational framework activity under integrating various types of decision-making. The characteristic is that the peer effect of green management will encompass all kinds of past decision-making patterns and interest mechanisms. The behavior motivations behind the peer effect must be examined in the context of historical experience to promote increased green governance effectiveness.
1 Introduction
Against the backdrop of a volatile international situation and a significant increase in external uncertainties, the course of human history has entered a period of considerable change unprecedented in a century. The historical intersection between the world’s significant changes and China’s remarkable development has promoted the maintenance and extension of the strategic opportunity period for China’s development. However, the international environment is treacherous, the task of domestic reform, development, and stability are arduous, and multiple issues and contradictions are intertwined, resulting in a significant increase in unpredictable factors. The key to tackling these crises and resolving development risks lies in renewing national governance concepts. Around this issue, the Third Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central Committee adopted the Decision of the CPC Central Committee on Several Major Issues of Comprehensively Deepening Reform, which put forward the critical thesis of promoting the modernization of the national governance system and governance capacity. It made the modernization of the national governance system and governance capacity the “fifth transformation” after the modernization of industry, agriculture, national defense, science, and technology (Bardhan, 2020). As China’s development enters a new era and the main contradictions in Chinese society are transformed, China’s primary national conditions and social practices enable national governance with Chinese characteristics. With a new governance structure and system, federal administration achieves integrated management in the economic, political, cultural, ecological civilization, and social spheres, becoming a concrete, practical tool to deal with economic, political, cultural, environmental, and social crises. And in the modernization and shaping of the national governance system, a construction pattern echoing the Five-in-One has been formed, with a prominent place given to the construction of ecological civilization. The reasons for this are the environmental problems caused by the unbalanced development model that constrain the sustainable development of our economy and society (Liu et al., 2021a), the low quality of products, and the lack of innovative power due to the weak accumulation of industrial knowledge (Liu et al., 2021b), which in turn leads to insufficient political, cultural and social construction. The key to resolving the contradictions between ecological environment and economic development and optimizing the coordinated development of politics, culture, and society lies in enhancing green governance capacity (Thoyre, 2021).
Green governance by local governments has become a key element and core part of national green governance. At present, local governments are forced by the ambiguity of green governance orientation, and there are many chaotic phenomena such as the loss of governance resources and internal conflict in governance competition. This has exacerbated the regional fragmentation of green governance by local governments due to the “blurring of powers and responsibilities and the division of powers.” To overcome this shortcoming, some of the “backward” places hope to follow the example of the whole range of government actions and strategies, thus forming a homogeneous development of green governance, which has to a certain extent revolutionized the model of green governance but has further intensified the struggle between horizontal governments. Based on this, this paper, through the perspective of the historical system, comprehensively composes the connotation of green governance and the historical experience of the peer effect of administrative decision-making, summarizes the formation mechanism of the peer effect of green governance of local governments through the transmutation and integration of the two, and lays down theoretical ideas for regional green governance and integrated arrangement.
Green governance is a microcosm and an essential practice of the Chinese program for global governance and the modernization of the national governance system and capacity, as well as a strategic choice for coordinating the contradictions of China’s domestic development and balancing economic, political, cultural, social, and ecological issues. Local governments, as the key actors and core leaders of green governance, are bound to influence China’s governance pattern with their green governance initiatives and results. However, the strong ‘local characteristics’ of local governments make them biased in understanding the connotation of green governance and balancing green governance with other administrative work, and the centralized decision-making of green governance often affects the path of local transformation and development. Focusing on green governance, we have formed the following research objectives: how to interpret the connotation of green governance and its peer effect? To what extent do green governance assessments and factor inputs contribute to the efficiency of green governance? Is there a peer effect of green governance and what are the sources of the influencing factors? How can green governance peer effects be channeled and implemented? Analyzing these questions can provide a reference for promoting regional cooperation on green governance and strengthening national green governance capacity. Local activities on green governance have been discussed in various countries.
Green governance activities are largely derived from the global construction of sustainable development. With the extension of sustainability activities, it shifted to government-led green administrative activities. And then evolved into green governance. The theory of sustainability (development) originated from the combination of foreign sustainability theory and Chinese development theory. The concept of sustainability was first proposed by Letcher Carson in 1962 in Silent Spring, which argues that the goal of sustainability is to get rid of the environmental pressures caused by the human economy, urbanization, population, and resources, and ultimately to achieve a balanced pattern of growth and development (Rennings and Wiggering, 1997). In 1972, the Club of Rome presented the environmental analysis ‘The Limits to Growth’, which for the first time expanded the concept of sustainability to ‘sustainable economic growth’ and ‘sustainable balanced development’. 1987, the World Commission on Environment and Development officially defined the concept of sustainable development and promoted it as an important term. In 1987, the World Commission on Environment and Development formally defined the concept of sustainability and promoted it as an important term in theory. 21st century, with the decline of China’s crude economic model, China and other developing countries have formed a new green paradigm: sustainable development refers to the process of development that can satisfy the current generation’s real needs without harming the development of future generations, and does not create structural resource hazards to the ability of future generations to satisfy their needs. The theory of sustainable development is based on the three fundamental principles of equity, continuity and commonality, with the ultimate goal of achieving coordinated, equitable, efficient, common and multidimensional development of societies (Zhao, 2017). As a result, countries around the globe have embarked on green governance activities with sustainability as the main theme. In terms of its internal theoretical structure, the theory of sustainable (green) development is in fact a unification of the theory of the limits of economic growth, the theory of the knowledge economy, the theory of sustainable ecology, the theory of the carrying capacity of the population, and the theory of the human-earth system. The theory clearly indicates the dialectical unity and coexistence of development and the environment, and emphasises the mutual constraints and limitations of the two (Li et al., 2020). That is, population expansion requires the reconciliation of human-land conflicts, and population, as an important economic factor, cannot grow indefinitely. In the context of environmental constraints and the limits of economic growth, a knowledge-driven sustainable model will break through the limitations of both sides, which is essentially an economic slowdown in disguise to sustained growth (Opschoor, 2010). The successful practice of the theory of sustainable (green) development is guided by the theory of the perpetuation of resources, the theory of externalities, the theory of the equitable intergenerational distribution of wealth, and the theory of production in the context of human production, material production and environmental production. On the one hand, the real realisation of sustainable development requires the scientific allocation of resources and the guarantee of a constant and stable use of resources. On the other hand, it is important to recognise the economic significance of resources and not to iterate them as free public goods to be used by society. Finally, the ‘development’ of sustainable (green) development still depends on the operation of the theory of production, which generates the real value of resources and distributes this value equitably between present and future generations, i.e., deals with the issues of production and distribution (Deslatte and Stokan, 2019). In this context, the discussion of green governance activities can shed deep light on countries around the globe in order to form a new green governance framework.
An important contribution of this paper is to refine the core connotation of green governance, and through qualitative research and other methods, to sort out the origins of the formation of the peer effect in the past administrative decision-making of local governments, and then refine the connotation of the peer effect of local government decision-making. Under the guidance of peer theory, administrative theory, public management, and other systemic perspectives, and considering the subject and identity characteristics of local governments, we construct the connotation structure of the peer effect of local governments’ green governance along with the research idea of “green governance + peer effect of administrative decision-making = peer effect of green governance”, and identify the outward manifestation and key characteristics of the effect. The research idea is to construct the connotation structure of the local government green governance peer effect and identify the external manifestation and key characteristics of the effect. Using the methods of literature analysis and practical research, we will continue to identify the driving factors of local governments’ green governance peer effect and clarify the whole process of the formation of the green governance peer effect and the path of differentiation of the effect. This will provide new ideas for the global practice of green and sustainable development.
2 Literature review
2.1 Research on green governance
Green governance is a governance activity or process in which all parties cooperate in public affairs based on the principles of mutual trust, mutual reliance, and shared governance, guided by green values, to achieve the harmonious and sustainable development of ‘economy-politics-society-culture-ecology’. ‘The governance activity or process of harmonious and sustainable development. The Government is the core subject and key actor of green governance, and is also the key field for realising the value of green connotation and implementing the new concept of green development (Guo and Chen, 2021). The following literature study focuses on the concept of green governance, quantitative and assessment measures, and research generalisation.
Green governance, as an important part of the theory of socialism with Chinese characteristics, reflects the strategic position of ecological civilization construction in the overall layout of the ‘Five-sphere Integrated Plan’ (Liu, 2017). From a deeper perspective, the fundamental starting point of green governance is to guide society from resource scarcity to environmental sustainability, and from unilateral solicitation and consideration of human needs to bilateral consideration of the environment as an equal subject (Shi and Liu, 2018). Through the overlapping consensus of green values, the optimal construction of a green governance system, and the profound depiction of the spectrum of green governance mechanisms (Shi and Tang, 2019), green governance portrays the development path of social construction in the ‘Five-sphere Integrated Plan’. In the transition from green development to green governance, social consensus, values, behavioral norms, and political mechanisms have gradually guided the formation of green culture and green politics under the linkage of institutional and non-institutional factors, laying the foundation of the cultural system of green governance (Li et al., 2019), and clarifying the direction of the promotion of political construction and cultural construction. In the context of the change of the main contradiction in society and the economic situation entering a new normal, green governance also needs to achieve balanced, coordinated, and compatible development of the economic system based on taking into account the social and ecological systems. Green governance is based on the premise of reversing the trend of ecological and environmental deterioration, achieving high-quality economic construction, and promoting the formation of a synergistic mechanism between the construction of ecological civilization and green development, which opens up a wider development prospect for economic construction under the Five-sphere Integrated Plan approach. It can be seen that green governance is an important deployment of the overall layout of the ‘Five-sphere Integrated Plan’, and is also the practical impetus for the formation of the organic whole of the ‘Five-sphere Integrated Plan’.
With the proposal of the five development concepts, the action path and core connotation of green governance have achieved the condensation and sublimation of regular understanding. The implementation of green governance is not to constrain the economic efficiency of enterprises and society with green regulations but to promote the sustainable development of the economy with green innovation based on coordination, openness, and sharing (Jiang and Guo, 2017). Liao et al. (2019) analyzed the dynamic relationship between science and technology innovation and the coordinating effect of green governance, and found that there is a significant positive and sustained impact of green governance on science and technology innovation, and science and technology innovation will also have a reverse effect on green governance. Sun et al. (2019) used hierarchical regression models to emphasize that green governance affects green innovation and corporate performance, and high-quality green governance helps to promote corporate green transformation. Li and Niu (2017) discuss the practical strategy of green governance and argue that green governance requires enterprises and other micro-bodies to continuously optimize the development structure, highlight innovation and development, and actively respond to the direction of economic-based governance of enterprise reform. In the context of increasing stakeholder pressure and tightening development resource constraints, green innovation has become a key behavior of green governance (Kong et al., 2016). In summary, at the strategic and theoretical levels, green governance links the ‘Five-sphere Integrated Plan’ construction requirements. At the tactical and operational levels, green governance implements the five development concepts. As a public affairs activity of the government, green governance creates an atmosphere of green innovation for society and promotes the scientific development of the ‘Five-sphere Integrated Plan’ of the whole society based on the productivity and creativity generated by green innovation.
The connotation of green governance is initially highlighted: green governance is based on the principle of mutual trust and mutual reliance, and the principle of building, governing, and sharing, with the green value as the guiding concept, through green technological innovation and institutional change, and efficient cooperation in all aspects of social affairs, to achieve economic, political, cultural, social and ecological harmony and sustainability governance process (De Lucia, 2015). In this process, the government, as the core of green governance, guides or leads enterprises to carry out green innovation through management functions and other means of governance, and then realizes the construction of a new pattern of ‘Five-sphere Integrated Plan’ through social changes and progress triggered by green innovation, which leads to the integrated development of politics, culture, society and economy. The green technology and productivity triggered by green innovation subvert the traditional development model of sloppy, thus truly realizing the green development of society. The core connotation of green governance indicates that the essence of green governance is the link relationship between the government and enterprises in the process of green development, the government participates in the capacity of an investor, while enterprises face society in the image of an exporter, and the outward effectiveness of green governance is precisely the degree of promotion of green innovation. As a result, the green transformation chain of green governance - green innovation - and green development is formally formed. In this process, if green governance wants to achieve the goal of green development of society, the key lies in more micro-factors and micro-units to strengthen green innovation to support the need for green development. The specific micro-factors and micro-units are precisely enterprises, and the landing point of green governance is to take the government’s call, policy action, and political guidance as the main, to encourage and support enterprises to carry out green transformation and innovation, and ultimately to achieve the green upgrading of social governance, and thus the direct outputs and effects of green governance is the increase and change of the enterprise’s green innovation capacity. From the perspective of high-quality economic and social development, green governance is not only the first step in the green transformation chain, but also a marker for judging the green progress and innovation of the society, and the scientific measurement of green governance will be of great significance. Considering that the core of green governance is a governance process, the government, as the initial promoter and builder of the green transformation chain, guides the maturity of green governance activities through the input of a large amount of government resources, and the final product is the results of green innovations and the atmosphere of green innovation in the society, i.e., the green governance opens up the second link in the green transformation chain.
The concept of green governance has been enriched with economic and social development, led by the connotation that the essence of green governance is sustainable innovation, and that this conceptual perspective originates from the social dimension, i.e., it emphasizes the broad coverage of green governance and green innovation. Green governance stimulates the formation of a national renewable economy and leads to a significant increase in manufacturing production through technological innovation (Brunel, 2019). Domestic scholars also interpret green governance at the macro and micro levels: at the macro level, it is emphasized that green governance is a combination of innovation-driven and green development strategies, and a strategic expression of green innovation, i.e., green governance is an important way to deal with ecological problems such as environmental degradation, and development problems such as industrial competitiveness (Schiederig et al., 2012). At the micro level, green governance refers to the corresponding actions taken by enterprises on their own economic performance and social environmental protection (He et al., 2019). It can be seen that the definition of green governance by foreign scholars focuses on the perspective of ‘sustainability’, while domestic scholars are mostly based on the perspective of ‘unity of economy and environment’. The two views are the same, and both emphasize that green governance can achieve the goal of sustainable development at the social level, as well as bring about changes and promotion in the economy and other fields.
To review the current state of research on green governance based on a holistic view perspective, this study utilizes Citespace with Vos-viewer for the work of combing and cleaning the relevant literature. Literature data were collected from the web of science core database. Choose green governance as the keyword. A total of 2,316 articles were retrieved, and 1,523 valid records were retained for analysis after subject selection and software clear automatic cleaning.
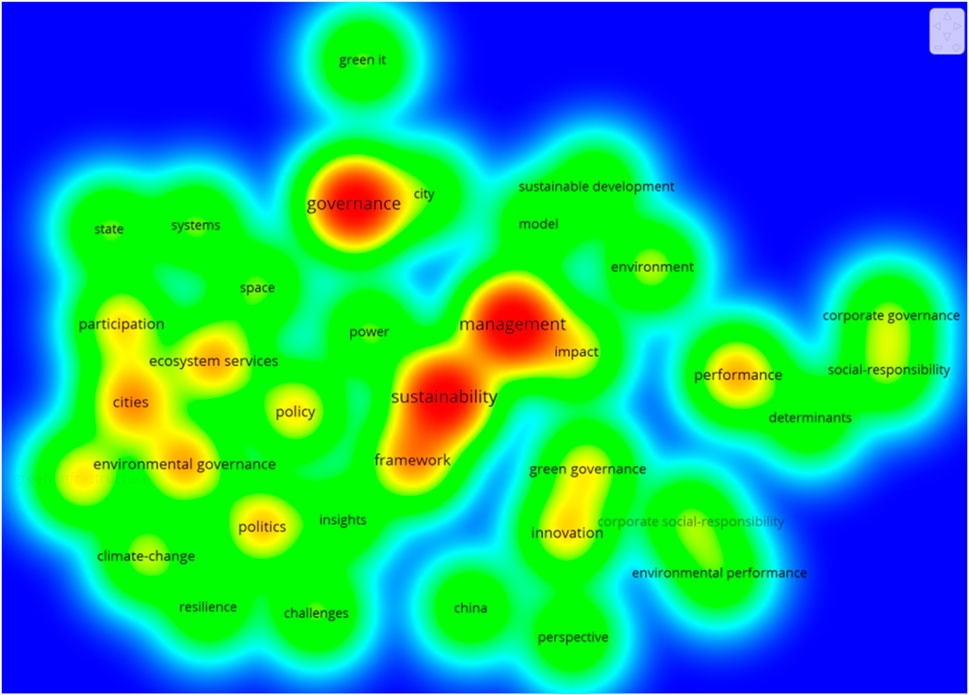
As can be seen from the figures, as far as hot topics are concerned (Figure 1), green governance research is highly focused on the topic of sustainable management, with the formation of a management framework as the core objective; at the sub-hot level, the construction of ecological management at the city level is discussed, including ecological services and environmental control, and analyses in subfields such as policy design and public management have been formed around this objective. In terms of the time zone clustering display, (Figure 2), the hotspot and sub-hotspot topics were generated earlier and accumulated a large number of research results, but the research frontiers focus on the levels of environmental performance, social responsibility, collaborative governance, and determinants analysis, which corresponds to the level of green governance assessment analyzed in the previous section. In the further downscaled hotspot clustering map, exploring the evolution of the time zone of the key terms (Figure 3), the starting point of green governance research is ‘environmental regulation’, starting in 2005, which includes the ecological scope of environmental governance, legal regulation, and governmental pressure in economic adjustment. Environmental regulation emphasizes the external diseconomies of environmental pollution and the need for governments to regulate the ecologically depleting economic activities of enterprises around mandatory policies and measures, whereas the urgency of environmental governance lies in the fact that it is based on the introduction of policies and measures, rather than focusing on economic activities. With the emergence of environmental regulation, research has emerged on participation, policy effectiveness, sustainability, citizenship, and many more, and the environmental discourse surrounding China entered the international arena in 2009. In 2010, the theme of green governance shifted to a corporate perspective, focusing on topics such as green manufacturing, environmental performance, green economy, land, business, corporate certification, and environmental accounting. In this respect, the paradigm followed by the Green Governance Institute is the concept-idea-practice path.
2.2 Research on peer effects
The concept of peer effect has been rapidly expanding with the development of peer theory and its application in different fields. The peer effect first appeared in the field of education, when the peer phenomenon refers to the phenomenon that with the increasing pressure of competition in education, many students will be crowded to compete for certain specific schools, i.e., the current concept of ‘school districts’ (Zabel, 2008). The emergence of the peer phenomenon creates a double-sided peer effect on society: on the one hand, due to the fierce competition in public schools, the quality of education has been significantly enhanced, and students are also divided in the process of ‘those who are close to the vermilion are red, and those who are close to the ink are black,’ resulting in groups of good and bad students. This means that even without social ‘natural selection’, the classification of students on their own will facilitate social advancement: that is to say, the elites and intellectuals will be washed out by cohesion; on the other hand, however, the stratification of students and schools will lead to a departure from the theory of equity in education. It can be seen that the peer effect is a positive or negative social impact of divesting the peer phenomenon and is guided by the peer theory, which is an important measure of feedback on the allocation of social resources, regulating the structure of internal operations, and equalizing opportunities in the field (Feld and Zölitz, 2015). With the depth of research in the field of education, scholars have begun to pay attention to the peer effect in education and other areas of the connection, such as proposed that college students in the choice of employment will also show the peer effect, due to the definition of a specific group of excellent mapping presented in the group of college students, college students will coincidentally follow the excellent group of the regional convergence of employment choices, industry convergence, and convergence of employment readiness. Feedback to the reality, that is, the formation of the so-called employment red and black list, the prevalence of public examination and other issues. This employment peer effect will affect the development of social knowledge class reserves, and even unfavorable to the structural change of national development, a swarm’ to follow the ‘excellent group’ gradually leads to the imbalance of social development (Li et al., 2020).
Entering the era of dual innovation, as well as the updating of foreign innovation theories, scholars have begun to pay attention to the existence of disorderly innovation activities and discuss the formation mechanism of certain irrational decisions. In this process, the peer effect was introduced into the above topic due to presenting the perceptual mechanism of decision-making. First proposed the existence of a peer effect of low-carbon willingness in consumers’ payment activities: with the clustering of individual socio-economic characteristics and low-carbon attitudes, the group of low-carbon consumers gradually expands. This positive peer effect has led to the emergence of groups of consumers with special preferences and short-term difficulties in meeting their needs, and the size of such groups will continue to increase. The sweet ‘share of the cake’ makes many enterprises take the lead in attempting to cater to the ‘preference will’ of such consumers, and once the pilot venture of some enterprises succeeds, it will trigger the willingness of other enterprises to make the transition, which completes the accumulation of the initial perceptual decision-making. Constructed a model of the influence of the peer effect on entrepreneurial activities and proved this consumer-enterprise peer effect transfer mechanism, which also marks the shift of the subject of the peer effect from individuals (students) to organizations (groups of enterprises), and the applicability and explanatory power of the peer effect is significantly enhanced. Enterprises or organizations, like individuals, will make group decisions due to a conservative or emulative mindset in the process of profit-seeking, which is particularly evident in topics such as investment and financing, innovation choices, dividend distribution, and leadership building. The main reason is that these perspectives are the key to the establishment of differentiated competitive advantages of enterprises, and once the enterprises are too isolated, rational, and without reference to the decision-making, that is, the so-called ‘eating crabs alone’ strategy, it is easy for enterprises to embark on the road of no return (Sassi and Gasmi, 2014). Therefore, most enterprises focus on imitation behavior in the above areas, based on extreme observation and emulation to protect their vested and available interests. This peer effect produces two effect results of complementing the strengths and blindly following the trend, the former is the scientific perceptual analyses after learning decision-making and obtaining significant benefit growth, while the latter is the loss of the competitive opportunities of differential advantages and being reduced to the servant of other leading firms.
The refinement of the peer effect at the organizational level has led to its application at the governmental decision-making level. Combined with the previous analysis of the cohort theory, it can be seen that the rationality of organizations’ decision-making will be more ambiguous in light of the multiple orientations of prices, revenues, and economic interests. The multiple responsibilities and complexity of the government’s role puts a great deal of administrative pressure on it to make decisions. The government’s risk appetite is also weaker than that of enterprises, which makes the ‘safeguard advantage’ of the peer effect more obvious, and based on the ideological guidance of the compromise route, the government shows a strong peer effect in new issues such as change and transformation (Cca et al., 2018). Under the fiscal decentralization system, market segmentation makes the government’s peer effect more obvious. In governmental activities, the concept of the cohort theory is expressed as the government’s homogeneous decision-making to avoid harm and to avoid lagging behind other governments in the decision-making administration, and any changes brought by such decisions to the society (resulting in the expansive increase and rapid decay of a certain kind of benefits of the original society) are the peer effect.
In order to review the current state of research on the peer effect based on a holistic view, this study utilises Citespace and Vos-viewer for combing and cleaning the relevant literature. Literature data were collected from the web of science core database. Select peer effect/s as the keyword. A total of 1,927 literatures were retrieved. After subject selection and software clear automatic cleaning, a total of 1,063 valid records were retained for analysis.
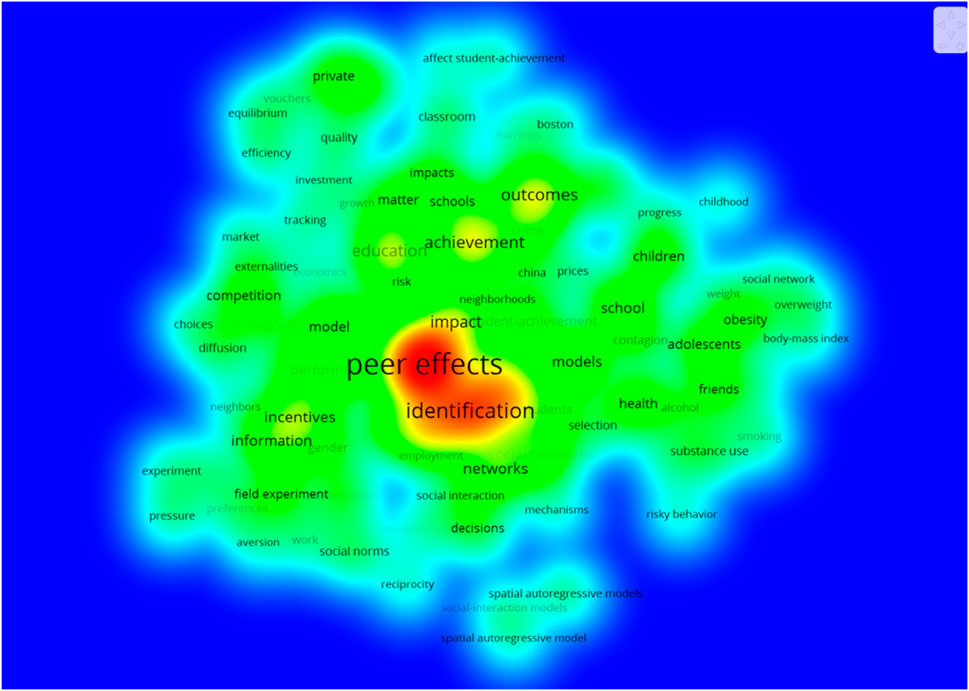
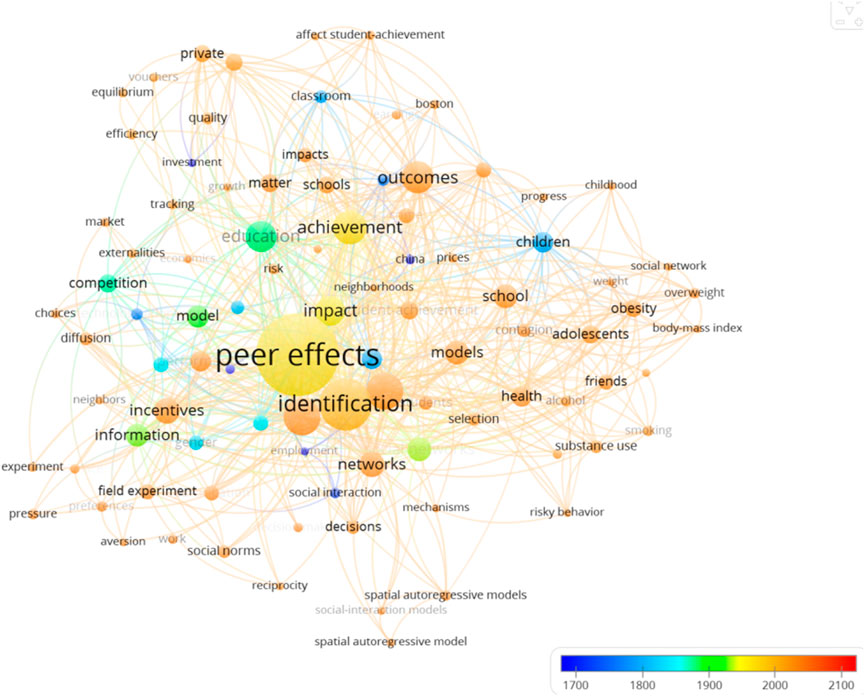
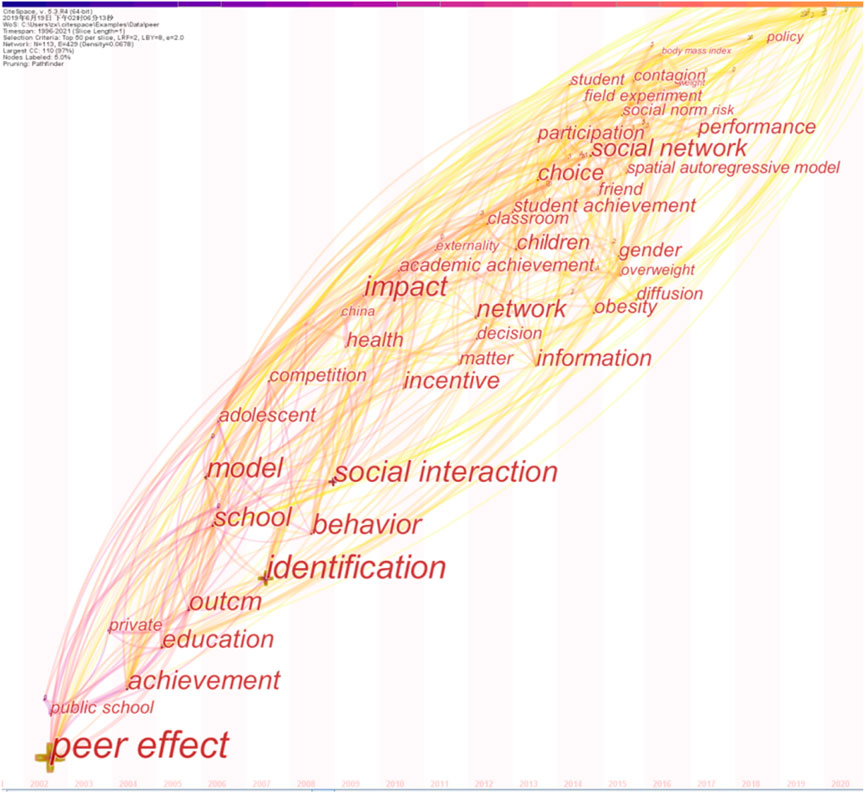
As can be seen from Figures, in terms of hot topics (Figure 4), the heavy focus of peer effects is on effect identification; at the sub-hot level, it is the methodological system of models, networks, information, factors, etc., that endeavors to be constructed around effect identification. In terms of the time zone clustering display (Figure 5), the peer effect in education disciplines continues to be the prior topic, including classroom, children, gender, and social relations perspectives. As the timeline lengthens, peer effect topics show explosive growth, including health and wellness topics such as overweight, health, and friendship, and evaluation topics such as efficiency, quality, competition, and market. As far as the most cutting-edge topics are concerned, the analyses of peer effects are clustered in terms of discussion of effect outcomes. Compared to green governance, the novelty of the peer effect is relatively weak, but the richness of topics is much higher than the former. Further downscaling of the hotspot clustering map to explore the time-zone variation of key topic terms shows (Figure 6) that the starting point of the study of the peer effect is the peer effect itself, which surfaces the primitive and pure creation of the theory, which is the direct peeling off of social phenomena, rather than the evolution of the formation of the topic of green governance. Peer effect research began in 2002, before 2009, the topic was concentrated in the field of education. 2009–2015 shifted to the enterprise dimension and maintained the expansion of other fields and mining of education science. 2016, the peer effect formally shifted to the stage of quantitative analysis, began the original formation of the connotation of the mechanism to be empirically examined, the formation of the peer effect of performance, performance, correlation model, and other high-frequency topics. High-frequency topics. It is worth noting that in 2020 the peer effect began to appear in isolated policy subject terms, indicating both the combination of the peer effect and government topics, but also the relative isolation and lack of the study, which is worthy of in-depth analysis.
3 Analysis of the formation mechanism of the same group effect of local government green governance
3.1 Global context of green governance and peer effect environment
3.1.1 Ecological environment construction leads green governance
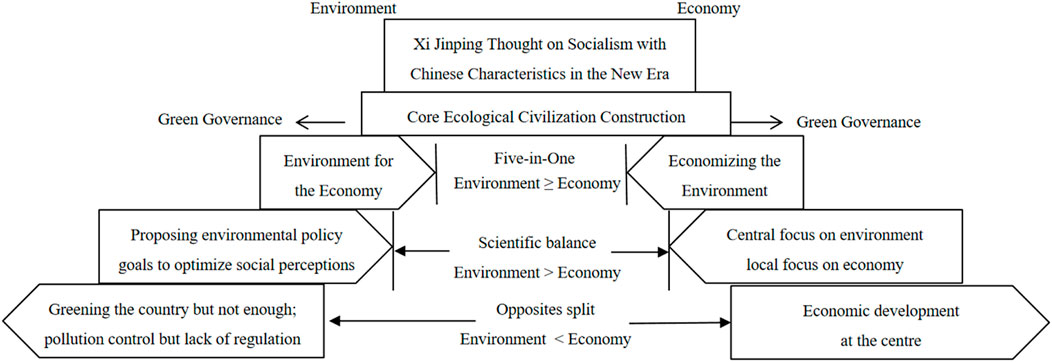
Since the 18th National Congress, China’s economy has faced downward pressure, and the contradiction between economic development and ecological construction has become increasingly acute. The heterogeneous confrontational rhetoric of “environmental protection excesses” and “one-size-fits-all governance” has further intensified the sentiment that the economy and the environment are divided and governed separately. The divergence of economic and environmental development has been accompanied by a certain degree of resource loss in the positioning of main functions, territorial spatial development, technological innovation, and structural adjustment (Sun and Wang, 2021). On 18 May 2018, the National Conference on Ecological Protection of the Environment was officially held. As the highest-profile, the largest scale, and most far-reaching ecological civilization conference, it established the “Thought on Ecological Civilization.” It made it an important part of China Socialist Thought with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, comprehensively summarizing and scientifically summarizing the sustainable development of the new era from the height of new concepts, new ideas, and new strategies. The far-reaching connotation of sustainable development in the new era. China’s thought on ecological civilization marks forming a new position and a new model for green development in China (Liu et al., 2021c). Based on its insight into the great development situation and objective laws of the historical leap from industrial civilization to ecological civilization, it takes the harmonious development of man and nature as its primary starting point. It coalesces to form the concept of green development. This is essentially a new Marxist ecological civilization theory practice combined with Chinese characteristics. As a result, new ways of production and life, new economic and political relations, and new cultural values and ethical systems collide and stir in a green context. Ecological and environmental protection, as the basic landing point of ecological civilization thought, becomes the core issue under green development and rises to the central position of green development (Xiao et al., 2021). The new productive life, the new economic politics, and the new cultural values correspond to the social construction, economic construction, political construction, and cultural construction (Huang et al., 2021). under the comprehensive guidance of green change thinking and action after breaking the contradictions of environmental, economic differentiation. The synergistic development of the five major constructions and the Five-in-One further highlights the green undertones of building a well-off society. During the deliberations of several delegations at the 19th National Congress, General Secretary pointed out that “the quality of the ecological environment determines whether a well-off society is comprehensive or not.” The battle to build a moderately prosperous society is the unified construction of the multi-dimensional requirements of social balance, inclusiveness, and sustainability and the global construction of social quality improvement under the in-depth innovation-driven development strategy and significantly enhanced development coordination. The adjustment process of the ecosystem and the economic system of “good money” by “bad money. is also a process of adjustment of the ecosystem and the economic system in which the “good money” catches up with the “bad money” (Scalia et al., 2020). The first and foremost synergy between ecological and economical construction is to remove the black economy from ecological development and make the economic system purely constructive, rather than “black growth,” which is crude development at the expense of the ecological environment. General Secretary put forward the theory of ecological-economic synergy as early as 2005 when he investigated Anji, Zhejiang Province. After the 19th National Congress, this theory was formally incorporated into the 19th National Congress and the Party Constitution. The practical guidance of the Two Mountains Theory has reversed the dichotomy between economic and social development and ecological protection in the traditional industrialization revolution (Dani, 2014), and its sublimated scientific significance implies the dialectical unification and integration of ecology and economy. In this way, the Two Mountains Theory reconstructs the “good” and “bad” chasing of ecological and economic systems, opening up a new situation of green and high-quality development in the perspective of the Five-in-One. In general, the resolution of ecological and economic contradictions has liberated the reconfiguring and combining productive forces and modes of production. It has balanced the social, political, and cultural orientations of construction, ultimately achieving the ‘comprehensive’ goal of building a well-off society. In this process, the ‘green’ ethos empowered by ecological construction links economic, social, political, and cultural construction, making the direction and integration of each dimension clearer. It can be seen that research on green and high-quality development under the Five-in-One is essential.
3.1.2 China’s governance system extends to green activities
National governance capacity has long fed into the core objective in the political transformation of the country: through the design and integration of institutional structures under the governance system, the linkage of institutional mechanisms, laws, and regulations in various dimensions such as economy, ecological civilization, society, politics, and culture is gradually formed, and a closely interlinked and coordinated national system is eventually constructed. In 2013, the Third Plenary Session of the 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC), in its Decision, for the first time explicitly put forward the goal of promoting the modernization of the national governance system and governance capacity, with governance replacing the two traditional concepts of state rule and state management and leaping to become the core force and central guide for national development (Chen and Bao, 2014). With the adoption of the Decision of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on Several Major Issues on Adhering to and Improving the Socialist System with Chinese Characteristics and Promoting the Modernization of the State Governance System and Governance Capacity at the 19th Plenary Session of the 19th CPC Central Committee in 2019, the construction of the governance system and capacity has been further focused and the modernization line of governance in parallel has become increasingly clear: With “governance” as the means, the Party’s leadership and the state’s leading force are adhered to, and the enthusiasm and participation of all social details are coordinated, so that the legal, market and social pressures can achieve the overall “governance” of all affairs, and achieve scientific and high-quality development of the whole situation based on the critical areas of economy, ecological civilization, society, politics and culture (Wang and Bernell, 2013); with “reason” as the footing, the coordinated development and orderly operation of all fields are promoted, and the institutionalization, standardization, procedure and democratization of public affairs and functions are achieved. In this process, local governments have gradually become the main body for implementing national governance construction (Chien et al., 2017). In the Third Plenary Session of the 19th Party Central Committee, it was clearly stated for the first time that the structure of a “governmental governance system with clear responsibilities and administration following the law” was one of the objectives of the reform of the Party and state institutions. This goal integrates the urgent demand for modernization of the national governance system and governance capacity and is also a critical path for the overall layout of the Five-in-One. In constructing the governmental governance system, the optimization of structures and responsibilities, and the consolidation of reform achievements through institutional construction, require an adequate “response” from local governments (Ran and Ping, 2010). As the first provider and responsible for public services, local governments have become a direct field for feedback on economic, ecological civilization, social, political, and cultural construction. As the grassroots actor in the structure of national governance, local governments determine the extent to which the modernization of the national governance system and governance capacity is achieved. With the increase in economic pressure and the need to change the mode of social development, local governments, in the process of implementing the “two skins” of governance and development, have gradually condensed the adjustment model so that green growth is presented in governance and green governance is added to change. Along with green governance refining the construction kernel of green development, local governments have formally stepped out of the development path of green governance (Lin et al., 2019) in many grassroots practices such as coordinating the hammering of national governance capacity, high-quality development, and the construction of the Five-in-One, and are more confident in chasing the grand blueprint of building a moderately prosperous society in all aspects. Thus, it will be of great practical significance to explore the core concept and scientific interpretation of green governance and precisely study and judge the countermeasure ideas based on the critical identity of local governments.
3.1.3 Green governance behavior path generates same group results
With the integration of green governance and macro policies, local governments have been guided by performance pressure and social aspirations and have shown positive green governance patterns. 2015 saw a gradual increase in the reform of the green governance system after the Central Party and State Council issued the “Overall Programme for the Reform of the Ecological Civilisation System,” and the green governance and ecological market system was formally constructed. The new Five-in-One performance appraisal and accountability system under the leadership of environmental civilization was formed. The new five-in-one performance appraisal and accountability system has taken shape. Around the central document, various localities have also issued policies in response to green governance (Dressler et al., 2020). At the regional level, in 2019, the Yangtze River Delta issued the “Yangtze River Delta Ecological Green Integrated Development Demonstration Zone”; in 2021, the Yangtze River Delta issued “Several Policy Measures on Supporting the High-Quality Development of the Yangtze River Delta Ecological Green Integrated Development Demonstration Zone.” In 2018, Guangdong Province, together with Hong Kong and Macao, issued the Implementation Plan for the Construction of the National Green Development Demonstration Zone in the Pearl River Delta. 2016, the State Council guided the Yangtze River Economic Belt by issuing the Outline of the Development Plan for the Yangtze River Economic Belt. During the past 4 years, structural green development policies such as the Special Management Measures for Central Budgetary Investment in the Construction of Major Regional Development Strategies (Direction of Green Development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt) and the Programme on Comprehensive Promotion of Fiscal and Tax Support Policies for the Development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt were collated and formed around this outline. At the individual local level, in Jiangsu, for example, the “Rules for the Implementation of the Green Guarantee and Subsidy Policy in Jiangsu Province (for trial implementation)” will be issued in 2019 to lay the financial foundation for green governance, and the “Opinions of the Provincial Government on Promoting Green Industry Development” will be published in 2020 to form a comprehensive green governance mindset. In general, all regions have adopted green governance models to meet the needs of changing development patterns, with various government policies and development frameworks showing a trend of “homogeneity.” However, in a homogeneous framework, many regions have followed joining without regard to their transformation base (Wu et al., 2021). For example, the Yunnan-Guizhou region started the green governance matching work of the Chengdu-Chongqing region, but the industry sector covered almost all green manufacturing industries (Ma et al., 2018). However, the industrial structure system of the Yungui region itself is not yet mature enough to take on the overflow of green resources. In August 2021, Tibet announced the initial formation of a green development pattern, emphasizing the “ecological priority, green and low-carbon development-oriented” road of high-quality development to guide the future construction of Tibet in all dimensions officially. In 2005, Tibet issued a ban on logging. In 2010 it introduced ecotourism. It encouraged Tibetans to build ecological homestays, and after the 13th Five-Year Plan, Tibet built a national model city for ecological civilization and a national model area for tourism and created a national clean energy succession base. By 2020, clean energy in Tibet will reach 89.09% of the installed capacity of power generation, with ecological and environmental tourism revenues exceeding 24 billion yuan and 32 million tourists received. It can be seen that green governance is a development goal that each local government strives to pursue and must achieve. However, the homogeneous development of each province and the quick scramble for green resources under the homogeneous ideas have made it difficult to improve the quality of the overall macro situation of green governance, and even inefficient “grouping” and excessive “imitation. “However, the problems of homogeneous development across provinces and rapid competition for green resources under a homogeneous mindset make it difficult to improve the quality of the overall macro picture of green governance, and even inefficient ‘grouping’ and excessive ‘imitation’ under which local governments blindly join the same ‘pooling group’ and stiffen development will lead to more efficiency losses in green governance (Xiao et al., 2020). In this context, how to scientifically study the peer phenomenon of green governance of local governments and research and judge the positive or negative peer effects of local governments in the process of green governance will be necessary for the scientific improvement of the development situation of green governance.
3.2 Origin, main content and definition of green governance of local governments
The formation of the proprietary concept and term of green governance originated from a summary in China and the “Two Mountains Theory” by People’s Daily Online, Xinhua Online, and Communist Party of China News in June 2017, which summarized General Secretary many statements on ecological construction, such as “If ecology thrives, civilization thrives; if ecology fails, civilization fails,” “Building a good ecological civilization is a long-term plan for the wellbeing of the people and the future of the nation” and “Environmental governance and building a harmonious development of man and nature,” into General Secretary concept of green governance (Zhu et al., 2019). In the same month, the eighth Clean Energy Ministerial Conference and the second Innovation Mission Ministerial Conference were held, with General Secretary emphasizing in his congratulatory speech that the world should follow the path of low-carbon, circular and sustainable green governance. Since then, green governance has become an essential topic for academic and government research. Combining the conceptual and theoretical foundations of the previous section, this part will further clarify the originating process and main contents of green governance in local governments and define the critical connotations in a judgmental manner.
3.2.1 Origins of green governance in local government
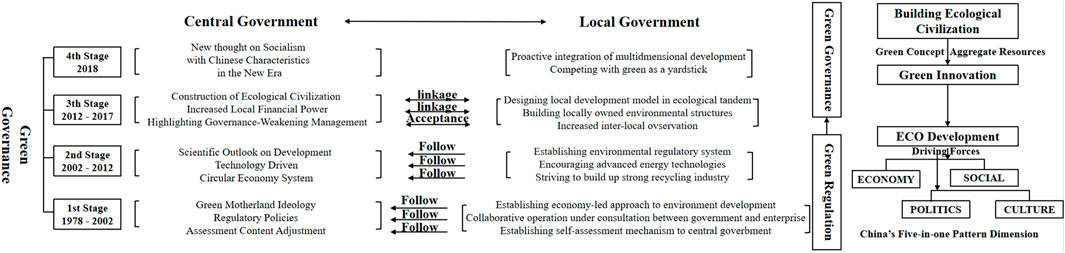
At the beginning of the 21st century, as global economic growth was sluggish and environmental resources were depleted, the dichotomy of economic and ecological development became unsustainable. International organizations, mainly the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the OECD, gradually put forward two central policy ideas, the “Global Green New Deal” and the “Green Economy,” to achieve a change in the theory and practice of sustainable development (Barbier et al., 2004). These green ideas focus on optimizing energy efficiency, resource restructuring, and green growth and emphasize the need for governments to construct scientific green policies and redeploy traditional development structures to achieve a green economic model driven by upward green mobility (Hassan et al., 2021). This is even though China has long been criticized for being a ‘sloppy economy,’ with problems such as energy pollution and resource inefficiency, which has led to a lack of recognition of the quality of our economy. It is undeniable that in the early days of our development, China seemed to have been given a unitary and social model of “economic dominance over the environment,” which also led to many environmental problems. In the eyes of scholars from abroad, such ecological problems were the key trigger for our determination to govern the environment and local governments’ source of green governance action. However, the formation of green governance activities in China has not been of a problem-oriented type, i.e., a strategic logic of solving problems after they have occurred. Instead, our country has always held a strategic ideology of ecological protection, and green governance is essentially a continuation of multiple environmental governance activities in a new era. This paper divides the evolution of green governance activities and policies since the reform and opening up into the following four stages and considers the role played by local governments in them, to fully trace the green governance of local governments: the first stage (1978–2002) is the stage of the embryonic green governance concept; the second stage (2002–2012) is the stage of the promotion of the green governance policy system and the adjustment of social ideas. The third stage (2012–2017) is the stage of green governance empowerment in the new era, and the fourth stage (2018-present) is the stage of green governance formal construction and maturity.
3.2.1.1 Embryonic stage of green governance concept (1978–2002)
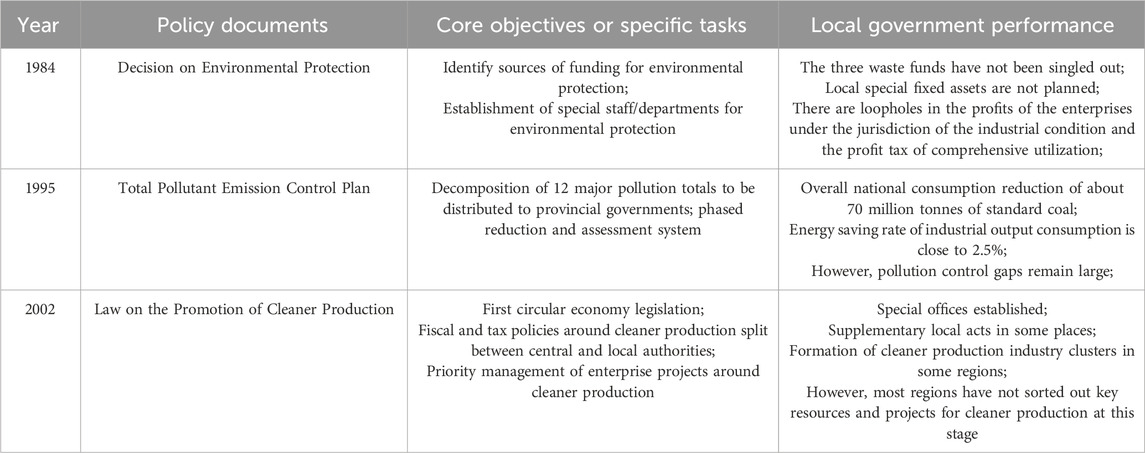
After China’s reform and opening up, the country established the idea of economic construction as the focus of development, but this does not mean abandoning the environment and disengaging from resources in favor of financial planning. In 1978, China leaders and other leading comrades first stated the need for a green barrier in China’s development process in their “Proposal for the Construction of Large Protective Forest Belts in the Northern Areas of China.” By 1997, the idea of greening the motherland had taken shape with China leader’s concept of “planting trees, greening the motherland and benefiting future generations” as its core. This strong statement became the source of China’s green development philosophy and marked China’s importance to environmental construction from the beginning to the end. In December 1983, at the Second National Conference on Environmental Protection, Vice-Premier Li Peng proposed that environmental protection was a basic state policy that China must adhere to in the long term and that environmental construction had thus been incorporated into the guidance of public values and regional government development. Under the direction of many leaders such as Deng and Li, a systematic policy system of “who pollutes, who treats” and “if there is pollution, treat it” was formed at that stage. However, at the local government level, the absence of a governance system and a management and control system driven by a robust administrative outlook led to a partial confrontation between central and local perceptions. The macro design of environmental construction was not fully implemented. The details of the policies are shown in Table 1.
Although none of these policies mentions ‘green governance,’ at their source, the objectives they address are essentially the scope of the subsequent construction of green governance. In terms of philosophy, these policies have always paved the way for the core of green governance: optimizing the dual goals of economy and environment, resolving the contradictions between the two rationally, and increasing the quality of society without sacrificing the development costs of both. Objectively speaking, the need for environmental management has not been neglected during the period of rapid economic growth, and this forward-looking view of the environment has guided the shaping of green governance. In addition, the environmental policy at this stage formed two core contributions at the practical level to the origins of green governance: 1) the so-called green governance was a practical action led by local governments and a multi-layered management action across sectors and industries (governance activities did not exist at that time); 2) the idea of green governance was to lead to a qualitative improvement of society and did not exist simply as optimization of any lone goal. This has resulted in many local governments not understanding the meaning of environmental management and prioritizing the economy, even interpreting the central government’s ‘economy-focused’ approach in a one-sided manner. The multi-level assessment system within local governments also gives economic indicators more weight than environmental indicators. As a result, the dichotomy between the social development goals of local governments is essentially antagonistic and unbalanced, and the differences between central and local environmental policy practices have led to many significant policies being ineffective and local governments performing unsatisfactorily.
3.2.1.2 Green governance policy system promotion and social concept adjustment phase (2002–2012)
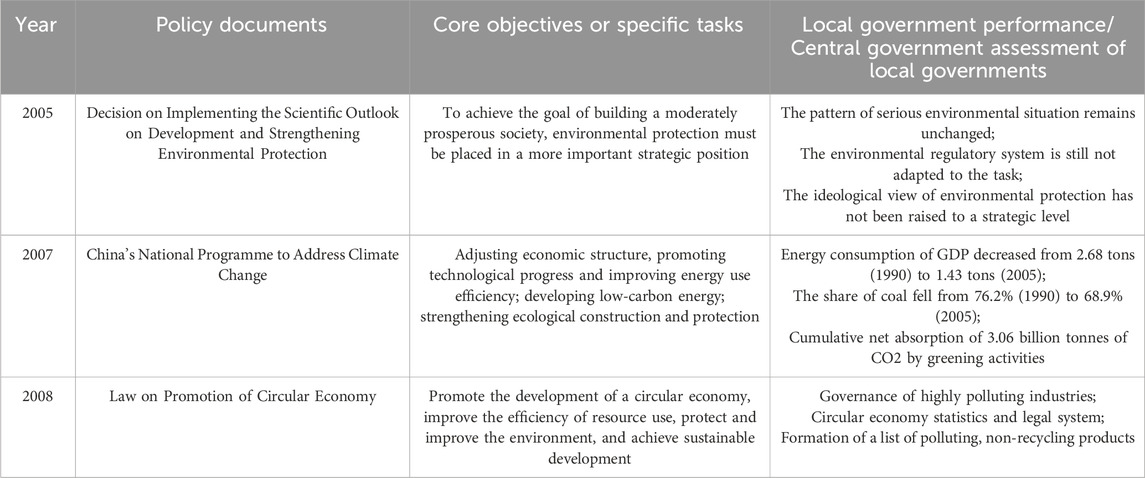
In the 21st century, China’s environmental problems have entered a phase of a concentrated explosion, and the contradictions between the environment and the economy have become increasingly acute. On the one hand, many local governments and members of society have made economic growth a synonym for the country’s international status, believing that a significant economic volume will hold the power of international discourse; on the other hand, the “hidden merits” of environmental innovation are not easy to please, and it is difficult to translate “a thousand years of work” into realistic assessment indicators to serve the prestige of local governments. On the other hand, the ‘hidden merits’ of environmental innovation are not easy to achieve, and it is difficult to translate them into realistic assessment indicators to serve the prestige of local governments. Combining these two factors has dramatically reduced the incentive for local governments to engage in green activities. However, as China’s international status has risen and it has become a reliable developing power on global environmental issues, the central government has once again leaped forward in its efforts to build the environment. In this context, the predecessor of green governance, environmental construction activities, entered a phase of systemic advancement and conceptual adjustment, with the central government focusing on formally reversing the negative behavior of local governments with a dual track of practice and conceptual parallelism. The central policies and local government performance in this phase are shown in Table 2.
In the context of Table 2, the most crucial contribution of this phase to the subsequent formation of green governance was its clear articulation of the strategic status of environmental protection, which was reinforced in the form of a codified text, thus preserving a social mechanism for balanced economic-environmental development. In addition, for the first time in China, the importance of environmental protection in the concept of the functioning of society was also emphasized, based on the restructuring of the policy system. The State Council’s successive national conferences on environmental protection have put forward the scientific assertion that “protecting the environment is protecting the productive forces” and “insisting on protection amid development and development amid protection,” which has helped build a healthy social and environmental outlook. Of particular concern is that this phase of environmental construction has laid down the core of green governance: firstly, the scientific perspective on development put forward by the central leaders during this phase is the first time in China’s history that the dialectical relationship between environmental construction, ecological resources, and economical construction has been systematically sorted out from the top level of design, which has changed the previous development pattern in which economic arguments took precedence. Secondly, for the first time in the history of the country, the government’s environmental management behavior has been transformed into governance behavior to integrate new economic development and new scientific development models, including the circular economy, low-carbon economy, and green economy, into the standard construction of society through market-oriented, softer and more efficient administrative activities. Scientific development is a high-quality development and meets long-term aspirations. Thirdly, for the first time in this phase of environmental policy, there is a specific reference to new tasks in ecological construction, a shift from a binding policy of simply reducing emissions and consumption and controlling resources, and a protective approach of restoring ecology and planting trees, to a proactive policy of technological leadership and structural optimization. This means that the future environmental system, including green governance, will take on the complex task of opening up a sustainable development model and integrating and promoting the overall construction of society. This leap in policy thinking signifies that green governance is not a passive tool of “polluting first and then treating later” (passive compensation for ecological restoration tasks), nor is it a cleansing tool of “not opening up sources but cutting costs” (elimination cleansing for emission reduction tasks), but instead, It must be an aggressive, science-based, proactive construction strategy. On this basis, the organizational performance of local authorities has improved, and the correct concept of development has been re-established.
3.2.1.3 New era green governance enabling phase (2012–2017)
Since the 18th National Congress, the new central leadership has formed a more profound exploration of green development. Particularly at the ideological level, General Secretary’s series of ecological outlooks and green theories have fantastically realized the internal empowerment of green governance, the most significant leap in China’s theoretical system of ecological thought. The manifestation of this empowerment stage is reflected in three places, firstly, the breadth of green activities. With the spread of easy-to-understand green concepts, the willingness of all social classes, organizations, and individuals to engage in green activities was strengthened, and the social forces in environmental construction were highlighted, easing the pressure on local governments. And with the reversal of corporate attitudes, the work of local governments has become significantly less complicated. Society has formed a green coordination system under a unified ideology and guidance. Second, green construction connectivity. The development concept represented by the “two mountains theory” has led to the improvement of the control system, along with the integration of dynamic market prices, maximum tax exemptions, and precise compensation mechanisms into the environmental policy system, the dynamic adjustment and complementation of economic and ecological advantages, mobilizing local governments and people to the greatest extent possible, with both (economic - environmental) benefits taking advantage of each other to produce maximum social utility. The mutual advantage of the two (economic-environmental) advantages has the most significant social utility. Thirdly, green development is normative. This stage focuses on the legal connotation of green governance, with a stringent legal system as a guarantee, actively exploring the normative path of third-party power and market integration, and laying the foundation for the construction of resource scarcity and quantitative characteristics based on a standardized evaluation system. As shown in Table 3, the policy system and local government performance in this stage are very abundant.
Overall, the elements of green governance, such as connotations and systems, are basically in place at this stage, completing all the work in the preceding sequence for the formal introduction of green governance in 2017. And thanks to the development of the elements of green power over the years, green administration has become a key leader in stringing together the development of all areas of society.
3.2.1.4 Formal building and maturing phase of green governance (2017-present)
In 2017, the introduction of green governance echoed China leader’s Thought on Chinese Specialties for a New Era and Thought on Ecological Civilisation, supporting what has become the platform for green development in contemporary China. After this stage, China’s economic-environmental binary relationship is optimized to its highest point, and with the complementary policies and guidelines of carbon peaking, carbon neutrality, and new energy, China has formed a construction pattern of ecological civilization. The green governance connotation of “community of life between human beings and nature” and “dialectical unity of environment and economy” has successfully shaped Eastern environmental theory and is a distinctive Chinese addition to the Marxist idea of human beings and nature, which has surpassed modern Western ecological approach at the ontological level. Through nearly 40 years of evolution and development, green governance has entered a formal construction and maturity phase.
Figure 7 shows the structural diagram of the origins of green governance constructed in this paper. The significance of green governance in China is gradually reinforced by the distancing and proximity of the economic-environmental dichotomy. Based on a holistic view, green governance in China is not a quick fix, nor is it a superficial response to a so-called international controversy, nor is it a reactive response to the problem at hand. The origins of green governance are essentially China’s long-term thinking and action on economic and environmental construction. The dynamics of green governance is an evolutionary process of enriching the meaning of green, clarifying the central idea, and exploring the task of greening. In general, the origins of green governance are a response to the economic-environmental dichotomy and the replacement of the traditional crude administrative management with the ultimate governance goal.
3.2.2 Key elements and connotations of green governance in local governments
Combining the origins of green governance by local governments, the study found that green governance first originated from environmental management actions in China. In the first stage (1978–2002), ecological construction laid down the concept of green governance and emphasized the status of green and sustainable development. In the second stage (2002–2012), dissenting social views were adjusted, and specific construction indicators were clarified in conjunction with the requirements of scientific development. In the third stage (2012–2017), the connotation of green governance was enriched, and the multidimensional areas of society were strung together. In the fourth stage (2017-), they were elevating the strategic status of green governance and integrating it into the socialist ecological theory system. Around its core tasks and changes in the realistic context, the main contents of green governance of local governments also differ in each stage.
In this section, the evolution of the main tasks of green governance is shown in Figure 8, taking into account the actual performance of central and local governments and the process of the origins of green management. As the diagram shows, the first and second stages have not yet developed an environmental governance structure, nor has the concept and construction system of national governance modernization been clarified, but instead a green/environmental regulation system. The main task of local governments in this stage is mostly to follow the central government’s design and encourage and guide green activities under limited local discretion and personnel advocacy, focusing on the innovation of self-concept and the acceptance of new green ideas. After the third and fourth stages, along with the relaxation of local discretion and the proposed modernization of governance, local governments accepted the active role of the central government and promoted green governance in a linked form. In these two stages, the main tasks of green governance for local governments include the following three aspects.
(1) Strategic level. Responding to China leader’s thought on socialism with Chinese characteristics in the new era and China leader’s thought on ecological civilization, we strive to construct a social development system under the green yardstick, mobilize the active release of green productivity of microelements in the whole society, coordinate the multidimensional development of regions and industries, and ultimately reverse the construction concept of environment-economy dichotomy in terms of ideas and thoughts. This process forms three sufficiencies: to fully understand the guidance of the Two Mountains Theory, to clarify the economic value of the environment and the environmental attributes of the economy, to build a circular economy model under the tandem of ecological construction; to fully understand the necessity of modernizing governance, combining decentralization and management, “governance” and “management” and learn to start environmental governance based on the overall situation with flexible means; fully understand the prominence of ecological civilization construction in the construction of the Five-in-One, and clarify the importance of ecological civilization construction in building a moderately prosperous society in all aspects and empowering its green undertones. Whether it is the building of a relatively prosperous society or the Five-in-One construction pattern and high-quality development, China’s requirements for local governments in the new era are complex and multidimensional, requiring local governments to find task links among the various intricate work. It is clear that green governance meets the demands of almost all construction tasks of local governments and effectively links all construction dimensions.
(2) Tactical level. Shaping the green governance process chain. Combined with the strategic thinking of green governance, it is clear that the landing point of green governance is to meet the tandem leading role of ecological civilization construction on economic, social, political, and cultural structure. Further, combining theories of sustainable development and government behavior, it is clear that the key to driving social progress is the formation of influential, productive forces. However, the local government itself is only a catalyst for productivity formation, not a producer of productive efficiency. Therefore, green governance, which wants to meet the ultimate governmental objectives, requires local governments to impose governance instruments on enterprises to generate green productivity. However, in a rigid industrial system, traditional green productivity is not effective enough, and new productivity aggregation comes from innovative technologies. Local governments link government-enterprise-society actors by building a green governance process chain by translating this complete process to the tactical level. In the green governance process chain, local governments first establish green concepts, gather green resources based on the construction of ecological civilization, and make every effort to promote green innovation in society. In the green governance-green innovation process, the local government establishes a green governance structure and green governance mechanism input system, serves the enterprises with the human, capital, and knowledge elements embraced by the government, and creates an excellent government-enterprise atmosphere to promote the formation of green results. As green innovation matures, the green innovation-green development chain takes shape, and local governments’ green governance inputs to enterprises and society form substantial outputs, both in green governance effectiveness and green governance social responsibility. These outputs create the momentum for green development and enable green productivity for the green transformation of society. Once the green transformation chain of green governance - green innovation - green growth is stabilized, the outputs of government green governance serve economic, social, political, and cultural construction and fully meet the ultimate strategic objectives.
(3) Practice implementation level. Precise gathering green resources to serve and assemble social micro-factor units and guide their green transformation and innovation. The direct output and effect of green governance is the increase and change in the green innovation capacity of enterprises. The core of green governance is a governance process. As the initial promoter and builder of the green transformation chain, the government matures green governance activities by investing in many government resources. The final product is the green innovation results and the green innovation atmosphere in society. To further refine, local governments’ specific practice of green governance is the integrated management of human resources, capital, and knowledge. In terms of human resources, the integration of talents in the environmental and economic fields will be undertaken to support green research and development and collaborative governance. In terms of capital: build a trading system for emissions activities, assist enterprises to make a market-based operation system based on local finance, and form a reasonable distribution of production and living space patterns. With the help of initial public resources, we will break the capital constraint of green innovation for small units such as enterprises. Knowledge: Form a long-term strategic plan for green governance, introduce relevant policies and plans to support the development of strategic emerging industries and advanced manufacturing industries, and strengthen management in a scientific and orderly manner with large projects and playing systems. From the above, it can be seen that green governance is a process of construction in which the local government, guided by the central government’s green philosophy, strives to achieve the goal of multidimensional and high-quality development of society. Green governance is a series of incentive, regulatory and collaborative human, capital, and knowledge resource deployment activities under the local government’s jurisdiction to secure resources as inputs, trigger green innovation and generate green productivity in society, and ultimately achieve green development. The output of green governance will meet the expected progress of society and the formation of the “Five-in-One” pattern.
3.3 The origin and definition of the peer effect of local government administrative decision-making
In the field of public administration, the American statesman Alison has argued that the success of a policy lies in its ability to promote social development. However, program planning contributes only 10 percent to achieve this policy objective, with effective implementation producing the remaining 90 percent. Thus, the key to real policy impact is at the practical level of performance. Chairman Mao Zedong also redefined public policy: a good theory is meaningless if correct but is only kept in a pile away from practice. Although the relationship between central and local governments is relatively harmonious in our particular social system compared to the West, there is no Western power structure with its confrontation and fragmentation, which avoids massive resistance to policy transmission from central to local governments and policy implementation at the bottom. The relationship between the central government and the local government is also relatively pure, and there is no interference in policy practice from the multiple interests, social groups, and complex perceptions of the West. However, the selective implementation of public policy by interest-driven subjects can also affect the ultimate policy performance. In our political environment, the dynamics of the central and local government’s interest objectives and relations are the key factors governing the effectiveness of our policies.
In China’s power structure, local governments are mostly the implementers of public policies and promoters of strategic ideas, and the effects generated by these landed policies are supposed to occur within the jurisdiction of local governments. However, the different mechanisms for distributing interests between the central and local governments can divide the relationship between the two, resulting in a significant government group that authoritatively distributes, portrays, and defends the public interests of society and the overall interests of the state with the general interests of the national economy. A local government group that autonomously distributes feeds back and expresses the public interests of the region and the overall interests of the area with local interests. The former is dominated by ministries and central authorities, while the latter is dominated by various local administrative and party-building departments. As the relationship between the two sides shifts from the consistency of interests to the autonomy of interests, local governments will seek to defend their interests by playing the game between the central government and the local authorities, weakening the implementation of significant policies and increasing the real power of local governments. This is a way for local governments to separate the effectiveness of central policies and transfer them to local energy and generate local gains. However, due to the weakness of local governments, this has led to the “collusion” and “synergy” of several local governments to transform their “local” status through consistent decision-making and benefit-sharing. The weakness of the identity of the local government and the collective power of the group to pool their interests to expand local effectiveness. This has formed the prototype of the peer phenomenon of local government administrative decision-making in China, and the total local energy synthesized by this view of group interests is the peer effect of local government managerial decision-making. This section will summarise the origins of the peer effect of local government administrative decision-making and its connotations at each stage, based on the main stages of social transformation and the realistic background of China.
3.3.1 Origins and connotations of the peer effect in local government administrative decision-making during the phase of institutional transition (1949–1978–1992)
In the early days of the founding of the People’s Republic, Chairman Mao Zedong put forward a discussion on how to deal with the relationship between the central and local governments in his “On the Ten Relations,” the core idea of which was to expand regional power, lead to an increase in the enthusiasm of local governments, and harmonize the interests of the central and local governments in the process of decentralization. The basic approach to the relationship between the central and local governments is to “take into account the interests of all parties and achieve dialectical unity.” However, the underlying principle is that “strong and unified leadership from the central government” is the core and that “under a unified national plan and discipline, “Local governments approach the masses and the positive factors to build the socialist cause. In the institutional context of the time, China had a planned economy model as its economic system, where directive plans led all financial and even other policies in the field, and the central government guided and regulated the functioning of society through planned major economic activities, in which the government determined the scheduling and production of all resources, or even essentially the central government. As an essential feature of the early socialist system, the planned economy followed the principle of linking the sectors of the national economy into an organic whole through the expansion of socialized production.
It is clear that in the purely planned economy of 1949–1978, local governments appeared in the central-territorial relationship in the sole capacity of ‘following’ and ‘implementing.’ Wherever and whatever the local government followed the principle of “unified financial revenue and expenditure, unified taxation, unified establishment, unified public food, unified trade, and unified banking.” Thus, in this context, the early phenomenon of a passive peer was formed: local government administrative decisions were coordinated by the central government, which did not consider regional heterogeneity and management differences. All started a template decision under the national plan. The policy effectiveness of such decisions, i.e., the peer effect, contributed to the balanced transformation and development of various regions and industries, macro-regulation and total balance to achieve superior values, and the country as a whole healed the vicious economic fluctuations left behind by the old China in a short period despite its fundamental disadvantages, and smoothly passed the difficult period of development; in addition, the peer group effect also integrated the limited resources of various localities into key strategic construction, so that In addition, the peer effect also consolidated the limited resources of each locality into the critical strategic building, so that “the power of the peer can do great things.” In short, the peer effect of local government administrative decisions was due to the poor development environment of the country and the highly centralized planned economic system of the central government. The connotation of the peer effect in the administrative decision-making of local governments was not the pursuit of local status and interests using grouping but the “support” of the central government by localities. It is synergistic cooperation between local governments, showing a state of positive synergy.
In 1978, the Third Plenary Session of the 11th Central Committee made a historic decision to gradually build a socialist market economic system based on the reform of state-owned enterprises and the public ownership system as the mainstay. From 1978 to 1992, China entered a mixed financial system. The coexistence of the planned economy and the market economy system led the central government to adjust to the political system around the economic reform. During this period, the power of local governments increased in two ways: firstly, the financial and administrative management of local governments increased, and the new central government system of “dividing revenues and expenditures, and grading and contracting” mobilized local executive potential; secondly, the autonomous power of enterprises to produce and operate was expanded, local dynamism increased, the local-enterprise distribution structure was optimized, and local governments The provincial government has been given economic-oriented management authority. The origin of this phase of local government administrative decision-making peer activity comes from the change in the appraisal mechanism of local governments under the institutional transformation: under the previous monotonous decision-making of acting “at the command of the central government,” the decision-making cohort of local governments was consistent, but the appraisal scale was also consistent, which did not induce local governments to “inwardly roll” their decisions. This does not cause “in-rolling” of local government decisions. At present, with the liberalization of authority and the rise of economic status, local governments have begun to focus on the effectiveness of administrative decision-making in the economic sphere, hoping to maximize the effectiveness of financial resources by organizational means and to take the lead in the development of the commodity economy and the regulatory role of the market. This change in orientation has led local governments with first-mover advantages and excellent performance to follow suit. In contrast, local governments with lagging performance and inexperience have “copied the work” and joined the administrative decisions of the same quality and content. This leads to the homogeneity of local government managerial decision-making at this stage, and the corresponding peer effect is the differentiation of market economy quality brought about by homogenous decision-making: under local autonomous decision-making, resource dispatch and planning arrangements are closely linked to regional characteristics, and simple imitation, conscious following, and abandonment of the rules of the market economy may lead to the better and the worse, and the gradual differentiation of local policy effectiveness. Therefore, the connotation of the peer effect in the administrative decision-making of local governments at this stage is the proactive action of local governments to avoid harm and pursue internal catching up, which is the result of “mutual competition” between localities in front of the central government. This peer is the decision of the disadvantaged localities to catch up with the prime localities, showing a specific positive peer state.
3.3.2 Origins and connotations of peer effect in local government administrative decision making in the stage of social structural transformation (1992–2012)
The transformation of the social structure refers mainly to the transformation of the social development structure, the adjustment of social interests, and the change of ideology. In the context of the analysis of the origins of green governance, it can be seen that this phase is a period of change in many elements of social thought and practice, with significant changes in social value systems and behavior. In terms of social interest adjustment, in 1994, China formalized the tax sharing system and the regularised central and local fiscal allocation mechanism gave local governments access to capital elements for autonomous development; in 1998, the People’s Bank of China reformed its management system, indirectly gaining access to external resources for local development despite the transfer of some local control over enterprises to the central government; in 2002 the administrative approval system was reformed and local -enterprise linkages gained more decision-making power. The nature of central-territory relations, as a combination of the structure of state power and the actual process of political operation, is the result of the distribution of the exercise of state power between the central and local levels arising from the relationship of interests. As a result of adjusting social claims at this stage, the provincial government takes the initiative in financial relations and the division of competences between the central and local levels. After the local governments have gained the initiative, their administrative decisions will not be fully presented to the central government. That is to say, the local governments at this stage will not take the initiative and “take credit” for the central government’s decisions, but rather some governments in resource-poor areas will be “enamored” of the model areas, hoping to gain financial favor, external resources from banks, and even good The government-enterprise relationship. Therefore, the phenomenon of peer in local government administrative decision-making during the social structural transformation phase stems from the horizontal role of local governments, and the effect it has is that local governments gain more social benefits through peer decision-making. In line with the mixed economy phase, this peer is still essentially a state of positive peer.
As for the structure of social development and the change in ideology, many new ideas led by the scientific concept of development were formed during this period, and the economic-environmental-dominated social dichotomy was adjusted. These macro forms of change have also led to an inevitable convergence in the decision-making activities of local governments. For example, the scientific development concept put forward the idea of people-centered, comprehensive, coordinated, and sustainable development, and various local governments have adopted corresponding construction ideas. The Shandong region took the new path of industrialization, putting quality and efficiency at the center of the first circular economy system; Guangdong drew on the financial advantages of Shenzhen to deepen reforms in its fiscal and investment strategies and to shape reforms in its science, education, culture, and health systems in just 20 years. Thus, the structural and ideological transformation of social development during this period led to a high degree of unity among local governments on the critical points of future scientific development and the implementation of these points in local administrative decisions. This convergence in decision-making is a natural consequence of the “different paths to the same end” and is a reform element that needs to be taken into account in the autonomous development of local governments under the advice of the central government. This peer phenomenon results from the inevitability of a new period of social development. The effect it has is a high degree of implementation of the scientific concept of development by local governments and a new socialist path under the central government’s guidance. Obviously, due to the differences in the implementation perspectives of the various localities, this peer may present a specific negative peer state, i.e., each writing a good “proposition essay” around the central instructions. However, the differentiated “writing style” leads to an eventual increase in the gap within the same group.
3.3.3 Origins and connotations of peer effect in local government administrative decision-making in the stage of social formation change (2012-present)
After the 18th National Congress in 2012, China has entered a stage of high quality development, with China leader’s thought on socialism with Chinese characteristics in the new era, the “Five-in-One” overall layout, the “Four Comprehensive” strategic layout, and the modernization of the national governance system and the ability to govern. The general layout of China leader’s New Era of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics, the “Five-in-One” strategic layout, the “Four-comprehensive” strategic layout, and the modernization of the national governance system and governance capacity are introductory statements that promote the upgrading of social forms to high quality. In 2021, China completed the goal of building a moderately prosperous society, and social form development entered its second century. With the change of the leading social contradictions and the upgrading of the social form, the conflicts and contradictions between central and local relations are gradually reduced. Economic dimension: China’s high-quality financial system has taken shape, and the local government’s domination of economic factors such as finance, materials, and prices has become more stable. The political dimension: the responsibility of localities to manage local affairs has increased, and the streamlining and optimization of the multi-level structure has led to an increase in the political voice of local governments. Cultural dimension: Cultural undertakings such as education, science, and literature are becoming more prosperous, localities are beginning to form cultural systems with regional characteristics, the soft power of local governments has increased significantly, and with a system of fairness and guarantees, including right in social opportunities, the confidence of local cultures is increasingly evident. The social dimension: the central government has fully decentralized issues of livelihood interest and reform, and the autonomy of local governments in their policies to benefit the people has been enhanced. Ecological civilization dimension: the main body of supervision of public policy implementation has changed from the central government to the central government, and the role of local control and the voice of the supervisory system has increased again.
Therefore, the emergence of the peer phenomenon in the administrative decision-making of local governments at this stage is the result of the central government’s decentralization and the co-decision making under the central government’s positive incentives and scientific supervision. The root of this peer phenomenon is the synergy between the central government and the local government. The prime localities help the disadvantaged localities progress the social form, forming a “new administrative decision-making group” through industrial transfer, decision sharing, and project construction. But there will also be disadvantaged places that continue to be in a phase of social structural transformation and reject the guidance of the dominant government. The former means that a positive peer state is formed, while the latter becomes a reverse peer state. Overall, the peer effect of the social form change phase is further to amplify the rate of improvement in social quality and continue to promote social form upgrading.
3.3.4 Sorting out the evolution of the peer effect in local government administrative decision-making
Based on the correlation analysis in this section, the study developed the evolution of the decision peer effect, as shown in Figure 9.
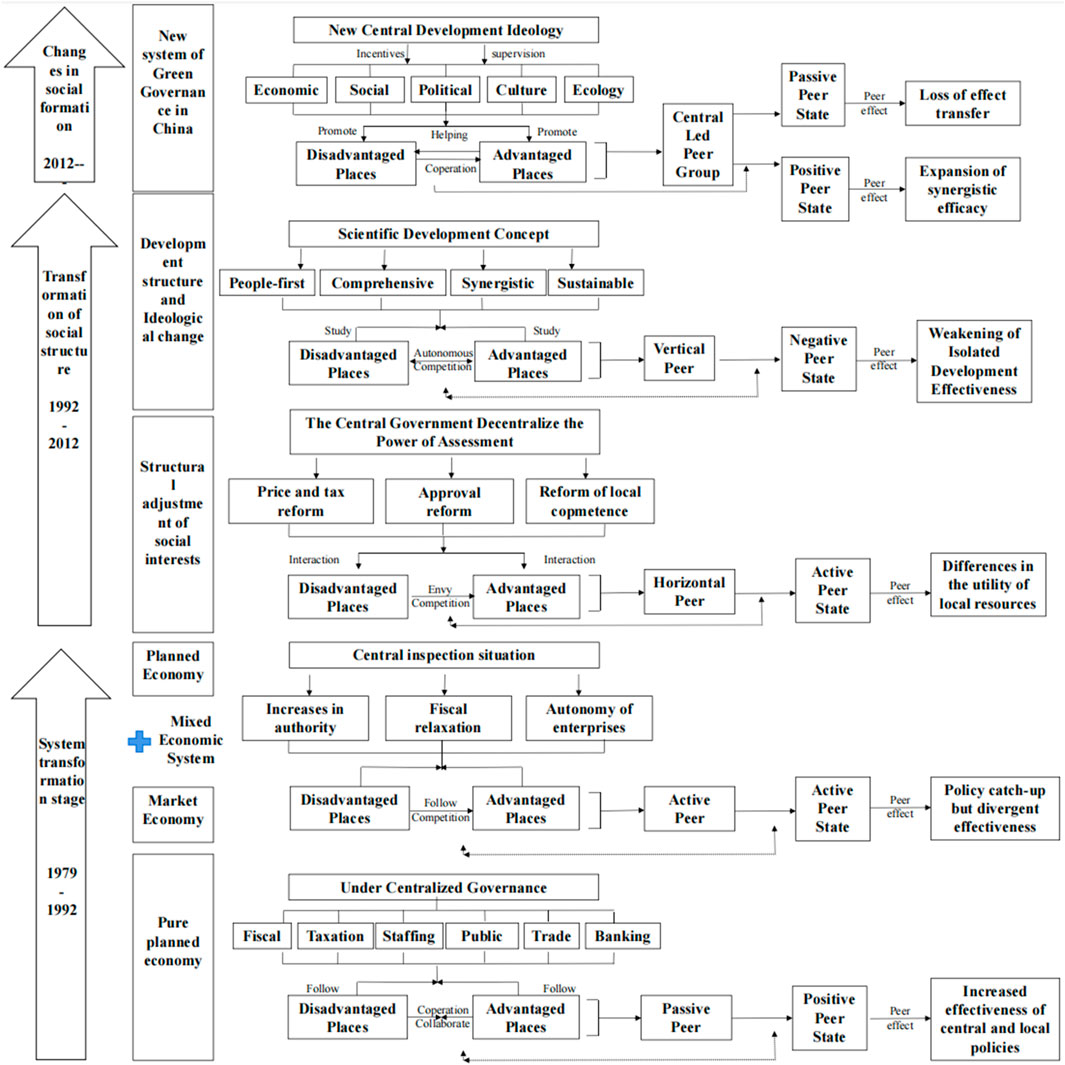
Figure 9. Changes in the origins and connotations of the peer effect in local government administrative decision-making.
As shown from Figure 9, with the background of China’s specific historical stage and the different roles played by the central government, local governments will coincidentally appear to make decisions peer phenomenon. During the period of the planned economy from 1949 to 1978, local governments were forced to form a unified decision-making front due to the solidification of the system, which is a passive type of peer. During the restructuring of social interests from 1992 to 2002, the disparity in resource advantages between local governments increased, causing disadvantaged areas to compete for the resources of regions advantaged through consistent decision-making. During the period of social change in 2012, the central government further clarified the decisions of local governments and began to take the initiative to lead and actively promote the quality of local governments’ decisions. The active support and cooperation among local governments also led to synergy and cross-content between the two sides in many choices. This kind of peer belongs to the solid central leadership peer. On the whole, due to the differences in the internal relationships (cooperation, emulation, competition, support, and autonomy) of local government administrative decision-making in each period, the peer state presents four forms, as positive, negative, active and passive, and the corresponding peer effect also produces positive or adverse effects. Therefore, mastering the code of the peer effect in local government administrative decision-making will provide empirical reference and practical guidance for government management effectiveness.
3.4 Definition of the connotation, external expression and characteristics of the green governance peer effect of local governments
China leader’s thought on ecological civilization profoundly elaborates that “ecological environment is a major political issue related to the Party’s mission and purpose, as well as a major social issue related to people’s livelihood.” The potential transformation between green and golden mountains reveals the dialectical unity between ecological protection and economic development. To strengthen the strategic determination of ecological civilization construction, balance the dynamic relationship between security and development, and run through the core demands of economic, political, social, and cultural benefits, there is an urgent need to enhance the effectiveness of green governance. General Secretary pointed out that to improve the ecological civilization system, social control capacity must be continuously improved, and the concept of green development is firmly practiced. In this context, the green governance system that has emerged has become an essential part of promoting the modernization of the national governance system and governance capacity, as well as achieving synergy between economic, political, social, cultural, and ecological development with the coordination and optimization of the spatial layout of production, living, and ecology.
With the receding of the crude economic growth method from the historical stage, the increasing pressure of ecological legacy and the increasingly sharp contradictions of economic adjustment have placed more constraints on local governments to transform, and an essential direction for local governments to break through the development dilemma is to strengthen green governance. However, green governance cannot be achieved overnight, and lags in economic, political, social, and cultural development may lead to ineffective governance (Lo, 2013). At the same time, the urgent need to transform local governments blurs the details of governance and weakens the integration power of green governance. With this orientation, some regions that have taken the lead in green governance have become excellent model templates for policy-making. The enthusiasm of local governments for green governance is a clear manifestation of China’s economic entry into a new era. At the beginning of the new development stage, as the pivot of the five development concepts, green governance is given a new direction in the top-level design for local governments to govern, i.e., to lead the construction of a resource-saving and environment-friendly society through green governance, and to achieve a coordinated development that can be carried by resources and the environment (Qi et al., 2021). Optimize the allocation of resource factors with the innovative product again, give new green supply under new technology and new business model, and eliminate grey and black production capacity. Reinforce the trend of deep economic integration into the world with open development and shared development, and guide the green extension of the industrial chain (Xu et al., 2014). The successful experiences of Zhejiang and Jiangsu have proven that green governance makes an essential contribution to the high-quality development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. As the transition progresses, green governance is being extended to the Yellow River and Pearl River basins to create green development ecological corridors and improve the effectiveness of environmental and environmental governance, further promoting balanced regional development and enhancing development connotations.
This analysis, combined with the previous section, shows that green governance belongs to the realm of administrative decision-making and inevitably converges with society’s ‘broad stream’ in all stages of transition. The peer effect of green governance by local governments formed under this orientation can be further defined. Under the premise of the central government’s strong emphasis on the new development concept in the new era, local governments have less room for free play in decision-making. Under the intervention of “competition with the ruler,” the individual behavior of local governments is more profoundly influenced by the behavior of the group (Balta-Ozkan et al., 2021), which makes green governance seem to be the “key straw” for local governments to get rid of the bottleneck of development. All places are in the “WeChat family group” of green governance. With the evolution of decision-making orientation and competition between disadvantaged and advantaged localities, this effect may have a positive effect: the synergy of multiple localities enhances the effectiveness of green governance and removes apparent black capacity. Or it can have a negative effect: the regional gap increases, and the efficacy of green administration decreases significantly. Therefore, the connotation of the peer effect of green governance by local governments refers to the phenomenon of convergence in the context of decisions made by local governments in the process of modernizing management, such as green governance, guided by changes in social form, China leader’s socialist ideology with Chinese characteristics in the new era and fundamental social contradictions. Along with the transformation of the dynamic relationship between governments, the social effects brought about by the peer phenomenon are thus transformed.
Further, combined with the previous analysis of the performance of green governance, administrative decision-making peer effect, this study considers that the external manifestations of the green governance peer impact of local governments are: (1) the suitable localities have formed a rich and mature policy decision-making system in green governance, whose activities include continuing to develop independently under the national green governance framework, or helping disadvantaged localities, through the transfer of green industries after cultivation, the green parks and the contribution of green resources, resulting in collaborative green governance decision-making. Under this linkage, the efficiency of local green governance is significantly improved, and the resulting green governance effectiveness leads to social progress. (2) Disadvantaged localities face philosophical problems such as an imbalance in decision-making and confusion in the direction in green governance, and their activities include continuing to develop independently under the national green governance framework, but most likely copying experiences and duplicating decisions, or even neighboring areas appearing to compete for green resources or linking up with advantaged localities to form cooperative green governance decisions through green resource undertaking and green experience learning. Under this linkage, both sides will continue to enjoy a pattern of green efficiency enhancement, creating a favorable green governance situation.
However, what is of concern is that green governance is a comprehensive administrative framework activity under the integration of various types of decision-making. Therefore, its characteristic is that the green governance peers effect will include the form and interest mechanism of all kinds of previous decisions: (1) it has the complex and uniform requirements of the central government in the era of planned economy, i.e., each local must build the system framework of green governance, which is the principal guidance for the formation of green governance peer effect of local government. (2) Local initiatives in the era of a mixed economy, i.e., localities clearly understand that green governance is the inevitable future of the national situation and a “novelty opportunity” for localities to seize the high ground for future development and therefore join the green governance sequence on their initiative. (3) Jealousy at the stage of restructuring of social interests, i.e., localities are influenced by prosperous regions and develop a logic of jealousy-driven incentives. (4) The competitive nature of the development structure and the mindset change, i.e., each locality clearly understands the positive impact of green governance on society and, guided by its own goals, wants to develop a locally appropriate governance path. (5) The social change phase is characterized by a great deal of integration, firstly, by the acceptance of the central government’s role as an incentive and supervisory function, and by a change from being “aligned with the central government” to being “driven by the central government,” and this drive is not a passive response to the central government’s strict rules, but a “soft drive” in collaboration with the central government. This push is not a passive “hard push” reaction under the strong regulations of the central government, but a “soft push” in cooperation and synergy with the central government. Secondly, there is a great deal of collaboration and synergy within the region, and the resulting mature green governance decisions will not be closed off by internal regional divisions.
3.5 The realization path of green governance peer effect of local government
3.5.1 Take the optimization of economic rights as an entry point to promote the activation of governance dynamics and enable rational decision-making on green governance
Give local governments greater fiscal and taxation authority to expand their green governance dynamics. Optimize the tax legislation authority and management mechanism of local public institutions at the provincial level, pay attention to the coordination between fiscal policies and other green governance policies, revitalize the strength of assets through fiscal restructuring, and activate the improvement of green governance effectiveness with the practical extension of budgetary support. The peer effect of green governance by local governments reflects the shortcomings of local financial management. In green control, local governments are highly dependent on fiscal output, while green governance wants to expand their economic power and “compete” with the central government for affairs. This confused approach to governance has led to irrational behavior: some disadvantaged regions only see prosperous areas expanding their fiscal revenues through green governance, ignoring in vain their existing mature and solid budgetary base, and distorting the path of green governance away from the concrete foundation and real development needs, which will eventually only lead to a systemic crisis of ineffective governance and fiscal shrinkage. Therefore, the internal logic of green governance should be clarified. Firstly, the central government may wish to expand the financial management authority of local governments and meet their demands in terms of motivation to enter green governance activities in a free and easy manner. Secondly, it should encourage local governments to invest in green governance and guide them to deepen their understanding of how successful regions operate financially so that they can support green governance with small-scale, high-energy assets. Lastly, the local government should adopt a zonal approach and precisely match the funding gap for green governance to avoid triggering significant debt risks in the financial turnaround.
3.5.2 Dialectical unification of regional interests and officials’ interests weakens the sentimental thinking of the exciting concept and promotes the linkage between the exciting concept and regional development
Reconstructing the performance appraisal system of local governments, strengthening the guiding role of regional interests, adjusting the driving mechanism of individual interests, enhancing the examination of the dynamic link between government inputs and outputs around the new tasks of high-quality development and the degree of social creation of green governance, and forming a new yardstick for local government assessment from the perspective of sustainability and strategic height. The peer effect of green governance by local governments is a combination of necessity and chance; from a necessity perspective, central and local governments choose green governance in response to development challenges, but from a chance perspective, the motives of local governments are not pure enough to ‘collide.’ In their green governance activities, local governments have become concerned with the regional benefits of green development. However, this motivation has not yet risen to the primary level. Therefore, resource use, environmental pollution control, environmental quality, ecological protection, and green living should be integrated into the government evaluation system, gradually shifting officials’ traditional views on economic growth and tax expansion to stimulate local governments’ rational motivation for the development and strengthen the starting and ending points of green governance for local governments, making their actions more realistic and unified in terms of people’s livelihood and social transformation. The central government must also pay attention to the financial discretion and promotion assessment of local governments as a pseudo-rational motive to drive the integration and synergy of green governance.
3.5.3 Paying attention to the special preferences of local governments and integrating special emotional mechanisms into a rational decision-making framework system, incorporating “differences” into “consistency”
We will pay attention to the concern of local governments for market players, protect the balanced relationship between local governments, enterprises, and entrepreneurs, actively face up to the legitimate interests of local governments towards business organizations, and affirm the particular preferences of local governments in the social atmosphere. Development can be achieved with half the effort by strengthening the “pro-clear” government-enterprise relationship and creating a better business environment. To a certain extent, local governments and their current leaders place great importance on establishing social resources and relationships, especially in the transition of government activities to the governance phase, where the softening of complex regulatory instruments allows local governments to have an intimate relationship with enterprises. Combined with the process of forming green governance efficiency, the output of local governments in achieving high-quality results in green governance is dependent on the expansion of green innovation products by enterprises, which means that local governments have a claim on enterprises in green governance. Therefore, it is essential to objectively acknowledge the preferential orientation of local governments in the business environment and social climate, which influences the final decisions of local governments and the mechanism of this invisible influence is within the realm of perception. Local governments can maintain this “ambiguous” government-enterprise linkage but should transform the “heterogeneity” of enterprises in various sectors into a “unified” consistency, i.e., the government can actively liaise, but The government can actively liaise, but it must be fair. The government can support key green industries in a biased manner and invest green resources purposefully but cannot neglect the quality enhancement of other sectors. The government can maintain a synergistic relationship with enterprises. However, it must maintain its status as a ‘leader,’ not as a co-conspirator or a blind decision-maker, and it cannot administratively force the interests of government and enterprises to be aligned. In short, local governments should focus on their role as referees in green governance. Individual localities should not be ‘enamored’ of the ‘corporate’ resources enjoyed by other governments, thus blindly following this particular preference and following suit to produce peer decisions. Enterprises are not production tools and performance resources for governments, but rather ‘athletes’ who work together for mutual benefit and progress.
4 Conclusion and implications
4.1 Conclusion
Based on the above analyses, this paper deeply explains the performance and formation path of local government green governance activities. It also explains the reasons for the eventual convergence of decision-making and the formation of the peer effect.
4.1.1 Analysis of the origin, content and connotation of local government green governance
The formation of local government green governance is marked by the proposal of General Secretary view of green governance. Tt has gone through the embryonic stage of the green governance concept (1978–2002), the stage of promoting the green governance policy system and adjusting the social concept (2002–2012), the stage of empowering the connotation of green governance in the new period (2012–2017), and the stage of formally constructing and maturing the green governance (2018-present), which comprise a total of four stages of development.
The change and enrichment of the main content and connotation of local government green governance is mainly the result of the adjustment of the role of the concept of green development at various stages and is essentially the mission of government construction given by the change of the economic-environmental dichotomy. With the formation of China leader’s thought of socialism with Chinese characteristics in the new period, the green governance of local governments has formed a chain of green governance-green innovation-green development to promote the construction of the five social transformations. In this process, local government green governance takes government resources as inputs and realizes the production of human, capital, and knowledge factors through green governance structures and green governance mechanisms; through the transformation of the factors, local enterprises and society realize the outputs of green governance effectiveness and green governance social responsibility, and such outputs are the results of green governance effectiveness.
4.1.2 The origin and connotation of local government administrative decision-making peer effect
Due to the weakness of local governments, many local governments ‘conspire’ and ‘cooperate’, many local governments through decision-making consistency, benefit sharing, and transforming the self ‘local’ identity. Weakness of the self ‘local’ identity, with the group power to collect the interests of the view, to expand the effectiveness of the local. This forms the prototype of the phenomenon of local government administrative decision-making cohort in China, and the increment of local effectiveness synthesized by this group interest view is the peer effect of local government administrative decision-making. Therefore, the local government administrative decision-making peer effect of change and transformation, in essence, is the central and local government interest view of the game and adjustment.
The development of the peer effect in administrative decision-making of local governments in China has gone through the stage of institutional transformation (1949–1992), the stage of social structural transformation (1992–2012), and the stage of social morphology change (2012-). Under the role of social forces, the local government thus appeared in the administrative decision-making peer effect: 1949–1978 planned economy period, the local government is forced by the solidification of the system and the formation of a unified decision-making front, belongs to the passive cohort; 1978–1992 mixed system period, the local government because of the = central assessment scale change, and the formation of emulation of the competition under the phenomenon of decision-making unanimity, belongs to active cohort; 1992–2002 social structure transformation stage (1992–2012), the stage of social formations change (1992-), the development of social formations. From 1992 to 2002, the social interest structure adjustment, the weaker regions hoped that the decision-making consistent and compete for the resources of the dominant regions, which led to the horizontal cohort among local governments; from 2002 to 2012, the development structure and ideological changes, the weaker decision-making generalization and vertical cohort; In 2012, the social changes, the local governments, and the central and local governments have created synergy and cooperation in many decisions. During the period of social change in 2012, local governments and central and local governments created synergies and cross-cutting contents in many decisions, forming a strong central-led cohort.
4.1.3 Connotation and characteristics of local government green governance peer effect
Because of the multiple attributes of administrative decision-making, local governments’ green governance also shows different degrees of cohort phenomenon and peer effect under the coupling effect of development stage and social background. As a comprehensive administrative framework activity under the integration of various types of decision-making, the green governance peer effect will include the previous forms of various types of decision-making and interest mechanisms, which not only presents the passive cohort characteristics under the central government’s mandatory unified requirements, but also presents the active cohort trend of the local government’s positive response, and also has the characteristics of the integration and complexity under the background of the interest structure, the ideological transformation, the social change, and other multiple institutional mechanisms.
4.2 Implications
The environmental foundation of local government green governance lays the material foundation for the generation of governance activities, but the direction and development of such activities depend on the motivational logic of local governments in green governance. Elements such as governance dynamics, regional interests, officials’ interests, and special preferences constitute the basic motivational factors for the formation of local governments’ green governance peer effect. When some regions are positively affected by the above elements, the green governance efficiency will show a highly correlated positive growth and the index of the peer effect will increase significantly. It is undeniable that the positive significance of these elements for the green governance peer effect and the broad motivation for the formation of a high-quality pattern of green governance; however, these elements are still essentially the most basic motivational factors, which are unable to go beyond the meaning of the governance activities and guide the local government to make pure decisions based on the local strategic height. Motivational factors are embedded in the administrative structure of the local government and are closely related to the ruling leadership and local interests. As a result of the inner subjective operation, the motivation factor contains too many ‘emotional’ ideas, although these ‘emotiona’ activities bring the positive side, but ultimately unsustainable. Therefore, building a rational and scientific decision-making mechanism for local government green governance is a key measure to guarantee the high quality and optimization of local government green governance, and also to guarantee that local government green governance activities can make rational subconscious decisions embedded in the self in the case of ‘emotional’ offline. Under the rational mechanism, the local government green governance peer effect will be objective and real, and the utility results will be more positive. Specific practices are encapsulated:
4.2.1 Optimisation of fiscal authority as an entry point to promote the activation of governance initiative and rational decision-making in green governance
Give local governments greater fiscal and tax authority to expand their green governance initiative. Optimize the tax legislation and management mechanism of local public institutions at the provincial level, pay attention to the coordination of fiscal policy and other green governance policies, revitalize assets through fiscal structural adjustment, and activate the enhancement of green governance efficiency through the effective extension of fiscal support. The local government green governance peer effect reflects the shortcomings of local financial management. Local governments in the practice of green governance are highly dependent on the financial output, and green governance process and want to use it to expand the financial power, and the central authority to achieve the ‘competition’, the financial both as the environmental basis of green governance, but also to the green governance of the incentive logic identity, the contradiction between the two makes the local government related system is confused, this kind of Confused governance ideas make it produce blindly follow the trend of irrational behavior: part of the vulnerable areas only see the successful areas through green governance to expand fiscal revenues, in vain, ignoring its original mature, solid financial foundation, detached from the reality of the foundation and the real development needs and distortion of the green governance path, and ultimately can only lead to ineffective governance, financial shrinkage of the systemic crisis. Therefore, when clarifying the internal logic of green governance. First of all, the central government may wish to expand the financial management authority of local governments, in the motivation to meet the demands of the local government, so that it is free and easy to enter the green governance activities; secondly, to encourage the local financial investment in green governance, to guide its deep understanding of the financial operation of successful regions, to support the green governance of the small-scale, high-energy asset operation; finally, the district policy, accurate docking of the green governance funding gaps and avoid local governments triggering major debt risks in financial turnover.
4.2.2 Dialectical unification of regional interests and officials’ interests, weakening the emotional thinking of the concept of interests, and promoting the connection between the concept of interests and regional development
Reconstruct the local government performance appraisal system, strengthen the guiding role of regional interests, adjust the driving mechanism of personal interests, focus on the new tasks of high-quality development, the degree of social creativity of green governance, and other connotations, strengthen the dynamic linkage between the government’s inputs and outputs, and form a new yardstick for the assessment of local governments from the perspective of sustainable and strategic height. The local government green governance peer effect is a combination of inevitable and accidental, from the inevitable point of view, the central and local governments to cope with the development of the problem will choose green governance, but from the accidental point of view, it is the local government is not pure enough motivation just ‘collision’. From the perspective of this paper, local governments have paid attention to the regional interest in green development, but the motivation has not yet risen to the main level. Therefore, the use of resources, environmental pollution control, environmental quality, ecological protection, green living, and other content into the government evaluation system, and gradually transfer the traditional view of economic growth, and tax expansion view of the officials, to stimulate the rational development of the local government motivation, strengthen the starting point of green governance of the local government, the starting point, the landing point, so that the deeds more real, unified to the people’s livelihood and social transformation. For the central government, it is also necessary to pay attention to the local government’s financial discretion, and promotion assessment, as a pseudo-rational motivation to drive the integration of green governance, and synergistic development.
4.2.3 Clearly understand the decision-making of the same group effect of green governance and avoid the loss of government resources
Resolve the structural redundancy of government resources, realize the simplification, efficiency and fit of input elements, promote the fine penetration of green governance elements, transform government functions, reshape governance thinking, and avoid the problem of resource inefficiency caused by blind investment. Green governance is not a “one size fits all” or “one size fits all” instantaneous governance activity, nor is it an effective management method. The improvement or growth of green governance efficiency itself is a “black box”. The operation process of the input-output ratio of green governance is different due to the different environment and characteristics in different regions, and the resource transformation trajectory in the “black box” is also different. Blindly promoting the expansion of input factors will not win the favor of the “black box”, on the contrary, it will damage the interests of the region. Only when formulating local development plans and green governance schemes, clearly recognizing their own “black box” operation mechanism, and accurately implementing policies according to local conditions, can the real effect of governance be expanded. As far as the current situation is concerned, the repeated setup of institutions, the imbalance of knowledge structure division, and the spread of green capital are all serious, and there is a long production cycle between green projects and green fixed capital. Treating various green governance activities with inclusive and patient governance concepts may eliminate the redundancy problem in the short term.
Author contributions
HG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. HL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Balta-Ozkan, N., Yildirim, J., Connor, P. M., Truckell, I., and Hart, P. (2021). Energy transition at local level: analyzing the role of peer effects and socio-economic factors on UK solar photovoltaic deployment. Energy Policy 148, 112004. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2020.112004
Barbier, E. B., Stern, D. I., and Common, M. S. (2004). Economic growth and environmental degradation: the environmental Kuznets curve and sustainable development. World Dev. 24 (7), 1151–1160. doi:10.1016/0305-750x(96)00032-0
Bardhan, P. (2020). The Chinese governance system: its strengths and weaknesses in a comparative development perspective. China Econ. Rev. 61, 101430. doi:10.1016/j.chieco.2020.101430
Brunel, C. (2019). Green innovation and green imports:Links between environmental policies, innovation, and production. J. Environ. Manag. 248, 109290. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109290
Cca, B., Rjb, E., Ns, C., and Boregowda, P. (2018). Government health insurance and spatial peer effects: new evidence from India. Soc. Sci. and Med. 196, 131–141. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.11.021
Chen, G., and Bao, J. (2014). Path dependence in the evolution of resort governance models in China. Tour. Geogr. 16 (5), 812–825. doi:10.1080/14616688.2014.949295
Chien, S. S., Hong, D. L., and Lin, P. H. (2017). Ideological and volume politics behind cloud water resource governance – weather modification in China. Geoforum 85, 225–233. doi:10.1016/j.geoforum.2017.08.003
Dani, R. (2014). Green industrial policy. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Pol. 30 (3), 469–491. doi:10.1093/oxrep/gru025
De Lucia, V. (2015). Green governance: ecological survival, human rights and the law of the commons. By burns weston and david bollier. J. Environ. Law 27 (02), 373–376. doi:10.1093/jel/eqv014
Deslatte, A., and Stokan, E. (2019). Hierarchies of need in sustainable development: a resource dependence approach for local governance. Urban Aff. Rev. 55 (04), 1125–1152. doi:10.1177/1078087417737181
Dressler, W. H., Smith, W., Kull, C. A., Carmenta, R., and Pulhin, J. M. (2020). Recalibrating burdens of blame: anti-swidden politics and green governance in the philippine uplands. Geoforum 1, 1–22. doi:10.1016/j.geoforum.2020.01.024
Feld, J., and Zölitz, U. (2015). “Understanding Peer Effects: On the Nature, Estimation and Channels of Peer Effects.“ Social Science Electronic Publishing 35. 2:387–428. doi:10.1086/689472
Guo, J. B., and Chen, F. L. (2021). Local government competition, environmental regulation and green development of urban agglomeration. Explor. Econ. (01), 113–123. doi:10.1002/sd.2610
Hassan, S. T., Xia, E., and Lee, C. C. (2021). Mitigation pathways impact of climate change and improving sustainable development: the roles of natural resources, income, and CO2 emission. Energy and Environ. 32, 338–363. doi:10.1177/0958305x20932550
He, X., Hung, S., Chau, K., et al. (2019). A study on the effect of environmental regulation on green innovation performance: a case of green manufacturing enterprise pearl river delta in China. Ekoloji 28 (07), 727–736.
Huang, Y., Aguilar, F., Yang, J., Qin, Y., and Wen, Y. (2021). Predicting citizens' participatory behavior in urban green space governance: application of the extended theory of planned behavior. Urban For. and Urban Green. 1, 127110. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2021.127110
Jiang, X., and Guo, X. (2017). Residents' experience and knowledge and Urban Green Governance -- Based on Mayer's theory and Finland's practice. Dialectics Nat. 33 (02), 114–118.
Kong, A., Ting, F., Feng, M., et al. (2016). Advanced manufacturing technologies and green innovation: the role of internal environmental collaboration. Sustainability 1689.
Li, Q., Zeng, F., Liu, S., Yang, M., and Xu, F. (2020). The effects of China's sustainable development policy for resource-based cities on local industrial transformation. Resour. Policy 71, 101940. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101940
Li, W., Zhang, Y., Zheng, M., Li, X., Cui, G., and Li, H. (2019). Research on Green Governance and its evaluation of Chinese listed companies. Manag. World 35 (05), 126–133+160. doi:10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2019.0070
Li, Y., Niu, X., et al. (2017). Green governance and governance transformation -- a summary of the 9th international symposium on corporate governance. Nankai Manag. Rev. 20 (05), 185–192.
Liao, K., Dai, S., and Duan, X. (2019). Research on the coordination effect evaluation and dynamic relationship between scientific and technological innovation and Green Governance. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 36 (16), 34–43.
Lin, R., Gui, Y., Xie, Z., and Liu, L. (2019). Green governance and international business strategies of emerging economies' multinational enterprises: a multiple-case study of Chinese firms in pollution-intensive industries. Sustainability 11, 1013. doi:10.3390/su11041013
Liu, H., Geng, J., and Yao, P. (2021c). Relationship of leadership and envy: how to resolve workplace envy with leadership—a bibliometric review study. J. Intell. 9, 44. doi:10.3390/jintelligence9030044
Liu, H., Yao, P., Wang, X., Huang, J., and Yu, L. (2021a). Research on the peer behavior of local government green governance based on seci expansion model. Land 10 (5), 472–526. doi:10.3390/land10050472
Liu, H., Zhang, J., and Zhang, X. (2021b). China's carbon emission responsibility and image from the perspective of global supply chain. Resour. Sci. 43 (04), 652–668.
Liu, Z. Y. (2017). General secretary xi jinping's view on green governance. People's Forum 25, 68–69.
Lo, A. Y. (2013). Carbon trading in a socialist market economy: can China make a difference? Ecol. Econ. 87, 72–74. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.12.023
Ma, L., Cai, B., Wu, F., and Zeng, H. (2018). Hourly disaggregation of industrial CO2 emissions from Shenzhen, China. Environ. Pollut. 236, 396–404. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.090
Opschoor, H. (2010). Sustainable development and a dwindling carbon space. Environ. and Resour. Econ. 45 (01), 3–23. doi:10.1007/s10640-009-9332-2
Qi, S., Zhou, C., Li, K., and Tang, S. (2021). The impact of a carbon trading pilot policy on the low-carbon international competitiveness of industry in China: an empirical analysis based on a DDD model. J. Clean. Prod. 281, 125361. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125361
Ran, T., and Ping, Q. (2010). How has rural tax reform affected farmers and local governance in China? China and World Econ. 15 (003), 19–32.
Rennings, K., and Wiggering, H. (1997). Steps towards indicators of sustainable development: linking economic and ecological concepts. Ecol. Econ. 20 (01), 25–36. doi:10.1016/s0921-8009(96)00108-5
Sassi, S., and Gasmi, A. (2014). The effect of enterprise and household credit on economic growth: new evidence from European Union countries. J. Macroecon. 39, 226–231. doi:10.1016/j.jmacro.2013.12.001
Scalia, M., Angelini, A., Farioli, F., Mattioli, G. F., Ragnisco, O., and Saviano, M. (2020). An Ecology and Economy Coupling Model. A global stationary state model for a sustainable economy in the Hamiltonian formalism. Ecol. Econ. 172, 106497. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.106497
Schiederig, T., Tietze, F., and Herstatt, C. (2012). Green innovation in technology and innovation management - an exploratory literature review. R&D Manag. 42 (02), 180–192. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9310.2011.00672.x
Shi, Y., and Liu, X. (2018). Finding the path to achieve a better life for the people Green Governance. Reform 2, 45–53.
Shi, Y., and Tang, E. (2019). On the construction of green governance culture system with Chinese characteristics. Adm. Forum 26 (02), 124–129.
Sun, L., Ren, X., and Li, Y. (2019). Strategic flexibility, green innovation and enterprise performance -- interaction and regulation effect model under dynamic environmental regulation. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 36 (22), 82–91.
Sun, Z. Q., and Wang, Q. (2021). The asymmetric effect of natural resource abundance on economic growth and environmental pollution: evidence from resource-rich economy. Resour. Policy 72 (2), 102085. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102085
Thoyre, A. (2021). Neoliberalizing negawatts: governance of energy efficiency as accumulation strategy. Geoforum 118, 140–149. doi:10.1016/j.geoforum.2020.12.012
Wang, H., and Bernell, D. (2013). Environmental disclosure in China: an examination of the green securities policy. J. Environ. and Dev. 22 (4), 339–369. doi:10.1177/1070496513506905
Wu, H., Hao, Y., Ren, S., Yang, X., and Xie, G. (2021). Does internet development improve green total factor energy efficiency? evidence from China. Energy Policy 153, 112247. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112247
Xiao, H., Wang, D., Qi, Y., Shao, S., Zhou, Y., and Shan, Y. (2021). The governance-production nexus of eco-efficiency in Chinese resource-based cities: a two-stage network dea approach. Energy Econ. 101, 105408. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105408
Xiao, J., Zhen, Z., Tian, L., Su, B., and Zhu, A. (2020). Green behavior towards low-carbon society: theory, measurement and action. J. Clean. Prod. 278, 123765. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123765
Xu, S., He, Z., and Long, R. (2014). Factors that influence carbon emissions due to energy consumption in China: decomposition analysis using LMDI. Appl. Energy 127, 182–193. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.093
Zabel, J. E. (2018). The impact of peer effects on student outcomes in New York city public schools. Educ. Finance and Policy 3 (02), 197–249. doi:10.1162/edfp.2008.3.2.197
Zhao, X. (2017). General secretary xi jinping's thought on sustainable development from the report of the 19th CPC national congress. South. Econ. 10, 13–15.
Keywords: green governance, local government, peer effect, transmutation logic, China
Citation: Gu H and Liu H (2025) Formation mechanism of local government green governance peer effect in China: evolution logic and basic experience. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1548458. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1548458
Received: 19 December 2024; Accepted: 13 May 2025;
Published: 30 May 2025.
Edited by:
Le Wen, Auckland University of Technology, New ZealandReviewed by:
Zhiheng Yang, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, ChinaShengqing Xu, Jiangsu Ocean Universiity, China
Copyright © 2025 Gu and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hengsheng Gu, Z3VoZW5nc2hlbmdAdG9uZ2ppLmVkdS5jbg==, MjIxMDQ3OUB0b25namkuZWR1LmNu
 Hengsheng Gu*
Hengsheng Gu* Hongda Liu
Hongda Liu