- 1Economics and Management College, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China
- 2School of Tourism Geography, History and Culture, Hulunbuir University, Hulunbuir, China
- 3Inner Mongolia Forest Industry Group Co., Ltd., Hulunbuir, China
- 4School of International Education, Wuhan University of Technoledgy, Wuhan, China
- 5School of Management and Economics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
With the advancement of sustainable development goals, digital technological innovation has emerged as a critical pathway for mitigating urban carbon emission intensity. Using balanced panel data from 282 Chinese cities spanning 2012-2019, this study employs fixed-effect models and mediating effect analysi to investigate the nonlinear impact of digital technology innovation on urban carbon intensity. The findings reveal the following. (1) There exists an inverted U-shaped relationship between digital technological innovation and carbon intensity. (2) A nonlinear mediation mechanism is identified, whereby digital technological innovation influences carbon intensity through its effects on energy intensity and governmental environmental attention. (3) Substantive digital technological innovation reaches the turning point more rapidly. (4) The inverted U-shaped relationship holds exclusively for non-key environmental protection cities, while it is not evident in key environmental protection cities. (5) This relationship is consistently observed across both Broadband China pilot cities and non-pilot cities, suggesting that the findings are robust and applicable to different types of cities. These findings not only deepen our understanding of the complex interplay between digital technological innovation and carbon intensity but also provide valuable theoretical insights and practical guidance for achieving sustainable development objectives.
1 Introduction
China’s rapid economic growth has spurred remarkable economic expansion, yet it has also given rise to substantial carbon emissions (Chang et al., 2023; Peng et al., 2023; Du et al., 2025; Xu et al., 2024). Particularly, the extensive use of fossil fuels has contributed to environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions (Zhu et al., 2025; Cheng et al., 2018; Kang et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2020). Moreover, inefficiencies in energy usage and san over-reliance on heavy industries in the economic structure have made it difficult to effectively control carbon emissions in the short term (Cui et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2022). In response to the critical challenge of carbon emissions, the Chinese government has set forth the “dual carbon” objectives (Bai et al., 2023; Ke et al., 2023; Tang et al., 2023; Jiang et al., 2024). These goals represent not only China’s commitment to addressing global climate change, but also a crucial lever for driving the green economic transformation. Balancing economic growth while effectively reducing carbon intensity has become a major issue for China’s development (Liu et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2022). In this context, the application of digital technologies has emerged as an essential means to enhance energy efficiency and facilitate the green transition (Pu et al., 2024; Yi et al., 2024). However, the implementation of digital transformation requires not only addressing the tension between technological innovation and environmental protection, but also carefully considering how effective policies can guide the transition toward genuine low-carbon and sustainable development (Li and Yue, 2024; Tang et al., 2024).
In recent years, digital technological innovation has garnered widespread attention globally and become one of the core drivers of high-quality economic development (Lu and Li, 2024; Yang et al., 2025). As a key player in the global digital economy, China has actively implemented a digital transformation strategy, gradually establishing a digital technology ecosystem characterized by big data, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (Chen and Lu, 2024). These technologies have not only been extensively applied in industries such as manufacturing, finance, transportation, and healthcare, but have also fundamentally transformed production processes and lifestyles (Zhao et al., 2024). The Chinese government has prioritized digital transformation as a national development strategy, particularly within the “14th Five-Year Plan” and the 2035 Vision, explicitly advocating for the acceleration of digital economy development and the construction of a “Digital China.” However, the rapid development of digital technologies has also brought forth new challenges, including issues such as the digital divide, information security, and privacy protection, which remain pressing concerns (Chen and Li, 2024; Zhu et al., 2024). Nevertheless, digital technologies, as the driving force behind the economic and social transformation, are providing significant momentum for China’s economic restructuring, industrial upgrading, and green development (Yang et al., 2025). As technologies such as 5G and artificial intelligence continue to mature, the digital economy is expected to play an increasingly critical role in the transition to a low-carbon economy, particularly in optimizing energy management and improving energy utilization efficiency (Gupta and Dey, 2024; Wang and Yang, 2024a).
Digital technological innovation holds significant potential in advancing the development of low-carbon economy. However, it also presents a “double-edged sword” (Xu et al., 2024). On one hand, the widespread application of digital technologies can effectively reduce carbon emissions by enhancing energy efficiency and minimizing resource waste. Technologies such as smart grids and big data enable intelligent energy dispatch and precise management, thus preventing overconsumption and waste of energy (Shen et al., 2024). For instance, cloud computing and artificial intelligence can optimize production processes, increase efficiency, and reduce high-carbon emission production stages, leading to a greener and more sustainable production model. Through digital management, firms can monitor emission sources in real-time and promptly implement corrective measures, further lowering their carbon footprint.
Furthermore, digital technological innovation may induce a “rebound effect”. In the short term, cost savings and efficiency improvements driven by digital technologies could stimulate increased energy consumption, potentially exacerbating carbon emissions. As production efficiency improves, firms may experience higher output, leading to an expansion in production scale and the creation of new market demands, which can, in turn, raise energy consumption (Hanelt et al., 2021). For example, emerging industries such as electric vehicles and shared mobility-enabled by digital technologies-may reduce carbon emissions from traditional combustion engines but could also increase electricity demand on a large scale (Lyytinen, 2022; Trocin et al., 2021). In particular, in China, where electricity generation is still heavily reliant on fossil fuels, this surge in demand may contribute to a rebound in carbon emissions (Liu Y. et al., 2023). Furthermore, the proliferation and widespread use of digital technologies may spur the expansion of data centers and server infrastructure, which, by themselves, represent a significant energy consumption concern. Thus, while digital technology innovation holds immense promise in fostering a low-carbon economy, it also introduces challenges that cannot be overlooked.
There are three possible innovations. First, while substantial research has explored the relationship between technological innovation and environmental outcomes, much of the existing work has focused primarily on how green technologies can reduce emissions by improving energy efficiency and minimizing resource waste. In contrast to traditional studies that focus on linear relationships (e.g., Zor, 2023; Chang et al., 2023), this paper is the first to reveal an inverted U-shaped nonlinear relationship between digital technology innovation and carbon emission intensity. The theoretical framework is expanded through the analysis of a dual mediating mechanism (energy intensity and government environmental attention). However, there is a notable gap in the literature regarding digital technology innovation, particularly in terms of its specific impact on carbon intensity. By examining the effect of digital technology innovation on carbon intensity, our paper not only enriches the literature on technological innovation and environmental governance, but also provides a new theoretical framework and empirical support for the role of digital technologies in low-carbon development. Second, this study identifies an inverted-U relationship between digital technology innovation and carbon intensity. This finding provides new empirical evidence for the long-standing academic discussion on the “rebound effect,” suggesting that the environmental impacts of digital technology innovation may vary substantially across different stages of development. Thus, this paper deepens our understanding of the complex role of digital technologies in the low-carbon economic transition and offers a fresh perspective for further academic exploration of sustainable development pathways driven by technological innovation. Finally, this paper demonstrates that digital technology innovation can indirectly influence urban carbon intensity through the government’s focus on environmental protection. This finding highlights the crucial role of digital technologies in enhancing environmental governance and policy responsiveness, thereby further enriching the theoretical understanding of how digital technology innovation contributes to carbon emission reductions. In sum, this study expands the boundaries of research on digital technology innovation and provides a scientific foundation for developing policy frameworks that promote the synergistic development of digitization and decarbonization.
The structure of the paper is as follows: the second section reviews the literature and puts forward research hypotheses, the third section includes sample selection, identification of variables and model specification, the fourth section presents empirical results and mechanism analysis, the fifth section discusses heterogeneous characteristics and policy implications, and the final section concludes the study with discussions on heterogeneous characteristics, policy implications and future research directions.
2 Literature review and research hypothesis
2.1 Literature review
2.1.1 Research related to digital technology innovation
Digital technology innovation is widely regarded as a key driver of economic development and social progress, primarily by leveraging advanced information technologies to optimize resource allocation and enhance production efficiency (Tortora et al., 2021). From a theoretical perspective, digital technology innovation spans several interdisciplinary fields, including technological innovation theory, information economics, and organizational change. Schumpeter’s innovation theory provides a foundational framework for understanding digital innovation, particularly its emphasis on the “reorganization of production factors”. In the digital era, this reorganizational power is exemplified by artificial intelligence-driven energy management systems, which restructure industrial processes through real-time data analysis and intelligent scheduling. For instance, smart grids enabled by digital technologies can optimize energy distribution across factories, reducing redundant consumption and lowering carbon emission intensity by reorganizing energy utilization patterns. Such applications demonstrate how digital technologies translate Schumpeter’s theoretical insights into practical reductions in environmental impact.
In recent years, with the rapid development of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, the scope of digital technology innovation has expanded beyond technological breakthroughs to include transformations in business models and governance structures (Firk et al., 2022). During the digital transformation process, profound changes have occurred in the interactions between enterprises, governments, and consumers, culminating in a new economic system centered around data as a core resource. Additionally, research on digital technology innovation is increasingly focusing on its social and environmental impacts, including its effects on labor markets, income distribution, and sustainable development (Huang et al., 2023b). However, there remains a lack of consensus in the academic community regarding a unified definition of digital technology innovation, particularly in distinguishing it from traditional technological innovation. As such, future research should seek to develop a more universally applicable theoretical framework by incorporating diverse technological application scenarios.
The realization of digital technology innovation is influenced by a range of factors, with three core drivers being technological supply, market demand, and institutional environment. In terms of technological supply, research and development investment and a highly skilled talent pool are direct catalysts for digital technology innovation. In particular, the intensification of R&D in fields such as artificial intelligence has significantly enhanced technological innovation capabilities (Mariani and Nambisan, 2021). Market demand incentivizes firms to meet consumer needs for intelligent products and services, thereby driving technological upgrades (Li et al., 2024). Meanwhile, the institutional environment-such as intellectual property protection policies, government subsidies, and regulatory frameworks-provides both the security and incentives necessary for digital technology innovation. However, the innovation paths for digital technology vary across countries and regions. For instance, developed countries tend to focus on basic research and technological breakthroughs, while developing nations often rely more heavily on technology imports and localized innovation (Huang et al., 2023a). Furthermore, globalization and cross-border cooperation are increasingly important in the landscape of digital technology innovation, with cross-border data flows and international R&D collaborations emerging as dominant trends. Future research should further explore the differential driving factors of digital technology innovation in varying contexts, particularly in balancing technological sovereignty with international cooperation in the globalized landscape.
The influence of digital innovation on economic development has become a focal point of research, demonstrating significant potential in driving economic growth, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing production efficiency (Goldfarb and Tucker, 2019). First, digital technologies reduce information asymmetry and transaction costs, creating more business opportunities for firms, thereby stimulating overall economic growth (Johnson et al., 2022). For example, the development of e-commerce and financial technology has facilitated the digital transformation of traditional industries, providing enterprises with new market access (Corvello et al., 2023). Second, digital innovation significantly enhances production and distribution efficiency through intelligent production processes and precise market analysis. Moreover, it generates new employment opportunities, although it also leads to the disappearance of certain traditional jobs. However, research has also shown that digital technology innovation may exacerbate income inequality, particularly when there is a mismatch between technology and labor skills. Furthermore, in some industries, the existence of technological barriers may reinforce market concentration. As a result, scholars advocate for a balanced approach to fostering digital technology innovation, emphasizing fairness and inclusivity to ensure that its economic benefits extend to a broader segment of society.
The environmental impact of digital technology innovation is dual-faceted, with the potential to both promote sustainable development and introduce new environmental challenges. Digital technologies have the potential to significantly promote sustainable development by enhancing energy efficiency and reducing resource waste. For example, smart grid technologies optimize energy distribution, while Internet of Things technologies enable real-time monitoring to reduce energy consumption in industrial production. On the other hand, the rapid advancement of digital technology innovation is accompanied by increased energy demand. This is particularly evident in the expansion of data centers and servers, which consume substantial amounts of electricity (Babilla, 2023). Furthermore, the widespread adoption of digital technologies may trigger a rebound effect. In this scenario, efficiency gains are offset by an overall increase in energy consumption, thereby undermining some of the emission reduction benefits (Cheng et al., 2023). As a result, there has been extensive academic discussion on the environmental effects of digital innovation, with proposed solutions including policy interventions to encourage the development of green technologies, optimizing the energy structure of data centers, and implementing more stringent environmental standards. However, research in this area remains in its early stages, and future studies will need to explore the multidimensional impacts of digital innovation on various environmental factors, providing a scientific foundation for achieving a synergistic development of technological advancement and environmental protection (Shojaei and Burgess, 2022).
2.1.2 Carbon intensity related studies
Carbon emission intensity is a key indicator for assessing the carbon efficiency of economic activities, typically defined as the amount of carbon emissions per unit of economic output (Aryai and Goldsworthy, 2024; Jiang et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2023). Carbon intensity is influenced by multiple factors, including economic conditions, technological advancements, energy structure, and policy interventions (Lee et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2021; Du et al., 2022). Among these factors, technological innovation is widely recognized as a primary driver for reducing carbon emission intensity, particularly in the contexts of clean energy technologies and industrial decarbonization (Porter and Linde, 1995). Moreover, optimizing the energy mix plays a critical role in influencing carbon emission intensity. For instance, the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources has been shown to significantly contribute to reducing carbon emissions (Lin and Teng, 2024; Liu et al., 2022; Duan et al., 2025). However, research indicates that the effects of these factors exhibit significant heterogeneity across regions (Zhao et al., 2023). For instance, in high-income countries, technological innovation has a more pronounced impact on reducing carbon emission intensity, whereas in regions with abundant energy resources, adjustments to the energy structure tend to have a more substantial effect (Grossman and Krueger, 1995; Wu et al., 2021).
From a dynamic perspective, changes in carbon intensity not only reflect the level of economic development and technological advancements, but are also significantly influenced by policy interventions (Xu et al., 2023). For instance, carbon taxes and carbon trading mechanisms are widely regarded as essential policy tools for driving corporate emissions reductions. By increasing corporate costs and optimizing resource allocation, these policies can substantially lower carbon emission intensity (Ren et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023). However, in certain energy-intensive industries, the rebound effect may undermine the effectiveness of these policies in reducing emissions (Zhang et al., 2022). Furthermore, the implementation strength of policies and the adequacy of complementary measures directly impact their real-world efficacy (Ali et al., 2022). In developing countries, for example, the effectiveness of policy implementation is often constrained by fluctuations in energy prices, government regulatory capacity, and public participation (Wu et al., 2024; Yan et al., 2022).
Recently, digital technology innovation has become a significant driver in reducing carbon emission intensity, profoundly impacting carbon emissions through optimized energy management, enhanced production efficiency, and the promotion of green technology transitions (Lian et al., 2024). Technologies such as smart grids and artificial intelligence enable precise energy scheduling and real-time monitoring, effectively reducing resource waste and lowering the carbon intensity per unit of output. However, the widespread adoption of digital technologies may also give rise to certain negative effects. For instance, the rapid expansion of digital infrastructure-such as data centers and servers-could increase carbon emissions, potentially offsetting some of the gains from technological advancements (Zhang et al., 2024). Additionally, digital innovation may lead to a rebound effect, where improved efficiency triggers higher energy demand, resulting in increased carbon emissions in the short term (Sun et al., 2024). Consequently, the academic discourse surrounding the environmental impacts of digital technology innovation has become increasingly vigorous, with many scholars suggesting that its role in reducing carbon emission intensity may exhibit nonlinear characteristics.
Based on the above literature, this study proposes the following hypothesis regarding the nonlinear relationship between digital technology innovation and carbon intensity.
2.2 Basic hypothesis
The rapid development of digital technologies is often accompanied by significant infrastructure investments, which, in the short term, may lead to an increase in carbon intensity. For instance, the deployment of data centers, cloud computing platforms, and large-scale Internet of Things devices requires substantial energy and resources to maintain their operations, with much of the energy consumption typically sourced from traditional fossil fuels, thereby contributing to higher carbon emissions (Wang et al., 2024b). This nonlinear pattern aligns with the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) theory proposed by Grossman and Krueger (1995), which posits an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic growth and environmental degradation. Analogously, digital technology innovation exhibits a “rebound effect” in its early stages (similar to EKC’s pollution increase phase), where infrastructure expansion and productivity growth driven by digitalization may transiently elevate carbon intensity. However, as digital technologies mature-characterized by widespread adoption of smart grids, big data analytics, and AI-driven efficiency tools-their energy-saving effects dominate, leading to a decline in carbon intensity (mirroring EKC’s pollution reduction phase) (Pu et al., 2024).
Furthermore, during the initial phase of digital technology adoption, a “rebound effect” may occur, wherein the resource savings and efficiency gains brought about by technological advancements stimulate increased productivity and consumption demand, thereby exacerbating carbon intensity. In this stage, although the application of digital technologies may improve energy efficiency in certain industries, the associated infrastructure development and rising market demand could keep carbon emission intensity at elevated levels or even cause it to rise (Du et al., 2024). This phenomenon aligns with the early pollution increase phase described by the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) theory, suggesting that digital technologies, in their early stages, may have a negative impact on carbon emissions.
As digital technologies mature, their positive impact on carbon emissions increasingly becomes more pronounced, gradually outweighing their initial negative effects. With the widespread integration of information technologies-particularly advancements in big data, smart grids, and artificial intelligence-digital technologies have demonstrated significant potential in optimizing resource allocation and improving energy efficiency. These technologies enable precise data analysis, real-time energy management, and intelligent production processes, all of which serve to minimize energy waste and excessive consumption (Geng et al., 2024). For example, the deployment of smart homes, intelligent buildings, and the industrial internet allows for precise monitoring and adjustment of energy usage, thereby supporting energy conservation and carbon reduction goals. Unlike traditional technological innovations, which typically exhibit linear or gradual environmental impacts, digital technologies show more pronounced nonlinearity due to their inherent network effects and infrastructure dependencies. For example, the marginal environmental benefit of digital tools increases exponentially as more firms and industries adopt interconnected digital systems, creating synergistic reductions in energy intensity. This contrasts with incremental innovations in traditional sectors, which often yield diminishing returns in emission reduction efficiency over time. For example, as digital technological innovations continue to evolve, industry supply chains are progressively shifting toward low-carbon, green practices, providing a more robust foundation for the green applications of digital technologies (Xu et al., 2024). These factors enable digital technologies to increasingly contribute to emissions reduction in the later stages, resulting in a gradual decline in carbon intensity. Consequently, over the long term, digital technology innovations not only play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions, but also drive the sustainable development of urban environments (Wu et al., 2022). So, we propose:
Hypothesis 1. There is an inverted “U” shaped relationship between digital technology innovation and urban carbon intensity.
3 Study design
3.1 Data source
In 2012, the construction of ecological civilization was officially elevated to the core of national governance. Moreover, considering that the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 shifted governmental priorities significantly towards pandemic prevention and control, the study period is limited to 2012-2019. Digital patent applications are obtained from CNRDS database, while information on carbon emissions and energy consumption are sourced from China Urban Statistical Yearbook, China Energy Statistical Yearbook. Environmental attention is derived from government work reports. Additional urban features are sourced from EPS database. Finally, we construct a balanced panel dataset covering 282 cities in China.
3.2 Variable metrics
3.2.1 Dependent variable
Urban carbon intensity (Ci). Urban carbon emissions primarily stem from two sources: direct emissions caused by the consumption of energy forms such as liquefied petroleum gas and coal, and indirect emissions linked to energy usage, including electricity and heat (Lv et al., 2024). Adopting the method proposed by Wu and Guo (2016), annual carbon emissions are computed by multiplying the consumption of different energy sources within cities by their corresponding carbon emission factors and aggregating the values. For indirect emissions from electricity consumption, the national average carbon emission factor for grid electricity (0.6101 kgCO2/kWh) was applied, as stipulated in the Provincial Greenhouse Gas Inventory Guidelines. The dependent variable is represented by the ratio of total urban carbon emissions to GDP. Therefore, the dependent variable is represented by the ratio of total urban carbon emissions to GDP.
3.2.2 Independent variable
Urban digital innovation (Digi). We employ the volume of urban digital economy patent applications as the core variable to measure the level of digital technological innovation at the city level. This indicator aims to capture both a city’s technological innovation capacity and its technological reserves within the digital economy domain. The number of digital economy patent applications reflects not only the intensity of investment in digital technology, but also the efficiency of innovation outputs, while simultaneously highlighting disparities in digital technological advancement across cities and its implications for regional competitiveness. As a core indicator of urban digital technology reserves, the number of digital economy patent applications correlates strongly with national policy orientations such as “Digital China”, reflecting both innovation investment and technological readiness in strategic fields like artificial intelligence and big data (Li and Yue, 2024). Moreover, this metric provides a direct measure of innovation activity in critical fields such as information technology, artificial intelligence, big data, and blockchain. As a key outcome of technological innovation, patent applications also serve as a proxy for a city’s ability to attract and support the digital economy’s industrial chain, revealing its overall strength in technology development, industrial agglomeration, and resource allocation. This study focuses on invention patents and utility model patents, as these categories most effectively capture technological innovation levels, thereby generating city-level data on digital economy patent applications.
3.2.3 Mechanism variables
Energy intensity (Ei). Drawing from references such as Chen et al. (2019) and Chen et al. (2022), this study employs “energy consumption/GDP” to measure energy intensity. Energy consumption is determined by converting the annual usage of electricity (measured in 10,000 kWh), liquefied petroleum gas (in tons), and natural gas (in 10,000 cubic meters) for each city into equivalent units of “10,000 tons of standard coal,” and then summing these values.
Government environmental attention (Er). When the government attaches great importance to environmental protection, the number of environment-related words in the government work report will increase accordingly, and the proportion will also increase (Chen et al., 2018). Similar to Chen et al. (2018), using the content analysis approach, we assess government attention to environmental issues by calculating the percentage of environmental terms to the total number of words in government work reports.
3.2.4 Control variables
Following the approach outlined by Zhang et al. (2023) and Zhang et al. (2020), we incorporate the following control variables into the model. Economic development level (Gdpr) is assessed using the city’s GDP growth rate. Foreign trade (Fore) is captured by the proportion of foreign direct investment to GDP. Educational expenditure (Edu) is proxied by the ratio of a city’s education investment relative to its GDP. Population density (Pode) is defined as the ratio of the total year-end population to the administrative area. Scientific expenditure (Scir) is represented by the share of a city’s scientific spending in its GDP. Industrial structure (Sec) is evaluated based on the share of the secondary sector’s value added in relation to GDP. Lastly, industrial sulfur dioxide emission intensity (So) is calculated as the proportion of industrial sulfur dioxide emissions to GDP.
3.3 Model setting
We designed the following model:
in Formula 1, Ciit indicates carbon intensity of city i in time t; Digiit represents digital technology innovation; Conit denotes a string of urban features; fixed effects for city and year are captured by μi and νt, respectively; εit represents the error term, α represents the constant term; β1 and β2 are the coefficients.
To examine the validity of the energy efficiency pathway and the environmental attention pathway, following the approach outlined by Baron (2022), we construct the mediating effects model as described below:
in Formula 2, Mechit is the mechanisms, Digiit represents digital technology innovation; Conit denotes a string of urban features; fixed effects for city and year are captured by μi and νt, respectively; εit represents the error term, α represents the constant term; β1 and β2 are the coefficients.
4 Analysis of results
4.1 Statistical analysis
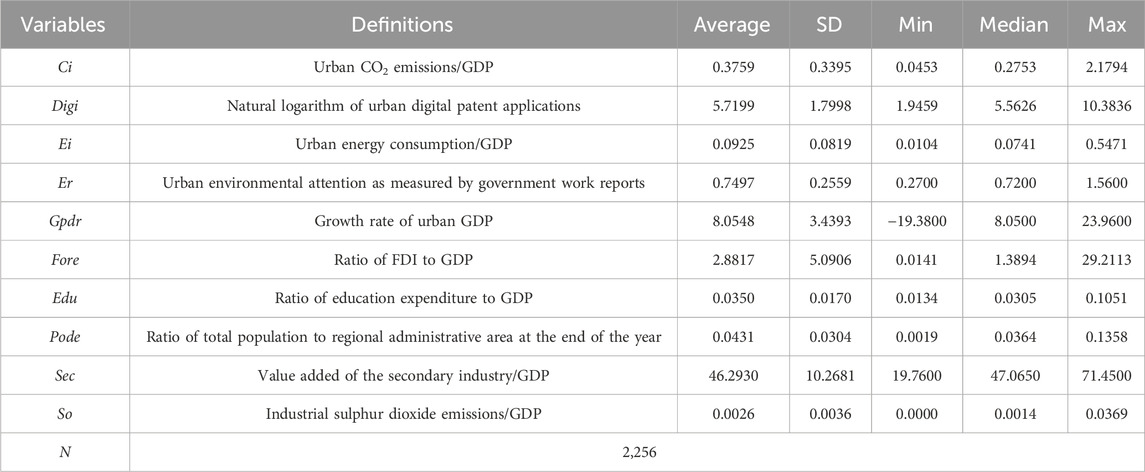
As shown in Table 1. The average carbon intensity (Ci) exceeds its median, reflecting a generally right-skewed distribution. The mean and median of digital technology innovation (Digi) are nearly identical, coupled with a low standard deviation, indicating that digital technology innovation levels across cities exhibit an approximately normal distribution pattern.
4.2 The spatial and temporal evolution of digital technological innovation and carbon intensity
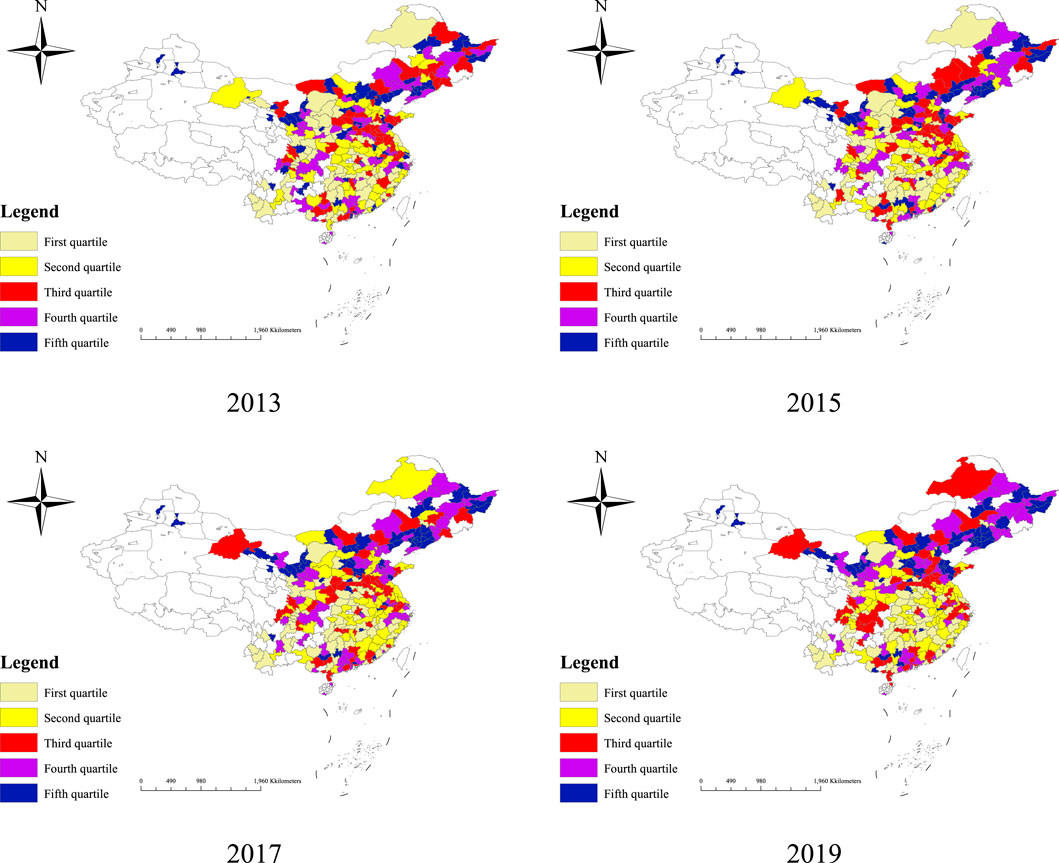
As shown in Figure 1, we examine the spatial distribution of digital technology for 2013, 2015, 2017, and 2019. Overall, cities with higher innovation capabilities were predominantly concentrated in the eastern provinces, particularly in the Yangtze River Delta region, during the period from 2013 to 2019. In contrast, cities with weaker innovation capabilities were primarily located in the southwestern, northwestern, and northeastern regions. This disparity can be attributed to the higher levels of openness, market dynamism, and a robust culture of innovation in the eastern regions, which have successfully attracted greater capital investment and corporate engagement in digital technology innovation. Conversely, the western and northeastern regions appear to have been constrained by relatively limited policy support and resource allocation, contributing to their lagging innovation capabilities.
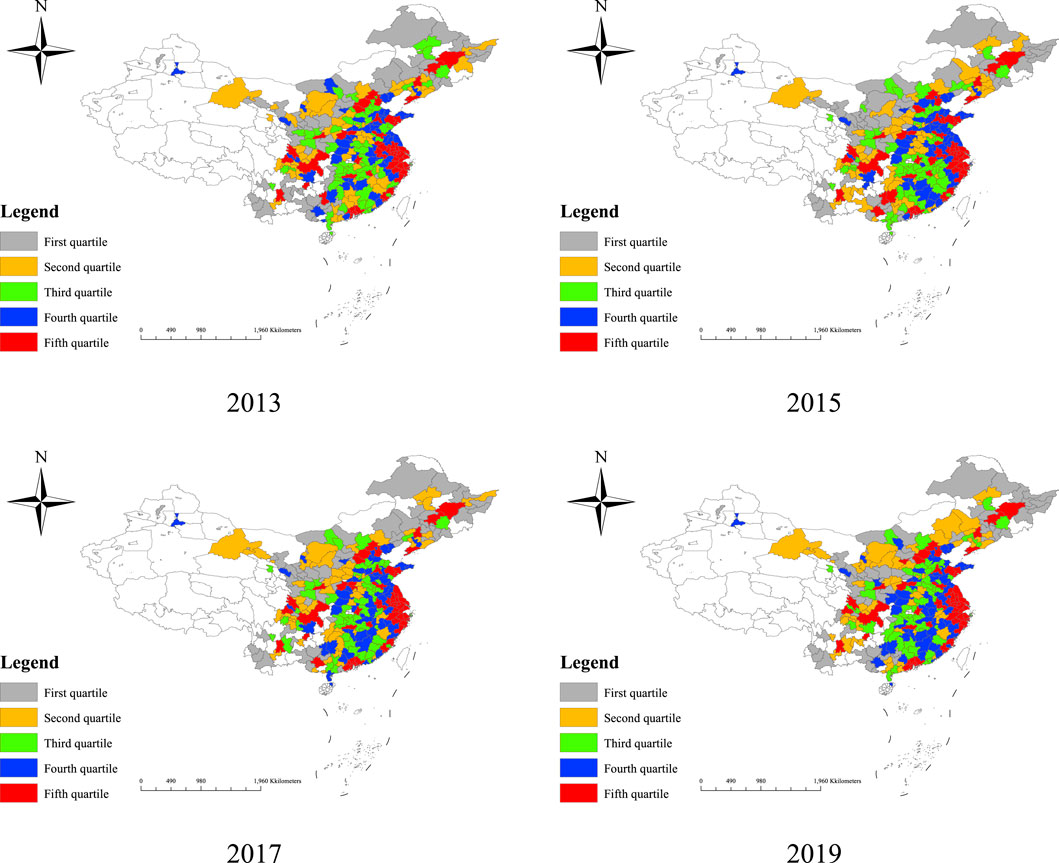
Figure 1. Spatial and temporal evolution of digital technological innovation. Note: The base map is from the National Center for Basic Geographic Information, review number is GS(2024) 0650, and the base map has not been modified. The same below.
As shown in Figure 2, we examine the spatial distribution of Ci in 2013, 2015, 2017, and 2019. Overall, areas with higher carbon intensity are predominantly located in northern China, particularly in the Northeast, Northwest, and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei regions. Northern regions, especially the Northwest and Northeast, possess abundant reserves of coal, oil, and natural gas, resulting in energy consumption that relies heavily on high-carbon fossil fuels and contributes to elevated emission intensity. Compared to southeastern coastal areas, northern cities have been slower to develop and adopt clean energy technologies, such as wind, solar, and nuclear power, which has further reinforced the dominance of fossil fuels and exacerbated their carbon emission intensity.
4.3 Benchmark result
The benchmark regression result is presented in Table 2. Column (1) reports the result without incorporating any urban features, where the coefficient of the independent variable Digi*Digi is significantly negative. Column (2) displays the results after including all control variables, showing that the coefficient of Digi*Digi and its significance remain largely unchanged. These findings indicate an inverted U-shaped relationship between digital technology innovation and carbon emission intensity, where innovation initially promotes but subsequently suppresses emission intensity. This result provides evidence of the rebound effect in the context of China, underscoring the critical role of digital technology innovation in driving low-carbon transitions and sustainable development. Furthermore, it supports Hypothesis 1, validating the proposed theoretical framework.
4.4 Robustness checks
First, as reported in column (1) of Table 3, we replace the independent variable with the number of authorized digital economy patents at the city level. Second, while numerous city-level control variables were included in the model, unobserved macro-level factors at the provincial level might still bias the findings. To address this issue, we adopted the method proposed by Yuan and Zhang (2015) by introducing province-year interaction fixed effects, which account for both time-varying and time-invariant provincial features. The result is shown in column (2). Third, we exclude four municipalities from the analysis to ensure more targeted results. The corresponding finding is presented in column (3). Finally, recognizing that a series of carbon reduction and environmental protection policies between 2012 and 2019 (e.g., the low-carbon city pilot programs), these policies could significantly influence carbon intensity. To control for their potential effects, we include these policies as control variables in the model. The result is reported in column (4).
4.5 Nonlinear mediating mechanism
4.5.1 Energy efficiency channel
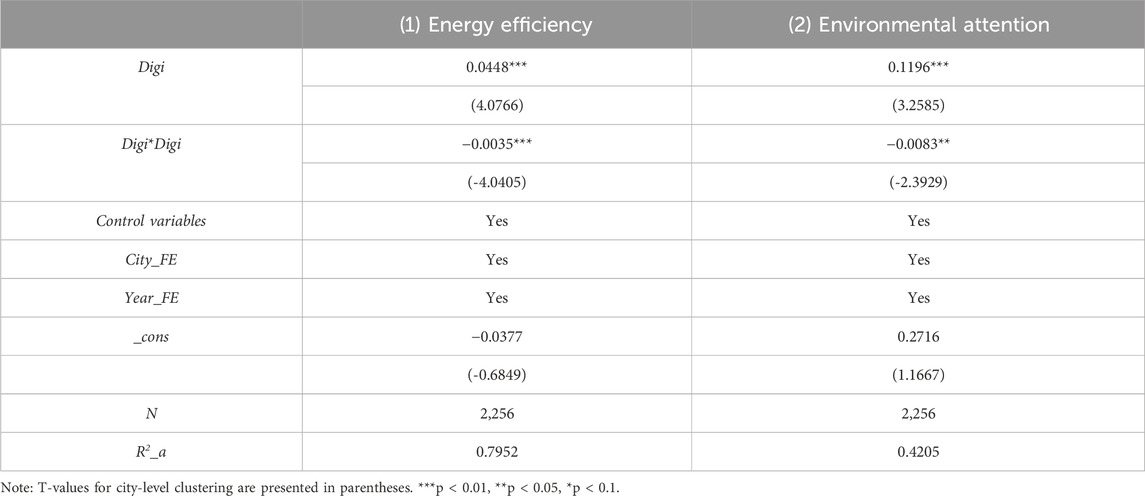
According to the result presented in column (1) of Table 4, the coefficient of Digi*Digi is significantly negative. This suggests that lower levels of digital technology innovation are linked to higher energy consumption. However, once digital innovation exceeds a certain threshold, it begins to reduce energy consumption. As digital technology innovation advances, it enables the development and adoption of more energy-efficient solutions, such as automation, data analytics, and smart technologies, which optimize energy usage and reduce consumption. Once digital innovation reaches a critical threshold, these technologies become widely implemented, leading to significant energy savings.
4.5.2 Environmental attention channel
Next, we examine the mediating role of government environmental attention. As reported in column (2) of Table 4. The coefficient of Digi*Digi is −0.0083, which is significantly negative at the 1% level. These results suggest that at initial stages of digital technology innovation, it may worsen environmental challenges. However, once digital innovation exceeds a certain threshold, it starts to alleviate environmental pollution and boosts government focus on environmental protection. This indicates that government attention to environmental issues acts as a mediator in the relationship between digital technology innovation and carbon intensity.
4.6 Heterogeneity analysis
4.6.1 Substantial or symbolic digital technology innovation
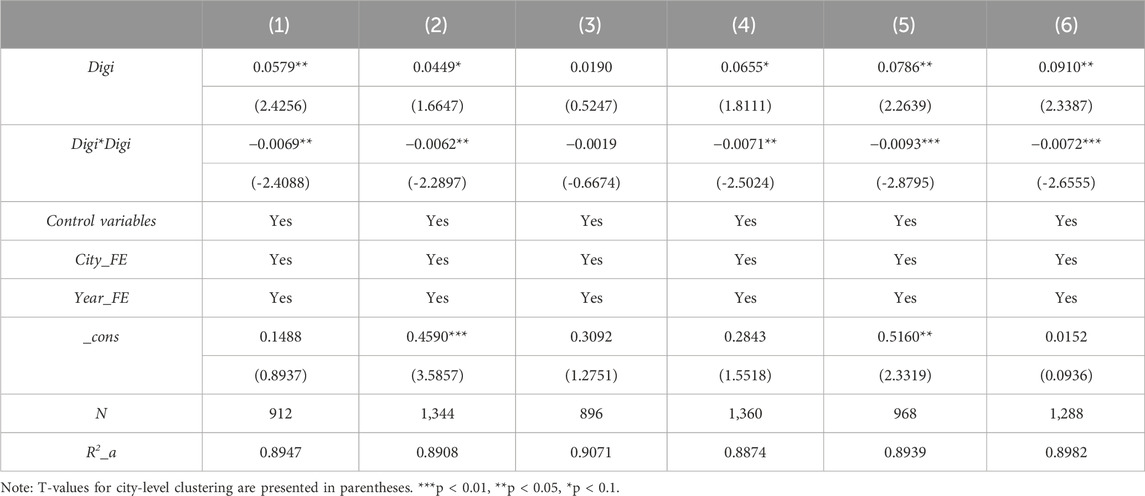
We categorize invention-based digital technology patents as substantial digital technological innovations and utility model patents as strategic digital technological innovations. Columns (1) and (2) of Table 5 present the result for substantial and strategic digital technological innovations, respectively. In both cases, the relationship between digital innovation and carbon intensity follows an inverted U-shape. However, a key distinction emerges: the turning point for substantial digital technological innovation occurs at a much earlier stage than for strategic digital technological innovation. This suggests that innovations with stronger technological capabilities, such as substantial innovations, reach the critical threshold more quickly, leading to a more rapid reduction in carbon intensity. This finding underscores the transformative potential of substantial digital innovations, which focus on fundamental changes in products or technologies, and highlights their greater potential and advantages in promoting environmental, corporate, and societal benefits.
4.6.2 Key environmental protection cities vs. other cities
The list of key cities for environmental protection comes from the 11th Five-Year Plan for National Environmental Protection, totaling 113 cities (A detailed list can be found in Supplementary Appendix SA). Column (3) of Table 5 represents these key environmental protection cities, while column (4) represents other cities. The results indicate that digital technological innovation exhibits a significant inverted U-shaped relationship with carbon intensity in other cities. This may be attributable to the fact that non-key cities typically face lower environmental regulatory pressures, which affords firms greater flexibility in their selection and application of technological innovations. These cities may be more effective in promoting the application of digital technologies through market-based mechanisms, optimizing energy efficiency, and reducing carbon intensity.
4.6.3 Broadband China pilot vs. non-broadband China pilot
Columns (5)–(6) of Table 5 correspond to the cities included in the “Broadband China” pilot program and those that are not. In both categories of cities, the inverted U-shaped relationships all hold. However, it is evident that in the pilot cities, digital innovation reaches the turning point more rapidly. This phenomenon may stem from the advantages that Broadband China pilot cities possess in terms of digital infrastructure, policy support, and innovation capacity. These cities typically benefit from greater government investment, policy backing, and early advantages in digital technology applications, enabling them to more quickly realize technological innovations and translate these into tangible carbon emission reduction effects. As a result, pilot cities are able to reach the turning point more swiftly, thereby playing a significant role in reducing carbon intensity.
5 Conclusion and implications
Our analysis reveals a significant inverted U-shaped relationship between digital technology innovation and carbon intensity. Specifically, in the early stages of digital technology innovation, the increased deployment of technology and resource inputs may lead to a rise in carbon intensity. However, as digital technologies mature and become more widely adopted, they contribute to a reduction in carbon intensity. Furthermore, our nonlinear mediation analysis indicate that digital technology innovation influences carbon intensity indirectly through two key channels: energy intensity and increased government attention to environmental protection. Notably, substantive digital technology innovation is observed to reach the turning point more quickly, yielding more pronounced improvements in carbon intensity. This underscores the critical role of technology quality in driving green development. The study also demonstrates that the inverted U-shaped relationship holds consistently across both broadband pilot and non-pilot cities but is limited to non-key environmental protection cities. These findings deepen our understanding of the relationship between digital technology innovation and carbon intensity, offering valuable policy recommendations and practical guidance for advancing urban sustainability objectives.
Based on the conclusions, we propose the following recommendations. First, during the early stages of digital technology innovation, it is crucial to enhance policy support, particularly in the areas of technology research and development (R&D) and commercialization. This can be achieved through government subsidies, tax incentives, and venture capital. These measures will encourage businesses to increase their investments in digital technologies and accelerate their maturation and application. Simultaneously, regulatory oversight should be strengthened to address potential negative effects during the innovation process, such as high energy consumption or environmental pollution. This can be done by establishing stringent energy consumption standards and environmental impact assessment mechanisms. These measures will ensure that early-stage digital innovation does not exacerbate carbon intensity.
Second, it is essential to promote the deep integration of digital technologies in energy management and environmental governance. For example, the development of intelligent energy systems based on artificial intelligence and big data should be prioritized to improve energy efficiency. The government should also enhance its environmental oversight by establishing regulatory indicators and regular evaluation mechanisms to integrate environmental performance into governmental assessments.
Third, substantial innovation projects should be given priority, concentrating resources on developing efficient and practical digital technology applications while avoiding the dispersion of resources and redundant investments. Special funds should be established to support R&D and application of digital technologies with significant carbon reduction potential. Additionally, incentive mechanisms should be created to encourage businesses to prioritize innovation quality rather than merely pursuing the quantity of technologies. It is important to acknowledge that patent applications mainly reflect technological potential rather than actual implementation. Future research could incorporate micro-level data on corporate digital transformation to more comprehensively assess the real-world impact of digital technologies on carbon intensity, bridging the gap between innovation output and application efficacy.
Fourth, in non-key environmental protection cities, policy support and special incentives should be leveraged to enhance investments in digital infrastructure, especially in regions with technological backwardness. In key environmental protection cities, it is essential to optimize existing environmental governance policies and explore the synergy between technology and policy, with a view to establishing an efficient environmental technology innovation model that consolidates their existing environmental governance advantages.
Lastly, the successful practices of Broadband China pilot cities should be replicated, including increasing investments in digital infrastructure, refining technology promotion policies, and fostering digital industry clusters. For non-pilot cities, this study recommends strengthening policy guidance and financial support, particularly for small- and medium-sized cities with substantial potential for digital transformation and resource-based cities. Accelerating the construction of infrastructure such as broadband networks can effectively enhance their technological absorption capacity.
While this study offers valuable insights into the impact of digital innovation on carbon intensity, several limitations merit acknowledgment. First, the analysis is confined to the city-level perspective, failing to account for potential spatial effects across regions. The influence of digital innovation may extend beyond individual cities, exerting spillover effects on neighboring areas through spatial interdependencies. Future research could incorporate spatial econometric models to systematically examine the intercity relationships. Second, the study relies on macro-level city-scale data, overlooking micro-level data at the county or firm level. Future studies may refine the data granularity to reveal intra-city variations and deliver more precise analytical results. Additionally, this research does not differentiate between various types of digital technology innovations. Future studies could categorize digital innovations into distinct categories and explore their heterogeneous mechanisms on carbon intensity, which would provide more targeted policy recommendations for decision-makers.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
SX: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Resources, Visualization. JL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JY: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. HL: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. DX: Investigation, Software, Writing – review and editing. SZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is funded by the Shanghai Planning Office of Philosophy and Social Science under its Youth Project: “Resource Allocation Measurement in ‘Four Chains’ Integration and Policy Target Selection: A Case Study of the Green and Low-Carbon Industry (2024EJC001)”.
Conflict of interest
Author HL was employed by Inner Mongolia Forest Industry Group Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ali, U., Guo, Q. B., Kartal, M. T., Nurgazina, Z., Khan, Z. A., and Sharif, A. (2022). The impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on carbon emission intensity in China: fresh evidence from novel dynamic ARDL simulations. J. Environ. Manag. 320, 115782. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115782
Aryai, V., and Goldsworthy, M. (2024). Real-time high-resolution modelling of grid carbon emissions intensity. Sustain. Cities Soc. 104, 105316. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105316
Babilla, T. U. K. (2023). Digital innovation and financial access for small and medium-sized enterprises in a currency union. Econ. Model. 120, 106182. doi:10.1016/j.econmod.2022.106182
Bai, L., Guo, T. R., Xu, W., Liu, Y. B., Kuang, M., and Jiang, L. (2023). Effects of digital economy on carbon emission intensity in Chinese cities: a life-cycle theory and the application of non-linear spatial panel smooth transition threshold model. Energy Policy 183, 113792. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2023.113792
Baron, E. J. (2022). School spending and student outcomes: evidence from revenue limit elections in Wisconsin. Am. Econ. Journal-Economic Policy 14 (1), 1–39. doi:10.1257/pol.20200226
Chang, H., Ding, Q. Y., Zhao, W. Z., Hou, N., and Liu, W. W. (2023). The digital economy, industrial structure upgrading, and carbon emission intensity -- empirical evidence from China's provinces. Energy Strategy Rev. 50, 101218. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2023.101218
Chen, D. X., and Li, X. M. (2024). The impact of institutional proximity on digital technology innovation linkages: empirical evidence on the guangdong-hong kong-macao greater Bay area of China. Technol. Analysis and Strategic Manag., 1–14. doi:10.1080/09537325.2024.2369565
Chen, X. H., and Lu, K. B. (2024). How does digital technology administrative penalty affect big data technology innovation: evidence from China. Humanit. and Soc. Sci. Commun. 11 (1), 601–613. doi:10.1057/s41599-024-03089-z
Chen, Z., Kahn, M. E., Liu, Y., and Wang, Z. (2018). The consequences of spatially differentiated water pollution regulation in China. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 88, 468–485. doi:10.1016/j.jeem.2018.01.010
Chen, Z. F., Huang, W. J., and Zheng, X. (2019). The decline in energy intensity: does financial development matter? Energy Policy 134, 110945. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2019.110945
Chen, S. S., Zhang, H. Y., and Wang, S. H. (2022). Trade openness, economic growth, and energy intensity in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 179, 121608. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121608
Cheng, Y., Zhang, N., Lu, Z., and Kang, C. (2018).Planning multiple energy systems toward low-carbon society: a decentralized approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, 10(5): 4859–4869. doi:10.1109/tsg.2018.2870323
Cheng, C., Wang, L. M., Xie, H. M., and Yan, L. L. (2023). Mapping digital innovation: a bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 194, 122706. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122706
Corvello, V., Belas, J., Giglio, C., Iazzolino, G., and Troise, C. (2023). The impact of business owners' individual characteristics on patenting in the context of digital innovation. J. Bus. Res. 155, 113397. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.113397
Cui, Y., Khan, S. U., Deng, Y., and Zhao, M. J. (2022). Spatiotemporal heterogeneity, convergence and its impact factors: perspective of carbon emission intensity and carbon emission per capita considering carbon sink effect. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 92, 106699. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106699
Du, M., Antunes, J., Wanke, P., and Chen, Z. (2022). Ecological efficiency assessment under the construction of low-carbon city: a perspective of green technology innovation. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 65 (9), 1727–1752. doi:10.1080/09640568.2021.1945552
Du, Z. L., Xu, J., and Lin, B. Q. (2024). What does the digital economy bring to household carbon emissions? -From the perspective of energy intensity. Appl. Energy 370, 123613. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123613
Du, M., Zhang, J., and Hou, X. (2025). Decarbonization like China: how does green finance reform and innovation enhance carbon emission efficiency? J. Environ. Manag. 376, 124331. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.124331
Duan, D., Wei, R., Wang, C., and Xia, B. (2025). Opportunity or obstacle? Climate risk disclosure and corporate ESG performance. Int. Rev. Econ. and Finance 100, 104101. doi:10.1016/j.iref.2025.104101
Firk, S., Gehrke, Y., Hanelt, A., and Wolff, M. (2022). Top management team characteristics and digital innovation: exploring digital knowledge and TMT interfaces. Long. Range Plan. 55 (3), 102166. doi:10.1016/j.lrp.2021.102166
Geng, W., Liu, X. Q., and Liao, X. C. (2024). Mechanism analysis of the influence of intelligent manufacturing on carbon emission intensity: evidence from cross country and industry. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 26 (6), 15777–15801. doi:10.1007/s10668-023-03273-2
Goldfarb, A., and Tucker, C. (2019). Digital economics. J. Econ. Literature 57 (1), 3–43. doi:10.1257/jel.20171452
Grossman, G. M., and Krueger, A. B. (1995). Economic growth and the environment. Q. J. Econ. 110 (2), 353–377.
Gupta, S., and Dey, D. K. (2024). Risk perception and adoption of digital innovation in Mobile stock trading. J. Consumer Behav. 23 (2), 639–654. doi:10.1002/cb.2225
Hanelt, A., Firk, S., Hilebrandt, B., and Kolbe, L. M. (2021). Digital M&A, digital innovation, and firm performance: an empirical investigation. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 30 (1), 3–26.
Huang, Q. Y., Fang, J. L., Xue, X. L., and Gao, H. M. (2023a). Does digital innovation cause better ESG performance? An empirical test of a-listed firms in China. Res. Int. Bus. Finance 66, 102049. doi:10.1016/j.ribaf.2023.102049
Huang, Q. Y., Xu, C. H., Xue, X. L., and Zhu, H. (2023b). Can digital innovation improve firm performance: evidence from digital patents of Chinese listed firms. Int. Rev. Financial Analysis 89, 102810. doi:10.1016/j.irfa.2023.102810
Jiang, L., Yang, L. S., Wu, Q. Y., and Zhang, X. Y. (2024). How does extreme heat affect carbon emission intensity? Evidence from county-level data in China. Econ. Model. 139, 106814. doi:10.1016/j.econmod.2024.106814
Johnson, P. C., Laurell, C., Ots, M., and Sandström, C. (2022). Digital innovation and the effects of artificial intelligence on firms' research and development-automation or augmentation, exploration or exploitation? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 179, 121636. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121636
Kang, C., Zhou, T., Chen, Q., Wang, J., Sun, Y., and Yan, H. (2015). Carbon emission flow from generation to demand: a network-based model. IEEE Trans. smart grid 6 (5), 2386–2394. doi:10.1109/tsg.2015.2388695
Ke, N., Lu, X. H., Kuang, B., and Zhang, X. P. (2023). Regional disparities and evolution trend of city-level carbon emission intensity in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 88, 104288. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2022.104288
Lee, C. C., Chang, Y. F., and Wang, E. Z. (2022). Crossing The Rivers by feeling the stones: the effect of China's green credit policy on manufacturing firms' carbon emission intensity. Energy Econ. 116, 106413. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106413
Li, X., and Yue, S. J. (2024). Blessing or curse? The role of digital technology innovation in carbon emission efficiency. J. Environ. Manag. 365, 121579. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121579
Li, H. T., Lu, L. T., Lin, Z., and Meng, T. Z. (2024). Digital innovation and corporate social responsibility performance: evidence from firms' digital patents. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 207, 123626. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2024.123626
Lian, W. W., Sun, X. Y., Wang, Y. X., Duan, H. M., Gao, T. M., and Yan, Q. (2024). The mechanism of China's renewable energy utilization impact on carbon emission intensity: evidence from the perspective of intermediary transmission. J. Environ. Manag. 350, 119652. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119652
Lin, B. Q., and Teng, Y. Q. (2024). Industrial chain division and carbon emission intensity: the moderating effect of digitization. Energy 286, 129573. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.129573
Liu, J. G., Li, S. J., and Ji, Q. (2021a). Regional differences and driving factors analysis of carbon emission intensity from transport sector in China. Energy 224, 120178. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2021.120178
Liu, P. T., Liu, L. Y., Xu, X., Zhao, Y. Y., Niu, J. M., and Zhang, Q. (2021b). Carbon footprint and carbon emission intensity of grassland wind farms in Inner Mongolia. J. Clean. Prod. 313, 127878. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127878
Liu, Q. F., Song, J. P., Dai, T. Q., Shi, A., Xu, J. H., and Wang, E. R. (2022). Spatio-temporal dynamic evolution of carbon emission intensity and the effectiveness of carbon emission reduction at county level based on nighttime light data. J. Clean. Prod. 362, 132301. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132301
Liu, K., Dong, S. M., and Han, M. F. (2023a). Exploring the impact of green innovation on carbon emission intensity in Chinese metropolitan areas. Ecol. Indic. 156, 111115. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111115
Liu, Y., Dong, J. Y., Mei, L., and Shen, R. (2023b). Digital innovation and performance of manufacturing firms: an affordance perspective. Technovation 119, 102458. doi:10.1016/j.technovation.2022.102458
Lu, J., and Li, H. (2024). Can digital technology innovation promote total factor energy efficiency? firm-Level evidence from China. Energy 293, 130682. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2024.130682
Lu, F. Z., Li, Z. W., and Zhang, S. (2023). Does digital finance development affect carbon emission intensity: evidence from China. Int. Rev. Econ. and Finance 88, 1272–1286. doi:10.1016/j.iref.2023.07.036
Lv, T. G., Zhao, Q., Fu, S. F., Jin, G., Zhang, X. M., Hu, H., et al. (2024). Deciphering flows: spatial correlation characteristics and factors influencing carbon emission intensity in the yangtze river Delta. J. Clean. Prod. 483, 144290. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.144290
Lyytinen, K. (2022). Innovation logics in the digital era: a systemic review of the emerging digital innovation regime. Innovation-Organization and Manag. 24 (1), 13–34. doi:10.1080/14479338.2021.1938579
Mariani, M. M., and Nambisan, S. (2021). Innovation analytics and digital innovation experimentation: the rise of research-driven online review platforms. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 172, 121009. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121009
Peng, J. C., Wen, L., Mu, X. Y., and Xiao, J. Z. (2023). The evolving centres of gravity in China?s oil and gas industry: evidence from infrared radiation imaging gas flaring data. Energy Sustain. Dev. 73, 263–279. doi:10.1016/j.esd.2023.02.002
Porter, M. E., and Linde, C. v. d. (1995). Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 9 (4), 97–118. doi:10.1257/jep.9.4.97
Pu, Z. N., Qian, Y., and Liu, R. H. (2024). Is digital technology innovation a panacea for carbon reduction? Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 31, 496–524. doi:10.3846/tede.2024.22208
Ren, Y. F., Yuan, W. R., Zhang, B. T., and Wang, S. J. (2022). Does improvement of environmental efficiency matter in reducing carbon emission intensity? Fresh evidence from 283 prefecture-level cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 373, 133878. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133878
Shen, Y. C., Fu, Y. Y., and Song, M. L. (2024). Digital finance promotes sustainable total factor eco-efficiency: evidence from China. Appl. Econ. 56 (36), 4389–4403. doi:10.1080/00036846.2023.2211337
Shojaei, R. S., and Burgess, G. (2022). Non-technical inhibitors: exploring the adoption of digital innovation in the UK construction industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 185, 122036. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122036
Sun, J. J., Cui, J., Dong, F., and Liu, Y. J. (2024). Regional decomposition and attribution analysis of carbon-emission intensity using an extended approach combined with a meta-frontier non-radial malmquist-luenberger productivity index. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 106, 107473. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2024.107473
Tang, P., Wang, C., Jiang, Q., Liu, X., and Wang, J. (2023). Symbol or substance? Environmental regulations and corporate environmental actions decoupling. J. Environ. Manag. 346, 118950. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118950
Tang, P., Jiang, Q., and Wang, C. (2024). Beyond environmental actions: how environmental regulations stimulate strategic-political CSR engagement in China? Energy Econ. 129, 107171. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107171
Tortora, D., Chierici, R., Briamonte, M. F., and Tiscini, R. (2021). 'I digitize so I exist'. Searching for critical capabilities affecting firms' digital innovation. J. Bus. Res. 129, 193–204. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.02.048
Trocin, C., Hovland, I. V., Mikalef, P., and Dremel, C. (2021). How artificial intelligence affords digital innovation: a cross-case analysis of Scandinavian companies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 173, 121081. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121081
Wang, L., and Yang, H. Y. (2024a). Digital technology innovation and corporate ESG performance: evidence from China. Econ. Change Restruct. 57 (6), 207. doi:10.1007/s10644-024-09791-x
Wang, Y., Qiu, J., Tao, Y., and Zhao, J. (2020). Carbon-oriented operational planning in coupled electricity and emission trading markets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 35 (4), 3145–3157. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2020.2966663
Wang, Y., Qiu, J., and Tao, Y. (2022). Robust energy systems scheduling considering uncertainties and demand side emission impacts. Energy 239, 122317. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2021.122317
Wang, Y. T., Yuan, Y. K., Qian, X., and Chi, Y. Y. (2024b). The impact of China's digital economy industry development and its structural indicators on carbon emission intensity. Front. Environ. Sci. 12, 1438927. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2024.1438927
Wu, J., and Guo, Z. (2016). Research on the convergence of carbon dioxide emissions in China: a continuous dynamic distribution approach. Stat. Res. 33 (1), 54–60.
Wu, Y., Chen, C. L., and Hu, C. (2021). Does the belt and road initiative increase the carbon emission intensity of participating countries? China and World Econ. 29 (3), 1–25. doi:10.1111/cwe.12374
Wu, R. J., Hua, X., Peng, L., Liao, Y. Y., and Yuan, Y. (2022). Nonlinear effect of digital economy on carbon emission intensity-based on dynamic panel threshold model. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 943177. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.943177
Wu, Y., Zong, T., Shuai, C. Y., and Jiao, L. D. (2024). How does new-type urbanization affect total carbon emissions, per capita carbon emissions, and carbon emission intensity? An empirical analysis of the yangtze river economic belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 349, 119441. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119441
Xu, P., Ye, P. H., Jahanger, A., Huang, S. W., and Zhao, F. (2023). Can green credit policy reduce corporate carbon emission intensity: evidence from China's listed firms. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 30 (5), 2623–2638. doi:10.1002/csr.2506
Xu, C. Z., Zhu, Q. Y., Li, X. C., Wu, L. P., and Deng, P. (2024a). Determinants of global carbon emission and aggregate carbon intensity: a multi-region input-output approach. Econ. Analysis Policy 81, 418–435. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2023.12.002
Xu, Q., Zhong, M. R., and Dong, Y. (2024b). Digital finance and rural revitalization: empirical test and mechanism discussion. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 201, 123248. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2024.123248
Yan, B., Wang, F., Dong, M. R., Ren, J., Liu, J., and Shan, J. (2022). How do financial spatial structure and economic agglomeration affect carbon emission intensity? Theory extension and evidence from China. Econ. Model. 108, 105745. doi:10.1016/j.econmod.2021.105745
Yang, B., Huang, J. F., and Chen, Y. Z. (2025a). The relationship between ESG ratings and digital technological innovation in manufacturing: insights via dual machine learning models. Finance Res. Lett. 71, 106362. doi:10.1016/j.frl.2024.106362
Yang, S. J., Lu, W. X., and Wan, L. Q. (2025b). The heterogeneous effect of digital economy on ecological resilience: considering the mediating role of technological innovation. Environ. Dev. Sustain., 1–27. doi:10.1007/s10668-024-05932-4
Yi, M., Chen, D. H., Wu, T., Tao, M. M., Sheng, M. S., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Intelligence and carbon emissions: the impact of smart infrastructure on carbon emission intensity in cities of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 112, 105602. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105602
Yuan, C., and Zhang, L. (2015). Public education spending and private substitution in urban China. J. Dev. Econ. 115, 124–139. doi:10.1016/j.jdeveco.2015.02.006
Zhang, F., Deng, X. Z., Phillips, F., Fang, C. L., and Wang, C. (2020). Impacts of industrial structure and technical progress on carbon emission intensity: evidence from 281 cities in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 154, 119949. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2020.119949
Zhang, A. X., Deng, R. R., and Wu, Y. F. (2022). Does the green credit policy reduce the carbon emission intensity of heavily polluting industries? -Evidence from China's industrial sectors. J. Environ. Manag. 311, 114815. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114815
Zhang, Q. F., Li, J. F., Li, Y., and Huang, H. (2023a). Coupling analysis and driving factors between carbon emission intensity and high-quality economic development: evidence from the yellow river basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 423, 138831. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138831
Zhang, W. K., Fan, H. X., and Zhao, Q. W. (2023b). Seeing green: how does digital infrastructure affect carbon emission intensity? Energy Econ. 127, 107085. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107085
Zhang, S. L., Miao, X. E., Zheng, H. Q., Chen, W. H., and Wang, H. F. (2024). Spatial functional division in urban agglomerations and carbon emission intensity: new evidence from 19 urban agglomerations in China. Energy 300, 131541. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2024.131541
Zhao, H., Chen, S. W., and Zhang, W. K. (2023). Does digital inclusive finance affect urban carbon emission intensity: evidence from 285 cities in China. Cities 142, 104552. doi:10.1016/j.cities.2023.104552
Zhao, S., Guan, Y. F., Zhou, H. Y., and Hu, F. (2024). Making digital technology innovation happen: the role of the ceo's information technology backgrounds. Econ. Model. 140, 106866. doi:10.1016/j.econmod.2024.106866
Zhu, Y. H., Xu, Y. Q., and Yin, S. G. (2024). How does digital technology innovation drive synergies for reducing pollution and carbon emissions? Sustain. Cities Soc. 116, 105932. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105932
Zhu, S. W., Lv, K. J., and Zhao, Y. (2025). Trust (in)congruence, digital technological innovation, and firms' ESG performance: a polynomial regression with response surface analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 373, 123689. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.123689
Keywords: digital economy, digital technology innovation, carbon emissions, carbon intensity, government environmental attention
Citation: Xu S, Li J, Ya J, Li H, Xia D and Zhang S (2025) Digital technological innovation and urban carbon emission intensity: a nonlinear path toward sustainability. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1579459. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1579459
Received: 19 February 2025; Accepted: 11 August 2025;
Published: 09 September 2025.
Edited by:
Jiachao Peng, Wuhan Institute of Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Xu, Li, Ya, Li, Xia and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiapeng Li, amlhcGVuZ0BjdWcuZWR1LmNu
 Shujing Xu1,2
Shujing Xu1,2 Jiapeng Li
Jiapeng Li Song Zhang
Song Zhang