- 1School of Business, Henan University of Science and Technology, Henan, China
- 2Hainan University, Haikou, Hainan, China
Reducing carbon emissions is crucial for combating climate change, and low-carbon consumption is vital for carbon reduction. While intelligence technologies may reshape consumption, how they affect low-carbon consumption behavior and the underlying mechanisms are underexplored. Using the Attitude-Context-Behavior (ACB) theory, this study investigated whether intelligence technologies can promote low-carbon consumption, focusing on attitudinal factors’ mediating effect. With 399 Ant Forest users, models were constructed and regression analyses were carried out. The results showed that: (1) Attitudinal factors positively influence consumers’ low-carbon consumption behavior; (2) Contextual factors, including intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives all positively affect low-carbon consumption behavior; (3) These contextual factors enhance low-carbon consumption behavior via attitudinal factors. To promote low-carbon consumption among Chinese residents, accelerating intelligence technology development, maintaining awareness campaigns, and enhancing self-efficacy are essential for a low-carbon societal shift.
1 Introduction
Excessive greenhouse gas emissions have caused severe harm to human society through climate warming. Countries worldwide have reached a consensus to reduce carbon emissions and address the climate crisis. China accounts for over one-third of global carbon emissions, making it the world’s largest carbon emitter. To tackle this, China has proposed the strategic goals of “achieving carbon peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060.” Realizing these goals requires joint efforts from businesses and consumers, particularly widespread adoption of sustainable green lifestyles. However, a key challenge lies in encouraging behaviors that generate greater environmental benefits (Stern, 2000). In recent years, the Chinese government has prioritized ecological conservation, implementing environmental policies and carbon reduction measures that have significantly advanced digital ecological civilization and enhanced smart governance capabilities. In February 2024, China released the Overall Plan for Digital China Development, explicitly targeting “substantial progress in digital ecological civilization by 2025,” which sets higher requirements for applying next-generation digital technologies in ecological governance and guides the nation’s digital sustainability efforts.
Promoting green consumption transformation is also an effective pathway to mitigate global warming. The Green Consumption Promotion Plan outlines that by 2025, green consumption concepts will be deeply rooted, wasteful practices will be curtailed, market shares of green products will rise significantly, and green consumption systems will take shape. The widespread adoption of low-carbon consumption behaviors is critical to achieving China’s carbon peaking and neutrality goals and slowing global climate change.
Empirical studies in China reveal that environmental cognition positively influences socially conscious consumption but negatively affects individually conscious consumption, suggesting that enhancing environmental awareness can effectively promote low-carbon behaviors (Chen et al., 2014; Tian et al., 2024b). Research on the cultural and behavioral dimensions of low-carbon consumption indicates that social consumption culture negatively moderates self-preferences, behavioral intentions, and individual actions (Guan, 2014). Emotional fluctuations significantly impact low-carbon consumption behaviors (Wang, 2018). Most Chinese citizens hold positive attitudes toward green consumption, with women and residents in developed regions showing greater concern (Huang et al., 2022). Key drivers include environmental education, air pollution control, and online shopping. Urban residents’ low-carbon behaviors are shaped by personal, familial, and societal factors (Ding et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2019; Mi et al., 2018).
Existing research predominantly examines low-carbon consumption from policy or corporate perspectives, with limited attention to the role of intelligence in shaping consumer behavior-a gap increasingly salient amid rapid advancements in intelligence technologies.
In recent years, China’s digital technologies have leapfrogged development, leveraging unique advantages to drive green product innovation, guide low-carbon choices, and foster sustainable markets. Consumer trends are shifting toward green and intelligent consumption. Digital platforms, with their robust data analytics and scenario-based applications, enable personalized services, carbon footprint tracking, and incentives for low-carbon actions like e-commerce and shared mobility, accelerating the transition to sustainable consumption models. As a flagship feature of Alipay (China’s leading mobile payment app), Ant Forest embeds environmental stewardship into daily transactions. This feature encourages users to adopt low-carbon habits by rewarding virtual “energy points” for eco-friendly behaviors, which can be redeemed to plant trees in arid regions. By engaging the public in collective environmental actions, Ant Forest bridges individual contributions to broader ecological goals (Li and Peng, 2019).
This study examines the role of intelligence technologies in facilitating low-carbon consumption behaviors, evaluates the applicability of the Attitude-Context-Behavior (ACB) theory in this context, and investigates the impact of Ant Forest on promoting sustainable practices among Chinese residents. The research framework is structured as follows: Firstly, we synthesize existing literature to establish a robust theoretical foundation and formulate hypotheses. Secondly, we develop a conceptual model of low-carbon consumption behavior grounded in the ACB theory. Thirdly, we outline empirical methods comprehensively, encompassing data sources, processing techniques, statistical analyses, and model outcomes. Lastly, we interpret the findings and provide actionable recommendations.
The theoretical contribution of this study resides in the application of the Attitude-Context-Behavior (ACB) theory to dissect the mechanisms by which intelligence technologies propel low-carbon behaviors. Moreover, it validates a novel conceptual model through the utilization of survey data collected from Chinese consumers. The results disclose that contextual factors, encompassing intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives, have a positive impact on enhancing low-carbon consumption behaviors via the mediating effect of attitudes. These findings not only provide theoretical underpinning for China’s ecological modernization but also offer practical guidelines for the attainment of its dual-carbon goals.
2 Literature review
With the advancement of information technology and the digital economy, the impact of intelligence technologies on consumption has become increasingly significant. As a smart technology application, Ant Forest employs gamified interactions and social sharing to notably influence low-carbon consumption behaviors and incentivize users to adopt environmentally friendly practices. By synthesizing domestic and international research, this section reviews three key themes.
2.1 Research on the impact of digital technologies on consumption
Digital technologies stimulate consumption potential and inject new vitality into expanding consumer markets. Digitization and sustainability are widely recognized as two transformative forces shaping economies and societies, with digitization offering opportunities for sustainable consumption patterns (Gossen and Lell, 2023; Tian et al., 2025). The digital economy facilitates clean energy consumption, thereby promoting high-quality economic development (Ren and Zhang, 2023). It also improves energy consumption structures by driving green technological innovation (Zeng et al., 2023). The adoption of digital twin technologies has been shown to reduce residential energy consumption and carbon emissions, as validated in tropical urban communities (Mohamad Zaidi et al., 2024). Enhancing rural digitalization and farmers’ digital literacy upgrades rural consumption patterns (Zhang and Ma, 2022). Implementing digital technologies in food supply chains enables sustainable production and consumption (Sharma et al., 2023). Recommendation systems powered by digital tools effectively nudge consumers toward green fashion choices (Cossatin et al., 2024). Digital content consumption significantly impacts environmental sustainability, accounting for approximately 40% of per capita carbon budgets (Istrate et al., 2024). Furthermore, algorithms and digital technologies optimize green energy consumption pathways (Yuan et al., 2023) and address climate challenges (George et al., 2021). Innovations such as social media platforms, autonomous devices, mobile apps, wearables, blockchain, and cryptocurrencies expand consumer choices (Buhalis et al., 2019), with extensive empirical evidence highlighting consumers’ growing reliance on technology in daily life (Priporas et al., 2017).
2.2 Research on Ant Forest’s influence on low-carbon consumption behaviors
Ant Forest, a gamified “internet plus voluntary tree-planting” application with over 500 million users, represents a successful model contributing to China’s ecological restoration. It translates users’ environmental awareness and low-carbon actions—such as walking, cycling, and reducing plastic/paper use—into tangible environmental benefits, offering a global reference for ecosystem recovery through digital engagement (Wang N. et al., 2022). While technology is often viewed as a double-edged sword in sustainability discourse, it increasingly serves as a catalyst for positive change (Al-Emran, 2023; Tian et al., 2024a). Among such innovations, Ant Forest stands out as a scalable tool for promoting sustainable behaviors (Obuobi et al., 2024), demonstrating significant potential to mitigate environmental harm (Ashfaq et al., 2022). The app strengthens users’ low-carbon purchasing and habitual consumption patterns, with its online-offline integration fostering replicable eco-friendly habits (Xiong et al., 2024).
By leveraging information technology, Ant Forest enables mass participation in green actions, with millions of trees planted through user engagement. AI technologies transcend spatial-temporal barriers in environmental protection, and Ant Forest’s “green energy” mechanism motivates public participation in energy-saving initiatives (Cao and Liu, 2023). Digital-driven environmental campaigns cultivate online green users (OGUs), positioning digital tools as pivotal for climate action (Chen et al., 2020). Users’ perceptions of Ant Forest’s hedonic, social, altruistic, and biospheric values positively shape their attitudes toward the platform (Zhang et al., 2022). The concept of a low-carbon digital economy, driven by green innovation and renewable energy consumption, further reduces carbon dioxide emissions (Alam et al., 2023). Although the integration of gamification and environmentalism presents new opportunities, the direct effectiveness of gamification in promoting sustainable behaviors among Chinese youth remains to be examined, and it still has limitations in driving green actions (Huang et al., 2023).
2.3 Research on the continuous usage behavior of Ant Forest users
Ant Forest is a new generation of persuasive system that incorporates functions such as social media and gamification, which promotes public participation in this green welfare initiative. Perceived persuasiveness and the intention to continue using it can lead to ultimate behavior change (Yang et al., 2018). Ant Forest offers various gamification features (such as points, leaderboards, badges, tasks, and teamwork) to encourage users to participate in environmental protection and public welfare activities. These gamification mechanisms, combined with the dissemination through social media, enable the co-creation of user brand value (Huang et al., 2024). The development of the Internet has led to a new form of integration between gamification and environmental protection, and the influence of gamification participation motivation on consumers’ green consumption behavior is becoming increasingly significant (Sun and Xing, 2022). The Ant Forest game platform can actively promote users to adopt pro-environmental behaviors, as it explores users’ needs from their own perspectives and gives full play to the role of game incentives in users’ environmental behaviors (Xiong et al., 2022). Intrinsic motivations (enjoyment, social interaction, satisfaction, altruism) and extrinsic motivations (external rewards, competition) influence Alipay users’ participation in the Ant Forest project (Wang S. et al., 2022). The increase in the usage of environmental protection applications has become a powerful tool for promoting offline environmental protection activities and a green lifestyle. Users’ satisfaction is an important psychological motivation that encourages continuous usage behavior in Ant Forest (Mi et al., 2021). Under the moderating effect of environmental knowledge, users’ values have an important impact on their attitudes towards Ant Forest and their intention to continue using it (Ashfaq et al., 2021).
The extant literature has explored digital technologies and Ant Forest, yielding numerous research outcomes. Nevertheless, the academic community has yet to engage in in-depth deliberations regarding whether intelligence technologies can promote low-carbon consumption behaviors. Moreover, there is relatively scant research on the influencing factors of low-carbon consumption from the perspective of the Attitude-Context-Behavior (ACB) theory. Drawing on the survey data of 399 Chinese Ant Forest users, this paper applies the ACB theory to investigate the influencing factors of residents’ low-carbon consumption and endeavors to address the question of whether intelligence technologies and intelligent applications can enhance low-carbon consumption behaviors.
3 Theoretical foundation and research hypotheses
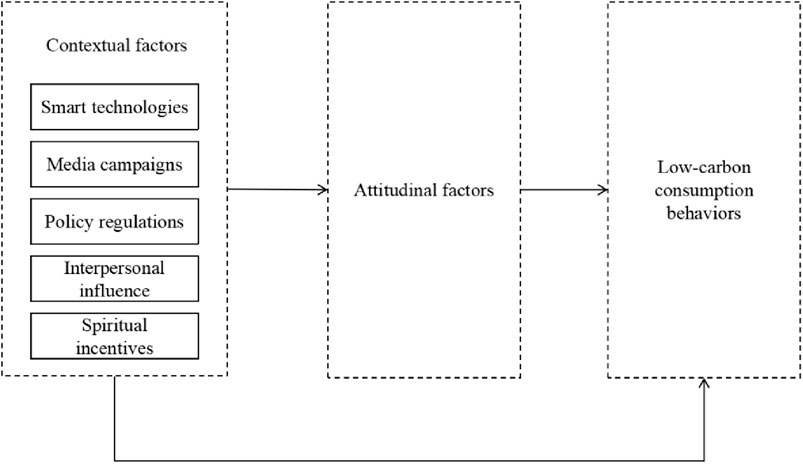
The Attitude-Context-Behavior (ACB) theory is a classic theory in social psychology, aiming to explain the formation and change of individual behaviors (Guagnano et al., 1995). This theory posits that an individual’s behavior is the result of the interaction between attitude and contextual factors. According to this model, the realization of consumer behavior is simultaneously influenced by both individual internal attitudes and external contextual factors, and different combinations of attitude and contextual factors determine different forms of behavior. Generally speaking, when the influence of contextual factors is neutral, attitude can almost independently influence the decision-making of low-carbon consumption behaviors; when contextual factors are relatively positive or negative, they can significantly promote or hinder the implementation of low-carbon consumption behaviors. Therefore, the gap between low-carbon consumption attitude and behavior can be explained by the negative effects of contextual factors, as shown in Figure 1. Based on the Attitude-Context-Behavior theory, this paper constructs a theoretical framework for the influencing factors of consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors from three aspects: attitude, context, and behavior.
3.1 The direct influence of contextual factors on residents’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Contextual factors generally refer to a set of factors associated with the physical or social environment, which are independent of individual consumers and product attributes, such as media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence (persuasion, demonstration, etc.), and spiritual incentives that support low-carbon consumption behaviors. On this basis, most Chinese scholars have explored the influence of contextual factors on low-carbon consumption behaviors mainly focusing on aspects such as public norms, policies and regulations, behavioral constraints, and reward and punishment mechanisms. Subsequently, some scholars have also found that contextual factors such as social policies can affect residents’ environmentally friendly behaviors. When social policies are favorable, residents will adopt more environmentally friendly behaviors (Meyer, 2015). Therefore, this paper chooses five variables, namely, intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives, with the aim of reflecting the impact of contextual factors. Intelligence technologies reflect the influence at the technical level. Through digital empowerment and energy conservation and consumption reduction, they bring convenience to residents. Media campaigns reflect the influence at the information and communication level. Through publicity and guidance, they improve residents’ awareness and understanding of low-carbon consumption behaviors. Policy regulations reflect the influence at the institutional and economic levels. Through normative guidance and economic regulatory means, they encourage residents to engage in low-carbon consumption behaviors. Interpersonal influence reflects the influence at the social and psychological levels. Through group norms and the effect of demonstration and imitation, it prompts residents to adjust their behaviors. Spiritual incentives reflect the influence at the social and cultural levels. By emphasizing the significance of low-carbon consumption behaviors for the environment and society, they help residents form environmental protection values and internalize them in their hearts and externalize them in their actions. The Attitude-Context-Behavior theory points out that when contextual factors are extremely favorable or unfavorable, they may greatly promote or prevent the occurrence of environmental behaviors, and at this time, the influence of environmental attitudes on environmental behaviors will approach zero (that is, there is an inverted U-shaped functional curve between environmental attitudes and environmental behaviors). Therefore, grounded in the foregoing analysis, it is posited that intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives exert a positive influence on residents’ low-carbon consumption behaviors. Consequently, the following hypotheses are put forward:
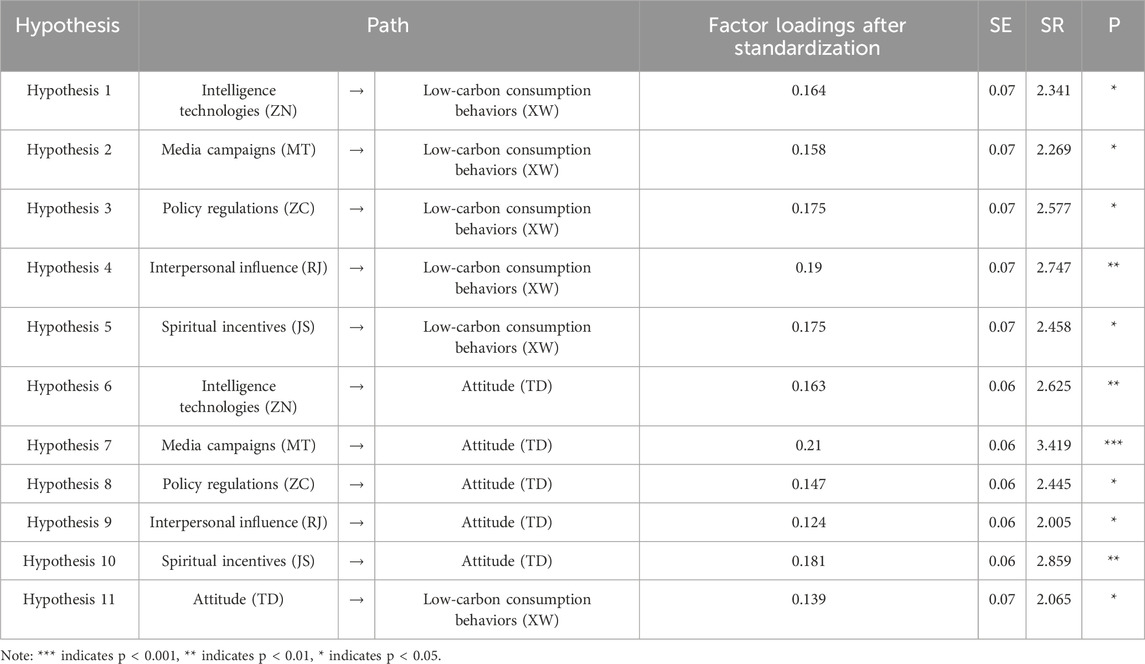
Hypothesis 1. Intelligence technologies have a positive impact on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Hypothesis 2. Media campaigns have a positive impact on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Hypothesis 3. Policy regulations have a positive impact on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Hypothesis 4. Interpersonal influence has a positive impact on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Hypothesis 5. Spiritual incentives have a positive impact on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
3.2 The indirect influence of contextual factors on residents’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
The Attitude - Context - Behavior theory posits that attitude and context interact with each other and jointly exert an effect on behavior. In a supportive context, a positive attitude is more prone to trigger corresponding behavior; conversely, in an unsupportive context, the impact of attitude on behavior may be attenuated. Therefore, this paper holds the view that contextual factors have a positive impact on attitudinal factors. Moreover, through this positive influence on attitudinal factors, they exert an indirect impact on residents’ low-carbon consumption behaviors. The following hypotheses are proposed:
Hypothesis 6. Intelligence technologies have a positive impact on attitude
Hypothesis 7. Media campaigns have a positive impact on attitude
Hypothesis 8. Policy regulations have a positive impact on attitude
Hypothesis 9. Interpersonal influence has a positive impact on attitude
Hypothesis 10. Spiritual incentives have a positive impact on attitude
3.3 The direct influence of attitudinal factors on residents’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Attitude is a stable psychological tendency that an individual holds towards a specific object (person, concept, emotion, or event, etc.). This psychological tendency contains the individual’s subjective evaluation and the resulting behavioral tendency. The Attitude-Context-Behavior theory holds that when the influence of contextual factors is neutral, attitude can almost independently influence the decision-making of low-carbon consumption behaviors. Based on the above analysis, this paper believes that attitude has a positive impact on low-carbon consumption behaviors and proposes the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 11. Attitude has a positive impact on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
According to the previous hypotheses, it can be known that the influence of contextual factors on residents’ low-carbon consumption behaviors mainly occurs through two channels: one is the direct channel, that is, contextual factors directly act on individuals, prompting them to adopt low-carbon consumption behaviors; the other is the indirect channel, that is, contextual factors influence individuals’ internal attitudes and then affect their low-carbon consumption behaviors. In the path of the indirect effect, individuals’ internal attitudes play a bridging role, connecting the relationship between contextual factors and low-carbon consumption behaviors. As a mediating variable, attitudinal factors moderate the influence of contextual factors on low-carbon consumption behaviors. In other words, contextual factors do not influence low-carbon consumption behaviors in isolation, but rather indirectly promote the occurrence of low-carbon consumption behaviors by influencing internal attitudinal factors. Therefore, this paper proposes the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 12. Attitude plays a mediating role between intelligence technologies and consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Hypothesis 13. Attitude plays a mediating role between media campaigns and consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Hypothesis 14. Attitude plays a mediating role between policy regulations and consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Hypothesis 15. Attitude plays a mediating role between interpersonal influence and consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
Hypothesis 16. Attitude plays a mediating role between spiritual incentives and consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors
According to the proposed research hypotheses, the theoretical model of this paper is shown in Figure 2.
4 Research methods and results analysis
4.1 Questionnaire design and survey
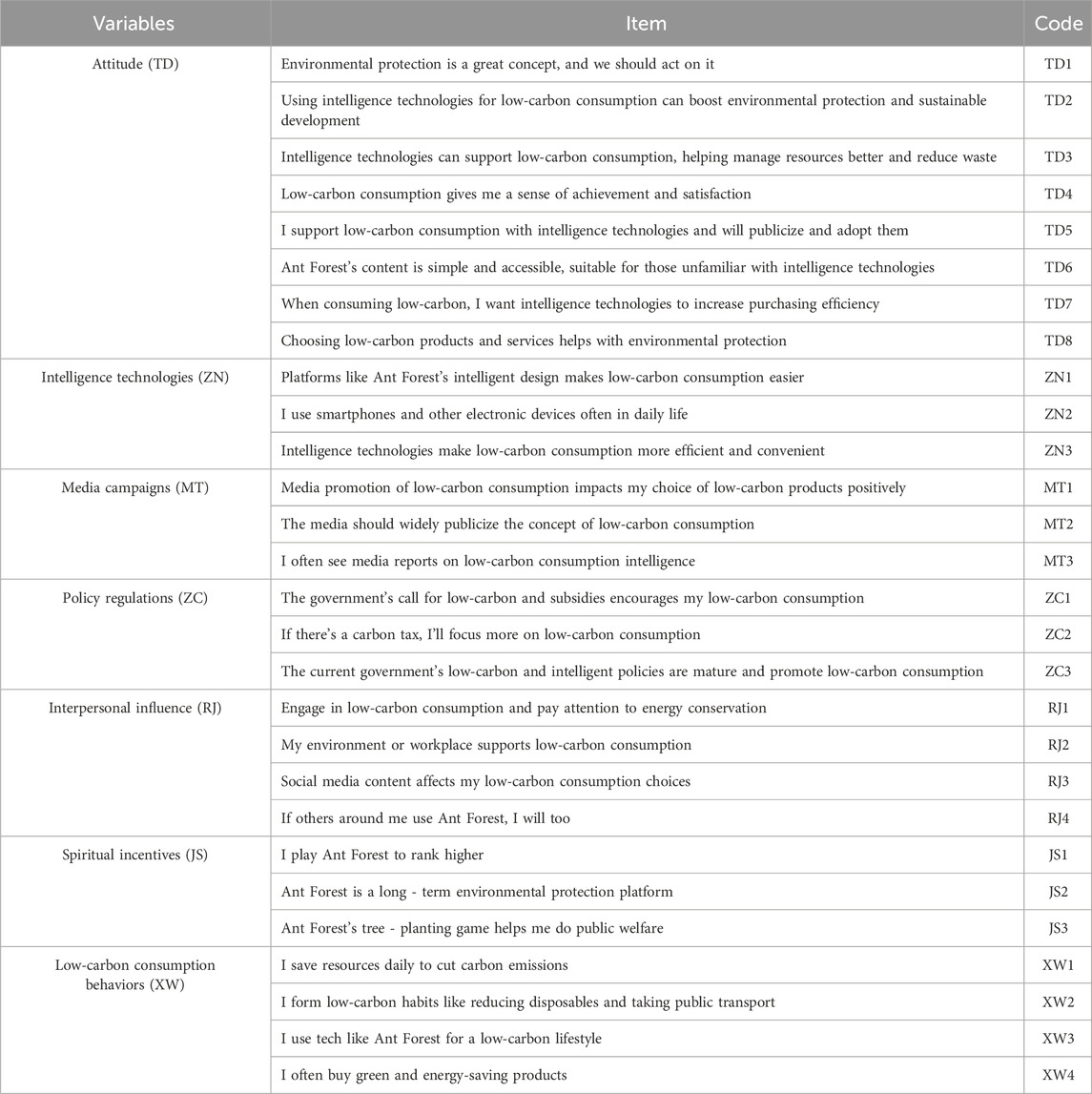
Drawing on relevant literature, conducting pre - surveys, and employing other research methods, this study determines the measurement items for each variable and designs the corresponding questionnaire. The questionnaire used in this study can be generally categorized into four main parts. The first part pertains to the demographic characteristics of the participants. The second part consists of the scale for attitudinal factors. The third part is the scale for contextual factors, which mainly encompasses five dimensions: intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives. The fourth part is the scale for low-carbon consumption behaviors. Each scale adopts a five - point Likert scale, and the final scale design is presented in Table 1.
Firstly, relevant journal articles and online resources are consulted to collect questionnaires and scales related to this study. On the basis of organizing these materials, the measurement indicators for each variable are determined by referring to existing mature scales, and a preliminary questionnaire is designed accordingly. The target respondents are set as users who have used or are currently using Ant Forest. In order to verify the correctness of the questionnaire in terms of wording, language expression, and logical structure, and to ensure the smooth implementation of the subsequent formal survey, this paper conducts a small-scale pre-survey of the initial questionnaire online and collects feedback through interviews, recording the improvement suggestions put forward by the participants for the questionnaire. Finally, according to the feedback results of the pre-survey, the initial questionnaire is adjusted and improved as necessary to ensure the quality and applicability of the questionnaire, and then a large-scale formal survey is carried out.
The survey of this study spans a period of 3 months. Relying on online community platforms related to Ant Forest, such as the relevant topic sections of Ant Forest on Baidu Tieba and the super topics of Ant Forest on Sina Weibo, the questionnaires are distributed. In terms of personnel arrangement, a survey team consisting of 5 people is established. Among them, 2 people are responsible for posting the questionnaire links on various platforms and promptly answering netizens’ questions; 1 person is responsible for the preliminary sorting and classification of the recovered questionnaires; and the other 2 people are specifically responsible for the quality control of the questionnaires, identifying invalid questionnaires through the set lie-detection questions. During the 3-month survey process, in the first month, the main task is to distribute questionnaire information frequently on various platforms to attract more users to participate in filling it out; in the second month, the exposure of the questionnaire is continued, and at the same time, a preliminary screening of the existing questionnaires is carried out; in the third month, the focus is on recovering the remaining questionnaires and conducting a final validity review of all the recovered questionnaires.
Given the time-consuming nature of recruiting and surveying Ant Forest users, a total of 430 questionnaires were distributed in this survey. After the team members carefully screened the lie-detection questions and excluded some invalid questionnaires, a total of 399 valid questionnaires were finally obtained, with an effective rate of 92.8%.
Among the valid samples, in terms of gender, males account for 47.4% and females account for 52.6%; in terms of age, the group aged 20–39 is the main body, accounting for 43.9%, because individuals in this group are generally more exposed to and engaged with intelligence technologies. They are often early adopters of new digital services and are more likely to be influenced by technological advancements in their consumption patterns; in terms of educational background, undergraduate and junior college education levels are the main ones, accounting for 50.9% and 34.8% respectively, Education is an important factor that can shape an individual’s awareness and understanding of environmental issues as well as their ability to access and utilize intelligence technologies. Higher levels of education are often associated with greater environmental awareness and a better understanding of the benefits of low-carbon consumption; in terms of residence, urban and rural areas account for 55.1% and 44.9% respectively, the distinction between urban and rural areas is important because there are significant differences in the availability and adoption of intelligence technologies, as well as in consumption cultures and environmental awareness. The monthly income level is mainly concentrated in the range of 4000–6000 yuan, accounting for 33.6%, income is a crucial factor in consumption behavior as it determines an individual’s purchasing power and ability to afford certain products and services related to low-carbon consumption.
4.2 Reliability analysis
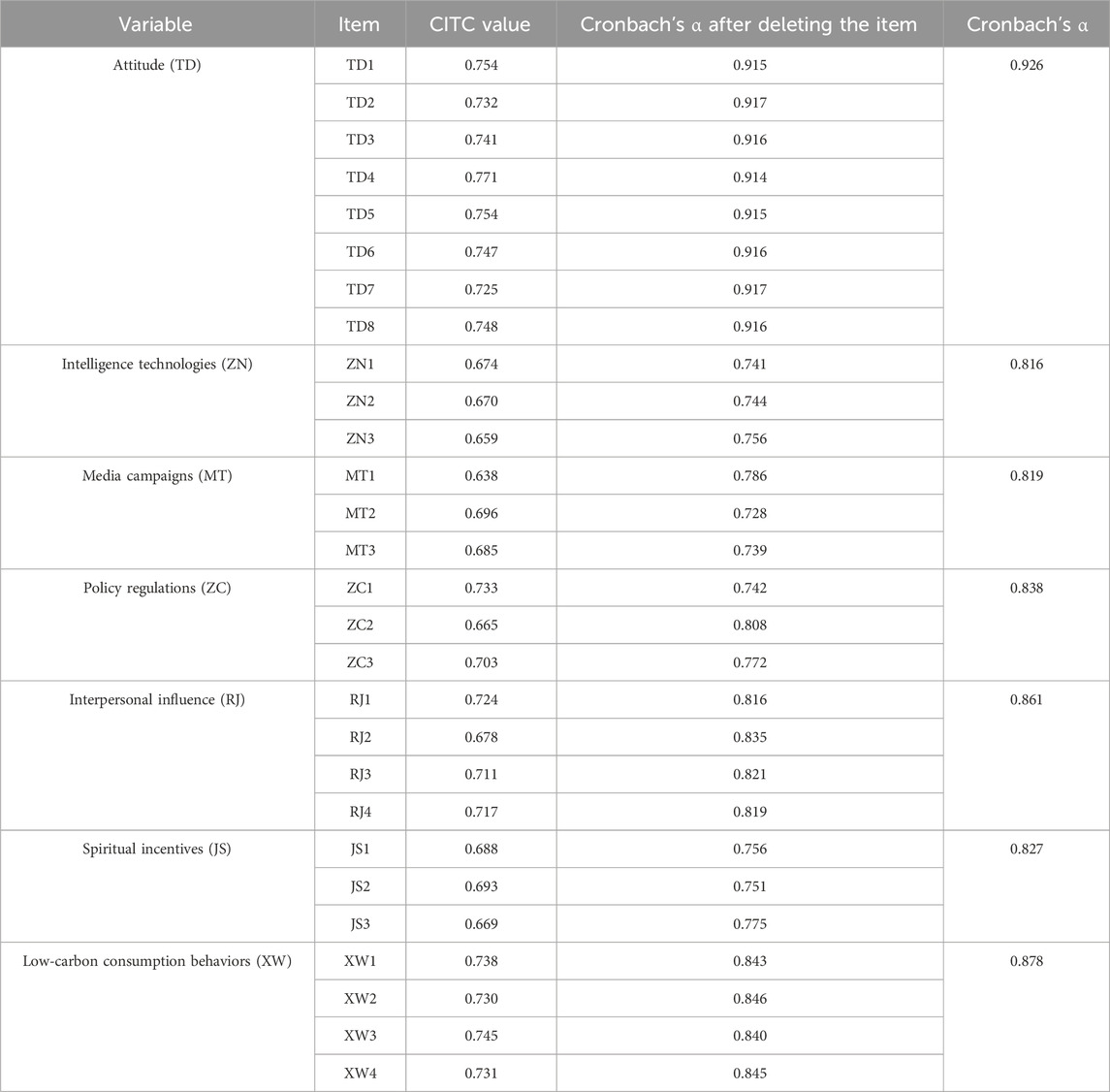
In this study, SPSS 27 was utilized to perform a reliability test on the scales of attitudinal factors, intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, spiritual incentives, and low-carbon consumption behaviors. The test results are presented in Table 2.
As can be seen from Table 2, the CITC value of each measurement item exceeds 0.6, and the Cronbach’s α coefficient does not increase after deleting the item, indicating that the items of these scales all meet the research requirements. At the same time, the overall Cronbach’s α coefficient of each variable is greater than 0.7 and all higher than 0.8, suggesting that these 7 scales all have relatively good reliability.
4.3 Validity analysis
4.3.1 Convergent validity
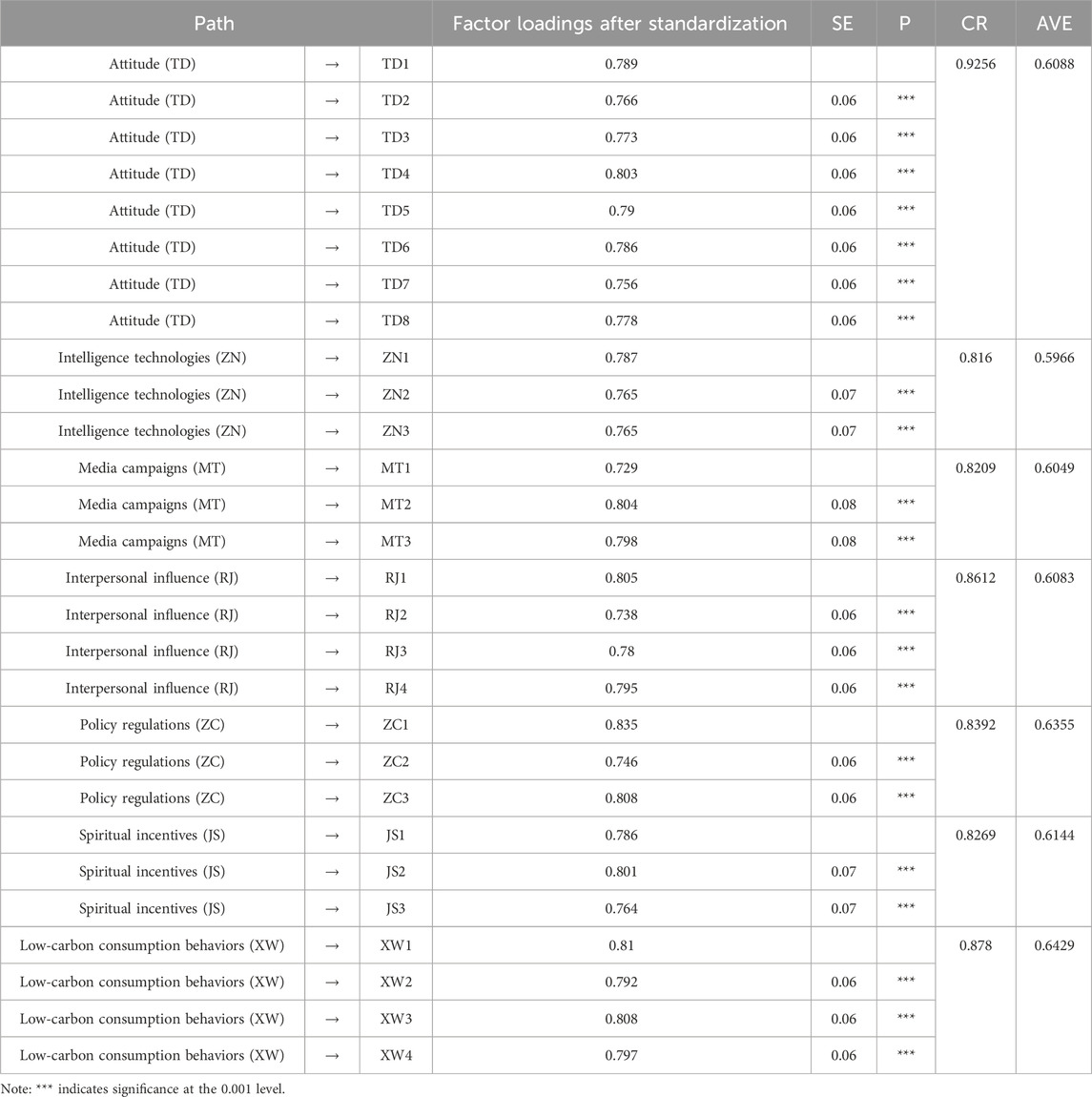
The standardized factor loadings of the items corresponding to the 7 variables of attitude, intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, spiritual incentives, and low-carbon consumption behaviors are all greater than 0.7, indicating that the structural validity of the questionnaire is good; the average variance extracted (AVE) of the variables is greater than 0.5 and the CR value is greater than 0.7, indicating good convergent validity. The results of convergent validity are shown in Table 3.
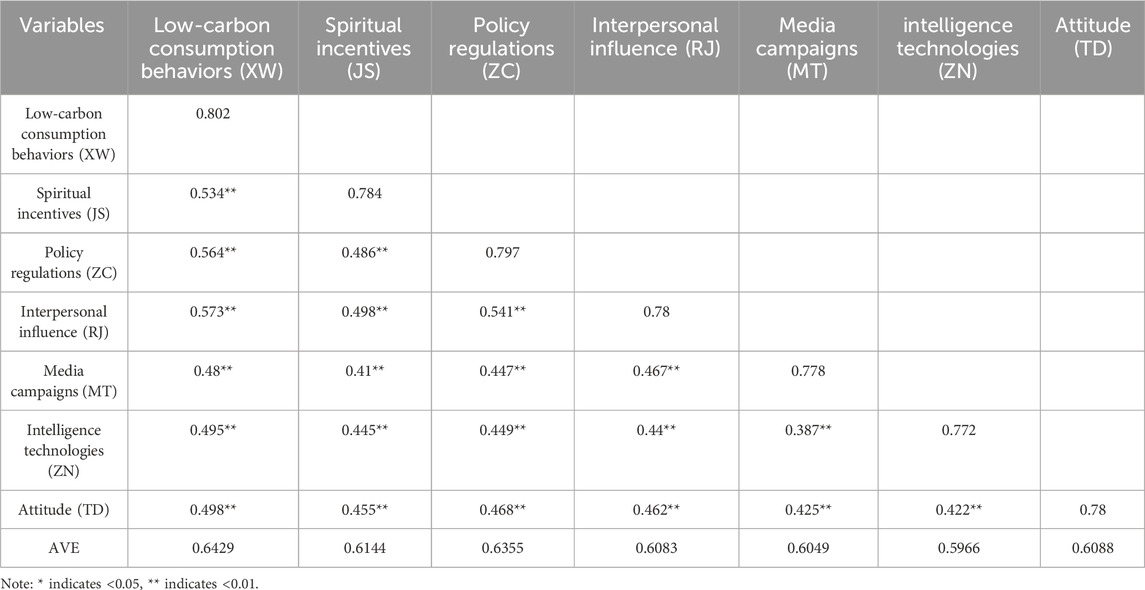
4.3.2 Discriminant validity
According to the results in Table 4, the standardized correlation coefficients between each pair of variables are all smaller than the square root values of the corresponding Average Variance Extracted (AVE) of the variables, indicating good discriminant validity.
4.4 Correlation analysis
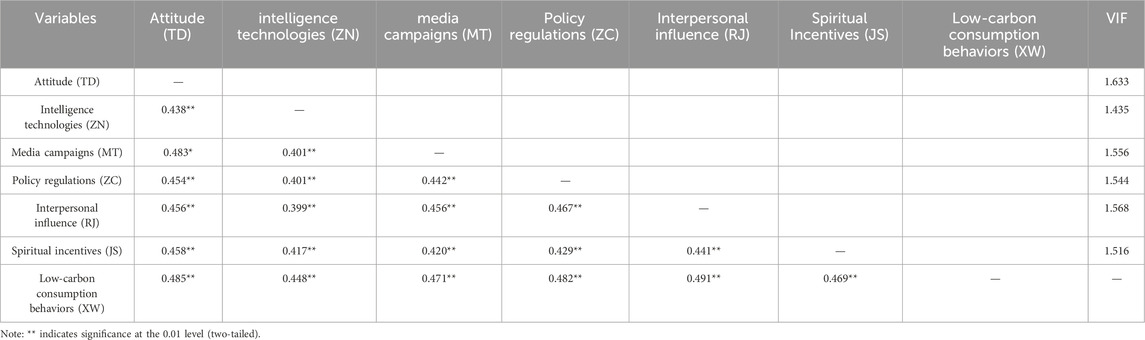
Before conducting the structural equation model analysis, this paper first carried out a correlation analysis between low-carbon consumption behaviors and the variables of their influencing factors. The correlation analysis can not only help us preliminarily identify whether there is a certain trend of connection between the independent variables and the dependent variables, but also provide a basis for further in-depth exploration of the exact relationships among the variables. Through the correlation analysis, we can determine whether there is a correlation between variables. When there is no correlation between variables, conducting subsequent causal relationship analysis is redundant; while when there is a correlation between variables, the structural equation model can be used to further analyze the effects among them. This paper uses the Pearson correlation coefficient to measure the correlation between variables, and the results of the correlation analysis are shown in Table 5.
According to the results of the correlation analysis, looking at the correlation coefficient between the attitudinal factor (TD) and low-carbon consumption behavior (XW), the correlation coefficient is 0.438, and it is significant at the 0.01 level (two-tailed), indicating that there is a certain degree of positive correlation between the two. From the perspective of the correlation coefficients between the contextual factors and low-carbon consumption behavior (XW), the correlation coefficients between intelligence technologies (ZN), media campaigns (MT), policy regulations (ZC), interpersonal influence (RJ), spiritual incentives (JS) and low-carbon consumption behavior (XW) are all positive values, and all are significant at the 0.01 level, indicating that there are also significant positive correlations among these variables. In addition, this paper uses SPSS27 to calculate the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) among the variables of the influencing factors of low-carbon consumption behavior. Generally speaking, when the VIF value is greater than 10, it indicates a serious problem of multicollinearity. The VIF values of all variables in the table are around 1.4–1.6, which is much smaller than 10, indicating that the problem of multicollinearity among the variables is not serious, and the reliability of the model is high. The results of the correlation analysis among the variables are basically consistent with the research hypotheses proposed in this paper, laying the foundation for the structural equation path and analysis in the following text.
4.5 Research methods and results
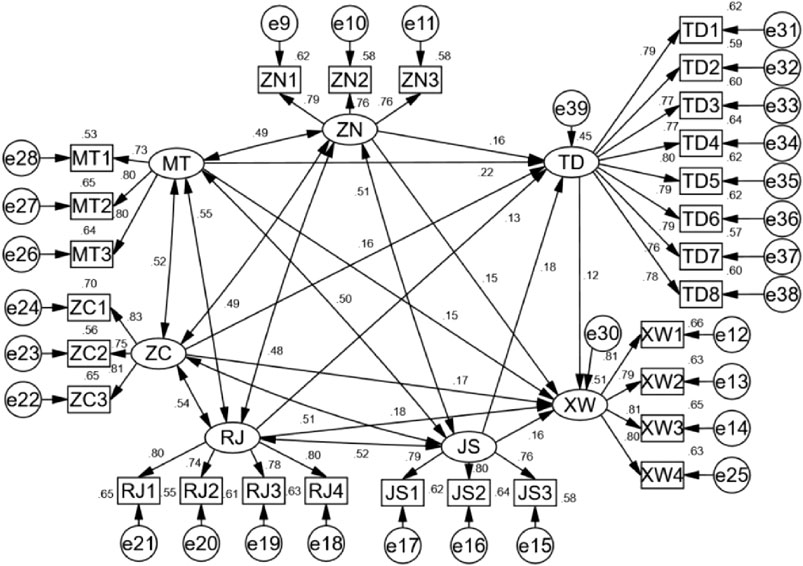
This paper constructs a structural equation model on AMOS, and the results are shown in Figure 3.
According to the results of the structural equation model, latent variables such as intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives respectively affect attitudes and low-carbon consumption behaviors through their corresponding observed variables ZN1-ZN3, MT1-MT3, etc. Among them, the path coefficient between intelligence technologies and attitude is 0.16, and the path coefficient between media campaigns and attitude is 0.22, etc. These indicate that there are differences in the degrees of influence of various contextual factors on attitudes and low-carbon consumption behaviors. Moreover, attitudes also have a certain influence on low-carbon consumption behaviors, with a path coefficient of 0.12.
4.5.1 Model fit test
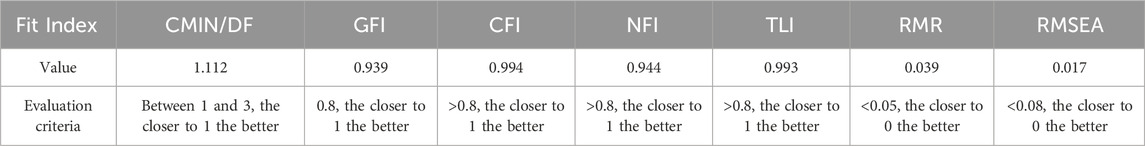
According to the model fit coefficients in Table 6, the chi-square to degrees of freedom ratio (CMIN/DF) = 1.112, which is between 1 and 3 and close to 1; the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) = 0.017, which is close to 0; the values of the other fit indices all reach the acceptable range, and the fitting effect is good.
4.5.2 Results of the hypothesis test of the path relationships in the SEM model
According to the results of the path coefficient test, as shown in Table 7, in terms of the direct effects of contextual factors on low-carbon consumption behaviors, the path coefficients between intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, spiritual incentives and low-carbon consumption behaviors are 0.164, 0.158, 0.175, 0.19, and 0.175 respectively, and they have passed the significance test, indicating that contextual factors have a positive impact on low-carbon consumption behaviors, and hypotheses Hypothesis 1, Hypothesis 2, Hypothesis 3, Hypothesis 4 and Hypothesis 5 are verified; from the indirect effects of contextual factors on low-carbon consumption behaviors, the standardized path coefficients are 0.163, 0.21, 0.147, 0.124, and 0.181 respectively, and they have passed the significance test, so hypotheses Hypothesis 6, Hypothesis 7, Hypothesis 8, Hypothesis 9, and Hypothesis 10 are verified. Regarding the relationship between attitudinal factors and low-carbon consumption behaviors, the path coefficient between attitude and low-carbon consumption behaviors is 0.139, which also passes the significance test, indicating that attitude has a positive impact on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors, and hypothesis Hypothesis 11 is verified.
4.5.3 Test of the mediating effect
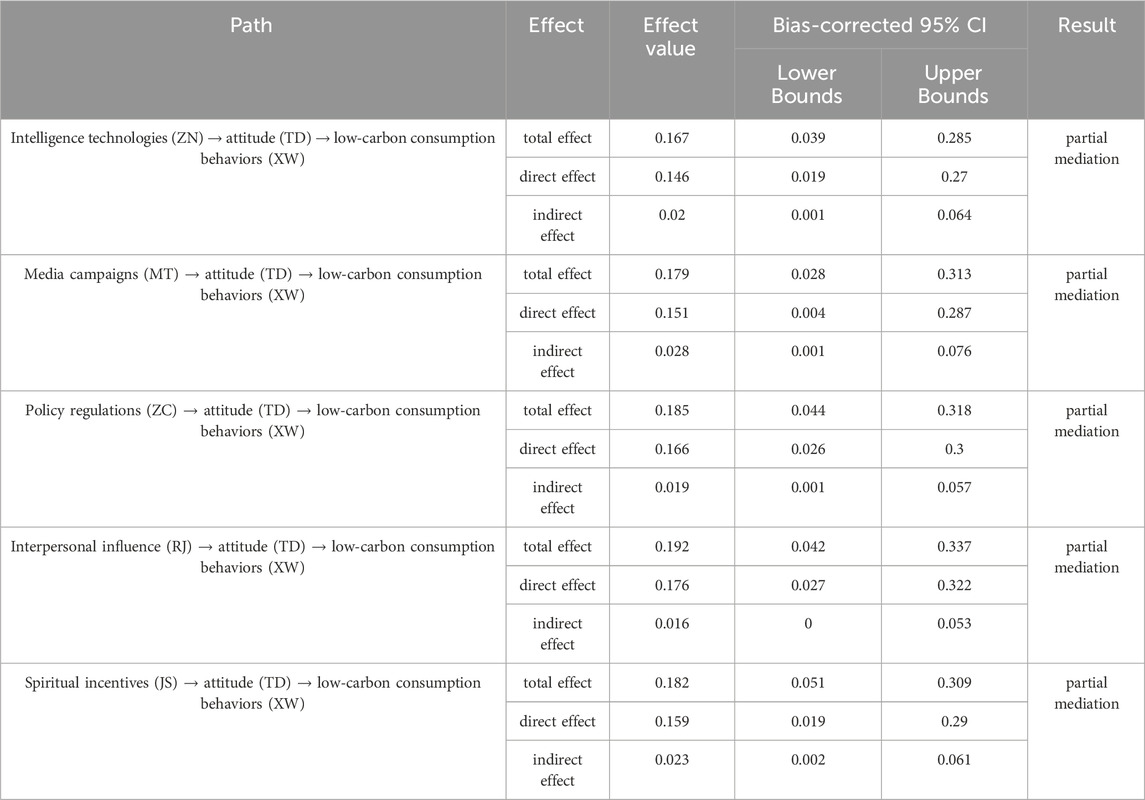
This paper uses the Bootstrap method to test the mediating effect of attitudinal factors between contextual factors and low-carbon consumption behaviors. The results of the mediating effect test are shown in Table 8.
According to the results of the mediating effect test, the mediating effects of attitudinal factors between each contextual factor variable and low-carbon consumption behaviors all pass the significance test, indicating that intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives can influence low-carbon consumption behaviors through attitudinal factors. Hypothesis 12, Hypothesis 13, Hypothesis 14, Hypothesis 15, and Hypothesis 16 are verified.
4.6 Regression analysis
This paper takes low-carbon consumption behaviors as the dependent variable, and attitude, intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives as the independent variables to conduct a linear regression analysis, further verifying the results of the previous structural equation model.
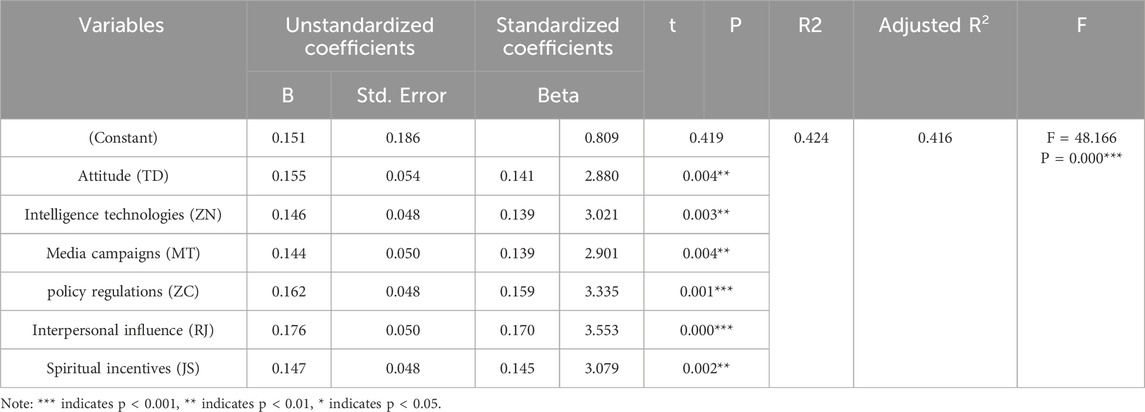
According to Table 9, the significance P value is 0.000***, showing significance at this level, and the model basically meets the requirements.
The formula of the model is as follows:
Among them, TD represents attitude, ZN represents intelligence technologies, MT represents media campaigns, ZC represents policy regulations, RJ represents interpersonal influence, JS represents spiritual incentives, and ε represents the error term. The regression analysis results indicate that attitudinal factors, intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives all exert significant positive impacts on low-carbon consumption behaviors, which is consistent with the findings of the previous structural equation model. In the regression analysis results, the unstandardized coefficient of intelligence technologies is 0.146. This implies that, when other variables are controlled, for every one-unit increase in intelligence technologies, low-carbon consumption behaviors will experience a positive change of 0.146 units. Meanwhile, the standardized coefficient Beta is 0.139, suggesting that among all independent variables, intelligence technologies have a certain degree of relative influence on low-carbon consumption behaviors and play a non - negligible role in promoting such behaviors. This also implies that the development and application of intelligence technologies, such as the various intelligent functions in Ant Forest (e.g., carbon footprint calculation, energy collection reminder), can effectively promote users’ low-carbon consumption behaviors.
5 Discussion
The conclusions of this paper are different from those of previous studies. Low-carbon awareness and low-carbon intention have a positive impact on the low-carbon behaviors of residents (Yang et al., 2020). In a model that encompasses individual and group-level factors as well as the perception of psychological empowerment, factors such as normative internalization have a positive impact on positive low-carbon consumption behaviors, and the perception of psychological empowerment plays a partial mediating role (Cheng et al., 2022). Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior, the factors influencing consumers’ willingness to purchase low-carbon products from the perspective of carbon labels were explored, including factors related to carbon labels, attitudes, norms, etc (Li et al., 2017). The influencing factors of urban residents’ low-carbon consumption behaviors were analyzed by sorting out relevant studies based on classic theories and summarizing factors such as the self, family, and context (Ding et al., 2018).
Nevertheless, this study, utilizing data from 399 Ant Forest users and grounded in the theoretical framework of the Attitude-Context-Behavior theory, comprehensively analyzes the relationships among the three elements. It not only focuses on the impacts of contextual and attitudinal factors on behaviors but also delves deeply into the mediating role of attitudinal factors, thus contributing novel insights in terms of theoretical foundation and research focus. This study reveals that both attitudinal and contextual factors exert a positive influence on low-carbon consumption behaviors, with attitudinal factors mediating the relationship between contextual factors and low-carbon consumption behaviors. Contextual factors not only directly impact consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors but also significantly affect attitudinal factors, and can indirectly influence behaviors through the mediating effect of attitudinal factors.
The advantage of intelligence technologies lies in their ability to provide accurate and real-time information feedback, which is crucial for consumers’ decision-making processes. The lack of sufficient information is one of the important factors hindering consumers from taking environmental protection behaviors, and intelligence technologies can exactly make up for this deficiency (Kollmuss and Agyeman, 2002). Via data logging and presentation, Ant Forest empowers users to gain a clear understanding of the environmental benefits engendered by their low-carbon behaviors. Consequently, this fortifies users’ environmental protection stances and serves to further propel low-carbon consumption behaviors.
However, this paper solely utilizes data from 399 Ant Forest users, and the relatively small sample size restricts the generalizability of the findings. Given that Ant Forest is a locally - oriented application and the majority of the surveyed respondents are Chinese, it is challenging to eliminate the potential impact of culture on the results, particularly the effect of the national conformist mindset. People from diverse cultural backgrounds may possess distinct values and behaviors, which could influence their intention to use Ant Forest and their environmental protection behaviors (Xiong et al., 2024). Moreover, Ant Forest represents merely a single intelligent application in the environmental protection domain. The study fails to encompass the impacts of other intelligent scenarios, such as smart homes and intelligent transportation, on low-carbon consumption behaviors, and thus cannot fully demonstrate the promotional effect of intelligence technologies on low-carbon consumption.
Consequently, future research should further broaden the sample scope, incorporate more user data from different regions with varying consumption habits and levels of environmental awareness, conduct comparative analyses, and enhance the general applicability of the research results. Additionally, the impacts of intelligent applications in different fields, such as smart grids and intelligent logistics, on low-carbon consumption behaviors ought to be investigated, and a multi - dimensional research model of intelligence and low-carbon consumption behaviors should be constructed to comprehensively disclose the relationship between the two. Owing to their unique advantages, intelligence technologies hold great potential in shaping and promoting low-carbon consumption behaviors. Subsequent research should further explore their underlying action mechanisms to provide more robust theoretical support and practical guidance for promoting low-carbon consumption.
6 Conclusion
Drawing on the Attitude-Context-Behavior theory, this study selects Ant Forest users as the research subjects. It conducts reliability and validity tests, as well as correlation analysis, on 399 valid samples. Subsequently, the constructed theoretical model is analyzed and tested using methods such as the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) and the Bootstrap method, followed by a linear regression analysis. Eventually, the 16 hypotheses proposed in this study are verified, and the following conclusions are reached.
(1) Attitudinal Factors and low-carbon Consumption Behaviors. Attitudinal factors exert a positive influence on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors. This implies that as the positivity of consumers’ attitudes intensifies, they are more likely to engage in low-carbon consumption behaviors.
(2) Contextual Factors and Low-carbon Consumption Behaviors. Results from the reliability and validity tests, correlation analysis, and path coefficients of the structural equation model consistently demonstrate that among the contextual factors, intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives all have a positive impact on low-carbon consumption behaviors. Specifically, intelligence technologies promote low-carbon consumption behaviors. Media promotion of low-carbon consumption can encourage consumers to adopt such behaviors. Under the government’s advocacy for low-carbon living and the prevailing social low-carbon atmosphere, consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors are enhanced. The low-carbon consumption behaviors of an individual’s relatives and friends can prompt the individual to engage in similar behaviors. To a certain degree, spiritual incentives can facilitate the occurrence of consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors.
(3) The Mediating Role of Attitudinal Factors. Findings from the direct effect and mediating effect tests indicate that among the contextual factors, intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives can all positively influence low-carbon consumption behaviors through the mediating role of attitudinal factors.
7 Implication
The foregoing research reveals that attitudinal factors, along with intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives among the contextual factors, all exert positive impacts on consumers’ low-carbon consumption behaviors. Moreover, intelligence technologies, media campaigns, policy regulations, interpersonal influence, and spiritual incentives within the contextual factors can positively influence low-carbon consumption behaviors via the mediating role of attitudinal factors. Based on these findings, this paper proposes suggestions from the following aspects.
7.1 Optimize data monitoring and feedback and enhance the social interaction experience
Establish a real-time intelligent feedback system to provide users with prompt feedback on the environmental benefits and personal gains resulting from their low-carbon consumption behaviors. For instance, present users’ emission reduction amounts through dynamic charts and illustrate the positive environmental impacts of these amounts. Concurrently, offer corresponding points or virtual rewards. Further optimize the social functions of Ant Forest to encourage interaction and sharing among users. Incorporate features such as low-carbon behavior competitions and team-based tree-planting cooperation among users, enabling them to engage in low-carbon consumption activities jointly with friends or colleagues.
7.2 Strengthen intelligent decision-making support and expand intelligent application scenarios
Develop intelligent decision-making tools to assist users in making more low-carbon choices during the consumption process. For example, analyze the carbon footprints of different products using intelligent algorithms and recommend more low-carbon products to users, helping them more intuitively understand the environmental implications of different choices when making purchase decisions. Simultaneously, utilize big data to analyze users’ living habits and push customized low-carbon consumption scenarios tailored to users. For example, for users who frequently order takeout, intelligently push reminders of low-carbon scenarios such as “bringing your own tableware.”
7.3 Promote the construction and supervision of intelligent platforms and improve the infrastructure for intelligent low-carbon consumption
The government assumes guiding, restrictive, and supervisory roles in the low-carbon transformation of consumption. This is crucial for shaping residents’ low-carbon consumption behaviors. The government should commence with top - level design and the construction of the legal and regulatory system. It should formulate relevant laws and regulations to promote the transformation of the consumption field towards intelligence and low-carbonization, thus accelerating the change in residents’ lifestyles, consumption patterns, and travel modes. Simultaneously, the government should increase investment in the infrastructure for intelligent low-carbon consumption. For example, construct more charging piles for new energy vehicles, intelligent garbage-sorting and recycling facilities, etc., to facilitate residents’ low-carbon consumption, reduce the cost and difficulty of low-carbon consumption, and provide favorable hardware-based contextual support for low-carbon consumption behaviors.
7.4 Continuously carry out publicity and build a low-carbon consumption market with multi-party participation and mutual benefits
Within the government-led governance framework for low-carbon transformation, give full play to the role of market mechanisms. Form an effective incentive and restraint mechanism for consumers and other market participants, and fully mobilize the enthusiasm of all stakeholders. Encourage enterprises to implement green supply chain management, integrating the low-carbon concept throughout the entire process from raw material procurement, production and processing to product sales and after - sales service. Provide market-related policy support and honorary commendations for enterprises that actively practice low-carbon production and operation, and set industry benchmarks.
7.5 Commend the achievements of low-carbon behaviors and create a wave of low-carbon consumption
Actively organize activities such as low-carbon consumption lectures and sharing sessions. Deeply explore the innovative measures and successful experiences of various regions, industries, and enterprises in promoting low-carbon consumption and widely disseminate them. Through these activities, comprehensively explain to residents the significance and practical feasibility of low-carbon consumption, enabling residents to truly realize that practicing low-carbon consumption in daily life is not difficult. Simultaneously, establish relevant awards and honors for typical cases of successful low-carbon living practices. Commend individuals and organizations that demonstrate outstanding performance and remarkable achievements in low-carbon consumption practices to strengthen residents’ determination to engage in low-carbon consumption. Additionally, through multi-channel publicity, ensure that their deeds reach communities, schools, and enterprises, making residents truly feel that low-carbon is within reach. When residents observe these real and tangible cases, they will be inspired to follow suit, gradually creating a low-carbon consumption trend throughout society and embedding the concept of green living in everyone’s mind.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the patients/participants OR patients/participants legal guardian/next of kin was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JY: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – review and editing. RZ: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by The National Social Science Fund of China: ”Research on the Dynamic Mechanism and Implementation Path of Digital Intelligence Empowering Residents Low-Carbon Consumption” (Grant number:24BJY036).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alam, I., Lu, S., Sarfraz, M., and Mohsin, M. (2023). The interplay of green technology and energy consumption: a study of China’s carbon neutrality and sustainable digital economy. Energies 16, 6184. doi:10.3390/en16176184
Al-Emran, M. (2023). Beyond technology acceptance: development and evaluation of technology-environmental, economic, and social sustainability theory. Technol. Soc. 75, 102383. doi:10.1016/j.techsoc.2023.102383
Ashfaq, M., Zhang, Q., Ali, F., Waheed, A., and Nawaz, S. (2021). You plant a virtual tree, we’ll plant a real tree: understanding users’ adoption of the Ant Forest mobile gaming application from a behavioral reasoning theory perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 310, 127394. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127394
Ashfaq, M., Zhang, Q., Zafar, A. U., Malik, M., and Waheed, A. (2022). Understanding Ant Forest continuance: effects of user experience, personal attributes and motivational factors. IMDS 122, 471–498. doi:10.1108/IMDS-03-2021-0164
Buhalis, D., Harwood, T., Bogicevic, V., Viglia, G., Beldona, S., and Hofacker, C. (2019). Technological disruptions in services: lessons from tourism and hospitality. JOSM 30, 484–506. doi:10.1108/JOSM-12-2018-0398
Cao, P., and Liu, S. (2023). The impact of artificial intelligence technology stimuli on sustainable consumption behavior: evidence from Ant forest users in China. Behav. Sci. 13, 604. doi:10.3390/bs13070604
Chen, B., Feng, Y., Sun, J., and Yan, J. (2020). Motivation analysis of online green users: evidence from Chinese “Ant forest.”. Front. Psychol. 11, 1335. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01335
Chen, H., Wei, J., Zhu, D., Fen, Q., and Niu, W. (2014). How to achieve a low-carbon economy in China: from individual attitudes to actual consumption behaviors. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 13, 1165–1172. doi:10.30638/eemj.2014.121
Cheng, X., Yang, J., Jiang, Y., Liu, W., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Determinants of proactive low-carbon consumption behaviors: insights from urban residents in eastern China. IJERPH 19, 6307. doi:10.3390/ijerph19106307
Cossatin, A. G., Mauro, N., and Ardissono, L. (2024). Promoting green fashion consumption through digital nudges in recommender systems. IEEE Access 12, 6812–6829. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3349710
Ding, Z., Jiang, X., Liu, Z., Long, R., Xu, Z., and Cao, Q. (2018). Factors affecting low-carbon consumption behavior of urban residents: a comprehensive review. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 132, 3–15. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.01.013
George, G., Merrill, R. K., and Schillebeeckx, S. J. D. (2021). Digital sustainability and entrepreneurship: how digital innovations are helping tackle climate change and sustainable development. Entrepreneursh. Theory Pract. 45, 999–1027. doi:10.1177/1042258719899425
Gossen, M., and Lell, O. (2023). Sustainable consumption in the digital age: a plea for a systemic policy approach to turn risks into opportunities. GAIA - Ecol. Perspect. Sci. Soc. 32, 71–76. doi:10.14512/gaia.32.S1.11
Guagnano, G. A., Stern, P. C., and Dietz, T. (1995). Influences on attitude-behavior relationships: a natural experiment with curbside recycling. Environ. Behav. 27, 699–718. doi:10.1177/0013916595275005
Guan, C. (2014). Research on residents’ low-carbon consumption in heilongjiang province. IERI Procedia 8, 35–40. doi:10.1016/j.ieri.2014.09.007
Huang, H., Long, R., Chen, H., Sun, K., and Li, Q. (2022). Exploring public attention about green consumption on Sina Weibo: using text mining and deep learning. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 30, 674–685. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2021.12.017
Huang, M., Mohamad Saleh, M. S., and Zolkepli, I. A. (2023). The moderating effect of green advertising on the relationship between gamification and sustainable consumption behavior: a case study of the Ant forest social media app. Sustainability 15, 2883. doi:10.3390/su15042883
Huang, M., Mohamad Saleh, M. S., and Zolkepli, I. A. (2024). The moderating effect of environmental gamification on the relationship between social media marketing and consumer-brand engagement: a case study of Ant Forest Gen Z users. Heliyon 10, e25948. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25948
Istrate, R., Tulus, V., Grass, R. N., Vanbever, L., Stark, W. J., and Guillén-Gosálbez, G. (2024). The environmental sustainability of digital content consumption. Nat. Commun. 15, 3724. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-47621-w
Kollmuss, A., and Agyeman, J. (2002). Mind the Gap: why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behavior? Environ. Educ. Res. 8, 239–260. doi:10.1080/13504620220145401
Li, L., and Peng, Z. (2019). Research on sustainable development——take “Ant forest” for example. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 242, 052031. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/242/5/052031
Li, Q., Long, R., and Chen, H. (2017). Empirical study of the willingness of consumers to purchase low-carbon products by considering carbon labels: a case study. J. Clean. Prod. 161, 1237–1250. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.154
Liu, Y., Liu, R., and Jiang, X. (2019). What drives low-carbon consumption behavior of Chinese college students? The regulation of situational factors. Nat. Hazards 95, 173–191. doi:10.1007/s11069-018-3497-3
Meyer, A. (2015). Does education increase pro-environmental behavior? Evidence from Europe. Ecol. Econ. 116, 108–121. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.04.018
Mi, L., Xu, T., Sun, Y., Zhao, J., Lv, T., Gan, X., et al. (2021). Playing Ant Forest to promote online green behavior: a new perspective on uses and gratifications. J. Environ. Manag. 278, 111544. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111544
Mi, L., Yu, X., Yang, J., and Lu, J. (2018). Influence of conspicuous consumption motivation on high-carbon consumption behavior of Residents——an empirical case study of Jiangsu province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 191, 167–178. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.109
Mohamad Zaidi, N. H., Lim, C. H., and Razali, H. (2024). Mitigating the energy consumption and carbon emissions of a residential area in a tropical city using digital twin technology: a case study of bertam, penang. Buildings 14, 638. doi:10.3390/buildings14030638
Obuobi, B., Tang, D., Awuah, F., Nketiah, E., and Adu-Gyamfi, G. (2024). Utilizing Ant Forest technology to foster sustainable behaviors: a novel approach towards environmental conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 359, 121038. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121038
Priporas, C.-V., Stylos, N., and Fotiadis, A. K. (2017). Generation Z consumers’ expectations of interactions in smart retailing: a future agenda. Comput. Hum. Behav. 77, 374–381. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.058
Ren, Z., and Zhang, J. (2023). Digital economy, clean energy consumption, and high-quality economic development: the case of China. Sustainability 15, 13588. doi:10.3390/su151813588
Sharma, M., Joshi, S., and Govindan, K. (2023). Overcoming barriers to implement digital technologies to achieve sustainable production and consumption in the food sector: a circular economy perspective. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 39, 203–215. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2023.04.002
Stern, P. C. (2000). New environmental theories: toward a coherent theory of environmentally significant behavior. J. Soc. Issues 56, 407–424. doi:10.1111/0022-4537.00175
Sun, Y., and Xing, J. (2022). The impact of gamification motivation on green consumption behavior—an empirical study based on Ant forest. Sustainability 15, 512. doi:10.3390/su15010512
Tian, P., Feng, K., Sun, L., Hubacek, K., Malerba, D., Zhong, H., et al. (2024a). Higher total energy costs strain the elderly, especially low-income, across 31 developed countries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 121, e2306771121. doi:10.1073/pnas.2306771121
Tian, P., Ma, H., Zhang, Z., Yu, Y., and Li, D. (2025). China’s current carbon inequality is predominantly determined by capital disparity. Ecol. Econ. 230, 108515. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2024.108515
Tian, P., Zhong, H., Chen, X., Feng, K., Sun, L., Zhang, N., et al. (2024b). Keeping the global consumption within the planetary boundaries. Nature 635, 625–630. doi:10.1038/s41586-024-08154-w
Wang, N., Hou, W., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., and Yang, L. (2022a). Quantifying the effects of the ‘Internet plus Ecology’ framework on carbon sink in the digital age: a representative study of Ant Forest in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 17, 124005. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/aca2bf
Wang, Q. (2018). Study of emotional changes based on neural management and electroencephalogram experiments on low-carbon consumption behavior. Neuroquantology 16. doi:10.14704/nq.2018.16.2.1184
Wang, S., Ibrahiem, M. H., and Li, M. (2022b). Motivations influencing Alipay users to participate in the Ant forest campaign: an empirical study. IJERPH 19, 17034. doi:10.3390/ijerph192417034
Xiong, N., Ren, P., Sun, B., He, S., Jiang, L., and Cui, H. (2022). Influence of incentive mechanism and fit degree on user’s environmental behavior—taking Alipay “Ant Forest” in China as an example. Front. Psychol. 13, 1033553. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1033553
Xiong, W., Liu, D., Li, Z., Wang, Q., and Yao, S. (2024). How does Ant forest influence low carbon consumption behavior: an analysis based on the S-O-R model. Sustainability 16, 1736. doi:10.3390/su16051736
Yang, Y., Guo, Y., and Luo, S. (2020). Consumers’ intention and cognition for low-carbon behavior: a case study of hangzhou in China. Energies 13, 5830. doi:10.3390/en13215830
Yang, Z., Kong, X., Sun, J., and Zhang, Y. (2018). Switching to green lifestyles: behavior change of Ant forest users. IJERPH 15, 1819. doi:10.3390/ijerph15091819
Yuan, J., Gao, Z., and Xiang, Y. (2023). Green energy consumption path selection and optimization algorithms in the era of low carbon and environmental protection digital trade. Sustainability 15, 12080. doi:10.3390/su151512080
Zeng, Y., Xu, X., Zhao, Y., and Li, B. (2023). Impact of digital economy on the upgrading of energy consumption structure: evidence from mainland China. Sustainability 15, 5968. doi:10.3390/su15075968
Zhang, B., Hu, X., and Gu, M. (2022). Promote pro-environmental behaviour through social media: an empirical study based on Ant Forest. Environ. Sci. and Policy 137, 216–227. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2022.08.020
Zhang, L., and Ma, X. (2022). Analysis on the path of digital villages affecting rural residents’ consumption upgrade: based on the investigation and research of 164 administrative villages in the pilot area of digital villages in zhejiang province. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2022/9928030
Keywords: low-carbon consumption behavior, Ant forest, attitude-context-behavior theory, intelligence technology, structural equation mode
Citation: Ding C, Ye J, Wu X and Zhang R (2025) Intelligence technologies and low-carbon consumption behavior: evidence from Chinese app “Ant Forest”. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1596697. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1596697
Received: 20 March 2025; Accepted: 06 May 2025;
Published: 30 May 2025.
Edited by:
Ji Lu, Dalhousie University, CanadaReviewed by:
Peipei Tian, Institute of Blue and Green Development, Shandong University, ChinaAileen Orbecido, De La Salle University, Philippines
Copyright © 2025 Ding, Ye, Wu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiawen Ye, MTUyMTIzMDIxMDhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Ruidan Zhang, ODY3NTgyNjkwQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Chaoxun Ding
Chaoxun Ding Jiawen Ye
Jiawen Ye Xuepin Wu2
Xuepin Wu2