- 1College of Logistics and Management Engineering, Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, Kunming, China
- 2College of Public Finance and Management, Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, Kunming, China
- 3College of Public Administration and Law, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China
To determine the source apportionment and ecological risk of heavy metals in water from a spatiotemporal perspective, the 7 samples were monitored from 2020 to 2022 in Taihu Lake. The correlation analysis and principal component analysis were employed to identify the sources of heavy metals, and the temporal and spatial characteristics of ecological risk were analyzed using the Mann-Kendall test, mean gravity center, and standard-deviation ellipse. The results indicated an increase in median concentration of heavy metals in the following order: Cd < Pb < Hg < Cu < As < Ni < Zn, These metals were primarily derived from industrial and agricultural activities. Overall, the ecological risks posed by heavy metals were deemed acceptable, with the exception of Hg, which showed considerable potential ecological risk. Furthermore, the potential ecological risk exhibited a significant decreasing trend, with Z-values passing the 95% confidence interval significance test, except for S3. The mean gravity centers of the potential ecological risk were located within an ellipse with center coordinates of (120.2553, 31.3718), major axis of 44,525 m, minor axis of 28,225 m, and a direction of 0.4463°. This study contributes to the enrichment of research perspectives for ecological risk and provides valuable insights for the development of mitigation strategies for heavy metals in Taihu Lake.
1 Introduction
Heavy metal contamination caused by intense anthropogenic perturbations is considered a troublesome problem due to its widespread distribution, long-lasting toxicity, and bio-accumulation (Zhao et al., 2020; Khanom and Hayashi, 2021; Xu et al., 2019). Extensive industrialization and urban sprawl can lead to the introduction of heavy metals into lakes, resulting in undesired environmental outcomes such as inhibiting plant photosynthesis, restraining animal growth, and threatening human health (Khanom and Hayashi, 2021; Bian et al., 2017; Uluturhan and Kucuksezgin, 2007; Xie et al., 2016). Therefore, it is essential to understand the characteristics, sources, and risks associated with heavy metals in water for proper function division, pollution prevention, and risk control.
In recent decades, the combination of natural factors and human activities, including industrial waste, sewage runoff, and agricultural discharge, has resulted in heavy metal pollution in water. (Ding et al., 2020; Wang and Zang, 2014; Zhang et al., 2020; Li Y. et al., 2020). For example, the total amount of wastewater discharged in China amounted to 73.53 billion tons, containing 3.59 billion tons in the Taihu Lake Basin in 2020. In order to reduce the harm caused by heavy metals to the aquatic environment, numerous studies have been implemented to address concerns regarding aquatic heavy metals over the past years, including ecological risk, resources, biological toxicity, and health risk (Li B. et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2019; Xia et al., 2012). The content focuses on the monitoring, transfer, treatment, and risk assessment of heavy metals in water or sediment (Xu et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2017; Biswal and Balasubramanian, 2023; Li et al., 2021), and the methods mainly include the enrichment factor, geo-accumulation index, contamination factor, potential ecological risk index, principal component analysis, and health risk assessment model (Zhao et al., 2020; Ji et al., 2021b; Rahman et al., 2014; Zhan et al., 2020). The current research perspective primarily concentrates on environmental science, while the continuous time variation characteristics analyzed from a geographical approach is relatively less explored.
Generally, Heavy metals entering the lake are difficult to be discharged in a short time due to the slower water velocity and longer water exchange recycle, and then the lake ecosystem is more susceptible to cumulative heavy metals, for instance, the heavy metal subsequently enter the aquatic flora, fauna, and microorganisms, of which some tissues are accumulated by heavy metals with several orders of magnitude higher than the corresponding background value of lakes after long-term exposure even at a low concentration level (Uluturhan and Kucuksezgin, 2007; Xia et al., 2020). Indeed, it is significantly important to explore the spatial-temporal variation characteristics for reducing the hazard of heavy metals by analyzing the sources and ecological risk of heavy metals in the water environment based on continuous time change from the perspective of geography (Ji et al., 2021a), especially for Taihu Lake with a complex aquatic ecosystem and a long history of anthropogenic impacts (Yuan et al., 2019).
Recently, various methods such as principal component analysis, correlation analysis, and positive matrix factorization have been employed to analyze the sources of heavy metals (Li Y. et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2017; Fang et al., 2019). However, there is a lack of studies that analyzed the sources of heavy metals from the temporal perspective. Principal component analysis is commonly utilized to condense the original metal data into a minimal number of factors (Qiao et al., 2020). On the other hand, correlation analysis could analyze the degree of correlation between the heavy metals (Xiang et al., 1987). Considering that the sources of heavy metals in the lake environment may vary over time, a combination of qualitative and quantitative analysis is essential for effectively identifying these sources (Zhang et al., 2017; Niu et al., 2021). Therefore, principal component analysis and correlation analysis are critical and practical methods for investigating the long-term sources of heavy metals in Taihu Lake from 2020 to 2022. Additionally, the potential ecological risk index, which is based on theoretical water environment sedimentology (Hakanson, 1980), has been widely used by researchers worldwide to assess the ecological risks associated with heavy metals in lake sediments, including lakes like Taihu, Bourget, Poyang, Mariout, and Veeranam (Li Y. et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2017; Abu El-Magd et al., 2021; Lécrivain et al., 2018; Suresh et al., 2012). In order to enhance its applicability to Taihu Lake, the parameters of the potential ecological risk index should be optimized, specifically the toxicity coefficient and classification criteria (Ma et al., 2020). Meanwhile, the Mann-Kendall test, also known as the distribution-free test, is a non-parametric statistical method used to determine the presence of significant temporal variations in variables such as vegetation, temperature, and precipitation (Kaushik et al., 2020; Rahman and Dawood, 2017; Yuan et al., 2020; Cavadias et al., 2002). And spatial-temporal characteristics of crop yield, climate variation, and economic development can be qualitatively assessed using methods such as the mean gravity center and standard-deviation ellipse (Balsa-Barreiro et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020; Cao et al., 2021). The overall spatial-temporal variations of ecological risk posed by heavy metals in Taihu Lake could be effectively revealed by employing the Mann-Kendall test, mean gravity center, and standard-deviation ellipse.
Therefore, principal component analysis and correlation analysis were applied to analyze the sources of heavy metals in Taihu Lake from 2020 to 2022. Additionally, a modified potential ecological risk index was obtained to assess the potential threats posed by these metals. Furthermore, the Mann-Kendall test, mean gravity center, and standard-deviation ellipse were utilized to assess the spatial-temporal characteristics of ecological risk. The goals of this research were (a) to analyze the characteristics and possible sources of heavy metal elements (including As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn) monitored in Taihu Lake from 2020 to 2022 and (b) to identify the spatial-temporal variation characteristics of ecological risk. To achieve these goals, a long-term monitoring study was conducted around Taihu Lake from 2020 to 2022, and the sources were investigated using correlation analysis and principal component analysis. In order to explore the ecological risk, the traditional potential ecological risk index proposed by Hakanson (1980) was optimized. Finally, the Mann-Kendall test, mean gravity center, and standard-deviation ellipse were employed to detect the spatial-temporal variation characteristics of ecological risk in Taihu Lake. This work aims to provide scientific evidence for risk management and pollution prevention in Taihu Lake and to enrich the researching perspective of heavy metals in water.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area and sampling sites
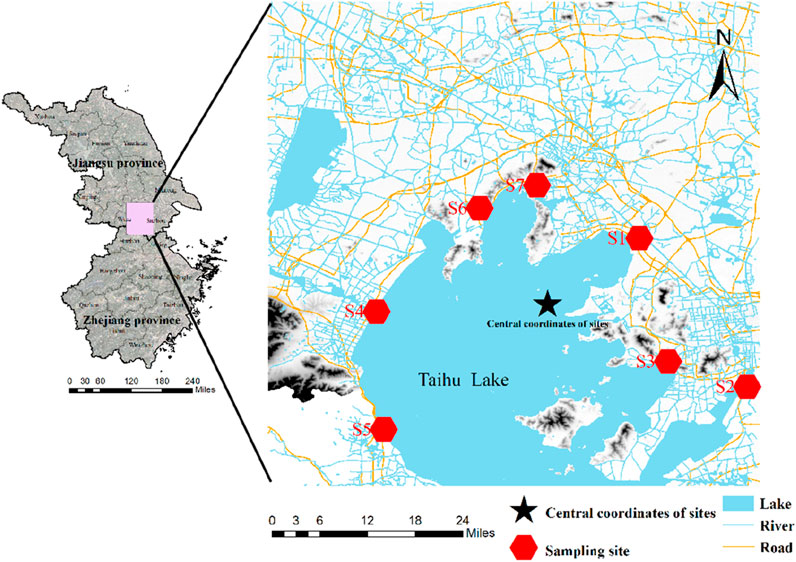
Located on the southern edge of the Yangtze River Delta, Taihu Lake covers an approximate water area of 2,338 km2 and has a subtropical monsoon climate with average precipitation ranging from 1,100 to 1,150 mm and temperatures ranging from 16.0°C to 18.0°C. The surrounding region of Taihu Lake comprises a network of water bodies, with hilly and mountainous terrain primarily located in the west and southwest, and plains dominating the eastern area. Additionally, the northeast region is characterized by a high concentration of population and industrial production, while agricultural production is primarily distributed in the northwest. With the rapid industrialization and agricultural practices that have taken place since the 1980s, Taihu Lake has gradually become polluted. Furthermore, Taihu Lake plays a vital role as a water source for agricultural production and the wellbeing of the local population in China (Li Y. et al., 2020; Xia et al., 2012; Niu et al., 2020; Zhu, 2017; Zhang S. et al., 2018). Therefore, Understanding the migration mechanisms and the spatial-temporal characteristics of ecological risk of heavy metal in Taihu Lake is crucial for enhancing our comprehension of the stability of the lake ecosystem and providing valuable insights into the sustainable use of water. Seven sampling sites, positioned at the inlets of the main rivers of Taihu Lake, were chosen as the subjects of this study (Figure 1). Additionally, the sampling sites were evenly distributed around Taihu Lake and the central site, situated at coordinates (120.249571, 31.322114), served as the reference point for the sampling sites.
2.2 Samples measurement and analysis
The automatic monitoring instrument, based on anodic stripping voltammetry, was utilized to obtain electric signals indicative of heavy metal concentrations in the water environment. Through analysis and evaluation of these signals, the concentration of heavy metals in the water could be directly determined. The instrument effectively eliminated interference from organic matter during the monitoring process of surface water. In conjunction with the automatic water quality monitoring station, the automatic monitoring instrument was employed to monitor heavy metal concentrations at the sampling sites. The accuracy, precision, and detection limit of the monitoring data were ensured by checking the instrument’s performance every 6 months. Additionally, instrument calibration was conducted monthly, following the regulations outlined in the Chinese technical specifications for automatic monitoring of surface water (HJ/T 91-2002). Meanwhile, the monitoring data from the sampling points were examined at least once every morning and afternoon by the workers at the monitoring stations. These data were analyzed and used as the fundamental dataset for this study, consisting of the monthly mean concentrations of As, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn from January 2020 to December 2022 for each sampling point.
2.3 Modified potential ecological risk index
Hakanson (1980) proposed the concept of potential ecological risk, where toxicity coefficients are determined using the elemental abundance and release capacity of sediment (Hakanson, 1980). The ecological risk can be calculated using the following formula.
Where the RI combines the Eri values for all of the heavy metals; Eri represents the potential ecological risk of each heavy metal; Ti corresponds to the toxic response coefficient, Pi represents the contamination factor of the heavy metal; Cmi and Csi are the actual concentration and the background concentration or baseline value of each heavy metal respectively. In this study, the Csi values were based on the grade Ⅳ standard outlined in the Chinese environmental quality standards for surface water (GB 3838-2002), as specified in the “action plan for comprehensive treatment of water environment in Taihu Lake Basin during the 13th 5-year plan.”
The abundance and release of heavy metals in sediment impact the toxicity coefficient, as discussed in Hakanson’s (1980) study. Unlike sediment, the toxicity coefficient of heavy metals in water does not involve the release effect, we modified the toxicity coefficient and the classification criteria of RI and Ei based on previous research studies (Hakanson, 1980; Ma et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2008). The specific formula is as following.
Where R refers to the response to the regularization treatment, Amin represents the minimum abundance of heavy metals in this study; Ai denotes the abundance of heavy metals. The optimized toxicity coefficients for As, Cd, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn were determined to be 11, 16, 2, 33, 3, 3, and 1, respectively. Additionally, the updated classification criteria were derived and are presented in Table 1 (Hakanson, 1980; Abu El-Magd et al., 2021; Lécrivain et al., 2018; Suresh et al., 2012).
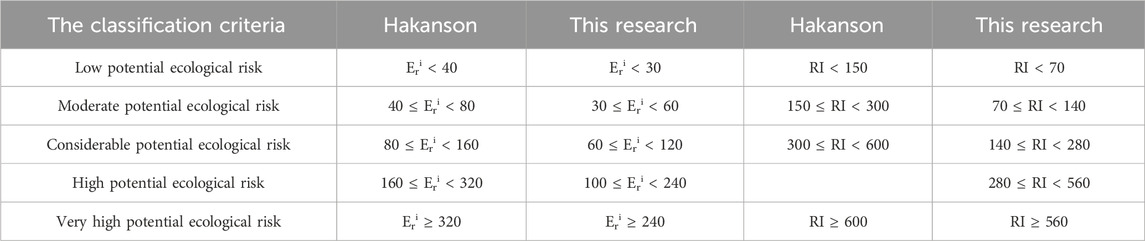
Table 1. Comparative analysis of the ecological risk classification criteria between Hakanson’s method and the approach proposed in this study.
2.4 Spatial-temporal dynamics analysis
2.4.1 Mann-Kendall test
The Mann-Kendall test was employed to assess the significance of the temporal trend regarding the potential ecological risk posed by heavy metals in Taihu Lake from 2020 to 2022. The Mann-Kendall test is defined by the following equations.
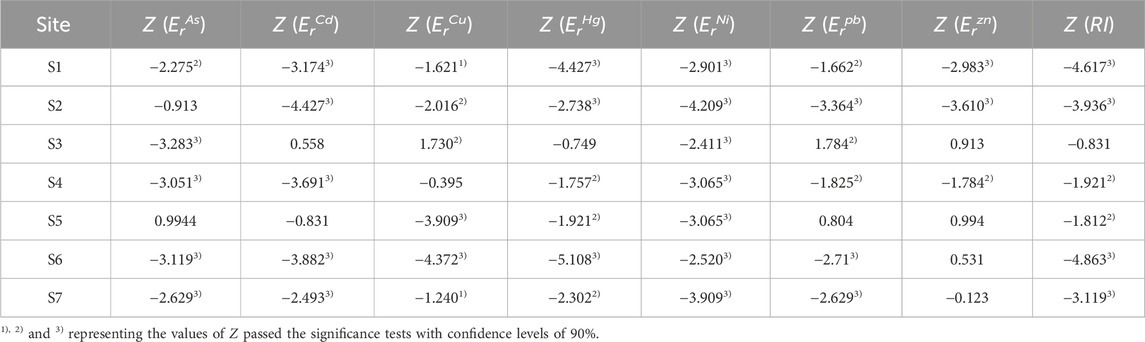
The variables xk and xj represent the Eri or RI in the kth and jth month of each sampling. The significance of the temporal trend of Eri or RI in the sampling site is determined by the absolute value of Z. When Z is greater than or equal to 1.28, 1.64, and 2.32, the trend passes the significance test with reliability levels of 90%, 95%, and 99%, respectively (Yuan et al., 2020; Gocic and Trajkovic, 2013).
2.4.2 Mean gravity center and standard-deviation ellipse
The temporal changes of the RI between 2020 and 2022 were analyzed by calculating the mean gravity center. This mean gravity center was computed using the following relationship.
Where n represents the number of surveying points; PRIj is the monthly percentage of RI for heavy metals in the water environment at a specific site; xj and yj correspond to the longitude and latitude, respectively; the (xm, ym) represents the mean gravity center. In order to clarify the directional distribution of the mean gravity center, we adopted the standard deviation ellipse, which was described in the previous studies (Cao et al., 2021; Gong, 2002).
2.5 Statistical analysis
In this study, IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, United States) was utilized to analyze the correlation analysis, principal component analysis of heavy metals. We employed correlation analysis to identify any significant associations between the heavy metals. Additionally, we performed principal component analysis to elucidate the original variations using fewer new and independent variables. Through a combination of correlation analysis and principal component analysis, we were able to identify possible sources of metals (Li Y. et al., 2020; Zhang P. et al., 2018). Furthermore, we utilized ArcGIS 10.3 to analyze the sampling sites map, mean gravity center, and standard deviation ellipse.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Overall characteristics of heavy metals in Taihu lake
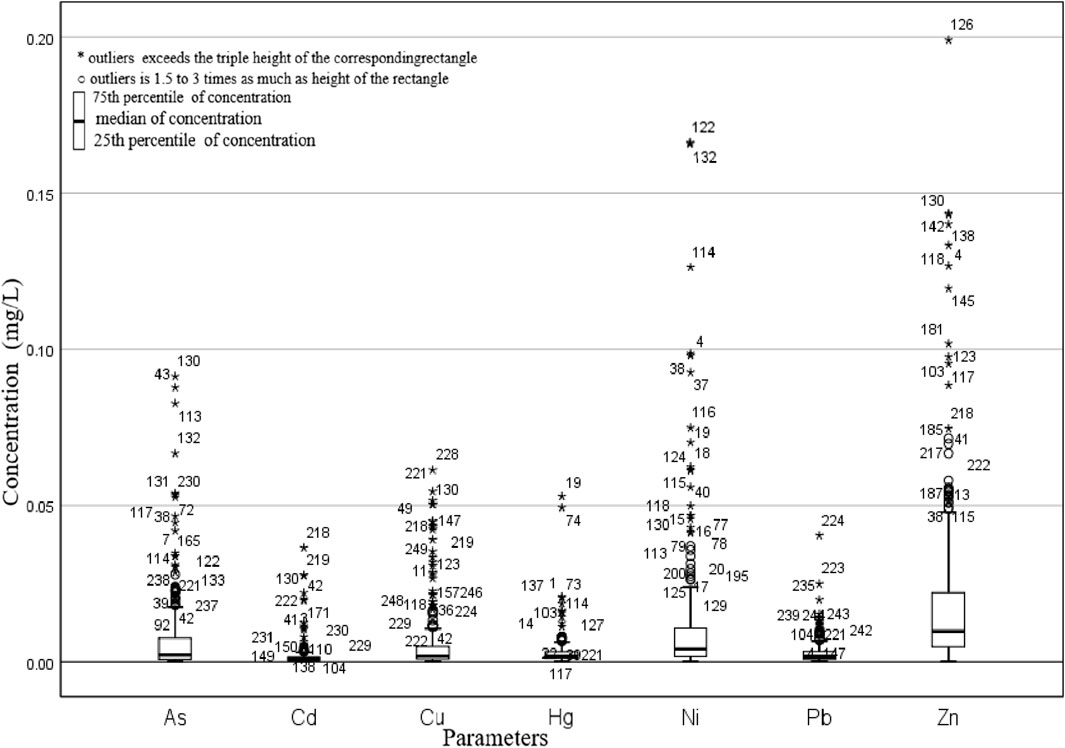
The concentrations of heavy metals were analyzed monthly from 2020 to 2022, and the results are summarized in Supplementary Table S1. The maximum concentrations of As, Cu, Pb, and Zn were 0.0913, 0.3536, 0.0404, and 0.3816 mg L−1, respectively. All of these concentrations were below the referenced standard values of 0.1, 1.0, 0.05, and 1.0 mg L−1. However, the mean concentration of Hg was relatively high at 0.0031 mg L-1, which is three times higher than the corresponding national standard. In contrast, the mean concentrations of the other elements were lower than their respective standards. Considering the cumulative effect of ecological risk associated with heavy metals (Zhang et al., 2019), it is necessary to analyze all of the heavy metals using the potential ecological risk index.
The coefficient of variation revealed that the high level of spatial-temporal variation for the seven heavy metals exceeded 1 during the monitoring period. Additionally, the skewness values were higher than 3, indicating that most of the monthly concentrations of heavy metals were less than the mean concentration. The kurtosis values ranged from 14.1070 to 127.3560, suggesting the presence of a certain number of extreme values of heavy metal concentrations at the seven sampling sites (Zhang P. et al., 2018). The analysis of box plots for the metal concentrations, including parameters, medians, outliers, and the 25th and 75th percentiles, was conducted (Figure 2). The outliers further verified that there were relatively large changes in heavy metal concentrations from 2020 to 2022, which may be attributed to the governance efforts in the Taihu Lake Basin (Zhu, 2017). Furthermore, aquatic heavy metals can originate from both external sources and sediment release (Zhao et al., 2020). Therefore, it is important to further investigate the sources and ecological risks of heavy metals from a spatial-temporal perspective.
3.2 Source identification
3.2.1 Correlation analysis
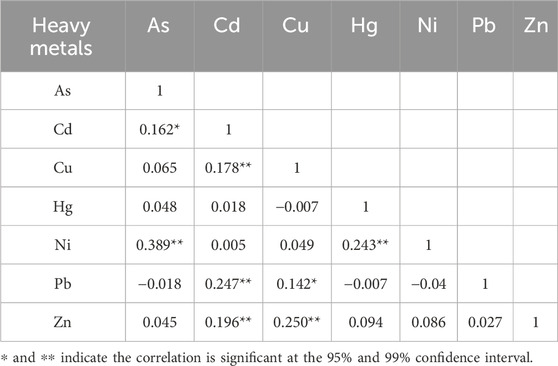
Table 2 presents the results of the correlation analysis. The pairs As-Ni, Cd-Cu, Cd-Pb, Cd-Zn, Cu-Zn, and Hg-Ni showed significant positive correlations (P < 0.01) with coefficients of 0.389, 0.178, 0.247, 0.196, 0.250, and 0.243, respectively, indicating the possibility of shared sources (Zhao et al., 2020). Moreover, the As-Cd and Cu-Pb pairs exhibited significant positive relationships at the 0.05 level, with correlation coefficients of 0.162 and 0.142, respectively. Although these positive correlations were relatively low, they were statistically significant (P < 0.05) and suggested a potential common origin (Chai et al., 2021). All significant correlation coefficients were less than 0.4, indicating a relatively weak correlation. In contrast, other pairs of heavy metals such as As-Cu, As-Hg, As-Pb, Cd-Hg, Cd-Ni, Cu-Hg, and Cu-Ni did not show significant correlations (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), implying that they likely originated from different sources (Zhang Z. et al., 2018).
3.2.2 Principal component analysis
As mentioned earlier, the study employed principal component analysis (PCA) to further investigate the relationships among the heavy metals from 2020 to 2022. The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin value was 0.529, and Bartlett’s test of sphericity was highly significant (p < 0.001), indicating the suitability of PCA for this study. The rotation method used was the Kaiser Normal Maximum Variance method, which converged after five iterations. The results are presented in Figure 3 and Supplementary Table S2. Based on these results, three principal components were extracted, which accounted for the majority of the original information, with a cumulative contribution rate of approximately 58.003%. The first principal component had high positive loadings for As, Hg, and Ni, contributing 20.933% of the total variance. The second principal component, dominated by Cd and Pb, explained 18.706% of the total variance. The third principal component, with a contribution rate of 18.364%, was characterized by Cu, Hg, and Zn.
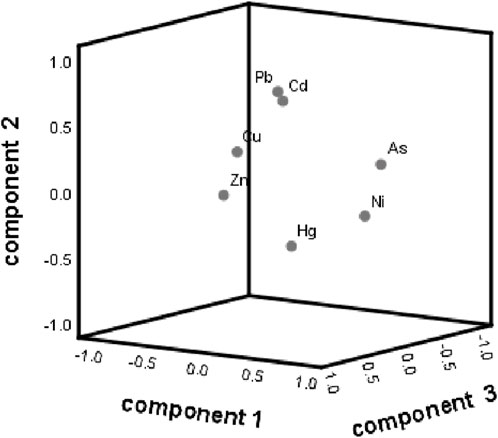
Figure 3. Principal components PC1, PC2 and PC3 showing three groups of heavy metals in Lake Taihu from 2020 to 2022.
3.2.3 Analysis of the source of the heavy metals
According to the correlation analysis and principal component analysis the heavy metals in Taihu Lake from 2020 to 2022, the loading of As and Ni on principal component 1 were respectively 0.808 and 0.81. Factors such as metal smelting, manufacturing, paper-making, and printing and dyeing might contribute to the presence of As and Ni in the water environment. Hg had a loading of 0.350 and showed a significant positive correlation with Ni, indicating that industrial enterprises could be a source of As, Hg, and Ni (Niu et al., 2020; Vu et al., 2017). Moreover, the cities surrounding Taihu Lake are key areas for economic development in China, with more than 3,000 large-scale enterprises involved in paper-making, printing and dyeing, non-ferrous smelting, and metal manufacturing in 2020, according to the Statistical Yearbook 2020 of Suzhou and Wuxi. Therefore, the manufacturing industry, including activities such as non-ferrous melting, metal fabrication, paper-making, and textile production, was inferred as the probable source of principal component 1, which may involve the burning of fossil fuels.
The loading of Cd, Pb, and Cu were 0.694, 0.340, and 0.711, respectively, and the relationships between Cd-Cu, Cd-Pb, and Cu-Pb were significantly positive. The Pearl River Delta, Yangtze River Delta, and Bohai Rim regions are prominent hubs for the manufacturing and processing of electronic products in China, and cities surrounding Taihu Lake hold a pivotal position within the Yangtze River Delta (Fu, 2011). Moreover, electroplating plays a critical role in electronic manufacturing, often resulting in the discharge of wastewater, gas, and residue containing the heavy metals Cd, Pb, and Cu (Bian et al., 2017; Guo et al., 2015). Therefore, the sources of principal component 2 was dominated by electronic manufacturing. Consequently, the dominant sources of principal component 2 can be attributed to electronic manufacturing.
Principal Component 3 predominantly comprised Cu, Hg, and Zn, with loadings of 0.600, 0.417, and 0.815, respectively. The area surrounding Taihu Lake is critical for grain production in China, experiencing extensive use of fertilizers and pesticides. This practice can result in the potential introduction of Cd, Hg, and Zn into the soil, subsequently leading to the transmission of these heavy metals into Taihu Lake through surface runoff (Li Y. et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2020). Statistical data reveals that the average fertilizer consumption in Suzhou and Wuxi exceeded 124 kilotons, while pesticide usage was larger than 6 kilotons in 2020. As a result, Principal Component 3 is characterized as originating from agricultural sources.
Overall, the heavy metal concentrations at the sampling sites in Taihu Lake were primarily attributed to industrial and agricultural activities during the monitoring period. It is worth noting that certain months exhibited elevated levels of heavy metals, which can also be attributed to these contributing factors. To address this issue, it is crucial to strengthen management practices in the future.
3.3 Potential ecological risk index
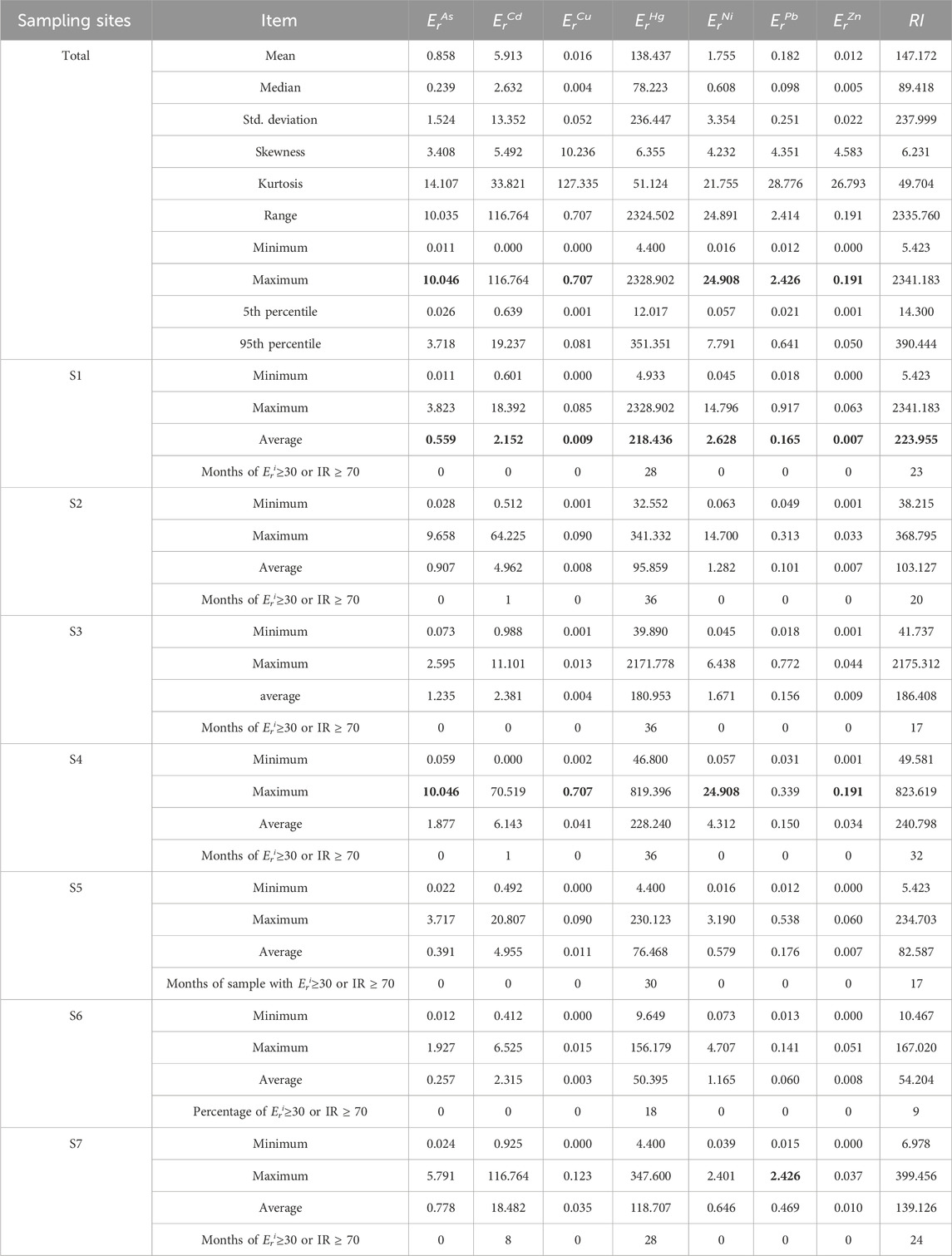
The potential ecological risk of heavy metals in different months and sampling sites was assessed by Equations 1, 2, and presented in Supplementary Table S3. Descriptive statistics were analyzed and shown in Table 3. The results showed that the maximum and 95th percentile of the RI were 2341.183 and 390.444, significantly surpassing the threshold value of 280. The mean and median RI values were 147.172 and 89.418, slightly higher than 140 and 70, respectively. These findings collectively indicated the presence of substantial potential ecological risk in certain months of Taihu Lake between 2020 and 2022.
Specifically, regarding the potential ecological risk of different heavy metals, the maximum values of potential ecological risk for As Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn were 10.046, 0.707, 24.908, 2.426, and 0.191, respectively. These maximum values were observed at the sampling sites S4 or S7. The maximum, mean, and 95th percentile of ErCd were 116.764, 5.913, and 19.237, respectively. This indicates that the ecological risk of Cd needs attention, particularly at S7, where the ErCd exceeded 30 with the time of 8 months. In terms of the potential ecological risk associated with Hg, the maximum, mean, and median values of the ErHg were 2328.902, 138.437, and 78.223, respectively. These values were significantly higher than those of the other heavy metals. Moreover, the month of ErHg in sampling sites exceeded 30 were 18 at least. Additionally, the kurtosis and skewness of the ErHg were calculated to be 51.124 and 6.355, respectively. The corresponding standard errors were 0.306 and 0.153, indicating that the distribution of the ErHg exhibited right-skewness and asymmetry. Therefore, it is without a doubt that Cd and Hg in the Taihu Lake should be considered as priority factors of ecological risk.
In terms of the potential ecological risk at different sampling sites, it was observed that the month which the ErHg exceeding 30, was emerging in the 7 sampling sites during the monitoring period. And the amount of the month was 28, 36, 36, 36, 30, 18, and 28 at S1, S2, S3, S4, S4, S5, S6, and S7, respectively. Additionally, the ErCd exceeded 30 in sampling sites S2, S3, and S7 with the month 1, 1, and 8 months, respectively. Notably, the RI higher than 70 appearing in the 7 sampling site, and the contribution rate of ErHg were more than 90% in the different sampling sites, except the S7 with 85.32% (Figure 3). This further reinforces the idea that Hg and Cd were the primary factors contributing to the ecological risk in Taihu Lake. These findings align with previous studies on Taihu Lake sediments (Li Y. et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2019; Niu et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2017), emphasizing the need to consider sediment and water management in controlling the ecological risk associated with heavy metals in Taihu Lake.
The maximum values of the RI, ErCd and ErHg surpassed the minimum threshold for high or very high potential ecological risk, respectively. Conversely, the minimum value among them was significantly lower than the maximum value for the low ecological risk level. Moreover, all of the sampling sites exhibited the aforementioned characteristics, except for the ErHg in S2, S3, and S4. Hence, a comprehensive analysis of the temporal and spatial characteristics of ecological risk from heavy metals in Taihu Lake during the period from 2020 to 2022 is necessary.
3.4 Temporal variations analysis of risk
To examine the temporal variation characteristics of the ecological risk posed by heavy metals in Taihu Lake, we performed the Mann-Kendall test to quantitatively analyze the RI and Eri of the sampling sites from 2020 to 2022 (Equations 3, 4 and 5). The results are displayed in Table 4. We observed a decreasing trend in the RI and Eir values for sampling sites S1, S2, S4, and S7, which were statistically significant at a 90% confidence interval, except for ErAs at S2, ErCu at S4, and ErZn at S7. The corresponding Z-scores were −4.862,659(ErAs), −3.119,185(ErCd), −3.881,955(ErCu), −4.372,307(ErHg), −5.107,835(ErNi), and −2.519,865(Erpb) at S6 respectively, These values indicate that the potential ecological risk has significantly decreased (Yuan et al., 2020). At S3, we found a significant increasing trend in ErCu and Erpb, while ErAs and ErNi exhibited a significant decreasing trend. Additionally, the decreasing trends of ErCd, ErCu, and ErHg were statistically significant at a 95% confidence level, while the increasing trends in ErAs, Erpb, and ErZn were not statistically significant at S5 (Gocic and Trajkovic, 2013; Frazier et al., 2018).
Although there were significant increasing trends of Erpb and ErCu, and non-significant increasing trends of ErAs, ErCd, ErHg, and ErNi at certain sampling sites, the dominant temporal variation characteristic of Eri for heavy metals in Taihu Lake was a significant decreasing trend. Furthermore, the temporal trends of RI showed significant decreases, with significant values of Z(RI) passing the 99% confidence interval test at S1, S2, S6, and S7, and the 95% confidence interval test at S4 and S5. This phenomenon may be attributed to a series of measures implemented to prevent and control environmental pollution around Taihu Lake, such as the closure of heavy polluting enterprises in printing and dyeing, electroplating, and paper-making (Zhu, 2017), the establishment of large-scale circular (organic) agricultural projects (Xu et al., 2018), and the implementation of wetland protection and recovery projects (Jiang et al., 2017). Additionally, future targeted measures should be taken to reduce the ecological risk of Cd and Hg based on the results of the source and potential ecological risk assessment in Taihu Lake from 2020 to 2022. To obtain a spatial perspective for risk control, we further conducted an analysis of the temporal characteristics of the sampling sites in Taihu Lake between 2020 and 2022. This analysis allowed us to further examine the spatial distribution characteristics of the sampling sites, providing valuable reference for risk control.
3.5 Spatial distribution characteristics of risk
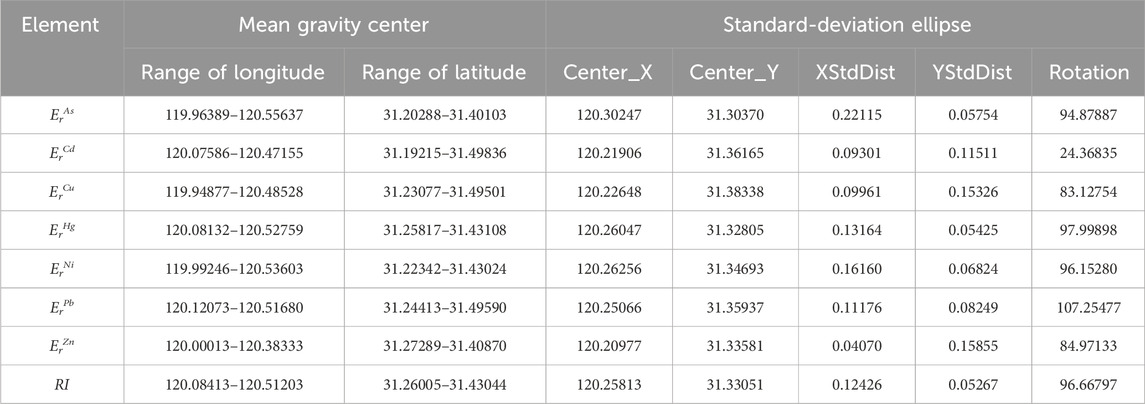
The spatial variation characteristics of the Eri and RI were analyzed of ecological risk caused by heavy metals in Taihu Lake from 2020 to December 2022 (Equation 6). The mean gravity centers of Eri and RI were found to be concentrated within the geographical coordinates of 120.55637–119.94878 N and 31.49836–31.19215 E, as determined through the analysis of spatial characteristics (Table 5). The major axis of the standard-deviation ellipse indicates the direction, while the minor axis represents the magnitude of dispersion (Peng et al., 2016). Therefore, the concentration degree of the mean gravity centers of the Eri and RI was increasing according to the ErCu, ErAs, ErN,i ErCd, ErPb, ErHg, RI, and ErZn. Moreover, a significant proportion of the mean gravity centers was found in the northeastern region of Taihu Lake from 2020 to 2022. The spatial aggregation patterns of ecological risk associated with heavy metals need to be further analyzed due to the spatial heterogeneity present in different sampling sites.
Therefore, the standard deviation ellipses of the mean gravity centers of ecological risk were analyzed using ArcGIS 10.3, and the results are presented in Table 5 and Figure 4. The results indicate that the center coordinates of the standard deviation ellipse of the ErNi, ErPb, ErHg, and RI were in the northeast of the central site, while the ErAs was in the southeast, and the ErCu, ErCd, and ErZn were in the northwest. This suggests that the northeastern part around Taihu Lake played a more significant role in terms of ecological risk from 2020 to 2022 (Shi et al., 2018). These findings are consistent with the results of previous studies (Xia et al., 2012; Ohore et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2019).
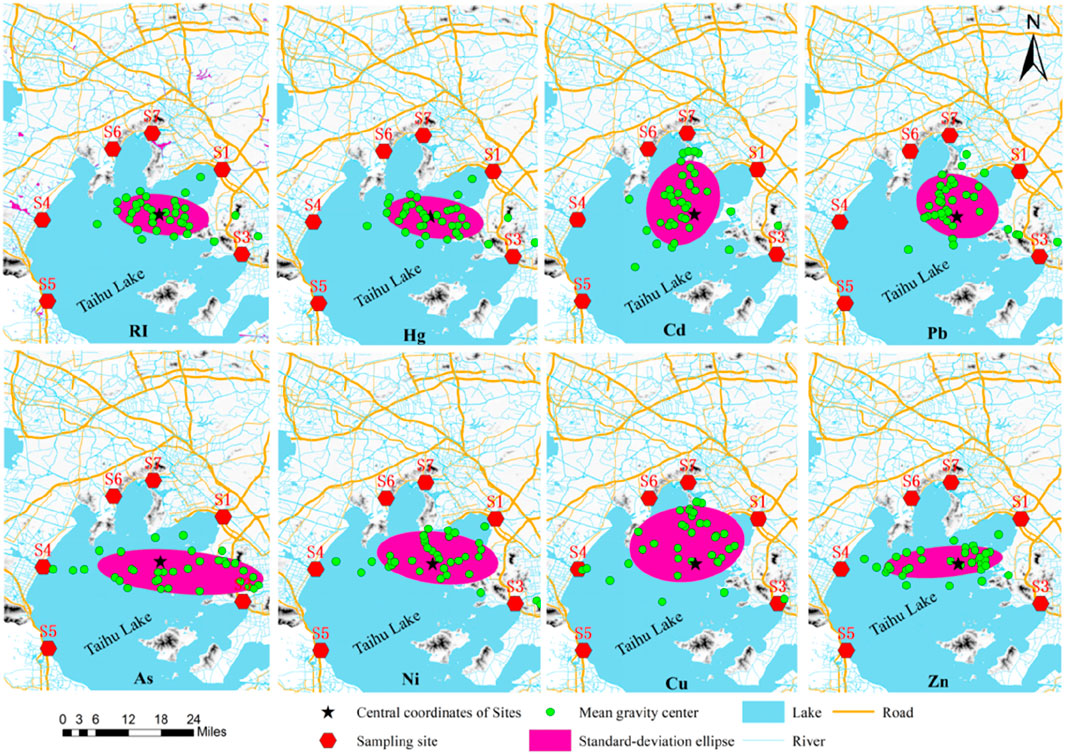
Figure 4. Analysis of weighted average gravity center and standard deviation ellipse about the ecological risk of aquatic heavy metals.
The pollutants in the basin indirectly indicate the pollution level of lake due to the river acting as a conduit between the lake and the basin. The pollutants entering the lake through the river have a significant impact on the overall water quality of Taihu Lake, particularly considering its numerous water networks, dense population, and substantial industrial activities (Li B. et al., 2020; Cotte and Vennemann, 2020; He et al., 2020). Consequently, heavy-metal pollutants from the basin, even those located far from Taihu Lake, can enter the lake through the river network, resulting in water pollution. According to the aforementioned analysis, Hg, which predominantly stems from industrial activities and poses a primary ecological risk, is primarily influenced by the northeastern part of Taihu Lake. However, despite the relocation of pollution-intensive enterprises surrounding Taihu Lake to suburban areas or farther away from the lake in recent years as a result of Taihu’s water pollution prevention and control regulations (Yuan et al., 2019), these enterprises cannot be disregarded in water pollution management due to the extensive water network of Taihu Lake (Niu et al., 2020; Zhang S. et al., 2018). Hence, in order to minimize the ecological risk of Taihu Lake, the stricter regulations and enforcement should be implemented to regulate pollutant discharge, particularly in the northeastern part of the lake, with special attention given to the pollution-intensive enterprises located around the river network. Moreover, comprehensive efforts are required to prevent pollutants from entering the lake within the Taihu basin, while simultaneously enhancing the treatment methods for heavy metal pollution from industrial operations and efficiently reducing and eliminating outdated production capacity (Bian et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2019; Xia et al., 2012; Fu, 2011).
4 Conclusion
Based on a continuous investigation conducted from 2020 to 2022 of heavy metals in Taihu Lake, this study analyzes the sources apportionment, spatiotemporal variation characteristics of ecological risk of heavy metals in Taihu Lake though the modified potential ecological risk model, principal component analysis, Mann-Kendall test, mean gravity center and standard-deviation ellipse. Firstly, compared to the referenced standard, Cd, Hg, and Ni were found to exceed that standard. These heavy metals predominantly originated from industrial production and agricultural activities, including non-ferrous melting, metal fabrication, paper-making, textile production, electronic manufacturing, and the use of fertilizers and pesticides. Secondly, the assessment of Eri and RI highlighted that Cd and Hg primary factors of ecological risk according to the modified potential ecological risk model. Special attention should be given to Hg, as the average ErHg value was 218.436. Thirdly, the overall ecological risk of heavy metals significantly decreased, as indicated by the absolute values of Z (Eri) and Z (RI) in most sites being higher than 1.64. These results indicate that a series of environmental control measures have achieved progress in mitigating the impact of heavy metals in Taihu Lake—suggesting that these measures should continue to be implemented. Finally, the northeastern part of Taihu Lake plays a critical role in causing the ecological risk of heavy metals. Therefore, the management and control of the ecological risk associated with heavy metals should primarily focus on the northern part of Taihu Lake, particularly with regards to Hg and Cd. This study provides valuable and in-depth insights for the ecological risk management of heavy metals in Taihu Lake and contributes to the research perspective and foundational theory of ecological risk associated with heavy metals in the water environment.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
GB: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. CJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. DH: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. YH: Data curation, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. YL: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. DL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review and editing. XF: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund Key Program (No. U2102208) Scientific Research Fund Project of Yunnan Provincial Department of Education (2025J0554), the data supports from the Scientific Research Program for Environmental Protection of Jiangsu Province [2018001], and Scientific Research of Environmental Monitoring of Jiangsu [1625 and 1905].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. All generated content has been carefully reviewed and verified by the authors, who take(s) full responsibility for the final content.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1604407/full#supplementary-material
References
Abu El-Magd, S. A., Taha, T. H., Pienaar, H. H., Breil, P., Amer, R., and Namour, P. (2021). Assessing heavy metal pollution hazard in sediments of Lake mariout, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 176, 104116. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2021.104116
Balsa-Barreiro, J., Li, Y., Morales, A., and Pentland, A. S. (2019). Globalization and the shifting centers of gravity of world's human dynamics: implications for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 239, 117923. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117923
Bian, B., Yan, Z., and Qin, Z. (2017). Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals from river network sediment in Western area of Taihu Lake. Environ. Sci. 38 (04), 1442–1450. doi:10.13227/j.hjkx.201608078
Biswal, B. K., and Balasubramanian, R. (2023). Use of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for removal of heavy metals from water and wastewater: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11 (5), 110986. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2023.110986
Cao, D., Feng, J., Bai, L., Xun, L., Jing, H. t., Sun, J. k., et al. (2021). Delineating the rice crop activities in northeast China through regional parametric synthesis using satellite remote sensing time-series data from 2000 to 2015. J. Integr. Agric. 20 (2), 424–437. doi:10.1016/s2095-3119(20)63458-x
Cavadias, G., Yue, S., and Pilon, P. (2002). Power of the mann-kendall and spearman's rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J. Hydrology 259 (1/4), 254–271. doi:10.1016/s0022-1694(01)00594-7
Chai, L., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Ma, L., Cheng, Z., and Su, L. (2021). Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 125, 107507. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107507
Cotte, G., and Vennemann, T. W. (2020). Mixing of rhône river water in Lake Geneva: seasonal tracing using stable isotope composition of water. J. Gt. Lakes. Res. 46 (4), 839–849. doi:10.1016/j.jglr.2020.05.015
Ding, H., Qiao, M., Zhong, J., Zhu, Y., Guo, C., Zhang, Q., et al. (2020). Characterization of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community in selected municipal and industrial sewage treatment plants beside Poyang Lake. Water Res. 174, 115603. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2020.115603
Fang, X., Peng, B., Wang, X., Song, Z., Zhou, D., Wang, Q., et al. (2019). Distribution, contamination and source identification of heavy metals in bed sediments from the lower reaches of the Xiangjiang river in Hunan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 689, 557–570. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.330
Frazier, R. J., Coops, N. C., Wulder, M. A., Hermosilla, T., and White, J. C. (2018). Analyzing spatial and temporal variability in short-term rates of post-fire vegetation return from landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 205, 32–45. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2017.11.007
Fu, J. (2011). Geographic agglomeration of China's electronic manufacturing industry chain. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. Sci. Ed. 13 (06), 35–40. doi:10.16822/j.cnki.hitskb.2011.06.007
Gocic, M., and Trajkovic, S. (2013). Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and sen's slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Change 100, 172–182. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.10.014
Gong, J. (2002). Clarifying the standard deviational ellipse. Geogr. Anal. 34 (2), 155–167. doi:10.1353/geo.2002.0010
Guo, P., Lei, Y., Zhou, Q., Wang, C., and Pan, J. c. (2015). Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in environmental samples around electroplating factories and the health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. 36 (09), 3447–3456. doi:10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.09.041
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 14 (8), 975–1001. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
He, J., Wu, X., Zhang, Y., Zheng, B., Meng, D., Zhou, H., et al. (2020). Management of water quality targets based on river-lake water quality response relationships for Lake Basins-a case study of Dianchi Lake. Environ. Res. 186, 109479. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.109479
Ji, C., Hou, D., and Xie, L. (2021a). Analysis and prediction of health risk from heavy metals in drinking water sources based on time series model. Environ. Sci. 42 (11), 265–275. doi:10.13227/j.hjkx.202103122
Ji, C., Hou, D., Xie, L., Sun, H., Li, F. Z., Zhou, Y., et al. (2021b). Analysis and prediction of health risk from heavy metals in drinking water sources based on time series model. Environ. Sci. 42 (11), 5322–5332. doi:10.13227/j.hjkx.202103122
Jiang, W., Lv, J., Wang, C., Chen, Z., and Liu, Y. (2017). Marsh wetland degradation risk assessment and change analysis: a case study in the Zoige Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 82, 316–326. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.06.059
Kaushik, S., Rafiq, M., Joshi, P. K., and Singh, T. (2020). Examining the glacial Lake dynamics in a warming climate and glof modelling in parts of Chandra Basin, Himachal Pradesh, India. Sci. Total Environ. 714, 136455. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136455
Khanom, S., and Hayashi, N. (2021). Removal of metal ions from water using oxygen plasma. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 9175. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-88466-3
Lécrivain, N., Aurenche, V., Cottin, N., Frossard, V., and Clément, B. (2018). Multi-contamination (heavy metals, polychlorinated biphenyls and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) of Littoral sediments and the associated ecological risk assessment in a large Lake in France (lake bourget). Sci. Total Environ. 619-620, 854–865. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.151
Li, B., Wan, R., Yang, G., Wang, S., and Wagner, P. D. (2020b). Exploring the spatiotemporal water quality variations and their influencing factors in a large floodplain Lake in China. Ecol. Indic. 115, 106454. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106454
Li, X., Yang, J., Fan, Y., Xie, M., Qian, X., and Li, H. (2021). Rapid monitoring of heavy metal pollution in Lake water using nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients and physicochemical indicators by support vector machine. Chemosphere 280, 130599. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130599
Li, Y., Chen, H., and Teng, Y. (2020a). Source apportionment and source-oriented risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of an urban river-lake system. Sci. Total Environ. 737, 140310. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140310
Ma, J., Han, X., and Jiang, Y. (2020). Some problems in the application of potential ecological risk index. Geogr. Res. 39 (06), 1233–1241. doi:10.11821/dlyj020190632
Niu, Y., Jiang, X., Wang, K., Xia, J., Jiao, W., et al. (2020). Meta analysis of heavy metal pollution and sources in surface sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 700, 134509. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134509
Niu, Y., Wang, F., Liu, S., and Zhang, W. (2021). Source analysis of heavy metal elements of Pm2.5 in canteen in a university in winter. Atmos. Environ. 244, 117879. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117879
Ohore, O. E., Addo, F. G., Zhang, S., Han, N., and Anim-Larbi, K. (2019). Distribution and relationship between antimicrobial resistance genes and heavy metals in surface sediments of taihu Lake, China. J. Environ. Sci. 77, 323–335. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2018.09.004
Peng, J., Chen, S., Lü, H., Liu, Y., and Wu, J. (2016). Spatiotemporal patterns of remotely sensed pm 2.5 concentration in China from 1999 to 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 174, 109–121. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.008
Qiao, D., Wang, G., Li, X., Wang, S., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Pollution, sources and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface amd water, sediments and surface soils around unexploited rona Cu deposit, Tibet, China. Chemosphere 248, 125988. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125988
Rahman, A. U., and Dawood, M. (2017). Spatio-statistical analysis of temperature fluctuation using Mann-Kendall and sen's slope approach. Clim. Dyn. 48 (3), 783–797. doi:10.1007/s00382-016-3110-y
Rahman, M. S., Saha, N., and Molla, A. H. (2014). Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediment and water body around Dhaka export processing zone, Bangladesh. Environ. Earth Sci. 71 (5), 2293–2308. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2631-5
Shi, Y., Matsunaga, T., Yamaguchi, Y., Zhao, A., Li, Z., and Gu, X. (2018). Long-term trends and spatial patterns of Pm2.5-Induced premature mortality in south and southeast Asia from 1999 to 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 631–632, 1504–1514. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.146
Suresh, G., Sutharsan, P., Ramasamy, V., and Venkatachalapathy, R. (2012). Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of veeranam Lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 84, 117–124. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.06.027
Uluturhan, E., and Kucuksezgin, F. (2007). Heavy metal contaminants in red pandora (pagellus erythrinus) tissues from the eastern aegean sea, Turkey. Water Res. 41 (6), 1185–1192. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.11.044
Vu, C. T., Lin, C., Shern, C., Yeh, G., Le, V. G., and Tran, H. T. (2017). Contamination, ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments and water of a contaminated river in Taiwan. Ecol. Indic. 82, 32–42. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.06.008
Wang, X., and Zang, S. (2014). Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of toxic heavy metals and metalloid in surface water of Lakes in daqing Heilongjiang province, China. Ecotoxicology 23, 609–617. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1177-y
Wang, Z., Liu, M., Liu, X., Meng, Y., Zhu, L., and Rong, Y. (2020). Spatio-temporal evolution of surface urban heat islands in the Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration. Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 117, 102865. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2020.102865
Wu, T., Qin, B., Brookes, J. D., Yan, W., Ji, X., and Feng, J. (2019). Spatial distribution of sediment nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake taihu from a hydrodynamics-induced transport perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 650, 1554–1565. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.145
Xia, J. W. W. S., Wang, W., Wang, S., Zhang, B., and Hu, J. (2012). Initial identification of heavy metals contamination in taihu Lake, a eutrophic Lake in China. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 24 (9), 1539–1548. doi:10.1016/s1001-0742(11)60986-8
Xia, P., Ma, L., Sun, R., Yang, Y., Tang, X., Yan, D., et al. (2020). Evaluation of potential ecological risk, possible sources and controlling factors of heavy metals in surface sediment of caohai wetland, China. Sci. Total Environ. 740, 140231. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140231
Xiang, M., Li, Y., Yang, J., Lei, K., Li, F., et al. (1987). Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 116911. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116911
Xie, Z., Jiang, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, D., Qi, S., Du, Z., et al. (2016). Assessing heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in Poyang Lake area, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 75 (7), 549. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-5240-7
Xu, J., Liu, C., Hsu, P., Zhao, J., Wu, T., Tang, J., et al. (2019). Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by asymmetrical alternating current electrochemistry. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 2440. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-10472-x
Xu, Z., Li, T., Bi, J., and Wang, C. (2018). Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of antibiotic pollution and ecological risk assessment in taihu Lake basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 643, 12–20. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.175
Xu, Z., Ni, S., and Tuo, X. (2008). Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 112–115. doi:10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2008.02.030
Yu, J., Yin, H., and Gao, Y. (2017). Characteristics of nutrient and heavy metals pollution in sediments of taihu watershed. China Environ. Sci. 37 (06), 2287–2294. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.06.037
Yuan, F., Wei, Y. D., Gao, J., and Chen, W. (2019). Water crisis, environmental regulations and location dynamics of pollution-intensive industries in China: a study of the Taihu Lake watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 216, 311–322. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.177
Yuan, J., Bian, Z., Yan, Q., Gu, Z., and Yu, H. (2020). An approach to the temporal and spatial characteristics of vegetation in the growing season in Western China. Remote Sens. 12 (6), 945. doi:10.3390/rs12060945
Zhan, S., Wu, J., Wang, J., and Jing, M. (2020). Distribution characteristics, sources identification and risk assessment of N-Alkanes and heavy metals in surface sediments, Tajikistan, central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 709, 136278. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136278
Zhang, H., Jiang, Y., Ding, M., and Xie, Z. (2017). Level, source identification, and risk analysis of heavy metal in surface sediments from river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24 (27), 21902–21916. doi:10.1007/s11356-017-9855-y
Zhang, J., Guo, X., Zeng, Y., and Deng, J. C. (2019). Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in river sediments from Lake taihu basin. Environ. Sci. 40 (5), 2202–2210. doi:10.13227/j.hjkx.201809168
Zhang, P., Qin, C., Hong, X., Kang, G., Qin, M., Yang, D., et al. (2018b). Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of yellow river irrigation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 633, 1136–1147. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.228
Zhang, S., Zhang, L., and Zhang, L. (2018a). Coupling relationship between polluting industrial agglomeration and water environment pollution in southern Jiangsu of taihu Lake basin. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 38 (06), 954–962. doi:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.06.015
Zhang, X., Li, B., Deng, J., Qin, B., Wells, M., and Tefsen, B. (2020). Regional-scale investigation of dissolved organic matter and lead binding in a large impacted Lake with a focus on environmental risk assessment. Water Res. 172, 115478. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2020.115478
Zhang, Z., Lu, Y., Li, H., Tu, Y., Liu, B., and Yang, Z. (2018c). Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the zijiang river, China. Sci. Total Environ. 645, 235–243. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.026
Zhao, L., Gong, D., Zhao, W., Lin, L., Yang, W., Guo, W., et al. (2020). Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of the three gorges reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 704, 134883. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134883
Zhou, Q., Yang, N., Li, Y., Ren, B., Ding, X., Bian, H., et al. (2020). Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and Lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Glob. Ecol. Conservation 22, e00925. doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e00925
Keywords: water heavy metals, potential ecological risk, Mann-Kendall test, mean gravity center, standard-deviation ellipse
Citation: Bao G, Ji C, Hou D, He Y, Li Y, Lei D and Fan X (2025) Source apportionment and ecological risk of heavy metals in Taihu lake from 2020 to 2022. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1604407. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1604407
Received: 03 April 2025; Accepted: 11 July 2025;
Published: 31 July 2025.
Edited by:
Zhi Wang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Bayram Yuksel, Giresun University, TürkiyeGordana Čanadi Jurešić, University of Rijeka, Croatia
Copyright © 2025 Bao, Ji, Hou, He, Li, Lei and Fan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chao Ji, MjA4ODYwNzg4QHFxLmNvbQ==; Dawei Hou, MzU2MDUyMDYxQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Guangjing Bao1
Guangjing Bao1 Chao Ji
Chao Ji