- 1China National Chemical Construction Investment Group Co., Ltd., Beijing, China
- 2Changjiang Survey, Planning, Design and Research Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China
- 3Hubei Provincial Engineering Research Center for Comprehensive Water Environment Treatment in the Yangtze River Basin, Wuhan, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Yangtze River Management and Protection of Ministry of Water Resources, Wuhan, China
- 5School of Resources and Civil Engineering, Gannan University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
Efficient removal of environmental endocrine disruptors (EDCs) from water is crucial for both human health and aquatic ecosystems security. In this study, MOFs were successfully loaded into granular acicular mullite, and then carbonized to synthesize MOF-derived carbon embedded granular acicular mullite (MOF-M-C). The SEM, FTIR, XPS, TGA were used to characterize the modified ceramsite. The adsorption performance of MOF-M-C for BPA and EE2 in aqueous solutions was systematically evaluated through batch experiments, investigating parameters such as contact time, temperature, pH, ionic strength, and coexisting anions. Kinetic, thermodynamic, and isotherm models were applied to analyze the adsorption mechanism. Results showed that the loading capacity of MOFs derived carbon on acicular mullite was 11.81% (w/w). The adsorption kinetics revealed that the process follows a pseudo-second-order model, indicating chemisorption as the dominant mechanism. In the single system, the adsorption capacity for BPA by MOFs derived carbon (MOF-CB) and the MOF-M-C were 51.704 and 71.68 mg·g−1, respectively. While for EE2, the values were 85.414 and 53.78 mg·g−1, respectively. In the binary system, EE2 and BPA competed for adsorption sites, with EE2 showing stronger affinity due to its higher hydrophobicity. Thermodynamic analysis confirmed that the adsorption was spontaneous, endothermic, and entropy-driven. The material’s performance was minimally affected by pH and ionic strength, making it robust for practical applications. Additionally, MOF-M-C demonstrated excellent regeneration efficiency, retaining over 80% of its adsorption capacity after four cycles. These findings highlight MOF-M-C as a promising, reusable adsorbent for the effective removal of endocrine-disrupting compounds from water.
1 Introduction
Environmental endocrine disruptors (EDCs) have garnered increasing attention due to their detrimental effects on human health and aquatic ecosystems, including reproductive disorders, nervous system damage, and disruptions to metabolic processes (Duan et al., 2019; Surana et al., 2022). Among these EDCs, bisphenol A (BPA) and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) are two prominent contaminants (Javidan et al., 2022). EE2, a synthetic estrogen widely used in oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapies, exhibits higher toxicity compared to natural estrogens such as estrone (E1) and 17β-estradiol (E2) (Song et al., 2023). BPA, a key component in the production of epoxy resins, polycarbonates, and plastic stabilizers (Jiang et al., 2023), has also become a pervasive environmental pollutant. In recent years, BPA and EE2 have been frequently detected in surface water (Goeury et al., 2022; Zhong et al., 2022), river sediment (Yang et al., 2024), sewage plant effluent (Moreira et al., 2023) and even drinking water supplies (Ismanto et al., 2022; Tomei Torres and Masten, 2023). These findings highlight the inefficiency of conventional water treatment processes in removing BPA and EE2, underscoring the urgent need for advanced technologies to enhance their removal efficiency.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), a class of coordination polymers formed by the self-assembly of metal ions or clusters with organic ligands, have emerged as a promising class of porous materials. MOFs are highly valued for their exceptional properties, including large specific surface areas, tunable pore structures, and versatile synthesis methods (Khalil et al., 2023; Hayat et al., 2024). By selecting different metal nodes and organic linkers, a wide variety of MOFs can be tailored for specific applications (Liu et al., 2023). To date, MOFs have demonstrated significant potential in gas capture and storage (Kang and Lee, 2023), liquid-phase adsorption (Liang et al., 2023), and catalytic water splitting (Li YY. et al., 2019; Poonia et al., 2023). Their unique physicochemical properties, such as high porosity and abundant adsorption sites, make them ideal candidates for the adsorption of environmental pollutants (Ahmadijokani et al., 2024). Furthermore, MOFs can be pyrolyzed under inert conditions to produce porous carbon materials while retaining their structural integrity and high surface area, offering an excellent precursor for functional carbon-based materials (Xu et al., 2023). The ease of synthesis and post-modification of MOFs has further driven their adoption in both scientific research and industrial applications (Daglar and Keskin, 2022; Jo et al., 2023). A variety of functionalized MOFs-derived porous carbon materials have been synthesized, some of which exhibit exceptional performance in removing water contaminants (Chang et al., 2022; Ding et al., 2022; Ahmed et al., 2024). For instance, Bhadra et al. carbonized Bio-MOF-1 at 1000°C for 12 h to produce BMDC-12h, which demonstrated an ultrahigh BPA adsorption capacity of 710 mg g−1 (Bhadra et al., 2018). Similarly, Ma et al. utilized ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 to prepare heteroatom-doped carbon catalysts, significantly enhancing the peroxymonosulfate-mediated catalytic oxidation of BPA (Ma et al., 2018a; Ma et al., 2018b). Duan et al. synthesized a polypyrrole-modified ZIF-8-derived porous carbon material (IHNPC), which exhibited remarkable selectivity and a maximum adsorption capacity of 455.95 mg g−1 for E2 (Duan et al., 2019). Additionally, Bhadra et al. developed a porous carbon material (CDM-6) from a metal-azolate framework (MAF-6), capable of adsorbing various emerging organic pollutants through hydrogen bonding (Bhadra and Jhung, 2017). Ahsan et al. prepared graphene oxide and carbon nanotube-doped Cu-BDC MOFs, both of which could increase the adsorption capacity of BPA by Cu-BDC MOFs, and the adsorption capacity of BPA on Cu-BCD@GrO could reach 182.2 mg g−1 (Ahsan et al., 2019).
Despite their remarkable potential, the practical application of MOFs and MOF-derived carbon materials is often hindered by their fine particulate or powdery nature, which complicates solid-liquid separation processes (Mon et al., 2018). To address this limitation, embedding MOFs into porous supports to form composite adsorbents has been proposed as a viable strategy to enhance their applicability (Huang et al., 2024). Ideal support materials should possess high porosity, large specific surface area, excellent chemical stability, and robust mechanical properties. Acicular mullite ceramics (M, 3Al2O3·2SiO2), an aluminosilicate mineral characterized by its needle-like microstructure, meet these criteria. Acicular mullite ceramics can form highly porous structures with substantial surface areas while maintaining mechanical integrity, making it an excellent candidate for use as a support material and filter medium (Gao et al., 2024).
Although ceramsite filter materials are widely used in water treatment plants, their effectiveness in removing endocrine-disrupting pollutants remains limited. Moreover, few studies have explored the application of MOFs for modifying filter media. In this study, we aim to address this gap by embedding MOFs into acicular mullite and subsequently carbonizing the composite to produce MOF-derived carbon-modified acicular mullite. The synthesized adsorbent was characterized using various techniques to analyze its morphology, structure, and elemental composition. Batch adsorption experiments were conducted to evaluate the performance and underlying mechanisms of BPA and EE2 removal by the composite material.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and reagents
Acicular mullite (M) ceramics with the diameter of 0.8–1.2 mm was synthesized in the laboratory, and the detailed synthesis method is provided in the Supplementary Material. Carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC), cobalt (Co(NO3)2·6H2O), zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2·6H2O), 2-methylimidazole (C4H6N2) and hydrochloric acid (HC) of analytical grade were purchased from Chengdu Kelong Chemical Reagent Factory. Standard substances of BPA (>99%) and EE2 (>99%) were obtained from Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH (Augsburg, Germany). Stock solutions of BPA and EE2 were prepared by dissolving their powders in methanol (chromatographic grade).
2.2 Sample preparation
Firstly, the acicular mullite was pretreated by soaking in 1 M HCl for 2 h, followed by rinsing with deionized water. It was then soaked in methanol for another 2 h, rinsed again with deionized water, and dried for further use. Then the acicular mullite (10 g) was immersed in 50 mL of a 3 g L−1 CMC solution and subjected to vacuum for 20 min. After 2 h, the CMC solution was discarded, and the sample was dried overnight in an oven at 60°C. Solution A: 3.492 g of Co(NO3)2·6H2O and 1.158 g of Zn(NO3)2·6H2O were dissolved in 40 mL methanol; Solution B: 5 g of 2-methylimidazole was dissolved in 30 mL methanol. The dried acicular mullite was placed in Solution A, and Solution B was quickly added under continuous stirring. The mixture was allowed to react at room temperature for 24 h. The solid samples were then collected, washed with methanol, and dried in an oven at 60°C for 12 h to obtain MOF-embedded acicular mullite (MOF-M). The same method was used to synthesize Zn/Co-ZIF powder (MOF) without acicular mullite particles.Finally, MOF-M was heated in a tubular furnace at 800°C for 3 h under a nitrogen atmosphere with a heating rate of 5°C min−1 to obtain MOF-derived nanoporous carbon-embedded acicular mullite (MOF-M-C). The MOF powder was carbonized using the same method to obtain MOF derived carbon (MOF-BC).
2.3 Characterization
The microstructure of pure acicular mullite, MOF-M, and MOF-M-C was examined using a JEOL JSM-7800F scanning electron microscope (SEM) at an acceleration voltage of 3.0 kV. Elemental analysis was performed using an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis system attached to the SEM instrument. X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra were collected using a PANalytical X’Pert Power diffractometer with Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å) at a scan rate of 0.013° per second over a 2θ range of 10°–80°, operating at 40 kV and 40 mA. Functional groups were analyzed using a Thermo Fisher Nicolet Is5 FTIR spectrometer in transmission/ATR mode. The zeta potential of the samples was measured at various pH values using a Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS. Specific surface area and pore size distribution were determined using a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 analyzer. Thermal stability was assessed using a Mettler Toledo thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) instrument. Acicular mullite and MOF-M were analyzed in air, while MOF-M-C was analyzed under a nitrogen atmosphere, with a heating rate of 10°C min−1 from 30°C to 900°C.
2.4 Batch adsorption experiment
2.4.1 Analytical methods for BPA and EE2
Water samples contained BPA and EE2 were extracted by solid phase extraction (SPE, Oasis HLB, 3cc/60 mg, Water, United States). The concentration of BPA and EE2 were quantified using a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system (Agilent 1260 Infinity) equipped with a ZORBAX SB-C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm) and a UV detector. The mobile phase for single-component analysis was 100% methanol, while for binary systems, a mixture of acetonitrile (50%) and water (50%) was used at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1. The injection volume was 10 μL, and the detection wavelength was set at 230 nm.
2.4.2 Adsorption equilibrium
A series of BPA and EE2 solutions (0.02–10 mg L−1) were prepared by diluting stock solutions. Then, 0.1 g of MOF-M-C was added to 100 mL of each solution in 250 mL conical flasks. The flasks were shaken at 120 rpm for 24 h at three temperatures (288 K, 298 K, and 308 K). After adsorption, the mixtures were filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane, and the residual concentrations of BPA and EE2 in the filtrate were measured.
2.4.3 Kinetic studies
For kinetic studies, 0.1 g of MOF-M-C was added to 100 mL of BPA or EE2 solutions (2 mg L−1). Samples were collected at predetermined time intervals (5, 15, 30, 60, 120, 180, 300, 500, 900, 1500, and 2000 min) for analysis.
2.4.4 Effect of ionic strength and coexisting anions
The effect of ionic strength was evaluated by adding NaCl at concentrations of 0.01, 0.1, 0.3, and 0.5 mol L−1 to the adsorption system. The influence of coexisting anions was studied by adding 0.05 mol L−1 of NaNO3, Na2CO3, Na2SO4, and Na3PO4·12H2O to 100 mL of 1 mg L−1 BPA or EE2 solutions.
2.4.5 Effect of solution pH
The pH effect was investigated by adding 0.1 g of MOF-M-C to 100 mL of BPA or EE2 solutions (2 mg L−1) at pH values ranging from 3.0 to 11.0. After shaking at 120 rpm for 24 h, the samples were filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane, and the residual concentrations of BPA and EE2 in the filtrate were measured.
2.4.6 Regeneration study
Two regeneration methods were employed: one was ethanol Regeneration, where the adsorption-saturated MOF-M-C was soaked in methanol and ultrasonicated for 30 min, followed by thorough rinsing with deionized water, drying at 80°C, and reuse for four cycles; and the other was Alkaline Regeneration, where the saturated MOF-M-C was treated with 0.1 M NaOH solution, shaken at 120 rpm for 24 h, filtered, rinsed, dried overnight, and reused for four cycles.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Materials characterization
The Zn/Co-ZIF particles synthesized in this study exhibited uniform rhombohedral dodecahedral morphology (Figure 1), with particle sizes ranging from 466 to 969 nm. The surface of the freshly prepared Zn/Co-ZIF particles was smooth; however, after carbonization under a nitrogen atmosphere, the particle surfaces became rough, and smaller particles were observed. As shown in Figure 1C, the well-defined MOF crystal structure was not distinctly visible on the surface of the acicular mullite. Instead, the pore structure of the acicular mullite became less pronounced, and numerous crumb-like substances were interspersed within the needle-like structure. Following carbonization, the pore structure of the acicular mullite became more evident, likely due to the volatilization of organic linkers such as CMC and 2-methylimidazole. Additionally, during the acquisition of SEM images, it was observed that before carbonization, the MOF-M material required gold sputtering to visualize the structure, whereas after carbonization, gold sputtering was no longer necessary for clear structural observation. It has been reported that after the carbonization of MOFs materials, functional groups such as carboxyl and hydroxyl groups can be removed, which can greatly improve the stability and conductivity of the materials (Xiao et al., 2020; Ding et al., 2025). Therefore, it was speculated that the electrical conductivity of MOF-M-C was significantly enhanced compared to that of MOF-M and pure acicular mullite (M).
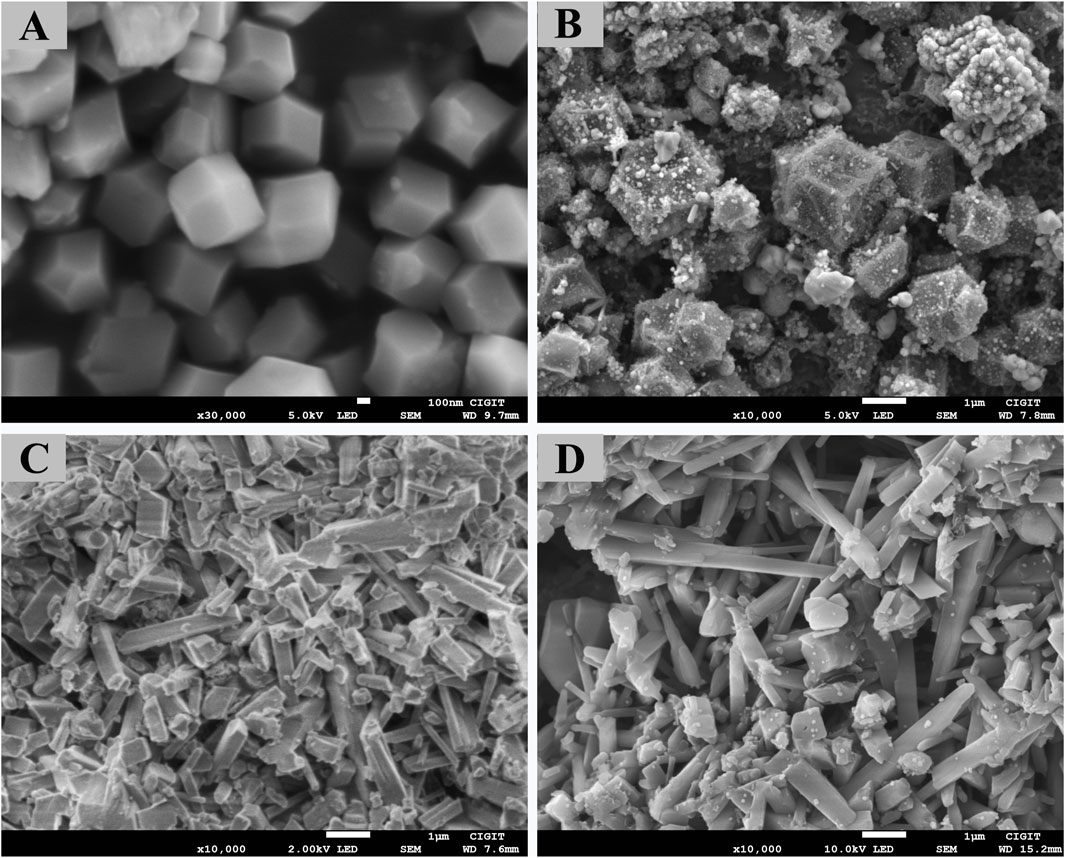
Figure 1. SEM images of MOF and MOF loading ceramsite, (A) MOF, (B) MOF-CB, (C) MOF-M and (D) MOF-M-C.
The EDS results confirmed the successful embedding of MOFs into the acicular mullite. The MOF particles were primarily composed of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), cobalt (Co), zinc (Zn), and oxygen (O) (Figure 2A). The N content in the MOF was 26.9%, but it nearly disappeared after carbonization. Following carbonization, the Co content increased significantly from 11.65% to 29.79%, while the C content decreased slightly, and other elements remained relatively unchanged. These results indicate that the synthesized MOFs were predominantly ZIF-67. Prior to MOF embedding, the mullite contained no detectable C or N; however, after MOF embedding, the C and N contents increased to 8.12% and 3.83%, respectively. After carbonization, the N content was no longer detectable in MOF-M-C, while the C content further increased to 13.02%, and the Co content was approximately 2.6%. Notably, Zn was not observed in the final product. Under an atmosphere of nitrogen at 800°C, the reduced Zn atoms undergo high-temperature sublimation in situ within the MOF material and are released from the system as vapor (Li X. et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2021). This process facilitates the creation of mesoporous and macroporous structures within the material, thereby increasing its specific surface area and thus enhancing pollutant adsorption performance. Furthermore, due to the limited precision of EDS detection, if the Zn content in the sample is low and falls below the detection limit, it cannot be detected.
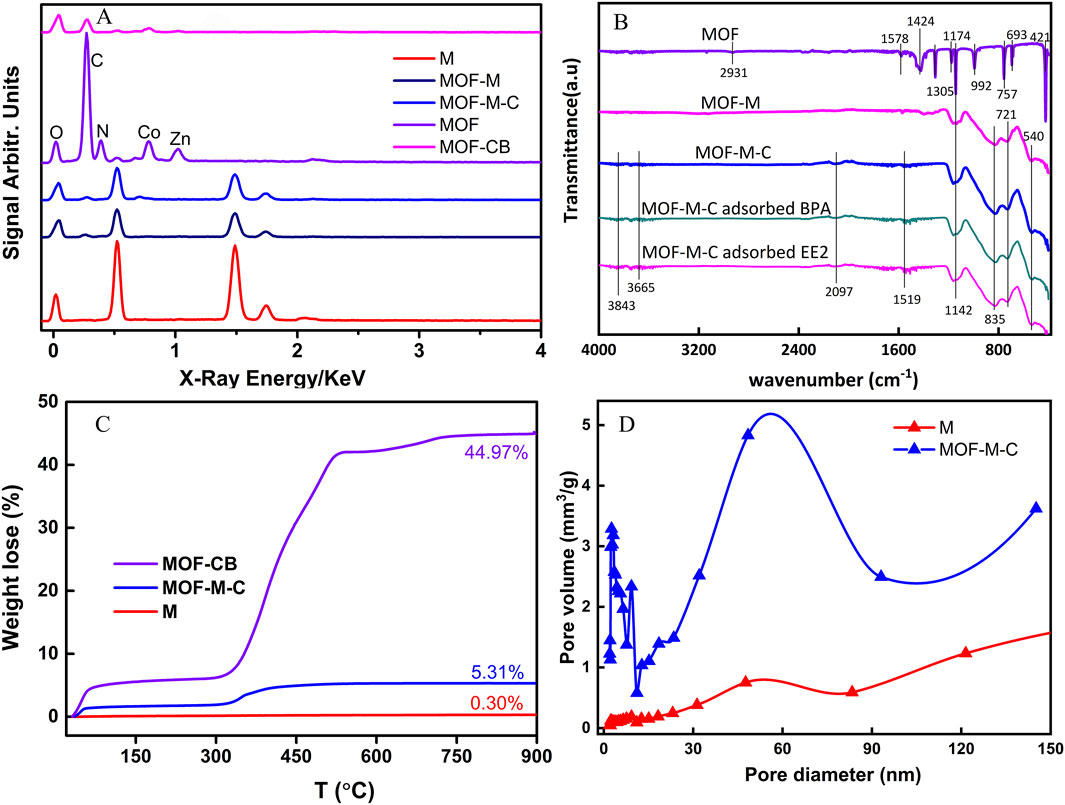
Figure 2. Characterization of MOF and MOF embedded acicular mullite: (A) EDX spectra; (B) FTIR spectra; (C) TGA analysis (heating rate 10 °C min−1 from 30 to 900 °C); (D) Pore distribution.
In Figure 2B, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was performed on the as-prepared MOF, MOF-M, and MOF-M-C. The characheristic peaks at 2931 cm−1 for C-H stretching, 1573 cm−1 and 1142 cm−1 for C42 cmmetching, corresponding to MOF structure. MOF-M, and MOF-M-C both exhibit characteristic peaks at 1573 cm−1 and 1142 cm−1, attributed to C-N stretching, confirming the MOF structure and its successful embedding in the mullite matrix to form MOF-M composites. Notably, In MOF-M-C, the disappearance of the NMOF structure and its successful−1) and the C-H stretching peak (2931 cm−1) (Ibrar et al., 2023), characteristic of coordinated amine ligands, alongside the emergence of a carbonyl peak (1520 cm−1) and a weak Cc of coordinated amine ligands, along−1). These spectral changes suggest ligand degradation or oxidation during modification, leading to alterations in the original amine structure and the formation of new functional groups. Additionally, carbonization effectively removed nitrogen from both the MOFs and MOF-M. Yang et al. (2018) reported that pre-loading carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) could enhance the attachment between the substrate and the Zn/Co-ZIF crystal precursors through interactions between the hydroxyl groups of CMC and Zn2+/Co2+ ions.
The results of hermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of M, MOF-CB, and MOF-M-C were listed in Figure 2C. As can be seen from the figure, the weight of needle-like mullite remains nearly unchanged as the temperature increases. In contrast, the weights of MOF-BC and MOF-M-C continuously decrease with rising temperature when the temperature exceeds 300°C. This downward trend continues until the temperature rises to around 600°C, after which the weight no longer decreases with further temperature elevation and stabilizes (reaching equilibrium). Ultimately, within the experimental temperature range, the weight losses of M, MOF-BC, and MOF-M-C are 0.30%, 44.97%, and 5.31% respectively. Based on these results, the MOF-derived carbon embedded in MOF-M-C accounted for approximately 11.81% of the total mass. TGA reveals MOF-M-C’s stability up to 300°C, with no significant decomposition below 300°C (Figure 2C). Ensuring MOF-M-C was fully applicable in water treatment processes. After coating with MOF-derived carbon, the specific surface area of the needle-like mullite increased by 19.85-fold, from 2.401 to 47.659 m2 g−1 (Supplementary Table S1). Pore structure analysis indicated that the pores were predominantly mesoporous both before and after modification. The increase in specific surface area was primarily attributed to the formation of mesopores, with a minor contribution from micropores and a slight increase in macropores (Figure 2D). Micropores (<2 nm) dominate adsorption via high surface area and confinement effects, mesopores (2–50 nm) facilitate rapid mass transport, and macropores (>50 nm) from particle stacking contribute minimally to adsorption capacity but aid diffusion kinetics. A larger specific surface area generally correlates with a higher adsorption capacity for contaminants (Boulanger et al., 2024). Previous studies have found that micropores in carbon-based materials are particularly effective for organic adsorption, especially when the pore size is 1.3–1.8 times the kinetic diameter of the target organic molecules (Pavlenko et al., 2022). Similarly, Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2015) demonstrated that larger pore diameters and volumes can enhance the diffusion rate within particles, leading to higher adsorption rates and equilibrium capacities. The hierarchical porosity (micropores/mesopores) confirmed by N2 sorption, coupled with TGA-derived thermal stability (≤300°C), directly enables MOF-M-C’s high adsorption capacity and reusability.
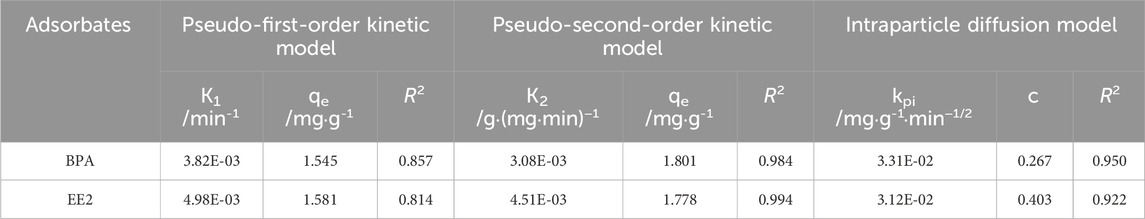
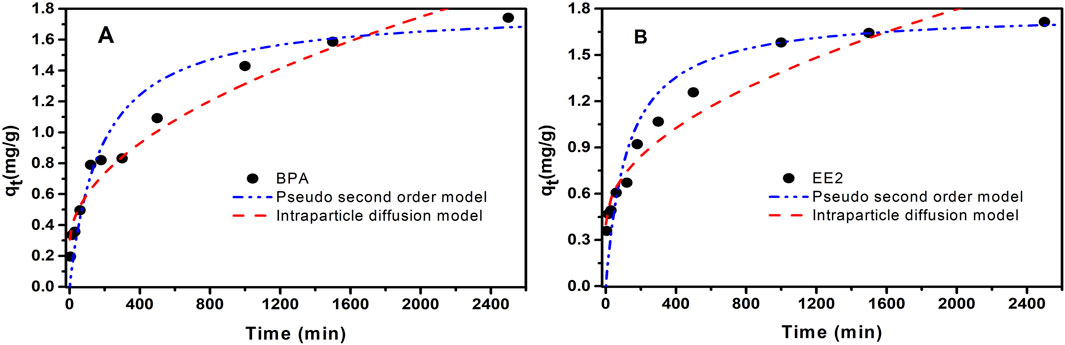
3.2 Adsorption kinetics study
Adsorption kinetics is a crucial method for elucidating adsorption mechanisms and determining key operational parameters in practical applications. Pseudo-first-order kinetic model, pseudo-second-order kinetic model and intraparticle diffusion model were employed to fit the kinetic data of EE2 and BPA adsorption by MOF-M-C, and the kinetic parameters were summarized in Table 1. According to the correlation coefficients (R2), the adsorption data for BPA and EE2 was best fit with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, followed by the intraparticle diffusion model (Figure 3). This indicated that the adsorption process was primarily controlled by the number of unoccupied active sites on the adsorbent surface, and the adsorption of BPA and EE2 on MOF-M-C tended to be chemisorption, generally involving electron sharing or transfer. Figure 3 illustrates the adsorption kinetics curves of BPA and EE2 on MOF-M-C. Initially, the adsorption capacities of both BPA and EE2 increased rapidly within the first 200 min. After this period, the adsorption rates slowed, with BPA reaching equilibrium at 1200 min and EE2 at 600 min. The equilibrium times observed in this study were longer than those reported for hierarchically nitrogen-doped porous carbon (IHNPF, 30 min) (Duan et al., 2019), magnetic biochar nanoparticles (Mag-BCP, 25 min) (Dong et al., 2018), and Fe3O4/graphene oxide hybrids (Fe3O4/GO, 110 min) (Ouyang et al., 2015), but comparable to beta-cyclodextrin/poly (L-glutamic acid) supported magnetic graphene oxide (CGMG, 480 min) (Jiang et al., 2017), bone charcoal (390 min) (Patel et al., 2015), and 17 beta-estradiol by few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets (GO, 720 min) (Jiang et al., 2016). The extended equilibrium time can be attributed to the larger particle size of the porous acicular mullite, which increases the diffusion path length for BPA and EE2 molecules. The rapid initial adsorption is likely due to the occupation of high-energy adsorption sites on the outer surface of MOF-M-C, followed by slower diffusion into the internal pores of the acicular mullite.
3.3 Adsorption isotherms
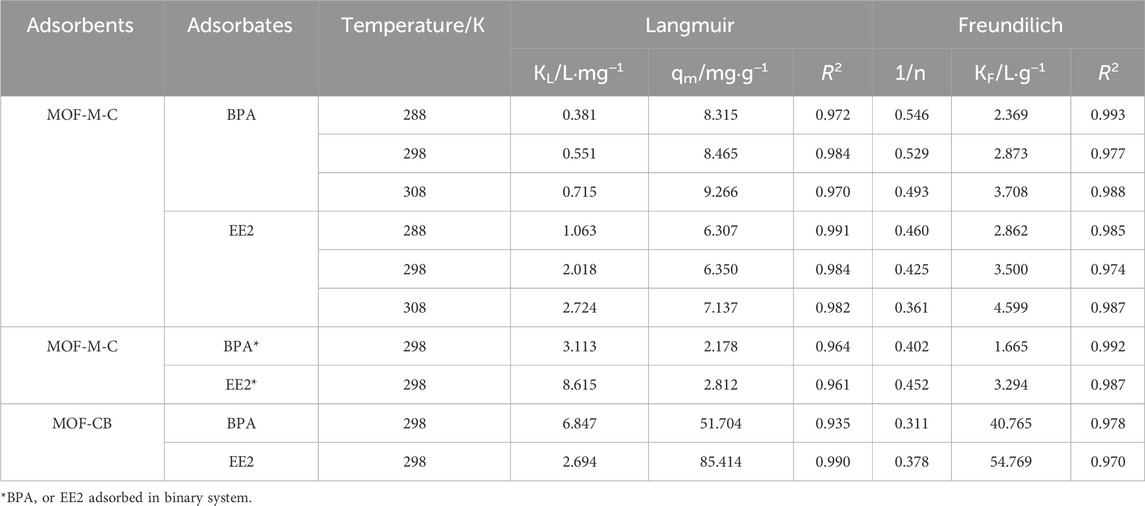
Adsorption isotherms for BPA and EE2 on MOF-M-C and MOF-CB were conducted at 288 K, 298 K, and 308 K in a single-component system. The data were fitted using Langmuir and Freundlich models (Table 2). The isothermal adsorption models can be found in the Supplementary Material. As shown in Figure 4, the adsorption capacity increased with the equilibrium concentration of BPA and EE2, with a slightly faster rate for EE2 than BPA. This can be attributed to higher contaminant concentrations favoring diffusion to the MOF-M-C surface. The Langmuir model provided a better fit for EE2 adsorption, while the Freundlich model was more suitable for BPA adsorption. The theoretical maximum adsorption capacities (qm) calculated from the Langmuir model at 298 K were 51.704 mg g−1 for BPA and 85.414 mg g−1 for EE2 on MOF-CB, and 8.465 mg g−1 and 6.35 mg g−1, respectively, on MOF-M-C. Our prior research has demonstrated that acicular mullite itself exhibited negligible adsorption capacity for EE2 and BPA (Zhou et al., 2022), we attribute the entire adsorption capacity of MOF-M-C toward these pollutants to the supported carbonized MOF. As determined by thermogravimetric analysis (Section 3.1), the loading percentage of carbonized MOF on MOF-M-C is approximately 11.81%. The observed adsorption capacity of BPA and EE2 on MOF-M-C is 8.465 mg g−1 and 6.35 mg g−1. Therefore, the adsorption capacity of BPA attributable to carbonized MOF supported on needle-cluster mullite is calculated as 8.465 mg g−1/0.1181 = 71.68 mg g−1. The adsorption capacity of EE2 attributable to carbonized MOF supported on needle-cluster mullite is 6.35 mg g−1/0.1181 = 53.78 mg g−1. The higher adsorption of EE2 on MOF-CB and lower adsorption on MOF-M-C may be due to changes in mass exchange pathways after embedding MOF-CB into the internal pores of the acicular mullite.
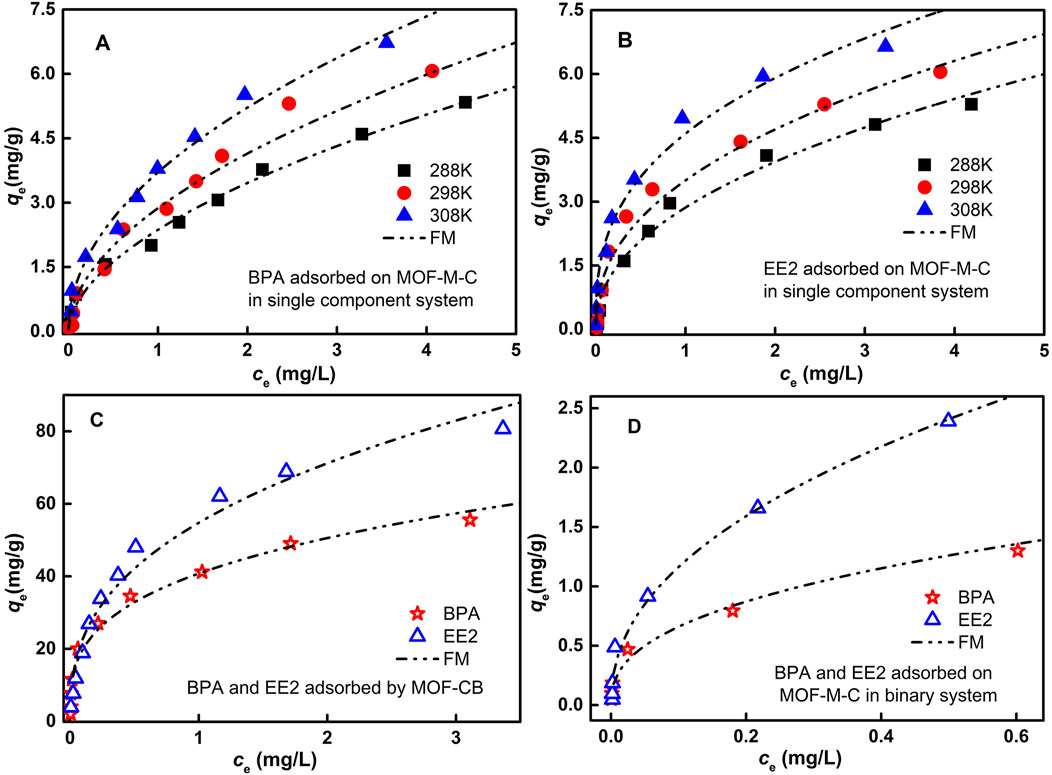
Figure 4. Adsorption isotherms of (A) BPA adsorbed by MOF-M-C, (B) EE2 adsorbed by MOF-M-C, (C) BPA and EE2 adsorbed on MOF-CB, and (D) BPA and EE2 co-adsorption on MOF-M-C.
The Freundlich parameter 1/n represents the adsorption affinity between the adsorbent and adsorbate. A value of 1/n < 1 indicates favorable adsorption, with smaller values suggesting easier adsorption (Ouyang et al., 2015). Table 2 shows that MOF-M-C has strong affinity for both BPA and EE2. As temperature increased, 1/n decreased and qm increased, indicating that higher temperatures favor adsorption. Additionally, at the same temperature, 1/n for EE2 was smaller than for BPA, suggesting stronger affinity but fewer reactive sites for EE2 adsorption.
In binary systems, the co-adsorption of BPA and EE2 on MOF-M-C was studied (Figure 4D; Table 2). EE2 exhibited higher adsorption than BPA, and the adsorption capacities for both were lower than in single-component systems. This indicates competition for adsorption sites, with EE2 being more readily adsorbed, consistent with its stronger affinity.
3.4 Effects of water chemistry
Solution pH significantly influences the surface charge distribution of the adsorbent and the speciation of the adsorbate, making it a critical factor in adsorption studies, especially for systems with functional groups (Bhadra et al., 2018). Figure 5A shows the effect of pH on BPA and EE2 adsorption on MOF-M-C. Solution pH significantly influences BPA adsorption on MOF-M-C. The adsorption capacity increases with rising pH under acidic conditions (pH < 5.0), shows negligible variation in the near-neutral range (5.0 < pH < 9.0), and decreases sharply under alkaline conditions (pH > 9.0). When pH < 5.0, high H+ concentration competes with phenolic groups of BPA molecules for adsorption sites (Jin et al., 2023). Which was consistent with the solvent shielding experiments (Zhou et al., 2014) demonstrating water and BPA competition for hydrogen-bonding sites. At pH 5.0–9.0, predominantly molecular BPA maintains stable adsorption. When pH > 9.0, enhanced BPA electronegativity combined with electrostatic repulsion causes rapid decline. The point of zero charge (PZC) of MOF-M-C was approximately 10.2 (Figure 5B). At pH > 10.2, electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged MOF-M-C and BPA anions (pKa: 9.6–10.2) significantly reduced adsorption. when pH > 10.2, both MOF-M-C (negatively charged surface) and BPA (doubly deprotonated) exhibited strong electrostatic repulsion, causing the observed sharp decline in adsorption.
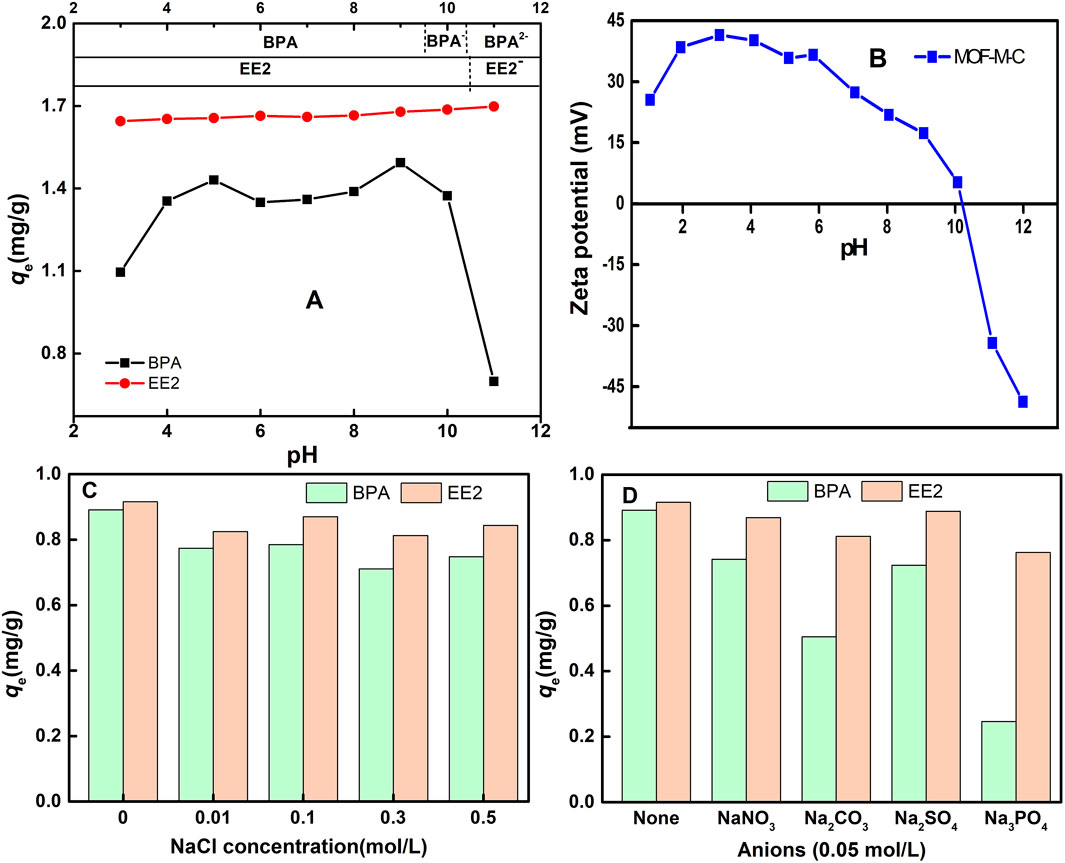
Figure 5. Effects of water chemistry parameters on the adsorption of BPA and EE2 on MOF-M-C: (A) the pH values, (B) zeta potential of MOF-M-C, (C) the ionic strength, and (D) the co-existing anions.
In contrast, EE2 adsorption on MOF-M-C remains stable across the tested pH range. This pH-independent behavior originates from EE2 pronounced hydrophobicity (lgkow: 3.67), where hydrophobic interactions dominate the adsorption mechanism. Unlike electrostatic forces, these hydrophobic driving forces remain unaffected by pH variations.
The presence of salts and ionic compounds can influence adsorption through mechanisms such as the salting-out effect (Duan et al., 2019). Figure 5C shows that ionic strength had little effect on EE2 adsorption but slightly reduced BPA adsorption. The decrease in BPA adsorption capacity with increasing ionic strength can be attributed to screens π-π/coulombic interactions for BPA and disrupts H-bonding with phenolic groups (Sun et al., 2020). Figure 5D demonstrates that coexisting anions (CO32-, PO43-, NO3−, SO42-) enhanced BPA adsorption, particularly in the presence of CO32- and PO43-, while EE2 adsorption was minimally affected by NO3− and SO42- and slightly reduced by CO32- and PO43-. These results indicate that MOF-M-C can effectively remove EE2 under varying pH and ionic conditions.
3.5 Adsorption thermodynamic analysis
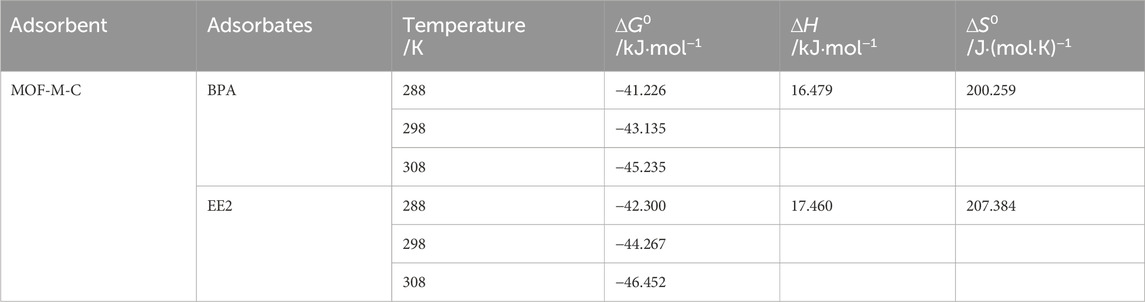
Thermodynamic parameters, including the standard Gibbs free energy change (∆G0), enthalpy change (∆H0), and entropy change (∆S0), were calculated by Equations 1–3 (Zhou and Zhou, 2014) to characterize the adsorption process (Table 3). Negative ∆G0 values indicated that BPA and EE2 were spontaneous adsorption, with EE2 being more readily adsorbed than BPA. ∆H0 > 0 indicated an endothermic adsorption process. Positive ∆S0 values confirmed the adsorption was entropy-increasing process. Thus, the adsorption of BPA and EE2 on MOF-M-C is a spontaneous with increasing enthalpy (∆H0 > 0) and increasing entropy (∆S0 > 0) process, primarily driven by increasing entropy.
where R is the universal gas constant, 8.314 J·(mol·K)−1, T is the absolute temperature (K), K0 is the isothermal adsorption constant calculated by isotherm models. K here is the KF, which is the Freundlich constant related to the sorption affinity, L·mg-1. Mw is the molecular weight of BPA or EE2, 55.5 is the mole number of 1 L water.
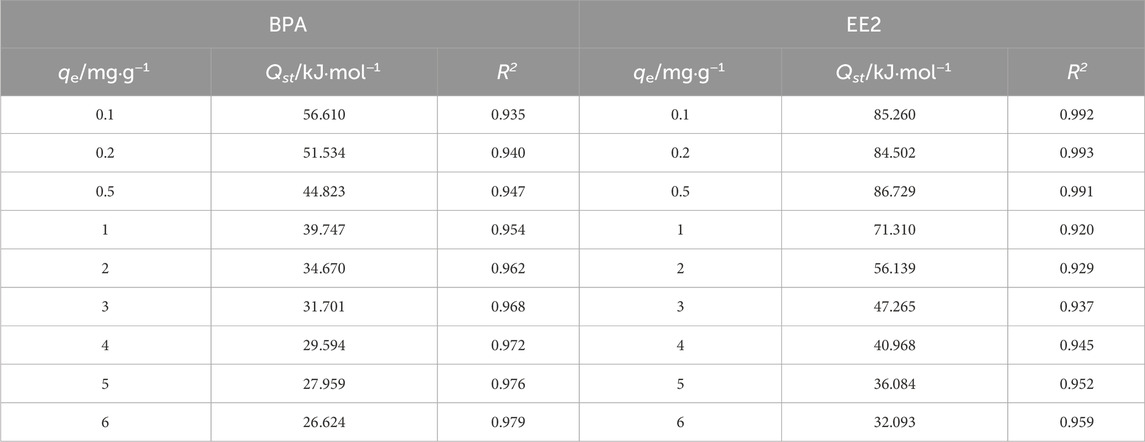
The isosteric heat of adsorption (Qst) was calculated using the Clausius-Clapeyron equation (Pan et al., 1998) (Equation 4) to quantify adsorption energy. Qst values for BPA (26.624–56.610 kJ mol−1) were lower than those for EE2 (32.093–85.260 kJ mol−1), consistent with the higher adsorption affinity of EE2 (Table 4; Figure 6). Qst values below 80 kJ mol−1 indicate physical adsorption, while values between 80 and 400 kJ mol−1 suggest chemical adsorption (Chowdhury et al., 2011; Jung et al., 2017). Thus, BPA adsorption is primarily physical, driven by hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions, and electrostatic attraction, while EE2 adsorption includes a chemical component (with Qst up to 85.26 kJ/mol), but barely crosses into chemisorption. Therefore, it was speculated that the adsorption of EE2 is mainly due to physical adsorption, such as hydrophobic interaction.
Where, ce is the concentration at equilibria, mg·L-1; T is the temperature, K; R is universal gas constant, J·(mol·K)−1; Qst is isosteric heat of adsorption, kJ·mol-1; N is the mole amount of the adsorption.
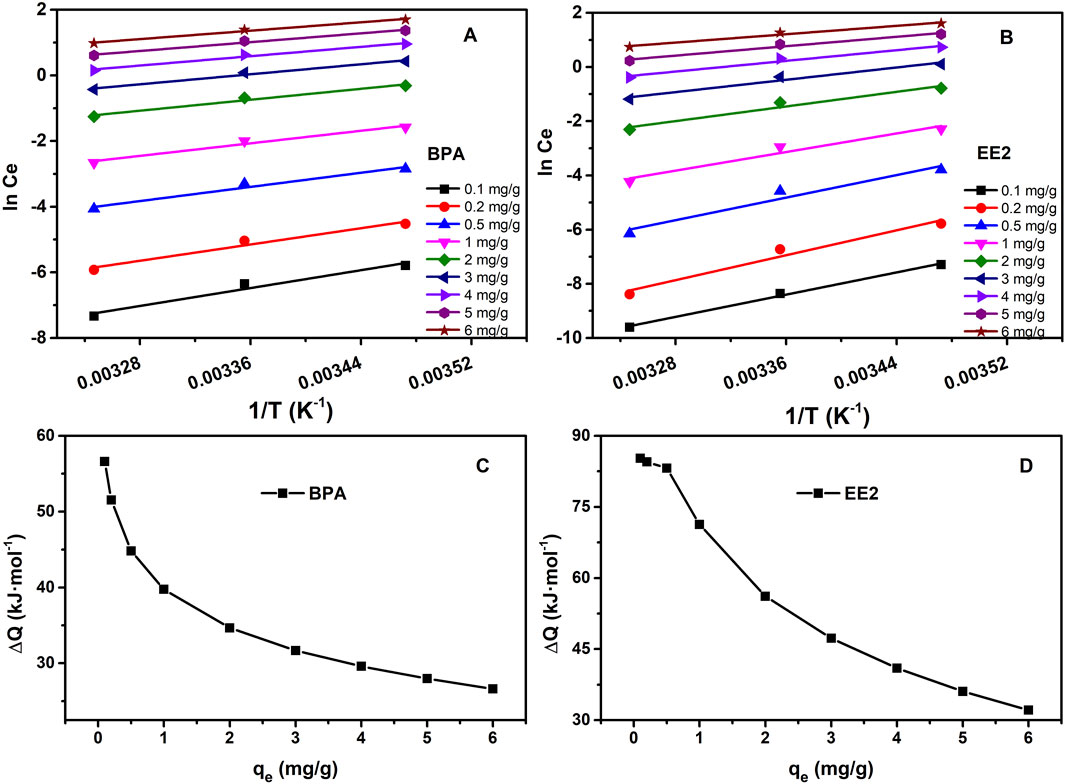
Figure 6. (A) and (B) are plots of lnce against 1/T for BPA and EE2 adsorbed on MOF-M-C, (C) and (D) are plot of isoteric heat of adsorption against equilibrium absorption capacity for BPA and EE2 adsorbed on MOF-M-C.
3.6 Regeneration
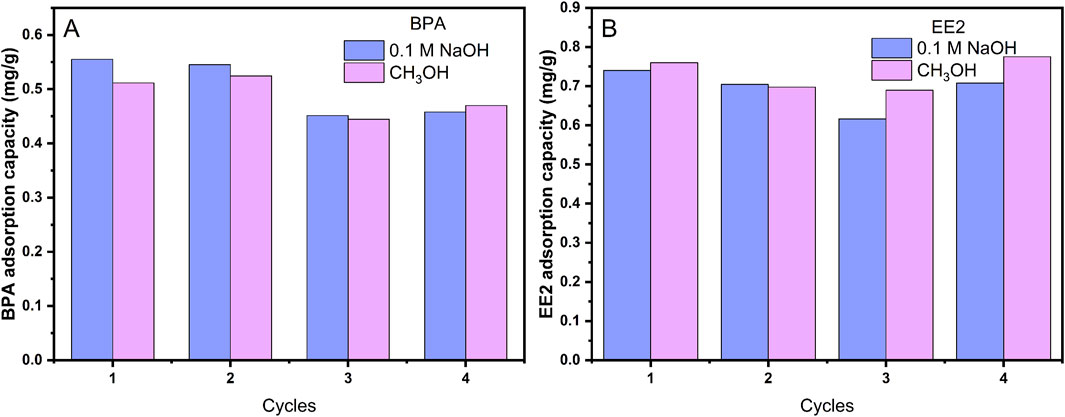
Regeneration is a critical factor in evaluating adsorbent applicability. The regeneration efficiency of adsorbents is quantified by the adsorption capacity retention rate (%) of pollutants on the adsorbent. MOF-M-C was regenerated using 0.1 mol L−1 NaOH or 100% methanol (Figure 7). Both methods demonstrated excellent regeneration efficiency, with BPA adsorption capacity remaining above 80% and EE2 adsorption capacity nearly unchanged after four cycles. These results highlight the reusability of MOF-M-C for BPA and EE2 removal.
4 Conclusion
MOF-derived carbon embedded in granular acicular mullite (MOF-M-C) was synthesized, characterized, and applied for the adsorption of BPA and EE2 from water. The adsorption capacity of MOF-CB remained high after embedding into acicular mullite, making it an ideal modifier for water treatment filter materials. The adsorption of BPA and EE2 on MOF-M-C was temperature-dependent and entropy-driven. Co-adsorption studies revealed competition between BPA and EE2, with EE2 exhibiting higher affinity. Thermodynamic analysis indicated that adsorption is primarily physical, involving hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions, and electrostatic attraction. MOF-M-C demonstrated excellent reusability, making it a promising material for water treatment applications.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
LD: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. XG: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. XX: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XQ: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LL: Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft. WC: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZQ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the Independent Innovation Research Program of Changjiang Survey, Planning, Design and Research Co., Ltd. (CX2023Z06-2 and CX2021Z65).
Conflict of interest
Authors LD, XX, and LL were employed by China National Chemical Construction Investment Group Co., Ltd. Authors XG, XQ, WC, and ZQ were employed by Changjiang Survey, Planning, Design and Research Co., Ltd.
The authors declare that this study received funding from Changjiang Survey, Planning, Design and Research Co., Ltd. The funder had the following involvement in the study: mainly participating in material procurement, the preparation and characterization of synthetic samples, as well as the drafting and revision of the manuscript.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1605083/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmadijokani, F., Ghaffarkhah, A., Molavi, H., Dutta, S., Lu, Y., Wuttke, S., et al. (2024). COF and MOF hybrids: advanced materials for wastewater treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34 (43), 2305527. doi:10.1002/adfm.202305527
Ahmed, I., Lee, G., Lee, H. J., and Jhung, S. H. (2024). Adsorption of pharmaceuticals from water using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), MOF-Derived carbons, covalent-organic frameworks (COFs), COF-Derived carbons: comparison of the four adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 488, 151022. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.151022
Ahsan, M. A., Jabbari, V., Islam, M. T., Turley, R. S., Dominguez, N., Kim, H., et al. (2019). Sustainable synthesis and remarkable adsorption capacity of MOF/Graphene oxide and MOF/CNT based hybrid nanocomposites for the removal of bisphenol A from water. Sci. total Environ. 673, 306–317. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.219
Bhadra, B. N., and Jhung, S. H. (2017). A remarkable adsorbent for removal of contaminants of emerging concern from water: porous carbon derived from metal azolate framework-6. J. Hazard. Mater. 340, 179–188. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.011
Bhadra, B. N., Lee, J. K., Cho, C. W., and Jhung, S. H. (2018). Remarkably efficient adsorbent for the removal of bisphenol A from water: bio-MOF-1-Derived porous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 343, 225–234. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.004
Boulanger, N., Talyzin, A. V., Xiong, S., Hultberg, M., and Grimm, A. (2024). High surface area activated carbon prepared from wood-based spent mushroom substrate for supercapacitors and water treatment. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 680, 132684. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132684
Chang, H., Shi, L.-N., Chen, Y.-H., Wang, P.-F., and Yi, T.-F. (2022). Advanced MOF-Derived carbon-based non-noble metal oxygen electrocatalyst for next-generation rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Coord. Chem. Rev. 473, 214839. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214839
Chowdhury, S, Mishra, R, Saha, P, and Kushwaha, P (2011). Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk, Desalination, 265, 159–168.
Daglar, H., and Keskin, S. (2022). Combining machine learning and molecular simulations to unlock gas separation potentials of MOF membranes and MOF/Polymer MMMs. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 14 (28), 32134–32148. doi:10.1021/acsami.2c08977
Ding, J., Tang, Y., Zheng, S., Zhang, S., Xue, H., Kong, Q., et al. (2022). The synthesis of MOF derived carbon and its application in water treatment. Nano Res. 15 (8), 6793–6818. doi:10.1007/s12274-022-4327-1
Ding, Z., Bu, W., and Tan, W. (2025). MOF-Derived porous carbon composite cathodes for lithium-ion capacitors: fabrication, applications and perspectives. J. Energy Storage 129, 117298. doi:10.1016/j.est.2025.117298
Dong, X. W., He, L. Z., Hu, H., Liu, N., Gao, S., and Piao, Y. X. (2018). Removal of 17 beta-estradiol by using highly adsorptive magnetic biochar nanoparticles from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 352, 371–379. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.025
Duan, Q., Li, X., Wu, Z., Alsaedi, A., Hayat, T., Chen, C., et al. (2019). Adsorption of 17β-estradiol from aqueous solutions by a novel hierarchically nitrogen-doped porous carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 533, 700–708. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2018.09.007
Gao, J.-M., Yan, Z., Wang, B., Ma, Z., and Guo, Y. (2024). Preparation of whisker mullite ceramic membrane from coal fly ash for efficient oil-water separation. Ceram. Int. 50 (18), 32727–32736. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.06.082
Goeury, K., Munoz, G., Duy, S. V., Prévost, M., and Sauvé, S. (2022). Occurrence and seasonal distribution of steroid hormones and bisphenol A in surface waters and suspended sediments of Quebec, Canada. Environ. Adv. 8, 100199. doi:10.1016/j.envadv.2022.100199
Hayat, A., Rauf, S., Al, A. B., El Jery, A., Almuqati, N., Melhi, S., et al. (2024). Recent advance in MOFs and MOF-Based composites: synthesis, properties, and applications. Mater. Today Energy 41, 101542. doi:10.1016/j.mtener.2024.101542
Huang, Y.-F., Wu, P., Tang, J.-P., Yang, J., Li, J., Chen, S., et al. (2024). MOF-Derived Cu embedded into N-doped mesoporous carbon as a robust support of PdAu nanocatalysts for ethanol electrooxidation. Rare Met. 43 (3), 1083–1094. doi:10.1007/s12598-023-02512-9
Ibrar, S., Ali, N. Z., Ojegu, E. O., Odia, O. B., Ikhioya, L., and Ahmad, I. (2023). Assessing high-performance energy storage of the synthesized ZIF-8 and ZIF-67. J. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 3 (4), 294–307. doi:10.48309/JAOC.2023.421600.1128
Ismanto, A., Hadibarata, T., Kristanti, R. A., Maslukah, L., Safinatunnajah, N., and Sathishkumar, P. (2022). The abundance of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in downstream of the bengawan solo and brantas Rivers located in Indonesia. Chemosphere 297, 134151. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134151
Javidan, P., Baghdadi, M., Torabian, A., and Goharrizi, B. A. (2022). A tailored metal–organic framework applicable at natural pH for the removal of 17α-ethinylestradiol from surface water. Desalination Water Treat. 264, 259–269. doi:10.5004/dwt.2022.28563
Jiang, H., Li, Q.-Y., Sun, J.-X., Huang, Y.-Y., Zhang, P., Mao, Y.-F., et al. (2023). Studies on competitive adsorption characteristics of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinylestradiol on thermoplastic polyurethane by site energy distribution theory. Environ. Geochem. Health 45 (7), 5181–5194. doi:10.1007/s10653-023-01566-z
Jiang, L. H., Liu, Y. G., Liu, S. B., Hu, X. J., Zeng, G. M., Hu, X., et al. (2017). Fabrication of beta-cyclodextrin/poly (L-glutamic acid) supported magnetic graphene oxide and its adsorption behavior for 17 beta-estradiol. Chem. Eng. J. 308, 597–605. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.067
Jiang, L. H., Liu, Y. G., Zeng, G. M., Xiao, F. Y., Hu, X. J., Hu, X., et al. (2016). Removal of 17 beta-estradiol by few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets from aqueous solutions: external influence and adsorption mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 284, 93–102. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.139
Jin, R., Zhao, C., Song, Y., Qiu, X., Li, C., and Zhao, Y. (2023). Competitive adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and bisphenol A on magnetic biochar: mechanism and site energy distribution. Environ. Pollut. 329, 121662. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121662
Jo, Y. M., Jo, Y. K., Lee, J. H., Jang, H. W., Hwang, I. S., and Yoo, D. J. (2023). MOF-based chemiresistive gas sensors: toward new functionalities. Adv. Mater. 35 (43), 2206842. doi:10.1002/adma.202206842
Jung, K.W., Lee, S., and Lee, Y.J (2017). Synthesis of novel magnesium ferrite (MgFe2O4)/biochar magnetic composites and its adsorption behavior for phosphate in aqueous solutions, Bioresource Technol, 245, 751–759.
Kang, D.-Y., and Lee, J. S. (2023). Challenges in developing MOF-Based membranes for gas separation. Langmuir 39 (8), 2871–2880. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c03458
Khalil, I. E., Fonseca, J., Reithofer, M. R., Eder, T., and Chin, J. M. (2023). Tackling orientation of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): the quest to enhance MOF performance. Coord. Chem. Rev. 481, 215043. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215043
Li, X., Guan, B. Y., Gao, S., and Lou, X. W. D. (2019a). A general dual-templating approach to biomass-derived hierarchically porous heteroatom-doped carbon materials for enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Energy and Environ. Sci. 12 (2), 648–655. doi:10.1039/c8ee02779j
Li, Y. Y., Fang, Y., Cao, Z. L., Li, N. J., Chen, D. Y., Xu, Q. F., et al. (2019b). Construction of g-C3N4/PDI@MOF heterojunctions for the highly efficient visible light-driven degradation of pharmaceutical and phenolic micropollutants. Appl. Catal. B-Environmental 250, 150–162. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.03.024
Liang, Y., Yang, X., Wang, X., Guan, Z.-J., Xing, H., and Fang, Y. (2023). A cage-on-MOF strategy to coordinatively functionalize mesoporous MOFs for manipulating selectivity in adsorption and catalysis. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 5223. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40973-9
Liu, L., Chen, L., Thummavichai, K., Ye, Z., Wang, Y., Fujita, T., et al. (2023). Amino-functionalized MOF-on-MOF architectural nanocomplexes composed for radioactive-iodine efficient adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 474, 145858. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2023.145858
Ma, W. J., Wang, N., Fan, Y. A., Tong, T. Z., Han, X. J., and Du, Y. C. (2018a). Non-radical-dominated catalytic degradation of bisphenol A by ZIF-67 derived nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes frameworks in the presence of peroxymonosulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 336, 721–731. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.164
Ma, W. J., Wang, N., Tong, T. Z., Zhang, L. J., Lin, K. Y. A., Han, X. J., et al. (2018b). Nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur tri-doped hollow carbon shells derived from ZIF-67@poly (cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4 '-sulfonyldiphenol) as a robust catalyst of peroxymonosulfate activation for degradation of bisphenol A. Carbon 137, 291–303. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2018.05.039
Mon, M., Bruno, R., Ferrando-Soria, J., Armentano, D., and Pardo, E. (2018). Metal–organic framework technologies for water remediation: towards a sustainable ecosystem. J. Mater. Chem. A 6 (12), 4912–4947. doi:10.1039/c8ta00264a
Moreira, C. G., De Souza, L. C., Castor Neto, T. C., Gomes, G., Bila, D. M., and Fonseca, F. V. (2023). Combined reverse osmosis and UV/H2O2 treatment of aqueous solutions of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinylestradiol: assessment of estrogenic activity. Environ. Technol. 44 (20), 3108–3120. doi:10.1080/09593330.2022.2051608
Pan, H H, Ritter, J A, and Balbuena, P B (1998). Examination of the approximations used in determining the isosteric heat of adsorption from the Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Langmuir, 14, 6323–6327.
Ouyang, K., Zhu, C. H., Zhao, Y., Wang, L. C., Xie, S., and Wang, Q. (2015). Adsorption mechanism of magnetically separable Fe3O4/graphene oxide hybrids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 355, 562–569. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.109
Patel, S., Jie, H., and Wei, G. (2015). Sorption of 17β-estradiol from aqueous solutions on to bone char derived from waste cattle bones: kinetics and isotherms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 3 (3), 1562–1569. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2015.04.027
Pavlenko, V., Żółtowska, S., Haruna, A., Zahid, M., Mansurov, Z., Supiyeva, Z., et al. (2022). A comprehensive review of template-assisted porous carbons: modern preparation methods and advanced applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 149, 100682. doi:10.1016/j.mser.2022.100682
Poonia, K., Patial, S., Raizada, P., Ahamad, T., Khan, A. a. P., Van Le, Q., et al. (2023). Recent advances in metal organic framework (MOF)-Based hierarchical composites for water treatment by adsorptional photocatalysis: a review. Environ. Res. 222, 115349. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.115349
Song, J., Shi, M., Xia, L., Dai, J., Luo, L., Wang, H., et al. (2023). The comparative study on inhibitory effect of natural organic matters on the TiO2 and activated carbon/TiO2 composites for the removal of 17α-ethinylestradiol. Chemosphere 333, 138930. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138930
Sun, Z., Zhao, L., Liu, C., Zhen, Y., and Ma, J. (2020). Fast adsorption of BPA with high capacity based on π-π electron donor-acceptor and hydrophobicity mechanism using an in-situ sp2 C dominant N-doped carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122510. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2019.122510
Surana, D., Gupta, J., Sharma, S., Kumar, S., and Ghosh, P. (2022). A review on advances in removal of endocrine disrupting compounds from aquatic matrices: Future perspectives on utilization of agri-waste based adsorbents. Science of The Total Environment, 826, 154129.
Tomei Torres, F. A., and Masten, S. J. (2023). Endocrine-disrupting substances: I. Relative risks of PFAS in drinking water. J. Water Health 21 (4), 451–462. doi:10.2166/wh.2023.153
Wang, J., Li, H. B., Shuang, C. D., Li, A. M., Wang, C., and Huang, Y. (2015). Effect of pore structure on adsorption behavior of ibuprofen by magnetic anion exchange resins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 210, 94–100. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.02.026
Xiao, F., Yang, X., Wang, D., Wang, H., Yu, D. Y., and Rogach, A. L. (2020). Metal–organic framework derived CoS2 wrapped with nitrogen-doped carbon for enhanced lithium/sodium storage performance. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 12 (11), 12809–12820. doi:10.1021/acsami.9b22169
Xu, S., Dong, A., Hu, Y., Yang, Z., Huang, S., and Qian, J. (2023). Multidimensional MOF-Derived carbon nanomaterials for multifunctional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 11 (18), 9721–9747. doi:10.1039/d3ta00239j
Yang, J., Bissett, M. A., and Dryfe, R. A. (2021). Investigation of voltage range and self-discharge in aqueous zinc-ion hybrid supercapacitors. ChemSusChem 14 (7), 1700–1709. doi:10.1002/cssc.202002931
Yang, Q., Liao, W., Wei, Z., Qiu, R., Zheng, Q., Wu, Q., et al. (2024). Degradation and humification of steroidal estrogens in the soil environment: a review. Chemosphere 357, 142043. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.142043
Yang, W. X., Wang, J., Yang, Q. F., Pei, H. N., Hu, N., Suo, Y. R., et al. (2018). Facile fabrication of robust MOF membranes on cloth via a CMC macromolecule bridge for highly efficient Pb(II) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 339, 230–239. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.126
Zhong, M., Wang, T., Zhao, W., Huang, J., Wang, B., Blaney, L., et al. (2022). Emerging organic contaminants in Chinese surface water: identification of priority pollutants. Engineering 11, 111–125. doi:10.1016/j.eng.2020.12.023
Zhou, Q., Luo, X., He, J., Guo, J., Xu, C., Wan, Y., et al. (2022). Bisphenol A and 17α-Ethinylestradiol removal from water by hydrophobic modified acicular mullite. Sustainability 14 (21), 14248. doi:10.3390/su142114248
Zhou, X., Wei, J., Liu, K., Liu, N., and Zhou, B. (2014). Adsorption of bisphenol A based on synergy between hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interaction. Langmuir 30 (46), 13861–13868. doi:10.1021/la502816m
Keywords: adsorption, bisphenol A, 17α-ethinylestradiol, acicular mullite, matal-organic framework derived carbon, isosteric heat
Citation: Deyong L, Guangcheng X, Xingcan X, Qi X, Lisheng L, Chu W and Qiuhong Z (2025) Novel MOF-Derived carbon-embedded acicular mullite for efficient removal of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinylestradiol: adsorption mechanisms and thermodynamic studies. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1605083. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1605083
Received: 03 April 2025; Accepted: 09 July 2025;
Published: 31 July 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaofei Tan, Hunan University, ChinaReviewed by:
V. N. Meena Devi, Noorul Islam University, IndiaSneha Nayak, NMAM Institute of Technology (Nitte Deemed to be University), India
Copyright © 2025 Deyong, Guangcheng, Xingcan, Qi, Lisheng, Chu and Qiuhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhou Qiuhong, emhvdXFpdWhvbmc1QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Liu Deyong1
Liu Deyong1 Zhou Qiuhong
Zhou Qiuhong