- 1School of Economics, North Minzu University, Yinchuan, China
- 2Common Modernization Research Center, Key Research Base of Humanities and Social Sciences of the State Ethnic Affairs Commission, Yinchuan, China
Introduction: Investigating the relationship between green technology innovation (GTI) and urban carbon emission (CEI) is crucial for sustainable economic development and achieving the dual carbon goal.
Methods: Using panel data from 272 cities in China between 2006 and 2022, this paper empirically analyzes the impact of GTI on urban CEI by applying the fixed effects and chain mediation models. Furthermore, the chain mediating effect of environmental regulations and energy consumption structure is explored.
Results: GTI significantly reduces urban CEI, particularly in the eastern region, non-resource-based, and large-scale cities, where its carbon reduction effect is more pronounced. The mechanism analysis reveals that environmental regulations and energy consumption structure not only play an independent mediating role, but also exert a chain mediation effect.
Discussion: These findings enhance our understanding of the intrinsic mechanisms underlying green technology innovation-driven carbon emission reduction in China. Besides, they offer theoretical insights for policy formulation, demonstrating a pivotal role in environmental governance and sustainable development.
1 Introduction
As global climate change becomes more severe, countries confront the dual challenges of environmental degradation and rising CEI when pursuing sustainable green development (Liao and Li, 2022). According to data from the International Energy Agency, global CO2 emissions related to energy reached a record 37.4 billion tons in 2023, a 0.9% increase compared to the previous year. Over 75% of these emissions resulted from fossil fuel combustion. At the same time, the frequency of extreme weather events and the reduction in nuclear power generation have further intensified carbon emission pressures (Chen and Wang, 2024). As the world’s second-largest economy and largest carbon emitter, China has maintained the highest carbon emissions since surpassing the United States in 2005 (Liang et al., 2019). With the ongoing expansion of China’s economy, the cost of this high-pollution growth is rising at an alarming rate. In response to the growing costs of high-pollution growth driven by economic expansion, the Chinese government has proposed dual carbon. The goal is to achieve carbon peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060.
In this macro context, the strategic importance of cities as drivers of economic and social activities is increasing (Tang and Zhou, 2025). Although cities occupy only 0.4%–0.9% of global land, they account for 60% of global resource consumption and contribute 70% of total carbon emissions (Wu et al., 2024). It results in a rigid growth trend in resource demand and consumption. Furthermore, this is further compounded by China’s resource endowment, which is marked by abundant labor but scarce capital, technology, and natural resources. It is unlikely that this situation will change in the short term (Wu et al., 2023). As a result, cities will face more severe carbon reduction challenges. Consequently, the key issue for urban sustainable development is achieving effective carbon control while maintaining economic growth.
GTI is considered a key pathway to achieving economic development and environmental protection goals (Lu and Lu, 2024). In the Porter Hypothesis, Porter and van der Linde (1995) proposed that appropriate environmental regulations can stimulate corporate innovation. This leads to a win-win situation of environmental and ecological improvement and economic benefits through technological progress. As climate change has intensified recently, GTI has been recognized as a core tool for reducing urban CEI and addressing climate risks. It encompasses a range of innovative activities, from clean energy to emission reduction and circular economy technologies. These activities are characterized by synergies, environmental friendliness, and sustainability (Chen et al., 2023). On one hand, through technological improvements and applications, GTlI can save energy, reduce pollution, and improve environmental performance. Simultaneously, it enhances the green competitiveness of market entities, thereby achieving win-win development for both the economy and the environment. On the other hand, GTI also improves residents’ quality of life and health and enhances urban livability and attractiveness (Lu and Xia, 2024). Ultimately, it drives the development of related industrial chains, creating agglomeration and scale effects (Birol, 2013). The International Energy Agency confirms that green technologies account for over 60% of carbon emission reductions in climate mitigation programs (IEA, 2013). For China, actively promoting GTI helps alleviate environmental pressure and achieve the dual carbon goals. Additionally, it enables China to gain a competitive edge in the new technological revolution. This will establish a new advantage in green development.
However, there are still significant differences in the academic understanding of the relationship between GTI and urban CEI. Although GTI is theoretically capable of promoting carbon reduction, the rebound effect suggests that GTI may lead to increased energy consumption. This may offset or even exceed the energy savings and emission reduction effects of GTI (Dai et al., 2023). Additionally, the varying levels of GTI development in different regions result in significant spatial heterogeneity in its emission reduction effects. As a result, drawing comprehensive conclusions is challenging (Feng et al., 2025). Furthermore, GTI is a typical public good with high input costs, technical risks, and long payback periods. Its carbon emission reduction effects often require realization through specific mediating pathways (Manso, 2011). While existing research has acknowledged the crucial roles of environmental regulation and energy consumption structure, there is insufficient analysis of how these factors play a chain mediation role in GTI’s impact on CEI.
Based on the above analysis, this study primarily examines the following research questions: Can GTI reduce carbon emissions at the urban level? What are the intrinsic mechanisms through which GTI affects urban carbon emissions? Do environmental regulations and energy consumption structure play a mediating role in the chain? Are there significant regional differences in the effects of emission reduction? Clarifying these questions is crucial for promoting high-quality development and carbon reduction in China under the dual-carbon goal. Given this, this paper uses panel data from 272 cities in China from 2006 to 2022. It constructs a chain mediation mechanism linking GTI, environmental regulation, energy consumption structure, and CEI. This not only helps clarify the theoretical debate on GTI’s carbon reduction effects but also reveals its underlying mechanisms. More importantly, it provides theoretical and empirical evidence for formulating precise and effective urban carbon reduction policies.
2 Literature review
2.1 GTI and CEI
As the concept of CTI has deepened in recent years, many scholars have recognized its significant positive impact on reducing urban CEI. From a theoretical perspective, the Natural Resource-Based View suggests that GTI helps firms gain competitive advantages. It also makes their environmental strategies valuable, scarce, difficult to imitate, and irreplaceable strategic resources (Hu et al., 2023). Recent empirical research has confirmed that GTI promotes high-quality economic development and enhances environmental sustainability across various countries and regions (Wang et al., 2022). For instance, in terms of Wei and Ma (2024), R&D expenditures increase CO2 emissions in APEC countries, while the number of patents reduces carbon emissions. After the discussion, it was found that GTI can effectively enhance a region’s carbon emission reduction capacity. Moreover, it also has significant spatial spillover effects on neighboring regions’ carbon emission reduction levels. At the international level, some scholars have used the CS-ARDL method to conclude that GTI positively impacts Thailand’s CEI and overall environmental improvement (Xuan et al., 2024). Research on developed countries, including the G7, also highlights that progress in green technology helps these countries achieve carbon emission reduction targets (Hu and Wu, 2022). This emphasizes the interdependence between technological innovation and environmental protection.
However, some research holds an opposing view on the emission reduction effects of GTI. They claim that GTP does not explicitly ensure CO2 emission reductions. From the perspective of Rennings and Rammer (2011), the market cannot effectively promote GTI. Companies may require sufficient incentives or penalties to drive GTI. Lu and Lu (2024) observed that GTI exhibits an inverted U-shaped impact on the carbon intensity across Chinese provinces from the perspective of energy output growth. Furthermore, Mongo et al. (2021) proposed an indirect rebound effect of GTI. If this effect is significant enough, energy demand growth may outweigh supply-side efficiency gains. This could undermine GTI’s role in reducing CEI. On the international level, Suki et al. (2022) emphasized that while GTI improved the environmental performance of Italian cities, it did not obviously reduce CEI.
Additionally, a study in Malaysia employing the Bootstrapped ARDL method found that GTI significantly increases CEI in the short and long term (Li H et al., 2024). Other scholars contend that the reduction of carbon emissions by GTI occurs in distinct phases. Although GTI positively affects carbon reduction in the short term, its effectiveness diminishes over time and even becomes ineffective (Chen et al., 2023). Relevant research has shown that GTI can effectively reduce CEI, but it is established in developed countries. Besides, Lin and Ma (2022) pointed out a non-linear relationship between GTI and CEI. Significant reductions occur only when the GTI and human capital level reach a specific threshold. Zhu and Zhang (2023) assessed the single-threshold effect of income on GTI effectiveness using a threshold regression model based on data from 71 economies. The results showed that GTI led to significant CEI only when the income level exceeded a specific threshold. Moreover, Wang et al. (2023) found differences in the carbon reduction effects of GTI across sectors. In the construction sector, GTI likely increases CEI, while in the industrial sector, it produces relatively fewer emissions.
2.2 GTI, environmental regulation (ER), and CEI
Porter (1991) contended that stringent, well-designed environmental regulations can stimulate GTI. This offsets compliance costs, increases firm productivity, and creates a win-win scenario. In this situation, both profitability and emission reduction targets are improved. Public Health Policy provides a new perspective on the impact of environmental regulations. It emphasizes how such regulations influence firms’ innovative behavior and contribute to emission reductions. Numerous studies have empirically tested this hypothesis (Li Q et al., 2024). The Innovation Offsets perspective suggests that under a well-functioning environmental regulatory system, the environmental benefits of resource efficiency improvements can outweigh the costs. These costs are associated with internalizing environmental impacts (Hart et al., 2022). Fragkiadakis and Paroussos (2021) confirmed a positive correlation between the intensity of environmental regulation and innovation output. Their study, which is based on data from the manufacturing sector of 17 European countries, supports this finding. Other research shows that stringent environmental policies, such as carbon taxes on excessive emissions, positively impact environmental sustainability. These policies also lead to increased environmental costs. Moreover, these policies significantly enhance environmental sustainability. It also increases investment in green technologies, further promoting sustainability in the G-7 economies (Aybudak et al., 2025). Chhabra et al. (2023) emphasized that implementing environmental laws, such as carbon pricing or taxation, is crucial for countries heavily reliant on importing non-renewable energy sources to meet consumption needs. Tang et al. (2025) found that the marginal impact of environmental policy synergies on per capita carbon emissions in China exhibits clear structural features at different levels. These synergies effectively lower per capita emissions and contribute to carbon neutrality targets.
However, due to the inherent uncertainty and high capital requirements of innovative activities, some argue that environmental regulation is necessary to reduce CEI (Wang et al., 2025). Research based on Neoclassical Economics argues that ecological regulations increase compliance costs, such as pollution fees. This forces firms to redirect limited resources from innovation to basic emission reduction projects, possibly reducing overall innovation efficiency (Yin et al., 2022). Some research has examined the mechanism of environmental regulation. They conclude that regulation, acting as a driver, can mediate the role of GTI in promoting a low-carbon transition (Wang H. J et al., 2024). Furthermore, Wu and Yu (2025) argued that market-based environmental regulatory instruments, such as IERs, are most effective in promoting green innovation and emission reductions among Chinese firms.
2.3 GTI, energy consumption structure (ECS) and CEI
Achieving carbon neutrality through GTI has become the consensus of most countries. The existing literature primarily focuses on two aspects of the relationship between GTI, energy consumption structure, and CEI. On the one hand, it examines the impact of GTI on the structure of energy consumption. Xu et al. (2022) emphasized a non-linear dynamic relationship between GTI and energy efficiency. When innovation levels exceed a critical threshold, CEI will be reduced significantly. From the perspective of Guo et al. (2024), stronger policy support is required when technological innovation levels are low. Once innovation levels improve, policy intensity should be reduced once innovation levels improve to promote green energy transformation. Yang et al. (2023) emphasized that GTI fosters the development of new energy sources. It will contribute to the reduction of fossil fuel consumption. Other scholars argue that GTI, as a key energy-saving mechanism, can guide resource flow from high-pollution, high-energy-consumption industries to low-energy, environmentally friendly industries. The process strongly promotes the energy transition (Cao and Xu, 2023).
Another aspect is that research has also focused on the impact of energy consumption structure on CEI. Zhang and Xu (2022) constructed an energy security index system and found that improving energy security helps decouple carbon emissions in the Yellow River Basin. Liu H. Z. et al. (2022) stated that an unreasonable energy consumption structure inhibits the low-carbon economic transformation regionally and in neighboring areas. Some scholars argue that reducing the cost of clean energy and promoting energy structure reform can eliminate dependence on traditional sources (Chen L et al., 2024). This paves the way for developing and using clean energy, such as solar energy. It also encourages the gradual replacement of high-carbon sources with low-carbon alternatives, thus reducing CEI.
In addition, some scholars have analyzed the impact of related policies and argued that energy quota trading has a dual green effect. It reduces carbon inequality within and between cities. The effect is more pronounced in national low-carbon pilot cities than in non-pilot cities (Haowei, 2025). Some scholars have examined the new energy city demonstration policy from constraint and incentive perspectives. They found that the carbon reduction effect of the NECDP becomes significant only after the second year, indicating a time lag (Che et al., 2023). Besides, some studies emphasize the potential complexity of GTI. Gu et al. (2019) argued that GTI improves energy efficiency, but its marginal effect gradually diminishes. Moreover, economic growth stimulates higher energy demand. This increases pollutant emissions in production processes and poses greater climate change risks. Some scholars have found that GTI may encourage residents to use energy-efficient products more frequently by reducing energy consumption costs. It will lead to increased CEI in turn (Pu et al., 2022).
In summary, existing research has examined the impact of CTI on CEI from different perspectives, providing a solid theoretical foundation for this study. However, there is still significant room for further exploration. Firstly, regarding the effectiveness of GTI in reducing carbon emissions, significant academic debate remains, and no consensus has been reached. Secondly, most existing research focuses on the effects of carbon emission reduction at the provincial level. However, as cities are the main drivers of economic development and the primary sources of carbon emissions, the carbon reduction mechanisms of GTI at the urban level remain underexplored. Thirdly, in terms of the mechanisms, although some scholars have highlighted the vital role of environmental regulation in the relationship between technological innovation and carbon emissions, most studies focus on its moderating effect. There has been relatively limited discussion on the mediation effect pathways. In addition, while existing research has examined the mediating roles of environmental regulation and energy consumption structure in the impact of GTI on CEI, few studies have integrated these factors into a unified framework. This limitation hinders the exploration of whether they form a chain mediation of GTI-environmental regulation-energy consumption structure-CEI.
Building on the research gaps mentioned above, this study focuses on whether GTI can reduce urban CEI at the city level. It also examines whether environmental regulation and energy consumption structure can play a chain mediation role in achieving urban carbon reduction goals. The potential contributions of this paper are as follows. Firstly, in terms of research methodology, this study differs from traditional single mediation analysis. It reveals that GTI affects CEI through a chain path. This path involves environmental regulation and energy structure transformation, enriching the research perspective. Secondly, existing research has mainly focused on the provincial level, while cities have not been adequately explored as the main battleground for carbon reduction. In the context of increasing resource and environmental constraints, the urban carbon reduction effects of CTI urgently need to be studied. Thirdly, this paper differs from previous research that focuses on the economic impact of environmental regulation. It treats environmental regulation as a policy incentive variable and explores its mediation paths. It suggests that GTI only provides the direction for enterprises. The innovation compensation effect and environmental compliance cost of environmental regulation policies drive this transformation. This study aims to provide references for regulatory institutions to develop low-carbon development strategies suited to China’s actual conditions.
3 Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
3.1 The direct impact of GTI on urban CEI
GTI is an innovation seeking to mitigate the conflict between economic expansion and ecological degradation. It is crucial to promote green, low-carbon economic development and achieve the dual-carbon goal (He et al., 2025). This view is supported by the theory of technology spillover, suggesting that green technology produces significant positive spillover effects as a special public good (Rong et al., 2023). On the one hand, applying key technologies such as renewable energy and energy storage can transform urban energy supply from centralized fossil energy systems to distributed clean energy. This shift breaks the traditional dependence on high-carbon pathways. Combined with e-mobility technology, this creates a chain system of emission reduction at the source and control at the end. Consequently, production costs for enterprises will decrease. This will stimulate production motivation, attract broader participation in GTI activities, and generate economies of scale (Colombelli et al., 2025). On the other hand, the potential of GTI to reduce emissions is also supported by Externality Theory. This theory argues that the environmental costs of corporate carbon emissions and the social benefits of green innovation are inadequately reflected in market pricing mechanisms (Hu and Tian, 2024). Similarly, using R&D subsidies, tax incentives, and other measures will encourage enterprises to adopt cleaner and more efficient green technologies. As a result, both capital and human investments in GTI will be increased. This will enhance individual enterprises’ ability to reduce emissions. In addition, a significant spillover effect will be generated, ultimately promoting the industry’s emission reduction process (Zhang et al., 2024).
The impact of GTI on carbon emissions remains controversial at the theoretical level. The Rebound Effect theory suggests that by reducing the cost of green products, GTI may stimulate larger-scale consumption. This may lead to an increase in overall carbon emissions instead of a decrease (Wang Q et al., 2024). According to the time-lag effect theory, it is a lengthy process for GTI to move from research and development to industrial application. This delay makes it challenging to achieve significant emission reductions in the short term (Yang Y. et al., 2023). Additionally, under resource constraints, large-scale investments in GTI may crowd out the improvement of traditional emission reduction technologies. This includes energy efficiency enhancements and other proven emission reduction paths. As a result, overall efficiency may decline (Li C et al., 2024). What is the actual emission reduction effect of GTI in the context of China’s rapid urbanization? Due to theoretical controversies and situational complexity, the exact impact of GTI on urban carbon emission reduction requires empirical testing. Therefore, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1. GTI has a significant effect on urban carbon emissions
3.2 Analysis of the mediating effects of environmental regulation
Environmental regulation refers to the administrative and legal measures governments use to guide firms in following specific policies. According to Porter’s hypothesis, technological progress reduces the costs of environmental monitoring and pollution control. This makes previously unaffordable or technologically infeasible environmental standards achievable (Song et al., 2022). The application of GTI prompts the government to set carbon emission caps. Consequently, mandatory constraints are imposed on high-emission industries, forcing them to adopt emission reduction measures (Cui et al., 2022). In addition, GTI has expanded the scope of environmental standards. Using tools such as carbon tax systems and green financial subsidies has shifted the regulatory approach towards multi-incentive mechanisms. This has accelerated the internalization of price mechanisms, directed resources toward low-carbon sectors, and reduced per-unit carbon emissions in urban areas (Ai et al., 2023). By utilizing institutional constraints and incentives, environmental regulation motivates market participants to reduce emissions, enhancing carbon reduction effectiveness. From the perspective of resource allocation, strict environmental regulations increase the costs and risks for high-carbon industries. Thus, their marginal returns decline. At the same time, the green technology sector benefits from high returns due to policy support (Zhang et al., 2024). This drives the concentration of factors such as capital, talent, and land in low-carbon industries, accelerating the translation of innovations into the marketplace.
However, the mediating mechanism of environmental regulation is not always effective. As regulators, information asymmetry theory suggests governments often lack sufficient technical and cost information. This makes it difficult to accurately assess firms’ abatement potential and compliance costs, leading to indiscriminate implementation of regulations (Tian et al., 2025). Additionally, environmental regulatory policies encounter practical constraints during implementation, including high costs and resistance from interest groups (Alexander et al., 2024). Such constraints significantly weaken the mediating effect. In the early stage of technological innovation, the lack of maturity and limited market acceptance of green technologies may result in overly advanced policies that are disconnected from reality. Therefore, compliance costs for enterprises increase, creating a compliance burden effect and inhibiting short-term incentives to reduce emissions (Han and Shao, 2022). More critically, behavioral distortion theory suggests that stringent environmental regulations may cause enterprises to develop a regulatory avoidance mindset. This leads them to circumvent regulations through industrial shifts, data falsification, and exploiting policy loopholes, rather than invest in GTI (Yu et al., 2021). Given the academic disagreement on the mediating role of environmental regulation, it is essential to verify whether GTI can reduce urban CEI through this pathway. Consequently, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2. Environmental regulation plays a mediating role in GTI and reducing urban CEI, though its direction remains uncertain.
3.3 Analysis of the mediating effect of energy consumption structure
Resource allocation theory holds that the market serves as a fundamental mechanism for distributing resources. It guides the flow of resources to more efficient and lower-cost areas through price signals (Struben et al., 2020). Based on this theory, GTI can reduce carbon emissions by optimizing the energy consumption structure. On the supply side, GTI adjusts the relative prices of energy sources and reduces the production cost of renewable energy. With the rise of emerging energy supply modes, market choices are becoming more diversified, and competition among enterprises is intensifying. Under the market price mechanism, the cost advantage of clean energy will be transmitted to various industries (Liu et al., 2021). As a result, the development of the energy system towards decarbonization is accelerated. From the demand management perspective, this advantage will be passed to consumers as clean energy costs decrease. It will incentivize them to reduce the use of high-carbon energy. Carbon pricing and other tools will amplify price signals, further guiding consumers to make low-carbon choices (Li et al., 2024). From the perspective of energy efficiency improvement, the energy substitution theory suggests that enterprises can adjust their energy structure. The optimization of energy consumption structure promotes the concentration of energy use in high-efficiency sources, reduces energy losses, improves energy use efficiency, and enhances emission reduction effectiveness (Zhang et al., 2023).
However, significant challenges have been encountered in the practical application of this theoretical expectation. The effectiveness of the mediating role of the energy consumption structure remains a subject of intense debate in existing research. Path-dependence theory emphasizes high sunk costs, technological lock-in, and interest groups’ resistance to the established energy system. Accordingly, the energy consumption structure becomes highly rigid. Breaking free from the established path remains difficult for GTI, even when driven by technological innovation, particularly in the short term (Mi et al., 2021). Traditional high-carbon energy sources maintain a dominant position in the energy consumption structure (Yong et al., 2023). Market failure theory further suggests that information asymmetry, monopoly power, and externalities in the energy market imply that the market mechanism alone may not achieve effective energy structure transformation. In addition, the capacity of technological innovation to optimize the structure may be weakened by market failures (Wang et al., 2020). More importantly, some scholars contend that adjusting the energy consumption structure frequently lags behind GTI. In some cases, this delay may render the mediating role insignificant and even hinder carbon emission reduction (Huang et al., 2022). Given the divergence in existing research on the mediating mechanism of energy consumption structure, it remains to be tested whether GTI can reduce urban carbon emissions through this pathway. Thus, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 3. Energy consumption structure plays a mediating role in GTI and reducing urban CEI, though its direction remains uncertain.
3.4 Analysis of chain mediation between environmental regulation and energy consumption structure
The mechanism through which GTI influences urban carbon emission reduction is viewed differently in academia. The supporting view is that GTI can optimize the energy consumption structure and achieve the carbon reduction target. This is achieved through dual regulation: policy guidance and the demonstration effect. Regarding policy guidance, the government provides signals to market players by formulating green innovation development plans and related policies (Chen F et al., 2024). This reduces the cost of technology application and accelerates the market penetration of low-carbon technologies. At the level of the demonstration effect, industrial ecology theory suggests that technological innovation networks and industrial ecosystems incentivize upstream enterprises to provide cleaner raw materials. They also encourage downstream enterprises to offer more environmentally friendly products and services (Chen and Jiang, 2025). Environmentally friendly products and services promote the efficient utilization of energy. Furthermore, the synergistic development of upstream and downstream enterprises is facilitated, forming carbon synergy and emission reduction effects within the industrial chain. According to Porter’s hypothesis, clean energy gains policy advantages as environmental standards gradually rise with technological support. In contrast, high-carbon energy faces elimination pressure. As a result, key market players are forced to invest in high-efficiency, low-carbon clean energy technologies (Gu et al., 2022). As the proportion of clean energy increases, the policy resistance of traditional high-pollution industries weakens. This creates conditions for the implementation of stricter environmental standards. With the support of technology, a positive feedback loop of regulatory reinforcement and structural optimization forms, ultimately achieving carbon reduction.
However, skeptical views challenge the effectiveness of such chained mediating mechanisms. Resource curse theory suggests that local governments may rely more on traditional taxes and employment in resource-rich regions. This can lead to insufficient enforcement of environmental regulations. Therefore, even when available, advanced green technologies may not be effectively translated into strict environmental constraints (Rammer et al., 2017). Neoclassical economics further suggests that excessive environmental regulations may create a crowding-out effect. This effect diverts resources away from technological innovation and weakens firms’ capacity for structural adjustment (Zhang and Fan, 2024). In addition, some scholars using cross-country panel data have found that, in many developing countries, environmental regulations are often reduced to policy instruments. The intensity of these regulations is driven more by political cycles and economic interests than by GTI. More critically, institutional economics theory emphasizes that the effectiveness of the chain mediation mechanism depends heavily on institutional quality. In regions with lower institutional quality, a broken chain may exist among GTI, environmental regulation, and energy restructuring (Zeng et al., 2022). Most existing research focuses on single-path analysis and lacks an in-depth examination of the multiple mediation effect (Liu et al., 2025). As a result, consensus has not been reached regarding whether GTI can upgrade the energy consumption structure and achieve carbon emission reduction through strengthened environmental regulation. This controversy requires clarification through more comprehensive empirical research. Accordingly, this paper proposes the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 4. (H4). Whether GTI can reduce CEI by strengthening environmental regulation and thus promoting energy structure upgrades remains to be verified.
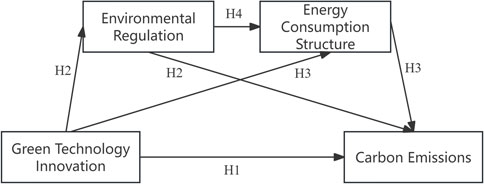
In summary, the mechanism of GTI on urban CEI is shown in Figure 1.
4 Research design and data description
4.1 Model construction
4.1.1 Benchmark regression model
In order to test whether GTI reduces urban CEI (i.e., direct impact), the following benchmark model is constructed for empirical research:
In Equation 1, the subscripts i and t denote the city serial number and year, respectively,
4.1.2 Mediation effect model
Based on the benchmark regression from Equation 1, drawing on the relevant research (Jiang, 2022), we establish a mediation model to identify the influence of GTI on CEI. The specific model is as shown in Equations 2, 3:
where mediator is the mediating variable, which in this paper is the energy consumption structure (CES) and the level of environmental regulation (ER); other variables have the same meanings as in Equation 1.
4.1.3 Chain mediation effect model
Equations 2, 3 demonstrate the impact of GTI on CEI through two independent mediating variables. However, these variables can not only function independently but may also generate chain effects. Drawing on relevant research findings (Ma et al., 2024; Li and Guo, 2024), this paper aims to clarify the mediating effect and construct a chain mediation model. This model analyzes the complex pathways by which GTI influences CEI via mediating variables, as shown in Equations 4–6:
where
4.2 Variable measurement and description
4.2.1 Explained variables
Urban carbon emissions (CEI). To accurately reflect the environmental pollution caused by urban economic development, referring to related research (Fan et al., 2023), and introducing the CO2 emission to quantify total carbon emissions. Following the IPCC-Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the carbon emission rate measures CO2 emissions from both direct sources (e.g., coal, natural gas, liquefied petroleum) and indirect sources (e.g., electricity, heat). Finally, the carbon emissions of each city are summed to obtain the total carbon emissions. The calculation formula is as shown in Equation 7:
In Equation 7, where
4.2.2 Core explanatory variables
The level of green technological innovation (GTI) is measured by the number of green patent applications in the IPC Green Inventory-WIPO. Based on the research by Xu and Chen. (2024), this measure is chosen because it reflects the dynamics of GTI more directly and promptly, while reducing risk and uncertainty.
4.2.3 Mediating variables
1. Environmental regulation (ER), Porter’s hypothesis suggests that it can force companies to eliminate inefficient and high-carbon capacity. Simultaneously, it also stimulates new industries such as renewable energy conservation and environmental protection. This, in turn, promotes technological diffusion, contributing to emission reductions throughout the industrial chain. Drawing on Zhang and Chen (2021), this study uses the level of importance assigned to environmental protection in government work reports as a measurement.
2. The structure of energy consumption (CES), which is measured by the proportion (%) of coal consumption in total energy consumption, drawing on the study of Fu (2010). Specifically, coal consumption is adjusted at the prefecture and municipal levels based on provincial nighttime lighting data and its quantitative correlation with energy statistics; energy consumption, drawing on relevant research (Lin and Meng, 2020), is adjusted at the prefecture and municipal levels based on the share of industrial output value. Then, inverse provincial energy consumption will be used for positive normalization.
4.2.4 Control variables
To avoid the negative impact of omitting important variables on regression results, this paper follows relevant research and selects the following control variables (Zhang et al., 2024):
1. The density of population (DOP) is measured by the ratio of the resident population to the area of the city. According to the theory of urban agglomeration, urbanization can improve energy efficiency through scale effects (Glaeser and Kahn, 2010). However, it may also exacerbate carbon lock-in due to rapid infrastructure expansion (Levine, 2005).
2. The degree of financial development (FD) is measured by the ratio of RMB loan balances of financial institutions to GDP. A well-developed financial market eases corporate financing constraints for innovation (Wang and Yi, 2023) and promotes clean technology R&D and application (Wang and Ullah, 2024). However, the technology lock-in effect may slow the transformation of traditional high-carbon industries.
3. The level of foreign investment (OP) is measured by the ratio of total imports and exports to GDP. International trade theory suggests foreign investment can generate technology spillover effects (Ding et al., 2019). However, the carbon leakage theory indicates that foreign investment may promote the transfer of high-carbon industries (Khanna et al., 2025).
4. The government intervention level (GL) is measured by the ratio of government fiscal expenditure to GDP (Chen et al., 2024). According to Peguy’s tax theory, a higher GL indicates the government has greater financial capacity and willingness to intervene in the market. This may include a carbon or environmental tax to correct market externalities.
5. The human capital level (HE) is measured by the logarithm of the number of students enrolled in general undergraduate and tertiary education. Investment in education enhances the ability to manage the environment (Zhang and Hussain, 2021). However, the theory of consumption upgrading suggests that individuals with higher human capital tend to favor lifestyles with a higher carbon footprint, such as frequent travel and high-end consumption. This may offset the effects of technological emission reduction (Liu et al., 2023).
6. The level of economic agglomeration (LEA) is measured by GDP and regional land area. High LEA promotes knowledge spillovers, economies of scale, and specialization (Glaeser and Kahn, 2010). However, environmental pressure theory suggests that a dramatic expansion of the absolute scale of economic activity often accompanies increases in LEA. This expansion may generate carbon emissions that far exceed the efficiency gains. The incremental increase in carbon emissions may outweigh the reduction effect of efficiency improvements (Romero-Lankao et al., 2014).
4.3 Data handling and description
Research focuses on Chinese cities at the prefecture level and above. However, due to numerous missing values in cities from Qinghai and Xinjiang, only provincial capitals were included in the data analysis. The final research sample consists of 272 cities at the prefecture level in China, excluding alliances and states. The GTI data primarily comes from the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA). The remaining variables are sourced from the China City Statistical Yearbook, China Energy Statistical Yearbook, China Regional Economic Statistical Yearbook, China Industrial Statistical Yearbook, China Labor Statistical Yearbook, China Environmental Statistical Yearbook, the National Bureau of Statistics of China, and the EPS database.
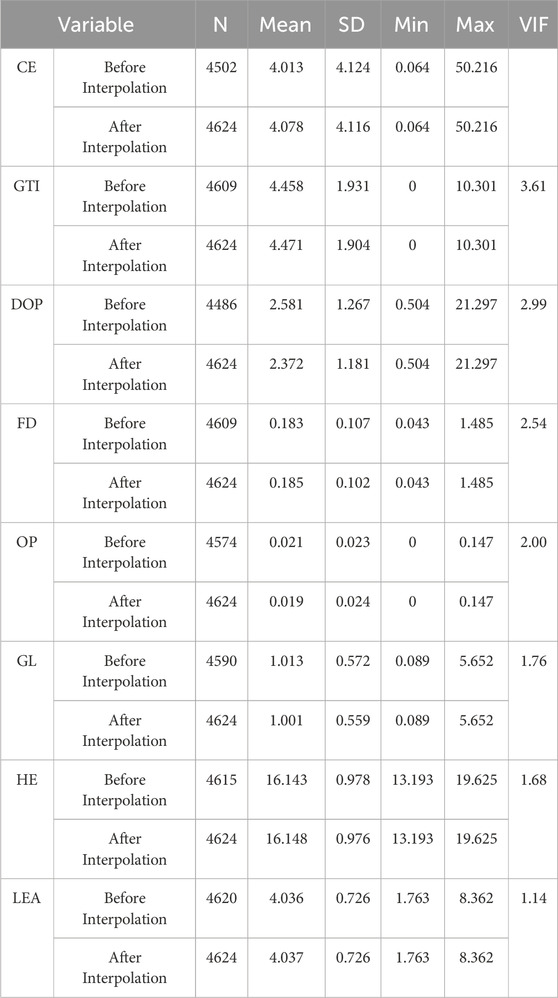
Before the analysis, the data for certain variables (GTI, DOP, and HE) were log-transformed. Simultaneously, selected variables were winsorized at the 1st and 99th percentiles (CEI and GTI). The risk of systematic bias was minimized due to the low proportion of missing values in the raw data (<1%). Missing values mainly occurred in isolation within a single year. To ensure data completeness, missing values were supplemented using interpolation. Additionally, to assess potential correlation issues between the variables, a VIF test was conducted. The descriptive statistics of the variables are presented in Table 1.
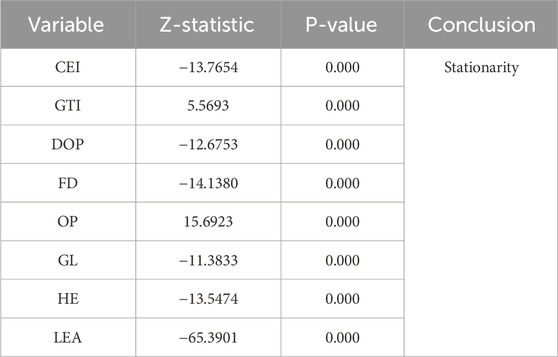
Table 1 shows that the maximum VIF value is 3.61, and the average is 2.24. These values are relatively stable, indicating no multicollinearity in the data. Additionally, the sample data used in this paper is short panel data. A Unit Root Test was conducted on the panel data to prevent pseudo-regression issues caused by a unit root in the data. The results are shown in Table 2. The results show that each variable rejects the unit root hypothesis at the 1% significance level. Therefore, the data is stationary and does not require further processing. Simultaneously, robust standard errors clustered at the city level address the potential heteroskedasticity issue.
5 Empirical results and analysis
5.1 Benchmark regression results
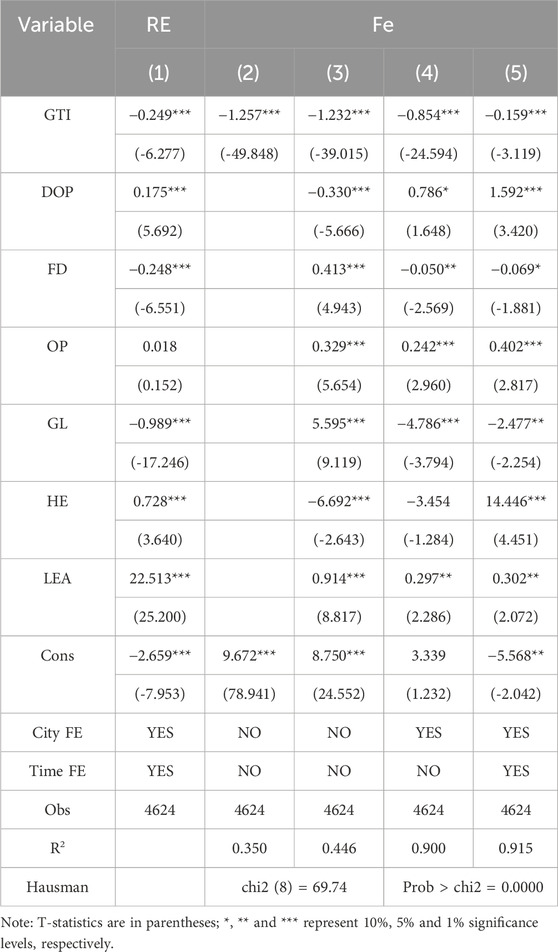
Before conducting the benchmark regression, model selection is performed. The results of the Hausman test, shown in Table 3, reveal that the P-value is less than 0.01, rejecting the null hypothesis. Therefore, the panel fixed-effect model is selected for regression. Columns (2) and (3) show that when control variables are added sequentially without fixed effects, the regression coefficients for carbon emission levels are significantly negative at the 1%. This indicates that GTI substantially reduces urban CEI. Columns (4) and (5) include individual and year fixed effects, respectively. The impact of GTI on CEI remains significantly negative and passes the 1% significance level. This finding provides preliminary support for hypothesis H1. This finding aligns with multiple studies (Zhang et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2022), which confirm the significant emission reduction effect of GTI. This effect is realized through recycling, reuse, and waste reduction, which lower resource consumption and carbon emissions during production. Furthermore, this finding confirms Porter’s theoretical expectation, which suggests that technological innovation can create a win-win situation for both the environment and economy (Porter and van der Linde, 1995). However, unlike Miao et al. (2024), which resulted from a short period and limitations in indicator selection, this study uses a more extended time window, effectively avoiding the discrepancies due to differing time methods. This approach effectively mitigates discrepancies in results arising from variations in measurement methodology (Li et al., 2023). It provides more robust empirical evidence for the carbon reduction effect of GTI.
5.2 Independent mediation effect test
Columns (1) and (2) in Table 4 validate the role of environmental regulation in urban carbon emissions. The results show that the regression coefficient for environmental regulation is 2.213, significantly positive at the 1% level. Meanwhile, the regression coefficient for carbon emissions remains significantly negative at the 1% level. Furthermore, after performing the Bootstrap mediation effect test, the estimated coefficient is −0.663, and the 95% confidence interval excludes 0. This suggests that GTI reduces carbon emissions by enhancing environmental regulation, thereby verifying hypothesis H2. This result aligns with Hu and Xiong (2024), which indicates that GTI can improve local government enforcement of environmental regulations and significantly reduce carbon emissions. It also confirms how environmental regulations incentivize enterprises to reduce emissions by lowering technology costs. However, unlike Ma et al. (2022) and Lu et al. (2023), which focus primarily on the direct impact of environmental regulations on GTI, this paper reverses the trend. It explores how GTI can strengthen the enforcement of environmental regulations, revealing the dynamic role of technological progress in institutional improvement.
The test results on the mediating role of the energy consumption structure are presented in columns (3) and (4) of Table 4. Table 4 shows that the coefficient for GTI’s influence on the energy consumption structure is 0.023, significantly positive at the 1% level. The absolute value of its negative influence on carbon emissions is smaller than the benchmark coefficient of 0.159. This indicates that the energy consumption structure plays a partial mediating role. The estimated coefficient in Bootstrap’s 1000 tests is −0.187, and the 95% confidence interval excludes 0. This indicates that GTI can reduce carbon emissions by optimizing the energy consumption structure, thereby verifying hypothesis H3. These findings align with the study by Guo and Tan. (2024), which suggests that new technologies reduce the cost of clean energy development and improve its economic feasibility and competitiveness. However, unlike Zhao et al. (2025), who examined the impact of green innovation on the energy mix from the perspective of corporate investment, this paper systematically verifies the mediating mechanism at the city level. It quantifies the magnitude of the mediating effect through a Bootstrap test, providing more rigorous empirical evidence for GTI’s indirect emission reduction pathway.
5.3 Chain mediation effect test
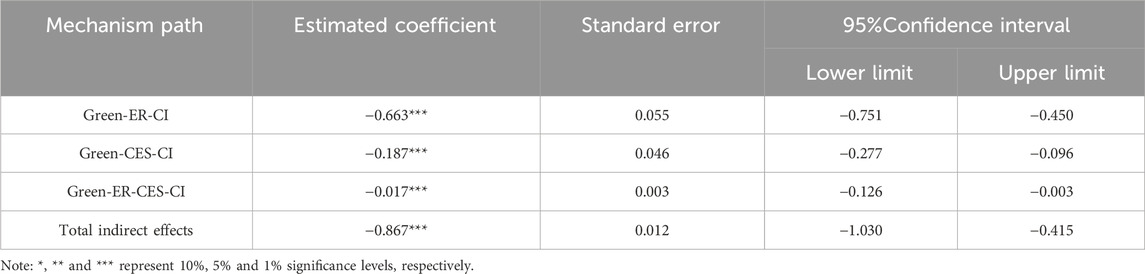
This paper examines the direct effect of GTI on CEI using Model 6 from the SPSS plug-in PROCESS. We conducted a Bootstrap test at the 95% confidence level, with 5000 sampling repetitions. The results are shown in Table 5. The coefficient of environmental regulation on energy consumption structure is 2.272, with a positive significance level. This indicates a significant chain mediation effect between environmental regulation and energy consumption structure. The indirect impact is greater than 0. Moreover, the Bootstrap test results in Table 5 show that the estimated coefficient of GTI is −0.017. The 95% confidence interval excludes 0, indicating that GTI can optimize the energy consumption structure by improving the environmental regulation level, thus reducing CEI. Hypothesis H4 is verified. The chain mediation aligns with Li et al. (2024), which argues that GTI enhances the technical feasibility of environmental regulation. Strengthened environmental regulation, in turn, guides market players to shift to cleaner energy options through the price mechanism (Liu et al., 2020). Unlike Zhang et al. (2024), who focus on the direct emission reduction effect of and Esperon-Rodriguez et al. (2022), who emphasize the independent impacts of environmental regulation and energy structure. This paper demonstrates that GTI achieves emission reductions and efficiency gains through two key pathways: regulatory reinforcement and structural optimization.
5.4 Robustness tests
5.4.1 Replacement of explained variables
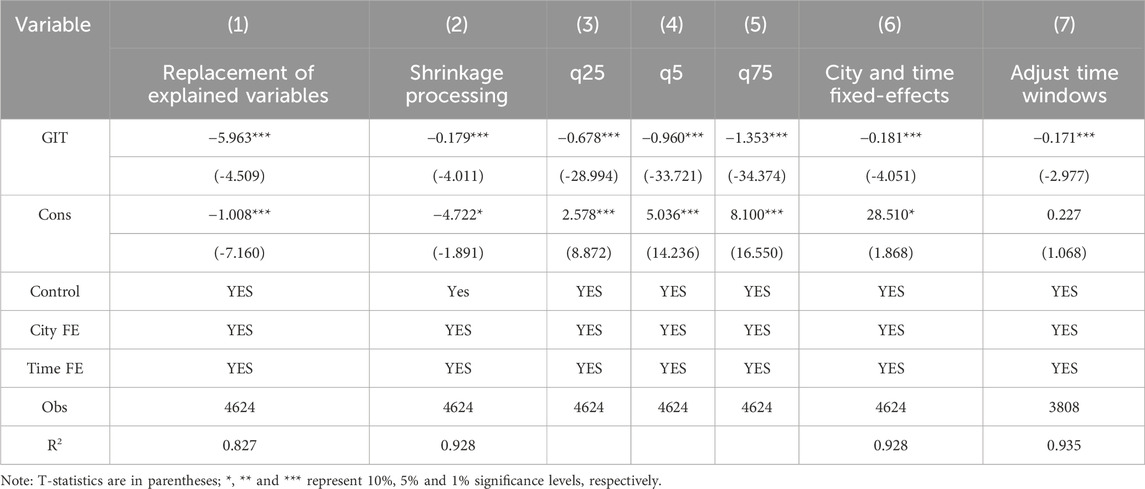
Consumers are the primary beneficiaries of production activities. Their consumption capacity and structure influence production and affect urban carbon emissions. Therefore, this paper follows the approach of Wu et al. (2024), using per capita carbon emissions as a proxy for carbon emissions to test the effect of GTI on carbon emission reduction. The regression results are presented in column (1) of Table 6. The regression coefficient of GTI remains significantly negative, confirming the robustness of the previous benchmark regression results.
5.4.2 Sample shrinkage processing
The sample data’s descriptive statistics show that each variable’s standard deviation is significant. To mitigate the impact of extreme values, the data undergo 1% shrinkage and are regressed again. The results in column (2) of Table 6 indicate that after sample shrinkage, the direction of GTI’s effect on carbon emissions remains at the 1% significance level, confirming the robustness of the regression results.
5.4.3 Quantile regression
To further investigate the trend in GTI’s impact on CEI at different stages, three specific quantile points (0.25, 0.5, 0.75) were selected using quantile regression. This method reflects the effect of GTI on carbon emissions at various development levels, as shown in Table 6, columns (3), (4), and (5). The results indicate a consistent and significant reduction in carbon emissions due to GTI at different quantile points, all of which pass the significance test.
5.4.4 Add individual and time fixed-effects
The time and region fixed-effects model is retested to eliminate the influence of time-varying factors and individual differences. In addition, it also controls for the differences caused by multidimensional shocks in different cities. The results in Table 6 show that the regression coefficient for GTI is −0.181, with a significance level of 1%. This confirms the robustness of the previous results.
5.4.5 Adjust time windows dynamically
At the beginning of 2020, the COVID-19 Pandemic Shock caused volatility in China’s economic development, so regressions are conducted using sample data from 2006 to 2019. The results in column (7) of Table 6 show that the coefficient of GTI is still significant at the 1% level, i.e., the previous benchmark regression result is robust.
5.5 Endogeneity treatment
5.5.1 Core explanatory variables lagged one period
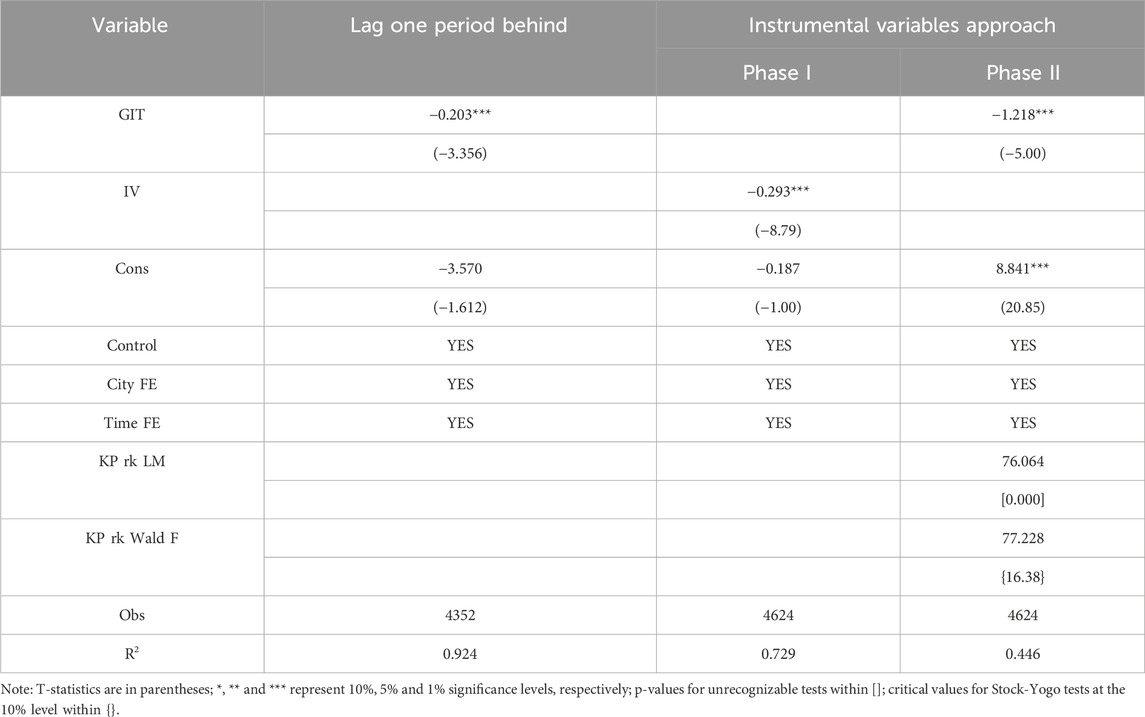
The GTI level in the previous period may affect current carbon emissions, as GTI can reduce emissions through long-term accumulation effects. Thus, following the approach of Yu (2023), the GTI level lagged by one period is selected for the robustness test based on time series principles. The results are shown in Table 7. It reveals that the regression coefficient of the lagged GTI level is −0.203, significantly negative at the 1% level. It confirms the robustness of the previous benchmark regression results.
5.5.2 Instrumental variables approach
A reverse causality may exist between GTI and CEI. Regions with lower emissions are often more inclined to promote green technology development. Therefore, this study selects terrain ruggedness (TR) as an instrumental variable for GTI. The rationale is that cities with complex topography often face spatial constraints, transportation challenges, and resource allocation problems. This makes them more inclined to technological innovation as a solution. Additionally, topography is a naturally occurring geographic feature, unaffected by contemporary economic activities or policies. It aligns with the principles of correlation and exogeneity for instrumental variables. Thus, the regression was performed using the two-stage least squares method. The results (see Table 7) show that the regression coefficient of GTI in the second stage is −1.218, which is significant at the 1% level. The Kleibergen-Paap rk LM statistic of the instrumental variable is 76.064 (p-value = 0.000), rejecting the hypothesis of non-identifiability. Meanwhile, the Kleibergen-Paap rk Wald F statistic exceeds the critical value at the 10% level of the Stock-Yogo weak identification test. This further supports the robustness of the benchmark regression result, indicating that GTI reduces urban CEI.
5.6 Heterogeneity test
Regional variations in GTI capacity arise due to differences in geographic environment, resource type, and economic development. Therefore, the heterogeneity effect of GTI on urban CEI is analyzed based on geographic location, resource type, and urban scale.
5.6.1 Geographic location heterogeneity
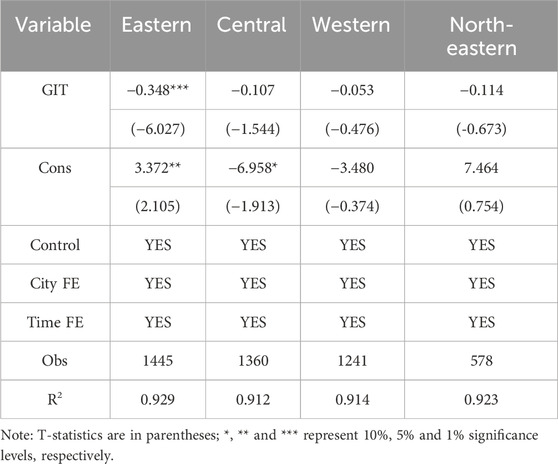
Based on the geographic location division of the National Bureau of Statistics, the sample cities were categorized into four regions (east, central, west, and northeast) for regression analysis. The results (see Table 8) show that, in the eastern region, the regression coefficient of GTI on carbon emissions is −0.348, significant at the 1% level. Additionally, the coefficients in the central, western, and northeastern regions are insignificant. This finding aligns with the heterogeneity analyses of Ran and Zhang (2023). This result is expected because the abatement effect in the eastern region arises primarily from the post-industrialization development stage and well-established innovation networks. In contrast, the central area is influenced by relevant strategies, with resource allocation more inclined to industrial transfer, resulting in insufficient investment in GTI (Wang Y et al., 2024). Unlike Zou et al. (2025), who argue that GTI in the central and western regions has significant potential for emission reduction, and Yang et al. (2024), who emphasize the resource advantages in the west. This study finds that the economy of the western region is highly dependent on resource extraction, leading to the “resource curse” effect, as shown in Su et al.’s (2024) study. Meanwhile, in contrast to Li et al.’s (2021) view that SOE reform in Northeast China enhances green innovation efficiency. This paper emphasizes that the high proportion of state-owned enterprises, low marketization, and severe cold climate hinder the effectiveness of GTI (Gao et al., 2022). It provides empirical support for the development of locally tailored low-carbon policies.
5.6.2 Resource types heterogeneity
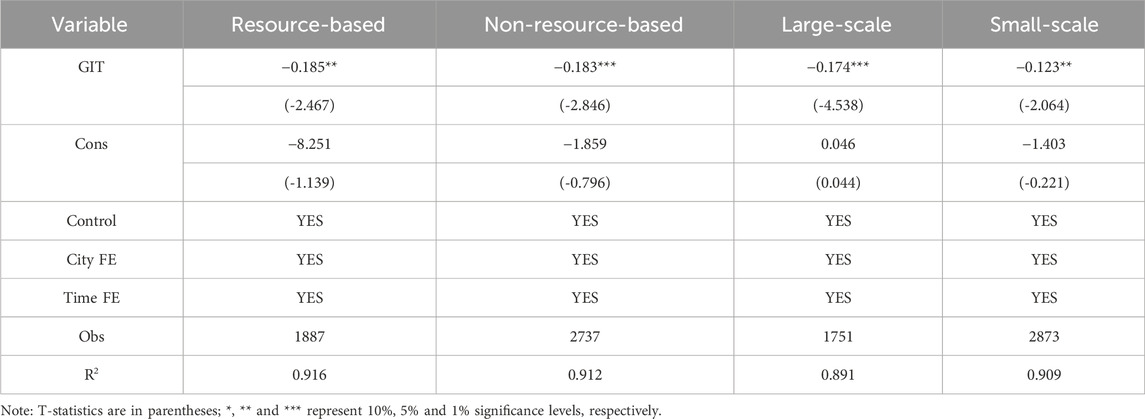
Resource-based cities represent a unique category in China’s urban development. Constrained by traditional industrial structures, these cities rely excessively on conventional industries. It hinders capacity in GTI. Based on the Central People’s Republic of China, resource-based cities are assigned a value of 1, while non-resource-based cities are assigned a value of 0. The results are presented in Table 9. The results indicate that, compared to resource-based cities, the carbon reduction effect of GTI is more pronounced in non-resource-based cities. The coefficient difference of 0.156 is statistically significant. This result aligns with Zhu et al. (2025), who found that non-resource-based cities perform better in green transitions due to stronger innovation capacity and industrial flexibility. Similarly, Hou et al. (2025) confirmed that the resource curse effect in resource-based cities hinders GTI. In contrast to Xu et al. (2021), who argue that financial and infrastructure advantages in resource-based cities promote green technology diffusion. This study finds that path dependence in resource-based cities weakens the carbon reduction effect of GTI. It highlights the constraining mechanism of resource type on the environmental impact of GTI.
5.6.3 Heterogeneity of city scale
Based on the National Bureau of Statistics, cities are classified as large-scale if their population exceeds 3 million and as small-scale if their population is less than 3 million. These cities were then regressed using the benchmark model (Equation 1). The results (see Table 9) show that the estimated regression coefficient for large-scale cities is −0.174, surpassing the 1% significance level. In contrast, although small-scale cities are significant, they are less effective than large cities in reducing CEI. The results of this heterogeneity analysis strongly align with existing literature, supporting Li et al. (2025), who found that GTI achievements in large cities can be applied to broader areas at lower unit costs. Promoting GTI in large cities leads to economies of scale and more significant emission reductions. Meanwhile, it also supports the theory of Zhu et al. (2024), who state that commercial demonstration effects are more significant, market demand is greater, and green innovations are more widely applied. However, most urban classifications use GDP or industrial structure as criteria, while this study categorizes cities based on population size, providing a new empirical perspective for research on urban scale heterogeneity.
6 Conclusion and policy implications
6.1 Conclusion
With the deepening of the dual-carbon goal and the innovation-driven development strategy, GTI has become a key driving force for urban low-carbon transformation. This paper examines 272 prefecture-level cities in China from 2006 to 2022 based on resource allocation and externality theories. The study applies a panel fixed-effect model and a chain mediation model to investigate the effect and path of CEI in cities empowered by GTI. The following key findings are obtained:
1. GTI can significantly reduce CEI. The conclusion holds even after replacing the explained variable, lagging the core explanatory variable by one period, and using the instrumental variable method.
2. The mechanism test shows that environmental regulation and energy consumption structure play independent and chain mediation roles between GTI and urban CEI. Specifically, GTI optimizes the energy consumption structure by improving the level of environmental regulation, ultimately achieving the goal of carbon reduction.
3. The heterogeneity results indicate that GTI significantly reduces CEI in the eastern region, non-resource-based and large-scale cities, compared to central and western areas, resource-based and small-scale cities.
6.2 Policy recommendations
Based on the above conclusions, the following recommendations are proposed:
Firstly, establishing a mechanism for green innovation entities to enhance the effectiveness of carbon reduction through technology. To achieve the dual-carbon goal, it is necessary to deepen the integration among industry, academia, and research. This includes creating a green technology transfer platform, reducing information barriers to technology diffusion, and promoting the adequate flow of green technologies among various innovation entities. Simultaneously, policy tools such as consumption subsidies and tax reductions should be used to raise consumer awareness and acceptance of green technologies. This would incentivize consumers to choose green products and services, thus creating stable market demand. Furthermore, mechanisms such as carbon trading and tax subsidies should be improved to internalize the positive externalities of GTI, thus enhancing corporate innovation incentives and achieving dual benefits for the environment and society. Additionally, an innovative insurance system needs to be established to address the negative externalities resulting from market failures. By improving risk-sharing mechanisms, the investment risks for innovation entities can be reduced, creating a favorable environment for GTI.
Secondly, environmental regulation policies should be strengthened to facilitate the energy structure and foster new urban carbon reduction activities. The study has shown that environmental regulation ensures the complete realization of GTI’s carbon reduction potential. Therefore, while developing green technologies, the government should strengthen the top-level design of environmental regulations. Based on the economic development level of each city, targeted environmental standards should be designed and effectively implemented. Furthermore, the energy consumption structure is a critical pathway for carbon reduction. Governments at all levels should leverage regional comparative advantages to accelerate energy-saving technology upgrades. They should guide the integration of green technologies into high-energy, high-pollution traditional sectors and drive the energy industry toward green and low-carbon development. Last but not least, the decisive role of the market in resource allocation must be emphasized. For high-carbon industries, strict emission standards and total volume control should be implemented. Market-based tools such as carbon trading and green finance should guide capital flow toward clean energy and low-carbon technologies, achieving synergies between environmental regulation and energy structure optimization and improving emission reduction efficiency.
Thirdly, implementing a region-specific development strategy and shaping a diverse environment for GTI. Given the different stages and characteristics of development in various cities, a new development paradigm should be established. It is characterized by clear features, complementary advantages, and efficient collaboration. Eastern cities should focus on accelerating the aggregation of green technology resources, optimizing energy supply and demand structures, and maximizing the diffusion of innovation outcomes to create regional demonstration effects. For central cities, it is essential to strengthen environmental regulations and leverage geographic proximity to diffuse eastern technologies. Meanwhile, the conversion rate of clean energy technologies should be improved, and cooperation with eastern cities should be enhanced. Although the GTI system in Western cities is relatively underdeveloped, the region is abundant in resources. Hence, the development strategy should focus on exploring renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Moreover, support for green finance, tax incentives, and other related policies should be intensified. The study also found that the carbon reduction effect of GTI is not significant in resource-based, small-scale cities. This indicates a path dependence in fossil-fuel-rich regions with high transformation costs. Therefore, a gradual environmental regulation strategy should be implemented, with transitional periods and phased targets. This approach would avoid the economic impact of one-size-fits-all environmental standards and enable green, low-carbon development.
7 Discussions
This paper provides relevant insights by analyzing the impact of GTI on CEI. However, there are some limitations in both the data and the conclusions. Firstly, the data primarily comes from urban statistical data in China. Due to data availability constraints, samples with many missing values were excluded. Furthermore, this study focuses on Chinese data, which may not fully reflect the effects of GTI emission reduction in different countries and regions. This limits the generalizability of the conclusions. Secondly, despite adopting the panel fixed-effect model, independent mediating effects, and chain mediation effects, these models still struggle to capture the dynamic relationship between GTI and CEI, particularly the long-term effects. Thirdly, in addition, as an empirical study at the macro level, this paper mainly relies on econometric analysis and lacks the corresponding mathematical model derivation to explore the theoretical transmission mechanism. Fourth, since the paper addresses urban carbon emission reduction, it is essential to consider whether policy changes, such as low-carbon pilot city policies, affect the impact of GTI on carbon reduction. The paper does not yet incorporate such a heterogeneity test.
Based on the limitations of this study, future research should incorporate data from more countries and regions. It will broaden data sources and improve the comprehensiveness of findings. Moreover, future studies should enrich relevant theories by constructing mathematical models and explaining the intrinsic mechanisms of GTI impacting CEI. Additionally, more complex models, such as GMM or time series approaches, can be introduced to capture the long-term dynamic relationship between GTI and CEI. Furthermore, it is crucial to explore the potential U-shaped nonlinear relationship or spatial spillover effects between GTI and CEI. Last but not least, future research should investigate whether the dominant industries or low-carbon pilot cities affect the relationship between GTI and CEI. By adopting these research methods, future studies are expected to more comprehensively reveal the mechanisms and effects of GTI on CEI under various policy environments and market conditions. It will enhance the validity and reliability of the research. We hope the above research directions can offer inspiration for further research in this field.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SL: Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – original draft. XC: Methodology, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Software, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Social Science Foundation Project of China (Grant No. 20BMZ110), Ningxia Natural Science Foundation Program (Grant No. 2023AAC03307) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 72561001).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ai, H., Tan, X., Zhou, S., Zhou, Y., and Xing, H. (2023). The impact of environmental regulation on carbon emissions: evidence from China. Econ. Anal. Policy 80, 1067–1079. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2023.09.032
Alexander, A., De Vito, A., and Menicacci, L. (2024). At what cost? Environmental regulation and corporate cash holdings. Financ. Res. Lett. 61, 104960. doi:10.1016/j.frl.2023.104960
Aybudak, H. G., Khalid, W., Usman, M., Seraj, M., Rafay, A., and Ali, Q. S. (2025). Assessing the impacts of economic growth, stringent environmental policies, renewable energy, and non-renewable energy on environmental sustainability in G-7 economies: insights from the Method of Moments Quantile Regression. Asia-Pacific J. Regional Sci. 9, 743–772. doi:10.1007/s41685-025-00388-4
Birol (2013). World energy outlook special report 2013: redrawing the EnergyClimate map. Paris, France: IEA. Available online at: https://www.iea.org/reports/redrawing-the-energy-climate-map.
Cao, J., and Xu, Y. (2023). Carbon emission reduction alliance, green technology, and emission reduction performance: an empirical study based on the synergistic perspective of environment and economy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (19), 55864–55883. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-25796-x
Che, S., Wang, J., and Chen, H. (2023). Can China’s decentralized energy governance reduce carbon emissions? Evidence from new energy demonstration cities. Energy 284, 128665. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.128665
Chen, X., and Jiang, Y. (2025). The effects of digitization and environmental regulation on energy consumption in China. Pol. J. Environ. Res. 34 (4), 3565–3575. doi:10.15244/pjoes/189370
Chen, X., and Wang, H. (2024). Do China’s ecological civilization advance demonstration zones inhibit fisheries’ carbon emission intensity? A quasi-natural experiment using double machine learning and spatial differencein-differences. J. Environ. Manage. 370, 122682. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122682
Chen F, F., Shao, M., Chen, W., and Wang, F. (2024). Environmental regulation, energy consumption structure, and industrial pollution emissions. Environ. Res. Commun. 6 (1), 015011. doi:10.1088/2515-7620/ad1ed5
Chen, H., Yi, J., Chen, A., Peng, D., and Yang, J. (2023). Green technology innovation and CO2 emission in China: evidence from a spatial-temporal analysis and a nonlinear spatial durbin model. Energy Policy 172, 113338. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113338
Chen L, L., Chen, D., Gong, N., and Qin, J. (2024). Assessing the influence of environmental regulation on carbon sequestration in China: towards a sustainable future. J. Environ. Manage. 368, 122177. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122177
Chhabra, M., Giri, A. K., and Kumar, A. (2023). Do trade openness and institutional quality contribute to carbon emission reduction? Evidence from BRICS countries. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 30 (17), 50986–51002. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-25789-w
Colombelli, A., D’Ambrosio, A., Le Masle, B., Ravetti, C., and Tubiana, M. (2025). Knowledge spillovers, green entrepreneurship and the demand for sustainability: evidence from Italian innovative startups. J. Technol. Transf., 1–26. doi:10.1007/s10961-025-10224-8
Cui, L., Ding, Y., and Li, X. (2022). Environmental regulation competition and carbon emissions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 20 (1), 736. doi:10.3390/ijerph20010736
Dai, W., Cheng, M., and Zheng, L. (2023). The effect exerted by environment regulation on industrial structure optimization: evidence of 286 China’s cities on the prefecture level. Heliyon 9 (5), e16406. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16406
Ding, X., Fu, Z., and Jia, H. (2019). Study on urbanization level, urban primacy and industrial water utilization efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 11 (23), 6571. doi:10.3390/su11236571
Esperon-Rodriguez, M., Tjoelker, M. G., Lenoir, J., Baumgartner, J. B., Beaumont, L. J., Nipperess, D. A., et al. (2022). Climate change increases global risk to urban forests. Nat. Clim. Change 12 (10), 950–955. doi:10.1038/s41558-022-01465-8
Fan, H., Pan, N., and Wu, T. (2023). Research on the effect of the development of digital economy on carbon emission reduction: empirical analysis based on 223 prefecture-level cities in China. J. Beijing Technol. Bus. Univ. Sci. 38 (03), 25–38. doi:10.12085/j.issn.1009-6116
Feng, W., Guo, B., and Yu, Y. (2025). The impact of green finance reform on industrial water pollution: evidence from innovation pilot zones in China. Water. Econ. Policy, 2440010. doi:10.1142/S2382624X24400101
Fragkiadakis, K., and Paroussos, L. (2021). Reducing the decarbonisation cost burden for EU energy-intensive industries. Energies 14 (1), 236. doi:10.3390/en14010236
Fu, L. (2010). An empirical research on industry structure and economic growth. Stat. Res. 27 (08), 79–81. doi:10.19343/j.cnki.11-1302/c.2010.08.011
Gao, P., Wang, Y., Zou, Y., Su, X., Che, X., and Yang, X. (2022). Green technology innovation and carbon emissions nexus in China: does industrial structure upgrading matter? Front. Psychol. 13, 951172. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.951172
Glaeser, E. L., and Kahn, M. E. (2010). The greenness of cities: carbon dioxide emissions and urban development. J. Urban Econ. 67, 404–418. doi:10.1016/j.jue.2009.11.006
Gu, W., Zhao, X., Yan, X., Wang, C., and Li, Q. (2019). Energy technological progress, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 236, 117666. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117666
Gu, G., Zheng, H., Tong, L., and Dai, Y. (2022). Does carbon financial market as an environmental regulation policy tool promote regional energy conservation and emission reduction? Empirical evidence from China. Energy Policy 163, 112826. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112826
Guo, L., and Tan, W. (2024). Analyzing the synergistic influence of green credit and green technology innovation in driving the Low-Carbon transition of the energy consumption structure. Sustain. Energy. Techn. 63, 103633. doi:10.1016/j.seta.2024.103633
Guo, L., Tan, W., Xu, Y., and Tang, Q. (2024). Curbing regional carbon emissions through green technology innovation: an empirical analysis in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain 27, 9477–9500. doi:10.1007/s10668-024-05243-8
Han, Y., and Shao, Y. (2022). Impact mechanisms of carbon emissions, industrial structure and environmental regulations in the Yellow River Basin. Pol. J. Environ. Res. 31 (6), 5693–5709. doi:10.15244/pjoes/152147
Haowei, C. (2025). Synergy effects of the energy quota trading system and carbon emissions trading system: a case study of China. Energy. Sustain. Dev. 87, 101733. doi:10.1016/j.esd.2025.101733
Hart, P. S., Campbell-Arvai, V., Wolske, K. S., and Raimi, K. T. (2022). Moral hazard or not? The effects of learning about carbon dioxide removal on perceptions of climate mitigation in the United States. Energy. Res. Soc. Sci. 89, 102656. doi:10.1016/j.erss.2022.102656
He, W., Chen, S., and Wu, Y. (2025). Green finance, green technology innovation, and carbon emission reduction. Environ. Res. Commun. 7 (4), 045018. doi:10.1088/2515-7620/adc905
Hou, M., Xie, Y., Lu, W., Cui, X., Xi, Z., and Han, Y. (2025). Green finance drives the synergy of pollution control and carbon reduction in China: dual perspective of effect and efficiency. Energy 330, 136873. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2025.136873
Hu, Y., and Tian, Y. (2024). The role of green reputation, carbon trading and government intervention in determining the green bond pricing: an externality perspective. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 89, 46–62. doi:10.1016/j.iref.2023.10.007
Hu, Y., and Wu, W. (2022). Spatiotemporal variation and driving factors of embodied carbon in China-g7 trade. Sustainability 14 (12), 7478. doi:10.3390/su14127478
Hu, L., and Xiong, P. (2024). How green technology innovation helps promote low-carbon transformation of manufacturing industry: based on the testing mediation effect of environmental regulation in the beijing-tianjin-hebei region. Ecol. Econ. 40 (12), 63–70.
Hu, J., Hu, M., and Zhang, H. (2023). Has the construction of ecological civilization promoted green technology innovation? Environ. Technol. Innov. 29, 102960. doi:10.1016/j.eti.2022.102960
Huang, H., Hong, J., Wang, X., Chang-Richards, A., Zhang, J., and Qiao, B. (2022). A spatiotemporal analysis of the driving forces behind the energy interactions of the Chinese economy: evidence from static and dynamic perspectives. Energy 239, 122104. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2021.122104
IEA (2013). World energy outlook 2013. Paris: IEA. Available online at: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2013.
Jiang, T., and Luo, Z. B. (2022). LOC102724163 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion by stimulating MUC19 expression. China Ind. Econ. 23 (05), 100–120. doi:10.3892/ol.2022.13220
Khanna, G., Liang, W., Mobarak, A. M., and Song, R. (2025). The productivity consequences of pollution-induced migration in China. Am. Econ. J. Appl. Econ. 17 (2), 184–224. doi:10.1257/app.20220655
Levine, R. (2005). Finance and growth: theory and evidence. Handb. Econ. growth 1, 865–934. doi:10.3386/w10766
Li, S., and Guo, Y. T. (2024). Impact of new quality productivity on the high quality development of private enterprises:based on the chain multiple mediation model. J. North Minzu Univ. Soc. Sci. (05), 168–176. doi:10.20076/j.cnki.64-1065/G4.2024.05.018
Li, C., Wang, Y., and Wang, L. (2024). Guided by the goal of “double carbon”. what is carbon Emiss. Reduct. Eff. Promot. Appl. green Technol. China? Environ. Res. 245, 117974. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.117974
Li, F., Xu, X., Li, Z., Du, P., and Ye, J. (2021). Can low-carbon technological innovation truly improve enterprise performance? The case of Chinese manufacturing companies. J. Clean. Prod. 293, 125949. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125949
Li, M., Hou, Y., Jia, Z., and Li, J. (2023). Role of green technological innovation in the green economic growth in China's natural resource markets. Resour. Policy. 86, 104187. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.104187
Li, J., Liu, X., and Shao, X. (2024). Collaborative carbon emission reduction in power supply and demand entities based on blockchain technology. Int. J. Elec Power. 157, 109840. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2024.109840
Li, J., Liu, Z., Li, X., and Guo, N. (2024). Research on the low-carbon effect of technological innovation. Environ. Policy 26 (9), 3127–3149. doi:10.1007/s10098-024-02787-1
Li, T., Li, G., Zeng, S., and Hao, Y. (2025). Towards a low-carbon economy: how can green technological innovation affect carbon productivity in China? J. Environ. Manage. 392, 126685. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.126685
Li, H., Su, Y., Ding, C. J., Tian, G. G., and Wu, Z. (2024). Unveiling the green innovation paradox: exploring the impact of carbon emission reduction on corporate green technology innovation. Technol. Forecast Soc. Change 207, 123562. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2024.123562
Li, Q., Qian, T., Wang, H., Bai, L., and Long, R. (2024). Environmental forcing and policy synergy: a multidimensional approach in the governance of air pollution and carbon emission. Environ. Res. 261, 119747. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2024.119747
Liang, L., Wang, Z., and Li, J. (2019). The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 237, 117649. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117649
Liao, B., and Li, L. (2022). Spatial division of labor, specialization of green technology innovation process and urban coordinated green development: evidence from China. Sustain. Cities. Soc. 80, 103778. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2022.103778
Lin, B., and Ma, R. (2022). Green technology innovations, urban innovation environment and CO2 emission reduction in China: fresh evidence from a partially linear functional-coefficient panel model. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change. 176, 121434. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121434
Lin, P., and Meng, N. (2020). Quality measurement and dynamic deconstruction of regional economic development in beijing-tianjin-hebei region under environmental constraints:from the perspective of green total factor productivity. Econ. Geo 40 (09), 36–45. doi:10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2020.09.004
Liu, X., Liu, X., Luo, X., Fu, H., Wang, M., and Li, L. (2020). Impact of different policy instruments on diffusing energy consumption monitoring technology in public buildings: evidence from Xi’an, China. J. Clean. Prod. 251, 119693. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119693
Liu, L., Wang, Z., and Zhang, Z. (2021). Matching-game approach for green technology investment strategies in a supply chain under environmental regulations. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 28, 371–390. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2021.06.001
Liu, H. Z., Yu, W. Q., and He, X. (2022). The impact of public transportation on carbon emissions—from the perspective of energy consumption. Sustainability 14 (10), 6248. doi:10.3390/su14106248
Liu, C., Xin, L., Li, J., and Sun, H. (2022). The impact of renewable energy technology innovation on industrial green transformation and upgrading: beggar thy neighbor or benefiting thy neighbor. Sustainability 14 (18), 11198. doi:10.3390/su141811198
Liu, L., Meng, Y., Wu, D., Ran, Q., Cao, J., and Liu, Z. (2023). Impact of haze pollution and human capital on economic resilience: evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 25 (11), 13429–13449. doi:10.1007/s10668-022-02625-8
Liu, H., Cai, X., Zhang, Z., and Wang, D. (2025). Can green technology innovations achieve the collaborative management of pollution reduction and carbon emissions reduction? Evidence from the Chinese industrial sector. Environ. Res. 264, 120400. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2024.120400
Lu, H., and Lu, Z. (2024). How does green technology innovation affect urban carbon emissions? Evidence from Chinese cities. Energy Build. 325, 115025. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2024.115025
Lu, Y., and Xia, Z. (2024). Digital inclusive finance, green technological innovation, and carbon emissions from a spatial perspective. Sci. Rep. 14, 8454. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-59081-9
Lu, M., Daixu, L., Peng, W., and Ruiqi, M. (2023). Heterogeneous environmental regulation tools and green economy development: evidence from China. Environ. Res. Commun. 5 (1), 015007. doi:10.1088/2515-7620/acb1f9
Ma, R., Li, F., and Du, M. (2022). How does environmental regulation and digital finance affect green technological innovation: evidence from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 928320. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.928320
Ma, L., Gao, J., and Li, Y. (2024). Digitalization empowering manufacturing enterprises to GreenTransformation and upgrade: green entrepreneurship orientationand GreenInnovationina chain mediation role. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy. 41 (17), 76–86. doi:10.6049/kjjbydc.2023010137
Manso, G. (2011). Motivating innovation. J. Financ. 66 (5), 1823–1860. doi:10.1111/j.1540-6261.2011.01688.x
Mi, L., Sun, Y., Qiao, L., Jia, T., Yang, Y., and Lv, T. (2021). Analysis of the cause of household carbon lock-in for Chinese urban households. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 18 (4), 2201. doi:10.3390/ijerph18042201
Miao, C., Chen, Z., and Zhang, A. (2024). Green technology innovation and carbon emission efficiency: the moderating role of environmental uncertainty. Sci. Total Environ. 938, 173551. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173551
Mongo, M., Belaid, F., and Ramdani, B. (2021). The effects of environmental innovations on CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy. 118, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2020.12.004
Porter, M. E. (1991). Towards a dynamic theory of strategy. Strateg. Manage J. 12 (S2), 95–117. doi:10.1002/smj.4250121008
Porter, M. E., and van der Linde, C. (1995). Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 9 (4), 97–118. doi:10.1257/jep.9.4.97
Pu, Z., Liu, J., and Yang, M. (2022). Could green technology innovation help economy achieve carbon neutrality development-evidence from Chinese cities. Front. Env. Sci. 10, 894085. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.894085
Rammer, C., Gottschalk, S., Peneder, M., Wörter, M., Stucki, T., and Arvanitis, S. (2017). Does Energy Policy hurt international competitiveness of firms? A comparative study for Germany, Switzerland and Austria. Energy Policy 109, 154–180. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2017.06.062
Ran, C., and Zhang, Y. (2023). The driving force of carbon emissions reduction in China: does green finance work. J. Clean. Prod. 421, 138502. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138502
Rennings, K., and Rammer, C. (2011). The impact of regulation-driven environmental innovation on innovation success and firm performance. Ind. Innov. 18 (3), 255–283. doi:10.1080/13662716.2011.561027
Romero-Lankao, P., Gurney, K. R., Seto, K. C., Chester, M., Duren, R. M., Hughes, S., et al. (2014). A critical knowledge pathway to low-carbon, sustainable futures: integrated understanding of urbanization, urban areas, and carbon. Earth's Future. 2 (10), 515–532. doi:10.1002/2014EF000258
Rong, J., Hong, J., Guo, Q., Fang, Z., and Chen, S. (2023). Path mechanism and spatial spillover effect of green technology innovation on agricultural CO2 emission intensity: a case study in Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 157, 111147. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111147
Song, J., Li, M., Wang, S., and Ye, T. (2022). To what extent does environmental regulation influence emission reduction? Evidence from local and neighboring locations in China. Sustainability 14 (15), 9714. doi:10.3390/su14159714
Struben, J., Lee, B. H., and Bingham, C. B. (2020). Collective action problems and resource allocation during market formation. Strateg. Sci. 5 (3), 245–270. doi:10.1287/stsc.2020.0105
Su, Y., Liu, M., Deng, N., Cai, Z., and Zheng, R. (2024). Rural digital economy, agricultural green technology innovation, and agricultural carbon emissions-based on panel data from 30 provinces in China between 2012 and 2021. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 33 (6). doi:10.15244/pjoes/184630
Suki, N. M., Suki, N. M., Afshan, S., Sharif, A., and Meo, M. S. (2022). The paradigms of technological innovation and renewables as a panacea for sustainable development: a pathway of going green. Renew. Energy 181, 1431–1439. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2021.09.121
Tang, W., and Zhou, Q. (2025). Can green financial policy drive urban carbon unlocking efficiency? A causal inference approach based on double machine learning. Front. Environ. Sci. 13, 1608475. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2025.1608475
Tang, Y., Hu, Y., and Cui, A. (2025). Research on the synergistic effects of market-oriented environmental regulations on pollution and carbon emission reduction. J. Environ. Manage. 380, 125115. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.125115
Tian, P., Wu, Y., Shang, B., Qi, C., Xu, Z., Li, G., et al. (2025). LCA as a decision support tool for the environmental improvement of organic fraction of municipal solid waste composting in China. J. Clean. Prod. 495, 145068. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.145068
Wang, Y., and Ullah, S. (2024). Effects of digitalization on energy security risk: do financial development and environmental trade matter? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31 (1), 249–261. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-31055-w
Wang, S., and Yi, X. (2023). Can the financial industry “anchor”carbon emission reductions? the mediating and moderating effects of the technology market. Energy Environ. 34 (3), 533–559. doi:10.1177/0958305X211061810
Wang, M., Cheng, Z., Li, Y., Li, J., and Guan, K. (2020). Impact of market regulation on economic and environmental performance: a game model of endogenous green technological innovation. J. Clean. Prod. 277, 123969. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123969
Wang, N., Yu, H., Shu, Y., Chen, Z., and Li, T. (2022). Can green patents reduce carbon emission intensity? an empirical analysis based on China’s experience. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 1084977. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.1084977
Wang, B., Chen, H., Ao, Y., and Liao, F. (2023). Spatiotemporal differentiation and influencing factors of green technology innovation efficiency in the construction industry: a case study of chengdu–chongqing urban agglomeration. Buildings 13 (1), 73. doi:10.3390/buildings13010073
Wang, Y., Qu, X., Zhang, H., Wang, K., Qu, Z., Li, N., et al. (2025). Dual environmental regulation and carbon emission reduction in pig breeding industry: synergistic effect or crowding-out effect? Evidence from China. Agriculture 15 (7), 787. doi:10.3390/agriculture15070787
Wang, H. J., Zheng, M. Q., Yin, H. T., and Chang, C. P. (2024). Green innovation, industrial structure and urban eco-efficiency in Chinese cities. Econ. Anal. Policy 82, 1011–1024. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2024.04.028
Wang, Q., He, Z., and Liu, T. (2024). Assessment of carbon emission reduction potential in new-type urbanization policy: a perspective on carbon rebound effect. Urban Anal. City Sci. 52 (6), 1498–1516. doi:10.1177/23998083241301855
Wang, Y., Zhao, Z., Shi, M., Liu, J., and Tan, Z. (2024). Public environmental concern, government environmental regulation and urban carbon emission reduction—analyzing the regulating role of green finance and industrial agglomeration. Sci. Total Environ. 924, 171549. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171549
Wei, W., and Ma, Y. (2024). The impact of green technology innovation on carbon emission reduction capacity in China: based on spatial econometrics and threshold effect analysis. PloS One 19 (12), e0310208. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0310208
Wu, J., and Yu, Z. (2025). The impact of market-based environmental regulation on carbon emission intensity: an analysis based on policy texts. Sustainability 17 (2), 465. doi:10.3390/su17020465
Wu, W., Cai, H., Liu, J., and Qin, Z. (2023). Dual effects of technological innovation and green transformation and upgrading of heavily polluting industries —from the perspective of carbon emissions. Res. Econ. Manage. 44 (11), 45–61. doi:10.13502/j.cnki.issn1000-7636.2023.11.003
Wu, K., Geng, Y., and Guo, T. (2024). The impact of green technology innovation on carbon emissions from the perspective of urban agglomeration: the moderating effect of human capitals. J. Nat. Resour. 39 (09), 2121–2139. doi:10.31497/zrzyxb.20240907
Xu, J., and Chen, Z. (2024). The effect of green technology innovation on carbon emission: an analysis based on nonlinear mediating effects and moderating effects. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 41 (08), 22–32. doi:10.6049/kjjbydc.H202307149
Xu, L., Fan, M., Yang, L., and Shao, S. (2021). Heterogeneous green innovations and carbon emission performance: evidence at China's city level. Energy Econ. 99, 105269. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105269
Xu, Y., Li, J., and Zhong, S. (2022). Can green technology innovation alleviate the regional energy dilemma? Evidence from 30 provinces in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 980519. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.980519
Xuan, V. N., Thu, N. T. P., and Hoa, P. X. (2024). Carbon dioxide emissions, population, foreign direct investment, and renewable energy nexus: new insights from Thailand. Energy Rep. 11, 4812–4823. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2024.04.045
Yang, A., Yang, M., Zhang, F., Kassim, A. A. M., and Wang, P. (2024). Has digital financial inclusion curbed carbon emissions intensity? Considering technological innovation and green consumption in China. J. Knowl. Econ. 15 (4), 19127–19156. doi:10.1007/s13132-024-01902-3
Yang, S., Wang, J., Dong, K., and Jiang, Q. (2023). A path towards China’s energy justice: how does digital technology innovation bring about a just revolution? Energy Econ. 127, 107056. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107056
Yang, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, T., Jia, Z., and Jia, W. (2023). “MOVES-based carbon emissions reduction measurement for urban green wave Traffic,” in In CICTP, 158–167. doi:10.1061/9780784484869.016
Yin, K., Liu, L., and Gu, H. (2022). Green paradox or forced emission reduction—the dual effects of environmental regulation on carbon emissions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 19 (17), 11058. doi:10.3390/ijerph191711058
Yong, C., Hu, W., and Wang, H. (2023). Factors influencing carbon emissions in high carbon industries in the zhejiang province and decoupling effect analysis. Sustainability 15 (22), 15975. doi:10.3390/su152215975
Yu, X. (2023). The nonlinear effect of green technological innovation on green transformation. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 40 (08), 22–31. doi:10.6049/kjjbydc.2022110240
Yu, H., Liao, L., Qu, S., Fang, D., Luo, L., and Xiong, G. (2021). Environmental regulation and corporate tax avoidance: a quasi-natural experiments study based on China’s new environmental protection law. J. Environ. Manage. 296, 113160. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113160
Zeng, F., Yan, L., and Tan, Y. (2022). Consequences and drivers of differentiated environmental regulation policies on hog production in China: a spatial econometrics approach. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 845147. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.845147
Zhang, J., and Chen, S. (2021). Financial development, environmental regulations and green economic transition. J. Finance Econ. 47 (11), 78–93. doi:10.16538/j.cnki.jfe.20210918.301
Zhang, X., and Fan, D. (2024). Is multi-pronged better? Research on the driving effect of the combination of environmental regulation in mining cities. J. Clean. Prod. 436, 140689. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.140689
Zhang, D., and Hussain, H. I. (2021). Nexus between fiscal imbalance and emissions reduction: new evidence from developing economies. J. Environ. Manage. 297, 113360. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113360
Zhang, Y., and Xu, X. (2022). Carbon emission efficiency measurement and influencing factor analysis of nine provinces in the Yellow River basin: based on SBM-DDF model and Tobit-CCD model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29 (22), 33263–33280. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-18566-8
Zhang D, D., Zhao, M., Wang, Y., Vigne, S. A., and Benkraiem, R. (2024). Technological innovation and its influence on energy risk management: unpacking China’s energy consumption structure optimisation amidst climate change. Energy Econ. 131, 107321. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2024.107321
Zhang, Q., Gu, B., Zhang, H., and Ji, Q. (2023). Emission reduction mode of China’s provincial transportation sector: based on “Energy+” carbon efficiency evaluation. Energy Policy 177, 113556. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2023.113556
Zhang, Y., Liu, X., and Yang, J. (2024). Digital economy, green dual innovation and carbon emissions. Sustainability 16 (17), 7291. doi:10.3390/su16177291
Zhang, H., Qi, R., Liu, Y., Wang, T., Zhong, F., Zhou, Q., et al. (2024). The spatial impact of digital economy on carbon emissions reduction: evidence from 215 cities in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 12, 1370938. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2024.1370938
Zhang, Y., Cui, X., and Liu, L. (2024). Environmental regulation, green technology progress and haze reduction and carbon reduction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 31 (25), 36367–36383. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-29903-w
Zhang, Z., Luo, X., Du, J., and Xu, B. (2024). Substantive or strategic: government R&D subsidies and green innovation. Financ. Res. Lett. 67, 105796. doi:10.1016/j.frl.2024.105796
Zhao, S., Cao, J., Sui, Y., and Liu, M. (2025). Digital transformation of construction enterprises and carbon emission reduction: evidence from listed companies. Front. Environ. Sci. 13, 1570182. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2025.1570182
Zhu, P. H., and Zhang, K. (2023). How does income and green technology innovation influence the emissions reduction effect of renewable energy: evidence from Chinese provincial data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (29), 74056–74069. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-27677-9
Zhu, Y., Xu, Y., and Yin, S. (2024). How does digital technology innovation drive synergies for reducing pollution and carbon emissions? Sustain Cities Soc. 116, 105932. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105932
Zhu, X., Che, J., Niu, X., Cao, N., and Liu, M. (2025). Study on the effect of technological innovation on carbon emission intensity in 278 prefecture-level cities in China. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 14917–17. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-99370-5
Keywords: green technology innovation, carbon emissions, energy consumption structure, environmental regulation, chain mediation effect
Citation: Li S and Cao X (2025) Can green technology innovation empower urban carbon mission reduction? Evidence from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1616667. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1616667
Received: 23 April 2025; Accepted: 29 August 2025;
Published: 22 September 2025.
Edited by:
Saige Wang, University of Science and Technology Beijing, ChinaReviewed by:
Bingnan Guo, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, ChinaEyob Mulat-Weldemeskel, London Metropolitan University, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Li and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Cao, c3VwZXIwODA5MTZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Su Li
Su Li Xin Cao
Xin Cao