- 1School of Accounting, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, Wu’han, China
- 2Bryant University - BITZH, Zhuhai, China
Introduction: Reducing carbon emission intensity is a crucial element in advancing sustainable development in China. In the context of continuous technological progress, the expansion of the digital economy may provide avenues for emissions reduction.
Methods: This paper constructs an index to measure digital economy progress using the entropy approach, based on data from 30 Chinese provinces from 2010 to 2024. Panel data regression models are then applied to examine the relationship between digitalization and carbon emission intensity, along with the mediating mechanisms involved.
Results: Baseline regression estimates suggest that both the overall digital economy index and its three core sub-components (with coefficients of −1.801, −7.784, −6.904, and −3.165, respectively) are associated with declines in carbon emission intensity, pointing to a potential mitigating effect. Considerable regional heterogeneity is observed, with the eastern and central regions exhibiting a more pronounced and statistically significant negative association, while the effect appears weaker and statistically insignificant in the western region.
Discussion: Further analysis of mediating pathways indicates that improvements in economic structure and innovation capacity may serve as channels through which digital economy development contributes—albeit to varying degrees—to reducing carbon emission intensity.
1 Introduction
Since the 1860s, when the industrial revolution occurred, enormous volumes of carbon dioxide have been emitted into the atmosphere by human activity. This has sparked a series of global environmental issues, posing significant challenges to human survival and development (Acheampong, 2018). Firstly, the greenhouse effect has gotten stronger due to the significant rise in carbon dioxide. Secondly, it has led to the frequent occurrence of extreme weather events, including high temperatures, severe cold spells, snowstorms, and typhoons. Thirdly, it has sped up the melting of polar ice, which has caused sea levels to increase steadily and endangering coastal communities and their residents. In response to environmental challenges linked to carbon output, several global entities—including the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)—have undertaken efforts aimed at promoting discussions and cooperative engagement among governments regarding potential strategies for emission reduction (Zhang et al., 2024a).
In response to the worldwide movement supporting low-carbon and green transformation, China, being a nation with the highest carbon emissions and the second-largest economy in the world, introduced its “3060” dual-carbon objective at the 75th United Nations General Assembly in September 2020. Reinforcing its previously stated intentions, China announced in December 2020 a goal to lower the intensity of its carbon emissions by more than 65% compared to 2005 levels by the year 2030—a target that, while notable, aligns with broader international trends and expectations (Chen et al., 2022b; Zhu and Lan, 2023). It follows, that accelerating China’s transition to a low-carbon economy is of critical importance to achieving those aims.
China has aggressively implemented successful policies and initiatives to lower its carbon emission intensity (Liu et al., 2022), but encounters a range of obstacles in pursuing its carbon intensity objectives, particularly those related to reaching peak emissions and progressing toward long-term carbon neutrality (Guan et al., 2018; Qian et al., 2022). A promising strategy for balancing environmental objectives with economic growth is the development of the digital economy (Li et al., 2023). The acceleration of industrial digitalization and digital industrialization has become essential in the digital age. One crucial method for nations to secure a competitive edge in the global market is by advancing their digital economies (Nathan and Rosso, 2015; Wang and Chen, 2023). Emerging as a new economic form, digital economy has become a new growth point, new driving force, and novel opportunity for China’s future economic development (Pan et al., 2022). The environmental impact of the digital economy has sparked considerable debate within the academic community. At the micro level, the digital economy can enhance the diffusion of low-carbon digital technologies, accelerate the adoption of green and clean energy solutions, and foster the transformation and development of green, low-carbon enterprises, thereby contributing to a reduction in carbon emission intensity. From a macro perspective, it can also reduce carbon emissions at a regional level, supporting green and low-carbon development through various mechanisms such as industrial restructuring, green technological innovation, optimization of resource allocation, and improvements in energy efficiency (Tang et al., 2021). In sum, when compared to traditional economic models, the digital economy offers innovative methods and tools for energy management by integrating advanced information technologies, which ultimately reduce overall energy emissions. In addition, as the largest developing country, China’s efforts and explorations in decarbonization and green transformation can provide meaningful practical experience for other developing countries. All in all, it is essential to study the impact of China’s digital economy development on carbon emission intensity.
Managing a gradual decline in carbon emission intensity presents an ongoing difficulty amid efforts to balance peak emissions, long-term neutrality goals, and the pursuit of higher-quality economic growth (Lange et al., 2020; Yuan et al., 2021). This paper investigates the possible role of digital economic development in moderating carbon emissions, providing a comprehensive analysis of the mechanisms via which digitalisation may affect emission intensity. Additionally, variations in attitudes and initial conditions for digital economy development among regions, coupled with pronounced spatial disparities in China’s economic, lead to notable regional divergences in the relationship between the digital economy and carbon emissions and their reciprocal influences (Liu X. et al., 2024; Sun et al., 2025). A thorough examination of carbon emissions in the Chinese digital economy, including regional heterogeneity analysis, is essential for a more profound knowledge of the subject.
The global economic landscape is experiencing gradual adjustments and structural shifts in the context of ongoing scientific innovation and industrial evolution. Luo et al. (2023) assert that the digital economy is increasingly pivotal in transitioning from conventional growth drivers to new sources of economic dynamism. Currently, a lot of nations are giving this shift priority by designating the digital economy as a national strategic project and stepping up measures to support its growth (Zhao et al., 2022; Han et al., 2022). China is turning its attention from merely encouraging economic growth to boosting development, and the digital economy is becoming a significant approach (Wang et al., 2022).
This research aims to investigate the potential correlation between the expansion of the digital economy and fluctuations in carbon emission intensity. Firstly, in-depth understanding of the development overview of the digital economy plays an important role in the construction of a comprehensive evaluation index system. Based on the constituent elements of the digital economy, we disaggregate the indicator into three components, mainly including the foundation, the scope of application and the prospects for development of digital economy, to form an integrated and comprehensive evaluation framework, which helps to comprehensively understand the composition and extension of the digital economy. Secondly, this study examines the possible impact of a composite digital economy development index and its three sub-components on carbon emission intensity, while conducting a series of robustness checks to evaluate the stability of the findings. Thirdly, it examines regional differences by comparing how the digital economy may relate to emission intensity across eastern, central, and western areas, offering preliminary insights that could assist local policymakers in considering region-specific strategies for low-carbon development. Lastly, the investigation examines potential pathways via which the digital economy may influence carbon emission intensity, taking into account mediating factors such as energy composition and innovation capacity.
The structure of the paper is arranged as follows. Section 2 offers a concise review of relevant literature. Section 3 outlines the theoretical foundation and introduces the proposed hypotheses. Section 4 details the data sources and the criteria for variable selection. Section 5 discusses the empirical findings based on the analysis. Finally, Section 6 summarizes the key observations and reflects on their broader implications.
2 Literature review
2.1 Review of previous studies
Given the rising significance of environmental issues, scholarly interest in the possible environmental consequences of the digital economy has consistently increased. Existing research has addressed a range of issues, including the determinants influencing carbon emission intensity (Marbuah et al., 2021; Li et al., 2021; Rodríguez and Pena-Boquete, 2017; Li and Zhou, 2024), as well as the underlying mechanisms through which such impacts may occur (Zhang et al., 2022; Wang X. et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2022). Additionally, several studies have explored spatial spillover dynamics, further enriching the understanding of regional interactions (Yi et al., 2022; Bai et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2023; Cheng et al., 2023; Tao et al., 2023).
With regard to economic determinants, in addition to the traditionally emphasized role of overall economic development (Murshed et al., 2022; Adebayo and Ullah, 2023), a growing body of research has begun to explore how digital transformation may be associated with carbon emission outcomes. Some studies indicate that improvements in digital infrastructure and related technologies may contribute to reductions in carbon emission intensity, though the extent of this relationship varies across contexts (Yu et al., 2024b; Li and Zhou, 2024; Khan and Hou, 2021). Moreover, certain findings suggest that the mitigating influence of the digital economy on emissions appears more evident in parts of central and western China (Gao and He, 2024; Liu X. et al., 2024). In parallel, international trade and financial development have also been examined for their dual roles, potentially acting either in support of or as alternatives to digitalization in limiting emissions (Ibrahim, 2018). In addition, previous research has established a unidirectional causal link from energy use to economic growth, further complicating the dynamics between development and environmental performance (Acheampong, 2018).
Regarding institutional factors, previous research has identified structural components, such as industrial composition (Liao and Liu, 2024; Chang et al., 2023) and the energy structure (Gigova et al., 2019; Wang and Chen, 2023; Li et al., 2025), as significant determinants of carbon emission intensity. Numerous scholars have shown that alterations in industrial structure and enhancements in the energy mix can substantially reduce urban carbon emissions (Chen et al., 2022a; Zhang et al., 2024b). Nevertheless, the magnitude of this effect significantly differs across various geographies (Zhang et al., 2022). For instance, Jiang et al. (2023) noted that the more economically advanced eastern regions incur higher abatement costs for the same level of emissions reduction than the less developed central and western provinces. Moreover, Liu M. et al. (2024) suggested that government involvement may reinforce the influence of digital economic development in moderating carbon intensity, potentially contributing to the broader process of transitioning toward lower-carbon urban systems.
Additionally, technological innovation is also a focus of attention in the established literature. Relevant studies have shown that innovation capacity has a direct and significant carbon intensity suppression effect (Mngumi et al., 2024; Wang Q. et al., 2023; Adebayo et al., 2023; Ahmed et al., 2022; Ren et al., 2021). For example, Ma et al. (2022) discovered that investment in research and development (R&D) not only lowers carbon emissions but also acts as a moderating factor between digitization and CO2 emissions, with technological advancement playing a similar role. Acheampong and Boateng (2019), by developing an artificial neural network to analyse the factors influencing carbon intensity, identified R&D expenditures as the most influential factor on carbon emission intensity in certain countries. Utilizing the quantile autoregressive distributed lag model, Wang et al. (2025a) demonstrated technological innovation is a more influential catalyst for promoting sustainability at most quantiles. Similarly, Wang et al. (2025b) proved that artificial intelligence contributes to an uptick in carbon emissions on account of the necessary digital infrastructure, while playing a pivotal role in aiding the realization of carbon neutrality over long term.
2.2 Research gap and contributions
Through a synthesis of the existing literature, it is evident that substantial research has been conducted on digital economy, carbon emissions, and the impact of the digital economy on carbon emissions, providing a solid theoretical foundation for this study. However, current research still faces several limitations: (1) There has been no uniformity index system in the quantitative research literature, and it is important to measure the current state of digital economy development through an appropriate index. (2) Past studies analyzed the role of energy structure and innovation capacity in the impact of digital economy development on carbon emission intensity separately, lacking integrated assessment of their complex mechanisms. (3) Although some studies have explored the spatial spillover effects of the digital economy, regional variations in this effect remained understudied, with insufficient recommendations for sustainability development strategies.
Against this backdrop, this study seeks to address the following three gaps in the existing literature: (1) Based on the constituent elements of the digital economy, we establish the digital economy index from three dimensions: the digital foundation, the digital technology development, and the digital industry development, providing a comprehensive evaluation framework for measuring digital economy development. (2) This study incorporates digital economy, carbon emission intensity, energy structure and innovation capacity into a unified research framework, exploring the mediating role of energy structure and innovation capacity, and clarifying them on the effects of digital economy development on carbon emission intensity, which enriches the mechanism study. (3) This study examines heterogeneous impacts across Chinese provinces, focusing on the regional coordination effects of the digital economy in facilitating carbon reduction, which provides empirical evidence to support collaborative mitigation strategies, as well as a valuable reference for the scientific formation of carbon emission reduction policies.
3 Theoretical analysis and hypothesis formulation
3.1 Digital economy and carbon emission intensity
As an emerging component of economic activity, the digital economy has gradually contributed to revitalizing aspects of China’s economic growth and has been increasingly recognized for its potential relevance to advancing low-carbon development efforts (Song et al., 2022).
From a macroeconomic perspective, the digital economy—propelled by emerging technologies such as big data and artificial intelligence—has been linked to initiatives aimed at advancing the digital transformation of urban infrastructure (Yang et al., 2021). This transition may contribute to more coordinated energy use and, potentially, to reductions in overall carbon emission intensity.
At the meso level, advancements in the digital economy may contribute to adjustments in the industrial structure, potentially supporting a shift toward greater efficiency and sustainability. In this context, digitalisation may enable the progressive transformation of conventional sectors and promote the expansion of nascent low-carbon industries, and thereby play a role—albeit indirectly—in moderating carbon emission intensity.
At the micro level, firms may utilize digital platforms to improve resource allocation, which can potentially enhance operational efficiency and reduce the likelihood of energy misallocation, thereby contributing to lower carbon intensity. Additionally, the digital economy may support the diffusion of technologies across industries, indirectly encouraging upgrades in equipment and gradual improvements in energy efficiency (Freire-González et al., 2017).
Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes research hypothesis 1:
H1
The digital economy has a significant inhibitory effect on carbon emission intensity.
3.2 The regional heterogeneity impacts of the digital economy development on carbon emission intensity
In the context of the digital economy, regional economic theory—which seeks to explain the patterns and drivers of spatial economic development—may offer a useful lens through which to examine strategies aimed at moderating carbon emission intensity across regions.
Firstly, agglomeration economy theory posits that firms and industries with shared characteristics often gravitate toward geographic concentration, enabling the formation of interlinked industrial networks and fostering collaborative dynamics. Such spatial clustering may facilitate efficiency gains and incremental innovation, which can gradually support the modernization of regional economic structures. These developments, under certain conditions, have the potential to contribute to a reduction in carbon emission intensity.
Secondly, modern economic geography theory emphasizes the spatial organization of economic activity, focusing on how trade flows, labor mobility, and regional development patterns shape agglomeration effects across cities and regions. From this perspective, the new economic geography framework suggests that developments associated with the digital economy—particularly those driven by advances in information and communication technologies—may indirectly support improvements in energy efficiency and contribute to more sustainable patterns of urban and regional growth. These dynamics could, under specific conditions, be linked to a moderation in carbon emission intensity.
Thirdly, given the vastness of China’s territory, substantial regional disparities can be found in the economic development levels, resource endowments, and the degree of development of the digital economy. The eastern region is generally more developed than the central and western regions, exhibiting higher levels of industrialization and urbanization. These developmental disparities have resulted in a greater maturity of the digital economy, energy efficiency, and green technologies in the eastern region, which has established relatively advanced infrastructure and innovation systems for the digital economy. Such advancements contribute to enhanced energy efficiency and a reduction in carbon emissions. In contrast, the central and western regions are still in the early stages of digital transformation, and, as a result, the carbon emission reduction benefits of the digital economy are less pronounced compared to those in the eastern regions. Both the digital economy and carbon emission levels demonstrate considerable regional heterogeneity. Consequently, the carbon emission reduction effects associated with the digital economy are also likely to exhibit regional variation.
Therefore, the evolution of the digital economy is intricately linked to a region’s economic framework and developmental status. More developed regions typically exhibit elevated levels of digitisation, hence expediting the expansion of the digital economy, whereas less developed areas often lag behind in this aspect (Shen et al., 2021). Furthermore, the digital economy may indirectly affect carbon emission intensity through various interconnected channels. These include facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources, enhancing energy-use efficiency, and contributing to the gradual refinement of energy management systems (Thompson et al., 2013). Additionally, local governments can introduce a range of policies to support digital economy growth, including encouraging clean energy technologies and strengthening carbon emissions trading systems to foster sustainable regional economic development (Cai et al., 2024). Jiang et al. (2024) also emphasize that subsidizing renewable energy and implementing carbon pricing are among the most effective strategies for achieving carbon neutrality.
Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes research hypothesis 2:
H2
There is regional heterogeneity in the impact of the digital economy development on carbon emission intensity.
3.3 Digital economy, energy structure and carbon emission intensity
The optimization of energy structures is made possible in large part by the digital economy. First and foremost, its advancement provides a framework and technological support for the investigation and application of novel energy sources. Leveraging digital technology enables the efficient management and utilization of renewable energy resources, thereby stimulating their development and deployment. Moreover, the applications of the digital economy enable businesses to improve their energy management practices while promoting energy conservation and enhancing efficiency by optimizing production and transportation processes (Kennedy, 2022). For example, with the use of data analysis and predictive technologies, companies can monitor and fine-tune their energy consumption, ultimately increasing overall energy efficiency.
Additionally, adjustments in the composition of energy sources can contribute to moderating carbon emission intensity. Reducing reliance on coal while gradually increasing the proportion of cleaner alternatives—such as natural gas, nuclear power, and various renewable energies including hydropower, solar, and wind—can support this transition. Expanding the role of these energy types within the overall consumption mix may help lessen dependence on traditional fossil fuels. The incorporation of sophisticated and efficient energy technology can enhance energy conversion and utilisation, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and related emissions.
Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes research hypothesis 3:
H3
The digital economy reduces carbon emission intensity by optimizing the energy structure.
3.4 Digital economy, innovative capacity and carbon emission intensity
The advancement of the digital economy may facilitate the incremental improvement of regional innovation capacity. The increasing adoption of digital technologies can streamline information acquisition processes within enterprises, potentially improving their ability to respond to shifts in market conditions, industry dynamics, and consumer preferences. In parallel, digital infrastructure may indirectly encourage firms to pursue innovation. Technologies such as virtual reality and artificial intelligence, for example, could lower some of the costs and uncertainties associated with research and development, thus offering new avenues for experimentation. Additionally, the utilisation of digital tools—such as remote work systems and digital documentation—may assist in promoting innovation at the regional level.
On the other hand, increased innovation capacity contributes to reduce carbon emission intensity. Firstly, bolstered innovation capacity can engender more efficient, energy-saving, and environmentally sustainable production and management methodologies. By integrating advanced production technologies, refining production processes, and enhancing product design, it facilitates the more effective utilization of energy and resources, consequently reducing carbon emission intensity. Secondly, innovation capacity stimulates the advancement and adoption of clean energy technologies, thereby diminishing carbon emission intensity through increased clean energy usage. Moreover, it offers enterprises access to lower-cost and more sustainable energy supplies. Finally, innovation capacity encourages cooperation and cooperative innovation across businesses, consequently generating more favorable conditions for the gradual development and commercialization of low-carbon technology and products, which may lead to a moderate reduction in overall carbon emissions and intensity over time.
Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes research hypothesis 4:
H4
The digital economy reduces carbon emission intensity by enhancing innovation capacity.
4 Data
4.1 Dependent variable
This study examines carbon emission intensity (CEI), defined as the ratio of carbon emissions to GDP, as the principal outcome variable. The carbon emissions are typically categorized into two types: those resulting from direct energy consumption (e.g., oil, natural gas, and liquefied petroleum gas) and those generated from indirect energy sources, such as electricity and thermal energy.
4.2 Explanatory variable
The explanatory variable examined in this paper is the Digital Economy (DIGE). We construct an index system for the digital economy from three dimensions: the digital foundation, the digital technology development, and the digital industry development (Table 1). Employing the entropy approach ensures an impartial evaluation of the stages of digital economic development. Data normalization must be done before moving on to the index selection process. Next, we employ the entropy weight technique to allocate weights to every index, ultimately ascertaining the digital economic development status of every province by means of the cumulative score commensurate with its weight.
4.2.1 The digital infrastructure
The advancement of the digital economy is significantly dependent on information infrastructure. As key factors, four indicators are typically used to assess this support: the average mobile telephone exchange capacity, the average long-distance fiber-optic lines, the average fiber-optic line length, and the average number of cell phone base stations. The average long-distance fiber-optic lines and fiber-optic line length are used to measure a region’s wired communication capacity, while the average mobile telephone exchange capacity and the number of cell phone base stations assess its wireless communication capability.
4.2.2 The digital technology development
The growth of digital technology has helped to the progressive advancement of the digital economy by encouraging innovation and boosting operational efficiency. Innovations in digital technology have fundamentally transformed traditional economic service models, allowing companies to diversify their operations at lower costs and accelerating overall economic development. To comprehensively assess the development of digital technology, we selected 7 key indicators: the mobile internet penetration rate, the level of enterprise digital applications, the digital finance index, the number of domain names per capita, the number of pages per capita, the internet broadband access ports per capita, and the per capita internet access traffic.
4.2.3 The digital industry development
The growth of the digital industry can be viewed as a general reflection of the evolving landscape and performance of the digital economy. Within this framework, the software sector largely embodies the transformation of knowledge into commercial products and services, whereas electronic information manufacturing primarily signifies the material foundation supporting digital infrastructure. Analogously, the industrialization of information processing and communication is reflected in the information technology services sector. Furthermore, the burgeoning information security sector embodies the industrialization of emerging technologies resulting from the maturation of modern information technology. Together, these elements make up the digital industry. This paper evaluates the development of the digital industry in terms of the level of development of the electronic information manufacturing industry, the software business income as a share of GDP, the IT services as a share of GDP, and the telecommunications as a share of GDP.
4.3 Control variables
1. Population Density (POPD). Cities with higher population densities typically require more residential, transportation, recreational, and other structures that require a lot of resources to create and maintain. At the same time, higher population densities require more water supply and treatment of wastewater, which brings about a large consumption of electricity and chemicals. Population density must therefore be included as a control variable.
2. Energy Consumption (EC). Energy consumption stands as a primary contributor to carbon emissions, exerting a substantial influence on carbon output. Fossil fuels, constituting a principal source of energy consumption, often result in elevated carbon emissions, particularly in developing nations undergoing rapid industrialization. This trend can be ascribed to a number of things, such as the necessity of industrial progress and technical advancement.
3. Level of urbanization (URBD). Urbanization exerts a notable influence on carbon emissions, with higher levels of urbanization correlating to increased numbers of automobiles and private transport, thereby amplifying carbon emissions. Moreover, elevated levels of urbanization entail greater demand for public infrastructure, further heightening carbon emission pressures.
4. Industrial Structure (INDS). The industrial structure delineates the relative proportions and distribution of various industries within a country or region’s economy. As different industries emit varying amounts of carbon, disparities in industrial composition directly influence the efficacy and intensity of carbon emissions across regions. For instance, tourist-centric cities typically exhibit lower carbon emissions compared to their traditional industrial counterparts.
5. Government intervention (GOVP). Government intervention holds the potential to yield positive outcomes regarding carbon emissions. This can be achieved through the formulation of tailored tax policies, targeting high-carbon emitting enterprises for taxation. In addition, policy measures implemented by the government may assist in directing the development of low-carbon sectors and encourage the emergence of industries such as renewable energy and tourism, both of which have the potential to support carbon emission mitigation efforts.
6. Environmental regulation (ENYR). Environmental regulation significantly influences carbon emissions. Primarily, it curbs carbon emissions by imposing restrictions on enterprise emissions. Additionally, it establishes compulsory laws, regulations, and environmental emission standards, mandating enterprises to integrate environmentally friendly technologies and equipment to mitigate carbon emissions. For instance, regulations governing automobile tailpipe emissions for manufacturers and fuel producers and initiatives promoting enterprises’ research and development of low-carbon and eco-friendly technologies serve to reduce carbon emissions effectively.
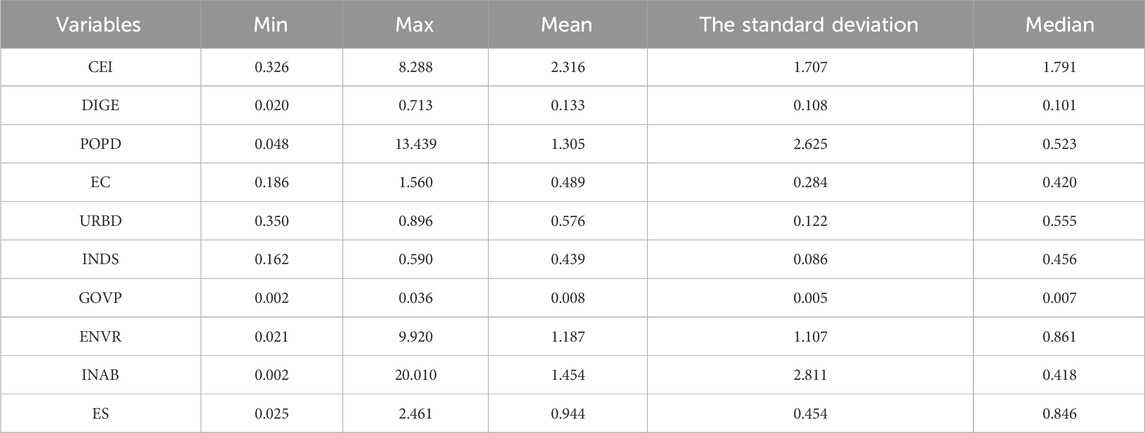
4.4 Descriptive statistics
For the purpose of this analysis, province panel data from China covering the years 2010–2024 are utilised. Carbon emission intensity figures are sourced from the Carbon Emission Accounts and Datasets (CEADs), while indicators representing the digital economy and control variables are primarily derived from the China Statistical Yearbook, the China City Statistical Yearbook, and the Digital Finance Research Center of Peking University. The dataset includes information from 30 provinces, selected based on the consistency and availability of data. Data for Tibet were excluded due to limitations in data accessibility. Table 2 displays the descriptive statistics for the pertinent variables.
Table 2 reveals that the explanatory variable CEI exhibits significant variability, characterized by a mean exceeding the median and a slight right-skewed distribution. Similarly, the explanatory variable DIGE displays a right-skewed distribution, with a mean surpassing the median. The control variables POPD, EC, URBD, INDS, GOVP, and ENAVR, as well as the mechanism variables INAB and ES, have means greater than the median, with an overall right-skewed distribution. And INAB has the largest standard deviation and the most discrete data, while GOVP has the smallest standard deviation and the most stable data.
5 Empirical results
5.1 Benchmark regression results
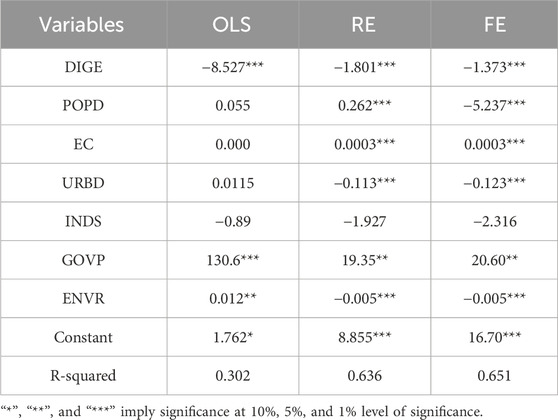
To enhance the credibility of the empirical findings, this study applies multiple standard estimation techniques frequently utilized in panel data analysis. Specifically, the ordinary least squares (OLS) approach is adopted alongside fixed effects (FE) and random effects (RE) models to provide comparative insights and test the consistency of the results. The specific outcomes are presented in Table 3.
The regression outputs derived from the three econometric models reveal that the Digital Economy Composite Index (DIGE) is significantly associated with a reduction in carbon emission intensity at the 1% level, suggesting a potential linkage between digital economic advancement and lower emissions. However, the estimated impacts of control variables—such as energy consumption (EC) and population density (POPD)—exhibit variation across the models, indicating underlying heterogeneity. To improve the interpretation of these results and determine the most suitable specification, the analysis subsequently evaluates and compares the performance of the OLS, fixed effects (FE), and random effects (RE) estimators.
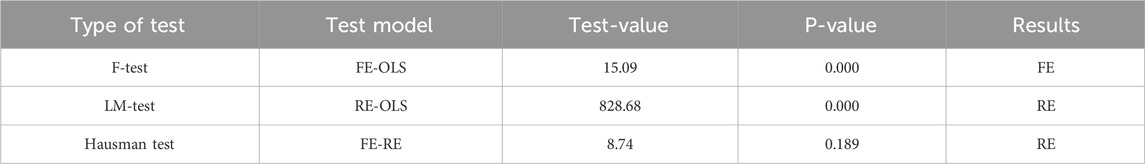
The F-test, LM-test, and Hausman test are often employed techniques for selecting a panel data model; specific outcomes are presented in Table 4. Both the F-test and LM-test reveal significant individual effects in the econometric model, suggesting the superiority of the FE and RE models over the OLS model. Moreover, the Hausman test’s P-value indicates the RE model’s superiority to the FE model. The RE model is the best option when taking into account the outcomes of all three tests. As a result, the RE model is chosen for further empirical research in this work.
This paper investigates the effects of the three main sub-indices that make up the comprehensive digital economy index: digital infrastructure (DI), digital technology application (DTA), and digital industry development (DID) in order to fully understand the relationship between the development of the digital economy and carbon emission intensity.
Table 5 presents regression coefficients for DID, DTA, and DI, each of which demonstrates a statistically significant negative association with carbon emission intensity. This suggests that the core components of the digital economy may be linked to a downward influence on emissions. Among them, DI appears to exert the most substantial effect, followed by DID and then DTA, indicating a relative ranking of DI > DID > DTA in terms of their respective contributions. Notably, the impact of DI reaches significance at the 1% threshold, whereas the associations observed for DID and DTA are significant at the 5% level, pointing to differences in the strength of influence across these digital economy indicators.
Digital infrastructure plays a crucial role in the advancement of the digital economy, providing essential technical support during its initial stages. The widespread deployment of digital technologies, such as sensors and smart manufacturing systems, can significantly enhance existing production and operational methods, thereby facilitating the low-carbon transformation of enterprises. However, the impact of technological and industrial development on carbon emissions is primarily indirect, and their mitigating effects are less pronounced compared to those of infrastructure development.
5.2 Regional heterogeneity analysis
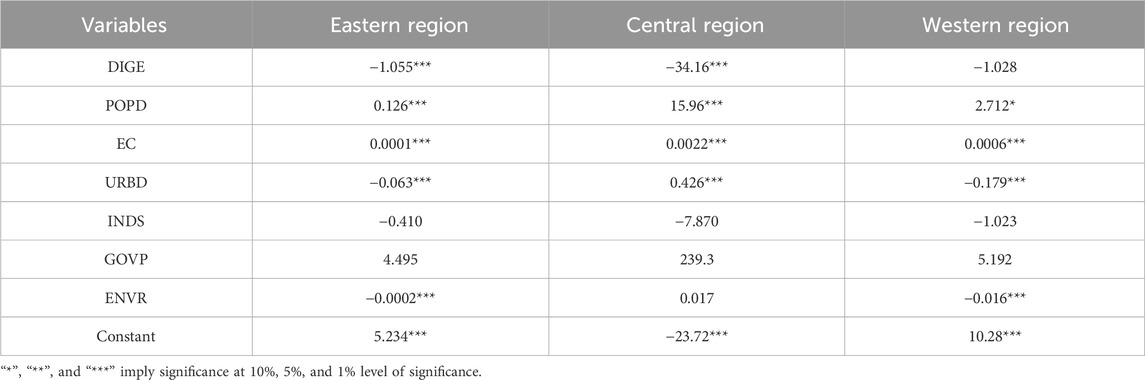
A heterogeneity analysis must be carried out in order to assess the model’s changes among various samples and conditions and to obtain a deeper understanding of the model’s behavior and performance. The economic belt of China is separated into three zones in this study: eastern, central, and western. For every region, separate RE model regressions are performed. Table 6 displays the outcomes.
Table 6 illustrates considerable geographical variability in the relationship between the digital economy and carbon emission intensity. The disparities are chiefly influenced by factors including the level of industrialisation, energy composition, and economic growth stage in various regions. The eastern and central regions, distinguished by superior infrastructure and greater integration of digital technology, demonstrate relatively higher digital economy maturity compared to the less-developed western provinces. Consequently, these regions show a stronger association between digital economic activity and emission reduction. The regression outcomes suggest that greater digital maturity may reinforce the capacity to mitigate carbon intensity, although the extent of this effect appears to vary with regional development conditions.
Given China’s rapid digital economy growth, there’s an imminent demand for infrastructure like data centers. The central region, benefiting from lower electricity costs compared to the east, has shouldered significant digital economy construction tasks. Consequently, its digital economy possesses the greatest potential for reducing carbon emissions. Conversely, non-significant results suggest that the west is lagging in digital economy expansion, resulting in a lesser impact on carbon emissions.
5.3 Analysis of impact mechanisms
The mechanism analysis seeks to delve deeper into the causal relationship between variables by examining their intrinsic connections. Building on earlier studies, this study investigates the energy structure optimization mechanism as a means of elucidating the mechanism by which the digital economy influences the intensity of carbon emissions.
5.3.1 Optimization of energy structure
The energy mix, which represents the proportion of various energy sources—fossil, wind, solar, and nuclear—used in a region or economy, significantly impacts carbon emission intensity. Under similar economic conditions, different energy structures yield disparate carbon emission impacts. It is worth noting that areas with high renewable energy concentrations have lower carbon intensities since these sources emit very little CO2. Conversely, regions with substantial nuclear energy proportions tend to have comparatively lower carbon emission intensity. Presently, our country is actively advancing nuclear energy development with a focus on safety. Conversely, regions heavily reliant on fossil fuels demonstrate higher carbon emission intensity, as evidenced by countries like the United States and India. Simultaneously, fossil fuels persist as primary energy sources for many developing nations due to their lower cost and the ease of adoption compared to cleaner alternatives like nuclear energy. This reliance on fossil fuels places significant pressure on global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and decrease emission intensity.
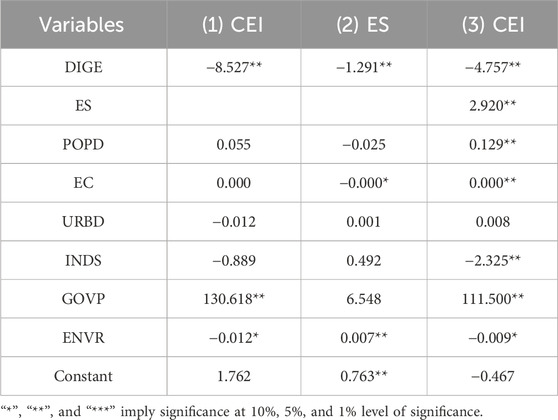
Within the context of the digital economy, this study delves into the intricate connection between energy structure and the reduction in carbon emission intensity, building on the prior analysis by employing the Bootstrap approach to assess the mediating effects. In light of this, three regression models are created:
Equation 1 represents a regression model in which additional factors serve as control variables and the independent variable Digital Economy (DIGE) is regressed against the dependent variable Carbon Emission Intensity (CEI). Equation 2 extends this analysis by including the mediating variable energy structure (ES) alongside the independent variable digital economy (DIGE), with other variables remaining as control variables. Finally, Equation 3 integrates both the independent variable digital economy (DIGE) and the mediating variable energy structure (ES) into the regression model, along with the dependent variable carbon emission intensity (CEI), while other variables retain their status as control variables. Here,
The regression outcomes presented in model (1) of Table 7 indicate that the digital economy (DIGE) is associated with a statistically significant reduction in carbon emission intensity (CEI), with significance observed at the 5% level, thereby supporting the mediating effects hypothesis with a regression coefficient of −8.527. Furthermore, in regression model (2), regression coefficient −1.291 shows that, at a 5% significance level, the digital economy (DIGE) significantly negatively affects the energy structure (ES). Meanwhile, with a regression coefficient of 2.920, the energy structure (ES) exhibits a substantial positive impact on carbon emission intensity (CEI) at the same significance level, indicating a strong mediating effect. This mediating effect has a computed value of −3.770.
In summary, the energy structure functions as a mediator in the correlation between the development of the digital economy and fluctuations in carbon intensity. As the digital economy progresses, there tends to be a gradual shift toward a more diversified energy portfolio, which may contribute to less dependence on coal and, consequently, to lower carbon intensity. This observation is broadly consistent with theoretical perspectives suggesting that digitalization can facilitate improvements in the composition of energy use, potentially supporting carbon intensity reduction.
5.3.2 Enhancement of innovation capacity
There exists a robust correlation between innovation capacity and carbon intensity. Innovation capacity, in this context, denotes the region’s adeptness in leveraging its resources—including land, minerals, population, and transportation—to enhance its economic competitiveness and development prowess through advancements in technology, knowledge, and other domains. It encompasses the generation, dissemination, and exchange of knowledge, along with the invention and innovation of products and processes, as well as policy, institutional, and industrial innovations. Technological innovation, on one hand, drives the enhancement of energy efficiency, leading directly to a reduction in carbon emissions. It also encourages the development, adoption, and research of low-carbon technologies, which reduces carbon emissions. Moreover, innovation capacity facilitates the identification and oversight of carbon emissions, enabling the detection of trends and problematic areas, and the formulation of appropriate measures to mitigate carbon emission intensity.
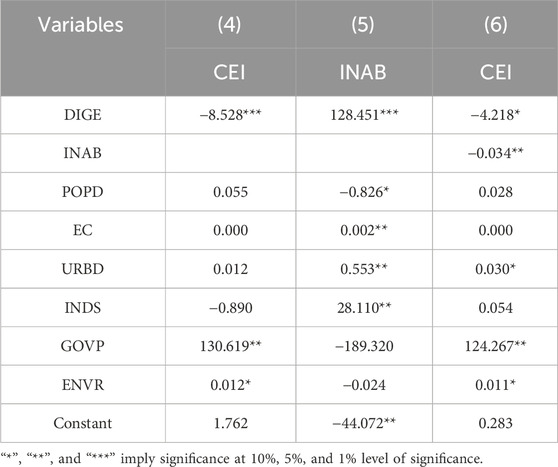
To further explore the potential pathway through which innovation capability may affect carbon intensity within the context of digital economy development, this study applies the Bootstrap approach to assess mediation effects. Accordingly, three separate regression models are constructed to facilitate this analysis.
Equation 4 represents a regression model in which other variables act as control variables and the independent variable Digital Economy (DIGE) is regressed against the dependent variable Carbon Emission Intensity (CEI). Equation 5 models the independent variable digital economy (DIGE) and the mediating variable innovation ability (INAB), while controlling for other variables. Equation 6 explores the digital economy (DIGE) affects carbon emission intensity (CEI) through the path of innovation ability (INAB), while other variables serve as controls. Here,
Table 8 offers several relevant observations. First, results from regression model (4) suggest a statistically significant inverse association between the digital economy (DIGE) and carbon emission intensity (CEI) at the 1% level, with a corresponding coefficient of −8.528. This is broadly consistent with the theoretical framework suggesting a potential mediating mechanism. Second, model (5) reveals a positive and statistically significant relationship between DIGE and innovation capacity (INAB), reflected in a coefficient of 128.451 at the 1% level. Moreover, the link between INAB and CEI appears to be negatively correlated, with a coefficient of −0.034, though the significance level here is more modest at 10%. These findings point to the presence of an indirect effect, estimated at −4.367, suggesting a potential mediation function of innovation ability in the correlation between digital progress and emission intensity.
In conclusion, innovation capacity facilitates the digital economy’s endeavours to diminish carbon emission intensity. By fostering innovation, the digital economy facilitates enterprise upgrading and technological advancements, thereby lowering carbon emission intensity. This outcome aligns with our theoretical examination. Consequently, it can be suggested that the advancement of the digital economy may contribute to a reduction in carbon emission intensity, primarily through its potential to support and enhance innovation activities.
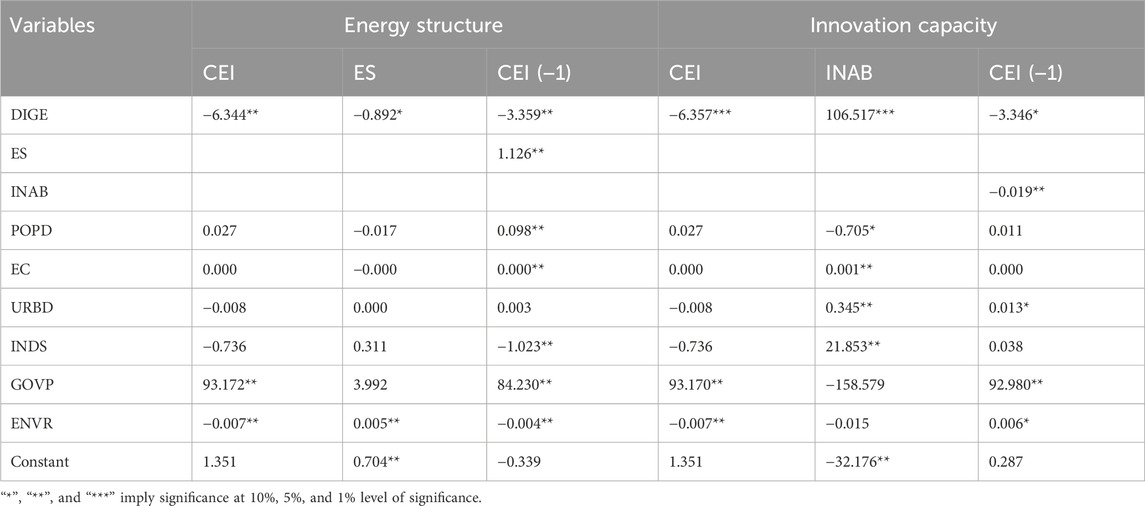
5.3.3 Robustness tests
To validate the robustness of the findings, we conducted rigorous checks using a one-period lag method for robust regression analysis. The test results are shown in Table 9. The output results indicate that the regression results of the two mediating variables are basically consistent with the previous results, and with only slight changes in the coefficient values of each variable, but the direction remains unchanged, which confirms the robustness of the empirical results.
6 Conclusion and policy implication
6.1 Conclusions
This study use the entropy approach to create a digital economy development index for 30 provinces in China from 2010 to 2024. Based on this index, panel data models are subsequently utilized to explore the potential associations between the evolution of the digital economy and carbon emission intensity, while considering possible influencing factors. The main observations from the analysis can be summarized as follows:
1. The analysis indicates that the growth of the digital economy correlates with a mitigating effect on carbon emission intensity, as evidenced by the regression coefficients derived from the random effects panel model. Furthermore, disaggregating the digital economy into sub-indices reveals varying levels of influence: digital infrastructure appears to exert a comparatively greater impact, while the effect linked to digital technology application is relatively more limited.
2. The impact of the digital economy on carbon emission intensity seems to vary by geographical region. In particular, the central region exhibits a notably greater correlation between digital development and lower carbon intensity than the eastern region. Conversely, this relationship is less evident in the western region, which may be partially attributed to relatively slower regional development, less diversified industrial structures, and a more traditional energy mix.
3. Enhancing innovative capabilities and optimising energy structure are the main ways that the digital economy lowers carbon emission intensity. On the one hand, the digital economy decreases carbon emission intensity by refining the energy structure, promoting low-carbon mobility, and enhancing energy intelligence. On the other hand, through advancements in science, technology, policy, and products, the digital economy stimulates reductions in carbon emission intensity, consequently bolstering innovation capacity.
6.2 Policy implications
Based on the above conclusions and in light of the characteristics of urban development in China, the following policy recommendations are proposed:
1. Establishment of a mechanism for regional coordination and development of the digital economy to narrow the digital economy gap between regions. For eastern and central regions with a mature digital economy, the focus should be on greening digital infrastructure and accelerating the substitution of clean energy. In contrast, the western region in the early stages of digitalization should invest more in building digital infrastructure, such as tax exemptions and financial subsidies, to prioritize the coordinated planning of digital infrastructure while guiding the development of low-carbon-oriented digital industries. In addition, it is necessary to strengthen the training and introduction of talents in the digital economy, encourage technical talent to move toward western region and create new strategic industrial clusters, thereby promoting innovation and development in the digital economy industry.
2. It is suggested that optimize industrial structure and promote low-carbon transition strategies. It is recommended that policymakers develop a system of incentives to encourage digital economy enterprises to accelerate the research and application of renewable energy, promoting traditional high-energy-consuming industries to adopt smart manufacturing, automation, and information technologies. This would result in a gradual reduction in their energy dependence and facilitate a transition towards low-carbon, high-value-added, technology-intensive industries. By providing policy support, the government can facilitate the structural adjustments of these industries, thereby promoting a low-carbon transition in the industrial structure and reducing carbon emissions.
3. The governments should strengthen the cultivation of innovation capacity in the digital economy. One approach is reduce the cost of innovation for enterprises and individuals by provide financial support, increase their enthusiasm to participate in low-carbon innovation. Another possible approach is set up a low-carbon innovation fund to support the research, development and application of low-carbon technologies with potential. Through so doing, it will gradually realize the prosperity of digital technology talents and technology research and development, and promote green and sustainable development.
6.3 Limitations and future directions
Although the study provides critical conclusions and policy implications, some limitations still exist. Firstly, this paper primarily examines the digital economy’s impact on carbon emission intensity through the intermediary role of energy structure and innovation capacity. However, a growing body of literature emphasizes the importance of artificial intelligence, which has a significant impact on both energy efficiency and innovation pathways. Future research may concentrate on the impact of the digital economy on carbon emissions intensity through the intermediary role of artificial intelligence, thus enriching both the depth and breadth of existing research. Secondly, this paper focus solely on regional differences, not considering other meaningful dimensions of heterogeneity. Comprehensive consideration of more research perspective is needed in future studies, to further uncover the behavioral mechanisms and institutional foundations through which the digital economy affects carbon emissions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
W-SC: Writing – original draft. Y-TJ: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Acheampong, A. O. (2018). Economic growth, CO2 emissions and energy consumption: what causes what and where? Energy Econ. 74, 677–692. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2018.07.022
Adebayo, T. S., and Ullah, S. (2023). Formulating sustainable development policies for China within the framework of socioeconomic conditions and government stability. Environ. Pollut. 328, 121673. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121673
Adebayo, T. S., Ullah, S., Kartal, M. T., Ali, K., Pata, U. K., and Ağa, M. (2023). Endorsing sustainable development in BRICS: the role of technological innovation, renewable energy consumption, and natural resources in limiting carbon emission. Sci. Total Environ. 859, 160181. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160181
Ahmed, Z., Ahmad, M., Murshed, M., Shah, M. I., Mahmood, H., and Abbas, S. (2022). How do green energy technology investments, technological innovation, and trade globalization enhance green energy supply and stimulate environmental sustainability in the G7 countries? Gondwana Res. 112, 105–115. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2022.09.014
Acheampong, A. O., and Boateng, E. B. (2019). Modelling carbon emission intensity: application of artificial neural network. J. Clean. Prod. 225, 833–856. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.352
Bai, T., Qi, Y., Li, Z., and Xu, D. (2023). Digital economy, industrial transformation and upgrading, and spatial transfer of carbon emissions: the paths for low-carbon transformation of Chinese cities. J. Environ. Manag. 344, 118528. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118528
Cai, Q. H., Jiang, F. X., and Lei, P. F. (2024). Evaluating the synergistic effects of the digital economy and carbon emission trade exchange on enterprise high-quality development. Int. Rev. Econ. Finance 95, 103431. doi:10.1016/j.iref.2024.103431
Chang, H., Ding, Q., Zhao, W., Hou, N., and Liu, W. (2023). The digital economy, industrial structure upgrading, and carbon emission intensity—empirical evidence from China’s provinces. Energy Strategy Rev. 50, 101218. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2023.101218
Chen, S., Ding, D., Shi, G., and Chen, G. (2022a). Digital economy, industrial structure, and carbon emissions: an empirical study based on a provincial panel data set from China. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 20, 316–323. doi:10.1016/j.cjpre.2022.11.002
Chen, S., Liu, J., Zhang, Q., Teng, F., and McLellan, B. C. (2022b). A critical review on deployment planning and risk analysis of carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) toward carbon neutrality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 167, 112537. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2022.112537
Cheng, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., and Jiang, J. (2023). The impact of the urban digital economy on China's carbon intensity: spatial spillover and mediating effect. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 189, 106762. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106762
Freire-González, J., Vivanco, D. F., and Puig-Ventosa, I. (2017). Economic structure and energy savings from energy efficiency in households. Ecol. Econ. 131, 12–20. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.08.023
Gao, F., and He, Z. (2024). Digital economy, land resource misallocation and urban carbon emissions in Chinese resource-based cities. Resour. Policy 91, 104914. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2024.104914
Gigova, T., Valeva, K., and Nikolova-Alexieva, V. (2019). “Digital transformation–opportunity for industrial growth”, in International conference on creative business for smart and sustainable growth (CREBUS). IEEE, 1–4.
Guan, D., Meng, J., Reiner, D. M., Zhang, N., Shan, Y., Mi, Z., et al. (2018). Structural decline in China’s CO2 emissions through transitions in industry and energy systems. Nat. Geosci. 11, 551–555. doi:10.1038/s41561-018-0161-1
Han, D., Ding, Y., Shi, Z., and He, Y. (2022). The impact of digital economy on total factor carbon productivity: the threshold effect of technology accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 55691–55706. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-19721-x
Ibrahim, M. H. (2018). Trade-finance complementarity and carbon emission intensity: panel evidence from middle-income countries. Environ. Syst. Decis. 34 (4). doi:10.1007/s10669-018-9675-8
Jiang, H. D., Purohit, P., Liang, Q. M., Liu, L. J., and Zhang, Y. F. (2023). Improving the regional deployment of carbon mitigation efforts by incorporating air-quality co-benefits: a multi-provincial analysis of China. Ecol. Econ. 204, 107675. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2022.107675
Jiang, H. D., Basanta, K. P., Dong, K. Y., Yu, Y. Y., and Liang, Q. M. (2024). An economy-wide impacts of multiple mitigation pathways toward carbon neutrality in China: a CGE-based analysis. Energy Econ. 129, 107220. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107220
Kennedy, C. (2022). Capital, energy and carbon in the United States economy. Appl. Energy 314, 118914. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.118914
Khan, I., and Hou, F. (2021). The impact of socioeconomic and environmental sustainability on CO2 emissions: a novel framework for thirty IEA countries. Soc. Indic. Res. 155 (3), 1045–1076. doi:10.1007/s11205-021-02629-3
Lange, S., Pohl, J., and Santarius, T. (2020). Digitalization and energy consumption. Does ICT reduce energy demand? Ecol. Econ. 176, 106760. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2020.106760
Li, C., and Zhou, W. (2024). Can digital economy development contribute to urban carbon emission reduction? - empirical evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 357, 120680. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120680
Li, J., Huang, X., Chuai, X., and Yang, H. (2021). The impact of land urbanization on carbon dioxide emissions in the Yangtze River Delta, China: a multiscale perspective. Cities 116, 103275. doi:10.1016/j.cities.2021.103275
Li, C., Liu, J., Liu, Y., and Wang, X. (2023). Can digitalization empowerment improve the efficiency of corporate capital allocation? —evidence from China. Econ. Analysis Policy 80, 1794–1810. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2023.11.014
Li, W., Fang, S., Yan, C., Gong, W., and Wang, C. (2025). Research on the impact of digital economy on industrial carbon emission efficiency – an analysis based on spatial threshold model. J. Clean. Prod. 515, 145755. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.145755
Liao, K., and Liu, J. (2024). Digital infrastructure empowerment and urban carbon emissions: evidence from China. Telecommun. Policy 48, 102764. doi:10.1016/j.telpol.2024.102764
Liu, J., Yu, Q., Chen, Y., and Liu, J. (2022). The impact of digital technology development on carbon emissions: a spatial effect analysis for China. Resour. Conservation Recycl. 185, 106445. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106445
Liu, M., Li, S., Li, Y., Shi, J., and Bai, J. (2024). Evaluating the synergistic effects of digital economy and government governance on urban low-carbon transition. Sustain. Cities Soc. 105, 105337. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105337
Liu, X., He, Z., Deng, Z. X., and Poddar, S. (2024). Analysis of spatiotemporal disparities and spatial spillover effect of a low-carbon economy in Chinese provinces under green technology innovation. Sustainability 16 (21), 9434. doi:10.3390/su16219434
Luo, S., Yimamu, N., Li, Y., Wu, H., Irfan, M., and Hao, Y. (2023). Digitalization and sustainable development: how could digital economy development improve green innovation in China? Bus. Strategy Environ. 32, 1847–1871. doi:10.1002/bse.3223
Ma, Q., Tariq, M., Mahmood, H., and Khan, Z. (2022). The nexus between digital economy and carbon dioxide emissions in China: the moderating role of investments in research and development. Technol. Soc. 68, 101910. doi:10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101910
Marbuah, G., Gren, I. M., and Tirkaso, W. T. (2021). Social capital, economic development and carbon emissions: empirical evidence from counties in Sweden. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 152, 111691. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2021.111691
Mngumi, F., Huang, L., Xiuli, G., and Ayub, B. (2024). Financial efficiency and CO2 emission in BRICS. Dose digital economy development matter? Heliyon 10, e24321. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24321
Murshed, M., Apergis, N., Alam, S., Khan, U., and Mahmud, S. (2022). The impacts of renewable energy, financial inclusivity, globalization, economic growth, and urbanization on carbon productivity: evidence from net moderation and mediation effects of energy efficiency gains. Renew. Energy 196, 824–838. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.07.012
Nathan, M., and Rosso, A. (2015). Mapping digital businesses with big data: some early findings from the UK. Resour. Policy 44, 1714–1733. doi:10.1016/j.respol.2015.01.008
Pan, W., Xie, T., Wang, Z., and Ma, L. (2022). Digital economy: an innovation driver for total factor productivity. J. Bus. Res. 139, 303–311. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.09.061
Qian, Y., Wang, H., and Wu, J. (2022). Spatiotemporal association of carbon dioxide emissions in China’s urban agglomerations. J. Environ. Manag. 323, 116109. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116109
Ren, S., Hao, Y., Xu, L., Wu, H., and Ba, N. (2021). Digitalization and energy: how does internet development affect China’s energy consumption? Energy Econ. 98, 105220. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105220
Rodríguez, M., and Pena-Boquete, Y. (2017). Carbon intensity changes in the Asian Dragons. Lessons for climate policy design. Energy Econ. 66, 17–26. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2017.05.028
Shen, Y., Hueng, C. J., and Hu, W. (2021). Measurement and spillover effect of digital financial inclusion: a cross-country analysis. Appl. Econ. Lett. 28 (20), 1738–1743. doi:10.1080/13504851.2020.1853663
Song, M., Zheng, C., and Wang, J. (2022). The role of digital economy in China’s sustainable development in a post-pandemic environment. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 35 (1), 58–77. doi:10.1108/jeim-03-2021-0153
Sun, H., Tang, C., Gao, P., and Zhou, G. (2025). Digital economy, energy consumption and urban carbon emission reduction: empirical evidence from 278 cities in China. Sustain. Futur. 10, 100858. doi:10.1016/j.sftr.2025.100858
Tang, C., Xu, Y., Hao, Y., Wu, H., and Xue, Y. (2021). What is the role of telecommunications infrastructure construction in green technology innovation? A firm-level analysis for China. Energy Econ. 103, 105576. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105576
Tao, M., Poletti, S., Wen, L., Selena Sheng, M., Wang, J., Wang, G., et al. (2023). Appraising the role of the digital economy in global decarbonization: a spatial non-linear perspective on globalization. J. Environ. Manag. 347, 119170. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119170
Thompson, P., Williams, R., and Thomas, B. (2013). Are UK SMEs with active web sites more likely to achieve both innovation and growth? J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 20 (4), 934–965. doi:10.1108/jsbed-05-2012-0067
Wang, L., and Chen, L. (2023). Impacts of digital economy agglomeration on carbon emission: a two-tier stochastic frontier and spatial decomposition analysis of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 95, 104624. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2023.104624
Wang, J., Dong, K., Dong, X., and Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. (2022). Assessing the digital economy and its carbon-mitigation effects: the case of China. Energy Econ. 113, 106198. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106198
Wang, X., Wang, K., Xu, B., and Jin, W. (2025a). Digitalisation and technological innovation: panaceas for sustainability? Int. J. Prod. Res. 16 (63). doi:10.1080/00207543.2025.2468883
Wang, X., Adnan, S., and Ge, F. (2025b). Towards carbon neutrality: will artificial intelligence and green bond become catalysts? Energy Econ. 148, 108711. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2025.108711
WangQ., , Sun, J., Pata, U. K., Li, R., and Kartal, M. T. (2023). Digital economy and carbon dioxide emissions: examining the role of threshold variables. Geosci. Front. 15, 101644. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101644
Wang, X., Qin, C., Liu, Y., Tanasescu, C., and Bao, J. (2023). Emerging enablers of green low-carbon development: do digital economy and open innovation matter? Energy Econ. 127, 107065. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.107065
Xu, Q., Zhong, M., and Cao, M. (2022). Does digital investment affect carbon efficiency? Spatial effect and mechanism discussion. Sci. Total Environ. 827, 154321. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154321
Yang, X., Wu, H., Ren, S., Ran, Q., and Zhang, J. (2021). Does the development of the internet contribute to air pollution control in China? Mechanism discussion and empirical test. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 56, 207–224. doi:10.1016/j.strueco.2020.12.001
Yang, Z., Gao, W., Han, Q., Qi, L., Cui, Y., and Chen, Y. (2022). Digitalization and carbon emissions: how does digital city construction affect China’s carbon emission reduction? Sustain. Cities Soc. 87, 104201. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2022.104201
Yi, M., Liu, Y., Sheng, M. S., and Wen, L. (2022). Effects of digital economy on carbon emission reduction: new evidence from China. Energy Policy 171, 113271. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113271
Yu, H., Wang, J., and Xu, J. (2023). Assessing the role of digital economy agglomeration in energy conservation and emission reduction: evidence from China. Energy 284, 128667. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.128667
Yu, Z., Liu, S., and Li, S. (2024b). Research on the spatial effect of digital economy development on urban carbon reduction. J. Environ. Manag. 357, 120764. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120764
Yuan, S., Musibau, H. O., Genç, S. Y., Shaheen, R., Ameen, A., and Tan, Z. (2021). Digitalization of economy is the key factor behind fourth industrial revolution: how G7 countries are overcoming with the financing issues? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 165, 120533. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120533
Zhang, J., Lyu, Y., Li, Y., and Geng, Y. (2022). Digital economy: an innovation driving factor for low-carbon development. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 96, 106821. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106821
Zhang, Z., Ling, D., Yang, Q., Feng, Y., and Xiu, J. (2024a). Central environmental protection inspection and carbon emission reduction: a tripartite evolutionary game model from the perspective of carbon neutrality. Petroleum Sci. 21 (3), 2139–2153. doi:10.1016/j.petsci.2023.11.014
Zhang, Z., Li, P., Wang, X., Ran, R., and Wu, W. (2024b). New energy policy and new quality productive forces: a quasi-natural experiment based on demonstration cities. Econ. Analysis Policy 84, 1670–1688. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2024.10.039
Zhao, S., Peng, D., Wen, H., and Wu, Y. (2022). Nonlinear and spatial spillover effects of the digital economy on green total factor energy efficiency: evidence from 281 cities in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 81896–81916. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-22694-6
Keywords: the digital economy, carbon emission intensity, theoretical analysis, panel regression model, the mediating mechanism analysis
Citation: Chen W-S and Jiang Y-T (2025) Effect of digital economy development on carbon emission intensity: evidence from Chinese provinces. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1618432. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1618432
Received: 28 May 2025; Accepted: 29 August 2025;
Published: 17 September 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaolei Sun, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Xiaoqing Wang, Ocean University of China, ChinaZhenhua Zhang, Lanzhou University, China
Copyright © 2025 Chen and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yu-Tong Jiang, eXRwZzEyQDE2My5jb20=
 Wen-Shuo Chen
Wen-Shuo Chen Yu-Tong Jiang
Yu-Tong Jiang