- Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Centre for WEEE Recycling, School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Shanghai Polytechnic University, Shanghai, China
Introduction: MNBs (MNBs), relying on its special chemical and physical properties, such as high surface potential, long stability and free radical generation capacity, have shown broad application prospects in environmental remediation.
Methods: Based on 508 related papers in the Web of Science database, this paper conducts a scientific knowledge mapping analysis using VOSviewer and CiteSpace software to reveal the research situation and trends. Researches show that MNB technology demonstrates remarkable effects in water pollution control (industrial wastewater, surface water, and groundwater) and soil pollution remediation.
Results and Discussion: For instance, ozone MNBs can increase the removal rate of plastic pollutants in industrial wastewater to 94.18% and enhance the degradation efficiency of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons through interfacial reactions. In soil remediation, their synergistic effect with surfactants can improve the petroleum pollutants’ removal efficiency. From the perspective of research hotspots, the coupling of MNBs with advanced oxidation technologies (such as Fenton, plasma, and photocatalysis) has become the mainstream direction, significantly enhancing the degradation efficiency of pollutants through interfacial effects and radical generation mechanisms. The author collaboration network indicates that Chinese scholars have made outstanding contributions. The team led by Hu Liming from Tsinghua University has achieved fruitful results in groundwater remediation using ozone MNBs. However, the international cooperation network still needs to be strengthened. In terms of institutional collaboration, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) leads in both the volume of publications and academic influence, with its research covering multiple application areas such as semiconductor cleaning and membrane treatment. Keyword co-occurrence analysis divides the research topics into three major categories: degradation mechanisms, ozone MNB technology, and multi-technology coupling applications. Among them, “free radicals”, “mass transfer”, and “photocatalysis” are the core keywords. Although MNB technology has achieved phased progress, its long-term stability in complex environments, large-scale application costs, and cross-disciplinary collaborative mechanisms still need in-depth exploration.
1 Introduction
With the acceleration of global urbanization and industrialization, environmental pollution issue is becoming increasingly severe, posing a serious threat to ecosystems and human health (Hoang et al., 2022; Wei et al., 2021). Among various pollution issues, water and soil pollution stand out prominently, making the search for efficient pollution control technologies an urgent matter. MNB technology, with its unique chemical and physical characteristics, has shown great environmental remediation potential and has become a research hotspot in recent years (Xiao et al., 2025; Haris et al., 2020; Xia et al., 2018; Xiao et al., 2019).
MNBs are bubbles with diameters at the micrometer and nanometer ranges. Compared with traditional macroscopic bubbles, they possess numerous superior characteristics, such as a high internal pressure, a large specific surface area, a longer residence time in liquids, and a high surface Zeta potential (Azuma et al., 2019; John et al., 2022; Loh et al., 2021; Temesgen et al., 2017). The large specific surface area of MNBs significantly increases the gas-liquid interface area, greatly enhancing various mass transfer efficiencies and rates (Xiao et al., 2022). Additionally, the surface of MNBs carries a charge, forming a double electric layer structure with a high interface potential. This property enables them to adsorb pollutants and promote their oxidative decomposition. Moreover, MNBs exhibit excellent stability in solutions and can persist for long periods due to their slow rising speed and charged surface. Some studies have shown that the existence time of oxygen MNBs (180–350 nm) can exceed 5 days, with the longest reaching 60 days (Zhou et al., 2021a), nitrogen MNBs (200–300 nm) can remain stable for a month (Ulatowski et al., 2019), and the existence time of air nano bubbles exceeds 3 months (Michailidi et al., 2020). When MNBs dissolve under pressure, they generate free radicals with strong oxidation capabilities, effectively degrading many refractory organic pollutants and enhancing the removal effect of pollutants (Li et al., 2009).
In the field of environmental remediation, MNB technology demonstrates broad application potential. In water pollution control, whether it is industrial wastewater, surface water, or groundwater pollution, this technology can play a significant role. For industrial wastewater, MNB ozonation can significantly increase the oxidation rate of ozone and effectively degrade organic pollutants (Kim et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2018), with a removal rate of plastic reaching 94.18% (Masry et al., 2021). In surface water purification, MNBs can perform multiple functions such as aeration mass transfer, air flotation, advanced oxidation, and sterilization and disinfection, effectively removing suspended degrading organic and solids pollutants from water (Wang et al., 2024a). For groundwater pollution, MNBs can carry oxidants into the aquifer to achieve in-situ remediation (Chen and Chang, 2022; Shen et al., 2024).
In soil pollution remediation, MNBs also have significant application value. They can serve as carriers to transport oxygen and nutrients into the soil, enhancing the degradation ability of microorganisms towards organic pollutants (Kwon et al., 2020; Pa et al., 2009). Additionally, MNBs can improve the treatment effect on petroleum-contaminated soil and oil sludge by synergistically acting with surfactants, increasing the removal efficiency of petroleum pollutants (Chen et al., 2018; Ji et al., 2018; Sun et al., 2020a).
In summary, MNB technology holds broad application prospects in environmental remediation, but further in-depth research and improvement are still needed. This study utilized software like CiteSpace and VOSviewer to conduct a comprehensive analysis of relevant literature and create a scientific knowledge graph, including source journals, keywords, hotspots, publication trends, research frontiers, author contributions and collaborations, etc. The analysis identified and tracked the research frontiers and hotspots in this field, identified scientific hotspots, research topics and their dynamic evolution, and paid attention to existing and emerging research topics and trends. By understanding the current research hotspots and challenges in the technology, it is expected to promote its large-scale practical application and provide effective technical support for solving global environmental pollution problems.
2 Data sources and research methods
2.1 Data source
Web of Science is a globally renowned comprehensive academic information resource database, covering numerous disciplines. The literature it includes has high academic influence and wide representativeness, effectively reflecting the cutting-edge trends and development directions of international academic research. This article conducts a bibliometric analysis using Web of Science as the data source. In the advanced search interface of Web of Science, the search conditions are set as: the subject contains “Micro nano bubble”, “nano bubble”, and “micro bubble”, and on the basis of the above search results, further search for literature with the full text containing “degradation”. The search mode is set to exact match, and the search time range is from the establishment of the database to 1 April 2025. After the search, a total of 509 articles related to the management of hazardous waste in small and micro enterprises were obtained. After duplicate removal using Note Express software, 508 articles were finally obtained for subsequent in-depth analysis. The search scope is set as “subject” (TS): TS = [“Micro nano bubble” or “nano bubble” or “micro bubble” AND TS = (“degradation”)]. The specific screening items are shown in Table 1, excluding irrelevant research topics and directions such as “endocrinology and metabolism” and “agriculture”, while Table 1 presents the final data results.
2.2 Research methods
Compared with traditional bibliometric methods, visualization methods can more intuitively present citation information of literature and its inherent hierarchical structure, facilitating in-depth exploration of interaction relationships in complex networks. This paper, by means of the scientific knowledge mapping method, uses CiteSpace and VOSviewer software to conduct trend analysis of publications, research institutions, scholars, and keyword co-occurrence analysis based on the obtained 508 related literature data, and draw corresponding knowledge maps, thereby comprehensively and intuitively presenting the research situation in this field.
3 Basic article information architecture
3.1 Author information
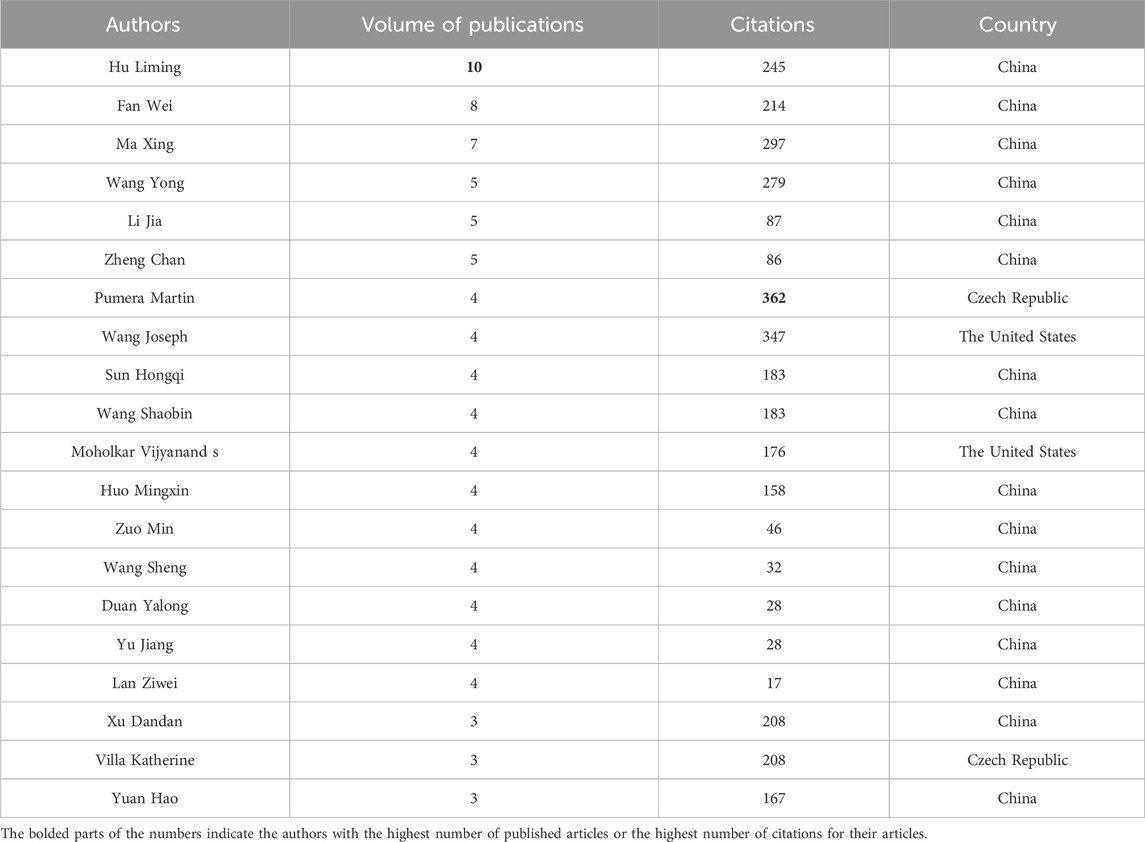
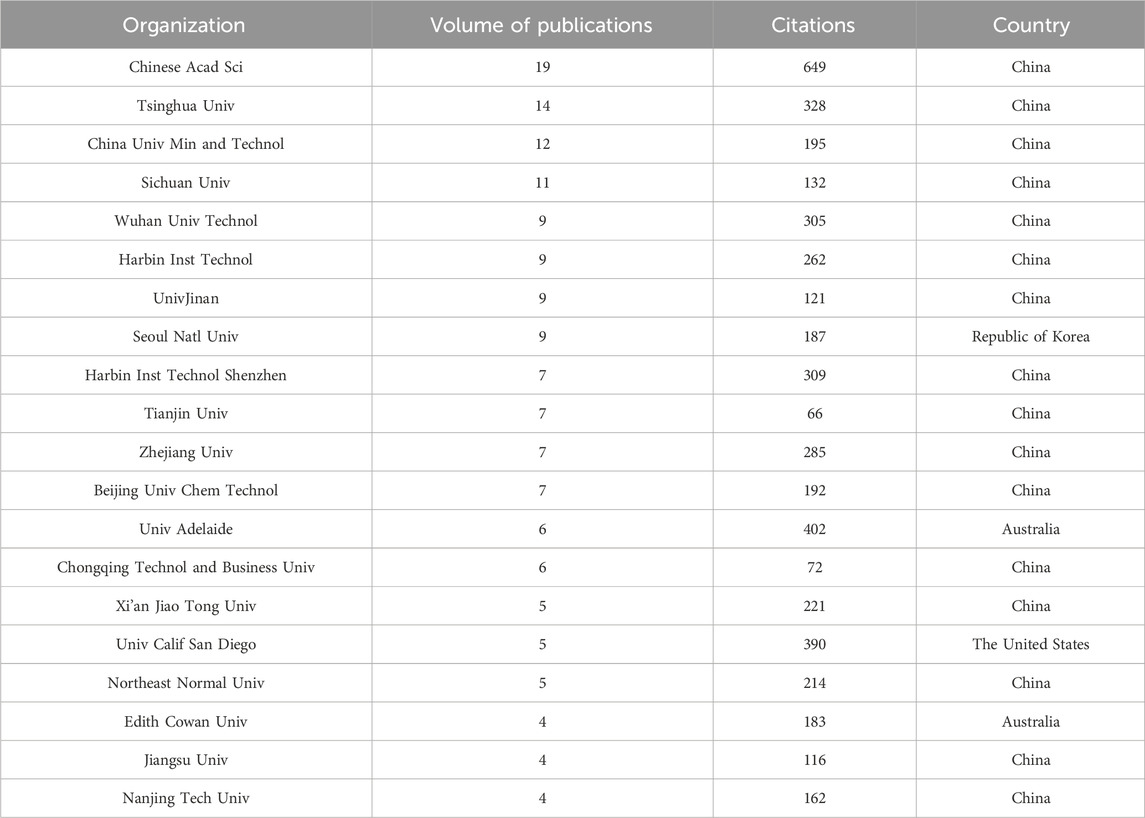
Authors and their collaborations within a certain research field are key factors in promoting academic progress and spreading knowledge. Bibliometric analysis can identify authors who have contributed to a specific research field and their collaboration patterns. Table 2 shows the top 20 authors who have published the most papers in photocatalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). There are 16 authors from China, demonstrating China’s outstanding contributions to this field. Hu Liming from Tsinghua University has published the most papers, with a total of 10. His most influential paper studied the characteristics of ozone MNBs, including their bubble number, size distribution, and zeta potential. The experiment investigated the ozone MNBs’ mass transfer rate. They used ozone MNBs to deal with water contaminated with organic matter, which showed significant purification efficiency. They also conducted the column tests to research the efficiency of ozone MNBs in the remediation of groundwater contaminated with organic matter. Field monitoring was carried out on a site contaminated with trichloroethylene (TCE). The results indicated that ozone MNBs could significantly enhance the remediation efficiency and are an innovative in-situ remediation technology of groundwater contaminated with organic matter (Hu and Xia, 2018). His team mainly focuses on the ozone MNB technology application in groundwater pollution treatment, confirming the groundwater pH influence and salinity on the treatment capacity of the technology (Xia and Hu, 2019; Li et al., 2013). They believe that ozone MNBs have great oxidation capacity and low secondary pollution (Cao et al., 2023), and possess the ability to transport and dissolve in porous media (Li et al., 2014), making it a promising in-situ remediation technology of groundwater contaminated with organic matter. Fan Wei from Jiangnan University ranks second with eight papers. The representative research direction of this author with the second-highest influence integrates MNB and photocatalytic technology. They found that the MNBs’ interfacial photoelectric effect was also proved to be beneficial for pollutant degradation. MNBs guided strong light scattering, increasing 54.8% of the light path length in the photocatalytic medium at 700 nm and strengthening the photocatalyst light adsorption (Fan et al., 2021; Fan et al., 2019).
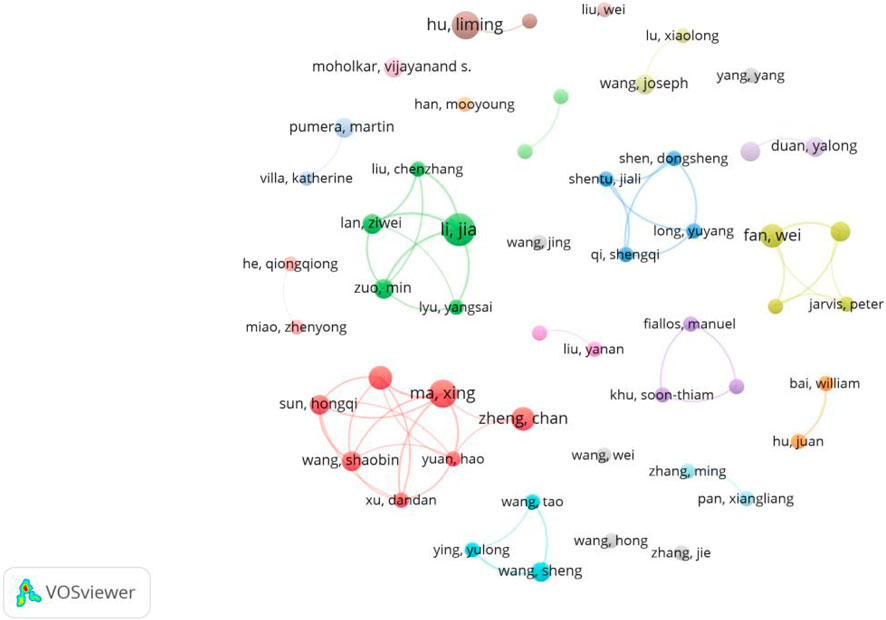
The author collaboration distribution map can well reflect the cooperation and joint research in environmental industrial pollution treatment using MNB technology (Figure 1). Each node’s size in the figure represents the paper number published by the author (the larger node means that the author has published more papers), while the connecting lines represent the authors’ collaboration. Figure 1 shows the degree of author collaboration, with several closely collaborating author groups emerging, including the teams of Ma Xing and Zheng Chan, as well as Li Jia and Lan Ziwei. Unlike the author with the highest volume of publications, their main research direction is nanomotors (Ma et al., 2016; Ye et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2023a). The closeness of the connections between different authors is shown in the figure, meaning that the international cooperation intensity in this field still needs to be strengthened. Analyzing the collaboration level among researchers is important because such collaboration not only helps to collect expertise from different disciplines, promoting innovation and progress, but also improves the reliability, quality and efficiency of research through peer review, knowledge transfer and resource sharing, etc. Moreover, collaboration can promote the scientific research internationalization, help solve complicated interdisciplinary problems, and accelerate the transformation of research outcomes into practical applications, especially in the fields of pollution control and environmental protection.
3.2 Information graphic of the issuing institution
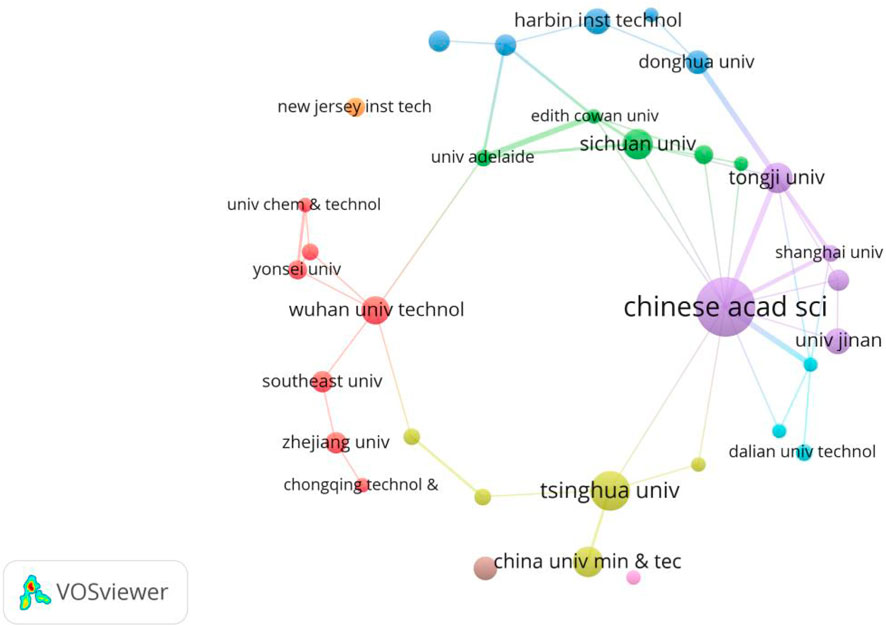
Research institution analysis provides information on the most influential and productive research institutions in a certain research field, which could make scholars well understand the current situation and field trends, and guide how to solve important problems and promote innovation. Figure 2 shows the knowledge domain of collaborative organizations using the software VOSviewer. Every circular node represents an organization, and the circle size indicates the published paper number. Inter-institutional collaboration is represented by a line between two nodes, with the thickness of the line indicating the degree of collaboration. The CAS occupies the highest ranking and has published the most papers in Table 3, which has a critical academic influence. In its latest research, it reviewed the benefits of MNB in the cleaning process, then analyzed in depth the factors affecting its cleaning effect and the possible mechanisms involved. Additionally, it summarized the production and application of MNB in various cleaning scenarios and elaborated on its applications in semiconductor cleaning (Takahashi et al., 2015), membrane cleaning (Lee et al., 2015) and metal cleaning (Ulatowski et al., 2024). In its latest research, it was found that the MNB technology enhanced the vacuum ultraviolet degradation rate by improving the mixing and mass transfer within the solution, optimizing the light performance in the solution, and increasing the dissolved oxygen level (El Aswar et al., 2025). Moreover, as shown in Figure 2, the CAS, Shanghai University, and Tongji University have relatively close cooperative relationships. Their works mainly focus on the application of MNB technology in treating polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution in groundwater, where the technology can enhance the surfactants transfer and thus improving the degradation capacity (Dai et al., 2023; Han et al., 2025).
3.3 Journal information
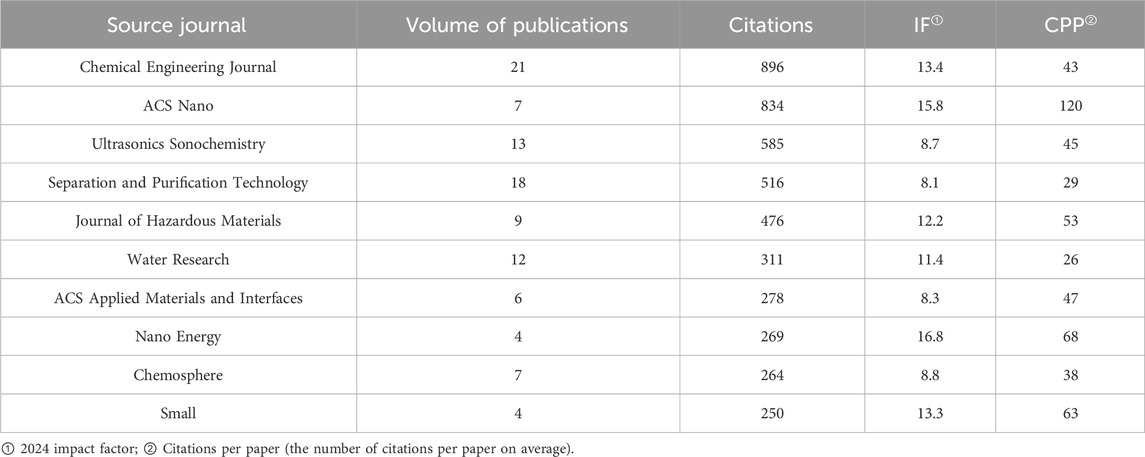
Journals in a research field help researchers understand the main academic resources and knowledge dissemination channels. The h-index is a hybrid quantitative indicator which could be used to evaluate the academic output quantity and quality. It was proposed by George Hirsch, a physicist at the University of California, San Diego, in 2005. As it can be seen in Table 4, the analysis of the journals has identified the top ten publications with the highest citation counts in the field of MNB technology for environmental pollution degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal is the journal with the highest number of articles published in this field, with 21 articles, and it is also the publication with the highest citation count, indicating its importance in the field. Next are Separation and Purification Technology and Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, which have published 18 and 13 articles respectively. Additionally, although ACS Nano has only published seven research papers on MNBs, its citation count ranks second, suggesting that this publication is highly trusted by readers in the field and the articles published in it have significant influence within the field.
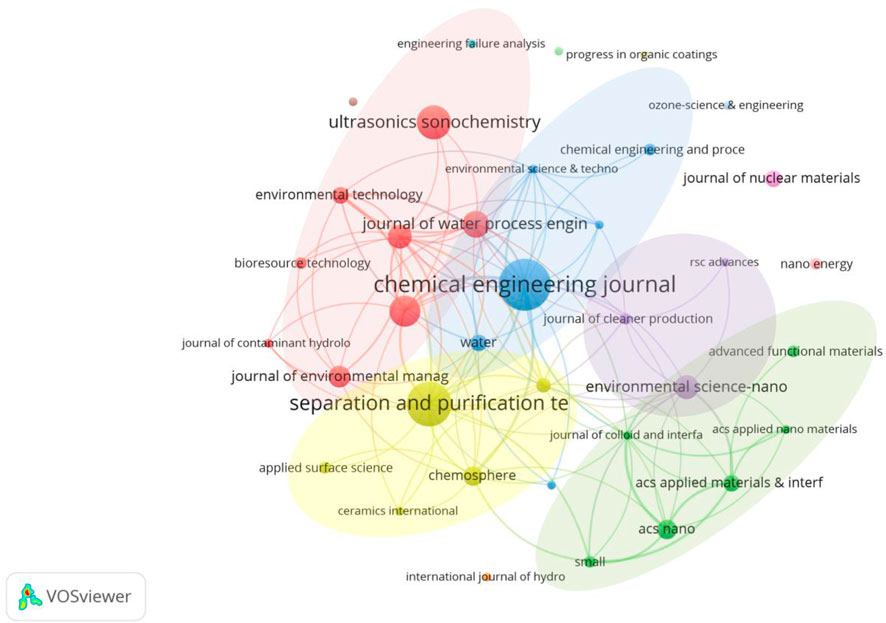
The different colored areas in the Figure 3 represent the different research preferences of various publications on the article’s research direction. The publications in the red area led by Ultrasonics Sonochemistry mainly focus on the generation mechanism and methods of MNBs. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry mainly uses ultrasound to generate MNBs for water pollution treatment, with two main approaches: activating intermediate substances [such as quantum dots (Entezari and Ghows, 2011), nanomaterials (Bao et al., 2023), etc.] to enhance their oxidation capacity and enhancing the generation of free radicals through sonochemistry (Pétrier et al., 2010), to strengthen the effect of wastewater treatment. The publications in the yellow area led by Separation and purification technology mainly focus on the technology of using MNBs to clean dirt. This journal mainly studies the use of MNB technology to clean filter membranes, solve the problem of membrane fouling, thereby improving the stability of the membrane and enhancing the degradation capacity of water treatment (Duan et al., 2025; Duan et al., 2022; Mo et al., 2024). The publications in the green area led by Acs nano mainly focus on the R&D of water treatment materials and equipment. This journal mainly studies the nanoscale micro-motors application in water pollution treatment (Villa et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2024; Soler et al., 2013). The publications in the blue area led by Chemical engineering journal have a relatively comprehensive research direction, covering various aspects of MNB technology.
4 The development of MNB technology
4.1 Trend of annual publications
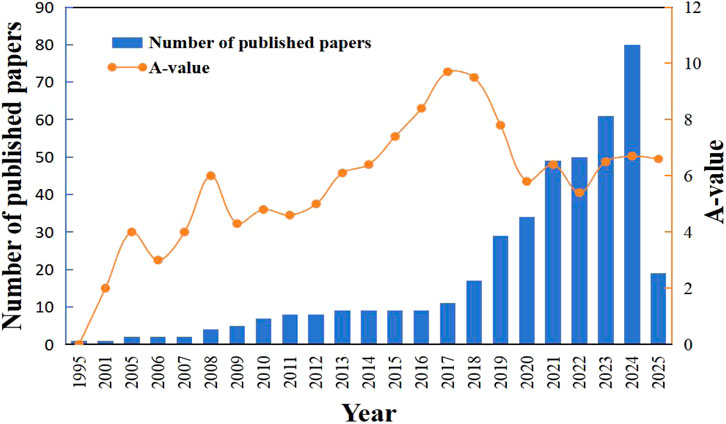
By conducting a statistical analysis of the published paper number from 1995 to 2025, the status, maturity and development trend of MNB technology research achievements can be clearly shown. Figure 4 presents the research result distribution on MNB technology in environmental treatment based on the time series. From 1995 to 2007, less than five articles on MNB technology were published each year. From 2008 to 2017, this field showed a overall slow growth trend, and the annual publication volume in this field exceeded 10 for the first time in 2017. After that, research related to MNB technology gradually became a hot topic, which is inseparable from the pollution control and environmental protection policies of many countries as well as major technological breakthroughs. From 2017 to 2024, the published paper number increased significantly, with an annual publication volume of over 50 for five consecutive years, and the publication volume reached 80 in 2024. As of 2025, 508 papers have been published in VOCs photocatalytic oxidation research. The continuous increase in the number of papers in this field indicates that researchers have paid more attention to the application of MNB technology in environmental pollution degradation.
4.2 Research technology trends over the years
Based on the timeline (Figure 5), the development process of MNB technology has been sorted out, covering its key progress from the theoretical assumption to the exploration of applications in multiple fields such as water treatment and disinfection, demonstrating the continuous expansion of its application boundaries and the deepening of research. In the theoretical assumption stage, Parker et al. first hypothesized the MNBs existence in 1994, laying the theoretical foundation for subsequent related research and opening the door to the study of this special type of bubble (Parker et al., 1994). During the early application exploration period of MNB technology (1999–2007), Ishida et al. imaged bulk MNBs using atomic force microscopy (AFM), providing a direct understanding of the physical morphology of MNBs (Ishida et al., 2000). Chu et al. reported the application of ozone MNBs in dye removal and water disinfection, expanding the application ideas of MNBs in water treatment (Chu et al., 2007).
From 2009 to 2018, it was the development period of MNB technology. Tasaki et al. studied the degradation effect of MNBs under ultraviolet (UV) irradiation on methyl orange, exploring the water treatment technology of light-MNB synergy (Utaka et al., 2009). In 2011, the first review on the application of MNB technology in water treatment was conducted, systematically summarizing the application achievements and prospects of this technology in water treatment at that time. In 2016, Agarwal et al. reviewed the history of MNBs, retrospectively summarizing its development trajectory from a more macroscopic perspective (Agarwal et al., 2016).
As shown in the figure, it is the time distribution map of key words related to MNB technology. During the explosive period after 2018, due to its excellent mass transfer ability and the ability to produce active oxidative species, MNB technology was coupled with different environmental pollution degradation technologies and applied in multiple fields. There were studies on the degradation of aniline using non-thermal plasma/MNBs, further enriching the technical means of MNBs in the treatment of refractory organic pollutants. In 2019, Fenton/MNBs were used for dye separation and microplasma bubbles for inactivating microorganisms, exploring new directions for the combination of MNBs with other technologies. MNBs were used to enhance the degradation of oxytetracycline under visible light, broadening the application scope of MNBs in the field of photocatalytic degradation. In 2021, it was found that MNBs could promote the photocatalytic disinfection of microbial spores, and the stability of oxygen-containing MNBs in fresh water was confirmed, providing new evidence for their application in the disinfection field. In 2022, the exploration of ultraviolet C (UV-C)/hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)/MNBs as a new disinfection technology further explored the potential of MNBs in disinfection technology innovation.
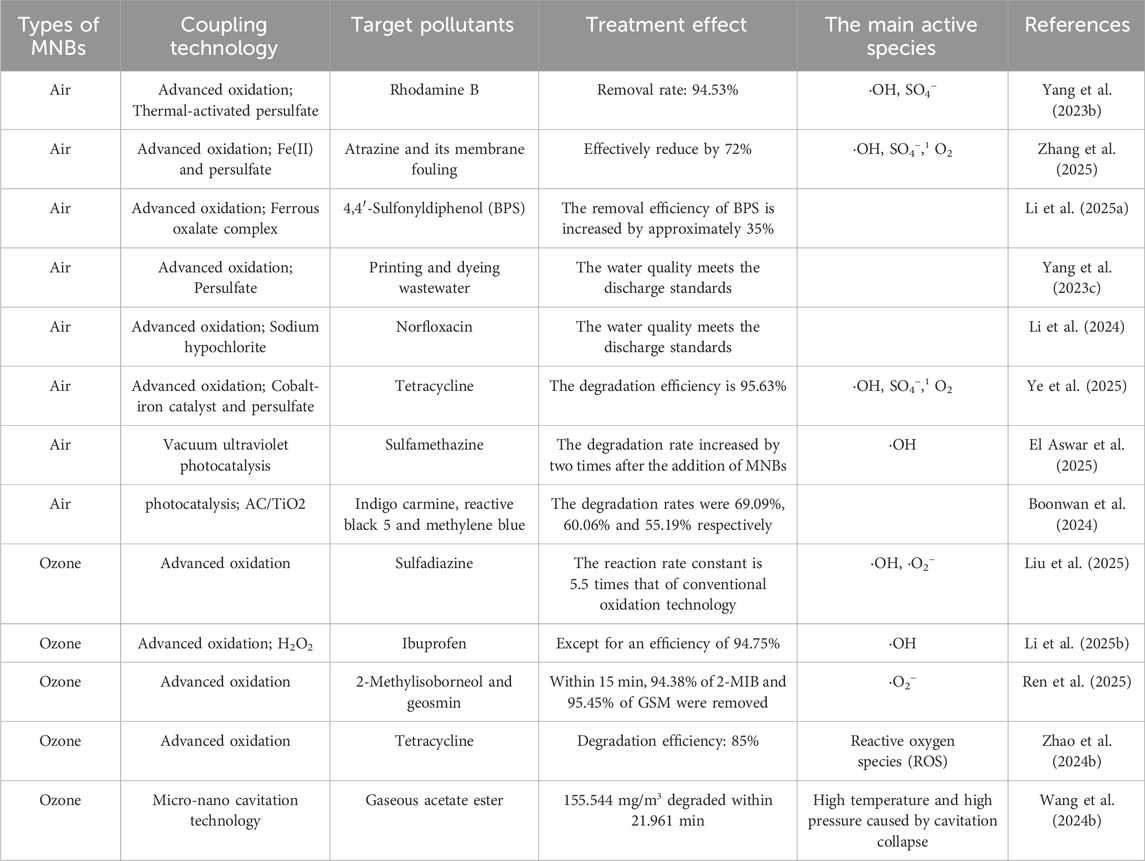
From 2023 to 2025, the development of MNB technology has been rapid, and research has delved deeper. The focus of research on the applicability of MNB technology has mainly been on exploring the coupling effect of MNBs with other technologies. In previous studies, it was found that MNBs can effectively enhance gas mass transfer and the production of active species. Scholars have thus focused on the coupling effect between MNBs and various oxidants, using the strong oxidation effect of MNBs to activate different oxidants (such as persulfate, ferrous ions, and nano zero-valent iron) and treat complex pollutants in different media, continuously expanding the application scope of MNB technology. Jing et al. utilized MNBs to enhance the immobilized Chlorella technology. Thanks to the excellent mass transfer capacity of MNBs, the biomass of Chlorella increased by 2.48 times, significantly improving the removal efficiency of ofloxacin (Jing et al., 2025). Chi et al. studied the degradation of tetracycline, a commonly used antibiotic in wastewater, using a system based on zero-valent nano-iron assisted by MNBs. MNBs can serve as an ideal carrier for zero-valent nano-iron. When they burst, they generate shock waves and highly reactive substances (such as •OH), which can significantly enhance the degradation efficiency (Chi et al., 2024). Table 5 presents a portion of the relevant research on MNB technology in various application scenarios over the past 2 years.
Meanwhile, due to the mature development of ozone MNB technology, in recent studies, scholars no longer confine their research to the laboratory and have conducted many practical application studies, mainly exploring the influence of factors such as air intake rate, air intake volume, and pollutant concentration (Hu et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2024a). Ponce-Robles et al. actively promoted the practical application of MNB technology. By adjusting the size of ozone MNBs, the air intake volume, and the air intake rate, they conducted experiments in large-scale pharmaceutical wastewater. They replaced the traditional tertiary sewage treatment equipment with ozone MNB technology, which enhanced the treatment capacity and reduced costs (Ponce-Robles et al., 2023).
5 Analysis of hotspots in MNB technology
5.1 Keyword clustering analysis
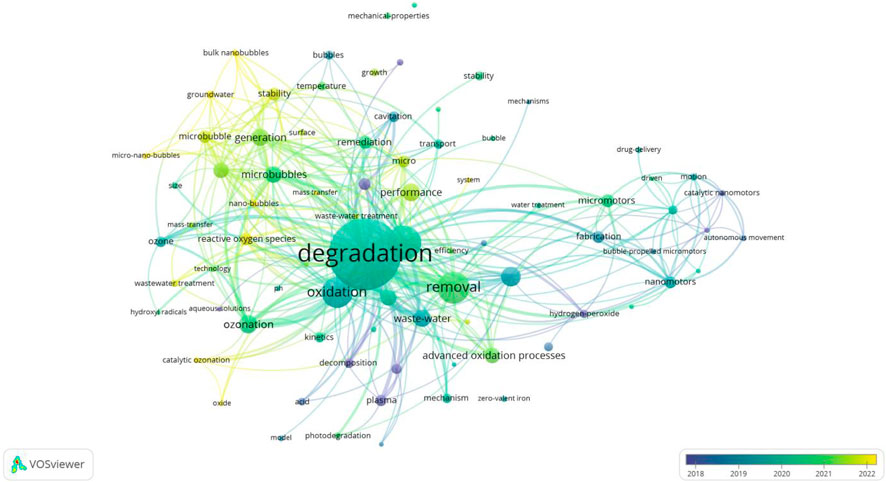
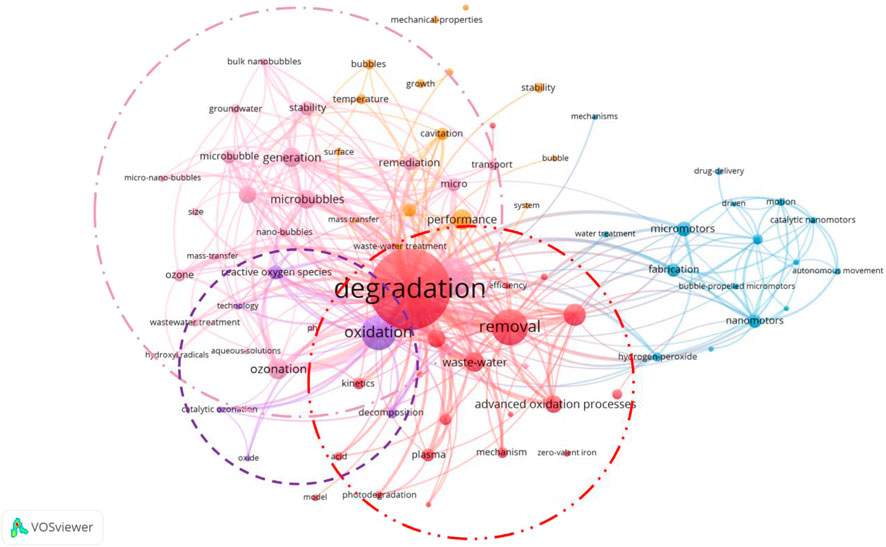
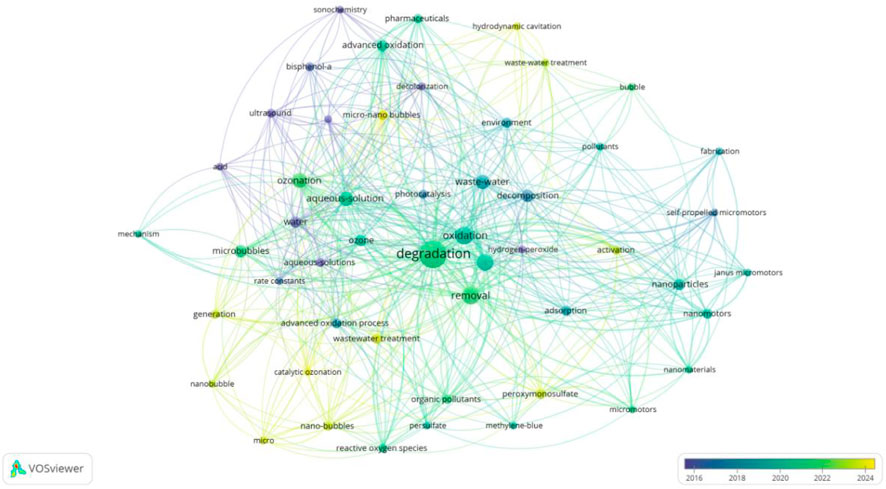
In the keyword spectrum diagram, VOSviewer has classified the keywords. Co-occurrence analysis of keywords helps to understand the basic themes and concepts in the literature or dataset. It assists researchers in positioning their research, decision-making, and collaboration to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities in a specific field or topic. As shown in Figure 6, the keywords in the MNB field are divided into five categories. The three main categories are the red area led by “degradation”, which mainly focuses on the application of MNB technology to assist other different treatment technologies, such as non-thermal plasma bubbles, advanced oxidation, photocatalysis, etc., and ultimately focuses on the degradation effect of pollutants. The second category is the pink area, mainly summarizing the development of ozone MNB technology. The combination of ozone and MNB technology is the most developed technology. Between these two areas is the purple area, mainly summarizing the core keywords of MNB technology, “oxides” and “reactive oxygen species”. Next, we will further analyze the three key categories.
5.2 The principle of MNB technology
First, let’s discuss the purple area section (Figure 6), which outlines the core principle of MNB technology. Now, two representative views explains the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) during MNB oxidation: one is the view of interface ion accumulation during the MNB contraction process (Takahashi et al., 2007a; Yang et al., 2023d). As MNBs contract, the surface Zeta potential increases with the increase in the contraction rate, which is inversely proportional to the bubble size. This indicates that the surface charge migration rate is insufficient to counteract the increase in the MNB contraction rate, leading to the accumulation of charges at the gas-liquid interface and the formation of a high chemical potential (Takahashi et al., 2015). According to this theory, under a wide range of pH conditions, MNBs carry a negative charge. Therefore, during the bubble contraction process, OH− is more easily adsorbed onto the bubble surface than H+, resulting in an interface environment with high ion concentration and a double-layer structure (Takahashi et al., 2007b). When ozone gas diffuses and dissolves into the liquid phase within MNBs, the high concentration of OH− at the interface triggers the ozone self-decomposition chain reaction, leading to the generation of ·OH (Cheng et al., 2018; Khuntia et al., 2012; Cheng et al., 2019). This theory is applicable to ozone MNBs. Since ozone itself is a highly reactive oxidizing species, when ozone gas diffuses and dissolves into the liquid phase within MBs, the high concentration of OH− at the interface triggers the ozone self-decomposition chain reaction, leading to the generation of •OH (Cheng et al., 2018; Khuntia et al., 2012; Cheng et al., 2019). During the accumulation of air and oxygen MNBs at the bubble interface, the reaction between oxygen and OH− is slow and inefficient, and thus cannot generate a large amount of reactive oxygen free radicals. Zhao et al. revealed the main free radicals produced and the pathways of ozone generating free radicals (Equations 1–4) when using ozone MNB technology to treat tetracycline wastewater, verifying the working mechanism of ozone MNBs (Zhao et al., 2024b).
The other view is the adiabatic compression during the MNB collapse process (Shi et al., 2021; Yasui et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2020). As MNBs contract, the reduction in volume increases the internal gas pressure. Before reaching the critical collapse state, MNBs typically withstand an internal pressure of 0.83–1.65 MPa, which is over 50 times the atmospheric pressure (Yasui et al., 2019). At this point, ozone molecules remain in a dense state, colliding more frequently in a smaller space, resulting in a higher energy state. Simultaneously, the MNB wall contraction speed reaches 90 m/s, raising the critical temperature inside the bubble to 3,000 K and the temperature of the liquid near the bubble to 360 K. Although these extreme conditions of high temperature and pressure only last for approximately 19 picoseconds, a quasi-adiabatic compression effect is formed at the MNB interface, which is sufficient to trigger the thermal decomposition of gas molecules, thereby leading to the generation of free radicals. The applicability of this theory is not only limited to ozone MNBs, but also applies to MNBs composed of oxygen and air. Although the free radical yield of oxygen is far less than that of ozone, with the support of adiabatic compression theory, it can be coupled with different types of other technologies (such as advanced oxidation, photocatalysis, etc.) to enhance the oxidation capacity and assist other water treatment technologies. Considering the cost, oxygen MNBs are cheaper than ozone MNBs and more suitable for coupling with other technologies. Li et al. found in the experiment of using divalent iron to catalyze the treatment of 4,4′-sulfonyl diphenol (BPS) that the degradation efficiency of pollutants increased by 35% after the addition of MNBs for co-treatment (Li et al., 2025a). El Aswad et al. utilized MNBs to assist in the ultraviolet photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethazine in water, doubling the degradation efficiency (El Aswar et al., 2025). During the treatment process, the presence of hydroxyl radicals was detected using pCBA, CCl4, and MDE probe compounds to identify •OH, •O2−, and 1O2 respectively. The discovery of hydroxyl radicals indicates that the energy and free radicals generated during the collapse of MNBs are conducive to the oxidative degradation of water pollution. This inexpensive and simple bubble technology is expected to become an auxiliary means to enhance existing environmental pollution treatment technologies and engineering.
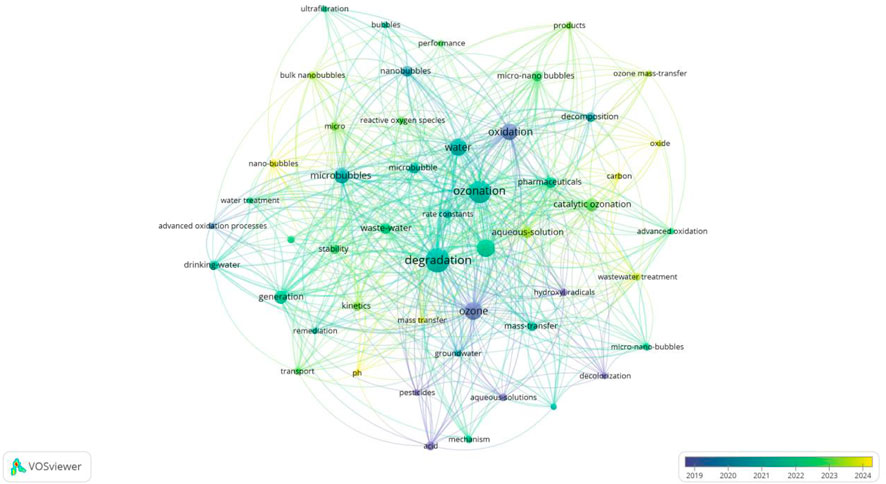
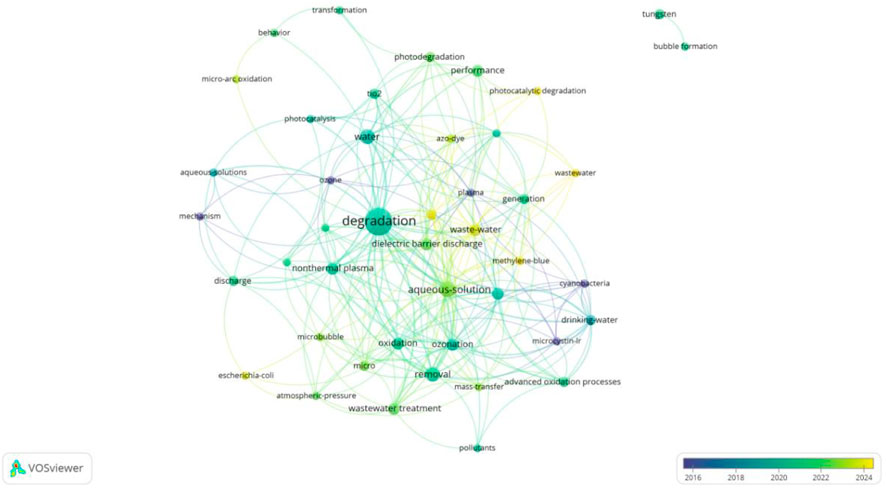
5.3 Ozone MNB technology
5.3.1 The principle of ozone MNB technology
The pink area (Figure 6) mainly focuses on the research of ozone MNB technology. By adding ozone as a search term and connecting it with “and” in the search formula, the keyword distribution map as shown in Figure 7 is obtained. The appearance of “Oxide” in the figure indicates that ozone is a strong oxidant with a high oxidation-reduction potential of 2.07 V, which can rapidly oxidize various organic and inorganic pollutants and convert them into harmless or low-harm substances. However, in traditional ozone water treatment technology, due to the low solubility of ozone in water and its easy decomposition, its utilization rate is not high (≤10 mg L-1) and it is only suitable for water treatment under neutral pH and room temperature conditions (Khan and Carroll, 2020; Levanov et al., 2017). Therefore, a higher O3 addition amount greatly increases the cost of gas preparation. The emergence of MNBs technology provides a new way to improve the utilization efficiency of ozone. Keywords such as “Mass transfer”, “Stay time”, and “ROS” imply the advantages of ozone MNBs. After ozone is integrated into the MNB system, the special properties of MNBs can effectively improve the dissolution and dispersion state of ozone in water, extend its residence time in water, significantly increase the contact probability and reaction efficiency between ozone and pollutants, and thereby enhance the removal ability of pollutants. The high stability in aqueous solutions and efficient mass transfer coefficient can overcome the problems of low solubility, short half-life, and low mass transfer coefficient of conventional O3 (Deng et al., 2021; Seridou and Kalogerakis, 2021). The ozone oxidation assisted by MNBs includes three main steps: (i) generating O3 by sequentially guiding gaseous oxygen through a traditional ozone generator and an MNBs generator to produce MNBs; (ii) transferring O3 from MNBs to water molecules; (iii) using dissolved O3 to target pollutants and generate ROS.
5.3.2 Control factors of ozone MNB technology
The characteristics of ozone microbubbles (MBs), such as small size and long residence time, can promote the decomposition of ozone and gas-liquid mass transfer, thereby enhancing the removal effect of refractory organic compounds. Therefore, any parameters that affect the characteristics of MBs, such as bubble size, stability, mass transfer efficiency, and interfacial environment, will indirectly affect the treatment efficiency.
First, within a certain temperature range, the influence of temperature on the removal rate of pollutants is not significant. In the experiments of phenol and TOC removal, the temperature change has a negligible effect on the degradation rate, as the positive and negative effects cancel each other out (Cheng et al., 2021; Mohite and Garg, 2017). Rising temperature will reduce the solubility of ozone in water, accelerate the escape of ozone, and lower the gas-liquid mass transfer rate. At the same time, it will decrease the mechanical strength of the bubble walls of MBs, making them more prone to rupture and accelerating the release of ozone. The temperature increase will significantly enhance the ozone oxidation rate (in line with the Van’t Hoff equation, for every 10 °C increase in temperature, the reaction rate approximately doubles). Therefore, the optimal temperature should be determined based on the actual situation.
The influence of gas-liquid ratio on MNBs shows a phased pattern. Increasing the gas-liquid ratio enhances the air flow rate and the number of MBs, strengthens gas-liquid mass transfer, raises the dissolved ozone concentration, accelerates the oxidation process, and significantly boosts the degradation rate in the PhOH degradation experiment. When the gas flow rate exceeds the critical point, the increase in degradation rate and mass transfer efficiency slows down as the mass transfer flux has exceeded the reaction demand. Excessively high gas-liquid ratios may also lead to an increase in bubble size and a decrease in specific surface area, which in turn reduces mass transfer efficiency. The ozone MBs process can enhance mass transfer efficiency through small bubbles and long residence time at a low gas-liquid ratio. Therefore, in practical applications, the gas-liquid ratio and bubble size need to be optimized to maximize the effect.
Surface tension mainly affects the size and stability of MBs. The lower the surface tension of the solution, the easier it is to generate small-diameter MBs. The average diameter of MBs generated by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) with a surface tension of 29.5 mN/m is 13.3 μm, which is significantly smaller than that in high surface tension systems, and small bubbles are usually beneficial for mass transfer (Melich et al., 2019). Surfactants can slow down the contraction, coalescence and rupture of bubbles, prolong the lifespan of MBs and enhance the stability of the interface, but they may reduce the mass transfer rate at the gas-liquid interface.
Finally, pH significantly alters the removal efficiency by influencing ozone decomposition, free radical generation, and the ionization state of organic compounds. A high pH promotes the self-decomposition of ozone and accelerates the generation of ·OH radicals, thereby enhancing the degradation rate of refractory organic compounds. The degradation rate constant of PhOH at pH 11 is 2.7 times that at pH 3 (Lim et al., 2022).
5.3.3 The application of ozone MNB technology
Ozone MNB technology has unique advantages in water treatment, being capable of removing organic pollutants in water and inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, ensuring the chemical and biological safety of drinking water. This technology oxidizes organic pollutants through the generation of ·OH, converting them into harmless substances, while also destroying the cell structure of microorganisms to achieve disinfection and sterilization. Compared with traditional drinking water treatment technologies, ozone MNB technology is green and clean, does not cause secondary pollution, and meets the strict requirements of drinking water treatment, providing a reliable technical means for ensuring drinking water safety. Studies have found that ozone MNB technology shows significant advantages in treating antibiotic wastewater. At an ozone concentration of 8 mg/L, it can completely degrade 100 mg/L of tetracycline within 20 min (Koundle et al., 2024). The degradation process not only relies on the direct oxidation effect of ozone but also benefits from the large amount of hydroxyl radicals (·OH) generated when MNBs burst. ·OH has extremely strong oxidation ability and can rapidly oxidize tetracycline molecules, converting them into harmless substances. In the treatment of wastewater containing aromatic hydrocarbons, ozone MNB technology also performs well. According to research, compared with ordinary ozonated water, ozone MNB water increases the oxidation rate of aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene, ethylbenzene, o-xylene, and p-xylene by 13.6%–22.6% (Shen et al., 2023). This is mainly because the interface effect of MNBs promotes the contact between aromatic hydrocarbons and ·OH, making the oxidation reaction easier to proceed. Studies have shown that ozone MNB technology can effectively penetrate low-permeability aquifers and oxidize and degrade organic pollutants in them (Shen et al., 2024). In the remediation of low-permeability aquifers contaminated by toluene, the removal rate of toluene is significantly improved by injecting encapsulated ozone MNB water (EOMBW).
Ozone MNB technology can also be applied to the treatment of organic petroleum pollution in soil. The micro-nano bubble oxidation process features short duration, low cost and high efficiency. It can enhance the effectiveness of surfactants and additives, providing a practical solution for the efficient remediation of petroleum pollution. MNBs can increase the negative zeta potential on the surface of soil particles, thereby enhancing the electrostatic repulsion between oil droplets and soil particles and weakening their adsorption, making it easier for oil droplets to detach from the soil surface. MNBs (such as 1 μm bubbles) can withstand extremely high pressure (about 390 kPa, four times the atmospheric pressure), and their collapse will generate intense pressure waves and micro-jets. This local impact force can directly act on the surface of soil particles such as sand grains, physically stripping off the adhered oil films or oil droplets. The small size characteristics of MNBs (large specific surface area and long residence time in the liquid phase) can significantly increase the collision probability with oil droplets and enhance the adhesion between particles and bubbles, enabling more oil droplets to be carried by bubbles and detached from the soil matrix. Finally, MNBs can capture dispersed oil stains and carry them to the soil surface or treatment system through buoyancy, facilitating subsequent separation and removal. Huang et al. utilized the saponin and cyclodextrin + MNBs enhanced system to degrade diesel in soil. The enhancement of MNBs increased the sand erosion diesel removal rate by more than 20% (Huang et al., 2021). Sun et al. utilized ozone MNB technology to degrade TPH in petroleum waste sludge, achieving a removal rate of 71.7%–79.5% (Sun et al., 2020b).
5.3.4 The application of ozone MNB technology
Ozone micro-nano bubble (MBs) technology has demonstrated high efficiency in oxidation and environmental friendliness in wastewater treatment, but it still has significant shortcomings. Technically, the generation devices of MBs are difficult to achieve uniform and controllable bubble sizes, making it hard to clearly distinguish the characteristics and degradation patterns of MBs of different sizes, which restricts the research on the mechanism. The correlation between the dynamic characteristics of MBs (such as residence time, contraction and expansion) and the oxidation effect has not been systematically analyzed, and there are theoretical disputes about the generation pathways and core mechanisms of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (such as the hypotheses of interface ion accumulation and adiabatic compression). In terms of application, most existing studies are limited to laboratory or pilot-scale, lacking long-term operation data in actual scenarios, making it difficult to deal with complex conditions such as water quality fluctuations; economic feasibility analysis is insufficient, and the quantitative assessment of the full life cycle cost, including equipment maintenance and energy consumption, is lacking, which limits large-scale promotion.
In future research, it is first necessary to optimize the generation device to achieve precise control of bubble size, and combine ERT, CFD and other technologies to analyze the dynamic characteristics of MBs of different sizes. Secondly, the degradation mechanism should be verified, the action path of ROS clarified, and a structure-activity relationship model constructed. Finally, a full life cycle cost analysis should be carried out to enhance economic sustainability and promote large-scale field trials to verify the technical stability. With the resolution of these issues, ozone MNB technology is expected to become a core technology for advanced wastewater treatment and the removal of refractory pollutants, providing important support for environmental resource protection.
5.4 The application of MNB technology
The red area of the keyword spectrum (Figure 6) mainly focuses on the application of MNB technology in combination with various other technologies. It summarizes the excellent auxiliary degradation ability of MNBs. The functionalization of MNBs, their ability to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), and their light scattering effect also contribute to assisting oxidation degradation reactions. Specifically, for instance, in the Fenton reaction, a Fe(II) catalytic layer can be constructed on the surface of MNBs, which not only adsorbs pollutants but also promotes the Fenton reaction in situ while adsorbing pollutants (Zhang et al., 2022a), thereby enhancing the oxidation reaction rate (Yi et al., 2023). Additionally, during the interface contraction process of MNBs, ROS can also be generated at the interface, directly leading to the degradation of pollutants (Wu et al., 2019). Moreover, the light scattering effect at the interface of MNBs can effectively extend the effective path length of light, thereby improving the photocatalytic efficiency (Fan et al., 2021). These indicate that the application of MNBs plays a crucial role in enhancing oxidation performance.
5.4.1 Fenton oxidation
Adding “Fenton” as a search term in the search formula and connecting it with “and”, the keyword distribution map as shown in Figure 8 is obtained. The Fenton oxidation process generates non-selective degradation of organic pollutants. Under acidic conditions, H2O2 is activated by the single-electron transfer of Fe(II) to form ·OH, while Fe(III) is reduced to Fe(II) by H2O2, ensuring the regeneration of Fe ions and the continuous progress of the Fenton reaction (Huang et al., 2019). However, the limited active sites restrict the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Chen et al., 2023), and the short lifetime of ·OH reduces the degradation efficiency (Zhang et al., 2023). The keywords such as “Specific surface area” and “Interface reaction” in the figure imply that MNBs may enhance the Fenton oxidation process due to their huge specific surface area and dynamic interface reactions (Zhang et al., 2022b). The Fenton process assisted by MNBs has been proven to be effective in the removal of organic pollutants.
5.4.2 Plasma technology
Adding “plasma” as a search term in the search formula and connecting it with “and”, the keyword distribution map as shown in Figure 9 is obtained. “Advanced oxidation” indicates that plasma technology, as one of the AOPs, can effectively degrade organic pollutants in water by generating active species with strong oxidation capacity, such as hydroxyl radicals (·OH), ozone (O3), superoxide anions (O2−), etc. Plasma is a partially or fully ionized gas composed of electrons, free radicals, ions, and neutral substances, which can be generated through various discharges (Jiang et al., 2014; Rao et al., 2023). Plasma bubble technology combines the advantages of plasma and bubbles, bringing new breakthroughs to water pollution control. The key term “Dielectric barrier discharge” (DBD) is the most common driving method for generating non-thermal plasma (NTP), which is typically used in water treatment (Zhou et al., 2021b). Traditional plasma water treatment technologies, such as surface discharge and submerged discharge, have problems such as low transfer efficiency of active species and short contact time with pollutants (Zhang et al., 2021a). However, plasma bubble technology encapsulates the active species generated by plasma within bubbles, using the bubbles as carriers to extend the residence time of active species in the solution and increase the gas-liquid interface area, thereby significantly improving the degradation efficiency of pollutants (Zhang et al., 2022a). The highly reactive substances inside can be continuously released into the water and interact with pollutants through the annihilation of bubbles. The MNB-assisted method avoids the early consumption of ROS, thereby enhancing the removal efficiency of pollutants and reducing energy consumption. In the MNB-assisted plasma oxidation process, for plasma MNBs at room temperature, the bubbles must be larger than 30 μm to remain stable (Liu et al., 2018). After the formation of plasma MNBs, the presence of liquid films inside or between the MNBs under the influence of the streamer generated by the plasma can produce micro-discharge effects, thereby increasing the production of plasma reactive species (Chen et al., 2017).
Liu et al. constructed a plasma-microbubble system (BE-plasma), which demonstrated a strong synergistic effect in treating wastewater contaminated with diclofenac (DCF) (Liu et al., 1999). Under optimized process parameters, the degradation efficiency of DCF reached 90.9% within 45 min, far exceeding the treatment efficiency of using plasma or microbubbles alone. In the treatment of antibiotic pollution, Zhou et al. utilized non-thermal plasma bubbles to degrade cefixime antibiotics (Zhang et al., 2021b). The study found that this technology had a significant degradation effect on cefixime, with an energy yield of 1.5 g/kWh in a micro-porous reactor after 30 min of plasma treatment, and ·OH radicals played a key role in the degradation process.
In terms of gas pollution control, although related research is relatively scarce, plasma bubble technology also shows certain potential. In the treatment of VOCs, plasma bubble technology can degrade VOCs molecules into harmless small molecules through the reaction of active species generated. The principle is that high-energy electrons, free radicals, and other active species produced during the plasma discharge can break the chemical bonds in VOCs molecules, causing oxidation and decomposition reactions. Compared with traditional gas treatment technologies, plasma bubble technology has the advantages of mild reaction conditions and no need for catalysts, and is expected to become an efficient method for gas pollution control.
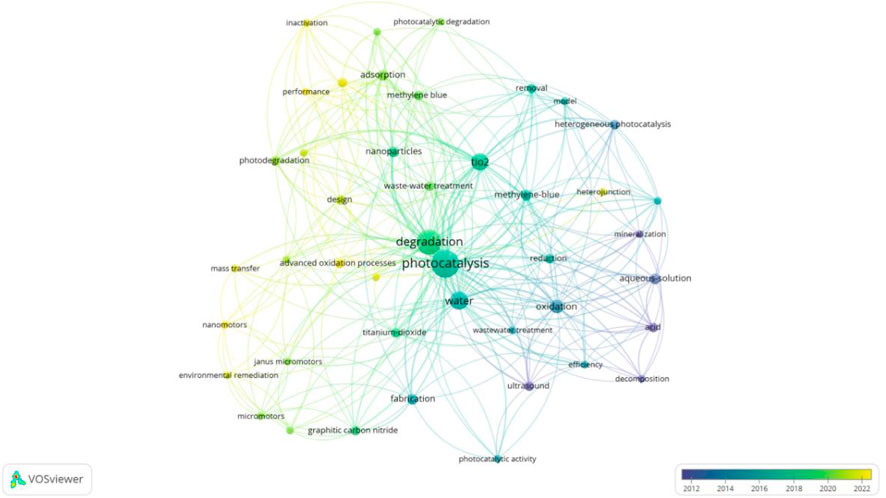
5.4.3 Photocatalytic technology
Photocatalytic technology is an advanced oxidation technology based on semiconductor materials. When semiconductor catalysts (such as “TiO2”, “heterojunctions”, etc.) are exposed to light with energy greater than their band gap energy, electrons are excited from the valence band to the conduction band, leaving holes in the valence band, thereby generating electron-hole pairs with strong oxidation capacity (Fu et al., 2019). These electron-hole pairs can react with substances such as water and oxygen adsorbed on the catalyst surface, generating ROS such as hydroxyl radicals (·OH), superoxide anions, etc.) (Liu et al., 2020; Weng et al., 2019). These reactive oxygen species have extremely high redox potentials and can oxidize and decompose various organic pollutants into harmless small molecules such as CO2 and H2O, achieving the degradation and mineralization of pollutants. However, photocatalytic technology still faces some challenges in practical applications. For example, photogenerated carriers (electrons and holes) are prone to recombination, reducing their efficiency in participating in photocatalytic reactions; the adsorption capacity of photocatalysts for pollutants is limited, and their dispersion in the reaction system is poor, affecting the rate and effect of photocatalytic reactions (Hao et al., 2021).
Coupling photocatalytic technology with MNB technology can achieve complementary advantages. The key to the combined application of photocatalytic technology and micro-nano bubble technology is demonstrated in Figure 10. On the one hand, MNBs can provide abundant oxygen for photocatalytic reactions, promote the separation of photogenerated carriers, and reduce the recombination of electron-hole pairs, thereby improving the efficiency of photocatalytic reactions (Agarwal et al., 2011; Dong et al., 2022). On the other hand, the reactive species generated by photocatalysis can synergize with the reactive species produced by the rupture of MNBs to enhance the oxidation and degradation of pollutants. Additionally, the presence of MNBs can improve the dispersion of photocatalysts in the solution, increase the contact opportunities between photocatalysts and pollutants, and further enhance the degradation effect.
In water pollution control, this coupled technology has shown significant advantages. Studies have shown that this technology has high efficiency in degrading various organic pollutants, such as dyes, antibiotics, and pesticides. When treating wastewater containing methylene blue, the photocatalytic and MNB coupled system can achieve efficient decolorization and mineralization of methylene blue in a relatively short time (Yang et al., 2022). MNBs not only increase the dissolved oxygen content in the system, promoting the progress of photocatalytic reactions, but also directly participate in the degradation of pollutants through the reactive species produced by their own rupture. At the same time, the reactive oxygen species generated by photocatalysis can also synergize with MNBs to improve the degradation efficiency (Selihin and Tay, 2022). In the treatment of wastewater containing bacteria, this coupled technology has a good inactivation effect on microorganisms. By destroying the cell structure of bacteria through various reactive oxygen species, they lose their activity, thereby achieving disinfection and purification of water bodies (Fan et al., 2021).
In the field of air pollution control, the coupled technology of photocatalysis and MNBs also has potential application value. For the degradation of VOCs, MNBs can carry oxygen and other oxidants, increasing the contact opportunities between VOCs and oxidants. Under light conditions, photocatalytic reactions generate a large number of reactive species, oxidizing and decomposing VOCs into harmless substances.
5.4.4 The advantages and prospects of the combined application of MNB technology
At present, the combination of MBs with various environmental treatment technologies is the most suitable development direction for MNB technology. The standalone MNB technology cannot generate sufficient active free radicals to degrade most pollutants in the environment. Although the ozone MNB technology is relatively mature, due to the uncertainty of control factors such as bubble existence form, stability, and size, as well as the lack of large-scale experimental data for complex polluted environments, the single MNB technology cannot be put into practical large-scale use yet. However, as an auxiliary technology coupled with other mature environmental treatment technologies, it benefits from its excellent free radical generation capacity and mass transfer efficiency, providing a better oxidation environment and enhancing the efficiency of other treatment technologies in degrading pollutants. It is a relatively practical auxiliary treatment technology. Especially, the combination of MBs with various advanced oxidation methods or photocatalytic methods has attracted increasing attention. This technology overcomes the limitations of ozone mass transfer utilization, effectively improving the oxidation efficiency of ozone. The presence of MBs keeps the catalyst particles in a dynamic dispersed state, effectively increasing the contact frequency between the catalyst and refractory organic compounds, significantly enhancing the mineralization efficiency of refractory organic compounds, and achieving efficient wastewater treatment.
6 Conclusion
MNB technology, with its unique physicochemical properties (such as large specific surface area, high surface Zeta potential, long stability and strong ability to generate oxidative free radicals), has demonstrated significant advantages in water pollution control (industrial wastewater, surface water, groundwater) and soil pollution remediation, and has become a research hotspot in the environmental field. By coupling with technologies such as ozone oxidation, photocatalysis, Fenton reaction and plasma technology, its pollutant degradation efficiency is significantly enhanced. For instance, the removal rate of plastic pollutants in industrial wastewater by ozone MNBs reaches 94.18%, and when combined with photocatalysis, it can increase the light absorption efficiency at a 700 nm light path by 54.8%.
China holds a dominant position in research in this field. Institutions such as Tsinghua University and the CAS have achieved remarkable results in applications such as groundwater remediation with ozone MNBs and semiconductor cleaning. However, the international cooperation network still needs to be strengthened. Keyword clustering analysis indicates that “degradation”, “ozone MNBs”, “free radicals”, and “photocatalysis” are the core research themes, and the coupling mechanism of technologies and interface reaction theory are the current exploration focuses.
However, the long-term stability of MNB technology in complex environments, the energy consumption and cost issues in large-scale applications, as well as the cross-disciplinary collaborative mechanisms (such as the interaction between microorganisms and bubbles) still require further research. In the future, efforts should be focused on technological optimization and adaptation to actual scenarios to promote its transformation from laboratory research to industrial applications, providing efficient solutions for global environmental pollution control.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
QC: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation. XZ: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation. YG: Project administration, Validation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition. QZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The present work was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (52270129), Oriental Talent Youth Program, Shanghai Shuguang Program (23SG52), and Guizhou Provincial Key Technology R&D Program [QKHZC(2024)153]. Guo also thanks the financial support of Science and Technology Development Fund of Pudong New Area (PKJ2022-C07), and Scientific Research Fund Project of Shanghai Polytechnic University (A10GY25G004-02).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Agarwal, A., Ng, W. J., and Liu, Y. (2011). Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 84, 1175–1180. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.054
Agarwal, M., Dikshit, P. K., Bhasarkar, J. B., Borah, A. J., and Moholkar, V. S. (2016). Physical insight into ultrasound-assisted biodesulfurization using free and immobilized cells of Rhodococcus rhodochrous MTCC 3552. Chem. Eng. J. 295, 254–267. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.042
Azuma, T., Otomo, K., Kunitou, M., Shimizu, M., Hosomaru, K., Mikata, S., et al. (2019). Removal of pharmaceuticals in water by introduction of ozonated microbubbles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 212, 483–489. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2018.11.059
Bao, J. F., Guo, S. S., Fan, D. D., Cheng, J. L., Zhang, Y., and Pang, X. (2023). Sonoactivated nanomaterials: a potent armament for wastewater treatment. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 99, 106569. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106569
Boonwan, C., Rojviroon, T., Rojviroon, O., Rajendran, R., Paramasivam, S., Chinnasamy, R., et al. (2024). Micro-nano bubbles in action: AC/TiO2 2 hybrid photocatalysts for efficient organic pollutant degradation and antibacterial activity. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 61, 103400. doi:10.1016/j.bcab.2024.103400
Cao, Y. Z., Hu, L. M., Jing, S., Wang, M. J., Wu, Z. X., Ji, L. J., et al. (2023). “Field Test Study of organics-contaminated groundwater In-Situ remediation by ozone micro-nano-bubbles,” in Proceedings of the 14th congress of the international-association-for-engineering-geology-and-the-environment (IAEG) (Chengdu: PEOPLES R CHINA), 709–719.
Chen, Y. C., and Chang, J. E. (2022). Removal of chlorine-contaminated groundwater by two-stage ozonation and biostimulation methods. J. Environ. Manag. 317, 115417. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115417
Chen, C., Li, F. Y., Chen, H. L., and Kong, M. G. (2017). Aqueous reactive species induced by a PCB surface micro-discharge air plasma device: a quantitative study. J. Phys. D-Applied Phys. 50, 445208. doi:10.1088/1361-6463/aa8be9
Chen, T. F., Yavuz, B. M., Delgado, A. G., Montoya, G., Van Winkle, D., Zuo, Y., et al. (2018). Impacts of moisture content during ozonation of soils containing residual petroleum. J. Hazard. Mater. 344, 1101–1108. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.060
Chen, C., Wang, Y. Y., Huang, Y. J., Hua, J., Qu, W., Xia, D. H., et al. (2023). Overlooked self-catalytic mechanism in phenolic moiety-mediated Fenton-like system: formation of Fe(III) hydroperoxide complex and co-treatment of refractory pollutants. Appl. Catal. B-Environment Energy 321, 122062. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122062
Cheng, W., Quan, X. J., Li, R. H., Wu, J., and Zhao, Q. H. (2018). Ozonation of phenol-containing wastewater using O3/Ca(OH)2 system in a micro bubble gas-liquid reactor. Ozone-Science and Eng. 40, 173–182. doi:10.1080/01919512.2017.1399791
Cheng, W., Jiang, L., Quan, X. J., Cheng, C., Huang, X. X., Cheng, Z. L., et al. (2019). Ozonation process intensification of p-nitrophenol by in situ separation of hydroxyl radical scavengers and microbubbles. Water Sci. Technol. 80, 25–36. doi:10.2166/wst.2019.227
Cheng, C., Huang, X. X., Cheng, W., Quan, X. J., Cheng, Z. L., Jiang, L., et al. (2021). Ozonation of biologically-treated municipal solid waste leachate using an integrated process of O3/Ca(OH)2 and microbubble reactor. Environ. Technol. 42, 2402–2412. doi:10.1080/09593330.2019.1703143
Chi, C. B., Huo, B. Q., Liang, Z. D., Hu, C. X., Sun, Q. Y., and Zhou, S. F. (2024). Study on tetracycline degradation in wastewater based on zero-valent nano iron assisted micro-nano bubbles. Alexandria Eng. J. 86, 577–583. doi:10.1016/j.aej.2023.12.004
Chu, L. B., Xing, X. H., Yu, A. F., Zhou, Y. N., Sun, X. L., and Jurcik, B. (2007). Enhanced ozonation of simulated dyestuff wastewater by microbubbles. Chemosphere 68, 1854–1860. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.014
Dai, C. M., Han, Y. M., Zhang, Y. L., Duan, Y. P., Tong, W. K., Liu, S. G., et al. (2023). Cyclic solubilization and release of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using gemini photosensitive surfactant combined with micro-nano bubbles: a promising enhancement technology for groundwater remediation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 309, 123042. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2022.123042
Deng, S. H., Jothinathan, L., Cai, Q. Q., Li, R., Wu, M. Y., Ong, S. L., et al. (2021). FeOx@GAC catalyzed microbubble ozonation coupled with biological process for industrial phenolic wastewater treatment: catalytic performance, biological process screening and microbial characteristics. Water Res. 190, 116687. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2020.116687
Dong, G. H., Chen, B., Liu, B., Hounjet, L. J., Cao, Y. Q., Stoyanov, S. R., et al. (2022). Advanced oxidation processes in microreactors for water and wastewater treatment: development, challenges, and opportunities. Water Res. 211, 118047. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2022.118047
Duan, Y. L., Yu, J., Zhang, R. X., Han, P. F., Ren, P., Liu, M., et al. (2022). Integrated MnO2 nanosheet ultrafiltration ceramic membrane with micro-nano bubbles for catalytic treatment of dye wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 300, 121786. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121786
Duan, Y. L., Zhao, D., Liu, Z. Y., and Yu, J. (2025). Hydrogen peroxide enhancing the process of MnO2-modified ceramic membrane catalyzing micro-nano bubble. Sep. Purif. Technol. 353, 128320. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2024.128320
El Aswar, E. I., Li, M. K., Huang, Y. Y., Sun, Z., Li, W. T., and Qiang, Z. M. (2025). Enhanced vacuum ultraviolet/ultraviolet process for advanced water treatment by using air micro/nano bubbles. J. Hazard. Mater. 489, 137602. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137602
Entezari, M. H., and Ghows, N. (2011). Micro-emulsion under ultrasound facilitates the fast synthesis of quantum dots of CdS at low temperature. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 18, 127–134. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.04.001
Fan, W., Zhou, Z., Wang, W. T., Huo, M. X., Zhang, L. L., Zhu, S. Y., et al. (2019). Environmentally friendly approach for advanced treatment of municipal secondary effluent by integration of micro-nano bubbles and photocatalysis. J. Clean. Prod. 237, 117828. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117828
Fan, W., Cui, J. Y., Li, Q., Huo, Y., Xiao, D., Yang, X., et al. (2021). Bactericidal efficiency and photochemical mechanisms of micro/nano bubble-enhanced visible light photocatalytic water disinfection. Water Res. 203, 117531. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2021.117531
Fu, Y. S., Li, J., and Li, J. G. (2019). Metal/semiconductor nanocomposites for photocatalysis: fundamentals, structures, applications and properties. Nanomaterials 9, 359. doi:10.3390/nano9030359
Han, Y. M., Dai, C. M., Li, J. X., Li, Z., Zhang, Y. L., Hon, L. K., et al. (2025). Reversible surfactant combined with micro-nano bubbles and peroxymonosulfate: a method for cyclic remediation of PAHs contaminated soil and groundwater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 354, 129491. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2024.129491
Hao, L., Huang, H. W., Zhang, Y. H., and Ma, T. Y. (2021). Oxygen vacant semiconductor photocatalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2100919. doi:10.1002/adfm.202100919
Haris, S., Qiu, X. B., Klammler, H., and Mohamed, M. M. A. (2020). The use of micro-nano bubbles in groundwater remediation: a comprehensive review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 11, 100463. doi:10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100463
Hoang, S. A., Bolan, N., Madhubashani, A. M. P., Vithanage, M., Perera, V., Wijesekara, H., et al. (2022). Treatment processes to eliminate potential environmental hazards and restore agronomic value of sewage sludge: a review. Environ. Pollut. 293, 118564. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118564
Hu, L. M., and Xia, Z. R. (2018). Application of ozone micro-nano-bubbles to groundwater remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 342, 446–453. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.08.030
Hu, L. L., Chen, B. Y., and Ma, J. (2023). Micro-/nano-bubbles ozonation for effective industrial wastewater remediation: from lab to pilot-scale application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11, 110807. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2023.110807
Huang, X. P., Chen, Y., Walter, E., Zong, M. R., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2019). Facet-specific photocatalytic degradation of organics by heterogeneous fenton chemistry on hematite nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 53, 10197–10207. doi:10.1021/acs.est.9b02946
Huang, Z. L., Chen, Q. Y., Yao, Y., Chen, Z., and Zhou, J. (2021). Micro-bubbles enhanced removal of diesel oil from the contaminated soil in washing/flushing with surfactant and additives. J. Environ. Manag. 290, 112570. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112570
Ishida, N., Inoue, T., Miyahara, M., and Higashitani, K. (2000). Nano bubbles on a hydrophobic surface in water observed by tapping-mode atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 16, 6377–6380. doi:10.1021/la000219r
Ji, H. D., Gong, Y. Y., Duan, J., Zhao, D. Y., and Liu, W. (2018). Degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in seawater by simulated surface-level atmospheric ozone: reaction kinetics and effect of oil dispersant. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 135, 427–440. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.047
Jiang, B., Zheng, J. T., Qiu, S., Wu, M. B., Zhang, Q. H., Yan, Z. F., et al. (2014). Review on electrical discharge plasma technology for wastewater remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 236, 348–368. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.090
Jing, M. Y., Zhang, J. P., Li, G. J., Zhang, D., Liu, F. J., and Yang, S. K. (2025). Micro-nano bubbles enhanced immobilized Chlorella vulgaris to remove ofloxacin from groundwater. J. Contam. Hydrology 268, 104458. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2024.104458
John, A., Brookes, A., Carra, I., Jefferson, B., and Jarvis, P. (2022). Microbubbles and their application to ozonation in water treatment: a critical review exploring their benefit and future application. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 1561–1603. doi:10.1080/10643389.2020.1860406
Khan, N. A., and Carroll, K. C. (2020). Natural attenuation method for contaminant remediation reagent delivery assessment for in situ chemical oxidation using aqueous ozone. Chemosphere 247, 125848. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125848
Khuntia, S., Majumder, S. K., and Ghosh, P. (2012). Microbubble-aided water and wastewater purification: a review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 28, 191–221. doi:10.1515/revce-2012-0007
Kim, S. Y., Park, J. W., Noh, J. H., Bae, Y. H., and Maeng, S. K. (2022). Potential organic matter management for industrial wastewater guidelines using advanced dissolved organic matter characterization tools. J. Water Process Eng. 46, 102604. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102604
Koundle, P., Nirmalkar, N., Momotko, M., Makowiec, S., and Boczkaj, G. (2024). Tetracycline degradation for wastewater treatment based on ozone nanobubbles advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) - focus on nanobubbles formation, degradation kinetics, mechanism and effects of water composition. Chem. Eng. J. 501, 156236. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.156236
Kwon, H., Mohamed, M. M., Annable, M. D., and Kim, H. (2020). Remediation of NAPL-contaminated porous media using micro-nano ozone bubbles: bench-scale experiments. J. Contam. Hydrology 228, 103563. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2019.103563
Lee, E. J., Kim, Y. H., Kim, H. S., and Jang, A. (2015). Influence of microbubble in physical cleaning of MF membrane process for wastewater reuse. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 8451–8459. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3928-y
Levanov, A. V., Isaikina, O. Y., Gasanova, R. B., and Lunin, V. V. (2017). Coefficient of ozone mass transfer during its interaction with an aqueous solution of formic acid in a bubble column reactor. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 91, 1427–1431. doi:10.1134/s0036024417080167
Li, P., Takahashi, M., and Chiba, K. (2009). Degradation of phenol by the collapse of microbubbles. Chemosphere 75, 1371–1375. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.03.031
Li, H. Z., Hu, L. M., and Xia, Z. R. (2013). Impact of groundwater salinity on bioremediation enhanced by micro-nano bubbles. Materials 6, 3676–3687. doi:10.3390/ma6093676
Li, H. Z., Hu, L. M., Song, D. J., and Al-Tabbaa, A. (2014). Subsurface transport behavior of micro-nano bubbles and potential applications for groundwater remediation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 11, 473–486. doi:10.3390/ijerph110100473
Li, G. J., Cheng, Y., Jing, M. Y., Zhang, D., Ma, Y. F., and Yang, S. K. (2024). Degradation of norfloxacin by the synergistic effect of micro-nano bubbles and sodium hypochlorite: kinetics, influencing factors and pathways. Environ. Science-Processes and Impacts 26, 2189–2202. doi:10.1039/d4em00490f
Li, P., Huang, X. J., Yang, Q., Xia, H. Z., Li, C. B., Zhang, Z. Q., et al. (2025a). Micro-nano bubbles enhanced degradation of emerging contaminants by ferrous-oxalate complexes: synergistic interaction between oxidation and coagulation. Front. Environ. Sci. and Eng. 19, 66. doi:10.1007/s11783-025-1986-7
Li, L. N., Fang, L. L., Shen, J. M., Wang, B. Y., Yuan, L., and Guo, Y. Q. (2025b). Removal of ibuprofen via the O3/H2O2 oxidation system: performance, degradation mechanism, and toxicity evaluation. Water 17, 1414. doi:10.3390/w17101414
Lim, S., Shi, J. L., von Gunten, U., and McCurry, D. L. (2022). Ozonation of organic compounds in water and wastewater: a critical review. Water Res. 213, 118053. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2022.118053
Liu, J., Lam, Y. L., Chan, Y. C., Zhou, Y., and Yao, J. (1999). Fabrication of high-performance dispersion compensating fiber by plasma chemical vapor deposition. Fiber Integr. Opt. 18, 63–67. doi:10.1080/014680399244703
Liu, Y. A., Zhang, H., Sun, J. H., Liu, J. X., Shen, X., Zhan, J. X., et al. (2018). Degradation of aniline in aqueous solution using non-thermal plasma generated in microbubbles. Chem. Eng. J. 345, 679–687. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.057
Liu, B. S., Wu, H., and Parkin, I. P. (2020). New insights into the fundamental principle of semiconductor photocatalysis. Acs Omega 5, 14847–14856. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c02145
Liu, S. T., Yang, J. W., Zhang, Y. L., Wu, T. L., and Chen, C. M. (2025). High-efficiency degradation mechanism of sulfadiazine by ozone micro-nano bubbles: the effect of gas flow rate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 376, 134140. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2025.134140
Loh, W. H., Cai, Q. Q., Li, R., Jothinathan, L., Lee, B. C. Y., Ng, O. H., et al. (2021). Reverse osmosis concentrate treatment by microbubble ozonation-biological activated carbon process: organics removal performance and environmental impact assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 798, 149289. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149289
Ma, X., Jang, S., Popescu, M. N., Uspal, W. E., Miguel-López, A., Hahn, K., et al. (2016). Reversed janus micro/nanomotors with internal chemical engine. Acs Nano 10, 8751–8759. doi:10.1021/acsnano.6b04358
Masry, M., Rossignol, S., Roussel, B. T., Bourgogne, D., Bussi, P. O., R'Mili, B., et al. (2021). Experimental evidence of plastic particles transfer at the water-air interface through bubble bursting. Environ. Pollut. 280, 116949. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116949
Melich, R., Valour, J. P., Urbaniak, S., Padilla, F., and Charcosset, C. (2019). Preparation and characterization of perfluorocarbon microbubbles using Shirasu Porous Glass (SPG) membranes. Colloids Surfaces a-Physicochemical Eng. Aspects 560, 233–243. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.09.058
Michailidi, E. D., Bomis, G., Varoutoglou, A., Kyzas, G. Z., Mitrikas, G., Mitropoulos, A. C., et al. (2020). Bulk nanobubbles: production and investigation of their formation/stability mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 564, 371–380. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.093
Mo, J. C., Lin, T., Liu, W., Zhang, Z. B., and Yan, Y. (2024). Cleaning efficiency and mechanism of ozone micro-nano-bubbles on ceramic membrane fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 331, 125698. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125698
Mohite, R. G., and Garg, A. (2017). Performance of heterogeneous catalytic wet oxidation for the removal of phenolic compounds: catalyst characterization and effect of pH, temperature, metal leaching and non-oxidative hydrothermal reaction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5, 468–478. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.024
Park, J. Y., Choi, Y. J., Moon, S., Shin, D. Y., and Nam, K. (2009). Microbubble suspension as a carrier of oxygen and acclimated bacteria for phenanthrene biodegradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 163, 761–767. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.024
Parker, J. L., Claesson, P. M., and Attard, P. (1994). Bubbles, cavities, and the long-ranged attraction between hydrophobic surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. 98, 8468–8480. doi:10.1021/j100085a029
Pétrier, C., Torres-Palma, R., Combet, E., Sarantakos, G., Baup, S., and Pulgarin, C. (2010). Enhanced sonochemical degradation of bisphenol-A by bicarbonate ions. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 17, 111–115. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.05.010
Ponce-Robles, L., Pagán-Muñoz, A., Lara-Guillén, A. J., Masdemont-Hernández, B., Munuera-Pérez, T., Nortes-Tortosa, P. A., et al. (2023). Full-scale O3/Micro-Nano bubbles system based advanced oxidation as alternative tertiary treatment in WWTP effluents. Catalysts 13, 188. doi:10.3390/catal13010188
Rao, N., Chu, X., Hadinoto, K., Angelina, A., Zhou, R., Zhang, T., et al. (2023). Algal cell inactivation and damage via cold plasma-activated bubbles: mechanistic insights and process benefits. Chem. Eng. J. 454, 140304. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.140304
Ren, Y. H., Wang, Y. L., Wang, X. L., Liu, B. Z., He, G. L., Gong, Y. L., et al. (2025). The degradation of 2-methylisobornyl alcohol and geosmin through a micro-nano bubble-activated ozone process: the dual mechanism of enhanced degradation efficiency. Environ. Science-Water Res. and Technol. 11, 1177–1185. doi:10.1039/d4ew00944d
Selihin, N. M., and Tay, M. G. (2022). A review on future wastewater treatment technologies: micro-nanobubbles, hybrid electro-Fenton processes, photocatalytic fuel cells, and microbial fuel cells. Water Sci. Technol. 85, 319–341. doi:10.2166/wst.2021.618
Seridou, P., and Kalogerakis, N. (2021). Disinfection applications of ozone micro- and nanobubbles. Environ. Science-Nano 8, 3493–3510. doi:10.1039/d1en00700a
Shen, D. S., Xie, Z. M., Shentu, J., Long, Y. Y., Lu, L., Li, L. L., et al. (2023). Enhanced oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons by ozone micro-nano bubble water: mechanism and influencing factors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11, 110281. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2023.110281
Shen, D. S., Li, L. L., Luo, J., Jia, J., Tang, L., Long, Y. Y., et al. (2024). Enhanced removal of toluene in heterogeneous aquifers through injecting encapsulated ozone micro-nano bubble water. J. Hazard. Mater. 468, 133810. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133810
Shi, X. N., Xue, S., Marhaba, T., and Zhang, W. (2021). Probing internal pressures and long-term stability of nanobubbles in water. Langmuir 37, 2514–2522. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c03574
Soler, L., Magdanz, V., Fomin, V. M., Sanchez, S., and Schmidt, O. G. (2013). Self-propelled micromotors for cleaning polluted water. ACS Nano 7, 9611–9620. doi:10.1021/nn405075d
Sun, Z. Y., Chen, X. L., Yang, K. Y., Zhua, N. W., and Lou, Z. Y. (2020a). The progressive steps for TPH stripping and the decomposition of oil refinery sludge using microbubble ozonation. Sci. Total Environ. 712, 135631. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135631
Sun, Z. Y., Xia, F. J., Lou, Z. Y., Chen, X. L., Zhu, N. W., Yuan, H. P., et al. (2020b). Innovative process for total petroleum hydrocarbons reduction on oil refinery sludge through microbubble ozonation. J. Clean. Prod. 256, 120337. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120337
Takahashi, M., Chiba, K., and Li, P. (2007a). Free-radical generation from collapsing microbubbles in the absence of a dynamic stimulus. J. Phys. Chem. B 111, 1343–1347. doi:10.1021/jp0669254
Takahashi, M., Chiba, K., and Li, P. (2007b). Formation of hydroxyl radicals by collapsing ozone microbubbles under strongly acidic conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 111, 11443–11446. doi:10.1021/jp074727m
Takahashi, M., Horibe, H., Matsuura, K., and Tatera, K. (2015). Effect of microbubbles on ozonized water for photoresist removal. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 28, 293–298. doi:10.2494/photopolymer.28.293
Temesgen, T., Bui, T. T., Han, M., Kim, T. I., and Park, H. (2017). Micro and nanobubble technologies as a new horizon for water-treatment techniques: a review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 246, 40–51. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2017.06.011
Ulatowski, K., Sobieszuk, P., Mróz, A., and Ciach, T. (2019). Stability of nanobubbles generated in water using porous membrane system. Chem. Eng. Processing-Process Intensif. 136, 62–71. doi:10.1016/j.cep.2018.12.010
Ulatowski, K., Szczygielski, P., and Sobieszuk, P. (2024). Impact of water purity and oxygen content in gas phase on effectiveness of surface cleaning with microbubbles. Materials 17, 6046. doi:10.3390/ma17246046
Utaka, Y., Okuda, S., and Tasaki, Y. (2009). Configuration of the micro-layer and characteristics of heat transfer in a narrow gap mini/micro-channel boiling system. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 2205–2214. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2008.11.020
Villa, K., Palenzuela, C. L. M., Sofer, Z., Matejková, S., and Pumera, M. (2018). Metal-free visible-light photoactivated C3N4 bubble-propelled tubular micromotors with inherent fluorescence and On/Off capabilities. Acs Nano 12, 12482–12491. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b06914
Wang, B. G., Wang, L. J., Cen, W. X., Lyu, T., Jarvis, P., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024a). Exploring a chemical input free advanced oxidation process based on nanobubble technology to treat organic micropollutants. Environ. Pollut. 340, 122877. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122877
Wang, Y. L., Wei, J. J., Hu, J., Guo, Z. M., and Bai, W. L. (2024b). Research on the kinetics and degradation pathways of gaseous acetic acid ester organics. Environ. Technol. 45, 2721–2734. doi:10.1080/09593330.2023.2185819
Wei, Z. H., Le, Q. V., Peng, W. X., Yang, Y. F., Yang, H., Gu, H. P., et al. (2021). A review on phytoremediation of contaminants in air, water and soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 403, 123658. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123658
Weng, B., Qi, M. Y., Han, C., Tang, Z. R., and Xu, Y. J. (2019). Photocorrosion inhibition of semiconductor-based photocatalysts: basic principle, current development, and future perspective. Acs Catal. 9, 4642–4687. doi:10.1021/acscatal.9b00313
Wu, C., Li, P., Xia, S. J., Wang, S., Wang, Y., Hu, J., et al. (2019). The role of interface in microbubble ozonation of aromatic compounds. Chemosphere 220, 1067–1074. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.174
Xia, Z. R., and Hu, L. M. (2019). Treatment of organics contaminated wastewater by ozone micro-nano-bubbles. Water 11, 55. doi:10.3390/w11010055
Xia, Z. R., Hu, L. M., Kusaba, S., and Song, D. J. (2018). “Remediation of TCE contaminated site by ozone micro-nano-bubbles,” in Proceedings of the 8th international Congress on environmental geotechnics (ICEG) (Hangzhou: PEOPLES R CHINA), 796–803.
Xiao, Z. G., Bin Aftab, T., and Li, D. X. (2019). Applications of micro-nano bubble technology in environmental pollution control. Micro and Nano Lett. 14, 782–787. doi:10.1049/mnl.2018.5710
Xiao, W., Zhang, H., Wang, X. H., Wang, B., Long, T., Deng, S., et al. (2022). Interaction mechanisms and application of Ozone micro/nanobubbles and nanoparticles: a review and perspective. Nanomaterials 12, 1958. doi:10.3390/nano12121958
Xiao, Y. T., Liu, H. L., Sun, C. X., Wang, D. Z., Li, L. H., Shao, L., et al. (2025). Research progress of micro-nano bubbles in environmental remediation: mechanisms, preparation methods, and applications. J. Environ. Manag. 375, 124387. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.124387
Yang, C. Y., Xue, Z. W., Yin, H., Lu, K., and Liu, W. (2022). Aqueous foam loaded TiO2 nano-catalysts for promoting photodegradation of methylene blue. J. Nanoparticle Res. 24, 59. doi:10.1007/s11051-022-05441-3
Yang, X. D., Li, J., Song, R., Zhao, B., Tang, J. M., Kong, L. A., et al. (2023a). Highly reproducible van der Waals integration of two-dimensional electronics on the wafer scale. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 471–478. doi:10.1038/s41565-023-01342-1
Yang, Y., Yao, X., Wu, S. H., Wang, X., Feng, L., Feng, X. D., et al. (2023b). Enhanced treatment of azo dyes in wastewater using heat-activated persulfate with micro-nano bubble aeration. Chem. Eng. Res. and Des. 197, 24–37. doi:10.1016/j.cherd.2023.07.013
Yang, Y., Wang, X., Wu, S. H., Yao, X., Feng, L., Feng, X. D., et al. (2023c). Insight into the application of micro-nano bubbles combined with heat-activated persulfate oxidation for removing dissolved organic matter from printing and dying wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 56, 104463. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.104463
Yang, X. L., Chen, L., Oshita, S., Fan, W. H., and Liu, S. (2023d). Mechanism for enhancing the ozonation process of Micro- and nanobubbles: bubble behavior and interface reaction. Acs Es&T Water 3, 3835–3847. doi:10.1021/acsestwater.3c00031
Yasui, K., Tuziuti, T., and Kanematsu, W. (2016). Extreme conditions in a dissolving air nanobubble. Phys. Rev. E 94, 013106. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.94.013106
Yasui, K., Tuziuti, T., and Kanematsu, W. (2019). High temperature and pressure inside a dissolving oxygen nanobubble. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 55, 308–312. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.01.013
Ye, H., Wang, Y., Xu, D. D., Liu, X. J., Liu, S. M., and Ma, X. (2021). Design and fabrication of micro/nano-motors for environmental and sensing applications. Appl. Mater. Today 23, 101007. doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2021.101007
Ye, J., Ling, Z. X., Li, C., Dai, M. Y., Chen, Q., Gu, Y. L., et al. (2025). Micro-nanobubble-assisted tetracycline degradation by biochar-supported FeCo-metal-organic framework derivatives/persulfate system. Colloids Surfaces a-Physicochemical Eng. Aspects 718, 136911. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2025.136911
Yi, H., Almatrafi, E., Ma, D. S., Huo, X. Q., Qin, L., Li, L., et al. (2023). Spatial confinement: a green pathway to promote the oxidation processes for organic pollutants removal from water. Water Res. 233, 119719. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2023.119719
Zhang, J., Huang, G. Q., Liu, C., Zhang, R. N., Chen, X. X., and Zhang, L. (2018). Synergistic effect of microbubbles and activated carbon on the ozonation treatment of synthetic dyeing wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 201, 10–18. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2018.02.003
Zhang, H., Li, P., Zhang, A., Sun, Z. Y., Liu, J. X., Héroux, P., et al. (2021a). Enhancing interface reactions by introducing microbubbles into a plasma treatment process for efficient decomposition of PFOA. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 55, 16067–16077. doi:10.1021/acs.est.1c01724
Zhang, T. Q., Zhou, R. W., Wang, P. Y., Mai-Prochnow, A., McConchie, R., Li, W. S., et al. (2021b). Degradation of cefixime antibiotic in water by atmospheric plasma bubbles: performance, degradation pathways and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 421, 127730. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.127730
Zhang, M., Liu, J. Y., Tang, L. F., Hu, N., Zhang, D. Y., and Pan, X. L. (2022a). Fenton micro-reactor on a bubble: a novel microbubble-triggered simultaneous capture and catalytic oxidation strategy for recalcitrant organic pollutant removal. Sci. Total Environ. 835, 155556. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155556
Zhang, Y., Fan, W. H., Li, X. M., Wang, W. X., and Liu, S. (2022b). Enhanced removal of free radicals by aqueous hydrogen nanobubbles and their role in oxidative stress. Environ. Sci. and Technol. 56, 15096–15107. doi:10.1021/acs.est.2c03707
Zhang, M., Yu, B. L., Fang, Q. K., Liu, J. Y., Xia, Q. Y., Ye, K., et al. (2023). Microbiome recognition of virulence-factor-governed interfacial mechanisms in antibiotic resistance and pathogenicity removal by functionalized microbubbles. Water Res. 242, 120224. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2023.120224
Zhang, J. H., Fang, Y. M., Lin, J. W., Du, W. X., Feng, Z. Y., Lin, Y., et al. (2024). Generalized and scalable synthesis of manganese dioxide-based tubular micromotors for heavy metal ion removal. Acs Nano 18, 29248–29260. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c11716
Zhang, B., Chen, Q. H., Tang, H. L., Qi, R. Q., and Shi, W. X. (2025). Micro-nano bubbles enhance the Fe(II)/persulfate process for ultrafiltration membrane fouling control: performance and mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 733, 124371. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2025.124371
Zhao, M. Y., Cui, H. N., Wang, C., and Song, Q. J. (2024a). Development of a 10-litre pilot scale micro-nano bubble (MNB)-enhanced photocatalytic system for wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. 45, 6200–6209. doi:10.1080/09593330.2024.2328660
Zhao, K., Padervand, M., Ren, H. T., Jia, T. T., Guo, Q. Q., Yang, L. P., et al. (2024b). Enhancing tetracycline removal efficiency through Ozone micro-nano bubbles: environmental implication and degradation pathway. Acs Es&T Eng. 4, 1860–1870. doi:10.1021/acsestengg.4c00102
Zhou, L. M., Wang, X. Y., Shin, H. J., Wang, J., Tai, R. Z., Zhang, X. H., et al. (2020). Ultrahigh density of gas molecules confined in surface nanobubbles in ambient water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 5583–5593. doi:10.1021/jacs.9b11303
Zhou, Y. L., Han, Z. Y., He, C. L., Feng, Q., Wang, K. T., Wang, Y. B., et al. (2021a). Long-term stability of different kinds of gas nanobubbles in deionized and salt water. Materials 14, 1808. doi:10.3390/ma14071808
Keywords: MNBs, environmental remediation, ozone oxidation, photocatalysis, free radicals, multi-technology coupling
Citation: Chen Q, Zhu X, Guo Y and Zhou Q (2025) Research progress of micro-nano-bubbles in environmental remediation field. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1623566. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1623566
Received: 06 May 2025; Accepted: 11 August 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Nsikak U. Benson, Topfaith University, NigeriaReviewed by:
Jin Qian, Northwestern Polytechnical University, ChinaV N Meena Devi, Noorul Islam University, India
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Zhu, Guo and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yaoguang Guo, eWdndW9Ac3NwdS5lZHUuY24=; Quanfa Zhou, emhvdXF1YW5mYUAxNjMuY29t
 Qin Chen
Qin Chen Xinjie Zhu
Xinjie Zhu Yaoguang Guo
Yaoguang Guo