- 1Institute of Climate and Environment, SIMAD University, Mogadishu, Somalia
- 2Faculty of Economics, SIMAD University, Mogadishu, Somalia
- 3Center for Sustainable and Inclusive Development Studies (SID), Faculty of Economics and Management, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
Introduction: Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) faces growing pressure to align economic progress with environmental sustainability, as the region contends with climate stress, industrial expansion, and resource-driven growth. Yet, there remains a limited understanding of the combined influence of clean energy, digitalization, foreign direct investment (FDI), and industrial development on the region’s sustainable transition.
Methods: This study explores the association between clean energy usage, FDI, economic growth, digitalization, industrialization, urbanization, and environmental sustainability across 38 SSA countries from 2001 to 2020. It applies econometric techniques including the pooled mean group estimator and method of moments quantile regression.
Results: The analysis affirms the transformative potential of renewable energy, which significantly reduces both ecological footprints and environmental pollution. FDI demonstrates dual effects-fostering technological improvements while amplifying ecological footprints through resource-intensive investments. Economic growth is consistently related to increased emissions and ecological impact. Strikingly, digitalization proposes promising pathways for sustainability, while industrialization and urbanization exacerbate environmental challenges. Quantile regression results reveal that these effects vary across different levels of environmental impact. The Dumitrescu–Hurlin panel causality test affirms bidirectional causalities in at least one cross-section.
Discussion: Sustainable development in SSA requires prioritizing renewable energy adoption, regulating FDI to align with environmental goals, integrating sustainability into economic and industrial policies, and expanding digitalization for smarter resource management.
1 Introduction
Environmental sustainability has recently become a paramount global concern. However, despite considerable emphasis on sustainable development, issues such as climate change and biodiversity loss continue to undermine global efforts (Guo et al., 2023; Moreno et al., 2023; Saleem et al., 2024). These persistent environmental challenges demonstrate the imperative to understand and develop strategies that ensure development aligns with ecological preservation. In response to these pressing needs, digitalization—particularly information and communication technology (ICT)—delivers innovative solutions to mitigate environmental degradation (Anser et al., 2021; N’dri et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Advancements in ICT provide practical avenues for responding to environmental challenges by improving the efficiency of resource use, strengthening systems for environmental monitoring, and supporting the uptake of sustainable practices (Wang et al., 2023). ICT also contributes to the optimization of energy systems through the deployment of smart grids, which rely on sensors and communication infrastructure to regulate electricity usage and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. These systems reduce reliance on fossil fuels, contribute to lower greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, enhance energy performance, and expand access to cleaner cooking fuels (Chang et al., 2022a; Elkhorchani and Grayaa, 2016; Murshed, 2020).
FDI can play a pivotal role in achieving environmental sustainability by facilitating the transfer of advanced technologies, encouraging innovation, and promoting environmentally friendly practices in host countries (Abbas et al., 2021; Demena and Afesorgbor, 2020). It is widely recognized that foreign investments can drive the adoption of cleaner technologies, improve energy efficiency, and elevate regulatory standards through the diffusion of best practices and environmentally sound innovations (Huang et al., 2019; Islam et al., 2021; Uche et al., 2023). For instance, green FDI, which emphasizes renewable energy and sustainable industrial processes, has been shown to significantly reduce ecological footprints in some developing nations. However, the environmental effects of FDI are not universally positive. Some multinational corporations exploit weaker environmental regulations in host countries to minimize operational costs, which leads to unsustainable practices such as resource depletion, deforestation, and the establishment of high-emission manufacturing facilities (Ben-David et al., 2021; Liu A. et al., 2024). These activities often result in increased CO2 emissions and ecological degradation, which undermines long-term sustainability goals. This dual nature of FDI illuminates the critical need for stringent environmental policies and enforcement mechanisms to ensure that foreign investments align with sustainable development objectives and contribute positively to environmental quality.
Industrial growth is a key driver of economic development, but it often imposes significant environmental pressures through heightened emissions, resource depletion, and pollution (Sarkodie et al., 2020; Usman and Balsalobre-Lorente, 2022). The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis identifies that economic growth initially worsens environmental degradation but later leads to improvements as income levels rise beyond a certain threshold (Mohamed et al., 2025; Ahmed et al., 2025; Grossman and Krueger, 1995). To address these challenges, the adoption of sustainable industrial practices, including energy-efficient technologies and stricter environmental regulations, can mitigate the negative impacts of industrialization (Chen and Cheng, 2017; Chen et al., 2021). Additionally, industrial diversification toward less polluting sectors enhances environmental outcomes while maintaining economic growth (Ren et al., 2024; Yu and Wang, 2021). Moreover, urbanization presents complex interactions with the environment (Abdi and Hashi, 2024). While urban growth often increases pollution and resource consumption, it also enables the development of sustainable infrastructure, renewable energy utilization, climate-smart agriculture, and innovations in industrial technologies. These outcomes contribute to employment generation, economic diversification, and poverty reduction, which alters environmental outcomes (Dingru et al., 2023; Ogwu, 2019; Salahuddin et al., 2019). Comprehending these dynamics is paramount for balancing economic and environmental preferences in swiftly urbanizing regions.
Environmental degradation in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) arises from multiple sources, including deforestation, dependence on non-renewable energy, rapid urbanization, and inadequate waste management practices (Abdi, 2023; Wang and Dong, 2019). The region’s heavy reliance on fossil fuels for energy production exacerbates air pollution and contributes significantly to climate change, which creates substantial barriers to achieving sustainable development (Cai, 2024; IRENA, 2024; Low Carbon Power, 2022). In 2023, FDI inflows to SSA totaled approximately USD 38 billion, shaping both the region’s economic growth and environmental outcomes (World Bank Open Data, 2024a). Industrialization, particularly in the construction and manufacturing sectors, accounted for 38.6% of SSA’s GDP in 2023 (World Bank Open Data, 2024b; World Bank Open Data, 2024c). However, these economic activities often aggravate environmental degradation unless they are aligned with sustainable practices. Transitioning to renewable energy sources deliver a promising pathway for mitigating environmental degradation in SSA (Abdi, 2023; Owusu and Asumadu-Sarkodie, 2016; Rahman et al., 2022). These energy sources reduce dependence on fossil fuels, lower GHG emissions, and contribute to long-term environmental sustainability (Acheampong et al., 2019; Adams and Acheampong, 2019; Deng et al., 2020; Güney, 2019; Rahman et al., 2022). Furthermore, renewable energy projects stimulate economic growth, generate employment opportunities, and enhance energy security, which handles both environmental and developmental challenges simultaneously (AlNemer et al., 2023; Mohamud and Mohamud, 2023; Riti et al., 2022; Saidi and Omri, 2020).
Despite these promising avenues, SSA continues to face significant challenges in achieving environmental sustainability. According to Global Footprint Network, the dynamics of ecological footprint and biocapacity across SSA reveal distinct trends over the past half-century. Western and Southern Africa experience escalating ecological deficits as footprints surpass biocapacity. Eastern Africa followed this pattern after 2005, while Central African countries sustained an ecological surplus, with biocapacity balancing or exceeding its footprint. High dependency on non-renewable energy sources, insufficient investment in renewable energy infrastructure, and inadequate regulatory frameworks exacerbate environmental degradation and hinder the implementation of effective sustainability measures (Byaro et al., 2022; Moyo and Oree, 2024; Oluoch et al., 2021; Pueyo, 2018). Limited access to financing for green energy projects further restricts the region’s transition to renewable energy, particularly for low-income countries. The lack of cohesive energy policies undermines efforts to adopt sustainable technologies, leaving SSA vulnerable to rising carbon footprints and ecological degradation (Abdi and Hashi, 2024). The digital divide in ICT adoption and environmentally detrimental FDI amplify environmental inequalities, which reflects the interaction of economic, technological, and environmental factors impeding progress (Zhang and Choi, 2025). Poorly regulated FDI often prioritizes resource extraction and pollution-intensive industries. Simultaneously, limited digital infrastructure prevents the adoption of technologies that could enhance resource efficiency. Rapid urbanization compounds these issues, with inadequate planning leading to unchecked pollution, deforestation, and inefficient waste management (Ahmed et al., 2025). While existing literature broadly examines the relationship between economic growth and environmental sustainability (Abdi, 2023; Adzawla et al., 2019; Iheonu et al., 2021; Qudrat-Ullah and Nevo, 2021; Tenaw and Beyene, 2021), little attention is given to how digitalization, FDI, industrialization, urbanization, and renewable energy collectively shape environmental outcomes in SSA.
This study engages with these gaps in the literature by investigating the roles of digitalization, FDI, and renewable energy in mitigating environmental degradation in SSA. It offers several contributions to the current body of research and policy discourse. Initially, the study utilizes panel data from 38 SSA countries spanning 2001 to 2020, which provides the first detailed and robust dataset to explore the combined effects of digitalization and FDI on environmental quality in SSA, an area with limited empirical research. Digitalization is measured through an ICT index constructed from multiple indicators, moving beyond the reliance on single-variable proxies that often fail to capture the full scope of technological diffusion. Subsequently, the study focuses on both ecological footprints and environmental pollution, which provides a broader assessment of environmental stress than prior research that tends to emphasize carbon emissions alone (Warsame et al., 2023; Ahmed et al., 2025). This distinction is particularly relevant in SSA, where comparatively low emission levels coexist with substantial ecological strain. Following this, the analysis applies a range of econometric techniques to enhance methodological robustness. These include tests for cross-sectional dependence and heterogeneity, cointegration diagnostics, and estimators such as the pooled mean group (PMG) for dynamic effects over time, the method of moments quantile regression (MMQR) for distributional analysis, and the Dumitrescu–Hurlin causality test. Finally, the policy-relevant evidence of the study identifies mechanisms through which digital infrastructure, renewable energy, and guided FDI can contribute to more sustainable environmental practices. The results inform strategies aimed at integrating ecological considerations within broader economic and development planning in SSA.
The structure of the paper is as follows. The next section reviews key contributions from the existing literature relevant to the study’s focus. The subsequent section outlines the data sources and explains the methodological approach adopted for the analysis. This is followed by a detailed presentation of the empirical results. The final section discusses the findings in relation to broader policy implications and identifies areas for future research.
2 Literature review
A substantial body of empirical literature, drawing on diverse analytical techniques and regional datasets, demonstrates that renewable energy use meaningfully improves environmental conditions across regions. In China, Xie et al. (2022) identified a 0.688% reduction in pollution levels for every one percent increase in renewable energy consumption between 1985 and 2019, while Zhang et al. (2025) provided fresh evidence that energy efficiency and the sharing economy increasingly drive sustainable economic development as development levels advance. Analyzing 27 African nations with linear and nonlinear models, Yang et al. (2022) found ecological footprints declined by 0.17% in deficit regions and 0.2% in nations with ecological reserves. In India, Akadiri and Adebayo (2022) linked renewable energy to emission reductions but noted adverse effects from fossil fuel reliance and financial expansion. Zafar et al. (2020) exhibited that in 27 OECD countries, the environmental benefits of renewable energy were most significant where education and research infrastructures were stronger. Through quantile-on-quantile analysis, Chang et al. (2022b) demonstrated that wind energy consumption substantially reduced ecological footprints in eight of the top ten EU wind energy-consuming nations, with effects varying across quantiles. Using PMG cointegration and Dumitrescu–Hurlin panel causality methods, Abdi (2023) confirmed that renewable energy reduced pollution in both the short and long run in 41 SSA nations. Moreover, Abdi et al. (2024) found similar patterns at the national level in Somalia, where renewable energy consumption was tied to lower pollution and ecological footprints.
A considerable number of studies suggest that FDI can, under specific conditions, promote sustainable development. Lazreg and Zouari (2018) found that FDI in Tunisia not only reduce CO2 emissions but also alleviated inequality and poverty. Using augmented mean group and bootstrap panel causality techniques, Zhang et al. (2021) demonstrated that outward FDI contributes to environmental sustainability when supported by technological progress, trade openness, and improvements in human wellbeing. Similarly, Huan and Qamruzzaman (2022) identified a significant positive relationship between FDI inflows and innovations in financial, technological, and environmental domains in both the short- and long-run. Dornean et al. (2022) observed that EU countries with strong sustainability-oriented business environments attract more FDI. In Turkey, Udemba and Keleş (2022) found a negative association between FDI and carbon emissions, while Renyong and Sedik (2023), using regional data from East Africa, concluded that FDI improves environmental quality when aligned with institutional and sustainability frameworks, albeit with more impact in the long run. Conversely, other studies reveal negative environmental consequences of FDI. Tariq et al. (2018), using a panel ARDL model for Pakistan and India, found a positive relationship between FDI and CO2 emissions. Ochoa-Moreno et al. (2021) supported the Pollution Haven Hypothesis in Latin America, linking FDI inflows to environmental degradation, and Chiriluş and Costea (2023) similarly reported increased pollution from FDI in Romania by pointing to the importance of regulatory quality in mediating FDI’s environmental effects.
The EKC hypothesis remains a central framework for understanding the relationship between economic growth and environmental sustainability, though empirical evidence varies by development level. Le and Quah (2018) confirmed the EKC in 14 Asia-Pacific nations, indicating that emissions decline as income increases, while Sarkodie and Strezov (2018) found similar patterns in developed countries but noted limited applicability in developing nations due to reliance on non-renewable energy and weak governance. In the Visegrád group, Rabbi and Abdullah (2024) observed the EKC in most countries, with Poland as an exception where emissions continued to rise. Tenaw and Beyene (2021) found that in SSA, economic growth initially harms environmental quality but improves with better resource governance. Mohamed et al. (2025) similarly found in Somalia that ecological footprints first rise with GDP but decline at higher income levels, which reinforces the EKC’s non-linear pattern. Critics such as Rashid Gill et al. (2018) argue that the EKC’s “grow now, clean later” approach is environmentally unsustainable, while Bibi and Jamil (2021) as well as Dogan and Inglesi-Lotz (2020) found no EKC evidence in SSA without strong environmental policies and renewable energy transitions. Complementing these perspectives, Liu et al. (2025) suggest that aligning economic growth with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) may support more inclusive and sustainable development pathways.
Research on the linkage between digitalization and environmental sustainability presents that that the relationship depends on context and technological applications. Majeed (2018) disclosed that while ICT holds transformative potential for global ecological sustainability, its benefits are more evident in developed economies, with less favourable outcomes in developing nations. Chatti (2021) supported this, showing that ICT use effectively reduces emissions, especially in transport. Xie et al. (2022) also found that technological innovation supports environmental sustainability. Zhu and Ye (2018) revealed that outward FDI to developed countries fosters green technology spillovers, though this effect is limited in developing countries due to weak institutions and human capital. In contrast, Khan et al. (2021) found that technological progress increased energy use and ecological damage across 69 BRI countries. In Bangladesh, Raihan et al. (2022) exhibited that innovation’s benefits are offset by industrialization and urbanization. Hu et al. (2019) observed that stricter environmental policies in China reduced FDI’s negative effects but failed to encourage green spillovers. Extending this discourse, Sibt-e-Ali et al. (2025) demonstrated that digitalization, fintech, governance, and SDG13 commitments jointly enhance environmental conservation and long-term carbon neutrality in emerging economies, with effects varying by development stage. Similarly, Wang et al. (2025) employed a panel nonlinear ARDL model and found asymmetric effects of renewable energy, technological innovation, infrastructure, and policy uncertainty on transport CO2 emissions in QUAD countries.
While industrialization is often linked to economic development, its environmental effects are highly context-dependent. When combined with renewable energy and technological innovation, industrialization can support sustainability. For example, Aquilas et al. (2024) presented that renewable energy moderates the environmental impact of manufacturing in 46 African countries, which promotes long-term sustainable development. Similarly, Saba et al. (2023) argued that technological innovation, renewable energy, and trade openness significantly improve environmental outcomes from industrial growth in Africa. By extending this view in the Asian context, Zhi-qiang et al. (2024) demonstrated that industrial upgrading, green technologies, and green finance interact positively to enhance environmental quality. Conversely, unregulated industrial expansion—especially reliant on non-renewable energy—worsens environmental degradation. Hossain and Huggins (2021) and Sikder et al. (2022) reported the ecological costs of such growth. Sumaira and Siddique (2023) found that industrialization and energy use significantly increased pollution in South Asia from 1984 to 2016. Voumik and Sultana (2022) observed similar challenges in BRICS countries, though sustainable industrial practices offered mitigating effects. Opoku and Boachie (2020), studying 36 African nations, noted that while industrialization itself had limited direct environmental effects, FDI targeting industry was environmentally detrimental. Ahmed et al. (2022) also linked poor urban-industrial planning to worsening environmental quality in Brazil. Likewise, Chikezie Ekwueme et al. (2023) found that in Asia, industrialization coupled with fossil fuel dependence contributed significantly to environmental damage.
Urbanization often leads to increased energy consumption, higher pollution, and greater environmental degradation (Chang et al., 2024). Adebayo et al. (2021) revealed that urbanization significantly contributed to increased CO2 emissions in Latin America from 1980 to 2017. Similarly, Qi et al. (2023) examined urbanization’s effects in six Asian countries from 1997 to 2019. They found that urbanization, population density, and real income increased environmental degradation. In SSA, Iheonu et al. (2021) found that urbanization led to higher CO2 emissions, particularly in countries with initially low emissions. However, their study indicated that international trade could promote environmental sustainability in both extremes of the emissions spectrum, though it may contribute to degradation in countries at the median level. Despite the predominance of studies pointing to the negative effects of urbanization, there is also evidence suggesting that urbanization’s impact on environmental sustainability can be moderated through strategic planning and the integration of green technologies (Rasool et al., 2022; Xin et al., 2023). Utilizing a quantile-based ARDL approach, Liu K. et al. (2024) found that while urbanization negatively affected environmental sustainability, the use of financial technology could mitigate some of these effects in China. Danish and Hassan (2023) similarly find that, in Pakistan, the interaction between urbanization and natural resource rent moderates the reduction of carbon footprints. Lastly, Ma and Qamruzzaman (2022) reported that while urbanization harms the environment, renewable energy and technological innovation can counteract these negative effects in developing African economies.
Building on the insights from the literature review, it is apparent that while digitalization, FDI, renewable energy, industrialization, and urbanization have been extensively studied, their combined effects on environmental sustainability remain underexplored, particularly in the context of SSA (Abdi, 2023; Iheonu et al., 2021). Existing studies often concentrate on these factors in isolation, overlooking their interconnected impacts and regional disparities. Moreover, the dual role of FDI—as both a driver of green innovation and a contributor to environmental degradation—discloses the necessity for more analysis, especially where institutional frameworks are weak (Ben-David et al., 2021; Ochoa-Moreno et al., 2021; Tariq et al., 2018). Similarly, while digitalization presents transformative potential, its environmental benefits are contingent upon adequate technological infrastructure and energy efficiency, which remain uneven in SSA (Majeed, 2018). This study handles these crucial gaps by exploring the integrated roles of digitalization, FDI, and renewable energy in mitigating environmental degradation across SSA. By embracing a thorough approach that accounts for both ecological footprints and pollution, this research provides a more precise understanding of how these factors interact and delivers practical insights for facilitating sustainable development in SSA (Akadiri and Adebayo, 2022; Yang et al., 2022).
3 Data and methodology
3.1 Data and variables
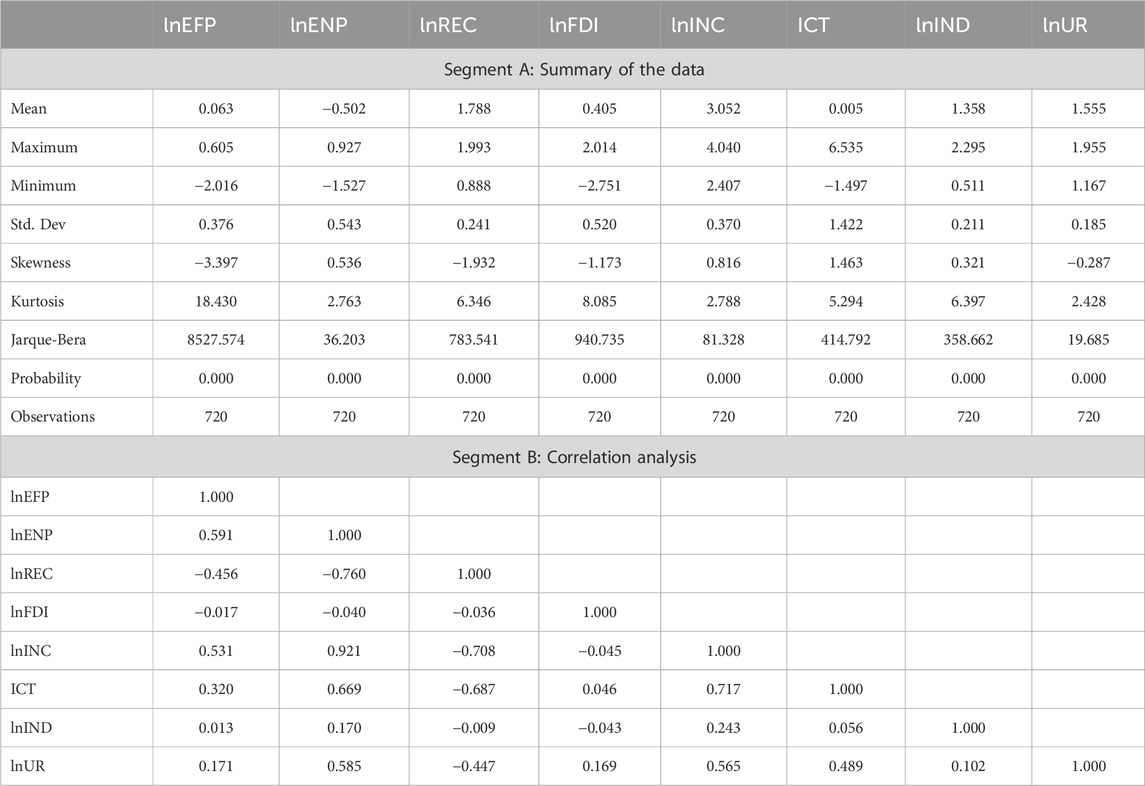
This study employs annual panel data from 2001 to 2020 covering 38 SSA countries to investigate the roles of digitalization, FDI, renewable energy adoption, and industrialization in shaping environmental sustainability. The outcome variables are ecological footprints and environmental pollution (Warsame et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2022). The explanatory variable includes renewable energy consumption, FDI, economic growth, digitalization, industrialization, and urbanization. Renewable energy consumption measures the share of energy derived from clean sources (Abdi et al., 2024; Sharma et al., 2021). Besides, FDI accounts for the environmental implications of capital inflows, which reflects its potential to facilitate technological progress or increase resource exploitation depending on regulatory environments (Demena and Afesorgbor, 2020; Tariq et al., 2018). Economic growth, expressed as income per capita, reflects income levels and allows for an assessment of its relationship with environmental outcomes (Sarkodie and Strezov, 2018). Digitalization is represented through an ICT index constructed using PCA, which aggregates mobile subscriptions, fixed telephone lines, and internet users to provide a comprehensive measure of ICT adoption (Majeed, 2018; Wang et al., 2023). Industrialization captures the industrial sector’s contribution to economic activity, which influences environmental sustainability depending on production processes and energy use (Aquilas et al., 2024; Opoku and Boachie, 2020). Finally, urbanization measures the concentration of population in urban areas, which reflects its effects on resource consumption and infrastructure development (Danish and Hassan, 2023). All data were obtained from the World Development Indicators (WDI) and the Global Footprint Network (GFN). Table 1 provides details on the variables, measures, and data sources.
3.2 Model specification
The model specification of this study is grounded in the frameworks of Zhang et al. (2021), Abdi et al. (2024), Sarkodie and Strezov (2018), Yang et al. (2022), Majeed (2018), and Tariq et al. (2018), extending their frameworks to examine the impact of renewable energy consumption, FDI, economic growth, digitalization, industrialization, and urbanization on environmental sustainability in SSA countries. All variables, except for ICT, are transformed into natural logarithmic forms to stabilize variance, mitigate heteroscedasticity, and allow for elasticity-based interpretation of coefficients. Model I investigate the determinants of ecological footprints as a broad measure of environmental pressure, while Model II focuses on carbon emissions to capture specific pollution levels resulting from human activities. The two models are specified as shown in Equations 1, 2.
In both equations,
3.3 Empirical strategy
3.3.1 Cross-sectional dependence and slope heterogeneity test
In panel data analysis, detecting cross-sectional dependence (CD) is crucial as unobserved common shocks, spillovers, or interconnected economic activities can create dependencies among cross-sectional units. Failing to address CD may lead to misleading results, biased estimates, and invalid inferences (Sarkodie and Owusu, 2020). To enhance the reliability of the results, the Breusch-Pagan Lagrange Multiplier (LM) test is applied, particularly because it is well-suited for datasets where the number of cross-sectional units (N) is smaller relative to the periods (T). In contrast, the Pesaran CD test is appropriate for larger panels and remains effective even when N is large and T is relatively small. The Breusch-Pagan LM test statistic is given by Equation 3.
where
Given that finite sample biases can affect the scaled LM test, Pesaran also proposed the bias-corrected scaled LM test. This refinement adjusts for small-sample bias using a correction factor
Finally, the study employs the Pesaran CD test, which is widely preferred for its robustness across both small and large panel settings. The test statistic is signified in Equation 6.
When working with panel data, assessing whether slope coefficients vary across cross-sectional units is a critical step. Assuming uniformity in slopes without testing for it can result in inaccurate inferences, especially in the presence of underlying heterogeneity. To account for this possibility, slope variability is assessed using Equation 7, as proposed by Pesaran and Yamagata (2008). This approach is based on a standardized dispersion statistic, given by the following expression:
where
3.3.2 Panel unit root and cointegration tests
In view of the possibility of cross-sectional dependence among units, this study applies the cross-sectionally augmented Dickey-Fuller (CADF) and cross-sectional augmented IPS (CIPS) tests (Pesaran, 2007). These second-generation panel unit root tests are designed to control for unobserved common factors, which makes them appropriate for settings where cross-sectional units exhibit interdependencies. Under the null hypothesis, all series are assumed to be non-stationary, while the alternative allows for stationarity in a subset of the panels. The CADF model used is described in Equation 8.
where
To examine the existence of long-run relationships among the variables, this study applies the cointegration tests proposed by Pedroni (1999), Pedroni (2004) and Kao (1999). The Pedroni approach accommodates heterogeneity across cross-sectional units by allowing for individual-specific intercepts and slope coefficients, whereas the Kao test assumes a homogeneous panel structure. Both tests evaluate the null hypothesis of no cointegration against the alternative that a stable long-term association exists among the variables. Evidence against the null suggests that, despite short-term fluctuations, the variables tend to move together over the long run.
3.3.3 Pooled mean group (PMG) and mean group (MG) techniques
This study investigates both short-run dynamics and long-run equilibrium relationships using dynamic panel estimators, specifically the PMG and MG approaches introduced by Pesaran et al. (1999). The PMG estimator constrains long-run coefficients to be identical across countries while allowing short-run adjustments, intercepts, and error variances to differ. In contrast, the MG estimator calculates unweighted averages of individual country coefficients, which imposes no restrictions on either the short-run or long-run relationships and thereby accommodating substantial heterogeneity across groups. The choice between these two estimators is determined by the Hausman (1978) test, which assesses whether the assumption of long-run homogeneity holds. If the null hypothesis of homogeneity is not rejected, the PMG estimator is preferred for its greater efficiency; otherwise, the MG estimator is employed to capture heterogeneous long-run dynamics. Based on the results of the Hausman test, this study applies the PMG technique, which offers the flexibility to model both short-term fluctuations and stable long-run relationships within the panel framework. The PMG specifications for ecological footprints and pollution are presented in Equations 9, 10.
Model I:
Model II:
where
3.3.4 Dumitrescu–Hurlin panel causality test
To analyze the direction of causality among the variables, this study applies the Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012) panel causality test, which is designed for heterogeneous panel settings. The test is employed to investigate causal linkages among renewable energy usage, FDI, income per capita, digitalization, industrialization, and urbanization. It enables an assessment of whether changes in one variable systematically lead to changes in another across countries. Importantly, the Dumitrescu–Hurlin test accommodates heterogeneity by allowing individual-specific coefficient variations while maintaining a shared structure under the null hypothesis. The causality test framework is represented by Equation 11.
where
In this study, causality direction is established by applying the test twice for each variable pair—once with
4 Analysis and discussion
4.1 Descriptive statistics and correlation analysis
The descriptive statistics and correlation analysis provide insights into the distribution and relationships of the fundamental variables. As illustrated in Segment A of Table 2, the average values reveal that income per capita has the highest mean of 3.052, while environmental pollution report the lowest mean at −0.502. Among all variables, ICT has the largest standard deviation (1.422) and maximum value (6.535), which indicates significant variations in technological advancements across countries. In contrast, FDI shows the lowest minimum value (−2.751). Skewness results reveal that ecological footprints, renewable energy use, FDI, and urbanization are negatively skewed, while environmental pollution, income per capita, ICT, and industrialization are positively skewed. Additionally, ecological footprints exhibit the highest kurtosis value (18.430), indicating a heavy-tailed distribution. The Jarque-Bera test results confirm that all variables are significantly different from a normal distribution at the 1% level. Segment B of Table 2 displays the correlation analysis. Renewable energy use and FDI are negatively correlated with ecological footprints and environmental pollution, which indicates their potential role in mitigating environmental pressures. On the other hand, income per capita, ICT, and urbanization exhibit positive correlations with ecological footprints and environmental pollution, which suggests that economic growth, technological expansion, and urbanization are associated with increased environmental pressures.
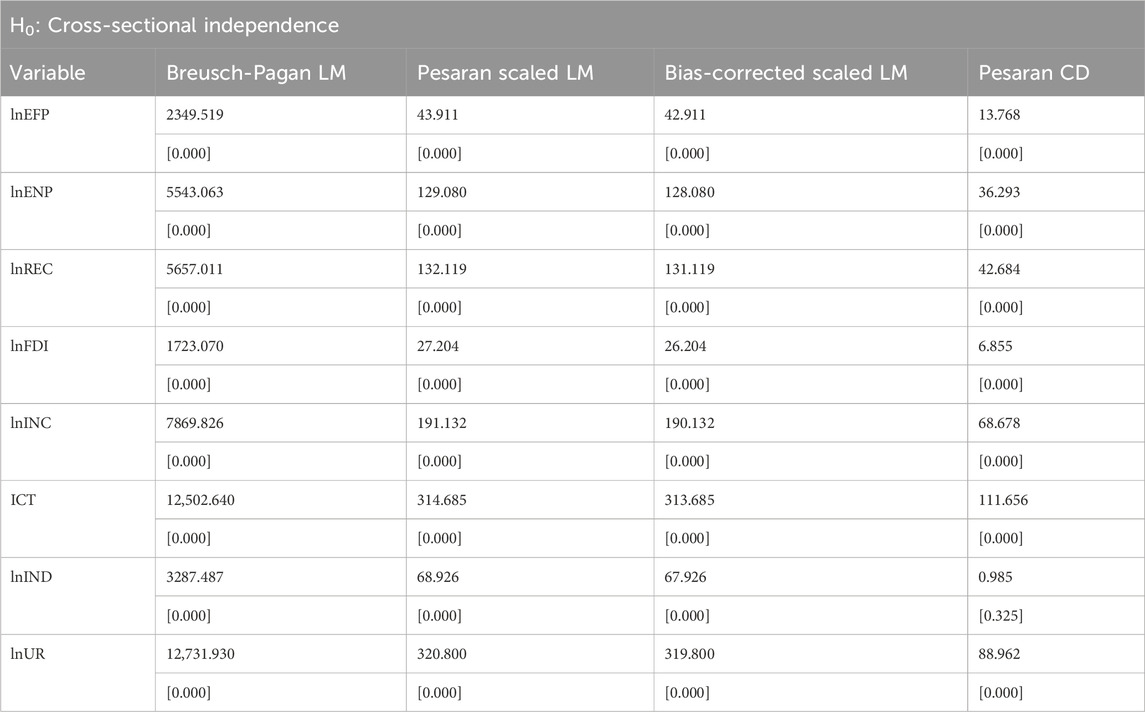
4.2 Cross-sectional dependence (CD) and heterogeneity tests
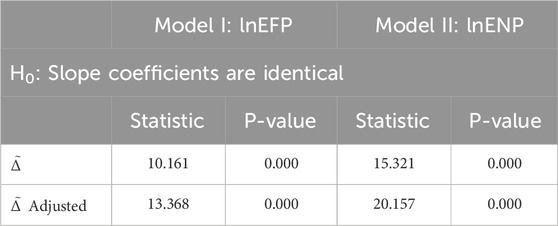
The empirical analysis begins by testing for CD and slope heterogeneity among the variables influencing environmental outcomes. As reported in Table 3, the results of the CD test reject the null hypothesis of independence. This suggests that the variables are interconnected across countries, potentially due to regional spillovers, shared policy environments, or other forms of economic and environmental interdependence. To further assess structural differences, the Pesaran and Yamagata (2008) slope homogeneity test is employed to determine whether slope coefficients vary across cross-sectional units. The outcomes presented in Table 4, based on both the.
4.3 Second-generation panel stationarity and cointegration analysis
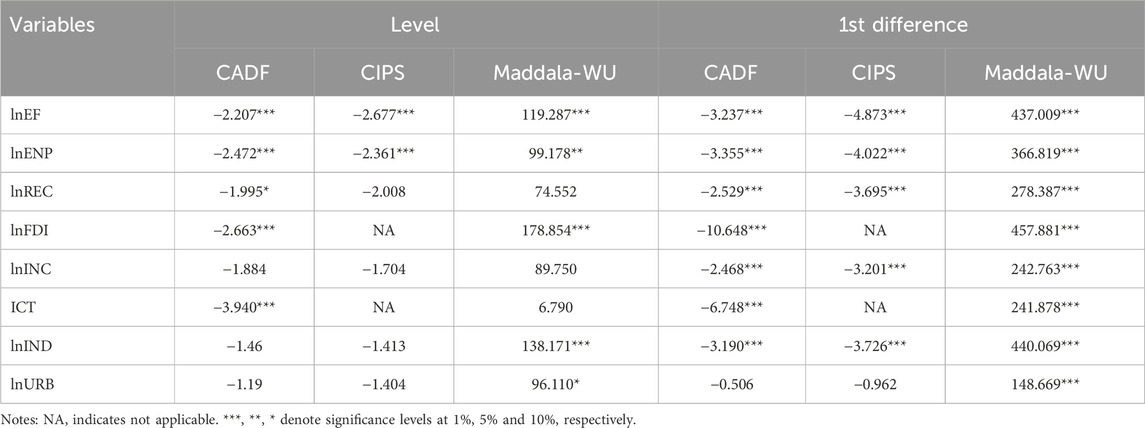
Following the confirmation of cross-sectional dependence and heterogeneity, the stationarity properties of the variables are analyzed using second-generation panel unit root tests, including the CADF and CIPS tests, alongside the Maddala and Wu (1999) Fisher-based χ2 statistic. The results, presented in Table 5, reveal mixed orders of integration. At the level, variables such as ecological footprints and environmental pollution are stationary at the 1% significance level, while renewable energy consumption, income per capita, industrialization, and urbanization remain non-stationary. However, after taking the first difference, all variables achieve stationarity across the CADF, CIPS, and Maddala-Wu tests, with significant t-statistics and χ2 values confirming their integration at I (1). These results suggest that the variables exhibit a combination of I (0) and I (1) properties. Given this mixed stationarity, traditional cointegration techniques are unsuitable for the current analysis. Instead, the PMG estimator is adopted, as it effectively accommodates variables integrated at different orders.
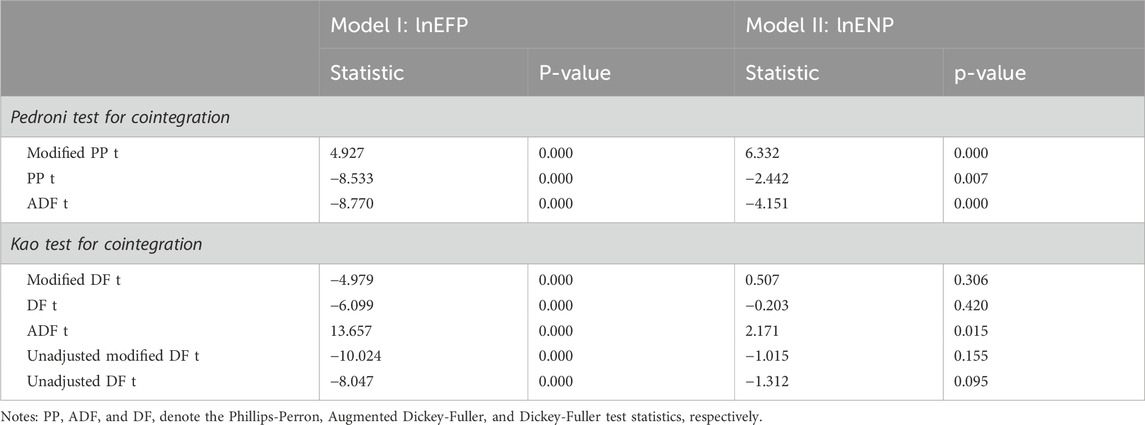
The results of the Pedroni and Kao cointegration tests, summarized in Table 6, assess the existence of long-run equilibrium relationships among the variables. The Pedroni test results provide strong evidence of cointegration in both models. Specifically, the Modified Phillips-Perron (PP) t-statistic, Phillips-Perron (PP) t-statistic, and Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) t-statistic are all statistically significant at the 1% level, which leads to the rejection of the null hypothesis of no cointegration. Similarly, the Kao cointegration test generally supports these findings, although some variations are observed. For Model I, the Modified Dickey-Fuller (DF) t-statistic, DF t-statistic, and Unadjusted DF t-statistic are all significant, which confirms the presence of cointegration. For Model II, although the ADF t-statistic remains significant at the 5% level, the Modified DF and Unadjusted DF statistics are insignificant. Overall, the combined evidence from the Pedroni and Kao tests supports the existence of long-run relationships among the studied variables, thereby justifying the application of the PMG estimator to capture both short- and long-run dynamics.
4.4 Long-run and short-run results from the PMG estimator
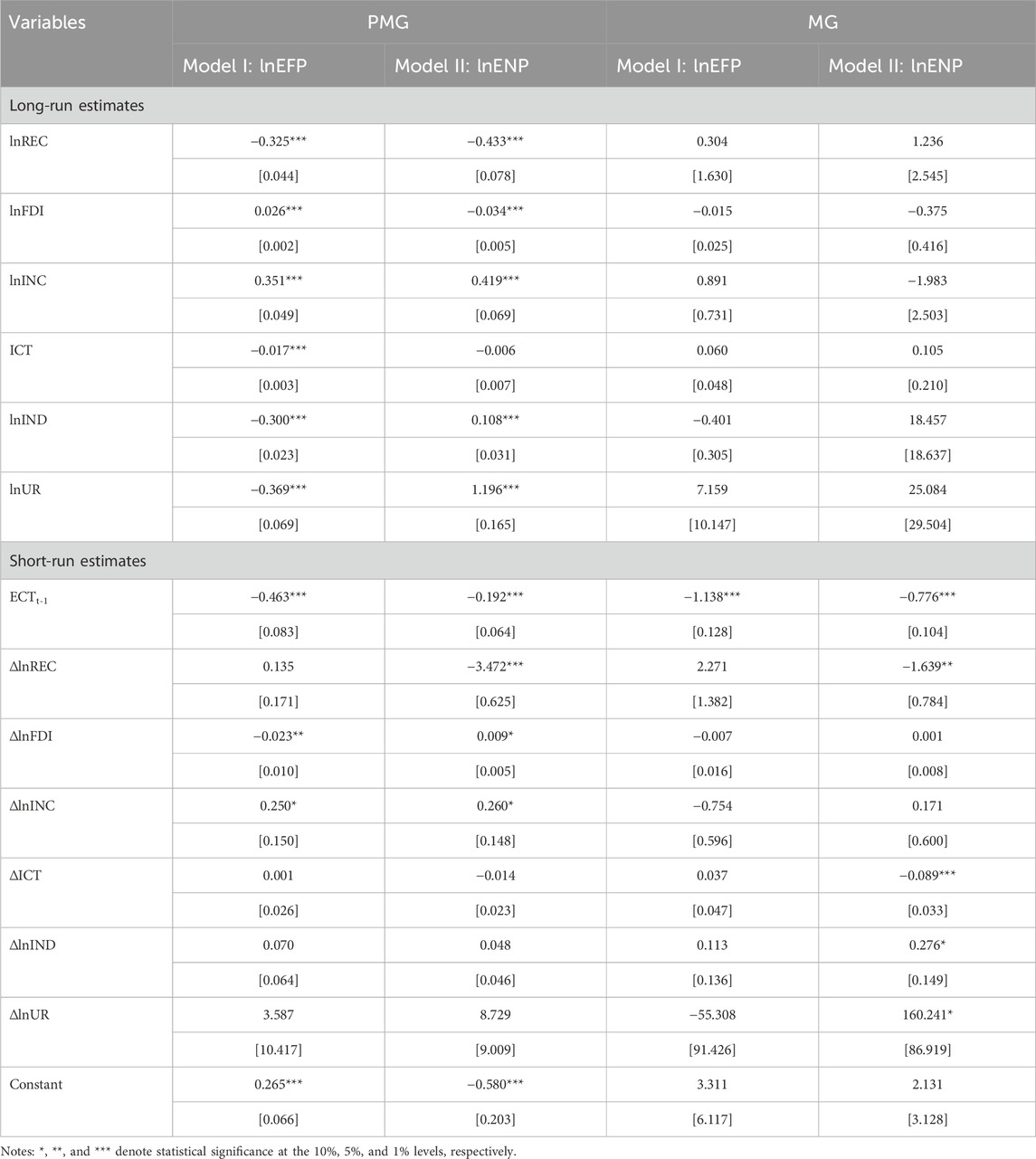
The findings from the PMG estimator, as presented in Table 7 reveal significant outcomes in how the explanatory variables affect ecological footprints (Model I) and environmental pollution (Model II) in SSA. While some variables demonstrate uniform effects across the two environmental indicators, others reveal notable differences. The chi-squared statistic for the Hausman test, with its corresponding probability value, confirms the robustness and reliability of the PMG estimator. In Model I, renewable energy consumption demonstrates its long-run effectiveness in reducing ecological footprints by 0.325%, significant at the 1 percent level. Similarly, Model II reveals an even stronger long-run reduction in environmental pollution by 0.433%, also significant at the 1 percent level. These findings align with Yang et al. (2022), who demonstrated renewable energy’s role in reducing ecological footprints in African nations, and Abdi (2023), who confirmed its pollution-reducing effects across 41 SSA countries. Comparable results were also observed by Zafar et al. (2020) and Akadiri and Adebayo (2022) for OECD and Indian contexts, respectively. In practice, this indicates that accelerating renewable energy adoption can effectively alleviate ecological pressures and reduce pollution levels across SSA in the long-run. In addition, FDI presents mixed effects between the two models. In Model I, FDI increases ecological footprints by 0.026%, significant at the 1% level, which reflects its association with resource-intensive activities under weak environmental regulation. This result is consistent with Tariq et al. (2018) for Pakistan and Ochoa-Moreno et al. (2021) under the Pollution Haven Hypothesis. In contrast, Model II reveal that FDI reduces environmental pollution by 0.034%, significant at the 5 percent level, signals its role in facilitating cleaner technologies, as evidenced by Zhang et al. (2021) and Renyong and Sedik (2023). In the short-run, FDI reduces ecological footprints (0.023%) but increases environmental pollution (0.009%), which pinpoints transitional trade-offs. For SSA, this suggests that FDI inflows must be accompanied by technology transfer and strong environmental governance to mitigate its adverse impacts while enhancing its pollution-reducing benefits.
Income per capita, representing economic growth, emerges as a consistent driver of environmental degradation across both models. In the long-run, a 1 percent increase in economic growth raises ecological footprints by 0.351% in Model I and environmental pollution by 0.419% in Model II, both significant at the 1 percent level. These findings align with Sarkodie and Strezov (2018) for developed countries and Le and Quah (2018) for Asia-Pacific nations. However, critics such as Bibi and Jamil (2021) argue that SSA’s weak regulatory frameworks hinder the translation of economic growth into environmental benefits. For SSA, this result implies that economic expansion remains resource- and pollution-intensive, which requires stronger investments in clean technologies and sustainable practices to decouple growth from environmental degradation. However, ICT delivers a promising contribution to environmental improvement in SSA. In Model I, digitalization reduces ecological footprints by 0.017%, which is significant at the 1 percent level, while in Model II, it lowers environmental pollution by 0.006%. These findings are consistent with Majeed (2018) and Chatti (2021), who highlighted ICT’s role in fostering resource efficiency and emissions reductions through smarter industrial processes. However, Raihan et al. (2022) and Khan et al. (2021) caution that technological progress can increase energy consumption in developing economies. For SSA, these results indicate that digital advancements can improve environmental efficiency over time, but their full potential can only be realized by expanding ICT infrastructure, particularly in underdeveloped regions.
Industrialization produces contrasting results across the two models. In Model I, industrialization reduces ecological footprints by 0.300%, which is significant at the 1 percent level, suggesting that sustainable industrial practices and cleaner technologies are being adopted in certain areas of SSA. Similar results were observed by Aquilas et al. (2024) and Saba et al. (2023) in Africa. Conversely, in Model II, industrialization increases environmental pollution by 0.108%, significant at the 1 percent level, which reflects continued reliance on fossil fuels, as noted by Sumaira and Siddique (2023) for South Asia and Hossain and Huggins (2021) for other developing regions. These contrasting effects imply that while industrial processes in SSA have begun incorporating sustainability measures, fossil fuel dependency remains a barrier to achieving broader environmental benefits. On the other hand, urbanization displays the most dynamic and contrasting effects across both models. In Model I, urbanization reduces ecological footprints by 0.369% in the long-run, which reflects improvements in urban resource efficiency and infrastructure. In Model II, urbanization has a pronounced positive effect on environmental pollution, increasing them by 1.196% in the long-run, significant at the 1 percent level. These findings align with Adebayo et al. (2021) for Latin America and Qi et al. (2023) for Asian economies, which indicate the environmental strain caused by rapid urban growth. Liu K. et al. (2024) and Ma and Qamruzzaman (2022) further reveal the importance of sustainable urban planning and renewable energy integration to moderate these effects. For SSA, the results imply that urbanization has yet to deliver large-scale environmental benefits due to rising energy demands, deforestation, and waste generation.
4.5 Method of moments quantile regression (MMQR)
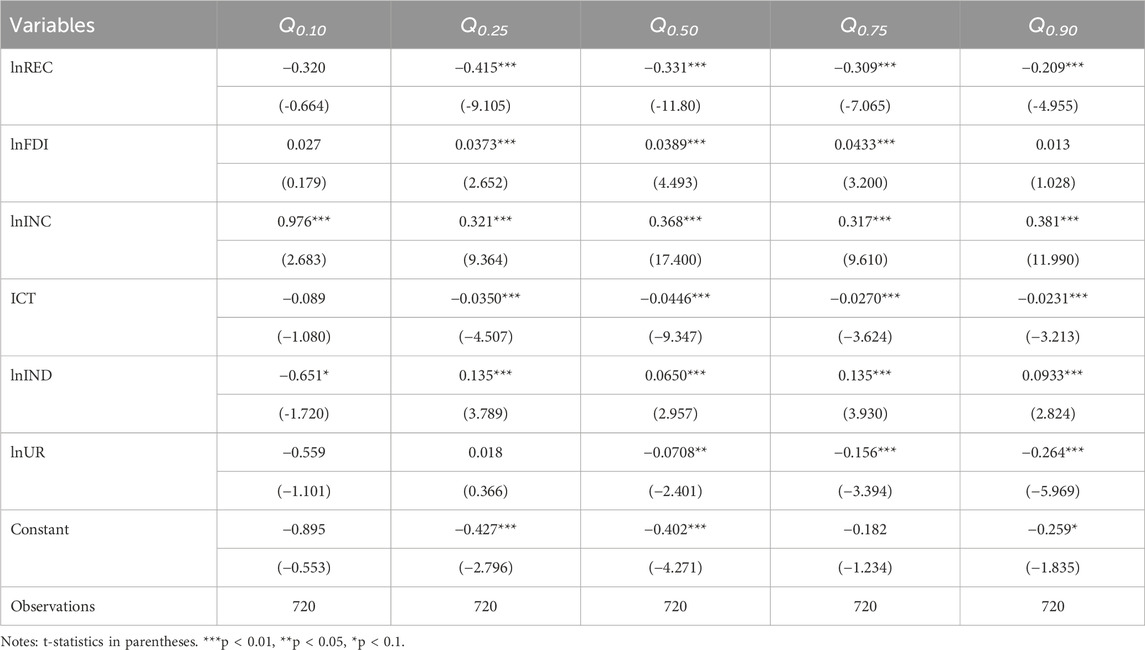
The MMQR analysis in Table 8 illuminates how fundamental factors influence ecological footprints across quantiles by capturing variations in environmental impacts. Renewable energy consumption reduces ecological footprints at all quantiles, with the strongest effects at Q0.25 (−0.415) and weaker reductions at Q0.90 (−0.209), which reiterates its effectiveness in mitigating ecological pressures across different environmental conditions. FDI increases ecological footprints, with notable impacts at Q0.75 (0.0433) and Q0.50 (0.0389), which echoes its association with resource-intensive activities in areas of higher ecological strain. Economic growth consistently raises ecological footprints, with the highest effect at Q0.10 (0.976) and significant impacts across all quantiles. However, ICT adoption reduces ecological footprints, with the most significant reductions observed at Q0.50 (−0.0446) and Q0.25 (−0.0350), which identifies its potential to enhance resource efficiency and sustainable practices. Industrialization shows mixed impacts, reducing footprints at Q0.10 (−0.651) but increasing them at higher quantiles like Q0.75 (0.135) and Q0.90 (0.0933), illustrating the dual role of industrial activities in SSA. Urbanization reduces ecological footprints at higher quantiles, particularly Q0.90 (−0.264) and Q0.75 (−0.156), which suggests improved resource management in urbanized regions while showing limited or negligible effects at lower quantiles like Q0.25 (0.018).
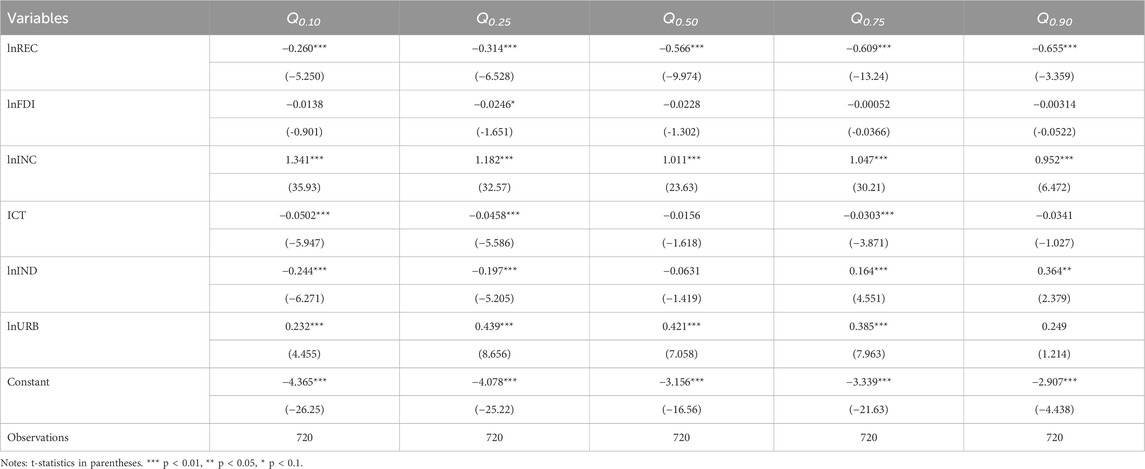
The MMQR results for environmental pollution (Table 9) reveal diverse impacts of key factors across quantiles. For instance, renewable energy utilization consistently reduces environmental pollution, with the strongest effects observed at the highest quantile (−0.655%) and Q0.75 (−0.609%). Moreover, FDI shows a minor reduction in emissions at Q0.25 (−0.0246%), though its influence is inconsistent across quantiles. Additionally, economic output exerts a consistently positive and significant effect on emissions across all quantiles, ranging from Q0.10 (1.341%) to Q0.90 (0.952%). However, ICT adoption reduces environmental pollution at lower quantiles, such as Q0.10 (−0.0502%) and Q0.25 (−0.0458%), but its impact diminishes at higher quantiles. In addition, industrialization presents mixed results: reducing emissions at Q0.10 (−0.244%) and Q0.25 (−0.197%) but increasing them at higher quantiles such as Q0.75 (0.164%) and Q0.90 (0.364%), which illustrates the dual role of industrial activities in SSA. Finally, urbanization consistently increases emissions, with the highest impact at Q0.25 (0.439%) and significant effects across all other quantiles.
4.6 Panel causality analysis
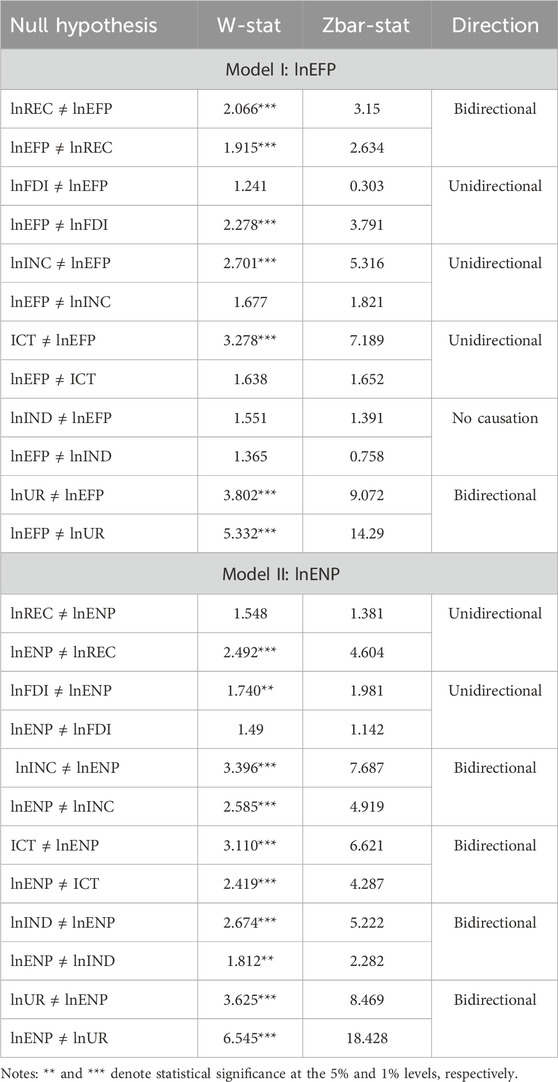
The Dumitrescu–Hurlin panel causality tests in Table 10 reveal significant outcomes in the directional relationships between variables in Model I and Model II. In Model I, the analysis identifies a bidirectional relationship between ecological footprints and renewable energy consumption, as evidenced by the rejection of the null hypothesis for both directions. This implies that renewable energy adoption and ecological footprints mutually influence one another. Additionally, ecological footprints significantly cause, while FDI does not reciprocally affect ecological footprints. Furthermore, urbanization exhibits a bidirectional relationship with ecological footprints, which indicates a mutual influence between urban expansion and ecological pressures. Interestingly, income per capita and ICT display a unidirectional relationship, where economic growth and digitalization significantly impact ecological footprints but are not influenced in return. No causal relationship is observed between industrialization and ecological footprints. In Model II, renewable energy consumption is influenced by environmental pollution (unidirectional causality), which emphasizes the role of emissions in driving renewable energy adoption. Conversely, environmental pollution has a bidirectional causal linkage with income per capita, ICT, industrialization, and urbanization. This indicates a reciprocal relationship, where economic activities and technological advancements both impact and are influenced by emissions. FDI, however, exhibits a unidirectional relationship, where environmental pollution is affected by FDI inflows but not vice versa. Notably, urbanization’s bidirectional impact on environmental pollution reflects the complex linkage of urban growth, energy demand, and emissions.
5 Conclusion and policy implications
Despite increasing global attention on environmental sustainability, SSA continues grappling with balancing economic growth and ecological preservation. This study examined the impacts of renewable energy consumption, FDI, economic growth, digitalization, industrialization, and urbanization on ecological footprints and environmental pollution across 38 SSA countries from 2001 to 2020. Utilizing a thorough methodological approach, the analysis employed the PMG estimator, MMQR, and Dumitrescu–Hurlin causality test to explore the dynamic relationships among the variables. Second-generation unit root tests such as CADF and CIPS confirmed the mixed stationarity of the data, while Pedroni and Kao cointegration tests verified long-run equilibrium relationships. The results exhibit renewable energy’s transformative role in reducing ecological footprints and environmental pollution across SSA. FDI demonstrated dual effects, positively contributing to technological advancement and reducing environmental pollution while simultaneously increasing ecological footprints due to resource-intensive activities. In addition, economic growth emerged as a key driver of environmental pressures, as it significantly increased both ecological footprints and environmental pollution, which reflects the resource-heavy nature of SSA’s growth models. Remarkably, digitalization showed promise in enhancing sustainability through efficiency gains. Conversely, industrialization and urbanization were found to exacerbate environmental degradation, significantly raising both ecological footprints and environmental pollution. The MMQR analysis delivered profound insights by illustrating how these effects vary across different levels of environmental impact. Additionally, the Dumitrescu–Hurlin causality test revealed bidirectional relationships between renewable energy, urbanization, economic growth, and environmental indicators.
In light of these findings, the results of this study equip paramount implications for policymakers in SSA aiming to achieve sustainable development. Firstly, renewable energy consumption emerges as a cornerstone for reducing both ecological pressures and emissions. Governments should prioritize large-scale renewable energy projects, improve grid infrastructure, and implement supportive policies such as subsidies and incentives to accelerate clean energy adoption. Secondly, while FDI contributes to reducing emissions, it risks exacerbating ecological degradation if left unregulated. Policymakers must strengthen environmental governance and attract environmentally responsible investments that facilitate technology transfer, promote cleaner production processes, and align with sustainability goals. Thirdly, economic growth, as indicated by income per capita, remains a double-edged sword. While fostering development, it intensifies environmental degradation. To break this link, SSA countries must integrate sustainability into their economic policies, focusing on green growth strategies, circular economies, and investments in low-carbon technologies to ensure long-term environmental and economic benefits. Fourthly, digitalization delivers a promising pathway to enhance environmental efficiency, though its current impact remains modest. Expanding ICT infrastructure, particularly in rural and underdeveloped regions, can facilitate smart resource management, climate monitoring, and the adoption of technology-driven solutions to environmental challenges. Fifthly, industrialization requires careful management to ensure it aligns with sustainable development. Policymakers should promote green industrialization by encouraging the adoption of energy-efficient technologies, cleaner production methods, and innovation in manufacturing processes to minimize environmental strain. Lastly, urbanization, while critical for economic transformation, poses significant environmental challenges. To address these, SSA countries must prioritize sustainable urban planning, develop climate-resilient infrastructure, and integrate renewable energy into urban systems to mitigate the adverse effects of rapid urban growth, such as pollution and resource depletion.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators.
Author contributions
AA: Validation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Software, Resources, Visualization, Formal Analysis. MZ: Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Supervision. MH: Writing – original draft. SA: Writing – review and editing, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbas, H. S. M., Xu, X., and Sun, C. (2021). Role of foreign direct investment interaction to energy consumption and institutional governance in sustainable GHG emission reduction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (40), 56808–56821. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-14650-7
Abdi, A. H. (2023). Toward a sustainable development in Sub-Saharan Africa: do economic complexity and renewable energy improve environmental quality? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (19), 55782–55798. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-26364-z
Abdi, A. H., and Hashi, M. A. (2024). Fostering a sustainable future in Somalia: examining the effects of industrialization, energy consumption, and urbanization on environmental sustainability. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 14 (6), 384–394. doi:10.32479/ijeep.16339
Abdi, A. H., Sheikh, S. N., and Elmi, S. M. (2024). Pathways to sustainable development in Somalia: evaluating the impact of agriculture, renewable energy, and urbanisation on ecological footprints and CO2 emissions. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 43 (1), 2411832. doi:10.1080/14786451.2024.2411832
Acheampong, A. O., Adams, S., and Boateng, E. (2019). Do globalization and renewable energy contribute to carbon emissions mitigation in Sub-Saharan Africa? Sci. Total Environ. 677, 436–446. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.353
Adams, S., and Acheampong, A. O. (2019). Reducing carbon emissions: the role of renewable energy and democracy. J. Clean. Prod. 240, 118245. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118245
Adebayo, T. S., Ramzan, M., Iqbal, H. A., Awosusi, A. A., and Akinsola, G. D. (2021). The environmental sustainability effects of financial development and urbanization in Latin American countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (41), 57983–57996. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-14580-4
Adzawla, W., Sawaneh, M., and Yusuf, A. M. (2019). Greenhouse gasses emission and economic growth nexus of Sub-Saharan Africa. Sci. Afr. 3, e00065. doi:10.1016/j.sciaf.2019.e00065
Ahmed, S., Abdi, A. H., Sodal, M., Yusuf, O. A., and Mohamud, M. H. (2025). Assessing the energy-economy-environment nexus in Somalia: the impact of agricultural value added on CO2 emissions. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 15 (1), 221–232. doi:10.32479/ijeep.17426
Ahmed, Z., Le, H. P., and Shahzad, S. J. H. (2022). Toward environmental sustainability: how do urbanization, economic growth, and industrialization affect biocapacity in Brazil? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 24 (10), 11676–11696. doi:10.1007/s10668-021-01915-x
Akadiri, S. S., and Adebayo, T. S. (2022). RETRACTED ARTICLE: Asymmetric nexus among financial globalization, non-renewable energy, renewable energy use, economic growth, and carbon emissions: impact on environmental sustainability targets in India. EBSCOhost 29, 16311–16323. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-16849-0
AlNemer, H. A., Hkiri, B., and Tissaoui, K. (2023). Dynamic impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on CO2 emission and economic growth in Saudi Arabia: fresh evidence from wavelet coherence analysis. Renew. Energy 209, 340–356. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2023.03.084
Anser, M. K., Ahmad, M., Khan, M. A., Zaman, K., Nassani, A. A., Askar, S. E., et al. (2021). The role of information and communication technologies in mitigating carbon emissions: evidence from panel quantile regression. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (17), 21065–21084. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-12114-y
Aquilas, N. A., Ngangnchi, F. H., and Mbella, M. E. (2024). Industrialization and environmental sustainability in Africa: the moderating effects of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption. Heliyon 10 (4), e25681. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25681
Ben-David, I., Jang, Y., Kleimeier, S., and Viehs, M. (2021). Exporting pollution: where do multinational firms emit CO2? Econ. Policy, eiab009. doi:10.1093/epolic/eiab009
Bibi, F., and Jamil, M. (2021). Testing environment kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis in different regions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (11), 13581–13594. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-11516-2
Byaro, M., Nkonoki, J., and Mafwolo, G. (2022). Exploring the nexus between natural resource depletion, renewable energy use, and environmental degradation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (8), 19931–19945. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-23104-7
Cai, K. (2024). Harnessing renewables in Sub-Saharan Africa. Staff Clim. Notes 2024 (005), 1. doi:10.5089/9798400290107.066
Chang, G., Yasin, I., and Naqvi, S. M. M. A. (2024). Environmental sustainability in OECD nations: the moderating impact of green innovation on urbanization and green growth. Sustainability 16 (16), 7047. doi:10.3390/su16167047
Chang, L., Saydaliev, H. B., Meo, M. S., and Mohsin, M. (2022a). How renewable energy matter for environmental sustainability: evidence from top-10 wind energy consumer countries of european union. Sustain. Energy, Grids Netw. 31, 100716. doi:10.1016/j.segan.2022.100716
Chang, L., Taghizadeh-Hesary, F., and Saydaliev, H. B. (2022b). How do ICT and renewable energy impact sustainable development? Renew. Energy 199, 123–131. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.08.082
Chatti, W. (2021). Moving towards environmental sustainability: information and communication technology (ICT), freight transport, and CO2 emissions. Heliyon 7 (10), e08190. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08190
Chen, B., and Cheng, Y. (2017). The impacts of environmental regulation on industrial activities: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in Chinese prefectures. Sustainability 9 (4), 571. doi:10.3390/su9040571
Chen, M., Sinha, A., Hu, K., and Shah, M. I. (2021). Impact of technological innovation on energy efficiency in industry 4.0 era: moderation of shadow economy in sustainable development. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 164, 120521. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120521
Chikezie Ekwueme, D., Lasisi, T. T., and Eluwole, K. K. (2023). Environmental sustainability in Asian countries: understanding the criticality of economic growth, industrialization, tourism import, and energy use. Energy and Environ. 34 (5), 1592–1618. doi:10.1177/0958305X221091543
Chiriluş, A., and Costea, A. (2023). The effect of FDI on environmental degradation in Romania: testing the pollution haven hypothesis. Sustainability 15 (13), 10733. doi:10.3390/su151310733
Danish, , and Hassan, S. T. (2023). Investigating the interaction effect of urbanization and natural resources on environmental sustainability in Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20 (8), 8477–8484. doi:10.1007/s13762-022-04497-x
Demena, B. A., and Afesorgbor, S. K. (2020). The effect of FDI on environmental emissions: evidence from a meta-analysis. Energy Policy 138, 111192. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111192
Deng, Q., Alvarado, R., Toledo, E., and Caraguay, L. (2020). Greenhouse gas emissions, non-renewable energy consumption, and output in South America: the role of the productive structure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 (13), 14477–14491. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-07693-9
Dingru, L., Onifade, S. T., Ramzan, M., and AL-Faryan, M. A. S. (2023). Environmental perspectives on the impacts of trade and natural resources on renewable energy utilization in sub-sahara Africa: accounting for FDI, income, and urbanization trends. Resour. Policy 80, 103204. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.103204
Dogan, E., and Inglesi-Lotz, R. (2020). The impact of economic structure to the environmental kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis: evidence from European countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 (11), 12717–12724. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-07878-2
Dornean, A., Chiriac, I., and Rusu, V. D. (2022). Linking FDI and sustainable environment in EU countries. Sustainability 14 (1), 196. doi:10.3390/su14010196
Dumitrescu, E.-I., and Hurlin, C. (2012). Testing for granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ. Model. 29 (4), 1450–1460. doi:10.1016/j.econmod.2012.02.014
Elkhorchani, H., and Grayaa, K. (2016). Novel home energy management system using wireless communication technologies for carbon emission reduction within a smart grid. J. Clean. Prod. 135, 950–962. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.179
Grossman, G. M., and Krueger, A. B. (1995). Economic growth and the environment. Q. J. Econ. 110 (2), 353–377. doi:10.2307/2118443
Güney, T. (2019). Renewable energy, non-renewable energy and sustainable development. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. and World Ecol. 26 (5), 389–397. doi:10.1080/13504509.2019.1595214
Guo, Q., Abbas, S., AbdulKareem, H. K. K., Shuaibu, M. S., Khudoykulov, K., and Saha, T. (2023). Devising strategies for sustainable development in Sub-Saharan Africa: the roles of renewable, non-renewable energy, and natural resources. Energy 284, 128713. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.128713
Hausman, J. A. (1978). Specification tests in econometrics. Econ. J. Econ. Soc. 46, 1251–1271. doi:10.2307/1913827
Hossain, Md. A., and Huggins, R. (2021). The environmental and social impacts of unplanned and rapid industrialization in suburban areas: the case of the greater Dhaka region, Bangladesh. Environ. Urbanization ASIA 12 (1), 73–89. doi:10.1177/0975425321990319
Hu, J., Wang, Z., Huang, Q., and Zhang, X. (2019). Environmental regulation intensity, foreign direct investment, and green technology spillover—an empirical study. Sustainability 11 (10), 2718. doi:10.3390/su11102718
Huan, Y., and Qamruzzaman, M. (2022). Innovation-led FDI sustainability: clarifying the nexus between financial innovation, technological innovation, environmental innovation, and FDI in the BRIC nations. Sustainability 14 (23), 15732. doi:10.3390/su142315732
Huang, Y., Zhang, Y., Lin, L., and Wan, G. (2019). Foreign direct investment and cleaner production choice: evidence from Chinese coal-fired power generating enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 212, 766–778. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.211
Iheonu, C. O., Anyanwu, O. C., Odo, O. K., and Nathaniel, S. P. (2021). Does economic growth, international trade, and urbanization uphold environmental sustainability in Sub-Saharan Africa? Insights from quantile and causality procedures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (22), 28222–28233. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-12539-z
IRENA (2024). “Sub-saharan Africa: policies and finance for renewable energy deployment,”. Abu Dhabi.Int. Renew. Energy Agency. Available online at: https://www.sipotra.it/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/SUB-SAHARAN-AFRICA-POLICIES-AND-FINANCE-FOR-RENEWABLE-ENERGY-DEPLOYMENT.pdf.
Islam, Md. M., Khan, M. K., Tareque, M., Jehan, N., and Dagar, V. (2021). Impact of globalization, foreign direct investment, and energy consumption on CO2 emissions in Bangladesh: does institutional quality matter? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (35), 48851–48871. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-13441-4
Kao, C. (1999). Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J. Econ. 90 (1), 1–44. doi:10.1016/s0304-4076(98)00023-2
Khan, A., Chenggang, Y., Hussain, J., and Kui, Z. (2021). Impact of technological innovation, financial development and foreign direct investment on renewable energy, non-renewable energy and the environment in belt and road initiative countries. Renew. Energy 171, 479–491. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2021.02.075
Lazreg, M., and Zouari, E. (2018). The relationship between FDI, poverty reduction and environmental sustainability in Tunisia. Available online at: https://hal.science/hal-01756733/.1 p114. doi:10.30560/jems.v1n1p114
Le, T.-H., and Quah, E. (2018). Income level and the emissions, energy, and growth nexus: evidence from Asia and the Pacific. Int. Econ. 156, 193–205. doi:10.1016/j.inteco.2018.03.002
Liu, A., Chen, C., Wen, Y., Mu, Q., Li, H., and Chai, L. (2024a). Foreign multinational enterprises pose hidden environmental pressures on China. J. Clean. Prod. 468, 143103. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.143103
Liu, K., Mahmoud, H. A., Liu, L., Halteh, K., Arnone, G., Shukurullaevich, N. K., et al. (2024b). RETRACTED: exploring the nexus between fintech, natural resources, urbanization, and environment sustainability in China: a QARDL study. Resour. Policy 89, 104557. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.104557
Liu, S., Islam, H., Ghosh, T., Ali, M. S. e., and Afrin, K. H. (2025). Exploring the nexus between economic growth and tourism demand: the role of sustainable development goals. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 12 (1), 441. doi:10.1057/s41599-025-04733-y
Low Carbon Power (2022). Understand low-carbon energy in Sub-Saharan Africa through data | low-carbon power. Available online at: https://lowcarbonpower.org/region/Sub-Saharan_Africa.
Ma, C., and Qamruzzaman, M. (2022). An asymmetric nexus between urbanization and technological innovation and environmental sustainability in Ethiopia and Egypt: what is the role of renewable energy? Sustainability 14 (13), 7639. doi:10.3390/su14137639
Maddala, G. S., and Wu, S. (1999). A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Statistics 61 (S1), 631–652. doi:10.1111/1468-0084.0610s1631
Majeed, M. T. S. (2018). Information and communication technology (ICT) and environmental sustainability in developed and developing countries, 758–783.
Mohamed, A. A., Abdi, A. H., Mohamud, S. S., and Osman, B. M. (2025). Institutional quality, economic growth, and environmental sustainability: a long-run analysis of the ecological footprint in Somalia. Discov. Sustain. 6 (1), 490. doi:10.1007/s43621-025-01063-6
Mohamud, I. H., and Mohamud, A. A. (2023). The impact of renewable energy consumption and economic growth on environmental degradation in Somalia. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 13 (5), 533–543. doi:10.32479/ijeep.14488
Moreno, J., Van De Ven, D.-J., Sampedro, J., Gambhir, A., Woods, J., and Gonzalez-Eguino, M. (2023). Assessing synergies and trade-offs of diverging Paris-compliant mitigation strategies with long-term SDG objectives. Glob. Environ. Change 78, 102624. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2022.102624
Moyo, B., and Oree, V. (2024). “Renewable energy policies in Sub-Saharan Africa: an analysis of strategies, challenges, and pathways to sustainable development,” in 2024 1st international conference on smart energy systems and artificial intelligence (SESAI), 1–6. doi:10.1109/SESAI61023.2024.10599404
Murshed, M. (2020). An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-Trade openness on renewable energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in south Asia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 (29), 36254–36281. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-09497-3
N’dri, L. M., Islam, M., and Kakinaka, M. (2021). ICT and environmental sustainability: any differences in developing countries? J. Clean. Prod. 297, 126642. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126642
Ochoa-Moreno, W.-S., Quito, B. A., and Moreno-Hurtado, C. A. (2021). Foreign direct investment and environmental quality: revisiting the EKC in Latin American countries. Sustainability 13 (22), 12651. doi:10.3390/su132212651
Ogwu, M. C. (2019). “Towards sustainable development in Africa: the challenge of urbanization and climate change adaptation,” in The geography of climate change adaptation in urban Africa. Editors P. B. Cobbinah, and M. Addaney (Springer International Publishing), 29–55. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-04873-0_2
Oluoch, S., Lal, P., and Susaeta, A. (2021). Investigating factors affecting renewable energy consumption: a panel data analysis in sub Saharan Africa. Environ. Challenges 4, 100092. doi:10.1016/j.envc.2021.100092
Opoku, E. E. O., and Boachie, M. K. (2020). The environmental impact of industrialization and foreign direct investment. Energy Policy 137, 111178. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111178
Owusu, P. A., and Asumadu-Sarkodie, S. (2016). A review of renewable energy sources, sustainability issues and climate change mitigation. Cogent Eng. 3 (1), 1167990. doi:10.1080/23311916.2016.1167990
Pedroni, P. (1999). Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Statistics 61 (s1), 653–670. doi:10.1111/1468-0084.61.s1.14
Pedroni, P. (2004). Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Econ. Theory 20 (3), 597–625. doi:10.1017/s0266466604203073
Pesaran, M. H. (2004). General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. Available online at: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=572504.
Pesaran, M. H. (2007). A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J. Appl. Econ. 22 (2), 265–312. doi:10.1002/jae.951
Pesaran, M. H., Shin, Y., and Smith, R. P. (1999). Pooled mean group estimation of dynamic heterogeneous panels. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 94 (446), 621–634. doi:10.1080/01621459.1999.10474156
Pesaran, M. H., and Yamagata, T. (2008). Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J. Econ. 142 (1), 50–93. doi:10.1016/j.jeconom.2007.05.010
Pueyo, A. (2018). What constrains renewable energy investment in Sub-Saharan Africa? A comparison of Kenya and Ghana. World Dev. 109, 85–100. doi:10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.04.008
Qi, F., Abu-Rumman, A., Al Shraah, A., Muda, I., Huerta-Soto, R., Hai Yen, T. T., et al. (2023). Moving a step closer towards environmental sustainability in Asian countries: focusing on real income, urbanization, transport infrastructure, and research and development. Econ. Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja 36 (2), 2111317. doi:10.1080/1331677X.2022.2111317
Qudrat-Ullah, H., and Nevo, C. M. (2021). The impact of renewable energy consumption and environmental sustainability on economic growth in Africa. Energy Rep. 7, 3877–3886. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2021.05.083
Rabbi, M. F., and Abdullah, M. (2024). Fossil fuel CO2 emissions and economic growth in the visegrád region: a study based on the environmental kuznets curve hypothesis. Climate 12 (8), 115. doi:10.3390/cli12080115
Rahman, A., Farrok, O., and Haque, M. M. (2022). Environmental impact of renewable energy source based electrical power plants: solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, geothermal, tidal, ocean, and osmotic. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 161, 112279. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2022.112279
Raihan, A., Muhtasim, D. A., Farhana, S., Pavel, M. I., Faruk, O., Rahman, M., et al. (2022). Nexus between carbon emissions, economic growth, renewable energy use, urbanization, industrialization, technological innovation, and forest area towards achieving environmental sustainability in Bangladesh. Energy Clim. Change 3, 100080. doi:10.1016/j.egycc.2022.100080
Rashid Gill, A., Viswanathan, K. K., and Hassan, S. (2018). The environmental kuznets curve (EKC) and the environmental problem of the day. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 1636–1642. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.247
Rasool, S. F., Zaman, S., Jehan, N., Chin, T., Khan, S., and Zaman, Q. U. (2022). Investigating the role of the tech industry, renewable energy, and urbanization in sustainable environment: policy directions in the context of developing economies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 183, 121935. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121935
Ren, Y., Hu, G., and Wan, Q. (2024). Environmental protection tax and diversified transition of heavily polluting enterprises: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Econ. Analysis Policy 81, 1570–1592. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2024.02.031
Renyong, H., and Sedik, A. A. (2023). Environmental sustainability and foreign direct investment in East Africa: institutional and policy benefits for environmental sustainability. Sustainability 15 (2), 1521. doi:10.3390/su15021521
Riti, J. S., Riti, M.-K. J., and Oji-Okoro, I. (2022). Renewable energy consumption in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA): implications on economic and environmental sustainability. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 4, 100129. doi:10.1016/j.crsust.2022.100129
Saba, C. S., Djemo, C. R. T., Eita, J. H., and Ngepah, N. (2023). Towards environmental sustainability path in Africa: the critical role of ICT, renewable energy sources, agriculturalization, industrialization and institutional quality. Energy Rep. 10, 4025–4050. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2023.10.039
Saidi, K., and Omri, A. (2020). The impact of renewable energy on carbon emissions and economic growth in 15 major renewable energy-consuming countries. Environ. Res. 186, 109567. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.109567
Salahuddin, M., Ali, Md. I., Vink, N., and Gow, J. (2019). The effects of urbanization and globalization on CO2 emissions: evidence from the Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26 (3), 2699–2709. doi:10.1007/s11356-018-3790-4
Saleem, A., Anwar, S., Nawaz, T., Fahad, S., Saud, S., Ur Rahman, T., et al. (2024). Securing a sustainable future: the climate change threat to agriculture, food security, and sustainable development goals. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. doi:10.1007/s43994-024-00177-3
Sarkodie, S. A., and Owusu, P. A. (2020). How to apply the novel dynamic ARDL simulations (dynardl) and Kernel-based regularized least squares (krls). MethodsX 7, 101160. doi:10.1016/j.mex.2020.101160
Sarkodie, S. A., Owusu, P. A., and Leirvik, T. (2020). Global effect of urban sprawl, industrialization, trade and economic development on carbon dioxide emissions. Environ. Res. Lett. 15 (3), 034049. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/ab7640
Sarkodie, S. A., and Strezov, V. (2018). Empirical study of the environmental kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. J. Clean. Prod. 201, 98–110. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.039
Sharma, R., Sinha, A., and Kautish, P. (2021). Does renewable energy consumption reduce ecological footprint? Evidence from eight developing countries of Asia. J. Clean. Prod. 285, 124867. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124867
Sibt-e-Ali, M., Xia, X., Yi, W., and Vasa, L. (2025). Quantifying the role of digitalization, financial technology, governance and SDG13 in achieving environment conservation in the perspective of emerging economies. Environ. Dev. Sustain. doi:10.1007/s10668-024-05940-4
Sikder, M., Wang, C., Yao, X., Huai, X., Wu, L., KwameYeboah, F., et al. (2022). The integrated impact of GDP growth, industrialization, energy use, and urbanization on CO2 emissions in developing countries: evidence from the panel ARDL approach. Sci. Total Environ. 837, 155795. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155795
Sumaira, , and Siddique, H. M. A. (2023). Industrialization, energy consumption, and environmental pollution: evidence from south Asia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (2), 4094–4102. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-22317-0
Tariq, G., Sun, H., Haris, M., Kong, Y., and Nadeem, A. (2018). Trade liberalization, FDI inflows economic growth and environmental sustanaibility in Pakistan and India. J. Agric. Environ. Int. Dev. (JAEID) 112 (2). doi:10.12895/jaeid.20182.722
Tenaw, D., and Beyene, A. D. (2021). Environmental sustainability and economic development in Sub-Saharan Africa: a modified EKC hypothesis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 143, 110897. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2021.110897
Uche, E., Das, N., Bera, P., and Cifuentes-Faura, J. (2023). Understanding the imperativeness of environmental-related technological innovations in the FDI – environmental performance nexus. Renew. Energy 206, 285–294. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2023.02.060
Udemba, E. N., and Keleş, N. İ. (2022). Interactions among urbanization, industrialization and foreign direct investment (FDI) in determining the environment and sustainable development: new insight from Turkey. Asia-Pacific J. Regional Sci. 6 (1), 191–212. doi:10.1007/s41685-021-00214-7
Usman, M., and Balsalobre-Lorente, D. (2022). Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Energy Policy 162, 112780. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112780
Voumik, L. C., and Sultana, T. (2022). Impact of urbanization, industrialization, electrification and renewable energy on the environment in BRICS: fresh evidence from novel CS-ARDL model. Heliyon 8 (11), e11457. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11457
Wang, J., and Dong, K. (2019). What drives environmental degradation? Evidence from 14 sub-saharan African countries. Sci. Total Environ. 656, 165–173. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.354
Wang, S., Rahman, S. U., Zulfiqar, M., Ali, S., Khalid, S., and Sibt e Ali, M. (2025). Sustainable pathways: decoding the interplay of renewable energy, economic policy uncertainty, infrastructure, and innovation on transport CO2 in QUAD economies. Renew. Energy 242, 122426. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2025.122426
Wang, Y., Qamruzzaman, Md., and Kor, S. (2023). Greening the future: harnessing ICT, innovation, eco-taxes, and clean energy for sustainable ecology—insights from dynamic seemingly unrelated regression, continuously updated fully modified, and continuously updated bias-corrected models. Sustainability 15 (23), 16417. doi:10.3390/su152316417
Warsame, A. A., Abdi, A. H., Amir, A. Y., and Azman-Saini, W. N. W. (2023). Towards sustainable environment in Somalia: the role of conflicts, urbanization, and globalization on environmental degradation and emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 406, 136856. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136856
World Bank Open Data (2024a). World bank open data. Available online at: https://data.worldbank.org.
World Bank Open Data (2024b). World bank open data. Available online at: https://data.worldbank.org.
World Bank Open Data (2024c). World bank open data. Available online at: https://data.worldbank.org.
Xie, Q., Adebayo, T. S., Irfan, M., and Altuntaş, M. (2022). Race to environmental sustainability: can renewable energy consumption and technological innovation sustain the strides for China? Renew. Energy 197, 320–330. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.07.138
Xin, L., Vu, T. L., Phan, T. T. H., Sadiq, M., Xuyen, N. T. M., and Ngo, T. Q. (2023). Nexus of natural resources, urbanization and economic recovery in Asia: the moderating role of innovation. Resour. Policy 81, 103328. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103328
Yang, L., Bashiru Danwana, S., and Issahaku, F. Y. (2022). Achieving environmental sustainability in Africa: the role of renewable energy consumption, natural resources, and government effectiveness—evidence from symmetric and asymmetric ARDL models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (13), 8038. Article 13. doi:10.3390/ijerph19138038
Yu, X., and Wang, P. (2021). Economic effects analysis of environmental regulation policy in the process of industrial structure upgrading: evidence from Chinese provincial panel data. Sci. Total Environ. 753, 142004. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142004
Zafar, M. W., Shahbaz, M., Sinha, A., Sengupta, T., and Qin, Q. (2020). How renewable energy consumption contribute to environmental quality? The role of education in OECD countries. J. Clean. Prod. 268, 122149. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122149
Zhang, T., and Choi, C. H. (2025). Will digital trade be friend or foe of the green economy? Unveiling the complexities of green growth. J. Appl. Econ., 28 (1), 2464591. doi:10.1080/15140326.2025.2464591
Zhang, Q., Naqvi, S. A. A., and Shah, S. A. R. (2021). The contribution of outward foreign direct investment, human well-being, and technology toward a sustainable environment. Sustainability 13 (20), 11430. doi:10.3390/su132011430
Zhang, X., Sibt e Ali, M., Niu, H., Iqbal, A., and Wenbo, G. (2025). Assessing the impact of energy efficiency and the sharing economy on sustainable economic development in China: a QARDL analysis from 1991 to 2020. Energy Strategy Rev. 59, 101729. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2025.101729
Zhi-qiang, J., Ximei, K., Javaid, M. Q., Sibt-e-Ali, M., Chishti, M. Z., and Ali, A. (2024). Revealing the effects of industrial structure upgrading and environmental technologies on environmental quality: evidence from Asia. Environ. Dev. Sustain. doi:10.1007/s10668-024-05815-8
Keywords: digitalization, foreign direct investment, industrialization, renewable energy, urbanization, ecological footprint, environmental pollution
Citation: Abdi AH, Zaidi MAS, Hassan MA and Ahmed S (2025) Accelerating sustainable transformation in sub-Saharan Africa: the role of clean energy, digitalization, foreign direct investment, and industrialization. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1624721. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1624721
Received: 09 May 2025; Accepted: 14 July 2025;
Published: 08 August 2025.
Edited by:
Dillip Das, University of KwaZulu-Natal, South AfricaReviewed by:
Ismail Suardi Wekke, Institut Agama Islam Negeri Sorong, IndonesiaMuhammad Sibt E. Ali, Zhengzhou University, China
Copyright © 2025 Abdi, Zaidi, Hassan and Ahmed. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abdikafi Hassan Abdi, YWJkaWthZmloYXNhbjc5QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Abdikafi Hassan Abdi
Abdikafi Hassan Abdi Mohd Azlan Shah Zaidi3
Mohd Azlan Shah Zaidi3 Mandeq Abdullahi Hassan
Mandeq Abdullahi Hassan