- 1School of International Trade and Economics, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing, China
- 2School of Economics and Management, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China
By optimizing the mechanism of farmland transfer, digital technology promotes large-scale and mechanized operation, significantly improves agricultural production efficiency and resource utilization rate, which provides key support for ensuring food security. Using panel data of Rural Fixed Observation Point in Henan Province from 2009 to 2022, this study empirically investigates the impact of Internet access on farmland transfer and constructs a mathematical theoretical model to study the potential mechanism. This study finds that the Internet access of farmers can promote the transfer of farmland. The potential mechanisms are the resource reallocation effect triggered by increased non-farm employment and income, the efficiency-enhancing effect of agricultural production driven by digital technology, and the transaction facilitation effect brought about by lower information costs. Heterogeneity analysis shows that in terms of policy support, the increase of grain purchase price and direct subsidy positively regulate the willingness to transfer; In terms of farmers’ capital endowment, the groups with high human capital and physical capital are more inclined to transfer out of farmland, while the households with high land capital show the characteristics of farmland dependence, and the households with high information capital have a stronger willingness to transfer farmland; In terms of economic and cultural attributes, farmers located in agricultural areas, underdeveloped areas and traditional villages also have stronger willingness to transfer farmland. These findings not only help to release the potential of land factors but also provide a feasible path for small farmers to connect with modern agriculture through technology empowerment, which has dual practical value for ensuring food security and promoting rural revitalization.
1 Introduction
Digital technology promotes the concentration of scattered arable land to new business entities and accelerates the process of agricultural scale and mechanization, which not only improves land output rate and labor productivity but optimizes resource allocation through intensive production, and enhances comprehensive grain production capacity and resilience to risks, providing key support for ensuring national food security and realizing sustainable agricultural development (Huang et al., 2024). In the field of agricultural production, the mobility of factors such as land, labor and capital has been inhibited for a long time due to information barriers, especially in the market of agricultural land transfer, where inefficient matching of supply and demand and high cost of contract execution are common (Fayet et al., 2022). Digital technology through accurate information transfer, real-time data interaction and intelligent algorithm matching, significantly alleviate the incomplete and asymmetric information in the traditional transaction (Zhang et al., 2022a), so that the factor price discovery mechanism tends to be perfect, and the efficiency of resource allocation can be improved by Pareto. This technology-driven institutional change essentially builds a more inclusive and competitive factor trading platform, which provides a new technological path to break through the predicament of farmland fragmentation (Lu et al., 2022). This study constructs a mathematical model of rural households’ farmland transfer decision-making, incorporates digital technology and farmland transfer tendency into the model, analyzes the impact and mechanism of digital technology on farmland transfer decision-making of farm households under the classical labor, land, and technological factor configurations.
In this paper, digital technology is defined as the technology application form in which farmers access the Internet and use digital tools to conduct information acquisition, production management and market transactions. In the traditional agricultural economy, the mobility of land factors has long been limited by geographic segmentation, information asymmetry and transaction cost constraints, resulting in the fragmentation of the agricultural land transfer market (Deininger et al., 2012). Digital technology has substantially compressed the information search cost and contract execution cost through technical means such as big data analysis, blockchain depository and intelligent algorithm matching (Susarla, 2012), making the pricing mechanism of land factors tend to be transparent and standardized. As a tangible carrier of digital technology, the penetration depth of Internet application directly determines the transformation efficiency of technological dividend to agricultural economy (Deichmann et al., 2016). According to the Statistical Report on China’s Internet Development, the Internet penetration rate in rural China has jumped from 30.1% in 2015 to 65.6% in 2022. As a large agricultural province, Henan is under the dual pressure of land fragmentation degree and labor outflow (Lv et al., 2025), which makes the large-scale circulation solution provided by Internet technology have significant marginal improvement value.
The existing literature has primarily analyzed the theoretical mechanisms of farmland transfer through dual perspectives: farm household characteristics and institutional environment. Family resource allocation forms the foundation for choice formulation (Han et al., 2023). The increase in non-farm employment proportion promotes land transfer-out by elevating opportunity costs (Wang et al., 2023); farmers with stronger management capacity tend to transfer in land to achieve economies of scale (Guo et al., 2023). However, the insufficient demand for farmland transfer has persisted. At the institutional level, the property rights system represents a key constraint. The confirmation and certification of contracting rights have significantly increased farmers’ willingness to transfer (Zhang, 2023), while digital finance has enhanced the contractual attributes of farmland transfer markets (Shen et al., 2023). Some scholars have initiated investigations into digital systems, and their findings demonstrate that transfer platforms can significantly reduce transaction costs and improve the quality and efficiency of rural land transfers (Wu et al., 2023). While existing research focuses on household resource endowment and property rights systems, the underlying logic of digital technology’s impact on farmland transfer requires further exploration.
This paper fills the gaps in existing research in three ways. First, in terms of data methodology, this study utilizes long-term tracking panel data from Rural Fixed Observation Points in Henan Province from 2009 to 2022, incorporates farmland transfers out and farmland transfers in into the same analytical framework, and applies a two-fixed-effects model to examine the impact of digital technology on the farmland transfer decisions of farm households. And village construction grid costs are selected as instrumental variations to solve the potential endogeneity problem using two-stage least squares. Second, in terms of theoretical model, a mathematical model of rural households’ farmland transfer decision is constructed to incorporate digital technology and farmland transfer tendency into the model, and based on the equilibrium results of the mathematical model, the role paths of digital technology influencing farmland transfer decision are verified in terms of income from non-farm employment, the level of production organization, and the access to information. Third, in terms of heterogeneity analysis, the heterogeneous effect of digital technology affecting farmland transfer decision is tested from the aspects of policy support (food purchase price/food direct subsidy), capital endowment of farmers (human/physical/land/information), and economic and cultural attributes (agricultural area/underdeveloped area/traditional village).
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypotheses
2.1 Decision-making model for farmland transfer
To clarify the systematic linkages between digital technology and agricultural land reallocation processes among rural households, this paper constructs a decision-making model for farmland transfer of rural households, incorporates digital technology and land transfer tendency into the model, and analyzes the effects and causal pathways of digital technology on the decision-making of farmland transfer under the classical configuration of labor, land, and technology factors.
Assuming that farmers’ decisions are based on utility maximization, each farmer has the same time endowment h and allocates time to agricultural labor l, non-farm employment e, and leisure r, i.e.,:
In Equation 1,
Households’ farmland transfer income is mainly rental income, and the transfer rental income function is as follows:
In Equation 2,
The cost function of farmland transfer is as follows:
In Equation 3,
The household utility function is as follows:
In Equation 4, U represents the household utility,
In Equation 5,
The optimal farmland transfer ratio
In Equation 6 illustrates that the ratio of farmland transfer
2.2 Theoretical mechanism
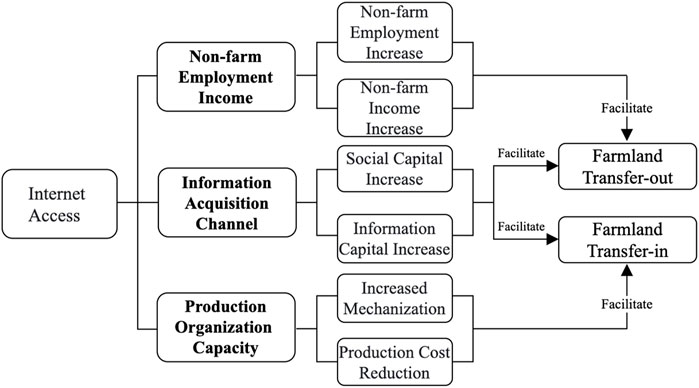
Building upon theoretical model findings, this section analyzes the theoretical mechanisms of digital technology affecting farmland transfer of farm households from three aspects: non-farm employment income, production organization capacity, and information acquisition channel (Figure 1). It also considers the fact that the grain purchase price and household farmland endowment may affect the transfer decision of farm households, which are included in the heterogeneity analysis.
2.2.1 Digital technology and farmland transfer
The effects of digital technology on farmland transactions depend on the dynamic game between the two forces of “efficiency improvement” and “market activation”, and its net effect realizes two-way regulation by reshaping the production function and transaction environment. Regarding farmland transfer-out, digital technology improves returns from alternative occupational engagement by expanding access to off-farm job information and reducing transition barriers during professional shifts, strengthening the incentive for resource reallocation and prompting farmers to turn out their farmland to release their labor force (Ren et al., 2023); the application of technologies such as smart farm machinery and precision agriculture significantly improves marginal farmland output, prompting operating entities to realize economies of scale through farmland transfer, while tools such as blockchain contracts reduce the risk of property rights transactions (Xu et al., 2025) and strengthen the feasibility of transfer. Although digital technology may inhibit transfer out by improving the efficiency of self-farming, the stimulating effect of digital technology on the transfer market and off-farm job prospects tends to prevail among agricultural workers, culminating in expanded agricultural land leasing transactions (Zhang et al., 2022b), and promoting the agglomeration of land resources to high-efficiency main bodies to form a synergistic optimization pattern of “market-driven transfers out and technology-driven transfers in”. Consequently, Hypothesis 1 is advanced as follows:
Hypothesis 1. Digital technology has a positive facilitating effect on the farmland transfer of households.
2.2.2 Non-farm employment income adjustment mechanism
Digital technology has expanded non-farm employment opportunities, elevated rural household incomes, and prompted farmland transfer-out decisions. First, geospatial constraints are eliminated by digital platforms via online recruitment systems and skills training, empowering farmers to access trans-regional labor markets and obtain multi-sector employment information, thereby enhancing labor mobility (Idowu and Elbanna, 2022). Second, new businesses such as e-commerce and the odd-job economy have given rise to diversified non-farm jobs, creating skill premium opportunities for rural young adults and increasing the proportion of off-farm earnings in rural households (Liu and Zhou, 2023). Finally, according to the theory of household resource allocation, the ongoing expansion of non-agricultural earnings drives rising opportunity costs in farm operations, and farmers are likely to transfer out their farmland to release labor to invest in high-return fields, and at the same time, realize the transformation of asset value through rental income (Grzelak and Staniszewski, 2025). Building upon these findings, Hypothesis 2 is advanced as follows:
Hypothesis 2. The increase in non-farm employment opportunities and income enhances the promoting effect of digital technology on farmland transfer-out, but inhibits farmland transfer-in.
2.2.3 Production organization capacity adjustment mechanism
Digital technology can enhance agricultural mechanization efficiency while decreasing operational expenditures, thereby improving crop yield efficiency while amplifying agricultural producers’ propensity to acquire additional arable land. First, the application of intelligent agricultural machinery and equipment and IoT monitoring systems (e.g., drone plant protection, precision irrigation) significantly improves the output efficiency per unit of farmland, shifts the marginal revenue curve to the right, and incentivizes operators to achieve economies of scale through land expansion (Kan, 2021). Second, the blockchain traceability system reduces quality control costs, big data analysis optimizes planting decisions, and socialized service platforms reduce management complexity through specialized division of labor, which together improve the feasibility of scale operations. Finally, when digital technology enables the output rate of inputs per unit of labor capital to exceed the traditional model, agricultural producers demonstrate a heightened propensity to expand operational acreage, thereby distributing fixed expenditures across enhanced productive scales (Foster and Rosenzweig, 2022). That is, digital technology increases the mechanization of agriculture and reduces production costs, thus elevating agricultural producers’ propensity to acquire additional farmland. Particularly within core grain cultivation zones, the combined influence of governmental incentives and digital technological frameworks elevates the incremental advantages of arable land acquisition (Huttunen, 2019), thereby driving the progression toward modernized and intensified farming practices. Building upon these findings, Hypothesis 3 is advanced as follows:
Hypothesis 3. Enhanced productive organizational increases the facilitating effect of digital technology on farmland transfer-in but inhibits the farmland transfer-out.
2.2.4 Information acquisition channel adjustment mechanism
Digital technology systematically reduces the cost of farmland transfer while bidirectionally stimulating farmland transfer markets. First, the digitalization of information channels breaks the time and space constraints, and farmers can instantly obtain cross-regional farmland supply and demand information through the online transfer platform, and use the intelligent matching function of big data to accurately dock with the trading object, eliminating the information monopoly of the traditional acquaintance society, while lowering information acquisition costs among households engaged in land transactions but also enhances the transferring main body’s efficiency of discovering high-quality plots of farmland (Su et al., 2023). Second, tools such as blockchain deposits and electronic contracts standardize the transaction process and reduce moral hazard and dispute-handling costs through automated ownership verification and smart contract execution (Michaelson, 2020). Finally, market transparency leads to Pareto improvement, whereby farmers transferring out of farmland maximize rent through the bidding mechanism, while farmers transferring in farmland accurately evaluate the value of land parcels with the help of remote sensing monitoring and other data services, optimizing the efficiency of resource allocation in both directions (Hou et al., 2019). Digital technology has broadened farmers’ access to information and enhanced farmers’ willingness to transfer out and in farmland. Digital technology promotes the transformation of potential transfer demand into actual transaction behavior and ultimately realizes the dynamic equilibrium of farmland factors in the transfer-out and transfer-in markets. In summary, Hypothesis 4 is advanced as follows:
Hypothesis 4. Broadened access to information reinforces the facilitating effect of digital technology on the farmland transfer-out and transfer-in.
3 Methods
3.1 Data
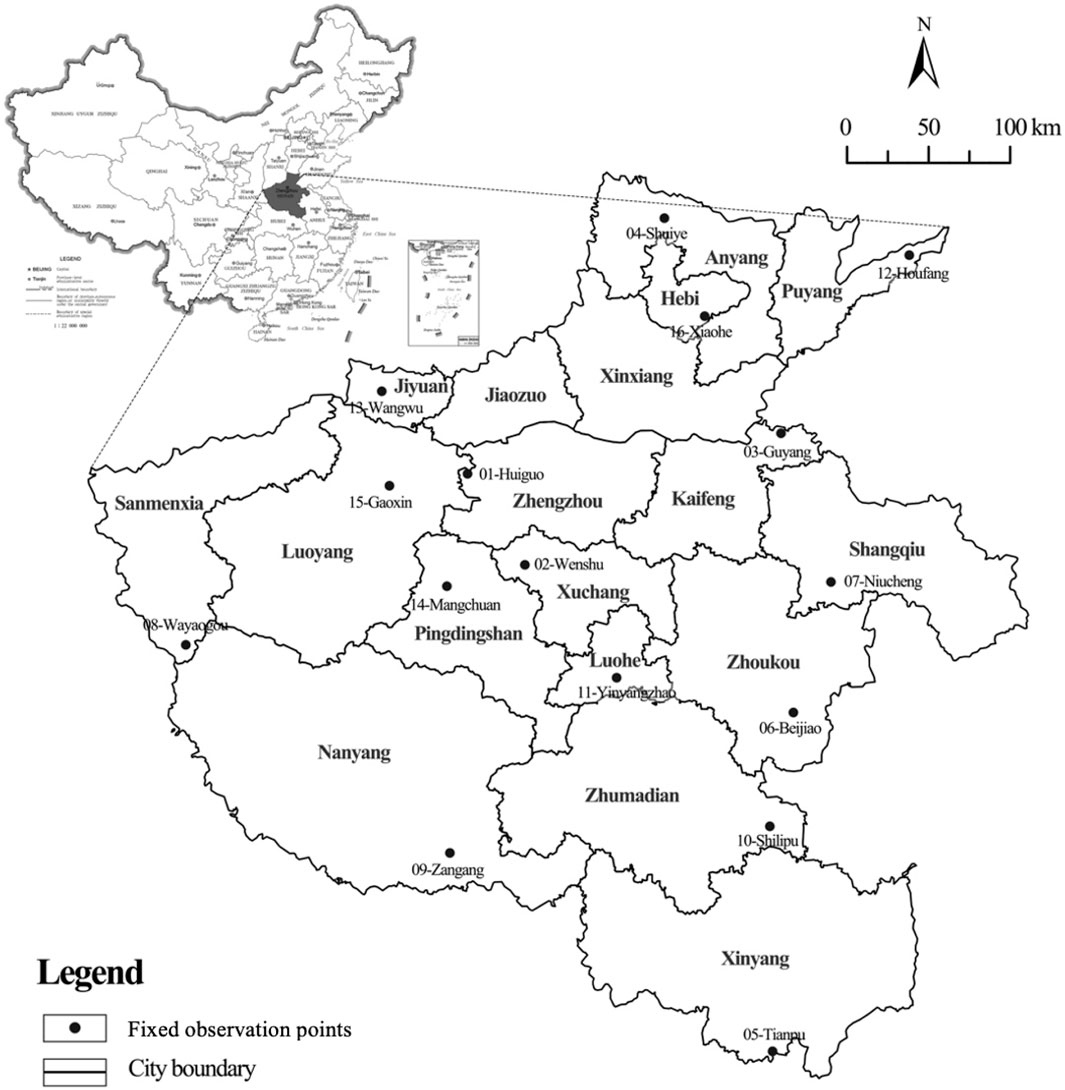
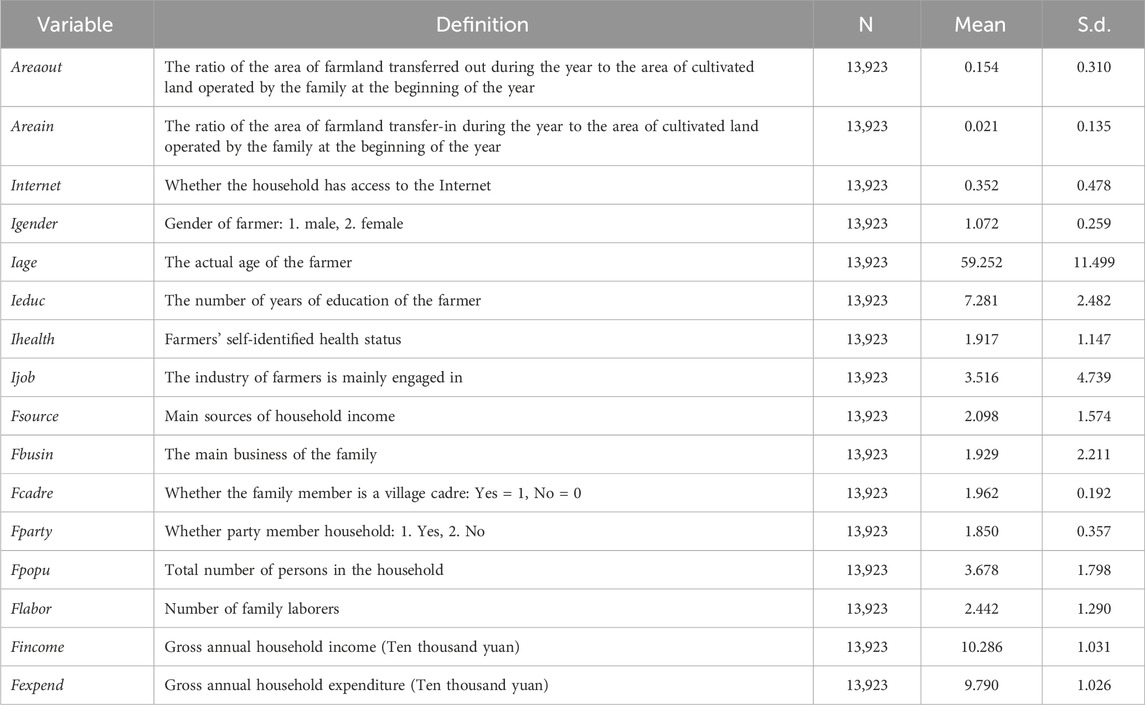
The data of Rural Fixed Observation Points in Henan Province of China from 2009 to 2022 are selected as the research sample. China’s rural fixed observation point is an authoritative and continuous rural social and economic survey system jointly established by the Policy Research Office of the CPC Central Committee and the Ministry of Agriculture of China, approved by the National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. The survey covers many fields of rural economic and social development, including population, labor force, land, fixed assets, crop planting area, household management overview, household annual income and expenditure, and the consumption level of surveyed farmers. Limited by data availability, this study focuses on Henan Province. There are a total of 16 Rural Fixed Observation Points in Henan Province, which are located in different prefecture-level cities in Henan Province, including all cities except Xinxiang and Jiaozuo, the specific location distribution is shown in Figure 2. Since the latest available data is in 2022, and the questionnaires of farmers before and after 2009 are quite different, this paper examines the impact of Internet use on farmers’ farmland transfer based on the survey data from 2009 to 2022. After summarizing and sorting, a total of 13,923 valid questionnaire data were obtained. This data has many advantages, such as high stability, wide coverage, large sample size and rich indicators, and scholars at home and abroad have carried out extensive and influential research with this data.
3.2 Variables
3.2.1 Dependent variable
This study operationalizes agricultural land transfer as the dependent variable, which is categorized into farmland transfer-out (Areaout) and farmland transfer-in (Areain) according to the increase or decrease of cultivated land area under household management. Farmland transfer-out constitutes the contractual process whereby landholders transfer operational rights to third-party agricultural operators, not participating in the cultivation and harvesting of the farmland, and only receiving the rent of the farmland, calculated as the proportion of leased-out agricultural land area within the calendar year relative to the total cultivated acreage managed by households; Farmland transfer-in constitutes the acquisition of cultivation rights from other landholders to enable scaled agricultural production, quantified by the proportion of leased-in acreage recorded within the calendar year relative to total cultivated land managed by households.
3.2.2 Core explanatory variable
Household Internet access (Internet) is the core explanatory variable, which is assigned a value based on “Whether or not your home has Internet access (1. Yes, 2. No)” in the questionnaire. If the farmer chooses “Yes”, the Internet access is coded as 1; if not, it is coded as 0. As the basic technical facility of digital technology application, Internet access’s coverage and intensity of use can systematically represent the breadth and depth of digital technology penetration, so it has multi-dimensional appropriateness in measuring the real effect of technology empowerment.
3.2.3 Control variables
Following the existing literature (Lv et al., 2025), this study selects control variables from both individual and household characteristics. Individual variables encompass farmers’ gender (Igender), chronological age (Iage), educational attainment (Ieduc), physiological condition (Ihealth), and occupation type (Ijob); household characteristics include the source of household income (Fsource), the main business of the family (Fbusin), whether it is a village cadre household (Fcadre), whether it is a party member household (Fparty), total population (Fpopu), the number of family laborers (Flabor), total annual income (Fincome), and total annual expenditure (Fexpend).
Variable corresponding descriptive statistics are comprehensively detailed in Table 1.
3.3 Model
This research investigates the effects of digital connectivity on agricultural land transactions and the specification is constructed as follows:
In Equation 7,
4 Results
4.1 Baseline results
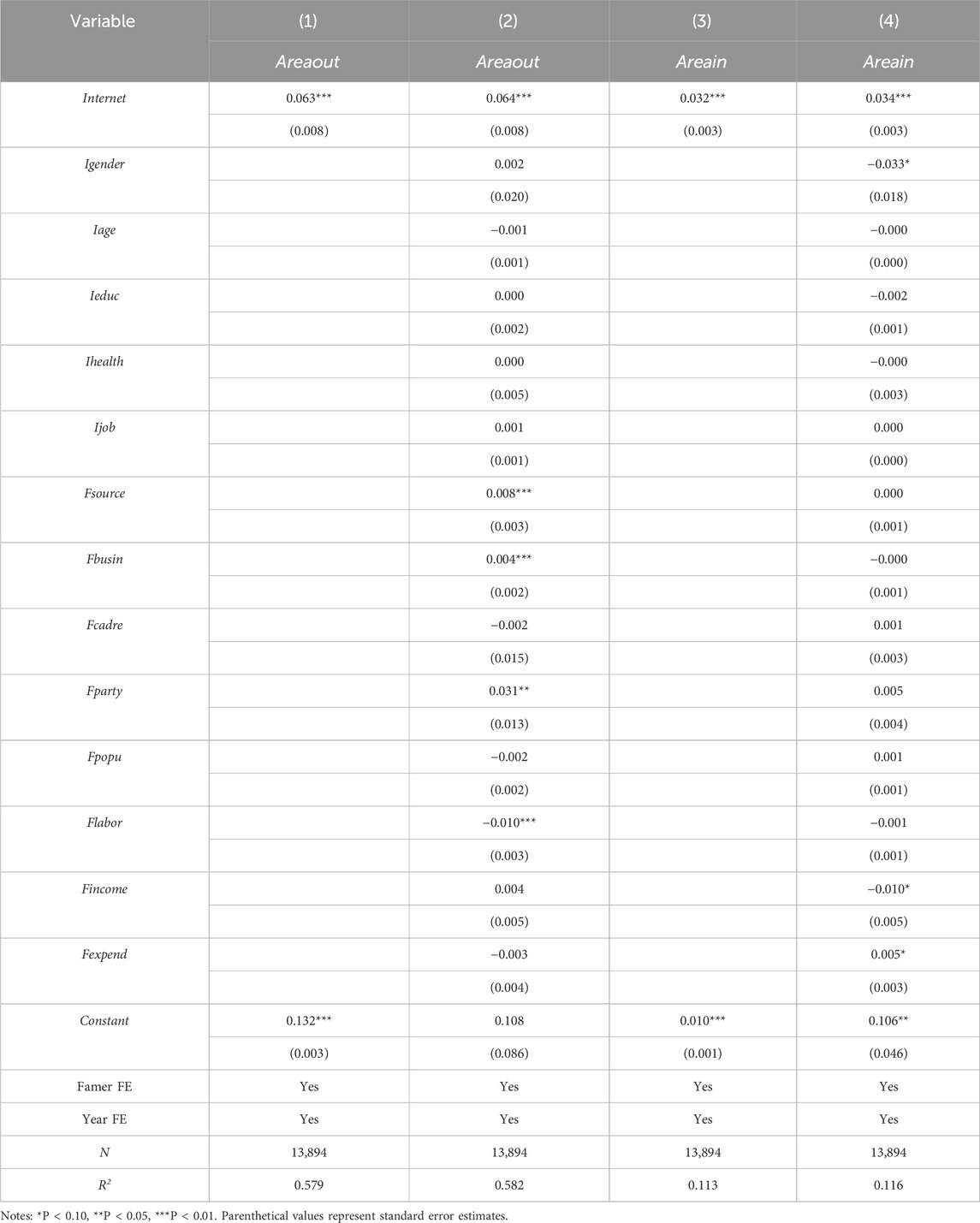
Baseline regression outcomes are methodically organized in columns (1) and (3) of Table 2, which exclude control variables. The Internet accessibility coefficient demonstrates statistical significance at the 1% level with a positive sign, suggesting that residential Internet adoption substantially enhances both farmland transfer-out and transfer-in processes. The regression analysis incorporating control variables reveals that in columns (2) and (4) of Table 2, the coefficients associated with Internet access maintain a statistically significant positive association at conventional levels, demonstrating the robustness of Internet connectivity’s facilitative effect on agricultural land transactions, and in terms of the coefficient magnitude, the facilitating effect on the transfer-out of farmland is significantly larger than the facilitating effect on the transfer-in of farmland. Internet access increases farmland transfer-out by about 6.4% and farmland transfer-in by about 3.4%, indicating that in rural areas of Henan Province, the adoption of digital technologies exerts a substantial influence on streamlining agricultural land transactions among rural households, thereby confirming the validity of Hypothesis 1.
Regarding control variables in farmland transfer models, coefficient estimates reveal that households deriving greater income from non-agricultural sectors exhibit a positive association with farmland transfer-out (reflecting reduced agricultural dependence), as do those specializing in non-farming activities (indicating occupational reallocation) and party member households (suggesting political capital advantages); conversely, larger labor force size correlates negatively with farmland transfer-out (implying higher farmwork capacity). For farmland transfer-in, female-headed households show negative association (potentially reflecting gendered resource constraints), while higher household income corresponds negatively (consistent with capital diversification strategies) yet greater household expenditure predicts positive engagement (signifying production capacity investment), collectively underscoring how socioeconomic characteristics distinctly shape farmland reallocation decisions beyond core variables.
The modest R-squared values observed in our farmland transfer-in regressions (0.11–0.12) highlight the need for future research to enhance predictive power by integrating three currently underrepresented dimensions: institutional factors such as standardized land transfer contracts and regulatory frameworks, social networks facilitating informal kinship-based transfers that dominate rural transactions, and behavioral characteristics of operators including risk tolerance thresholds and entrepreneurial aptitude—all essential for developing next-generation models of agricultural land reallocation.
In addition, this study leverages Henan’s predominantly plains-based topography—with sparsely distributed mountainous and hilly areas in its western regions—to conduct grouping regressions stratified by county-level terrain, examining differential impacts of digital technology adoption on farmland transfer. Results in Supplementary Appendix Table A1 demonstrate that while digital technologies significantly promote farmland transfer-out and transfer-in across plains, mountainous, and hilly zones, their effect intensity exhibits a diminishing gradient: impacts in mountainous and hilly areas are attenuated relative to plains. This difference may stem from dual topographical limitations: (1) signal obstruction and inadequate infrastructure coverage in mountainous areas reduce technological accessibility, thereby diminishing digital tool efficacy; (2) plot fragmentation in hilly terrain inhibits scale economies, curtailing productivity gains from technology-enabled operations. Consequently, the conclusions of this paper are conditionally applicable to mountainous and hilly areas but require terrain-adjusted implementation frameworks.
4.2 Robustness test
4.2.1 Instrumental variable
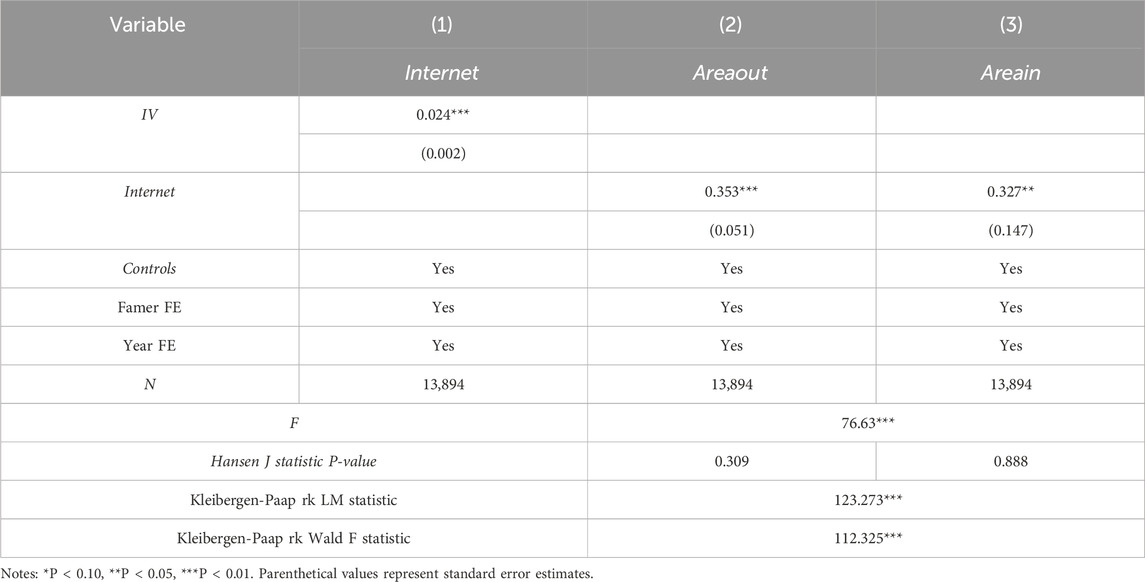
To address potential endogeneity concerns, village construction grid costs and the topography of the county in which the village is located are selected as instrumental variables (Lv et al., 2025), with the model re-estimated using the 2SLS method. Regarding correlation, higher village construction grid costs are associated with more comprehensive Internet infrastructure, increasing farmers’ likelihood of Internet access, thereby satisfying the relevance condition; the elevation of the village terrain increases the installation and maintenance cost of network infrastructure and telecommunication services, thus restricting the development of rural Internet and meeting the relevant conditions. Concerning exogeneity, village construction grid costs are not directly associated with farmland transfer decisions, as these decisions primarily correlate with farmers’ health status and household characteristics (He et al., 2021), thus satisfying the exogeneity principle; as an exogenous geographic characteristic, county topography exerts no causal influence on farmers’ farmland transfer decisions (Zhou and Xiong, 2018), fulfilling the exclusion restriction.
The instrumental variable regression estimates are reported in Table 3. The first column results show a significant positive relationship between the instrumental variables and independent variable. The second-stage regression outcomes in columns (2) and (3) demonstrate methodological consistency with baseline estimates, showing statistically significant positive coefficients at standard confidence levels. That is, Internet adoption substantially enhances both farmland transfer-out and transfer-in processes. These results demonstrate that digital connectivity substantially enhances agricultural land reallocation efficiency among rural households.
4.2.2 Replacement of dependent variables
In the benchmark regression, the measurement of land transfer (out and in) employs the ratio between annual contracted-out (contracted-in) agricultural land area and initial household-operated cultivation area. This operationalization has been substituted with logarithmic transformations of the contracted-out (contracted-in) land area for robustness verification, with corresponding empirical outcomes documented in columns (1) and (2) of Supplementary Appendix Table A2. The estimates remain statistically significant and positive, demonstrating that digital connectivity enhances agricultural land reallocation efficiency and confirming the robustness of the benchmark results.
4.2.3 Changing model setting
The baseline regression has excluded the effect of village-level factors on the regression results, as the farmer code consists of a “village code” plus “household code”, controlling for farmer fixed effects also controls for village fixed effects. The clustering has been changed from the farmer level to the village level and the corresponding empirical outcomes are documented in Supplementary Appendix Table A2 columns (3) and (4). The coefficient magnitude and significance of Internet access are consistent with the baseline regression results, and the standard error has increased, this verification confirms the methodological stability of core empirical outcomes.
4.2.4 Changing sample interval
The dataset employed in this study covers the timeframe from 2009 to 2022. On the one hand, considering that it is relatively difficult for farmers to transfer farmland during the COVID-19 epidemic, and the event has caused a lot of inconvenience to farmers’ agricultural production, the Internet penetration rate was relatively low before 2011, which may have an impact on the regression results. Therefore, this paper reduces the sample interval to 2011–2019 to re-run the regression; the corresponding analytical findings are documented in Supplementary Appendix Table A2 columns (5) and (6), after excluding the effects of other factors, Internet access still significantly promotes the farmland transfer of farm households.
4.2.5 Excluding policy effects
Some digital economy policies are issued for the 2009–2022 period, such as the “Broadband China” strategy (2013), the “Smart City” pilot (2012), and the “E-commerce to the Countryside” program (2014). To eliminate the potential influence of policy interventions on the analytical outcomes, the baseline regression model is re-estimated with these policy variables incorporated as additional controls. The revised results are reported in Supplementary Appendix Table A3. The robust positive effect of digital connectivity on agricultural land reallocation persists after controlling for concurrent policy interventions, confirming the analytical independence of core results from extraneous policy factors.
4.3 Heterogeneity analysis
To examine the heterogeneous impacts of digital technological adoption on agricultural land reallocation behaviors, we conduct heterogeneity analysis across three dimensions: policy support intensity, capital endowment of farmers, and economic and cultural attributes. The policy supports intensity modulates farmers’ risk-return calculus by altering expected returns and risk perceptions in farmland transfer markets. Household capital endowment determines their agricultural production capacity, resource constraint intensity, and technology transformation efficiency. The economic and cultural attributes determine the compliance with social norms and the adaptability of digital technology, thus affecting the decision-making of farmers on the transfer of farmland.
Referring to the existing literature, the interaction term is introduced into the benchmark regression to analyze the heterogeneous effects of rural digital connectivity on agricultural land reallocation by household characteristics. The following econometric model is specified:
In Equation 8,
4.3.1 Strength of policy support
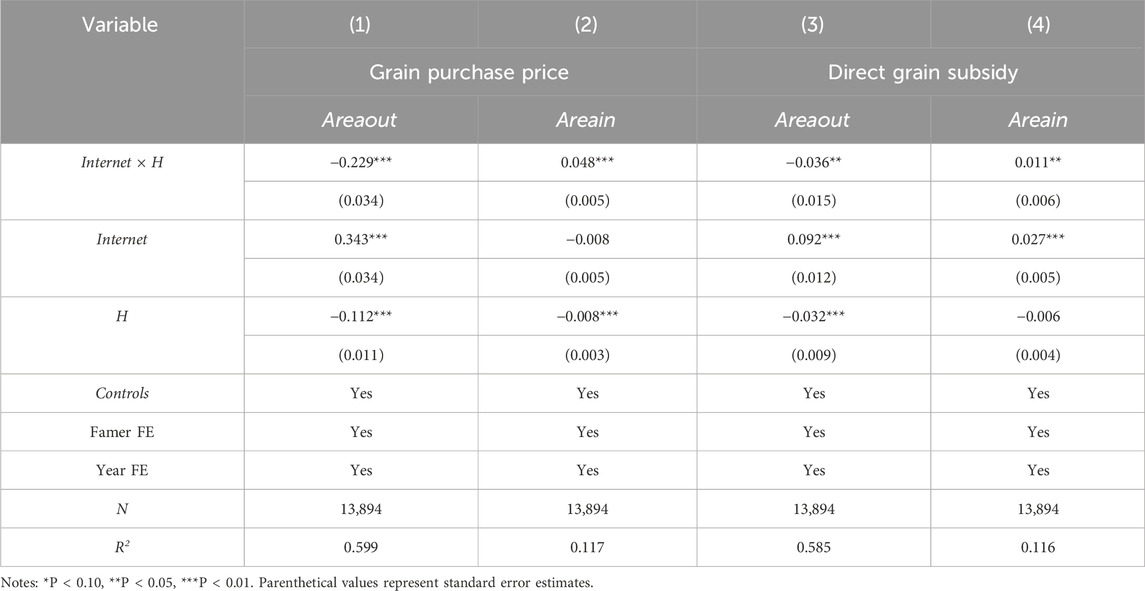
4.3.1.1 Grain purchase price
Agricultural business income constitutes the cornerstone of farmers’ livelihoods. Grain purchase prices directly determine agricultural income levels, consequently influencing farmland transfer decisions. The higher the grain purchase price, the more farmers are willing to transfer in more farmland to realize more income, and vice versa; these households demonstrate a greater propensity to divest their agricultural land holdings. According to the median grain purchase price, the dataset was stratified into two distinct analytical cohorts: high and low. Observations exceeding the sample median are dichotomized to 1; otherwise, it is 0. The analytical outcomes are systematically organized in Table 4, columns (1)–(2), which suggests that higher grain purchase prices correlate with farmers’ increased likelihood of engaging in farmland transfer-in activities and reduced propensity for transfer-out. When agricultural commodity prices reach elevated levels, farmers gain more by selling grain, and compared to transferring out their farmland, farmers are more willing to farm by themselves to obtain higher income and are even willing to transfer the farmland of other farmers in to increase business income through large-scale operation. This demonstrates that grain procurement pricing serves as a regulatory mechanism for agricultural producers’ crop supply availability, the high grain purchase price results in more grain supply, and farmers are more willing to transfer in more farmland (Zhou et al., 2021).
4.3.1.2 Direct grain subsidy
As a policy instrument supporting agricultural development and ensuring grain security, grain subsidies significantly influence farmland transfer decisions. Direct grain subsidies enhance farmers’ incentives to transfer in farmland by improving agricultural net returns. According to the median amount of direct grain subsidy, the sample is categorized into high and low subsidy groups, with binary values assigned (1 = high subsidy level, 0 = low subsidy level), respectively. The analytical outcomes are systematically organized in Table 4, columns (3) and (4), and indicate that when the grain direct subsidy is high, the farm household is more willing to transfer in farmland instead of transferring out of farmland. Since the amount of direct grain subsidy is positively related to the cultivated area of farmers (Yang et al., 2023), the greater the agricultural land expanse, the higher the corresponding governmental subsidy allocation, if all the cultivated land is subcontracted to others, they cannot get any direct grain subsidy, agricultural producers demonstrate greater propensity to expand operational acreage, thereby accessing enhanced governmental subsidy allocations.
4.3.2 Farmers’ capital endowment
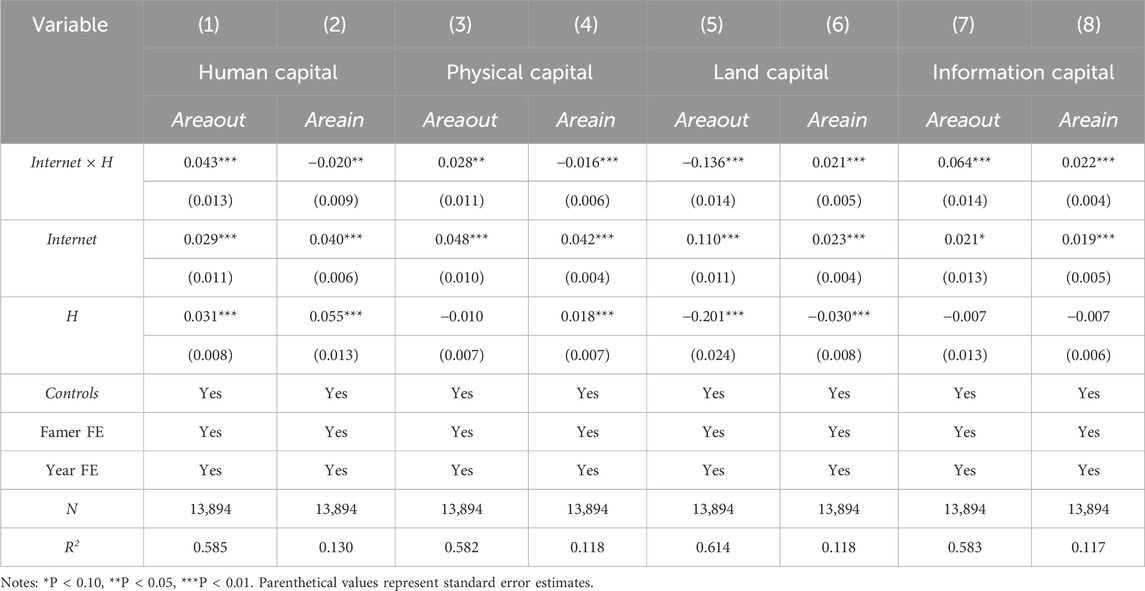
4.3.2.1 Human capital
Human capital quantifies agrarian households’ economic reliance on agricultural land operations-derived revenue, which affects the willingness to participate in the transfer of farmland, and this paper measures human capital by household income. The median amount of household income is divided into two groups of high-income households and low-income households, and assigned the values of 1 and 0. The empirical results in columns (1) and (2) of Table 5 demonstrate a significantly positive coefficient for transfer-out farmland, whereas land transferring-in exhibits statistically negative estimates, which indicates that for the high-income households, there is a greater tendency to transfer farmland out. That is, compared to low-income households, high-income households have a stronger willingness to transfer farmland out and a weaker willingness to transfer farmland in. The observed phenomenon may be attributed to the income composition patterns of affluent households, wherein non-agricultural revenue streams constitute a predominant share of total earnings, effectively displacing farm-derived income as the principal economic foundation, agricultural producers demonstrate heightened engagement in secondary and tertiary industries (Lv et al., 2025), resulting in diminished labor allocation for cultivation activities, while concurrently obtaining rental income through farmland divestment.
4.3.2.2 Physical capital
Physical capital reflects the household economic level of farmers; the higher the physical capital, the stronger their economic strength and the lower their willingness to engage in agricultural production. This study measures physical capital using farm households’ consumption expenditure, the sample is dichotomously stratified by median consumptive expenditure levels. Households with elevated consumption expenditures were coded as 1, while those demonstrating lower expenditure levels were assigned a value of 0. The heterogeneous physical capital endowment patterns detailed in Table 5, columns (3) and (4), which are the same as those of the human capital, indicating agricultural producers with substantial physical assets exhibit heightened propensity toward arable land divestment, while those with low physical capital are more inclined to transfer in the farmland. This phenomenon is primarily attributable to agricultural producers with substantial physical capital endowments typically maintaining diversified off-farm revenue streams and consolidated asset portfolios, and transferring out of farmland can exchange for stable rent and release labor to be invested in high-value-added industries (Donovan and Poole, 2014); Low physical capital farmers are limited by non-farm opportunities, and transferring farmland in can expand the scale of cultivation to improve marginal returns and alleviate the pressure on their livelihoods.
4.3.2.3 Land capital
Land capital fundamentally shapes agricultural production scale and resource allocation. This study quantifies land capital using households cultivated land area. Households are classified into high-land endowment (coded 1) and low-land endowment (coded 0) groups based on whether their cultivated area exceeds the median. Columns (5) and (6) of Table 5 demonstrate statistically significant parameter estimates, indicating land-abundant households demonstrate a lower propensity to transfer farmland out and a higher willingness to acquire additional farmland. Smallholders face higher input-output ratios and lower productivity in land management, incentivizing farmland transfer-out for resource optimization (Mutoko et al., 2014). Conversely, land-abundant households pursue scale economies through mechanized operations, reducing unit costs while enhancing productivity.
4.3.2.4 Information capital
Information capital reflects the ability of farmers to acquire, process, and utilize information, and in this paper, we measure farmers’ information capital by expenditure on communication. The higher the information capital, the better they can make strategic adjustments according to market information and policy dynamics, thus affecting their decision-making on farmland transfer. According to the median expenditure on maintaining rural social relationships, the sample is divided into high and low information capital groups and assigned the values of 1 and 0. The analytical outcomes are documented in columns (7) and (8) of Table 5, with the interaction term coefficients demonstrating statistically significant positive associations, which indicates that farmers with high information capital are significantly likely to transfer not only out of the farmland but also into the farmland. If farmers have non-farm employment opportunities, they will quit inefficient farming and shift to higher-paying fields (Chapagain and Raizada, 2017); Conversely, if farmers anticipate that large-scale operation can improve returns through real-time access to information on planting technology, price fluctuations, and policy subsidies, Agricultural producers actively expand cultivated land holdings to enhance production efficiency. Demonstrating that increased informational asset accessibility among rural households positively correlates with agricultural land reallocation.
4.3.3 Economic and cultural attributes
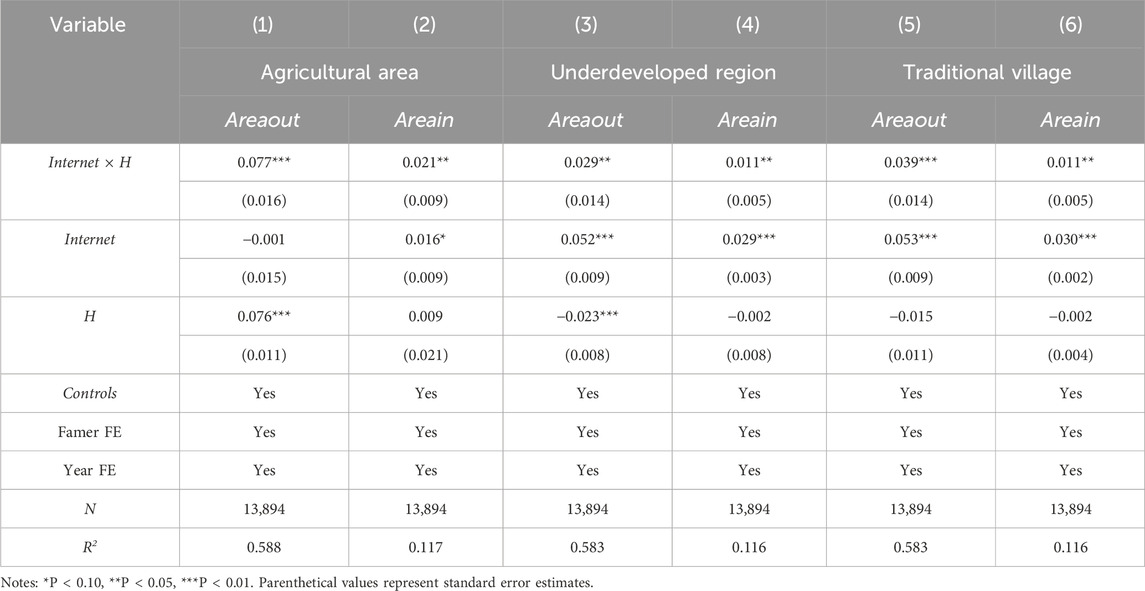
4.3.3.1 Agricultural area
Agricultural areas are regions with a primary focus on agricultural activities, often experience limited availability of non-farm employment options due to the predominant emphasis on crop cultivation and livestock rearing, so the fact that a farmer’s village belongs to an agricultural area reflects the unitary nature of the economic structure and the dependence on land resources. The values are 1 and 0 according to whether the village of the farmer belongs to the agricultural area, The findings, presented in the initial two columns of Table 6, show that the farmers in agricultural areas have significantly increased their willingness to transfer their farmland out and in when they have access to the Internet. The fundamental reason is that Internet access breaks the closed information environment in agricultural areas. On the one hand, the diffusion of technical information reduces the threshold of large-scale operation (Zhang Q. et al., 2022), which motivates production-oriented farmers to expand their farmland scale; On the other hand, market opportunity spillovers push livelihood transition farmers to leave the farmland bondage, forming a flexible transfer pattern of “leaving the farmland but not leaving the hometown”.
4.3.3.2 Underdeveloped region
The vulnerability of livelihoods and difficulties in accessing markets is reflected in the fact that the villages in which the farmers live are in less developed areas, which are often characterized by poor infrastructure, a lack of non-farm employment channels, and an information silo effect, whereby farmers rely on the farmland for their livelihoods and find it difficult to break out of their inefficient patterns of production. Values of 1 and 0 are assigned according to whether the village is an underdeveloped area. Columns (3) and (4) exhibit the results. The analysis demonstrates that farmers in underdeveloped areas’ inclination to transfer their farmland out and in significantly increases after accessing the Internet. This is mainly because Internet access improves returns to agricultural production through technological empowerment (Ahmad et al., 2024), driving farmers to transfer in farmland; and information empowerment activates the potential labor force, engaging in non-farm production to bring higher returns (Deichmann et al., 2016), and thus, more inclined to transfer out of farmland.
4.3.3.3 Traditional village
Traditional villages are usually linked by clan networks, and the land carries the functions of ethical identity and social capital accumulation, so farmers in traditional villages are constrained by cultural roots and institutional inertia. Depending on whether the farmer’s village belongs to a traditional village or not, assigned a value of 1 or 0, respectively. Columns (5) and (6) exhibit the results, the empirical evidence reveals that enhanced digital connectivity stimulates bidirectional land transfer activities within conventional rural agricultural populations. The possible reason is that Internet access breaks through the traditional binding of land and identity, and the flow of information spawns a game of economic rationality and cultural tradition. Farmers who are capable of realizing large-scale operations integrate fragmented farmland with the help of digital platforms (Zhao et al., 2024), transform the cultural attributes of farmland into productive assets, and realize large-scale farming for greater returns; Farmers who are unable to engage in agricultural production are informed of non-farm opportunities and pension costs, the findings suggest these mechanisms trigger demands for land value realization, promoting farmland transfers to acquire livelihood capital in non-agricultural sectors.
4.4 Mechanism analysis
Theoretical examination establishes that digital technology shapes agricultural land transactions by delineating three distinct mechanisms: non-farm employment income, production organization capacity, and information accessibility. First, enhanced non-farm employment opportunities increase labor shifts to secondary or tertiary sectors, driving farmland transfer-out. Second, improved production organization capacity boosts agricultural productivity while lowering operational costs, strengthening incentives for farmland transfer-in. Third, expanded information access reduces transaction costs and search frictions, while facilitating contractual agreements that accelerate farmland transfer processes.
This research utilizes a moderating effect model (Equation 9) to investigate the theoretical mechanism of digital technology affecting farmers’ farmland transfer, and constructs the model as follows:
The mechanism variable
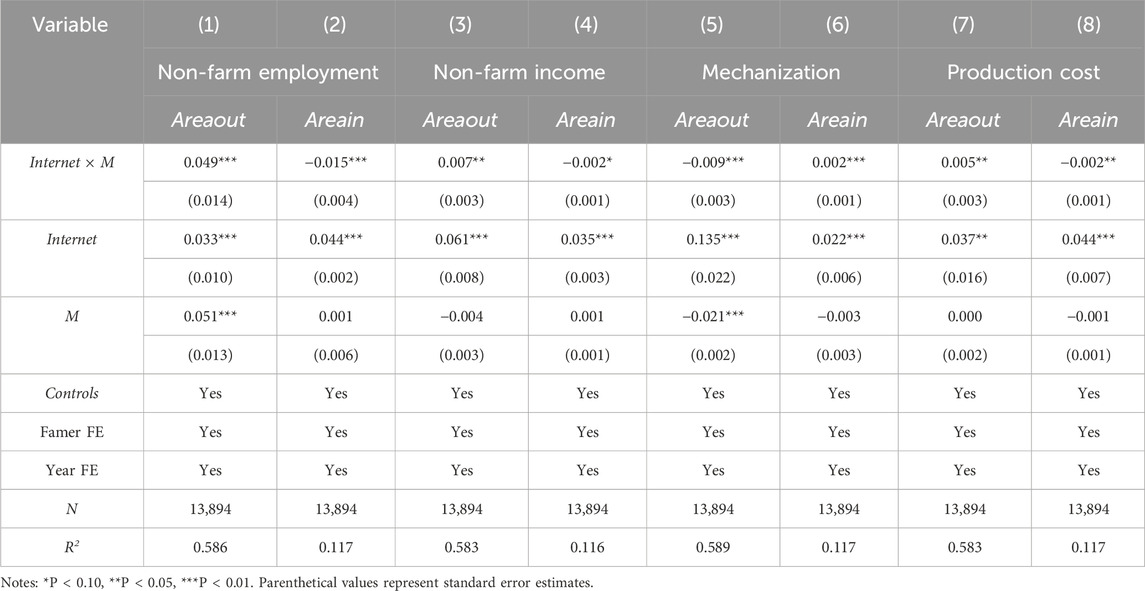
4.4.1 Non-farm employment and income
Table 7 presents the findings from the analysis of off-farm occupations and income mechanisms. The interaction term coefficients exhibit statistically significant positive effects across columns (1) and (3), whereas statistically significant negative effects are observed in columns (2) and (4), the empirical findings indicate that the enhancing impact of household Internet adoption on farmland transfer-out becomes more pronounced as off-farm occupational engagement and income levels rise, whereas its promotional influence on farmland transfer-in concurrently diminishes under equivalent conditions. Digital technology utilization expands off-farm occupational opportunities while enhancing their earnings from non-agricultural sources, which contributes to an increased propensity among rural households toward relinquishing their agricultural land holdings, and Hypothesis 2 is verified. Because farmers with higher non-agricultural income usually have a higher degree of part-time employment, longer non-agricultural working time, and lower demand for income from agricultural production (Mondal et al., 2021), this elevates the probability of these farmers entering employment within the manufacturing and service sector domains, which significantly augments the potential for occupational transition processes. Furthermore, structural transformations within sectoral compositions have been catalyzed by the progression of digitally enabled economic systems (Yang and Meseretchanie, 2024), which provide more employment channels for farmers, and the increase of non-farm income provides sufficient livelihood security, which encourages farmers to gradually leave agricultural production and stop small-scale farmland cultivation.
4.4.2 Production organization capacity
The results of production organization capacity mechanism are also shown in Table 7. The analytical outcomes in columns (5)–(6) reveal mechanization-related dynamics: interaction coefficients display statistically inverse relationships, with negative associations manifesting in farmland transfer-out models and positive correlations emerging in transfer-in counterparts, suggesting that mechanization intensification corresponds with heightened farmland retention propensities but inversely correlates with land relinquishment tendencies. Internet access demonstrates mechanization-dependent duality: Its promotional effect on farmland outflow diminishes inversely with mechanization intensity, while concurrently amplifying land inflow. Second, columns (7) and (8) present the production cost test findings, the promotional effects of household Internet access exhibit cost-contingent bidirectionality: positively reinforcing farmland outflow as operational expenses escalate, while inversely attenuating land inflow under equivalent cost increments, i.e., the lower the production cost is, farmers are significantly more likely to transfer-in more farmland. In summary, the higher the production organization capacity, the stronger the facilitating effect of Internet access on farmland transfer-in, and Hypothesis 3 is verified. Farmers with a high production organization capacity also have a higher degree of mechanization of agricultural production, while concurrently maintaining foundational proficiency in core agronomic techniques and accumulated practical expertise (Peng et al., 2022). This facilitates large-scale agricultural production, and due to the diminishing marginal cost, it is easier to obtain excess profits from agricultural production (Zhang Q. et al., 2022), which motivates farmers to increase farmland area within their agricultural activities.
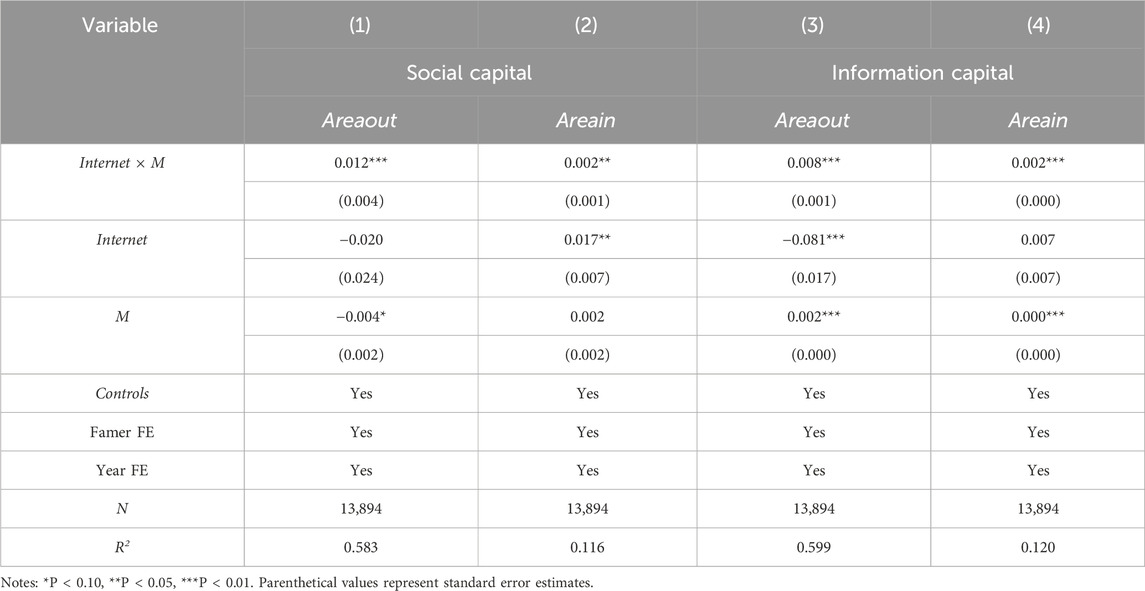
4.4.3 Information acquisition channel
Table 8 delineates the analytical findings of information accessibility mechanisms, with columns (1) and (2) quantifying social capital assessments and columns (3) and (4) measuring informational capital evaluations, respectively. The interaction variables demonstrate statistically significant positive coefficients, revealing that the promotional impact of digital connectivity on bidirectional farmland transfer dynamics intensifies proportionally with expanded information accessibility channels, and Hypothesis 4 is verified. Internet access expands farmers’ information acquisition channels, improves information dissemination efficiency, and broadens the scope of information dissemination, thus reducing information asymmetry and making it easier to reach farmland transfer contracts among farmers. With the diversification of information acquisition channels, farmers no longer rely solely on the oral transmission of the same village to obtain farmland transfer information. In addition to the introduction of relatives and friends, WeChat friend circle, social media, agricultural professional websites, government announcements, intermediary organizations, etc., also provide a wealth of information on the transfer of farmland, so that farmers have more options and comparison space when choosing to transfer farmland out or in (Zou et al., 2022). Thus, it is conducive to improving the opportunities for transferring out and in farmland, thereby contributing to the mitigation of empirical patterns of rural farmland fragmentation.
While our operationalization of information capital (via communication expenditure) and social capital (through relationship maintenance costs) aligns with established practices in rural development economics (e.g., Lv et al., 2025), we acknowledge these monetary proxies may not fully capture households’ strategic access to land-specific information; Nevertheless, contextual evidence confirms their functional relevance, suggesting these measures effectively reflect capital-driven opportunity structures despite potential noise in capturing qualitative dimensions like information relevance or trust depth, a limitation future studies could address through digital trace data or experimental designs.
5 Conclusion
Using the survey data of Rural Fixed Observation Points in Henan Province from 2009 to 2022, this study empirically examines the impact of digital technology on farmers’ farmland transfer. The findings reveal that households’ access to the Internet significantly facilitates both farmland transfer-out and transfer-in, demonstrating an overall enhancement in farmland reallocation dynamics. The potential mechanism is mainly manifested in three aspects. First, strengthen the willingness of farmers to reallocate resources by expanding non-agricultural employment opportunities and income growth; Second, improve the level of production organization with the help of digital agricultural technology, and promote the transformation of agricultural operation to scale, specialization and mechanization; Third, break the information barriers, reduce the transaction costs of circulation, broaden the channels of information acquisition, and increase the opportunities of agricultural land subcontracting. Heterogeneity analysis shows that the increase of policy support can enhance the incentive effect of farmers to expand production scale; Households with high human capital and physical capital are more likely to transfer out of farmland due to non-agricultural employment opportunities and higher economic base advantages, while households with high land capital are more likely to transfer into farmland due to land dependence. Households with high information capital have stronger intention to transfer out and into farmland. In terms of economic and cultural attributes, farmers in agricultural areas, underdeveloped areas and traditional villages have stronger willingness to transfer farmland.
There are several limitations to this paper. First, our theoretical model assumes linear productivity effects for analytical tractability, and future work should explore heterogeneous treatment effects across digital technology adoption stages using nonparametric approaches or dynamic threshold models. Second, the inability to disentangle cost-reduction versus rent-premium effects remains a constraint, attributable to missing micro-level cost and productivity variables in nationally representative rural surveys. We recommend collecting the necessary cost and productivity data in future research to further disaggregate the cost reduction and rent premium effects of digital technologies.
The paper makes the following targeted recommendations. First, the construction of digital infrastructure and the promotion of agricultural technology applications should be accelerated. Government departments should focus on improving Internet coverage and access quality in rural areas and reduce the cost of Internet use for farmers through special subsidies. Simultaneously promote the construction of digital agricultural technology demonstration bases and carry out targeted training programs to help farmers master digital skills such as the operation of smart farm machinery and precision planting. Encourage leading agricultural enterprises to build production hosting platforms to provide small farmers with full-process socialized services, accelerating the transformation of traditional agriculture to scale and intensification.
Second, improve the market service system and policy support for agricultural land transfer. Build a farmland transfer information platform covering provinces, cities, counties and villages, integrating land supply and demand information, ownership certification, contract templates and other modules to reduce transaction friction costs. Optimize the structure of grain subsidy policy by implementing Zhejiang-tested stepped subsidies for farmers transferring land to large-scale grain production, strengthening policy incentives through differentiated compensation. Besides, to address farmland fragmentation, promote Shandong-style government-led production hosting platforms that enable “small pieces to large pieces” transfer models, enhancing continuous operation feasibility through coordinated land integration.
Third, implement differentiated policy guidance and risk prevention and control mechanisms. For peri-urban areas with more non-agricultural employment opportunities, guide high-income families to standardize their transfer behavior, and support vocational training and social security policies to avoid land abandonment. In the main grain-producing areas, a market-expectation guidance mechanism has been set up to stabilize operators’ confidence through a system of dynamic adjustment of the purchase price. Regarding resource endowment constraints, a special transfer compensation fund has been set up for farmers with less than five acres of arable land, and agricultural insurance innovations have been used to reduce natural risks and market fluctuation risks for large-scale business entities, forming a virtuous cycle of “transferring out of the market with security, and transferring into the market with motivation”.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
XG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. JL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. RZ: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42371314) and the Education and Major project of Applied Research of Philosophy and Social Sciences in colleges and universities of Henan Province (No. 2022-YYZD-08).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1631305/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmad, B., Zhao, Z., Jile, X., Gultaj, H., Khan, N., and Yunxian, Y. (2024). Exploring the influence of internet technology adoption on the technical efficiency of food production: insight from wheat farmers. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8, 1385935. doi:10.3389/fsufs.2024.1385935
Chapagain, T., and Raizada, M. N. (2017). Agronomic challenges and opportunities for smallholder terrace agriculture in developing countries. Front. plant Sci. 8, 331. doi:10.3389/fpls.2017.00331
Deichmann, U., Goyal, A., and Mishra, D. (2016). Will digital technologies transform agriculture in developing countries? Agric. Econ. 47 (S1), 21–33. doi:10.1111/agec.12300
Deininger, K., Savastano, S., and Carletto, C. (2012). Land fragmentation, cropland abandonment, and land market operation in Albania. World Dev. 40 (10), 2108–2122. doi:10.1016/j.worlddev.2012.05.010
Donovan, J., and Poole, N. (2014). Changing asset endowments and smallholder participation in higher value markets: evidence from certified coffee producers in Nicaragua. Food Policy 44, 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.foodpol.2013.09.010
Fayet, C. M., Reilly, K. H., Van Ham, C., and Verburg, P. H. (2022). What is the future of abandoned agricultural lands? A systematic review of alternative trajectories in Europe. Land use policy 112, 105833. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105833
Foster, A. D., and Rosenzweig, M. R. (2022). Are there too many farms in the world? Labor market transaction costs, machine capacities, and optimal farm size. J. Political Econ. 130 (3), 636–680. doi:10.1086/717890
Grzelak, A., and Staniszewski, J. (2025). Relative return on assets in farms and its economic and environmental drivers. Perspective of the european union and the polish region wielkopolska. J. Clean. Prod. 493, 144901. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.144901
Guo, Y., Cui, M., and Xu, Z. (2023). Effect of spatial characteristics of farmland plots on transfer patterns in China: a supply and demand perspective. Land 12 (2), 444. doi:10.3390/land12020444
Han, W., Zhang, Z., and Zhang, X. (2023). The impact of farmland transfer participation on farmers’ livelihood choices–an empirical study of the effectiveness of the 2014 three property rights separation reform. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 15 (3), 534–562. doi:10.1108/caer-12-2021-0236
He, Q., Deng, X., Li, C., Kong, F., and Qi, Y. (2021). Does land transfer improve farmers’ quality of life? Evidence from rural China. Land 11 (1), 15. doi:10.3390/land11010015
Hou, J., Huo, X., and Yin, R. (2019). Does computer usage change farmers’ production and consumption? Evidence from China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 11 (2), 387–410. doi:10.1108/caer-09-2016-0149
Huang, Q., Guo, W., and Wang, Y. (2024). A study of the impact of new quality productive forces on agricultural modernization: empirical evidence from China. Agriculture 14 (11), 1935. doi:10.3390/agriculture14111935
Huttunen, S. (2019). Revisiting agricultural modernisation: interconnected farming practices driving rural development at the farm level. J. Rural Stud. 71, 36–45. doi:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2019.09.004
Idowu, A., and Elbanna, A. (2022). Digital platforms of work and the crafting of career path: the crowdworkers’ perspective. Inf. Syst. Front. 24 (2), 441–457. doi:10.1007/s10796-020-10036-1
Kan, K. (2021). Creating land markets for rural revitalization: land transfer, property rights and gentrification in China. J. Rural Stud. 81, 68–77. doi:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2020.08.006
Liu, Y., and Zhou, M. (2023). Can rural e-commerce narrow the urban–rural income gap? Evidence from coverage of Taobao villages in China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 15 (3), 580–603. doi:10.1108/caer-09-2022-0221
Lu, H., Chen, Y., Huan, H., and Duan, N. (2022). Analyzing cultivated land protection behavior from the perspective of land fragmentation and farmland transfer: evidence from farmers in rural China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 901097. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.901097
Lv, J., Guo, X., and Jiang, H. (2025). Rural E-Commerce and income inequality: evidence from China. Sustainability 17 (10), 4720. doi:10.3390/su17104720
Michaelson, P. (2020). Arbitrating disputes involving blockchains, smart contracts, and smart legal contracts. Dispute Resolut. J. 74 (4), 89–133. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3720876
Mondal, R. K., Selvanathan, E. A., and Selvanathan, S. (2021). Nexus between rural nonfarm income and agricultural production in Bangladesh. Appl. Econ. 53 (10), 1184–1199. doi:10.1080/00036846.2020.1827138
Mutoko, M. C., Hein, L., and Shisanya, C. A. (2014). Farm diversity, resource use efficiency and sustainable land management in the western highlands of Kenya. J. Rural Stud. 36, 108–120. doi:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2014.07.006
Peng, J., Zhao, Z., and Liu, D. (2022). Impact of agricultural mechanization on agricultural production, income, and mechanism: evidence from Hubei province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 838686. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.838686
Ren, J., Gao, T., Shi, X., Chen, X., and Mu, K. (2023). The impact and heterogeneity analysis of digital financial inclusion on non-farm employment of rural labor. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 21 (2), 103–110. doi:10.1016/j.cjpre.2023.06.006
Shen, Y., Guo, X., and Zhang, X. (2023). Digital financial inclusion, land transfer, and agricultural green total factor productivity. Sustainability 15 (8), 6436. doi:10.3390/su15086436
Su, Y., Li, Y., Chen, X., Wang, Y., and Zang, L. (2023). Farmland titling, farmland adjustment and rural collective action: application of institutional analysis and development framework using evidence from China's irrigation commons. J. Rural Stud. 102, 103089. doi:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2023.103089
Susarla, A. (2012). Contractual flexibility, rent seeking, and renegotiation design: an empirical analysis of information technology outsourcing contracts. Manag. Sci. 58 (7), 1388–1407. doi:10.1287/mnsc.1110.1493
Wang, B., Shao, X., Yang, X., and Xu, H. (2023). How does land transfer impact rural household income disparity? An empirical analysis based on the micro-perspective of farmers in China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7, 1224152. doi:10.3389/fsufs.2023.1224152
Wu, Y., Duan, K., and Zhang, W. (2023). The impact of internet use on farmers’ land transfer under the framework of transaction costs. Land 12 (10), 1855. doi:10.3390/land12101855
Xu, K., Yi, X., and Zhou, L. (2025). Impacts of agricultural production services on green grain production efficiency: factors allocation perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 380, 125136. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.125136
Yang, J., and Meseretchanie, A. (2024). The intermediate role of farmland transfer in the impact of digital financial inclusion on agricultural total factor productivity in China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8, 1345549. doi:10.3389/fsufs.2024.1345549
Yang, T., Chandio, A. A., Zhang, A., and Liu, Y. (2023). Do farm subsidies effectively increase grain production? Evidence from major grain-producing regions of China. Foods 12 (7), 1435. doi:10.3390/foods12071435
Zhang, W. (2023). Circulation expectations, farmer trust, and farmers’ contract choice behavior. Land 12 (8), 1588. doi:10.3390/land12081588
Zhang, F., Bao, X., Deng, X., and Xu, D. (2022a). Rural land transfer in the information age: can internet use affect farmers’ land transfer-in? Land 11 (10), 1761. doi:10.3390/land11101761
Zhang, F., Bao, X., Guo, S., Deng, X., Song, J., and Xu, D. (2022b). Internet use and land transfer in: empirical evidence from China’s rural panel data. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29 (58), 88288–88301. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-21917-0
Zhang, Q., Razzaq, A., Qin, J., Feng, Z., Ye, F., and Xiao, M. (2022c). Does the expansion of farmers’ operation scale improve the efficiency of agricultural production in China? Implications for environmental sustainability. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 918060. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.918060
Zhao, S., Li, M., and Cao, X. (2024). Empowering rural development: evidence from China on the impact of digital village construction on farmland scale operation. Land 13 (7), 903. doi:10.3390/land13070903
Zhou, L., and Xiong, L. Y. (2018). Natural topographic controls on the spatial distribution of poverty-stricken counties in China. Appl. Geogr. 90, 282–292. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2017.10.006
Zhou, B. B., Aggarwal, R., Wu, J., and Lv, L. (2021). Urbanization-associated farmland loss: a macro-micro comparative study in China. Land Use Policy 101, 105228. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.105228
Keywords: food security, scale economy, production efficiency, internet access, farmland transfer, decision making model
Citation: Guo X, Liu X, Lv J and Zhu R (2025) Impact of digital technology on farmland transfer and food security: an empirical study in rural China. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1631305. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1631305
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 04 August 2025;
Published: 21 August 2025.
Edited by:
Idowu Oladele, Global Center on Adaptation, NetherlandsCopyright © 2025 Guo, Liu, Lv and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xianghua Liu, bGl1eGlhbmdodWFAaGVuYXUuZWR1LmNu
 Xinyu Guo
Xinyu Guo Xianghua Liu2*
Xianghua Liu2* Jinwei Lv
Jinwei Lv