- College of Architecture and Art Design, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou, China
Introduction: Under China’s strategic initiative for ecological conservation and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, establishing Ecological Security Patterns (ESPs) has emerged as a crucial approach to reconcile ecological preservation with socioeconomic growth.
Methods: This paper takes Lanzhou city in the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin in China as an example. First, we employed the InVEST-HQ module to assess habitat quality and extract the ecological sources. Second, we constructed resistance surfaces reflecting the expansion dynamics of ecological and urban sources. Third, the Minimum Cumulative Resistance (MCR) model, GIS Hydrological Analysis module and Spatial Analysis module were used to divide ecological suitability zones, determine ecological corridors, and identify ecological nodes, so as to construct ESPs and propose optimization strategies.
Results: The results showed as follows: 1 Spatial differentiation of ecological sources (1388.73 km2, 10.61%) predominantly in northwestern and southern regions, contrasting with urban sources (527.66 km2, 4.03%) concentrated along the Yellow River Valley and Qinwangchuan Basin; 2 According to the MCR difference between ecological sources and urban sources, the study area was divided into ecological core zone (ECZ), ecological buffer zone (EBZ), optimized construction zone (OCZ), and suitable construction zone (SCZ), with the proportions of 37.05%, 25.68%, 18.53% and 18.74%, respectively; 3 Based on the theory of “matrix - patch - corridor - node” in landscape ecology, the ESPs of Lanzhou City was constructed with the framework of “One belt, Two rings, Four screens, Six districts and multiple corridors”.
Discussion: The results can provide reference for ecological environment protection and ecosystem restoration in the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin in China.
1 Introduction
The accelerated industrialization and urbanization in China have substantially elevated economic development, yet simultaneously triggered severe ecological degradation, such as the sharp reduction of forest resources, serious environmental pollution and loss of biodiversity (Cetin et al., 2019; He J. F. et al., 2017; Peng et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2019), which have seriously threatened regional ecological security and sustainable development (Ding et al., 2022; Fu et al., 2020; Su et al., 2011). Therefore, determining the ecological core protection area, restoring the self-regulation ability of the ecosystem, enhancing the stability and functionality of the ecosystem, constructing the Ecological Security Patterns (ESPs), and realizing the coupling and coordinated development of the natural ecosystem and the socioeconomic system have become urgent tasks for ecological protection (Baloch et al., 2019). ESPs is the basic guarantee for sustainable development and the ecological environment foundation, and support for regional economic security and social stability (Dai et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023). Meanwhile, as a bridge between ecosystem services and the development of human society, ESPs is a key link to ensure regional ecological security and human wellbeing, and has received wide attention (Zhang Y. L. et al., 2022).
The National Program for Ecological and Environmental Protection issued by the State Council of China in 2000 proposed that ecological protection areas should be established to prevent the destruction of the ecological environment and the degradation of ecological functions. In 2011, China officially promulgated the National Functional Zoning Plan, which pointed out that important ecological functional zones are restricted development zones, with the protection and restoration of the ecological environment and the provision of ecological products as the primary task, and all types of development activities are strictly controlled. In 2020, the General Office of the Ministry of Natural Resources of China issued the Guide for Evaluation of the Carrying Capacity of Resources and Environment and the Suitability of Territorial Space Development (referred to as the “Double Evaluation”), which provides a reference basis for the delineation and spatial governance of the “Three Zones and Three Lines” (the three zones are urban space, agricultural space, ecological space, and the three lines: urban development boundary, permanent basic farmland protection red line, ecological protection red line). Therefore, building an ESPs based on the background of territorial spatial planning is an important means to maintain regional ecosystem stability, improve the sustainable supply capacity of ecosystem services, and coordinate economic development and ecological environmental protection, which is of great significance for implementing the strategy of ecological civilization.
The construction of ESPs is based on landscape ecology, and through the analysis of ecological elements and ecological suitability, the spatial pattern is constructed to realize the coupling of landscape ecological structure, ecological process and ecological function, so as to ensure the stability and sustainability of the ecosystem (Ding et al., 2022; Fu et al., 2020; Li et al., 2023; Yu, 1996). ESPs was constructed mainly from the perspectives of biodiversity conservation (Zhao and Xu, 2015), ecological sensitivity assessment (Yang et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022), ecological network analysis (Chen et al., 2023; Wang Y. S. et al., 2023), land use optimization (Kang et al., 2021; Li Q. G. et al., 2021; Li et al., 2020), and ecological service supply and demand matching analysis (Gao et al., 2024; Wang Z. Y. et al., 2023). The research scales were mainly concentrated in various types of regions, such as urban agglomeration (Li et al., 2020; Ouyang et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2024), river basins (Yang et al., 2024; Zhang Y. L. et al., 2022), provincial (Sun et al., 2020), city (Li S. C. et al., 2021), county (Fu et al., 2020), coastal zones (Qian et al., 2023), arid zones (Li Q. G. et al., 2021; Pan et al., 2022), and karst region (Yang et al., 2022).
With the improvement of ESPs construction model, a research paradigm of “identifying sources - constructing resistance surface - extracting corridors - identifying ecological nodes” has been formed (Fu et al., 2020; Zhang C. X. et al., 2022). Among them, scientific identification of ecological sources is the basis for ESPs construction (Ding et al., 2022), including qualitative research methods and quantitative research methods. The qualitative method is to directly select patches with higher habitat quality such as nature reserves and scenic spots to determine ecological sources (Vergnes et al., 2013). The quantitative method is to determine the ecological sources by assessing the importance of ecosystem services, ecological sensitivity, landscape connectivity and habitat quality (Li et al., 2023; Wang Z. Y. et al., 2023; Zhai et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2021). Among them, habitat quality, as the main basis for identifying ecological sources, is essentially based on the needs of species survival. It is not only the theoretically optimal indicator, but also the basis of ecological protection practice due to its quantifiable and dynamically monitored characteristics (Zhai et al., 2024). As another core element of ESPs construction, resistance surface is generally obtained by land use type assignment. However, due to the multi-suitability of land use functions and the difference of ecological processes (Hepcan and Ozkan, 2011), resistance surface correction has become a research hotspot in recent years (Jiang et al., 2021). Ecological corridors refers to the belt area in the ecological network system that plays an important role in connecting the flow of matter, energy and information, and its identification methods include circuit theory (Chen et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2020; Zhang Y. L. et al., 2022), gravity model (Li S. C. et al., 2021), and MCR model (Li Y. Y. et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2022). Among them, the MCR model can better simulate the magnitude of landscape obstruction in the spatial movement process of species, and has visual analysis effect, becoming the main method to identify ecological corridors (Yang et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2023). The ecological nodes is at the intersection of the minimum cost path and the maximum cost path and the weakest point of the ecological corridors, which is the key point of species migration and diffusion (Chen et al., 2023). In summary, scholars have conducted extensive theoretical analysis and practical research on the construction of ESPs, achieving fruitful research results. However, further in-depth exploration is needed. Firstly, the construction of ESPs is crucial for the ecological environment construction of ecologically sensitive and fragile areas, and there is a lack of existing relevant research literature; Secondly, most studies use qualitative methods to directly delineate ecological sources, while this article uses quantitative methods to assess habitat quality and delineate ecological sources, resulting in more accurate delineation results; Thirdly, the impact of urban expansion on the construction of ESPs has been fully considered, greatly alleviating the contradiction between ESPs construction and urban expansion; Fourthly, based on the identification of the elements for constructing the ESPs, an optimization path for the regional ESPs has been proposed, which provides a reference for the future construction of the regional ESPs.
Lanzhou City, located in the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin in China, is an important part of China’s ESPs and a hub of ecological construction in western China. However, due to its location in arid region, less precipitation and scarce vegetation, the ecosystem is relatively fragile (Dong et al., 2022). At the same time, with the improvement of urbanization level, urban space expansion is rapid, and the high-intensity development of land resources has a profound impact on the terrestrial ecosystem (Zhang et al., 2025). Based on this, taking Lanzhou City as an example, the InVEST-HQ module was used to evaluate the habitat quality and extract the ecological sources. Secondly, based on MCR model, GIS Hydrological Analysis module and Spatial Analysis module, the ecological suitability zones were divided, the ecological corridors were determined, and the ecological nodes were identified. Finally, the ESPs was constructed and optimized to provide countermeasures for the coordinated development of ecological protection and economic development in the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin in China.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area
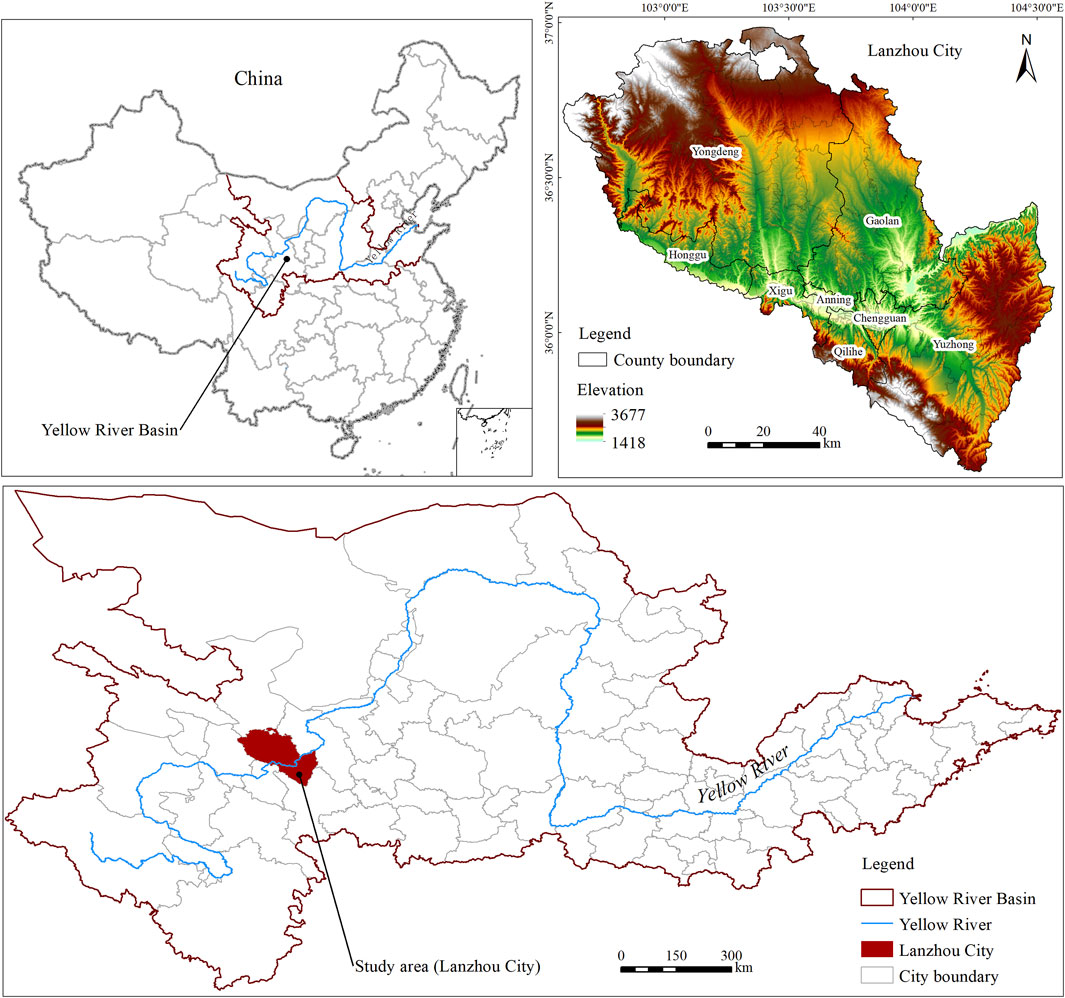
Lanzhou City (102°35′–104°34′E, 35°34′–37°07′N), situated in the upper reaches of the Yellow River Basin in China (Figure 1), covers a total area of 13,080 km2 with a permanent population of 4.425 million (2024 estimate). Characterized by a temperate continental climate, the region exhibits an annual precipitation of 324 mm, contrasting with substantial evaporation reaching 1,676 mm, and maintains an average temperature of 10.3°C. The terrain of Lanzhou City is high in the northwest and low in the southeast, with various topographic types, mainly dominated by mountains, hills and basins. The main land use types are grassland, cultivated land and forest land. The Yellow River passes through the urban area of Lanzhou City from southwest to northeast, and the urban layout is in the valley basin with relatively closed terrain. With the construction of Lanzhou National New District in 2012, the urban spatial expansion is obvious, which has an important impact on the ecosystem. The contradiction between ecological protection and urban expansion needs to be solved urgently.
2.2 Methods
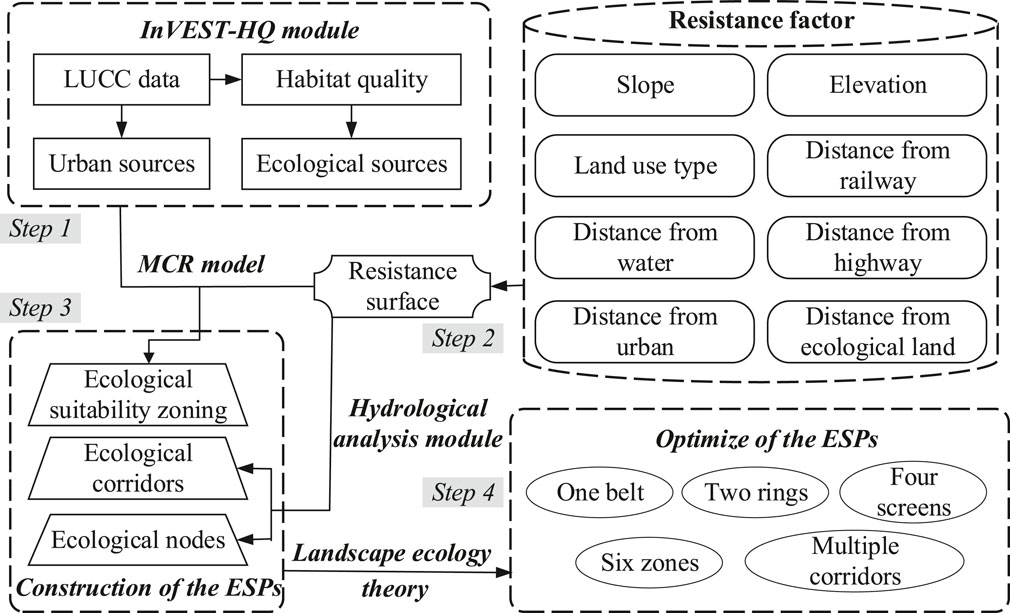
This study implemented a four-stage analytical framework (Figure 2): 1 Ecological source identification through habitat quality assessment using InVEST-HQ; 2 The resistance surface was constructed based on MCR model; 3 According to the MCR difference between ecological land expansion and urban land expansion, ecological suitability zones were divided in the study area, and ecological corridors and ecological nodes were extracted through GIS hydrological analysis and Spatial Analysis, and finally the ESPs was constructed; 4 Guided by the “matrix-patch-corridor-node” framework in landscape ecology, ESPs optimization was systematically conducted.
2.2.1 Ecological source identification method
The steps for identifying ecological source areas in the study area are as follows: Firstly, based on existing research (Ding et al., 2022; Wei et al., 2022), this article evaluates the habitat quality of the study area using the InVEST model; Secondly, the Jenks Break method is used to classify habitat quality into five categories: low, relatively low, medium, relatively high, and high; Finally, extract relatively high and high habitat quality categories as ecological sources (excluding areas less than 1 square kilometer). The formula for calculating habitat quality is as follows (Li et al., 2018):
In Formula 1, where Qxj, Hj and Dxj are habitat quality, habitat suitability and habitat degradation of land use type j, respectively, k is the half-saturation constant, and z is a normalized constant and is the default parameter of the model. More details about these calculations can be found in the InVEST VERSION User’s Guide or existing related studies (Dong et al., 2022; He J. H. et al., 2017; Sun et al., 2019).
2.2.2 Resistance surface construction method
The resistance surface was constructed based on The Minimum Cumulative Resistance model (MCR) model. The MCR quantifies the least resistance that must be overcome when moving through different types of landscape units from a designated source. Initially proposed by Knaapen et al. (1992) to study species diffusion processes, this model has since been refined through integration with GIS-based cost distance analysis. Subsequent scholars have enhanced the MCR framework and successfully applied it to various domains including landscape ecological security patterns (ESPs), urban spatial expansion studies, and ecological suitability assessments for urban land use (Yu, 1996). Its mathematical formulation can be expressed as follows (Knaapen et al., 1992):
In Formula 2,
2.2.3 The method of ecological suitability zoning
According to the minimum cumulative resistance difference between ecological land expansion and urban land expansion, the ecological suitability zoning was divided by using the Jenks Natural breaks method, and its calculation formula is as follows:
In Formula 3,
2.2.4 The ecological corridors and ecological nodes identification method
Based on the resistance surfaces between ecological sources, the hydrological analysis module in ArcGIS was utilized to extract MCR corridors with high connectivity. The workflow included depression filling, non-depression flow direction calculation, and flow accumulation calculation. Subsequently, ecological corridors were generated through vectorization and smoothing within the study area. Based on the extraction of corridors, the intersection point of the maximum cost path and the minimum cost path or the intersection point of the minimum cost path are extracted as ecological nodes.
2.3 Data source
Geospatial datasets were sourced from authoritative repositories: 1 Land use vector data from the Resource and Environment Data Cloud Platform (RESDC, http://www.resdc.cn); 2 30 m-resolution DEM from the Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn), processed through municipal boundary masking. Slope gradients (in degrees) were algorithmically derived from DEM using surface analysis tools. Proximity metrics (railways, waterways, highways, urban centers, ecological zones) were computed ArcGIS Pro’s Spatial Analyst module (Euclidean Distance toolset). All geospatial layers underwent standardization through: a) UTM projection unification, b) 30 m grid alignment by resampling.
3 Results
3.1 Sources identification
3.1.1 Ecological sources identification
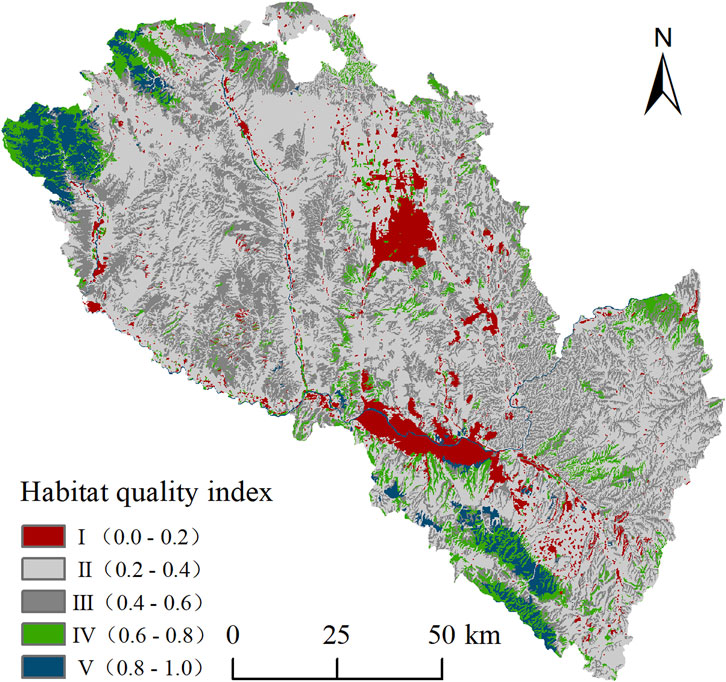
The spatial distribution of habitat quality in Lanzhou City was generated using the InVEST-HQ module (Figure 3), categorized into five grades: Ⅰ (low), Ⅱ (relatively low), Ⅲ (medium), Ⅳ (relatively high), and Ⅴ (high), accounting for 6.10%, 54.39%, 26.93%, 8.33%, and 4.25% of the total area, respectively. The analysis revealed that habitat quality in Lanzhou City was predominantly low-grade, with a relatively fragile overall ecological environment and notable spatial distribution disparities.
The grade I habitat quality areas were primarily concentrated in the densely populated Yellow River Valley and the rapidly developing Yuzhong and Qinwangchuan Basins. Intense human activities and intensive development in these regions have directly contributed to habitat destruction. The grade Ⅱ and Ⅲ habitat quality areas were predominantly located in the loess hilly regions north of the Yellow River and the Northern Yuzhong Mountain within the study area’s southwestern sector. These areas experience intensive agricultural practices combined with limited precipitation, rendering their ecosystems particularly vulnerable. The grade Ⅳ and Ⅴ habitat quality areas were primarily concentrated in the Rocky Mountains of the study area’s northwestern and southern regions, where woodland and grassland constituted the predominant land cover types. These zones exhibited generally high habitat quality, supported by steep terrain features, minimal human interference, dense vegetation cover, and the enforcement of ecological conservation measures. In summary, combined with the actual ecological environment situation in Lanzhou City, the regions with habitat quality levels Ⅳ and Ⅴ were selected as ecological sources and the fragmented patches with an area of less than 1 km2 were removed. According to the extraction of ecological sources, the area of ecological sources in Lanzhou City was 1388.73 km2, accounting for 10.61% of the total study area, which is mainly distributed in the northwest and south of Lanzhou City (Figure 4).
3.1.2 Urban sources identification
At present, most of the existing studies have selected urban built-up areas as the source for urban expansion. In this paper, the urban construction land and other construction land were selected as the urban sources (the patch area was larger than 1 km2). Based on the extraction of urban sources, it is finally obtained that the urban sources of Lanzhou City was 527.66 km2, accounting for 4.03% of the study area, mainly concentrated in the Yellow River Valley basin and Qinwangchuan basin of the study area (Figure 5).
3.2 Ecological suitability zoning
3.2.1 Selection and weight determination of resistance factors
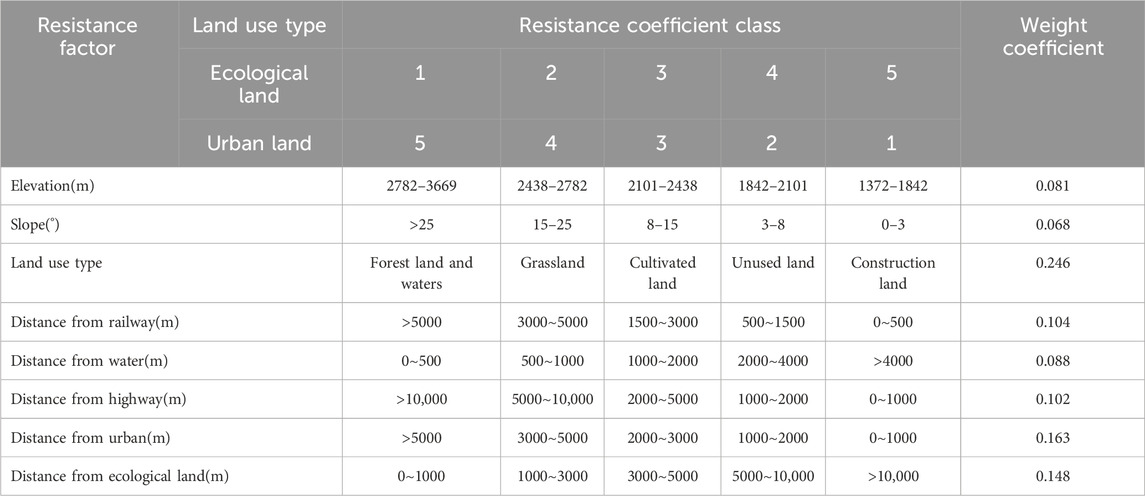
Based on the existing studies (Li Q. G. et al., 2021; Qian et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024), eight factors including elevation, slope, land use type, distance from railway, distance from water, distance from highway, distance from urban and distance from ecological land were selected as resistance evaluation factors. In order to make ecological land expansion and urban land expansion proceed under the same standard, a resistance evaluation system with the same resistance factor and opposite resistance coefficient is established. The resistance coefficient is represented by 5 grades respectively, and the smaller the score, the smaller the resistance. According to the impact of each resistance factor on the ecological land and urban land expansion process, the weights were determined using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) analysis method (Table 1).
3.2.2 Resistance surface construction
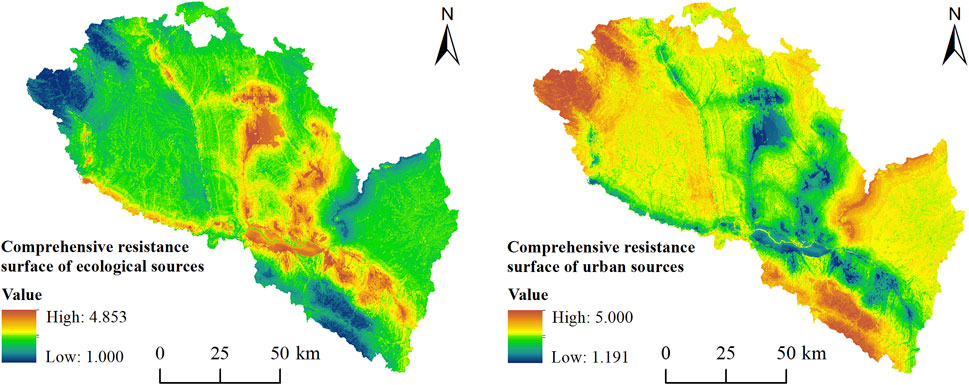
Using ArcGIS software, resistance factor data from Table 1 were processed into raster formats (Figures 6, 7), and according to the determined weight coefficient of the resistance factor, the Raster Caculator tool of the Spatial Analysis module of ArcGIS software was used for weighted superposition analysis. Therefore, the comprehensive resistance value of ecological land and urban land expansion was obtained (Figure 8). It can be seen that the spatial pattern of the comprehensive resistance values of ecological land and urban land expansion is opposite, which is consistent with the evaluation system of resistance factors.
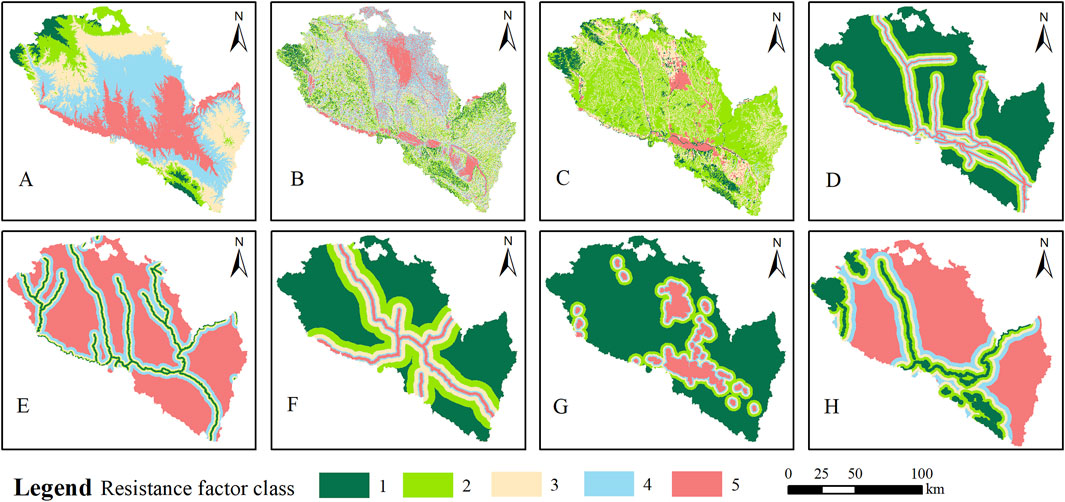
Figure 6. Ecological sources expansion resistance factors. (A) Elevation; (B) Slope; (C) Land use type; (D) Distance from railway; (E) Distance from water; (F) Distance from highway; (E) Distance from urban; (H) Distance from ecological land.
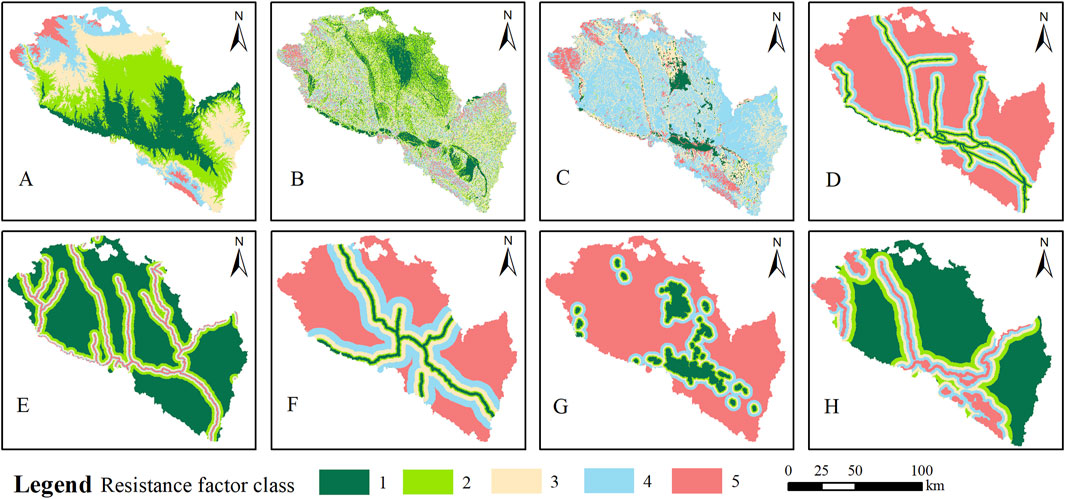
Figure 7. Urban sources expansion resistance factors. (A) Elevation; (B) Slope; (C) Land use type; (D) Distance from railway; (E) Distance from water; (F) Distance from highway; (E) Distance from urban; (H) Distance from ecological land.
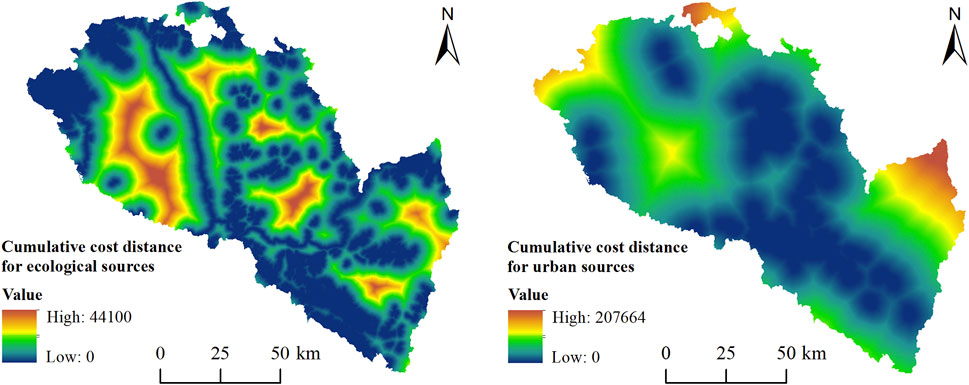
3.2.3 Minimum cumulative resistance value
Building upon the comprehensive resistance values of ecological and urban land expansion, the Cost Distance tool in ArcGIS’s Spatial Analyst module was employed to calculate their respective minimum cumulative resistance surfaces (Figure 9). The results indicate that low-resistance areas for ecological land expansion are primarily distributed in the northwest and southeast of the study area, as well as along the Zhuanglang River and the Yellow River. In contrast, high-resistance areas for ecological expansion cluster in the loess hilly terrain north of the Yellow River, the Yuzhong Basin, and the Qinwangchuan Basin. Regarding urban expansion, low-resistance areas are concentrated in the Huangshui Valley, Yellow River Valley Basin, Yuzhong Basin, and Qinwangchuan Basin, while high-resistance areas are predominantly located in the northwest, southeast, and the northern mountainous region of Yuzhong County.
3.2.4 Ecological suitability zoning
Based on the minimum cumulative resistance differences between ecological land and urban land expansion, the study area was classified into four functional zones: ecological core zone (ECZ), ecological buffer zone (EBZ), optimized construction zone (OCZ), and suitable construction zone (SCZ), covering areas of 4888.99 km2, 3389.33 km2, 2445.47 km2, and 2472.04 km2, respectively. These zones account for 37.05%, 25.68%, 18.53%, and 18.74% of the total study area.
The ECZ is concentrated and distributed in contiguous areas, mainly located in the north and south of the study area, the north Mountain of Yuzhong County and the west loess area of Zhuanglang River, including the Liancheng National Nature Reserve, Xinglong Mountain National Nature Reserve and other important ecological functional areas. The ecosystem structure is relatively stable and the ecosystem service capacity is strong, so it should be used as a prohibited and restricted development zone to strengthen ecological protection and ecological restoration. The EBZ is distributed between the ECZ and the OCZ, serves as a restricted development zone where ecological construction should be enhanced, and large-scale industrialization, urbanization, or mineral exploitation must be prohibited. The OCZ encircles the outer edges of existing urban built-up areas. As a potential space for future urban expansion, this zone requires balanced management of ecological protection and urban development. The SCZ is mainly located in the central urban area, Lanzhou New Area, Yuzhong, Gaolan, Yongdeng and other key urban built-up areas, the ecological environment is degraded due to urbanization, and the anti-interference ability of the ecosystem is weak (Figure 10).
3.3 Ecological corridors and ecological nodes identification
Identify the ecological corridors in the study area by using the hydrological analysis module in ArcGIS. The results show that a total of 15 key corridors (with a total length of 674.77 km) and 62 secondary corridors (with a total length of 769.58 km) have been determined. Based on the extraction of corridors, 40 ecological nodes were identified and extracted (Figure 11).
Comparing the identified ecological corridors and ecological nodes with the land use map and basic geographic information base map, it is found that: 1 The ecological base of Lanzhou City is mainly grassland, and forest land is relatively scarce. The ecological source areas were deficient in patches, with high fragmentation and unbalanced spatial distribution. The number of ecological corridors is fewer and the connectivity is poor, which reduces the connectivity of the regional landscape. 2 The identified ecological corridors are mainly river corridors, and the corridors are generally narrow, which is not conducive to the free migration of species. 3 Due to the special valley topography of Lanzhou City, urban land and agricultural land are distributed along the Yellow River Valley, and rapid urban development constantly cuts and occupies cultivated land and habitat patches, resulting in fragmentation of ecological land, continuous degradation of habitat quality, reduced connectivity between ecological patches, and continuous weakening of ecological corridor connectivity.
4 Discussion
4.1 The optimization framework for ESPs
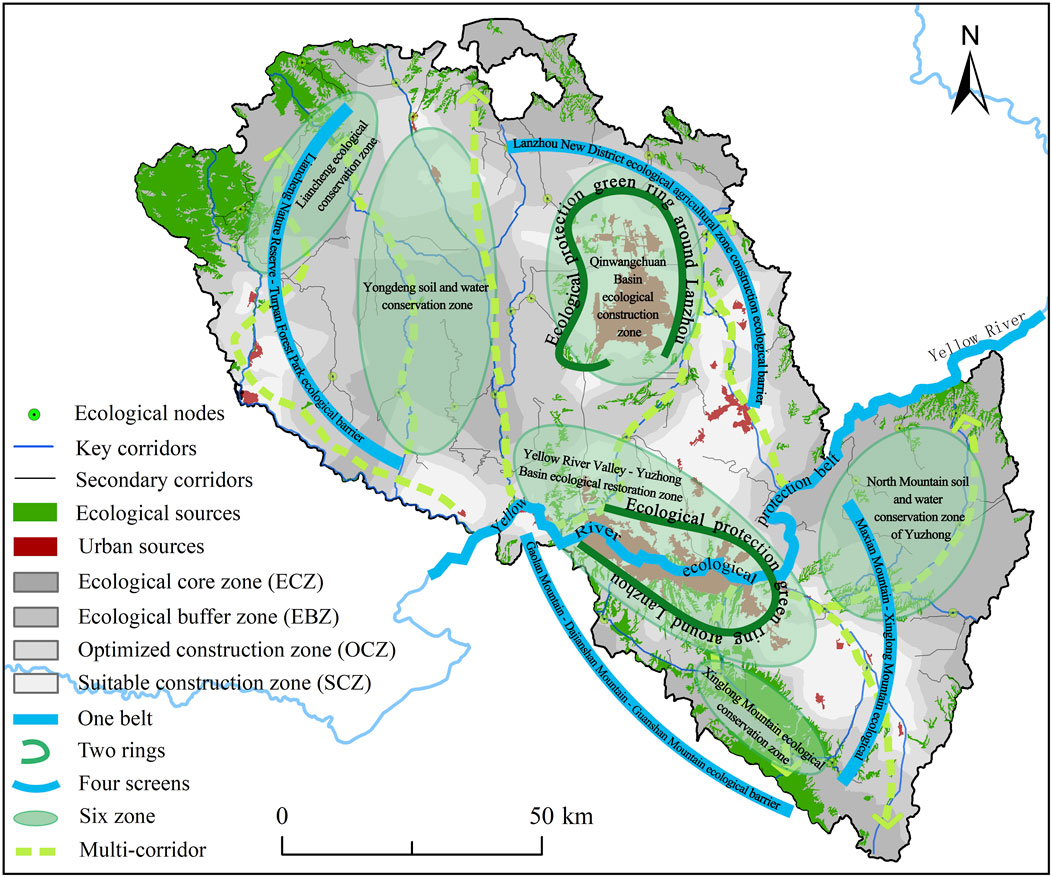
This study first diagnosed the ecological security issues in the study area, including identification of ecological sources, construction of resistance surfaces, and extraction of ecological corridors and ecological nodes. Secondly, based on the current situation of ESPs and the policy orientation of ecological protection in Lanzhou City, the “matrix-patch-corridor-node” theory in landscape ecology is applied (Zhang C. X. et al., 2022). From the aspects of protecting ecological sources, unblocking ecological corridors, and cultivating ecological nodes, a multi-level composite ecological network spatial structure is established by optimizing the combination of different ecological elements. Ultimately, this study proposes constructing an optimized ecological spatial layout framework for Lanzhou City characterized as “One Belt, Two Rings, Four Screens, Six Zones, and Multiple Corridors” (Figure 12). This framework aims to create a functional and networked regional ecological spatial pattern while maintaining the original structural organization and content focus.
4.2 The optimization measures for ESPs
1. The “One Belt” refers to the Yellow River Ecological Protection Belt. While serving as a crucial channel connecting major ecological sources and nodes, it also functions as the primary pathway for species migration and energy transportation in the study area, requiring comprehensive management. Specific measures include: First, implementing comprehensive pollution prevention and control measures for the Yellow River’s main channel and tributaries, enhancing monitoring of river discharge outlets, advancing renovation of key outlets, and addressing prominent water environment issues in the basin; Second, strengthening ecological protection and wetland restoration along the Yellow River’s main stream, reserving ecological wetlands at estuary areas where major tributaries converge, enhancing waterfront shoreline protection, preserving natural water bodies and wetlands, and progressively restoring ecological service functions; Third, enforcing water resource management systems to build water-efficient cities through improved urban water management and supply network upgrades, expanding adoption of water-saving technologies in high-standard farmland, optimizing water rights trading mechanisms, enhancing reclaimed water treatment infrastructure and pipe networks, developing storm-flood water management facilities, and reducing conventional water consumption; Fourth, rationally constructing flood control systems for main and tributary channels, strengthening flood capacity management in the Yellow River’s urban sections and tributary estuaries, improving drainage systems, enhancing flood risk management and operational protocols, upgrading flood control command systems with early warning mechanisms, and ensuring regional water security.
2. The “Two Rings” refers to establishing ecological protection green ring encircling Lanzhou’s urban core and the Lanzhou New Area. As a characteristic valley city flanked by northern and southern mountain ranges, Lanzhou requires ecological restoration of these bordering highlands through enhanced vegetation coverage and the creation of mountain-encircling green ring. These measures will simultaneously improve urban ecological conditions and elevate living environment quality. Concurrently, leveraging the development of shelterbelts and ecological landscape forests in the Lanzhou New Area, this initiative aims to establish an ecological conservation zone that enhances regional environmental quality while advancing the construction of a demonstration area for ecological development in the upper Yellow River basin.
3. The “Four screens” refers to Liancheng Nature Reserve - Turpan Forest Park ecological barrier, Gaolan Mountain - Dajianshan Mountain - Guanshan Mountain ecological barrier, Lanzhou New District ecological agricultural zone construction ecological barrier, and Maxian Mountain - Xinglong Mountain ecological barrier. The Liancheng Nature Reserve-Turpan Forest Park Barrier situated at the ecological transition between the Qilian Mountains and Loess Plateau, this zone features complex geomorphology that supports diverse natural conditions, abundant flora and fauna, and intact forest ecosystems. The Gaolan Mountain-Dajianshan Mountain-Guanshan Mountain Barrier located in the study area’s southwestern sector, this dual-function zone serves both as an ecological leisure destination for cultural experiences and as a natural environmental buffer. The Lanzhou New District Ecological Agricultural Zone Barrier occupying the northern study region, this infrastructure fulfills critical ecological roles including sandstorm mitigation, water conservation, and microclimate regulation. The Maxian Mountain-Xinglong Mountain Barrier positioned in the eastern study area as the Qilian Mountains’ eastern extension, this corridor maintains essential biological diversity while performing vital watershed conservation functions.
4. The “Six zone” refers to the North Mountain soil and water conservation zone of Yuzhong, Xinglong Mountain ecological conservation zone, Liancheng ecological conservation zone, Qinwangchuan Basin ecological construction zone, Yellow River Valley - Yuzhong Basin ecological restoration zone, and Yongdeng soil and water conservation zone. Yuzhong North Mountain is a typical loess hilly area. Due to drought and water shortage, scarce vegetation and high cost of ecological construction, barren and drought-tolerant species should be planted to achieve soil and water conservation and gradually restore its ecological environment. Xinglong Mountain ecological conservation zone and Liancheng ecological conservation zone belong to national nature reserves, which are important ecological functional areas and habitats of precious species in the research area. Ecological conservation should strengthen forest land construction projects, improve biodiversity and water conservation capacity according to local conditions, improve the supply capacity of ecosystem services, and ensure regional ecological security. The ecological construction area of Qinwangchuan Basin is located in the north of Lanzhou City. With the development of Lanzhou New District, the scale of construction land in the basin has gradually expanded, so it is of great significance to restore ecological space and build protective forest belt. At the same time, this zone is also an important agricultural production area, through the implementation of rural low-efficiency farmland remediation projects, not only improve the efficiency of farmland use, but also play the function of farmland ecosystem. In the ecological restoration zone of the Yellow River Valley and Yuzhong Basin, the population is dense, human activities are frequent, and land use conflicts are serious. Coupled with the relatively poor natural resources in the area, the supply capacity of ecosystem services is difficult to meet the demand, and the contradiction between supply and demand of ecosystem services is prominent. Therefore, the region should focus on ecological improvement, attach importance to ecological restoration and the enhancement of ecosystem service functions, adhere to land conservation and intensive development, constantly improve green infrastructure and corridor landscape in the urban area, increase the area of parks and recreational green spaces, improve vegetation coverage, expand ecological land space, and comprehensively balance ecological construction and economic development. Yongdeng soil and water conservation zone is located on the west bank of Zhuanglang River. Ecological cultivation should be the main process of ecological restoration in this area. On the one hand, land use types with high ecosystem services should be protected comprehensively to improve their ecological benefits. On the other hand, measures such as mountain closure and grazing ban, cultivated land leveling and gully management should be taken to strengthen the protection and management of the mountain and its vegetation, and maintain the integrity of the regional ecosystem.
5. The “Multi-corridors” initiative involves developing river corridors along the Datong, Huangshui, Zhuanglang, and Wanchuan river systems, interconnecting them with the Yellow River Ecological Protection Belt to enhance regional hydrological connectivity. Concurrently, greenbelt corridors will be established along strategic routes connecting Lanzhou’s urban core to the New District, Yuzhong North Mountain, Xinglong Mountain Ecological Conservation Zone, and Yongdeng Soil Conservation Area, jointly strengthening ecological connectivity between urban systems and surrounding ecosystems to facilitate material-energy exchange. Furthermore, ecological node development will be intensified through expanded ecological land allocation, creation of buffer zones and protective belts, and optimization of node scale-functionality to reinforce their pivotal bridging role in the ecological network.
4.3 Limitations and future perspectives
Firstly, in terms of data processing, the resistance factors faced by the expansion of ecological sources and urban sources are multi-faceted and relatively complex (Li Q. G. et al., 2021). When constructing the resistance surface, we took into account all the influencing factors as much as possible, but there was still a certain degree of subjectivity. In future research, field investigations can be added to further supplement and improve the resistance factors and construct a resistance surface that conforms to the expansion characteristics of the source area. Secondly, in terms of the adoption of methods, a Hydrological Analysis model was used in the process of identifying ecological corridors and ecological nodes, and the analysis results provided a reference basis for the optimization of ecological corridors and ecological nodes in river valley cities. In addition to this method, scholars have identified ecological corridors and ecological nodes by using Circuit Theory (Chen et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2020), Gravity Models (Li S. C. et al., 2021), etc. Therefore, in the subsequent research, Circuit Theory and Gravity Models were adopted to supplement and optimize the identification of ecological corridors and ecological nodes. Thirdly, our research only analyzed the current ESPs based on historical land use data. In subsequent studies, different development scenarios can be set to better simulate and predict future ecological security trends (Kang et al., 2021), so as to provide references for future regional ecological protection. In addition, population growth and rapid socio-economic development have led to a reduction in available water resources for the ecosystem, causing ecological degradation in many regions and affecting the sustainable development of the ecosystem (Yuan et al., 2025). The study area is located in the arid and semi-arid region of northwest China (Dong et al., 2022). The rational allocation and efficient utilization of water resources are of great significance for the construction of the regional ecological security pattern. To sum up, as a crucial ecological functional zone in the upper Yellow River Basin, Lanzhou City bears the critical responsibility of safeguarding regional ecological security, maintaining human settlement sustainability, and preserving biodiversity. The habitat quality assessment and ESPs construction methodology developed in this study provides operational guidance for ecological space optimization, core conservation area protection, and sustainable territorial spatial utilization, ultimately supporting coordinated regional development.
5 Conclusion
This paper takes Lanzhou City in China as an example, according to the research paradigm of “identifying the sources - constructing the resistance surface - extracting the corridors - identifying the strategic nodes”. The ecological sources were extracted by the habitat quality assessment method, and the resistance surface was constructed based on the resistance model. MCR model and hydrological analysis model were used to divide ecological suitability zones, extract ecological corridors and identify ecological nodes. Finally, ESPs was constructed and optimized. The following conclusions are drawn:
1. The ecological sources of Lanzhou City was 1388.73 km2, accounting for 10.61% of the total study area, mainly distributed in the northwestern and southern parts of Lanzhou City; The urban sources was 527.66 km2, accounting for 4.03%, mainly concentrated in the Yellow River valley basin and Qinwangchuan basin of the study area.
2. The areas of ecological core zone (ECZ), ecological buffer zone (EBZ), optimized construction zone (OCZ), and suitable construction zone (SCZ) are 4888.99 km2, 3389.33 km2, 2445.47 km2 and 2472.04 km2, respectively, accounting for 37.05%, 25.68%, 18.53% and 18.74% of the total area of Lanzhou City.
3. Based on the theory of “strom–patch - corridor - node” in landscape ecology, combined with the spatial distribution characteristics of ecological sources, ecological corridors and ecological nodes in the study area, it was proposed to construct an optimized ecological spatial layout structure of Lanzhou City with “One belt, Two rings, Four screens, Six districts and multiple corridors” as the framework.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JD: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. LL: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision. WY: Software, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Investigation. BL: Writing – review and editing, Validation, Project administration, Formal Analysis. XZ: Writing – original draft, Resources, Visualization, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Innovation Fund of Gansu Provincial Department of Education (Project No. 2025A-036); The 2024 Humanities and Social Science Cultivation Fund of Lanzhou University of Technology: The theoretical logic and governance model of organic renewal of old communities from the perspective of residents’ behavior; The Research Project of Gansu Provincial Department of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (JK2024-31); The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 42261034 and 41961029).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Baloch, M. A., Zhang, J. J., Iqbal, K., and Iqbal, Z. (2019). The effect of financial development on ecological footprint in BRI countries: evidence from panel data estimation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26 (6), 6199–6208. doi:10.1007/s11356-018-3992-9
Cetin, M., Adiguzel, F., Gungor, S., Kaya, E., and Sancar, M. C. (2019). Evaluation of thermal climatic region areas in terms of building density in urban management and planning for Burdur, Turkey. Air Qual. Atmos. and Health 12 (9), 1103–1112. doi:10.1007/s11869-019-00727-3
Chen, J. Z., Mei, Z. X., Wang, B., and Wei, J. C. (2022). Construction of ecological security patterns based on circuit theory under the resistance distance principle. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (10), 6298. doi:10.3390/ijerph19106298
Chen, Z. J., Chen, H., Yang, M. A., Wang, X., Jiang, Y. F., and Zhang, W. (2023). Heterogeneity and optimization of ecological security pattern on a mountain town: a case of tianzhu county in the hexi corridor, China. Front. Env. Sci-Switz. 10. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2022.1106379
Dai, Y. C., Diao, Y. Y., Dai, C. Y., Li, Y., Sun, G. Y., Zahoor, B., et al. (2022). Spatial-temporal dynamics and evolution of ecological security in a rapid urbanization city, southwest China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 10. doi:10.3389/fevo.2022.914567
Ding, M. M., Liu, W., Xiao, L., Zhong, F. X., Lu, N., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). Construction and optimization strategy of ecological security pattern in a rapidly urbanizing region: a case study in central-south China. Ecol. Indic. 136, 108604. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108604
Dong, J. H., Zhang, Z. B., Liu, B. T., Zhang, X. H., Zhang, W. B., and Chen, L. (2022). Spatiotemporal variations and driving factors of habitat quality in the loess hilly area of the yellow river basin: a case study of lanzhou city, China. J. Arid Land 14 (6), 637–652. doi:10.1007/s40333-022-0097-6
Fu, Y. J., Shi, X. Y., He, J., Yuan, Y., and Qu, L. L. (2020). Identification and optimization strategy of county ecological security pattern: a case study in the loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 112, 106030. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.106030
Gao, X., Guo, Z. Y., Zhang, M. M., Liang, X. Y., Zhao, M. R., and Qin, L. (2024). Ecological source identification and ecological security pattern construction from the perspective of ecosystem service supply and demand: a case study of baiyangdian basin in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. doi:10.1007/s10668-024-05302-0
He, J. F., Yao, Y. K., Huang, G., and Duan, C. L. (2017a). Intensification of the density stability in the air dense medium gas–solid fluidized bed based on a binary dense media. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 122, 58–67. doi:10.1016/j.cep.2017.09.014
He, J. H., Huang, J. L., and Li, C. (2017b). The evaluation for the impact of land use change on habitat quality: a joint contribution of cellular automata scenario simulation and habitat quality assessment model. Ecol. Model. 366, 58–67. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.10.001
Hepcan, C. C., and Ozkan, M. B. (2011). Establishing ecological networks for habitat conservation in the case of Çeşme-urla peninsula, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 174, 157–170. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1447-y
Huang, J. M., Hu, Y. C., and Zheng, F. Y. (2020). Research on recognition and protection of ecological security patterns based on circuit theory: a case study of jinan city. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 27 (11), 12414–12427. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-07764-x
Jiang, H., Peng, J., Dong, J. Q., Zhang, Z. M., Xu, Z. H., and Meersmans, J. (2021). Linking ecological background and demand to identify ecological security patterns across the guangdong-hong kong-macao greater Bay area in China. Landsc. Ecol. 36 (7), 2135–2150. doi:10.1007/s10980-021-01234-6
Kang, J. M., Zhang, X., Zhu, X. W., and Zhang, B. L. (2021). Ecological security pattern: a new idea for balancing regional development and ecological protection. A case study of the jiaodong peninsula, China. Glob. Ecol. Conservation 26, e01472. doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01472
Knaapen, J. P., Scheffer, M., and Harms, B. (1992). Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plann. 23, 1–12. doi:10.1016/0169-2046(92)90060-D
Li, F. X., Wang, L. Y., Chen, Z. J., Clarke, K. C., Li, M., and Jiang, P. (2018). Extending the SLEUTH model to integrate habitat quality into urban growth simulation. J. Environ. Manage. 217, 486–498. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.109
Li, Z. T., Li, M., and Xia, B. C. (2020). Spatio-temporal dynamics of ecological security pattern of the pearl river Delta urban agglomeration based on LUCC simulation. Ecol. Indic. 114, 106319. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106319
Li, Q. G., Wang, L. C., Gul, H. N., and Li, D. (2021a). Simulation and optimization of land use pattern to embed ecological suitability in an oasis region: a case study of ganzhou district, Gansu province, China. J. Environ. Manage 287, 112321. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112321
Li, S. C., Zhao, Y. L., Xiao, W., Yue, W. Z., and Wu, T. (2021b). Optimizing ecological security pattern in the coal resource-based city: a case study in shuozhou city, China. Ecol. Indic. 130, 108026. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108026
Li, Y. Y., Zhang, Y. Z., Jiang, Z. Y., Guo, C. X., Zhao, M. Y., Yang, Z. G., et al. (2021c). Integrating morphological spatial pattern analysis and the minimal cumulative resistance model to optimize urban ecological networks: a case study in shenzhen city, China. Ecol. Process. 10 (1). doi:10.1186/s13717-021-00332-2
Li, J. T., Liu, Y., Gani, A. A., Wu, J. L., and Dai, Y. C. (2023). Identification of ecological security patterns for the qiandongnan ecotourism area in southwest China using InVEST and circuit theory. Forests 14 (7), 1316. doi:10.3390/f14071316
Liu, Q. H., Sun, Y. J., Mei, Y. A., Jian, Z., Pan, F., and Zhang, L. G. (2022). Construction and analysis of ecological security pattern of qingdao based on MSPA and MCR models. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 32 (1), 155–169. doi:10.15244/pjoes/153431
Ouyang, X., Wang, Z. B., and Zhu, X. (2019). Construction of the ecological security pattern of urban agglomeration under the framework of supply and demand of ecosystem services using bayesian network machine learning: case study of the changsha–zhuzhou–xiangtan urban agglomeration, China. Sustainability 11 (22), 6416. doi:10.3390/su11226416
Pan, N. H., Du, Q. Q., Guan, Q. Y., Tan, Z., Sun, Y. F., and Wang, Q. Z. (2022). Ecological security assessment and pattern construction in arid and semi-arid areas: a case study of the hexi region, NW China. Ecol. Indic. 138, 108797. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108797
Peng, J., Pan, Y. J., Liu, Y. X., Zhao, H. J., and Wang, Y. L. (2018). Linking ecological degradation risk to identify ecological security patterns in a rapidly urbanizing landscape. Habitat Int. 71, 110–124. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.11.010
Qian, W. Q., Zhao, Y., and Li, X. Y. (2023). Construction of ecological security pattern in coastal urban areas: a case study in qingdao, China. Ecol. Indic. 154, 110754. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110754
Su, S. L., Li, D., Yu, X., Zhang, Z. H., Zhang, Q., Xiao, R., et al. (2011). Assessing land ecological security in shanghai (China) based on catastrophe theory. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 25 (6), 737–746. doi:10.1007/s00477-011-0457-9
Sun, X. Y., Jiang, Z., Liu, F., and Zhang, D. Z. (2019). Monitoring spatio-temporal dynamics of habitat quality in nansihu Lake basin, eastern China, from 1980 to 2015. Ecol. Indic. 102, 716–723. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.03.041
Sun, M. Y., Li, X. H., Yang, R. J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Song, Z. W., et al. (2020). Comprehensive partitions and different strategies based on ecological security and economic development in Guizhou province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 274, 122794. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122794
Vergnes, A., Kerbiriou, C., and Clergeau, P. (2013). Ecological corridors also operate in an urban matrix: a test case with garden shrews. Urban Ecosyst. 16 (3), 511–525. doi:10.1007/s11252-013-0289-0
Wang, C. L., Jiang, Q. O., Shao, Y. Q., Sun, S. Y., Xiao, L., and Guo, J. B. (2019). Ecological environment assessment based on land use simulation: a case study in the heihe river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 697, 133928. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133928
Wang, Y. S., Zhang, F., Li, X. Y., Johnson, V. C., Tan, M. L., Kung, H.-T., et al. (2023a). Methodology for mapping the ecological security pattern and ecological network in the arid region of Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 15 (11), 2836. doi:10.3390/rs15112836
Wang, Z. Y., Zhang, J., Chen, J. C., Gao, H. Z., Li, J. M., and Li, M. H. (2023b). Determining the ecological security pattern and important ecological regions based on the supply–demand of ecosystem services: a case study of xuzhou city, China. Front. Public Health 11. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1087588
Wei, L., Zhou, L., Sun, D. Q., Yuan, B., and Hu, F. N. (2022). Evaluating the impact of urban expansion on the habitat quality and constructing ecological security patterns: a case study of jiziwan in the yellow river basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 145, 109544. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109544
Yang, Y. P., Chen, J. J., Huang, R. J., Feng, Z. H., Zhou, G. Q., You, H. T., et al. (2022). Construction of ecological security pattern based on the importance of ecological Protection-A case study of Guangxi, a karst region in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (9). doi:10.3390/ijerph19095699
Yang, X. W., Wei, G. Y., Liang, C. Z., Yang, Z., Fang, H. Y., and Zhang, S. M. (2023). Construction of ecological security pattern based on ecosystem service evaluation and minimal cumulative resistance model: a case study of hefei city, China. Environment. Dev. Sustain. 26 (4), 10681–10700. doi:10.1007/s10668-023-03170-8
Yang, J., Wang, S. Y., Zhou, J., Zhang, J., and Zhang, W. L. (2024). Optimisation of ecological security patterns in ecologically transition areas under the perspective of ecological resilience − a case of taohe river. Ecol. Indic. 166, 112315. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112315
Yu, K. J. (1996). Security patterns and surface model in landscape ecological planning. Landsc. Urban Plann. 36, 1–17. doi:10.1016/S0169-2046(96)00331-3
Yuan, L., Zhou, Z. J., He, W. J., Wu, X., Degefu, D. M., Cheng, J., et al. (2025). A fuzzy logic approach within the DPSIR framework to address the inherent uncertainty and complexity of water security assessments. Ecol. Indic. 170, 112984. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112984
Zhai, Y. P., Zhai, G. Q., Yu, Z. J., Ma, X. Y., Lu, Z. Y., Chen, Y. M., et al. (2024). Constructing the ecological security pattern of the daqing river basin for the high-standard ecological construction of Xiong'an new area, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. doi:10.1007/s10668-024-04635-0
Zhang, Y. Z., Jiang, Z. Y., Li, Y. Y., Yang, Z. G., Wang, X. H., and Li, X. B. (2021). Construction and optimization of an urban ecological security pattern based on habitat quality assessment and the minimum cumulative resistance model in shenzhen City, China. Forests 12 (7), 847. doi:10.3390/f12070847
Zhang, C. X., Jia, C., Gao, H. G., and Shen, S. G. (2022a). Ecological security pattern construction in hilly areas based on SPCA and MCR: a case study of nanchong city, China. Sustainability 14 (18), 11368. doi:10.3390/su141811368
Zhang, Y. L., Zhao, Z. Y., Fu, B. J., Ma, R. M., Yang, Y. Y., Lü, Y. H., et al. (2022b). Identifying ecological security patterns based on the supply, demand and sensitivity of ecosystem service: a case study in the yellow river Basin, China. J. Environ. Manage. 315, 115158. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115158
Zhang, R., Chen, T. Y., Su, F., Liu, Y. H., and Zheng, G. Q. (2024). Simulating the impact of urban expansion on ecological security pattern from a multi-scenario perspective: a case changsha–zhuzhou–xiangtan urban agglomeration, China. Sustainability 16 (21), 9382. doi:10.3390/su16219382
Zhang, X. H., Zhang, N., Wang, S. H., Dong, J. H., and Pan, X. F. (2025). Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of carbon emission efficiency in Western Valley cities in China. Sustainability 17 (11), 5025. doi:10.3390/su17115025
Zhao, X. Q., and Xu, X. H. (2015). Research on landscape ecological security pattern in a eucalyptus introduced region based on biodiversity conservation. Russ. J. Ecol. 46 (1), 59–70. doi:10.1134/s106741361501018x
Zhou, Y., Chang, J., Chen, Z. C., and Zheng, G. D. (2022). Construction of ecological security pattern based on ecological sensitivity assessment in jining city, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 31 (6), 5383–5404. doi:10.1159/000151866
Keywords: ESPS, habitat quality, ecological sources, ecological corridors, Lanzhou city
Citation: Dong J, Li L, Yang W, Liu B and Zhang X (2025) Construction and optimization of ecological security patterns in ecologically fragile areas: a case study of Lanzhou City, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1639986. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1639986
Received: 03 June 2025; Accepted: 05 August 2025;
Published: 21 August 2025.
Edited by:
Chong Jiang, Guangdong Academy of Science (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Liang Yuan, China Three Gorges University, ChinaQinghui Huang, Tongji University, China
Ying Zheng, China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, China
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Li, Yang, Liu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianhong Dong, ZG9uZ2poQGx1dC5lZHUuY24=
 Jianhong Dong
Jianhong Dong Lina Li
Lina Li