- 1College of Soil and Water Conservation, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
- 2College of Ecology and Environment (College of Wetlands), Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
- 3College of Economics and Management, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
As an important part of China’s ecological security barrier on the plateau, the rational configuration of landscape patterns and a good ecological environment are crucial guarantees for the high-quality development of national parks. Using Landsat image data from 2000 to 2024, this study analyzes pudacuo national park as an example. The study uses Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis (MSPA) to analyze the evolution characteristics of the landscape pattern and the Remote Sensing Ecological Index (RSEI) to evaluate the ecological environment quality(EEQ). In the meantime, the geodetector, bivariate spatial autocorrelation, and Spearman correlation coefficient were combined to investigate and ascertain the geographic relationship between the two. The results of the research indicate that: (1) the park’s core area is primarily forested and far away from populated regions, with high stability in its, Aggregation Index (AI) and Largest Patch Index (LPI); in the contrary, the edge area’s grassland and unused land are heavily impacted by human disturbances like grazing and tourism, and the landscape pattern is distinguished by fragmentation and degradation of ecological functions; (2) From 2000 to 2024, the ecological environment quality of pudacuo national park continued to improve. The ecological environment quality in the study area was mainly rated as “good,” accounting for up to 49.04% of the total, with the trend in ecological environment quality remaining “basically stable.” (3) Correlation analysis showed that ecological environment quality was significantly positively correlated with LPI, AI, and Patch Cohesion Index (COHESION). The spatiotemporal evolution of ecological environment quality in pudacuo national park is not only constrained by landscape fragmentation and core patch patterns but is also closely related to landscape diversity and overall spatial structure. This study aims to provide a scientific basis and decision support for the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development of pudacuo national park.
1 Introduction
The ecological environment is a fundamental supporting element for the sustainable development of human society, and its quality evolution process profoundly affects the level of regional socio-economic development and the quality of the human environment (Wang Q. et al., 2023). With the continuous expansion of human economic activities, high-intensity anthropogenic interference has led to significant changes in the pattern of land cover, posing a serious threat to the stability of the ecosystem. In order to accurately assess the risk to regional ecological security, it is necessary to discover the spatial and temporal evolution pattern of ecological environment quality and its driving mechanism. The result will also serve as a crucial scientific basis and technical assistance in advancing the development of an ecological civilization. Previous studies have primarily employed single ecological indicators, such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) (Jiang et al., 2021), Net Primary Productivity (NPP) (Ma et al., 2023), and the Modified Vegetation Index (MSAVI) (Zhao et al., 2025), to reflect ecological conditions. While these indicators excel at revealing vegetation cover and productivity dynamics, they often fail to comprehensively characterize ecological quality in complex ecosystems. In recent years, comprehensive ecological indicators have gained increasing attention. For example, the InVEST model (Wei et al., 2022a) can assess ecosystem services, but its high parameter requirements and complex data needs limit its application in high-altitude regions or areas with limited data. In contrast, the Remote Sensing Ecological Index (RSEI) has emerged as a core technical tool for dynamic monitoring of ecological environment quality due to its multi-dimensional and multi-scale comprehensive assessment advantages (Guo et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2022; Maimaitituersun et al., 2025). This method has been widely applied in fields such as urban agglomeration ecological environment quality assessment (Xu et al., 2024), highland lake ecological environment evolution (Xiong et al., 2021), and spatiotemporal evolution of plain ecological fragile areas (Yi et al., 2023). Extensive research regions indicate that RSEI demonstrates higher applicability and stability in ecological fragile areas and regions with significant human disturbance, enabling a more comprehensive characterization of regional ecological quality. pudacuo national park is located on the northwestern plateau of Yunnan Province, characterized by complex topography and fragile ecological environments. In recent years, tourism development and human disturbance have continued to intensify, leading to increasing ecological pressure (Xie et al., 2023). In this context, the comprehensiveness and sensitivity of RSEI enable it to more accurately reflect the spatiotemporal characteristics of ecological environment quality changes. In the meantime, the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform, with its robust data storage and parallel processing capabilities, offers an effective technical support platform for the large-scale implementation of RSEI(Xu et al., 2022; Huang Y. et al., 2024).
In the context of rapid expansion of land use demand and increasing ecosystem degradation, land use/cover change (LUCC) has become one of the core drivers affecting the quality of the ecological environment (Wang et al., 2021). Especially in the context of resource development and other human activities, the significant fragmentation, heterogeneity, and functional degradation of landscape patterns caused by LUCC have become more and more prominent (Yang et al., 2022), seriously threatening the structural stability and service functions of regional ecosystems. In recent years, landscape pattern, as a core indicator characterizing the spatial heterogeneity and spatial organization of the land surface (Liu et al., 2021), has been widely used in the evaluation of ecological environment quality and analysis of ecological processes (Yohannes et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2022; Guo et al., 2024). Landscape pattern is regarded as an important indicator affecting various ecological processes with certain ecological effects (Boongaling et al., 2018). Studies have shown that elements such as landscape type composition, landscape configuration characteristics, and landscape spatial configuration have significant effects on ecological environment quality at different spatial scales (Ji et al., 2020). Landscape patterns serve as an important indicator of surface spatial heterogeneity (Qiu et al., 2024), directly revealing the evolution of landscape fragmentation, aggregation, and diversity, thereby reflecting the potential impact of human activities on ecosystem stability. pudacuo national park is subject to dual influences from natural conditions and human disturbances, resulting in a significant trend toward landscape fragmentation. Landscape pattern indices can be used to visually reveal the processes of landscape spatial heterogeneity and functional degradation, which is particularly important for understanding the relationship between tourism development and ecological environmental effects.
Currently, many scholars have carried out studies on the correlation between ecological quality and landscape pattern at different spatial scales, mainly using correlation analysis (Ji et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2024), Partial least squares regression (PLSR) (Zhang and Chen, 2022), Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression (GTWR) and Multiscale Geographic Weighted Regression (MGWR) (Hu et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024), etc., and the research scales cover administrative regions (Hu et al., 2022), urban agglomerations (Ji et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2024), and watershed ecosystems (Zhang and Chen, 2022). However, there is still a lack of research on national parks.
As an important part of the nature reserve system, national parks are the core areas of nationally representative natural ecosystems, and have an important strategic position in biodiversity conservation and ecological security barrier construction (Li et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2025). Currently, national parks are facing multiple challenges such as landscape fragmentation, ecological function degradation (Qi et al., 2024), biodiversity maintenance (Dendup et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2024), and increased anthropogenic interference (Zhou and Grumbine, 2011). As an important spatial carrier for ecosystem protection, national parks are often located in ecologically sensitive, highland mountainous, and other fragile areas, and the evolution of their landscape patterns has a more significant impact on ecological quality. However, there is a lack of systematic research on the coupled relationship between landscape pattern and ecological quality in such protected areas. Therefore, there is an urgent need to construct a scientific and systematic analytical framework to enhance the understanding of the coupling mechanism between landscape pattern and ecological environment quality in the context of ecologically fragile areas and significant human disturbances. Therefore, exploring the response mechanism of ecological environment quality and landscape pattern in national parks has important theoretical value and practical significance for enhancing the ecological barrier function of national parks and optimizing the development and protection pattern of national land space. pudacuo national park, as the only pilot park in Yunnan Province, is located in the ecologically sensitive area of the Northwest Yunnan Plateau, with typical alpine and canyon geomorphology, diverse biomes, and complex climatic conditions, which play an important supporting role for the regional ecological security pattern. Since the pilot reform of the national park system was carried out in 2015 (Xie et al., 2023), it has attracted a large number of Chinese and foreign tourists, and as the intensity of tourism development continues to increase and the scope of human interference continues to expand, the landscape pattern of the region has undergone significant changes, and its ecological environment quality is facing multiple pressures. In this context, there is an urgent need to deeply explore the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of the landscape pattern of pudacuo national park and its influence mechanism on the quality of the ecological environment.
Based on the above background, the research objectives of this paper include: (1) to quantify the evolution of land use pattern in pudacuo national park, and analyze the characteristics of its landscape pattern changes from landscape scale and class scale, respectively; (2) to analyze the characteristics of the spatial and temporal evolution of ecological environment quality in pudacuo national park; (3) to explore the response mechanism of the ecological environment quality and the landscape pattern changes, and to identify their spatial relationships. The results of the study can provide a scientific basis for the sustainable management of the ecosystem in the national park and promote the coordinated development of ecological environmental protection and regional economic and social development.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area
pudacuo national park is located in the eastern part of Shangri-La City, Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan Province, between longitudes 99°52′12″∼100°11′43″E and latitudes 27°44′34″∼28°04′30″N, with a total area of about 602.11 km2, 22 km away from the city of Shangri-La (Xie et al., 2023) (Figure 1). pudacuo national park is located in the core area of the “Three Parallel Rivers” World Natural Heritage Site and is one of the first batches of pilot areas for the reform of the national park system in China. Due to its unique geological structure and diverse climatic conditions, the park contains a variety of ecosystems such as forests, thickets, wetlands, lakes, and alpine meadows (Zhang et al., 2023). pudacuo national park, as one of the 11 pilot parks, has been established so far, attracting a large number of Chinese and foreign tourists, promoting local development, bringing considerable economic income to Shangri-La, and promoting the establishment of the national park system and providing corresponding experience.
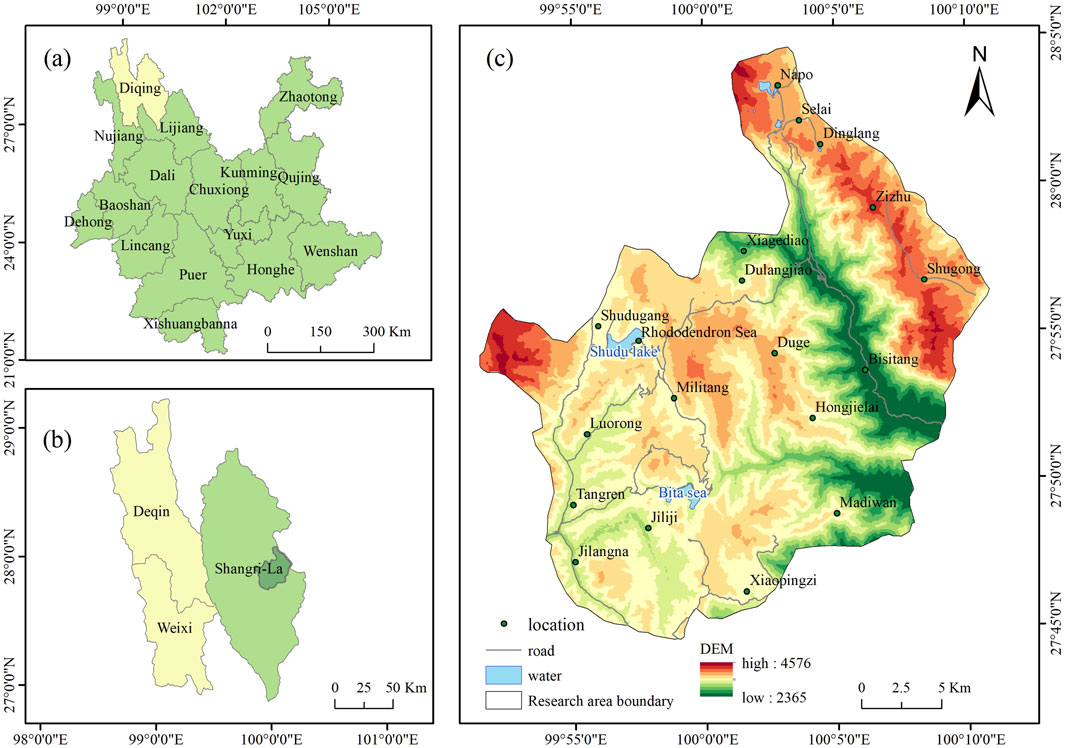
Figure 1. Overview of the study area. (a) Yunnan Province. (b) Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. (c) pudacuo national park.
2.2 Data methods
As a typical nature reserve, the ecosystem of national parks is of unique importance. By studying the ecological environment quality and landscape pattern influence mechanism of national parks, we can gain a deeper understanding of the interactions of different ecosystems, and help to promote the exploration of national park management theories and systems suitable for China’s national conditions. In this study, firstly, based on the land use/land cover (LULC) data in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020 and 2024, we analyzed the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of landscape pattern using the landscape pattern index and MSPA, and secondly, we analyzed the spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of ecological environment quality based on the GEE platform using the Remote Sensing Ecological Index (RSEI). Finally, the two were analyzed,and their spatial relationships were identified, and landscape pattern optimization suggestions were made from the perspective of ecological environment quality improvement. The research framework is shown in Figure 2.
2.2.1 Classification of land use types
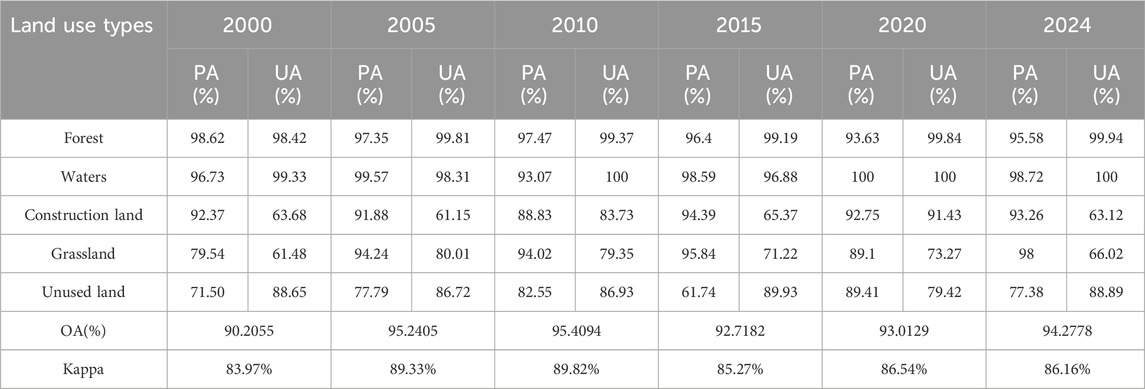
Referring to previous literature (Otukei et al., 2010; Hussain et al., 2020), the maximum likelihood method in supervised classification was adopted. This method has a sound theoretical foundation and is one of the most classic methods for remote sensing image classification. It has been proven effective in remote sensing image classification. The land use types in the study area were classified into five categories: forest, waters, construction land, grassland, unused land. The land use classification maps for the study area in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020, and 2024. The accuracy of the classification results was evaluated, and the overall accuracy of the six image interpretations was above 80% (Table 1). The classification results were relatively accurate and could provide relatively accurate data support for subsequent analysis.
2.2.2 Landscape pattern index
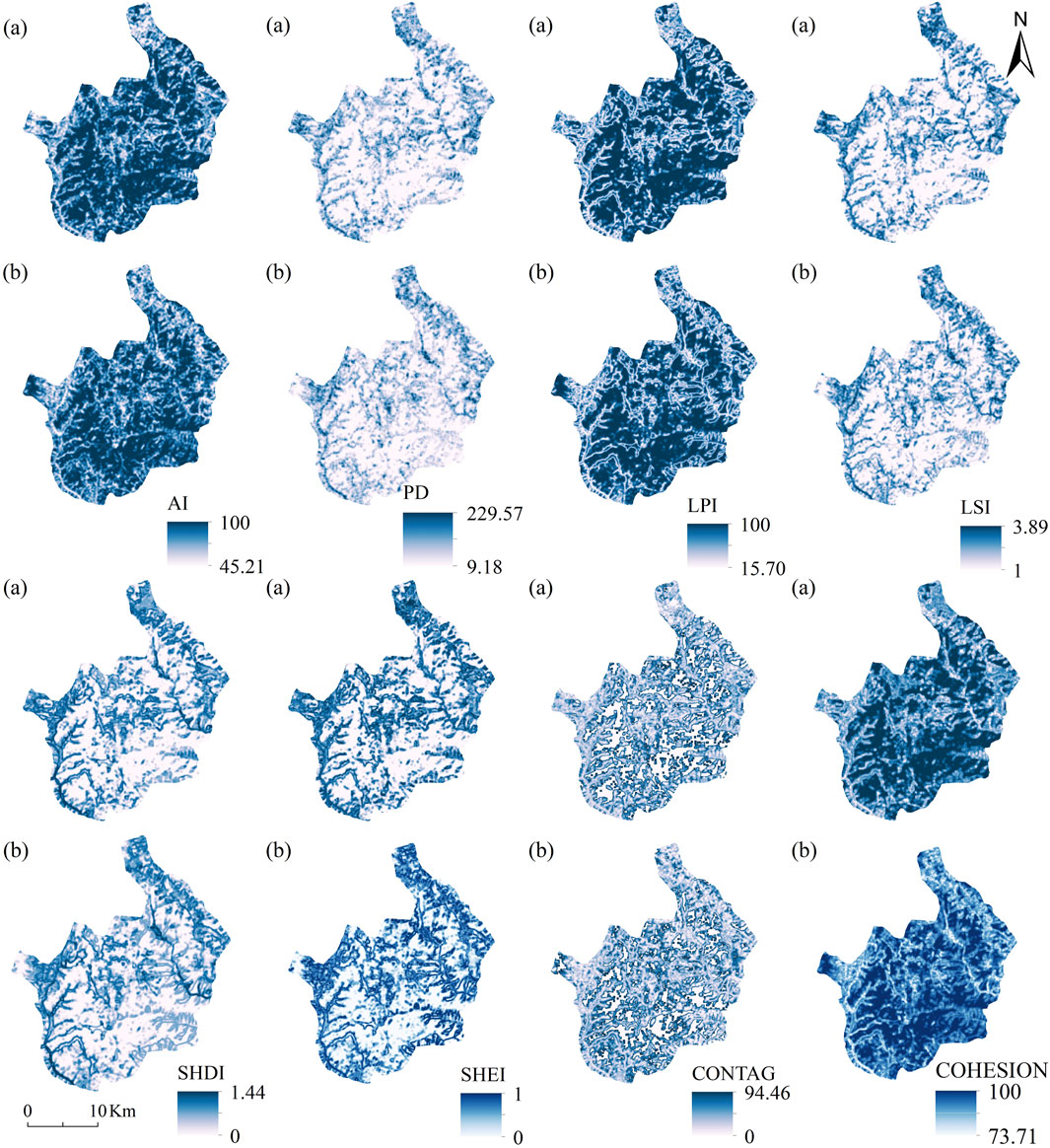
The influence of land ecological processes is reflected in the spatial expression of landscape pattern, which is a mosaic of patches with different land use types (Masoudi et al., 2024). For ecologically sensitive areas such as pudacuo national park that are significantly affected by tourism development, the landscape pattern index can intuitively reflect the evolution of landscape structure under the influence of human activities and the natural environment, thereby revealing its potential impact on ecosystem stability. Referring to relevant studies (Li et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2024), Fragstats 4.2 was used to calculate landscape pattern indices at both the class and landscape levels. At the class level, indicators reflecting landscape structural characteristics, fragmentation levels, and edge effects were first selected: Patch Density (PD), Largest Patch Index (LPI), Landscape Shape Index (LSI). Additionally, indicators reflecting overall landscape diversity and evenness were selected: Shannon Diversity Index (SHDI) and Shannon Evenness Index (SHEI). To enhance the explanatory power of landscape patterns for ecological quality, functional and connectivity indicators were added: Aggregation Index (AI) to measure the spatial aggregation of landscape types, and Patch Cohesion Index (COHESION) to characterize connectivity between patches. At the landscape level, the Contagion Index (CONTAG) has been added to measure the aggregation of landscape patches.
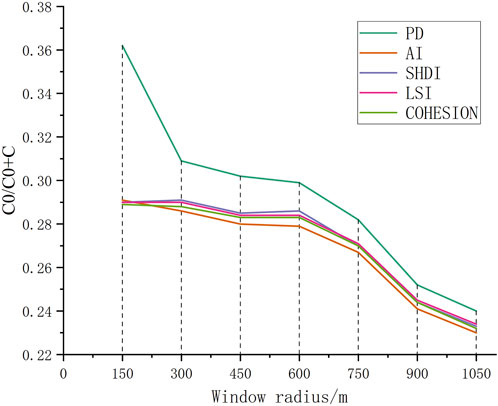
To comprehensively understand the evolution of the landscape spatial pattern in the study area, the selected landscape indices were calculated using the moving window function of FRAGSTATS 4.2 software. Referring to relevant literature (Li et al., 2021; Ai et al., 2022), to avoid data processing errors caused by non-integer pixels, typical parameters PD, AI, LSI, SHDI, and COHESION were selected from four dimensions: density, shape, aggregation, and diversity. The moving window radius were set to 150, 300, 450, 600, 750, 900, and 1050 m, and the landscape index semi-variogram simulation was conducted using GS + software under different moving window radius (Figure 3). When the moving window side length was within the range of 300–600 m, the fluctuation amplitude began to decrease, and 300 m was determined as the moving window side length for analysis.
2.2.3 Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis, MSPA
Based on the principles of mathematical morphology, MSPA is a technique for analyzing landscape spatial patterns that can efficiently recognize and categorize the spatial structural properties of landscape elements, thereby exposing the spatial arrangement and interconnectedness of landscape patterns (Wei et al., 2022b). pudacuo national park has a complex terrain, and ecological processes are highly dependent on landscape connectivity. MSPA can effectively supplement the shortcomings of traditional landscape indices in spatial functional connectivity analysis. This study is based on six periods of land use type data, forest land was used as foreground data and assigned a value of 1; other land use types were non-forested land, which was used as background data and assigned a value of 2. Forest/non-forested binary raster images with a spatial resolution of 30 m were generated. Using Guidos Toolbox 2.8 software, a structure with an edge width of 1 image element and 8 adjacent image elements connected was used to characterize the landscape type to which each forest pixel belonged. The landscape patches were categorized into 7 types of landscape spatial patterns: Core, Perforation, Islet, Bridge, Edge, Branch, and Loop.
2.2.4 Remote sensing ecological index (RSEI)
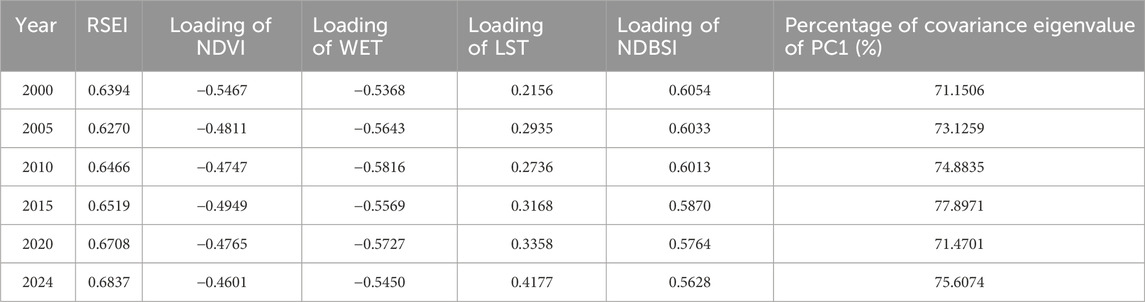
In the comprehensive assessment of regional environmental quality, the indicators closely related to human survival are usually selected, and the index uses principal component analysis coupled with the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), the Wetness (WET), the heat index (LST), and the dryness index (NDBSI). Before the principal component analysis, the indicators need to be normalized so that the scale of each indicator belongs to the same range of numerical fluctuations. By integrating multi-dimensional information, this approach demonstrates higher stability and sensitivity in regions where ecological fragility and human disturbance coexist, thereby providing a more comprehensive reflection of the spatiotemporal evolution of ecological quality in pudacuo national park. The calculation formula is as follows (Duo et al., 2024; Huang S. et al., 2024).
2.2.4.1 NDVI
where
2.2.4.2 WET
where
2.2.4.3 LST
where
2.2.4.4 NDBSI
where SI is the bare soil index, IBI is the applied building index, ρSWIR1 is the short-wave infrared 1-band reflectance, ρred is the red-band reflectance, ρblue is the blue-band reflectance, ρNIR is the near-infrared band reflectance, and ρgreen is the green-band reflectance.
2.2.4.5 Normalization process
2.2.5 Spatial correlation analysis
Spatial autocorrelation analysis is a statistical method used to quantify the spatial dependence of variable values in geographic spatial data (Zhou et al., 2024). Spatial autocorrelation reflects the correlation between a specific geographic phenomenon or attribute value in a given geographic unit and the same phenomenon or attribute value in adjacent geographic units. It is typically categorized into global spatial autocorrelation and local spatial autocorrelation. In this study, the GEODA software was utilized to define spatial proximity relationships based on a spatial weight matrix derived from the Queen contiguity criterion (Queen contiguity, order = 1), thereby reasonably characterizing the spatial proximity relationships among study area units. This study first employed the global Moran’s I index to measure the overall spatial correlation of ecological environment quality in pudacuo national park; second, it utilized local spatial autocorrelation and cluster maps to reveal spatial aggregation characteristics in local areas, identifying whether significant “high-high” or “low-low” aggregation patterns exist; Finally, it further introduces bivariate spatial autocorrelation analysis to calculate the spatial correlation between ecological environment quality and landscape pattern indices, exploring their spatial distribution coupling relationships and local interaction characteristics. Through a multi-level spatial correlation analysis combining global and local perspectives, this study comprehensively reveals the spatial pattern characteristics of ecological environment quality in pudacuo national park and its spatial coupling mechanisms with landscape pattern indices.
2.2.6 Geodetector
By analyzing the variations among geographical data, Geodetector quantitatively investigates the extent to which the independent variable influences the dependent variable (Zhang et al., 2024). This can effectively explain the effect of the landscape pattern index (X) on the level of ecological environment quality (Y), the study used factor probes to explain the effect of landscape pattern index AI (X1),PD (X2),LPI (X3),LSI (X4),SHEI (X5),SHDI (X6),CONTAG (X7)and COHESION (X8) on the quality of ecological environment Y.
where q is the explanatory power of the metric, h is the category or partition of the variable, L is the number of subregions, Nh and N are the number of sample units in the subregion and the whole region, respectively, and the variance of a single variable in the whole region and subregion.
2.3 Data sources
In this study, based on the T2 level surface reflectance dataset provided by the GEE platform (https://earthengine.google.com/), Landsat 5 TM and Landsat 8 OLI series remote sensing images were used, and the vegetation growing season (April-September) images of 2000–2024 were selected, de-clouded, median synthesized, and image cropped (Huang et al., 2024b). DEM data, remote sensing image data for land use classification, were obtained from Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn), and remote sensing images with no cloud coverage were selected for the study area. The dataset includes Landsat-5 TM imagery from 9 January 2000, 6 January 2005, and 12 February 2010; Landsat-8 OLI imagery from 9 November 2015, and 24 December 2020; and Landsat-9 OLI-2/TIRS-2 data from 23 March 2024. The road network vector data and POI (point of interest) data were obtained from the BIGEMAP GIS Office (http://www.bigemap.com). All the images and data are unified to the WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_47N coordinate system with a spatial resolution of 30 m.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of the spatial and temporal evolution of landscape patterns
3.1.1 Land use
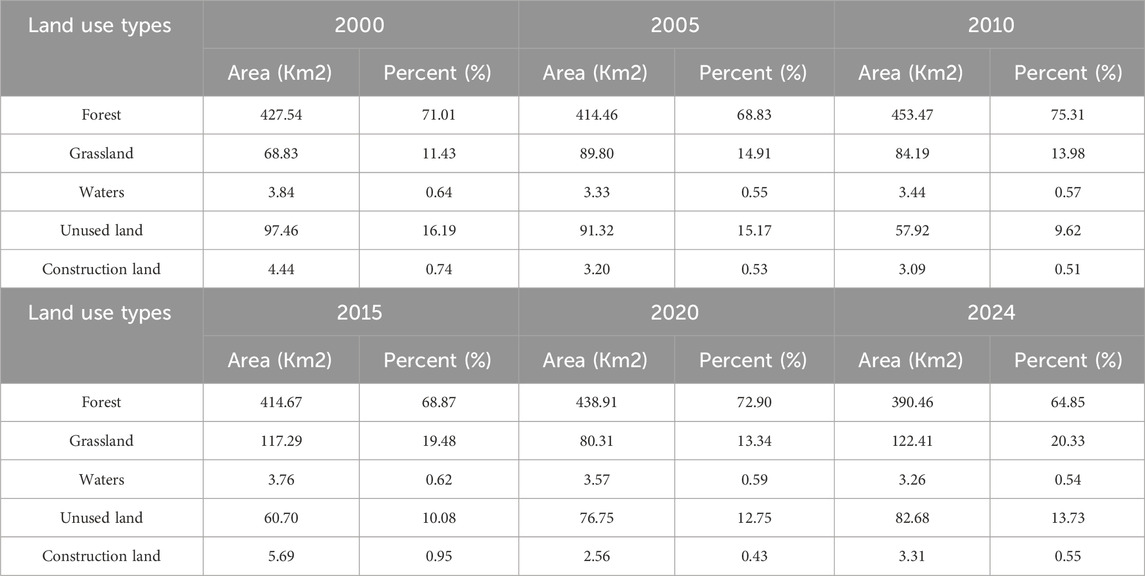
Based on land use types and areas (Table 2) and spatial distribution (Figure 4), forest land is the primary land use type in the study area, accounting for 64.85%–75.31% of the total area. It is widely distributed in areas such as Duluojiao in the central region and is the primary land use type affecting ecological environment quality. The area of water bodies and construction land changed less during the research period, and their proportion remained almost unchanged. Building land is generally distributed in the western Luolong Ethnic Eco-cultural Tourism Village, where human activities are the strongest. The water bodies are mainly located in the Shudu Lake and the Bita Sea, with a small number of water bodies in the northern part of Napo. Grassland and Unused land are mostly distributed in Madiwan in the east of the park, and the Xiagediao areas in the north, with relatively significant changes. In general, the percentage of unused land area has dropped while the percentage of grassland area has increased.
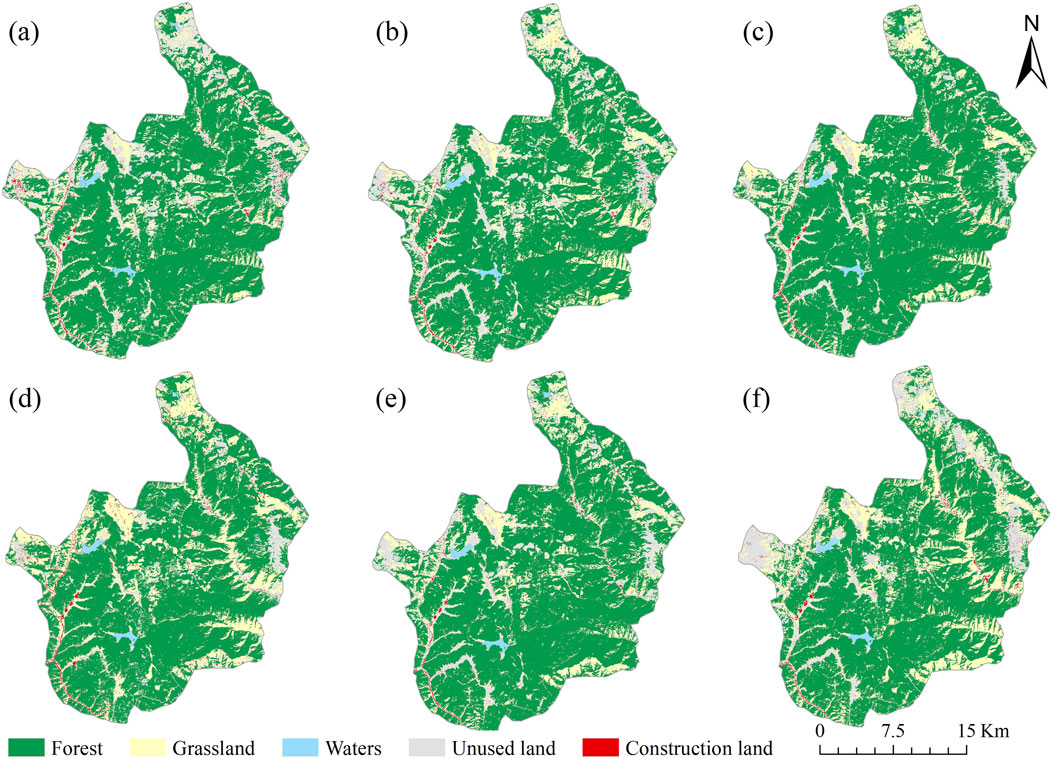
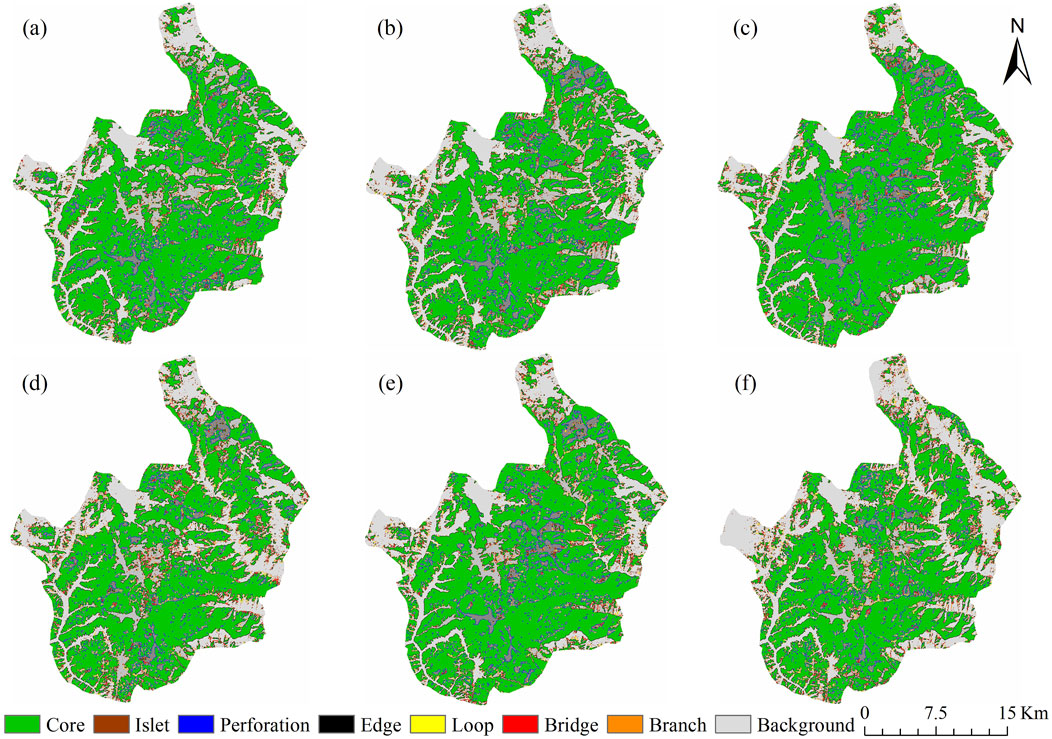
Figure 4. Land use types in Pudacuo National Park (a) 2000 (b) 2005 (c) 2010 (d) 2015 (e) 2020 (f) 2024.
3.1.2 Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis
Comparative analysis of the landscape pattern maps in 2000–2024 (Figure 5) revealed that the landscape pattern of pudacuo national park was dominated by the core area, but the core area showed a gradual decrease between 2000 and 2024, indicating an increase in landscape fragmentation and a decrease in the completeness of the ecological environment, which is closely related to human activities such as tourism development in the park. Meanwhile, the Perforation, Islet, and Bridge areas decreased from 2000 to 2024, further confirming the process of shrinking core ecological areas. The degree of disturbance to the natural boundaries increased along with the expansion of Edge and Loop. Overall, the landscape pattern of pudacuo national park was gradually fragmented from 2000 to 2024, which was mainly influenced by anthropogenic factors such as tourism activities, infrastructure construction, and land use changes. To be able to develop an environmentally friendly plan that works for the park’s growth, the planning department should concentrate on coordinating environmental preservation with economic development.
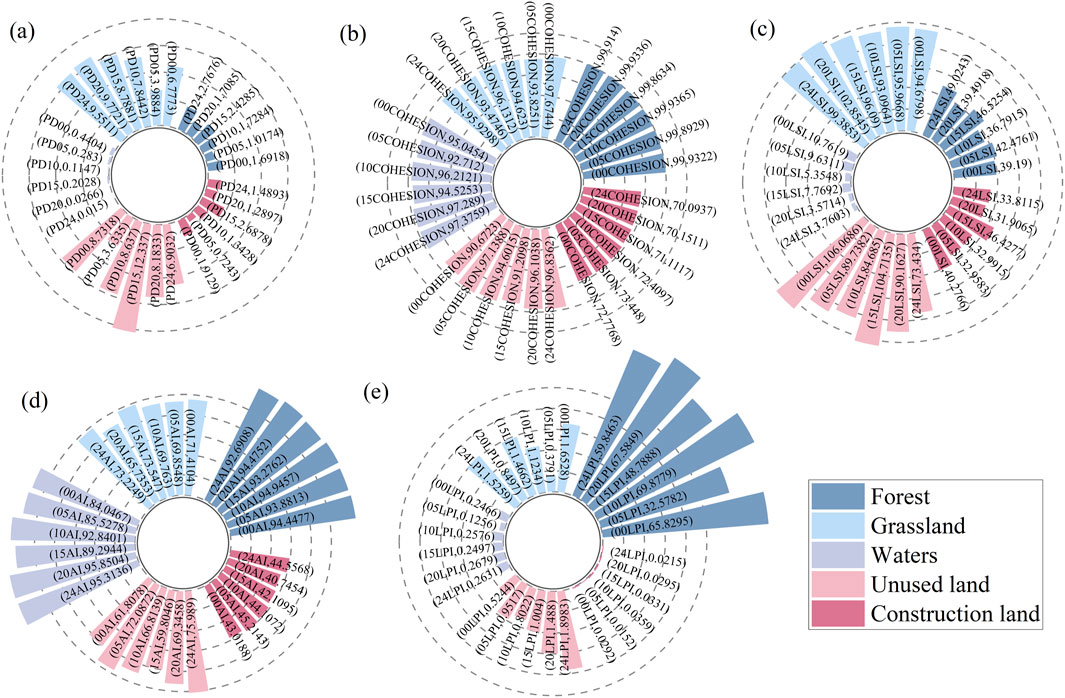
3.1.3 Landscape pattern index analysis
As shown in Figure 6, throughout the study period, forest PD remained at a low level, while COHESION was the highest, indicating the lowest degree of fragmentation and the strongest habitat connectivity. LPI was significantly higher than other land use types and the high value of AI, reflecting the dominant role of forests in the landscape and the presence of large, continuous habitats. LSI was relatively high, indicating irregular patch boundaries, primarily influenced by natural factors such as terrain variations. Overall, forests have consistently been the core ecological component in the study area, providing stable and well-connected habitats, while being distant from residential areas, resulting in a relatively stable landscape. Grasslands have slightly higher PD values than forests, but COHESION and AI remain at high levels, indicating that although they exhibit some fragmentation, connectivity remains good. LPI is lower than forests, indicating that the dominant patches in grasslands are smaller in scale. The LSI is moderately high, reflecting irregular patch boundaries. Overall, grassland spatial structure is stable with moderate fragmentation, serving as an important supplementary habitat to forests.
Water bodies have low PD, high COHESION, and are spatially concentrated with strong connectivity, but their area is smaller than that of forests and grasslands. The LSI is low and shapes are regular. The main water bodies within the park are Bita Lake and Shudu Lake. Unused land has high PD, low COHESION and AI, severe fragmentation, scattered distribution, long-term low LPI, and fluctuating LSI, indicating an unstable overall pattern and weak ecological function. Construction land has the low PD, lowest COHESION and AI, poor connectivity, weak aggregation, extremely low LPI with dispersed patches, and relatively high LSI, reflecting strong disturbance from infrastructure construction.
3.1.4 Spatial and temporal evolution of landscape patterns
From 2000 to 2024, the landscape pattern index of pudacuo national park exhibited distinct spatiotemporal evolution characteristics in its spatial distribution (Figure 7). From a regional distribution perspective, the AI was relatively high in the central forest areas, indicating strong patch aggregation and continuous distribution of similar landscapes in these regions. The LPI and CONTAG were also relatively high, particularly in areas with concentrated forests and grasslands, suggesting highly concentrated landscape types with large and continuous patch areas. Additionally, the high values of COHESION and low values of PD further reflect a small number of patches and a complete spatial pattern, indicating good ecological connectivity. This area is concentrated in the core zone of the park, which features rugged terrain, predominantly forested and grassland distributions, high vegetation coverage, and is distant from tourist access areas. The ecosystem exhibits strong integrity and stability, with high ecological conservation value. The southeastern and high-mountain forest areas exhibit the lowest PD values, with a relatively intact landscape pattern, and both AI and CONTAG are relatively high, indicating highly concentrated landscape types, large and continuous patches, a stable ecosystem, and prominent natural conservation value. COHESION is also high, ensuring the integrity of ecological corridors. However, due to the single vegetation cover, SHDI and SHEI are relatively low, reflecting the single structural characteristics of the ecosystem. In contrast, the tourist development areas in the east have exposed rocks, the highest PD, and significant landscape fragmentation. AI is low, with scattered patch distribution and significantly reduced COHESION, reflecting the weakening of ecological connectivity due to human activities. Nevertheless, these areas have relatively high SHDI and SHEI values, indicating diverse landscape types and relatively balanced area proportions. LSI is relatively high, indicating complex and irregular patch boundaries, with some structural complexity in the ecosystem, but overall ecological functions are limited. The local landscape morphology is relatively complex, with high landscape fragmentation and significant human disturbance. This region is located within the Shudu Lake Scenic Area, the only tourist zone open to the public within the park, where frequent tourist activities and extensive construction of tourist facilities have led to highly fragmented landscapes. This indicates that tourism development has a significant impact on landscape patterns. Future efforts should seek a balance between tourism development and ecological conservation to minimize human disturbance to landscape ecosystems.
3.2 Characteristics of spatial and temporal evolution of ecological environment quality
3.2.1 Results of principal component analysis
The results of principal component analysis (Table 3) show that the contribution rate of PC1 band was above 70% from 2000 to 2024, which indicates that the majority of the data pertaining to the four main ecological elements can be represented by PC1. The remotely sensed eco-index can be built using PC1, RSEI, of which NDVI and WET are negative, while LST and NDBSI are positive. The positive impacts of NDVI and WET on the environment are expressed using the “1-PC1”.
3.2.2 Characteristics of the spatial and temporal distribution of ecological environmental quality
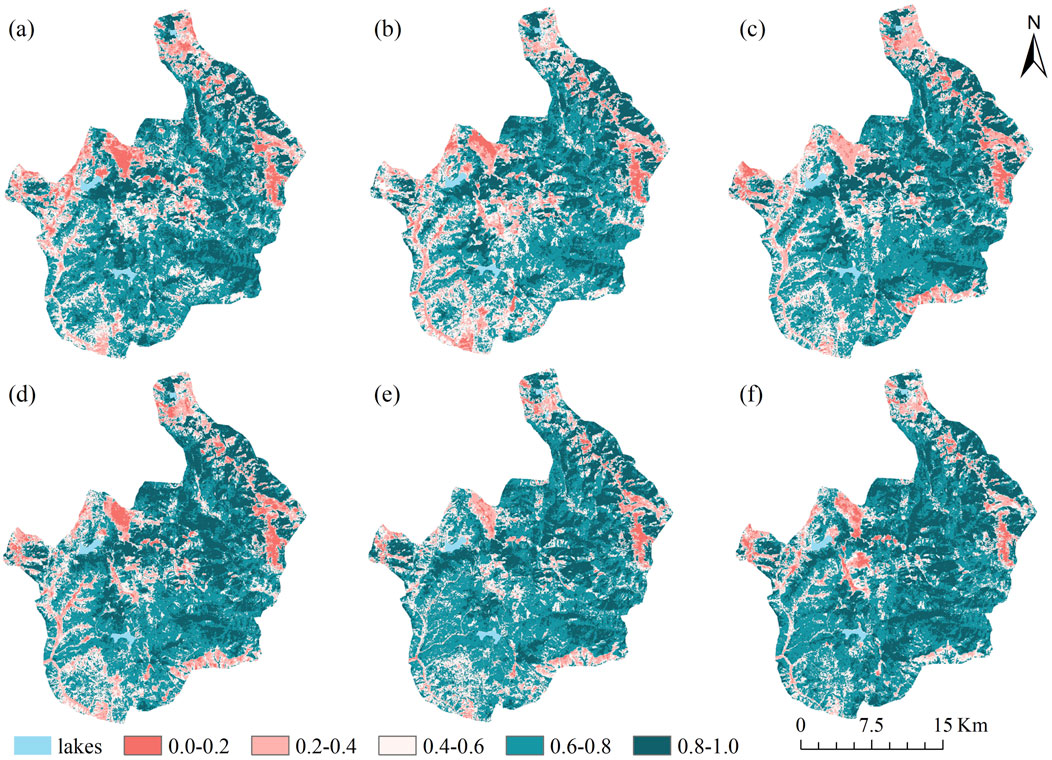
Five grades were assigned to the RSEI: Poor [0, 0.2), Fair [0.2, 0.4), Moderate [0.4, 0.6), Good [0.6, 0.8), and Excellent [0.8, 1.0]. At the same time, five grades were assigned to the situational change in order to further analyze the ecological environment change in the study area: Sharp Decline, Slight Decline, Relative Stable, Slightly Increase, and Drastic Increase. The RSEI ratings (Table 4) and changes (Table 5) of pudacuo national park were statistically analyzed. The spatial distribution of RSEI ratings and changes is shown in Figures 8, 9.
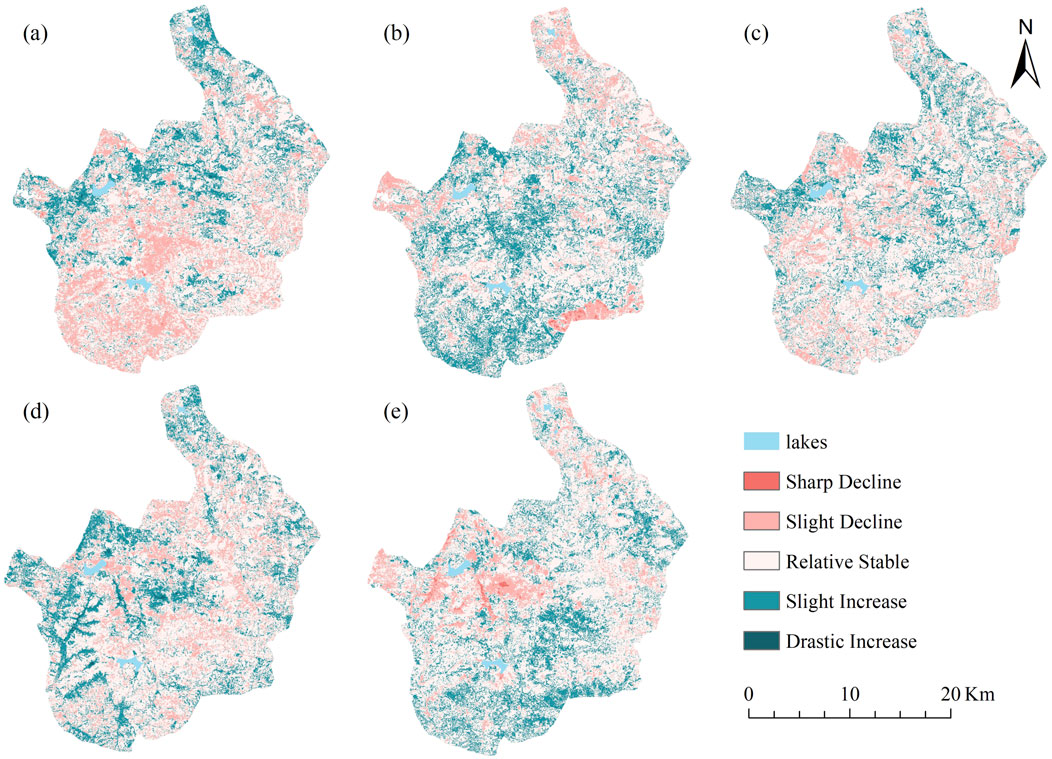
Figure 9. Ecological environment quality changes (a) 2000–2005 (b) 2005–2010 (c) 2010–2015 (d) 2015–2020 (e) 2020–2024.
The RSEI averaged between 0.6270 and 0.6837 from 2000 to 2024, indicating an overall improvement in environmental quality. Areas with excellent environmental quality accounted for 19.84%–29.12% of the total area, while areas with good environmental quality accounted for 42.06%–49.04%, primarily concentrated in the Donglangjiao region of central-eastern China. As the core protected region of pudacuo national park, the area’s rocky topography and many biological species are rigorously protected, thereby preserving the stability of the local ecology. The ecological changes are primarily “Relative Stable” and “Slightly increased.” Areas with medium ecological quality are mainly distributed in the ecological hiking experience area on the west side of the park, accounting for 22.91%–15.56% of the total area. As the only tourist attraction open to the public in the park, it clearly reflects the impact of local tourism activities on the ecology. Especially since 2020, as a famous tourist attraction, frequent tourism activities and the construction of tourism facilities in pudacuo national park have caused serious degradation of the ecological environment around Shudu Lake. The poor natural environment’s quality ranges from 4.09% to 2.00%, with fair quality falling between 6.90% and 11.42%, which is primarily found in the western area, where the local bedrock is exposed, dominated by unutilized land, and the terrain is low for the river valley area, so the EEQ is poor. The degradation of grassland brought on by excessive grazing is the reason for the ecological environment’s trend of deterioration and change in the north-central and southeast regions of pudacuo national park.
3.2.3 Spatial autocorrelation analysis of ecological environment quality
This study conducted a spatial autocorrelation analysis of the distribution patterns of ecological and environmental quality from 2000 to 2024. The results showed that the global Moran’s I indices for habitat quality in pudacuo national park were 0.709 (Figure 10a), 0.691 (Figure 10b), 0.693 (Figure 10c), 0.718 (Figure 10d), 0.679 (Figure 10e), and 0.704 (Figure 10f). Significance tests indicate that the ecological environment quality in pudacuo national park exhibits strong spatial positive correlation and relatively stable spatial clustering characteristics.
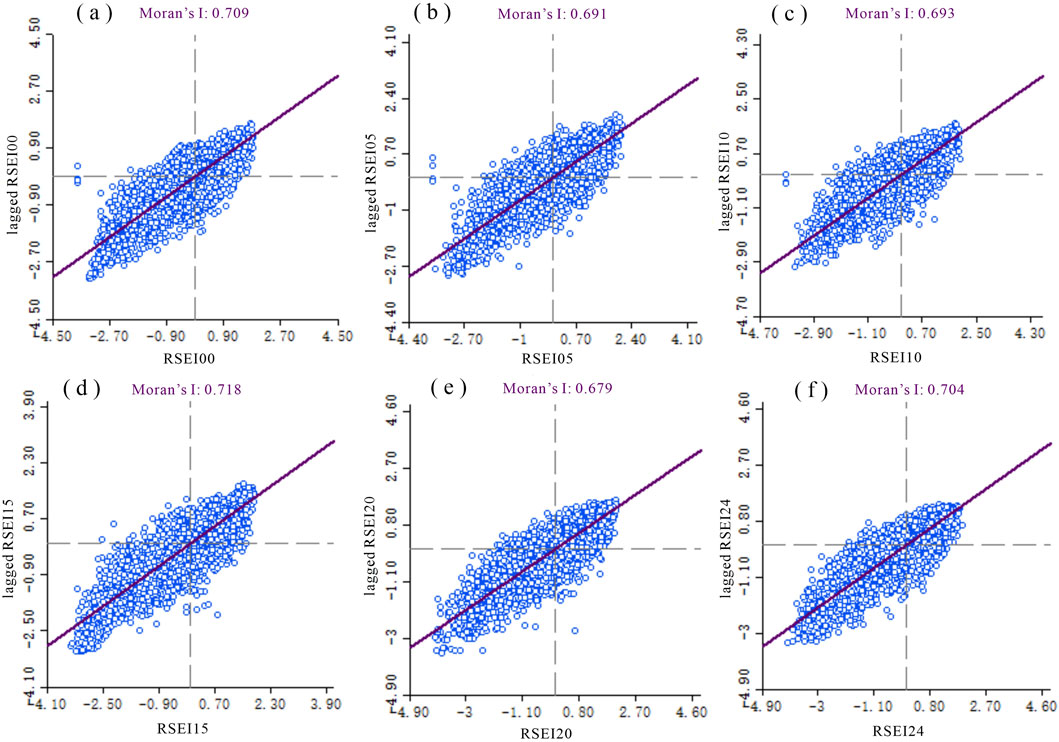
Figure 10. Moran's I index of ecological quality (a) 2000 (b) 2005 (c) 2010 (d) 2015 (e) 2020 (f) 2024.
The results of the LISA clustering analysis of pudacuo national park (Figure 11) show that the ecological environment quality of the park has H-H and L-L clustering characteristics, which show positive spatial autocorrelation. H-H clustering is distributed in the core area of the forest with high ecological environment quality, and the high-quality habitat in the core area positively affects the surrounding areas through the functions of species migration and water conservation, forming a high level of ecological environment quality. The L-L cluster is distributed in the valley area in the southeast with poor ecological quality, which has infertile soils and is susceptible to erosion and has low coverage of natural vegetation, with a weaker ecological carrying capacity. A low-value patchy distribution is formed in the left section, surrounding the open tourist area of Shudu Lake, as a result of human activity disruption in the low-value area spreading to the perimeter and causing a synchronous reduction in the quality of habitats in the surrounding areas.
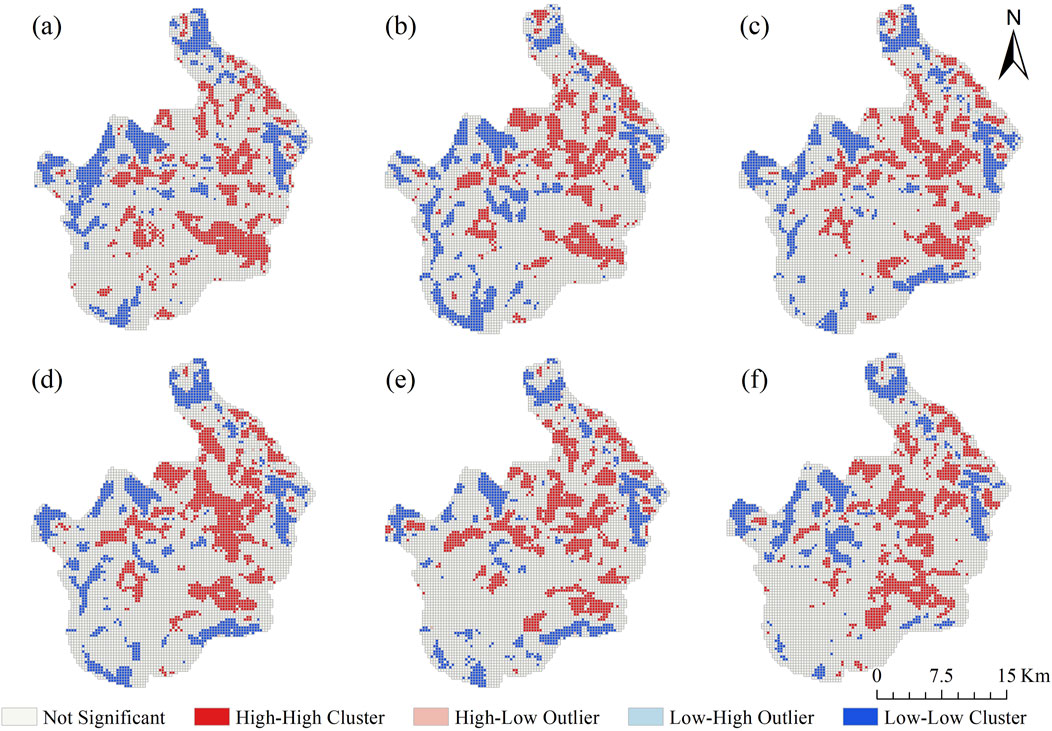
Figure 11. Localised spatial autocorrelation analysis of ecological quality (a) 2000 (b) 2005 (c) 2010 (d) 2015 (e) 2020 (f) 2024.
3.3 Ecological environment quality response to landscape pattern changes
3.3.1 Correlation between landscape pattern and ecological environment quality
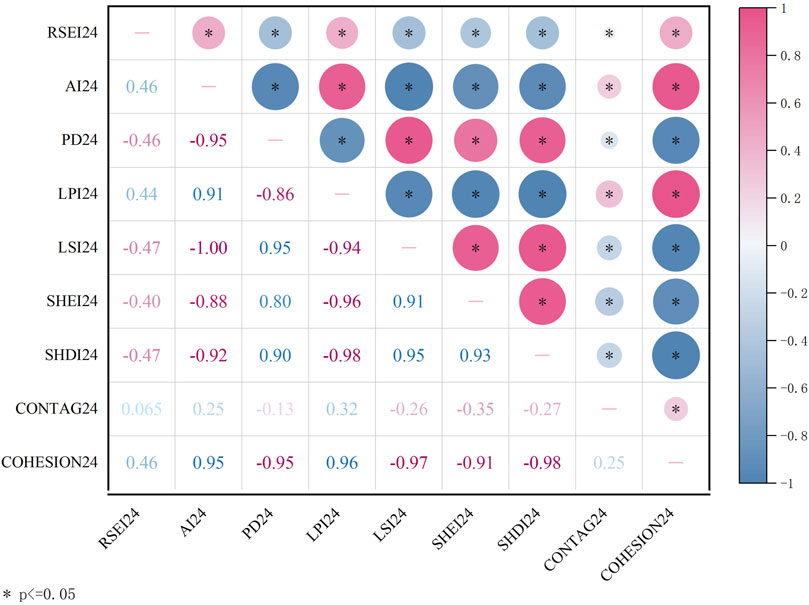
Using SPSS software, a Spearman correlation analysis was conducted on the RSEI and landscape pattern index within each grid after the fishing net was divided. This analysis examined the correlation between the landscape pattern index and ecological environment quality in the study area from 2000 to 2024 (Table 6) and generated a correlation heatmap for 2024 (Figure 12) to analyze the relationship. The results indicate that the correlation analysis shows significant differences in the impact of different landscape pattern indices on ecological environment quality. AI, LPI, and COHESION are all significantly positively correlated with RSEI, indicating that higher patch aggregation, larger dominant patches, and stronger landscape connectivity contribute to improving ecological environment quality. Conversely, PD, LSI, SHEI, and SHDI were significantly negatively correlated with RSEI, indicating that highly fragmented, complexly shaped, and overly uniform and diverse landscapes may weaken ecosystem stability and health, potentially due to landscape fragmentation caused by human disturbance. In contrast, the correlation between CONTAG and RSEI did not reach a significant level, suggesting that the overall landscape aggregation at the scale of this study has a relatively limited impact on ecological environment quality. In general, improvements in ecological environment quality depend more on landscape pattern aggregation and connectivity rather than mere diversity and uniformity.
From a time series perspective, overall analysis shows that the absolute values of the correlation coefficients of various indices are trending downward, indicating that although the ecological environment and landscape patterns of pudacuo national park are somewhat correlated, this correlation is weakening. This may be related to external disturbances such as tourism activities and ecological restoration projects.
3.3.2 Local spatial autocorrelation analysis of landscape pattern characteristics and ecological environment quality
To analyze the aggregation relationship and spatial aggregation characteristics between the two, bivariate local spatial autocorrelation was used with the GeoDA software. Because the aggregation effect of bivariate local spatial autocorrelation did not differ much over the years, only the local spatial autocorrelation analysis of RSEI and landscape pattern indices in 2024 was carried out in this study (Figure 13).
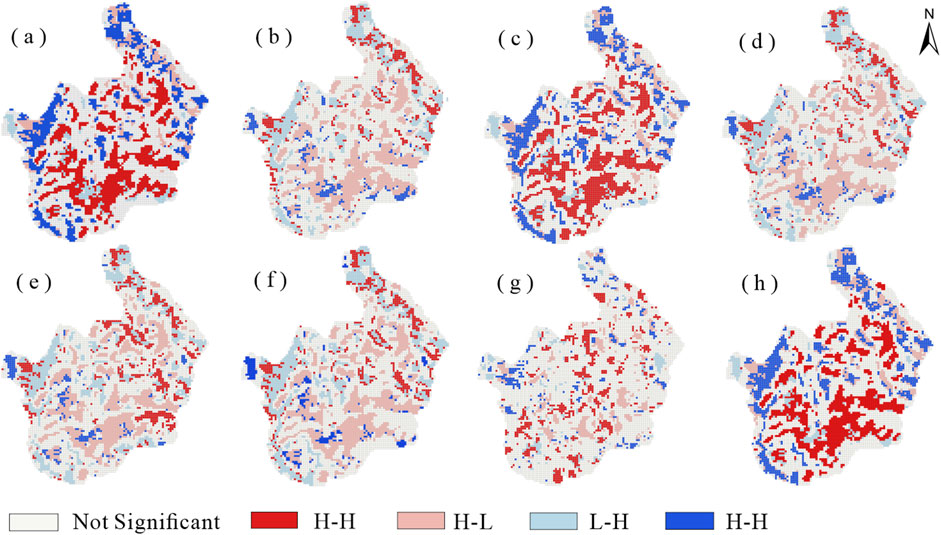
Figure 13. Localized spatial autocorrelation analysis of ecological quality and landscape pattern indices in 2024 (a) RSEI-AI (b) RSEI-PD (c) RSEI-LPI (d) RSEI-LSI (e) RSEI-SHEI (f) RSEI-SHDI (g) RSEI-CONTAG (h) RSEI-COHESION.
In Figure 13, the first parameter represents ecological environment quality, and the second parameter represents various landscape indices. Using LISA aggregation maps to explore the spatial coupling relationship between ecological environment quality and landscape pattern indices, it was found that the spatial correlation between different indices and RSEI varies significantly. AI, LPI, and COHESION exhibit a large-scale H-H aggregation pattern with RSEI, indicating that in areas with high patch aggregation, large maximum patch size, and strong landscape connectivity, ecological environment quality is generally better, highlighting the important role of large patches and good connectivity in maintaining regional ecological functions. This indicates that the region has good ecological environment quality and integrity, primarily distributed in the central and southern parts of the park. This area features dense forests, good vegetation coverage, rugged terrain, and minimal human impact. Conversely, PD, LSI, SHEI, and SHDI primarily exhibit an H-L aggregation pattern, indicating that in areas with high PD, LSI, SHEI and SHDI, ecological quality is often lower, further validating the adverse effects of landscape fragmentation and complexity on ecosystem health. Additionally, the spatial coupling relationship between CONTAG and RSEI did not reach a significant level, suggesting that the overall landscape aggregation at the scale of this study has limited spatial explanatory power for ecological quality. Overall, the spatial distribution of ecological quality is more dependent on landscape aggregation and connectivity, while excessive uniformity and diversity do not necessarily enhance ecological levels and may even weaken ecosystem stability.
3.3.3 Time-series characterization of the influence of landscape pattern index on RSEI
The impact of the Landscape Pattern Index on RSEI in pudacuo national park can be seen through the usage of geodetectors. As can be seen from the single-factor detection results (Figure 14), AI (X1), PD (X2), LPI (X3), LSI (X4), SHEI (X5), SHDI (X6), CONTAG (X7), and COHESION (X8) have a significant driving effect on the evolution of ecological environment quality (P < 0.05).

Figure 14. The determinant power q value of the landscape pattern index on the RSEI from 2000 to 2024. (a) 2000 (b) 2005 (c) 2010 (d) 2015 (e) 2020 (f) 2024.
Overall, AI, PD, and LPI consistently maintained high explanatory power across different stages, indicating that landscape aggregation, fragmentation levels, and core patch stability are key drivers of changes in ecological environment quality. Meanwhile, SHEI and SHDI exhibited enhanced explanatory power during certain periods, reflecting the important role of landscape type diversity and distribution balance in maintaining ecosystem stability. CONTAG and COHESION remained at moderate levels in most periods, but their driving effects approached or exceeded those of core factors in certain years, indicating that landscape connectivity and cohesion exert significant influences on ecological processes during specific stages. Thus, the spatiotemporal evolution of ecological quality in pudacuo national park is not only constrained by landscape fragmentation and core patch patterns but is also closely related to landscape diversity and overall spatial structure. This finding suggests that national park management should prioritize maintaining the integrity of large patches, optimizing landscape diversity and balance, and enhancing aggregation and connectivity between patches to sustain regional ecosystem stability and the continuous provision of ecological services.
4 Discussion
4.1 Landscape pattern and ecological quality changes
This study reveals the spatial heterogeneity characteristics of ecosystems and their driving mechanisms under the special management mode of the national park by analyzing the landscape pattern response mechanism of ecological environment quality to environmental stress in pudacuo national park, providing an important scientific basis for the protection of high-altitude fragile ecological zones. Overall, the ecological quality of pudacuo national park improved during the study period, and the spatial pattern of ecological quality presented a spatial pattern dominated by the high-quality ecological core area in the center, and secondary to the scenic area of Shudu Lake in the west and the two low-quality ecological patches in the east, a finding that is consistent with the results of a previous study (Ma et al., 2022).
The core protected area effectively maintains a high level of remote sensing ecological index (RSEI >0.6) and exhibits strong ecological stability due to the implementation of the most restrictive human disturbance policy, which verifies the scientific validity and effectiveness of the national park management model in the protection of plateau ecosystems (Zhou and Grumbine, 2011). The stability of core ecological patches plays a key role in maintaining regional ecological environment quality, and under the condition of proper protection of core ecological patches, the region still has the potential to maintain a high level of ecological environment quality even in the context of global climate change. Therefore, in the future ecological management of the national park, the protection of the core area should be further strengthened, and anthropogenic interference should be strictly controlled in order to maintain the ecological integrity and resilience of the core protected area.
For the marginal areas, such as the western part of the Shudu Lake, the region has excessive tourism activities, is significantly disturbed by human activities, the ecosystem is disturbed to varying degrees, and the RSEI of some areas continues to be at a low level. Although the original intention of the national park system was to improve environmental quality and protect biodiversity, its effectiveness has been mixed (Wang et al., 2012). In order to mitigate the negative impacts of tourism development on the ecological environment, it is recommended to construct landscape buffer zones. Damschen et al. pointed out that neglecting landscape connectivity will fail to realize the substantial, complementary, and long-lasting biodiversity benefits of landscape connectivity (Damschen et al., 2019). Specifically, a three-tier management system comprising “core protection zones–ecological restoration zones–recreational use zones” can be established, with enhanced ecological restoration and functional zoning management in the peripheral areas. On one hand, establish a tourism carrying capacity threshold monitoring and early warning mechanism in high-frequency use areas such as Shudu Lake to scientifically control visitor numbers and tourism facility density, preventing them from exceeding the ecosystem’s recovery capacity threshold. On the other hand, establish clearly defined ecological buffer zones between recreational use zones and core protection zones to achieve a dynamic balance between protection and utilization. In addition, for the exposed bedrock and severely degraded land in the southeast, ecological restoration and vegetation restoration strategies should be implemented, taking into account the topography, climate, and soil conditions. According to the ecological restoration program proposed by (Duan et al., 2024) in Northwest Yunnan province, cold-resistant, drought-resistant, and barren-tolerant native vegetation, such as Huashan pine (Pinus armandii) and Lijiang spruce (Picea likiangensis), should be planted in the areas of barren land and extreme climate to enhance the ecosystem service function while improving the biodiversity of the region.
4.2 Correlation between landscape pattern and EEQ
Landscape pattern indices were significantly correlated with ecological quality, which is consistent with previous studies (Wu et al., 2024). Specifically, PD, LSI, SHDI, and SHEI showed a significant negative correlation with ecological environment quality, while LPI, AI, and COHESION showed a significant positive correlation with ecological environment quality, which is consistent with the results of previous studies (Wu et al., 2024), indicating that large-scale, highly continuous dominant ecological patches are critical for maintaining regional ecological quality. However, from a time-series perspective, the correlation between landscape pattern indices and ecological environment quality showed a weakening trend. Through comparative analysis, it was found that the areas with weakened correlation were mainly concentrated in the sections with strong interference from human activities. The high intensity of human activities in pudacuo national park and its appeal to economic development and ecological balance make the relationship between ecological environment quality and landscape pattern in this region unique. This phenomenon may be closely related to the large-scale construction of tourism facilities and ecological trekking experience areas, for example, in the case of Shudu Lake, where wooden trestles were built along the lake to facilitate tourists’ visits (Xie et al., 2023). Artificial intervention cut the originally continuous unused land, grassland, and other landscapes into patches with complex shapes and diverse types, which made the landscape pattern index tend to be naturalized, but the actual ecological environment quality did not improve simultaneously. This result reveals that the morphology tends to be close to nature driven by high-intensity human activities; however, the function continues to be degraded, suggesting that there may be limitations in the ecological indications of the traditional landscape pattern index in artificially intervened areas.
4.3 Ecological maintenance under the national park system
As a foundational component of China’s ecological protection system, nature reserves at all levels have long played a critical role in maintaining biodiversity, optimizing landscape patterns, and sustaining ecosystem stability (Zhang et al., 2017). However, existing research indicates (Zhou and Grumbine, 2011; Li et al., 2016) that under the traditional protection model, most nature reserves are managed by the government, resulting in a series of issues such as redundant administrative work, lack of professional capacity, unclear responsibilities, and inefficient resource allocation. This management model not only weakens the overall coherence and scientific rigor of conservation efforts but also limits the coupled regulatory capacity between ecological functions and landscape structures. In contrast, national parks have enhanced representativeness and management effectiveness through expanded and optimized boundaries, streamlined institutions, and cohesive management (Zang et al., 2022). This system provides a more systematic and comprehensive governance framework for protecting ecosystems and biodiversity regions (Chen et al., 2023), demonstrating significant advantages in enhancing ecosystem stability and environmental quality. Since the implementation of the national park system, the ecological environment quality in the core area of pudacuo national park has significantly improved, with the RSEI consistently maintaining a level above 0.6. The pristine forest belt of Bita Lake and high-altitude wetlands have been effectively protected. This reflects the stabilizing effect of enhanced management intensity on high-quality ecological patches, indicating that the national park system has strong adaptability to high-altitude ecosystems.
Compared with research on national parks worldwide, Pudacuo national park’s practices share commonalities while also demonstrating unique characteristics. The Kainji National Park study found that effective protection of national parks and nature reserves contributes to improved biodiversity conservation, forest health, and urban air quality (Tang and Adesina, 2022). The Margalla Hills National Park study noted that the region possesses rich woody plant species diversity and abundance, with these species providing crucial ecological services to the entire ecosystem and playing a significant role in carbon sequestration (Ali et al., 2022). These cases align with the findings of this study, all indicating that national parks possess institutional advantages in maintaining landscape stability and improving ecological environment quality. However, Pudacuo national park, located on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, faces unique geographical and social environmental conditions, with slow ecological recovery processes and strong community cultural embeddedness, thereby imposing higher demands on management models.
From a methodological perspective, this study employs a comprehensive framework combining “landscape pattern indices and MSPA to analyze landscape pattern evolution characteristics, using RSEI to evaluate ecological environment quality, and integrating Spearman correlation coefficients, bivariate spatial autocorrelation, and geographic detectors to analyze and identify their spatial relationships.” This approach demonstrates innovation in quantitatively revealing the coupling mechanisms between landscape patterns and ecological environment quality. Compared to the commonly used correlation analysis or single regression methods in existing studies, this combination not only captures the structural characteristics of landscape spatial patterns (MSPA) but also dynamically reflects the spatiotemporal evolution of ecological environment quality. Spearman’s correlation coefficient and bivariate spatial autocorrelation are used to analyze and identify the spatial relationship between the two, while the geodetector quantifies the multi-factor driving mechanisms. This methodological framework provides more explanatory evidence for the ecological-landscape coupling relationships in complex high-altitude national parks and offers a replicable research approach for future management evaluations of other national parks and protected areas.
Although the national park system has demonstrated its advantages, its implementation faces practical challenges, particularly in terms of balancing tourism economy, community development, and ecological protection, which still need to be further optimized. Excessive tourism development in many national parks is raising serious concerns about the natural environment (Xu and Fox, 2014). The trade-offs between ecological protection and economic development make the management objectives of national parks face substantial challenges (Xue et al., 2023). Taking pudacuo national park as an example, the overconstruction of infrastructure and high-frequency use by tourists in the area of the Shudu Lake Scenic Area have led to frequent problems such as hardening of the ground surface, deterioration of ecological quality, pollution of soil and water, and obvious compression of ecological and environmental functions. Similar phenomena are also common in other parks, such as in the Qilian Mountain National Park, where the environmental responsibility behaviors of residents and tourists play a significant role in the protection of natural resources and the sustainable development of ecotourism (Wang Y. et al., 2023). A study on the landscapes surrounding 159 national parks in 11 European countries indicates that high natural and landscape values influence the extent and rate of landscape fragmentation, necessitating the formulation and implementation of relevant policies to strictly regulate the buffer zones around national parks (Kubacka et al., 2022). Therefore, when drawing on international experience, pudacuo national park needs to refine management measures in a way that is tailored to local conditions.
In addition, national parks also carry the two basic responsibilities of environmental protection and community development (Tan et al., 2021), how to balance ecological safety, minority livelihoods, and cultural continuity has become a special challenge for the governance of national parks. Neglecting local culture and restricting access to resources can significantly affect local communities’ satisfaction with park management and conservation outcomes (Allendorf and Conservation, 2007; He and Su, 2022). pudacuo national park is located in Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, and local Tibetan residents have a close relationship with the natural environment, and the institutional spatial control of the national park may limit their original livelihoods. Wei et al. pointed out that the key point lies in the ability of the residents to recognize the benefits of the national park’s tourism development (Wei et al., 2024).
Given the geographical and social context of Pudacuo, the following more actionable policy implications can be proposed: First, establish scientific ecological compensation standards and ensure the reasonable interests of communities surrounding core protected areas through a tiered compensation mechanism, even under resource usage restrictions; Second, set tourism carrying capacity thresholds and dynamically adjust visitor numbers and infrastructure development intensity based on ecological monitoring data; Third, promote a “government + community” co-management model to engage local Tibetan residents in ecological patrols, tourism interpretation, and resource monitoring activities. Through ecological compensation, industrial support, and ecological tourism cooperatives, enhance community ecological benefits and development momentum to establish a new win-win framework for ecological protection and community development; Fourth, given the challenges of high-altitude vegetation restoration—which is difficult and time-consuming—strengthen in situ restoration of degraded wetlands and forests, as well as ecological corridor construction, to enhance overall landscape connectivity and ecological stability.
In summary, the management practices of pudacuo national park demonstrate that the national park system possesses significant advantages in improving ecological environment quality. However, achieving ecological system integrity and sustainable development requires a management mechanism characterized by systematization, refinement, and coordination. In the future, as the system is further developed, it is essential to strengthen the coupling logic between ecological and social systems, promoting the coordinated development of ecological conservation, cultural heritage preservation, and community symbiosis.
4.4 Significance and future prospects
This study reveals the close relationship between landscape patterns and ecological environment quality, providing scientific references and practical guidance for ecological protection and management in the northwestern Yunnan Plateau region. Additionally, the findings offer theoretical support and practical insights for ecological assessment and development within Yunnan Province’s national park system, holding significant practical implications. Based on this, it is recommended that national park management authorities prioritize the protection of ecologically sensitive areas, scientifically balance ecological conservation, tourism development, and community interests, and effectively enhance landscape connectivity and the overall stability of ecological systems.
Although this study has achieved certain results, it still has some limitations. First, the time span of the remote sensing imagery used in the study is relatively short, making it difficult to fully reflect the long-term evolution of ecological environment quality. Second, the direct impact of natural factors such as climate change has not been explicitly incorporated, yet such factors may play an important role in highland ecosystems. Additionally, due to limitations in data acquisition and the characteristics of the study area, the consideration of socioeconomic variables in this study was relatively limited, primarily focusing on land use/cover changes as a direct driving factor, without systematically quantifying the indirect effects of macro-socioeconomic indicators on the ecological environment.
Future research could be conducted in the following areas: first, extending the time series and incorporating climate data to more comprehensively characterize the dynamic evolution of the ecological environment under the combined effects of climate change and human activities; Second, combining more detailed socioeconomic data (such as population density, nighttime light intensity, tourism activity intensity, and community participation) to explore the specific mechanisms through which human activities influence ecological environment quality via different pathways; Third, strengthening research on policy implications for landscape pattern optimization, particularly for high-altitude protected areas where conflicts between tourism and ecological conservation are prominent. Differentiated management strategies should be developed to maintain the ecological integrity of core zones while reasonably guiding tourism development and community livelihood activities, thereby achieving a win-win outcome for conservation and development.
Overall, this study not only provides valuable insights for ecological management practices in pudacuo national park but also offers a theoretical framework and methodological references for similar research in other high-altitude and fragile ecosystems. In the face of increasingly severe global environmental changes and regional human disturbances, how to balance ecological stability with socio-economic development will be a key challenge for achieving sustainable development in national parks in the future.
5 Conclusion
This study utilized remote sensing imagery from 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020, and 2024, employing landscape pattern indices, RSEI, MSPA, spatial analysis, and geodetectors to investigate the response mechanisms of ecological environment quality to landscape patterns in pudacuo national park. The main conclusions are as follows:
1. The overall landscape pattern of the park remains stable, with the core area maintaining high ecological integrity. The core area is primarily forested and distant from human settlements. In contrast, the edge zone is significantly influenced by natural and human disturbances, resulting in notable changes in landscape structure. This is particularly evident in areas with frequent tourist activities and geologically exposed zones, where the landscape pattern exhibits fragmentation, increased heterogeneity, and ecological function degradation.
2. From 2000 to 2024, ecological environment quality continued to improve, with the study area primarily classified as “good” quality, and the trend in ecological environment quality remained relatively stable. High-quality areas are primarily concentrated in core protected zones such as forested areas, where forest ecosystems play a crucial role in maintaining ecological environment quality; low-quality areas are primarily due to the impacts of tourism activities and desertification. Spatial autocorrelation analysis results indicate that ecological environment quality exhibits significant spatial positive correlation (Moran’s I > 0.679), with high-high (H-H) and low-low (L-L) clusters maintaining stable spatial patterns.
3. Landscape pattern indices exhibit significant spatiotemporal heterogeneity in explaining ecological environment quality. The spatiotemporal evolution of ecological environment quality in pudacuo national park is not only constrained by landscape fragmentation and core patch patterns but is also closely related to landscape diversity and overall spatial structure.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SZ: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Methodology. XL: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition. KR: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YC: Writing – review and editing. XiH: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project was funded by Major scientific and technological projects of Yunnan Province: Research on Key Technologies of ecological environment monitoring and intelligent management of natural resources in Yunnan (202202AD080010).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the funding. Thanks to the editors for their hard work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ai, J., Yang, L., Liu, Y., Yu, K., and Liu, J. J. L. (2022). Dynamic landscape fragmentation and the driving forces on haitan island, China. Land 11 (1), 136. doi:10.3390/land11010136
Ali, S., Khan, S. M., Siddiq, Z., Ahmad, Z., Ahmad, K. S., Abdullah, A., et al. (2022). Carbon sequestration potential of reserve forests present in the protected margalla hills national park. J. King Saud University-Science 34 (4), 101978. doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101978
Allendorf, T. D. J. B.Conservation (2007). Residents’ attitudes toward three protected areas in Southwestern Nepal. Biodivers. Conservation 16 (7), 2087–2102. doi:10.1007/s10531-006-9092-z
Boongaling, C. G. K., Faustino-Eslava, D. V., and Lansigan, F. P. J. L. u.p. (2018). Modeling land use change impacts on hydrology and the use of landscape metrics as tools for watershed management: the case of an ungauged catchment in the Philippines. Land use policy 72, 116–128. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.12.042
Chen, X., Yu, L., Cao, Y., Xu, Y., Zhao, Z., Zhuang, Y., et al. (2023). Habitat quality dynamics in China's first group of national parks in recent four decades: evidence from land use and land cover changes. J. Environ. Manag. 325, 116505. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116505
Damschen, E. I., Brudvig, L. A., Burt, M. A., Fletcher Jr, R. J., Haddad, N. M., Levey, D. J., et al. (2019). Ongoing accumulation of plant diversity through habitat connectivity in an 18-year experiment. Science 365 (6460), 1478–1480. doi:10.1126/science.aax8992
Dendup, P., Wangdi, L., Jamtsho, Y., Kuenzang, P., Gyeltshen, D., Tashi, T., et al. (2021). Bird diversity and conservation threats in jigme dorji national park, Bhutan. Glob. Ecol. Conservation 30, e01771. doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01771
Duan, H., Zheng, X., Li, S., Li, Y., Ye, L., Jing, H., et al. (2024). Vegetation restoration model and suggestions on its optimization in rocky desertification areas of Yunnan province. CARSOLOGICA Sin. 43 (1), 137–146. doi:10.11932/karst2021y13
Duo, L., Wang, J., Zhong, Y., Jiang, C., Chen, Y., Guo, X. J. I. J. o.C. S., et al. (2024). Ecological environment quality assessment of coal mining cities based on GEE platform: a case study of shuozhou, China. Int. J. Coal Sci. and Technol. 11 (1), 75. doi:10.1007/s40789-024-00723-8
Guo, B., Fang, Y., Jin, X. J. L. u.p., and zhou, Y. (2020). Monitoring the effects of land consolidation on the ecological environmental quality based on remote sensing: a case study of chaohu Lake basin, China. Land use policy 95, 104569. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104569
Guo, J., Shen, B., Li, H., Wang, Y., Tuvshintogtokh, I., Niu, J., et al. (2024). Past dynamics and future prediction of the impacts of land use cover change and climate change on landscape ecological risk across the mongolian Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 355, 120365. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120365
He, S., and Su, Y. J. L. (2022). Understanding residents’ perceptions of the ecosystem to improve park–people relationships in Wuyishan national Park, China. Land 11 (4), 532. doi:10.3390/land11040532
Hu, J., Zhang, J., and Li, Y. J. E. I. (2022). Exploring the spatial and temporal driving mechanisms of landscape patterns on habitat quality in a city undergoing rapid urbanization based on GTWR and MGWR: the case of nanjing, China. Ecol. Indic. 143, 109333. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109333
Huang, S., Li, Y., Hu, H., Xue, P., and Wang, J. J. G. I. (2024a). Assessment of optimal seasonal selection for RSEI construction: a case study of ecological environment quality assessment in the beijing-tianjin-hebei region from 2001 to 2020. Geocarto Int. 39 (1), 2311224. doi:10.1080/10106049.2024.2311224
Huang, Y., Yu, H., Xu, Y., and Jiang, Y. J. E. S.Technology (2024b). Evaluation of ecological environmental quality and analysis in linhai city based on GEE and remote sensing ecological index. Environ. Sci. Technol. (10036504) 47 (11). doi:10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.0767.24.338
Hussain, S., Mubeen, M., Ahmad, A., Akram, W., Hammad, H. M., Ali, M., et al. (2020). Using GIS tools to detect the land use/land cover changes during forty years in lodhran district of Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 (32), 39676–39692. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-06072-3
Ji, J., Wang, S., Zhou, Y., Liu, W., and Wang, L. J. I. A. (2020). Spatiotemporal change and landscape pattern variation of eco-environmental quality in jing-jin-ji urban agglomeration from 2001 to 2015. Ieee Access 8, 125534–125548. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3007786
Jiang, L., Liu, Y., Wu, S., and Yang, C. J. E. i. (2021). Analyzing ecological environment change and associated driving factors in China based on NDVI time series data. Ecol. Indic. 129, 107933. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107933
Kubacka, M., Żywica, P., Subirós, J. V., Bródka, S., and Macias, A. J. L. U. P. (2022). How do the surrounding areas of national parks work in the context of landscape fragmentation? A case study of 159 protected areas selected in 11 EU countries. Land Use Policy 113, 105910. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105910
Li, J., Wang, W., Axmacher, J. C., Zhang, Y., and Zhu, Y. J. S. (2016). Streamlining China's protected areas. science 351 (6278), 1160. doi:10.1126/science.351.6278.1160-a
Li, P., Zuo, D., Xu, Z., Zhang, R., Han, Y., Sun, W., et al. (2021). Dynamic changes of land use/cover and landscape pattern in a typical alpine river basin of the qinghai-tibet Plateau, China. Land Degrad. and Dev. 32 (15), 4327–4339. doi:10.1002/ldr.4039
Li, L., Tang, H., Lei, J., and Song, X. J. E. I. (2022). Spatial autocorrelation in land use type and ecosystem service value in Hainan tropical rain forest national park. Ecol. Indic. 137, 108727. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108727
Liu, C., Zhang, F., Johnson, V. C., Duan, P., and Kung, H.-t.J. E. I. (2021). Spatio-temporal variation of oasis landscape pattern in arid area: human or natural driving? Ecol. Indic. 125, 107495. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107495
Liu, Q., Qiao, J., Li, M., Dun, Y., Zhu, X., and Ji, X. J. J. o.C. P. (2024). Spatiotemporal evolution of ecological environmental quality and its dynamic relationships with landscape pattern in the zhengzhou metropolitan area: a perspective based on nonlinear effects and spatiotemporal heterogeneity. J. Clean. Prod. 480, 144102. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.144102
Ma, Y., Pan, J., Cai, S., Chen, Y., and Chen, Y. J. S. G. S. (2022). Trade-offs and synergies between social value and ecological value of ecosystem services: a case study of the potatso National park. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 42, 1283–1294. doi:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2022.07.015
Ma, B., Jing, J., Liu, B., Wang, Y., and He, H. J. G. E.Conservation (2023). Assessing the contribution of human activities and climate change to the dynamics of NPP in ecologically fragile regions. Glob. Ecol. Conservation 42, e02393. doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2023.e02393
Maimaitituersun, A., Yang, H., Aobuliaisan, N., Maimaitiaili, K., and Chenyu, O. J. E. I. (2025). Assessing subtle changes in arid land river basin ecological quality: a study utilizing the PIE engine platform and RSEI. Ecol. Indic. 170, 113035. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.113035
Masoudi, M., Richards, D. R., Tan, P. Y. J. J. o.G., and Analysis, S. (2024). Assessment of the influence of spatial scale and type of land cover on urban landscape pattern analysis using landscape metrics. J. Geovisualization Spatial Analysis 8 (1), 8. doi:10.1007/s41651-024-00170-8
Otukei, J. R., and Blaschke, T. J. I. J. o.A. E. O.Geoinformation (2010). Land cover change assessment using decision trees, support vector machines and maximum likelihood classification algorithms. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observation Geoinformation 12, S27–S31. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2009.11.002
Qi, T., Li, Y., Huang, M., Luo, B., Peng, Z., Wang, W., et al. (2024). Land intensification use scenarios based on urban land suitability assessment of the national park. Sustain. Cities Soc. 102, 105229. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105229
Qiu, M., Liu, Y., Chen, P., He, N., Wang, S., Huang, X., et al. (2024). Spatio-temporal changes and hydrological forces of wetland landscape pattern in the yellow River Delta during 1986–2022. Landsc. Ecol. 39 (3), 51. doi:10.1007/s10980-024-01850-y
Tan, S., Zhong, Y., Yang, F., and Gong, X. J. G. E.Conservation (2021). The impact of nanshan national park concession policy on farmers' income in China. Glob. Ecol. Conservation 31, e01804. doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01804
Tang, X., and Adesina, J. A. J. S. (2022). Biodiversity conservation of national parks and nature-protected areas in West Africa: the case of kainji national park, Nigeria. Sustainability 14 (12), 7322. doi:10.3390/su14127322
Wang, G., Innes, J. L., Wu, S. W., Krzyzanowski, J., Yin, Y., Dai, S., et al. (2012). National park development in China: conservation or commercialization? Ambio 41 (3), 247–261. doi:10.1007/s13280-011-0194-9
Wang, H., Liu, X., Zhao, C., Chang, Y., Liu, Y., and Zang, F. J. E. I. (2021). Spatial-temporal pattern analysis of landscape ecological risk assessment based on land use/land cover change in baishuijiang national nature reserve in Gansu province, China. Ecol. Indic. 124, 107454. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107454
Wang, Q., and Wang, H. J. E. g.health (2023a). Evaluation for the spatiotemporal patterns of ecological vulnerability and habitat quality: implications for supporting habitat conservation and healthy sustainable development. Environ. Geochem. health 45 (5), 2117–2147. doi:10.1007/s10653-022-01328-3
Wang, Y., Zhao, R., Yan, Z., Wang, M., Pan, Y., and Wu, R. J. P. o. (2023b). A comparative study of environmental responsibility behavior in ecotourism from the perceptions of residents and tourists: a case of Qilian Mountains national park in China. Plos one 18 (2), e0281119. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0281119
Wang, Q., Zhang, P., Chang, Y., Li, G., Chen, Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). Landscape pattern evolution and ecological risk assessment of the yellow river basin based on optimal scale. Ecol. Indic. 158, 111381. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111381
Wei, Q., Abudureheman, M., Halike, A., Yao, K., Yao, L., Tang, H., et al. (2022a). Temporal and spatial variation analysis of habitat quality on the PLUS-InVEST model for ebinur Lake basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 145, 109632. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109632
Wei, Q., Halike, A., Yao, K., Chen, L., and Balati, M. J. E. I. (2022b). Construction and optimization of ecological security pattern in ebinur Lake basin based on MSPA-MCR models. Ecol. Indic. 138, 108857. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108857
Wei, X., Pu, P., Cheng, L., Jiang, H., and Liu, Y. J. E. I. (2024). Ethnic community’s perception of benefit-sharing and participation intentions in national park tourism in China: an asymmetric modeling approach. Ecol. Indic. 166, 112257. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112257
Wu, Z., Zhu, D., Xiong, K., and Wang, X. J. E. I. (2022). Dynamics of landscape ecological quality based on benefit evaluation coupled with the rocky desertification control in south China karst. Ecol. Indic. 138, 108870. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108870
Wu, Z., Zhang, S., Liu, M., Wu, Z., Hu, X., and Lin, S. J. F. (2024). Impact of forest Landscape patterns on ecological quality in coastal cities of Fujian, China, from 2000 to 2020. Forests 15(11), 1925. doi:10.3390/f15111925
Xie, C., Zhao, M., Li, Y., Tang, T., Meng, Z., and Ding, Y. J. S. (2023). Evaluating the effectiveness of environmental interpretation in national parks based on visitors’ spatiotemporal behavior and emotional experience: a case study of pudacuo national park, China. Sustainability 15 (10), 8027. doi:10.3390/su15108027
Xiong, Y., Xu, W., Lu, N., Huang, S., Wu, C., Wang, L., et al. (2021). Assessment of spatial–temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: a case study in erhai Lake basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 125, 107518. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107518
Xu, F., and Fox, D. J. T. M. (2014). Modelling attitudes to nature, tourism and sustainable development in national parks: a survey of visitors in China and the UK. Tour. Manag. 45, 142–158. doi:10.1016/j.tourman.2014.03.005
Xu, H., Duan, W., Deng, W., and Lin, M. J. R. S. (2022). RSEI or MRSEI? Comment on Jia et al. Evaluation of eco-environmental quality in qaidam basin based on the ecological index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote sens. 2021, 13, 4543. Remote Sens. 14 (21), 5307. doi:10.3390/rs14215307
Xu, C., Li, B., Kong, F., and He, T. J. E. I. (2024). Spatial-temporal variation, driving mechanism and management zoning of ecological resilience based on RSEI in a coastal metropolitan area. Ecol. Indic. 158, 111447. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111447
Xue, S., Fang, Z., Bai, Y., Alatalo, J. M., Yang, Y., and Zhang, F. J. J. o.E. M. (2023). The next step for China's national park management: integrating ecosystem services into space boundary delimitation. J. Environ. Manag. 329, 117086. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117086
Yang, H., Zhong, X., Deng, S., and Nie, S. J. E. I. (2022). Impact of LUCC on landscape pattern in the yangtze river basin during 2001–2019. Ecol. Inf. 69, 101631. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2022.101631
Yang, H., Xu, W., Yu, J., Xie, X., Xie, Z., Lei, X., et al. (2023). Exploring the impact of changing landscape patterns on ecological quality in different cities: a comparative study among three megacities in eastern and Western China. Ecol. Inf. 77, 102255. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2023.102255
Yang, J., Deng, W., Zhang, G., and Cui, X. J. E. I. (2024). Linking endangered species protection to construct and optimize ecological security patterns in the national ecological civilization construction demonstration zone: a case study of yichang, China. Ecol. Indic. 158, 111579. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.111579
Yi, S., Zhou, Y., Zhang, J., Li, Q., Liu, Y., Guo, Y., et al. (2023). Spatial-temporal evolution and motivation of ecological vulnerability based on RSEI and GEE in the jianghan plain from 2000 to 2020. Front. Environ. Sci. 11, 1191532. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2023.1191532
Yohannes, H., Soromessa, T., Argaw, M., and Dewan, A. J. S. o.t.T. E. (2021). Impact of landscape pattern changes on hydrological ecosystem services in the beressa watershed of the Blue Nile basin in Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 793, 148559. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148559
Zang, Z., Guo, Z., Fan, X., Han, M., Du, A., Xu, W., et al. (2022). Assessing the performance of the pilot national parks in China. Ecol. Indic. 145, 109699. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109699
Zhang, T., and Chen, Y. J. F. i.p.s. (2022). The effects of landscape change on habitat quality in arid desert areas based on future scenarios: tarim river basin as a case study. Front. plant Sci. 13, 1031859. doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.1031859
Zhang, L., Luo, Z., Mallon, D., Li, C., and Jiang, Z. J. B. c. (2017). Biodiversity conservation status in China's growing protected areas. Biol. Conserv. 210, 89–100. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2016.05.005
Zhang, Y., She, J., Long, X., and Zhang, M. J. E. I. (2022). Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of eco-environmental quality based on RSEI in chang-zhu-tan metropolitan circle, central China. Ecol. Indic. 144, 109436. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109436
Zhang, X., Zhong, L., and Zhang, H.J Ecological Indicators (2023). Using propensity score matching models to assess the protection effectiveness in pudacuo national park, China. Ecol. Indic. 150, 110222. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110222
Zhang, X., Jia, W., Lu, S., and He, J. J. E. I. (2024). Ecological assessment and driver analysis of high vegetation cover areas based on new remote sensing index. Ecol. Inf. 82, 102786. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2024.102786
Zhang, Y., Vanclay, F., and Hanna, P. J. L. U. P. (2025). How communities and social impacts are considered in policies for protected areas in China. Land Use Policy 148, 107404. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2024.107404
Zhao, Z., Lu, C., Tonooka, H., Wu, L., Lin, H., and Jiang, X. J. S. R. (2025). Dynamic monitoring of vegetation phenology on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 2001 to 2020 via the MSAVI and EVI. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 25698. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-11821-1
Zhou, D., and Grumbine, R. E. J. B. C. (2011). National parks in China: experiments with protecting nature and human livelihoods in Yunnan province, peoples’ Republic of China (PRC). Biol. Conserv. 144 (5), 1314–1321. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2011.01.002
Keywords: ecological quality, landscape pattern, National Park, RSEI, MSPA
Citation: He X, Zhang S, Li X, Ran K, Chen Y and Huang X (2025) Evolution of landscape pattern and ecological environment effect in Pudacuo National Park, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1653103. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1653103
Received: 24 June 2025; Accepted: 28 August 2025;
Published: 26 September 2025.
Edited by:
Nina Lam, Louisiana State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Jianhua Xiao, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaZhongsheng Chen, China West Normal University, China
Kai Sun, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright © 2025 He, Zhang, Li, Ran, Chen and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoyuan Huang, aHh5MjFjbkBzd2Z1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Xuejuan He
Xuejuan He Shunmin Zhang1
Shunmin Zhang1 Xiaona Li
Xiaona Li