- 1School of Economics, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou, China
- 2School of Marxism, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
The artificial intelligence (AI) innovative application pilot policy is a key measure to promote energy saving and emission reduction in Chinese cities. This study employs a quasi-natural experiment approach, utilizing urban carbon emission data from 2003 to 2021 in China, to investigate the impact of the AI pilot policy on urban carbon emissions through a difference-in-differences (DID) model. After conducting a series of robustness tests, we find that the AI pilot policy exerts a significant inhibitory effect on urban carbon emissions. Mechanism analysis reveals that this policy reduces carbon emissions by enhancing the adoption of urban green technology and strengthening environmental regulations. Further analysis indicates that the carbon reduction effect of the AI pilot policy is more pronounced in cities with high levels of scientific and technological capacity, high market potential, advanced financial development, and well-established digital infrastructure. This study enriches and demonstrates the implementation effects of AI development in China, providing decision-making references for vigorously promoting AI innovation application policies and advancing urban sustainable development and the dual carbon goals.
1 Introduction
China’s economic development has transitioned from catching up to keeping pace with, and ultimately leading, the global economy. However, the pursuit of economic benefits has led to environmental degradation, which has become a significant constraint on sustainable development. Among these challenges, carbon emissions are a direct cause of frequent ecological problems such as extreme climate changes and the greenhouse effect. From the Kyoto Protocol to the Paris Agreement, the concept of sustainable development has been consistently emphasized, and global collaboration on ecological and environmental governance has become a fundamental consensus (Sethi et al., 2020). China’s urbanization rate had reached 67%1, with urban carbon emissions accounting for approximately 80% of the country’s total national emissions. Cities are thus the primary sources of carbon emissions. Therefore, studying carbon reduction in Chinese cities is both representative and rational. Faced with the global challenge of carbon emissions, China has pledged to achieve carbon peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060, thereby contributing its wisdom and experience to the sustainable development of other developing countries. Adhering to the principle that science and technology are the primary productive forces, China emphasizes “relying on scientific and technological power to strengthen environmental protection”. AI technology, with its powerful capabilities in data collection, information analysis, and scientific prediction, provides technical support and innovative momentum for green development.
In existing academic research, studies on factors influencing carbon emissions can be broadly categorized. The first category focuses on analyzing the diverse factors affecting carbon emissions (Wan and Yu, 2025). Existing research suggests a proportional relationship between urban population activity levels and carbon emissions (Wei and Liu, 2022). Overall, urban carbon emissions exhibit a decreasing trend from the city center to the periphery (Zeng et al., 2019). Local governments have formulated relevant environmental regulations to ensure institutionalized ecological construction (Zhang J. et al., 2022). In the information era, AI has emerged as a significant force in carbon reduction. It increasingly highlights the importance of new digital elements in environmental governance, such as the Internet of Things (Alpan et al., 2022). Industrial robots reduce pollutant emissions intensity by improving energy efficiency and enhancing pollution reduction technologies (Li et al., 2025).
The academic consensus maintains that the relationship between AI and the ecological environment follows an inverted U-shaped curve (Dong et al., 2024). This implies that in the early stages of AI application, establishing data centers during the integration of AI technology with industries such as automobile manufacturing, energy extraction, and smart factories consumes substantial amounts of computational resources and electrical energy (Zhang et al., 2023). According to data from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, by 2030, the total energy consumption of data centers in China is projected to reach approximately 380 billion kilowatt-hours,2 which may exacerbate urban carbon emissions. This suggests that AI technology may initially lead to an environmental rebound effect (Wu et al., 2023). However, once AI reaches a mature stage of long-term application, it is expected to exert a significant inhibitory effect on carbon emissions. The primary reason is that AI can rationally optimize industrial structures and resource allocation through big data analytics, thereby reducing resource waste and lowering carbon emissions (Alhasnawi et al., 2024). Additionally, AI can enhance energy efficiency and reduce energy consumption and pollution by promoting the innovative application of clean and renewable energy sources (Chen and Jin, 2023).
The second category of research focuses on the relationship between AI policy and carbon emissions. AI is widely applied in life, effectively promoting the digital transformation of production and lifestyle (Sharma and Sharma, 2024). However, it also introduces new social issues such as digital hegemony and information risks (Cheatham et al., 2019). Development-oriented policies emphasize government-led and market-led innovation applications of AI technology, while regulatory policies stress the scientific monitoring, assessment, and control of risks associated with AI (Wang K. et al., 2025). It has been found that AI significantly reduces carbon emissions through mechanisms such as industrial structure optimization, technological innovation, and resource allocation. This suppressive effect is influenced by factors such as regional heterogeneity and differences in resource endowments (Wu et al., 2021). AI policies are more effective in reducing carbon emissions in cities with higher levels of economic development, better resource endowments, and larger urban sizes. Based on preliminary research, scholars have proposed expanding the scope of pilot cities for AI policies, accelerating the application of green innovation technologies, and enhancing the construction of digital infrastructure (Zhong et al., 2024).
In this context, the goals of AI pilot policies are aligned with those of carbon emission reduction. As an essential policy for high-quality urban development, what effects do AI pilot policies exert on urban carbon emissions? Through which specific mechanisms do these effects operate? How can the impact of AI policy on carbon emissions be scientifically evaluated? These questions merit further exploration. Building on the preceding analysis, this study leverages the AI pilot policy as a quasi-natural experiment, utilizing urban carbon emission data from China spanning the period from 2003 to 2021 as the research sample. The study employs the DID model to examine the impact of the AI pilot policy on urban carbon emissions, thereby contributing to the accurate assessment of the policy’s environmental effects and informing policy optimization.
The marginal contributions of this paper are as follows:
First, this paper employs a more recent and comprehensive data sample. Specifically, this paper selects urban carbon emission data from 2003 to 2021. This timeframe is based on the issuance of China’s “Comprehensive Work Plan for Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction” in 2007 and the “AI Innovation Application Pilot Zone” in 2019. Compared with the existing studies on a country’s carbon emissions (Cao et al., 2025) and urban panels (Chen et al., 2022), the application of AI policies in China still needs further expansion. Since policy implementation requires a transition period, the sample period is extended from 2003 to 2021.
Second, this study focuses on carbon emission data of Chinese cities. There are 220 city samples in total, among which 12 are pilot cities. Existing research has primarily concentrated on carbon emissions data at the provincial (Hao et al., 2019) and enterprise levels in China (Lee et al., 2024). However, Chinese cities warrant attention because their panel data offer more detailed information than provincial data, providing greater reference value for policy recommendations. Moreover, as administrative units, Chinese cities possess more autonomy and can develop specific AI policies and carbon reduction strategies tailored to their unique conditions.
Third, the selection of key research mechanisms. Scholars have effectively analyzed the impact of AI technology on reducing carbon emissions (Wang et al., 2019), technological innovation (Zhang, 2021), and energy efficiency (Akram et al., 2020). This paper selects green innovation and environmental regulation as the key mechanisms because the link between green technology innovation and AI technology is powerful. The most direct manifestation of AI applications is the promotion of intelligent, digital, and precise innovations in relevant fields. National macroeconomic policies emphasize environmental protection primarily through ER as a key instrument. As a form of environmental regulation, AI policies should be promptly integrated into energy conservation and emission reduction tasks. This study provides an empirical evaluation of the policy implementation effects, laying a foundation for expanding pilot policies.
Fourth, the endogenous analysis of heterogeneous cities. Cities are inherently complex social entities, and Chinese cities, in particular, exhibit significant heterogeneity due to varying natural geographical conditions and levels of socioeconomic development. As relatively independent research subjects, Chinese cities display marked differences in various aspects, including technological development levels, market development potential, financial development status, and digital infrastructure. These intrinsic conditions are directly related to the implementation effects of AI pilot policies within urban economic and social contexts. The analysis of heterogeneity provides a basis for formulating specific strategies and identifying future development directions in the implementation of AI pilot policies.
2 Institutional background and research hypotheses
2.1 Institutional background
China is now in a new stage of development. It focuses on high-quality growth to meet people’s needs for a better life. AI technology has become a key driving force for high-quality development. However, the widespread application of AI necessitates not only robust policy support but also advanced hardware infrastructure. Therefore, it is imperative to innovate national AI policy frameworks and expedite the implementation of AI pilot programs. In 2017, the General Office of the State Council of China issued the Notice on the Development Plan for a New Generation of Artificial Intelligence, establishing a high-level strategic framework for AI development in the country. These policies have established a conducive policy environment for AI development and promoted its extensive integration into economic production, political construction, cultural advancement, social harmony, and ecological management. Since 2019, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China has supported the establishment of the Shanghai AI Innovation Application Pilot Zone to promote the innovative development and application of artificial intelligence.3 By the end of 2022, China had established 12 pilot zones. These include Shanghai (2019), Jinan (2019), Qingdao (2019), Shenzhen (2019), Beijing (2021), Tianjin (2021), Hangzhou (2021), Guangzhou (2021), Chengdu (2021); Nanjing (2022), Wuhan (2022), and Changsha (2022). During the same period, the Ministry of Science and Technology of China issued the “Guidelines for the Construction of National New Generation Artificial Intelligence Innovation Development Pilot Zones.” These policies effectively promote the organic integration of AI technology and urban sustainable development.
2.2 Theoretical foundations and research hypotheses
From a production perspective, the difficulty of reducing carbon emissions lies in local governments’ pursuit of high economic benefits without considering the environmental impact. This often leads to the extensive use of high-pollution resources and high-consumption energy in the production process, thereby directly increasing carbon emissions (Wang et al., 2016). Politically, the gap between national environmental regulations and their local implementation is a critical issue. Local governments may struggle to effectively curb carbon emissions and protect the ecological environment due to inadequate social conditions for policy implementation, insufficient awareness of policy importance, and a lack of attention to policy details. These factors result in environmental regulations failing to achieve their intended policy outcomes (Xu et al., 2014). AI technologies are evolving rapidly and being widely applied across diverse production and daily life scenarios. Their digitalization, intelligence, and autonomy provide new technological tools and opportunities for energy conservation and emission reduction. To seize the developmental advantages offered by technologies, China has introduced relevant policies aimed at establishing a series of digital platforms and digital industries. These initiatives leverage AI to drive new industrialization. AI technologies facilitate the upgrading and transformation of urban economic and industrial structures, foster technological innovation, and enhance energy efficiency, thereby reducing carbon emissions. Furthermore, AI technology can supply local governments with detailed and precise data on carbon emissions, energy utilization, and air quality indices, serving as a foundation for decision-making (Liu et al., 2019). Additionally, it can also drive the transformation of high-consumption and high-pollution energy industries toward greener and lower-carbon industries, thereby significantly mitigating urban carbon emissions (Lin and Zhou, 2021). From a macro perspective, cities implementing AI pilot policies can more effectively promote energy conservation and emission reduction efforts with the support of advanced information technologies, such as AI. Based on the theoretical analysis above, the following hypothesis can be proposed:
H1. AI pilot policies have a significant inhibitory effect on urban carbon emissions.
Green innovation represents a bidirectional integration of technology and ecology, incorporating the concepts of ecology, environmental protection, and sustainable development. It serves as a critique and reflection on the societal trends that celebrate technological rationality. Green innovation technologies refer to those technologies and products that are capable of reducing the negative impact of production while simultaneously enhancing economic benefits for enterprises (Yi et al., 2020). In summary, the essential characteristic of green innovation technology is its positive environmental impact, typically achieved by reducing energy consumption and improving energy efficiency to generate ecological benefits (Rennings, 2000). As an advanced technology, green innovation balances economic production with ecological conservation. Innovations in green clean technologies and manufacturing processes play a pivotal role in reducing environmental pollution. The number of green patent inventions in a city constitutes a robust metric for evaluating the level of green innovation technology. AI provides vast quantities of data and innovative directions for advancing green technology, facilitating the modernization and high-quality development of traditional industries in cities. By achieving large-scale application of AI, marginal costs are reduced (Biggi et al., 2025). This improves coordination efficiency among enterprises during economic production, reduces resource wastage in business operations, and enables the achievement of cleaner and more efficient business models (Otsuka et al., 2014). AI directly elevates the level of green innovation technologies in cities, thus offering a viable approach to reducing urban carbon emissions.
H2. AI pilot policies reduce carbon emissions by promoting green innovation technologies.
The Chinese government actively establishes relevant policies, laws, and environmental protection regulations to promote energy conservation and emission reduction efforts. Undoubtedly, the implementation of environmental regulations may increase costs for urban economic development. This could potentially lead to suboptimal outcomes in energy conservation and emission reduction, as well as insufficient development of green innovation. However, provided that a policy adaptation period is allowed, it can be observed that ecological protection policies can play a supervisory and managerial role in reducing carbon emissions. Nonetheless, specific issues require specific analysis, and the implementation of environmental regulations must be adapted to local conditions (Liu et al., 2022). Based on the mechanism of action, environmental regulations can be categorized into command-and-control, market-driven, and voluntary environmental regulations (Ren et al., 2018). All three types of environmental regulations require ecological and environmental data as the basis for policy formulation. The application of AI policies provides robust support for enhancing environmental regulations. Artificial intelligence technologies provide reference data for policy assessment in environmental regulations. This encompasses environmental monitoring standards, pollutant emission criteria, clean production benchmarks, green taxation, carbon emission trading schemes, environmental subsidies, and access to environmental protection information (Tang et al., 2020). Integrating artificial intelligence technology with environmental regulations helps to reduce the implementation cost associated with these regulations. For governments, this integration facilitates real-time monitoring of carbon emissions through digital and networked regulatory frameworks. For society and individuals, the internet enables the rapid dissemination and timely access to information on environmental regulations. This enhances public awareness and understanding of ecological and environmental protection and related scientific knowledge (Zhang L. et al., 2022). Moreover, this integration achieves a combination of institutional carbon emission regulations and voluntary compliance by stakeholders.
H3. AI pilot policies enhance the institutionalization and sustainability of urban carbon reduction efforts by refining environmental regulations, thereby effectively reducing carbon emissions.
3 Study design
3.1 Model
To examine the relationship between AI pilot policy and carbon emissions, this study employs a multi-period DID model. The model is constructed as follows:
In the model, CO2 represents the dependent variable, where i and t denote the city and the year, respectively. Treat is a dummy variable that takes one if the city is within the AI policy pilot area, and zero otherwise. Post is a dummy variable that equals 1 for the year when the policy is implemented in city i and for all subsequent years, and zero otherwise. X represents a set of control variables. φ denotes fixed city effects, μ represents fixed annual effects, and ε denotes the random error term.
3.2 Variable selection
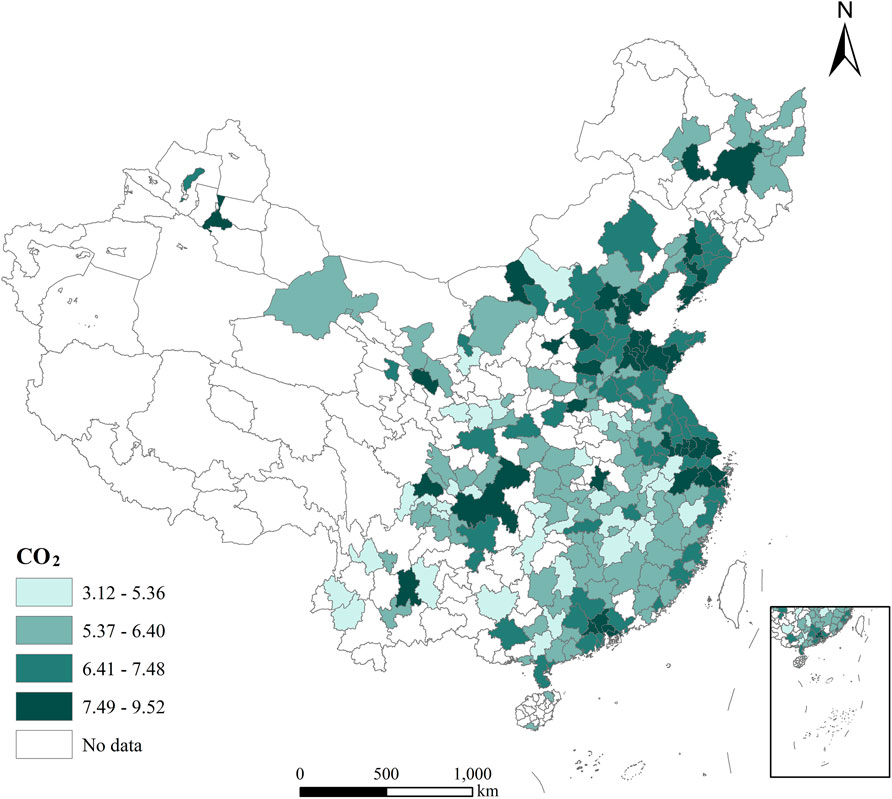
Dependent Variable (CO2): Carbon emissions. Carbon emissions are influenced by urban industrial production, economic structure, and transportation activities etc. The carbon emissions data are sourced from the cities’ CO2 emissions inventory published by the China Emissions Accounts and Datasets (CEADS). The spatial distribution map of carbon dioxide emissions in Chinese Cities is shown in Figure 1.
Independent Variable (DID): Artificial Intelligence Pilot Policy. Since 2019, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China has supported the establishment of the Shanghai AI Innovation Application Pilot Zone to promote the innovative development and application of artificial intelligence. By the end of 2022, China had established 12 pilot zones. These include Shanghai (2019), Jinan (2019), Qingdao (2019), Shenzhen (2019), Beijing (2021), Tianjin (2021), Hangzhou (2021), Guangzhou (2021), Chengdu (2021); Nanjing (2022), Wuhan (2022), and Changsha (2022). For cities that participated in the pilot after 2019, the interaction term Treat × Post is set to 1; otherwise, it is set to 0.
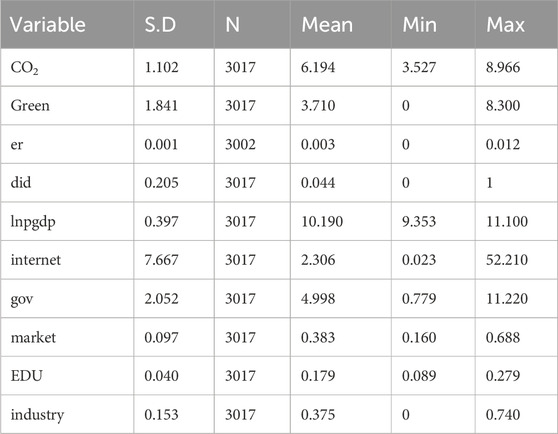
Control Variables: To better identify the impact of the AI pilot policy on urban carbon emissions, this study includes the following control variables, based on relevant literature (Ding et al., 2023): Financial support intensity (gov) is measured by the ratio of fixed asset investment to local government public budget expenditures. The industrialization level (industry) is measured by the ratio of industrial added value to local government GDP. Education Spending Level (EDU) is measured by the ratio of city educational expenditures to local government public budget expenditures. Economic Development Level (Inpgdp) is measured by the logarithm of per capita GDP. Internet Penetration Rate (internet) is measured by taking the logarithm of the number of internet users. Market potential level (market) is measured by the ratio of total social retail consumption to GDP. The descriptive statistics of these variables are presented in Table 1.
Mediating variables: Considering that green patent data can better respond to green innovation in cities, this paper draws on Wan (2024). According to the “Green List of International Patent Classification” launched by the WIPO in 2010, which aims at facilitating the retrieval of patent information related to environmentally friendly technologies, and based on the patent classification number of the State Intellectual Property Office (SIPO), the number of green patent applications filed by the city each year is matched. Green invention patents and green utility model patents are a core indicator of the city’s green innovation activities. This study adopts the research methods proposed by Hoffmann et al. (2022), utilizing the proportion of environmental protection content in annual summary reports produced by local governments to measure the intensity of local environmental regulations.
3.3 Data description
For empirical analysis, this paper uses carbon emission data from 220 cities in China from 2003 to 2021 as the initial research sample. The detailed data on carbon emissions for Chinese cities comes from the China Emission Accounts and Datasets (CEADS). Following the approach of Chen et al. (2020), the carbon emissions data in this study are derived from county-level CO2 emissions data calculated in the literature and aggregated to the city level to highlight regional differences in urban carbon emissions. The National Bureau of Statistics provides data on population, total foreign-invested industry investment, and GDP. Additional data are obtained from mainstream databases, including the National Bureau of Statistics, the National Intellectual Property Administration, the “China Statistical Yearbook”, the “China City Statistical Yearbook”, the “China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook”, the ESP database, and the Guotai’an database.
4 Empirical analysis
4.1 Parallel trend test
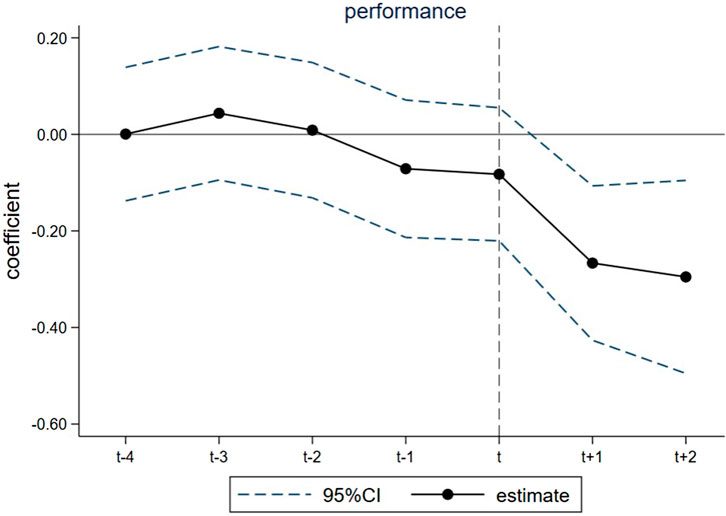
Satisfying the parallel trends assumption is a crucial prerequisite for conducting DID analysis. Figure 2 illustrates the trend of urban carbon emissions both before and after the policy’s implementation. At the policy implementation time point (t), the coefficient exhibits a significant decrease, indicating that the AI policy has an immediate and substantial impact on carbon emissions. As time progresses, the policy’s effect persists, suggesting that the AI policy has a long-term positive impact on urban carbon emissions.
4.2 Baseline regression results
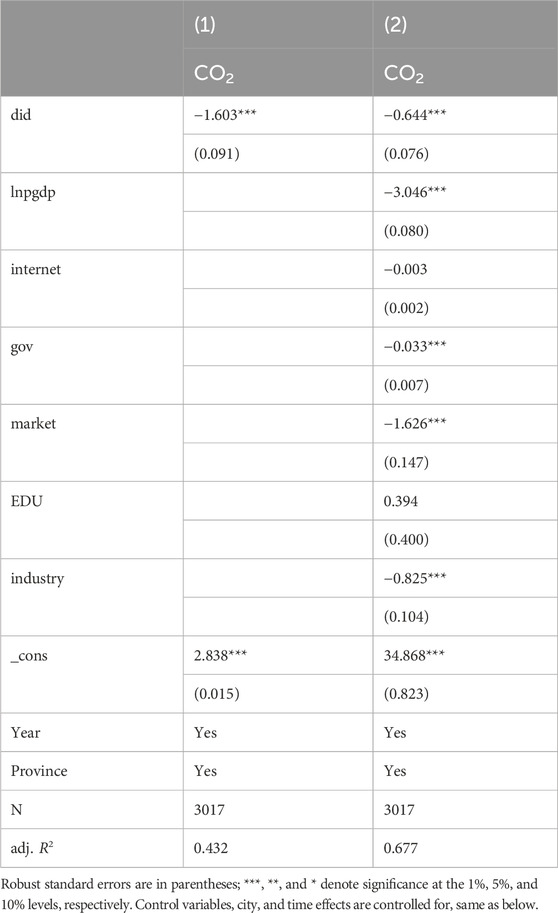
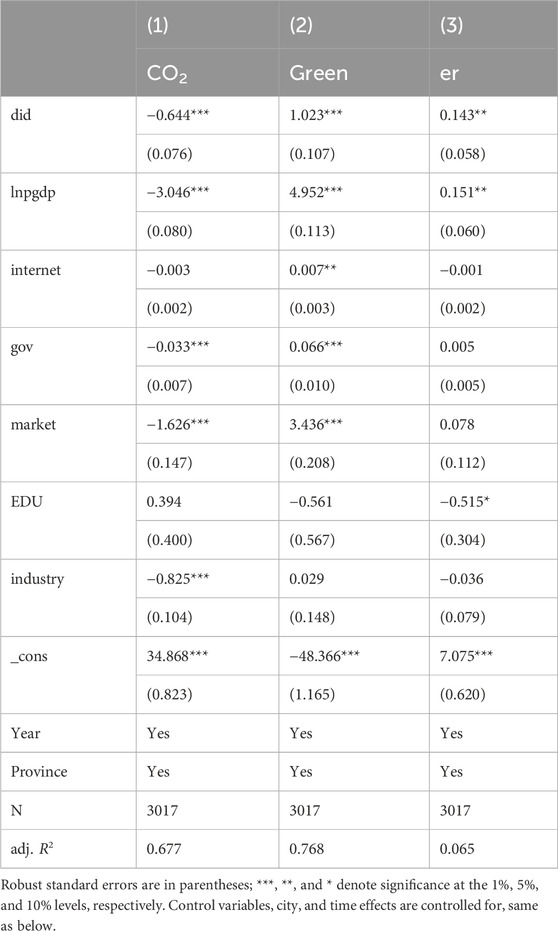
Table 2 displays the impact of the AI pilot policy on urban carbon emissions. Column (1) presents the estimated effects without considering control variables. The regression results indicate that incorporating control variables enhances the estimated effectiveness of the AI pilot policy in reducing urban carbon emissions. Specifically, the magnitude of the negative coefficient for the policy’s impact becomes more pronounced after accounting for these variables, suggesting a more potent effect. The observed enhancement in policy effectiveness can be attributed to several key control variables. First, economic development and fiscal support provide financial backing and policy assistance for advanced AI technologies (Lauterbach, 2019). Second, expenditures on education and internet penetration rates create a talent pool that supports the implementation of the AI pilot policy, facilitating the spillover of knowledge and skills (Sanusi et al., 2022). Third, market potential and the level of industrialization enhance market competitiveness for AI technological innovation. These control variables directly influence the implementation of the AI pilot policy and, consequently, its effectiveness in reducing urban carbon emissions.
4.3 Mechanism test
Consistent with the theoretical analysis presented earlier, the AI pilot policy is expected to have a significant impact on urban carbon emissions by promoting green technology and intensifying environmental regulations in cities.
1. Green Innovation. The AI pilot policy influences carbon emissions through green innovation, primarily by enhancing the level of green technology (Qu et al., 2024). According to China’s “Green Technology Patent Classification System” document, green technology patents refer to environmentally friendly green technology that can reduce energy consumption. Due to the large number of green patents, logarithmic statistical methods are used to analyze them in the study. The integration of AI technology provides a new impetus for green innovation, with mutual influence and promotion between the two (Wang Q. et al., 2025). Specifically, the capabilities of AI technology in big data analysis, algorithm optimization, and intelligent recommendation are applied to green technologies to enhance the level of intelligent monitoring of carbon emissions (Yi et al., 2024). The statistical accounting of carbon emissions is a crucial foundational task. The Chinese government has proposed the “Work Plan for Improving the Carbon Emission Statistical Accounting System,” which calls for establishing a national carbon emissions data platform by integrating AI with green innovation concepts. By leveraging the powerful computing capabilities of AI, big data, and cloud algorithms, it is possible to implement intelligent supervision of energy consumption, conduct scientific analysis of carbon emission data, and achieve precise tracking of carbon emission sources. This integration creates a green information AI management system (Cheng et al., 2025). According to China’s “National Carbon Market Development Report (2024)”, the national power sector’s carbon emission intensity decreased by 8.78% in 2023, achieving the dual goals of enhancing AI technology and protecting the ecological environment.
AI technology can facilitate the research and development of green innovation patents, promoting a green culture (Lin et al., 2024). By matching and identifying green patents through their classification codes, we can determine the number of green invention patents granted to enterprises. The application of green artificial intelligence patents can effectively enhance the carbon reduction rate of urban fossil fuels, improve the rational layout of industrial structures, increase the proportion of low-carbon emerging industries, and promote the full utilization of clean and renewable energy sources. This, in turn, facilitates the greening of the production process and the ecological production of products, thereby promoting the green transformation of social enterprise production (Liang et al., 2024). Green technologies based on AI should align with international green patent technologies to enhance the scientific accuracy and global recognition of carbon emission data monitoring and accounting. This alignment provides technical expertise for carbon reduction efforts in other countries (Sands, 2023). The results are shown in column 2 of Table 3.
2. Environmental Regulation. Ecological and environmental protection is a pressing issue that needs to be addressed in the pursuit of Chinese-style modernization. According to the 2024 Chinese government report, comprehensive governance of the ecological environment is emphasized as a key priority, with the implementation of a series of environmental regulations aimed at enhancing the modernization level of ecological governance. Environmental regulations are a set of systems proposed by the government to address ecological and environmental protection, adaptation to climate change risks, and other related issues (De Almeida et al., 2021). Chinese environmental regulations emphasize leveraging the principal capabilities of local governments, with cities serving as the leading construction carriers. There is a push to enhance the construction of digital and AI infrastructure to improve the level of intelligence in urban governance modernization (Roberts et al., 2021). From a content perspective, AI offers intelligent conditions for enhancing the effectiveness of environmental governance. Against the backdrop of pilot policies on AI, environmental regulation is exhibiting new characteristics, such as networking, intelligence, and digitalization. With the carbon emission data and its dynamic emission patterns provided by AI infrastructure, local governments can conduct digital monitoring of carbon emissions across various industries. This enhances the efficiency of environmental pollution monitoring and expands the scope of government environmental regulation (Makhkamov, 2022).
From a methodological perspective, the AI pilot policy has innovated the governance concept of environmental regulations. It has creatively proposed new methods of environmental protection in the cyberspace domain, such as “Internet courts” and “virtual space law” (Ramich and Piskunov, 2022). These innovations have improved the perfection of the environmental regulation system, creating a flexible, diverse, and complementary multi-tiered system that is well-suited to local conditions. From the perspective of stakeholders, environmental regulations outline the responsibilities of governments, societies, businesses, and individuals in environmental protection. These regulations emphasize the need for the entire society to integrate environmental consciousness into both production and daily life. The use of internet information technology accelerates and broadens the dissemination of environmental regulation content, which is beneficial for cultivating autonomous awareness and social consensus among all stakeholders involved in environmental protection (Nie et al., 2022). According to the data in column (3) of Table 3, cities that have adopted pilot AI policies have enhanced the digital and intelligent capabilities of their environmental regulation systems through modern network information technology. This enhancement supports the normalization and long-term effectiveness of urban carbon emission reduction efforts, thereby suppressing urban carbon emissions.
4.4 Robustness test
4.4.1 Placebo test
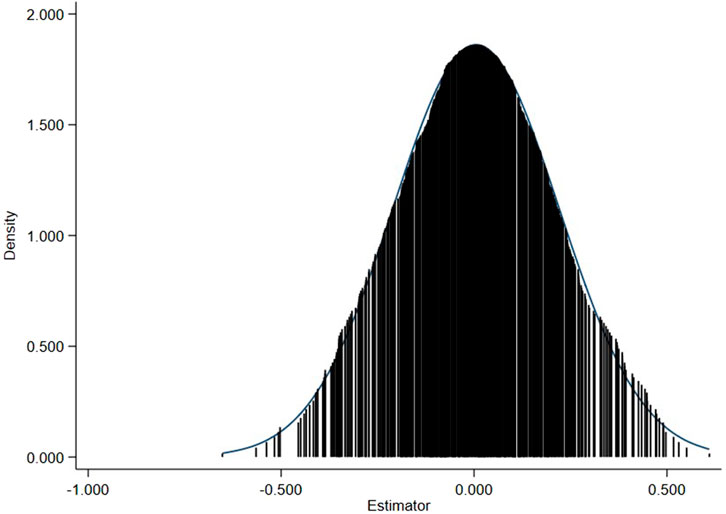
To ensure that the statistically significant results of the AI pilot policy on carbon emissions are not driven by unobserved confounding variables, this study conducted a placebo test. Specifically, a computer was used to generate new treatment groups randomly, and this process was repeated 500 times. The DID model was then applied to analyze the regression results. As shown in Figure 3, the results form a roughly normal distribution centered around zero. This indicates that, in the randomly generated treatment groups, most of the evaluation results are close to 0, showing no significant effect. Therefore, the robustness of the study’s results is confirmed.
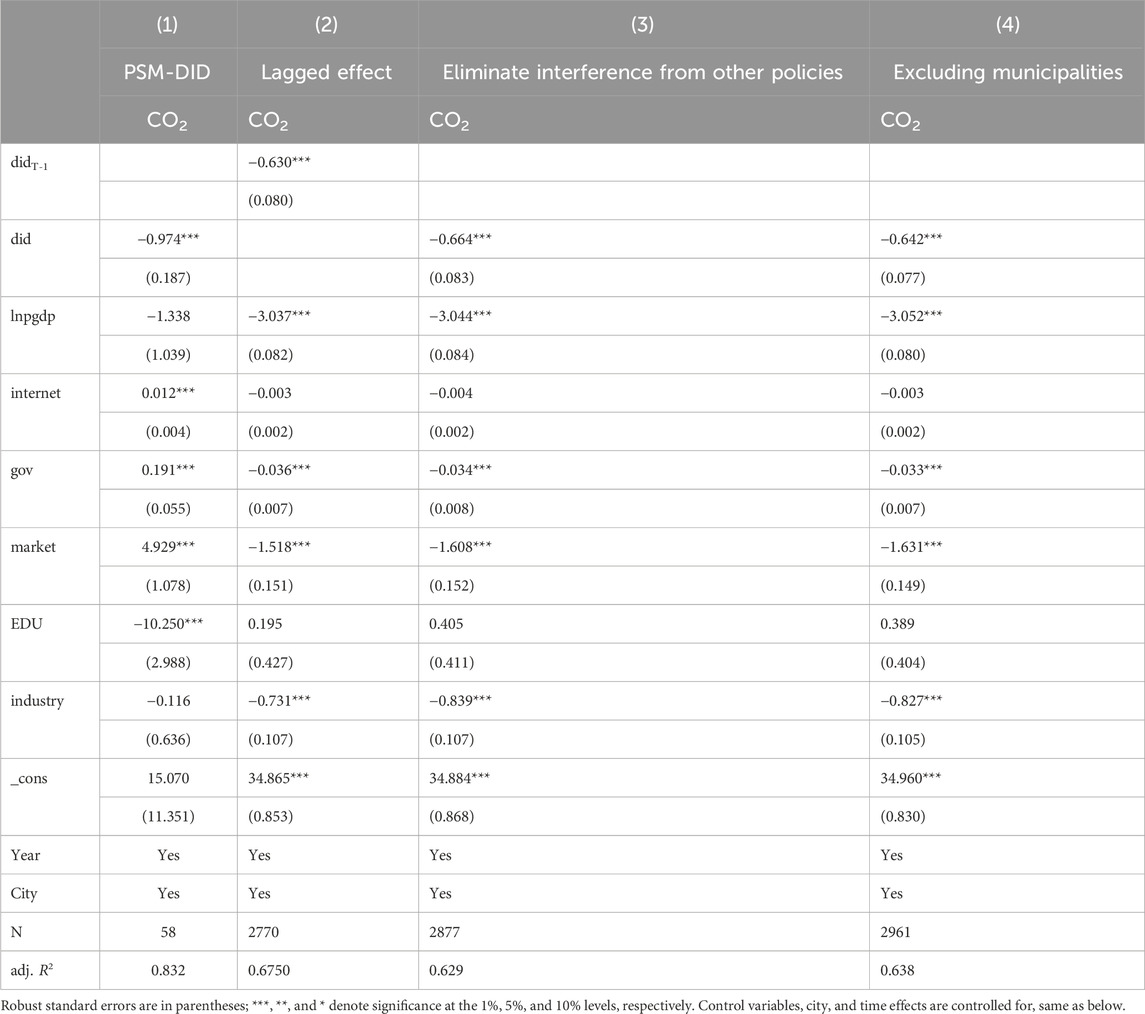
4.4.2 PSM-DID
This study conducted a PSM-DID test to enhance the credibility of the research conclusions. Specifically, the study incorporated fiscal support intensity (gov), educational expenditure (EDU), economic development level (lnpgdp), internet penetration rate (internet), market potential (market), and level of industrialization (industry) as control variables. The results are shown in column (1) of Table 4.
4.4.3 Lagged effect
From the issuance of notifications by the central government to the pilot phase, and then to the specific implementation of the promotion, a time lag is required; hence, the effects of policy implementation will exhibit significant latency. To more scientifically assess the impact of the AI innovation pilot policy on urban carbon emissions, it is necessary to conduct a one-period lag regression test. The data show that the AI innovation pilot policy still significantly inhibits urban carbon emissions. The results are shown in column (2) of Table 4.
4.4.4 Eliminate interference from other policies
During China’s carbon reduction reform to achieve the dual carbon goals of the new era, multiple policies often overlap or occur concurrently. For example, within the data sample period of this article (2003–2021), China initiated low-carbon city pilot policies in 2010. Starting in 2011, carbon emission trading pilots were implemented in economically developed regions, including Shenzhen, Shanghai, and Beijing. The carbon emission trading market was officially launched in 2017. In 2018, the “Environmental Protection Tax Law” was implemented formally. These policies have directly enhanced the effectiveness of China’s carbon reduction efforts (Zhang et al., 2020). During this period, some related policies were also introduced. For example, scholarly research has demonstrated the significant impact of the total pollutant emission control system, the Energy Conservation Law, China’s coal-to-gas policy, and competitive corporate policies (Xie and Wu, 2024). Although the forms and contents of policies are diverse, low-carbon cities, carbon emission trading, and environmental protection taxes are directly related to the issue of carbon emissions. Therefore, this study primarily focuses on mitigating the disruptive effects of these policies. These policies intersect with the AI pilot policy in terms of content and overlap in time, which may potentially affect the baseline regression results of this paper. To avoid the influence of these carbon emission-related policies, samples affected by other policy interferences were excluded, and the analysis was rerun. The results are shown in column (3) of Table 4.
4.4.5 Excluding municipalities
In China, municipalities hold a higher administrative status than ordinary cities. This elevated position enables them to attract more policy support, financial investment, technological resources, and talent, thereby creating advantageous conditions for the implementation of AI pilot policies. In comparison, ordinary cities often trail those directly under the Central Government in terms of technological progress and autonomy in policy implementation (Zhao and Wang, 2022). Failing to account for these differences may introduce bias into the study’s estimated results. To address this concern, the analysis excluded carbon emission data from Chinese municipalities and performed a new regression analysis. The findings indicate that AI pilot policies continue to significantly reduce urban carbon emissions at the 1% significance level. This result corroborates the robustness and reliability of the conclusion. The results are shown in column (4) of Table 4.
5 Further discussion
The heterogeneity analysis in this study encompasses four aspects: the level of urban scientific and technological capabilities, market potential, financial development, and digital infrastructure development. Using the median split method for group classification, the analysis divides groups based on scientific and technological capabilities, market potential, financial growth, and digital infrastructure. This method has proven highly effective in this study. The development of scientific and technological capabilities, market potential, economic development levels, and digital infrastructure varies significantly across cities. Given this imbalance, the median serves as a more robust measure of central tendency than the mean.
5.1 Heterogeneity in the level of scientific and technological development
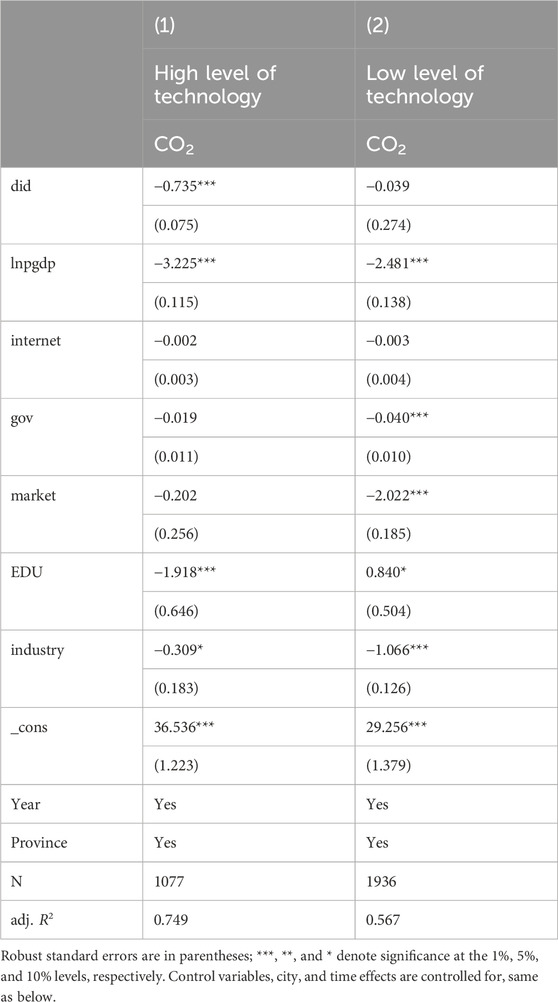
The level of scientific and technological development serves as a vital indicator of a nation’s comprehensive strength and constitutes a key element of a city’s core competitiveness (Popkova and Gulzat, 2019). In China, disparities in financial investment in urban development, higher education, and high-tech industries have caused uneven scientific and technological development across cities (Cao et al., 2019). The heterogeneity of technological development levels is measured using the level of urban scientific and technological patents as the measurement basis. A city with advanced scientific and technological development implies relatively mature and favorable conditions for implementing AI pilot policies. Such cities typically boast robust hardware infrastructure, scientific talent, and technological funding, all of which can facilitate the comprehensive integration of AI technologies.
Table 5 Column (1) shows that in cities with a high level of scientific and technological development, the implementation of AI pilot policies has proven more effective in significantly reducing urban carbon emissions. Conversely, in cities with a low level of scientific and technological development, the implementation of AI pilot policies often exhibits limited effectiveness in reducing carbon emissions. This is because cities with less developed technological capabilities typically lack the necessary hardware infrastructure, have insufficient AI-related talent pools, and are deficient in knowledge and concepts related to AI development. The “China Urban Artificial Intelligence Development Index Report” reveals that Beijing, with an overall AI development index of 92.93, ranks highest nationwide. This is primarily attributed to Beijing’s numerous universities, which boast a rich pool of scientific and technological talent, as well as the presence of high-tech companies such as Baidu and ByteDance. In contrast, cities with less developed technology industries, such as Lanzhou (61.78) and Changchun (65.61), have significantly lower AI development indices compared to Beijing and Shenzhen.
5.2 Heterogeneity in market potential levels
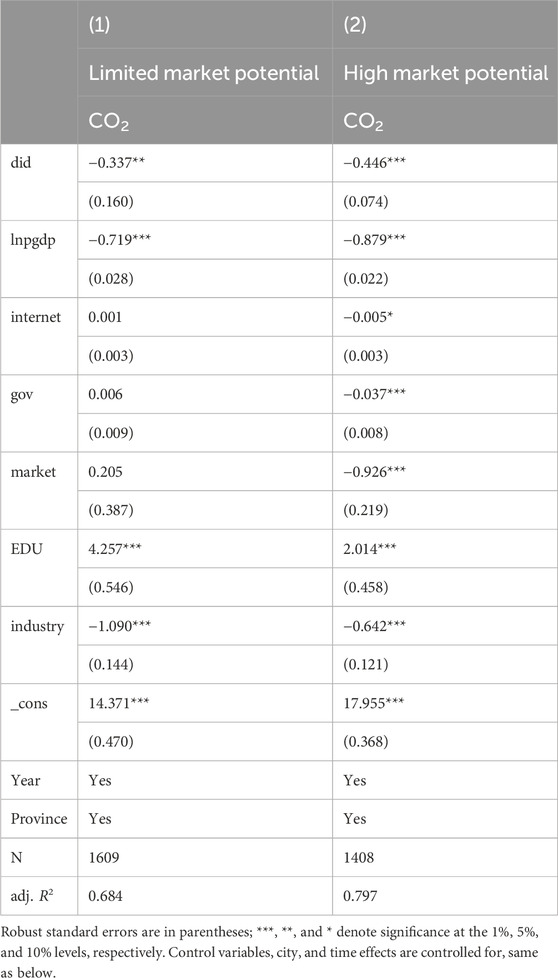
Due to differences in natural geography and historical development traditions, there is an imbalance in the level of market potential development among Chinese cities. The heterogeneity of market potential levels is determined using the marketization index as the criterion. Generally, cities in the southeastern coastal regions have higher market potential than those in the northwestern inland areas. The southeastern coastal regions are characterized by high population density, convenient water and land transportation, abundant natural geographical resources, and a long history of market-oriented traditions. In contrast, cities in the northwestern inland regions are marked by sparse populations, inconvenient transportation, and a lack of market vitality (Yan et al., 2021). Additionally, the level of market potential is closely related to city size, with megacities typically having higher market potential than medium and small cities. China classifies cities, including megacities, large cities, and huge cities, based on the number of permanent residents in urban areas as an objective criterion (Shuang and Zheng, 2024). Megacities accumulate large resident populations, and higher population density typically correlates with greater energy consumption and larger overall market demand. Consequently, megacities exhibit higher market potential. Intelligent applications such as unmanned supermarkets and robotic delivery have significantly enhanced the efficiency of market operations and consumer allocation, thereby reducing carbon emissions during the social consumption process. As shown in Table 6, in cities with low market potential, AI pilot policies suppress carbon emissions at the 5% significance level. In contrast, in cities with high market potential, the effect is more pronounced, reaching the 1% significance level.
5.3 Heterogeneity in financial development levels
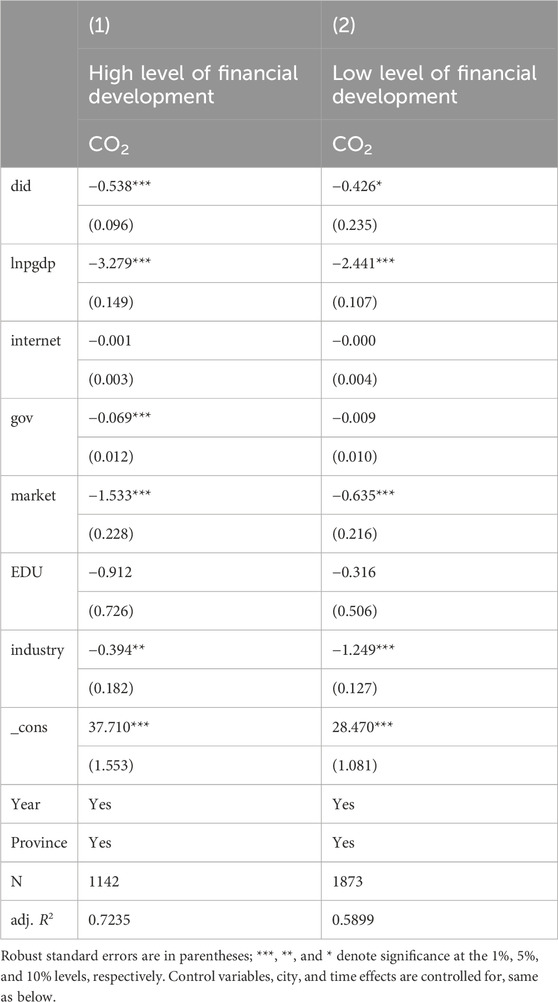
Varying levels of financial development influence the effect of AI pilot policies on curbing urban carbon emissions. The heterogeneity of urban financial development levels is examined using the amount of urban loan balances as the criterion. Financial support directly impacts the implementation of AI enterprises and technologies. Cities like Beijing and Shanghai, with their well-developed economic environments, have established AI industry development funds exceeding 1 billion yuan, creating favorable conditions for the development of AI. This financial backing not only encourages innovation but also attracts investments and talents, thereby fostering a sustainable and competitive AI ecosystem within these cities. In cities with advanced financial development, a well-established credit system supports the innovation and research of green, clean technologies and renewable resources. Financial institutions can utilize AI and digital technologies to evaluate green projects of enterprises promptly and identify the impacts of green industries (Chen and Chen, 2021). During financial investment, more emphasis is also placed on a healthy and sustainable green investment environment. To attract more financial enterprises to invest, local governments will enhance energy-saving and emission-reduction efforts, support the stable development of the carbon trading market, and thus improve the city’s green investment environment. As shown in Table 7, high levels of financial development are associated with a significant reduction in carbon emissions at the 1% significance level. However, column (2) shows that in cities with low financial development levels, the effect is weaker, occurring at the 10% significance level. This is due to limited investments and credit for green technology and renewable energy, resulting in a less pronounced suppressive effect on carbon emissions compared to cities with higher levels of financial development.
5.4 Heterogeneity of digital infrastructure levels
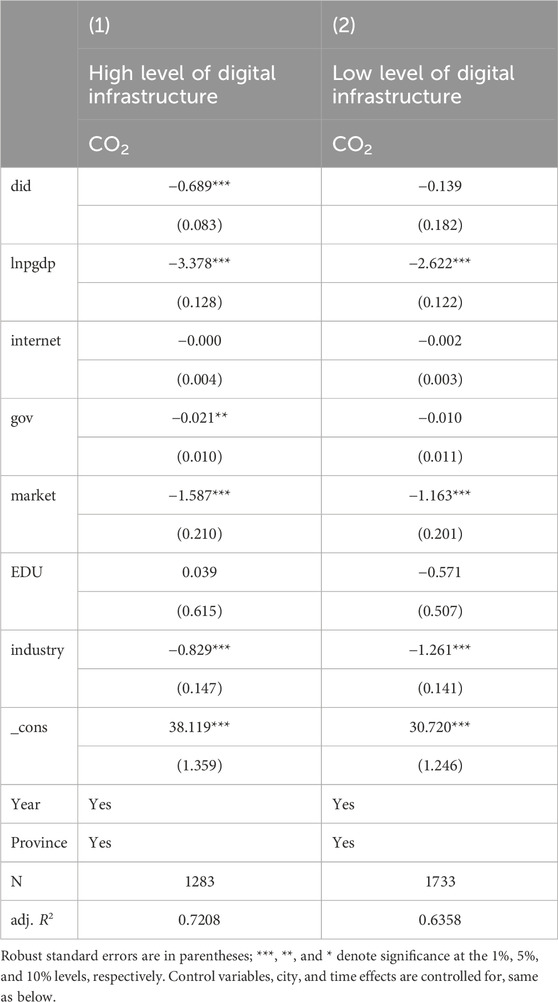
Digital infrastructure provides the necessary hardware support for implementing AI pilot policies. This study on the heterogeneity of urban digital infrastructure levels uses whether a city is a pilot city for the Broadband China and Smart City strategies as a criterion. It leverages digital technologies, such as 5G and AI, thereby aiding cities in the rational allocation of resources and enhancing energy efficiency (Hu et al., 2023). Under the strategic initiatives of Smart City, policies like the Broadband China Demonstration City and National Big Data Center Pilot Project have collectively advanced the level of digital infrastructure in Chinese cities. The integration of AI pilot policies with digital infrastructure has significantly promoted the development of urban AI + initiatives and enhanced the levels of smart city construction. This has driven the vigorous growth of the digital economy, optimized urban industrial structures, reduced the proportion of high-energy-consuming and high-polluting industries, and thus effectively lowered urban carbon emissions. Conversely, cities with weaker digital infrastructure lack the necessary hardware conditions to support the implementation of AI pilot policies, which can even be counterproductive. For instance, the implementation of AI pilot policies might increase the economic development burden of a city. The results are shown in Table 8.
6 Conclusions and policy recommendations
Utilizing AI technology to reduce carbon emissions and promote green ecological production and living has consistently drawn academic attention. This research employs the DID model, leveraging the AI pilot policy as a quasi-natural experiment. It examines the impacts, mechanisms, and heterogeneity of AI pilot policies on urban carbon emissions, utilizing data from 220 Chinese cities spanning the period from 2003 to 2021. The research concludes that AI policies significantly reduce urban carbon emissions through dual mechanisms: green, innovative technologies and environmental regulations. These effects are more pronounced in cities with higher levels of scientific and technological advancement, market potential, financial development, and digital infrastructure.
First, systematically summarize the experiences from the pilot cities of the artificial intelligence innovation application zones. Under the overarching goals of the “New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan,” rapidly advance the widespread application of AI technology in cities, integrating the specific hardware and software conditions of Chinese cities. Specifically, expand the pilot scope in cities with dense populations, well-developed industries, and convenient transportation. In cities where the pilot conditions are less favorable, enhance the effectiveness of policy guidance and strengthen economic development, technological innovation, and the development of digital infrastructure to ensure the smooth progression of AI innovation development pilot projects in these zones.
Second, to establish a green development concept across society. Local governments should encourage residents to adopt green and low-carbon lifestyles by promoting smart public transportation, energy-efficient smart home appliances, and paperless office practices. Additionally, environmental taxes and carbon trading mechanisms can encourage businesses to participate in carbon reduction efforts. This approach helps position governments, societies, businesses, and individuals as key players in energy conservation and emission reduction, fostering voluntary carbon reduction actions.
Third, a comprehensive environmental governance framework is crucial for building an ecological civilization and protecting the environment. Local governments should formulate policies and implementation strategies for AI applications, tailored to their specific economic development conditions, industrial layouts, and resource advantages. For example, Beijing has introduced the “Beijing Artificial Intelligence Empowerment New Industrialization Action Plan (2025)”, while Shenzhen has launched the “Shenzhen Action Plan to Accelerate the Construction of an Artificial Intelligence Pioneer City”. In the process of refining environmental regulations, a positive interaction between national policies and city strategies is established.
Fourth, fully leverage the convenience and intelligence of digital technologies to refine the national urban carbon emissions assessment system. The government should regularly track and evaluate the effects of AI pilot policies on carbon emissions in each pilot city. Since building a carbon emissions database requires funding and professional expertise, the government and businesses need to collaborate on this initiative. Joint efforts by the government and companies will ensure comprehensive, transparent access to carbon emissions data. It is recommended that the carbon emissions database be made publicly accessible. This would provide a convenient data-acquisition platform for government decision-makers, corporate managers, and researchers, thereby facilitating the co-construction and sharing of data.
7 Limitations and future research discussion
AI pilot policies are continuously being improved, and AI technology is increasingly permeating all aspects of production and daily lives. Emphasizing the development of AI aligns with the objective laws of social productivity development. It is a proactive strategy for achieving dual carbon goals and enhancing the quality of life. However, addressing carbon emissions is a complex socio-economic challenge, and the effectiveness of AI pilot policies also requires a more extended implementation period for robust validation. The limitations of this study are inevitably constrained by subjective and objective conditions. To address these limitations and guide future research, while the impact of individual policies on urban carbon emissions is crucial for policy evaluation, current research on urban carbon reduction remains incomplete. Therefore, future studies should focus on the combined effects of multiple policies and their differentiated responses to more accurately identify the mechanisms of urban carbon reduction. This study selected specific control variables for baseline regression in the DID model. However, urban carbon emissions are influenced by numerous factors, and ongoing research is necessary to adapt to evolving conditions and policies. The control variables chosen in this study are limited in scope. For instance, other important control variables such as energy structure, transportation structure, and industrial composition also impact carbon emissions. This highlights the need to expand the range of control variables in future research to capture a more comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing carbon emissions. Objectively speaking, due to the imbalanced development among cities, there are issues with the flow of population, resources, and capital. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the spatial spillover effects of urban carbon emissions in achieving the “Dual Carbon” goals. This requires coordinated planning and scientific layout across regions. Therefore, in future research, we will focus on these limitations and actively explore a more thorough and scientific evaluation of the policy effects of AI on carbon emissions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
KW: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Software, Investigation, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. JL: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Resources, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (grant number 24FKSB035).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
12025-03-05, The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China, State Council Gazette No. 9 of 2025. Visit the website: https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/2025/issue_11946/202503/content_7015861.html
22024-02-16, “Economic Daily”, “The Computing Power Industry Goes Green”-China National Radio. Visit the website: http://m.cnr.cn/tech/20240226/t20240226_526609114.html
32019-05-17, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology approved the establishment of the Shanghai (Pudong New Area) Artificial Intelligence Innovation Application Pilot Zone. Visit the website: https://www.miit.gov.cn/jgsj/kjs/gzdt/art/2020/art_18121dd4c1f743f292c325bca6a903c0.html
References
Akram, R., Chen, F., Khalid, F., Ye, Z., and Majeed, M. T. (2020). Heterogeneous effects of energy efficiency and renewable energy on carbon emissions: evidence from developing countries. J. Clean. Prod. 247, 119122. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119122
Alhasnawi, B. N., Almutoki, S. M. M., Hussain, F. F. K., Harrison, A., Bazooyar, B., Zanker, M., et al. (2024). A new methodology for reducing carbon emissions using multi-renewable energy systems and artificial intelligence. Sustain. Cities Soc. 114, 105721. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105721
Alpan, K., Tuncal, K., Ozkan, C., Sekeroglu, B., and Ever, Y. K. (2022). Design and simulation of global model for carbon emission reduction using IoT and artificial intelligence. Procedia Comput. Sci. 204, 627–634. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2022.08.076
Biggi, G., Iori, M., Mazzei, J., and Mina, A. (2025). “Green intelligence: the AI content of green technologies,” in Eurasian Business Review, 1–38.
Cao, X., Zhou, B., Shi, Y., and Pei, X. (2019). The unbalanced analysis of economic Urbanization—a case study of typical cities in China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 9 (1), 13. doi:10.3390/ijgi9010013
Cao, Q., Chi, C., and Shan, J. (2025). Can artificial intelligence technology reduce carbon emissions? A global perspective. Energy Econ. 143, 108285. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2025.108285
Cheatham, B., Javanmardian, K., and Samandari, H. (2019). Confronting the risks of artificial intelligence. McKinsey Q. 2 (38), 1–9.
Chen, X., and Chen, Z. (2021). Can green finance development reduce carbon emissions? Empirical evidence from 30 Chinese provinces. Sustain. 13 (21), 12137. doi:10.3390/su132112137
Chen, Y., and Jin, S. (2023). Artificial intelligence and carbon emissions in manufacturing firms: the moderating role of green innovation. Processes 11 (9), 2705. doi:10.3390/pr11092705
Chen, J., Gao, M., Cheng, S., Hou, W., Song, M., Liu, X., et al. (2020). County-level CO2 emissions and sequestration in China during 1997–2017. Sci. Data 7 (1), 391. doi:10.1038/s41597-020-00736-3
Chen, P., Gao, J., Ji, Z., Liang, H., and Peng, Y. (2022). Do artificial intelligence applications affect carbon emission performance? Evidence from panel data analysis of Chinese cities. Energies 15 (15), 5730. doi:10.3390/en15155730
Cheng, J., Xu, N. R., Khan, N. U., and Singh, H. S. M. (2025). The impacts of artificial intelligence literacy, green absorptive capacity, and green information system on green innovation. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environmental Management 32 (2), 2375–2389. doi:10.1002/csr.3017
De Almeida, P. G. R., dos Santos, C. D., and Farias, J. S. (2021). Artificial intelligence regulation: a framework for governance. Ethics Inf. Technol. 23 (3), 505–525. doi:10.1007/s10676-021-09593-z
Ding, T., Li, J., Shi, X., Li, X., and Chen, Y. (2023). Is artificial intelligence associated with carbon emissions reduction? Case of China. Resour. Policy 85, 103892. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103892
Dong, M., Wang, G., and Han, X. (2024). Impacts of artificial intelligence on carbon emissions in China: in terms of artificial intelligence type and regional differences. Sustain. Cities Soc. 113, 105682. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105682
Hao, Y., Huang, Z., and Wu, H. (2019). Do carbon emissions and economic growth decouple in China? An empirical analysis based on provincial panel data. Energies 12 (12), 2411. doi:10.3390/en12122411
Hoffmann, R., Muttarak, R., Peisker, J., and Stanig, P. (2022). Climate change experiences raise environmental concerns and promote green voting. Nat. Clim. Change 12 (2), 148–155. doi:10.1038/s41558-021-01263-8
Hu, J., Zhang, H., and Irfan, M. (2023). How does digital infrastructure construction affect low-carbon development? A multidimensional interpretation of evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 396, 136467. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136467
Lauterbach, A. (2019). Artificial intelligence and policy: quo vadis? Digital policy. Regul. Gov. 21 (3), 238–263. doi:10.1108/dprg-09-2018-0054
Lee, C. C., Wang, E. Z., and Tang, H. (2024). Green fiscal policy and carbon emission: enterprises’ level evidence from China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 203, 114795. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2024.114795
Li, H., Lu, Z., Zhang, Z., and Tanasescu, C. (2025). How does artificial intelligence affect manufacturing firms' energy intensity? Energy Econ. 141, 108109. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2024.108109
Liang, P., Sun, X., and Qi, L. (2024). Does artificial intelligence technology enhance green transformation of enterprises: based on green innovation perspective. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 26 (8), 21651–21687. doi:10.1007/s10668-023-04225-6
Lin, B., and Zhou, Y. (2021). Does the internet development affect energy and carbon emission performance? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 28, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2021.03.016
Lin, J., Zeng, Y., Wu, S., and Luo, X. R. (2024). How does artificial intelligence affect the environmental performance of organizations? The role of green innovation and green culture. Inf. Management 61 (2), 103924. doi:10.1016/j.im.2024.103924
Liu, C. M., Sun, Z., and Zhang, J. (2019). Research on the effect of carbon emission reduction policy in China’s carbon emissions trading pilot. China popul. Resour. Environ 29 (11), 49–58.
Liu, L., Li, M., Gong, X., Jiang, P., Jin, R., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Influence mechanism of different environmental regulations on carbon emission efficiency. Int. J. Environmental Res. Public Health 19 (20), 13385. doi:10.3390/ijerph192013385
Makhkamov, D. (2022). Modern trends in regulation of environmental and legal relations: digitalization and artificial intelligence. Am. J. Political Sci. Law Criminol. 4 (01), 41–46. doi:10.37547/tajpslc/volume04issue01-07
Nie, G. Q., Zhu, Y. F., Wu, W. P., Xie, W. H., and Wu, K. X. (2022). Impact of voluntary environmental regulation on green technological innovation: evidence from Chinese manufacturing enterprises. Front. Energy Res. 10, 889037. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2022.889037
Otsuka, A., Goto, M., and Sueyoshi, T. (2014). Energy efficiency and agglomeration economies: the case of J apanese manufacturing industries. Regional Sci. Policy and Pract. 6 (2), 195–213. doi:10.1111/rsp3.12039
Popkova, E. G., and Gulzat, K. (2019). “Technological revolution in the 21st century: digital society vs. artificial intelligence,” in Institute of scientific communications conference (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 339–345.
Qu, F., She, W., Li, D., Zheng, B., and Albitar, K. (2024). Mitigating excessive financialization or promoting innovation? Productivity effects of China's carbon emission trading scheme. Bus. Strategy Environ. 33 (7), 7427–7445. doi:10.1002/bse.3876
Ramich, M. S., and Piskunov, D. A. (2022). The securitization of cyberspace: From rulemaking to establishing legal regimes. V. RUDN Int. Relations 22 (2), 238–255. doi:10.22363/2313-0660-2022-22-2-238-255
Ren, S., Li, X., Yuan, B., Li, D., and Chen, X. (2018). The effects of three types of environmental regulation on eco-efficiency: a cross-region analysis in China. J. Clean. Prod. 173, 245–255. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.113
Rennings, K. (2000). Redefining innovation—Eco-innovation research and the contribution from ecological economics. Ecol. Econ. 32 (2), 319–332. doi:10.1016/s0921-8009(99)00112-3
Roberts, H., Cowls, J., Morley, J., Taddeo, M., Wang, V., and Floridi, L. (2021). The Chinese approach to artificial intelligence: an analysis of policy, ethics, and regulation. Springer International Publishing, 47–79.
Sands, P. (2023). “Environmental protection in the twenty-first century: sustainable development and international law,” in The global environment (London, United Kingdom: Routledge).
Sanusi, I. T., Olaleye, S. A., Agbo, F. J., and Chiu, T. K. (2022). The role of learners’ competencies in artificial intelligence education. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 3, 100098. doi:10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100098
Sethi, P., Chakrabarti, D., and Bhattacharjee, S. (2020). Globalization, financial development and economic growth: perils on the environmental sustainability of an emerging economy. J. Policy Model. 42 (3), 520–535. doi:10.1016/j.jpolmod.2020.01.007
Sharma, A. K., and Sharma, R. (2024). Assessing the influence of artificial intelligence on sustainable consumption behavior and lifestyle choices. Young Consumers Insight Ideas Responsible Marketers. doi:10.1108/YC-09-2024-2214
Shuang, Q., and Zheng, Z. (2024). Analysis on the impact of smart city construction on urban greenness in China’s megacities. J. Environmental Management 355, 120568. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120568
Tang, K., Qiu, Y., and Zhou, D. (2020). Does command-and-control regulation promote green innovation performance? Evidence from China's industrial enterprises. Sci. Total Environ. 712, 136362. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136362
Wan, K. (2024). Local governments competing for the environment and green innovation-evidence from China. J. Appl. Econ. 27 (1), 2358723. doi:10.1080/15140326.2024.2358723
Wan, K., and Yu, X. (2025). Green structural monetary policy and firms’ asymmetric carbon emission reduction: evidence from China. Econ. Analysis Policy 86, 1914–1928. doi:10.1016/j.eap.2025.05.031
Wang, Y., Li, L., Kubota, J., Han, R., Zhu, X., and Lu, G. (2016). Does urbanization lead to more carbon emission? Evidence from a panel of BRICS countries. Appl. Energy 168, 375–380. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.01.105
Wang, K., Wu, M., Sun, Y., Shi, X., Sun, A., and Zhang, P. (2019). Resource abundance, industrial structure, and regional carbon emissions efficiency in China. Resour. Policy 60, 203–214. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.01.001
Wang, K., Dong, K., Wu, J., and Wu, J. (2025a). Patterns of artificial intelligence policies in China: a nationwide perspective. Libr. Hi Tech. 43 (1), 295–325. doi:10.1108/lht-04-2022-0168
Wang, Q., Sun, T., and Li, R. (2025b). Does artificial intelligence promote green innovation? An assessment based on direct, indirect, spillover, and heterogeneity effects. Energy and Environ. 36 (2), 1005–1037. doi:10.1177/0958305x231220520
Wei, L., and Liu, Z. (2022). Spatial heterogeneity of demographic structure effects on urban carbon emissions. Environmental Impact Assess. Rev. 95, 106790. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106790
Wu, L., Sun, L., Qi, P., Ren, X., and Sun, X. (2021). Energy endowment, industrial structure upgrading, and CO2 emissions in China: revisiting resource curse in the context of carbon emissions. Resour. Policy 74, 102329. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102329
Wu, D., Xie, Y., and Liu, D. (2023). Rethinking the complex effects of the clean energy transition on air pollution abatement: evidence from China's coal-to-gas policy. Energy 283, 128413. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.128413
Xie, Y., and Wu, D. (2024). How does competition policy affect enterprise digitization? Dual perspectives of digital commitment and digital innovation. J. Bus. Res. 178, 114651. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2024.114651
Xu, S. C., He, Z. X., and Long, R. Y. (2014). Factors that influence carbon emissions due to energy consumption in China: decomposition analysis using LMDI. Appl. Energy 127, 182–193. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.093
Yan, D., Wu, S., Zhou, S., Li, F., and Wang, Y. (2021). Healthy city development for Chinese cities under dramatic imbalance: evidence from 258 cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 74, 103157. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2021.103157
Yi, M., Wang, Y., Sheng, M., Sharp, B., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Effects of heterogeneous technological progress on haze pollution: evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 169, 106533. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.106533
Yi, M., Chen, D., Wu, T., Tao, M., Sheng, M. S., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Intelligence and carbon emissions: the impact of smart infrastructure on carbon emission intensity in cities of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 112, 105602. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2024.105602
Zeng, L., Lu, H., Liu, Y., Zhou, Y., and Hu, H. (2019). Analysis of regional differences and influencing factors on China’s carbon emission efficiency in 2005–2015. Energies 12 (16), 3081. doi:10.3390/en12163081
Zhang, H. (2021). Technology innovation, economic growth and carbon emissions in the context of carbon neutrality: evidence from BRICS. Sustainability 13 (20), 11138. doi:10.3390/su132011138
Zhang, W., Li, G., Uddin, M. K., and Guo, S. (2020). Environmental regulation, foreign investment behavior, and carbon emissions for 30 provinces in China. J. Clean. Prod. 248, 119208. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119208
Zhang, J., Zhang, H., and Gong, X. (2022a). Government's environmental protection expenditure in China: the role of internet penetration. Environmental Impact Assess. Rev. 93, 106706. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106706
Zhang, L., Yan, Y., Xu, W., Sun, J., and Zhang, Y. (2022b). Carbon emission calculation and influencing factor analysis based on industrial big data in the “double carbon” era. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022 (1), 1–12. doi:10.1155/2022/2815940
Zhang, X., Ciais, P., Jian, X., Liu, X., Wang, R., Chen, K., et al. (2023). The carbon footprint response to projected base stations of China's 5G mobile network. Sci. Total Environ. 870, 161906. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161906
Zhao, B., and Wang, K. (2022). The differences between county, county-level City and municipal district in the system of administrative divisions in China. J. Geogr. Res. 5 (1). doi:10.30564/jgr.v5i1.3739
Keywords: artificial intelligence, carbon emissions, green technology, environmental regulation, China
Citation: Wan K and Li J (2025) How do AI pilot policies affect urban carbon emissions? A quasi-natural experiment in Chinese cities. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1683439. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1683439
Received: 14 August 2025; Accepted: 15 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Sawaid Abbas, University of the Punjab, PakistanReviewed by:
Xiaolin Yu, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, ChinaMuhammad Uzair Mahmood, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright © 2025 Wan and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiali Li, amlhbGlsZWVAY3F1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Kai Wan
Kai Wan Jiali Li
Jiali Li