- 1National Co-Innovation Center for Nuclear Waste Disposal and Environmental Safety, School of National Defence and Nuclear Science and Technology, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang, China
- 2School of Materials and Chemistry, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang, China
- 3School of Environment and Resource, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang, China
The efficient capture of radioactive iodine is critical for nuclear safety due to its high mobility and toxicity. Bismuth sulfide (Bi2S3) aerogel, synthesized via a one-step hydrothermal method, demonstrates exceptional iodine adsorption performance. Characterization by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and BET confirmed the material’s porous structure, which facilitated iodine uptake. Batch experiments revealed a high adsorption capacity of 1,204 mg/g, with kinetics and isotherms well described by the pseudo-second-order model and Freundlich isotherm, respectively, indicating that the adsorption process is dominated by chemisorption. The adsorption mechanism involves iodine phase transfer and subsequent formation of stable BiI3 phases, ensuring long-term immobilization. The Bi2S3 aerogel demonstrates superior chemical and thermal stability, high capture efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, further highlighting its practical potential for nuclear waste management. This work advances the design of bismuth-based adsorbents by combining high capacity, stability, and scalable synthesis, thereby offering a sustainable solution for radioactive iodine capture.
1 Introduction
Global energy demand has expanded dramatically over the past few decades. Benefiting from its high energy density, low carbon, no pollutant emissions, and other characteristics, nuclear energy is considered one of the most promising energy solutions to alleviate energy shortages and greenhouse effects (Parsons et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2024). Nonetheless, radioactive nuclear waste is an inevitable product of nuclear power plant operation, which seriously endangers the ecological and environmental security, and it must be effectively managed to ensure the sustainable development of nuclear energy (Wang et al., 2019). Radioactive waste from nuclear power plants primarily contains radionuclides such as 3H, 85Kr, 90Sr, 99Tc, 129I, 131I, 133Xe, and 137Cs. Among these, iodine is particularly hazardous due to its volatility and bioaccumulation and poses great risks to human health and ecosystems. Notably, 129I has a half-life of 15.7 million years, meaning that even a single release could cause permanent radioactive contamination and therefore requires stringent containment during spent fuel reprocessing (Subrahmanyam et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2023a). Therefore, the development of safe and efficient gaseous radioactive iodine removal technology is of great practical significance.
At present, the treatment of gaseous radioactive iodine can be divided into two categories: wet scrubbing and solid adsorption (Riley et al., 2016). Contrary to wet scrubbing, solid absorption has the advantages of simple process equipment, mild reaction conditions, and almost no secondary pollution, and it is the most popular method of iodine treatment in current research (Moore et al., 2020). Solid iodine adsorbent materials have evolved from early limited types, such as silver-coated silica gel (Liao et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2022) and silver-containing zeolites (Nan et al., 2018; Chapman et al., 2010), rapidly expanding to diverse material categories including activated carbon (Hirota et al., 2021; Tang et al., 2025), zeolites (Zhao et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2024), graphene (Liu et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2024), macroporous resins (Zhang et al., 2025a), aerogels (Yang et al., 2025; Cao et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2025; Fang et al., 2022), layered hydrides (Ma et al., 2014), porous organic polymers (Xie et al., 2019), metal–organic frameworks (Chen et al., 2025; Zhang et al., 2025b), and covalent organic frameworks (He et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2023b). Among the above materials, the aerogels demonstrate the best adsorption performance due to their large specific surface area, high porosity, and easily controllable structure. Moreover, aerogels are widely available in various raw material forms and can be prepared using simple procedures, making them highly promising for large-scale application in engineering practices of iodine adsorption during spent fuel reprocessing (Yuvaraja et al., 2025).
Bismuth-based materials not only have good affinity for iodine but also have the advantages of low price and low environmental toxicity, so approaches utilizing these materials have been rapidly emerging in the research field of iodine adsorbents in recent years (Reda et al., 2021). Xiao et al. developed three bismuth-based carbon nano-membranes through electrospinning technology to coat carbon nano-membranes with bismuth or bismuth oxide (Chee et al., 2020). All materials demonstrated exceptional iodine adsorption performance, with the elemental bismuth-coated membrane achieving the highest iodine adsorption capacity of 732 mg/g. This remarkable result is attributed to the coating process significantly enhancing bismuth atom utilization efficiency, thereby accelerating the adsorption process. Luan et al. synthesized a 3D-ordered macroporous bismuth-loaded silica aerogel material which achieved an adsorption capacity of 696 mg/g for gaseous iodine, which is more than three times that of commercial silver-containing zeolite (Chang et al., 2022). It has been shown that bismuth-based materials have unique advantages in iodine adsorption and separation. Al-Mamoori et al. (2025) synthesized a type of bismuth-SBA-15 derived from rice husk exhibiting an iodine capture capacity of as much as 3,956 mg/g at 200 °C. Extensive research demonstrates that bismuth-based materials hold significant potential for the adsorption of radioactive iodine, offering a promising approach for nuclear waste remediation.
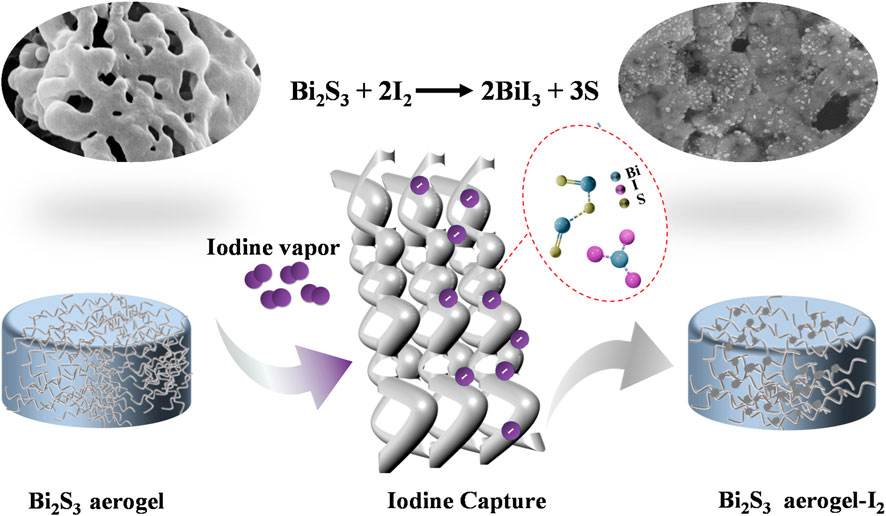
Herein, we developed a type of bismuth sulfide (Bi2S3) aerogel using chitosan as a 3D template agent. Through a combination of freeze-drying and subsequent calcination, we successfully obtained bare Bi2S3 aerogel with enhanced production efficiency and yield. The morphology, pore structure, and chemical composition of the prepared aerogel were systematically characterized. The iodine capture performance was evaluated under various conditions, demonstrating exceptional adsorption capacity and chemical stability. The adsorption mechanism and potential applications for radioactive iodine removal in harsh environments were further investigated.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
In this work, bismuth nitrate pentahydrate (Bi(NO3)3⋅5H2O, AR), thiourea (CH4N2S, AR) and iodine (I2, AR) were purchased from Aladdin (Shanghai). Cyclohexane (C6H12, AR) was purchased from Macklin. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, K30) was purchased from Chron Chemicals (Chengdu), and chitosan was purchased from Shanghai Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (China). All chemicals were of analytical reagent grade and used without further purification.
2.2 Preparation of Bi2S3 aerogel
Bi2S3 aerogel was prepared using the hydrothermal method (Li et al., 2023). First, 0.485 g Bi(NO3)3·5H2O was added to 30 mL of deionized water and stirred for 1 h; then, 0.6 g thiourea and 0.15 g chitosan were added to the solution with continuous stirring for 30 min. Subsequently, 0.2 g polyvinylpyrrolidone was added to the solution and stirred until completely dissolved. Afterward, the mixture was transferred to the reaction kettle and heated in the oven at 200 °C for 200 min. After the reactor cooled to room temperature, the solution was transferred to a centrifuge tube, mixed thoroughly, and then subjected to quick-freeze pretreatment by liquid nitrogen before being placed in a freeze dryer for 3 days to obtain the Bi2S3/chitosan aerogel sample. Finally, the lyophilized samples were placed in a crucible for calcination to remove chitosan. Four groups of samples were calcined at 180 °C, 200 °C, 250 °C, and 300 °C, respectively. Supplementary Figure S1 shows a schematic diagram of the synthesis process of Bi2S3 aerogel.
2.3 Characterization
The powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern was performed on DMAX1400 with the range of 3°–80° (2θ), and the scan rate was set to 8°/min. An ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum on UV2600A was used to record the absorbance of the sample. Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy was recorded on a Nicolet-5700 FT-IR spectrometer with a range of 400–4,000 cm−1. Morphological characterization and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy element mapping of the samples were performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Ultra 55). The specific surface area and pore size information of the sample were obtained using a gas sorption analyzer (Quantachrome, Autosorb iQ).
2.4 Iodine adsorption
2.4.1 Iodine vapor adsorption
The iodine vapor adsorption experiments were conducted according to the following procedure. Approximately 1 g of solid iodine (I2) was placed in a large corundum crucible. A small corundum crucible containing 50 mg of the Bi2S3 aerogel sample was then positioned inside the large crucible, after which the assembly was sealed with a lid and transferred to a dedicated adsorption oven. The system was maintained at 75 °C under ambient pressure for predetermined time intervals. After the completion of the heating process, the samples were allowed to cool to room temperature, removed, and weighed to determine the amount of iodine captured. Each adsorption test was performed in duplicate, and the average value was used for data analysis. The capture amount of iodine vapor by the sample is calculated as following Equation 1:
where Q (wt%) is the iodine absorption amount and m1 (mg) and m2 (mg) are the weights of the sample before and after adsorption, respectively.
2.4.2 Adsorption of iodine in an organic solution
According to a certain solid–liquid ratio, 10 mg of Bi2S3 aerogel was added to glass bottles containing iodine in cyclohexane solutions of different concentrations (50, 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, and 1,000 ppm). The mixtures were then stirred at ambient temperature for 24 h. After a certain period of time, solid-liquid separation was performed via filtration through a 0.22 µm microporous organic membrane, and then the iodine concentration in the adsorption solution was measured using a UV2600A ultraviolet spectrometer (λ = 522 nm). The equilibrium adsorption capacity as following Equation 2:
where C0 (mg/L) and Ce (mg/L) are the initial I2 concentration and the I2 concentration after adsorption, respectively. V is the volume of the solution in milliliters, and m is the weight of the adsorbent in milligrams.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization of Bi2S3 aerogel
The SEM images of Bi2S3 aerogel calcined at 200 °C are shown in Figure 1. A typical 3D network structure is presented in Figure 1a, which coincided with the aerogel structure characteristics and preliminarily confirmed the successful synthesis of Bi2S3 aerogel (Riley et al., 2013). Moreover, the SEM image with higher resolution, shown in Figure 1b, more clearly showed that Bi2S3 nanoparticles are self-assembled into a 3D network structure through cross-linking stacking (Zhou et al., 2023).
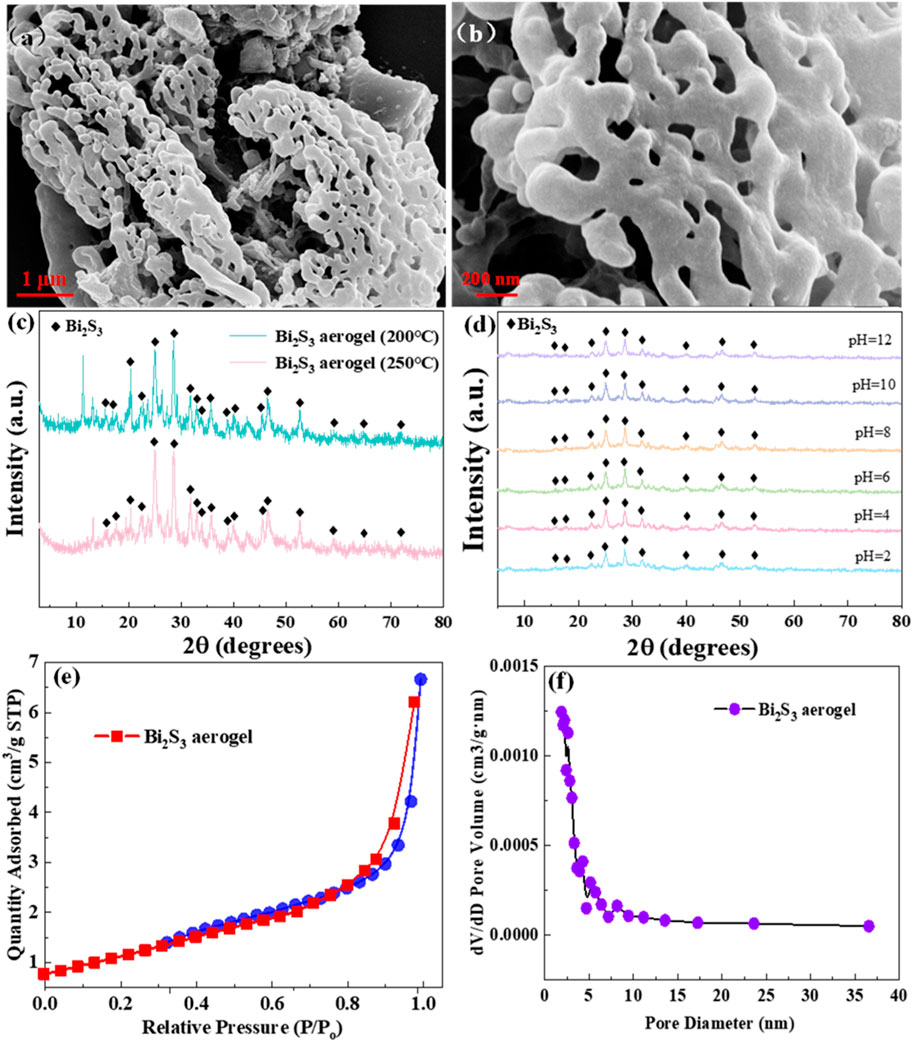
Figure 1. SEM images of Bi2S3 aerogel (a,b). (c) XRD patterns of Bi2S3 aerogel treated at different temperatures. (d) XRD patterns of Bi2S3 aerogel immersed in various pH solutions. (e) N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms. (f) Pore size distribution curves of Bi2S3 aerogel.
XRD was used to analyze the effects of different calcination temperatures and immersion in various pH solutions on the structure of Bi2S3 aerogel. As shown in Figure 1c, the XRD patterns of Bi2S3 aerogels calcined at 200 °C and 250 °C are almost identical, and significant diffraction peaks belonging to the (210), (021), (230), and (431) crystal planes of Bi2S3 (JCPDS no. 75–1360) were observed at 17.87°, 27.43°, 28.65°, and 46.81°, respectively (Ouyang et al., 2018). Further comparison revealed that the intensity of some characteristic peaks of Bi2S3 aerogel calcined at 250 °C was reduced, which may be attributed to the decrease in crystallinity caused by the increase in calcination temperature (Ananthakrishnan and Goswami, 2024). The XRD patterns of Bi2S3 aerogel before and after soaking in solutions across a wide pH range (2–12) show negligible shifts in characteristic peaks (Figure 1d), confirming its excellent acid–base stability under extreme conditions (Jiang et al., 2022).
Figures 1e,f depict the N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms and the BJH pore size distribution of Bi2S3 aerogel. Figure 1e shows a sharp rise in the nitrogen adsorption curve within the relative pressure range of 0.8–1.0 exhibiting type-IV isotherms, which indicated abundant meso-macroporous structure in Bi2S3 aerogel (Thommes et al., 2015). This could be confirmed by the pore size distribution curves (Figure 1f). Calculations reveal an average specific surface area of 4.6942 m2/g, a pore volume of 0.0103 cm3/g, and an average pore diameter of 9.3038 nm, which further confirmed that the structure of Bi2S3 aerogel is mesoporous along with the presence of some macroporous structures (Hu et al., 2024).
3.2 Adsorption performance
The influence of different calcination temperatures on the iodine adsorption performance of Bi2S3 aerogel during synthesis was investigated. Bi2S3 aerogels prepared by calcination at different temperatures (180 °C, 200 °C, 250 °C, and 300 °C) were placed in iodine vapor for 24 h to obtain saturation adsorption at 75 °C. As shown in Figure 2a, Bi2S3 aerogels obtained by calcination at 180 °C and 200 °C exhibited high iodine vapor adsorption capacities of 1,006 mg/g and 1,204 mg/g, respectively, demonstrating excellent adsorption performance for gaseous iodine. However, when the calcination temperature was increased further, the adsorption capacity of the samples decreased sharply. The adsorption capacity of the samples calcined at 300 °C decreased by 67% to 463 mg/g for iodine vapor.
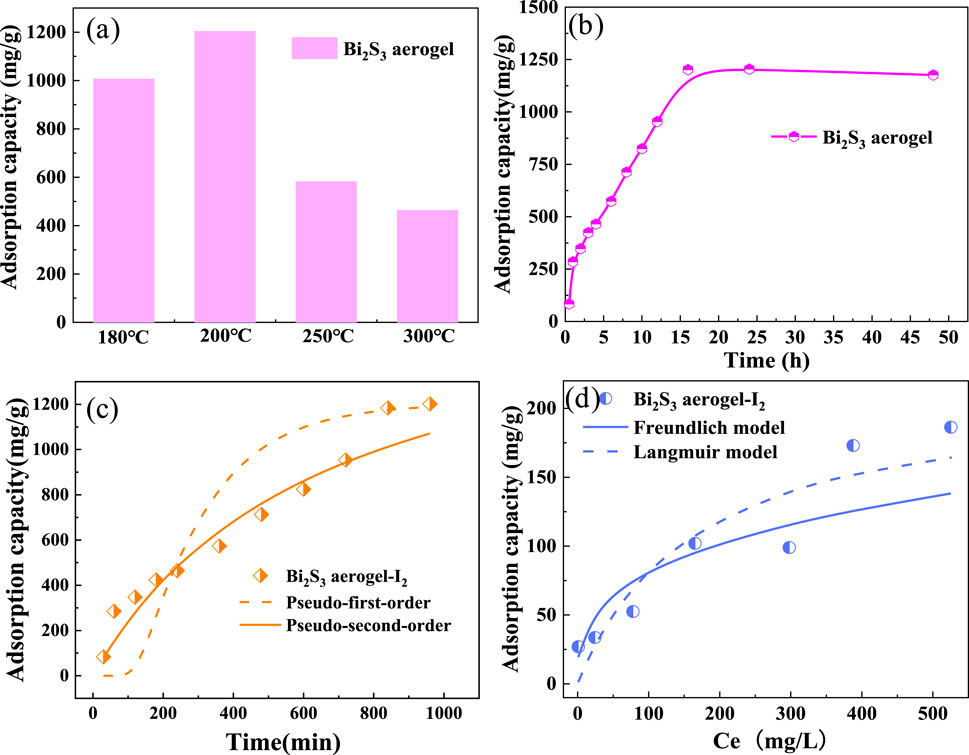
Figure 2. (a) Iodine adsorption capacity of Bi2S3 aerogel calcined at different temperatures. (b) Adsorption of iodine vapor by Bi2S3 aerogel calcined at 200 °C. (c) Effect of contact time on the iodine vapor adsorption performance of Bi2S3 aerogel. (d) Effect of iodine concentrations in cyclohexane on the adsorption performance of Bi2S3 aerogel.
The Bi2S3 aerogel calcined at 200 °C exhibited a maximum iodine adsorption capacity of 1,204 mg/g when tested in iodine vapor at 75 °C. The adsorption process is shown in Figure 2b. The mass of iodine adsorbed by the sample increased steadily during the initial stage, and the adsorption rate gradually declined in the later stage. It was inferred that the rapid increase in adsorption during the initial stage was attributed to surface reaction, whereas the slow adsorption rate in the later stage was dominated by pore filling controlled by mass transfer diffusion (Al-Mamoori et al., 2019; Al-Mamoori et al., 2025). The adsorption process reached equilibrium in 16 h, and the maximum iodine adsorption capacity of the sample reached 1,204 mg/g, indicating a good performance among the reported iodine adsorbents (Supplementary Table S1). Following this, the adsorption capacity decreased slightly because of the desorption of part of the physically adsorbed iodine. To further investigate the iodine adsorption behavior of Bi2S3 aerogel, the pseudo-first-order model and pseudo-second-order model (Figure 2c; Supplementary Equations S1,S2) were exploited to fit the experimental data. The fitting results and calculations are shown in Figure 2c and Supplementary Table S2, respectively, which indicate that the adsorption kinetics of iodine by Bi2S3 aerogel fit the pseudo-second-order model better, with a higher R2 value (0.84) compared to the pseudo-first-order model (0.72). The results indicate that the adsorption of iodine by Bi2S3 aerogel was dominated by the chemisorption process (Wang and Guo, 2020).
To investigate the adsorption capacity of Bi2S3 aerogel for liquid iodine, we carried out isothermal adsorption experiments with iodine in a cyclohexane solution at room temperature and fitted the experimental data with Langmuir and Freundlich models (Supplementary Equations S3,S4). As shown in Figure 2d, with the increase in the equilibrium concentration of iodine in the cyclohexane solution, the adsorption capacity of iodine per unit mass of adsorbent gradually increases until it reaches the maximum adsorption capacity for liquid iodine. According to the parameters fitted by the two adsorption models (Supplementary Table S3), the Freundlich model (R2 > 0.80) is more suitable than the Langmuir model (R2 > 0.76) (Pham et al., 2016), and the maximum adsorption capacity of Bi2S3 aerogel for iodine in cyclohexane is 186 mg/g.
3.3 Adsorption mechanism
As shown in Figure 3a, electron image and elemental mapping of Bi2S3 aerogel after iodine adsorption can be used for the preliminary analysis of its capture mechanism. The mapping images of Figure 3(a-1, a-2, a-3) showed that the adsorbed iodine was evenly distributed in the sample, and the distribution was completely consistent with that of bismuth, indicating that bismuth plays a major role in the iodine adsorption process (Al-Mamoori et al., 2020). The FT-IR spectra of the samples before and after iodine adsorption (Figure 3b) showed that the characteristic vibration peaks corresponding to Bi–S bonds at 1,623, 1,372, and 718 cm-1 either disappeared or exhibited significant shifts after iodine adsorption (Cao et al., 2012), indicating that the bond was cracked to generate new adsorbed products during the adsorption process. Furthermore, XRD analysis (Figure 3c) showed that the characteristic peaks of Bi2S3 disappeared in the samples after iodine adsorption, whereas the new characteristic peaks corresponding to BiI3 were detected at 2θ values of 12.8°, 26.9°, 35.2°, 41.5°, 46.2°, and 50.3° (JCPDS no. 48–1795) (Chen et al., 2024). Based on the peaks, it is speculated that the product was BiI3 after iodine adsorption and that Bi2S3 and I2 reacted to form BiI3. Therefore, as depicted in Figure 4, the mechanism of iodine adsorption by Bi2S3 aerogel involves the chemical reaction: Bi2S3 + 3I2 → 2BiI3 + 3S (Jiang et al., 2022).
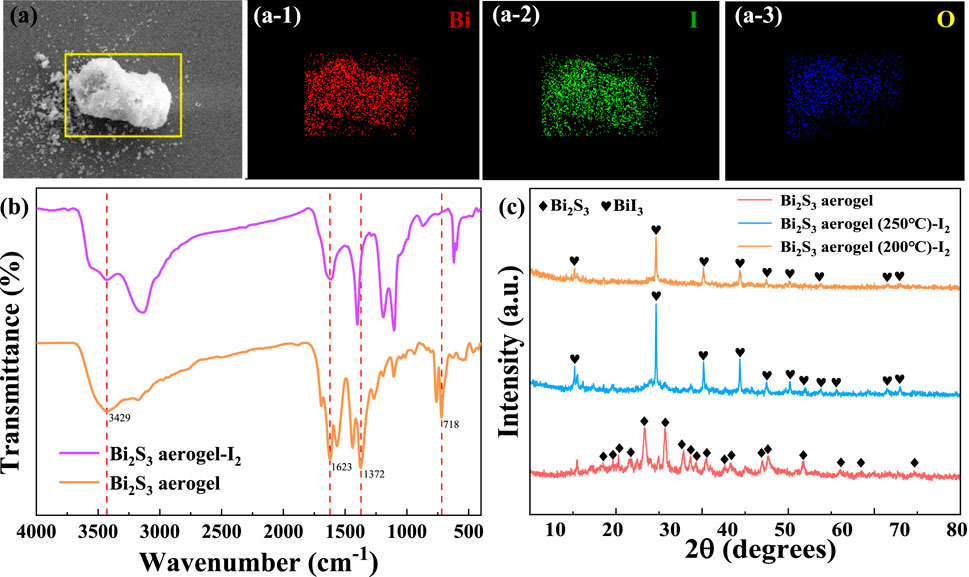
Figure 3. Electron image (a) and elemental mapping (a-1, a-2, and a-3) of Bi2S3 aerogel after iodine adsorption. FT-IR (b) and XRD (c) of Bi2S3 aerogel before and after iodine adsorption.
4 Conclusion
In summary, this study demonstrates the successful synthesis of Bi2S3 aerogel via a template removal method, with optimal structural integrity and iodine adsorption performance achieved at a calcination temperature of 200 °C. The aerogel exhibits exceptional adsorption capabilities, including a gaseous iodine adsorption capacity exceeding 1,204 mg/g and a solution-phase-removal efficiency of 186 mg/g. It also outperforms conventional adsorbents such as activated carbon. Mechanistic studies confirm that the adsorption process is dominated by chemisorption, where iodine reacts with Bi2S3 to form stable BiI3. The Bi2S3 aerogel’s robust stability across a wide pH range (2–12) and its resistance to structural degradation under acidic/alkaline conditions highlight its suitability for nuclear waste reprocessing, which involves the capture of volatile iodine in complex environments. Furthermore, the formation of thermodynamically stable BiI3 ensures long-term iodine immobilization. These results position porous Bi2S3 aerogel as a promising candidate for spent nuclear fuel treatment, combining high capacity, chemical stability, and sustainable synthesis.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
RW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. HX: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. YT: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. LC: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YZ: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RX: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. CT: Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. YY: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. CL: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. HW: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JY: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. TD: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22476164), the Central Guidance for Local Science and Technology Development Projects (2023ZYDF074), the Postgraduate Innovation Fund Project by Southwest University of Science and Technology (24ycx3005), and the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students of Sichuan Province (S202510619006).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2025.1709936/full#supplementary-material
References
Al-Mamoori, A., Lawson, S., Rownaghi, A. A., and Rezaei, F. (2019). Improving adsorptive performance of CaO for high-temperature CO2 capture through Fe and Ga doping. Energy Fuels. 33, 1404–1413. doi:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b03996
Al-Mamoori, A., Alsalbokh, M., Lawson, S., Rownaghi, A. A., and Rezaei, F. (2020). Development of bismuth-mordenite adsorbents for iodine capture from off-gas streams. Chem. Eng. J. 391, 123583. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2019.123583
Al-Mamoori, A., Mohammed, I. S., Kader, H. D. A., Al-sadoon, A. M., and Majdi, H. S. (2025). Novel Bi-SBA-15 derived rice husk for iodine adsorption from off-gas stream. Results Chem. 13, 101972. doi:10.1016/j.rechem.2024.101972
Ananthakrishnan, R., and Goswami, K. (2024). Deciphering the effect of calcination temperature on crystallinity, morphology, oxygen vacancy and photocatalytic activity of bi-phasic ZnO/ZnCo2O4 heterostructured nanomaterials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 327, 129792. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2024.129792
Cao, J., Xu, B., Lin, H., Luo, B., and Chen, S. (2012). Novel heterostructured Bi2S3/BiOI photocatalyst: facile preparation, characterization and visible light photocatalytic performance. Dalton Trans. 41, 11482–11490. doi:10.1039/C2DT30883E
Cao, J., Duan, S., Zhao, Q., Chen, G., Wang, Z., Liu, R., et al. (2023). Three-dimensional-network-structured bismuth-based silica aerogel fiber felt for highly efficient immobilization of iodine. Langmuir 39, 12910–12919. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c02041
Chang, S., Wang, K., Gao, L., Liu, J., Wang, L., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Highly efficient adsorption of radioiodine by a three-dimensional ordered macroporous bismuth-silica composite aerogel. Chem. Eng. Sci. 260, 117856. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2022.117856
Chapman, K. W., Chupas, P. J., and Nenoff, T. M. (2010). Radioactive iodine capture in silver-containing mordenites through nanoscale silver iodide formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 8897–8899. doi:10.1021/ja103110y
Chee, T., Tian, Z., Zhang, X., Lei, L., and Xiao, C. (2020). Efficient capture of radioactive iodine by a new bismuth-decorated electrospinning carbon nanofiber. J. Nucl. Mater. 542, 152526. doi:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2020.152526
Chen, K., Zhou, X., Dai, X., Chen, Y., Li, S., Gong, C., et al. (2024). Sulfur vacancy-rich bismuth sulfide nanowire derived from CAU-17 for radioactive iodine capture in complex environments: performance and intrinsic mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 473, 134584. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134584
Chen, G., Wu, L., Wang, Z., Liu, R., Tan, C., Tan, Y., et al. (2025). Aluminum-based MOF for efficient iodine and methyl iodide capture from NO2-containing gas streams. Chem. Eng. J. 507, 160829. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2025.160829
Fang, Y., Ren, G., Ma, Y., Wang, C., Li, M., Pang, X., et al. (2022). Adsorption and reutilization of Pb(II) based on acid-resistant metal-organic gel. Sep. Purif. Technol. 295, 121253. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121253
He, L., Li, B., Ma, Z., Zhao, F., Zhang, M., Chen, J., et al. (2024). Task-driven tailored covalent organic framework for dynamic capture of trace radioactive CH3131I under high-flow rate conditions. ACS Cent. Sci. 10, 2072–2081. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.4c01318
Hirota, M., Higaki, S., Ito, S., Ishida, Y., and Terao, K. (2021). Effects of 2-hydroxypropyl α-cyclodextrin on the radioactive iodine sorption on activated carbon. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 328, 659–667. doi:10.1007/s10967-021-07672-5
Hu, A., Xie, Q., Chen, L., and Li, Y. (2024). Hierarchically ordered meso-/macroporous MOF-based materials for catalysis and energy applications. EnergyChem 6, 100137. doi:10.1016/j.enchem.2024.100137
Jiang, M., Zhu, L., Zhao, Q., Chen, G., Wang, Z., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). Novel synthesis of NaY-NH4F-Bi2S3 composite for enhancing iodine capture. Chem. Eng. J. 443, 136477. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.136477
Li, X., Wang, X., Dong, L., Zou, Q., He, C., Zhu, Y., et al. (2023). Combining electrospinning and hydrothermal methods to prepare Bi2S3@SiO2 nanostructure-based membranes for enhanced capture capacity of off-gas iodine from a nuclear plant. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 6, 4328–4336. doi:10.1021/acsanm.2c05438
Liao, L., Song, S., Liang, G., Wang, X., Pan, N., Lei, H., et al. (2025). Resource recovery from iodine-containing silver-loaded silica gel: recycling of silver and immobilization of iodine. J. Hazard. Mater. 493, 138306. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138306
Liu, B., Ren, X., Chen, L., Ma, X., Chen, Q., Sun, Q., et al. (2019). High efficient adsorption and storage of iodine on S, N co-doped graphene aerogel. J. Hazard. Mater. 373, 705–715. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.005
Ma, S., Islam, S. M., Shim, Y., Gu, Q., Wang, P., Li, H., et al. (2014). Highly efficient iodine capture by layered double hydroxides intercalated with polysulfides. Chem. Mater. 26, 7114–7123. doi:10.1021/cm5036997
Moore, R. C., Pearce, C. I., Morad, J. W., Chatterjee, S., Levitskaia, T. G., Asmussen, R. M., et al. (2020). Iodine immobilization by materials through sorption and redox-driven processes: a literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 716, 132820. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.166
Nan, Y., Liu, J., Tang, S., Lin, R., and Tavlarides, L. L. (2018). Silver-exchanged mordenite for capture of water vapor in off-gas streams: a study of adsorption kinetics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 57, 1048–1058. doi:10.1021/acs.iecr.7b04420
Ouyang, H., Chen, N., Chang, G., Zhao, X., Sun, Y., Chen, S., et al. (2018). Selective capture of toxic selenite anions by bismuth-based metal–organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 13197–13201. doi:10.1002/anie.201807891
Parsons, J., Buongiorno, J., Corradini, M., and Petti, D. (2019). A fresh look at nuclear energy. Science 363, 105. doi:10.1126/science.aaw5304
Pham, T. C. T., Docao, S., Hwang, I. C., Song, M. K., Choi, D. Y., Moon, D., et al. (2016). Capture of iodine and organic iodides using silica zeolites and the semiconductor behaviour of iodine in a silica zeolite. Energy Environ. Sci. 9, 1050–1062. doi:10.1039/C5EE02843D
Reda, A. T., Pan, M., Zhang, D., and Xu, X. (2021). Bismuth-based materials for iodine capture and storage: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 105279. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2021.105279
Riley, B. J., Chun, J., Um, W., Lepry, W. C., Matyas, J., Olszta, M. J., et al. (2013). Chalcogen-based aerogels as sorbents for radionuclide remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 7540–7547. doi:10.1021/es400595z
Riley, B. J., Vienna, J. D., Strachan, D. M., McCloy, J. S., and Jerden, J. L. (2016). Materials and processes for the effective capture and immobilization of radioiodine: a review. J. Nucl. Mater. 470, 307–326. doi:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2015.11.038
Subrahmanyam, K. S., Sarma, D., Malliakas, C. D., Polychronopoulou, K., Riley, B. J., Pierce, D. A., et al. (2015). Chalcogenide aerogels as sorbents for radioactive iodine. Chem. Mater. 27, 2619–2626. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b00413
Tang, Z., Xie, D., Li, S., and Huang, L. (2025). The directions of enhanced activated carbon fibers for iodine capture from humid gas streams: synergistic mechanisms of microporosity, hydrophobicity, and nitrogen sites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 354, 129032. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2024.129032
Thommes, M., Kaneko, K., Neimark, A. V., Olivier, J. P., Rodriguez-Reinoso, F., Rouquerol, J., et al. (2015). Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 87, 1051–1069. doi:10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Wang, J., and Guo, X. (2020). Adsorption kinetic models: physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 390, 122156. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122156
Wang, X., Chen, L., Wang, L., Fan, Q., Pan, D., Li, J., et al. (2019). Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides. Sci. China Chem. 62, 933–967. doi:10.1007/s11426-019-9492-4
Wang, J., Li, M., Feng, Y., Liu, Y., and Liu, J. (2022). Efficient capture of radioactive iodine by Ag-attached silica gel and its kinetics. Nucl. Mater. Energy 33, 101270. doi:10.1016/j.nme.2022.101270
Wang, X., Meng, R., Zhao, S., Jing, Z., Jin, Y., Zhang, J., et al. (2024). MIL-88A(Al)/chitosan/graphene oxide composite aerogel with hierarchical porosity for enhanced radioactive iodine adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 277, 134456. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134456
Wang, R., Tan, Y., Xiao, H., Zeng, Z., Liu, S., Tan, C., et al. (2025). Recent advances in aerogel materials for the capture of radioactive iodine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 376, 134118. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2025.134118
Xie, W., Cui, D., Zhang, S., Xu, Y., and Jiang, D. (2019). Iodine capture in porous organic polymers and metal–organic frameworks materials. Mater. Horiz. 6, 1571–1595. doi:10.1039/C8MH01656A
Yang, L., Fu, H., Dong, L., Ma, M., Deng, Y., Wu, H., et al. (2025). Moldable SnS2/polyimide aerogel as fixed-bed adsorbent: efficient immobilization of radioiodine vapor with resistance to high-temperature and high-humidity conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 370, 133159. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2025.133159
Yuvaraja, G., Wen, C., Subbaiah, M. V., Wen, J., Venkateswarlu, S., Yarramuthi, V., et al. (2025). Advances in next gen aerogel materials for radionuclides cleanup: from functional design to computational insights. Coord. Chem. Rev. 545, 217047. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2025.217047
Zhang, Y., He, L., Pan, T., Xie, J., Wu, F., Dong, X., et al. (2023a). Superior iodine uptake capacity enabled by an open metal-sulfide framework composed of three types of active sites. CCS Chem. 5, 1540–1548. doi:10.31635/ccschem.022.202201966
Zhang, Z., Shi, X., Wang, X., Zhang, Z., and Wang, Y. (2023b). Encapsulating covalent organic frameworks (COFs) in cellulose aerogels for efficient iodine uptake. Sep. Purif. Technol. 309, 123108. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123108
Zhang, E., Wang, C., Yang, H., Mo, F., Wei, L., and Tang, Q. (2025a). Efficient removal of iodide from medical wastewater by D201 resin. Water Air Soil Pollut. 236, 437. doi:10.1007/s11270-025-08087-8
Zhang, J., Wang, X., Guo, X., Sang, W., He, Q., and Zhang, W. (2025b). Crystal- and pore-size dependent iodine adsorption properties in MOFs. Small 21, 2410678. doi:10.1002/smll.202410678
Zhao, Q., Liao, C., Chen, G., Liu, R., Wang, Z., Xu, A., et al. (2022). In situ confined synthesis of a copper-encapsulated Silicalite-1 zeolite for highly efficient iodine capture. Inorg. Chem. 61, 20133–20143. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c03582
Zhao, Q., Li, X., Chen, G., Wang, Z., Tan, C., Liu, C., et al. (2024). Hydrophobic nanosheet silicalite-1 zeolite for iodine and methyl iodide capture. J. Hazard. Mater. 472, 134496. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134496
Zhou, X., Jin, H., Yun, S., Huang, W., Mao, P., Chen, J., et al. (2023). A novel Cu nanoporous aerogel for high-efficient immobilization of iodide in water. Chem. Eng. J. 454, 140217. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.140217
Keywords: bismuth sulfide aerogel, biotemplated, iodine, adsorption, immobilization
Citation: Wang R, Xiao H, Tan Y, Chen L, Zhou Y, Xie R, Tan C, Yang Y, Liu C, Wang H, Yang J, Duan T and Zhu L (2025) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of bismuth sulfide aerogel for efficient iodine capture. Front. Environ. Sci. 13:1709936. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2025.1709936
Received: 21 September 2025; Accepted: 11 November 2025;
Published: 03 December 2025.
Edited by:
Andrew Hursthouse, University of the West of Scotland, United KingdomCopyright © 2025 Wang, Xiao, Tan, Chen, Zhou, Xie, Tan, Yang, Liu, Wang, Yang, Duan and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lin Zhu, emh1bGluQHN3dXN0LmVkdS5jbg==
 Renren Wang1,2
Renren Wang1,2 Lin Zhu
Lin Zhu