Abstract
Pine wilt disease (PWD) is a devastating forest disease that severely impacts pine trees, with widespread outbreaks leading to catastrophic damage in pine forests worldwide. Our study aims to investigate the dynamics of PWD infection on soil physicochemical properties and biological activities, as well as the interrelationships between them. Soil samples were collected from 0 to 10 cm and 10 to 20 cm depths in subtropical Pinus massoniana (Masson pine) forests with PWD infection years of 0 (non-infection), 6, 10, and 16 years. The physicochemical properties, microbial biomass, and enzymatic activities of these soil samples were measured. The results revealed that soil non-capillary porosity, clay, microbial biomass carbon and microbial biomass nitrogen decreased significantly in 6 years forests. Available potassium consistently decreased with longer invasion periods, while soil polyphenol oxidase, leucine amino peptidase, and available phosphorous peaked in 6 years forests and then declined over time. The soil physicochemical properties, biological activities all decreased as soil depth increased. Redundancy analysis and Mantel tests underscored the critical role of Total potassium, pH, Total phosphorous, and bulk density in shaping microbial activities. This study demonstrated that PWD infection significantly effect on soil physicochemical properties, microbial biomass, and enzymatic activities with the chronosequence progresses. These finding contribute to a deeper understanding of how invasive pathogens like PWD can reshape soil environments, with implications for forest conservation and restoration practices.
Introduction
Pine wilt disease (PWD) is a globally significant quarantine forest disease caused by the Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (pine wood nematode, PWN) that primarily affects pine trees (Yang et al., 2014). Originating in North America, PWD was first reported in Japan in the early 20th century. It has since become established in several countries, including China, Japan, South Korea, the United States, Portugal, and Mexico, causing widespread pine mortality as well as significant ecological and economic losses (Liu J. et al., 2023; Back et al., 2024). In Europe, PWD has been detected in Portugal, where it has led to significant pine mortality, raising concerns about the potential for further spread across the continent (Seidl et al., 2018; Calvão et al., 2019). In China, PWD was first found in the Nanjing city in 1982, then it has rapidly spread to many other regions, particularly in the southern provinces (Hao et al., 2021). The subtropical climate of these areas, characterized by warm temperatures and high humidity, creates an ideal environment for the proliferation of the PWN and its vector beetles (Tang et al., 2021). As a result, large-scale pine die-offs have occurred, severely affecting the landscape and local economies dependent on pine forests (Hao et al., 2022).
Soil is a critical component of forest ecosystems, serving as a reservoir of nutrients, organic matter, and microbial communities that support plant growth and maintain ecosystem balance (Binkley and Fisher, 2019). PWN is transmitted by insect vectors, which introduce the nematode into pine trees during feeding (de la Fuente and Beck, 2019; Liu Y. et al., 2023). An infected pine tree typically exhibits reduced or halted resin secretion alongside rapid needle dehydration and yellowing, impairing its photosynthetic capacity and potentially causing death within a few months (Tian et al., 2022). The loss of pine trees due to PWD not only reduces forest cover but also disrupts the ecological balance of affected areas (Binkley and Fisher, 2019). Moreover, the death of pine trees has cascading effects on other ecological processes, particularly those related to the soil environment, including soil properties and biological activities (Wu et al., 2023; Baek and Kim, 2023). Research has shown that PWD can cause significant alterations in the soil chemical composition, affecting not only nutrient availability but also soil pH and the balance of soil minerals (Chu et al., 2016). Gao et al. (2015) reported shifts in soil nutrient elements following pine mortality: due to decreased litter input and increased nutrient leaching, the levels of elements such as nitrogen and potassium declined with the duration of the PWD invasion. The decomposition of dead pine trees also influences the soil’s physical properties, including its structure and water-holding capacity. The loss of tree roots also can lead to increased soil erosion and compaction (Kim et al., 2010). These changes in physical and nutrient conditions can impact microbial communities essential for nutrient cycling, potentially altering both their diversity and function of the soil ecosystem (Jiao et al., 2023).
Soil biological activity plays a crucial role in organic matter metabolism and is closely linked to soil properties (Gispert et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2018). It is generally recognized that soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity increase with the length of cultivation and serve as effective indicators for assessing soil quality (Lucas-Borja et al., 2016). In addition to changes in nutrient dynamics, the death of trees and the subsequent changes in soil conditions can disrupt these microbial communities, leading to shifts in their structure and function (Back et al., 2024; Mabuhay and Nakagoshi, 2012). Previous studies have indicated that PWD can lead to an initial boost in microbial activity, as decomposing wood and needles provide a source of organic carbon (Baek and Kim, 2023). However, as the decomposition process progresses and the availability of easily decomposable organic matter decreases, microbial activity may decline, leading to changes in the composition and function of the microbial communities (Qu et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2023). Zhang et al. (2021) reported a marked increase in soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels following the removal of dead trees affected by PWD. PWD infection also accelerates forest succession, leading to significant changes in soil microbial community composition and structure at different stages of succession (Qu et al., 2020).
Pinus massoniana (Masson pine) is a keystone species in subtropical forests, particularly in southern China (Chi et al., 2023). These forests are not only economically valuable, providing timber and non-timber forest products, but they also play crucial roles in maintaining regional ecological balance (Pan et al., 2021). They contribute to carbon sequestration, soil conservation, water regulation, and biodiversity preservation (Gao et al., 2015). The latest survey data shows that the planting area of Masson pine has exceeded 8 million hectares (National Forestry and Grassland Administration, 2020). Statistics indicate that PWD currently affects about 650,000 hectares annually, with the majority of the dead pine trees being Masson pines in China (Wang et al., 2022). Previous research has primarily focused on changes in soil physicochemical properties (Bashir et al., 2021; Siegert et al., 2024), and microbial activities (Shi et al., 2015a; Qu et al., 2022) by PWD infection. However, there remains a paucity of studies examining the temporal dynamics—and their interrelationships—of soil physicochemical properties, microbial biomass, and soil enzyme activities in PWD-infected Masson pine forests.
It is crucial to develop effective strategies for managing forests affected by PWD by understanding its impact on soil nutrient characteristics and biological activities (Qu et al., 2022). Previous research has provided valuable insights into the immediate effects of PWD on soil and forest ecosystems, but there is limited understanding of the interactions between soil nutrient changes and microbial activity within the context of pest disturbances and the long-term resilience and sustainability of forest ecosystem (Jeong et al., 2013; Holden and Treseder, 2013). Furthermore, the chronosequence of PWD infection—referring to the progression of infection over time—provides a opportunity to study the temporal dynamics of soil nutrient properties and biological activities (Gao et al., 2015), which allow researchers to infer the long-term effects of PWD by examining soils at different stages of infection (Anderson-Teixeira et al., 2021). The primary aims of this study sought to (i) characterize the changes in soil nutrient properties along a PWD infection chronosequence and across different soil layers in subtropical Masson pine forests, (ii) investigate the associated changes in soil biological activities—including microbial biomass and enzyme activities critical for nutrient cycling, and (iii) determine the response of microbial biomass and enzymatic activities to soil physicochemical properties and the relationships among the three along the chronosequence.
Materials and methods
Study region
Our research was conducted in Yichang City, Hubei Province, China (Table 1). This area has an eastern mid-subtropical monsoon climate, with a with a mean annual temperature of 16.9°C and a mean annual precipitation of 1215.6 mm, respectively. Before the PWD invasion, Masson pine was the dominant tree species in the region, widely distributed at elevations between 45 and 1500 m, playing a crucial role in ecological and environmental protection (Gao et al., 2015). Moreover, since the area is a key environmental protection zone, these Masson pines have not been subjected to any human-induced logging since their planting, and there are no records of significant natural disasters (such as fires or snowstorms). The PWD is currently the only recorded severe natural disaster affecting the Masson pine forests. Since 2006, PWD attacked the Masson pines in this area and has since spread rapidly (Gao et al., 2018).
TABLE 1
| Infection years | Latitude (N) |
Longitude (E) |
Altitude (m) | DBH (cm) | Pine density (tree⋅ha–1) |
Stand age (year) |
| 0 | 30.86 | 110.78 | 900∼911 | 25.38 ± 1.34a | 592 ± 101a | 33 |
| 6 | 30.85 | 111.01 | 285∼302 | 18.62 ± 0.81b | 516 ± 14a | 30 |
| 10 | 30.85 | 110.92 | 562∼574 | 17.13 ± 2.65b | 450 ± 152a | 26 |
| 16 | 30.87 | 110.90 | 340∼387 | 19.61 ± 1.05b | 366 ± 138a | 30 |
General information on each site in the Masson pine forests.
DBH and pine density was the plot level’s mean value ± standard deviation (n = 3). Stand attributes, including DBH and stand age, represented the value of the selected Masson pine. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between PWD infection years (p < 0.05).
Soil sampling
We selected four stands which had consistent stand age and initial planting density based on the PWD invasion data provided by the local forestry department. The four stands selected were Masson pine forests that had not been invaded by PWD (non-infection, 0 years) and had been invaded by PWD for 6, 10, and 16 years, respectively. Three plots (20 × 20 m) for each site were randomly established for the subsequent soil sampling. There were 12 plots (four PWD infection years × three replicate plots). Detail information for each period of Masson pine forest is shown in Table 1.
In each plot, 5 sampling points were selected along an S-shaped curve, with each point at least 1 meter away from the trees. Soil samples were taken from 0 to 10 cm and 10 to 20 cm depths after removing forest litter and herbaceous plants. Firstly we collected the soil by cutting ring (100 cm3) method for bulk density and non-capillary porosity analyses (Zhang et al., 2018). Soil samples were collected using a soil auger with a 5 cm inner diameter. Samples from the same plot and soil layer were thoroughly mixed and evenly divided into two portions: one portion was immediately stored at 4°C for the analysis of soil biological properties, while the other was reserved for chemical analysis.
Laboratory analysis
Soil non-capillary porosity (NCP) and bulk density (BD) were determined within the cutting ring in the laboratory. Soil pH was measured in soil-water (1:2.5 w/v) suspension using a pH meter (PHS–25, REX, China) (Zhang et al., 2018). Clay was measured by the hydrometer method. The soil organic carbon (SOC), total N (TN) and available N (AN) were measured using an elemental analyzer (Euro EA, Germany). The determination of total P (TP) and available P (AP) was conducted with a UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (UV-2550, Japan) using ammonium molybdate. Total K (TK) was measured using the NaOH fusion–molybdenum antimony colorimetric method (Chen et al., 2022). Available K (AK) content was analyzed by plasma emission spectroscopy following digestion with a 1 mol⋅L−1 NH4OAc solution (IRIS Intrepid II XSP, USA).
The chloroform fumigation-extraction method was used to estimate the microbial biomass (C, N, and P) (Bao, 2000). Soil enzyme activities were analyzed by Saiya-Cork et al. (2002) using a microtiter plate fluorescence assay for the determination of four hydrolases and two oxidoreductases including β-glucosidase (BG), acid phosphatase (ACP), N-acetyl-glucosidase (NAG), leucine amino peptidase (LAP), polyphenol oxidase (POX) and peroxidase (PER).
Statistical analyses
A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to assess the differences in stand density and DBH between stands of infection years, followed by post hoc multiple comparisons using the Tukey-HSD method. A linear mixed-effects model (LMM) was used to analyze differences in soil physicochemical properties, microbial biomass, and enzyme activities, with the duration of PWD infection specified as a fixed effect and replicate plots within each stand treated as a random effect.
Data analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 and JMP 17. All plots were performed in Origin 2024 Mantel test analysis between soil physicochemical properties and microbial activity was conducted using the “ggcor” R package, and correlation heatmaps were generated using ChiPlot (accessed on August 21, 2022)1. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was conducted using CANOCO 5.0 to assess the relationships among soil physicochemical properties, microbial biomass, and biological activities.
Results
Soil physical and chemical properties
The physicochemical properties in different soil depth of the Masson forests showed significant changes with increasing PWD infection years (Table 2). NCP in 10–20 cm was significantly reduced in 6-year infection forests of PWD, and gradually recovered with increasing years of invasion. Soil clay in 0–10 and 10–20 cm depth in infected forests were significantly decreased. Soil pH showed an increasing, then decreasing, then increasing trend with the number of years of PWD infection in 0–10 and 10–20 cm depth. The SOC in the 10–20 cm depth increased in 10 years infection forests. TP and AP were both significantly increased in 6 years forests of PWD invasion, and then decreased with increasing years of invasion. AK showed a decreasing trend in 0–10 and 10–20 cm soil depth with increasing years of PWD invasion. Soil nutrient elements decreased with increasing soil depth.
TABLE 2
| Soil properties | 0–10 cm | 10∼20 cm | ||||||
| 0 | 6 years | 10 years | 16 years | 0 | 6 years | 10 years | 16 years | |
| BD (g⋅cm–3) |
1.41 ± 0.14 | 1.39 ± 0.02 | 1.19 ± 0.13 | 1.4 ± 0.05 | 1.50 ± 0.12 | 1.50 ± 0.02 | 1.34 ± 0.05 | 1.45 ± 0.04 |
| NCP (%) |
9.85 ± 0.36 | 6.43 ± 2.74 | 10.81 ± 4.47 | 9.23 ± 2.32 | 8.73 ± 0.51a | 5.27 ± 0.52b | 10.43 ± 0.96a | 7.92 ± 2.03a |
| Clay (%) |
24.22 ± 0.30a | 7.48 ± 2.11b | 10.94 ± 3.74b | 12.38 ± 1.48b | 25.80 ± 1.39a | 7.36 ± 2.15b | 11.23 ± 7.09b | 12.80 ± 1.17b |
| pH | 4.91 ± 0.22bc | 5.40 ± 0.11a | 4.63 ± 0.09c | 5.13 ± 0.19ab | 4.85 ± 0.14b | 5.80 ± 13a | 4.77 ± 0.21b | 5.45 ± 0.29a |
| SOC (g⋅kg–1) |
18.77 ± 2.15 | 19.36 ± 3.17 | 21.79 ± 2.77 | 19.67 ± 3.59 | 9.52 ± 0.30b | 8.52 ± 1.48b | 14.84 ± 2.60a | 11.75 ± 1.28b |
| TN (g⋅kg–1) |
1.66 ± 0.16 | 1.82 ± 0.20 | 1.77 ± 0.10 | 1.67 ± 0.23 | 0.92 ± 0.03 | 0.92 ± 0.14 | 1.18 ± 0.07 | 1.06 ± 0.17 |
| TP (g⋅kg–1) |
0.26 ± 0.01b | 0.78 ± 0.03a | 0.35 ± 0.09b | 0.38 ± 0.01b | 0.19 ± 0.01b | 0.73 ± 0.14a | 0.34 ± 0.12b | 0.36 ± 0.11b |
| TK (g⋅kg–1) |
6.36 ± 0.64 | 4.67 ± 0.31 | 5.73 ± 0.45 | 6.81 ± 2.53 | 7.29 ± 0.77 | 5.10 ± 1.15 | 5.10 ± 0.72 | 6.79 ± 1.38 |
| AN (g⋅kg–1) |
0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.03 |
| AP (mg⋅kg–1) |
3.31 ± 0.04b | 18.63 ± 9.29a | 4.62 ± 1.65b | 6.39 ± 2.62b | 2.58 ± 1.26b | 21.21 ± 8.35a | 3.60 ± 2.28b | 6.18 ± 2.85b |
| AK (mg⋅kg–1) |
96.57 ± 16.64a | 48.32 ± 5.68b | 71.90 ± 19.38ab | 60.90 ± 16.99ab | 63.44 ± 9.91a | 32.67 ± 2.43b | 59.28 ± 13.01a | 39.81 ± 7.40b |
Soil physiochemical properties between different PWD infection years.
Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among forests with varying PWD infection years at the same soil depth (p < 0.05). BD, bulk density; NCP, non-capillary porosity; SOC, soil organic carbon; TN, total N; AN, available N; TP, total P; AP, available P; TK, total P; AK, available K. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between stands with varying durations of PWD infection at the same soil depth (p < 0.05).
Soil microbial biomass and enzymatic activities
The microbial biomass and enzyme activity in different soil depth of the Masson forests showed significant changes with the increase in PWD infection years (Figure 1). Compared to non-infection stands, there was a significant increase in BG activities in 10–20 cm soil depth of the 16-year infection forests. PWD infection significantly increased LAP activities in 0–10 cm soil depth. At the same time, during the initial stages of PWD invasion, the POX activities also significantly increased, reaching its peak in 6 years infection forests.
FIGURE 1

Soil enzymatic activities (A–F) and microbial biomass (G–I) between different PWD infection years. MBP, microbial biomass P; MBC, microbial biomass C; MBN, microbial biomass N; BG, β-glucosidase activities; ACP, acid phosphatase activities; NAG, N-acetyl-glucosidase activities; LAP, leucine amino peptidase activities; POX, polyphenol oxidase activities; PER, peroxidase activities. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between stands with varying durations of PWD infection at the same soil depth (p < 0.05).
In 10–20 cm soil depth, MBC and MBN showed a trend of initially decreasing and then increasing with increasing years of PWD invasion, and the lowest values were observed after 10 years infection forests.
Relationships between soil physicochemical properties and biological activities
Mantel tests and RDA analysis were used to examine the relationship between the soil biological variables and the physicochemical variables (Figures 2, 3 and Supplementary Table 1). TK was significantly positively correlated with enzyme activity in 0–10 cm soil depth (Figure 2A). SOC and BD exhibited a significant positive correlation with microbial biomass (Figure 2B) in 10–20 cm soil depth. Mantel tests further revealed a highly significant negative correlation between TP and clay, and a highly significant positive correlation between TP and AP, AN and TN (Figures 2A, B).
FIGURE 2
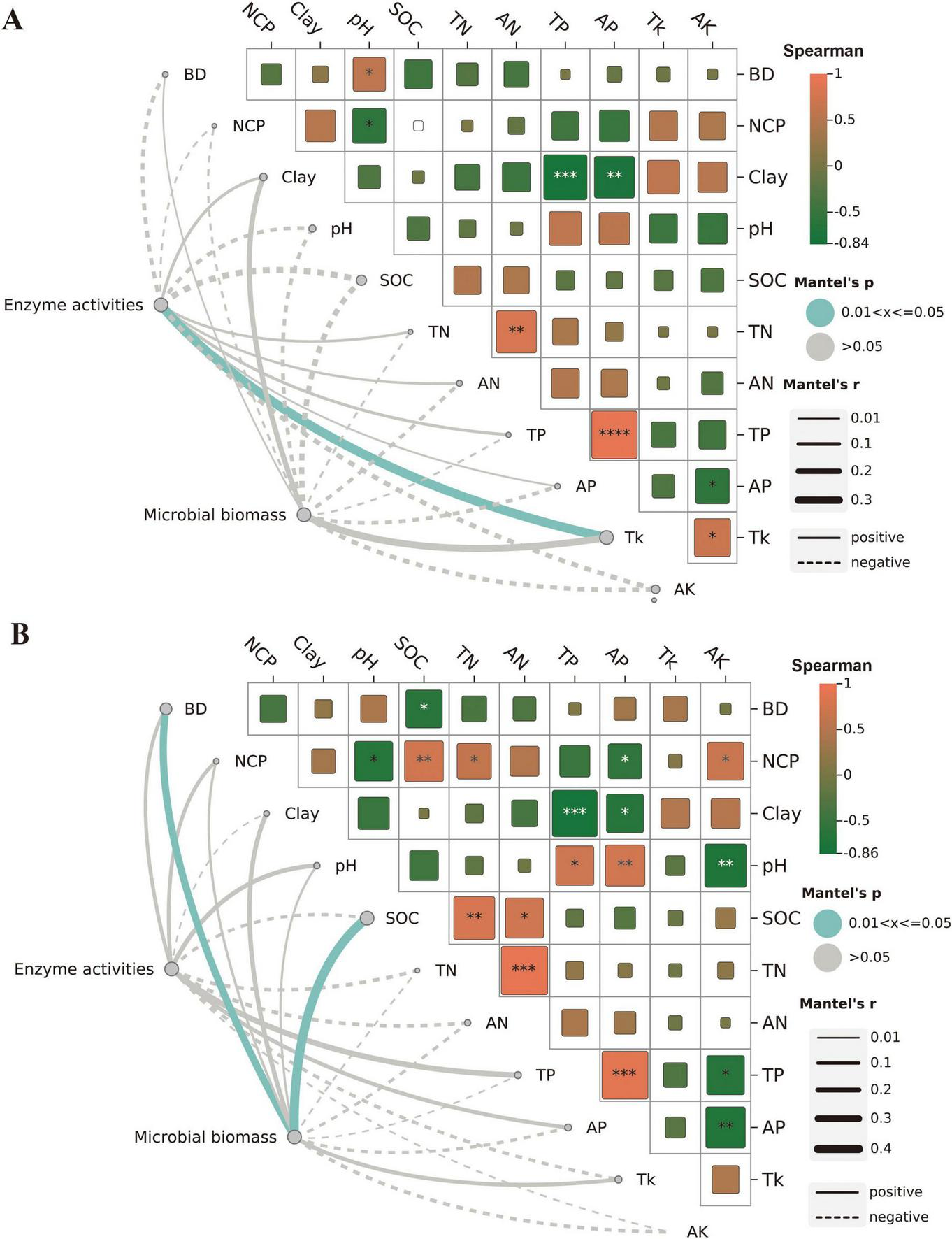
Correlations among the soil biological activities and physical-chemical properties in 0–10 cm (A) and 10–20 cm (B) depth. Significance levels of each predictor are *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
FIGURE 3
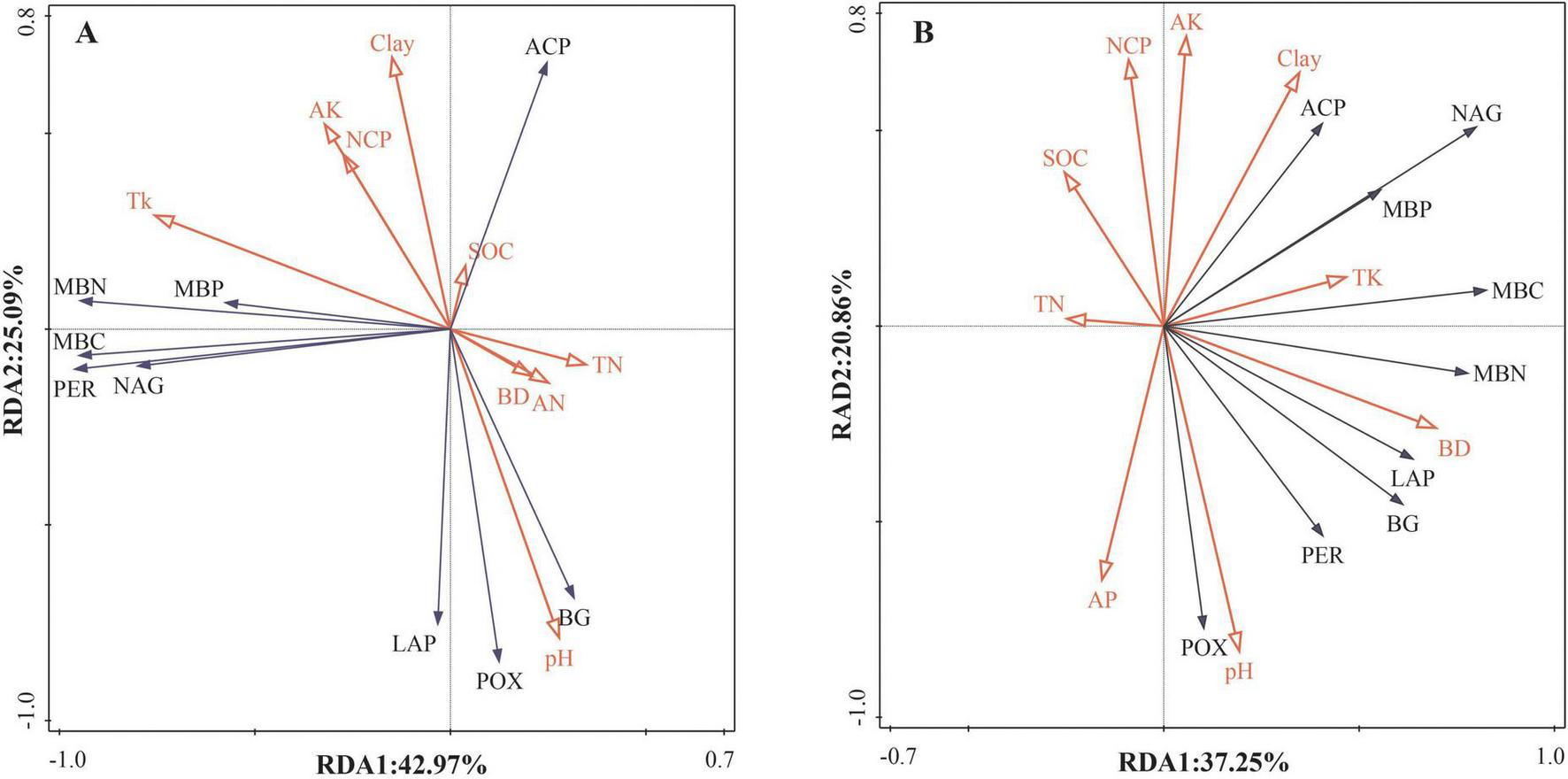
Relationships between soil biological activities and physicochemical properties at soil depths of 0–10 cm (A) and 10–20 cm (B) were identified by RDA.
The results of RDA showed that the first two axes of the plot explained 42.97 and 25.09% of the variation in soil biological activities (soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities) in 0–10 cm soil depth (Figure 3A), and 37.25 and 20.86% in 10–20 cm soil depth (Figure 3B). In particular, the TK and pH were important soil factors affecting soil biological activities in 0–10 cm soil depth. BD and AP important soil factors affecting soil biological activities in 10–20 cm soil depth.
Discussion
Effects of PWD infection on soil physicochemical properties
The reduction in NCP and clay during the early stages of PWD infection, particularly noticeable in 6 years infected forests, indicates significant soil structure disruption (Table 2). Coarser soils may experience increased erosion risks and reduced ability to retain organic matter and nutrients, influencing overall soil fertility and ecosystem stability. This initial compaction is likely due to the loss of plant biomass, resulting in reduced soil aeration and water infiltration capacity (Gao et al., 2015). Furthermore, the decrease in tree canopy cover caused by widespread pine mortality enhances understory light availability and increases water evaporation, contributing further to soil compaction (Sakamoto et al., 2003; Fukasawa, 2016). However, the gradual recovery of porosity over time indicates a resilience of soil structure, potentially due to the re-establishment of plant or microbial activity that helps to re-aggregate soil particles (Liu J. et al., 2023; Guo et al., 2023).
We observed that soil nutrients exhibited a complex interaction between soil chemistry and disease progression (Table 2). The early increase in TP and AP in PWD-infected soils indicates an initial phase of nutrient release, possibly due to the breakdown of organic matter and root tissues. The peak phosphorus levels in the 6-year infection forests emphasize the rapid nutrient cycling during the early infection stages, which could temporarily enhance soil fertility (Hok et al., 2015). Conversely, the decreasing trend in soil AK with prolonged PWD infection underscores ongoing nutrient depletion (Table 2). These changes may be due to the increased nutrient consumption resulting from the recovery of vegetation biomass as the duration of PWD infection progresses (Fukasawa, 2016). Previous studies have suggested that soil nutrients are generally higher in non-infection stands compared to infected ones (Kim et al., 2011; Mabuhay and Nakagoshi, 2012). Differences in research results may be due to variations in soil properties arising from changes in observation time, forest conditions, and vegetation structure (Ge et al., 2014; Gao et al., 2018). These variations might be due to changes in soil physical properties, like BD, resulting from PWD infection, which influence microbial community composition and activity. Consequently, this can impact the availability of essential nutrients for plants, ultimately affecting nutrient cycling and ecosystem functions within the forest (Cobb et al., 2016). Notably, the absence of significant changes in soil BD, TN, TK, and AN across different years of PWD infection suggests that these properties are less sensitive to PWD impacts or may reflect a balance between nutrient inputs and losses. This stability might indicate a resilient aspect of soil properties that can buffer against the disturbances caused by PWD, maintaining certain critical soil functions, or that their responses are more delayed and require longer observation periods to manifest (Siegert et al., 2024; Anderson-Teixeira et al., 2021).
Effects of PWD infection on soil microbial biomass and enzymatic activities
The observed significant increases in LAP and POX activities during the early stages of PWD infection, with peaks observed at 6 years (Figures 1D, E), highlight notable shifts in microbial enzymatic profiles. These findings suggest that the initial stages of PWD invasion introduce substantial amounts of dying and decaying tree material into the soil (Fujihara, 1996; Fukasawa, 2018). This influx likely stimulates microbial activity related to lignin and nitrogen degradation, as microbes increase the production of LAP and POX to process the newly available substrates (Wan et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020). Conversely, the long-term effects of PWD infection are reflected in the changes observed in BG and NAG activities (Figures 1A, C). The increased activities of these enzymes indicate that long-term PWD infection likely alters the composition and input of organic matter, prompting microbial communities to enhance BG and NAG activities to meet their carbon and nitrogen needs. This will benefit the restoration of the soil ecosystem in affected forests, as the increased enzyme activities help promote the decomposition of organic matter and the cycling of nutrients, thereby improving soil health and ecological function (Chen et al., 2024).
Our observations also revealed that changes in microbial biomass did not consistently correlate with changes in enzyme activity levels (Figures 1G–I). The invasion of PWD involves not only biotic disturbances but also abiotic disturbances (Fukasawa, 2016). Firstly, the invasion of PWD leads to tree mortality, which alters the underground soil environment and impacts soil ecosystem functions (Shi et al., 2015b). Secondly, abiotic disturbances can also exert significant influence during biotic disturbances (Holden and Treseder, 2013; Wen et al., 2022). For example, human activities such as felling diseased trees can result in severe soil compaction (Veldkamp et al., 2020). Soil compaction alters soil porosity, potentially impairing gas exchange, reducing drainage, and inhibiting soil microbial growth (Nazari et al., 2021). The burning of infected wood can damage the soil by heating and scorching the surface layer (Whitman et al., 2019). The direct impact of abiotic disturbances on soil properties can partly explain the alterations in soil characteristics observed after such events (Fichtner et al., 2014). However, biotic disturbances generally do not cause direct physical alterations to the soil but can lead to significant indirect effects on soil properties (Zhang et al., 2024). We hypothesize that during the initial stages of PWD invasion, alterations in soil physicochemical properties—including pH, SOC, and clay — along with fluctuating pH levels, created a stressful environment for microbial communities. This stress may have influenced microbial metabolic processes and enzyme stability. Although soil conditions appeared to improve subsequently, leading to a more favorable environment for microbial growth and activity, the initial decline in biological activities may have resulted from a delayed microbial response to these environmental changes (Norris et al., 2023).
Relationship between physicochemical properties and biological activities
The results from Mantel test and RDA analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between soil physicochemical properties and biological activity (Figures 2, 3). These findings emphasize that maintaining adequate levels of these soil properties could be crucial for sustaining soil function in PWD-affected forests. For example, Potassium is essential for microbial metabolism and enzyme production, and its availability directly influences enzyme activities involved in nutrient cycling (Hou et al., 2018). Increased soil nutrient content levels can enhance microbial growth and enzymatic activity, thereby supporting the soil’s ability to process organic matter and potentially suppress pathogen populations through competitive interactions (Guo et al., 2023; Yan et al., 2024). High BD can restrict root growth, reduce pore space for microbial activities, and limit nutrient availability (Gérard, 2016), which can exacerbate the effects of PWD infection. BD was positively correlated with microbial activities in 10–20 cm depth (Figure 2B), suggesting that despite increased compaction, microbial biomass and activity can persist if other conditions are favorable. This resilience indicates that deeper soil layers may support substantial microbial communities, which can contribute to nutrient cycling and ecosystem functioning even under stress conditions induced by PWD infection (Liu Y. et al., 2023).
Previous studies have suggested that pH is a critical factor influencing soil biological activities (Mabuhay and Nakagoshi, 2012). Conifer species, through their mycorrhizal associations, can release organic acids and absorb basic cations, contributing to soil acidification (Rigueiro Rodríguez et al., 2012). The decline in mycorrhizal activity under the influence of PWD may have contributed to a marked increase in the pH of the affected soil (Ma et al., 2020). Fan et al. (2023) found that adjusting soil pH significantly alleviates the incidence and severity of PWD. In the context of PWD infection, pH fluctuations can influence microbial populations differently, potentially altering enzyme activities and overall soil health (Figure 2 and Table 2). A favorable pH range can enhance enzyme activities and microbial processes, contributing to a more resilient soil ecosystem (Chen et al., 2022). In subtropical Masson pine forests, managing soil pH within an optimal range can enhance microbial functions and improve the soil’s resilience to PWD infection (Fan et al., 2023).
The observed relationships between soil properties and biological activities have significant implications for forest management and disease control strategies in subtropical Masson pine forests (Holden and Treseder, 2013; Norris et al., 2023; Fan et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024). In the topsoil, enhancing organic matter inputs, optimizing phosphorus availability, and managing soil pH can bolster microbial activity and enzyme functions, improving the soil’s ability to cope with PWD infection (Zhang et al., 2018). Practices such as compost application, pH adjustment, and balanced fertilization can support microbial health and potentially suppress pathogen populations through competitive and antagonistic mechanisms (De Corato, 2020). For deeper soil layers, strategies to manage phosphorus levels and alleviate soil compaction are crucial. Implementing practices to reduce BD, such as minimizing understory vegetation disturbance or enhancing biological control, can improve soil structure and microbial habitat, thereby enhancing resistance to PWD infection (Yang et al., 2014; Back et al., 2024).
Conclusion
Our results demonstrated that the duration of PWD infection significantly influence the soil physicochemical properties, microbial biomass, and enzymatic activities. These changes reflect the adaptive response of the microbial community to changes in soil conditions after PWD infection. The strong correlations between physicochemical properties and microbial activities emphasize the interdependence of soil properties and biological processes under PWD stress. In summary, our results reflect the impact of prolonged PWD infection on soil physicochemical properties and microbial activity, as well as their potential interrelationships. They enhance our understanding of soil conditions and processes across different soil depths under PWD infection, which is crucial for the restoration of Masson pine forest ecosystems.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
XS: Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZJ: Writing – review and editing. KW: Writing – review and editing. XW: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. WX: Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds of CAF (CAFYBB2021ZG001) and National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFD1400900).
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff who provided assistance in sampling and investigations and the Hubei Zigui Three Gorges Reservoir National Forest Ecosystem Observation and Research Station that provided support in investigations, and samples process.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/ffgc.2025.1544221/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1
Anderson-Teixeira K. J. Herrmann V. Cass W. B. Williams A. B. Paull S. J. Gonzalez-Akre E. B. et al (2021). Long-term impacts of invasive insects and pathogens on composition, biomass, and diversity of forests in virginia’s blue ridge mountains.Ecosystems2489–105. 10.1007/s10021-020-00503-w
2
Back M. A. Bonifácio L. Inácio M. L. Mota M. Boa E. (2024). Pine wilt disease: A global threat to forestry.Plant Pathol.731026–1041. 10.1111/ppa.13875
3
Baek G. Kim C. (2023). Comparisons of different regeneration approaches on soil respiration of Chamaecyparis obtusa planted in pine wilt disease-disturbed stands.J. For. Res.28168–176. 10.1080/13416979.2022.2141860
4
Bao S. (2000). Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis.Beijing: China Agriculture Press.
5
Bashir O. Ali T. Baba Z. A. Rather G. H. Bangroo S. A. Mukhtar S. D. et al (2021). “Soil organic matter and its impact on soil properties and nutrient status,” in Microbiota and Biofertilizers, Vol 2: Ecofriendly Tools for Reclamation of Degraded Soil Environs, edsHamid DarG.BhatR.MehmoodM. (Berlin: Springer), 129–159. 10.1007/978-3-030-61010-4_7
6
Binkley D. Fisher R. F. (2019). Ecology and Management of Forest Soils.Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons.
7
Calvão T. Duarte C. M. Pimentel C. S. (2019). Climate and landscape patterns of pine forest decline after invasion by the pinewood nematode.For. Ecol. Manag.43343–51. 10.1016/j.foreco.2018.10.039
8
Chen H. Zhang S. Ma C. Xiang Y. Wu J. (2024). Restoring farmland to forest increases phosphorus limitation based on microbial and soil C: N: P stoichiometry-a synthesis across China.Forest Ecol. Manag.556:121745. 10.1016/j.foreco.2024.121745
9
Chen Y. Wei T. Sha G. Zhu Q. Liu Z. Ren K. et al (2022). Soil enzyme activities of typical plant communities after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China.Appl. Soil Ecol.170:104292. 10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104292
10
Chi Y. Wang G. G. Zhu M. Jin P. Hu Y. Shu P. et al (2023). Potentially suitable habitat prediction of Pinus massoniana Lamb. in China under climate change using Maxent model.Front. Forests Glob. Change6:1144401. 10.3389/ffgc.2023.1144401
11
Chu H. Wang C. Wang H. Chen H. Tang M. (2016). Pine wilt disease alters soil properties and root-associated fungal communities in Pinus tabulaeformis forest.Plant Soil404237–249. 10.1007/s11104-016-2845-x
12
Cobb R. C. Meentemeyer R. K. Rizzo D. M. (2016). Wildfire and forest disease interaction lead to greater loss of soil nutrients and carbon.Oecologia182265–276. 10.1007/s00442-016-3649-7
13
De Corato U. (2020). Agricultural waste recycling in horticultural intensive farming systems by on-farm composting and compost-based tea application improves soil quality and plant health: A review under the perspective of a circular economy.Sci. Total Environ.738:139840. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139840
14
de la Fuente B. Beck P. S. (2019). Management measures to control pine wood nematode spread in Europe.J. Appl. Ecol.562577–2580. 10.1111/1365-2664.13486
15
Fan Y. Liu L. Wu C. Yu G. Wang Z. Fan J. et al (2023). The effect of regulating soil pH on the control of pine wilt disease in a black pine forest.Forests14:1583. 10.3390/f14081583
16
Fichtner A. Von Oheimb G. Härdtle W. Wilken C. Gutknecht J. (2014). Effects of anthropogenic disturbances on soil microbial communities in oak forests persist for more than 100 years.Soil Biol. Biochem.7079–87. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.12.015
17
Fujihara M. (1996). Development of secondary pine forests after pine wilt disease in western Japan.J. Vegetation Sci.7729–738. 10.2307/3236384
18
Fukasawa Y. (2016). Seedling regeneration on decayed pine logs after the deforestation events caused by pine wilt disease.Ann. Forest Res.59191–198. 10.15287/afr.2016.572
19
Fukasawa Y. (2018). Pine stumps act as hotspots for seedling regeneration after pine dieback in a mixed natural forest dominated by Chamaecyparis obtusa.Ecol. Res.331169–1179. 10.1007/s11284-018-1631-z
20
Gao R. Luo Y. Wang Z. Yu H. Shi J. (2018). Patterns of biomass, carbon, and nitrogen storage distribution dynamics after the invasion of pine forests by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) in the three Gorges Reservoir Region.J. Forestry Res.29459–470. 10.1007/s11676-017-0432-5
21
Gao R. Shi J. Huang R. Wang Z. Luo Y. (2015). Effects of pine wilt disease invasion on soil properties and masson pine forest communities in the Three Gorges reservoir region, China.Ecol. Evol.51702–1716. 10.1002/ece3.1326
22
Ge P. Da L. J. Wang W. B. Xu X. N. (2014). Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic carbon, nitrogen and other nutrients in soil of Pinus massoniana stands after pine wilt disease disturbance.J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr.1475–87. 10.4067/S0718-95162014005000006
23
Gérard F. (2016). Clay minerals, iron/aluminum oxides, and their contribution to phosphate sorption in soils—A myth revisited.Geoderma262213–226. 10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.08.036
24
Gispert M. Emran M. Pardini G. Doni S. Ceccanti B. (2013). The impact of land management and abandonment on soil enzymatic activity, glomalin content and aggregate stability.Geoderma20251–61. 10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.03.012
25
Guo J. Gong X. Yu S. Wei B. Chu L. Liu J. et al (2023). Responses of soil microbial diversity to forest management practices after pine wilt disease infection.Forests14:862. 10.3390/f14050862
26
Hao Z. Huang J. Li X. Sun H. Fang G. (2022). A multi-point aggregation trend of the outbreak of pine wilt disease in China over the past 20 years.Forest Ecol. Manag.505:119890. 10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119890
27
Hao Z. Huang J. Zhou Y. Fang G. (2021). Spatiotemporal pattern of pine wilt disease in the Yangtze river Basin.Forests12:731. 10.3390/f12060731
28
Hok L. de Moraes Sá J. C. Boulakia S. Reyes M. Leng V. Kong R. et al (2015). Short-term conservation agriculture and biomass-C input impacts on soil C dynamics in a savanna ecosystem in Cambodia.Agric. Ecosyst. Environ.21454–67. 10.1016/j.agee.2015.08.013
29
Holden S. R. Treseder K. K. (2013). A meta-analysis of soil microbial biomass responses to forest disturbances.Front. Microbiol.4:163. 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00163
30
Hou E. Chen C. Luo Y. Zhou G. Kuang Y. Zhang Y. et al (2018). Effects of climate on soil phosphorus cycle and availability in natural terrestrial ecosystems.Global Change Biol.243344–3356. 10.1111/gcb.14093
31
Jeong J. Kim C. Lee K. Bolan N. S. Naidu R. (2013). Carbon storage and soil CO2 efflux rates at varying degrees of damage from pine wilt disease in red pine stands.Sci. Total Environ.465273–278. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.080
32
Jiao Z. Gao Z. Liao Y. Liu Y. Dong L. Sun H. (2023). Effects of pine wilt disease on rhizosphere microbiota and fine root fungi: Insights into enzyme activity, ectomycorrhizal infection and microbial composition.Forests14:1884. 10.3390/f14091884
33
Kim C. Jang K. Kim J. Byun J. Lee C. Jeon K. (2010). Relationship between soil properties and incidence of pine wilt disease at stand level.Landsc. Ecol. Eng.6119–124. 10.1007/s11355-009-0087-2
34
Kim C. Jeong J. Cho H. Lee K. Park N. (2011). Carbon and nitrogen status in litterfall of a red pine stand with varying degrees of damage from pine wilt disease.J. Ecol. Environ.34215–222. 10.5141/JEFB.2011.023
35
Liu J. Liu W. Wu J. Wei B. Guo J. Zhong L. et al (2023). Responses of plant species diversity and biomass to forest management practices after pine wilt disease.Forests14:1636. 10.3390/f14081636
36
Liu Y. Huang J. Yang T. (2023). Natural factors play a dominant role in the short-distance transmission of pine wilt disease.Forests14:1059. 10.3390/f14051059
37
Lucas-Borja M. E. Hedo J. Cerdá A. Candel-Pérez D. Viñegla B. (2016). Unravelling the importance of forest age stand and forest structure driving microbiological soil properties, enzymatic activities and soil nutrients content in Mediterranean Spanish black pine (Pinus nigra Ar. ssp. salzmannii) forest.Sci. Total Environ.562145–154. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.160
38
Ma Y. Qu Z. Liu B. Tan J. Asiegbu F. O. Sun H. (2020). Bacterial community structure of Pinus Thunbergii naturally infected by the nematode Bursaphelenchus Xylophilus.Microorganisms8:307. 10.3390/microorganisms8020307
39
Mabuhay J. A. Nakagoshi N. (2012). Response of soil microbial communities to changes in a forest ecosystem brought about by pine wilt disease.Landsc. Ecol. Eng.8189–196. 10.1007/s11355-011-0165-0
40
National Forestry and Grassland Administration (2020). China Forest Resources Report (2014-2018).Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House.
41
Nazari M. Eteghadipour M. Zarebanadkouki M. Ghorbani M. Dippold M. A. Bilyera N. et al (2021). Impacts of logging-associated compaction on Forest soils: A meta-analysis.Front. Forests Glob. Change4:780074. 10.3389/ffgc.2021.780074
42
Norris C. E. Quideau S. A. Oh S. Swallow M. J. B. Kishchuk B. E. (2023). Post-fire and harvest legacy on soil carbon and microbial communities in boreal forest soils.Forest Ecol. Manag.542:121136. 10.1016/j.foreco.2023.121136
43
Pan J. Guo Q. Li H. Luo S. Zhang Y. Yao S. et al (2021). Dynamics of soil nutrients, microbial community structure, enzymatic activity, and their relationships along a chronosequence of Pinus massoniana plantations.Forests12:376. 10.3390/f12030376
44
Qu Z. L. Liu B. Ma Y. Xu J. Sun H. (2020). The response of the soil bacterial community and function to forest succession caused by forest disease.Functional Ecology342548–2559. 10.1111/1365-2435.13665
45
Qu Z. Braima A. Liu B. Ma Y. Sun H. (2022). Soil fungal community structure and function shift during a disease-driven forest succession.Microbiol. Spectrum10:e00795-22. 10.1128/spectrum.00795-22
46
Rigueiro Rodríguez A. Mosquera Losada M. R. Fernández Núñez E. (2012). Afforestation of agricultural land with Pinus radiata D. Don and Betula alba L. in NW Spain: Effects on soil pH, understorey production and floristic diversity eleven years after establishment.Land Degradation Dev.23227–241. 10.1002/ldr.1072
47
Saiya-Cork K. R. Sinsabaugh R. L. Zak D. R. (2002). The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil.Soil Biol. Biochem.341309–1315. 10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00074-3
48
Sakamoto K. Miki N. Tsuzuki T. Nishimoto T. Yoshikawa K. (2003). Comparison of stand dynamics after dieback caused by pine wilt disease among pine forests with different management regimes in western Japan.J. For. Res.8303–309. 10.1007/s10310-003-0044-0
49
Seidl R. Klonner G. Rammer W. Essl F. Moreno A. Neumann M. et al (2018). Invasive alien pests threaten the carbon stored in Europe’s forests.Nat. Commun.91610–1626. 10.1038/s41467-018-04096-w
50
Shi C. Gao Y. Wang Y. Xu X. Huang B. (2015a). Soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities in Pinus massoniana forest infected by pine wood nematode.Chinese J. Ecol.341046–1051. 10.13292/j.1000-4890.20150311.024
51
Shi C. Wang C. Xu X. Huang B. Wu L. Yang D. (2015b). Comparison of bacterial communities in soil between nematode-infected and nematode-uninfected Pinus massoniana pinewood forest.Appl. Soil Ecol.8511–20. 10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.08.008
52
Siegert C. Clay N. Pace K. Vissa S. Hofstetter R. W. Leverón O. et al (2024). Bark beetle-driven community and biogeochemical impacts in forest ecosystems: A review.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am.117163–183. 10.1093/aesa/saae009
53
Tang X. Yuan Y. Li X. Zhang J. (2021). Maximum entropy modeling to predict the impact of climate change on pine wilt disease in China.Front. Plant Sci.12:764–778. 10.3389/fpls.2021.652500
54
Tian H. Zhao L. Koski T. M. Sun J. (2022). Microhabitat governs the microbiota of the pinewood nematode and its vector beetle: Implication for the prevalence of pine wilt disease.Microbiol. Spectrum10:e00783-22. 10.1128/spectrum.00783-22
55
Veldkamp E. Schmidt M. Powers J. S. Corre M. D. (2020). Deforestation and reforestation impacts on soils in the tropics.Nat. Rev. Earth Environ.1590–605. 10.1038/s43017-020-0091-5
56
Wan P. He R. Wang P. Cao A. (2022). Implementation of different forest management methods in a natural forest: Changes in soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities.Forest Ecol. Manag.520:120409. 10.1016/j.foreco.2022.120409
57
Wang W. Peng W. Liu X. He G. Cai Y. (2022). Spatiotemporal dynamics and factors driving the distributions of pine wilt disease-damaged forests in China.Forests13:261. 10.3390/f13020261
58
Wen X. Gu T. Qi H. Zhang F. (2022). Incineration or pulverization? Evolutionary game model of management of nematode-infected pine wood in China in the carbon neutrality context.Front. Environ. Sci.10:1041357. 10.3389/fenvs.2022.1041357
59
Whitman T. Whitman E. Woolet J. Flannigan M. D. Thompson D. K. Parisien M. (2019). Soil bacterial and fungal response to wildfires in the Canadian boreal forest across a burn severity gradient.Soil Biol. Biochem.138:107571. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107571
60
Wu C. Tu C. Wang Z. Fan J. Lv Z. Fan Y. (2023). The effect of clearing diseased wood on the soil’s physicochemical properties in black pine forests.Sustainability15:15980. 10.3390/su152215980
61
Xu Y. Du A. Wang Z. Zhu W. Li C. Wu L. (2020). Effects of different rotation periods of Eucalyptus plantations on soil physiochemical properties, enzyme activities, microbial biomass and microbial community structure and diversity.Forest Ecol. Manag.456:117683. 10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117683
62
Yan L. Wen Y. Zhou X. Li H. Wu W. Sunoj V. S. J. et al (2024). Adding Castanopsis hystrix to a Pinus massoniana plantation changed leaf phosphorus and nitrogen investment and soil nitrogen concentrations.Plant Soil49631–49. 10.1007/s11104-023-06097-1
63
Yang Z. Wang X. Zhang Y. (2014). Recent advances in biological control of important native and invasive forest pests in China.Biol. Control68117–128. 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2013.06.010
64
Zhang W. Qiao W. Gao D. Dai Y. Deng J. Yang G. et al (2018). Relationship between soil nutrient properties and biological activities along a restoration chronosequence of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation forests in the Ziwuling Mountains, China.Catena16185–95. 10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.021
65
Zhang X. Zhao Z. Chen T. Zhao T. Song L. Mei L. (2021). Fertilization and clear-cutting effects on greenhouse gas emissions of pinewood nematode damaged Masson pine plantation.Ecosyst. Health Sustainabil.7:1868271. 10.1080/20964129.2020.1868271
66
Zhang Y. Sun Z. Yin S. (2024). Response of soil physicochemical properties and microbial community composition in Larix olgensis plantations to disturbance by a large outbreak of bark beetle.Forests15677–685. 10.3390/f15040677
Summary
Keywords
pine wilt disease, Pinus massoniana , soil physicochemical properties, soil enzymatic activities, infection chronosequence
Citation
Song X, Jian Z, Wei K, Wang X and Xiao W (2025) Dynamics of soil nutrients and biological activities along an infection chronosequence of pine wilt disease in subtropical Masson pine forests. Front. For. Glob. Change 8:1544221. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2025.1544221
Received
12 December 2024
Accepted
05 May 2025
Published
23 May 2025
Volume
8 - 2025
Edited by
Anna Maria Vettraino, University of Tuscia, Italy
Reviewed by
Cameron Ducayet McIntire, United States Department of Agriculture, United States
Laith Khalil Tawfeeq Al-Ani, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia
Ruihe Gao, Shanxi Agricultural University, China
Mia Miranti, Padjadjaran University, Indonesia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Song, Jian, Wei, Wang and Xiao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoyi Wang, xywang@caf.ac.cnWenfa Xiao, xiaowenf@caf.ac.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.