- 1College of Forestry, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Tree Genetics and Breeding, Key Laboratory of Tree Breeding and Cultivation of State Forestry and Grassland Administration, Research Institute of Forestry, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China
Height to crown base is a main component of crown structure to understand the growth of the tree. It is essentially important to construct a comprehensive height to crown base model to facilitate the application in forest management practice decision making. Measurements from a total of 13,822 trees across 159 sample plots developed in the forest stands of Larix kaempferi plantations in Liaoning and Hubei provinces were used to fit the model. Variables of tree size, competition, climate, and thinning practice were considered in the model development. A dummy variable approach was used to analyze the effects of initial planting density and study area on height to crown base, and the interaction between initial planting density and competition was also considered in the height to crown base model. A nonlinear mixed effects model was developed to eliminate heteroscedasticity at the sample plot level. The results showed that the logistic model had the best performance and was therefore selected as the base model. Total tree height and height-diameter ratio from tree level variables, stand basal area of competition variables, spring degree-days below 0°C (DD_0_sp) of climate variables, and thinning variables showed significant contributions to height to crown base and were finally included in the final model. Height to crown base increased with the increase in total tree height, competition, height-diameter ratio, thinning intensity, and decreased with the increase in DD_0_sp and logarithmic transformation of altitude. Large initial planting density resulted in a rise in height to the crown base. The relative contributions of each group of variables to height to crown base were as follows: tree size (41.7%) > competition (27.3%) > thinning (24.5%) > interaction of competition and thinning (3.2%) > climate (2.4%) > site quality (0.9%). The model reveals that thinning mitigates the impact of competition on height to crown base, especially for trees from Hubei province.This comprehensive model provides a robust tool for optimizing Larix kaempferi plantation management strategies and will lay a foundation to conduct forest management strategies decision.
1 Introduction
Forest canopy is important in determining the structures of the forest stand and affecting tree development within stand (Pan et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022; Qin et al., 2022). The distribution of tree crowns affects the canopy structure and photosynthesis capacity through its effects on light penetration and absorption (Monsi and Saeki, 2005; Gao et al., 2023a). Crown dimensions are generally characterized by horizontal characteristic (e.g., crown width) (Sharma et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2025), vertical feature (e.g., crown length) (Sattler and LeMay, 2011) and three-dimensional occupation (e.g., crown volume) (Aryal et al., 2023), and is a reflection of tree interactions with their surrounding environment (Martin et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2024). Crown length or height to crown base indicated the vitality of the tree and has been successfully incorporated into tree growth models (Sporek and Sporek, 2023; Jia and Chen, 2019; Sattler and LeMay, 2011). Due to the complexity of topography and forest environment for a dense stand, directly measuring height to crown base is almost impossible (Fu et al., 2017). Therefore, it is essentially important to develop a height to crown base model to facilitate its incorporation into the forest growth and yield system (Shi et al., 2022; Yi et al., 2023). Despite many heights to crown base models for a variety of tree species having been developed (Rijal et al., 2012; Torita et al., 2024; Yan et al., 2024), a comprehensive model considering initial planting density and thinning practice is still limited.
The original motivation for developing height to crown base model is to simulate the recession of tree crown (Ledermann, 2011). The static model relies on allometric relationships between height to crown base and tree size, stand attributes, neighbor tree competition, as well as the climate variables (Garber et al., 2008). Otherwise, the dynamic approach directly predicts the change in height to crown base by developing a function including only initial forest stand conditions (Hann and Hanus, 2004). In addition, the dynamic height to crown base can be developed using the branch mortality technique, which seems more complicated (Jia and Chen, 2019). Due to the lack of repeated measurements, developing a static model is more common compared to the dynamic model (Garber et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2024). An accurate height to crown base model is more useful in the crown shape description and thus provides a reference for the forest management practice decision based on the crown thinning (Dagley et al., 2023; Tong et al., 2024). However, the application of static model is still limited because the information on historical forest stand structure has not been included in the model. Initial planting density is an important forest management practice that affects the inter-tree competition, mortality of individual trees, and stiffness of trees (Antony et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2017). The increasing stand density increases crown recession; otherwise, crown recession will be slowed in the condition of reducing stand density by thinning (Short and Burkhart, 1992). Thinning has been tested and regarded as an important practice to improve the performance of tree growth model (Barbeito et al., 2008; Jia et al., 2021; Dagley et al., 2023). However, initial planting density and thinning have not been incorporated into height to crown base model at present.
Height to crown base development is also attributed to competition, because the intense competition will result in more rapid mortality for the branches from the lower part of crown (Antos et al., 2010). Therefore, it is essentially important to avoid under-prediction in sparse forest stands and over-prediction in dense stands for height to crown base prediction. Sharma et al. (2018) developed a height to crown base model by comparing distance-related competition variables and distance-independent competition variables and found that the distance-related competition variables showed better performance. Climate is also an important factor that affects the characteristics of crown (Yan et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024; Yan et al., 2023; Chhin et al., 2008). Shi et al. (2022) evaluate the influence of tree height, forest stand competition, site conditions, and climate on height to crown base modeling. The results indicated that large tree height and intense competition increased the height to crown base, and climate also significantly affected the model performance. Exponential and logistic equations were commonly used as base models in the height to crown base model development (Rijal et al., 2012; Duan et al., 2018).
Larix kaempferi is a main economic tree species that has been introduced in China for more than 110 years (Gao et al., 2023b). Because of the characteristics of fast growth, good quality, strong resistance, and wide adaptability, Larix kaempferi is widely planted in northern China and sub-high mountainous areas of southern China. The initial planting density and thinning strategy for Larix kaempferi plantation across the planting area in China are sophisticated and inconsistent. Therefore, it is challenging to analyze the variations of forest management strategies on height to crown base. We aimed to develop a comprehensive nonlinear mixed effects height to crown base model for planted Larix kaempferi in China, incorporating initial planting density, thinning strategy, climate, and competition factors. The results will lay a foundation for linking the crown development, tree growth, and wood quality for Larix kaempferi.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area description
Dagujia forest farm and Changlinggang forest farm, characterized by different climate characteristics, were the locations to conduct our field investigation. Dagujia forest farm (124°47′–125°12′E, 42°22′–42°16′N) is from Liaoning province of Northeast China, and Changlinggang forest farm (110°00′–110°04′E, 30°47′–30°50′N) is from Hubei province of central China. The present study was conducted at these two forest farms because the two sites are nearly the northernmost and southernmost areas suitable for the normal growth of Larix kaempferi plantation. The elevation of Dagujia forest farm ranges from 200 to 600 meters. The annual average temperature is 6.3°C, the extreme maximum temperature is 34°C, and the extreme minimum temperature is −34°C. The average annual precipitation is 600 mm, mainly concentrated from July to September. Frost-free days in 1 year is about 137 days, and the type of soil is mainly Alfisol. Changlinggang forest farm is characterized by a north subtropical monsoon mountain temperate climate. The range of altitude is 1,600–1900 m. The annual average temperature is 13.5°C, the extreme maximum temperature is 29°C, and the extreme minimum temperature is −17.2°C. The average frost-free days per year is about 250 days. The annual precipitation is 1,600 mm, mainly concentrates from July to September. The type of soil is mountainous brown soil. Larix gmelinii, Pinus massoniana, and Cunninghamia lanceolata are the main tree species.
2.2 Data collection
An investigation at Dagujia forest farm was conducted in 2017 and 2018. A total of 17 forest stands with complete appearance and different ages were selected to develop permanent sample plots. In 2017, a total of 96 permanent sample plots, each with an area of 0.08 hectare (approximately 28.3 × 28.3 m2), were developed from 14 forest stands with ages ranging from 4 to 34 years. In 2018, a total of nine permanent sample plots with an area of 0.06 hectare for each plot (20 × 30 m2) were developed from the remaining three forest stands with age ranging from 12 to 20 years. Thus, 105 sample plots were developed with current densities from 388 to 2,850 trees per hectare, and with an initial planting density of 2,500 or 3,300 trees per hectare. The field investigation at Changlinggang forest farm was conducted from June to August in 2019 and 2022. In 2019, six permanent sample plots, each measuring 0.06 hectares (20 × 30 m2), were developed for each of the forest stands aged 5–42 years. In 2022, a supplementary field study was conducted at three additional forest stands aged 19–36 years. Six plots, each sized 0.06 hectare (20 × 30 m2), were developed from each forest stand. Therefore, a total of 78 permanent sample plots were developed at Changlinggang forest farm, with the current density ranging from 183 to 1,667 trees per hectare, and an initial planting density of forest stands of 1,667 or 2,500 trees per hectare. The detailed description of the initial planting density and historical forest management practices for each sample plot are shown in Table 1.
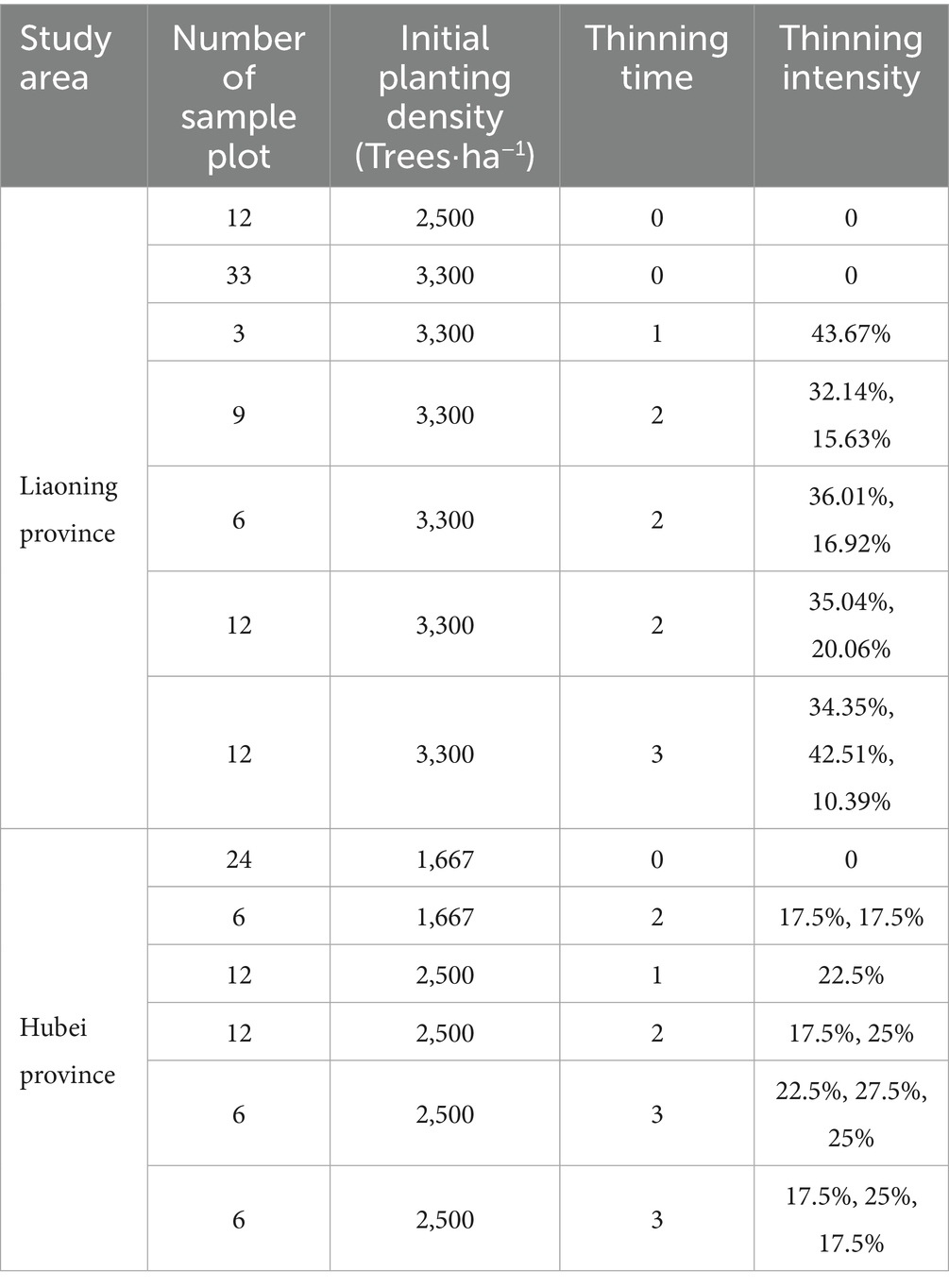
Table 1. Descriptive information of the initial planting density and thinning practice for the sample plots used in the height to crown model development.
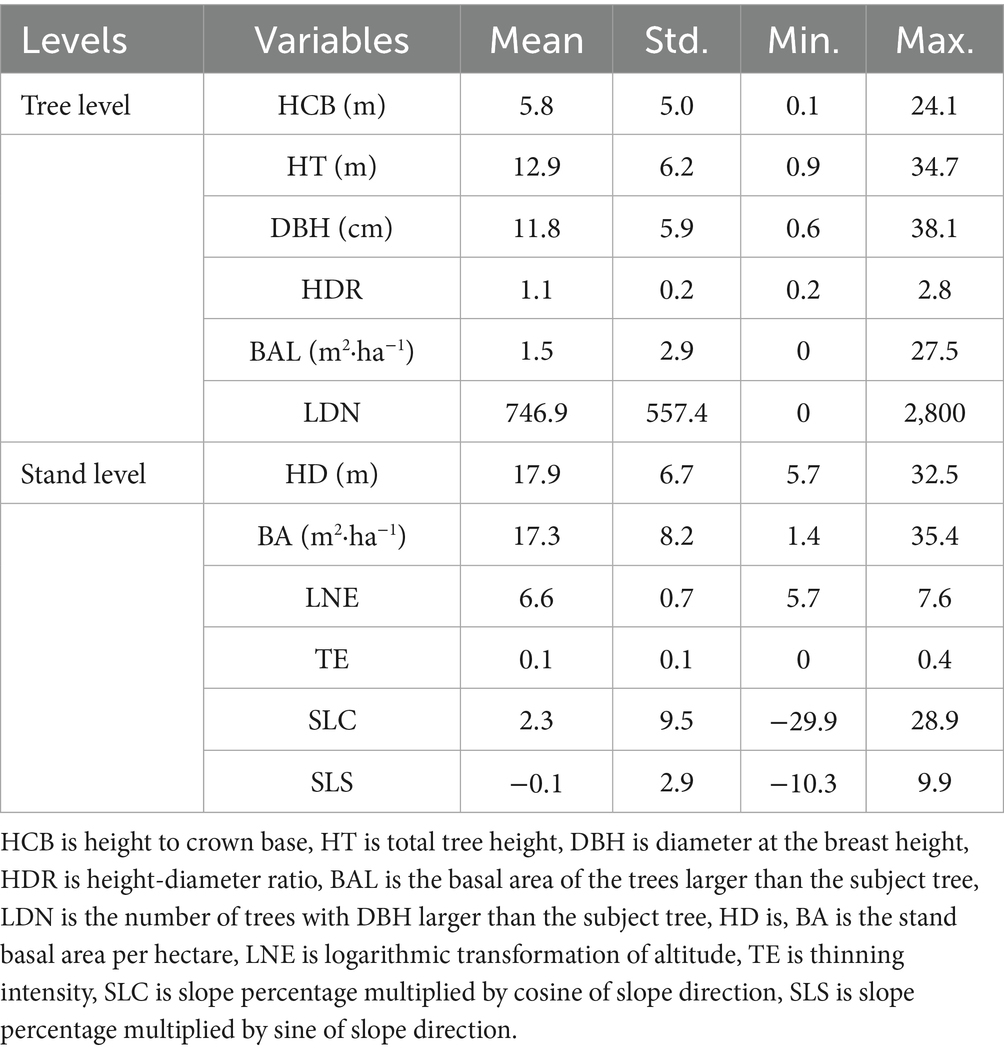
The measurements for the attributes of all trees from each plot were conducted and recorded in the field. Diameter at breast height (DBH, cm), tree height (HT, m), and height to the crown base (HCB, m) were measured. Crown width (CW, m) from four directions was measured with a measuring tape. Height-diameter ratio (HDR) was calculated as the ratio of total tree height to diameter at the breast height. Dominant tree height (HTdom, m) was defined as the average tree height for the eight trees with the largest tree height from the 0.08-hectare plots and six trees from the 0.06-hectare plots. The sum of the basal areas of trees larger than the subject tree (BAL, m2·ha−1), the number of trees with DBH larger than the subject tree (LDN, trees·ha−1) and the stand basal area per hectare (BA, m2·ha−1) defined as the ratio of the sum of basal area for each tree in the plot-to-plot area were calculated. Trees from each plot were screened for the preliminary inspection, and those with unreasonable measurements or other tree species in the sample plots were excluded. Only the plots with complete records of thinning times and thinning intensity were used in the height to crown base model development. Finally, a total of 87 plots from Dagujia forest farm and 78 plots from Changlinggang forest farm were used to fit the height to crown base model. Table 2 shows detailed information about the stand characteristics of each sample plot. A total of 13,822 trees from 165 sample plots were used to develop the height to crown base models for Larix kaempferi plantations.
2.3 Base model selection
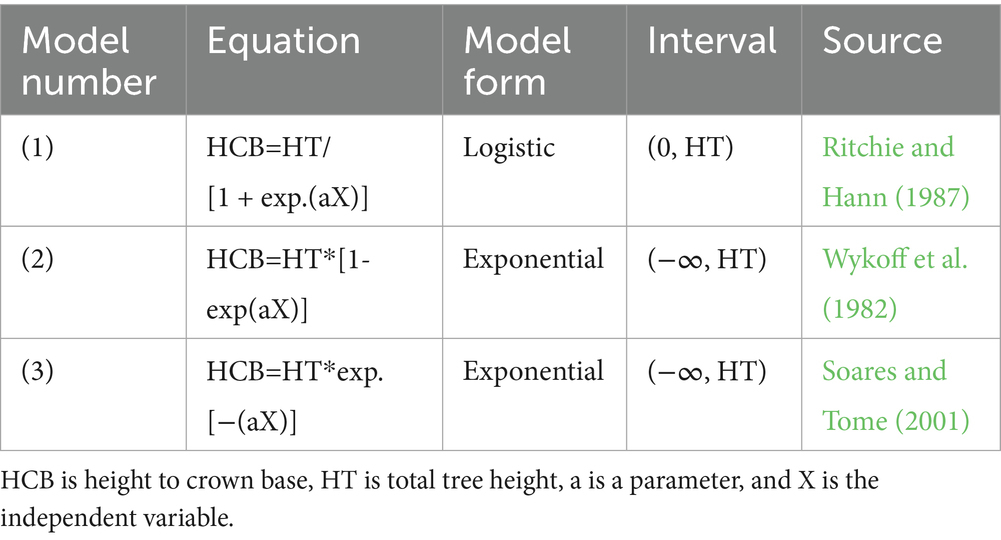
Among all the predictors, height to crown base is mostly related to tree height. Therefore, height to crown base is first modeled by using total tree height as the sole variable. Logistic function and exponential function (Wykoff et al., 1982; Soares and Tome, 2001) were used as base models, and the three models finally used and compared were listed in Table 3. All three base equations were fitted by ordinary least squares estimation. Ra2, AIC, and RMSE were used to compare models (Equations 1–3).
2.4 Base model extension
Tree variable, competition variable, site quality, climate variable, initial planting density, and thinning intensity were added to the base model. All the variables and combinations of different variables have been tried to incorporate into the model. The fitting accuracy of each model and significance of parameter test were combined to select the best model. In addition, the biological sense of the parameter estimates was also considered. In detail, the tree level variables included HT, DBH, CW, and HDR. The competition variables considered were BA and BAL, site factor of HTdom, logarithmic transformation of altitude (lnE), slope percentage multiplied by cosine of slope direction (SLC), slope percentage multiplied by sine of slope direction (SLS), and LDN. The climate variables were generated following Ma et al. (2024). Initial planting density was added using a dummy variable approach. To further analyze the effects of thinning on the change of height to crown base of individual trees, we further developed an index by considering the thinning intensity and the thinning intervals, and added it to the height to crown base model. Jia et al. (2021) developed an index for forest stands, conducted only once at the time of thinning, using a ratio between the thinning intensity and stand age when the thinning practice was implemented. In our study, we developed a comprehensive index for conducting two and three times of thinning by taking the thinning time effect into consideration. For the forest stands conducted thinning practice one, two, and three times, a comprehensive thinning effect could be shown as Equations 4–6.
Where TEi were the thinning indices for the forest stands conducting thinning for one (i = 1), two (i = 2), and three times (i = 3), respectively; TI1, TI2, and TI3 were the thinning intensities for the first time, second time, and third time, respectively; Age is forest stand age for the current time, Age1, Age2 and Age3 were the forest stand ages for the first thinning, second thinning and third thinning.
To avoid the problem of over-parameterization results from the increasing number of variables included in the model, only one variable from each type was selected and added to the final model. The multicollinearity of the model was examined using the variance inflation factor (VIF). VIF is larger than 10, indicating a problem of multicollinearity between variables. Considering the hierarchical structure and the possible correlation between the trees nested in the plots, a nonlinear mixed effects model was developed by introducing random effects at the plot level (Yan et al., 2024; Yang and Huang, 2018). A residual plot was used to detect the efficiency of heteroscedasticity elimination by using the power equation and exponential equation. All analyses were conducted through the R software using nlme package (R Core Team, 2023). Hierarchical partitioning analysis was used to quantify relative importance of the independent variables on height to crown base performed by “hier.part” package of R software (Tong et al., 2025).
3 Results
3.1 Model development of height to crown base
Based on estimates and biological sense of parameters, as well as goodness of fit for the three candidate models in Table 3, the logistic equation was regarded as the best base model with Ra2 of 0.76 and RMSE of 2.48 m. HDR from tree level variables and stand basal area per hectare from competition variables were finally incorporated into height to crown base model. DD_0_sp of climate and logarithmic transformation of altitude of site quality variables were included in the final model. Subsequently, the thinning index was successfully incorporated into the height to crown base model. Finally, initial planting density and study area were added into the model using a dummy variable approach. The final model is shown as Equation 7, and the parameter estimates and goodness of fit statistics are shown in Table 4. The final model had Ra2 of 0.9297, AIC of 46,789, and RMSE of 1.3137 m. All parameter estimates were significant at the significance level of 0.05, and they had biological significance. It indicated that competition, climate, site quality, and thinning practice significantly affected height to crown base. All parameters for the dummy variables were significantly different at the significance level of 0.05, indicating that initial planting density had a significant impact on the height to crown base of trees from Liaoning and Hubei provinces.
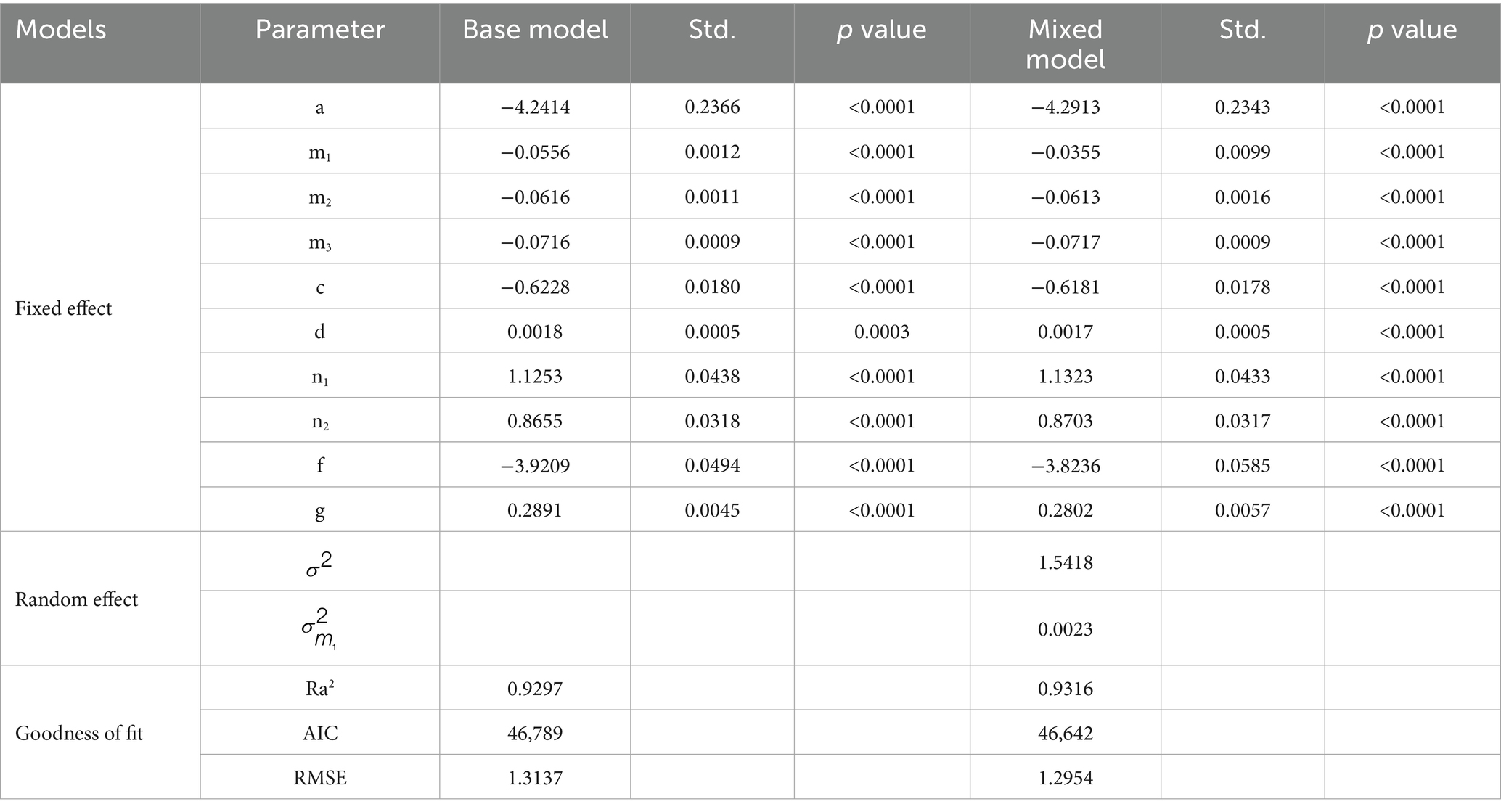
Table 4. Parameter estimates, random effects variance components, and goodness of fit for the mixed-effects HCB model.
Where HCB is height to crown base; HT is total tree height; BA is stand basal area per hectare; HDR is height-diameter ratio; DD_0_sp is spring degree-days below 0°C; TE is the comprehensive index related to thinning practice. Y1 = 1, Y2 = 0, Y3 = 0 indicated the initial planting density of 1,667 tree·ha−1; Y2 = 1, Y1 = 0, Y3 = 0 indicated the initial planting density of 2,500 tree·ha−1; Y3 = 1, Y1 = 0, Y2 = 0 indicated the initial planting density of 3,300 tree·ha−1, respectively; X1 = 1 and X2 = 0 represented Liaoning province, X1 = 0 and X2 = 1 represented Hubei province.
3.2 Mixed effect HCB model
A nonlinear mixed effects HCB model at the plot level for Larix kaempferi was developed. The combinations of more than two random effect parameters lead to non-convergence or insignificant estimates. Finally, the parameter of m1, regarded as a random effect, had the largest Ra2, and the smallest AIC and RMSE (Table 4). Compared to the base model, Ra2 of the final mixed model was 0.9316, AIC was 46,642, and RMSE was 1.2954 m, which were better than the base model. Based on the likelihood ratio test (LRT), the performance of nonlinear mixed effects model was significantly improved compared to the nonlinear model (LRT = 151.42, p < 0.0001). By comparing the residual graphs of the base model and nonlinear mixed effects model, it was shown that heteroscedasticity was improved and the range of residuals was reduced (Figure 1).
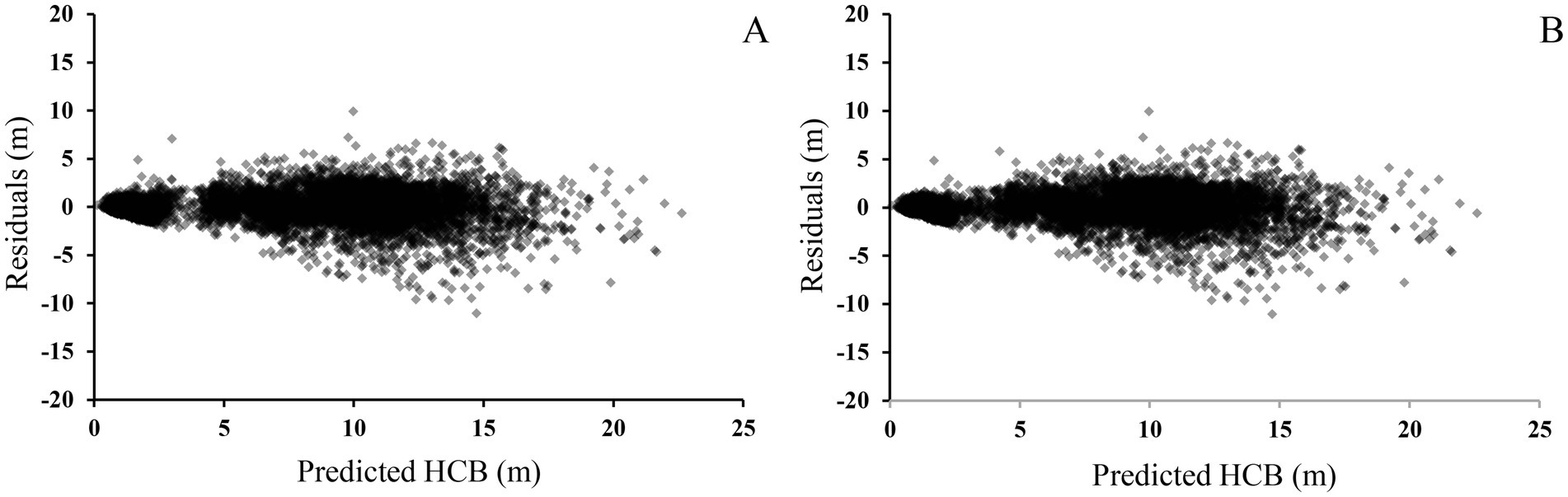
Figure 1. Residual plots of height to crown base model based on ordinary regression model (A) and mixed-effects model (B). HCB is height to crown base of individual trees.
3.3 Effects of variables on the HCB
Based on the parameter estimates for the fixed effect in the mixed model, we further analyzed the influence of each variable on height to crown base (Figure 2). The results revealed that height to crown base of individual trees increased with the increasing of total tree height (Figure 2A), competition level (Figure 2B), HDR (Figure 2C), and the thinning intensity (Figure 2F). Height to crown base decreased with the increasing of DD_0_sp (Figure 2D) and logarithmic transformation of altitude (Figure 2E). The results from Figure 2 also indicate that a large initial planting density will increase the height to crown base in both Liaoning province and Hubei province. Increased thinning intensity decreased the competition level, and the effect of interaction of thinning and competition on the height to crown base was also studied, as shown in Figure 3. It indicated that the height of crown base rose with the increase in thinning intensity for forest stands with all the kinds of initial planting densities. The intense competition level also increased the height to crown base. It firmly showed that the effect of competition on the height to crown base was reduced with an increase in thinning intensity, especially for trees from Hubei province.
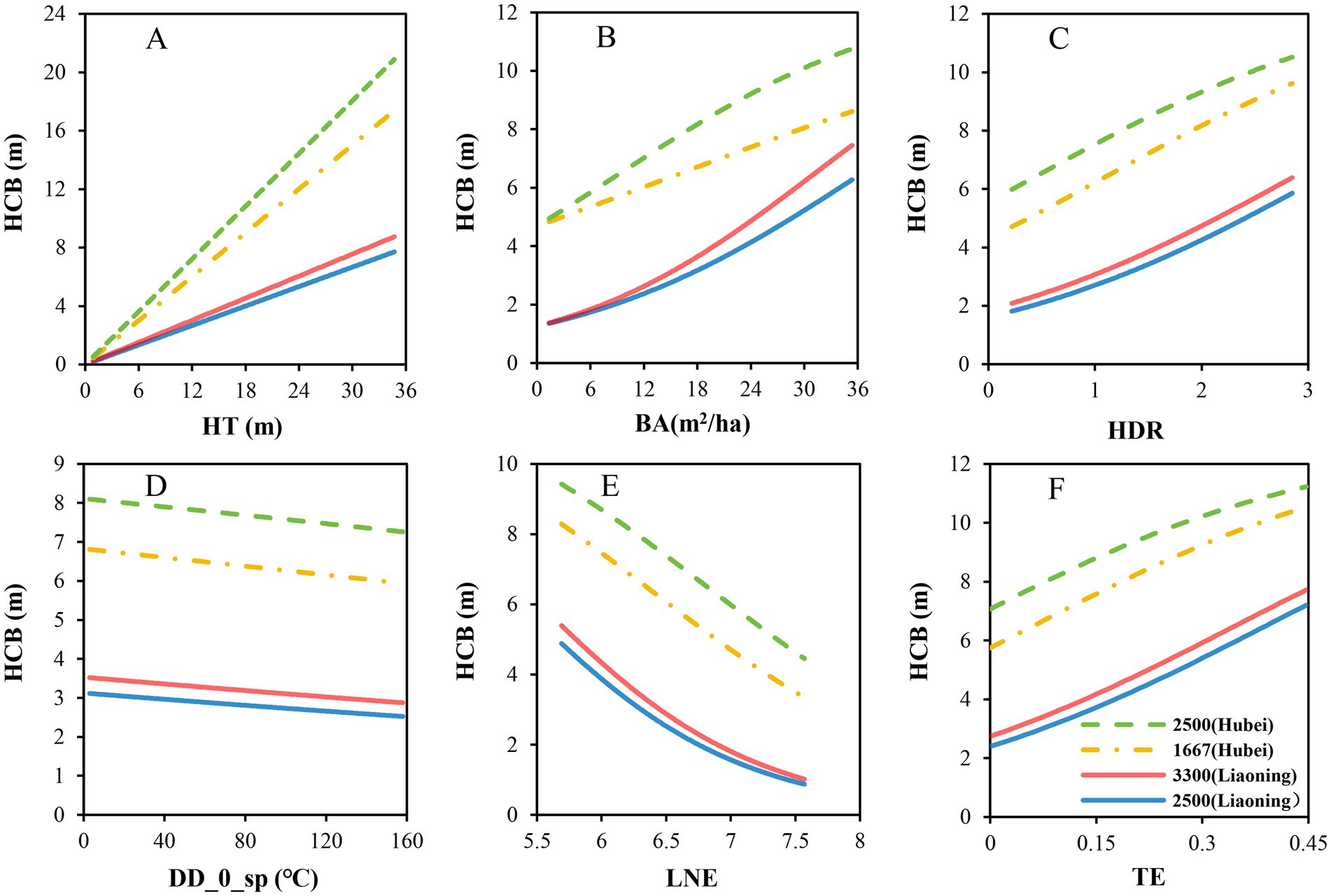
Figure 2. (A) represents the influence of HT on height to crown base, (B) represents the influence of BA on height to crown base, (C) represents the influence of HDR on height to crown base, (D) represents the influence of DD_0_sp on height to crown base, (E) represents the influence of LNE on height to crown base, F represents the influence of TE on height to crown base.
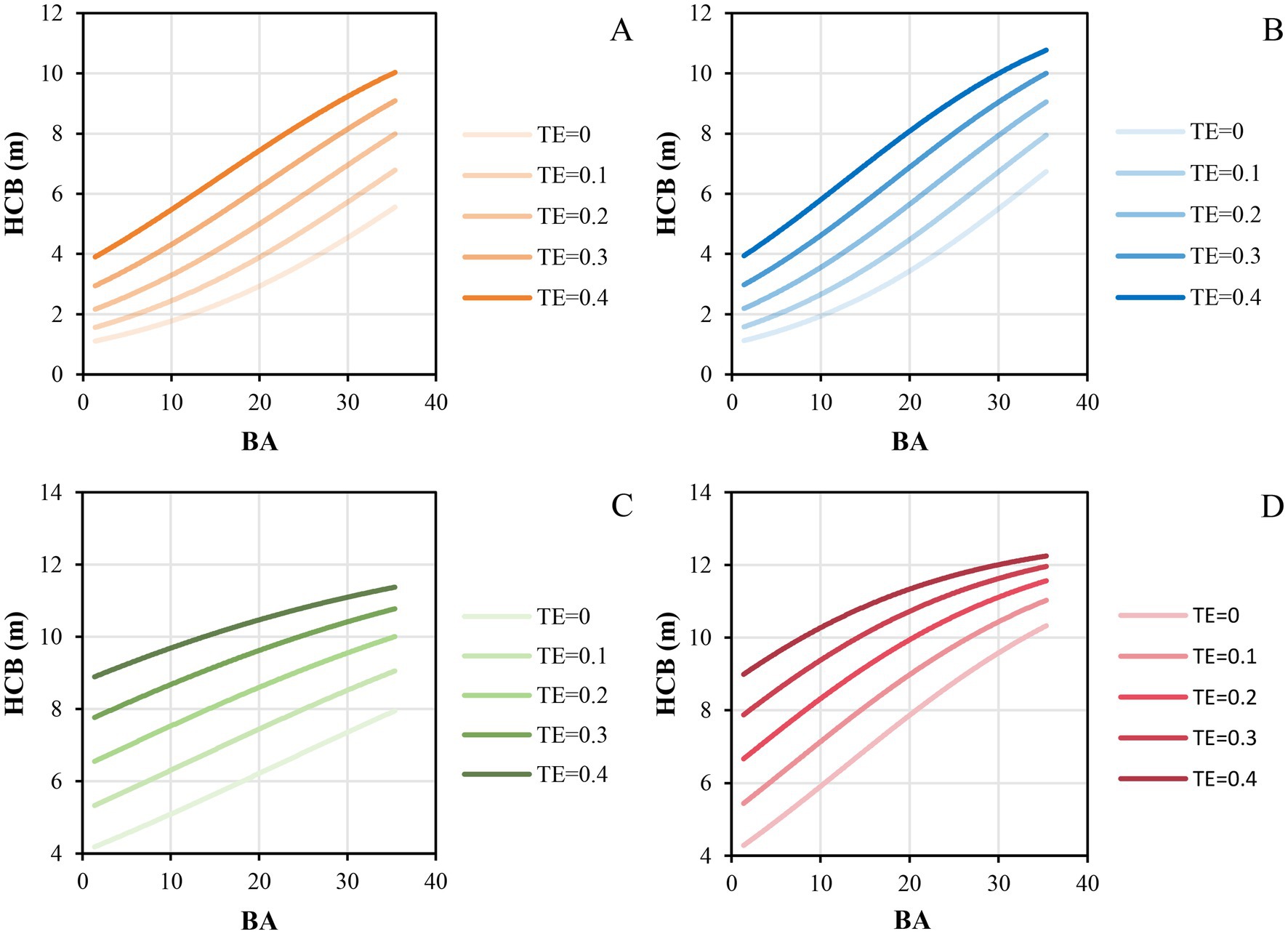
Figure 3. Effects of the interaction of thinning and competition on the height to crown base of individual trees, A represents trees from Liaoning province with the initial planting density of 2,500 trees per hectare, B represents trees from Liaoning province with the initial planting density of 3,300 trees per hectare, C represents trees from Hubei province with the initial planting density of 1,667 trees per hectare, and D represents trees from Hubei province with the initial planting density of 2,500 trees per hectare.
Relative contribution for each variable (Figure 4) and different groups of the data divided by different study areas (Figure 5, A1,A2), initial planting densities (Figure 5, B1–B3), and different thinning intensities (Figure 5, C1–C4) were studied. It indicated that the relative contributions of each group of variables to height to crown base were as follows: tree size (41.7%) > competition (27.3%) > thinning (24.5%) > interaction of competition and thinning (3.2%) > climate (2.4%) > site quality (0.9%). Total tree height, stand basal area per hectare and thinning intensity were the most important variables in determining height to crown base with tree height (36.9%) > stand basal area (24.6%) > thinning intensity (20.71%) for Liaoning province, and total tree height (33.8%) > thinning intensity (22.28%) > stand basal area (26.76%) for Hubei province. For the trees from different initial planting densities, the most important variables for the trees from the stand with initial planting density of 1,667 trees per hectare were thinning intensity (31.53%) > total tree height (28.97%) > stand basal area (27.57%), total tree height (23.28%) > logarithmic transformation of altitude (20.76%) > thinning intensity (19.05) for trees from the stand with initial planting density of 2,500 trees per hectare, and total tree height (39.67%) > stand basal area (24.30%) > thinning intensity (21.06%) for trees from the stand with initial planting density of 3,300 trees per hectare. We divided the thinning intensity into four groups; the most important variables for most of the groups were tree height, stand basal area, and thinning intensity.
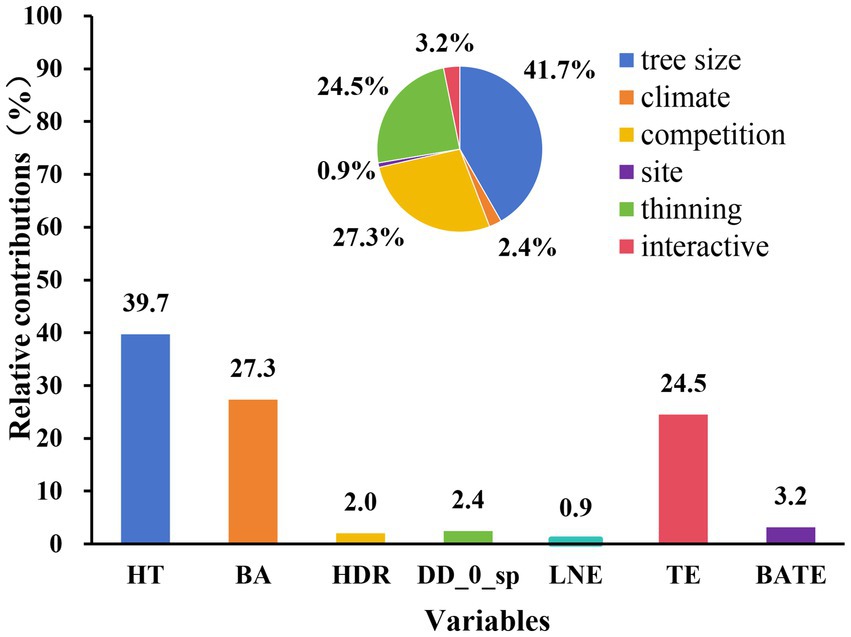
Figure 4. The relative contributions of variables to the height to crown base model. HT is total tree height, BA is the stand basal area per hectare, HDR is height-diameter ratio, DD_0_sp is spring degree-days below 0°C, LNE is the logarithmic transformation of altitude, TE is thinning intensity, and BATE is the interaction of initial planting density and competition.
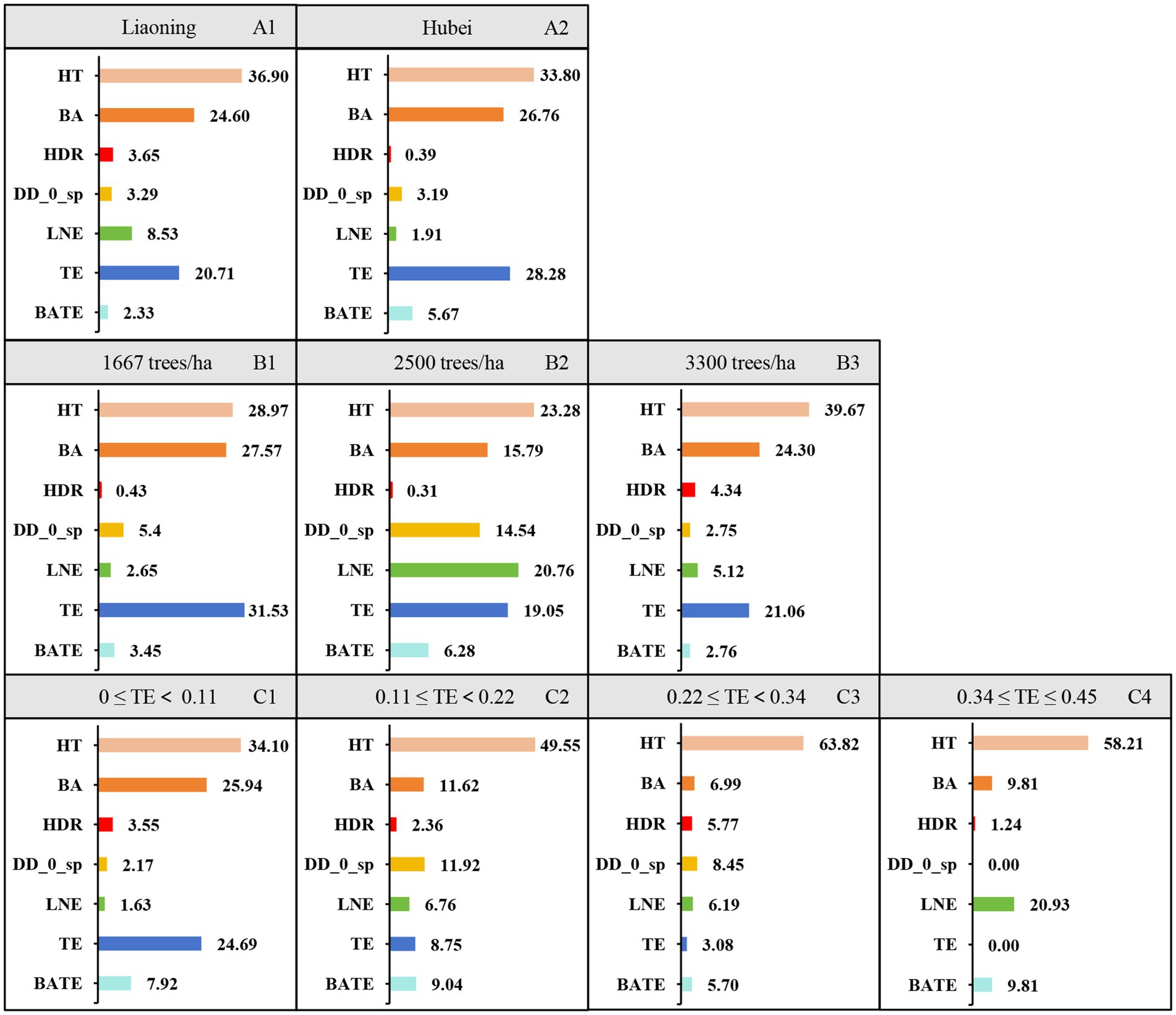
Figure 5. The relative contributions of each variable to height to crown base of individual trees by different groups, including different study area (Liaoning and Hubei province, A1,A2), different initial planting densities (1,667 trees/ha, 2,500 trees/ha, 3,300 trees/ha, B1–B3), and different thinning intensities (0 ≤ TE<0.11, 0.11 ≤ TE<0.22, 0.22 ≤ TE<0.34, 0.34 ≤ TE ≤ 0.45, C1–C4). HT is total tree height, BA is the stand basal area per hectare, HDR is height-diameter ratio, DD_0_sp is days below 0°C in spring, LNE is the logarithmic transformation of altitude, and TE is thinning intensity. BATE is the interaction of BA and TE.
4 Discussion
Height to the live crown base is an important crown dimension related to photosynthesis capacity, tree vigor, and wood quality (Ledermann, 2011; Kuprevicius et al., 2013). The low forest density increases the branch diameter, especially at the lower crown levels. Pruning is by far the most common practice to improve wood quality, resulting in an increased proportion of high-quality timber (Skovsgaard et al., 2018). However, high-pruning in young forest stands requires a high input of labor. Thus, the accurate height to crown base model will provide a prediction for the height to crown base and provide a reference for the height of pruning. Initial planting density and thinning intensity are two main factors in changing the height to crown base of individual trees. We therefore developed a comprehensive nonlinear mixed effects height to crown base model for planted Larix kaempferi in China by incorporating initial planting density and thinning intensity. The planted Larix kaempferi used for model development ranged from 30°N to 42°N, characterized by different climates. We used the dummy variable approach to characterize the two study regions. Therefore, the model developed in our study can be used in the planted regions for Larix kaempferi. The results will lay a foundation for the forest management strategy decision making for forest managers.
The logistic model with the best performance in the present study was selected to fit height to crown base of planted Larix kaempferi, which was consistent with the conclusions in most literature (Zhou et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2020; Pan et al., 2020; Shi et al., 2022; Yan et al., 2024). Tree size, including total tree height and HDR, emerged as the most influential factor with a relative contribution of 40.59% on height to crown base, which is similar to the study of Yan et al. (2024) and Shi et al. (2022). HDR is also a reflection of competition and can be interpreted as an indicator of social position in the forest stands (Rijal et al., 2012; Power et al., 2012). Larger HDR indicating intense competition and a highly competitive forest stand increase the possibility of crown recession resulting in a larger height to crown base (Dyer and Burkhart, 1987; Yang and Huang, 2018). In addition, HDR is also an important variable in estimating biomass and carbon stock, and assessing access of tree to light resources (Hulshof et al., 2015). As an indicator of symmetrical competition in size, the influence of stand basal area per hectare can be attributed to the competition for light, water, and nutrients (Yan et al., 2024). Some researchers have showed that tree facing intense competition tend to have shorter crown width (Sharma et al., 2016), and the greater competition for a tree in forest stand resulting in larger height to crown base which is consistent with the recent studies, such as Yan et al. (2024) and Shi et al. (2022). In our study, the relative importance of competition was 28.41%, just smaller than the tree level variable.
Climate has a significant impact on tree growth and stand dynamics (Bennett et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2021). The influence of climate also varies with the variables used and the time scales. In our study, the climate variable of DD_0_sp at the scale of season is selected, which is inversely proportional to HCB and is the same as that of the previous study (Yang et al., 2020). The reason may be that low temperature will affect the physiological activities of Larix kaempferi, and the more DD_0_sp., the longer the physiological activities will be inhibited. The terminal buds and lateral buds of trees grow slowly, and the rate of branch elongation decreases (Cortini et al., 2012; Bai et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2024). In order to maintain survival and basic physiological functions, more energy will be used to maintain cell activity and repair damage caused by low temperature, while less energy will be invested in upward growth. The relative contribution of climate variables in our research is only 2.59% which is not as great as in the study by Shi et al. (2022). The probable reason is that the study by Shi et al. (2022) has not considered the effect of thinning practice. Site factors can represent the site quality and vitality of sample plots. The better the site quality, the denser the stand density, and the stronger the growth vitality of trees (Li, 2018). The site quality showed best performance in our study, which conformed to the study of Shi et al. (2022). Our study revealed that the height to crown base of individual trees decreases with the increase of altitude, indicating that the crown recession rate is lower at high elevations.
Thinning is generally regarded as an effective forest silvicultural activity to regulate inter-tree competition (Pretzsch, 2009). Short and Burkhart (1992) developed a variable that expresses thinning effects by considering basal area before thinning, basal area immediately after thinning, current age of the forest stand, along with the age at thinning. Basal area ratio before and after thinning plus time effect representing the thinning effect on the prediction model of the crown height increase and decrease of loblolly pine (Short and Burkhart, 1992). Ganbaatar et al. (2021) mainly focused on the effect of thinning on the horizontal expansion of crown. However, the monitoring for the thinning effect was only conducted for 5 years, so it was difficult to reveal the long-term impact of thinning on crown. There was few relevant research to add thinning as a factor to the height to crown base model. Our study revealed that the height to crown base of individual trees increased with the thinning intensity which is consistent with our primary analysis between the observed height to crown base and the thinning intensity (Figure 6). The reason might be that thinning changed the structure of the stand, increased the growth environment of the stand, and thus increased the radial growth of the individual trees. The rise of height to crown base will increase the sunlight interception and the photosynthesis capacity of individual trees, leading to an increase in radial growth (Li, 2007). Based on the permanent sample plots by conducting thinning, the reasons why the increase of thinning intensity increased the height to crown base will be further studied in the future.
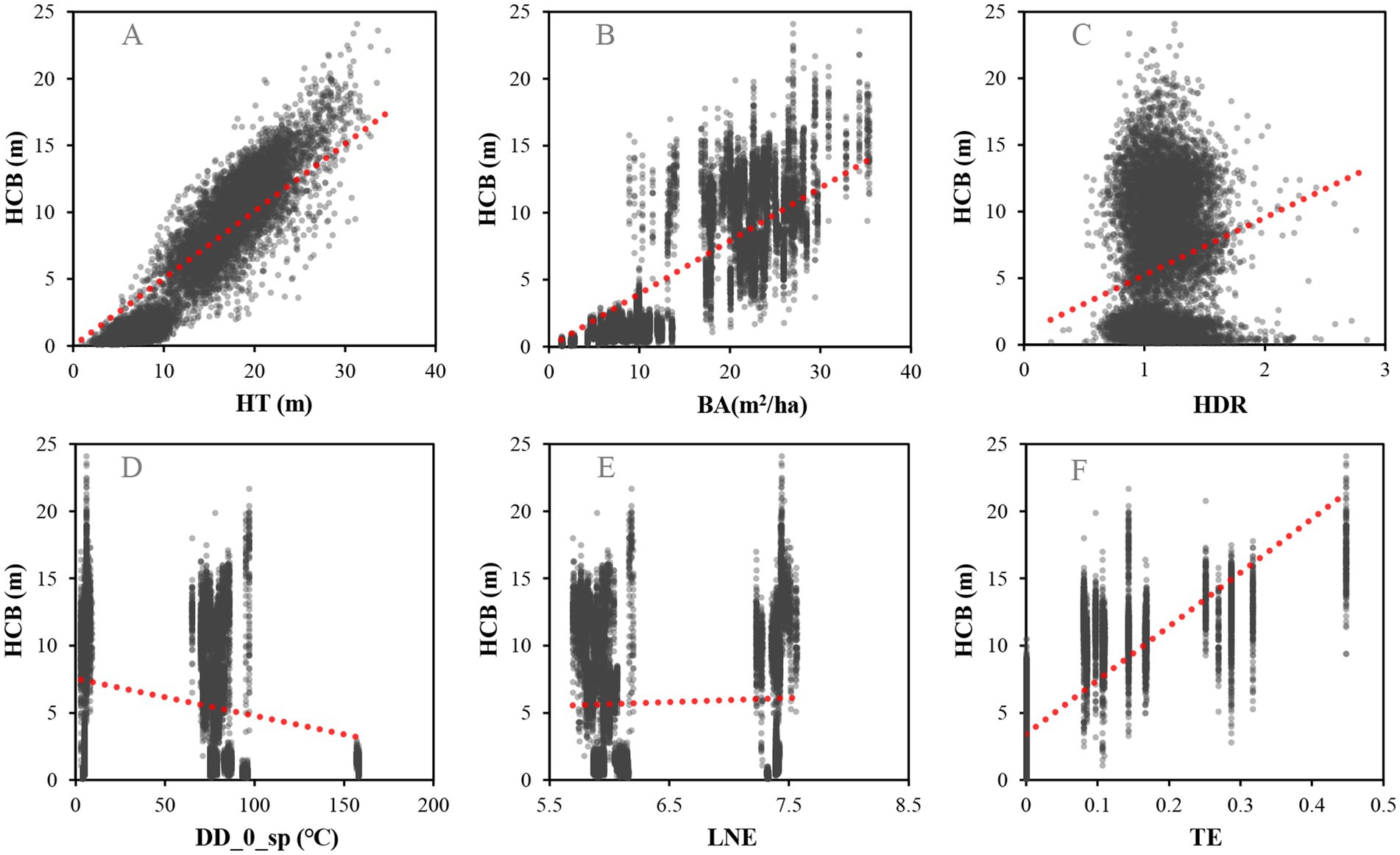
Figure 6. (A) represents the influence of HT on height to crown base, (B) represents the influence of BA on height to crown base, (C) represents the influence of HDR on height to crown base, (D) represents the influence of DD_0_sp on height to crown base, (E) represents the influence of LNE on height to crown base, F represents the influence of TE on height to crown base.
5 Conclusion
The height to crown base of an individual tree affects crown size, tree growth, and wood quality of trees. The logistic equation was selected as the base model to develop height to crown base model. The height to crown base increased with the increase in total tree height, competition, HDR, thinning intensity, and decreased with the increase in DD_0_sp and altitude. Large initial planting density led to a rise in height to crown base. The effect of competition on the height to crown base was reduced with an increase in thinning intensity. The relative contributions of the main variables, including tree size, competition, and thinning to height to crown base were 41.7, 27.3, and 24.5%, respectively.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
ZL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Data curation. JL: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. HG: Data curation, Supervision, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Validation, Formal analysis, Project administration, Funding acquisition. DC: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Validation. HL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work is funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFD2200801), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32471864), Liao Ning Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC2403180), Science and Technology Project for Excellent Young Scholars of Liaoning Province (2024JH3/10200036).
Acknowledgments
The authors also thank the students who have worked hard in data collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Antony, F., Schimleck, L. R., Jordan, L., Daniels, R. F., and Clark, A. (2012). Modeling the effect of initial planting density on within tree variation of stiffness in loblolly pine. Ann. For. Sci. 69, 641–650. doi: 10.1007/s13595-011-0180-1
Antos, J. A., Parish, R., and Nigh, G. D. (2010). Effects of neighbours on crown length of Abies lasiocarpa and Picea engelmannii in two old-growth stands in British Columbia. Can. J. For. Res. 40, 638–647. doi: 10.1139/X10-011
Aryal, K. R., Chapagain, T. R., Basukala, R. K., Khadka, S., Chaudhary, G., Budha, R. K., et al. (2023). Allometric tree volume models for Pinus roxberghii and Cedrus deodara in Karnali Province, Nepal. Forest Ecol. Manag. 546:121364. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2023.121364
Bai, X., Zhang, X., Li, J., Duan, X., Jin, Y., and Chen, Z. (2019). Altitudinal disparity in growth of Dahurian larch (Larix gmelinii Rupr.) in response to recent climate change in Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 670, 466–477. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.232
Barbeito, I., Paidos, M., Calama, R., and Cañellas, I. (2008). Effect of stand structure on stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) regeneration dynamics. Forestry 81, 617–629. doi: 10.1093/forestry/cpn037
Bennett, A. C., Penman, T. D., Arndt, S. K., Roxburgh, S. H., and Bennett, L. T. (2020). Climate more important than soils for predicting forest biomass at the continental scale. Ecography 43, 1692–1705. doi: 10.1111/ecog.05180
Chhin, S., Hogg, E. H., Lieffers, Y. J., and Huang, S. M. (2008). Potential effects of climate change on the growth of lodgepole pine across diameter size classes and ecological regions. For. Ecol. Manag. 256, 1692–1703. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2008.02.046
Cortini, F., Comeau, P. G., and Bokalo, M. (2012). Trembling aspen competition and climate effects on white spruce growth in boreal mixtures of Western Canada. For. Ecol. Manag. 277, 67–73. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2012.04.022
Dagley, C. M., Fisher, J., Teraoka, J., Powell, S., and Berrill, J. P. (2023). Heavy crown thinning in redwood/Douglas-fir gave superior forest restoration outcomes after 10 years. Can. J. For. Res. 53, 579–590. doi: 10.1139/cjfr-2022-0214
Duan, G. S., Li, X. D., Feng, Y., and Fu, L. Y. (2018). Generalized nonlinear mixed-effects crown base height model of Larix principis-rupprechtii natural secondary forests. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 42, 170–176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201703103
Dyer, M. E., and Burkhart, H. E. (1987). Compatible crown ratio and crown height models. Can. J. For. Res. 17, 572–574. doi: 10.1139/x87-096
Fu, L. Y., Zhang, H. R., Sharma, R. P., Pang, L. F., and Wang, G. X. (2017). A generalized nonlinear mixed-effects height to crown base model for Mongolian oak in Northeast China. For. Ecol. Manag. 384, 34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2016.09.012
Ganbaatar, B., Jamsran, T., Gradel, A., and Sukhbaatar, G. (2021). Assessment of the effects of thinnings in scots pine plantations in Mongolia: a comparative analysis of tree growth and crown development based on dominant trees. For. Sci. Technol. 17, 135–143. doi: 10.1080/21580103.2021.1963326
Gao, H. L., Chen, D. S., Sun, X. M., and Zhang, S. G. (2023b). Responses of the crown shape of Larix kaempferi plantations to site index in subtropical areas of China. Forests 14:2181. doi: 10.3390/f14112181
Gao, H. L., Feng, J., Chen, D. S., Hou, Y. M., Sun, Y. X., and Dong, G. J. (2023a). Effects of competition on the vertical distribution of foliage biomass within the crowns of planted Korean pine trees in Northeast China. Forests 14:1005. doi: 10.3390/f14051005
Garber, S. M., Monserud, R. A., and Maguire, D. A. (2008). Crown recession patterns in three conifer species of the northern Rocky Mountains. For. Sci. 54, 633–646. doi: 10.1093/forestscience/54.6.633
Guo, K. L., Zhang, T. W., Wang, Y. H., Gou, X. X., Yu, S. L., Shang, H. M., et al. (2024). Missing rings of Larix sibirica associated with climatic elements on the Altai Mountains, China. J. For. Res. 35:134. doi: 10.1007/s11676-024-01785-9
Hann, D. W., and Hanus, M. L. (2004). Evaluation of nonspatial approaches and equation forms used to predict tree crown recession. Can. J. For. Res. 34, 1993–2003. doi: 10.1139/x04-076
Hulshof, C. M., Swenson, N. G., and Weiser, M. D. (2015). Tree height–diameter allometry across the United States. Ecol. Evol. 5, 1193–1204. doi: 10.1002/ece3.1328
Jia, W. W., and Chen, D. S. (2019). Nonlinear mixed-effects height to crown base and crown length dynamic models using the branch mortality technique for a Korean larch (Larix olgensis) plantations in Northeast China. J. For. Res. 30, 2095–2109. doi: 10.1007/s11676-019-01045-1
Jia, W. W., Luo, T. Z., and Li, F. R. (2021). Branch density model for Pinus koraiensis plantation based on thinning effects. J. Beijing For. Univ. 43, 10–21. doi: 10.12171/j.1000−1522.20200057
Kuprevicius, A., Auty, D., Achim, A., and Caspersen, J. P. (2013). Quantifying the influence of live crown ratio on the mechanical properties of clear wood. Forestry 86, 361–369. doi: 10.1093/forestry/cpt006
Ledermann, T. (2011). A non-linear model to predict crown recession of Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) karst.] in Austria. Eur. J. For. Res. 130, 521–531. doi: 10.1007/s10342-010-0440-x
Li, C. Y. (2007). Effects of thinning on the undergrowth of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus tabulaeformis plantation in Beijing mountainous areas. Master’s thesis. Beijing forestry university, Beijing, China.
Li, X. (2018). The study of dynamic predicting model of height to crown base for Mongolian pine plantation in Heilongjiang Province. Master’s thesis. Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China.
Liu, J. T., Feng, J., Gao, H. L., and Chen, D. S. (2024). Nonlinear mixed-effect branch growth model development for planted Korean pine in Northeast China. Trees 38, 409–421. doi: 10.1007/s00468-024-02490-0
Liu, J. T., Tong, Y. W., Gao, H. L., Sun, X. M., and Chen, D. S. (2025). Nonlinear mixed effects crown width model for planted L. kaempferi at high altitudes in southern China. Trees 39:54. doi: 10.1007/s00468-025-02632-y
Ma, H., Cao, Y. S., Lyu, Y. T., Xu, G. J., He, Y. J., and Wang, J. J. (2024). Construction of individual tree DBH growth models for natural Betula platyphylla forests in Daxing’an mountains, Inner Mongolia of Northern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 46, 101–110. doi: 10.12171/j.1000−1522.20230086
Martin, J., Andreas, R., and Hans, P. (2021). How drought stress becomes visible upon detecting tree shape using terrestrial laser scanning (TLS). For. Ecol. Manag. 489:118975. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2021.118975
Monsi, M., and Saeki, T. (2005). On the factor light in plant communities and its importance for matter production. Ann. Bot. 95, 549–567. doi: 10.1093/aob/mci052
Pan, L., Mei, G. Y., Wang, Y. F., Saeed, S., Chen, L. P., and Cao, Y. S. (2020). Generalized nonlinear mixed-effect model of individual tree height to Crown Base for Larix Olgensis Henry in Northeast China. J. Sustain. For. 39, 827–840. doi: 10.1080/10549811.2020.1734026
Power, H., LeMay, V., Berninger, F., Sattler, D., and Kneeshaw, D. (2012). Differences in crown characteristics between black (Picea mariana) and white spruce (Picea glauca). Can. J. For. Res. 42, 1733–1743. doi: 10.1139/x2012-106
Pretzsch, H. (2009). Forest dynamics, growth and yield: From measurement to model. Berlin: Springer.
Qin, Y. P., He, X., Lei, X. D., Feng, L. Y., Zhou, Z. Y., and Lu, J. (2022). Tree size inequality and competition effects on nonlinear mixed effects crown width model for natural spruce-fir-broadleaf mixed forest in Northeast China. For. Ecol. Manag. 518:120291. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2022.120291
R Core Team (2023). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Rijal, B., Weiskittel, A. R., and Kershaw, J. A. (2012). Development of height to crown base models for thirteen tree species of the north American Acadian region. For. Chron. 88, 60–73. doi: 10.5558/tfc2012-011
Ritchie, M. W., and Hann, D. W. (1987). Equations for predicting height to crown base for fourteen tree species in southwest Oregon. Corvallis: Oregon State University.
Sattler, D. F., and LeMay, V. (2011). A system of nonlinear simultaneous equations for crown length and crown radius for the forest dynamics model SORTIE-ND. Can. J. For. Res. 41, 1567–1576. doi: 10.1139/x11-078
Sharma, R. P., Vacek, Z., and Vacek, S. (2016). Individual tree crown width models for Norway spruce and European beech in Czech Republic. For. Ecol. Manag. 366, 208–220. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2016.01.040
Sharma, R. P., Vacek, Z., and Vacek, S. (2018). Generalized nonlinear mixed-effects individual tree crown ratio models for Norway spruce and European beech. Forests 9:555. doi: 10.3390/f9090555
Shi, J. N., Liu, X. Z., and Xiang, W. (2022). Does climate play a more important role than competition in modeling height to Crown Base of Larix Principis-Rupprechtii in northern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 526:120564. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2022.120564
Short, E. A., and Burkhart, H. E. (1992). Predicting crown-height increment for thinned and Unthinned loblolly pine plantations. For. Sci. 38, 594–610. doi: 10.1093/forestscience/38.3.594
Skovsgaard, J. P., Markmann, J. J. M., Attocchi, G., and Talbot, B. (2018). High-pruning of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) and pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.): work efficiency for target pruning as a function of tree species, pruning height, branch characteristics, pole saw type and operator. Scand. J. For. Res. 33, 511–517. doi: 10.1080/02827581.2018.1441901
Soares, P., and Tome, M. (2001). A tree crown ratio prediction equation for eucalypt plantations. Ann. For. Sci. 58, 193–202. doi: 10.1051/forest:2001118
Sporek, M., and Sporek, K. (2023). Allometric model of crown length for Pinus sylvestris L. Stands in South-Western Poland. Forests 14:1779. doi: 10.3390/f14091779
Tong, Y. W., Chen, D. S., Gao, H. L., Xie, Y. H., and Liu, J. T. (2025). Developing branch diameter and length models for the planted Larix kaempferi from different latitude regions in China. J. For. Res. 36:77. doi: 10.1007/s11676-025-01878-z
Tong, Y. W., Chen, D. S., Sun, X. M., and Gao, H. L. (2024). A comprehensive crown profile model of planted Larix kaempferi from different latitudes in China. Eur. J. For. Res. 143, 1429–1446. doi: 10.1007/s10342-024-01703-y
Torita, H., Masaka, K., Tanaka, N., Igarashi, Y., Iwasaki, K., and Nakata, Y. (2024). Estimation of average crown base height of Japanese black pine (Pinus thunbergii Parlat.) coastal forests related to tsunami damage. J. Coast. Conserv. 28:83. doi: 10.1007/s11852-024-01085-8
Wang, J. J., Jiang, L. C., and Yan, Y. F. (2022). The impacts of climate, competition, and their interactions on crown width for three major species in Chinese boreal forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 526:120597. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2022.120597
Wang, Y. R., Liu, Z. H., Li, J. P., Cao, X. Y., and Lv, Y. (2024). Assessing the relationship between tree growth, crown size, and neighboring tree species diversity in mixed coniferous and broad forests using crown size competition indices. Forests 15:633. doi: 10.3390/f15040633
Wykoff, W. R., Crookston, N. L., and Stage, A. R. (1982). User’s guide to the stand prognosis model (general technical report INT-133). United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Intermountain Foerst and Range Experiment Station.
Yan, Y. F., Wang, J. J., Liu, S. M., Gaire, D., and Jiang, L. C. (2024). Modelling the influence of competition, climate, soil, and their interaction on height to crown base for Korean pine plantations in Northeast China. Eur. J. For. Res. 143, 1627–1640. doi: 10.1007/s10342-024-01710-z
Yan, Y. F., Wang, J. J., Mahardika, S. B., and Jiang, L. C. (2023). Effects of climate and competition on crown width: a case of Korean pine plantations. Eur. J. For. Res. 142, 231–244. doi: 10.1007/s10342-022-01515-y
Yang, Y. Q., and Huang, S. M. (2018). Effects of competition and climate variables on modelling height to live crown for three boreal tree species in Alberta, Canada. Eur. J. For. Res. 137, 153–167. doi: 10.1007/s10342-017-1095-7
Yang, Z. H., Liu, Q. W., Luo, P., Ye, Q. L., Sharma, R. P., Duan, G. S., et al. (2020). Nonlinear mixed-effects height to crown base model based on both airborne LiDAR and field datasets for Picea crassifolia Kom trees in Northwest China. For. Ecol. Manag. 474:118323. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118323
Yi, D., Li, F. R., Ma, A. Y., Lin, F. C., Hao, Y. S., and Dong, L. H. (2023). Model construction for height to crown base of Larix olgensis based on mixed-effects model and quantile regression. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 34, 1035–1042. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202304.007
Zhang, X. Q., Cao, Q. V., Duan, A. G., and Zhang, J. G. (2017). Modeling tree mortality in relation to climate, initial planting density, and competition in Chinese fir plantations using a Bayesian logistic multilevel method. Can. J. For. Res. 47, 1278–1285. doi: 10.1139/cjfr-2017-0215
Zhou, X., Chen, Q., Sharma, R. P., Wang, Y. H., He, P., Guo, J. P., et al. (2021). A climate sensitive mixed-effects diameter class mortality model for prince Rupprecht larch (Larix gmelinii var. principis-rupprechtii) in northern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 491:119091. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119091
Zhou, X., Zhang, X., Li, Z., Liu, L. Y., Sharma, R. P., and Guan, F. Y. (2024). A climate sensitive nonlinear mixed-effects height to crown base model: a study focuses on Phyllostachys pubescens. Trees 38, 849–862. doi: 10.1007/s00468-024-02514-9
Keywords: height to crown base, nonlinear mixed effects model, initial planting density, thinning intensity, Larix kaempferi
Citation: Liu Z, Liu J, Gao H, Chen D and Lyu H (2025) Nonlinear mixed effects height to crown base model for Larix kaempferi plantation in China by considering initial planting density and thinning intensity. Front. For. Glob. Change. 8:1635431. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2025.1635431
Edited by:
Ram P. Sharma, Tribhuvan University, NepalReviewed by:
Wei Xiang, Beijing Forestry University, ChinaJose Manuel Balderas, Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Liu, Gao, Chen and Lyu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huilin Gao, Z2hsMjAxN0BzeWF1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Zhiqi Liu1
Zhiqi Liu1 Huilin Gao
Huilin Gao Dongsheng Chen
Dongsheng Chen