Abstract
Introduction:
Wildfire detection and segmentation play a critical role in environmental monitoring and disaster prevention. However, existing deep learning-based segmentation models often struggle to identify wildfire boundaries accurately due to complex image features and limited annotated data.
Methods:
We propose a novel segmentation network called PPCNet, which integrates three key modules: a Panoramic Feature Fusion (PFF) module for multi-scale feature extraction, a Dense Feature Fusion Encoder (DFFE) to capture contextual details, and a Local Detail Compensation (LDC) loss function to enhance boundary accuracy. Additionally, we design a pseudo-label optimization framework to leverage unlabeled data effectively.
Results:
Experiments were conducted on multiple wildfire datasets, and the results show that PPCNet achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. Our model demonstrates significant improvements in segmentation accuracy and boundary localization, validated through quantitative metrics and visual comparisons.
Discussion:
The integration of PFF, DFFE, and LDC components enables PPCNet to generalize well across different wildfire scenarios. The use of pseudo-labeling further enhances performance without requiring additional labeled data, making it suitable for real-world deployment in wildfire monitoring systems.
1 Introduction
Forest fires, as a typical frequent and highly damaging global natural disaster, have shown an obvious increasing trend in frequency, affected area, and severity in recent years due to factors such as global climate change and intensified human activities (Zheng H. et al., 2023; Giannakidou et al., 2024). Forest fires not only directly destroy large amounts of forest resources, disrupt the structure and function of ecosystems, and severely threaten biodiversity, but also aggravate the greenhouse effect through carbon emissions, alter atmospheric components, and further intensify climate change (Wang H. et al., 2024). At the same time, forest fires pose serious negative impacts on human life, property safety, public health, and economic development. According to relevant statistical data, the ecological, economic, and social losses caused by forest fires worldwide continue to rise, making it urgent to develop effective technical means for early monitoring and rapid response (Samhitha et al., 2024). Against the background of interdisciplinary technological development, how to efficiently and accurately segment and identify forest fires by using advanced remote sensing methods, especially with high spatial and temporal resolution data acquisition and intelligent analysis techniques, has become an important research focus in remote sensing and intelligent information processing (Yandouzi et al., 2024).
In recent years, with the rapid development and widespread application of UAV remote sensing technology, it has become possible to obtain large-scale, high-resolution, and low-cost forest fire image data. Compared with traditional satellite remote sensing, UAVs have the advantages of high mobility, flexible imaging, and rapid response, making them an important information source for forest fire monitoring (Feng et al., 2025). Meanwhile, Deep learning, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), has shown strong performance in image recognition and semantic segmentation, significantly advancing research on forest fire detection and segmentation (Lin et al., 2024; Zheng et al., 2024). Unlike image classification and object detection, which only identify the presence or approximate location of a fire, image segmentation provides pixel-level delineation of fire and smoke regions, enabling accurate boundary extraction and dynamic monitoring. Such fine-grained spatial information is crucial for assessing fire extent, supporting early warning, and improving situational awareness in UAV-based forest fire management. Deep learning–based segmentation models can automatically extract multi-scale semantic features, enhancing robustness and accuracy under complex environmental conditions.
Nevertheless, building high-performance and robust forest fire segmentation models still faces many challenges. On the one hand, deep learning methods rely heavily on large-scale, high-quality annotated datasets for supervised training. However, due to the suddenness, danger, and complex field conditions of forest fires, the process of precise annotation of forest fire images is costly, inefficient, and highly subjective, resulting in a serious lack of publicly available high-quality forest fire datasets (Zheng Y. et al., 2023; Lee et al., 2024). On the other hand, in actual forest fire scenes, factors such as fire spreading patterns, smoke distribution, background vegetation types, and lighting conditions are complex and variable, often accompanied by image occlusion and low contrast, which further increases the difficulty of feature expression, boundary localization, and generalization under small-sample conditions (Mai et al., 2025). To address these problems, semi-supervised learning (SSL) has received widespread attention in image segmentation tasks in recent years as an effective learning paradigm to alleviate data scarcity and improve model performance (Yang L. et al., 2025). By jointly utilizing limited labeled and abundant unlabeled data, SSL can mine the potential information in unlabeled data, assisting models in learning more robust and discriminative feature expressions under weak supervision, thereby reducing dependence on large-scale annotated datasets and enhancing segmentation performance and model generalization.
In the task of forest fire image segmentation, how to fully utilize large amounts of unlabeled UAV images and combine them with semi-supervised learning strategies to improve segmentation accuracy and boundary recognition ability under complex environments has become an important research direction. Although some researchers have attempted to introduce semi-supervised learning methods into forest fire segmentation tasks (Lai et al., 2021; Koottungal et al., 2023), existing methods still have limitations in feature fusion, multi-scale information modeling, and consistency constraint design. For example, Sun et al. (2022) enhanced multi-scale feature representation by introducing an atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module, which effectively expanded the receptive field but still had deficiencies in preserving local details and improving the segmentation of fire boundaries and complex smoke structures. Rudz et al. (2013) designed a feature extraction and reconstruction framework for forest fire images based on an autoencoder structure combined with semi-supervised ideas, which alleviated data scarcity to some extent, but the weak multi-scale feature fusion ability made it difficult to cope with complex backgrounds and diverse fire scenes. Toulouse et al. (2015) introduced color and shape constraints in the pseudo-label generation process, which improved segmentation performance and the reliability of pseudo-labels by filtering high-confidence pseudo-labels and applying image augmentation strategies. However, there remains room for improvement in enhancing model consistency and suppressing pseudo-label noise propagation.
To address the existing problems of insufficient feature representation, inaccurate boundary segmentation, weak generalization, and inefficient utilization of semi-supervised information in current forest fire segmentation tasks, we propose a semi-supervised segmentation method for UAV remote sensing forest fire that integrates panoramic feature fusion and pixel-level contrastive learning. The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
-
(1)
A panoramic feature fusion (PFF) module is designed to efficiently integrate multi-level and multi-scale features, fully capturing global contextual information and local detail features in forest fire images.
-
(2)
A dual-frequency enhancement (DFE) mechanism is proposed to jointly extract low-frequency information (background structure and overall shape) and high-frequency information (boundary texture and detail changes), effectively enhancing the model’s sensitivity and expression ability for fire and smoke boundaries.
-
(3)
A pixel contrastive loss (PCL) is designed to construct positive and negative sample pairs based on pixel-level features, combined with directional constraints and confidence calibration mechanisms, which enhances the discriminative ability of the un-supervised branch.
-
(4)
A semi-supervised learning framework is proposed, which combines supervised cross-entropy loss with unsupervised contrastive loss to fully exploit the complementary information in limited labeled data and abundant unlabeled data, improving segmentation accuracy.
-
(5)
Extensive experiments on four forest fire remote sensing datasets show that the pro-posed method achieves superior segmentation performance, verifying its effective-ness.
2 Related work
In recent years, deep learning-based methods have become the mainstream approach for forest fire image segmentation, driven by the rapid development and success of deep learning techniques in image analysis tasks. However, challenges such as limited labeled data, complex background environments, and diverse fire shapes still hinder the performance of segmentation models. To address these issues, researchers have explored several technical directions within the deep learning framework. Semi-supervised learning strategies aim to alleviate the reliance on large-scale labeled datasets by effectively utilizing both labeled and unlabeled data. Meanwhile, feature fusion techniques enhance the model’s ability to capture contextual information and accurately delineate fire boundaries under complex scenarios. This section provides a systematic review of representative methods and recent advances in forest fire image segmentation, covering traditional image processing approaches, deep learning-based methods, semi-supervised learning strategies, and feature fusion strategies.
2.1 Traditional image processing methods for forest fire segmentation
Early research on forest fire detection and segmentation mainly relied on traditional image processing techniques. Typical methods include color threshold segmentation (Yang Z. et al., 2025), edge detection (Wei and Larsen, 2019), and morphological analysis. These methods usually utilize the distinctive color features of flames in visible images, such as red, orange, and yellow, to perform color space conversion and threshold segmentation. Some methods also use the structural differences between flames and the background for edge detection and morphological operations. In addition, certain studies have combined dynamic characteristics of flames, such as flicker frequency and contour deformation, to assist in detection and improve timeliness and accuracy. For instance, Tlig et al. (2020) proposed a multi-scale color image segmentation method based on the integration of PCA and Gabor filters, effectively enhancing flame region discrimination. Hossain et al. (2020) applied local binary patterns (LBP) from multiple color spaces and artificial neural networks to achieve joint smoke and flame detection. Zhao et al. (2011) combined Fourier descriptors with a dynamic support vector machine (SVM) to achieve dynamic flame detection based on flickering contour features. Although these methods offer advantages such as high computational efficiency and simple implementation, they rely heavily on low-level explicit features. As a result, they struggle to achieve accurate flame region segmentation under complex forest fire scenarios, such as illumination variations, smoke occlusion, and background interference, especially in terms of fine-grained boundary and internal structure representation (Darwish Ahmad et al., 2023). With the increasing demands for accuracy and real-time performance in practical applications, these traditional methods show significant limitations, highlighting the need for more advanced and expressive approaches.
2.2 Deep learning-based forest fire segmentation
The widespread application of deep learning techniques, especially CNNs, in image segmentation has improved the performance of forest fire segmentation methods (Saleh et al., 2024). Classic semantic segmentation architectures such as U-Net (Wu et al., 2022) and the DeepLab series (Yang, 2024) have become mainstream technical approaches in forest fire segmentation due to their powerful multi-scale feature extraction and spatial information recovery capabilities. U-Net employs an encoder-decoder architecture with skip connections, enabling effective feature fusion and spatial detail recovery. Originally designed for medical image segmentation, U-Net has been widely extended to forest fire segmentation tasks (Shirvani et al., 2023). Building upon this, FDE U-Net (Zou et al., 2025) integrates an ACmix convolutional mixing module and a CBAM attention mechanism to significantly enhance feature expression for small-scale fire regions, improving segmentation accuracy. The DeepLab series introduces atrous convolutions and ASPP modules, which effectively expand the receptive field and enhance the capture of multi-scale contextual information (Liu et al., 2024). Liu et al. (2023) designed a double-attention residual feature fusion (DARA) module within the DeepLabV3 architecture, further improving feature discrimination and boundary recognition for fire regions. Harkat et al. (2022) optimized the DeepLabV3+ framework to construct a real-time forest fire image segmentation system, achieving a balance between segmentation accuracy and speed for practical applications. Although deep learning methods have achieved remarkable results in forest fire segmentation, their strong reliance on large-scale, high-quality annotated data has become a bottleneck for their widespread application in real-world forest fire scenarios. Due to the dangerous, complex, and subjective nature of forest fire data collection and annotation, high-quality data resources remain extremely scarce, underscoring the need to explore new methods for efficient data utilization.
2.3 Semi-supervised learning strategies
To mitigate limited annotated data, SSL (semi-supervised learning) has been increasingly adopted in forest fire segmentation tasks as an effective strategy to reduce supervision dependence and improve model generalization (Ouali et al., 2020; Desai and Ghose, 2022; Yang et al., 2022). SSL combines limited labeled data with abundant unlabeled data to mine potential information from the unlabeled portion, assisting models in learning more robust feature representations under weak supervision and reducing the need for large annotated datasets. Current mainstream SSL strategies include pseudo-label generation (Zhang et al., 2021), consistency regularization (Wang et al., 2020), region-mixing data augmentation such as CutMix (Yun et al., 2019) and MixUp (Carratino et al., 2022), and masked image modeling (MIM) (Xie et al., 2022). For example, Wang et al. (2022) proposed the SemiFSNet model, which enhances segmentation performance and stability on unlabeled forest fire images through consistency regularization. Other studies (Xin et al., 2024) introduced perturbation mechanisms at the feature level to encourage models to learn more robust and discriminative features. Pseudo-label generation methods (Yan et al., 2024) further select high-confidence pseudo-labels dynamically, supporting effective training on unlabeled data and gradually narrowing the performance gap between supervised and unsupervised data. However, existing semi-supervised forest fire segmentation methods still face two main limitations: (1) insufficient exploitation of deep structural information in unlabeled data, leading to limited feature expression capability, and (2) a lack of robust feature constraints tailored to complex forest fire scenarios, such as occlusion, smoke, and background interference, making models prone to overfitting or boundary segmentation blur. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes a semi-supervised segmentation framework that combines supervised and unsupervised branches. In particular, a pixel contrastive loss with directional constraints is designed for the unsupervised branch, which leverages spatial structure information and confidence calibration to construct reliable positive and negative sample pairs, further enhancing boundary and detail segmentation for forest fires under complex environments.
2.4 Feature fusion strategies
Feature fusion is a key technical approach for improving segmentation accuracy and robustness (Shang et al., 2020). Representative methods such as skip connections in U-Net (Ronneberger et al., 2015) and the ASPP module in the DeepLab series (Liu et al., 2022) effectively integrate local and global information through architectural design. In recent years, researchers have explored advanced feature fusion strategies, including attention mechanisms, feature pyramid structures, and multi-modal information fusion. For example, the CBAM module (Chen et al., 2023) jointly applies channel and spatial attention to enhance the expression of key regions related to forest fires. Li et al. (2022) designed a multi-feature fusion framework that incorporates color and texture information, significantly improving model robustness and discrimination under complex backgrounds. Zhang et al. (2023) proposed a repeated deep-shallow feature fusion strategy to enrich overall semantic information and improve segmentation accuracy and boundary detail preservation. Although these methods demonstrate the importance of feature fusion in forest fire segmentation, most existing work remains limited to single-scale or local-level information integration, lacking systematic modeling of global forest fire image information. To address this, this paper introduces a panoramic feature fusion module that systematically integrates deep and shallow features at different levels and scales from a macro and global perspective. This enables comprehensive capture of contextual semantic information and local details in forest fire images, significantly enhancing segmentation performance and boundary expression under complex environments.
3 Methodology
3.1 Overall architecture
To address the challenges of forest fire image segmentation, including the difficulty of data acquisition, complex environmental interference, and insufficient boundary expression, we propose a semi-supervised forest fire segmentation method based on UAV remote sensing, named PPCNet (Panoramic Feature Fusion and Pixel Contrastive Learning Network). The proposed PPCNet aims to comprehensively improve the segmentation accuracy and robustness of the model in complex forest fire scenarios by integrating multi-level deep features and introducing pixel-level consistency constraints. By exploiting limited labeled and large-scale unlabeled data, PPCNet improves model performance.
The overall structure of PPCNet is shown in Figure 1. The model adopts a dual-branch framework consisting of a supervised branch and an unsupervised branch. Both branches share the same encoder network but adopt different optimization strategies to work collaboratively. In the supervised branch, labeled wildfire images are first processed by the encoder to extract multi-scale and multi-level deep features. To enhance the representation of complex object boundaries and local details, a Dual-Frequency Feature Enhancement (DFFE) module is introduced after the encoder. By jointly utilizing low-frequency structural information and high-frequency edge and texture information, the module optimizes the feature representation. The enhanced feature map is then fed into the classifier to generate the final segmentation prediction. This branch is optimized using a cross-entropy loss to ensure stable and reliable segmentation performance on labeled data. In the unsupervised branch, for unlabeled wildfire images, a dual random cropping strategy is adopted to generate two sub-images with partially overlapping regions. This design not only increases data diversity but also provides the basis for pixel-level contrastive learning. The two sub-images are passed through the encoder and feature enhancement modules to obtain their respective high-dimensional feature maps. Based on the spatial correspondence, the overlapping regions in the two feature maps are extracted, and pseudo-labels are generated by the classifier. Using this information, pixel-level positive and negative sample pairs are constructed. On this basis, the proposed Pixel Contrastive Loss (PCL) is introduced, which incorporates directional constraints and confidence calibration mechanisms. This loss guides the model to learn discriminative and structurally consistent feature representations from unlabeled data, further improving the model’s ability to accurately capture wildfire target boundaries and fine details.
FIGURE 1

Overall structure of the proposed PPCNet.
3.2 Basic feature extraction module
High-quality feature extraction is the foundation for achieving accurate image segmentation. In this study, we adopt the ResNet50 network as the backbone for the basic feature extraction of PPCNet. ResNet introduces residual connections to effectively alleviate problems such as gradient vanishing and network degradation in deep neural networks, providing strong feature representation capabilities and stable network performance. In particular, ResNet50 offers an optimal balance between feature richness and computational efficiency, making it well-suited for wildfire image segmentation, where flame targets often exhibit blurred boundaries, scale variation, and strong interference from smoke and vegetation. Its hierarchical feature maps naturally align with the design of the PFF and DFFE modules, facilitating the integration of spatial, semantic, and frequency-domain information for more precise fire region delineation. Specifically, the input image x is first processed through a 7×7 convolutional layer with a stride of 2, followed by a max-pooling layer, which reduces the spatial resolution while extracting low-level features. The resulting feature map is denoted as F0. Subsequently, the feature map F0 passes through four stages of residual blocks to progressively extract multi-level deep features. The structure of each stage is as follows: The first stage contains 3 residual blocks, and its output is denoted as F1, which mainly captures basic texture and edge information from the image. The second stage contains 4 residual blocks, and its output is denoted as F2, extracting richer intermediate features and structural information. The third stage consists of 6 residual blocks, generating the feature map F3, which captures high-level semantic information of the image. The final stage contains 3 residual blocks, followed by a global average pooling layer, producing the final deep feature map F4 with rich global semantic information and strong feature expression capabilities. Throughout the feature extraction process, the multi-level feature maps F1, F2, F3, and F4 retain rich hierarchical information from low-level edges and textures to high-level semantics and global structures. These feature maps are then fed into the PFF module to further integrate multi-scale, multi-level information.
In the supervised branch, PPCNet receives explicit guidance from pixel-level annotations of forest fire regions. Each labeled image is paired with a binary mask, where fire pixels are marked as 1 and background pixels as 0. The model learns to align its pixel-wise predictions with these annotations through the supervised cross-entropy loss, thereby establishing a direct mapping between visual features and fire occurrence regions. This explicit supervision enables the network to accurately learn the spatial distribution and boundaries of fire areas, while the PFF and DFFE modules further refine boundary and texture representations to enhance segmentation precision under complex backgrounds.
3.3 Panoramic feature fusion module
In the process of feature extraction using CNN, deep features with higher semantic information are gradually obtained through multiple layers of convolution. For wildfire image segmentation tasks, high-level semantic features, such as the overall shape of fire spots and their relationship with the background, are essential for accurate segmentation. However, shallow-level features obtained in the early layers of the network, including edge, color, and precise location information, also play a critical role in determining segmentation accuracy. In practical wildfire image segmentation tasks, complex environments such as occlusions, varying backgrounds, and smoke interference often occur. Meanwhile, the shape and location of fire spots are important segmentation targets. Simply relying on deeper convolution layers to extract high-level features may cause the network to lose important shallow features, such as edges, color contrast, and position information, which leads to blurred boundaries or inaccurate segmentation results. To address this issue, we propose a PFF module to effectively combine features extracted from different stages of the network, aiming to obtain more comprehensive and representative feature information. As shown in Figure 2, within the PFF module, features from different layers are progressively fused through a two-stage fusion structure called the PFF block.
FIGURE 2
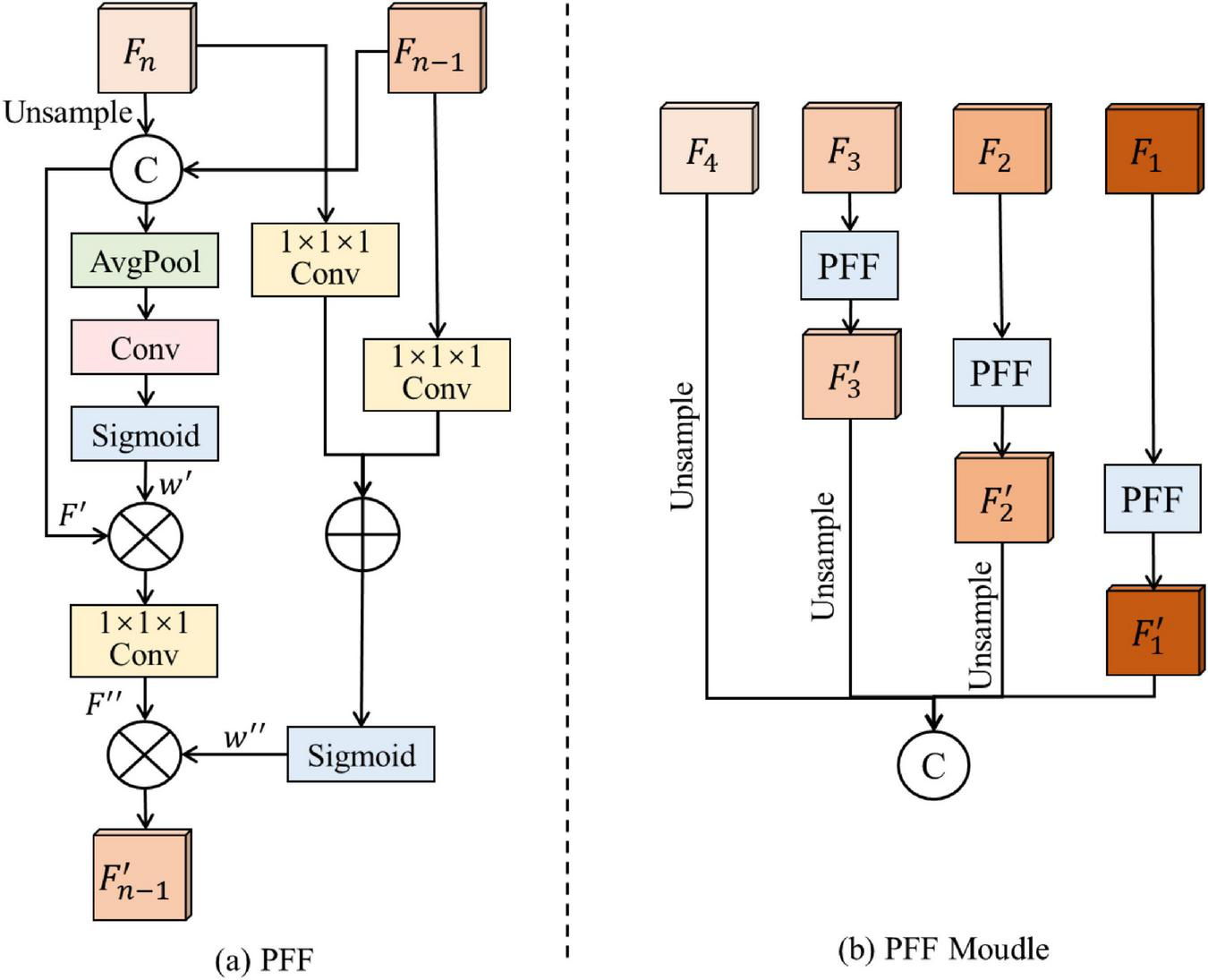
Structure of the panoramic feature fusion module. The diagram includes (a) the overall PFF (Panoramic Feature Fusion) structure with hierarchical feature fusion stages, and (b) the internal structure of a PFF block showing upsampling, concatenation, attention weighting, and local recalibration processes.
Specifically, four feature maps are extracted from different stages of the ResNet50 backbone, denoted as F1, F2, F3, and F4. These feature maps are fed into the PFF module, where different-level features are gradually fused to obtain rich panoramic features. For any two adjacent feature maps Fn and Fn–1 (1 ≤ n ≥ 4), the PFF Block performs a series of operations to fuse them and generate the updated feature map . First, to extract shared characteristics from different levels, the higher-level feature Fn is upsampled to match the spatial size of Fn–1, and then the two feature maps are concatenated along the channel dimension:
where Concat (⋅) denotes channel-wise concatenation, and indicates the upsampled version of Fn.
Next, to capture the channel-wise information of the concatenated feature map, F′ is passed through an average pooling layer (AvgPool), a convolutional layer (Conv), and a Sigmoid activation function to obtain channel attention weights:
The channel weights w′ are then used to recalibrate the concatenated feature map F′, enhancing important features while suppressing less informative ones:
where ⊗ denotes element-wise multiplication and Conv1×1×1 is a 1×1×1 convolution.
To further extract and fuse local structure information from different layers, the input features Fn and Fn–1 are separately passed through a 1×1×1 convolution and a Sigmoid activation to obtain local information weights:
where ⊗ represents element-wise addition.
Finally, the local weights w″ are used to recalibrate the feature map F″, producing the updated fused feature :
Through this two-step fusion process, the PFF block gradually integrates low-level details and high-level semantic information, ensuring that both boundary and contextual features are retained.
After three rounds of such fusion, the updated feature maps , and are obtained. Finally, the upsampled high-level feature map and the fused features from different stages are concatenated to generate the final panoramic feature representation:
This comprehensive feature F effectively combines global semantic information with local structural details, significantly enhancing the model’s ability to accurately distinguish flame regions, boundaries, and background areas in complex wildfire scenes.
3.4 Dual-frequency feature enhancement module
In computer vision, an image can be divided into high-frequency and low-frequency components, which reflect different types of information. High-frequency components mainly contain edge, texture, and fine details of the image. For wildfire images, these details, especially the flame edges and texture information, are crucial for accurate segmentation. By enhancing high-frequency components, the model can better capture flame contours and fine structures, thus reducing false positives and missed detections in segmentation tasks. However, high-frequency components may also contain noise, and directly enhancing them could amplify noise and negatively affect the segmentation results. Therefore, while enhancing high-frequency information, it is also important to incorporate low-frequency components to help suppress noise. Low-frequency components reflect the overall structure and background information of the image, which is very helpful for distinguishing the background areas and understanding the global context in wildfire scenes. By keeping low-frequency information, the model can better separate flames from complex backgrounds, thus improving segmentation stability. The combination of high-frequency and low-frequency features provides multi-scale information for the model, which is beneficial for improving segmentation accuracy. In this work, we propose a DFFE module, which separates the feature maps extracted by the encoder into high-frequency and low-frequency parts for further feature enhancement. The structure of the DFFE module is shown in Figure 3.
FIGURE 3
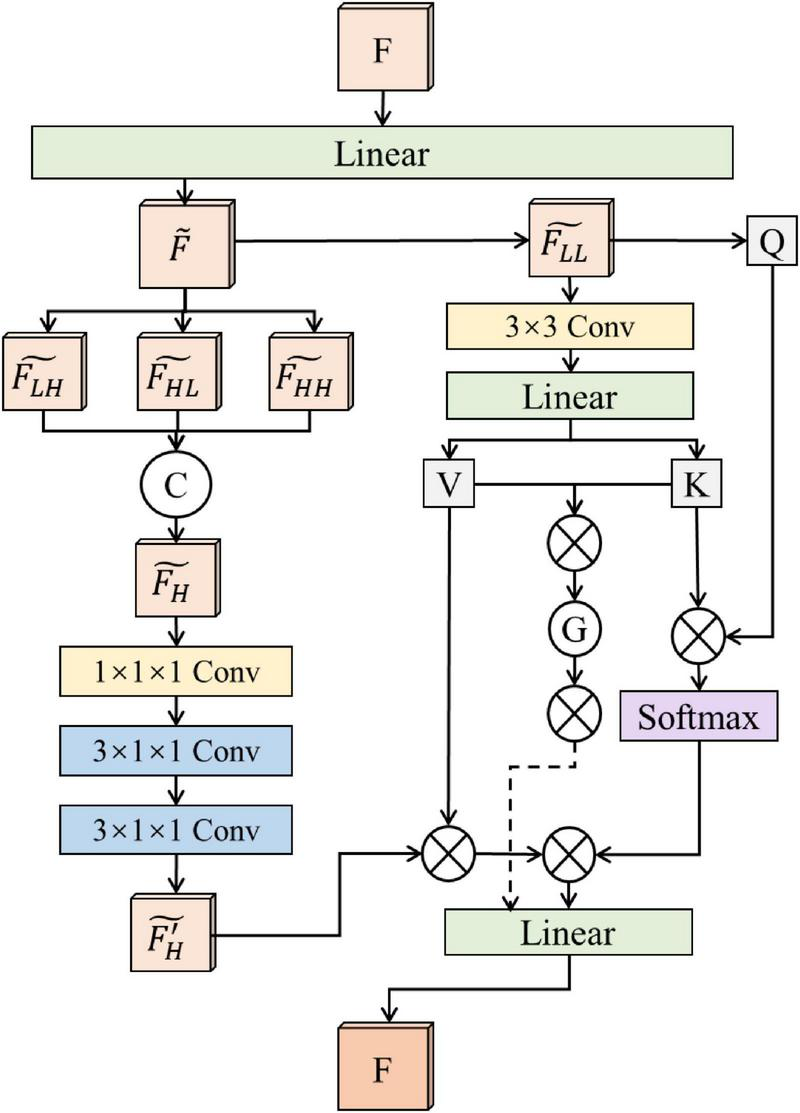
Structure of the dual-frequency feature enhancement module.
First, given an input feature map F, we apply a linear transformation to reduce the number of channels, and obtain a new feature map . Then, a wavelet transform is used to decompose the feature map into low-frequency and high-frequency components. Specifically, for the 2D feature map , a one-dimensional wavelet transform is first applied to each row:
Here, h and g are low-pass and high-pass filters, respectively, and * represents the convolution operation.
Next, another one-dimensional wavelet transform is applied to each column of Flow_h and Fhigh_h to further decompose the feature map:
In this work, we use Haar wavelets for decomposition, where the low-pass filter is and the high-pass filter is . Among the decomposed features, captures vertical edge and texture details, focuses on horizontal edges and textures, and reflects diagonal edges and texture information. These three components together represent the high-frequency details of the feature map, which are useful for expressing flame boundaries and fine structures.
We concatenate the three high-frequency features along the channel dimension to form an enhanced high-frequency feature map:
After that, we apply two 3×1×1 convolution layers to further refine these high-frequency features and obtain clearer boundary features . At the same time, the low-frequency feature is processed with a 3×3 convolution and a linear transformation to generate key and value features, which are then concatenated to form global context information G. To ensure boundary information is preserved in this process, we also add the boundary features to the value part.
Finally, we introduce a multi-path attention mechanism based on the original input feature F. Specifically, queries Q are generated from F, and used together with K (key) and V (value) to extract different levels of contextual information. The first path captures spatial dependencies, helping to distinguish flames from the background. The second path focuses on the channel-level semantic representation, enhancing multi-scale feature fusion. The third path highlights boundary information in the value features to ensure that flame contours are better preserved.
3.5 Pixel contrastive loss
To effectively utilize both the limited labeled data and abundant unlabeled data, this paper designs a dual-branch optimization framework consisting of a supervised branch and an unsupervised branch. The supervised branch employs a standard cross-entropy loss for pixel-level supervised learning, while the unsupervised branch introduces a Pixel Contrastive Loss (PCL) to enhance feature discriminability and consistency on unlabeled data through directional constraints and positive-negative sample selection.
In the supervised branch, the labeled wildfire image xl is first processed through the feature extraction, panoramic feature fusion, and dual-frequency feature enhancement modules to obtain the enhanced feature map FEl. The final prediction result is generated through the classifier 𝒞(⋅) as follows:
The difference between the predicted result and the ground truth yl is measured using the standard cross-entropy loss:
where N represents the total number of pixels, C is the number of categories, yli,c denotes the probability that the ith pixel belongs to category c, and represents the predicted probability for the same pixel and category.
In the unsupervised branch, the unlabeled wildfire image xu undergoes two independent random crops to generate two sub-images xu1 and xu2, which contain overlapping regions denoted as xo. These sub-images are passed through the feature extraction and panoramic feature fusion modules to obtain feature maps:
The overlapping regions in the feature maps are denoted as Ou1 and Ou2, respectively. For the same spatial position in Ou1 and Ou2, the corresponding features are considered positive sample pairs, while features from different objects are treated as negative sample pairs.
To enhance feature alignment, a directional contrastive loss ℒDC is introduced, which uses confidence-guided positive-negative sample selection to promote alignment between low-confidence and high-confidence features while suppressing noisy feature propagation. Specifically, the maximum category probability of each feature is used as the confidence measure, encouraging features with lower confidence to align with those with higher confidence:
where s(⋅,⋅) denotes the cosine similarity, τ is a temperature coefficient, h, w indicate spatial positions, FNeg represents the set of negative samples, and the directional mask is defined as:
indicating that only locations where the confidence of Ou2 exceeds that of Ou1 are considered for contrastive learning.
To further reduce errors from incorrect pseudo-labels in negative sample selection, pseudo-labels predicted by the unsupervised branch are utilized. The category probability of each feature is calculated as:
For a feature with pseudo-label and a negative sample On with pseudo-label yn, the negative sample mask is defined as:
Incorporating this mask, the updated directional contrastive loss is expressed as:
Furthermore, to mitigate the impact of low-confidence positive sample pairs, a confidence threshold τ is applied to filter them out. The final form of the directional contrastive loss becomes:
where the composite mask combines both directional and confidence constraints:
Finally, the overall pixel contrastive loss for a batch of size B is formulated as:
The final total loss function for the model is defined as:
where λ is a balancing hyperparameter that controls the contribution of the unsupervised loss.
4 Experiments and results
4.1 Datasets
To comprehensively evaluate the effectiveness and applicability of the PPCNet model, we conduct comparative and ablation experiments on four publicly available remote sensing forest fire datasets (Flame, Corsican, D-Fire, and M4SFWD). The Flame dataset was collected by Northern Arizona University and other institutions using UAVs in the pine forest areas of Arizona, USA, and contains 2003 images. This dataset effectively addresses the lack of forest fire recognition data under harsh environmental conditions such as haze and smoke, providing high practical application value. The Corsican dataset was organized by the Environmental Science Laboratory of the University of Corsica in France and consists of 1,136 real forest fire images. The dataset features diverse background environments, rich vegetation types, and significant variations in the scale of forest fire targets within the images, making it highly challenging for segmentation tasks. The D-Fire dataset was compiled by the Venancio research team in Brazil. The images were sourced from the internet, legally simulated fire experiments at the Belo Horizonte Technology Park in Brazil, surveillance equipment from the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG), and the Serra do Rola-Moça State Park in Belo Horizonte. The dataset contains a total of 21,527 images. To ensure data quality, 9869 images with clearly visible forest fire targets were selected for experiments. The M4SFWD dataset is a synthetic dataset specifically designed for remote sensing forest fire detection tasks. It contains 3974 images covering various fire patterns, scene backgrounds, and imaging conditions, providing an effective benchmark for evaluating model adaptability and generalization performance under diverse scenarios.
Representative image samples from the four datasets are shown in Figure 4. Overall, the datasets cover both real and synthetic data, diverse scenes, and complex environments, providing a comprehensive and systematic platform for validating the performance of the proposed PPCNet.
FIGURE 4
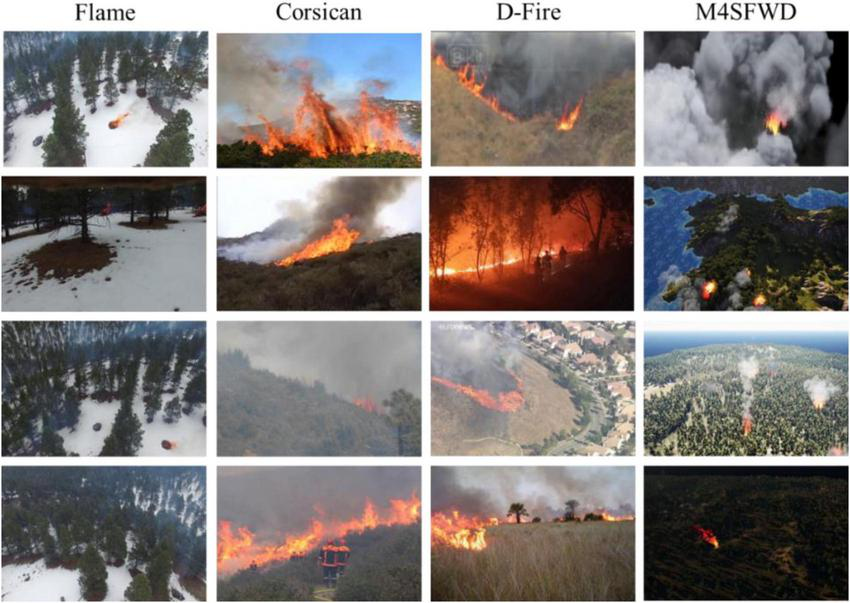

Sample images from the Flame, Corsican, D-Fire and M4SFWD datasets.
4.2 Experiment setup
In this study, ResNet50 is adopted as the backbone network. All labeled and unlabeled images are resized to 224=224 and normalized. The optimizer is set to SGD with a learning rate of 0.01, weight decay of 0.0001, and momentum of 0.9. The batch size is set to 14, and the model is trained for 60 epochs. Random horizontal flipping is applied to both the supervised and unsupervised branches for data augmentation. The temperature coefficient τ for contrastive loss is set to 0.1, the loss weight λ for the unsupervised branch is set to 0.5, and the positive sample filtering threshold γ is set to 0.75. All experiments are performed on a workstation with Ubuntu 18.04 and an NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU.
To evaluate the segmentation performance, Precision and IoU (Intersection over Union) of the fire region are used as the main metrics. The mathematical definitions of these metrics are given as follows:
where TP, FP, and FN represent the number of true positive, false positive, and false negative pixels in the fire region, respectively. Precision is calculated as the ratio of correctly predicted fire pixels to all predicted fire pixels. IoU is computed as the ratio of the intersection area between the predicted fire region and the ground truth to their union area. Since the segmentation task only contains two categories (background and fire), IoU of the fire region is adopted as the primary indicator to measure the model’s accuracy in locating the fire area.
4.3 Comparison with other methods
To comprehensively verify the performance advantages of the PPCNet model for forest fire image segmentation, five representative semi-supervised semantic segmentation methods are selected for comparison, including CAC (Lai et al., 2021), ST++ (Yang et al., 2022), CCT (Ouali et al., 2020), ALS4GAN (Desai and Ghose, 2022), and Allspark (Wang H. et al., 2024). These methods are widely recognized in semi-supervised image segmentation and have been extensively applied in complex scenarios such as remote sensing, providing strong reference value. The experiments are conducted on four publicly available aerial remote sensing forest fire datasets. The same data splitting strategy and evaluation metrics are adopted to ensure the fairness and comparability of the experimental results. Specifically, the training sets are divided into different proportions of labeled and unlabeled data (8:2, 7:3, and 5:5) to simulate real-world scenarios with varying degrees of annotated data availability, thereby further testing the stability and robustness of the models under different data conditions.
4.3.1 Results and visualization analysis on the Flame dataset
The Flame dataset mainly consists of images captured by UAVs at high altitudes. These images present typical challenges such as small fire targets, complex backgrounds, and severe occlusions, making the segmentation task highly difficult. In the experiment, the dataset is divided into training and testing sets with a ratio of 8:2. Within the training set, different labeled and unlabeled data proportions (8:2, 7:3, and 5:5) are further configured. The results are shown in Table 1. The results demonstrate that the PPCNet consistently outperforms all comparison methods across all three labeled and unlabeled data ratios in terms of both Precision and IoU. Notably, under the most challenging condition with 50% unlabeled data (5:5 split), the IoU of PPCNet reaches 71.6%, which is 1.1% higher than the second-best method, ALS4GAN. This fully validates the advantage of the proposed model in scenarios with limited labeled data and strong reliance on semi-supervised learning. Specifically, ALS4GAN and Allspark also show strong performance on this dataset, especially as the proportion of unlabeled data increases, reflecting their certain semi-supervised learning capabilities. In contrast, CAC and CCT exhibit relatively weaker overall performance, with significantly lower IoU values under the 8:2 labeled-unlabeled ratio, indicating limitations in their feature representation for small targets and complex backgrounds.
TABLE 1
| Model | 8:2 | 7:3 | 5:5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | |
| CAC (Lai et al., 2021) | 76.9% | 62.5% | 79.1% | 65.4% | 80.7% | 67.7% |
| ST++ (Yang et al., 2022) | 75.5% | 60.6% | 80.6% | 67.6% | 80.8% | 67.9% |
| CCT (Ouali et al., 2020) | 76.0% | 61.3% | 78.1% | 64.1% | 81.2% | 68.4% |
| ALS4GAN (Desai and Ghose, 2022) | 77.5% | 63.3% | 79.3% | 65.7% | 82.7% | 70.5% |
| Allspark (Wang H. et al., 2024) | 77.1% | 62.7% | 78.7% | 64.8% | 82.2% | 69.7% |
| PPCNet | 79.3% | 65.8% | 81.0% | 68.1% | 83.4% | 71.6% |
Experimental results on the Flame dataset.
Bold values indicate the best performance.
The visual comparison results shown in Figure 5 further illustrate the segmentation performance differences among different models. It can be clearly observed that although most semi-supervised methods can roughly locate the fire regions, PPCNet achieves more accurate and complete segmentation results in terms of fire boundary details and texture structure. This is mainly attributed to the PFF and DFFE modules integrated into PPCNet, which effectively capture the detailed features of small-scale fire targets and, through multi-scale information integration and frequency-domain feature enhancement, significantly improve the model’s segmentation performance under complex scene conditions.
FIGURE 5
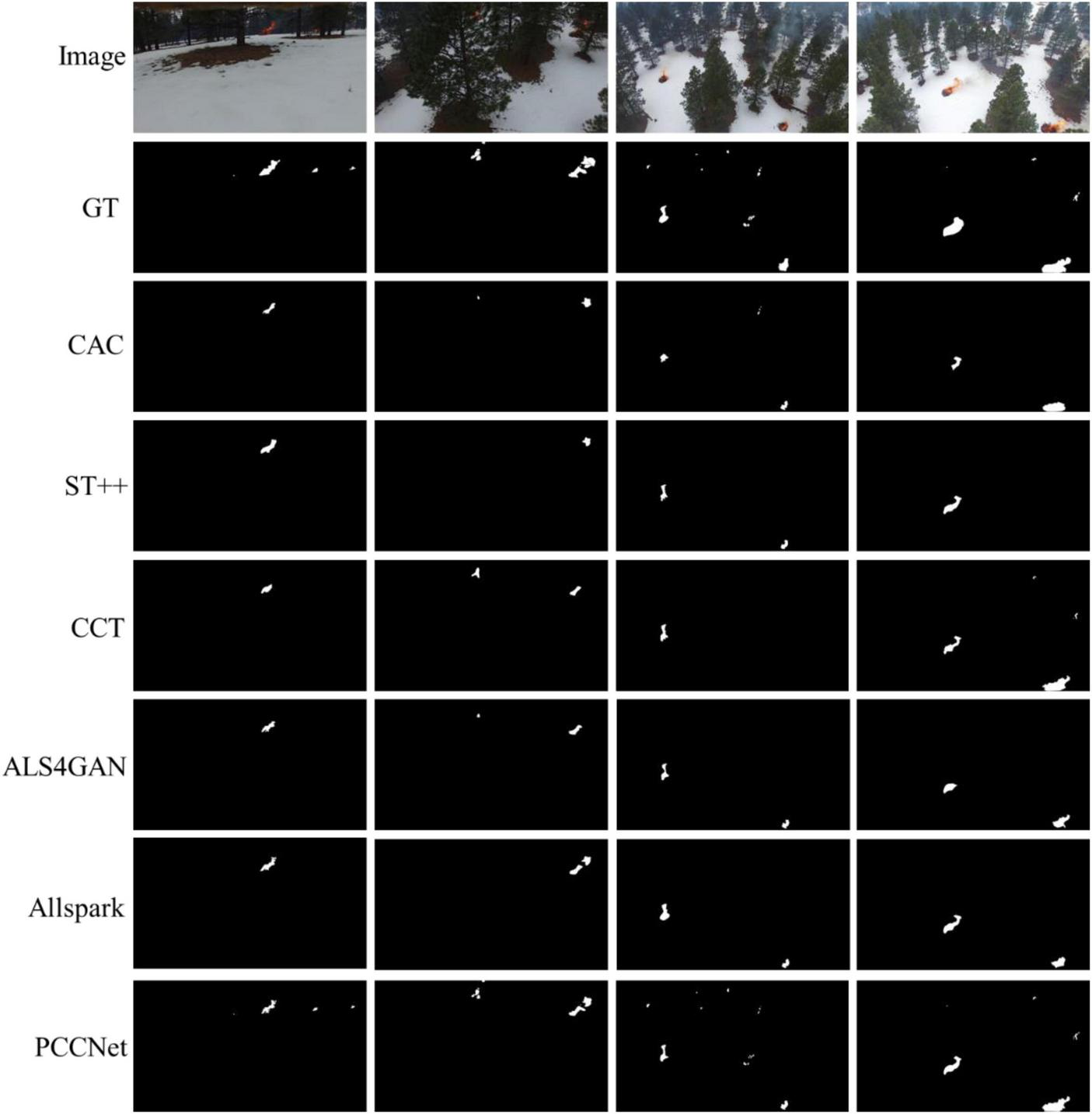
The visual comparisons of segmentation results on the Flame dataset.
4.3.2 Results and visualization analysis on the Corsican dataset
The Corsican dataset contains a large number of real forest fire images captured in natural environments under various weather conditions, lighting variations, and flame shapes. Fire targets in this dataset are generally large, with complex backgrounds, providing both high application value and significant challenges. The experimental setup follows that of the Flame dataset, with an 8:2 training-test split. Within the training set, labeled and unlabeled data are divided in proportions of 8:2, 7:3, and 5:5. The detailed results are shown in Table 2.
TABLE 2
| Model | 8:2 | 7:3 | 5:5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | |
| CAC (Lai et al., 2021) | 82.7% | 70.5% | 86.3% | 75.9% | 86.5% | 76.2% |
| ST++ (Yang et al., 2022) | 77.4% | 63.1% | 88.1% | 78.6% | 87.6% | 77.1% |
| CCT (Ouali et al., 2020) | 81.2% | 68.3% | 82.5% | 70.4% | 86.0% | 75.3% |
| ALS4GAN (Desai and Ghose, 2022) | 83.2% | 71.2% | 87.7% | 75.6% | 86.8% | 77.4% |
| Allspark (Wang H. et al., 2024) | 82.0% | 69.4% | 82.4% | 70.9% | 86.5% | 76.2% |
| PPCNet | 89.4% | 80.4% | 90.1% | 82.4% | 92.1% | 85.6% |
Experimental results on the Corsican dataset.
Bold values indicate the best performance.
The results clearly show that PPCNet achieves the best performance across all labeled-unlabeled data proportions in both Precision and IoU metrics. Particularly under the most challenging 5:5 split with 50% unlabeled data, PPCNet achieves an IoU of 85.6% and Precision of 92.1%, highlighting its outstanding stability and robustness under different levels of labeled data availability. Furthermore, ALS4GAN and ST++ demonstrate competitive performance, with ST++ even outperforming ALS4GAN in IoU under 7:3 and 5:5 splits, indicating its advantage in semi-supervised learning. CCT and Allspark deliver moderate performance, while CAC consistently performs the weakest.
The visualization results shown in Figure 6 further illustrate that the PFF module effectively combines shallow (e.g., edges, colors, positions) and deep (e.g., semantic, scene context) features, which is particularly beneficial for segmenting large-scale, diverse, and complex fire targets in this dataset. The shallow features assist in precise boundary localization, while the deep features enhance scene semantic understanding, working together to significantly improve the model’s overall expressive capability. Additionally, the DFFE module leverages high and low-frequency information to accurately capture fire boundaries and texture details. The incorporation of low-frequency information effectively suppresses background noise from lighting and weather variations, further enhancing segmentation robustness in complex scenes. These designs together contribute to the superior comprehensive performance of PPCNet on the Corsican dataset, demonstrating its strong potential for real-world forest fire segmentation tasks.
FIGURE 6
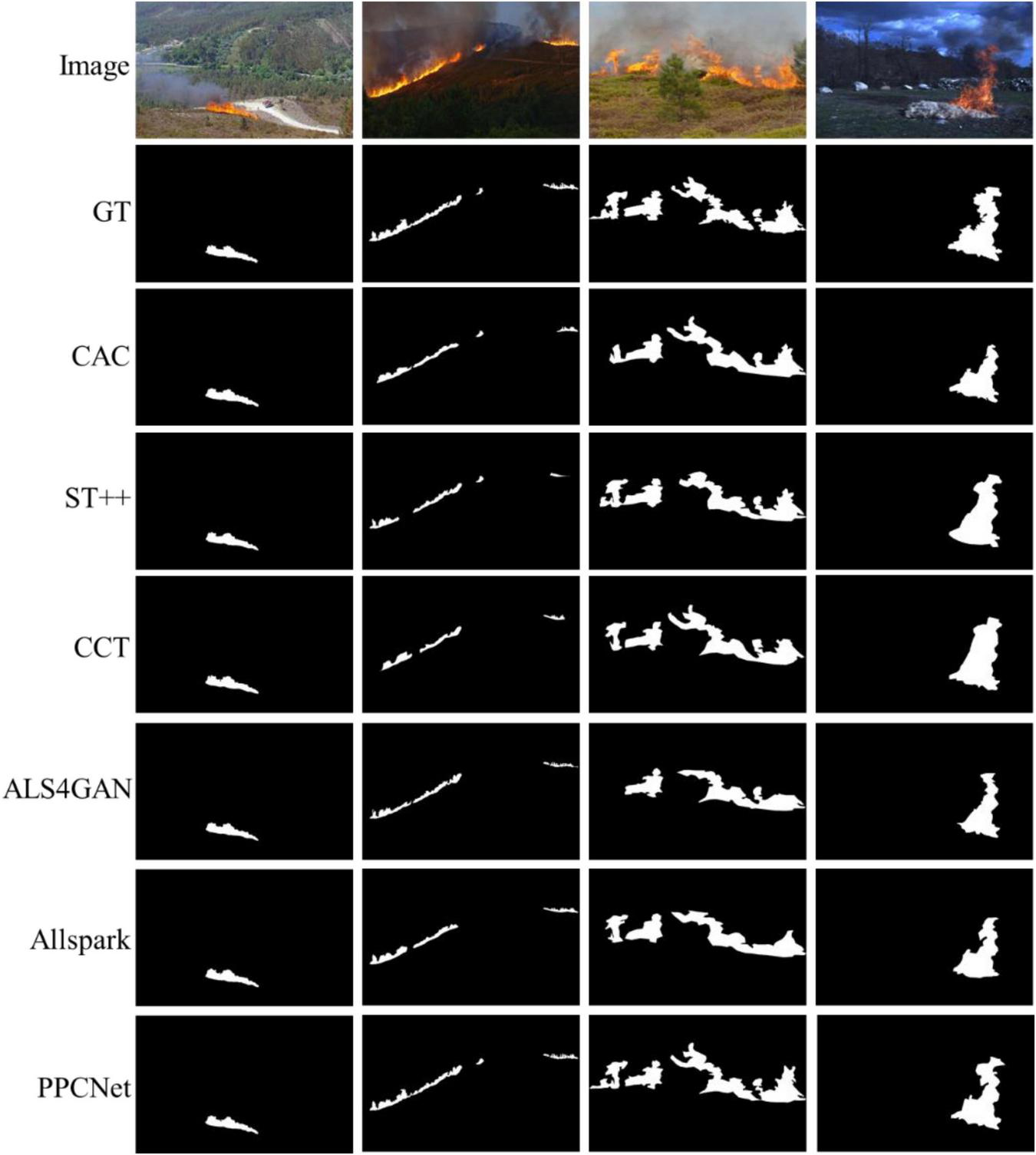
The visual comparisons of segmentation results on the Corsican dataset.
4.3.3 Results and visualization analysis on the D-Fire dataset
The D-Fire dataset covers a wide variety of real forest fire scenes, accounting for day-night lighting variations and different fire development stages, making it particularly challenging. The experiments adopt the same labeled-unlabeled data splits of 8:2, 7:3, and 5:5. Table 3 summarizes the results of all models under different conditions. As shown, PPCNet consistently outperforms all other models in both Precision and IoU across all data splits, demonstrating strong overall advantages. Notably, under the most challenging 5:5 split, PPCNet achieves an IoU of 75.3%, which is 0.8% and 3.2% higher than ALS4GAN and Allspark, respectively, further verifying its robustness and stability under limited labeled data and high reliance on unsupervised learning. Compared with the Corsican dataset, the overall IoU results on the D-Fire dataset are lower, reflecting additional challenges posed by lighting variations and fire development stages. Despite this, PPCNet maintains its performance lead, indirectly confirming the effectiveness of the PFF and DFFE modules in complex, variable environments. ALS4GAN shows noticeable improvement with high proportions of unlabeled data (5:5 split), suggesting its semi-supervised strategy offers some advantages under challenging conditions. However, ST++, CCT, and CAC exhibit relatively lower IoU values, particularly under 8:2 and 7:3 splits, indicating insufficient adaptability to lighting and fire stage variations.
TABLE 3
| Model | 8:2 | 7:3 | 5:5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | |
| CAC (Lai et al., 2021) | 79.1% | 65.4% | 80.7% | 67.7% | 76.9% | 73.4% |
| ST++ (Yang et al., 2022) | 80.6% | 67.6% | 80.8% | 67.9% | 75.5% | 70.8% |
| CCT (Ouali et al., 2020) | 78.1% | 64.1% | 81.2% | 68.4% | 76.0% | 71.6% |
| ALS4GAN (Desai and Ghose, 2022) | 79.3% | 65.7% | 82.7% | 70.5% | 77.5% | 74.5% |
| Allspark (Wang H. et al., 2024) | 78.7% | 64.8% | 82.2% | 69.7% | 77.1% | 72.1% |
| PPCNet | 81.0% | 68.1% | 83.4% | 71.6% | 79.3% | 75.3% |
Experimental results on the D-Fire dataset.
Bold values indicate the best performance.
The visual comparison results in Figure 7 reveal that even under varying lighting conditions and different fire development stages, PPCNet accurately locates fire regions and provides significantly better boundary delineation and texture detail preservation than other methods. This superior performance mainly results from the PFF module’s effective multi-level feature integration and the DFFE module’s combined enhancement of frequency-domain information, giving the model stronger adaptability to complex environments and boundary expression capabilities.
FIGURE 7
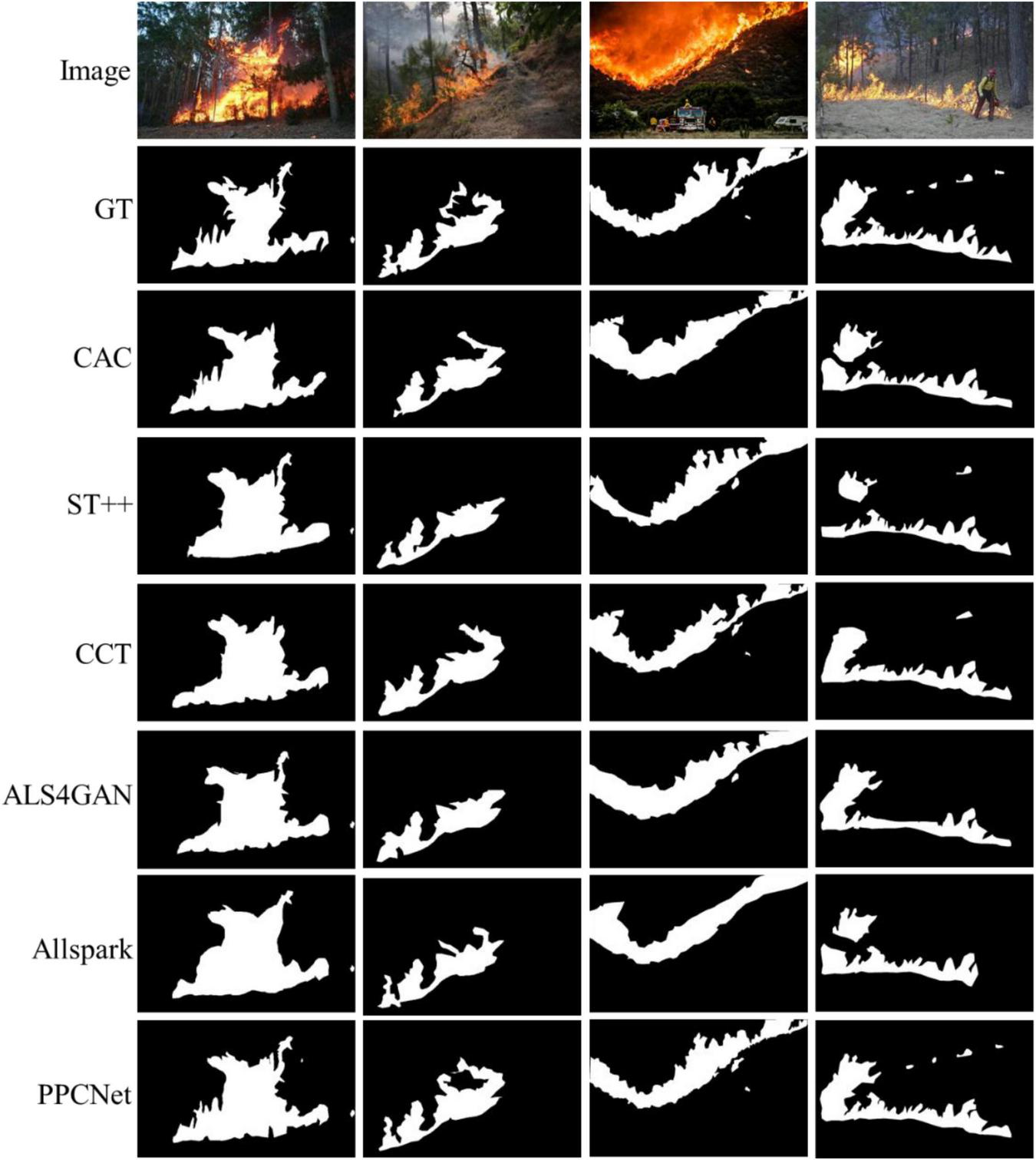
The visual comparisons of segmentation results on the D-Fire dataset.
4.3.4 Results and visualization analysis on the M4SFWD dataset
The M4SFWD dataset is a synthetic dataset designed to simulate forest fire scenarios under complex terrain, weather, and lighting conditions. It incorporates multi-scale and varying numbers of fire targets, providing a comprehensive evaluation of model performance under complex, realistic conditions. Table 4 presents the results of all models under three labeled-unlabeled data splits. Overall, the IoU values on the M4SFWD dataset are lower than those on the Corsican dataset but higher than those on the D-Fire dataset, indicating that the simulated complex environments present challenges, though not as severe as real-world lighting variations. PPCNet achieves the best performance in both Precision and IoU across all splits. Especially under the 5:5 split, PPCNet reaches an IoU of 78.1%, 2.2% higher than the second-best model, Allspark. Notably, the Precision scores are relatively high for all models, reflecting strong performance in coarse segmentation of large fire targets. However, the IoU results reveal that fine-grained segmentation and background discrimination remain challenging. Allspark and ALS4GAN perform similarly on this dataset, showing good stability with increasing proportions of unlabeled data. In contrast, ST++, CCT, and CAC lag behind in IoU, further confirming the comprehensive advantage of PPCNet in handling complex, realistic forest fire scenarios.
TABLE 4
| Model | 8:2 | 7:3 | 5:5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | |
| CAC (Lai et al., 2021) | 79.7% | 66.3% | 83.9% | 72.3% | 86.0% | 75.4% |
| ST++ (Yang et al., 2022) | 81.2% | 68.4% | 80.7% | 67.7% | 84.0% | 72.5% |
| CCT (Ouali et al., 2020) | 80.4% | 67.2% | 81.3% | 68.6% | 84.4% | 73.2% |
| ALS4GAN (Desai and Ghose, 2022) | 80.7% | 67.7% | 83.9% | 72.3% | 85.6% | 74.8% |
| Allspark (Wang H. et al., 2024) | 81.6% | 68.9% | 82.7% | 70.5% | 86.3% | 75.9% |
| PPCNet | 82.0% | 69.4% | 84.8% | 73.7% | 87.1% | 78.1% |
Experimental results on the M4SFWD dataset.
Bold values indicate the best performance.
Visualization results in Figure 8 show that PPCNet effectively preserves flame boundaries, textures, and overall contours under different terrain, weather, and lighting conditions. The model achieves significantly better segmentation accuracy and region continuity compared to other methods, further validating the effectiveness of its multi-scale and frequency-domain joint enhancement strategy.
FIGURE 8
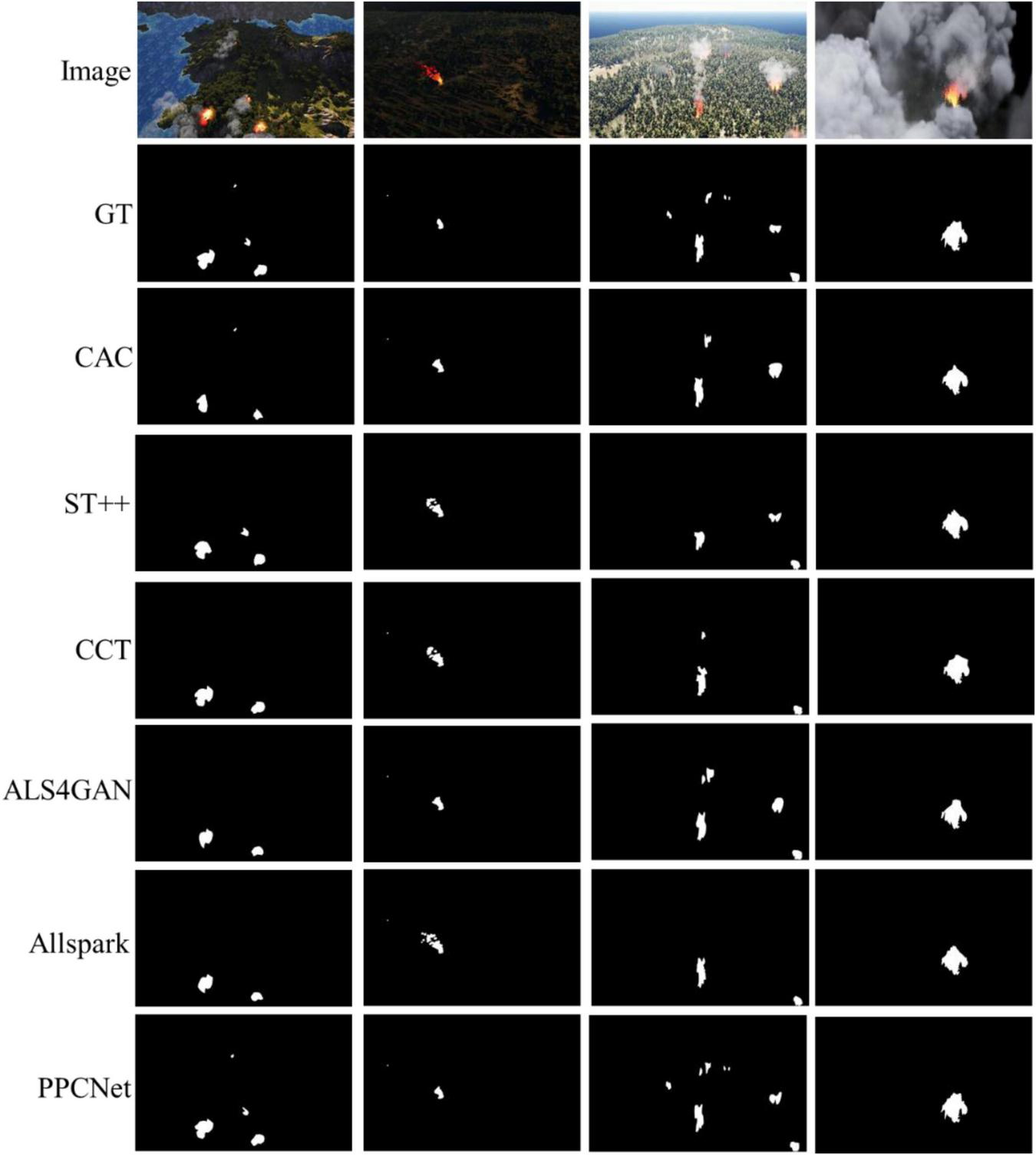
The visual comparisons of segmentation results on the M4SFWD dataset.
However, a closer inspection of the misclassified samples across all datasets reveals several consistent patterns. Most errors occur in scenes with highly complex backgrounds, such as vegetation, soil, or sunlight reflections that share similar spectral characteristics with flame regions. Low-visibility conditions, including dense smoke, haze, and nighttime illumination, also lead to boundary blurring and lower confidence in fire localization. In addition, small-scale or partially occluded flames tend to be merged with non-fire regions, producing fragmented boundaries. These observations indicate that PPCNet’s remaining errors are mainly caused by visual ambiguity rather than deficiencies in feature representation. The PFF and DFFE modules already alleviate these problems by enhancing texture and boundary cues, yet extremely challenging lighting and visibility conditions remain difficult cases for all models.
4.4 Ablation experiments
To further verify each core module in PPCNet, this study conducts ablation experiments focusing on the Panoramic Feature Fusion (PFF) module, the Dual-Frequency Feature Enhancement (DFFE) module, and the Pixel Contrastive Loss (LDC). These experiments comprehensively analyze the contribution of each component to segmentation performance. The Baseline model, used as a reference, adopts a conventional ASPP module for multi-scale feature fusion, and applies standard cross-entropy loss for the unlabeled data branch. Subsequently, PFF, DFFE, and LDC are individually or jointly introduced to replace the corresponding structures, and the impact of each module on model performance is evaluated. All ablation experiments adopt an 8:2 ratio of labeled to unlabeled data. The results are presented in Table 5.
TABLE 5
| Strategy | Flame | Corsican | D-Fire | M4SFWD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | Precision | IoU | |
| Baseline | 76.4% | 61.8% | 85.9% | 75.3% | 77.5% | 63.2% | 79.2% | 65.6% |
| Baseline+PFF | 77.8% | 63.7% | 87.5% | 77.8% | 79.2% | 65.6% | 81.3% | 68.5% |
| Baseline+DFEE | 78.0% | 63.9% | 87.6% | 78.0% | 79.4% | 65.8% | 80.8% | 67.8% |
| Baseline+LDC | 76.8% | 62.4% | 86.6% | 76.3% | 77.7% | 63.5% | 80.0% | 66.7% |
| Baseline+PFF+DFEE | 78.5% | 64.6% | 88.1% | 78.7% | 80.4% | 67.2% | 81.7% | 69.0% |
| Baseline+PFF+LDC | 78.0% | 63.9% | 87.8% | 78.2% | 79.9% | 66.5% | 81.5% | 68.8% |
| Baseline+DFEE+LDC | 78.2% | 64.2% | 88.3% | 79.1% | 80.2% | 66.9% | 81.1% | 68.2% |
| Full PPCNet | 79.3% | 65.8% | 89.4% | 80.4% | 81.0% | 68.1% | 82.0% | 69.4% |
Ablation results of different module combinations.
Bold values indicate the best performance.
The ablation study confirms the effectiveness of each core component within PCCNet. Among them, the PFF module contributes the most consistent and significant performance improvement across all datasets. Taking the Flame dataset as an example, Precision increases by 1.4% and IoU by 1.9%. Similar improvements are observed on Corsican, D-Fire, and M4SFWD datasets, where PFF helps the model better integrate multi-scale contextual information and local details, especially under complex backgrounds and large scale variations. The DFFE module also provides stable performance gains. By combining high- and low-frequency information, it effectively enhances the model’s ability to capture fire contours, edges, and texture details while preserving global structure. Across the four datasets, DFFE brings Precision improvements of around 1.6% to 1.9% and IoU gains of up to 2.7%, alleviating common issues such as blurred boundaries and missing details. In contrast, the LDC shows limited improvement when used alone. However, its combination with PFF and DFFE produces clear synergistic effects. On the D-Fire dataset, the complete combination of all three modules results in a 3.5% Precision gain and a 4.9% IoU improvement, much higher than the individual contributions of each module. This demonstrates that LDC enhances feature discrimination by enforcing pixel-wise contrastive learning, which becomes particularly beneficial when combined with improved feature extraction and fusion mechanisms. Overall, when all three components are integrated into the full PPCNet framework, the model achieves the best results across all datasets. On the most challenging M4SFWD dataset, the complete model reaches 82.0% Precision and 69.4% IoU, outperforming the Baseline by 2.8 and 3.8%, respectively. These results comprehensively validate the collaborative advantage of the proposed modules and the robustness of PPCNet under various complex forest fire scenarios.
The visual results of the ablation experiment on the D-Fire dataset under the 8:2 data split, shown in Figure 9, further illustrate the effectiveness of each module. In particular, the red-box areas highlight how the PFF module simulates a “panoramic view” to comprehensively observe the scene and mitigate the impact of complex terrain, lighting variations, and occlusions. For example, as shown in Figure 9c, although a firefighter’s leg partially occludes a fire region, PFF effectively analyzes the overall fire spread and infers the presence of occluded fire areas. The DFFE module enhances the extraction of fire texture and detail features, as evident in Figure 9b, where incorporating DFFE results in significantly finer and more detailed segmentation outcomes.
FIGURE 9
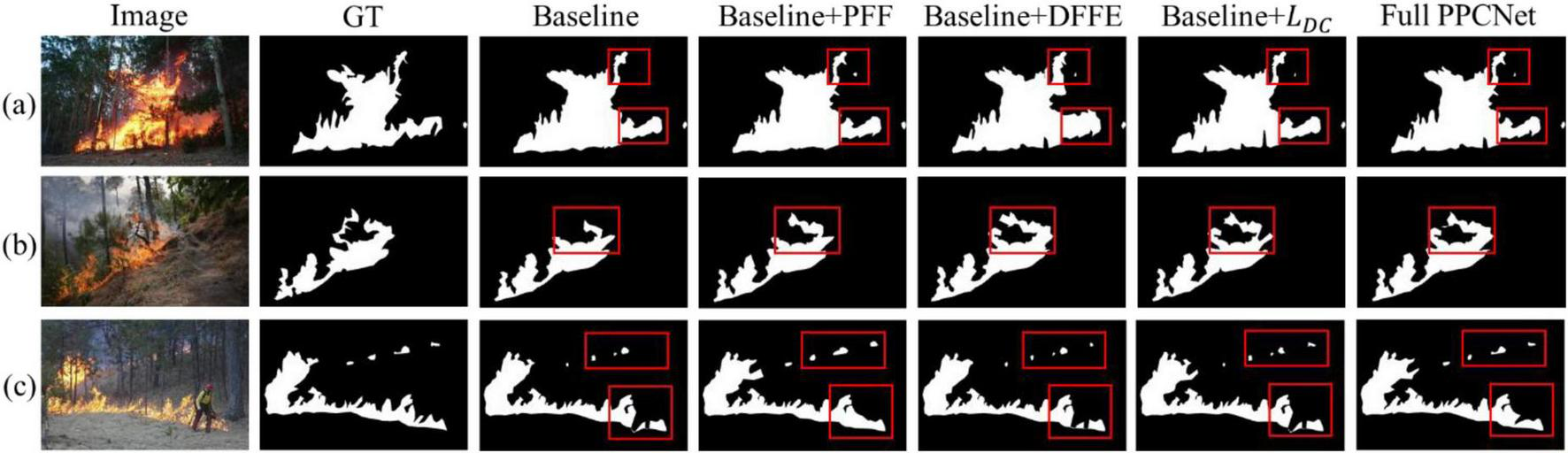
Segmentation results on three different wildfire image samples. (a–c) Represent three input wildfire samples respectively.
4.5 Convergence analysis
To further verify the training stability and optimization efficiency of PPCNet, a convergence analysis was conducted by comparing it with five representative semi-supervised segmentation methods, namely CAC, ST++, CCT, ALS4GAN, and Allspark, on the D-Fire dataset. In this experiment, the ratio of labeled to unlabeled data was set to 5:5. All models were trained under identical parameter configurations and data conditions, and the variation curves of training loss were recorded throughout the process, as shown in Figure 10. From the overall trend, it can be observed that PPCNet maintains a consistently lower loss value throughout the entire training process and achieves significantly faster convergence compared to other methods. Specifically, within the first 20 epochs, the loss value of PPCNet rapidly decreases to approximately 0.18, which is notably lower than that of CAC (approximately 0.27), Allspark (approximately 0.34), and ALS4GAN (approximately 0.37) over the same period. In contrast, both ST++ and CCT exhibit relatively slower declines in loss and more substantial fluctuations during the early training stages, indicating inferior stability.
FIGURE 10
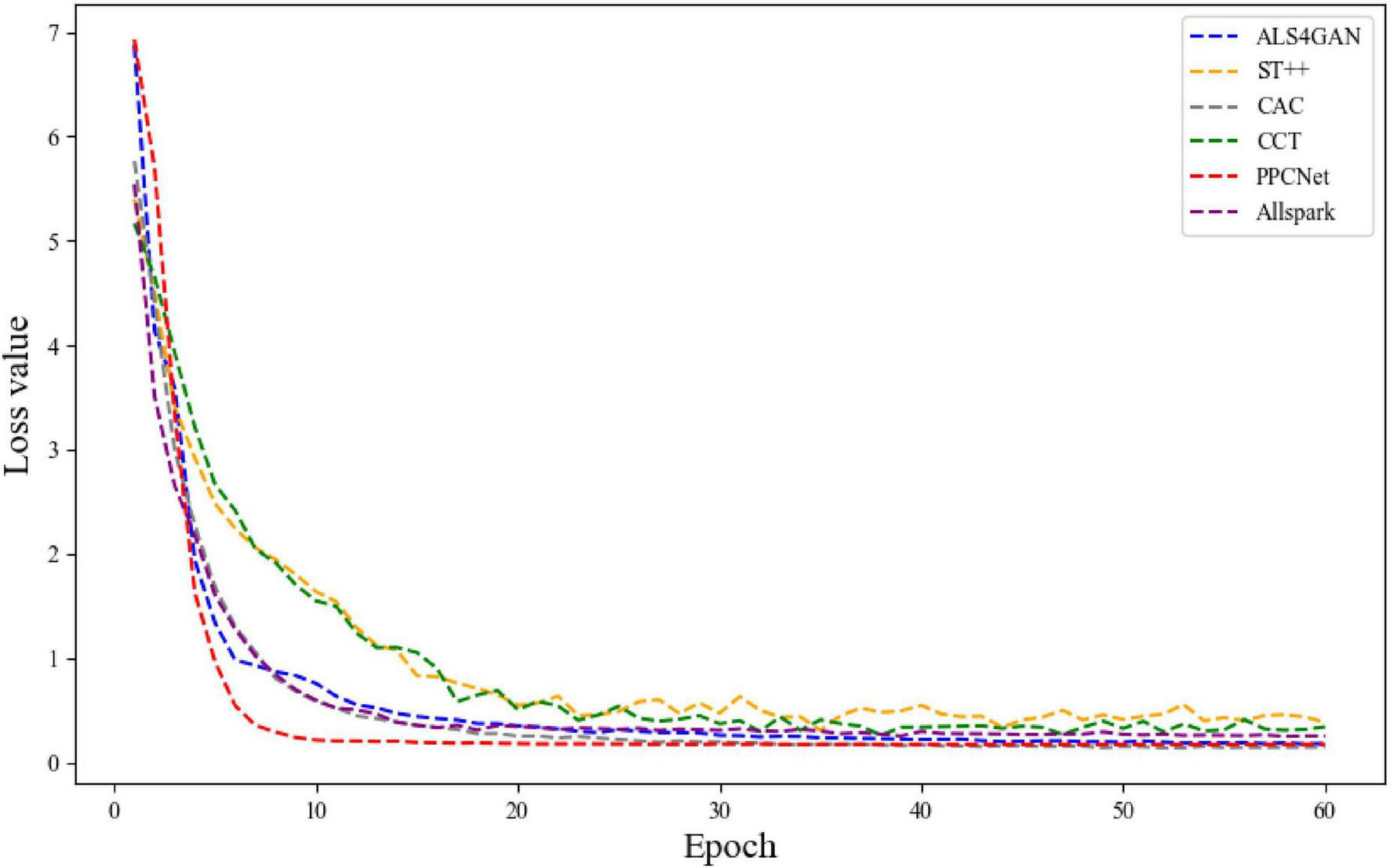
The variation curves of training loss on the D-Fire dataset.
To further verify the generalization and stability of PPCNet under different data conditions, an additional convergence analysis was conducted on the Corsican dataset. As shown in Figure 11, PPCNet exhibits a similarly smooth and rapid convergence trend.
FIGURE 11
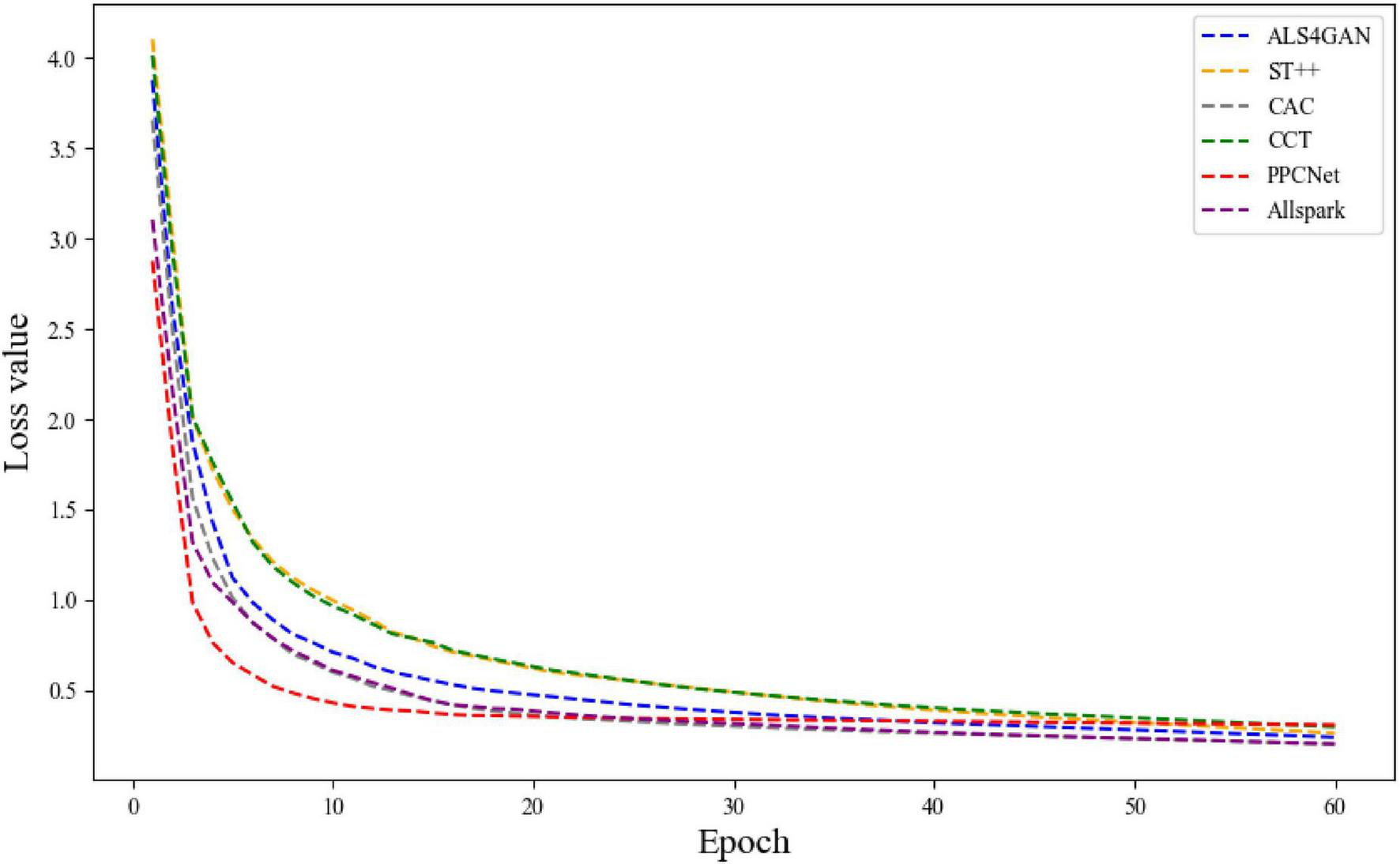
The variation curves of training loss on the Corsican dataset.
5 Conclusion
In this study, a semi-supervised segmentation method for forest fire images based on UAV remote sensing, named PPCNet, is proposed to address the limited labeled data, complex environmental interference, and insufficient boundary representation in forest fire segmentation tasks. The proposed method introduces several innovative components, including a Panoramic Feature Fusion (PFF) module, a Dual-Frequency Feature Enhancement (DFFE) module, and a Pixel Contrastive Loss (LDC). Through the effective integration of multi-scale, cross-level, and multi-frequency information, the model enhances its feature representation capability under complex forest fire scenarios. Extensive comparative experiments demonstrate that PPCNet achieves superior segmentation performance on four representative UAV remote sensing forest fire datasets: FLAME, Corsican, D-Fire, and M4SFWD.
In future work, we plan to further enhance and extend this research in the following directions. First, we will explore the incorporation of advanced structures such as Transformers and self-attention mechanisms to improve the ability to detect distant and weak fire targets. Second, we will investigate information fusion strategies based on multi-modal remote sensing data, including infrared, thermal, and multispectral images, to enrich input information and improve segmentation robustness under multi-source data conditions. Finally, we aim to construct a large-scale, multi-scenario, and multi-temporal UAV remote sensing forest fire dataset to promote the practical application and engineering deployment of semi-supervised forest fire segmentation methods in real-world scenarios.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. HL: Formal analysis, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province of China (Grant No. KYCX22_1105), and the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFD1000400).
Acknowledgments
We thank all the reviewers, and the preliminary and academic editors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Carratino L. Cissé M. Jenatton R. Vert J.-P. (2022). On mixup regularization.J. Mach. Learn. Res.231–31.
2
Chen B. Bai D. Lin H. Jiao W. (2023). Flametransnet: Advancing forest flame segmentation with fusion and augmentation techniques.Forests14:1887. 10.3390/f14091887
3
Darwish Ahmad A. Akafuah N. K. Forthofer J. Fuchihata M. Hirasawa T. Kuwana K. et al (2023). Large-scale fire whirl and forest fire disasters: Awareness, implications, and the need for developing preventative methods.Front. Mech. Eng.9:1045542. 10.3389/fmech.2023.1045542
4
Desai S. Ghose D. (2022). “Active learning for improved semi-supervised semantic segmentation in satellite images,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 553–563.
5
Feng H. Qiu J. Wen L. Zhang J. Yang J. Lyu Z. et al (2025). U3UNet: An accurate and reliable segmentation model for forest fire monitoring based on UAV vision.Neural Netw.185:107207. 10.1016/j.neunet.2025.107207
6
Giannakidou S. Radoglou-Grammatikis P. Lagkas T. Argyriou V. Goudos S. Markakis E. K. et al (2024). Leveraging the power of internet of things and artificial intelligence in forest fire prevention, detection, and restoration: A comprehensive survey.Internet Things26:101171. 10.1016/j.iot.2024.101171
7
Harkat H. Nascimento J. M. P. Bernardino A. Thariq Ahmed H. F. (2022). Assessing the impact of the loss function and encoder architecture for fire aerial images segmentation using deeplabv3+.Remote Sens.14:2023. 10.3390/rs14092023
8
Hossain F. M. A. Zhang Y. M. Tonima M. A. (2020). Forest fire flame and smoke detection from UAV-captured images using fire-specific color features and multi-color space local binary pattern.J. Unmanned Veh. Syst.8285–309. 10.1139/juvs-2020-0009
9
Koottungal A. Pandey S. Nambiar A. (2023). “Semi-supervised classification and segmentation of forest fire using autoencoders,” in International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, (Berlin: Springer), 27–39.
10
Lai X. Tian Z. Jiang L. Liu S. Zhao H. Wang L. et al (2021). “Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with directional context-aware consistency,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 1205–1214.
11
Lee K. van Leeuwen W. J. D. Gillan J. K. Falk D. A. (2024). Examining the impacts of pre-fire forest conditions on burn severity using multiple remote sensing platforms.Remote Sens16:1803. 10.3390/rs16101803
12
Li C. Liu Q. Li B. Liu L. (2022). Investigation of recognition and classification of forest fires based on fusion color and textural features of images.Forests13:1719. 10.3390/f13101719
13
Lin Q. Li Z. Zeng K. Fan H. Li W. Zhou X. (2024). FireMatch: A semi-supervised video fire detection network based on consistency and distribution alignment.Expert Syst. Appl.248:123409. 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.123409
14
Liu R. Tao F. Liu X. Na J. Leng H. Wu J. et al (2022). RAANet: A residual ASPP with attention framework for semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images.Remote Sens14:3109. 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.123409
15
Liu T. Chen W. Lin X. Mu Y. Huang J. Gao D. et al (2023). Defogging learning based on an improved deepLabV3+ model for accurate foggy forest fire segmentation.Forests14:1859. 10.3390/f14091859
16
Liu Y. Bai X. Wang J. Li G. Li J. Lv Z. (2024). Image semantic segmentation approach based on DeepLabV3 plus network with an attention mechanism.Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell.127:107260. 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107260
17
Mai H. Sun R. Wu F. (2025). “Relaxed class-consensus consistency for semi-supervised semantic segmentation,” in Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, (Washington, DC: AAAI Press), 6045–6053. 10.3390/s23020940
18
Ouali Y. Hudelot C. Tami M. (2020). “Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with cross-consistency training,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 12674–12684.
19
Ronneberger O. Fischer P. Brox T. (2015). “U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation,” in Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th international conference, Munich, Germany, (Berlin: Springer), 234–241.
20
Rudz S. Chetehouna K. Hafiane A. Laurent H. Séro-Guillaume O. (2013). Investigation of a novel image segmentation method dedicated to forest fire applications.Meas. Sci. Technol.24:075403. 10.1088/0957-0233/24/7/075403
21
Saleh A. Zulkifley M. A. Harun H. H. Gaudreault F. Davison I. Spraggon M. (2024). Forest fire surveillance systems: A review of deep learning methods.Heliyon10:e23127. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23127
22
Samhitha J. S. S. Sagar K. A. Yaswanth J. S. Haritha K. (2024). “Early forest fire prediction system using wireless sensor network,” in 2024 2nd International Conference on Device Intelligence, Computing and Communication Technologies (DICCT), (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 232–237.
23
Shang R. Zhang J. Jiao L. Li Y. Marturi N. Stolkin R. (2020). Multi-scale adaptive feature fusion network for semantic segmentation in remote sensing images.Remote Sens.12:872. 10.3390/rs12050872
24
Shirvani Z. Abdi O. Goodman R. C. (2023). High-resolution semantic segmentation of woodland fires using residual attention UNet and time series of Sentinel-2.Remote Sens.15:1342. 10.3390/rs15051342
25
Sun G. Wen Y. Li Y. (2022). Instance segmentation using semi-supervised learning for fire recognition.Heliyon8:e12375. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12375
26
Tlig L. Bouchouicha M. Tlig M. Sayadi M. Moreau E. (2020). A fast segmentation method for fire forest images based on multiscale transform and PCA.Sensors20:6429. 10.3390/s20226429
27
Toulouse T. Rossi L. Akhloufi M. Celik T. Maldague X. (2015). Benchmarking of wildland fire colour segmentation algorithms.IET Image Process91064–1072. 10.1049/iet-ipr.2014.0935
28
Wang H. Zhang Q. Li Y. Li X. (2024). “Allspark: Reborn labeled features from unlabeled in transformer for semi-supervised semantic segmentation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 3627–3636.
29
Wang J. Fan X. Yang X. Tjahjadi T. Wang Y. (2022). Semi-supervised learning for forest fire segmentation using UAV imagery.Forests13:1573. 10.3390/f13101573
30
Wang J. Hq Ding C. Chen S. He C. Luo B. (2020). Semi-supervised remote sensing image semantic segmentation via consistency regularization and average update of pseudo-label.Remote Sens12:3603. 10.3390/rs12213603
31
Wang Y. Wang Y. Xu C. Wang X. Zhang Y. (2024). Computer vision-driven forest wildfire and smoke recognition via IoT drone cameras.Wireless Netw.307603–7616. 10.1007/s11276-024-03718-0
32
Wei X. Larsen C. P. S. (2019). Methods to detect edge effected reductions in fire frequency in simulated forest landscapes.ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf.8:277. 10.3390/ijgi8060277
33
Wu X. Hong D. Chanussot J. (2022). UIU-Net: U-Net in U-Net for infrared small object detection.IEEE Trans. Image Process.32364–376. 10.1109/TIP.2022.3228497
34
Xie Z. Zhang Z. Cao Y. Lin Y. Bao J. Yao Z. et al (2022). “Simmim: A simple framework for masked image modeling,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 9653–9663.
35
Xin Y. Fan Z. Qi X. Geng Y. Li X. (2024). Enhancing semi-supervised semantic segmentation of remote sensing images via feature perturbation-based consistency regularization methods.Sensors24:730. 10.3390/s24030730
36
Yan Z. Zheng X. Li W. Wang L. Ding P. Zhang L. et al (2024). FireDA: A domain adaptation-based method for forest fire recognition with limited labeled scenarios.Forests15:1684. 10.3390/f15101684
37
Yandouzi M. Berrahal M. Grari M. Boukabous M. Moussaoui O. Azizi M. et al (2024). Semantic segmentation and thermal imaging for forest fires detection and monitoring by drones.Bull. Electrical Eng. Informatics132784–2796. 10.11591/eei.v13i4.7663
38
Yang H. (2024). Efficiency in constraint: A comparative analysis review of FCN and DeepLab models on small-scale datasets.Appl. Comput. Eng.7519–30. 10.54254/2755-2721/75/20240501
39
Yang L. Zhao Z. Zhao H. (2025). Unimatch v2: Pushing the limit of semi-supervised semantic segmentation.IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell.473031–3048. 10.1109/TPAMI.2025.3528453
40
Yang L. Zhuo W. Qi L. Shi Y. Gao Y. (2022). “St++: Make self-training work better for semi-supervised semantic segmentation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 4268–4277.
41
Yang Z. Cao S. Aibin M. (2025). Beyond sRGB: Optimizing object detection with diverse color spaces for precise wildfire risk assessment.Remote Sens17:1503. 10.3390/rs17091503
42
Yun S. Han D. Oh S. J. Chun S. Choe J. Yoo Y. (2019). “Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 6023–6032.
43
Zhang P. Zhang B. Zhang T. Chen D. Wang Y. Wen F. (2021). “Prototypical pseudo label denoising and target structure learning for domain adaptive semantic segmentation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 12414–12424.
44
Zhang Z. Guo Y. Chen G. Xu Z. (2023). Wildfire detection via a dual-channel CNN with multi-level feature fusion.Forests14:1499. 10.3390/f14071499
45
Zhao J. Zhang Z. Han S. Qu C. Yuan Z. Zhang D. (2011). SVM based forest fire detection using static and dynamic features.Comput. Sci. Information Syst.8821–841. 10.2298/CSIS101012030Z
46
Zheng H. Dembélé S. Wu Y. Liu Y. Chen H. Zhang Q. (2023). A lightweight algorithm capable of accurately identifying forest fires from UAV remote sensing imagery.Front. For. Glob. Change6:1134942. 10.3389/ffgc.2023.1134942
47
Zheng H. Wang M. Wang Z. Huang X. (2024). FireDM: A weakly-supervised approach for massive generation of multi-scale and multi-scene fire segmentation datasets.Knowl. Based Syst.290:111547. 10.1016/j.knosys.2024.111547
48
Zheng Y. Zhang G. Tan S. Yang Z. Wen D. Xiao H. (2023). A forest fire smoke detection model combining convolutional neural network and vision transformer.Front. For. Glob. Change6:1136969. 10.3389/ffgc.2023.1136969
49
Zou R. Xin Z. Liao G. Huang P. Wang R. Qiao Y. (2025). A Fire segmentation method with flame detail enhancement U-net in multispectral remote sensing images under category imbalance.Remote Sens.17:2175. 10.3390/rs17132175
Summary
Keywords
UAV remote sensing, fire, forest fire segmentation, semi-supervised learning, feature fusion
Citation
Ma Y and Lin H (2025) Semi-supervised segmentation of forest fires from UAV remote sensing images via panoramic feature fusion and pixel contrastive learning. Front. For. Glob. Change 8:1669707. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2025.1669707
Received
20 July 2025
Accepted
31 October 2025
Published
17 November 2025
Volume
8 - 2025
Edited by
María Menéndez-Miguélez, Instituto Nacional de Investigación y Tecnología Agroalimentaria (INIA), Spain
Reviewed by
Bijoy Vengasseril Thampi, Analytical Mechanics Associates, United States
Kunlong Niu, Guangzhou Institute of Geography, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Ma and Lin.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haifeng Lin, haifeng.lin@njfu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.