- 1Department of Oncology, Deqing People’s Hospital, Huzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Respiratory Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
- 3Department of Urology, Deqing People’s Hospital, Huzhou, Zhejiang, China
Endoplasmic reticulum is the primary site of eukaryotic cells involved in biosynthesis, lipid metabolism, glucose metabolism, protein folding and secretion. Multiple factors in the tumor microenvironment may induce the accumulation of unfolded and misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and trigger endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Adaptive mechanisms including unfolded protein response (UPR) and endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation (ERAD) are activated in response to ER stress. Previous studies have revealed that ER stress may participate in epithelial mesenchymal transformation, apoptosis, metabolic regulation and drug resistance of lung cancer cells. Herein, we summarized the potential effects and regulatory mechanisms of ER stress on the biological process of lung cancer, which may provide scientific significance and clinical value for elucidating the adaptability of lung cancer cells under stress and developing novel targeted therapies.
Introduction
Lung cancer is the most prevalent malignant tumor worldwide. The American Cancer Society has reported that lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer-related mortality in 2022, comprising the majority of cancer deaths globally, with around 81% of lung cancer cases being attributed to long-term smoking (1). Additional risk factors include a family history of pulmonary cancer, occupational exposure, previous exposure to infectious pathogens, and various aetiologic factors (2). The universal application of low-dose computed tomography, as an effective modality for lung cancer screening, has significantly improved the detection rate of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). However, even patients diagnosed with early-stage and undergo radical surgery, approximately 30%-50% of patients still develop postoperative recurrence, with a 5-year survival rate of less than 60% (3).
Malignant tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment (TME) exhibit reciprocal regulation and adaptation. Due to genomic instability, abnormal metabolism, immune destruction, and alteration of the tumor microenvironment, tumor cells are constantly exposed to exogenous stress (hypoxia, oxidative stress, etc.) and endogenous stress (oncogene activation, tumor suppressor gene inactivation, etc.) that may induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress (4). Stress may trigger autophagic apoptosis in tumor cells (5), while sustained ER stress contributes to the therapeutic resistance. This is largely attributed to high plasticity and adaptive capacity of tumor cells that enable them to survive and even convert the stress into a drive for self-renewal (6). Studies have demonstrated that ER stress is closely associated with immune regulation and drug resistance in lung cancer. The identification of stress-related signaling targets and regulatory mechanisms is of paramount scientific and clinical significance for elucidating the adaptive capacity of lung cancer cells under stress and developing novel targeted therapies.
UPR and ERAD
The endoplasmic reticulum is a crucial inner membrane structure in eukaryotic cells that plays a fundamental role in various cellular processes, including biosynthesis, lipid and glucose metabolism, protein folding, and secretion of over 30% of intracellular proteins (7). Previous studies have indicated that ER may serve as a “largest processing plant” in the cell, precisely regulating protein folding and modification processes, as well as cellular signals transduction. However, various physiological and pathological factors in the ER may cause disruption of calcium ion homeostasis and protein misfolding in the lumen, leading to an imbalance in ER homeostasis. The imbalance can cause unfolded and misfolded proteins to accumulate in the ER lumen and trigger the ER stress response (8). Under stress conditions, cells initiate a series of cascade response pathways, including the unfolded protein response (UPR) and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD), to adapt to protein folding alterations (9).
The UPR is an interconnected signaling pathway that involves three transmembrane proteins on the ER membrane, namely inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α), PKR-like ER kinase (PERK), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6). The primary function of UPR is to restore ER homeostasis by adapting to changes in protein folding within the ER (10). Glucose-regulated proteins 78 (GRP78), an ER resident chaperone also referred to as binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP), may serve as central receptors for ER stress (11). In the resting state of the ER, the luminal structural domains of ATF6, PERK, and IRE1α are bound with the chaperone protein GRP78/BiP in an inactive state. While accumulation of misfolded proteins in the ER lumen may trigger ER stress and contribute to the GRP78/BiP complex dissociating from the sensors, leading to the activation of UPR pathway to restore ER homeostasis and protect the cell from disruption (12).
ERAD is a crucial protein quality control system for the degradation of misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. In mammals, ERAD substrates are recognized through the synergistic cooperation of multiple proteins (13). Once identified, ubiquitin can be transferred to E2 enzymes via the ubiquitin-activating enzyme, and transferred to substrate proteins by ubiquitin ligases. Subsequently, ERAD substrates are translocated through the retro-translocation channel and released into the cytoplasm for degradation by the 26S proteasome (14). Derlins are a family of multi-transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum that share structural composition and physicochemical features like rhodopsin superfamily, and act in synergy with other proteins to regulate ERAD substrate recognition (15). For example, Derlin-1, a six-transmembrane protein, can form homo- or hetero-oligomers with homologs Derlin-2 and Derlin-3 to facilitate the retro-translocation of full-length defective proteins (16). Additionally, the ERAD-associated rhomboid proteins RHBDL4 cleaves specific membrane substrates into fragments, and subsequently retro-translocated to the cytoplasm for degradation by the proteasome.
To further clarify ERAD’s mechanistic core, the E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes Hrd1, gp78, and SEL1L-Hrd1synergize through modular specialization to mediate substrate recognition, ubiquitination, and retro-translocation: The conserved Hrd1 complex targets ERAD-L (misfolded luminal glycoproteins, via EDEM-dependent demannosylation and OS-9/XTP3B glycan sensing) and ERAD-M (membrane proteins with misfolded transmembrane domains, via Hrd1/Derlin-1 hydrophobic detection), catalyzing K48-linked polyubiquitination and driving retro-translocation via a Derlin-1/Hrd1 membrane-distorting channel coupled to the p97 ATPase (17). The specialized gp78 complex focuses on ERAD-M and ERAD-C, recognizing cytosolic hydrophobic motifs and recruiting endocytic machinery for mislocalized substrates; it generates mixed K48/K63 ubiquitin chain, with activity enhanced by mTORC1-mediated phosphorylation, and relies on a p97-binding VBM motif and helix-unfolding of transmembrane domains for translocation (17, 18). The mammalian SEL1L-Hrd1 hub uses SEL1L’s leucine-rich repeats to stabilize Hrd1 and screen for conformational defects, allosterically regulating Hrd1’s ubiquitination and integrating Derlin-1’s hydrophobic groove, p97 membrane anchoring, and dynamic deubiquitination (e.g., USP19) for fine-tuned retro-translocation (19). Collectively, these complexes couple substrate-specific recognition, ubiquitin chain diversity, and p97-dependent translocation to link ERAD with autophagy and metabolic stress responses, underpinning ER proteostasis and disease pathogenesis. Previous studies have demonstrated that ERAD regulates tumor immunomodulation, therapeutic resistance, and cell survival (20, 21). Targeting essential regulatory proteins of the ERAD system to regulate the survival and apoptosis of tumor cells may be a potentially attractive option for cancer therapy.
Drivers of ER stress in tumor microenvironment
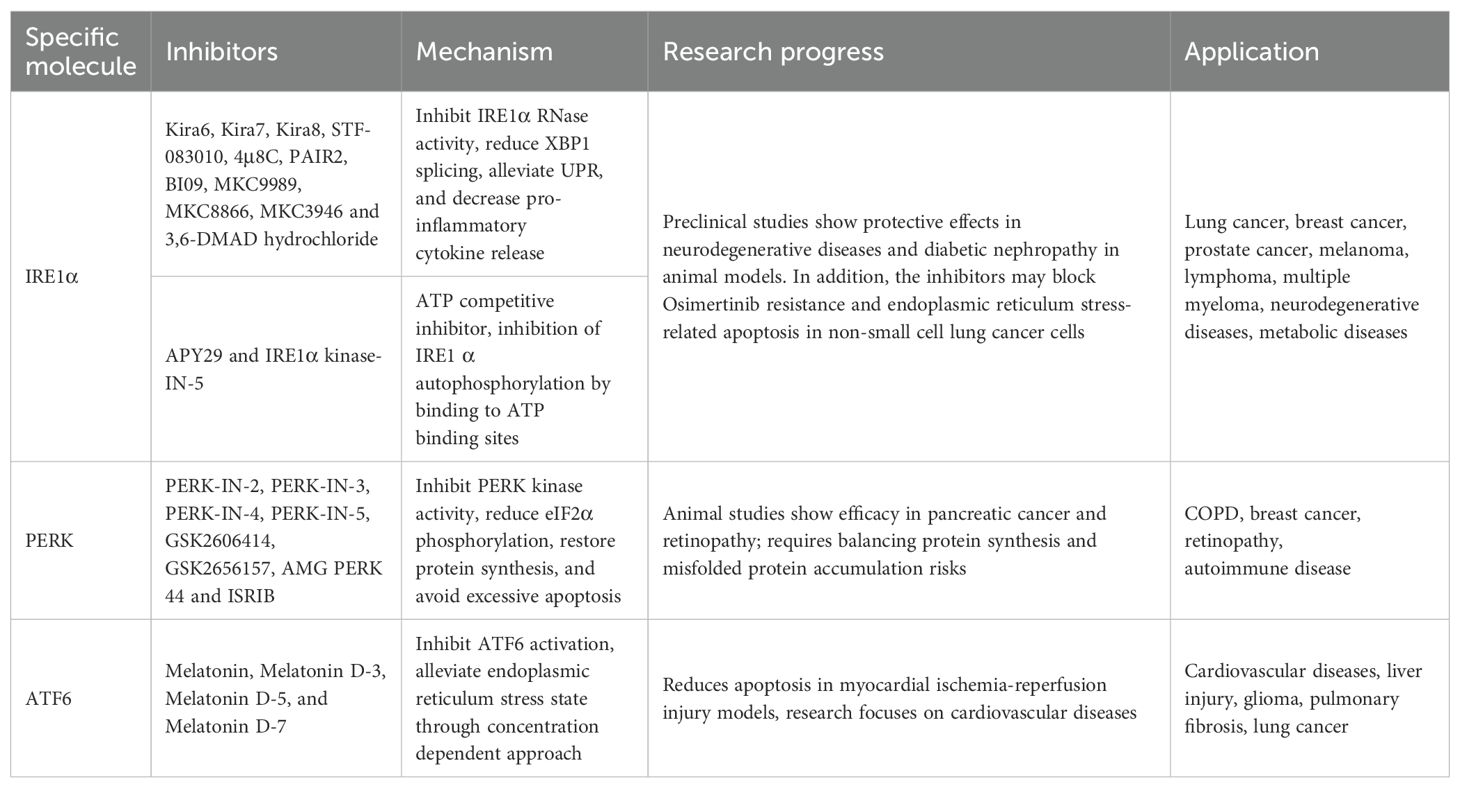
Multiple stressors in the tumor microenvironment, including hypoxia, oxidative stress, nutritional deficiencies, and acidosis, can disrupt the proper folding of intracellular proteins and trigger the accumulation of unfolded and misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. To address the challenge, the adaptive mechanisms, such as UPR and ERAD, are activated to maintain proper protein homeostasis within the endoplasmic reticulum (Figure 1).
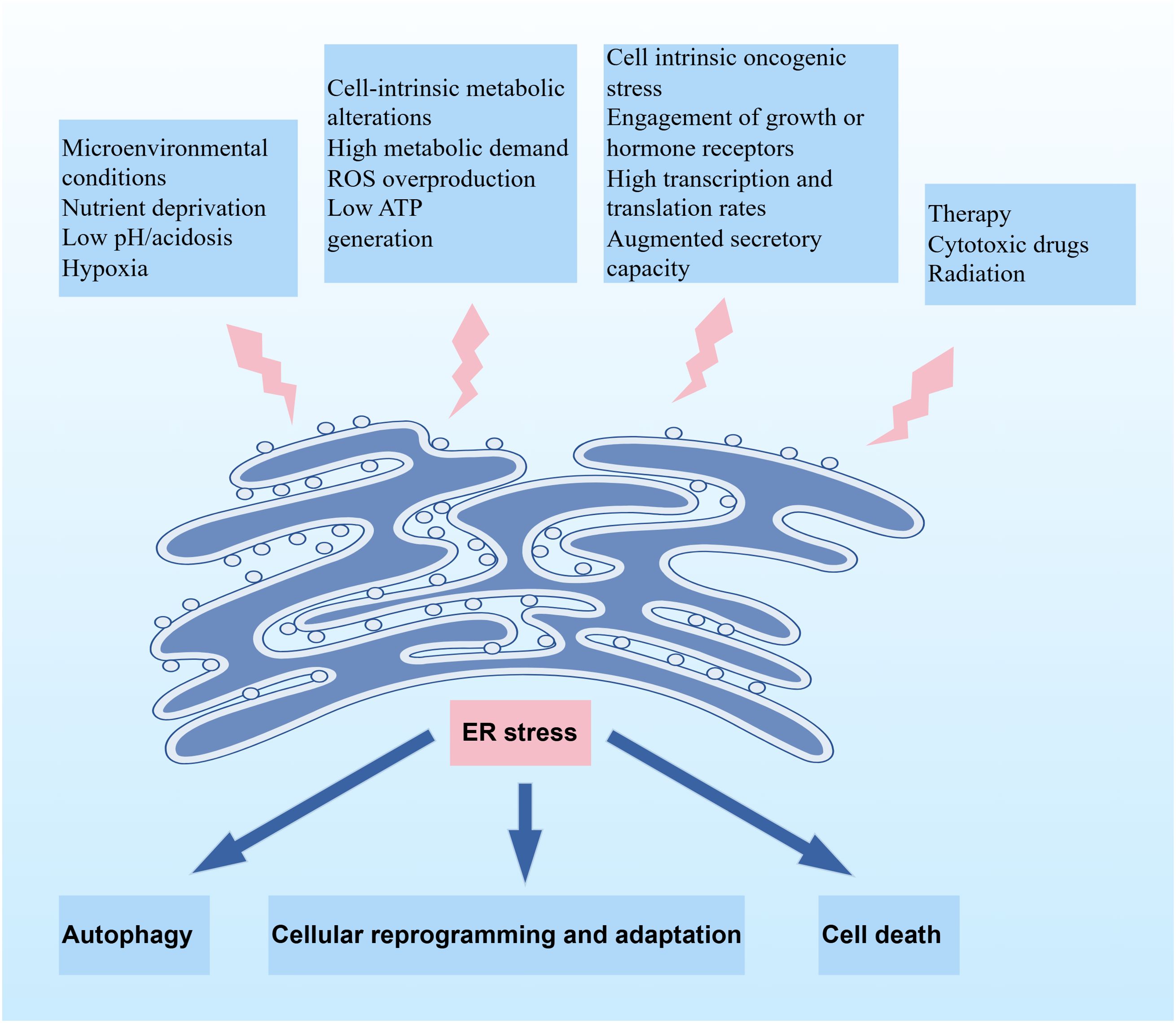
Figure 1. Schematic illustration depicting the induction of ER stress and its downstream cellular fates. Upstream factors triggering ER stress include microenvironmental conditions, cell-intrinsic metabolic alterations, cell-intrinsic oncogenic stress, and therapeutic interventions. ER stress elicits three principal outcomes: autophagy, cellular reprogramming and adaptation, or cell death, depending on the stress intensity and cellular context.
Hypoxia
The imbalance between high oxygen consumption and abnormal vascularization of malignant tumors in the microenvironment results in the generation of low oxygen regions in the center of solid tumors. Hypoxia, an essential characteristic of the microenvironment, disrupts the homeostasis of the endoplasmic reticulum by impairing post-translational modification processes such as glycosylation and disulfide bond formation (22). Disulfide bond formation is dependent on molecular oxygen, which is the ultimate acceptor for electron transfer during the process and is crucial for post-translational protein folding and isomerization (23). ERO-1α, a regulatory oxidoreductase in the endoplasmic reticulum, synergizes with protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and peroxiredoxin 4 (PRX4) to facilitate disulfide bond formation and protein folding (24, 25). The interaction between ERO-1α and PDI constitute the pivotal oxidative folding pathway in the ER. However, limited ATP production under hypoxic conditions may impair the oxygen-dependent protein folding process, leading to the accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen.
Oxidative stress
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are oxygen radicals in living organisms, including oxygen and highly reactive oxygen-containing molecules (e.g., superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxides, and free radicals). ROS are formed continuously in mitochondria by electron leakage from the respiratory chains, and contribute to cellular signaling, regulation of gene expression, and intracellular calcium levels (26, 27). Prior studies have shown that during the UPR, PDI synthesis is markedly increased to promote the formation of disulfide bonds in misfolded proteins, accompanied by the production of electrons (28). Simultaneously, intracellular reduced glutathione (GSH), with oxygen as the final electron acceptor, is oxidized to oxidized glutathione (GSSG) with the production of ROS (29). The redox imbalance caused by GSH depletion in the microenvironment is the key factor triggering ER stress in lung cancer cells. Elevated ROS levels caused by GSH deficiency exacerbate ER stress by activating the iNOS/ATF4/DDIT3 pathway, while promoting mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum interactions to further amplify stress signals (30, 31). Disruption of redox balance between GSH and GSSG may induce ER stress after oxidative stress. In addition, the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum promotes Ca2+ leakage from the ER lumen into the cytosol, which stimulates mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, leading to the overproduction of ROS in mitochondria. Oxidative stress resulting from excessive ROS can disrupt the homeostasis of endoplasmic reticulum and causes the formation of unfolded protein deposits.
Acidosis
Metabolic reprogramming is a hallmark of cancer, wherein tumor cells reprogram nutrient utilization to meet the cellular demands for bioenergetics and biosynthesis (32). Compared with normal cells, tumor cells may utilize the aerobic glycolysis pathway to adapt to low glucose levels, for example, they take up more glucose and convert glucose into pyruvate by aerobic glycolysis which ultimately generates adenosine with the inhibition of downstream glycolysis steps catalyzed by pyruvate kinase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. Such a phenomenon is referred to as “Warburg effect”, which facilitates the survival and growth of tumor cells under hypoxic conditions (33). The increased acid production in tumor microenvironment activates the acid-sensing ion channel 1α (ASIC1α) on the cell surface, leading to the activation of calcium ion channels and subsequent calcium overload. Calcium overload is a crucial initiator of ER stress (34). Calcium accumulation in mitochondria causes uncoupling of electron transport and obstructs ATP generation. Owing to insufficient cellular energy supply, an amount of the unfolded proteins may accumulate in the endoplasmic reticulum and further triggering calcium ion release, exacerbating intracellular calcium overload and inducing ER stress (35).
Glutamine deficiency
Glutamine serves as a vital precursor for the synthesis of proteins, nucleotides, and other macromolecules in mammals. Additionally, it generates nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and GSH, which help maintain redox homeostasis and defend against free radicals (36). There is an extensive consumption of glutamine in the tumor microenvironment. The “Warburg” effect suggests that tumor cells preferentially provide energy by means of glycolysis, even under conditions of sufficient oxygen. This preference for glycolysis affects the mitochondrial energy supply. To maintain mitochondrial energy supply, tumor cells rely on the glutamine transporter to uptake glutamine and replenish the metabolites of TCA, providing the necessary substrates for overactivated glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation reactions (37). Prior studies have shown that tumors consume glutamine at 5–10 times the rate of normal cells, highlighting the dependence on glutamine (38). However, the reprogramming of glutamine metabolism in tumors disrupts the balance of glutathione and NADPH, thereby perturbing intracellular redox homeostasis.
In addition, the deficiencies of glutamine and glucose in the microenvironment can disrupt the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway (HBP) (39). The HBP is an essential branch of intracellular glucose metabolism, integrating glucose metabolism, glutamine breakdown, fatty acid metabolism, and nucleotide metabolism. The pathway utilizes glucose, glutamine, acetyl-CoA, and UTP to produce uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc), which is an essential donor for the biosynthesis of polysaccharides, proteoglycans, glycolipids, and O-GlcNAc modifications (40, 41). The impact of the HBP is closely linked to the content and destination of UDP-GlcNAc. Studies have shown that glycosylation is not only a major post-translational protein modification mechanism, but also critical for maintaining protein structure and activity. O-GlcNAc is the primary source of glycosylation and folding of modified endoplasmic reticulum proteins (42). Glucose and glutamine deficiency in the TME may alter the production of glutathione and promote accumulation of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby increasing ER stress.
ER stress in lung cancer
The diverse drivers of ER stress within the TME do not act in isolation but instead converge on lung cancer cells to elicit context-specific perturbations in protein homeostasis. These TME-derived stressors directly impinge on the ER of lung cancer cells, activating UPR pathways that serve as critical nodes linking extracellular cues to intracellular phenotypic adaptations. Specifically, the cumulative effects of TME-induced ER stress reprogram key cellular processes in lung cancer, including the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to enhance metastatic potential, the regulation of apoptotic and autophagic machinery to balance survival and cell death, and the modulation of drug resistance mechanisms to evade therapeutic pressure (Figure 2).
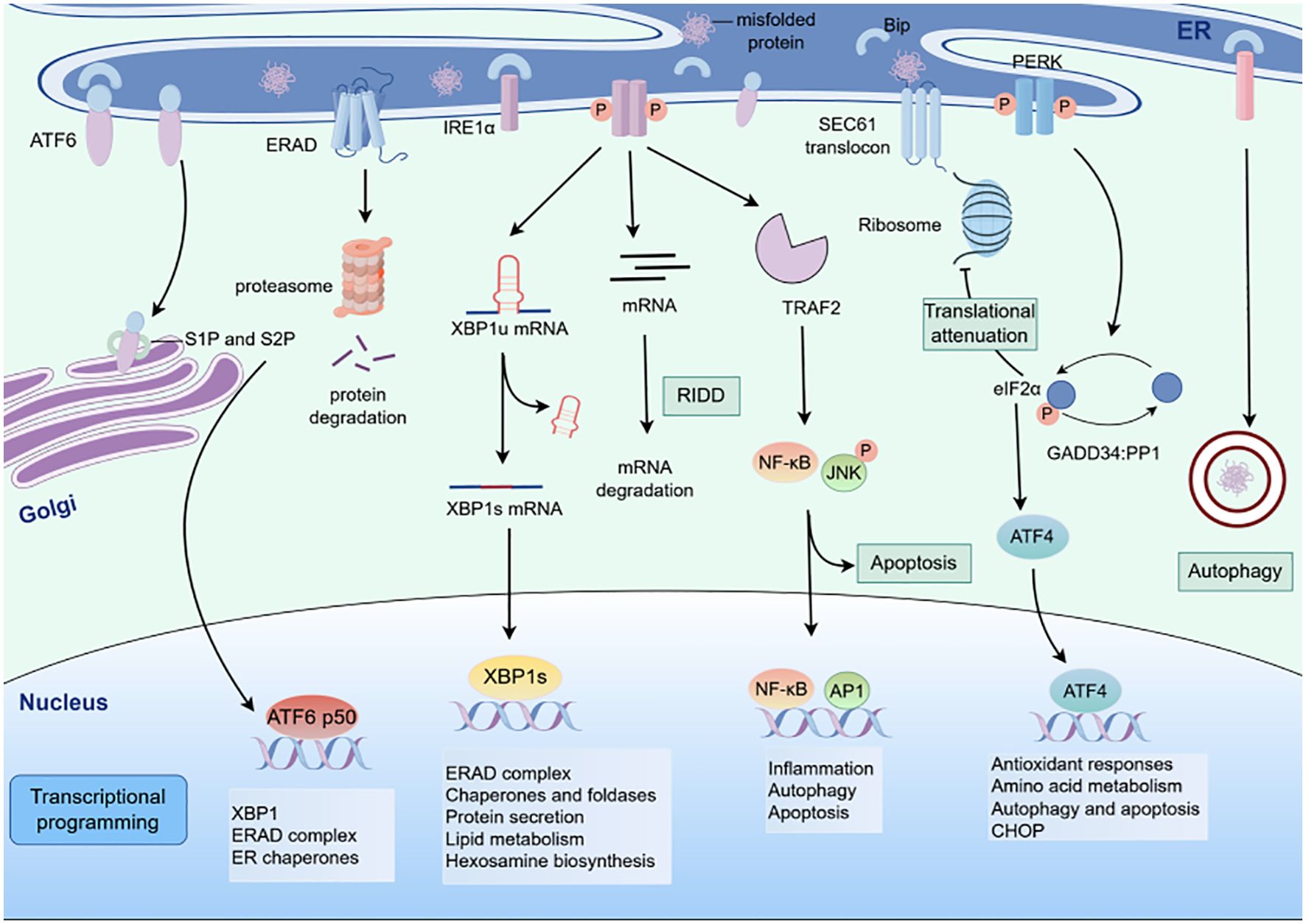
Figure 2. Schematic of ER stress - induced unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling pathways. The three canonical UPR signaling cascades activated by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. When misfolded proteins accumulate in the ER, three ER - resident sensors (IRE1α, PERK, and ATF6) initiate distinct signaling branches.
ER stress and EMT
EMT refers to a process in which epithelial cells lose their polarity, cytoskeletal structure, and intercellular adhesion, acquiring the migratory characteristics of mesenchymal cells (43). Recent studies have shown that ER stress can induce EMT in lung cancer cells. Tunicamycin (TM) and thapsigargin (TG), as ER stress inducers, can disrupt calcium homeostasis, redox balance, and N-glycan synthesis, leading to non-specific activation of the UPR. The activated UPR then induces EMT in a Smad2/3- and Src-dependent manner (44). The ubiquinone protein UBQLN1 plays a critical role in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPP), transporting polyubiquitin proteins to the proteasome and assisting the ERAD process in clearing unfolded proteins (45, 46). Shah et al. reported that the UBQLN1 deficiency in lung cancer cells promotes cytoskeleton formation, increases the expression of stromal phenotype-related proteins such as Vimentin, Snail, and ZEB1, and inhibits the expression of epithelial phenotypic markers such as E-Cadherin and Claudin1, ultimately regulating the EMT in lung cancer cells (47).
Abnormally activated EMT can modulate the sensitivity of tumor cells to ER stress. The expression of EMT-related genes is strongly associated with the extracellular matrix (ECM) and PERK-eIF2α pathway. Lung cancer cells undergoing EMT may remodel the ECM by secreting matrix proteases and scaffold proteins, and activate the PERK-eIF2α axis to enhance their sensitivity to ER stress. Furthermore, maintaining endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis via the PERK-eIF2α signaling pathway is also essential for EMT-mediated cell invasion and metastasis.
ER stress and apoptosis
The ER stress response is a protective cellular mechanism that helps to alleviate the accumulation of unfolded proteins and attenuate endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction. However, persistent and excessive stress can trigger intracellular apoptotic signals and promote apoptosis (48). ER stress induces apoptosis through the activation of multiple pathways, including the c/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), Caspase-12, and JNK pathways. The PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 signaling pathway is the primary pathway that facilitates CHOP protein expression. During ER stress, PERK dissociates from GRP78/BiP and activated through phosphorylation. Activated PERK further promotes ATF4 translation, which cooperates with ATF6 and XBP-1 to enter the nucleus and bind to the CHOP promoter to activate its transcriptional level (49). Overexpressed CHOP induces apoptosis by downregulating the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and upregulating the pro-apoptotic protein Bax, ultimately triggering apoptosis through Caspase-3 activation (50). Gan et al. reported that in tunicamycin-induced ER stress, mutant p53 lung cancer cells undergo apoptosis and autophagy by increasing the expression of CHOP, GRP78, IRE1α, and Caspase-3 (51). Besides, rolapitant may trigger the ER stress-CHOP-DR5 signaling pathway by targeting the OTUD3-GRP78 axis, enhancing TRAIL induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells (52).
The apoptosis of lung cancer cells mediated by JNK is predominantly driven by the IRE1α signaling pathway. Upon ER stress, IRE1α recruits TRAF2 and ASK1 to form the IRE1α-TRAF2-ASK1 complex, which then phosphorylates apoptosis regulatory kinases, resulting in the activation of pro-apoptotic IRE1-JNK signaling axis. JNK phosphorylation can activate the activities of pro-apoptotic proteins BIM and BMF, thereby enhancing their susceptibility to apoptosis (53, 54). Additionally, the IRE1α-TRAF2 complex triggers the dissociation of procaspase-12 from TRAF2 and activates Caspase-12. Caspase-12 further cleaves and activates Caspase-9, which in turn activates Caspase-3 to induce apoptosis (55). Zhang et al. have demonstrated that CSTMP-induced ER stress-related apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma mainly depends on the activation of Caspase-12, Caspase-4, and the IRE1α-TRAF2-ASK1-JNK signaling pathway (56).
ER stress and autophagy
ER stress and autophagy form a complex interplay network. Autophagy alleviates ER stress by clearing misfolded proteins to sustain tumor cell survival, for instance, Sestrin2, a stress-inducible protein, dualistically suppresses ER stress via PERK pathway inhibition while activating AMPK-mediated autophagy, effectively curbing apoptosis in lung cancer cells (57), whereas excessive autophagy may trigger apoptosis or ferroptosis. Lai et al. have demonstrated that the marine compound Crassolide triggers unresolved ER stress, leading to autophagosome overload and subsequent G2/M phase arrest via ATF4-CHOP-dependent ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Mechanistically, Crassolide disrupts ER-mitochondria contact sites, amplifying mitochondrial ROS and lipid peroxidation (58, 59).
The dynamic equilibrium between ER stress and autophagy is orchestrated by the unfolded protein response. PERK and IRE1α branches upregulate autophagy adaptors (LC3-II, Beclin1) through transcriptional activation of ER chaperones (GRP78, CHOP), enabling transient proteotoxic stress resolution (60, 61). However, persistent ER stress overwhelms this adaptive response, shifting autophagy toward apoptosis via calcium-mediated caspase-12 activation (62). Pharmacologically, the ER stress inhibitor 4-PBA attenuates both autophagy flux and apoptosis, rescuing chemotherapy-induced normal tissue damage (58, 60). Furthermore, ER stress-mediated autophagy enhancement serves as a critical mechanism of chemoresistance, and autophagy inhibition (e.g., chloroquine) can reverse drug resistance while amplifying ER stress-dependent apoptosis (63). Collectively, targeting the ERS-autophagy regulatory network provides novel therapeutic avenues for lung cancer treatment.
ER stress and drug resistance
ER stress can directly regulate the drug resistance in lung cancer cells. The molecular chaperone GRP78 mediates cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma endoplasmic reticulum stress tolerant (ERST) through the activation of the Akt cascade (64). GRP78 can also localize on the surface of tumor cells as surface GRP78 (sGRP78), which is preferentially overexpressed in invasive, metastatic, and chemotherapy-resistant cancers (65). sGRP78, as a receptor of multiple signal pathways on the cell surface, transmits signals to endow cancer cells with stem cells properties and epithelial-mesenchymal transition ability, and mediates gefitinib resistance (66, 67). The plasminogen Kringle5 domain may bind to sGRP78 of endothelia and tumor cells, reducing the proliferation and colony formation of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, and alleviating radiotherapy resistance (68).
CHOP is also an indispensable part of the ER stress response, and increased expression of CHOP enhances sensitivity to cisplatin in lung cancer cells (69, 70). Wang et al. have shown that CHOP regulates cisplatin resistance in NSCLC cells by promoting the expression of apoptotic proteins and inhibiting the Bcl-2/JNK signaling pathway (71). Cisplatin has also been demonstrated to induce ER stress in lung cancer cells through the PERK/IRE1 signaling pathway. Inhibition of ER stress with the ER stress inhibitors 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) or tauroursodeoxycholic acid sodium salt (TUDCA) has been found to increase the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to cisplatin (72).
ER stress and immune regulation
The UPR pathways-PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6 may modulate immune cell function within the tumor microenvironment. For instance, PERK activation in cancer cells upregulates PD-L1 expression, impairing cytotoxic T-cell activity and fostering immune evasion (73) Concurrently, ER stress in dendritic cells (DCs) disrupts antigen presentation by downregulating MHC class I molecules, as shown in preclinical lung adenocarcinoma models (74).
Paradoxically, ER stress may also trigger tumor immunogenic cell death (ICD). The ICD process induces tumor cell death under stress, resulting in the exposure of tumor-associated antigens that activate cytotoxic T cells and trigger anti-tumor immune responses (75). Calreticulin (CRT), a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule, is released and translocated from the endoplasmic reticulum to the tumor cell membrane during ICD. CRT may bind to low-density lipoprotein receptor on the surface of DCs, promoting the phagocytosis of tumor cells by DCs (76, 77). A retrospective analysis showed that high expression of CRT on tumor cells was strongly correlated with eIF2α phosphorylation and mature DC infiltration, which had a positive impact on the clinical prognosis of NSCLC patients (78). Additionally, Wang et al. reported that Ir1 anchored to the endoplasmic reticulum activates the ER stress response, contributing to ICD activation via CD8+ T cell-mediated immune responses and Foxp3+ T cell exhaustion, ultimately producing long-term anti-tumor immunity (79).
ER stress further amplifies immunosuppressive signals by recruiting regulatory T cells (Tregs). Notably, ER stress sustains Treg stability through molecules such as transmembrane protein TMED4. TMED4 deficiency destabilizes Foxp3 expression, impairing Treg immunosuppressive capacity and thereby enhancing antitumor immunity (80). Additionally, chronic ER stress fosters a metabolic niche favoring Treg dominance by suppressing mitochondrial respiration and cytotoxicity in CD8+ T cells, indirectly amplifying Treg-mediated immunosuppression (81). Furthermore, ER stress-activated tumor cells secrete immunosuppressive factors like sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), forming an “ER stress-S1P-CAMP axis” that drives Treg expansion and establishes an immunosuppressive TME (82).
In addition, ER stress can promote the polarization of M1 macrophage or inhibit the polarization of M2 macrophage by activating pathways such as PERK and IRE1α, thereby affecting the progression of lung cancer (83). Zhou et al. have also found that Piperlongumine (PL) inhibits the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages into the M2 phenotype by inducing ER stress in lung cancer cells, thereby reducing tumor cell migration. In vitro experiments have confirmed that the ER stress inhibitor 4-PBA can reverse the effects of PL, indicating the critical role of ER stress in macrophage polarization (84).
ER stress signal transduction pathway
The UPR primarily inhibits protein synthesis through ER stress sensors PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6 (Figure 3). In physiological conditions, the ER stress sensors are bound to the molecular chaperone GRP78/Bip. While when cells are exposed to internal and external stressors, misfolded or unfolded proteins accumulate and compete with the stress sensors for binding to GRP78, as a result PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6 dissociate from GRP78 and activate downstream signaling pathways.
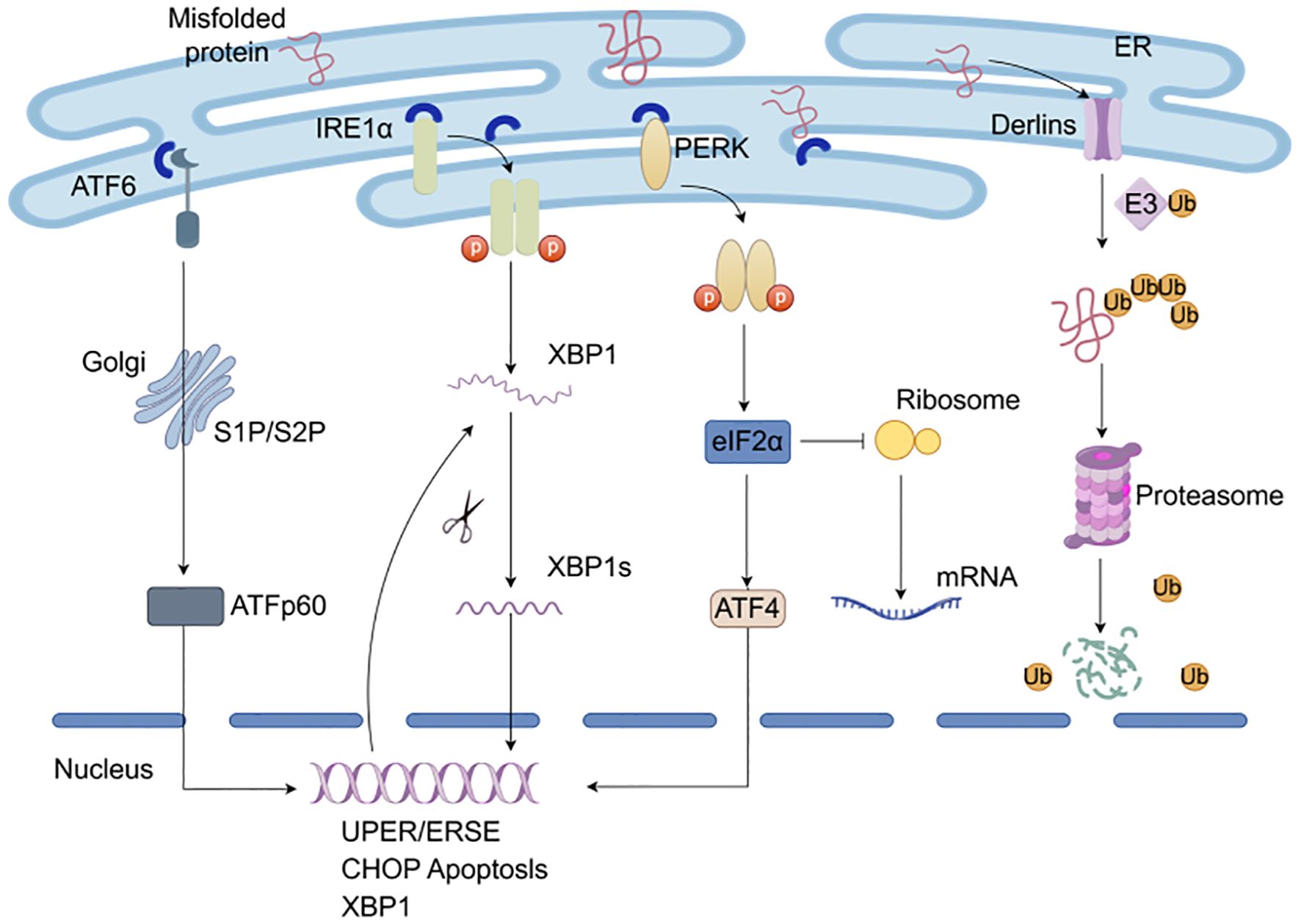
Figure 3. Protein quality control system. The UPR responsible for restoring ER homeostasis by adapting to changes in protein folding within the ER through ER stress sensors PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6. Misfolded or unfolded proteins accumulate and compete with the stress sensors for binding to chaperones and then activate downstream signaling pathways. In ERAD, misfolded substrates are recognized and shuttled from the ER lumen into the cytosol for degradation by the proteasome.
PERK-eIF2α signal pathway
PERK is a type I transmembrane protein located on the endoplasmic reticulum, with its N-terminal stress-sensing domain binding to GRP78 to prevent dimerization. When PERK dissociates from GRP78, its C-terminal serine/threonine protein kinase catalytic domain is activated through autophosphorylation. The activated PERK further phosphorylates downstream eIF2α, and the phosphorylated eIF2α inhibits the assembly of 80S ribosomal subunits and terminates mRNA translation, thereby effectively suppressing the rate of protein synthesis (85). Activated eIF2α may upregulate the translation of ATF4 and the expression of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 34 (GADD34) and CHOP. When excessive ER stress triggers overactivation of the unfolded protein response, it induces sustained phosphorylation-mediated inhibition of eIF2α, under which condition ATF4 exerts pro-apoptotic effects. Although the reduction in protein synthesis under ER stress may grant stressed cells additional time to resolve aberrant protein accumulation, prolonged PERK signaling–by persistently blocking protein translation–becomes detrimental to survival. To counteract this, ATF4 transcriptionally upregulates growth arrest and GADD34, a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), which dephosphorylates p-eIF2α. This restores the eIF2α-GTP-Met-tRNA ternary complex, thereby resuming mRNA translation and preserving cellular homeostasis (86). However, if ER stress remains unresolved, persistent PERK activation ultimately upregulates CHOP, a key mediator of apoptosis that disrupts redox balance and mitochondrial integrity. The highly expressed CHOP downregulates anti-apoptotic proteins (e.g., Bcl2) while upregulating pro-apoptotic members (e.g., Bax, Bim), thereby driving apoptotic cell death, ultimately initiating the process of ER stress-mediated programmed cell death (87).
IRE1α-XBP1 signal pathway
IRE1 is the most highly conserved UPR sensor in eukaryotic cells and possesses both serine/threonine protein kinase activity and endonuclease activity. When cells undergo ER stress, the IRE1α dissociates from GRP78/Bip and undergoes autophosphorylation and dimerization, which activates its endonuclease activity to splice and modify the XBP1 mRNA precursor. The process involved in the removal of introns and permission of the XBP1 translation. Subsequently, spliced XBP1 enters the nucleus to mediate ERAD, protein folding, and endoplasmic reticulum membrane expansion (88). Conversely, unresolved and persistent ER stress leads to sustained, high-level dimerization and autophosphorylation of IRE1α. This enhances the ribonuclease activity of IRE1α, primarily augmenting its splicing efficiency toward XBP1 mRNA. More critically, it concurrently reduces the substrate specificity of IRE1α’s ribonuclease domain, enabling nonspecific degradation of hundreds of mRNAs translated on the ER membrane–a process termed regulated IRE1α-dependent decay (RIDD) (89). While RIDD transiently alleviates ER protein-folding burden by degrading secretory pathway transcripts, the indiscriminate cleavage of ER-associated mRNAs ultimately depletes critical ER-resident enzymes and structural components (e.g., chaperones, translocon subunits), exacerbating ER dysfunction (90). Under severe ER stress, RIDD not only disrupts ER protein processing but also drives ER membrane destabilization and Caspase-12-mediated apoptosis, positioning it as a double-edged sword in cellular stress adaptation.
ATF6 signal pathway
ATF6 is a type II transmembrane transcription factor located on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, consisting of two subunits (ATF6α and ATF6β) and containing a basic leucine zipper domain (91). ATF6 is packaged into transport vesicles and transported from the ER to the Golgi apparatus during ER stress. In the Golgi, ATF6 is cleaved into transcription factor ATF6p50 by proteolytic enzymes S1P and S2P. The cleaved ATF6p50 migrates to the nucleus to activate unfolded protein response elements (UPREs) or ER stress elements (ERSEs) and promote the refolding of ERAD-related proteins (92). Additionally, ATF6 may activate the transcription of CHOP to induce apoptosis and enhance the expression of unspliced XBP1, thereby linking to the IRE1α pathway (93).
Drugs targeting ER stress
The PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6 signaling pathways play a crucial role in the immune regulation, invasion, and migration of tumor cells. To date, Existing studies have identified inhibitors targeting the UPR signaling pathway show the promising anti-tumor potential in lung cancer. Nonetheless, the efficacy and clinical translation of these drugs require verification through further basic and preclinical trials (Table 1).
PERK inhibitor
The PERK signaling pathway is activated in the cytoplasm in response to ER stress. Several highly efficient and selective PERK inhibitors with oral bioavailability have been identified, including PERK-IN-2, PERK-IN-3, PERK-IN-4, and PERK-IN-5 (94). GSK2606414 and GSK2656157 are ATP-competitive PERK inhibitors with high selectivity and cell permeability, which inhibit PERK Thr980 phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner (95, 96). Studies have shown that GSK2606414 can effectively inhibit the ER stress response of lung cancer cells and slow the growth of lung cancer allograft models in mice (97). Moreover, GSK2606414 inhibited nitrofurazone (NFZ)-induced elevation of ROS and Ca2+ levels, blocked the activation of the PERK-ATF4-CHOP signaling pathway, and consequently suppressed NFZ-induced apoptosis in NSCLC cells (98), which suggests that GSK2606414 may influence tumor cell fate through regulation of oxidative stress and calcium homeostasis. Additionally, GSK2606414 demonstrates potential in regulating the inflammatory microenvironment of lung cancer by inhibiting PERK, which concurrently attenuates both NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses and apoptosis (99). Other highly selective PERK inhibitors include AMGPERK44 and ISRIB, which can effectively reverse eIF2α phosphorylation (100). ISRIB increases DUSP6 levels to reduce TG-induced PERK/p-eIF2α activation and inhibit chemotherapy resistance of KRAS-driven lung cancer cells (101). Moreover, ISRIB can regulate lung cancer immunotherapy by inhibiting PD-L1 expression (102, 103). However, there are few reports on the research of AMGPERK44 in lung cancer. Currently, only studies have shown that the combination of AMGPERK44 and the Ref-1 inhibitor can significantly enhance the killing effect on pancreatic cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), especially in the 3D co-culture model (104).
IRE1α-XBP1 inhibitor
IRE1α inhibitors suppress the activation of IRE1α by targeting both its ribonuclease and serine/threonine kinase activities. Several compounds have been identified as IRE1α RNase inhibitors, including Kira6, Kira7, Kira8, STF-083010, 4μ8C, PAIR2, BI09, MKC9989, MKC8866, and MKC3946. These compounds have been extensively investigated for the potential in treating various types of cancer, including lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, melanoma, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma (105). STF-083010 inhibits IRE1 endonuclease activity, blocks osimertinib resistance in NSCLC cells induced by IRE1 signal transduction (106), and reverses ER stress-induced apoptosis through the PERK/IRE1α/ATF6 pathway (107). In addition, ATP-competitive inhibitors APY29 and IRE1α kinase-IN-5 are specific allosteric regulators of IRE1α kinase activity, which inhibits the autophosphorylation of IRE1α by combining its ATP binding sites (108). Sunitinib, a multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and its deuterated derivative, sunitinib-D10, effectively restrain the phosphorylation of IRE1α by competing with ATP binding and subsequently inhibiting its autophosphorylation and RNase activation (109).
3,6-DMAD hydrochloride and toyocamycin have been identified to reverse the ER stress by the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway. 3,6-DMAD hydrochloride, an acridine derivative, represses the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway (110, 111). It inhibits IRE1α oligomerization, RNase activity, and XBP1 splicing in vivo and has been demonstrated to prevent the growth of multiple myeloma (111, 112). However, there have been limited reports on the study of 3,6-DMAD hydrochloride in lung cancer at present. Toyocamycin, an adenosine analogue produced by Streptomyces, is an inhibitor of XBP1 (113). It can block RNA synthesis and ribosome function, inhibit XBP1 mRNA cleavage, and reduce the activity of tumor cells that have been activated by IRE1α (114).
ATF6 pathway inhibitor
There are several inhibitors of the ATF6 pathway, including melatonin and its deuterated derivatives, melatonin D-3, melatonin D-5, and melatonin D-7 (115). Melatonin is a hormone secreted by the pineal gland that regulates the circadian clock and primarily binds to melatonin receptors MT1 and MT2 (116). As a novel selective ATF6 inhibitor, melatonin can reduce the ER stress in a concentration-dependent manner and prevent glioma cell death caused by excessive ER stress activation (117). Studies have also indicated that melatonin alleviates ER stress and bleomycin-induced EMT in lung fibroblasts by inhibiting ATF6 and α-SMA (118). Notably, melatonin has ever demonstrated protective effects against lung cancer in multiple animal models. For example, in a passive smoking-induced lung injury model, it reduces lung tissue damage, apoptosis, and inflammatory responses by decreasing ATF6 activation while downregulating the expression of lung cancer-related genes (such as VEGF, CYP1A1, and CYP1B1) (119); in the Lewis lung cancer (LLC) mouse model, it significantly inhibits tumor growth by suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome and ATF6-related pathways, accompanied by reduced expression of pro-angiogenic and lymphangiogenic markers in tumor tissues (120). Additionally, the combination of melatonin and ortho-topolin riboside (oTR) has exerted synergistic anti-tumor effects by regulating metabolism and transcriptome in NSCLC cells (121). Moreover, melatonin combined with USP7 inhibitor P5091 may enhance anti-cancer activity in p53 deficient NSCLC (122).
Conclusion
This review has systematically summarized that various stress factors in vivo and in vitro, including hypoxia, oxidative stress, acidosis, glutamine and glucose deficiency, and other adverse factors, may activate the ER stress response to varying degrees during the progression of lung cancer. ER stress is extensively involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, drug resistance, apoptosis, as well as immune regulation of lung cancer cells, and modulates multiple signaling pathways of lung cancer. Inhibitors targeting the UPR signaling pathway also participate in the bioactivities of tumors.
Our study reveals a crucial mechanistic foundation for enhancing immunotherapy, revealing how ER stress drives immunosuppression and identifying strategies to exploit ER stress-induced ICD and reverse immune evasion for combination therapies with checkpoint inhibitors. In addition, in-depth exploration highlights the potential for molecularly guided personalized therapy, emphasizing how tumor heterogeneity influences ER stress responses, paving the way for biomarker-stratified treatment using UPR activity markers.
Despite significant advances in understanding ER stress in lung cancer, several limitations and challenges remain. First, current knowledge relies heavily on preclinical models. Translating mechanistic insights on ER stress-induced EMT, apoptosis, autophagy, drug resistance, and immune modulation into effective clinical strategies requires robust validation in human studies. Second, the UPR is a dynamic network with significant crosstalk. The net outcome is highly context-dependent, influenced by stress intensity, duration, cell type, genetic background, and the tumor microenvironment. This complexity makes therapeutic targeting inherently challenging and prone to unintended consequences. Finally, the influence of specific lung cancer driver mutations and histological subtypes on ER stress responses and dependencies is underexplored. Future research needs to define context-specific UPR roles to enable biomarker-driven therapies.
In summary, targeting the regulatory molecules of ER stress and UPR in lung cancer may provide a new direction for tumor therapy. While due to the complex interactions between the structure of proteins involved in ER stress and signaling pathways, the off-target phenomenon of targeted agents is also a new challenge. With the accumulation and integration of multi-omics data, the treatment of lung cancer will be gradually addressed.
Author contributions
DZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LL: Writing – original draft. HJ: Writing – original draft. HM: Writing – original draft. LW: Writing – original draft. WM: Writing – original draft. ZL: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rebecca LS, Kimberly DM, Hannah EF, and Ahmedin J. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. (2022) 72:7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
2. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, et al. NCCN guidelines insights: non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2021. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2021) 19:254–66. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.0013
3. Woodard GA, Jones KD, and Jablons DM. Lung cancer staging and prognosis. Cancer Treat Res. (2016) 170:47–75. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7933
4. Tan AC and Tan DSW. Targeted therapies for lung cancer patients with oncogenic driver molecular alterations. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:611–25. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01626
5. Xiaojing F, Juanjuan C, Xiangjun M, Piyu J, Qiuling Z, Wenwen Z, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, cell death and tumor: Association between endoplasmic reticulum stress and the apoptosis pathway in tumors (Review). Oncol Rep. (2021) 45:801–8. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7933
6. Oakes SA. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in cancer cells. Am J Pathol. (2020) 190:934–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.01.010
7. Dianne SS and Michael D B. The endoplasmic reticulum: structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2015) 73:79–94. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2052-6
8. Oakes SA and Papa FR. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol. (2015) 10:173–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104649
9. Sandes JM and de Figueiredo R. The endoplasmic reticulum of trypanosomatids: An unrevealed road for chemotherapy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:1057774. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1057774
10. da Silva DC, Valentao P, Andrade PB, and Pereira DM. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders: Tools and strategies to understand its complexity. Pharmacol Res. (2020) 155:104702. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104702
11. Ibrahim IM, Abdelmalek DH, and Elfiky AA. GRP78: A cell’s response to stress. Life Sci. (2019) 226:156–63. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.022
12. Li Y, Lu L, Zhang G, Ji G, and Xu H. The role and therapeutic implication of endoplasmic reticulum stress in inflammatory cancer transformation. Am J Cancer Res. (2022) 12:2277–92.
13. Roth J and Zuber C. Quality control of glycoprotein folding and ERAD: the role of N-glycan handling, EDEM1 and OS-9. Histochem Cell Biol. (2017) 147:269–84. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1513-9
14. Needham PG, Guerriero CJ, and Brodsky JL. Chaperoning endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) and protein conformational diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2019) 11. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033928
15. Nejatfard A, Wauer N, Bhaduri S, Conn A, Gourkanti S, Singh N, et al. Derlin rhomboid pseudoproteases employ substrate engagement and lipid distortion to enable the retrotranslocation of ERAD membrane substrates. Cell Rep. (2021) 37:109840. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109840
16. Daisuke M and Kazuhiro N. Pathogenic hijacking of ER-associated degradation: is ERAD flexible? Mol Cell. (2015) 59:335–44. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.010
17. Wu SA, Li ZJ, and Qi L. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein degradation by ER-associated degradation and ER-phagy. Trends Cell Biol. (2025) 35:576–91. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2025.01.002
18. Wiseman RL, Mesgarzadeh JS, and Hendershot LM. Reshaping endoplasmic reticulum quality control through the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:1477–91. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.025
19. Wang HH, Biunno I, Sun S, and Qi L. SEL1L-HRD1-mediated ERAD in mammals. Nat Cell Biol. (2025) 27:1063–73. doi: 10.1038/s41556-025-01690-1
20. Shi Y, Wang X, Meng Y, Ma J, Zhang Q, Shao G, et al. A novel mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress- and c-Myc-degradation-mediated therapeutic benefits of antineurokinin-1 receptor drugs in colorectal cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2021) 8:e2101936. doi: 10.1002/advs.202101936
21. Qin X, Denton WD, Huiting LN, Smith KS, and Feng H. Unraveling the regulatory role of endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation in tumor immunity. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. (2020) 55:322–53. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2020.1784085
22. Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen H, et al. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:157. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1089-9
23. Levitin F, Lee SCS, Hulme S, Rumantir RA, Wong AS, Meester MR, et al. Oxygen-independent disulfide bond formation in VEGF-A and CA9. J Biol Chem. (2021) 296:100505. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100505
24. Alise JP, Aeid I, Maxwell AD, Samia M, Caryn EO, Jakob RW, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum transport of glutathione by sec61 is regulated by Ero1 and Bip. Mol Cell. (2017) 67:962–73. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.08.012
25. Shergalis AG, Hu S, Bankhead A 3rd, and Neamati N. Role of the ERO1-PDI interaction in oxidative protein folding and disease. Pharmacol Ther. (2020) 210:107525. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107525
26. Moloney JN and Cotter TG. ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2018) 80:50–64. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.05.023
27. Cheung EC and Vousden KH. The role of ROS in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. (2022) 22:280–97. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00435-0
28. Alessandra F, Carolina Z, Marta DA, Lucia N, Anna Teresa P, Michele R, et al. Intracellular redox-modulated pathways as targets for effective approaches in the treatment of viral infection. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073603
29. Zeeshan HM, Lee GH, Kim HR, and Chae HJ. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and associated ROS. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17:327. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030327
30. Hu K, Xu Y, Fan J, Liu H, Di C, Xu F, et al. Feasibility exploration of GSH in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy from the aspects of pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and mechanism. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1387409. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1387409
31. Liu X, Hussain R, Mehmood K, Tang Z, Zhang H, and Li Y. Mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum communication-mediated oxidative stress and autophagy. BioMed Res Int. (2022) 2022:6459585. doi: 10.1155/2022/6459585
32. Xia L, Oyang L, Lin J, Tan S, Han Y, Wu N, et al. The cancer metabolic reprogramming and immune response. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01316-8
33. Huang Y. Targeting glycolysis for cancer therapy using drug delivery systems. J Control Release. (2023) 353:650–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.12.003
34. Krebs J, Agellon LB, and Michalak M. Ca(2+) homeostasis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress: An integrated view of calcium signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2015) 460:114–21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.004
35. Boyman L, Karbowski M, and Lederer WJ. Regulation of mitochondrial ATP production: Ca(2+) signaling and quality control. Trends Mol Med. (2020) 26:21–39. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.10.007
36. Ying M, You D, Zhu X, Cai L, Zeng S, and Hu X. Lactate and glutamine support NADPH generation in cancer cells under glucose deprived conditions. Redox Biol. (2021) 46:102065. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102065
37. Cluntun AA, Lukey MJ, Cerione RA, and Locasale JW. Glutamine metabolism in cancer: understanding the heterogeneity. Trends Cancer. (2017) 3:169–80. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.01.005
38. Wang J, Zhang Q, Fu H, Han Y, Li X, Zou Q, et al. ASCT2 regulates fatty acid metabolism to trigger glutamine addiction in basal-like breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173028
39. Lee JB, Pyo KH, and Kim HR. Role and function of O-glcNAcylation in cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215365
40. Lam C, Low JY, Tran PT, and Wang H. The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway and cancer: Current knowledge and future therapeutic strategies. Cancer Lett. (2021) 503:11–8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.01.010
41. Nie H and Yi W. O-GlcNAcylation, a sweet link to the pathology of diseases. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2019) 20:437–48. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900150
42. Yang X and Qian K. Protein O-GlcNAcylation: emerging mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2017) 18:452–65. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.22
43. Pastushenko I and Blanpain C. EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. (2019) 29:212–26. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.12.001
44. Bergmann TJ, Fregno I, Fumagalli F, Rinaldi A, Bertoni F, Boersema PJ, et al. Chemical stresses fail to mimic the unfolded protein response resulting from luminal load with unfolded polypeptides. J Biol Chem. (2018) 293:5600–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001484
45. Kurlawala Z, Shah PP, Shah C, and Beverly LJ. The STI and UBA domains of UBQLN1 are critical determinants of substrate interaction and proteostasis. J Cell Biochem. (2017) 118:2261–70. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25880
46. Liu Y, Lu L, Hettinger CL, Dong G, Zhang D, Rezvani K, et al. Ubiquilin-1 protects cells from oxidative stress and ischemic stroke caused tissue injury in mice. J Neurosci. (2014) 34:2813–21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3541-13.2014
47. Shah PP, Lockwood WW, Saurabh K, Kurlawala Z, Shannon SP, Waigel S, et al. Ubiquilin1 represses migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene. (2015) 34:1709–17. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.97
48. Song S, Tan J, Miao Y, Li M, and Zhang Q. Crosstalk of autophagy and apoptosis: Involvement of the dual role of autophagy under ER stress. J Cell Physiol. (2017) 232:2977–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25785
49. Rozpedek W, Pytel D, Mucha B, Leszczynska H, Diehl JA, and Majsterek I. The role of the PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway in tumor progression during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Curr Mol Med. (2016) 16:533–44. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160523143937
50. Hu H, Tian M, Ding C, and Yu S. The C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) transcription factor functions in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and microbial infection. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:3083. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03083
51. Gan PP, Zhou YY, Zhong MZ, Peng Y, Li L, and Li JH. Endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes autophagy and apoptosis and reduces chemotherapy resistance in mutant p53 lung cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2017) 44:133–51. doi: 10.1159/000484622
52. Du T, Gu Q, Zhang Y, Gan Y, Liang R, Yang W, et al. Rolapitant treats lung cancer by targeting deubiquitinase OTUD3. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22:195. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01519-8
53. Yu Y, Wu D, Li Y, Qiao H, and Shan Z. Ketamine enhances autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats and SV-HUC-1 cells via activating IRE1-TRAF2-ASK1-JNK pathway. Cell Cycle. (2021) 20:1907–22. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1966199
54. Lin T, Lee JE, Kang JW, Shin HY, Lee JB, and Jin DI. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and unfolded protein response (UPR) in mammalian oocyte maturation and preimplantation embryo development. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020409
55. Zhou Y, Jin Y, Wang Y, and Wu R. Hypoxia activates the unfolded protein response signaling network: An adaptive mechanism for endometriosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:945578. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.945578
56. Zhang J, Liang Y, Lin Y, Liu Y, YouYou, and Yin W. IRE1alpha-TRAF2-ASK1 pathway is involved in CSTMP-induced apoptosis and ER stress in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. BioMed Pharmacother. (2016) 82:281–9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.04.050
57. Ala M. Sestrin2 in cancer: a foe or a friend? biomark Res. (2022) 10:29. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00380-6
58. Lai KM, Wang JH, Lin SC, Wen Y, Wu CL, Su JH, et al. Crassolide induces G2/M cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy in human lung cancer cells via ROS-mediated ER stress pathways. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105624
59. Liao H, Liu S, Ma Q, Huang H, Goel A, Torabian P, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced autophagy in cancer and its potential interactions with apoptosis and ferroptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2025) 1872:119869. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119869
60. Zhang J, Tang Y, Xu W, Hu Z, Xu S, and Niu Q. Fluoride-induced cortical toxicity in rats: the role of excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress and its mediated defective autophagy. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2023) 201:3850–60. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03463-5
61. Shao S, Zhuang X, Zhang L, and Qiao T. Antidepressants fluoxetine mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy of non-small cell lung cancer cells through the ATF4-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:904701. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.904701
62. Zhang Z, Shan X, Li S, Chang J, Zhang Z, Dong Y, et al. Retinal light damage: From mechanisms to protective strategies. Surv Ophthalmol. (2024) 69:905–15. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2024.07.004
63. Wang L, Song R, Ma M, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Li J, et al. Inhibition of autophagy can promote the apoptosis of bladder cancer cells induced by SC66 through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Chem Biol Interact. (2023) 384:110725. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110725
64. Lin Y, Wang Z, Liu L, and Chen L. Akt is the downstream target of GRP78 in mediating cisplatin resistance in ER stress-tolerant human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. (2011) 71:291–7. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2010.06.004
65. Lager TW, Conner C, Keating CR, Warshaw JN, and Panopoulos AD. Cell surface GRP78 and Dermcidin cooperate to regulate breast cancer cell migration through Wnt signaling. Oncogene. (2021) 40:4050–9. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01821-6
66. Liao CH, Tzeng YT, Lai GM, Chang CL, Hu MH, Tsai WL, et al. Omega-3 fatty acid-Enriched fish oil and selenium combination modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress response elements and reverses acquired gefitinib resistance in HCC827 lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mar Drugs. (2020) 18. doi: 10.3390/md18080399
67. Xia S, Duan W, Liu W, Zhang X, and Wang Q. GRP78 in lung cancer. J Transl Med. (2021) 19:118. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02786-6
68. Dadey DYA, Kapoor V, Hoye K, Khudanyan A, Collins A, Thotala D, et al. Antibody targeting GRP78 enhances the efficacy of radiation therapy in human glioblastoma and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines and tumor models. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:2556–64. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1935
69. Cao S, Tang J, Huang Y, Li G, Li Z, Cai W, et al. The road of solid tumor survival: from drug-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress to drug resistance. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:620514. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.620514
70. Liu Y, Liang X, Zhang H, Dong J, Zhang Y, Wang J, et al. ER stress-related genes EIF2AK3, HSPA5, and DDIT3 polymorphisms are associated with risk of lung cancer. Front Genet. (2022) 13:938787. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.938787
71. Wang LL, Hu RC, Dai AG, Tan SX, Xu M, Kong CC, et al. CHOP overexpression sensitizes human non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin treatment by Bcl-2/JNK pathway. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13:6279–87.
72. Shi S, Tan P, Yan B, Gao R, Zhao J, Wang J, et al. ER stress and autophagy are involved in the apoptosis induced by cisplatin in human lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. (2016) 35:2606–14. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4680
73. Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2012) 13:89–102. doi: 10.1038/nrm3270
74. Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Silberman PC, Rutkowski MR, Chopra S, Perales-Puchalt A, Song M, et al. ER stress sensor XBP1 controls anti-tumor immunity by disrupting dendritic cell homeostasis. Cell. (2015) 161:1527–38. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.025
75. Ahmed A and Tait SWG. Targeting immunogenic cell death in cancer. Mol Oncol. (2020) 14:2994–3006. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12851
76. Rapoport BL and Anderson R. Realizing the clinical potential of immunogenic cell death in cancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040959
77. Zhou J, Wang G, Chen Y, Wang H, Hua Y, and Cai Z. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy: Present and emerging inducers. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:4854–65. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14356
78. Fucikova J, Becht E, Iribarren K, Goc J, Remark R, Damotte D, et al. Calreticulin expression in human non-Small cell lung cancers correlates with increased accumulation of antitumor immune cells and favorable prognosis. Cancer Res. (2016) 76:1746–56. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1142
79. Wang L, Guan R, Xie L, Liao X, Xiong K, Rees TW, et al. An ER-targeting iridium(III) complex that induces immunogenic cell death in non-small-cell lung cancer. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. (2021) 60:4657–65. doi: 10.1002/anie.202013987
80. Jiang Z, Wang H, Wang X, Duo H, Tao Y, Li J, et al. TMED4 facilitates regulatory T cell suppressive function via ROS homeostasis in tumor and autoimmune mouse models. J Clin Invest. (2024) 135. doi: 10.1172/JCI179874
81. Hwang SM, Awasthi D, Jeong J, Sandoval TA, Chae CS, Ramos Y, et al. Transgelin 2 guards T cell lipid metabolism and antitumour function. Nature. (2024) 635:1010–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08071-y
82. Park K, Shin KO, Kim YI, Nielsen-Scott AL, Mainzer C, Celli A, et al. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate-Cathelicidin axis plays a pivotal role in the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol. (2025) 145:854–63 e856. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2024.08.008
83. Peng C, Wang J, Wang S, Zhao Y, Wang H, Wang Y, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: triggers microenvironmental regulation and drives tumor evolution. Cancer Med. (2025) 14:e70684. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70684
84. Zhou Y, Teng W, Wu J, Luo Y, Wang Y, and Li Y. Piperlongumine inhibits lung cancer growth by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress leading to suppression of M2 macrophage polarization. Biol Proced Online. (2025) 27:18. doi: 10.1186/s12575-025-00279-0
85. Kim CY and Kim KH. Selenate prevents adipogenesis through induction of selenoprotein S and attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Molecules. (2018) 23. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112882
86. Cantoni O, Zito E, Guidarelli A, Fiorani M, and Ghezzi P. Mitochondrial ROS, ER stress, and Nrf2 crosstalk in the regulation of mitochondrial apoptosis induced by arsenite. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11. doi: 10.3390/antiox11051034
87. Li D, Wang WJ, Wang YZ, Wang YB, and Li YL. Lobaplatin promotes (125)I-induced apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating PERK-eIF2alpha-ATF4-CHOP pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:744. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1918-1
88. Shaheen A. Effect of the unfolded protein response on ER protein export: a potential new mechanism to relieve ER stress. Cell Stress Chaperones. (2018) 23:797–806. doi: 10.1007/s12192-018-0905-2
89. Hollien J, Lin JH, Li H, Stevens N, Walter P, and Weissman JS. Regulated Ire1-dependent decay of messenger RNAs in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. (2009) 186:323–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200903014
90. Upton JP, Wang L, Han D, Wang ES, Huskey NE, Lim L, et al. IRE1alpha cleaves select microRNAs during ER stress to derepress translation of proapoptotic Caspase-2. Science. (2012) 338:818–22. doi: 10.1126/science.1226191
91. Ge L, Wang T, Shi D, Geng Y, Fan H, Zhang R, et al. ATF6alpha contributes to rheumatoid arthritis by inducing inflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis resistance. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:965708. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.965708
92. Tam AB, Roberts LS, Chandra V, Rivera IG, Nomura DK, Forbes DJ, et al. The UPR activator ATF6 responds to proteotoxic and lipotoxic stress by distinct mechanisms. Dev Cell. (2018) 46:327–43.e327. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.04.023
93. Delmotte P and Sieck GC. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial function in airway smooth muscle. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2019) 7:374. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00374
94. Calvo V, Surguladze D, Li AH, Surman MD, Malibhatla S, Bandaru M, et al. Discovery of 2-amino-3-amido-5-aryl-pyridines as highly potent, orally bioavailable, and efficacious PERK kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. (2021) 43:128058. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128058
95. Zhang M, Gallego-Delgado J, Fernandez-Arias C, Waters NC, Rodriguez A, Tsuji M, et al. Inhibiting the plasmodium eIF2alpha kinase PK4 prevents artemisinin-induced latency. Cell Host Microbe. (2017) 22:766–76.e764. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.11.005
96. Zhao Q, Che X, Zhang H, Fan P, Tan G, Liu L, et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links endoplasmic reticulum stress to inflammatory brain injury and apoptosis after subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neuroinflamm. (2017) 14:104. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0878-6
97. Van Krieken R, Tsai YL, Carlos AJ, Ha DP, and Lee AS. ER residential chaperone GRP78 unconventionally relocalizes to the cell surface via endosomal transport. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2021) 78:5179–95. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03849-z
98. Li D, Liu L, Li F, Ma C, and Ge K. Nifuroxazide induces the apoptosis of human non−small cell lung cancer cells through the endoplasmic reticulum stress PERK signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. (2023) 25:248. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13834
99. Keramidas P, Papachristou E, Papi RM, Mantsou A, and Choli-Papadopoulou T. Inhibition of PERK kinase, an orchestrator of the unfolded protein response (UPR), significantly reduces apoptosis and inflammation of lung epithelial cells triggered by SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a protein. Biomedicines. (2023) 11. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061585
100. McGrath EP, Logue SE, Mnich K, Deegan S, Jager R, Gorman AM, et al. The unfolded protein response in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2018) 10. doi: 10.3390/cancers10100344
101. Ghaddar N, Wang S, Woodvine B, Krishnamoorthy J, van Hoef V, Darini C, et al. The integrated stress response is tumorigenic and constitutes a therapeutic liability in KRAS-driven lung cancer. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:4651. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24661-0
102. Suresh S, Chen B, Zhu J, Golden RJ, Lu C, Evers BM, et al. eIF5B drives integrated stress response-dependent translation of PD-L1 in lung cancer. Nat Cancer. (2020) 1:533–45. doi: 10.1038/s43018-020-0056-0
103. Suresh S and O’Donnell KA. Translational control of immune evasion in cancer. Trends Cancer. (2021) 7:580–2. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2021.04.002
104. Mijit M, Boner M, Cordova RA, Gampala S, Kpenu E, Klunk AJ, et al. Activation of the integrated stress response (ISR) pathways in response to Ref-1 inhibition in human pancreatic cancer and its tumor microenvironment. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1146115. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1146115
105. Kitakaze K, Taniuchi S, Kawano E, Hamada Y, Miyake M, Oyadomari M, et al. Cell-based HTS identifies a chemical chaperone for preventing ER protein aggregation and proteotoxicity. Elife. (2019) 8. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43302
106. Tang ZH, Su MX, Guo X, Jiang XM, Jia L, Chen X, et al. Increased expression of IRE1alpha associates with the resistant mechanism of osimertinib (AZD9291)-resistant non-small cell lung cancer HCC827/OSIR cells. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. (2018) 18:550–5. doi: 10.2174/1871520617666170719155517
107. Liu Y, Jiang ZY, Zhou YL, Qiu HH, Wang G, Luo Y, et al. beta-elemene regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress to induce the apoptosis of NSCLC cells through PERK/IRE1alpha/ATF6 pathway. BioMed Pharmacother. (2017) 93:490–7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.073
108. Feldman HC, Ghosh R, Auyeung VC, Mueller JL, Kim JH, Potter ZE, et al. ATP-competitive partial antagonists of the IRE1alpha RNase segregate outputs of the UPR. Nat Chem Biol. (2021) 17:1148–56. doi: 10.1038/s41589-021-00852-0
109. Ali MM, Bagratuni T, Davenport EL, Nowak PR, Silva-Santisteban MC, Hardcastle A, et al. Structure of the Ire1 autophosphorylation complex and implications for the unfolded protein response. EMBO J. (2011) 30:894–905. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.18
110. Siwecka N, Rozpedek-Kaminska W, Wawrzynkiewicz A, Pytel D, Diehl JA, and Majsterek I. The structure, activation and signaling of IRE1 and its role in determining cell fate. Biomedicines. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020156
111. Shao A, Xu Q, Spalek WT, Cain CF, Kang CW, Tang CA, et al. Development of tumor-targeting IRE-1 inhibitors for B-cell cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. (2020) 19:2432–44. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0127
112. Jiang D, Tam AB, Alagappan M, Hay MP, Gupta A, Kozak MM, et al. Acridine derivatives as inhibitors of the IRE1alpha-XBP1 pathway are cytotoxic to human multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther. (2016) 15:2055–65. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-1023
113. Park SG, Kim SH, Kim KY, Yu SN, Choi HD, Kim YW, et al. Toyocamycin induces apoptosis via the crosstalk between reactive oxygen species and p38/ERK MAPKs signaling pathway in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Pharmacol Rep. (2017) 69:90–6. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2016.10.014
114. Pandey S, Djibo R, Darracq A, Calendo G, Zhang H, Henry RA, et al. Selective CDK9 inhibition by natural compound toyocamycin in cancer cells. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143340
115. Qin DZ, Cai H, He C, Yang DH, Sun J, He WL, et al. Melatonin relieves heat-induced spermatocyte apoptosis in mouse testes by inhibition of ATF6 and PERK signaling pathways. Zool Res. (2021) 42:514–24. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2021.041
116. Bhattacharya S, Patel KK, Dehari D, Agrawal AK, and Singh S. Melatonin and its ubiquitous anticancer effects. Mol Cell Biochem. (2019) 462:133–55. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03617-5
117. Xu W, Lu X, Zheng J, Li T, Gao L, Lenahan C, et al. Melatonin protects against neuronal apoptosis via suppression of the ATF6/CHOP pathway in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Neurosci. (2018) 12:638. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00638
118. San-Miguel B, Crespo I, Sanchez DI, Gonzalez-Fernandez B, Ortiz de Urbina JJ, Tunon MJ, et al. Melatonin inhibits autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in mice with carbon tetrachloride-induced fibrosis. J Pineal Res. (2015) 59:151–62. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12247
119. Xiong J, Xie L, Huang Y, Zhu J, Hong Z, Qian H, et al. Therapeutic effects of melatonin on the lungs of rats exposed to passive smoking. Respir Res. (2024) 25:411. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03042-3
120. Zhao Z, Ma D, Qin Y, Xu Y, Li S, and Liu H. Melatonin downregulates angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by regulating tumor-associated macrophages via NLRP3 inflammasomes in lung adenocarcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). (2024) 16:12225–38. doi: 10.18632/aging.206057
121. Lee JW, Lee H, Noh SW, and Choi HK. Co-treatment with melatonin and ortho-topolin riboside reduces cell viability by altering metabolic profiles in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact. (2024) 391:110900. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.110900
Keywords: lung cancer, tumor microenvironment, endoplasmic reticulum stress, unfolded protein response, targeted therapy
Citation: Zhang D, Lin L, Jin H, Mao H, Wang L, Ma W and Lao Z (2025) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 15:1550075. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1550075
Received: 22 December 2024; Accepted: 25 August 2025;
Published: 05 September 2025.
Edited by:
S. Paul Gao, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Elia Ranzato, Università del Piemonte Orientale, ItalyDegan Lu, Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Lin, Jin, Mao, Wang, Ma and Lao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenghong Lao, bGFvemgxMjBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Donghuan Zhang
Donghuan Zhang Lanlan Lin2†
Lanlan Lin2†