- 1Department of Oncology, Yantaishan Hospital, Yantai, Shandong, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Technologies for Chinese Medicine Pharmaceutical Process Control and Intelligent Manufacture, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common dose-limiting side effect in patients undergoing chemotherapy. Many commonly used chemotherapeutic agents simultaneously induce neurotoxicity and modulate the immune system. Emerging evidence highlights a critical role of the innate immune system in the development of various neuropathic pain conditions. As a natural immune defense mechanism formed during phylogenetic evolution, innate immunity elicits a robust response during CIPN pathogenesis. This review summarizes the roles of the innate immune system—including the skin barrier, innate immune cells, and innate immune molecules—in the context of CIPN.
1 Introduction
Advances in cancer therapeutics have markedly improved patient survival rates; however, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) remains a prevalent, dose-limiting toxicity that significantly compromises quality of life and therapeutic continuity. Clinical epidemiological data indicate that the incidence of CIPN ranges between 50% and 90% (1–5). A comprehensive meta-analysis of 77 studies conducted across 28 countries, encompassing 10,962 patients, estimated a pooled prevalence of chronic painful CIPN at 41.22%, with substantial heterogeneity observed among studies. Subgroup analyses revealed higher prevalence in patients receiving platinum compounds or taxanes, and in those diagnosed with lung cancer (6).
Despite its high burden, current evidence-based preventive or disease-modifying interventions are lacking. According to the latest clinical practice guidelines issued by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), duloxetine is the only pharmacological agent recommended for the management of painful CIPN (7). However, randomized controlled trials have failed to demonstrate prophylactic efficacy. A recent prevention study in colorectal cancer patients showed that duloxetine (30 mg or 60 mg daily) did not reduce the incidence of acute oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy vs. placebo, with no significant difference in patient-reported symptoms. Moreover, the duloxetine arm exhibited poorer adherence, with fatigue and nausea as common adverse events (8). Consequently, duloxetine is currently endorsed solely for symptomatic pain relief and not for CIPN prevention.
Multiple pharmacological approaches have been investigated—including anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin), tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline), vitamin B supplementation, calcium–magnesium infusions, and diverse chemoprotective agents—yet none have demonstrated definitive neuroprotective effects in clinical trials (7). As a result, most guideline-based strategies for CIPN management are extrapolated from treatments for other neuropathic pain conditions, such as opioids, antiepileptics, and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) (9). However, their efficacy in alleviating CIPN-specific symptoms remains limited. In current clinical practice, modification of chemotherapy dosage, or even discontinuation, remains the primary recourse for severe or progressive disease cases.
Traditionally, pathogenesis research has primarily focused on the direct neurotoxic effects of chemotherapeutic agents, including mitochondrial dysfunction, ion channel abnormalities, and oxidative stress pathways (10). However, recent years have witnessed a critical paradigm shift in research approaches, with investigators actively pursuing novel interventions that can effectively preserve peripheral nerve function without compromising the antitumor activity of chemotherapeutic drugs. Preserving the integrity of neural function not only significantly enhances patients' quality of life but may also optimize overall oncological treatment outcomes by improving therapeutic tolerance. This research transition has positioned non-neuronal components within the nervous system—particularly neuroimmune interaction mechanisms—as pivotal breakthrough points for elucidating CIPN pathogenesis and developing targeted therapies (11–13).
In the complex pathogenic network of CIPN, aberrant activation of the innate immune system has been demonstrated to play a central regulatory role. As an evolutionarily conserved defense mechanism, innate immunity precisely identifies chemotherapy-induced damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), thereby triggering cascading immune responses. Clinical studies have demonstrated significantly elevated levels of innate immune-derived pro-inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and IL-1β in the peripheral blood of CIPN patients. Animal models further reveal that various innate immune cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, and mast cells, undergo specific recruitment to injured nerve tissues following chemotherapeutic exposure. Upon PRR-mediated recognition of DAMPs in the microenvironment, these immunocytes become activated and subsequently release abundant pro-inflammatory mediators (e.g., cytokines, chemokines, and reactive oxygen species), establishing a persistent neuroinflammatory milieu (4). Of particular significance, this immune-neural crosstalk not only induces neuroinflammatory states but also contributes to peripheral sensitization through modulation of nociceptor electrophysiological properties (14). The prolonged persistence of such pathological alterations may represent the mechanistic basis underlying the intractable chronic pain associated with CIPN.
To advance understanding of these mechanisms and their therapeutic implications, this review aims to comprehensively elucidate the contributions of the innate immune system to CIPN development, focusing on its multifaceted components as potential therapeutic targets. Specifically, we seek to: (1) delineate the skin's role as a dynamic neuro-immunological interface, where barrier disruption and keratinocyte-mediated DAMP signaling initiate local inflammatory cascades; (2) examine the recruitment and activation of key innate immune cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells, and microglia, which orchestrate neuroinflammatory milieus through phagocytosis, mediator release, and crosstalk with neural elements; (3) analyze the impact of cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and chemokines (e.g., CX3CL1/CX3CR1, CCL2/CCR2) in sustaining immune cell trafficking, nociceptor modulation, and chronic pain states; and (4) integrate these insights to highlight translational opportunities, such as targeted inhibition of PRR pathways or mediator antagonists, to restore neuro-immune homeostasis without compromising anticancer efficacy.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy
We performed a comprehensive narrative literature search to identify preclinical and clinical studies reporting pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), focusing on innate immune system involvement. Searches were conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase up to September 2025.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
Study type—Preclinical (in vivo rodent models) or clinical studies. Chemotherapeutic agents—Paclitaxel, oxaliplatin, cisplatin, vincristine.
Focus—Mechanistic investigations into innate immune cell involvement (macrophages, mast cells, microglia, neutrophils), chemokine signaling, skin barrier alterations, and interventions for CIPN.
Outcome—Includes histological evidence, molecular signaling pathways, neurobehavioral changes, or therapeutic interventions.
2.3 Presentation of results
Data were systematically extracted into a structured table recording: (1) Authors, year, reference number; (2) Study design and model; (3) Chemotherapy agent(s); (4) Immune cell type(s) or molecular pathways involved; (5) Intervention and outcomes; (6) Findings were organized by immune cell category (macrophages, mast cells, microglia, neutrophils) and innate immune mediators, with separate sections for skin barrier involvement and clinical evidence; (7) Key mechanistic and therapeutic findings are presented in summary tables and integrated into the discussion.
3 The role of skin
The skin, as the first line of defense between the body and external environment, has evolved beyond a simple physical barrier to become a dynamic neuro-immunological regulatory hub. Contemporary research demonstrates that this organ integrates mechanical protection, microbial defense, and neurosensory functions through a sophisticated cellular network comprising both immune and non-immune cells, serving as a central mediator in maintaining tissue homeostasis and responding to external insults (15, 16). This multifaceted protective system relies not only on physical barrier structures and antimicrobial molecules but also involves intricate immune surveillance and neural signaling mechanisms.
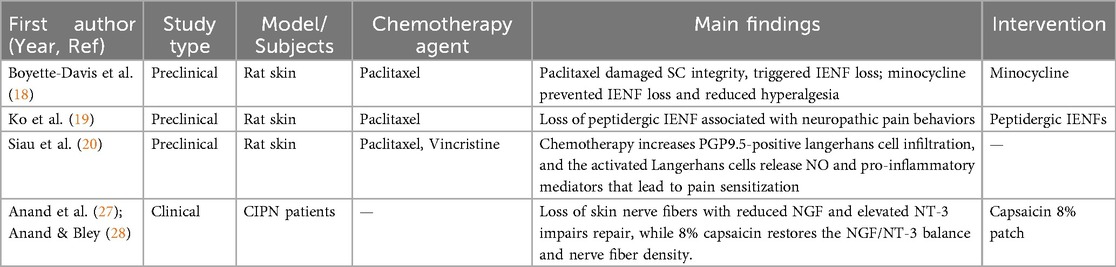
In the pathogenesis of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), skin-mediated neuro-immune interactions have recently emerged as critical contributors (17). Recent studies have revealed three pathological mechanisms by which the skin contributes to CIPN: Current evidence identifies three key pathological mechanisms through which the skin exacerbates CIPN: First, chemotherapeutic agents compromise stratum corneum integrity, triggering intraepidermal nerve fiber (IENF) degeneration and sensory nerve terminal exposure a finding corroborated by clinical biopsy studies (18–20). Damaged keratinocytes recognize damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) via Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling, subsequently upregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines [e.g., interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)] (21–23), while concurrently dysregulating antimicrobial peptide secretion (including β-defensins), thereby amplifying localized neuroinflammation (24–26). Second, experimental models reveal that paclitaxel and vincristine significantly enhance epidermal infiltration of PGP9.5-positive Langerhans cells, which directly promote pain sensitization through nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory mediator release (20). Third, imbalances in cutaneous neurotrophic factors—particularly reduced nerve growth factor (NGF) expression alongside elevated neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) levels—disrupt nerve repair mechanisms. Clinical evidence suggests that the high-concentration capsaicin exerts a biphasic therapeutic effect in CIPN. In the initial phase, high-concentration capsaicin induces a functional “defunctionalization” of nociceptive C fibers by disorganizing their cytoskeletal structure, leading to transient degeneration of intraepidermal nerve endings and temporary reduction in pain signaling. This early deactivation step is followed by a regenerative phase, in which a secondary increase in intraepidermal and subepidermal nerve fiber density reflects re-growth and functional recovery of the cutaneous nerve network. Mechanistically, capsaicin patch treatment has been shown to restore the disrupted NGF/NT-3 ratio to physiological levels, thereby supporting nerve repair processes. Post-treatment skin biopsies consistently demonstrate significant increases in both intraepidermal and subepidermal nerve fiber density (27, 28), indicating that targeted cutaneous interventions can not only promote structural regeneration but also effectively rebalance neuro-immune homeostasis. These findings underscore the therapeutic potential of skin barrier-protective strategies—including reinforcement of stratum corneum integrity and modulation of local immune responses—as innovative avenues for CIPN management. The key pathological mechanisms of skin involvement in CIPN and corresponding therapeutic strategies are systematically summarized in Table 1.
4 Innate immune cells
4.1 Macrophages
Macrophages originate from myeloid progenitor cells in the bone marrow and constitute essential components of the mononuclear phagocyte system. As principal effector cells of innate immunity, these versatile immune cells execute three cardinal functions: (i) pathogen and cellular debris clearance through phagocytosis; (ii) antigen processing and presentation to initiate adaptive immune responses; and (iii) cytokine secretion to modulate inflammatory processes (29).
Emerging evidence demonstrates that macrophages within the peripheral nervous system, particularly those localized in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG), exert pivotal regulatory roles in neuropathic pain pathogenesis (30, 31). Experimental investigations reveal that following peripheral nerve injury, the ipsilateral DRG demonstrates a marked increase in macrophage infiltration, primarily from circulating monocyte-derived populations. Yu et al. demonstrated that axotomy-induced neuropathic pain in both male and female murine models promotes DRG macrophage expansion, which is indispensable for neuropathic pain initiation and maintenance (32). Notably, this dynamic macrophage response within the DRG microenvironment also represents a key pathogenic mechanism in CIPN.
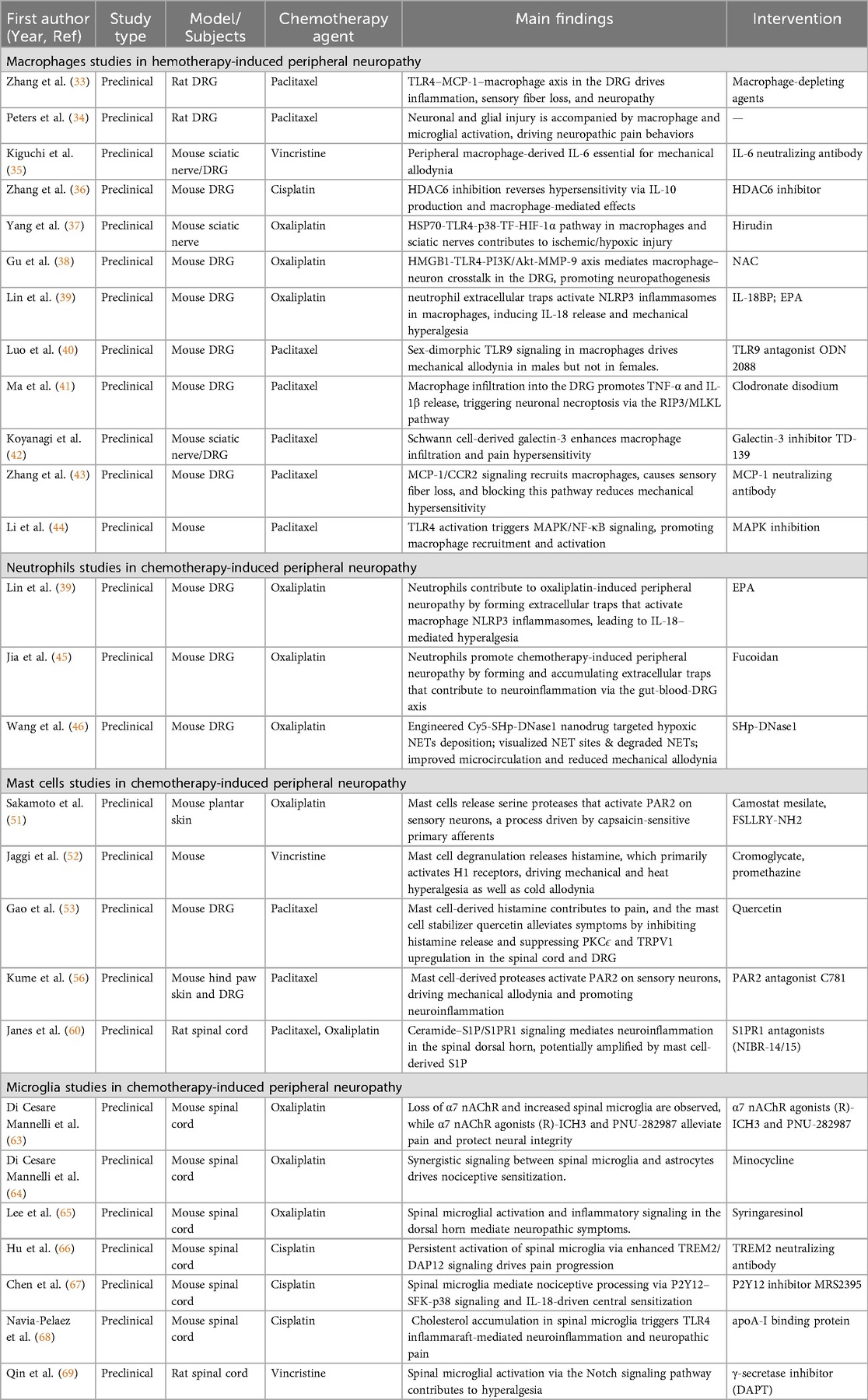
Current research establishes that paclitaxel-induced CIPN correlates with significant macrophage infiltration in the DRG. Longitudinal immunofluorescence analyses demonstrate that CD68+ macrophage accumulation in L4-L5 DRG segments begins to increase three days post-chemotherapy, reaches a zenith at day 14, and sustains elevated levels through day 21 (33). These activated macrophages exhibit characteristic morphological transformations, including cytoplasmic vacuolation, mitochondrial swelling, and increased cell volume, while preferentially localizing around neuronal somata (34). Importantly, this DRG macrophage infiltration pattern extends beyond paclitaxel, having been documented in CIPN models induced by platinum-based agents (cisplatin, oxaliplatin) and vinca alkaloids (vincristine) (35–38).
The pathogenic contribution of macrophages to CIPN involves complex molecular regulatory networks. Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathways represent critical mediators in this process. Paclitaxel administration triggers robust TLR4 signaling activation, which in turn propagates the p38/NF-κB inflammatory cascade in a TLR4-dependent manner, directly contributing to pain sensitization. In oxaliplatin-induced CIPN models, neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) within the DRG microenvironment engage TLR7 and TLR9 receptors on macrophages to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, culminating in IL-18 release and nociceptor hyperexcitability (39). Intriguingly, TLR9 signaling exhibits sexually dimorphic characteristics in paclitaxel-induced CIPN: it demonstrates pronounced disease-promoting effects in male mice while showing attenuated regulatory activity in females (40).
Beyond canonical TLR pathways, macrophages orchestrate CIPN pathogenesis through multifaceted molecular mechanisms. High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), a prototypical damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule, demonstrates dual-pathogenic effects in CIPN: it accelerates disease progression via ROS/p38 MAPK/NF-κB/HAT signaling activation, while simultaneously forming the HMGB1-TLR4-PI3K/Akt-MMP-9 signaling axis to synergistically amplify neuroinflammatory responses (38). Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β secreted by activated macrophages directly induce sensory neuron damage and pain sensitization through RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic pathways (41). Additionally, recent studies have shown that Schwann cell-derived galectin-3 modulates macrophage infiltration patterns, contributing to CIPN development (42).
Based on these mechanistic insights, multiple experiments have confirmed that targeted interventions—such as blocking TLR4 signaling with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) antagonists, inhibiting macrophage recruitment with MCP-1 neutralizing antibodies, or depleting macrophages using macrophage-depleting agents—can effectively suppress abnormal macrophage activation and pathological infiltration, thereby significantly alleviating chemotherapy-induced mechanical allodynia (33, 43, 44). These findings provide a crucial theoretical foundation for developing novel therapeutic strategies for CIPN.
4.2 Neutrophils
In recent years, the mechanisms by which neutrophils contribute to chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy have gradually garnered attention. Chemotherapeutic agents such as oxaliplatin can induce intestinal barrier damage, leading to the leakage of LPS and HMGB1 into the bloodstream, which subsequently activates neutrophils infiltrating the DRG to form NETs (45). These NETs exacerbate nerve damage through a dual mechanism: on the one hand, the tissue factor (TF) captured by NETs triggers microthrombus formation, resulting in microcirculatory disturbances and a hypoxic microenvironment in the DRG and peripheral nerves. This process aggravates axonal injury and mechanical hypersensitivity via the HIF-1α/MMP-9 signaling axis (46); on the other hand, NETs activate the TLR7/TLR9 receptors on macrophages, triggering NLRP3 inflammasome activation and promoting IL-18 release. This, in turn, induces abnormal phosphorylation of the GluN2B subunit at the Tyr1472 site in spinal dorsal horn neurons, ultimately leading to central sensitization. Clinical data further reveal elevated plasma levels of NETs markers (such as citrullinated histone H3) in CIPN patients, which positively correlate with pain intensity (39).
Targeting this mechanism, enzyme-based therapies for NETs degradation represent another promising intervention strategy. Wang et al. innovatively developed an ischemia-homing peptide (SHp, CLEVSRKNC)-modified DNase1 nanodrug (Cy5-SHp-DNase1) that specifically accumulates in hypoxic areas with NETs deposition, enabling highly efficient targeted degradation. Compared to conventional DNase1, this engineered enzyme exhibits dual functions: serving as an in vivo hypoxia probe to visualize NETs deposition sites while precisely degrading NETs to improve microcirculatory dysfunction. In animal studies, SHp-DNase1 significantly alleviated oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia, demonstrating superior efficacy to either standard DNase1 or the anticoagulant hirudin. This patented formulation shows strong clinical translation potential and may overcome the limited effectiveness of traditional anticoagulants against NETs-associated thrombosis (46).
4.3 Mast cells
Mast cells are tissue-resident immune cells widely distributed in the skin, around blood vessels of visceral organs, and throughout the peripheral nervous system. Located at the interface between the body and external environment, they serve as rapid responders to environmental threats (47). Although these cells are best known for their roles in allergic reactions and anti-parasitic immunity, recent studies have revealed their crucial function in neuro-immune interactions. Mast cells can sense tissue damage and inflammatory signals, bidirectionally modulating neural activity and immune responses through the release of mediators such as histamine, proteases, and cytokines (48, 49). Benefiting from their close anatomical and functional connections with neurons, mast cells have emerged as important bridges linking the nervous and immune systems.
In the pathogenesis of CIPN, neuroinflammation has been confirmed as a critical factor in disease development. As a key regulator of neuroinflammation, mast cells participate in the pathological process of CIPN through multiple pathways: On one hand, chemotherapeutic agents can directly activate perineural mast cells, triggering their degranulation and releasing large amounts of inflammatory mediators. These mediators can not only directly alter the excitability of sensory neurons but also recruit immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils to form an inflammatory cascade (14); On the other hand, neurotrophic factors (e.g., NGF) secreted by mast cells play a dual role in neuroprotection and nerve injury, and disruption of this dynamic balance ultimately leads to neurological dysfunction and hyperalgesia (50).
Emerging research has further elucidated the molecular mechanisms of mast cells in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. In oxaliplatin-treated models, significant mast cell degranulation and increased mast cell numbers were observed in the plantar epidermis of mice. Genetic studies revealed that congenital mast cell-deficient mice showed remarkable resistance to oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia (51). Similarly, vincristine was found to trigger mast cell degranulation, particularly promoting histamine release, which subsequently induced thermal hyperalgesia and cold allodynia through the H1/H2 receptor pathway (52). Paclitaxel, through a unique “histamine-H1 receptor-PKC-TRPV1” signaling axis, enhanced thermal sensitivity of TRPV1 channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons (53).
Beyond the histamine system, studies have also uncovered the mechanisms of novel mast cell-derived algogenic mediators. Oxaliplatin was found to significantly elevate skin serine protease activity, an effect markedly attenuated in mast cell-deficient mice. Crucially, the analgesic effects of serine protease inhibitors confirmed the pivotal role of these mediators in mechanical allodynia (51). Notably, the mast cell-specific protease tryptase can induce hyperalgesia by activating protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) receptors through a neurokinin-1 receptor-dependent pathway, while simultaneously promoting neuronal release of pain-related neuropeptides such as g calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P (SP) (54, 55). In paclitaxel-treated models, peripheral tissue tryptase activity showed significant positive correlation with thermal hyperalgesia severity. Both PAR-2 antagonists and inhibitors targeting its downstream signaling pathways (including PLCβ, PKCε and PKA) demonstrated promising analgesic effects (56).
The sphingolipid metabolite sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is another critical mediator in mast cell-mediated pain regulation (57, 58). Its synthesis is tightly controlled by FcεRI signaling, and it acts in an autocrine manner via S1P1/S1P2 receptors to modulate mast cell degranulation, chemotaxis, and neuropathic pain (59). Preclinical studies show that S1P1 receptor blockade alleviates cancer-induced bone pain and chemotherapy-induced neuropathy. Notably, the S1P1 modulator fingolimod exhibits neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects in both paclitaxel and oxaliplatin models, offering a promising therapeutic strategy for CIPN (60).
4.4 Microglia
Studies have demonstrated that microglial activation is a key pathological feature in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain, making it a novel potential therapeutic target for alleviating chemotherapy-related neuropathic pain (61–63). In animal models of oxaliplatin-induced CIPN, significant activation of spinal microglia has been observed. Notably, intrathecal administration of the microglial inhibitor minocycline effectively ameliorates oxaliplatin-induced CIPN symptoms. Temporal analysis reveals that microglial activation peaks on day 7 post-treatment but gradually returns to baseline levels by days 14 and 21 (64). Further research indicates that oxaliplatin treatment induces microglial activation in the mouse spinal cord, accompanied by upregulated expression of various inflammatory mediators, including pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α), inflammation-related enzymes (COX-2 and iNOS), and signaling molecules (p-ERK and p-NF-κB), a phenomenon validated in the BV-2 microglial cell line (65).
In cisplatin-induced neuropathic pain models, studies have uncovered a more complex regulatory network. Cisplatin activates the spinal TREM2/DAP12 signaling pathway, triggering microglial inflammatory responses and significantly elevating the expression of inflammatory markers such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, iNOS, and CD68. This persistent neuroinflammation can lead to intraepidermal nerve fiber (IENF) loss and may induce structural and functional changes in DRG neurons, ultimately mediating the development of pain symptoms. Importantly, blocking microglial activation or inhibiting TREM2 signaling effectively prevents IENF loss and significantly alleviates cisplatin-induced mechanical allodynia (66). Additionally, the P2Y12-SFK-p38 signaling pathway promotes spinal central sensitization through an IL-18-dependent mechanism, providing a theoretical basis for developing analgesic strategies targeting the P2Y12 receptor (67). Recent studies have also revealed that abnormal cholesterol accumulation in microglia is a critical mechanism underlying neuropathic pain in cisplatin-induced CIPN models. Targeted modulation of cholesterol metabolism pathways not only restores the normal state of inflammatory lipid rafts but also reprograms microglial phenotypes, thereby producing long-lasting analgesic effects (68). In vincristine-induced CIPN mouse models, intrathecal administration of the γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT alleviates neuropathic pain symptoms by inhibiting the NOTCH signaling pathway, which subsequently downregulates the activity of the microglial CX3CR1/p38/MAPK pathway (69). The key pathological mechanisms of innate immune cells involvement in CIPN and corresponding therapeutic strategies are systematically summarized in Table 2.
5 Cytokines
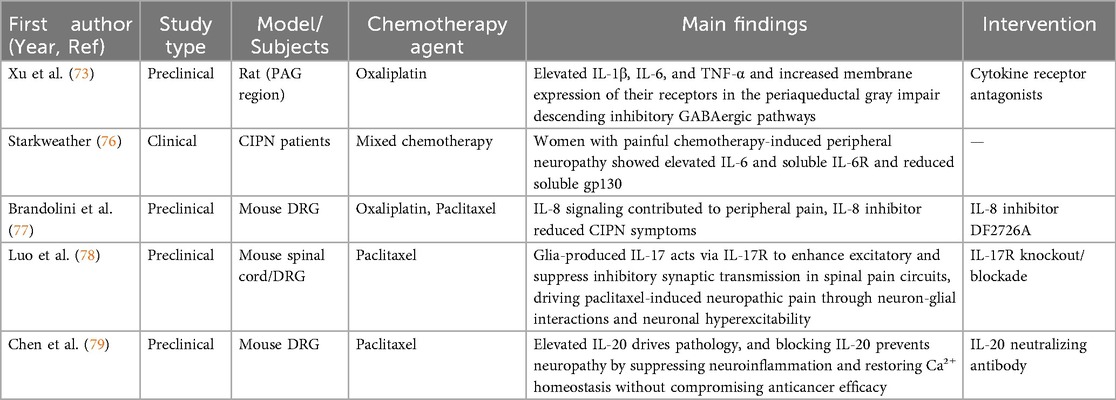
Chemotherapy-induced inflammatory responses are considered potential drivers of nociceptive processes in CIPN. Pro-inflammatory and chemotactic factors released after chemotherapy are recognized as key mechanisms regulating neuro-immune interactions, with downstream cytokine effects serving as critical triggers for neuroinflammation in the sensory nervous system (70–72). Chemotherapy leads to significant cytokine release, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. In oxaliplatin-induced rat CIPN models, elevated levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the periaqueductal gray (PAG) correlate with reduced γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Further experiments demonstrate that blocking pro-inflammatory cytokine receptors in the PAG of oxaliplatin-treated rats largely restores GABA concentrations and alleviates mechanical allodynia and cold hyperalgesia (73). Pro-inflammatory cytokines not only cause axonal damage and promote neuron-immune responses, increasing the release of bradykinin, serotonin, and histamine, but also exert direct toxic effects on neural cells by mediating the activity of neurons and glia through specific receptors (74, 75).
In breast cancer patients, serum levels of IL-6 and soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R) are significantly higher in those with CIPN compared to those without symptoms, suggesting that persistent CIPN and reduced quality of life may be linked to increased levels of the inflammatory mediator IL-6 and its soluble receptor (76). Studies have shown that the IL-8 signaling pathway contributes to peripheral pain development in oxaliplatin- and paclitaxel-induced CIPN models, and the IL-8 inhibitor DF2726A effectively alleviates CIPN symptoms (77).
Compared to inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, the role of IL-17 in pain remains less understood. Recently, IL-17 was found to regulate inflammatory responses associated with nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. In neuropathic pain models, IL-17 levels are upregulated in injured nerves, and IL-17 receptors (IL-17R) are detected in most neurons in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) sections and cultured DRG neurons. IL-17-deficient mice exhibit reduced mechanical pain sensitivity compared to wild-type mice after methadone injection or partial sciatic nerve ligation. Emerging research reports that astrocyte-derived IL-17 suppresses inhibitory synaptic transmission in spinal pain circuits and drives chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. IL-17 not only enhances excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in somatostatin-expressing neurons in mouse spinal cord slices but also inhibits inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs). Selective knockout of IL-17R in spinal neurons reduces paclitaxel-induced hypersensitivity. In DRGs, the expression of IL-17R in nociceptive neurons is both necessary and sufficient for paclitaxel-induced neuronal hyperexcitability (78).
In mouse models, serum and DRG levels of interleukin-20 (IL-20) fluctuate with paclitaxel treatment. Blocking IL-20 with neutralizing antibodies or genetic deletion of its receptor prevents CIPN, mitigates peripheral nerve damage, and suppresses inflammatory responses, including macrophage infiltration and cytokine release. Mechanistically, targeting IL-20 improves paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting neuroinflammation and restoring calcium homeostasis (79). The key pathological mechanisms of cytokines involvement in CIPN and corresponding therapeutic strategies are systematically summarized in Table 3.
6 Chemokines
Chemokines are regulators of peripheral immune cell trafficking and are also expressed on neurons and glial cells in the central nervous system. As potential mediators and contributors to CIPN pain signaling, chemokines and their receptors—including CX3CL1/CX3CR1, CCL2/CCR2, CXCL1/CXCR2, CXCL12/CXCR4, and CCL3/CCR5—exhibit altered expression under CIPN pathological conditions. Chemokine receptor antagonists have been shown to alleviate neuropathic pain behaviors, suggesting that innate immune activation may represent a broad mechanistic basis for CIPN (80).
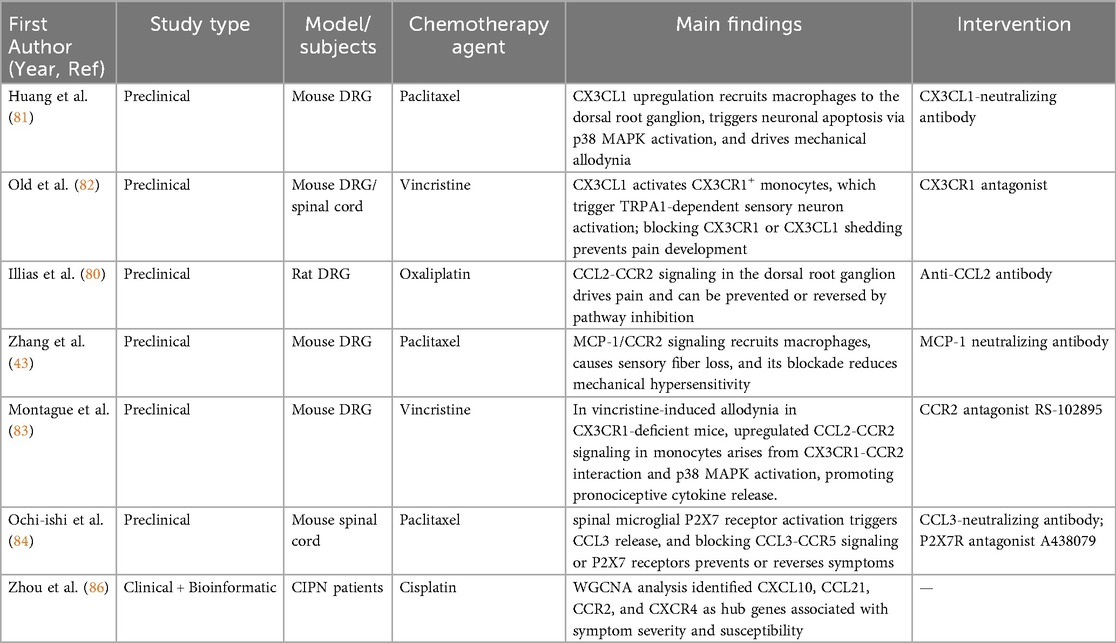
Paclitaxel has been found to significantly upregulate the chemokine CX3CL1 in A-fiber sensory neurons, thereby inducing macrophage infiltration into DRG. Intrathecal or systemic administration of CX3CL1-neutralizing antibodies blocks paclitaxel-induced macrophage recruitment, DRG neuronal apoptosis, and abnormal pain. Mechanistically, CX3CL1 inhibition reduces p38 MAPK activation in macrophages, thereby suppressing neuronal apoptosis and mechanical pain development. These findings provide novel evidence that CX3CL1-recruited macrophages contribute to paclitaxel-induced DRG neuronal damage and painful peripheral neuropathy (81). In vincristine-induced CIPN models, upregulated endothelial adhesion promotes infiltration of circulating CX3CR1+ monocytes into the sciatic nerve. At the endothelial-nerve interface, CX3CL1 activates CX3CR1+ monocytes to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), which subsequently activate TRPA1 receptors in sensory neurons, eliciting pain responses. Notably, CX3CR1-deficient mice exhibit delayed pain onset after vincristine treatment. Targeting CX3CR1 with antagonists or inhibiting CX3CL1 proteolytic shedding (via ADAM10/17 or cathepsin S) may serve as a therapeutic strategy for chemotherapy-induced peripheral pain (82).
The CCL2 (MCP-1)/CCR2 axis plays a critical role in paclitaxel-induced CIPN. Studies report increased expression of MCP-1 and its receptor CCR2 in DRGs of paclitaxel-treated animals. MCP-1 elevates intracellular calcium in large- and medium-sized DRG neurons, while anti-MCP-1 antibodies or CCR2 antisense oligonucleotides attenuate mechanical allodynia and prevent intraepidermal nerve fiber (IENF) loss. The MCP-1/CCR2 pathway is thus a promising therapeutic target (43). In oxaliplatin-induced CIPN, CCL2/CCR2 expression peaks at day 4 post-treatment and normalizes by day 15. Intrathecal anti-CCL2 antibody therapy prevents mechanical hypersensitivity and reverses established pain, highlighting the translational potential of this pathway (80).
In vincristine models, CX3CR1+ monocytes in the sciatic nerve mediate mechanical allodynia. While Cx3cr1−/− mice eventually develop pain due to compensatory CCL2/CCR2 upregulation, CCR2 antagonists effectively mitigate pain, revealing crosstalk between these chemokine pathways (83).
Paclitaxel increases spinal dorsal horn (SDH) microglia and upregulates CCL3/CCR5. Intrathecal CCL3-neutralizing antibodies prevent and reverse mechanical pain. P2X7 receptors (P2X7Rs) on microglia facilitate CCL3 release, and the P2X7R antagonist A438079 shows both prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy (84).
Vincristine and paclitaxel upregulate CXCL12 in DRGs. This chemokine, released from neuronal central terminals, attracts T cells and monocytes via CXCR4 activation, increasing intracellular calcium and promoting immune cell chemotaxis (85).
Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) identified CXCL10, CCL21, CCR2, CXCR4, TLR4, NPY1R, and GALR2 as hub genes linked to CIPN status, severity, and susceptibility. Chemokine regulators (e.g., CXCL10, CCL21, CCR2, CXCR4) are associated with peripheral immune cell trafficking in CIPN (86). The key pathological mechanisms of chemokines involvement in CIPN and corresponding therapeutic strategies are systematically summarized in Table 4.
7 Outlook and perspectives
Advances in anti-tumor therapies have markedly improved patient survival, yet chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy remains a major complication that compromises cancer patients' quality of life. Beyond causing neuropathic pain, paresthesia, and other debilitating symptoms, CIPN often necessitates chemotherapy dose modification or discontinuation, thereby undermining oncological treatment efficacy. This condition imposes a multidimensional burden—physical, psychological, and social—on affected individuals. However, current preventive and therapeutic strategies for CIPN remain largely inadequate.
Recent studies highlight the central role of aberrant innate immune activation in CIPN pathogenesis. This review has addressed two key dimensions: (1) mechanistic pathways by which innate immunity drives CIPN progression; and (2) the potential clinical utility of therapeutic approaches targeting innate immune components. These mechanistic insights provide a foundation for developing new interventions that preserve anti-tumor potency while alleviating symptom burden. Nonetheless, several critical challenges hinder progress. First, distinct chemotherapeutic agents (e.g., oxaliplatin, cisplatin, vincristine) trigger unique patterns of immune activation and cellular recruitment, complicating the development of broadly applicable therapies. Second, most preclinical studies employ tumor-free animal models, which fail to account for the modulatory effects of the tumor microenvironment on neuroimmune dynamics.
In addition, emerging evidence implicates adaptive immune responses in CIPN recovery. For example, CD8+ T cells within the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) are essential for resolution of paclitaxel-induced mechanical allodynia; T cell-deficient mice exhibit prolonged symptom duration compared to wild-type counterparts (87). In cisplatin-induced CIPN models, T cells mediate the protective effects of selective histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) inhibitors against mechanical hyperalgesia and mitochondrial dysfunction in DRG neurons (88). Furthermore, paclitaxel-exposed T cells stimulate macrophages to secrete interleukin-10 (IL-10) via interleukin-13 (IL-13), and macrophage-derived IL-10 engages IL-10 receptors (IL-10R) on DRGs to counteract paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy (89). Based on current evidence, future research priorities should include: (1) Developing precision interventions tailored to the distinct immune signatures of specific chemotherapeutic agents; (2) Validating therapeutic targets in tumor-bearing animal models to enhance clinical relevance; (3) Elucidating synergistic mechanisms between innate and adaptive immune systems; (4) Exploring novel therapies targeting key effector cells, such as DRG monocytes/macrophages and spinal microglia. Advancing these research directions will support the design of innovative strategies that effectively control CIPN while safeguarding anti-tumor efficacy—ultimately achieving the dual objectives of improving cancer treatment outcomes and enhancing patient quality of life.
Author contributions
ND: Writing – original draft. TL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Mattar M, Umutoni F, Hassan MA, Wamburu MW, Turner R, Patton JS, et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a recent update on pathophysiology and treatment. Life (Basel). (2024) 14(8):991. doi: 10.3390/life14080991
2. Bae EH, Greenwald MK, Schwartz AG. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: mechanisms and therapeutic avenues. Neurotherapeutics. (2021) 18(4):2384–96. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01142-2
3. Desforges AD, Hebert CM, Spence AL, Reid B, Dhaibar HA, Cruz-Topete D, et al. Treatment and diagnosis of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: an update. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 147:112671. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112671
4. Molinares D, Kurtevski S, Zhu Y. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: diagnosis, agents, general clinical presentation, and treatments. Curr Oncol Rep. (2023) 25(11):1227–35. doi: 10.1007/s11912-023-01449-7
5. Lee KT, Bulls HW, Hoogland AI, James BW, Colon-Echevarria CB, Jim HSL. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): a narrative review and proposed theoretical model. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16(14):2571. doi: 10.3390/cancers16142571
6. D’Souza RS, Saini C, Hussain N, Javed S, Prokop L, Her YF. Global estimates of prevalence of chronic painful neuropathy among patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: systematic review and meta-analysis of data from 28 countries, 2000–24. Reg Anesth Pain Med. (2025):rapm-2024-106229. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2024-106229
7. Loprinzi CL, Lacchetti C, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G, Chauhan C, Hertz DL, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: ASCO guideline update. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38(28):3325–48. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01399
8. Smith EML. Alliance A221805: duloxetine to prevent oxaliplatin-induced chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN)—a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II study. J Clin Oncol. (2025) 43(16_suppl):12010. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2025.43.16_suppl.12010
9. Jesus Palma AC, Antunes Júnior CR, Barreto ESR, Alencar VB, Souza A, Mathias CMC, et al. Pharmacological treatment of chemotherapy-induced neuropathy: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Pain Manag Nurs. (2025) 26(3):249–63. doi: 10.1016/j.pmn.2025.01.007
10. Yang Y, Zhao B, Gao X, Sun J, Ye J, Li J, et al. Targeting strategies for oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: clinical syndrome, molecular basis, and drug development. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 40(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02141-z
11. Ji RR, Chamessian A, Zhang YQ. Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science. (2016) 354(6312):572–7. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf8924
12. Lees JG, Makker PG, Tonkin RS, Abdulla M, Park SB, Goldstein D, et al. Immune-mediated processes implicated in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Eur J Cancer. (2017) 73:22–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.12.006
13. Uhelski ML, Li Y, Fonseca MM, Romero-Snadoval EA, Dougherty PM. Role of innate immunity in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Neurosci Lett. (2021) 755:135941. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135941
14. Ollodart J, Steele LR, Romero-Sandoval EA, Strowd RE, Shiozawa Y. Contributions of neuroimmune interactions to chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy development and its prevention/therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. (2024) 222:116070. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116070
15. Bos JD, Kapsenberg ML. The skin immune system its cellular constituents and their interactions. Immunol Today. (1986) 7(7–8):235–40. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(86)90111-8
16. Handler A, Ginty DD. The mechanosensory neurons of touch and their mechanisms of activation. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2021) 22(9):521–37. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00489-x
17. Lowy DB, Makker PGS, Moalem-Taylor G. Cutaneous neuroimmune interactions in peripheral neuropathic pain states. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:660203. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.660203
18. Boyette-Davis J, Xin W, Zhang H, Dougherty PM. Intraepidermal nerve fiber loss corresponds to the development of taxol-induced hyperalgesia and can be prevented by treatment with minocycline. Pain. (2011) 152(2):308–13. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.10.030
19. Ko MH, Hu ME, Hsieh YL, Lan CT, Tseng TJ. Peptidergic intraepidermal nerve fibers in the skin contribute to the neuropathic pain in paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. Neuropeptides. (2014) 48(3):109–17. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2014.02.001
20. Siau C, Xiao W, Bennett GJ. Paclitaxel- and vincristine-evoked painful peripheral neuropathies: loss of epidermal innervation and activation of Langerhans cells. Exp Neurol. (2006) 201(2):507–14. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.05.007
21. Amarante-Mendes GP, Adjemian S, Branco LM, Zanetti LC, Weinlich R, Bortoluci KR. Pattern recognition receptors and the host cell death molecular machinery. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2379. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02379
22. Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11(5):373–84. doi: 10.1038/ni.1863
23. Satoh T, Akira S. Toll-like receptor signaling and its inducible proteins. Microbiol Spectr. (2016) 4(6):10–128. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MCHD-0040-2016
24. Bayer A, Lammel J, Tohidnezhad M, Lippross S, Behrendt P, Klüter T, et al. The antimicrobial peptide human beta-defensin-3 is induced by platelet-released growth factors in primary keratinocytes. Mediators Inflamm. (2017) 2017::6157491. doi: 10.1155/2017/6157491
25. Li N, Yamasaki K, Saito R, Fukushi-Takahashi S, Shimada-Omori R, Asano M, et al. Alarmin function of cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL37 through IL-36γ induction in human epidermal keratinocytes. J Immunol. (2014) 193(10):5140–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302574
26. Tjabringa GS, Rabe KF, Hiemstra PS. The human cathelicidin LL-37: a multifunctional peptide involved in infection and inflammation in the lung. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. (2005) 18(5):321–7. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2005.01.001
27. Anand P, Elsafa E, Privitera R, Naidoo K, Yiangou Y, Donatien P, et al. Rational treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy with capsaicin 8% patch: from pain relief towards disease modification. J Pain Res. (2019) 12:2039–52. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S213912
28. Anand P, Bley K. Topical capsaicin for pain management: therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action of the new high-concentration capsaicin 8% patch. Br J Anaesth. (2011) 107(4):490–502. doi: 10.1093/bja/aer260
29. Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. (2013) 496(7446):445–55. doi: 10.1038/nature12034
30. Chen O, Donnelly CR, Ji RR. Regulation of pain by neuro-immune interactions between macrophages and nociceptor sensory neurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol. (2020) 62:17–25. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2019.11.006
31. Jain A, Gyori BM, Hakim S, Jain A, Sun L, Petrova V, et al. Nociceptor-immune interactomes reveal insult-specific immune signatures of pain. Nat Immunol. (2024) 25(7):1296–305. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01857-2
32. Yu X, Liu H, Hamel KA, Morvan MG, Yu S, Leff J, et al. Dorsal root ganglion macrophages contribute to both the initiation and persistence of neuropathic pain. Nat Commun. (2020) 11(1):264. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13839-2
33. Zhang H, Li Y, de Carvalho-Barbosa M, Kavelaars A, Heijnen CJ, Albrecht PJ, et al. Dorsal root ganglion infiltration by macrophages contributes to paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Pain. (2016) 17(7):775–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2016.02.011
34. Peters CM, Jimenez-Andrade JM, Jonas BM, Sevcik MA, Koewler NJ, Ghilardi JR, et al. Intravenous paclitaxel administration in the rat induces a peripheral sensory neuropathy characterized by macrophage infiltration and injury to sensory neurons and their supporting cells. Exp Neurol. (2007) 203(1):42–54. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.07.022
35. Kiguchi N, Maeda T, Kobayashi Y, Kondo T, Ozaki M, Kishioka S. The critical role of invading peripheral macrophage-derived interleukin-6 in vincristine-induced mechanical allodynia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. (2008) 592(1-3):87–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.07.008
36. Zhang J, Ma J, Trinh RT, Heijnen CJ, Kavelaars A. An HDAC6 inhibitor reverses chemotherapy-induced mechanical hypersensitivity via an IL-10 and macrophage dependent pathway. Brain Behav Immun. (2022) 100:287–96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.12.005
37. Yang Y, Hu L, Wang C, Yang X, Song L, Jiang C, et al. P38/TF/HIF-α signaling pathway participates in the progression of CIPN in mice. Biomed Res Int. (2019) 2019:5347804. doi: 10.1155/2019/5347804
38. Gu H, Wang C, Li J, Yang Y, Sun W, Jiang C, et al. High mobility group box-1-toll-like receptor 4-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B-mediated generation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in the dorsal root ganglion promotes chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Int J Cancer. (2020) 146(10):2810–21. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32652
39. Lin T, Hu L, Hu F, Li K, Wang CY, Zong LJ, et al. NET-triggered NLRP3 activation and IL18 release drive oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. Cancer Immunol Res. (2022) 10(12):1542–58. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0197
40. Luo X, Huh Y, Bang S, He Q, Zhang L, Matsuda M, et al. Macrophage toll-like receptor 9 contributes to chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain in male mice. J Neurosci. (2019) 39(35):6848–64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3257-18.2019
41. Ma D, Wang X, Liu X, Li Z, Liu J, Cao J, et al. Macrophage infiltration initiates RIP3/MLKL-dependent necroptosis in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Mediators Inflamm. (2022) 2022:1567210. doi: 10.1155/2022/1567210
42. Koyanagi M, Imai S, Matsumoto M, Iguma Y, Kawaguchi-Sakita N, Kotake T, et al. Pronociceptive roles of schwann cell-derived galectin-3 in taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy. Cancer Res. (2021) 81(8):2207–19. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2799
43. Zhang H, Boyette-Davis JA, Kosturakis AK, Li Y, Yoon SY, Walters ET, et al. Induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and its receptor CCR2 in primary sensory neurons contributes to paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Pain. (2013) 14(10):1031–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2013.03.012
44. Li Y, Zhang H, Kosturakis AK, Cassidy RM, Zhang H, Kennamer-Chapman RM, et al. MAPK signaling downstream to TLR4 contributes to paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. Brain Behav Immun. (2015) 49:255–66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.06.003
45. Jia R, Wan L, Jin L, Tian Q, Chen Y, Zhu X, et al. Fucoidan reduces NET accumulation and alleviates chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy via the gut-blood-DRG axis. J Neuroinflammation. (2025) 22(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03431-5
46. Wang CY, Lin TT, Hu L, Xu CJ, Hu F, Wan L, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps as a unique target in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. EBioMedicine. (2023) 90:104499. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104499
47. Krystel-Whittemore M, Dileepan KN, Wood JG. Mast cell: a multi-functional master cell. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:620. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00620
48. Yun HD, Goel Y, Gupta K. Crosstalk of mast cells and natural killer cells with neurons in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(16):12543. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612543
49. Gupta K, Harvima IT. Mast cell-neural interactions contribute to pain and itch. Immunol Rev. (2018) 282(1):168–87. doi: 10.1111/imr.12622
50. Forsythe P. Mast cells in neuroimmune interactions. Trends Neurosci. (2019) 42(1):43–55. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2018.09.006
51. Sakamoto A, Andoh T, Kuraishi Y. Involvement of mast cells and proteinase-activated receptor 2 in oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia in mice. Pharmacol Res. (2016) 105:84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.01.008
52. Jaggi AS, Kaur G, Bali A, Singh N. Pharmacological investigations on mast cell stabilizer and histamine receptor antagonists in vincristine-induced neuropathic pain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2017) 390(11):1087–96. doi: 10.1007/s00210-017-1426-8
53. Gao W, Zan Y, Wang ZJ, Hu XY, Huang F. Quercetin ameliorates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain by stabilizing mast cells, and subsequently blocking PKCε-dependent activation of TRPV1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2016) 37(9):1166–77. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.58
54. Déry O, Corvera CU, Steinhoff M, Bunnett NW. Proteinase-activated receptors: novel mechanisms of signaling by serine proteases. Am J Physiol. (1998) 274(6):C1429–52. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1998.274.6.C1429
55. Vergnolle N, Bunnett NW, Sharkey KA, Brussee V, Compton SJ, Grady EF, et al. Proteinase-activated receptor-2 and hyperalgesia: a novel pain pathway. Nat Med. (2001) 7(7):821–6. doi: 10.1038/89945
56. Kume M, Ahmad A, DeFea KA, Vagner J, Dussor G, Boitano S, et al. Protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) expressed in sensory neurons contributes to signs of pain and neuropathy in paclitaxel treated mice. J Pain. (2023) 24(11):1980–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2023.06.006
57. Prieschl EE, Csonga R, Novotny V, Kikuchi GE, Baumruker T. The balance between sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate is decisive for mast cell activation after Fc epsilon receptor I triggering. J Exp Med. (1999) 190(1):1–8. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.1.1
58. Jolly PS, Bektas M, Olivera A, Gonzalez-Espinosa C, Proia RL, Rivera J, et al. Transactivation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors by FcepsilonRI triggering is required for normal mast cell degranulation and chemotaxis. J Exp Med. (2004) 199(7):959–70. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030680
59. Grenald SA, Doyle TM, Zhang H, Slosky LM, Chen Z, Largent-Milnes TM, et al. Targeting the S1P/S1PR1 axis mitigates cancer-induced bone pain and neuroinflammation. Pain. (2017) 158(9):1733–42. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000965
60. Janes K, Little JW, Li C, Bryant L, Chen C, Chen Z, et al. The development and maintenance of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain require activation of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor subtype 1. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289(30):21082–97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569574
61. Pacini A, Micheli L, Maresca M, Branca JJ, McIntosh JM, Ghelardini C, et al. The α9α10 nicotinic receptor antagonist α-conotoxin RgIA prevents neuropathic pain induced by oxaliplatin treatment. Exp Neurol. (2016) 282:37–48. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.04.022
62. Lee JH, Kim W. The role of satellite glial cells, astrocytes, and microglia in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain. Biomedicines. (2020) 8(9):324. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8090324
63. Di Cesare Mannelli L, Pacini A, Matera C, Zanardelli M, Mello T, De Amici M, et al. Involvement of α7 nAChR subtype in rat oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy: effects of selective activation. Neuropharmacology. (2014) 79:37–48. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.10.034
64. Di Cesare Mannelli L, Pacini A, Micheli L, Tani A, Zanardelli M, Ghelardini C. Glial role in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol. (2014) 261:22–33. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.06.016
65. Lee JH, Choi JH, Kim J, Kim TW, Kim JY, Chung G, et al. Syringaresinol alleviates oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain symptoms by inhibiting the inflammatory responses of spinal microglia. Molecules. (2022) 27(23):8138. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238138
66. Hu LY, Zhou Y, Cui WQ, Hu XM, Du LX, Mi WL, et al. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) dependent microglial activation promotes cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice. Brain Behav Immun. (2018) 68:132–45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.10.011
67. Chen XT, Chen LP, Fan LJ, Kan HM, Wang ZZ, Qian B, et al. Microglial P2Y12 signaling contributes to cisplatin-induced pain hypersensitivity via IL-18-mediated central sensitization in the spinal cord. J Pain. (2023) 24(5):901–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2023.01.005
68. Navia-Pelaez JM, Choi SH, Dos Santos Aggum Capettini L, Xia Y, Gonen A, Agatisa-Boyle C, et al. Normalization of cholesterol metabolism in spinal microglia alleviates neuropathic pain. J Exp Med. (2021) 218(7):e20202059. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202059
69. Qin B, Li Y, Liu X, Gong D, Zheng W. Notch activation enhances microglial CX3CR1/P38 MAPK pathway in rats model of vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy. Neurosci Lett. (2020) 715:134624. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134624
70. Austin PJ, Moalem-Taylor G. The neuro-immune balance in neuropathic pain: involvement of inflammatory immune cells, immune-like glial cells and cytokines. J Neuroimmunol. (2010) 229(1-2):26–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.08.013
71. Gao YJ, Ji RR. Chemokines, neuronal-glial interactions, and central processing of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Ther. (2010) 126(1):56–68. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.01.002
72. Domingo IK, Latif A, Bhavsar AP. Pro-inflammatory signalling PRRopels cisplatin-induced toxicity. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(13):7227. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137227
73. Xu D, Zhao H, Gao H, Zhao H, Liu D, Li J. Participation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in neuropathic pain evoked by chemotherapeutic oxaliplatin via central GABAergic pathway. Mol Pain. (2018) 14:1744806918783535. doi: 10.1177/1744806918783535
74. Brandolini L, d'Angelo M, Antonosante A, Allegretti M, Cimini A. Chemokine signaling in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(12):2904. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122904
75. Ozaktay AC, Cavanaugh JM, Asik I, DeLeo JA, Weinstein JN. Dorsal root sensitivity to interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor in rats. Eur Spine J. (2002) 11(5):467–75. doi: 10.1007/s00586-002-0430-x
76. Starkweather A. Increased interleukin-6 activity associated with painful chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in women after breast cancer treatment. Nurs Res Pract. (2010) 2010:281531. doi: 10.1155/2010/281531
77. Brandolini L, Castelli V, Aramini A, Giorgio C, Bianchini G, Russo R, et al. DF2726A, a new IL-8 signalling inhibitor, is able to counteract chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Sci Rep. (2019) 9(1):11729. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48231-z
78. Luo H, Liu HZ, Zhang WW, Matsuda M, Lv N, Chen G, et al. Interleukin-17 regulates neuron-glial communications, synaptic transmission, and neuropathic pain after chemotherapy. Cell Rep. (2019) 29(8):2384–97.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.10.085
79. Chen LH, Yeh YM, Chen YF, Hsu YH, Wang HH, Lin PC, et al. Targeting interleukin-20 alleviates paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. Pain. (2020) 161(6):1237–54. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001831
80. Illias AM, Gist AC, Zhang H, Kosturakis AK, Dougherty PM. Chemokine CCL2 and its receptor CCR2 in the dorsal root ganglion contribute to oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hypersensitivity. Pain. (2018) 159(7):1308–16. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001212
81. Huang ZZ, Li D, Liu CC, Cui Y, Zhu HQ, Zhang WW, et al. CX3CL1-mediated macrophage activation contributed to paclitaxel-induced DRG neuronal apoptosis and painful peripheral neuropathy. Brain Behav Immun. (2014) 40:155–65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.03.014
82. Old EA, Nadkarni S, Grist J, Gentry C, Bevan S, Kim KW, et al. Monocytes expressing CX3CR1 orchestrate the development of vincristine-induced pain. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124(5):2023–36. doi: 10.1172/JCI71389
83. Montague K, Simeoli R, Valente J, Malcangio M. A novel interaction between CX(3)CR(1) and CCR(2) signalling in monocytes constitutes an underlying mechanism for persistent vincristine-induced pain. J Neuroinflammation. (2018) 15(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1116-6
84. Ochi-ishi R, Nagata K, Inoue T, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Tsuda M, Inoue K. Involvement of the chemokine CCL3 and the purinoceptor P2X7 in the spinal cord in paclitaxel-induced mechanical allodynia. Mol Pain. (2014) 10:53. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-10-53
85. Flatters SJL, Dougherty PM, Colvin LA. Clinical and preclinical perspectives on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): a narrative review. Br J Anaesth. (2017) 119(4):737–49. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex229
86. Zhou RH, Chen C, Jin SH, Li J, Xu ZH, Ye L, et al. Co-expression gene modules involved in cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy according to sensitivity, status, and severity. J Peripher Nerv Syst. (2020) 25(4):366–76. doi: 10.1111/jns.12407
87. Makker PG, Duffy SS, Lees JG, Perera CJ, Tonkin RS, Butovsky O, et al. Characterisation of immune and neuroinflammatory changes associated with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. PLoS One. (2017) 12(1):e0170814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170814
88. Krukowski K, Eijkelkamp N, Laumet G, Hack CE, Li Y, Dougherty PM, et al. CD8+ T cells and endogenous IL-10 are required for resolution of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. (2016) 36(43):11074–83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3708-15.2016
Keywords: chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, innate immune system, neurotoxicity, quality life, macrophage
Citation: Dong N and Lin T (2025) Innate immunity in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: recent advances. Front. Pain Res. 6:1642306. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2025.1642306
Received: 6 June 2025; Accepted: 8 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Wuping Sun, Affiliated Nanshan Hospital of Shenzhen University Health Science Center, ChinaReviewed by:
Ryan S. D'Souza, Mayo Clinic, United StatesFlorent Bienfait, Institut de Cancérologie de l'Ouest (ICO), France
Copyright: © 2025 Dong and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tongtong Lin, NTYwMDAzQG5qdWNtLmVkdS5jbg==
 Nana Dong1
Nana Dong1 Tongtong Lin
Tongtong Lin