- 1Pediatric Emergency Center, Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-Care Hospital (Gansu Provincial Central Hospital), Lanzhou, China
- 2Clinical Research Center, Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-Care Hospital (Gansu Provincial Central Hospital), Lanzhou, China
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-Care Hospital (Gansu Provincial Central Hospital), Lanzhou, China
- 4The First Clinical Medical College, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou, China
Objective: The aim of this study was to analyse the clinical characteristics and related risk factors of Pediatric Sepsis, construct a column-line diagram model to predict the likelihood of Pediatric Sepsis, and validate the model to facilitate primary care paediatricians to quickly and quantitatively assess the risk of Pediatric Sepsis.
Methods: This single-center retrospective study included children hospitalized for infections at Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-Care Hospital from January 2018 to June 2024. Data on 39 variables covering baseline characteristics, vital signs, and laboratory indicators were collected. The samples were randomized into training and validation groups in a 7:3 ratio. Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression was used for initial data screening and dimensionality reduction, followed by Logistic regression to identify independent risk factors for sepsis. Predictive modeling was then performed. The performance of the column-line plots was internally validated using ROC curves, calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: The development dataset included 834 patients with severe infections, of whom 212 (25.4%) developed sepsis. Seven predictors were identified as independent risk factors: respiratory rate, temperature, immature granulocyte percentage, platelets, procalcitonin, fibrinogen, and lactic acid. A predictive column-line diagram was created using these predictors. Internal validation showed that the column-line diagrams had good discriminatory ability, calibration, and clinical applicability.
Conclusion: A column-line diagram was successfully developed to predict the incidence of sepsis in children using seven commonly used clinical and laboratory indicators. The model demonstrated good performance and clinical validity through internal validation.
1 Introduction
Children possess immature immune systems that render them vulnerable to infectious illnesses (1, 2). In low- and middle-income nations, the mortality rate associated with Pediatric Sepsis can reach 25%, posing a significant hazard to children's well-being and survival (3).
Sepsis is characterized as a life-threatening dysfunction of organs resulting from an imbalanced host response triggered by an infection (4). The pathogenesis of sepsis is complex, and until the year 2020, clear diagnostic criteria for early pediatric sepsis were lacking. The publication of the International Guidelines of the Campaign to Save Sepsis in 2020 provided a framework for diagnosing sepsis in children (5), stipulating that a Pediatric Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (PSOFA) score of ≥2 in patients with infections or suspected infections indicates sepsis. However, this guideline is subject to limitations, as the PSOFA score is derived from the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score utilized in adults. Children cannot be considered as miniature versions of adults, hence a straightforward application of adult criteria to assess organ function in children may not be precise (2). The onset and progression of sepsis entail specific temporal dynamics and alterations. Children with sepsis may not exhibit typical septic presentations initially (6), thereby complicating early diagnosis.
Inadequate understanding of sepsis among some pediatric practitioners and the prevalent issue of delayed diagnoses underscore the ongoing challenge of enhancing early sepsis detection through routine laboratory assessments. There is a pressing need for a predictive model capable of accurately discerning individuals at risk of sepsis progression, enabling the prompt administration of standardized treatments to mitigate mortality rates. In this study, we conducted a retrospective analysis of laboratory findings from children with and without sepsis, and developed and validated a composite model utilizing Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression and multifactorial Logistic regression, which achieved favorable results.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population and design
This study was conducted at a single tertiary hospital in Gansu, China, focusing on children hospitalized for infections in 13 different subspecialty pediatric departments of the Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-Care Hospital (Gansu Provincial Central Hospital) between January 2018 and June 2024. The inclusion criteria comprised children aged 1 month to 14 years with complete case data. Exclusion criteria included children with advanced malignant tumors, congenital immunodeficiency, recent use of immunosuppressive drugs, severe combined congenital diseases, and those with missing clinical data. All enrolled patients were divided into sepsis group and non-sepsis group based on the presence or absence of sepsis. The diagnostic criteria for the sepsis group were defined as infection or suspected infection + PSOFA score ≥2. Of the initial 953 cases, 119 were subsequently excluded, resulting in a final cohort of 834 cases. These 834 infected patients were randomly divided into training and validation sets, with the training set comprising 583 cases (149 septic and 434 non-septic children) and the validation set consisting of 251 cases (63 septic and 188 non-septic children). Details of the data screening process are depicted in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Enrolment and allocation of study participants. Flowchart depicting the enrolment of 953 patients, exclusion, and eventual inclusion of 834 patients in the training set (n = 583) and validation set (n = 251) of the predictive model development.
This retrospective study solely entails the collection and analysis of existing data without influencing the treatment of any patients. The program has been reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-Care Hospital (Gansu Provincial Central Hospital) with the ethical filing number: (2023) GSFY Lun Audit (11).
2.2 Selected predictor variables
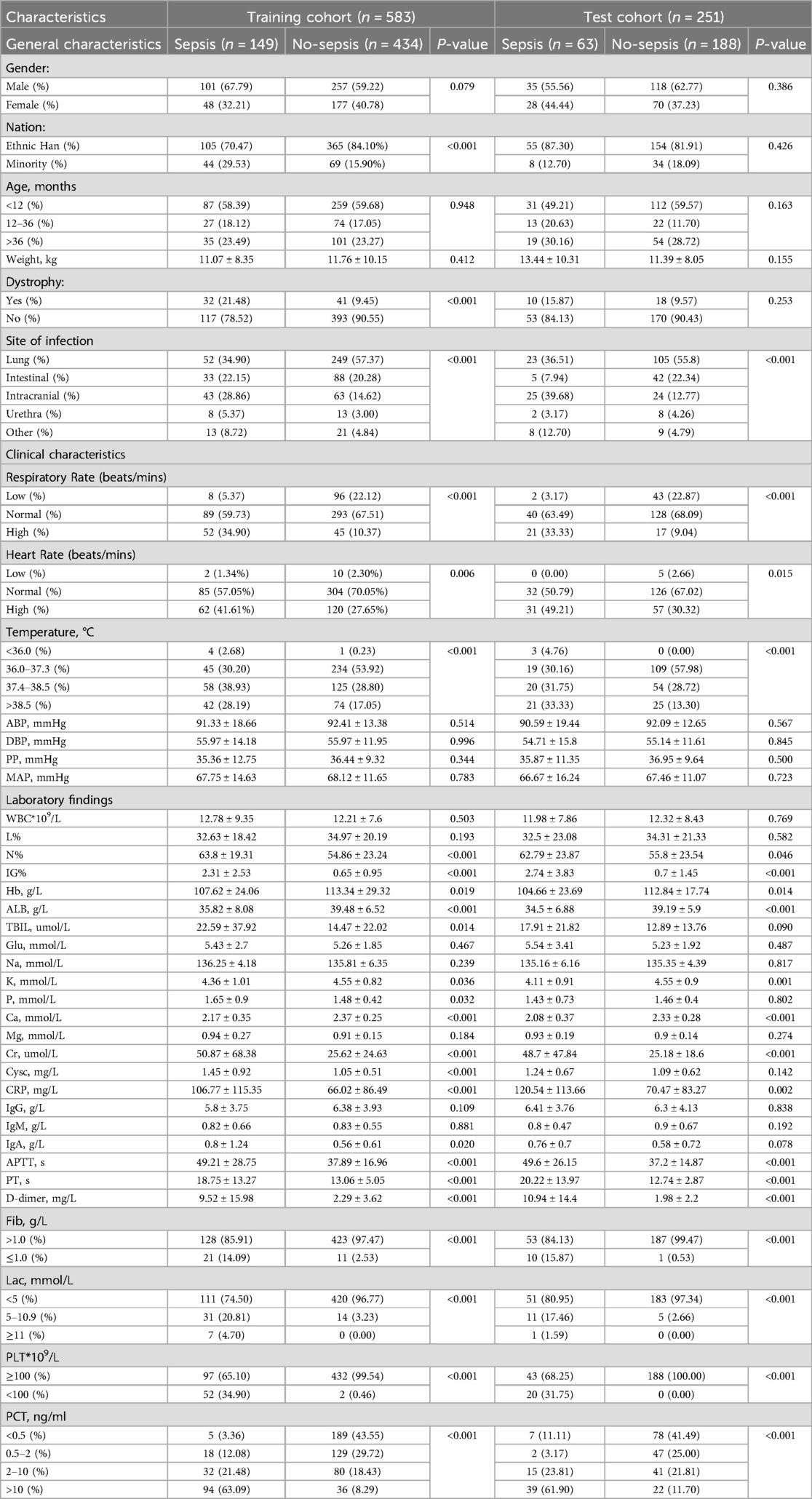
The researchers utilized a scientific research platform to gather pertinent clinical data of patients. All vital signs and laboratory tests were obtained within 24 h of hospital admission. encompassing: (1). fundamental information: age, gender, weight, ethnicity, nutritional status, and site of primary infection, etc; (2). vital signs: temperature (T), heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), differential pulse pressure (PP), and mean arterial pressure (MAP); Because the fluctuation range of respiratory rate and heart rate varies in children of different ages, respiration and heart rate were grouped according to the normal fluctuation range of different age groups, including below normal, normal, and above normal levels. The specific criteria for such divisions were derived from Chinese and American pediatric basic critical care support training materials (7) (Table 1). 3. Laboratory indices: white blood cells (WBC), haemoglobin (Hb), platelets (PLT), percentage of neutrophils (N%), percentage of lymphocytes (L%), immature granulocyte percentage (IG%), C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), albumin (ALB), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), Total bilirubin (TBIL), creatinine (Cr), urea nitrogen (BUN), cystatin C (CYSC), creatine kinase (CK), potassium (K), sodium (Na), phosphorus (P), magnesium (My), calcium (Ca), lactic acid (Lac), immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM, IgA), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), fibrinogen (Fib), and plasma D-dimer assay (D-dimer), all serological markers were tested within 24 h of admission. The subvariable categorization of PCT was based on the expert consensus stratification for the clinical use of calcitoninogen in emergency medicine (8) (Table 1), PLT, Lac and Fib grouping boundaries were delineated by the 2024 International Consensus Phoenix Scoring Criteria for Sepsis and Septic Shock in Children (9) (Table 1). All data were collected and cross-checked by two trained researchers, with any inconsistencies addressed and rectified. Following data collection, a database was established for subsequent statistical analyses.
2.3 Statistical methods
All statistical analyses were performed using R software (version 4.4.0) with dedicated packages, including “glmnet” for LASSO regression, “pROC” for ROC curve analysis, and “rms” for calibration plots. Statistical significance was defined as P-values below 0.05.
The distribution of continuous variables was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Normally distributed continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (Mean ± SD)), while categorical variables were expressed as percentages (%) and assessed using the Pearson chi-square or Fisher's exact test.
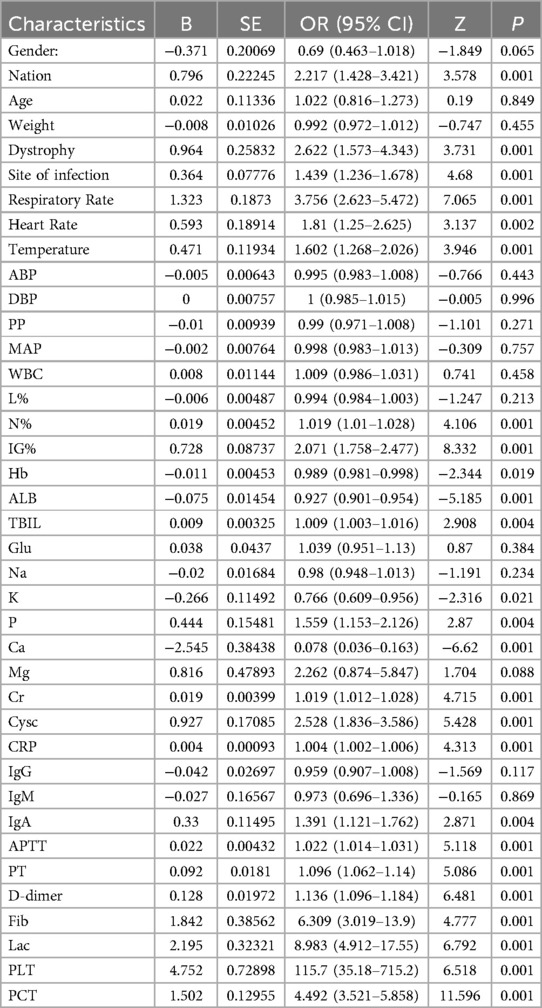
To mitigate potential issues of multicollinearity and overfitting, variables selection was conducted using the Least Absolute Shrinkage with Selection Operator Algorithm (LASSO) regression analysis method. Through LASSO regression, data dimensionality was reduced by shrinking the coefficients of uncorrelated variables to zero, while retaining variables with non-zero coefficients as potential predictor variables.Initially, all patients were randomly allocated to a training set and a validation set in a 7:3 ratio. Univariate analysis was performed on 39 variables. Variables achieving a significance level of P < 0.05 were subsequently incorporated into LASSO regression analysis. A logistic regression model was then developed using the training set. Following model development, the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration curve, and Decision Curve Analysis (DCA) were calculated in both the training set and the validation set. The optimal shrinkage parameter lambda was determined via 10-fold cross-validation using the “cv.glmnet” function within the “glmnet” package. In this study, lambda. 1se (within one standard error of the minimum lambda) was selected as the optimal lambda choice as it facilitates the selection of the minimum number of variables while maintaining good predictive performance.
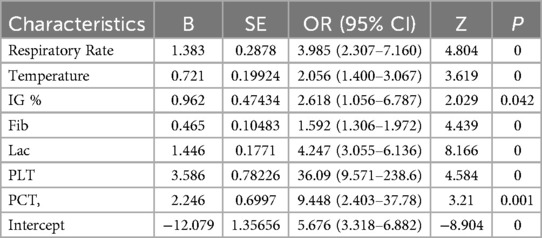
Predictors identified through LASSO regression were incorporated into a multivariate logistic regression analysis to ascertain independent risk factors associated with sepsis, along with their corresponding regression coefficients (b) and intercept values. Column plots were constructed based on the outcomes of the multivariate logistic regression analysis utilizing the “rms” package in R. Subsequently, patients within the development dataset were randomly split into 70% for training and 30% for internal validation using the “caret” package. The predictive model's clinical efficacy was assessed by evaluating the performance of the column plots in both the training and validation sets through “pROC”, “rms” and “rmda” packages, respectively.
3 Results
3.1 Comparison of general patient characteristics
A total of 834 children hospitalised for infection were included in the dataset. Table 1 illustrates that males accounted for 61.27% (511/834) of the cohort, while females comprised 38.73% (323/834). There were no statistically significant differences observed in the age and weight distributions between the sepsis and non-sepsis group (P > 0.05). However, the proportion of patients in the sepsis group with the nervous system as the primary site of infection was significantly higher compared to the non-sepsis group (28.86% vs. 14.62%, P < 0.001).
3.2 Comparison of patients' vital signs and laboratory tests
Significant differences were observed in various vital signs and laboratory test results between the sepsis and non-sepsis groups. The sepsis group exhibited a notably higher proportion of respiratory rate and heart rate above the normal range for the corresponding age group compared to the non-sepsis group (34.90% vs. 10.37%, P < 0.001), (41.61% vs. 27.65%, P = 0.006). Additionally, the sepsis group showed a higher incidence of hypothermia (<36°C) and hyperthermia (>38.5°C) than the non-sepsis group, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.001). Regarding laboratory tests, parameters including N%, IG%, Hb, ALB, TBIL, K, P, Ca, Cr, Cysc, CRP, IgA, APTT, PT, D-dimer, Fib, Lac, PLT, and PCT in the sepsis group were significantly different from those in the non-sepsis group (P < 0.05) (Table 1).
3.3 Variable selection and modelling of column-line plots
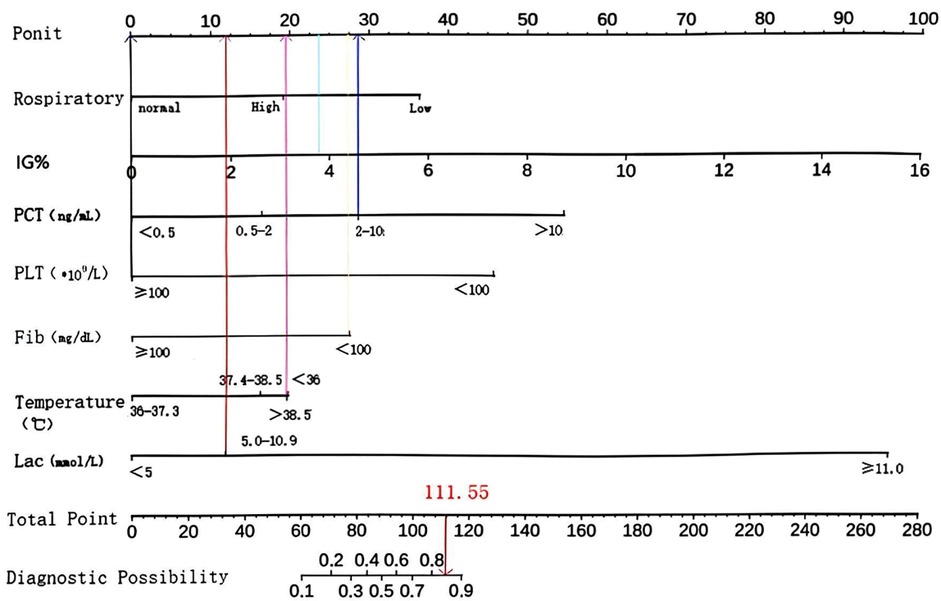
The primary objective of this study was to establish a predictive model for pediatric sepsis diagnosis.This model targets sepsis prediction within the first 48 h of hospital admission. A total of 39 variables pertinent to the diagnostic process underwent univariate analysis, revealing that ethnicity, nutritional status, site of primary infection, respiratory rate, heart rate, body temperature, N%, IG%, Hb, ALB, TBIL, K, P, Ca, Cr, Cysc, CRP, IgA, APTT, PT, D-dimer, Fib, Lac, PLT, PCT, 25 variables, were independent risk factors for the development of sepsis (P < 0.05) (Table 2). These 25 variables were included in the LASSO regression, with lambda. 1se being chosen as the optimal lambda. Subsequently, seven independent risk factors were identified, including respiratory rate (RR), temperature (T), immature granulocyte percentage (IG%), fibrinogen (Fib), lactic acid (Lac), platelets (PLT), and procalcitonin (PCT) (Figures 2A,B). These seven independent risk factors were then subjected to multifactorial analysis (Table 3). To enhance the intuitiveness and practicality of the predictive model, it was visualized as a column-line graph incorporating the seven independent predictors. Each variable's result on the graph corresponds to its respective test outcome, with the associated predictor score indicated at the top. By summing the scores for each indicator, the total predicted score can be determined, offering insight into the likelihood of sepsis occurrence in the child. For example, for an 8-month-old infant with a respiratory rate of 55 breaths/min (0 points), a temperature of 39°C (19.7 points), immature granulocyte percentage of 3.8% (23.75 points), a procalcitonin (PCT) level of 6 ng/ml (28.6 points), a platelet count (PLT) of 105*109/L (0 points), a fibrinogen (Fib) level of 90 mg/dl (27.5 points), and a lactate level of 6 mmol/L (12 points), the calculated total score would be 111.5, corresponding to a predicted sepsis risk of 0.84 (Figure 3).
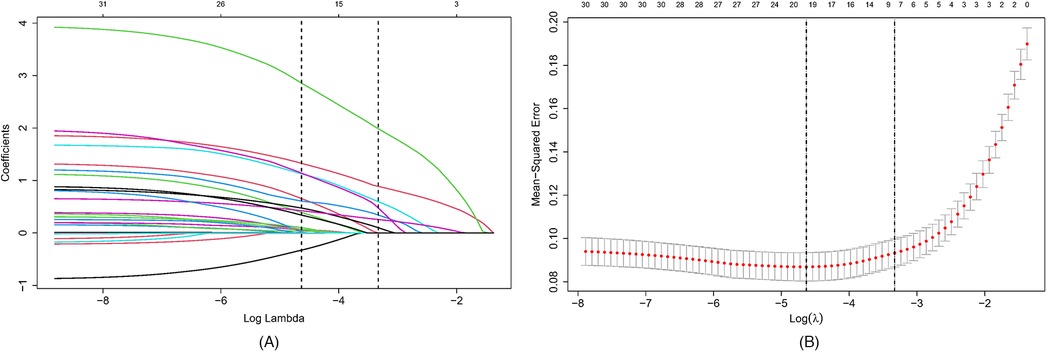
Figure 2. Selection of candidate predictor variables using LASSO regression. (A) Distribution of LASSO coefficients for 39 potential predictor variables. (B) Optimization of parameter (lambda) selection in the LASSO model using 10-fold cross-validation based on one standard error of the minimum criterion (lambda. 1se). Seven non-zero coefficient variables were selected as candidate predictors. LASSO, minimum absolute shrinkage and selection operator.
3.4 Internal validation of column line diagrams
In this study, patients were divided into a training set and a validation set in a ratio of 7:3. The validation set was used for internal validation to test the predictive performance of the model. The ROC curve for the training set exhibited an AUC of 0.949 (95% CI: 0.927–0.971, P < 0.001) with a sensitivity of 92.6%. The specificity was 84.3%, demonstrates good discriminative power for sepsis occurring within 48 h (Figure 4A). Similarly, the ROC curve for the validation set demonstrated an AUC of 0.924 (95% CI: 0.810–0.904, P < 0.001) with a sensitivity of 81.0% and specificity of 90.4% (Figure 4B). The column-line plot displayed good calibration based on the Hosmer-Lemeshow test results: training set 2 = 7.9663, P = 0.437; validation set 2 = 10.072, P = 0.260. The calibration curves were visually depicted (Figures 4C,D), indicating a favorable agreement between the predicted probability of sepsis occurrence in children using the column-line plot and the actual probability of sepsis occurrence, with good calibration in both the training and internal validation sets. A DCA analysis was performed using the threshold probability as the horizontal coordinate and the net benefit rate as the vertical coordinate to evaluate the clinical application value of the column-line diagram. As illustrated in Figures 4E,F, the column chart can provide a greater net benefit than the “all” and “none” scenarios, with the training set (threshold probability: >0.2) and the internal validation set (threshold probability: >0.2), indicating superior clinical utility.

Figure 4. (A,B) ROC curves. (C,D) Calibration curve. (E,F) DCA. ROC curve: subjects’ work characteristic curve; DCA: decision curve analysis.
4 Discussion
In this study, we developed and validated a new, simple and effective predictive model for the risk of sepsis onset up to 48 h in advance, updated continuously as new data is received. Utilizing fundamental vital signs and key laboratory parameters including respiratory rate, body temperature, percentage of naïve granulocytes, platelet count, procalcitonin, fibrinogen and lactate, column-line diagrams were constructed. The predictive model underwent internal validation, demonstrating strong predictive capabilities, and can serve as a valuable tool for pediatricians in evaluating children at risk of sepsis development.
Given the diverse clinical symptomatology in the early phases of sepsis, the limited specificity of laboratory markers, and the absence of definitive biomarkers, numerous researchers have advocated for combining multiple biomarkers to enhance early sepsis diagnosis through scoring systems. Sakyi (10) et al. conducted a case-control study involving 60 children aged 0–6 years with sepsis, and 30 non-septic children as controls. They identified CRP, PCT, and preprotease (sCD14-ST) as markers with substantial predictive value and as independent predictors of sepsis in children. While the predictive capacity of PCT aligns with our study's findings, we did not identify CRP as an independent predictor of sepsis, potentially attributed to the limited case numbers in their investigation. Several studies have indicated an association between preprotease (sCD14-ST) and sepsis development (11–13). However, the limited availability of presepsin testing, particularly in primary care settings, significantly hampers the practical application of the model. Our study's strengths lie in the ample sample size, well-defined variables, and the accessibility of their corresponding data. For instance, platelet count and immature granulocyte percentage can be obtained from CBC analyses, while lactate levels can be assessed through arterial blood gas (ABG) analyses. These routine laboratory tests are widely accessible in healthcare facilities across various settings. Florian's (14) team also developed a pediatric sepsis prediction model incorporating laboratory measures of IL-6, platelet count, PCT, CRP, and four clinical parameters including PICU length of stay, presence of central venous catheter, body temperature, and cumulative number of sepsis and SIRS episodes prior to diagnosis. The complexity of the variables in this model may hinder early diagnosis, for instance, PICU length of stay could impede sepsis identification in non-ICU settings. Moreover, the cumulative number of sepsis and SIRS episodes may not be easily interpreted by individuals with low literacy levels. In terms of early and accurate diagnosis, our predictive model surpasses the former. Other researchers have utilized sepsis-related genes to design diagnostic prediction models (15–18), but these models are primarily applicable in large, well-equipped hospitals. In less-developed regions and primary care settings, delayed sepsis diagnosis and elevated mortality rates are more prevalent.
Three of the seven variables screened in this study, including calcitoninogen, platelet count and lactate, are widely acknowledged for their strong association with sepsis diagnosis and severity, as supported by existing research. Platelets are crucial in diagnostic criteria such as the SOFA score and the newly proposed Phoenix score (9). Lactate holds significance in the Phoenix score. The lactate categorization in this study adhered to the latest Phoenix score criteria to ensure broad recognition. PCT exhibits rapid responsiveness post-bacterial infection, typically rising 2–4 h after sepsis onset (19). With its high sensitivity and specificity, PCT serves as a valuable biomarker for sepsis diagnosis and prognostication of disease severity (20). In the non-infected state of the organism, PCT concentrations <0.05 ng/ml are observed, while concentrations exceeding 10 ng/ml suggest severe sepsis or septic shock (8, 21, 22). In a randomized controlled trial by Ali et al. (23), PCT was found to exhibit higher accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity compared to CRP in sepsis diagnosis (80.79% vs. 69.45%, 36% vs. 28.7%, 87.6% vs. 72.4%). In a study by Doerflinger et al. (24) focusing on an early prediction model for pediatric sepsis diagnosis using procalcitonin and interleukin-10, the combination of PCT (≥0.425 ng/ml) and IL-10 (≥4.37 pg/ml) demonstrated a sensitivity of 100% (95% CI: 68.8%–100%) and a specificity of 89% (95% CI 80.0–95.0%). This study reported an 11-fold increase in PCT levels in the sepsis group compared to the non-sepsis group, aligning with the findings of the current investigation.
The present study also identified respiratory rate and body temperature as predictors of sepsis in children. The concept of SIRS was introduced as early as 1991 in sepsis 1.0 (25), indicating that a clinical response to non-specific injury (temperature > 38°C or <36°C; heart rate > 90 bpm; respiratory rate > 20 bpm; total white blood cell count > 12*10−9/L or <4*10−9/L, or proportion of immature (rod-shaped nuclei) neutrophils > 10%) meeting two criteria plus a suspected infection is adequate for sepsis diagnosis. Similarly, the diagnostic criteria of sepsis 2.0 in 2001 included assessment of respiratory rate and temperature (26), although these criteria were later deemed to lack specificity and are no longer in use. Nevertheless, they can still reflect the body's inflammatory response status and criticality level to some extent. Temperature changes can be influenced by various factors, including feeding, environmental temperature, and the level of immune stimulation, as demonstrated in animal studies (27, 28). Severe infections tend to induce more significant and varied temperature fluctuations compared to other causes. A large prospective study showed (29) a bimodal distribution of body temperatures in septic patients, with the development of sepsis linked to hyperthermia and increased mortality associated with hypothermia. This implies that hyperthermia and hypothermia may indicate a more severe and an excessive immune response. Consistent with the findings of this study, a body temperature <36°C or >38.5°C also resulted in a single high score of 20.9. Respiratory dysfunction can cause hypoxemia and dyspnea, with respiratory rate serving as an indicator of respiratory distress (30). Following the onset of sepsis, the respiratory system is commonly affected, and studies have indicated a significant association between abnormal respiratory rate and sepsis diagnosis (31).
Monitoring both temperature and respiratory rate is routine and easily accessible. In this study, alongside assessing sepsis likelihood using respiratory rate and body temperature status, we also combined PCT, PLT, and lactate with other laboratory indicators that are closely related to the development of sepsis to make a comprehensive determination, which is a highly effective guide for the identification of sepsis in children.
Sepsis and septic shock can lead to sepsis-induced coagulation dysfunction by activating inflammatory mediators and causing damage to endothelial cells (32). These fibrinolytic changes induced may lead to microthrombosis and microcirculatory disturbances, ultimately leading to organ failure and increased mortality (33). Fibrinogen plays a key role in haemostasis and antimicrobial host defence (34). In patients with sepsis, fibrinogen levels are often decreased and are associated with a poor prognosis (32). Signoff et al. (35) observed that children with sepsis combined with hypofibrinogenemia may have a more complicated disease course (73.7% vs. 29.2%; P < 0.001) and a higher 28-day mortality rate (26.3% vs. 7. 1%, P = 0.002). A retrospective study demonstrated a significant association between fibrinogen levels below 2 g/L upon PICU admission and an elevated risk of mortality in pediatric sepsis patients (36). The immature granulocyte percentage, often underappreciated in clinical settings, may rise in infected individuals, particularly in the presence of bacterial infections, as immature naive granulocytes are released prematurely into the peripheral blood. In a study on naive cells as the earliest biomarkers of sepsis, it was mentioned that absolute and immature granulocyte percentage serve as the earliest discriminators of sepsis (37). These markers exhibit an area under the curve of 0.81 and 0.82, respectively, and can be elevated up to 24 h prior to sepsis diagnosis. Therefore, absolute and immature granulocyte percentage represent readily accessible and cost-effective markers with high specificity and sensitivity for distinguishing septic from non-septic patients. A prospective study by Nierhaus et al. (38) similarly found that IG% could differentiate between infected and non-infected patients (P < 0.0001) with a sensitivity of 89.2% and a specificity of 76.4%, especially within 48 h following sepsis onset.
In this study, a set of seven variables closely associated with sepsis development and readily accessible were chosen to construct a column chart and an online calculator. To guarantee clinical reliability and practical applicability, the web-based interactive calculator is currently undergoing final stages of optimization and validation testing. Due to the complexity of consciousness impairment in children with severe sepsis, assessment cannot rely solely on the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) and delirium screening tools (39). Moreover, clinical evaluation of consciousness status demonstrates high variability and subjectivity, particularly considering age-related differences (40), Therefore, consciousness assessment was excluded from these variables. The column chart created in this study, based on seven quantifiable indicators, enhances clinical applicability and holds significant potential for reducing child mortality and disability, particularly in resource-limited settings. It should be emphasized that this model is primarily designed for sepsis screening in children upon hospital admission or during clinical deterioration. This approach may have limited clinical utility in children definitively diagnosed with sepsis and concomitant multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) in the PICU. While the model demonstrates strengths in operational utility and broad applicability, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations, for instance, the single-center retrospective design and lack of external validation may introduce bias in the study. Future endeavors should include external validation or larger prospective studies to enhance the accuracy and generalizability of the prediction model.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-care Hospital (Gansu Provincial Central Hospital). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from primarily isolated as part of your previous study for which ethical approval was obtained. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was not obtained from the minor(s)' legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article because This is a retrospective study, which only involves collecting and analysing the available data and does not affect the treatment of any patients. The program has been reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-Care Hospital (Gansu Provincial Central Hospital) with the ethical filing number: (2023) GSFY Lun Audit (11).
Author contributions
YJ: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Validation, Data curation. WW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Resources. RX: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. CW: Methodology, Visualization, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. XW: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation, Conceptualization. JZ: Data curation, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Gansu Provincial Major Science and Technology Special Project (Grant No. 22ZD6FA034).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge: Financial support from the Gansu Provincial Major Science and Technology Special Project (Grant No. 22ZD6FA034); Access to clinical data and resources provided by Gansu Provincial Maternity and Child-care Hospital and Gansu University of Chinese Medicine; Technical assistance from colleagues in the Department of Pediatrics and Clinical Research Center; Valuable suggestions from peer reviewers during manuscript preparation. We also extend our gratitude to all participating patients and their families.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2025.1624278/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Meyer Sauteur PM. Childhood community-acquired pneumonia. Eur J Pediatr. (2024) 183:1129–36. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05366-6
2. Tan B, Wong JJ-M, Sultana R, Koh JCJW, Jit M, Mok YH, et al. Global case-fatality rates in pediatric severe sepsis and septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. (2019) 173:352–62. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.4839
3. Miranda M, Nadel S. Pediatric sepsis: a summary of current definitions and management recommendations. Curr Pediatr Rep. (2023) 11:29–39. doi: 10.1007/s40124-023-00286-3
4. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315:801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
5. Weiss SL, Peters MJ, Alhazzani W, Agus MSD, Flori HR, Inwald DP, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign international guidelines for the management of septic shock and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction in children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2020) 21:e52–e106. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000002198
6. Mierzchała-Pasierb M, Lipińska-Gediga M. Sepsis diagnosis and monitoring—procalcitonin as standard, but what next? Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. (2019) 51:299–305. doi: 10.5114/ait.2019.88104
7. Madden MA, editors. Pediatric Fundamental Critical Care Support. Hangzhou, Zhejiang: Zhejiang University Press (2013).
8. Expert Consensus Group on the Emergency Clinical Use of Calcitoninogen. Expert consensus on the clinical application of procalcitonin (PCT) in emergency medicine. Chin J Emerg Med. (2012) 21:944–51. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2012.09.005
9. Schlapbach LJ, Watson RS, Sorce LR, Argent AC, Menon K, Hall MW, et al. International consensus criteria for pediatric sepsis and septic shock. JAMA. (2024) 331:665–74. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.0179
10. Sakyi SA, Enimil A, Adu DK, Ephraim RD, Danquah KO, Fondjo L, et al. Individual and combined bioscore model of presepsin, procalcitonin, and high sensitive C-reactive protein as biomarkers for early diagnosis of paediatric sepsis. Heliyon. (2020) 6:e04841. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04841
11. Zhou W, Rao H, Ding Q, Lou X, Shen J, Ye B, et al. Soluble CD14 subtype in peripheral blood is a biomarker for early diagnosis of sepsis. Lab Med. (2020) 51:614–9. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmaa015
12. Gad GI, Shinkar DM, Kamel El-Din MM, Nagi HM. The utility of soluble CD14 subtype in early diagnosis of culture-proven early-onset neonatal sepsis and prediction of outcome. Am J Perinatol. (2020) 37:497–502. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1683863
13. Chen M, Zhu Y. Utility of sTREM-1 and presepsin (sCD14-ST) as diagnostic and prognostic markers of sepsis. Clin Lab. (2020) 66:10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.190508. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.190508
14. Lamping F, Jack T, Rübsamen N, Sasse M, Beerbaum P, Mikolajczyk RT, et al. Development and validation of a diagnostic model for early differentiation of sepsis and non-infectious SIRS in critically ill children—a data-driven approach using machine-learning algorithms. BMC Pediatr. (2018) 18:112. doi: 10.1186/s12887-018-1082-2
15. Yang Y, Zhang G. Lysosome-related diagnostic biomarkers for pediatric sepsis integrated by machine learning. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:5575–83. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S437110
16. Ying J, Wang Q, Xu T, Lu Z. Diagnostic potential of a gradient boosting-based model for detecting pediatric sepsis. Genomics. (2021) 113(1 Pt 2):874–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.10.018
17. Zhang WY, Chen ZH, An XX, Li H, Zhang HL, Wu SJ, et al. Analysis and validation of diagnostic biomarkers and immune cell infiltration characteristics in pediatric sepsis by integrating bioinformatics and machine learning. World J Pediatr. (2023) 19:1094–103. doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00717-7
18. Zhang G, Zhang K. Screening and identification of neutrophil extracellular trap-related diagnostic biomarkers for pediatric sepsis by machine learning. Inflammation. (2024) 48(1):212–22. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02059-6
19. Meisner M. Update on procalcitonin measurements. Ann Lab Med. (2014) 34:263–73. doi: 10.3343/alm.2014.34.4.263
20. Barshilia D, Huang JJ, Komaram AC, Chen Y-C, Chen C-D, Syu M-Y, et al. Ultrasensitive and rapid detection of procalcitonin via waveguide-enhanced nanogold-linked immunosorbent assay for early sepsis diagnosis. Nano Lett. (2024) 24(8):2596–602. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c04762
21. Xu HG, Tian M, Pan SY. Clinical utility of procalcitonin and its association with pathogenic microorganisms. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. (2022) 59:93–111. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2021.1988047
22. Samsudin I, Vasikaran SD. Clinical utility and measurement of procalcitonin. Clin Biochem Rev. (2017) 38:59–68.29332972
23. Ali WA, Bazan NS, Elberry AA, Hussein RRS. A randomized trial to compare procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in assessing severity of sepsis and in guiding antibacterial therapy in Egyptian critically ill patients. Ir J Med Sci. (2021) 190:1487–95. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02494-y
24. Doerflinger M, Haeusler GM, Li-Wai-Suen CSN, Clark JE, Slavin M, Babl FE, et al. Procalcitonin and interleukin-10 may assist in early prediction of bacteraemia in children with cancer and febrile neutropenia. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:641879. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.641879
25. Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, et al. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM consensus conference committee. Chest. (1992) 101:1644–55. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644
26. Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS international sepsis definitions conference. Crit Care Med. (2003) 31:1250–6. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000050454.01978.3B
27. Steiner AA, Romanovsky AA. Energy trade-offs in host defense: immunology meets physiology. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 30:875–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.08.012
28. Ganeshan K, Nikkanen J, Man K, Leong YA, Sogawa Y, Maschek JA, et al. Energetic trade-offs and hypometabolic states promote disease tolerance. Cell. (2019) 177:399–413.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.050
29. Thomas-Rüddel DO, Hoffmann P, Schwarzkopf D, Scheer C, Bach F, Komann M, et al. Fever and hypothermia represent two populations of sepsis patients and are associated with outside temperature. Crit Care. (2021) 25:368. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03776-2
30. Lee CU, Jo YH, Lee JH, Kim J, Park SM, Hwang JE, et al. The index of oxygenation to respiratory rate as a prognostic factor for mortality in sepsis. Am J Emerg Med. (2021) 45:426–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.09.052
31. Lane DJ, Wunsch H, Saskin R, Cheskes S, Lin S, Morrison LJ, et al. Epidemiology and patient predictors of infection and sepsis in the prehospital setting. Intensive Care Med. (2020) 46:1394–403. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06093-4
32. Schupp T, Weidner K, Rusnak J, Jawhar S, Forner J, Dulatahu F, et al. Fibrinogen reflects severity and predicts outcomes in patients with sepsis and septic shock. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. (2023) 34:161–70. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000001197
33. Larsen JB, Aggerbeck MA, Larsen KM, Hvas CL, Hvas AM. Fibrin network formation and lysis in septic shock patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:9540. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179540
34. Ko YP, Flick MJ. Fibrinogen is at the interface of host defense and pathogen virulence in Staphylococcus aureus infection. Semin Thromb Hemost. (2016) 42:408–21. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1579635
35. Signoff JK, Fitzgerald JC, Teachey DT, Balamuth F, Weiss SL. Hypofibrinogenemia is associated with poor outcome and secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome in pediatric severe sepsis. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2018) 19:397–405. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000001507
36. Tang X, Shao L, Dou J, Zhou Y, Chen M, Cui Y, et al. Fibrinogen as a prognostic predictor in pediatric patients with sepsis. Mediators Inflamm. (2020) 2020:9153620. doi: 10.1155/2020/9153620
37. Bhansaly P, Mehta S, Sharma N, Gupta E, Mehta S, Gupta S. Evaluation of immature granulocyte count as the earliest biomarker for sepsis. Indian J Crit Care Med. (2022) 26:216–23. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23920
38. Nierhaus A, Klatte S, Linssen J, Eismann NM, Wichmann D, Hedke J, et al. Revisiting the white blood cell count: immature granulocytes count as a diagnostic marker to discriminate between SIRS and sepsis—a prospective, observational study. BMC Immunol. (2013) 14:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-14-8
39. Castro REV, Medeiros DNM, Murupudi N, de Magalhães-Barbosa MC, Prata-Barbosa A, Kawai Y. About acute disorders of consciousness in pediatric severe sepsis and organ failure. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2024) 25:e310–1. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000003443
Keywords: sepsis, pediatric, diagnosis, models, regression analysis
Citation: Jiang Y, Wang W, Xu R, Wang C, Wang Z, Wang X, Zhang J and Wang Y (2025) Construction and efficacy evaluation of a model for early diagnosis of pediatric sepsis based on LASSO-logistic regression. Front. Pediatr. 13:1624278. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1624278
Received: 7 May 2025; Accepted: 24 July 2025;
Published: 26 August 2025.
Edited by:
Zhixin Song, Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Qirui Guo, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, ChinaYu Wang, Anhui Medical University, China
Sotirios Liliopoulos, Technical University of Crete, Greece
Copyright: © 2025 Jiang, Wang, Xu, Wang, Wang, Wang, Zhang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weikai Wang, d2FuZ3drMjBAbHp1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Yan Jiang
Yan Jiang Weikai Wang1*
Weikai Wang1* Yanxia Wang
Yanxia Wang