- 1Shriners Hospital for Children Northern California, Sacramento, CA, USA
- 2Hospital Infantil Manuel de Jesus Rivera “la Mascota”, Managua, Nicaragua
Recent reports have demonstrated that nearly two-thirds of the world’s population do not have access to adequate surgical care, a burden that is borne disproportionately by residents of resource-poor countries. Although the reasons for limited access to surgical care are complex and multi-factorial, among the most substantial barriers is the lack of trained surgical providers. This is particularly true in surgical subspecialties that focus on life-improving, rather than life-saving, treatments, such as pediatric hand and upper extremity surgery, which manages such conditions as congenital malformations, trauma and post-traumatic deformities including burns, and neuromuscular conditions (brachial plexus birth palsy, spinal cord injury, and cerebral palsy). Many models of providing surgical care in resource-limited environments have been described and implemented, but few result in sustainable models of health-care delivery. We present our experience developing a pediatric hand and upper extremity surgery training program in Nicaragua, a resource-limited nation, that grew out of a collaboration of American and Nicaraguan orthopedic surgeons. We compare this experience to that of surgeons undergoing subspecialty training in pediatric upper limb surgery in the US, highlighting the similarities and differences of these training programs. Finally, we assess the results of this training program and identify areas for further growth and development.
Introduction
Although the origin of the adage “Give a man a fish, and you feed him for a day. Teach a man to fish, and you feed him for a lifetime,” is debated, the principle it conveys, that the acquisition of skills promotes self-sufficiency, can be found in numerous diverse philosophies. The ubiquity of this concept suggests that it is applicable to the acquisition of any scarce resource, including medical and surgical care.
Background and Rationale
In 2015, the Lancet Commission on Global Surgery estimates that nearly 5 billion people, approximately two-thirds of the world population, do not have access to adequate surgical care (1). Not surprisingly, this burden is borne disproportionately by people in resource-poor nations (1), with the poorest third of the world population receiving only 3.5% of all surgical procedures (2). Given that an estimated 30% of global diseases are treatable with surgical intervention, the lack of access to safe, timely, and appropriate surgical care results in substantial morbidity, mortality, and disability. Additionally, although the relationship between health and socioeconomic status is complex, several studies have established an association between poor health (especially in childhood) and poor socioeconomic status in both developed and developing nations (3, 4). Consequently, in addition to a moral imperative to address disparities in access to adequate surgical care, the dedication of resources to improve surgical care in resource-poor environments will likely have economic benefits at both the individual and societal level, the ramifications of which are likely to be far reaching.
The reasons for inadequate surgical care in resource-poor environments are multi-factorial, including inadequate infrastructure (facilities, electricity, water), limited physical resources (surgical and anesthesia supplies and equipment), lack of adequately trained anesthesia and surgical providers, and under-utilization of surgical services for financial, cultural, and religious reasons (5, 6). Moreover, strategies to improve global health often focus on infectious and communicable diseases, rather that surgically treated diseases, which are often characterized as expensive and technologically demanding to treat, despite emerging evidence that suggest that surgical care is cost effective (7). Although there are many reasons for lack of surgical care, the shortage of trained surgical providers is among the most significant barriers to essential surgical care worldwide (8).
If we accept the wisdom of the “teach a man to fish” philosophy, part of the solution to limited access to surgical care may be to increase the number of qualified surgeons by providing training experiences in surgical disciplines in which there are currently inadequate numbers of trained local providers. The goal of such a training program would be to develop surgeons who are not only capable to delivering surgical care but who are also able to mentor and train additional surgeons (residents, colleagues) to create a sustainable supply of knowledgeable, competent surgical providers. We describe our experience developing collaboration between American and Nicaraguan surgeons to provide pediatric hand and upper extremity surgery in Nicaragua.
Competencies and Standards
In the US, hand surgery fellowship training is available to graduates of ACGME-accredited residencies in orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery, and general surgery, and pediatric orthopedic training is available to orthopedic surgery residency graduates. Following hand surgery or pediatric orthopedic fellowship training, approximately five US surgeons each year elect to obtain an additional 6 months of training in pediatric hand surgery, to prepare them to care for children with congenital hand malformations, neuromuscular conditions such as brachial plexus birth palsy, spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, and post-traumatic deformities. These highly specialized surgeons acquire the diagnostic skill set of pediatric orthopedists by gaining an understanding of the impact of growth on musculoskeletal deformities, the treatment of syndromes, and the technical skill set of hand surgeons (training in complex reconstructive procedures that treat pediatric hand conditions).
While no formal accreditation of pediatric hand surgery exists, this discipline, a hybrid subset of pediatric orthopedic surgery and hand surgery, has become well established in the US. Most children’s hospitals now include a pediatric hand surgeon on their staff and the Pediatric Hand Study Group (PHSG), established in 1995, meets twice-yearly, performs multicenter research projects, and presents an international award each year for the best pediatric hand article (9–14). The senior author (Michelle A. James) is a founding member of the PHSG and has directed a pediatric hand fellowship training program at Shriners Hospital for Children Northern California since 2009, training eight pediatric hand fellows (http://shrinerschildrens.org/pediatric-hand-upper-extremity-surgery-fellowship). In this training program, pediatric hand fellows typically perform approximately 100 cases in a 6-month period (Table 1).
Learning Environment
Nicaragua and the Nicaraguan Health System
Nicaragua is the largest country in Central America by land mass area, approximately the size of the stat of New York in the US, and has a population of 6.1 million people. The majority of the population lives in the Pacific region of the country, along the western coast, with 25% of the total population in the capital city Managua (15). Nicaragua also is the poorest country in Central American and the second poorest country in the Western Hemisphere (16) with nearly 50% of the population living under the poverty line and a per capita gross national income of US $2,720 (17).
The Nicaraguan health-care system has three tiers with both private and public components. The private health-care sector serves Nicaraguans with the financial resources to pay for care, approximately 10% of the population. The public sector includes the Nicaraguan Social Security Institute (Instituto Nicaraguense de Seguridad Social or INSS), which covers salaried government workers (10–20% of the population) and the Ministry of Health (Ministerio de Salud or MINSA), which provides health-care services for the remainder (approximately 70–80% of the population). In addition to being the predominant health-care provider in Nicaragua, MINSA is also the health-care regulatory agency and is responsible for all matters related to the provision of healthcare, from establishing health-care policy and government priorities to the salary schedule for providers (16).
Medical Education and Orthopedic Surgery Residency in Nicaragua
There are both public and private medical schools in Nicaragua. Admission to public medical school is based on the results of a standardized admissions test, and tuition is covered by the government. Medical education in public medical schools lasts 8 years after high school (5 years of medical studies, 1 intern year, 2 years of social service). By contrast, private medical schools (American University, Catholic University, Military School) charge tuition and last 6 years (2 years of social service are not required). Following medical school, physicians wishing to become orthopedic surgeons must be accepted into an orthopedic surgery residency. These are administered by either MINSA or the National Autonomous University of Nicaragua (Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Nicaragua or UNAN). Most programs last 4 years. In 2015, 55 residents (including 10 women) were enrolled in orthopedic surgery residency in Nicaragua (18). In contrast to the US, where nearly 90% of graduating orthopedic surgery residents matriculate into an orthopedic subspecialty fellowship (19), there are no subspecialty orthopedic fellowships available in Nicaragua, although some residents complete an additional year of residency focusing on a particular subspecialty, and a small number seek subspecialty training in other countries, but due to financial and regulatory barriers, few surgeons pursue fellowship training.
According to the Asociación Nicaragűense Orthopaedia y Traumatología (ANOT), there were 210 actively practicing orthopedic surgeons in Nicaragua, about half of whom practice in Managua [3.5 orthopedic surgeons for every 100,000 people, compared with 8.5 per 100,000 in the US (19)]. However, not all Nicaraguan orthopedic surgeons belong to ANOT, so this estimate may not be accurate. Few Nicaraguan orthopedic surgeons have subspecialty training in pediatric orthopedic surgery or hand surgery, and no surgeons are trained specifically in pediatric hand surgery, a unique discipline that includes some of the most intricate and complex surgery in orthopedics. Other than service trips of surgeons from developed countries, pediatric hand surgeons are not available to treat congenital hand malformations, neuromuscular disorders (spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, brachial plexus palsy), and post-traumatic deformities.
La Brigada de las Manos
In 2009, under the auspices of Health Volunteers Overseas (20), a relationship was forged between three of the authors (Jairo J. Rios Roque, Gabriel Ramos Zelaya, and Michelle A. James), along with two additional members of the orthopedic and traumatology physician staff of a pediatric hospital in Managua, Nicaragua (Hospital Fernando Velez Paiz). In 2014, Hospital Velez Paiz was damaged by an earthquake, and the orthopedic staff and the pediatric hand surgery program (La Brigada de las Manos) transferred their services to Hospital Infantil Manuel de Jesus Rivera (Hospital “La Mascota”), the largest public children’s hospital in Nicaragua. Both Hospital Velez Paiz and Hospital La Mascota are administered by MINSA.
At the time of the first Brigada de las Manos trip in 2009, it was apparent that there existed in Nicaragua a large population of children with hand conditions, with little treatment available. The orthopedic surgeon sub-director of the children’s hospital (Gabriel Ramos Zelaya) requested that the Brigada provide hand surgery training to one of the junior orthopedic surgeons (Jairo J. Rios Roque), so that he could provide ongoing care between Brigada trips, and eventually gain expertise to care for complex pediatric hand problems independently. Jairo J. Rios Roque’s practice has been based at a public children’s hospital since 2009 and he has extensive experience, although no formal training, in pediatric orthopedic surgery, and a strong interest in hand surgery. The senior author (Michelle A. James) investigated various options for international hand fellowships in the US, and discovered that licensing and credentialing requirements virtually precluded hands-on training in the US for Jairo J. Rios Roque. Together, the sub-director and senior author developed a model of training that includes:
(1) Twice-yearly week-long Brigada visits. The Brigada includes two experienced pediatric hand surgeons (Michelle A. James and another member of the PHSG), a pediatric orthopedic occupational therapist, and additional volunteers. During these visits, the Brigada surgeons work with Jairo J. Rios Roque and the La Mascota staff to see approximately 100 children in clinic and to schedule and perform 20–25 operations (see Table 2). Jairo J. Rios Roque functions as a pediatric hand fellow, performing at least half of the cases together with a Brigada surgeon (Figure 1). The Brigada surgeons also train Nicaraguan residents. Jairo J. Rios Roque provides post-operative care for patients, communicating with Brigada surgeons by email as indicated. In addition, based on his performance in clinic and surgery, he is credentialed by the Brigada members to perform certain pediatric hand operations between trips.
(2) Nicaraguan surgeon visits to the US. As part of the planned training curriculum, Jairo J. Rios Roque visits the senior author every 1–2 years for 2–3 weeks (three visits between 2009 and 2016) where he observes clinic and surgery. He obtained a Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America international scholarship to attend a pediatric orthopedic meeting and visit two centers, in addition to attending the World Symposium on Congenital Hand Surgery in Dallas, TX, USA. At each Brigada visit, Jairo J. Rios Roque presents patients whom he has operated on since the previous visit to the visiting surgeons, who critique his results and provide feedback.
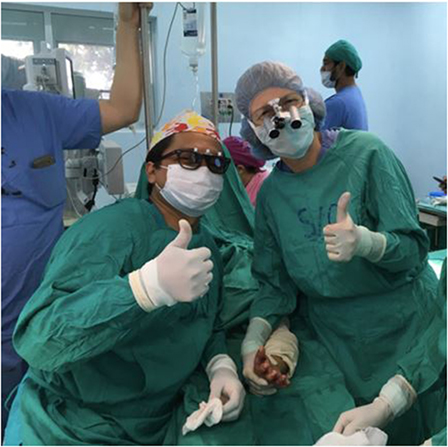
Figure 1. Jairo J. Rios Roque, MD and Michelle A. James, MD following a syndactyly release procedure performed at Hospital “La Mascota” in Managua, Nicaragua.
Results to Date/Assessment
Comparison to SHCNC Pediatric Hand Surgery Training Experience
Although Jairo J. Rios Roque’s experience is not a consolidated period of six contiguous months, but is rather occurring over years in a series of 1 week intervals, it is similar in number of cases and types of cases to a typical pediatric hand surgery training fellowship in the US (see Tables 1 and 2). There is substantial overlap in the most frequent diagnoses and procedures, with surgeries for polydactyly, syndactyly, sequelae of upper extremity trauma, and neuromuscular conditions (arthrogryposis, cerebral palsy) being among the most common procedures performed (Figures 2–6). Moreover, the volume of operative cases performed by Jairo J. Rios Roque is comparable to those of the typical US pediatric hand surgery fellow during his or her 6-month fellowship. SHCNC pediatric hand surgery fellows typically perform 100 surgical cases during their 6-month training experience and, after 7 years, Jairo J. Rios Roque has performed approximately half of the 220 cases with the Brigada during that time, and observed many of the other cases. Finally, the Nicaraguan training experience employs the concepts of graduated responsibility, such that Jairo J. Rios Roque’s responsibility and ability to independently care for patients in clinic and the operating room increases, commensurate with his experience, skills and core competencies, benchmarks for determining Jairo J. Rios Roque’s progress, and ability to practice pediatric hand surgery independently.
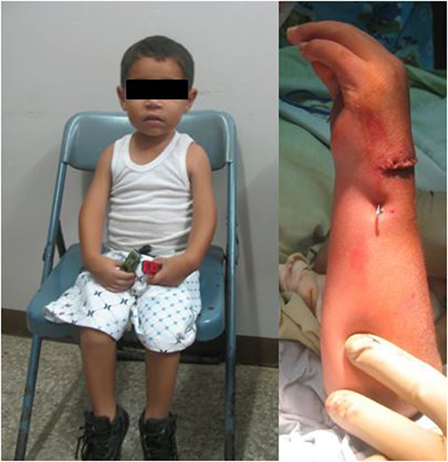
Figure 2. A patient with arthrogryposis, limited elbow flexion, and wrist extension. Note the flexed position of the wrists pre-operatively (image on the left). The patient was treated with a dorsal carpal wedge osteotomy to improve the position the wrist to neutral (image on the right).
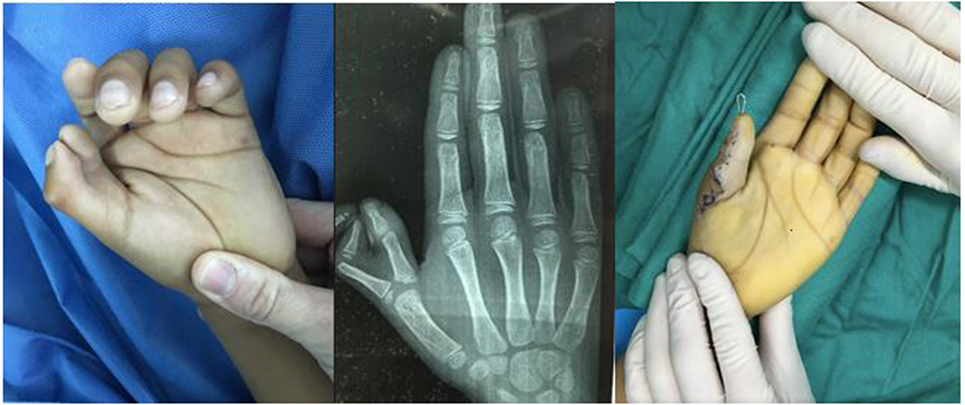
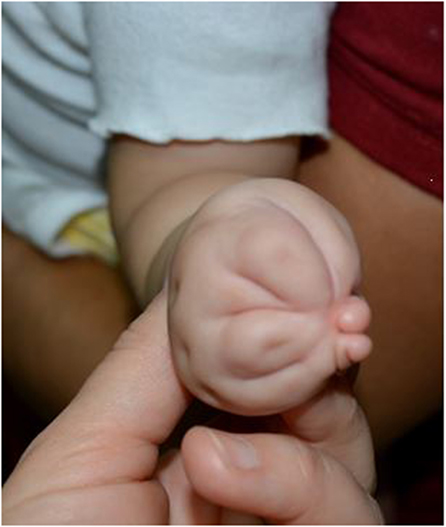
Figure 3. Radial (thumb) polydactyly treated with reconstruction of the thumb to form a single stable thumb.
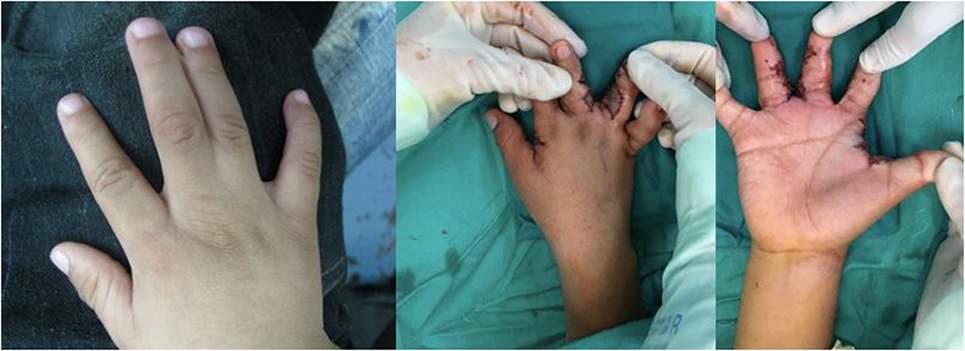
Figure 4. Syndactyly (webbed digits) affecting the ring and long fingers treated with syndactyly release and skin grafting.
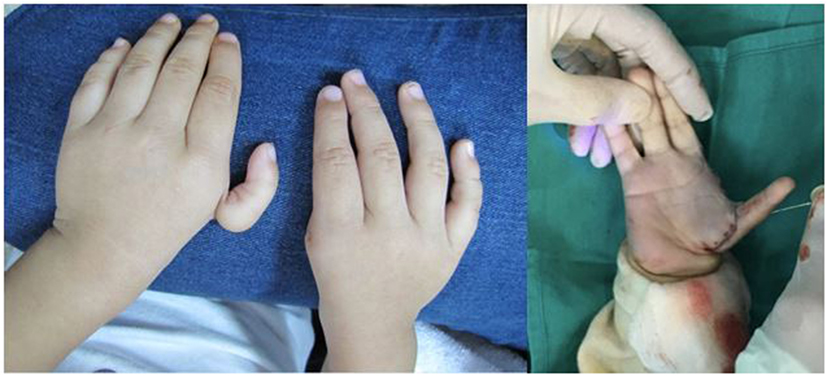
Figure 6. Bilateral thumb hypoplasia with a severely underdeveloped thumb on the left hand and an absent thumb on the right hand. This patient was treated with pollicization on both hands, in a staged fashion, which involves reconstructing and repositioning the index finger to function in the position of a thumb.
Nevertheless, there are differences between the Nicaragua training experience and the SHCNC experience. The biggest difference is the lack of availability of hand fellowship training for Jairo J. Rios Roque as a prerequisite to pediatric hand surgeon training. Although hand fellowships focus on the care of adult hand problems, they provide training in the basic hand surgical skills needed to perform most pediatric hand surgical procedures. For this reason, Jairo J. Rios Roque’s training is prolonged, and will likely not ultimately include the most complex procedures, especially those that require microsurgical skills. Table 2 does not include brachial plexus exploration and reconstruction surgeries, due in part to the fact that the hospital lacks a surgical microscope, which is required for brachial plexus reconstructions, and also due to the fact that Nicaraguan patient with brachial plexus birth palsy Brigada may present in a delayed fashion. In the US, brachial plexus surgeries are often performed around 6 months of age in the US, and the Nicaraguan patients present to hand clinic at an older age, making them less likely to benefit from brachial plexus reconstruction and more likely to require other procedures to minimize the sequelae of brachial plexus birth palsies (e.g., tendon transfers and contracture releases). Another difference is that Nicaraguan patients with syndromic congenital anomalies may be less likely to undergo surgery, as these patients may have a greater risk of anesthesia that precludes their ability to undergo surgery safely without the advanced monitoring and critical care technology available in the US. Several such patients in need of surgical intervention have been transferred to hospitals in the US where PHSG surgeons are able to care for them safely. Finally, surgeries requiring advanced technology, such as corrective forearm osteotomies using Materialise (Materialise NV, Leuven, Belgium), which utilizes 3D CT scanning, 3D printing, and advanced software technology to plan complex forearm reconstructions, are unable to be performed in Nicaragua due to the limited or absent availability of these resources.
Discussion
Sustainability
In addition to the mentor model of surgical education we have described here, several other methods to improve the availability and capacity of surgical providers in resource-poor environments are have been utilized, including: direct provision of surgical services (mission trips of visiting surgeons to resource-poor countries); fellowships (medical providers from resource-poor countries travel to the US to obtain experience and training not available in their home country); and attendance at international conferences and courses (which provide learning opportunities in the form of lectures and surgical simulations) (21). Each of these strategies, while beneficial, has certain limitations. Direct provision of surgical services (i.e., “parachute trips”) does not expand the skills or ability of local providers. Most US fellowships for foreign medical providers are limited to observerships, which do not allow hands-on training, and the provision of surgical services is not conducted in the context of their local resources, often relying on expensive technology that is not available in their home institution. Finally, international conferences and courses, like observerships, require substantial commitment of both time and resources, which is not feasible for many providers.
In contrast to the above surgical experiences, the training model we have implemented in Nicaragua results in sustainable delivery of health-care services to children with hand conditions. As Jairo J. Rios Roque’s responsibility and ability to independently care for patients in clinic and the operating room increase, patients with congenital and acquired hand conditions will be able to receive appropriate care from Jairo J. Rios Roque directly, throughout the year, without the services of the Brigada. Moreover, he will be able to educate and train the Nicaraguan residents and orthopedic surgeons in the care of patients with these conditions. Finally, the next step in sustainable surgical education is to establish research initiatives that investigate the outcomes of the treatment provided, to publish the results of these investigations, and allow the study findings to inform surgical decision making. Currently, we are planning to include Hospital La Mascota in the development of registry of congenital hand differences, which would ultimately be used to determine the outcomes and effective of surgical treatments for these conditions. Because Hospital La Mascota is the sole provider of surgical services for these complex conditions, a registry of the patients treated here will provide unique and comprehensive perspective into the incidence of these conditions, the need for surgical treatment, and outcomes of operative interventions; this could then be compared to similar registries in the US, enhancing our understanding of how to best improve the hands and lives of patients with these conditions.
Conclusion
The disparity between the need for surgical care and its availability in resource-poor countries is substantial, which has far reaching consequences for individual, social, political, and economic development. Although the reasons for this disparity are complex, solutions should focus on sustainable ways to increase the supply of scarce resources. In Nicaragua, as in other developing nations, there is an unmet need for surgeons adequately trained in the management of pediatric upper extremity surgery. We believe that the model of education and training presented here is a self-sustaining solution to lack of adequately trained pediatric hand and upper extremity surgeon in Nicaragua, which can be applied to other surgical specialties in other environments. We are hopeful that the establishment of such training models improves surgical education, enables and empowers surgeons in resource-poor environments to provide of desperately needed surgical care, and improves both the health and the lives of the patients treated.
Author Contributions
MM: primary author, responsible for data collection and analysis, drafting the work, approval of final work for submission and publication, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work. JR: contributed substantially to the data collection and interpretation, made important intellectual contributions through the writing and revision processes, approved the final work for submission and publication, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work. GZ: made considerable contributions to the conception and design of the training program and the written manuscript describing this program, participated in data interpretation and in critical analysis of the written work in the revising processes, approved the final work for submission and publication, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work. MJ: responsible for initiation and design of the training program, conceived the idea for the written manuscript describing this program, participated in data interpretation and in critical analysis of the written work in the revising processes, approved the final work for submission and publication, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Alkire BC, Raykar NP, Shrime MG, Weiser TG, Bickler SW, Rose JA, et al. Global access to surgical care: a modelling study. Lancet Glob Health (2015) 3:e316–23. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(15)70088-4
2. Weiser TG, Regenbogen ER, Thompson KD, Haynes AB, Lipsitz SR, Berry WR, et al. An estimation of the global volume of surgery: a modeling strategy based on available data. Lancet (2008) 372:139–44. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60878-8
3. Case A, Fertig A, Paxson C. The lasting impact of childhood health and circumstance. J Health Econ (2005) 24(2):365–89. doi:10.1016/j.jhealeco.2004.09.008
4. Belli PC, Bustreo F, Preker A. Investing in children’s health: what are the economic benefits? Bull World Health Organ (2005) 83(10):777–84. doi:10.1590/S0042-96862005001000015
5. Spiegel DA, Gosselin RA, Coughlin RR, Kushner AL, Bickler SB. Topics in global public health. Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:2377–84. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0413-2
6. Grimes CE, Bowman KG, Dodgion CM, Lavy CB. Systematic review of barriers to surgical care in low-income and middle-income countries. World J Surg (2011) 35(5):941–50. doi:10.1007/s00268-011-1010-1
7. Shirley ED, Sabharwal S, Schwend RM, Cabral C, Spiegel D. Addressing the global disparities in the delivery of pediatric orthopaedic services: opportunities for COUR and POSNA. J Pediatr Orthop (2016) 36(1):89–95. doi:10.1097/BPO.0000000000000400
8. Hoyler M, Finlayson SR, McClain CD, Meara JG, Hagander L. Shortage of doctors, shortage of data: a review of the global surgery, obstetrics, and anesthesia workforce literature. World J Surg (2014) 38:269–80. doi:10.1007/s00268-013-2324-y
9. James M. Symposium introduction. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg (2010) 14(1):2. doi:10.1097/BTH.0b013e3181e4612d
10. Goldfarb CA, Van Heest A, James MA, McCarroll HR. Paul R. Manske 2011 award for best upper extremity congenital research manuscript. J Hand Surg Am (2012) 37(6):1293. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.04.014
11. Goldfarb CA, Van Heest A, James M, McCarroll HR. Paul R. Manske 2012 award for the best upper extremity congenital research manuscript. J Hand Surg Am (2013) 38(9):1865–6. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.07.015
12. Goldfarb CA, Van Heest A, James M, McCarroll HR. Paul R. Manske 2013 award for the best upper extremity congenital research manuscript. J Hand Surg Am (2014) 39(10):2119. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.07.033
13. Goldfarb CA, Van Heest A, James M, McCarroll HR. Paul R. Manske 2014 award for the best upper extremity congenital research manuscript. J Hand Surg Am (2015) 40(8):1715. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2015.05.027
14. Goldfarb CA. Paul R. Manske 2015 award for the best upper extremity congenital research manuscript. J Hand Surg Am (2016) 41(9):e325. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2016.05.019
15. United Nations (UN) Data. Available from: http://data.un.org/CountryProfile.aspx?crName=NICARAGUA (accessed March 28, 2017).
16. Sequeira M, Espinoza H, Amador JJ, Domingo G, Quintanilla M, de los Santos T. The Nicaraguan Health System. Seattle, WA: PATH (2011).
17. CIA. World Factbook. Available from: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/nu.html (2016).
18. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Available from: http://www.aaos.org/AAOSNow/2007/Oct/reimbursement/reimbursement1/?ssopc=1 (accessed March 28, 2017).
19. AAOS Department of Research and Scientific Affairs. Orthopaedic Practice in the US 2014 (2015). 6 p. Available from: http://www.aaos.org/2014OPUS/
20. Health Volunteers Overseas. Available from: https://hvousa.org/ (accessed March 28, 2017).
Keywords: pediatric hand surgery, orthopedic surgery training, Nicaragua, resource-poor environment, surgical education
Citation: Manske MCB, Rios Roque JJ, Zelaya GR and James MA (2017) Pediatric Hand Surgery Training in Nicaragua: A Sustainable Model of Surgical Education in a Resource-Poor Environment. Front. Public Health 5:75. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00075
Received: 27 December 2016; Accepted: 22 March 2017;
Published: 11 April 2017
Edited by:
Jennifer Gail Audette, University of Rhode Island, USAReviewed by:
Jill Black, Widener University, USADean Smith, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, USA
Copyright: © 2017 Manske, Rios Roque, Zelaya and James. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mary Claire B. Manske, bWNsYWlyZW1hbnNrZUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Mary Claire B. Manske
Mary Claire B. Manske Jairo J. Rios Roque
Jairo J. Rios Roque Gabriel Ramos Zelaya
Gabriel Ramos Zelaya Michelle A. James
Michelle A. James