- 1School of Nursing, Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
- 2Department of General Practice, First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
- 3Nursing Department, No. 902 Hospital of the People’s Liberation Army Joint Logistics and Security Force, Bengbu, Anhui, China
- 4Nursing Department, First People's Hospital Affiliated with Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
- 5General Practice Education Development Research Center, Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui, China
- 6School of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China
Objective: To examine the heterogeneity and determinants of digital health literacy among older adult patients with chronic diseases and provide evidence for targeted interventions.
Methods: A convenience sample of 536 older adult patients with chronic diseases was recruited from three tertiary hospitals in Anhui Province between October 2023 and May 2024. Data were collected using structured questionnaires, including the Digital Health Literacy Assessment Scale, Social Support Rating Scale, General Self-Efficacy Scale, Brief Symptom Rating Scale, Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire, and the age-adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Index. Latent profile analysis (LPA) was conducted in Mplus 8.3. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0 to identify literacy profiles and their associated factors.
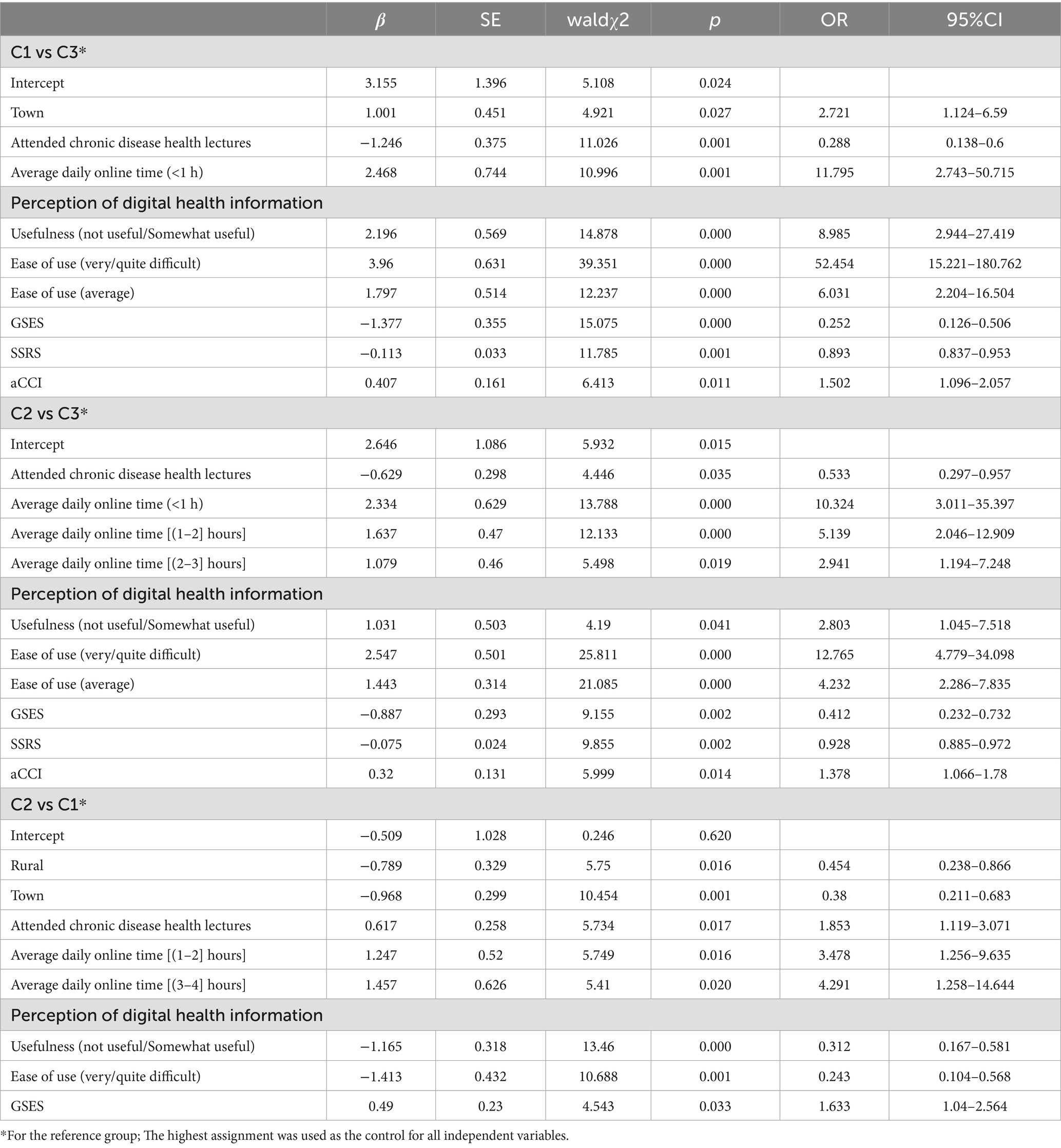
Results: The mean digital health literacy score was 41.36 (SD = 12.8), with an average item score of 2.76 (SD = 0.85). LPA identified three profiles: C1—Low Literacy, Passive Interaction (n = 142, 26.5%); C2—Moderate Literacy, Limited Interaction (n = 276, 51.5%); and C3—High Literacy, Active Interaction (n = 118, 22.0%). Multinomial logistic regression analysis showed that residence, participation in chronic disease health education, daily internet use, perceived ease of use and usefulness of digital health information, general self-efficacy, and social support were significant independent predictors of profile membership (p < 0.05). The model explained approximately 59.0% of the variance in profile classification (Nagelkerke R2 = 0.590).
Conclusion: Digital health literacy among older adult patients with chronic diseases was generally low, particularly in interactive skills, with significant heterogeneity across subgroups. Tailored strategies that address the unique needs of each profile are essential to improve digital health literacy in this population.
1 Introduction
The global population is aging; by 2080, persons aged 65 or older will outnumber children under 18 (1). As the country with both the largest older adult population and one of the fastest aging rates globally, China faces substantial challenges linked to population aging. By the end of 2024, China’s population aged 60 and above had reached 310.31 million, representing 22% of the total population. Among them, 220.23 million were aged 65 or older, accounting for 15.6% (2). This share is projected to rise to 25% by 2050 (1), indicating that China has entered a moderately aging society (3). With age, cognitive, motor, and sensory functions decline, and mental health issues become more prominent. Over 78% of older adults have at least one chronic disease, and the number of disabled older adults is rising (3). Meanwhile, China’s healthcare system continues to struggle with the mismatch between limited high-quality medical resources and the increasingly complex health needs of its aging population (4). Older adult patients with chronic diseases require timely medical care, eldercare services, and reliable health information, yet traditional healthcare models no longer fully meet these demands.
As population aging accelerates, the incidence of chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs) continues to grow. Characterized by high prevalence, long duration, low control rates, and high costs, chronic diseases have become a significant global public health burden. Each year, NCDs cause about 43 million deaths worldwide—75% of all deaths—including 18 million premature deaths (before age 70). Cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic respiratory disease, and diabetes account for more than 80% of these deaths. In China, chronic diseases are highly prevalent among older adults, often accompanied by comorbidities and mental health problems, contributing to high rates of disability and mortality. Currently, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory disease, and diabetes account for 88% of deaths in China and over 70% of the total disease burden. This poses a serious public health challenge with implications for national health and socioeconomic development (5). In response, improving chronic disease self-management has become a key strategy. Effective management slows disease progression, reduces complications, and improves quality of life. While demand for telemedicine, health management, and personalized medical services has surged in recent years, China still faces significant challenges in chronic disease prevention and control (3, 6).
In the context of accelerating digitalization, digital health governance is gaining global momentum (7), and China is rapidly advancing its digital health transition (4). As of December 2024, China had 1.108 billion internet users, with a penetration rate of 78.6%. Mobile users accounted for 1.105 billion, or 99.7% of total users. Among them, 61.2% demonstrated proficiency in at least one digital skill. Internet access among older adults reached 52.5%, with 47.4% capable of using “elder mode” features on mobile applications. Meanwhile, the internet healthcare sector expanded rapidly, with 418 million users—37.7% of total internet users—as service standardization and regulation continued to improve. Digital health technologies not only enhance health management efficiency but also drive the development of personalized care. The internet and social media have become key platforms for health information dissemination (8). Digital health literacy (DHL) refers to an individual’s ability to access, evaluate, interact with, and apply digital health information to maintain or improve health (9). Studies have shown that illness perception and social support significantly influence DHL (10, 11). In this study, illness perception was assessed using the Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire (BIPQ), which emphasizes the emotional and cognitive burden of disease. Therefore, higher BIPQ scores—indicating stronger perceived illness threat—may be associated with lower digital health literacy. Digital health interventions can improve self-management in patients with chronic diseases (12), thereby enhancing health outcomes and quality of life (13). According to social ecological systems theory (14, 15), individual development is shaped by multilayered systems, including the microsystem (individual factors such as self-efficacy, illness perception, internet use habits), the mesosystem (interpersonal factors such as participation in health education and perceived social support), and the macrosystem (societal and technological contexts such as digital infrastructure and the usability and usefulness of digital health platforms). This framework enables a comprehensive understanding of how personal, social, and contextual factors interact to influence digital health literacy in older adults with chronic diseases.
Most current domestic studies on DHL adopt a variable-centered approach, assuming population homogeneity and ignoring individual-level differences. This limits the identification of unique characteristics and needs. However, developing effective DHL interventions requires recognizing the heterogeneity of the target population. Latent Profile Analysis (LPA), a person-centered method, identifies shared patterns of responses, classifies individuals into subgroups, and reveals underlying population heterogeneity, thereby improving the precision of classification (16, 17). This study applies LPA to explore DHL profiles among older adult patients with chronic diseases and, based on social ecological systems theory, examines the influencing factors associated with each profile to inform tailored intervention strategies.
2 Participants and methods
2.1 Participants
This study used a convenience sampling method to recruit older adult patients with chronic diseases from three tertiary hospitals in Anhui Province between October 2023 and May 2024. Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) age ≥60 years; (2) diagnosis of a chronic disease according to the ICD-10, including but not limited to hypertension, diabetes, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and coronary artery disease; (3) ability to use smart devices (e.g., access the internet via mobile phone); (4) normal consciousness and the ability to read or communicate; and (5) voluntary participation with informed consent. Exclusion criteria included: (1) severe cognitive, speech, visual, auditory, or psychiatric impairments; (2) acute or critical illness with serious complications or organ failure during the study; (3) inability to engage in extended communication or having significant communication barriers; and (4) simultaneous participation in other related studies.
Sample size was estimated using the standard formula for cross-sectional studies: N (μα/2σ/δ)2 (18), where α = 0.05, μα/2 = 1.96, δ = allowable error, and σ = standard deviation. A pilot survey (n = 40) reported mean scores and standard deviations for digital health literacy (2.76 ± 0.85), social support (2.97 ± 0.63), general self-efficacy (2.26 ± 0.60), psychological status (2.16 ± 0.72), and illness perception (5.93 ± 0.88). The maximum standard deviation (σ = 0.88) was selected. With δ set to 0.25σ (19) (i.e., 0.22), the calculated minimum sample size was 62. Accounting for a 20% attrition rate, the adjusted sample size was 75. According to multivariable analysis guidelines (20), the recommended sample size is 5–10 times the number of variables. With 30 variables and a 20% attrition buffer, the target sample size was 180–360. Moreover, Nylund-Gibson et al. (21) emphasize that latent profile analysis (LPA) requires a sample size of at least 300 to ensure convergence and capture small profile groups. In total, 536 participants were included, satisfying the requirements for LPA. Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Bengbu Medical University (Approval No. [2023]369).
2.2 Research tools
2.2.1 General information questionnaire
This questionnaire was developed by the research team through literature review and consultation with clinical experts. It collected data on demographics (e.g., age, gender, education), disease characteristics (e.g., number of chronic conditions, self-rated health), and internet use, including digital device usage and attitudes toward digital health information.
2.2.2 Digital health literacy assessment scale (DHLS)
Developed by Liu (9), the DHLS consists of 15 items across three dimensions: the ability to access and evaluate digital health information, interaction ability, and application ability. Total scores range from 15 to 75, with higher scores indicating higher digital health literacy. The scale’s Cronbach’s α was 0.941 and 0.906 in the present study.
2.2.3 Social support rating scale (SSRS)
Developed by Xiao (22), the SSRS includes 10 items covering three dimensions: objective support, subjective support, and support utilization. Total scores range from 12 to 83, with higher scores reflecting greater social support. Cronbach’s α was 0.896 in previous studies (23), and 0.720 in this study.
2.2.4 10-item Kessler psychological distress scale (K10)
The K10, developed by Kessler (24) and translated into Chinese by Zhou et al. (25), assesses psychological distress over the past month. It includes 10 items, with total scores ranging from 10 to 50; higher scores indicate greater distress. Cronbach’s α was 0.8011 (26) and 0.900 in this study.
2.2.5 General self-efficacy scale (GSES)
Developed by Schwarzer et al. (27) and translated by Wang et al. (28), the 10-item GSES measures confidence in handling challenges. Total scores range from 10 to 40, with higher scores indicating stronger perceived self-efficacy. Cronbach’s α was 0.871 in previous studies and 0.873 in this study.
2.2.6 Brief illness perception questionnaire (BIPQ)
The BIPQ, developed by Broadbent et al. (29) and translated by Sun et al. (30), includes nine items measuring cognitive and emotional illness representations, illness understanding, and perceived causes. This study included only the first three dimensions, excluding the open-ended question on perceived causes. Total scores range from 0 to 80, with higher scores reflecting more negative illness perceptions. Cronbach’s α was 0.831 in prior studies and 0.751 here.
2.2.7 Age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity index (aCCI)
The aCCI quantifies comorbidity severity by incorporating both age and the number of chronic conditions. Disease scores are assigned values of 1, 2, 3, or 6 based on specific conditions. Age categories (<50, 50–59, 60–69, 70–79, 80–89, ≥90 years) are scored as 0–5, respectively. Higher scores indicate greater comorbidity burden (31, 32). Disease data were verified via electronic medical records and physician evaluations.
2.3 Data collection
Data were collected from the outpatient and inpatient departments of three tertiary hospitals in Anhui Province, China. The sample included both inpatients and patients attending regular follow-up visits for chronic disease management. Prior to recruitment, the research team obtained formal approval from the relevant hospital departments.
To enhance cultural and contextual sensitivity, the investigators—who were also trained clinical nurses—participated in routine care activities, enabling them to build rapport with patients and become familiar with their language habits and cultural backgrounds. Eligible participants were approached in a private setting, where the study’s purpose, procedures, confidentiality measures, and audio recording requirements were clearly explained in plain and accessible language. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants before enrollment.
After obtaining consent, participants completed the questionnaires independently in a quiet setting. For those with visual, literacy, or physical difficulties, trained researchers provided one-on-one assistance to ensure understanding without influencing responses. Additionally, disease-related information was verified and supplemented through medical record review.
A total of 550 eligible older adult patients were invited to participate, of whom 536 completed the questionnaire, yielding a response rate of 97.45%. The dropout rate was 2.25%, primarily due to invalid responses—such as patterned answering (e.g., identical scores across items), extreme values, or multiple selections in single-choice items. Completed questionnaires were collected immediately upon completion and reviewed on-site for completeness. Any missing or ambiguous responses were clarified in real time with the participants. Questionnaires were deemed invalid if they contained over 10% patterned or extreme responses or multiple answers to single-choice questions, as defined in previous literature (33, 34).
To minimize expectation bias, participation was entirely voluntary, and respondents were informed that their answers would remain anonymous and have no impact on their care. Researchers provided assistance only in terms of questionnaire delivery or completion support (e.g., reading questions), without influencing the content of responses.
2.4 Statistical methods
Data were double-checked, organized, and entered into a database. Latent profile modeling was conducted in Mplus 8.3 using the 15 DHLS items as observed variables. Models with increasing class numbers were tested, and the optimal solution was selected based on model fit and clinical interpretability. Evaluation criteria included:
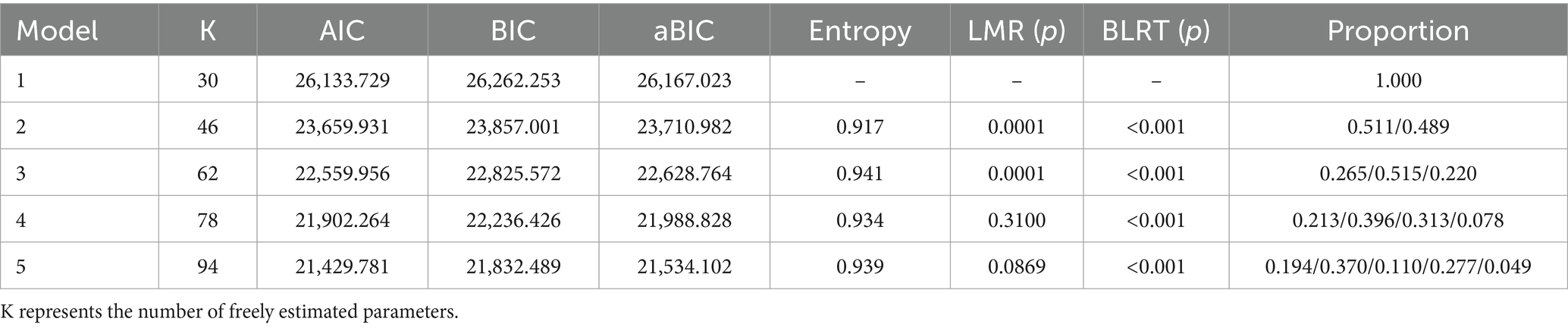
① Information criteria—AIC, BIC, and adjusted BIC (aBIC), with lower values indicating better fit; ② Classification accuracy—Entropy values (range: 0–1), with values closer to 1 indicating better precision; ③ Likelihood ratio tests—Lo–Mendell–Rubin (LMR) and bootstrap likelihood ratio test (BLRT), with p < 0.05 indicating that the K-class model outperforms the K − 1 class model. Common method bias was assessed using Harman’s single-factor test in SPSS 26.0. Skewness and kurtosis tested univariate normality; Mardia’s test assessed multivariate normality. Variables with normal or near-normal distributions were reported as mean ± SD and compared using one-way ANOVA. Categorical variables were expressed as frequencies or percentages and analyzed using χ2 or Fisher’s exact test. Variables significant in univariate analysis were included in multivariate logistic regression. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Common method bias test
Given the self-reported nature of the data, there was potential for common method bias. To mitigate this, participants were assured of anonymity and confidentiality before the survey. During the survey, item order was balanced, and disease-related information was corroborated through multiple sources, including electronic medical records, to reduce single-source bias. Harman’s single-factor test was employed, revealing 13 factors with eigenvalues exceeding 1. The first factor accounted for 22.049% of the variance, below the 40% threshold (35), indicating that common method bias was not a significant concern.
3.2 Normality test
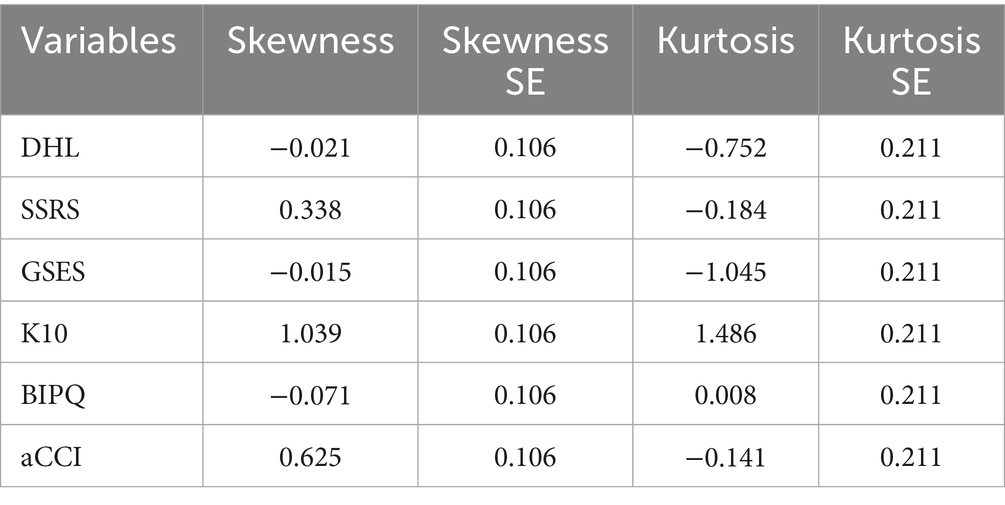
Univariate normality was evaluated using skewness and kurtosis. The absolute values of skewness for all variables were less than 3, and kurtosis values were below 10, meeting Kline’s criteria and suggesting an approximately normal distribution (36). Multivariate normality was assessed using the Mardia test. Additionally, the standardized multivariate kurtosis coefficient (|std-MK|) was 2.4423, which satisfies Byrne’s criterion of std-MK < 5 for multivariate normality (37) (see Table 1).
3.3 General information of the participants
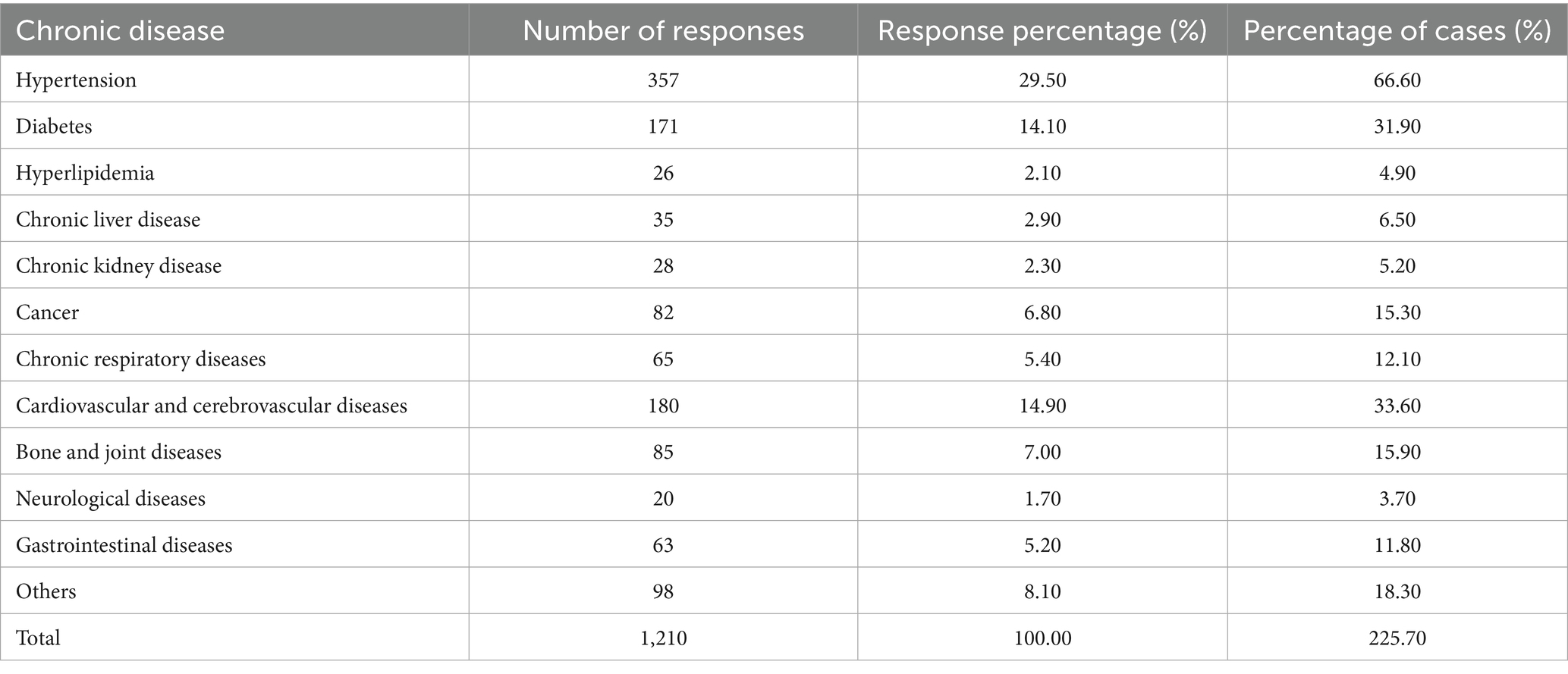
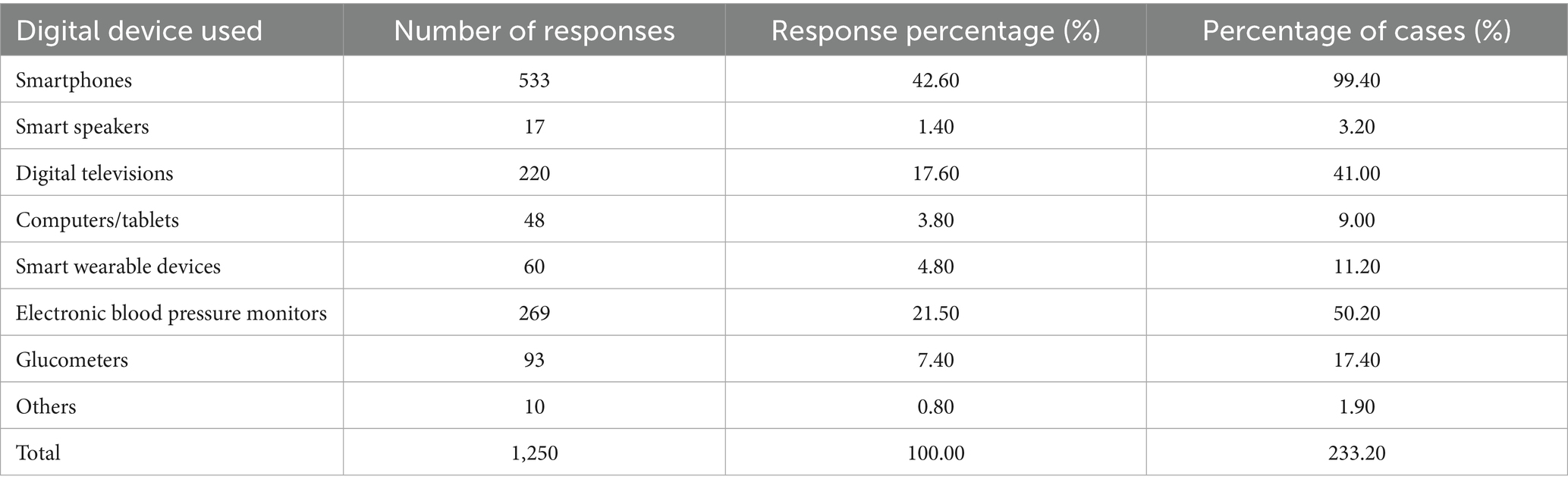
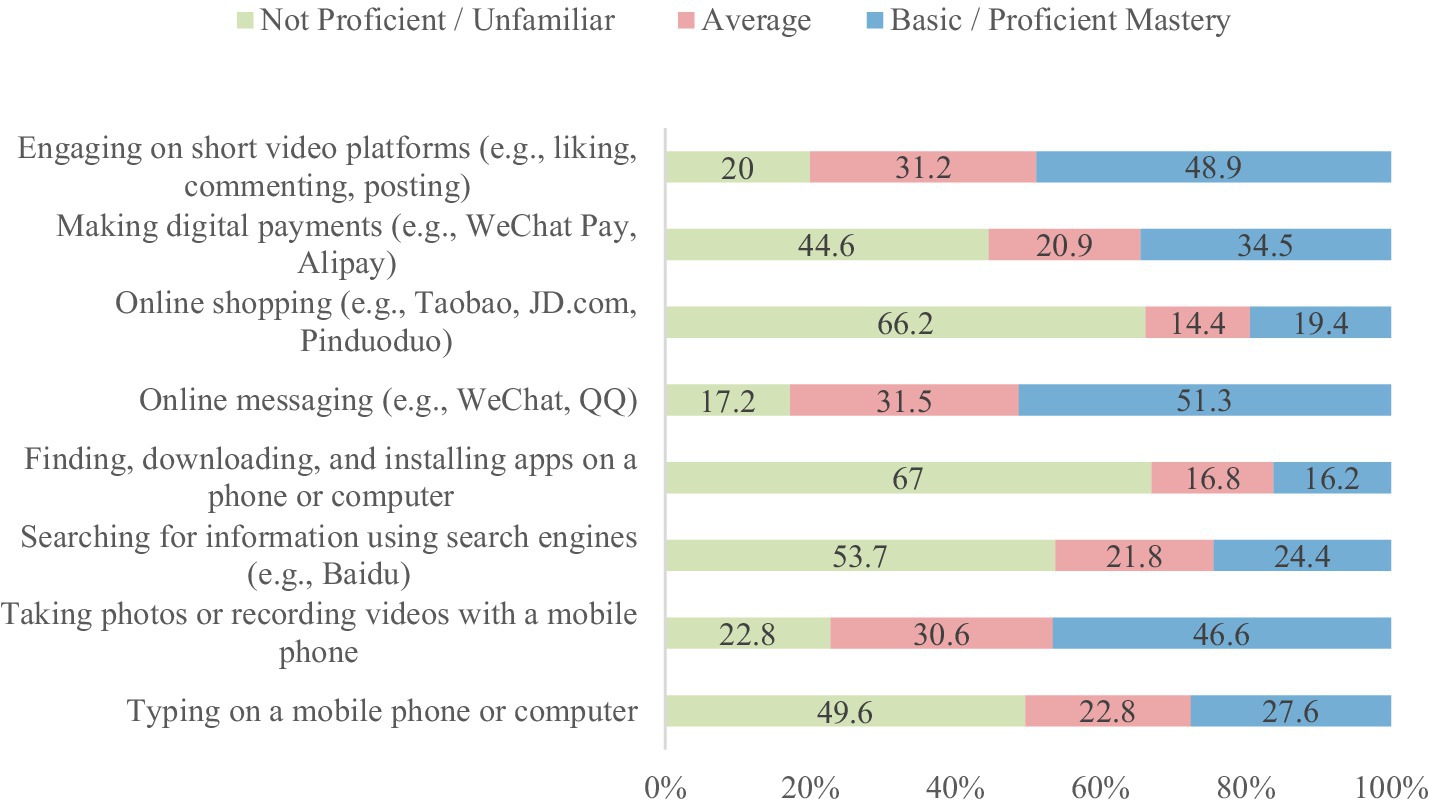
A total of 550 questionnaires were distributed; 14 were invalid, resulting in 536 valid responses and an effective response rate of 97.45%. The participants’ mean age was 67.4 ± 6.9 years. Additional demographic details are presented in Table 2. As shown in Table 3, hypertension was the most prevalent chronic disease among participants. The differences in chronic disease types were statistically significant (χ2 = 1,010.71, df = 11, p < 0.0001). Table 4 indicates that smartphones were the most commonly used smart devices, with usage differences also statistically significant (χ2 = 1,436.67, df = 7, p < 0.0001). Regarding digital literacy, Figure 1 illustrates that the highest proficiency rates were in online chatting (51.30%), interacting on short video platforms (48.90%), and taking photos/videos with a mobile phone (46.60%). Lower proficiency was observed in online shopping (19.40%) and software downloading/installation (16.20%). This suggests a stratification in digital skills, with social and entertainment-related abilities being more developed than utilitarian and complex operational skills.
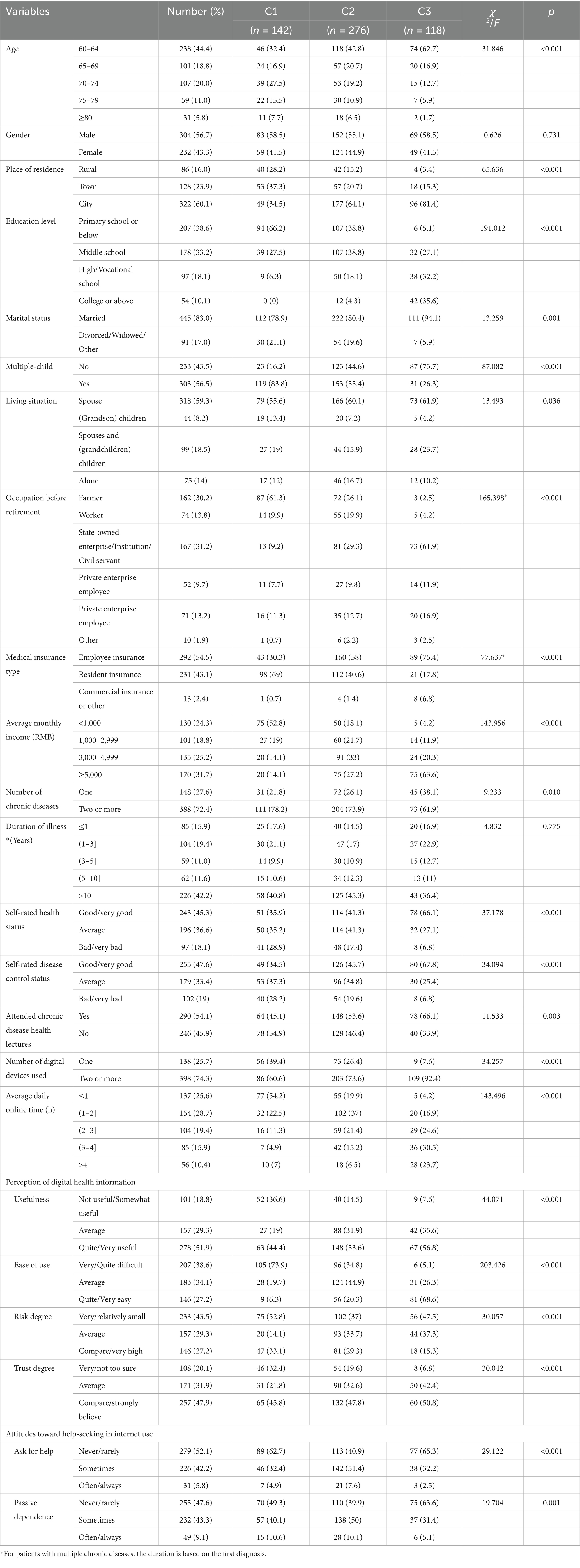
Table 2. Univariate analysis of general characteristics and latent categories of digital health literacy among older adult patients with chronic diseases.
3.4 Latent profile analysis and profile naming
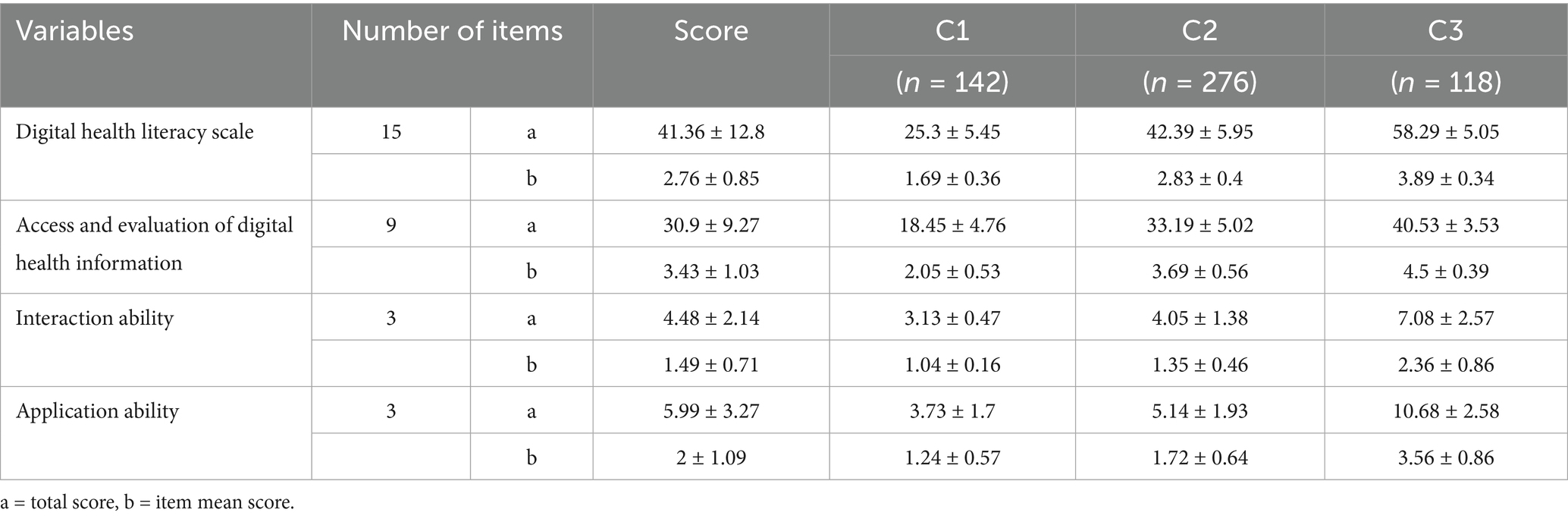
Utilizing the 15 items of the Digital Health Literacy Scale as indicators, latent profile analysis (LPA) was conducted with Mplus 8.3. Models with 1 to 5 classes were evaluated (see Table 5). As the number of classes increased, AIC, BIC, and aBIC values decreased, indicating improved fit. Entropy values exceeded 0.9, suggesting high classification accuracy. The LMR test for the 4-class model was not statistically significant (p > 0.05), indicating no superiority over the 3-class model. In the 3-class model, entropy was 0.941, with significant LMR and BLRT tests (p < 0.05). Class sizes were 142, 276, and 118, each exceeding 5% of the sample. Considering fit indices, sample distribution, and clinical relevance, the 3-class model was selected. Table 6 presents the mean scores of digital health literacy for the three profiles. Figure 2 depicts the profile plot, leading to the following classifications:
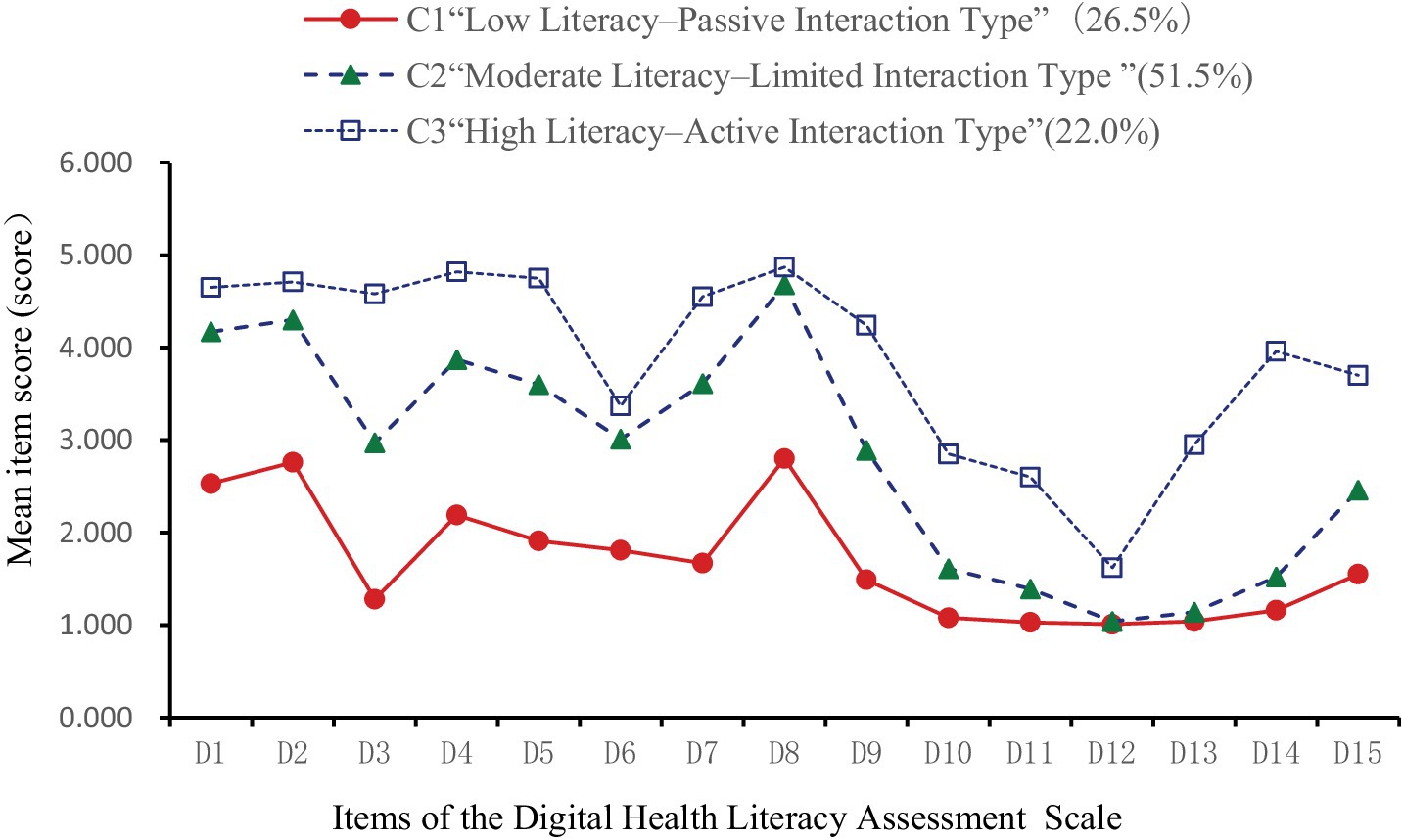
Figure 2. Latent profile chart of digital health literacy among older adult patients with chronic diseases.
C1: Low Literacy–Passive Interaction Type (142 participants, 26.5%): Consistently low scores across all items, notably in information acquisition and evaluation. Item 3 (“Actively searching for needed health information online”) was particularly low, indicating poor proactive information-seeking behavior. Despite low overall scores, item 8 was relatively higher, suggesting that participants considered the relevance of information to their conditions. Interaction abilities (items 10–12) were weak, especially in online sharing and communication. Application skills (items 13–15) were also low, notably in using online consultation functions. This group exhibited low digital health literacy with a tendency for passive information reception. C2: Moderate Literacy–Limited Interaction Type (276 participants, 51.5%): Moderate scores across all items, with improvements in information acquisition and evaluation (items 1–9). However, interaction abilities (items 10–12) remained relatively low, indicating limited engagement in online information exchange. Application skills showed enhancements, particularly in monitoring health indicators and accessing medical services digitally. This group demonstrated moderate digital health literacy with restricted interaction capabilities. C3: High Literacy–Active Interaction Type (118 participants, 22.0%): High scores across all items, especially in proactive health information acquisition (item 3). While item 12 scores suggested cautiousness in activities like online voting, overall interaction abilities were strong. Application skills were well-developed, indicating a high level of digital health literacy with active engagement in digital health activities.
3.5 Univariate analysis of the latent profiles of digital health literacy in older adult patients with chronic diseases
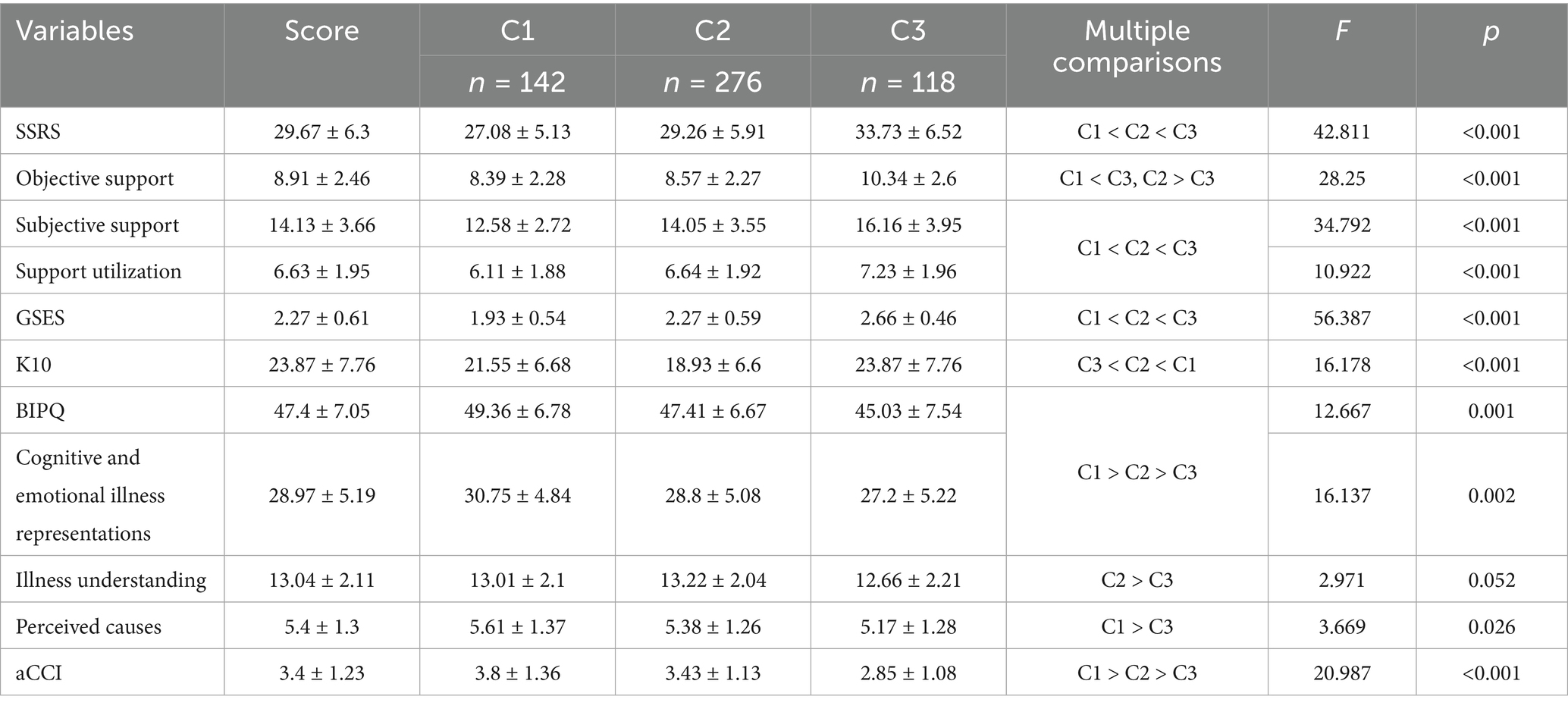
The univariate analysis revealed significant differences (p < 0.05) among the latent profiles in variables including age, place of residence, education level, marital status, number of children, cohabitation status, pre-retirement occupation, type of medical insurance, per capita monthly household income, number of chronic conditions, self-rated health status, self-rated disease control, participation in chronic disease health education, number of smart devices used, average daily internet use, perception of digital health information, and attitudes toward online health-seeking behavior (Table 2). Significant differences (p < 0.05) were also observed in total and subscale scores for social support, general self-efficacy, and illness perception (including cognitive representation and illness understanding) across the three latent profiles (Table 7).
3.6 Multivariate analysis of the latent profiles of digital health literacy in older adult patients with chronic diseases
Multinomial logistic regression was conducted using the latent profiles of digital health literacy (C1 = 1, C2 = 2, C3 = 3) as the dependent variable. Independent variables included all factors found significant in the univariate analysis. Original scores were used for social support, general self-efficacy, psychological distress, illness perception, and aCCI. Coding for other variables is detailed in Table 8. Results (Table 9) showed that, compared to C1 and C2, participants who had attended health education sessions and had higher levels of self-efficacy and social support were more likely to be classified as C3. Compared to C3, individuals living in urban areas, using the internet less than 1 h daily, perceiving digital health information as “not at all/slightly useful,” reporting usability as “very/somewhat difficult” or “neutral,” and having higher aCCI scores were more likely to belong to C1. Similarly, those with daily internet use up to 3 h, who rated digital health information as “not at all/slightly useful,” and perceived usability as “very/somewhat difficult” or “neutral,” with higher aCCI scores, were more likely to be in C2. Compared to C2, participants living in rural or urban areas, perceiving digital health information as “not at all/slightly useful,” and rating usability as “very/somewhat difficult,” were more likely to belong to C1. In contrast, attending health education sessions, using the internet for 1–4 h daily, and having higher self-efficacy scores increased the likelihood of being in C2.
Multinomial logistic regression analysis showed that residence, participation in chronic disease health education, daily internet use, perceived ease of use and usefulness of digital health information, general self-efficacy, and social support were significant independent predictors of profile membership (p < 0.05). The model explained approximately 59.0% of the variance in profile classification (Nagelkerke R2 = 0.590).
4 Discussion
4.1 Status of digital health literacy in older adult patients with chronic conditions
4.1.1 Overall level of digital health literacy
This study found that the mean digital health literacy score among older adult patients with chronic diseases was 41.36 ± 12.8, with an average item score of 2.76 ± 0.85 (range: 1–5). This score falls below the standard median of 3, suggesting generally low digital health literacy. However, it is slightly higher than those reported in previous studies of older adults in rural or community-based settings in China. Yang et al. (38) reported a score of 39.76 ± 13.82 (average item score: 2.65 ± 0.92) among rural older adults in Hebei Province. A study in rural Chengde (39) found a score of 34.90 ± 17.18 (item average: 2.33 ± 1.15). Liu (9) reported a total score of 37.10 ± 18.65 (item average: 2.47 ± 1.68) among community-dwelling older adults in Chongqing. These previous results suggest slightly lower digital health literacy levels compared to our findings. The discrepancy may stem from differences in sample characteristics. In our study, only 16.0% of participants were from rural areas, suggesting that rural older adults may have lower digital health literacy than their urban counterparts. Moreover, all participants were hospital outpatients, likely leading to greater attention to health information. The mean age (67.4 ± 6.9 years) and proportion living alone (14%) were also lower than in earlier studies (9), which reported 70.93 ± 5.51 years and a 22% rate of solitary living. These findings align with previous research (9), which also identified age, residence, and cohabitation as key influencing factors.
In terms of digital health literacy dimensions, mean item scores from highest to lowest were: information access and evaluation (3.43 ± 1.03), application (2.00 ± 1.09), and interaction (1.49 ± 0.71). Yang et al. (39) found a similar pattern: access and evaluation (2.43 ± 1.23), application (2.28 ± 1.17), interaction (2.05 ± 1.21). Liu (9), however, reported higher scores for interaction than application: access and evaluation (2.89 ± 1.71), interaction (2.18 ± 1.56), and application (1.51 ± 1.03).
This inconsistency may reflect contextual factors. In our setting, the hospital actively promotes digital health services, including volunteer support and user training, helping patients use online tools for appointments and payments. Despite these efforts, participants still reported low willingness and ability to engage in digital interactions. Many people lacked confidence. In using digital tools, one fears operational mistakes and privacy breaches. Concerns over personal data exposure and potential harassment led some to avoid online engagement entirely. As a result, participants viewed themselves more as passive information recipients than active communicators, which may explain the higher application score relative to interaction.
4.1.2 Digital health literacy among older adult patients with chronic diseases: three latent profiles identified
This study identified three distinct latent profiles of digital health literacy among older adult patients with chronic diseases: C1—Low Literacy–Passive Interaction, C2—Moderate Literacy–Limited Interaction, and C3—High Literacy–Active Interaction, reflecting marked heterogeneity in this population.
Category C1 (n = 142, 26.5%) demonstrated a low overall literacy level, with a mean score of 1.69 ± 0.3. Dimension scores were: 2.05 ± 0.5 (information access and evaluation), 1.24 ± 0.5 (application ability), and 1.04 ± 0.1 (interaction ability)—the lowest. Patients were mostly from rural or township areas, used the internet less than 1 h daily, perceived digital health information as “not at all/slightly useful,” and found it “very/somewhat difficult” or “neutral” to use. They also had higher adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Index (aCCI) scores. These individuals typically lacked digital skills, used smartphones mainly for entertainment or communication, and passively consumed health content. Influenced by frequent reports of online fraud, they lacked objective assessments of digital safety, often believing that browsing posed little risk while deeper engagement might lead to data breaches or financial loss. As a result, they preferred receiving rather than sharing information—aligning with prior research (9). Social alienation is common in this group and may contribute to reduced willingness or capacity for online interaction (40).
Category C2 (n = 276, 51.5%) had a moderate literacy level, with a mean score of 2.83 ± 0.4. Dimension scores were: 3.69 ± 0.5 (information access and evaluation), 1.72 ± 0.6 (application ability), and 1.35 ± 0.4 (interaction ability)—again, the lowest. This profile was defined as Moderate Literacy–Limited Interaction. Most participants lived in townships, had attended chronic disease education sessions, and used the internet for fewer than 4 h daily. They rated digital health information as “slightly useful” and “somewhat difficult” or “neutral” to use. These patients had relatively high self-efficacy and aCCI scores, strong social support, and moderate awareness of digital health risks. Aging-related cognitive decline makes adaptation to digital tools challenging, but younger seniors are more receptive to learning. Strong support systems enable access to information and technical help, boosting self-efficacy and encouraging engagement, even when actual interaction ability remains limited.
Category C3 (n = 118, 22.0%) had the highest overall literacy, with a mean score of 3.89 ± 0.3. Dimension scores were: 4.5 ± 0.39 (information access and evaluation), 2.36 ± 0.8 (application ability), and 3.56 ± 0.8 (interaction ability). This profile was labeled High Literacy–Active Interaction. Patients in this group were more likely to have attended health education programs and reported high levels of self-efficacy and social support. These individuals often received professional guidance from healthcare providers, demonstrated confidence in accessing and using digital tools, and actively engaged in health-related communication. Category C2 (n = 276, 51.5%) had a moderate literacy level, with a mean score of 2.83 ± 0.4. Dimension scores were: 3.69 ± 0.5 (information access and evaluation), 1.72 ± 0.6 (application ability), and 1.35 ± 0.4 (interaction ability)—again, the lowest. This profile was defined as Moderate Literacy–Limited Interaction. Most participants lived in townships, had attended chronic disease education sessions, and used the internet for fewer than 4 h daily. They rated digital health information as “slightly useful” and “somewhat difficult” or “neutral” to use. These patients had relatively high self-efficacy and aCCI scores, strong social support, and moderate awareness of digital health risks. Aging-related cognitive decline makes adaptation to digital tools challenging, but younger seniors are more receptive to learning. Strong support systems enable access to information and technical help, boosting self-efficacy and encouraging engagement, even when actual interaction ability remains limited. Category C3 (n = 118, 22.0%) had the highest overall literacy, with a mean score of 3.89 ± 0.3. Dimension scores were: 4.5 ± 0.39 (information access and evaluation), 2.36 ± 0.8 (application ability), and 3.56 ± 0.8 (interaction ability). This profile was labeled High Literacy–Active Interaction. Patients in this group were more likely to have attended health education programs and reported high levels of self-efficacy and social support. These individuals often received professional guidance from healthcare providers, demonstrated confidence in accessing and using digital tools, and actively engaged in health-related communication.
4.2 Influencing factors of digital health literacy profiles
This study found that residence, participation in chronic disease education, internet usage, perceived usefulness and ease of digital health tools, self-efficacy, and social support significantly influenced digital health literacy profiles in older adult patients.
4.2.1 Individual level factors
Patients in C1 often perceived digital health information as difficult to use and of limited value. Prior studies show that perceived usefulness and ease of use strongly influence technology adoption (9). Most older adult individuals possess only basic digital skills and remain affected by the digital divide, with limited access to or ability to apply health technologies (41). Lower education, reduced literacy, minimal exposure to digital media, and limited device proficiency contribute to poor digital health literacy and complicate chronic disease self-management (42). Younger older adult patients are generally more adaptable, and as digital health technologies proliferate, new forms of ageism may emerge (43). Digital health literacy declines with age and is negatively associated with trust in digital sources and perceived usability (9, 44, 45). Frequent use of multiple digital devices is linked to quicker adoption and improved literacy (46). Significant differences in disease perception were observed among the three profiles (p < 0.05). C1 patients often lacked accurate awareness of disease progression, held negative perceptions, and were more prone to anxiety or distress (47), reducing their motivation to engage with digital resources (48). Conversely, C3 patients demonstrated higher self-efficacy, enabling them to apply health information effectively in chronic disease management, consistent with previous findings (11). Prior successful experiences may have built their confidence in using digital tools. They were also more inclined to share personal experiences, fostering improved digital literacy. However, some older adults remain reluctant to share health information due to concerns about accuracy, privacy, or social stigma, which may hinder engagement.
4.2.2 Interpersonal relationships
Family support is the most immediate source of emotional and informational assistance for older adult patients. Younger family members generally possess higher levels of digital literacy. In families with strong intergenerational relationships, higher education levels, and financial stability, digital engagement and efficacy tend to be greater. Older adult individuals in such environments receive timely emotional and informational support when encountering difficulties accessing digital health resources. This support enhances their acceptance of digital technologies, improves self-efficacy, and reduces anxiety related to technology use (38, 49). However, in multigenerational households, older adult patients often assume caregiving roles or handle household responsibilities. These obligations consume time and energy, reducing their capacity to learn digital skills and improve digital health literacy. Peer support also plays a key role. Older adult patients tend to trust members of their social circles or fellow patients, which facilitates communication and mutual understanding. Information shared within these networks is perceived as vetted and reliable. Such peer interactions serve as both guidance and motivation, encouraging older adult individuals to develop their digital health literacy.
4.2.3 Social support systems
Social support—emotional, informational, and instrumental—reduces stress and promotes overall well-being among older adult patients. It significantly influences their willingness to adopt digital technologies and their level of digital health literacy, aligning with previous findings (42, 50, 51). Most older adult individuals seek care at nearby community health centers or pharmacies, where long-term relationships with primary healthcare providers offer trusted emotional and informational support. Patients who have participated in chronic disease health education are more likely to fall into the high-literacy group (C3). These individuals tend to receive professional guidance from healthcare providers, demonstrate higher health literacy, and better understand their own information needs. They are more proactive in seeking health information, communicating, and engaging with digital health platforms (52). China’s digital health sector is expanding rapidly, supported by improved infrastructure and technologies. Digital media now plays a major role in disseminating health information (8), creating a favorable environment for older adult access to digital health resources (53). However, the field still lacks standardized regulation. Some search engines and short video platforms prioritize paid content through ranking algorithms, resulting in uneven information quality. Additionally, frequent device updates, complex interfaces, and online scams raise concerns about data privacy and financial safety. These factors undermine trust and hinder older adult patients’ digital health engagement.
5 Limitations
This study has several limitations that may affect both internal and external validity. First, the sample was drawn exclusively from older adult patients attending tertiary hospitals in Anhui Province, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to individuals in rural areas or those receiving care in primary or secondary healthcare settings. Tertiary hospitals generally provide better access to digital infrastructure and health services, which may positively skew digital health literacy levels. Second, all participants were required to possess basic proficiency in using smartphones or other smart devices. This inclusion criterion may have inadvertently excluded individuals most affected by the digital divide—those with minimal or no experience using digital technologies—thus potentially overestimating the actual level of digital health literacy in the broader older adult population. Third, the study employed a cross-sectional and once-off survey design, which limits the ability to draw causal inferences from the observed associations. Longitudinal studies are warranted to verify the directionality and potential causality of the relationships among digital health literacy, self-efficacy, and related influencing factors. Fourth, all data were collected using self-administered questionnaires based on self-perceptions, which may be subject to common method bias, including social desirability and recall bias. Finally, although the digital health literacy scale and other instruments used in this study have been validated in Chinese populations, they are not widely adopted in international research. This may limit the comparability of findings across different cultural or healthcare contexts. Future studies should consider incorporating internationally recognized tools to enhance cross-cultural applicability and validity.
6 Conclusion
This study found that older adult chronic disease patients generally have low levels of digital health literacy. Using latent profile analysis (LPA), patients were classified into three categories: C1: “Low Literacy - Passive Interaction Type,” C2: “Medium Literacy - Limited Interaction Type,” and C3: “High Literacy - Active Interaction Type,” revealing significant heterogeneity among the groups. Healthcare providers should prioritize patients in category C1, and design targeted intervention plans based on the characteristics of each group to enhance digital health literacy. In the context of digitalization and technological advancements, improving the digital health literacy of older adult chronic disease patients is a complex, multi-faceted task that requires the collective effort of society.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the dataset generated and analyzed during the current study contains personal health information from older adult patients with chronic diseases, and its use is subject to strict confidentiality agreements. Due to privacy and ethical concerns, the data cannot be made publicly available. Access to the dataset is restricted and available only upon reasonable request, with approval from the ethics committee of the participating institutions, in compliance with applicable data protection regulations. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to Xiumu Yang, MDcwMDAxM0BiYm11LmVkdS5jbg==.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Bengbu Medical University ([2023] No. 369). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YS: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. XX: Investigation, Writing – original draft. HG: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XD: Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft. SZ: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Anhui Provincial Philosophy and Social Science Research Planning Project (AHSKY2023D048), the Major Philosophy and Social Sciences Project of the Anhui Provincial Department of Education (2024AH040341), the 2023 Medical Education Research Project of the Chinese Medical Association and the National Medical Education Development Center (2023B014), the Quality Engineering Projects of the Anhui Provincial Department of Education (2023zyxwjxalk139, 2023kcszsf146, and 2023jyxm0635), the National Social Science Fund Incubation Projects of Bengbu Medical University (2023byfy142sk and 2023byzd166sk), the Natural Science Foundation of Bengbu Medical University (2023byzd047), Bengbu Social Science Planning Key Project (BB25A018) and the Longhu Talent Project of Bengbu Medical University (LH250201001).
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants in this study for their sincere cooperation and the hospital’s clinical staff for their help and support. We also sincerely appreciate the valuable comments and suggestions from the reviewers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Nations U. World population prospects 2024: summary of results: United Nations. (2024). Available online at: https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/ (Accessed November 15, 2022).
2. Statistics NBo. Statistical communiqué of the People's Republic of China on the 2024 national economic and social development: National Bureau of Statistics. (2025). Available online at: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202502/t20250228_1958817.html (Accessed February 28, 2025).
3. Fifteen departments, Commission itNH. Notice on the issuance of the "14th Five-Year Plan" for Healthy Aging: Fifteen departments, including the National Health Commission. (2022). Available at: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-03/01/content_5676342.htm (Accessed February 07, 2022).
4. Commission CCA. 14th five-year national informatization plan: Central Cyberspace Affairs Commission. (2021). Available online at: http://www.cac.gov.cn/2021-12/27/c_1642205314518676.htm (Accessed December 27, 2021).
5. Council S. State Council's Opinions on Implementing the Healthy China Initiative: State Council. (2019). Available at: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2019-07/15/content_5409492.htm (Accessed July 15, 2019).
6. Xue, L, Cai, M, Liu, Q, Ying, X, and Wu, S. Trends and regional variations in chronic diseases and their risk factors in China: an observational study based on national health service surveys. Int J Equity Health. (2023) 22:120. doi: 10.1186/s12939-023-01910-w
7. Organization WH. Global strategy on digital health 2020–2025: World Health Organization. (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/documents/gs4dhdaa2a9f352b0445bafbc79ca799dce4d.pdf (Accessed August 18, 2021).
8. Fei, S, Xiang, Y, Wang, Y, Mei, H, and Sun, Y. Study on acceptance situation of we-media health information in elderly chronic patients. Front Soc Sci. (2023) 12:2319–25. doi: 10.12677/ass.2023.125314
9. Liu, S. Development and empirical research on the digital health literacy assessment scale for community elderly under the background of active aging. Chong Qing: Army Medical University (2022).
10. Slevin, P, Kessie, T, Cullen, J, Butler, MW, Donnelly, SC, and Caulfield, B. A qualitative study of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patient perceptions of the barriers and facilitators to adopting digital health technology. Digit Health. (2019) 5:5. doi: 10.1177/2055207619871729
11. Yang, Q, Xin, X, Wang, Y, Peng, D, and Tian, J. The impact of social support networks and self-efficacy on digital health literacy among urban and rural elderly. Bus Inf. (2022):0136–8.
12. Xiong, S, Lu, H, Peoples, N, Duman, EK, Najarro, A, Ni, Z, et al. Digital health interventions for non-communicable disease management in primary health care in low-and middle-income countries. NPJ Digit Med. (2023) 6:12. doi: 10.1038/s41746-023-00764-4
13. Li, S, Cui, G, Yin, Y, Wang, S, Liu, X, and Chen, L. Health-promoting behaviors mediate the relationship between eHealth literacy and health-related quality of life among Chinese older adults: a cross-sectional study. Qual Life Res. (2021) 30:2235–43. doi: 10.1007/s11136-021-02797-2
14. Bronfenbrenner, U. The ecology of human development: experiments by nature and design [M] Harvard University Press (1979).
15. Bronfenbrenner, U, and Ceci, SJ. Nature-nurture reconceptualized in developmental perspective: a bioecological model. Psychol Rev. (1994) 101:568–86. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.101.4.568
16. Schmiege, SJ, Masyn, KE, and Bryan, AD. Confirmatory latent class analysis: illustrations of empirically driven and theoretically driven model constraints. Organ Res Methods. (2018) 21:983–1001. doi: 10.1177/1094428117747689
17. Kui, Y, Jian, P, and Jun, Z. Application of latent profile analysis in the field of organizational behavior. Adv Psychol Sci. (2020) 28:1056–70. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01056
19. Ni, Y, and Zhang, J. How to determine permissible error δ value properly when computing sample sizes in hypothesis tests. J Evid Based Med. (2011) 11:370–2.
20. Bin, C. Sample size estimation for multivariate analysis design in medical research—a comprehensive estimation method for sample size in multivariate analysis design. Injury Med (Electron Ed). (2012) 1:58–60. doi: 10.3868/j.issn.2095-1566.2012.04.012
21. Nylund-Gibson, K, and Choi, AY. Ten frequently asked questions about latent class analysis. Transl Issues Psychol Sci. (2018) 4:440–61. doi: 10.1037/tps0000176
22. Xiao, S. Theoretical basis and research application of the social support rating scale. J Clin Psychiatry. (1994) 2:98–100.
23. Jiwen, L, Fuyue, L, and Yulong, L. Reliability and validity study of the social support rating scale. J Xinjiang Med Univ. (2008) 1:1–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2008.01.001
24. Kessler, RC, Barker, PR, Colpe, LJ, Epstein, JF, Gfroerer, JC, Hiripi, E, et al. Screening for serious mental illness in the general population. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2003) 60:184–9. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.60.2.184
25. Zhou, C, He, J, Xu, L, Sun, H, Zheng, W, Wang, X, et al. First application of Kessler 10 scale to measuring mental health status of the aged in China. Chin J Clin Psychol. (2009) 17:761–3. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2009.06.003
26. Zhou, C, Chu, J, Wang, T, Peng, Q, He, J, Zheng, W, et al. Reliability and validity of 10-item Kessler scale (K10) Chinese version in evaluation of mental health status of Chinese population. Chin J Clin Psychol. (2008) 16:627–9. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2008.06.026
27. Schwarzer, R, Bäßler, J, Kwiatek, P, Schröder, K, and Zhang, JX. The assessment of optimistic self-beliefs: comparison of the German, Spanish, and Chinese versions of the general self-efficacy scale. Appl Psychol. (1997) 46:69–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-0597.1997.tb01096.x
28. Wang, C, Hu, Z, and Liu, Y. Evidences for reliability and validity of the Chinese version of general self efficacy scale. Chin J Appl Psychol. (2001) 7:37–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6020.2001.01.007
29. Broadbent, E, Petrie, KJ, Main, J, and Weinman, J. The brief illness perception questionnaire. J Psychosom Res. (2006) 60:631–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2005.10.020
30. Sun, W, Lou, Q, Yuan, Y, Zou, Q, Dong, X, He, L, et al. Application of the simplified Chinese version of the illness perception questionnaire in patients with somatoform disorders. J Chongqing Med Univ. (2015) 40:1138–42. doi: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.000482
31. Koppie, TM, Serio, AM, Vickers, AJ, Vora, K, Dalbagni, G, Donat, SM, et al. Age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity score is associated with treatment decisions and clinical outcomes for patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Cancer. (2008) 112:2384–92. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23462
32. Charlson, M, Szatrowski, TP, Peterson, J, and Gold, J. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J Clin Epidemiol. (1994) 47:1245–51. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(94)90129-5
33. Meade, AW, and Craig, SB. Identifying careless responses in survey data. Psychol Methods. (2012) 17:437–55. doi: 10.1037/a0028085
34. Ward, MK, and Meade, AW. Dealing with careless responding in survey data: prevention, identification, and recommended best practices. Annu Rev Psychol. (2023) 74:577–96. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-040422-045007
35. Tang, D, and Wen, Z. Statistical approaches for testing common method bias: problems and suggestions. J Psychol Sci. (2020) 43:215–23. doi: 10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.20200130
36. Kline, RB. Becoming a behavioral science researcher: a guide to producing research that matters. 2nd ed. [M]. Guilford Press (2020).
37. Byrne, BM. Structural equation modeling with AMOS: basic concepts, applications, and programming. 3rd ed Routledge (2016).
38. Yang, Q, Xin, X, Li, X, and Zhang, L. The mediating effect of self-perceived aging between digital health literacy and technology anxiety in rural elderly. Modern Prevent Med. (2024) 51:471–5. doi: 10.20043/j.cnki.MPM.202309424
39. Yang, Q, Xin, X, Yang, J, Cao, J, Liu, C, Li, X, et al. The mediating effect of digital health literacy on the aging expectations and healthy aging of rural empty nest elderly. Modern Prevent Med. (2024) 51:2780–4. doi: 10.20043/j.cnki.MPM.202403037
40. Zhu, B, and Xu, Y. Research progress on social isolation in patients with chronic diseases. Gen Nurs. (2023) 21:1494–9. doi: 10.12104/ji.ssn.1674-4748.2023.11.013
41. Hu, M, and Xuan, H. Research on the online health information seeking behavior of elderly patients with chronic diseases based on grounded theory. Chinese Clin Nurs. (2020) 12:388–92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3768.2020.05.002
42. Estrela, M, Semedo, G, Roque, F, Ferreira, PL, and Herdeiro, MT. Sociodemographic determinants of digital health literacy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Med Inform. (2023) 177:105124. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2023.105124
43. Organization WH. Ageism in artificial intelligence for health: World Health Organization. (2022). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240040793 (Accessed February 9, 2022).
44. Papp-Zipernovszky, O, Horváth, MD, Schulz, PJ, and Csabai, M. Generation gaps in digital health literacy and their impact on health information seeking behavior and health empowerment in Hungary. Front Public Health. (2021) 9:635943. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.635943
45. Marzo, RR, Chen, HWJ, Abid, K, Chauhan, S, Kaggwa, MM, Essar, MY, et al. Adapted digital health literacy and health information seeking behavior among lower income groups in Malaysia during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:998272. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.998272
46. Zhao, BY, Huang, L, Cheng, X, Chen, TT, Li, SJ, Wang, XJ, et al. Digital health literacy and associated factors among internet users from China: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:908. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18324-0
47. Striberger, R, Zarrouk, M, Kumlien, C, and Axelsson, M. Illness perception, health literacy, self-efficacy, adherence and quality of life in patients with intermittent claudication - a longitudinal cohort study. BMC Nurs. (2023) 22:167. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01329-2
48. Lin, W, and Zhao, L. Digital health literacy and the resolution of anxiety in the elderly. J South China Normal Univ (Soc Sci Ed). (2022):72–83+206.
49. Tang, X, Guo, Y, Chen, X, Jie, CY, and Ying, ST. Status and influencing factors of technology anxiety in older adult patients with chronic diseases in a smart healthcare environment. Nurs Res. (2023) 37:3925–30. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2023.21.024
50. Zhu, Y, Song, Y, Wang, Y, Ji, H, Wang, D, Cai, S, et al. Relationships among patient activation, social support and online health information seeking of community-dwelling older adults living with coronary heart disease. J Adv Nurs. (2023) 79:161–9. doi: 10.1111/jan.15428
51. Shin, H, and Park, C. Social support and psychological well-being in younger and older adults: the mediating effects of basic psychological need satisfaction. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:1051968. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1051968
52. Mengiste, M, Ahmed, MH, Bogale, A, and Yilma, T. Information-seeking behavior and its associated factors among patients with diabetes in a resource-limited country: a cross-sectional study. Diab Metab Syndr Obes Targets Ther. (2021) 14:2155–66. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S289905
Keywords: older adult, chronic diseases, digital health literacy, influencing factors, latent profile analysis
Citation: Shao Y, Xu X, Guo H, Duan X, Zhang Z, Zhao S and Yang X (2025) Latent profile and determinants of digital health literacy among older adult patients with chronic diseases: a cross-sectional study. Front. Public Health. 13:1477314. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1477314
Edited by:
Steven Hoffman, Brigham Young University, United StatesReviewed by:
Orsolya Papp-Zipernovszky, University of Szeged, HungaryKen Wah Teo, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
Copyright © 2025 Shao, Xu, Guo, Duan, Zhang, Zhao and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiumu Yang, MDcwMDAxM0BiYm11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yujiao Shao
Yujiao Shao Xuejun Xu
Xuejun Xu Hongyan Guo2†
Hongyan Guo2† Xiaocui Duan
Xiaocui Duan Xiumu Yang
Xiumu Yang