- 1Department of Maternity, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2School of Health Science & Nursing, Wuhan Polytechnic University, Wuhan, China
Introduction: The health quotient (HQ) represents health awareness, health knowledge, and health ability. There are few studies on the HQ of women in the puerperium.
Methods: The convenience sampling method was used to select puerperium women.
Results: A total of 245 questionnaires were valid. The average scores of health awareness, health knowledge, and health ability of women were 15.0 ± 1.6 (maximum: 18), 26.6 ± 7.9 (maximum: 42), and 25.8 ± 5.3 (maximum: 33) points, respectively. The residence of rural (OR = 3.489, p = 0.018) and whether the perinatal caregiver was a nanny (OR = 2.538, p = 0.019) were independently associated with health awareness. The occupational status of on-the-job (OR = 2.573, p = 0.010) and whether the payment method was medical insurance (OR = 0.233, p = 0.048) were independently associated with health knowledge. The place of residence (OR = 3.090, p = 0.040) and parity ≥ 2 births (OR = 4.324, p = 0.001) were independently associated with health ability. The structural equation model showed that the maternal health knowledge had direct effects on maternal health ability (β = 0.316, p = 0.011) and baby health ability (β = 0.327, p = 0.029), the baby health knowledge directly affected the baby health ability (β = 0.462, p < 0.001), and the health awareness directly affected the maternal health ability (β = 0.569, p = 0.006).
Conclusion: Puerperium women had sufficient health awareness, suboptimal health knowledge, and suboptimal health ability. The residence, perinatal caregiver, occupational status, payment method, and parity were risk factors of HQ.
Introduction
The outline of the “Healthy China 2030” strategy pointed out that “the health problems of key groups such as women, children, the older adult, and the disabled should be highlighted to improve the health of the whole people” (1–5). Pregnant women represent a special population. Ensuring their physical and mental health reflects the quality of women’s healthcare work in China and will have repercussions on the physical and mental health of the children and the next generation of workers. Hence, improving the care of pregnant women and their children is a key measure to improve the overall quality of the nation.
The health quotient (HQ) was derived and developed based on the concept of health, reflecting the level of health awareness, health knowledge, and health ability of individuals or residents of a certain area (6, 7). In this study, health awareness captures personal perceptions and attitudes toward health and well-being; health knowledge refers to the individual’s understanding of health-related information and disease management; and health ability indicates practical skills related to maternal self-care and neonatal care. These domains align with the conceptual framework proposed by Wan et al. (8, 9).
HQ, like the intelligence quotient and emotional quotient, represents the basic health literacy of individuals, including self-care, health knowledge, health maintenance, and other aspects (6, 7). An important aspect of HQ is that it can be improved through the proper interventions (10–12). Maintaining HQ is beneficial for the self-management of patients with chronic conditions (6, 13). Studies have shown that introducing the concept of HQ into routine health education and nursing can fully mobilize the patients’ initiative, improve treatment compliance, and help patients rebuild a healthy lifestyle to promote and maintain health effectively (10–12, 14, 15).
The puerperium refers to the period from the end of childbirth to the time when all body organs (except the breast) gradually return to their pre-pregnancy state, which generally takes 6–8 weeks (14). The puerperium is an important period for the recovery of maternal organs and a critical period for the healthy growth of newborns (14, 15). Women in the puerperium are under great psychological pressure and hormonal changes and are prone to a sense of a lack of competence in their role as mothers, which can have a huge adverse impact on parenting health and family relationships (16–18). The HQ level of women in the puerperium period is of great significance to the health management of infants and the rehabilitation of mothers after childbirth (8). Still, there are few studies on the HQ of women in the puerperium. A better understanding of the HQ of such women is necessary to improve postpartum care and management and the health of mothers and their children.
Therefore, this study examined the HQ level of puerperium women. The results should provide a theoretical basis for the future development of puerperium health education and related interventions.
Materials and methods
Study design and participants
This study is based on the master’s thesis of Wan Shenxian, which involved the development and initial validation of the Postpartum Women Health Quotient Scale (PWHQS) (9). The present study further examines the scale’s applicability in a broader sample of puerperal women and explores the associated influencing factors.
The cross-sectional study included puerperium women by convenience sampling in the author’s Hospital between September 2020 and December 2020. This study was reviewed by the Medical Ethics Committee of the author’s Hospital. All participants signed the study informed consent form.
The inclusion criteria were (1) puerperium women, (2) ≥ 18 years of age, (3) able to communicate in writing or language, express thoughts clearly, and cooperate in completing the questionnaire, and (4) patients and their families gave informed consent and participated voluntarily. The exclusion criteria were (1) serious concomitant diseases, such as acute respiratory failure or (2) those who requested participation termination during the investigation.
Data collection
The general information questionnaire was designed by the research team to collect maternal age, education, occupational status, place of residence, income, healthcare payment method, preterm birth, parity, mode of delivery, complications during pregnancy, etc.
The HQ was assessed using the PWHQS scale, which includes 31 items covering five original subdimensions (9). In the original validation study, the scale demonstrated high internal consistency with a Cronbach’s α coefficient of 0.908 and strong content validity, with a scale-level content validity index (S-CVI) of 0.939 (9).
For the purposes of this study, the original five subdimensions were reorganized into three dimensions: health awareness (6 items), health knowledge (14 items, combining maternal and infant health knowledge), and health ability (11 items, combining maternal and infant health ability). The original item content remained unchanged. Each item is graded using a Likert-4 scoring. The score of each dimension is the sum of the corresponding item scores, and the total score of the scale is 93 points. Each dimension was divided into a high-score group and a low-score group according to the score (above or below the average for each dimension). A higher score represents higher HQ levels.
Before the formal survey, the convenience sampling method was adopted, and 30 puerperium women were selected for pre-survey. After a 2-week interval, the same survey method was used to conduct a second survey on the same group of subjects. Correlation analysis was used, the test–retest reliability of the two surveys was calculated, and the results showed that the r was 0.947. The Cronbach’s α coefficients of the total items of the questionnaire and health awareness, health knowledge, and health ability were 0.908, 0.914, 0.892, and 0.934, respectively, indicating that the questionnaire had good reliability.
Quality control
The inventory survey was carried out in strict accordance with the research plan. The personnel participating in the questionnaire survey were uniformly trained. Before issuing the questionnaires, the research purpose, content, and filling requirements were explained to the research subjects, and the informed consent form was signed to ensure the confidentiality of the data. The investigators distributed the questionnaires in person and collected them on the spot. The input data were double-checked.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 23.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for data analysis. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used for testing the continuous variables for normal distribution. The continuous variables were presented as means ± standard deviation. The categorical variables were expressed as n (%). The correlations between the dimensions of HQ were analyzed using the Spearman rank correlation. The influencing factors of each dimension of HQ were analyzed by multivariable logistic regression, and a forest plot was drawn. The results were expressed using the adjusted odds ratio (OR) and the corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI). A structural equation model (SEM) analysis was performed to examine how each dimension influenced each other; the hypotheses were that health knowledge directly influenced health awareness and ability, while health awareness directly influenced health ability. Two-sided p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
General information of the participants
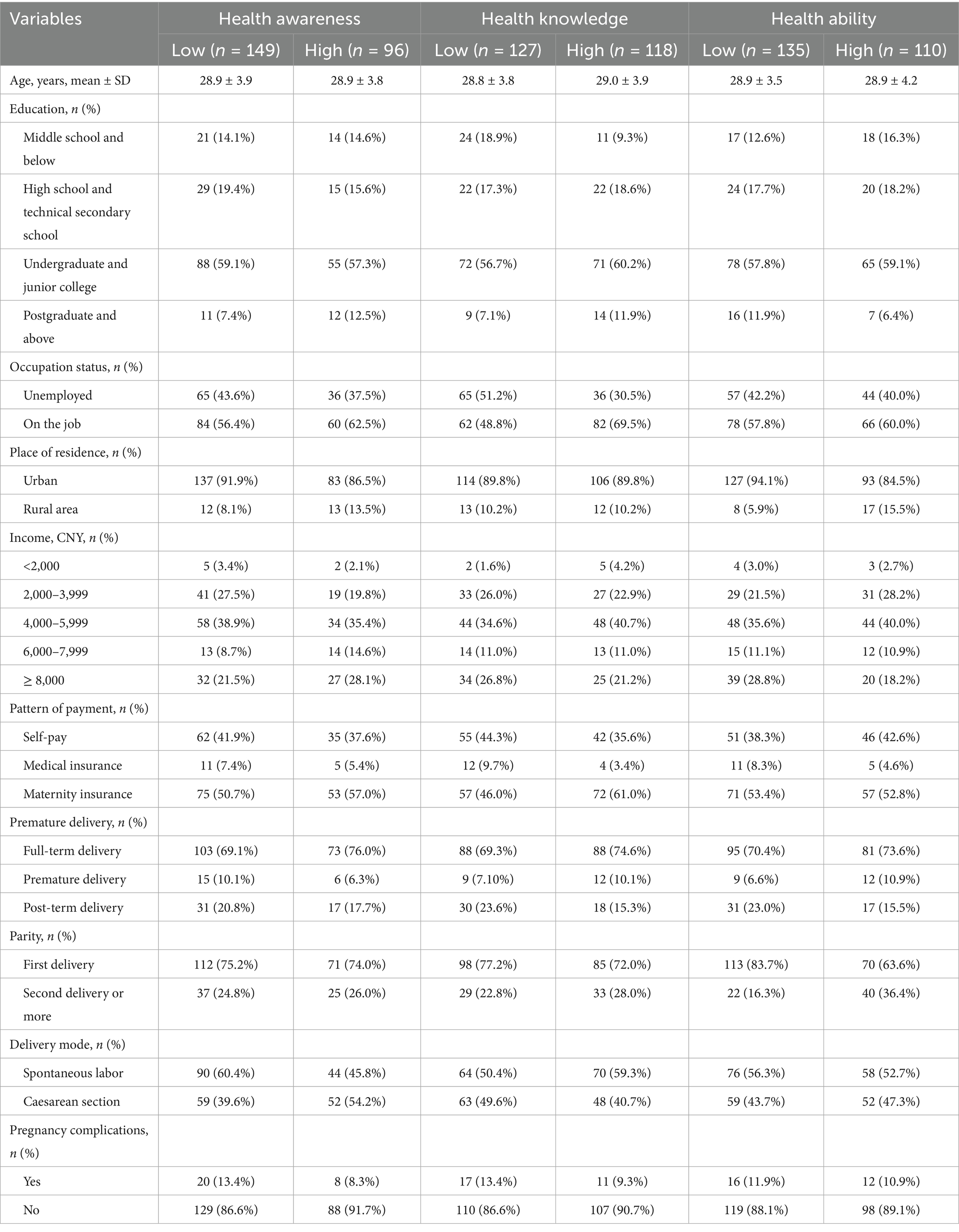
A total of 250 questionnaires were distributed, 245 valid questionnaires were retrieved, and the effective retrieval rate was 98.0%. The participants were 28.9 ± 3.8 years old, 143 (58.4%) had undergraduate and junior college education, and 23 (9.4%) had a master’s degree or above. About 90 and 10% of puerperal lived in urban and rural areas, respectively, and 8.6 and 19.6% of newborns were born premature and post-term, respectively. There were 134 (54.7%) and 111 (45.3%) mothers who delivered spontaneously and by cesarean section, respectively. There were 28 cases of maternal complications during pregnancy, accounting for 11.4%. The average scores of health awareness, health knowledge, and health ability of all subjects were 15.0 ± 1.6, 26.6 ± 7.9, and 25.8 ± 5.3, respectively. The general information of the participants is shown in Table 1.
Correlation analysis between dimensions of health quotient
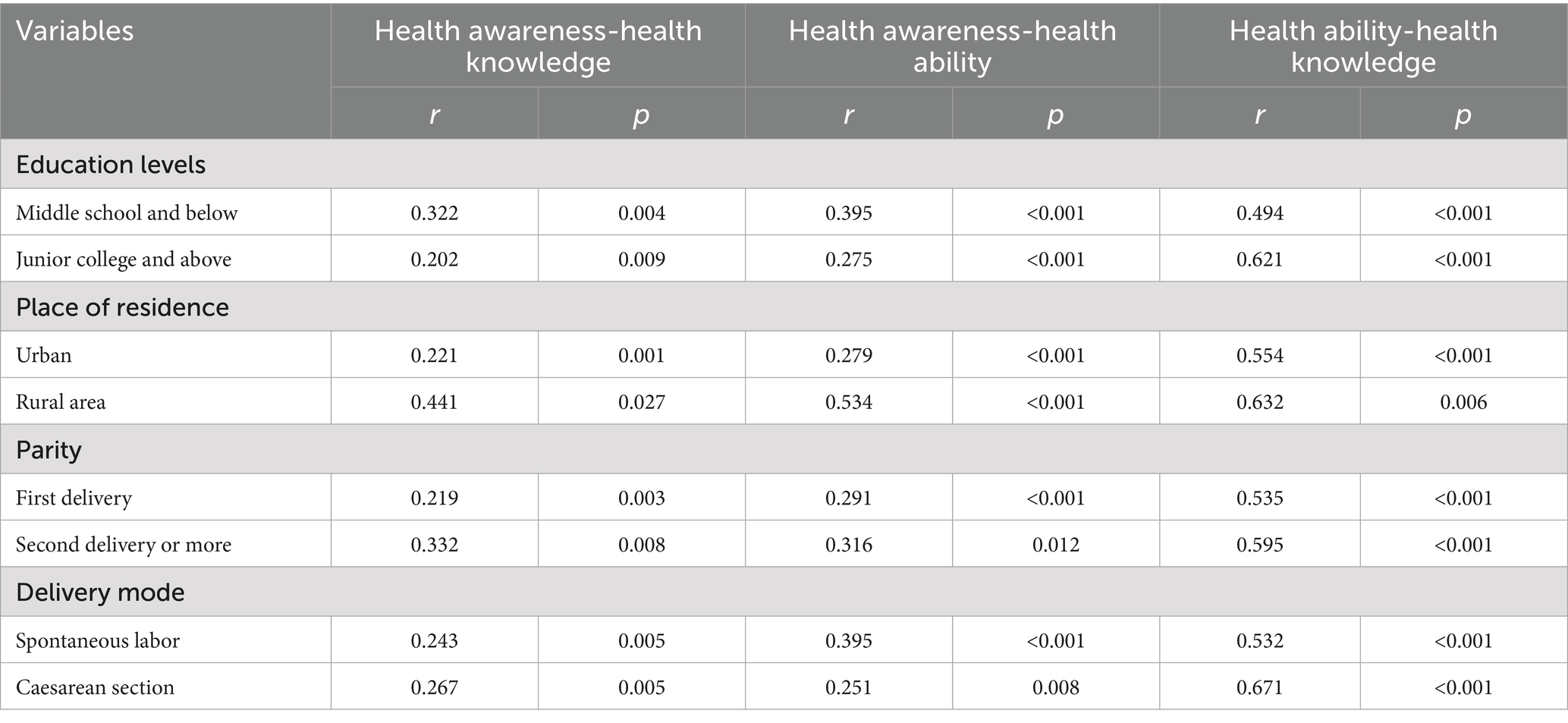
Spearman rank correlation was used to analyze the correlation between the various dimensions of HQ levels. There was a moderate correlation between health ability and health knowledge, while there was a weak correlation between health awareness and health knowledge, as well as between health awareness and health ability. To further explore subgroup differences, stratified Spearman correlation analyses were conducted. As shown in Table 2, women with a junior college education or above exhibited a stronger correlation between health ability and health knowledge (r = 0.621, p < 0.001) compared to those with a high school education or below (r = 0.494, p < 0.001). Similarly, urban residents demonstrated stronger interdimensional correlations than rural residents. The correlation between health ability and health knowledge was also stronger in women who delivered by cesarean section (r = 0.671, p < 0.001) compared to those with natural delivery (r = 0.532, p < 0.001). These findings are detailed in Table 2.
Risk factors of health quotient levels
The residence of rural (OR = 3.489, 95%CI: 1.234–9.864, p = 0.018) and whether the perinatal caregiver was a nanny (OR = 2.538, 95%CI: 1.165–5.530, p = 0.019) were independently associated with health awareness: mothers whose residence was in rural areas or whose caregiver was a nanny had lower health awareness. The occupational status of on-the-job (OR = 2.573, 95%CI: 1.255–5.276, p = 0.010) and whether the payment method was medical insurance (OR = 0.233, 95%CI: 0.055–0.989, p = 0.048) were independently associated with health knowledge: the puerperal on the job had lower health knowledge score, and the puerperal with the payment method of medical insurance had higher health knowledge score. The residence of rural (OR = 3.090, 95%CI: 1.052–9.075, p = 0.040) and parity ≥ 2 births (OR = 4.324, 95%CI: 1.864–10.031, p = 0.001) were independently associated with health ability: the puerperal living in rural areas had lower health ability score than those in urban areas, and the puerperal para >2 had lower health ability scores than women with a first parity (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Forest plot of the influencing factors of (A) health awareness, (B) health knowledge, and (C) health ability.
Structural equation model analysis
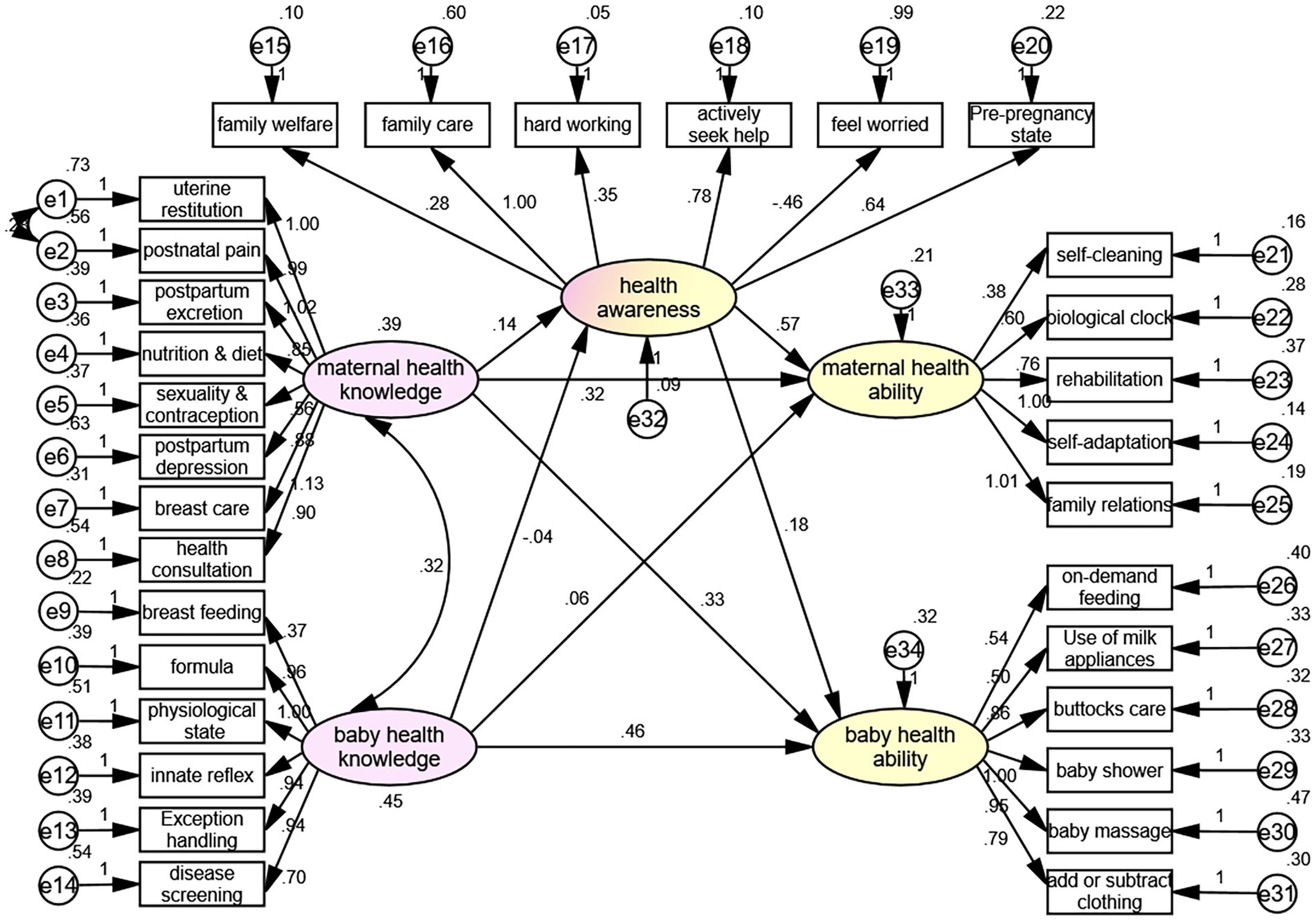
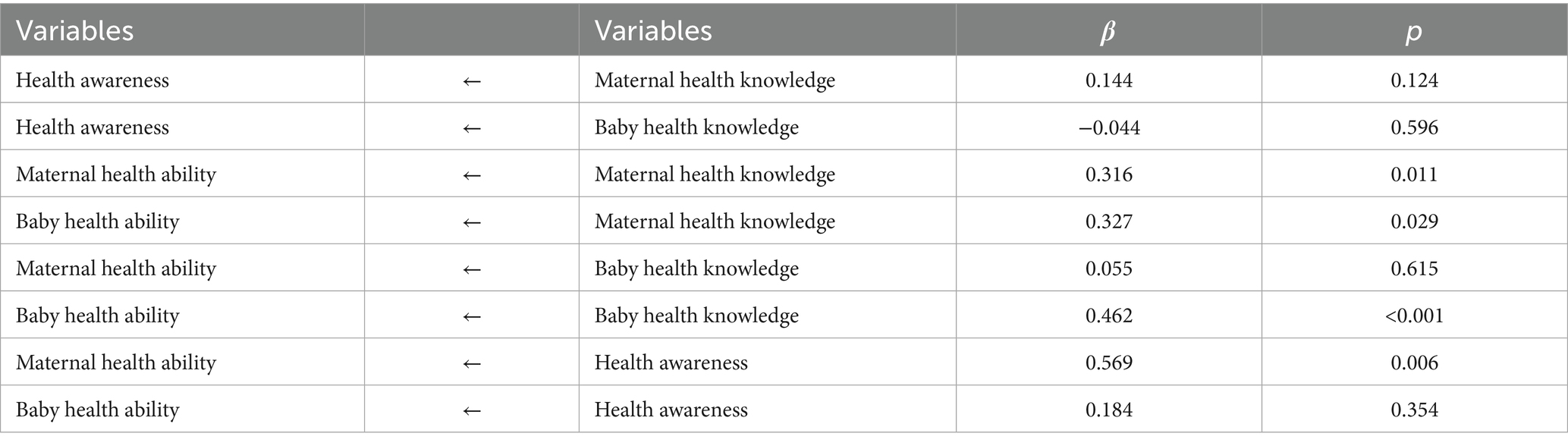
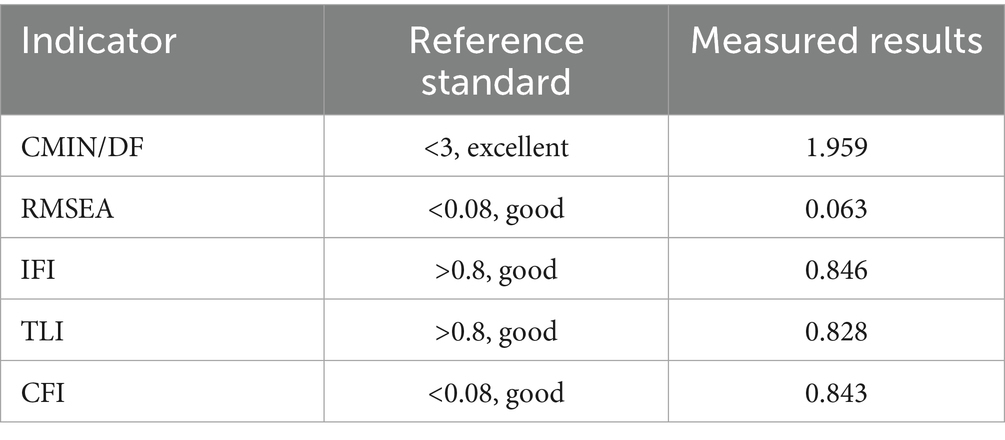
The SEM showed that the maternal health knowledge had direct effects on maternal health ability (β = 0.316, p = 0.011) and baby health ability (β = 0.327, p = 0.029), the baby health knowledge directly affected the baby health ability (β = 0.462, p < 0.001), and the health awareness directly affected the maternal health ability (β = 0.569, p = 0.006) (Figure 2, Table 3). Table 4 shows that the fit of the SEM was good.
Discussion
The results suggested that the HQ of puerperal women was intermediate, consistent with previous findings indicating that health literacy among pregnant women in China remains suboptimal (18–22). The present study identified key risk factors affecting HQ, including residence, perinatal caregiver type, occupational status, payment method, and parity. These findings align with previous research using the original PWHQS, which also emphasized the significant influence of socioeconomic factors on HQ levels (18, 23).
Most women have insufficient or lack maternal and child healthcare knowledge and nursing ability during the puerperium, especially primiparas, whose poor physical condition, hormonal changes, and psychological problems seriously affect their health and can also bring negative effects on the growth and development of newborns (15–17, 19, 20). The present study showed that the levels of health awareness, health knowledge, and health ability were interrelated, and positive correlations existed among these dimensions. Specifically, health knowledge was found to directly affect both maternal health ability (β = 0.316, p = 0.011) and baby health ability (β = 0.327, p = 0.029). This finding is in line with Wang Zhenzhen, who reported that infant-related health knowledge positively influences puerperal women’s HQ through infant-related health ability (19).
Furthermore, our study revealed that health awareness also directly influenced maternal health ability (β = 0.569, p = 0.006), a finding that extends previous literature by emphasizing the importance of health awareness in maternal self-care capacity. However, the correlation between health awareness and health knowledge was relatively weak, indicating that having health knowledge does not necessarily translate into heightened health awareness, particularly among women with lower educational backgrounds.
The residence of rural areas and having a nanny as a perinatal caregiver were independently associated with lower health awareness. This finding is consistent with Wan et al. and Wang Rong, who also found that urban residency and higher educational attainment are associated with better HQ levels (9, 23). The lower health awareness among women with nannies may reflect the delegation of maternal responsibilities to caregivers, potentially reducing the mother’s health management engagement.
In contrast, our study uniquely identified occupational status as a significant factor affecting health knowledge. Employed women demonstrated lower health knowledge scores compared to unemployed women, which may be attributable to the limited time and resources available for health education among working women. Previous studies have not emphasized this association, suggesting a new perspective for targeting health education interventions for employed mothers. Moreover, the present study highlighted that the payment method also impacted health knowledge. Women using medical insurance exhibited higher health knowledge scores, possibly due to greater access to health resources and educational materials associated with insurance coverage. This is a novel finding, as previous research primarily focused on educational and social factors without considering economic access as a determinant of health knowledge.
Parity was another significant factor affecting health ability, with women having two or more births showing lower health ability scores compared to primiparas. This is contrary to Wang et al., who reported that increased parity was associated with higher self-care ability due to accumulated maternal experience (23). However, our findings suggest that multiple births may impose a heavier physical and psychological burden on mothers, potentially reducing their capacity for effective health management.
The identification of risk factors and the interrelationship among health awareness, knowledge, and ability provide valuable insights for targeted health education programs. To improve HQ levels, specific attention should be given to women in rural areas, those with multiple births, and working mothers, as these subgroups are more likely to exhibit lower HQ scores. Additionally, integrating HQ-focused health education into digital platforms and community outreach programs could further enhance health literacy among postpartum women (24).
This study had limitations. Participants were recruited from a single tertiary hospital using a convenience sampling method, which may limit the generalizability of the results and introduce potential selection bias. Future studies should consider recruiting larger, more diverse samples across multiple centers to enhance external validity. Psychological factors such as depression and anxiety, which are common during the postpartum period and may influence health behaviors and self-management ability, were not assessed in this study. The absence of such measures may limit a more comprehensive understanding of the determinants of HQ. Future studies should consider incorporating validated psychological assessments to explore the potential mediating or moderating effects of mental health on HQ levels. Additional longitudinal data will also be helpful in identifying temporal relationships and designing more targeted interventions.
Conclusion
The health knowledge, health awareness, and health ability of puerperium women were positively correlated. The HQ levels of women during the puerperium were affected by the place of residence, caregiver, employment status, payment method, and parity. The SEM showed that maternal health knowledge directly affected maternal health ability and baby health ability, baby health knowledge directly affected the baby health ability, and health awareness directly affected the maternal health ability. Hence, improving knowledge is important.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Henan Provincial People’s Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
ZW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RN: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Joint Construction Project of Henan Provincial Medical Science and Technology Research Program; Risk factors analysis and prediction model construction of postpartum depression in Zhengzhou (LHGJ20220082) and Study on EIF1B AS1/miR-320/ULK1 regulatory Axis in the Pathogenesis and Diagnosis of Preeclampsia (Project No.: LHGJ20200050).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Dong, B, Zou, Z, Song, Y, Hu, P, Luo, D, Wen, B, et al. Adolescent health and healthy China 2030: a review. J Adolesc Health. (2020) 67:S24–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.07.023
2. Gao, C, Xu, J, Liu, Y, and Yang, Y. Nutrition policy and healthy China 2030 building. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2021) 75:238–46. doi: 10.1038/s41430-020-00765-6
3. Jiang, Z, and Jiang, W. Health education in the healthy China initiative 2019-2030. China CDC Wkly. (2021) 3:78–80. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2021.018
4. Tan, X, Liu, X, and Shao, H. Healthy China 2030: a vision for health care. Value Health Reg Issues. (2017) 12:112–4. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2017.04.001
5. Tan, X, Zhang, Y, and Shao, H. Healthy China 2030, a breakthrough for improving health. Glob Health Promot. (2019) 26:96–9. doi: 10.1177/1757975917743533
6. Guo, J, Whittemore, R, and He, GP. Factors that influence health quotient in Chinese college undergraduates. J Clin Nurs. (2010) 19:145–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2009.03044.x
7. Michie, S, Richardson, M, Johnston, M, Abraham, C, Francis, J, Hardeman, W, et al. The behavior change technique taxonomy (v1) of 93 hierarchically clustered techniques: building an international consensus for the reporting of behavior change interventions. Ann Behav Med. (2013) 46:81–95. doi: 10.1007/s12160-013-9486-6
8. Wan, SX, Li, HL, Wang, W, Shen, Q, Li, CH, Lyon, ME, et al. Psychometric properties of the postpartum women health quotient scale among Chinese post partum women. Midwifery. (2016) 39:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2016.04.004
9. Wan, SX, Li, HL, and Wang, W. The establishment of the puerperium women's health consultation scale and its reliability and validity test. PLA Nurs J. (2015) 32:27–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9993.2015.06.007
10. Michie, S, Abraham, C, Whittington, C, McAteer, J, and Gupta, S. Effective techniques in healthy eating and physical activity interventions: a meta-regression. Health Psychol. (2009) 28:690–701. doi: 10.1037/a0016136
11. Michie, S, Hyder, N, Walia, A, and West, R. Development of a taxonomy of behaviour change techniques used in individual behavioural support for smoking cessation. Addict Behav. (2011) 36:315–9. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2010.11.016
12. Michie, S, Whittington, C, Hamoudi, Z, Zarnani, F, Tober, G, and West, R. Identification of behaviour change techniques to reduce excessive alcohol consumption. Addiction. (2012) 107:1431–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.03845.x
13. Stein, AD, Shakour, SK, and Zuidema, RA. Financial incentives, participation in employer-sponsored health promotion, and changes in employee health and productivity: health plus health quotient program. J Occup Environ Med. (2000) 42:1148–55. doi: 10.1097/00043764-200012000-00005
14. Chauhan, G, and Tadi, P. Physiology, postpartum changes. Treasure Island (FL): Stat Pearls (2022).
15. Lopez-Gonzalez, DM, and Kopparapu, AK. Postpartum care of the new mother. Treasure Island (FL): Stat Pearls (2022).
16. Mughal, S, Azhar, Y, and Siddiqui, W. Postpartum Depression. Treasure Island (FL): Stat Pearls (2022).
17. Mughal, S, Azhar, Y, Siddiqui, W, and May, K. Postpartum depression (nursing). Treasure Island (FL): Stat Pearls (2022).
18. Schiller, CE, Meltzer-Brody, S, and Rubinow, DR. The role of reproductive hormones in postpartum depression. CNS Spectr. (2015) 20:48–59. doi: 10.1017/S1092852914000480
19. Badr, HA, and Zauszniewski, JA. Meta-analysis of the predictive factors of postpartum fatigue. Appl Nurs Res. (2017) 36:122–7. doi: 10.1016/j.apnr.2017.06.010
20. Almalik, MM. Understanding maternal postpartum needs: a descriptive survey of current maternal health services. J Clin Nurs. (2017) 26:4654–63. doi: 10.1111/jocn.13812
21. Zhou, YL, Liu, W, Li, Y, Qin, Y, Li, RJ, Yu, LL, et al. Establishment of nutrition literacy core items for Chinese pregnant women. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2020) 54:1081–1086. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20200327-00453
22. Hai, Y, Wu, WL, Yu, LW, and Wu, L. Health literacy and health outcomes in China\u0027s floating population: mediating effects of health service. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21:691. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10662-7
23. Wang, R, Tan, LL, Liao, DH, Tang, CX, and Wu, YP. Current status and influencing factors of health quotient in puerperium women. Modern Nurse. (2018) 25:40–43.
Keywords: puerperium, women, health quotient, inventory survey, fluencing factors
Citation: Wang Z, Nie R, Zhang Q, Zhou L, Zhao C and Cheng X (2025) Health quotient of puerperal women: a retrospective observational study. Front. Public Health. 13:1537392. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1537392
Edited by:
Mohammad Ali Zakeri, Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences, IranReviewed by:
Edwin Castillo Velarde, Hospital Base Guillermo Almenara Irigoyen, PeruAmin Hassanshahi Raviz, Bam University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Nie, Zhang, Zhou, Zhao and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xianghong Cheng, Y2hlbmd4aWFuZ2hvbmc2NjZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Zhenzhen Wang1
Zhenzhen Wang1 Rong Nie
Rong Nie Liping Zhou
Liping Zhou