- 1Department of Clinical Psychology, The Third People’s Hospital of Foshan, Foshan, Guangdong, China
- 2Department of Public Health, The Third People’s Hospital of Foshan, Foshan, Guangdong, China
- 3Xinshi Hospital of Gaoming District, Foshan, Guangdong, China
Background: Mental health literacy (MHL) is essential for enhancing mental well-being and addressing mental health challenges. In China, MHL levels remain low, and studies on gender differences in MHL are limited. This study aims to explore gender-specific differences in MHL and their influencing factors among residents of Foshan City, China, to provide a theoretical basis for targeted mental health interventions.
Methods: Data for this study were obtained from the 2022 Foshan City Residents’ Mental Health Survey. A comprehensive sample of 9,044 participants over 18 years old was included, collecting information on sociodemographic characteristics, lifestyle habits, health-related factors, and MHL assessments. Chi-square (χ2) tests and independent samples t-tests were used to analyze gender differences in MHL. Additionally, multi-factor logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify factors influencing MHL across genders.
Results: The overall MHL attainment rate was 8.46%. Male residents demonstrated a significantly lower attainment rate of 6.65%, compared to 10.14% among female residents. Across specific dimensions, including mental health knowledge, attitudes, and psychological skills, males consistently exhibited lower levels of MHL than females. Multi-factor logistic regression analysis identified protective factors for male MHL, including higher educational attainment, professional technical occupations, and retirement, while depression emerged as a significant risk factor. For females, protective factors included higher education, higher monthly household income, and engaging in exercise 3 to 5 times per week. Risk factors for females included being middle-aged or older and experiencing depression.
Conclusion: The MHL levels among residents of Foshan City are relatively low, with notable gender differences, particularly with males exhibiting significantly lower levels compared to females. These findings highlight the ongoing necessity to enhance the dissemination and accessibility of mental health knowledge. When developing relevant policies as well as measures, it is imperative to take into account gender differences and implement tailored programs aimed at enhancing MHL among both male and female residents.
Introduction
According to the 2019 report published by the World Health Organization, approximately 970 million people worldwide suffer from mental disorders, accounting for 13% of the global population (1). In China, it is reported that the weighted lifetime prevalence of various mental disorders among individuals aged 18 and above stands at an alarming rate of 16.57% (2). Mental disorders consistently rank as the second leading cause of Years Lived with Disability (YLDs) globally, emphasizing the urgent need for effective intervention strategies (3).
Among the various strategies to address this challenge, enhancing public mental health literacy (MHL) is regarded as one of the key factors in promoting mental well-being and preventing mental disorders (4, 5). MHL, defined as the capacity to effectively apply knowledge, skills, and attitudes related to mental health in order to maintain psychological well-being, plays a vital role in improving mental health outcomes (6–9). It encompasses not only the recognition, management, and prevention of mental disorders, but also an understanding of how to promote and sustain positive mental health (10). Higher levels of MHL are associated with earlier detection of mental health problems, reduced stigma, and increased likelihood of seeking timely and effective support, all of which contribute to improved mental health outcomes (11, 12). However, low levels of MHL remain a global challenge (13, 14). A meta-analysis found that the recognition rates for depression (25.4%), anxiety disorders (18.2%), and schizophrenia (18.4%) among the Chinese general population are alarmingly low (15). While most respondents agreed that professional help is necessary, fewer than 40% had actually utilized mental health services, and over 60% viewed psychiatric medications as harmful (15). Similar trends have been observed in other countries, where stigma and misconceptions surrounding mental illness remain pervasive (16–18).
Gender differences in mental disorders are well-documented, with females generally exhibiting higher rates of depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (19–21), while males are more likely to suffer from substance use disorders and antisocial behaviors (22, 23). And for females, they exhibit higher prevalence rates of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety disorders. A 2019 global study estimated that approximately 279.6 million people worldwide were affected by depressive disorders, including 109.2 million males and 170.4 million females (3). Anxiety disorders affected an estimated 301.4 million individuals globally, with 113.9 million males and 187.5 million females impacted (3). A recent meta-analysis also revealed that COVID-19 related fear and anxiety were more prevalent in females (24). Moreover, an epidemiological study in China found that from 1990 to 2021, the burden of depression and anxiety disorders continued to rise, with females exhibiting higher incidence rates and greater disease burden compared to males (25). These disparities are shaped by a combination of biological factors, such as hormonal differences, and sociocultural influences, including gender role expectations and exposure to violence, all of which disproportionately affect females (26).
Given the well-established association between MHL and mental health outcomes, gender differences in MHL may partly explain the observed gender disparities in mental health and mental disorders. MHL influences individuals’ ability to recognize symptoms, seek professional help, and manage psychological conditions effectively (27). These factors may contribute to the differences in how males and females experience and address mental health challenges (27).
In general, females tend to exhibit higher MHL levels than males. Prior evidence suggests that females are more likely to accurately recognize mental disorders, such as anxiety and depressive disorder (28, 29). Neuroimaging research indicates that these gender differences in recognition abilities may stem from higher neural activation in brain regions associated with emotion recognition in females (30). On the other hand, males are often less likely to seek professional help, are more prone to endorse alternative remedies, and exhibit higher levels of stigma toward mental illnesses (28, 31, 32). Cultural influences also play a significant moderating role in MHL. For instance, a study has shown that Arab males demonstrate superior knowledge, more positive attitudes, and a greater willingness to seek help for mental disorders compared to females, suggesting that gender differences in MHL are not universally consistent but rather shaped by cultural contexts (33). Despite these findings, most studies on gender differences in MHL have been conducted in Western contexts, with limited localized studies in China. Therefore, gender-specific differences in MHL within the Chinese population remain unclear.
In this study, we aim to comprehensively analyze gender differences in MHL and identify the factors that influence MHL in males and females, using data sourced from the 2022 Foshan City Residents’ Mental Health Survey. By investigating the distinct characteristics of gender differences in MHL within the Chinese context, this research endeavors to establish a foundation for formulating more targeted public health policies and mental health intervention strategies (7).
Materials and methods
Study population
The 2022 Foshan City Residents’ Mental Health Survey was conducted from June 2022 to October 2022. The survey participants were permanent residents of Foshan. The inclusion criteria for the survey encompassed individuals aged above 18 years, residing in Foshan for more than 6 months, and capable of understanding the questionnaire content and cooperating with the survey. Exclusion criteria included those unable to communicate effectively or comprehend the questionnaire due to cognitive impairments, mental disorders, or severe physical illnesses, as well as individuals who could not be located after at least three follow-up visits conducted at different times.
Sample size and sampling method
The sample size was calculated using the formula: , where the significance level of α = 0.05, μα = 1.96, p = 2.1% [the baseline prevalence of major depressive disorder outlined in the “Healthy China Action (2019–2030)”], δ = 0.024 (allowable error, calculated as 0.2p), and deff = 2 (design effect). The calculated sample size resulted in an approximate value of N = 8,954.
The survey employed a multi-stage stratified random sampling method. In the first stage, the five districts of Foshan City were stratified based on their financial revenue and expenditure status. Within each stratum, a specific number of villages or residents’ committees were chosen, taking into account their population size, leading to a total of 89 villages or residents’ committees being selected as the primary sampling units for the survey. In the second stage, within the selected villages or residents’ committees, households that were empty, commercial establishments, or had invalid addresses were excluded. The remaining households were subsequently numbered based on their door numbers, and a systematic sampling approach was conducted to determine both the starting point and the interval. This resulted in the selection of 105 households from each village or residents’ committee. In the third stage, all eligible adult residents from the sampled households were registered, and subsequently, one individual from each household was randomly selected to participate in the survey. After securing informed consent from the selected individuals, trained investigators assisted the participants in scanning a QR code on their mobile phones to access the electronic questionnaire on the Foshan City Mental Health Service Platform. For those participants who were unable to use mobile devices, paper questionnaires or face-to-face interviews were provided as alternative methods.
Data collection
The survey consisted mainly of socio-demographic data and questionnaire data. The former includes gender, age, education level, marital status, occupation, income, exercise frequency, diet, smoking habits, drinking habits, as well as the presence of chronic diseases. The latter includes assessments of MHL, depression, anxiety, and insomnia.
Mental health literacy was evaluated using the National Mental Health Literacy Questionnaire (NMHLQ), which comprises three distinct sections. The first section contains judgment questions to assess participants’ knowledge of mental health. The second section includes self-assessment questions aimed at assessing their positive mindset, acquisition of mental health information, as well as awareness of mental health issues. The third section features case-based questions designed to measure participants’ recognition of mental disorders, their ability to overcome stigma, and their attitudes toward seeking professional help. The measurement standards for the three dimensions of MHL are as follows: (1) a total score of 80 or above on the judgment questions; (2) a total score of 24 or above on the self-assessment questions; (3) a total score of 28 or above on the case questions. MHL is considered attainment only when all three criteria are met. The detailed content and scoring criteria of the NMHLQ have been previously described in a study (34).
The Chinese version of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) was utilized to assess depression. This questionnaire comprises 9 self-reported items, with each item scored on a scale from 0 to 3 points. The total score ranges from 0 to 27, and a score of 10 or above is considered indicative of current depression (35). The Chinese version of the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) was employed to evaluate anxiety. This questionnaire includes 7 self-reported items, with each item scored from 0 to 4 points. The total score ranges from 0 to 21, with a score of 10 or above being indicative of current anxiety (36). The Chinese version of the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) was used to assess insomnia. This questionnaire consists of 7 self-reported items, with each item scored on a scale from 0 to 4 points. The total score ranges from 0 to 28, and a score of 8 or higher is considered to indicate the presence of current insomnia (37).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 25.0. Measurement data were presented as Mean ± SD, and comparisons between groups were conducted using independent samples t-test. Count data were expressed as frequencies and percentages, with inter-group comparisons conducted using chi-square tests (χ2). Initially, univariate analysis was conducted to screen for potential factors associated with MHL levels. Subsequently, multivariate logistic regression analysis was employed to identify the influencing factors of MHL. The statistical significance level was set at α = 0.05 (two-tailed).
Results
Comparison of socio-demographic data, lifestyle, and health-related factors between male and female residents
A total of 9,251 questionnaires were initially completed in this survey, but 207 of them were deemed invalid and were therefore excluded. Ultimately, 9,044 valid responses were obtained, resulting in an effective response rate of 97.76%. Among the respondents, 4,359 (48.20%) were male, while 4,685 (51.80%) were female. Table 1 displays the variations in socio-demographic characteristics and health-related factors between male and female participants.
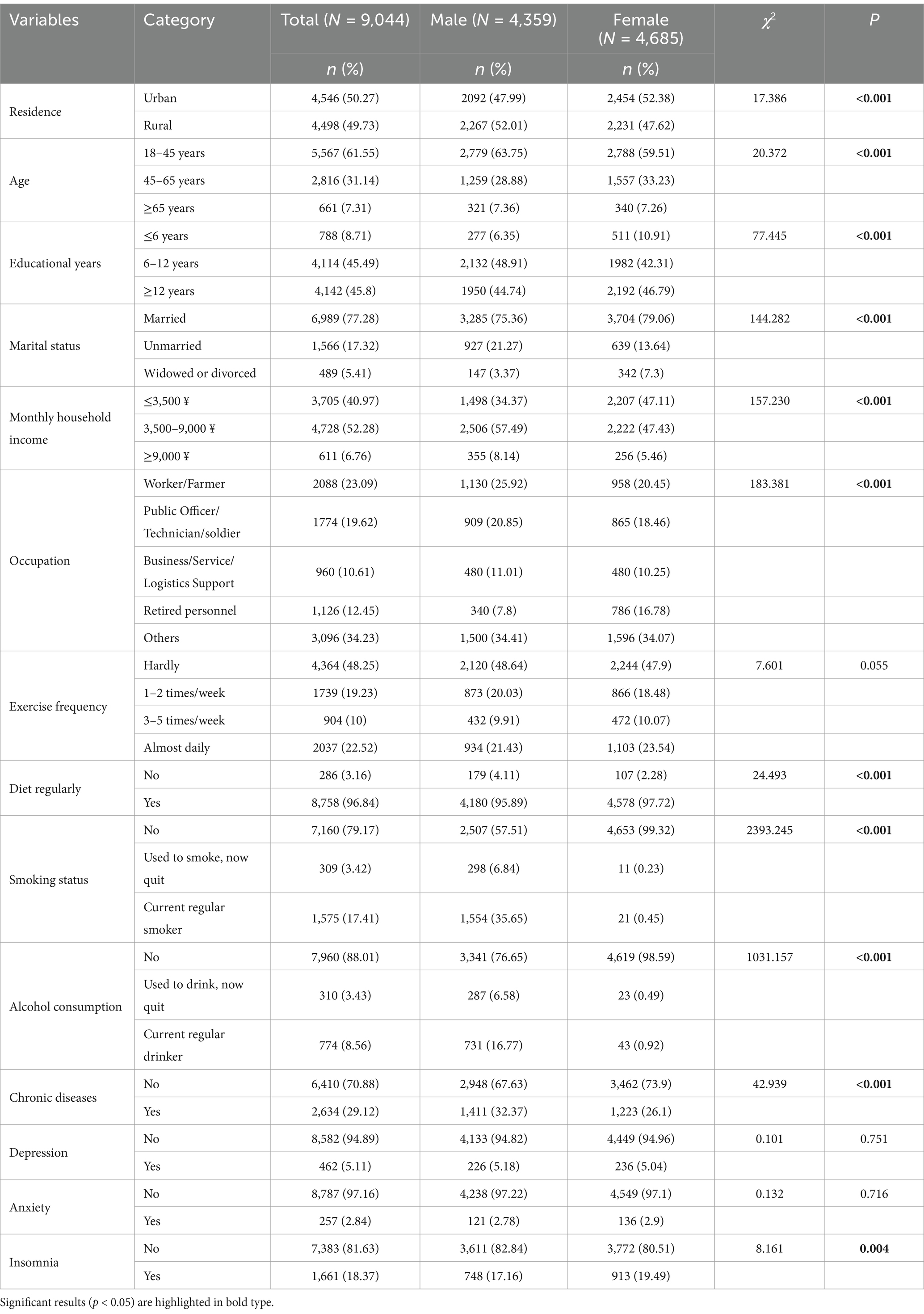
Table 1. Gender differences in socio-demographic information, lifestyle, and health-related factors.
No statistically significant differences were observed between males and females in terms of exercise frequency, anxiety levels, or depression. However, compared to their male counterparts, females were found to have a higher proportion of urban residents, individuals in the middle-age bracket, and retirees. Conversely, males were found to have a higher proportion of individuals with a moderate level of education, an unmarried status, and a higher average monthly household income. Furthermore, gender differences in lifestyle were noted, with females exhibiting healthier habits. Specifically, a higher proportion of females had regular dietary patterns and lower rates of smoking and drinking compared to males. Conversely, males were more likely to report chronic diseases, while females reported a higher incidence of insomnia (Table 1).
Comparison of mental health knowledge between male and female residents
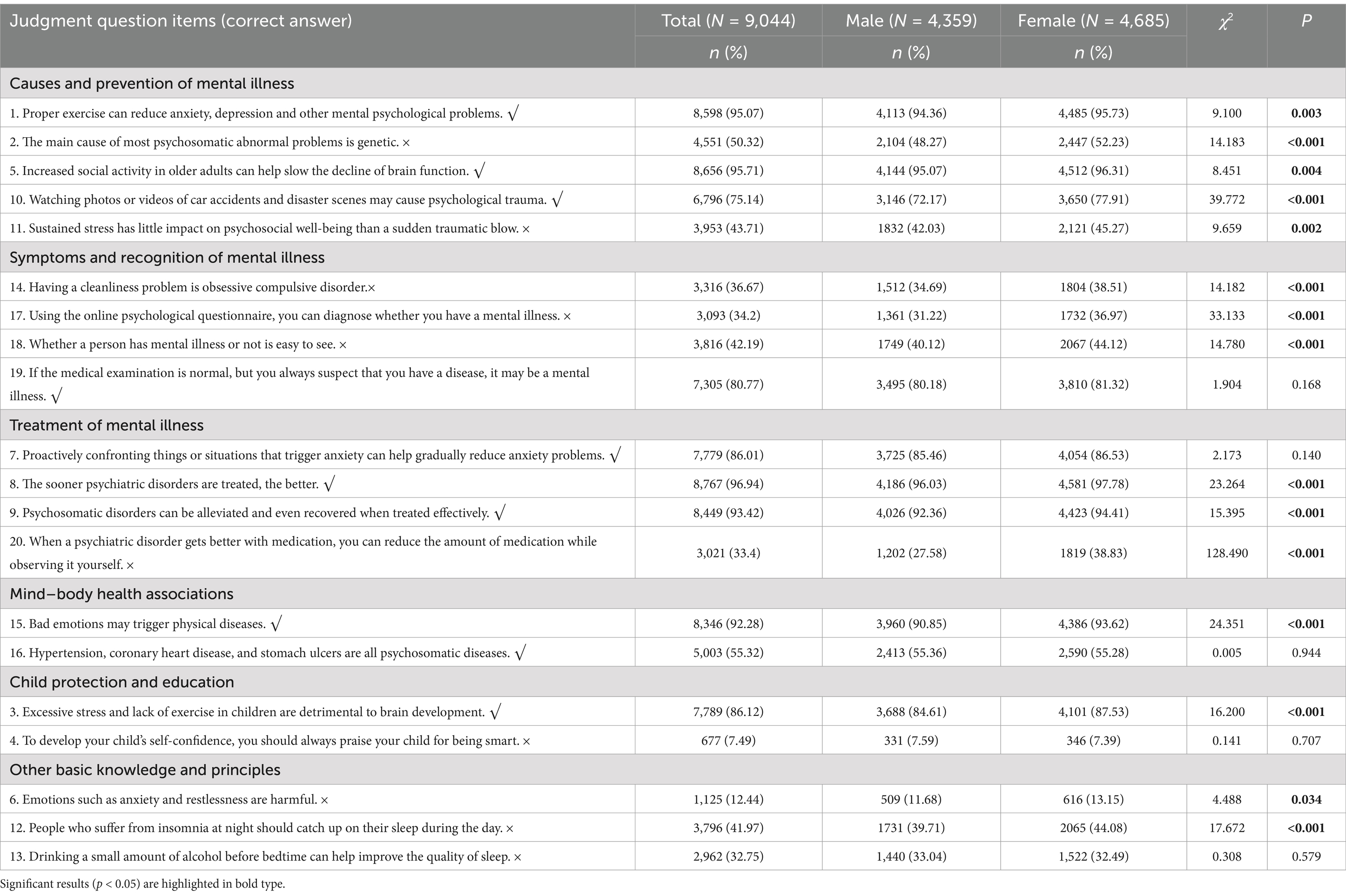
Out of the 20 judgment questions assessing mental health knowledge, 11 items demonstrated a correct response rate exceeding 50%, while nine items displayed a correct response rate below 50%. For items 4, 7, 13, 16, and 19, no statistically significant differences were found in the correct response rates between male and female respondents. Conversely, for the remaining 15 items, female respondents demonstrated a higher correct response rate compared to their male counterparts. Overall, these findings indicate that female participants exhibited a higher level of awareness and understanding regarding mental health knowledge compared to males (Table 2).
Comparison of MHL between male and female residents
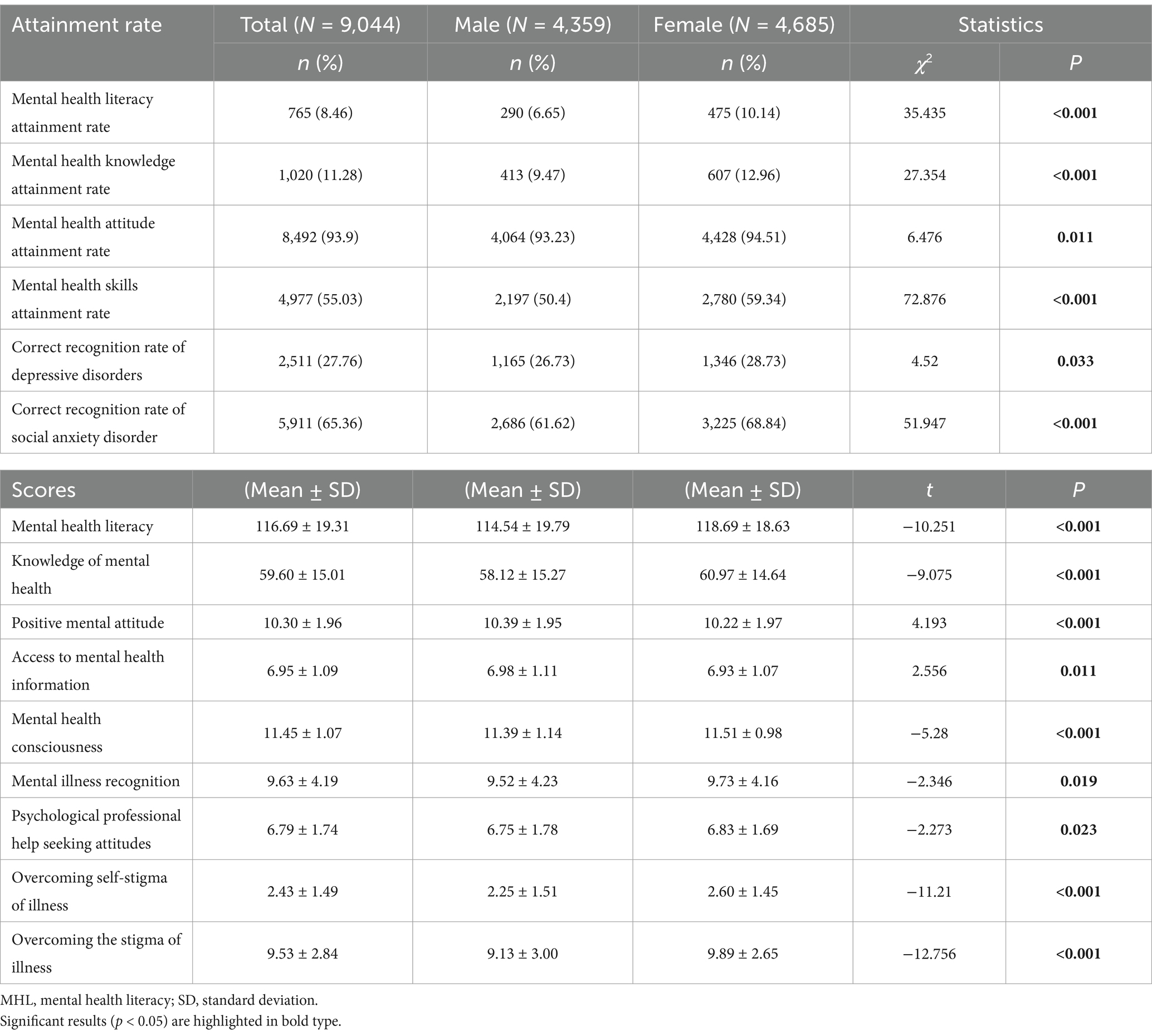
The overall attainment rate of MHL among residents in the study was a mere 8.46%. Specifically, male residents had a significantly lower rate of 6.65% compared to the 10.14% observed among female residents. Furthermore, females had significantly higher attainment rates than males in several domains, including mental health knowledge, mental health attitude, mental health skills, as well as correct recognition rates for depression and social anxiety (all p < 0.05) (Table 3).
Comparative analyses of scores on various subscales revealed that female residents performed significantly better than males in total MHL, mental health knowledge, mental health awareness, recognition of mental disorders, attitudes toward seeking professional psychological assistance, overcoming self-stigma, as well as general stigma (all p < 0.05). In contrast, male residents scored significantly higher in areas including maintaining a positive mental attitude and accessing mental health information (all p < 0.05) (Table 3).
Regression analysis of influencing factors on MHL levels among male and female residents
Univariate analysis revealed statistically significant differences in MHL levels among residents based on factors such as household registration types, age, marital status, occupation, exercise frequency, smoking status, drinking status, presence of chronic diseases, and depression (as displayed in Supplementary Table S1). These statistically significant factors were subsequently included as independent variables, with the attainment of MHL serving as the dependent variable (0 = non-attainment, 1 = attainment). Further analysis was conducted using multivariate logistic regression.
For male residents, the results of the logistic regression analysis demonstrated that higher education (≥12 years of education, OR = 2.217), engaging in professional technical work (OR = 1.767), and being retired (OR = 3.18) were protective factors for the attainment of MHL. In contrast, depression emerged as a risk factor (OR = 0.298) for the attainment of MHL (Table 4).
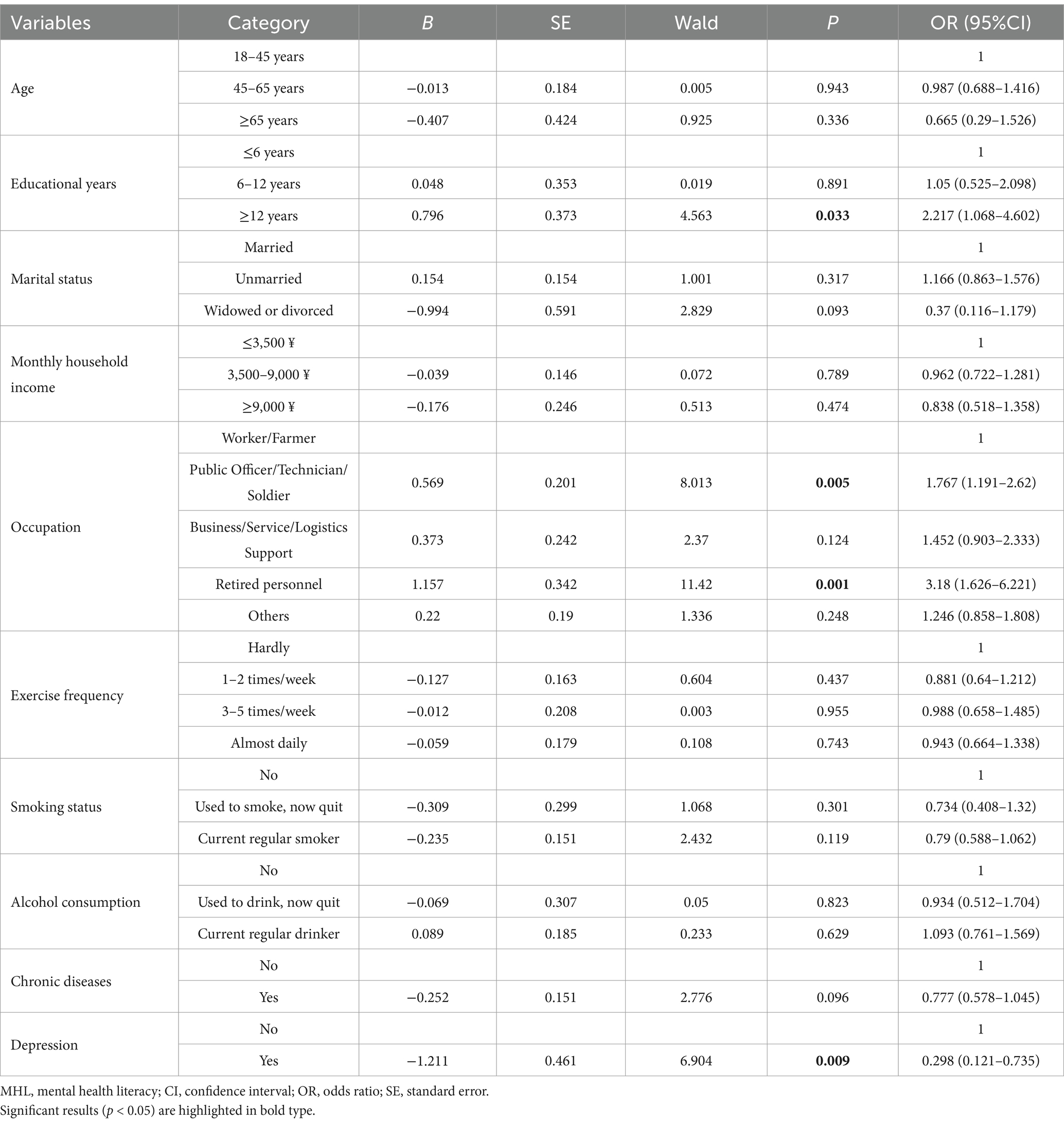
Table 4. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of factors influencing MHL levels among male residents.
For female residents, the logistic regression analysis results indicated that higher education (≥12 years of education, OR = 1.780), being unmarried (OR = 1.383), having a higher monthly household income (3500–9,000 ¥, OR = 1.299; ≥9,000 ¥, OR = 1.953), and engaging in exercise frequency of 3–5 times per week (OR = 1.568) were protective factors for the attainment of MHL. Conversely, the middle-aged and older age groups (45–64 years, OR = 0.488; ≥65 years, OR = 0.020) and the presence of depression (OR = 0.557) emerged as risk factors for the attainment of MHL among female residents (Table 5).
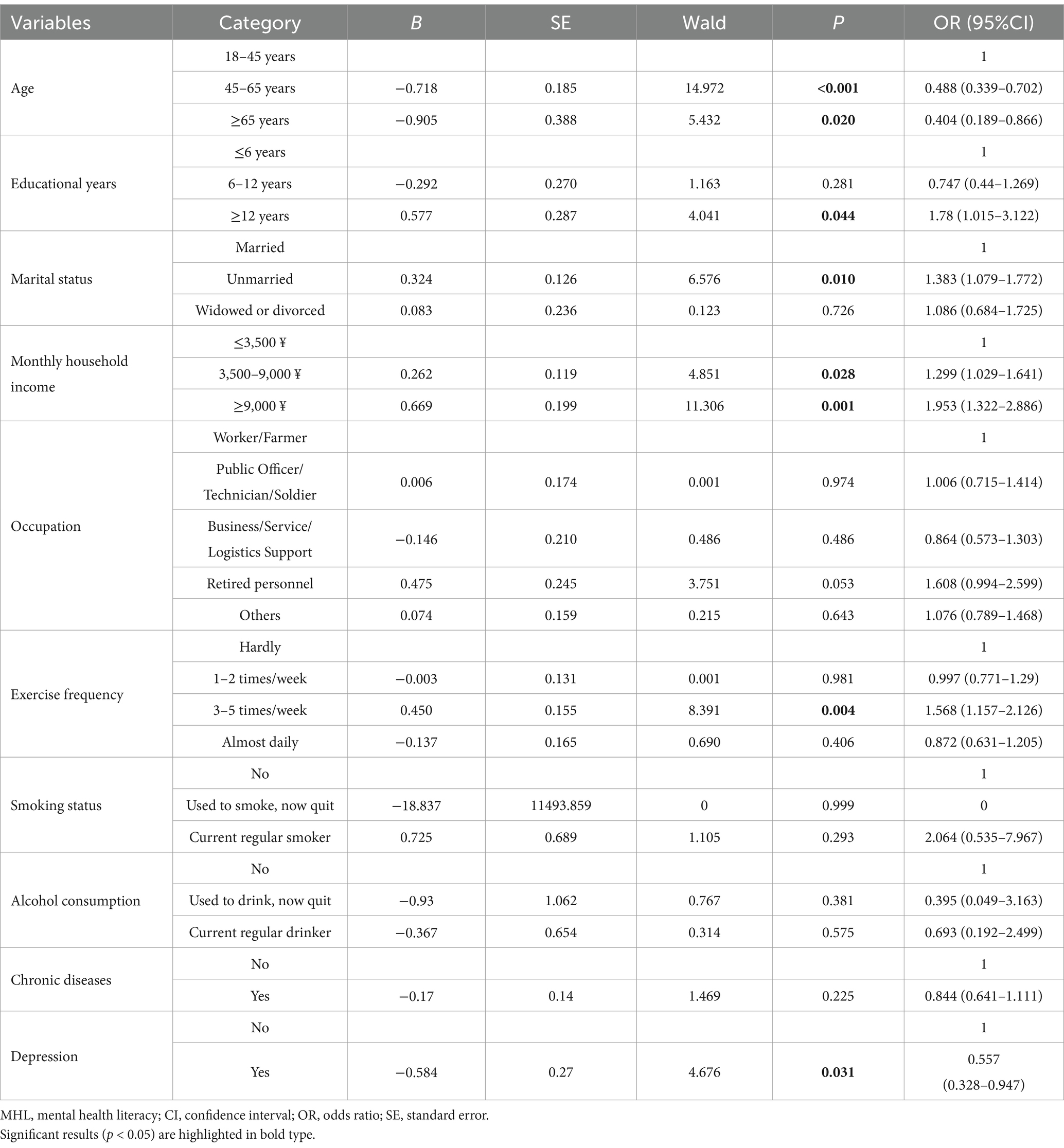
Table 5. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of factors influencing MHL levels among female residents.
Discussion
This study investigates gender differences in MHL using survey data collected from residents of Foshan City, China, in 2022. The results indicate that the overall attainment rate of MHL among Foshan City residents is relatively low, at only 8.46%. Specifically, the attainment rate among males is 6.65%, while it is slightly higher among females, at 10.14%. These values are far below the 20% target set by the Healthy China Initiative (2019–2030) for 2022, underscoring the urgent need for population-wide interventions to improve MHL across all groups. While females demonstrated relatively higher MHL levels than males, both groups remain well below the national benchmark, highlighting that low MHL is a widespread issue rather than one confined to a particular gender. Therefore, policymakers should adopt a “universal coverage with targeted reinforcement” approach – implementing broad-based measures, such as media campaigns and curriculum reforms, to increase MHL levels among the general population, while also designing targeted interventions to support gender-specific groups.
Regarding the three dimensions of MHL, the highest attainment rate is observed in mental health attitudes (assessed through self-assessment questions), with both male and female residents achieving over 90% in this area. The attainment rate for mental skills (case questions) is the second highest, with both genders achieving over 50%. However, the attainment rate for mental health knowledge (judgment questions) is the lowest, with male residents scoring 9.47% and female residents achieving 12.96%. These patterns align with previous research findings (34), indicating that although the public demonstrates a high level of awareness and a positive attitude toward mental health, a deficiency in comprehensive mental health knowledge hinders the translation of this awareness into practical skills and behavior. The lack of knowledge regarding mental health appears to be a crucial obstacle hindering the overall improvement of MHL.
An examination of the 20 judgment questions related to mental health knowledge (Table 2) indicates that both male and female respondents achieved a correct response rate below 50% for nine of the items. This implies that a significant number of residents possess misunderstandings regarding certain aspects of mental health knowledge. The statement “To develop your child’s self-confidence, you should always praise your child for being smart” exhibited the highest incidence of incorrect responses. This indicates a deficiency in understanding the suitable methods for fostering the psychological development of children and adolescents. Overpraising a child’s intelligence can cultivate a dependency on external affirmation, thereby undermining the cultivation of a growth mindset by diminishing the importance of personal endeavor. To address the issue, it is imperative to bolster the dissemination of mental health knowledge for children and adolescents at the societal, educational, and family levels. Additionally, the eight other items with substantial error rates were related to mental disorders. These included statements such as “Emotions like anxiety and restlessness are harmful” and “Drinking a small amount of alcohol before bedtime can help improve the quality of sleep.” These discoveries underscore that residents persist in holding misconceptions about common mental health conditions, their diagnosis, and their treatment. In light of these findings, it is essential to intensify public education efforts and disseminate precise mental health knowledge through diverse platforms, such as school syllabi, community engagements, and media outreach programs (11, 38). Additionally, there is an urgent requirement to enhance the education and training of mental health competencies to comprehensively raise the general standard of MHL (39).
In alignment with previous studies conducted on Western demographics (40–42), the results of this study reveal that female residents in Foshan, China, have higher levels of MHL than males. Specifically, female residents demonstrate superior knowledge and awareness of mental health compared to males. Additionally, females demonstrate more favorable outcomes in recognizing mental disorders, attitudes toward seeking professional psychological assistance, and overcoming stigma, including self-stigma. Conversely, male residents score higher in maintaining a positive mindset and in accessing mental health information compared to females. This finding partially aligns with previous research while demonstrating some heterogeneity (14, 28, 33, 43). The discrepancies observed in these findings may be attributed to variations in the assessment tools employed and the cultural backgrounds of the participants across various studies. Several factors can provide explanations for the observed gender differences. Firstly, females may inherently possess a heightened level of psychological awareness, introspection, and emotional sensitivity, which enhances their capacity to seek psychological assistance when confronted with mental health challenges (44). In contrast, males typically exhibit lesser capabilities in recognizing and expressing emotions, posing challenges in acknowledging and articulating their mental health concerns (45, 46). Moreover, traditional societal norms in China impose heightened expectations on males to embody “strength” and discourage the display of vulnerability, leading to an increased tendency to suppress emotions and a reluctance to seek assistance for mental health concerns. This aligns with males’ reduced ability to overcome both societal stigma and self-stigma. Lastly, males generally exhibit superior stress management skills, enabling them to maintain a more positive outlook when confronted with adverse events (47). Collectively, these results indicate that female residents possess a higher level of MHL than males, highlighting the pressing necessity for targeted mental health education initiatives aimed specifically at male residents to improve their MHL.
The results of the logistic regression analysis unveil distinct protective and risk factors that influence the MHL of male and female residents. For male residents, the protective factors include possessing a higher level of education, being employed in dedicated employment, and being retired, while depression stands out as the sole risk factor. For female residents, the protective factors encompass having a higher level of education, being unmarried, possessing a higher monthly family income, and engaging in moderate exercise frequency (3–5 times per week). In contrast, the risk factors for females include being within the middle-aged to older adult age range and experiencing depression. These findings are in alignment with previous studies which have demonstrated that individuals with higher education levels generally possess greater MHL (48, 49). This correlation is likely attributable to their exposure to more comprehensive education, which fosters an enhanced understanding of the significance of mental health, empowering them to actively acquire relevant knowledge and seek professional assistance. Furthermore, male residents who are engaged in professional technical occupations (such as public officer, technician, or soldier) and those who are retired demonstrate higher levels of MHL. This is likely due to their higher educational attainment, income levels, access to structured mental health education, psychological resilience training, as well as a greater availability of mental health resources. This finding underscores that employment significantly promotes psychological health, particularly for males (50, 51). For females, the status of being unmarried emerged as a protective factor for MHL, which aligns with the findings of previous research endeavors (52). In traditional Chinese culture, females are frequently expected to fulfill caregiving roles, encompassing responsibilities such as nurturing children, caring for older adult family members, and managing household duties. These societal expectations can impose substantial mental health burdens on married females, frequently leading them to prioritize the needs of their family over their own mental health. Consequently, married females may overlook self-care, resulting in a decline in their MHL. In contrast, unmarried females frequently enjoy greater economic independence and interpersonal freedom, which may contribute to higher levels of mental health awareness and understanding. Moreover, females with higher monthly family incomes were observed to have superior levels of MHL in comparison to those with lower incomes. This reflects the importance of economic independence in fostering improved mental health and enhancing MHL among females (53, 54). Interestingly, moderate exercise (3–5 times per week) emerged as a protective factor for female residents, potentially due to females’ heightened concerns regarding body image and overall health. Previous research has indicated that both a lack of exercise and excessive exercise frequency can lead to adverse mental health outcomes, which is consistent with our findings (55, 56).
In both males and females, recent depression was found to be associated with low levels of MHL, aligning with previous research findings (57, 58). This relationship can be attributed to the adverse effects of depression on an individual’s emotional and cognitive functions, often manifesting as symptoms such as difficulty concentrating and impaired decision-making abilities (59). These impairments obstruct the capacity to acquire knowledge and skills related to mental health, ultimately leading to decreased levels of MHL. Previous studies have demonstrated that individuals exhibiting significant depressive symptoms are only half as likely to accurately recognize their own depression compared to those with mild depressive symptoms. Moreover, individuals who accurately identify their depression are five times more likely to seek professional help than those who fail to do so (60). These findings emphasize the critical importance of early identification and treatment of depression, coupled with the provision of mental health education and support services, in bolstering the MHL of individuals experiencing depression. In addition, previous research indicates that MHL is a significant predictor of an individual’s mental health status. A positive correlation exists between higher levels of MHL and improved mental health outcomes (61). Conversely, low levels of MHL are closely linked to depression (58, 60, 62), indicating that improving MHL could act as an effective early intervention strategy for addressing mental health issues. These findings highlight the intricate relationship between MHL and depression, suggesting a pressing need for further exploration in future research. Finally, being middle-aged or older adult was identified as a risk factor for female MHL, potentially due to the generally lower levels of educational attainment within this demographic. The reintroduction of the college entrance examination in China in 1977, combined with the implementation of 9 years of compulsory education in 1986, led to comparatively lower levels of education among older individuals in comparison to younger generations. Additionally, traditional gender biases favoring males have historically constrained educational prospects for females, which may provide further insight into why this phenomenon is particularly evident among females.
Limitations
This study is also subject to certain limitations. Firstly, the cross-sectional design employed in this research fails to unveil the dynamic characteristics of MHL over time, and it does not establish causal relationships among the influencing factors. Therefore, it is imperative for future large-scale, high-quality longitudinal studies to conduct a more thorough exploration of these relationships. Secondly, despite the numerous factors that can impact MHL, this study only examined a limited subset of common factors due to constraints in the initial research design, neglecting other potential variables such as perceived stress and social support (60, 63, 64). Future research should incorporate a wider array of relevant factors to comprehensively evaluate their influence on residents’ MHL. Thirdly, significant differences were observed between male and female participants in terms of demographic and health-related variables, such as residence, age, marital status, and employment. This imbalance in baseline characteristics may have biased the results of gender comparisons. Future studies should consider employing gender-stratified sampling or propensity score matching to improve comparability between groups. Finally, the participants in the study were all from Foshan City, Guangdong Province, China, making this study less nationally representative.
Conclusion
In summary, this study reveals critically low levels of MHL among Foshan residents (8.46% overall attainment), with particularly severe deficits in mental health knowledge being the primary barrier to improving MHL. The observed gender differences (male: 6.65% vs. female: 10.14%), although statistically significant, should be interpreted in the broader context of universally inadequate MHL levels across all demographics. Intervention strategies must have a dual focus: population-wide interventions to address systemic knowledge gaps, such as mental health education and popular science initiatives, and targeted approaches for high-risk subgroups. For males, priority populations include those with limited education, unemployment status, or depressive symptoms. For females, at-risk groups include the less educated, married women, low-income earners, physically inactive, middle-aged to older adult and those experiencing depression. The development of targeted, population-specific interventions, coupled with the strengthening of educational initiatives aimed at improving mental health knowledge and skills, is essential to promote a comprehensive improvement in MHL.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was received for this study from the Ethics Committee of the Third People’s Hospital of Foshan (Approval No. FSSY-LS202212). The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
ZC: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. JX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. RL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. LO: Data curation, Writing – original draft. ZL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. GX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Foshan Science and technology innovation project (2220001005002) and High-Level Hospital Development Program for Foshan “Climbing” Project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1555615/full#supplementary-material
References
1. WHO. (2022). World mental health report: transforming mental health for all. Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240049338 (accessed January 4, 2025)
2. Huang, Y, Wang, Y, Wang, H, Liu, Z, Yu, X, Yan, J, et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry. (2019) 6:211–24. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(18)30511-x
3. Collaborators GMD. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry. (2022) 9:137–50. doi: 10.1016/s2215-0366(21)00395-3
4. Yeo, G, Reich, SM, Liaw, NA, and Chia, EYM. The effect of digital mental health literacy interventions on mental health: systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res. (2024) 26:e51268. doi: 10.2196/51268
5. Haeri-Mehrizi, A, Mohammadi, S, Rafifar, S, Sadighi, J, Kermani, RM, Rostami, R, et al. Health literacy and mental health: a national cross-sectional inquiry. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:13639. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64656-7
6. Jiang, G, Zhao, C, Wei, H, Yu, L, Li, D, Lin, X, et al. Mental health literacy: connotation, measurement and new framework. J Psychol Sci. (2020) 43:232–8. doi: 10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.20200132
7. Kutcher, S, Wei, Y, and Coniglio, C. Mental health literacy: past, present, and future. Can J Psychiatr. (2016) 61:154–8. doi: 10.1177/0706743715616609
8. Bjørnsen, HN, Eilertsen, MEB, Ringdal, R, Espnes, GA, and Moksnes, UK. Positive mental health literacy: development and validation of a measure among Norwegian adolescents. BMC Public Health. (2017) 17:717. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4733-6
9. Jorm, AF. Why we need the concept of "mental health literacy". Health Commun. (2015) 30:1166–8. doi: 10.1080/10410236.2015.1037423
10. Soria-Martínez, M, Navarro-Pérez, CF, Pérez-Ardanaz, B, and Martí-García, C. Conceptual framework of mental health literacy: results from a scoping review and a Delphi survey. Int J Ment Health Nurs. (2024) 33:281–96. doi: 10.1111/inm.13249
11. Jorm, AF. Mental health literacy: empowering the community to take action for better mental health. Am Psychol. (2012) 67:231–43. doi: 10.1037/a0025957
12. Jorm, AF, Barney, LJ, Christensen, H, Highet, NJ, Kelly, CM, and Kitchener, BA. Research on mental health literacy: what we know and what we still need to know. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. (2006) 40:3–5. doi: 10.1080/j.1440-1614.2006.01734.x
13. Ganasen, KA, Parker, S, Hugo, CJ, Stein, DJ, Emsley, RA, and Seedat, S. Mental health literacy: focus on developing countries. Afr J Psychiatry. (2008) 11:23–8. doi: 10.4314/ajpsy.v11i1.30251
14. Tay, JL, Tay, YF, and Klainin-Yobas, P. Mental health literacy levels. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. (2018) 32:757–63. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2018.04.007
15. Li, W, and Reavley, N. Recognition and beliefs about treatment for mental disorders in mainland China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. (2020) 55:129–49. doi: 10.1007/s00127-019-01799-3
16. Tambling, RR, and D'Aniello, C. Mental health literacy and relational health literacy among college students. J Am Coll Heal. (2025) 73:1–9. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2023.2228428
17. Rafal, G, Gatto, A, and DeBate, R. Mental health literacy, stigma, and help-seeking behaviors among male college students. J Am Coll Heal. (2018) 66:284–91. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2018.1434780
18. Kaneko, Y, and Motohashi, Y. Male gender and low education with poor mental health literacy: a population-based study. J Epidemiol. (2007) 17:114–9. doi: 10.2188/jea.17.114
19. Haering, S, Schulze, L, Geiling, A, Meyer, C, Klusmann, H, Schumacher, S, et al. Higher risk-less data: a systematic review and meta-analysis on the role of sex and gender in trauma research. J Psychopathol Clin Sci. (2024) 133:257–72. doi: 10.1037/abn0000899
20. Salk, RH, Hyde, JS, and Abramson, LY. Gender differences in depression in representative national samples: Meta-analyses of diagnoses and symptoms. Psychol Bull. (2017) 143:783–822. doi: 10.1037/bul0000102
21. Gao, W, Ping, S, and Liu, X. Gender differences in depression, anxiety, and stress among college students: a longitudinal study from China. J Affect Disord. (2020) 263:292–300. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.11.121
22. McHugh, RK, Votaw, VR, Sugarman, DE, and Greenfield, SF. Sex and gender differences in substance use disorders. Clin Psychol Rev. (2018) 66:12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2017.10.012
23. O’Dell, C, Charles, NE, and Barry, CT. Gender differences in links between antisocial features and forms and functions of aggression among at-risk youth. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. (2024) 46:357–72. doi: 10.1007/s10862-024-10134-3
24. Metin, A, Erbiçer, ES, Şen, S, and Çetinkaya, A. Gender and COVID-19 related fear and anxiety: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2022) 310:384–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.05.036
25. Tian, W, Yan, G, Xiong, S, Zhang, J, Peng, J, Zhang, X, et al. Burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in China and its provinces, 1990-2021: findings from the global burden of disease study 2021. Br J Psychiatry. (2025):1–11. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2024.267
26. Johnson, BE. Gender differences in mental health. Salem Press Encyclopedia of Health [Preprint]. (2025). Available at: http://research.ebsco.com/linkprocessor/plink?id=3515775b-f78d-372e-a529-f6de161ae4a7 (Accessed May 26, 2025).
27. Lee, HY, Hwang, J, Ball, JG, Lee, J, Yu, Y, and Albright, DL. Mental health literacy affects mental health attitude: is there a gender difference? Am J Health Behav. (2020) 44:282–91. doi: 10.5993/ajhb.44.3.1
28. Cotton, SM, Wright, A, Harris, MG, Jorm, AF, and McGorry, PD. Influence of gender on mental health literacy in young Australians. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. (2006) 40:790–6. doi: 10.1080/j.1440-1614.2006.01885.x
29. Haavik, L, Joa, I, Hatloy, K, Stain, HJ, and Langeveld, J. Help seeking for mental health problems in an adolescent population: the effect of gender. J Ment Health. (2019) 28:467–74. doi: 10.1080/09638237.2017.1340630
30. Derntl, B, Finkelmeyer, A, Eickhoff, S, Kellermann, T, Falkenberg, DI, Schneider, F, et al. Multidimensional assessment of empathic abilities: neural correlates and gender differences. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2010) 35:67–82. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.10.006
31. Schroeder, S, Tan, CM, Urlacher, B, and Heitkamp, T. The role of rural and urban geography and gender in community stigma around mental illness. Health Educ Behav. (2021) 48:63–73. doi: 10.1177/1090198120974963
32. Alluhaibi, BA, and Awadalla, AW. Attitudes and stigma toward seeking psychological help among Saudi adults. BMC Psychol. (2022) 10:216. doi: 10.1186/s40359-022-00923-4
33. Bener, A, and Ghuloum, S. Gender differences in the knowledge, attitude and practice towards mental health illness in a rapidly developing Arab society. Int J Soc Psychiatry. (2011) 57:480–6. doi: 10.1177/0020764010374415
34. He, XY, Tan, WY, Guo, LL, Ji, YY, Jia, FJ, and Wang, SB. Mental health literacy among urban and rural residents of Guangdong Province, China. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. (2024) 17:2305–18. doi: 10.2147/rmhp.S479868
35. Levis, B, Benedetti, A, and Thombs, BD. Accuracy of patient health questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for screening to detect major depression: individual participant data meta-analysis. BMJ. (2019) 365:1476. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l1476
36. Sapra, A, Bhandari, P, Sharma, S, Chanpura, T, and Lopp, L. Using generalized anxiety Disorder-2 (GAD-2) and GAD-7 in a primary care setting. Cureus. (2020) 12:e8224. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8224
37. Wong, ML, Lau, KNT, Espie, CA, Luik, AI, Kyle, SD, and Lau, EYY. Psychometric properties of the sleep condition Indicator and insomnia severity index in the evaluation of insomnia disorder. Sleep Med. (2017) 33:76–81. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2016.05.019
38. Lee, JE, Goh, ML, and Yeo, SF. Mental health awareness of secondary schools students: mediating roles of knowledge on mental health, knowledge on professional help, and attitude towards mental health. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e14512. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14512
39. Murthy, MKS, Kapanee, ARM, Desai, G, and Chaturvedi, SK. Exploring the knowledge and attitude of public about mental health problems: a pilot intervention for effective mental health promotion. J Educ Health Promot. (2019) 8:177. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_137_19
40. Gorczynski, P, and Sims-Schouten, W. Evaluating mental health literacy amongst US college students: a cross sectional study. J Am Coll Heal. (2024) 72:676–9. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2022.2063690
41. Chakraverty, D, Baumeister, A, Aldin, A, Seven, ÜS, Monsef, I, Skoetz, N, et al. Gender differences of health literacy in persons with a migration background: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e056090. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-056090
42. Gibbons, RJ, Thorsteinsson, EB, and Loi, NM. Beliefs and attitudes towards mental illness: an examination of the sex differences in mental health literacy in a community sample. Peer J. (2015) 3:e1004. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1004
43. Andrews, KL, Jamshidi, L, Shields, RE, Teckchandani, TA, Afifi, TO, Fletcher, AJ, et al. Examining mental health knowledge, stigma, and service use intentions among Royal Canadian Mounted Police cadets. Front Psychol. (2023) 14:1123361. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1123361
44. Petrides, KV, Furnham, A, and Martin, GN. Estimates of emotional and psychometric intelligence: evidence for gender-based stereotypes. J Soc Psychol. (2004) 144:149–62. doi: 10.3200/socp.144.2.149-162
45. Wingenbach, TSH, Ashwin, C, and Brosnan, M. Sex differences in facial emotion recognition across varying expression intensity levels from videos. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0190634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190634
46. Donges, US, Kersting, A, and Suslow, T. Women's greater ability to perceive happy facial emotion automatically: gender differences in affective priming. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e41745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041745
47. Tommasi, M, Sergi, MR, Picconi, L, and Saggino, A. The location of emotional intelligence measured by EQ-i in the personality and cognitive space: are there gender differences? Front Psychol. (2022) 13:985847. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.985847
48. Al-Qerem, W, Jarab, A, Khdour, M, Eberhardt, J, Alasmari, F, Hammad, A, et al. Assessing mental health literacy in Jordan: a factor analysis and Rasch analysis study. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1396255. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1396255
49. Snow, KSR, Merrill, K, Macintosh, J, Thomas, M, and Miles, L. Mental health literacy in Polynesian native Hawaiian and other Pacific islanders. Int J Ment Health Nurs. (2024) 33:683–92. doi: 10.1111/inm.13275
50. Drake, RE, and Wallach, MA. Employment is a critical mental health intervention. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. (2020) 29:e178. doi: 10.1017/s2045796020000906
51. Padrosa, E, Vanroelen, C, Muntaner, C, Benach, J, and Julià, M. Precarious employment and mental health across European welfare states: a gender perspective. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. (2022) 95:1463–80. doi: 10.1007/s00420-022-01839-7
52. Xiuzhen, S, Jie, L, Yi, X, Jingmin, Z, and Linghui, Z. Mental health literacy among residents in Jiaxing City. J Prev Med. (2023) 35:911–5. doi: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2023.10.018
53. Shekhawat, K, Sharma, P, and Menaria, P. Financial independence and maternal mental health-a right balance. Southeast Asian J Health Prof. (2022) 5:4–7. doi: 10.18231/j.sajhp.2022.002
54. Mellar, BM, Fanslow, JL, Gulliver, PJ, and McIntosh, TKD. Economic abuse by an intimate partner and its associations with women's socioeconomic status and mental health. J Interpers Violence. (2024) 39:4415–37. doi: 10.1177/08862605241235140
55. Golshani, S, Najafpour, A, Hashemian, SS, Goudarzi, N, Shahmari, F, Golshani, S, et al. When much is too much-compared to light exercisers, heavy exercisers report more mental health issues and stress, but less sleep complaints. Healthcare. (2021) 9:1289. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9101289
56. Senaratne, N, Stubbs, B, Werneck, AO, Stamatakis, E, and Hamer, M. Device-measured physical activity and sedentary behaviour in relation to mental wellbeing: an analysis of the 1970 British cohort study. Prev Med. (2021) 145:106434. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2021.106434
57. Zhong, SL, Wang, SB, Ding, KR, Tan, WY, and Zhou, L. Low mental health literacy is associated with depression and anxiety among adults: a population-based survey of 16, 715 adults in China. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:2721. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20020-y
58. Lam, LT. Mental health literacy and mental health status in adolescents: a population-based survey. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. (2014) 8:26. doi: 10.1186/1753-2000-8-26
59. Bredemeier, K, Berenbaum, H, Brockmole, JR, Boot, WR, Simons, DJ, and Most, SB. A load on my mind: evidence that anhedonic depression is like multi-tasking. Acta Psychol. (2012) 139:137–45. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2011.11.007
60. Kim, JE, Saw, A, and Zane, N. The influence of psychological symptoms on mental health literacy of college students. Am J Orthopsychiatry. (2015) 85:620–30. doi: 10.1037/ort0000074
61. Song, J, Feng, K, Zhang, D, Wang, S, Wang, W, and Li, Y. The relationship between mental health literacy, overall adaptation and mental health of university freshers. Psychol Res Behav Manag. (2023) 16:4935–47. doi: 10.2147/prbm.S437718
62. Huang, X, Wang, X, Hu, J, Xue, Y, Wei, Y, Wan, Y, et al. Inadequate mental health literacy and insufficient physical activity potentially increase the risks of anxiety and depressive symptoms in Chinese college students. Front Psych. (2021) 12:753695. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.753695
63. Li, S, Sheng, Y, and Jing, Y. How social support impact teachers' mental health literacy: a chain mediation model. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:851332. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.851332
Keywords: mental health literacy, gender differences, influencing factors, logistic regression analysis, cross-sectional study
Citation: Chu Z, Xie J, Liu R, Ou L, Lan Z and Xie G (2025) Gender-specific differences in mental health literacy and influencing factors among residents in Foshan City, China: a cross-sectional study. Front. Public Health. 13:1555615. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1555615
Edited by:
Iman Permana, Muhammadiyah University of Yogyakarta, IndonesiaReviewed by:
Li Zhou, Zunyi Medical University, ChinaKrzysztof Zdziarski, Pomeranian Medical University, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Chu, Xie, Liu, Ou, Lan and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guojun Xie, eGllZ2pmc0AxMjYuY29t
 Zhaosong Chu
Zhaosong Chu Jianling Xie2
Jianling Xie2 Guojun Xie
Guojun Xie