- 1School of Nursing, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Nursing Department, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 3School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Background: Due to aging, the use of antidiabetic drugs, and dietary restrictions following a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), the social interactions of older adults with T2DM are often limited. As a result, this population experiences a higher incidence of social isolation than the general older adult population. This study aims to analyze the prevalence and influencing factors of social isolation among older adults with T2DM using a structural equation model.
Patients and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted between January and November 2023. A total of 496 older adults with T2DM were recruited from hospitals or community health service centers in Beijing to investigate their social isolation status and related factors. The Lubben Social Network Scale-6, along with related scales, was used for data collection. The effects of different factors on social isolation were determined using a path analysis.
Results: Among 496 older adults with T2DM, 227 reported social isolation, resulting in a prevalence rate of 45.77%. Activity of daily living, cognitive function, loneliness, exercise management, smoking, social support, and social participation are all directly related to social isolation. Additionally, six factors—activity of daily living, loneliness, depression, diet management, blood glucose monitoring, and social support—were related to social isolation through social participation.
Conclusion: The incidence of social isolation among older adults with T2DM is high. For them, activities of daily living, loneliness, and social support are significant factors in their social isolation since they are directly or indirectly related to social isolation. Meanwhile, diabetes self-management, such as diet management, exercise management, blood glucose management, and smoking, is directly or indirectly related to social isolation. For older adults with T2DM, the important intermediary role of social participation between the factors and social isolation should be given due attention.
1 Introduction
With aging, the proportion of the older adult population with diabetes in China has gradually increased. Approximately 30% of Chinese older adults have diabetes, and 95% of them suffer from type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (1). Social isolation is a well-established risk factor for adverse health and psychological outcomes. A recent meta-analysis revealed that socially isolated individuals have a 1.88-fold higher risk of developing T2DM compared to non-isolated individuals (2). After being diagnosed with diabetes, some patients avoid communicating with others because they are worried that their diet is challenging to control, or it is inconvenient to use hypoglycemic drugs when going out. Moreover, those with diabetes complications, such as diabetic foot, are forced to reduce social activities due to physical restrictions (3). These situations may increase the difficulty of maintaining the social network of older adults with T2DM. Therefore, those with diabetes are at high risk of social isolation. Moreover, aging increases the risk of social isolation. In China, people aged 60 or above are classified as older adults (4). Due to retirement or changes in family structure (i.e., the passing away of a spouse or children away from home), older adults’ social network tends to shrink, and the risk of social isolation increases accordingly. Compared with older adults in Western society, the social network size of older adults in China is smaller, with a higher proportion of family members, and their social network is mainly based on kinship (5). However, since the 1970s, the continuously declining birth rate and intensified population mobility have led to a trend toward smaller households in China, which may increase the risk of social isolation among older adults in China (5). In 2019, a survey in Beijing, China, showed that the incidence of social isolation among older adults with T2DM was 22.7% (6).
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health not merely as the absence of disease or infirmity, but as a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing (7). Social isolation adversely affects both physical and mental health, contributing to suboptimal health status, increased incidence of physical and mental disorders, and ultimately higher mortality rates. At the societal level, it can drive detrimental shifts in social structure and impede socioeconomic and cultural development. Consequently, social isolation is widely recognized as a critical global public health challenge (8).
Social isolation is a state of disconnection from meaningful connections with others or society, which can manifest as a lack of marital status (unmarried, widowed or divorced), failure to participate in any social groups, community organizations, or interest-based activities, a lack of close ties with relatives and friends, or an emotional support network (9). This condition has significant implications for health and wellbeing. It is associated with negative emotional states (e.g., anxiety and depression), cognitive decline (10, 11), and unhealthy behaviors such as reduced physical activity and poor treatment adherence—factors that undermine effective diabetes self-management (12, 13). Moreover, poor self-management in diabetic patients leads to significant blood glucose fluctuations, which may further impair social interactions, reduce social network size, and exacerbate isolation (13). This cyclical relationship creates a self-perpetuating vicious cycle, worsening both health outcomes and social connectivity.
Social isolation in older adults with diabetes may be associated with self-management, physical activity, blood glucose fluctuation, and physical function (14), but few studies have reported the factors affecting social isolation in older adults with diabetes in China. In addition, existing studies focus on single or scattered factor categories related to social isolation, without exploring the relationships between these factors. This makes it difficult to provide a strong reference for intervention in social isolation for older adults with diabetes. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the factors associated with social isolation and their interplay in older adults with diabetes.
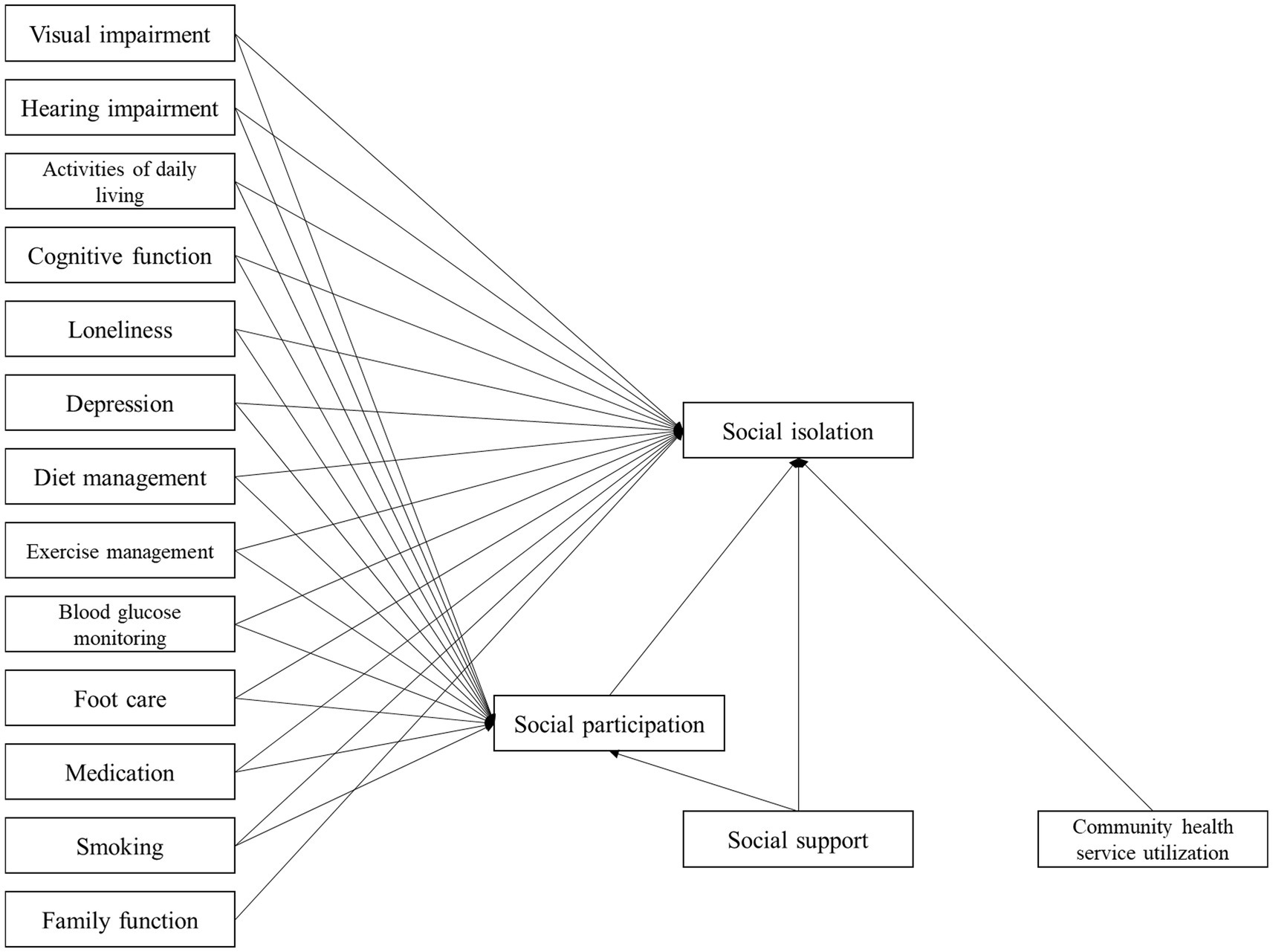
Wenger’s conceptual framework of social networks for older adults is mostly used for studying social networks (15). Social network refers to the mutual relationship between individuals and their family members, relatives, friends, and other interactive members. Social isolation is a special state of social network characterized by a low level of social interaction. In the framework, the structural characteristics of social network (i.e., frequency of contact, closeness, and distance) in older adults are impacted by various factors such as personal characteristics, external environment characteristics, and social support. Social support refers to the degree of spiritual and material connection between individuals and various aspects of society, including relatives, friends, colleagues, partners, and social organizations such as family units (16). Under the guidance of Wenger’s conceptual framework and combined with the related factors of social isolation of patients with diabetes shown in literature (6), we speculate that the social isolation of the older adults with T2DM are related to individual characteristics (visual impairment, hearing impairment, activity of daily living, cognitive function, self-management, depression, loneliness, etc.), external environment characteristics (family function and social participation, etc.), social support, and the use of formal services (community health service utilization).
Social participation refers to the behavior and process of an individual actively interacting with society and integrating into the family and social environment (17). Appropriate social participation increases the contact between individuals and others, expands their social network size, and helps individuals to maintain good social relationships. Conversely, impaired social participation ability reduces social participation and aggravates the degree of social isolation of the older patients (17). For older adults with T2DM, it was reported that social participation was associated with self-management, social support, loneliness, and the ability to perform daily living activities (18). From this inference, social participation may be a mediating variable in the model of social isolation-related factors; that is, other factors may indirectly affect the occurrence of social isolation through social participation.
This study used questionnaires to investigate the factors related to social isolation in 496 older adults with T2DM and conducted path analysis using a structural model to elucidate the mechanism of social isolation in these older adults and provide a basis for developing targeted interventions. We hypothesized that, after controlling for general demographic factors, 16 factors such as visual impairment, hearing impairment, self-management, diabetes self-management activities (such as diet, medication, exercise, blood glucose monitoring foot care, and smoking), social support, social participation may directly affect the occurrence of social isolation in the older adults with T2DM; meanwhile, some factors may affect the social isolation indirectly through social participation.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and sample
From January to November 2023, a cross-sectional study was carried out with a convenience sample of older adults with T2DM at the China–Japan Friendship Hospital, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, the Beijing Hospital, and the Fangzhuang Community Health Service Center.
The inclusion criteria for this study are as follows: ① Being ≥60 years old, ② having a diagnosis of T2DM (according to the diagnostic criteria of diabetes issued by the Chinese Medical Association (19)) for more than 1 year, ③ Chinese nationality, ④ score on the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) > 20 points. The exclusion criteria for this study are as follows: ① Having acute complications of diabetes, ② Having serious diseases caused by non-diabetes (such as a tumor), ③ Having a severe mental disorder or language communication barriers.
According to the sample size calculation method of the structural equation model (20), the sample size needs to be at least 10 times the number of observed variables. In this study, there were 31 observed variables in the study, and considering the possible invalid questionnaire, the sample size was increased by 10%. Therefore, the theoretical sample size was at least 341 cases. This study included a total of 496 samples.
2.2 Measurement
2.2.1 Lubben social network scale-6 (LSNS-6)
LSNS-6 is a brief version of the social network scale compiled by Lubben (21), which identifies an individual’s social isolation based on frequency and intimacy with their friends and family. It includes family and friend dimensions, each with six questions. The score for each question is 0–5. A total score lower than 12 indicates social isolation, and a score of less than 6 for each dimension indicates isolation in this dimension. Lower scores indicate a higher level of social isolation. The Chinese version of LSNS-6 and its subscales have good reliability and validity (22). Cronbach’s α coefficients for the total scale, and family and friend subscales, in this study were 0.856, 0.917, and 0.915, respectively.
2.2.2 Scale sets on factors related to social isolation
1. General Information Sheet: This is a self-designed sheet used to investigate part of the influencing factors of social isolation. The sheet includes demographic data (gender, age, education level, marital status, etc.), disease-related data (number of chronic diseases, fasting blood glucose value, diabetic complications, visual function, hearing function, etc.), and social data (living status, community transportation conditions, and health service utilization). Patients with poor vision or blindness due to cataract, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy were regarded as having visual impairment. Those with tinnitus, unclear hearing, and the use of hearing aids were regarded as having hearing impairment. The assessment of health service utilization refers to the assessment of patients’ attitudes and use of healthcare services, that is, the types of care services that older adults were aware of and/or received and were willing to accept.
2. Activity of Daily Living Scale (ADLs): ADLs is composed of the physical self-maintenance scale and instrumental activities of daily living scale to assess an individual’s physical self-care ability (such as walking and eating independently) and instrumental daily living ability (such as shopping, cooking, and transportation). It has 14 items, which are measured on a 4-point Likert scale (ranging from “fully capable” ~ to “completely impossible”). The higher the total score, the poorer the living ability (23). ADLs demonstrated good applicability in the Chinese older adult population, with Cronbach’s α of 0.894 (24).
3. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE): The MMSE was used to evaluate an individual’s cognitive function in five aspects: orientation (time and place), immediate memory, attention and computing power, delayed memory, and language, totaling 30 points. A total score of no less than 27 points indicates normal cognition, while 21–26 points indicates mild cognitive impairment, 10–20 indicates moderate cognitive impairment, and less than 10 indicates severe cognitive impairment (25). The MMSE demonstrated good reliability, with the intraclass correlation coefficient for inter-rater reliability reaching 0.99, and the test–retest reliability was 0.91 (26).
4. University of California at Los Angeles Loneliness Scale (UCLA-LS): The UCLA-LS consists of 20 items designed to evaluate an individual’s feelings of loneliness. All items are measured on a 4-point Likert scale (ranging from “never” to “always”), and some items are scored in reverse. The higher the total score, the more severe the loneliness (27). Cronbach’s α of UCLA-LS was 0.92 (28).
5. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-15): The GDS-15 is used to assess depressive symptoms in older adults over a week and consists of 15 items. Responses indicating depressive symptoms are scored as 1 point, while other responses are scored as 0. A higher score on the scale reflects more severe depressive symptoms. The Chinese version of the scale has demonstrated good reliability and validity among Chinese older adults. Cronbach’s α of the GDS-15 (Chinese version) was 0.763 (29).
6. Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities Scale (SDSCA): The SDSCA is a widely used tool to measure diabetes self-management behaviors. It comprises 13 items and 6 subscales of diet, exercise, medication, blood glucose monitoring, foot care, and smoking. Except for smoking, each item is scored on a scale of 0–7 points, and each dimension was scored as the average score for that dimension, with higher scores indicating better self-management behaviors. Cronbach’s α of each dimension in SDSCA was 0.62–0.92 (30).
7. Family Adaptation, Partnership, Growth, Affection, Resolve index (APGAR): This assessment tool evaluates family function from five aspects (five items): family fitness, cooperation, length, emotion, and intimacy. The three responses, “almost always,” “sometimes,” and “almost never,” correspond to 3–1 points, respectively (31). A higher total score suggests better family function. The test–retest reliability coefficient was 0.83 (32).
8. Social Support Rating Scale (SSRS): The SSRS questionnaire is used to assess the level of social support for an individual, including three dimensions and 10 items, which mostly uses a 4-level Likert scale. The higher the total score, the higher the level of social support (33). The internal consistency across items of SSRS was 0.89–0.94, and test–retest reliability was 0.92 (34).
9. Impact on Participation and Autonomy (IPA) Questionnaire: The IPA questionnaire is used to measure the level of an individual’s social participation with good reliability and validity, including four dimensions and 25 items. The higher the total score, the less social participation. Cronbach’s α of each dimension in IPA was 0.81–0.91 (35).
2.3 Data collection method
Older adults with T2DM were recruited from the outpatient or inpatient departments of the hospitals or the community health service center. The researchers introduced the purpose and content of the study to the older adults and issued the questionnaire after obtaining their oral consent. At first, the cognitive function of the older adults was evaluated using MMSE; those who scored an MMSE score of >20 points continued to complete the questionnaire. The older adults without cognitive impairment completed the questionnaire by themselves, while the caregivers assisted those with mild cognitive impairment. If the participant had difficulties with reading, writing, or handwriting, the researcher would read the questions and complete the questionnaire based on the participant’s answers. After the questionnaire was completed, it was collected and checked on the spot. If there was an obvious omission or incorrect filling, a timely follow-up and improvement of the questionnaire were conducted. The questionnaire with 10% missing items or logical errors was deemed invalid. In this study, 508 questionnaires were distributed, and 12 invalid questionnaires were excluded. Finally, a total of 496 questionnaires were included, with an effective return rate of 97.64%, and the mean was used to interpolate missing values.
2.4 Statistical analysis and path analysis
Data were analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 26.0 and Mplus 8.0 software. Count data were expressed by frequency and composition ratio (%), and the chi-squared test was used for comparison between groups. Measurement data were compared between groups using the Mann–Whitney U test. The Spearman rank correlation analysis was used to explore the correlation between social isolation and various factors; p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Model fitting was performed on the hypothesis model using Bayesian estimation. The model parameters were evaluated based on the posterior prediction distribution, trace map, autocorrelation map, and potential scale reduction (PSR). The fitting effect was evaluated based on posterior prediction p-value (PPp), the closer to 0.5, the better the model fit, and if less than 0.05, the model fit is considered poor (17). The insignificant path was adjusted to achieve the best-fitting effect to analyze the pathways through which different factors affect social isolation.
3 Results
3.1 Sample characteristics and social isolation status
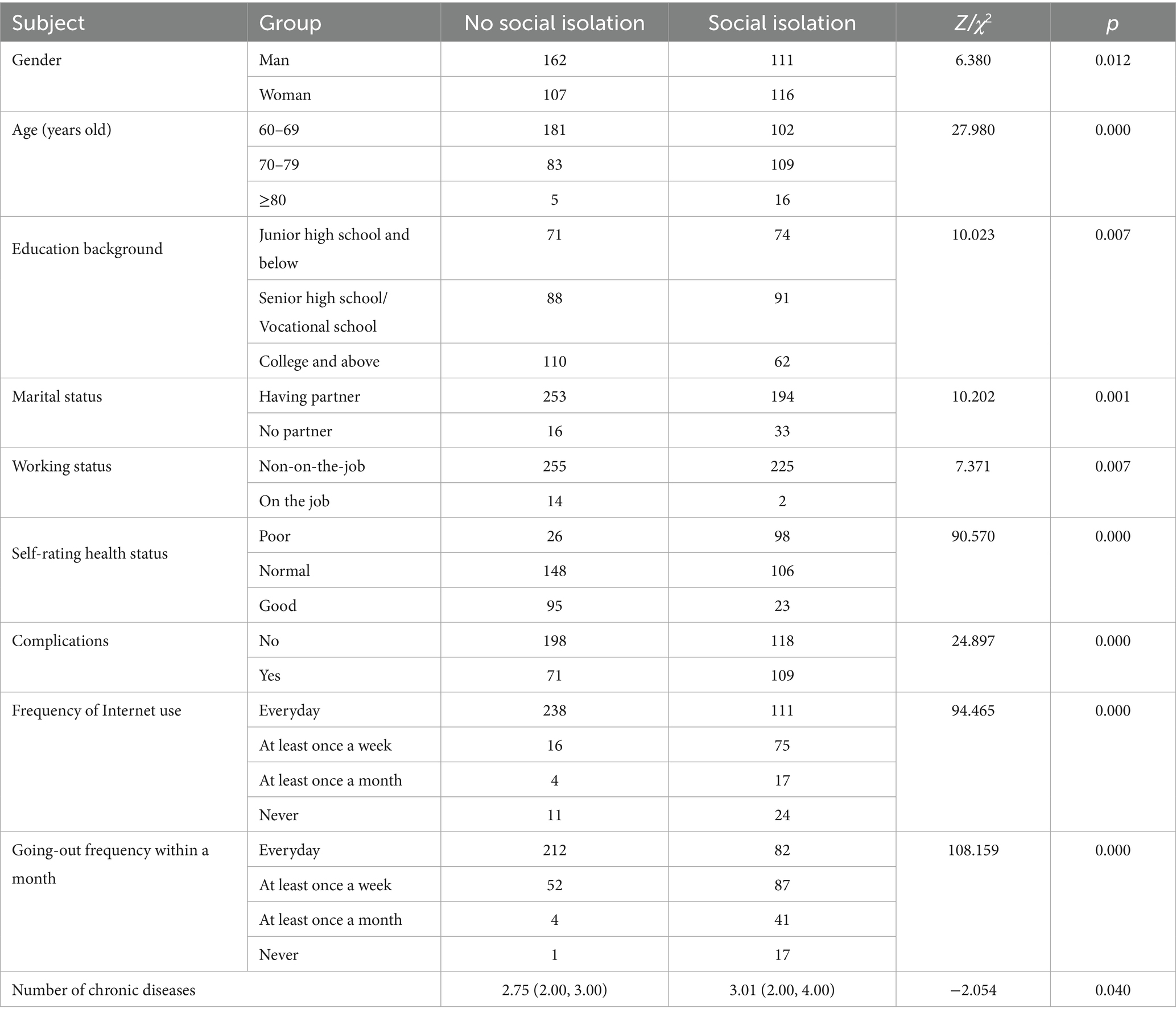
A total of 496 older adults with T2DM were 60–91 years old, with a mean age of 68.88 ± 5.81 years; 273 males and 223 females. Their T2DM duration was 1–47 years, with a mean of 14.35 ± 8.69 years. There were 296 participants without cognitive impairment and 200 with mild cognitive impairment. The total score for LSNS-6 was (13.15 ± 5.61), of which 227 had social isolation, with an incidence of 45.77%. Seventy-four participants (14.92%) had social isolation at the family dimension and 239 (48.19%) at the friend dimension.
Univariate analysis was performed to evaluate the variables associated with social isolation in older adults with T2DM. There were significant differences in gender, age, educational background, marital status, working status, self-rating health status, and complications between the social isolation group and the non-social isolation group (Table 1).
3.2 Correlation analysis between social isolation and other factors in older adults with T2DM
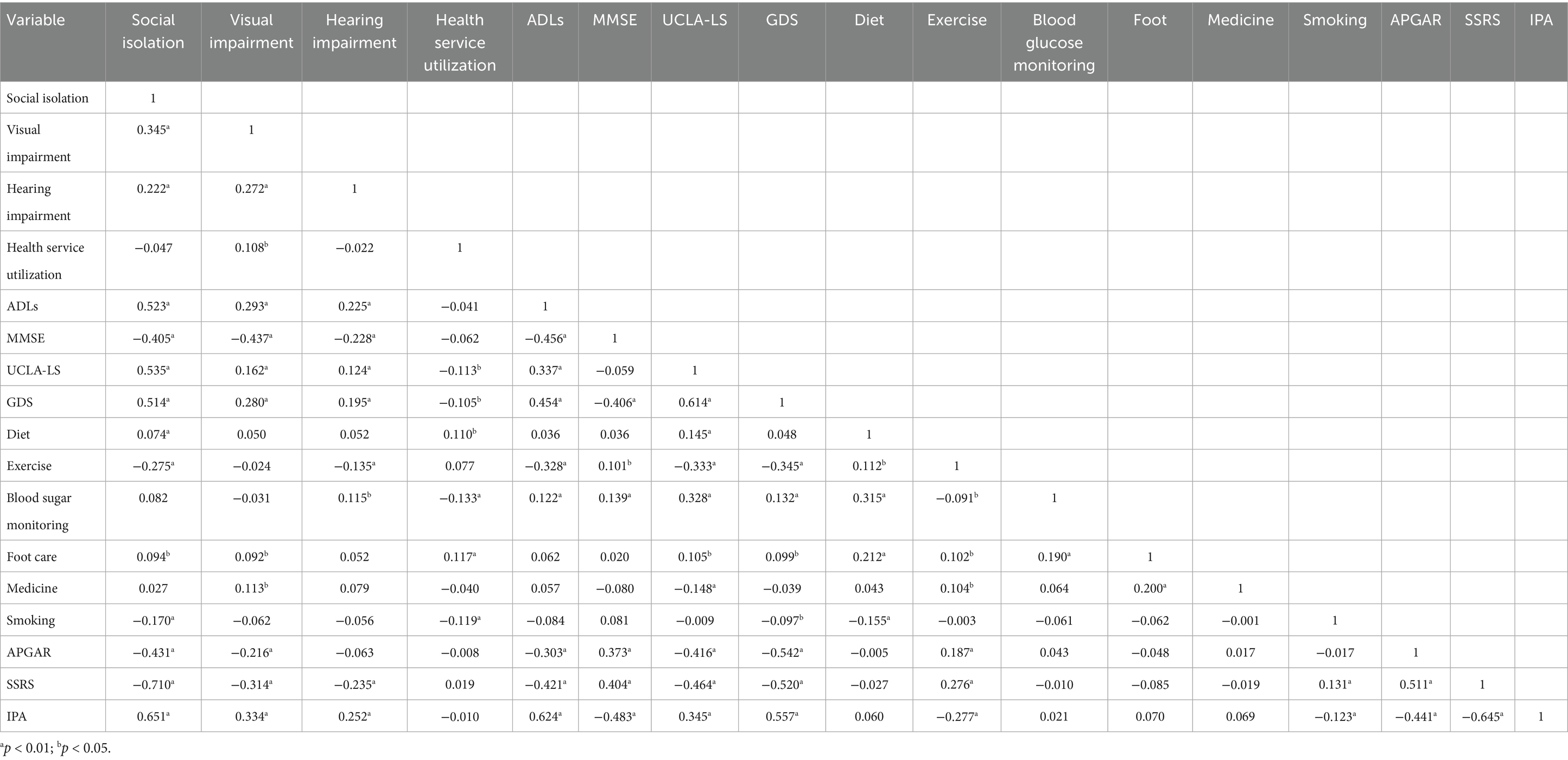
It was shown that the occurrence of social isolation was negatively related to MMSE score, SDSCA exercise-management dimension score, smoking, APGAR score, SSRS score, visual impairment, hearing impairment, ADLs score, UCLA-LS score, GDS score, SDSCA diet-management dimension score, foot-care dimension score, and IPA score; but it was not related to community health service utilization, SDSCA blood glucose monitoring dimension score, and medication management dimension score (Table 2).
3.3 Path analysis model
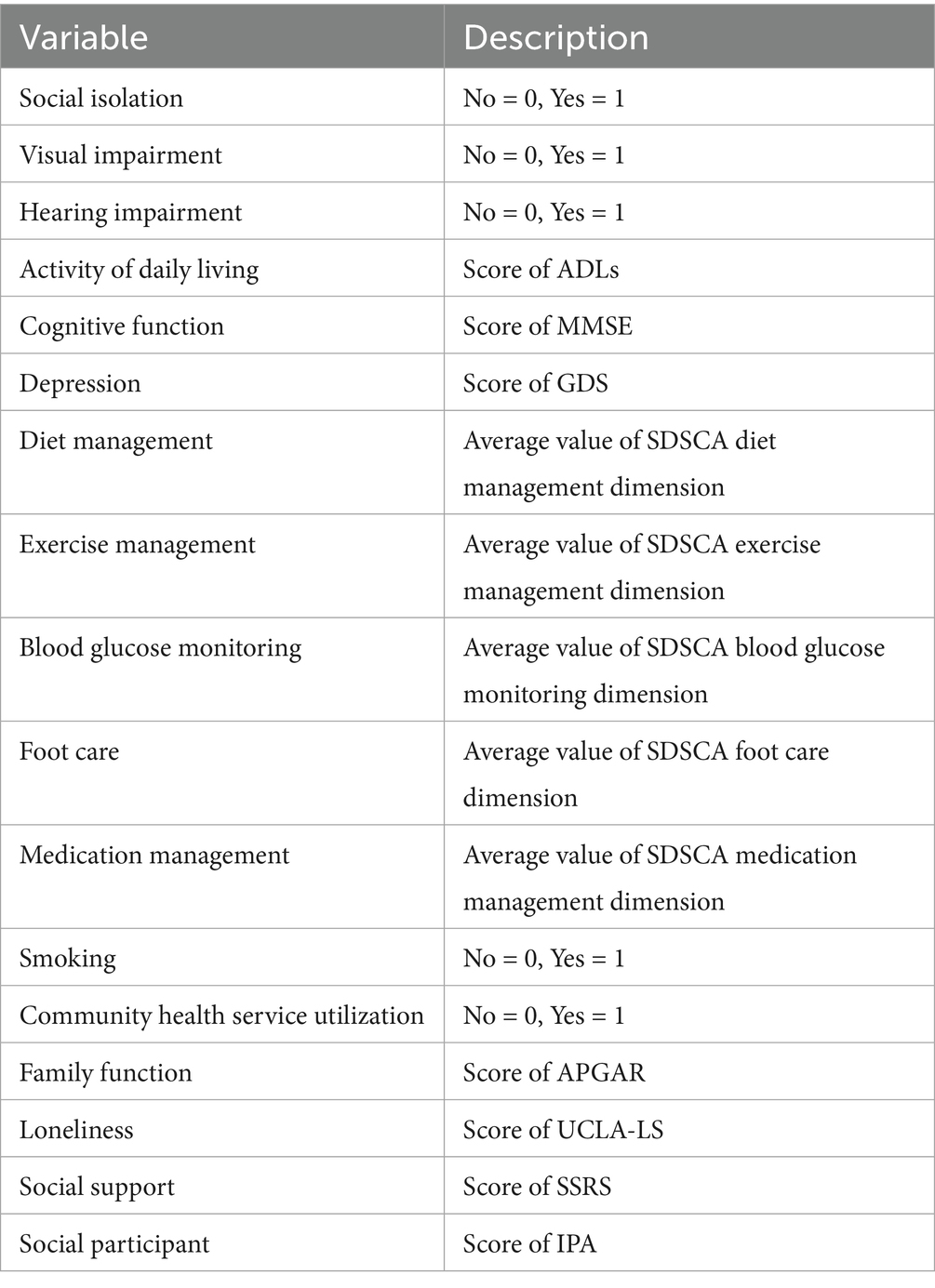
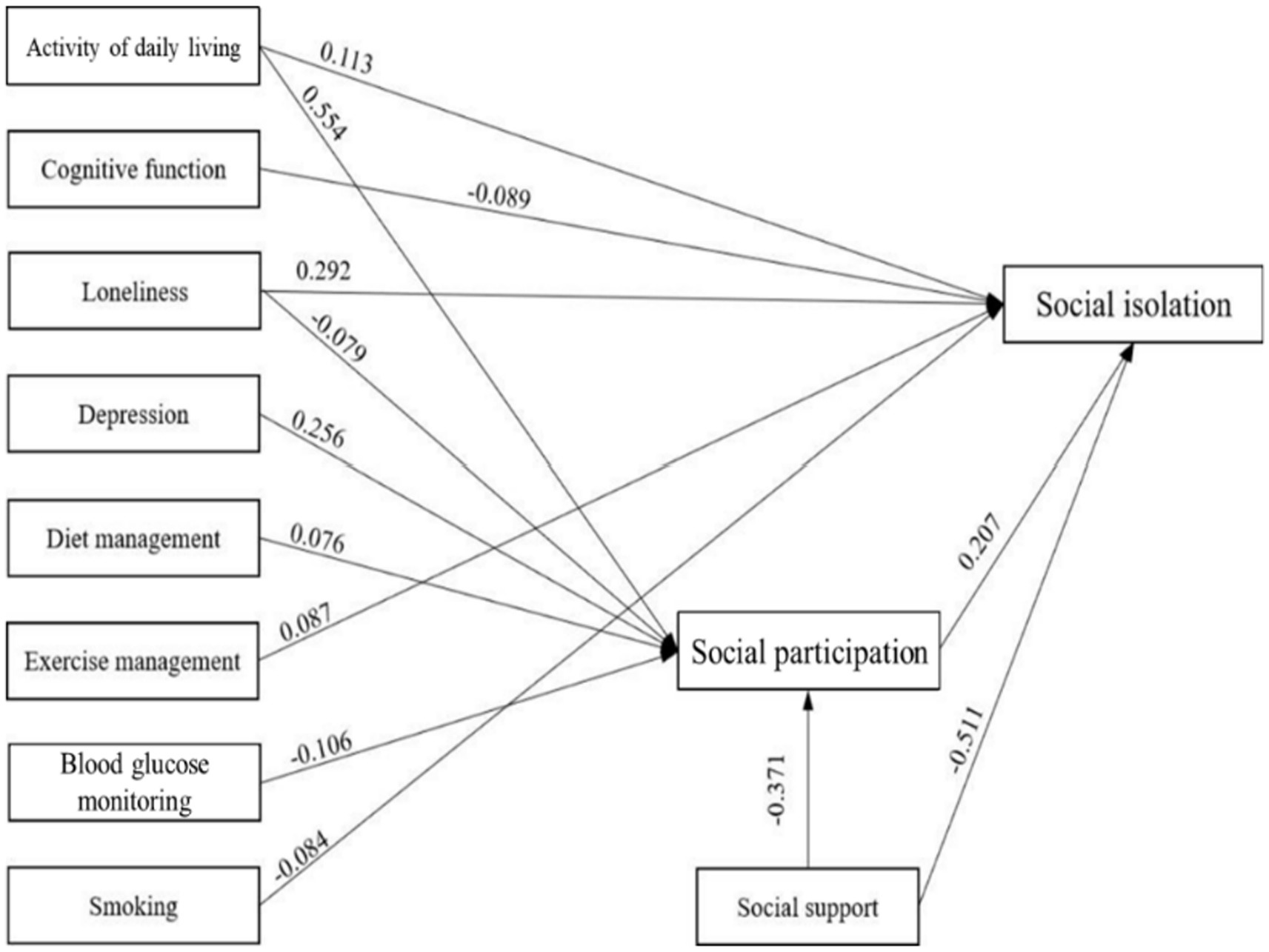
On the basis of the hypothesized path, with the occurrence of social isolation as endogenous variable, gender, age, education background, marital status, working status, self-rating health, complications, internet use frequency, number of chronic diseases as control variables, visual impairment, activity of daily living and other factors as exogenous variables, social participation as the mediator, the initial hypothesized model was established (Figure 1), and then model fitting was performed. The hypothesized model is shown to fit poorly. Non-significant paths were deleted, and the hypothesized model was corrected. Variable assignments of the model are shown in Table 3. The final model parameters exhibit good convergence and good fit (PPp = 0.071 > 0.05). The model shows the paths with statistically significant coefficients (Figure 2).
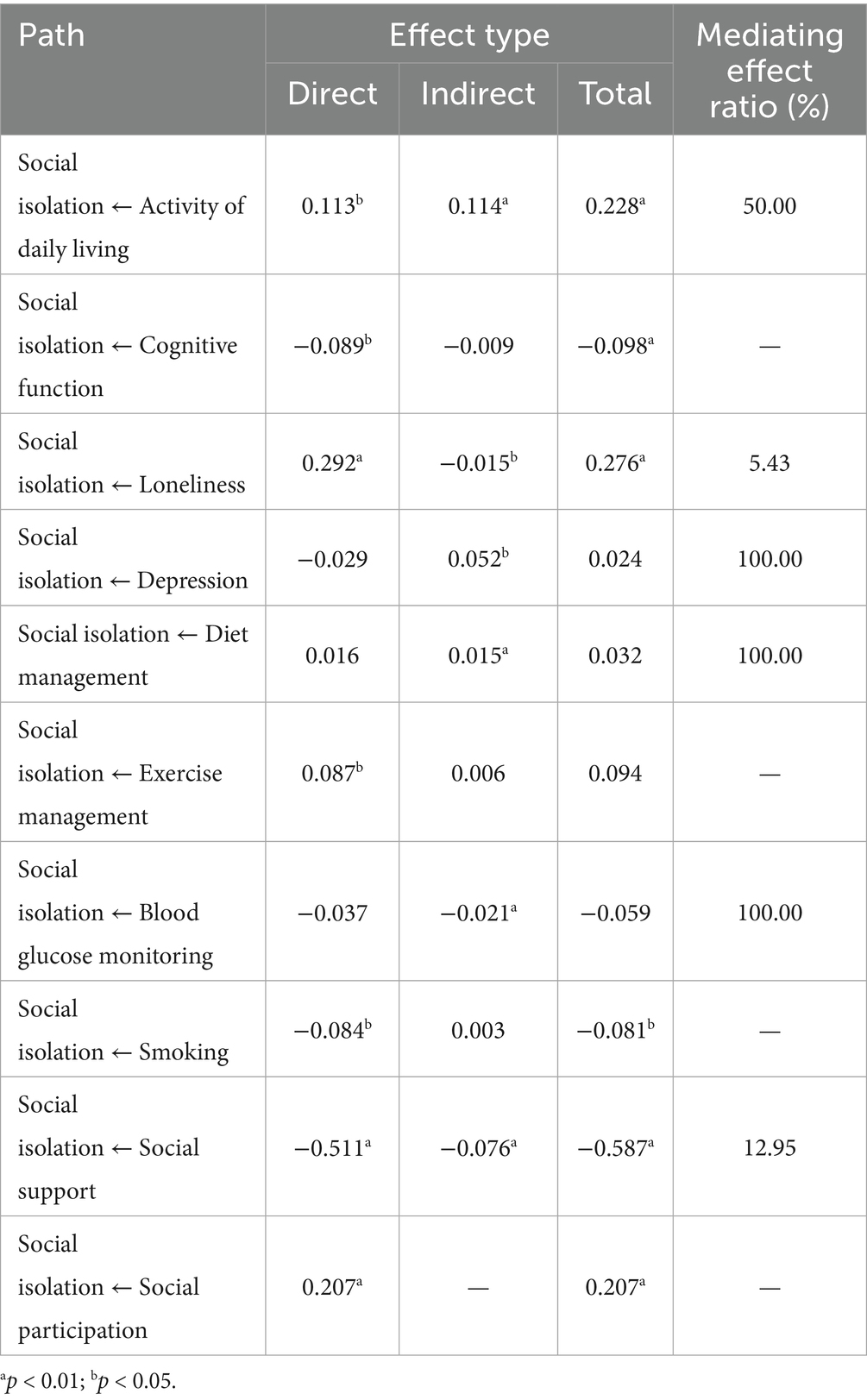
The direct, indirect, and total effects of factors on social isolation in older adults with T2DM are listed in Table 4. Cognitive function, SDSCA exercise management, and smoking only directly affect social isolation, while depression, SDSCA diet management, and blood glucose monitoring indirectly affect social isolation completely through social participation. Activity of daily living, loneliness, and social support not only directly affect social isolation but also influence it through social participation, with intermediary effect ratios of 50.00, 5.43, and 12.95%, respectively.
4 Discussion
Based on Wenger’s conceptual framework of social networks for older adults, this study used a Bayesian method to test a structural equation model to determine the path of the influencing factors to social isolation in older adults with T2DM. Among 496 older adults with T2DM, 227 (45.8%) reported developing social isolation. Activity of daily living, cognitive function, loneliness, exercise management, smoking, social support, and social participation were directly associated with social isolation. In addition, six factors—activity of daily living, loneliness, depression, diet management, blood glucose monitoring, and social support—were indirectly associated with social isolation through their impact on social participation. Our research broadens the theoretical research field of social isolation in older adults with T2DM and provides a theoretical basis for formulating targeted interventions.
In this study, 45.77% older adults with T2DM experienced social isolation, which is higher than 22.7% of older adults with T2DM in Beijing in 2019 (6), which may be related to the reduction of going out and social interaction in older adults after the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak (36). It is also higher than 24.3% for community-dwelling older adults during the COVID-19 outbreak (37), indicating that the impact of the epidemic on the social network of older adults with T2DM may be higher than that of the general older adult population. Older adults with T2DM tend to reduce communication with the outside world to avoid infection or glucose fluctuations, which may lead to social isolation.
We found that the occurrence of social isolation in the friend dimension in older adults with T2DM was significantly higher than that in the family dimension (48.19% vs. 14.92%), which was consistent with the results of other studies of social isolation in older adults (38, 39). In general, personal family networks gradually stabilize from adolescence, while the size of friend networks gradually decreases in adulthood (40). In the context of Chinese “filial piety culture” (a Confucian value emphasizing children’s obligation to respect and care for aging parents), the majority of older adults with T2DM live with family members such as spouses or children. In this study, 473 participants (95.36%) lived with their families. Even among those who live alone, regular contact is maintained through visits or communication via telephone, WeChat (a widely used social app in China), and other approaches. As a result, social isolation in the family dimension occurs less (41). However, due to retirement and the demands of glycemic control, especially after developing diabetic complications, older adults often experience reduced participation in social activities and a shrinking network of friends. As a result, social isolation is prone to occur in the friend dimension.
After controlling for gender, working status, complications, and number of chronic diseases, the older adults with T2DM with low-level activity of daily living, poor cognitive function, high-level loneliness and low-level social support were more likely to have social isolation, which is similar to the findings of studies in the general older adult population (42–44). Due to aging and diabetes, older adults with T2DM are prone to have impaired cognitive function, which affects their judgment of time and place and therefore affects their social communication ability (45). The older adults with loneliness and a low level of social support think that they are not close to others and cannot get support from the outside world, so they consciously alienate themselves from others. All of these may increase the risk of social isolation.
We found the occurrence of social isolation in older adults with T2DM was also directly related to diabetes self-management behaviors in exercise management and smoking; the older adults with a low exercise management level tended to suffer from social isolation. It was reported that 38.9% of the Chinese older adults with T2DM kept regular exercise (46), and they tended to engage in aerobic exercise mainly by walking, and more than half of them exercise alone (47). Moreover, due to diabetes complications (36.29% in this study), part of the older adults had no energy to participate in other social activities (48) after exercise. These situations may lead to difficulties in maintaining or even reducing the social activity level of older adults with T2DM, resulting in social isolation. In many social occasions in China, there is a habit of handing and receiving cigarettes. Smoking is often seen as a social means of building social relationships and then communicating with friends, and correspondingly, the risk of social isolation for smokers is reduced (49). However, smoking accelerates the occurrence of vascular distortion and complications, which leads to the deterioration of the condition (50). Therefore, it is not advocated that older adults with T2DM increase social interaction through smoking, and other suitable social means can be used instead, such as playing cards and square dancing (for those without diabetes complications).
In this study, we found social participation is a mediation variable, which is confirmed the initial hypothesis, and six factors (activity of daily living, loneliness, depression, diet management, blood glucose monitoring, and social support) strengthen or weaken its influence on the risk of social isolation through the intermediary of social participation. The lower the level of social participation among older adults, the less family participation, social contact, and interaction, and the higher the risk of social isolation (42). It is worth noting that for older adults with T2DM, diet management and blood glucose monitoring were not directly related to social isolation, but rather indirectly affected social isolation through their impact on social participation. DiNardo et al. reported that dietary restrictions were associated with social isolation in individuals with diabetes (51). Our study found that older adults with T2DM who adhered to more stringent dietary control regimens exhibited diminished social participation, while those demonstrating greater adherence to blood glucose monitoring showed increased social participation. These two factors, along with the other four factors, were related to social isolation through social participation. In China, dinner is an important way for people to socialize. However, the older adults with T2DM worry that taking dinner with others may destroy their diet control and cause abnormal blood glucose fluctuations. On the other hand, older adults are concerned about maintaining a low-sugar diet that is unsociable and consciously reduce social activities (52). As a result, individuals with good diet management may reduce social participation, and the risk of social isolation increases correspondingly. Older adults who frequently monitor their blood glucose may be able to adjust their activity plan in a timely manner according to their blood glucose status, which can increase their confidence in participating in social activities and indirectly reduce the risk of social isolation (53).
Variables such as activities of daily living, loneliness, and social support are directly related to social isolation, and are also indirectly related to it through social participation. The scope and degree of social participation of older adults with good activities of daily living are not limited, and those with high-level social support are willing to participate in various social activities (54). However, we found that the older adults with high levels of loneliness had high levels of social participation. It may be because older adults with high levels of loneliness consciously increase family and social activities to reduce loneliness. Even if social participation behavior has increased, older adults still feel lonely. This kind of socializing is likely to be ineffective. In the next step, qualitative interviews should be conducted with the older adults with T2DM to understand the forms and real feelings of their social participation, and corresponding interventions need to be developed to reduce social isolation in this population.
It is recommended that community healthcare providers should prioritize older adults with T2DM who exhibit impaired activities of daily living, poor cognitive function, and high levels of loneliness, with regular assessment of their social isolation status. Given the mediating role of social participation, healthcare professionals should encourage social engagement among older adults while simultaneously guiding them to maintain dietary control and enhance self-monitoring of blood glucose levels. Considering both diabetes exercise management principles and the physical capabilities of older adults with T2DM, medical staff may organize group activities such as walking sessions or regularly arrange cultural and recreational programs, including calligraphy and music appreciation, thereby providing appropriate opportunities for social participation. Furthermore, it is advisable to improve supporting infrastructure that facilitates social engagement for older adults, creating more favorable conditions for their social activities.
5 Conclusion
This study showed a high prevalence of social isolation in older adults with T2DM and severe social isolation in the friend dimension. For older adults with T2DM, activities of daily living, cognitive function, loneliness, exercise, smoking self-management, and social support are directly related to social isolation. Social participation has a direct correlation with social isolation and is an intermediary factor between activities of daily living, loneliness, depression, diet management, blood glucose monitoring, self-management, social support, and social isolation. Depression, diet management, and blood glucose monitoring are related to social isolation completely through social participation.
6 Limitations
First, as this is a cross-sectional study, it does not allow for the determination of causal relationships between social isolation and the related factors. Second, the older adults with T2DM in this study were from Beijing, the capital city and a first-tier city in China, which may limit the representativeness of the sample to a certain extent. In the future, a multicenter follow-up study will be necessary to further reveal the mechanisms through which social isolation influences various factors in older adults with T2DM.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine. IRB certificate number: 2023BZYLL0504. Our study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients or their legal representatives.
Author contributions
JW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XB: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. KL: Validation, Writing – review & editing. CS: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. QW: Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. RZ: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YL: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1674077.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Compilation team of Clinical Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Elderly Diabetes mellitus in China. Clinical guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes among the elderly in China (2022 edition). Chin J Intern Med. (2022) 61:12–50. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20211027-00751
2. Asif, M, Asif, A, Rahman, UA, Ajmal, H, Jafar, U, and Fatima, O. Social isolation, loneliness, and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. (2025) 19:221–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2025.03.006
3. Uchigata, Y. The still persistent stigma around diabetes: is there something we can do to make it disappear? Diabetol Int. (2018) 9:209–11. doi: 10.1007/s13340-018-0373-z
4. Yu, PL, Wang, JY, Hu, JZ, Liu, SX, Han, BX, He, Y, et al. The standard for healthy Chinese older adults (WS/T 802-2022). Chin J Geriatr. (2022) 41:1263. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2022.11.001
5. Zhang, WJ, and Liu, RP. Determinants of social isolation of the Chinese elderly. Popul Res. (2016) 40:75–91.
6. Yang, KL, Liu, Y, Yin, X, Wu, SS, Wu, QY, Wang, L, et al. A survey of social network status and its related factors for older adults with type 2 diabetes in Beijing, China. Nurs Open. (2022) 9:1005–14. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1138
7. World Health Organization. Constitution of the World Health Organization. Geneva: World Health Organization.
8. Ge, L, Yap, CW, and Heng, BH. Associations of social isolation, social participation, and loneliness with frailty in older adults in Singapore: a panel data analysis. BMC Geriatr. (2022) 22:26. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02745-2
9. Zhang, S, and Chen, G. Status and influencing factors of social isolation among urban elderly people in China. Popul J. (2015) 37:66–76. doi: 10.16405/j.cnki.1004-129X.2015.04.007
10. Kim, J, and Park, GR. Prolonged social isolation and cognitive function in older adults: lack of informal social contact versus formal social activity as the source of social isolation. Aging Ment Health. (2023) 27:2438–45. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2023.2202616
11. Kim, J, and Hwang, S. Separating the effects of transitions into and out of social isolation and loneliness on cognitive function in later life. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. (2024) 79:gbae082. doi: 10.1093/geronb/gbae082
12. Blazer, D. Social isolation and loneliness in older adults—a mental health/public health challenge. JAMA Psychiatry. (2020) 77:990–1. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.1054
13. Basmaz, SE, Dogan, F, and Sahin, F. Relationship between mental symptoms, dietary compliance and glucose levels of diabetic patients in isolation during COVID-19 pandemic. J Health Sci Med. (2020) 5:189–94. doi: 10.32322/jhsm.1011144
14. Ida, S, Kaneko, R, Imataka, K, Okubo, K, Shirakura, Y, Azuma, K, et al. Factors associated with social isolation and being homebound among older patients with diabetes: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. (2020) 10:e037528. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037528
15. Wenger, GC. A comparison of urban with rural support networks: Liverpool and North Wales. Ageing Soc. (1995) 15:59–81. doi: 10.1017/S0144686X00002129
17. Wang, P, Wang, Q, Zhao, C, Li, X, and Zhang, Y. Latent profile analysis and its influencing factors of social isolation among community older adults. J Nurs Sci (Chinese). (2024) 39:14–8. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2024.02.014
18. Fu, B, Xiao, Q, and Hu, H. Analysis of the social participation level and influencing factors of elderly diabetes patients. Chin J Prev Control Chronic Dis (Chinese). (2020) 28:48–52. doi: 10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2020.01.012
19. Chinese Diabetes Society. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition). Chin J Diabetes Mellit. (2021) 13:315–409. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210221-00095
20. Van de Schoot, R, Depaoli, S, King, R, Kramer, B, Märtens, K, Tadesse, MG, et al. Bayesian statistics and modelling. Nat Rev Methods Primers. (2021) 1:1. doi: 10.1038/s43586-020-00001-2
21. Lubben, J, Blozik, E, Gillmann, G, Iliffe, S, von Renteln Kruse, W, Beck, JC, et al. Performance of an abbreviated version of the Lubben social network scale among three European community-dwelling older adult populations. Gerontologist. (2006) 46:503–13. doi: 10.1093/geront/46.4.503
22. Chang, Q, Sha, F, Chan, CH, and Yip, PSF. Validation of an abbreviated version of the Lubben social network scale (“LSNS-6”) and its associations with suicidality among older adults in China. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0201612. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201612
23. Chen, Y, Ji, H, Shen, Y, and Liu, D. Chronic disease and multimorbidity in the Chinese older adults’ population and their impact on daily living ability: a cross-sectional study of the Chinese longitudinal healthy longevity survey (CLHLS). Arch Public Health. (2024) 82:17. doi: 10.1186/s13690-024-01243-2
24. Liao, Q, Gao, J, Zhong, YZ, Bai, DX, Liu, RR, Zhang, H, et al. Influencing factors of pre- and intra-frail daily living activities of the elderly in pension institutions. Modern Clin Nurs. (2020) 19:16–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8283.2020.07.003
25. Katzman, R, Zhang, MY, Ouang-Ya-Qu,, Wang, ZY, Liu, WT, Yu, E, et al. A Chinese version of the mini-mental state examination; impact of illiteracy in a Shanghai dementia survey. J Clin Epidemiol. (1988) 41:971–8.
26. Zhang, MY ed. Handbook of psychiatric rating scales. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press (1998).
27. Huang, Y, Zhu, X, Liu, X, and Li, J. The effects of loneliness, social isolation, and associated gender differences on the risk of developing cognitive impairment for Chinese oldest old. Aging Ment Health. (2022) 27:1360–7. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2022.2116396
28. Wang, DF. Reliability and validity of the Russell loneliness scale. Chin J Clin Psychol. (1995) 3:23–5.
29. Tang, D. Use of the brief geriatric depression scale (GDS-15) in Chinese elderly. Chin J Clin Psychol Chinese. (2013) 21:402–5. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2013.03.036
30. Sun, S. Study on the current situation and influencing factors of self-management in diabetes patients. Master’s thesis. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College (2010).
31. Sun, L, Sun, L, Sun, Y, Yang, L, Wu, H, Zhang, D, et al. Correlations between psychological symptoms and social relationships among medical undergraduates in Anhui Province of China. Int J Psychiatry Med. (2011) 42:29–47. doi: 10.2190/PM.42.1.c
32. Lv, F, and Gu, Y. Family APGAR questionnaire and its clinical applications. Foreign Med Sci (Hosp Manag Ed). (1995) 12:56–9.
33. Ke, X, Liu, C, and Li, N. Social support and quality of life: a cross-sectional study on survivors eight months after the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. BMC Public Health. (2010) 10:573–83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-573
34. Yan, J, Zhang, SG, Jin, SJ, and Chen, X. Effect of social support and depression on stages of dietary behaviors in diabetic patients. J Nurs Sci. (2018) 33:72–4. 79. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2018.04.072
35. He, Y. A longitudinal study of the level of social participation and influencing factors in first-episode stroke patients. (Master’s thesis). Shanghai: Naval Medical University (2013).
36. Xu, Z, Zhang, D, Xu, D, Li, X, Xie, Y, Sun, W, et al. Loneliness, depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder among Chinese adults during COVID-19: a cross-sectional online survey. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0259012. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259012
37. Li, Y, Han, Y, Liu, Y, Wang, X, Chu, M, Jia, Y, et al. Prevalence and influencing factors of social isolation among community elderly in Tangshan city. Chin J Public Health. (2021) 37:319–22. doi: 10.11847/zgggws1124142
38. Zhang, Y, Liu, F, Xu, R, Yi, M, and Guo, J. Relationship among social isolation, depression and frailty of the elderly in pension institutions. Chin Nurs Res. (2022) 36:1543–6. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2022.09.007
39. Fang, Y, Ma, L, Chen, H, Cai, S, Jiang, W, Luo, F, et al. The effect of social isolation on the cognitive ability of the oldest old in Chinese nursing homes in post-COVID-19: a moderated chain mediation model. Front Psychol. (2024) 15:1421729. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1421729
40. Wrzus, C, Hänel, M, Wagner, J, and Neyer, FJ. Social network changes and life events across the life span: a meta-analysis. Psychol Bull. (2013) 139:53–80. doi: 10.1037/a0028601
41. Dai, F, Liu, S, and Zhang, X. Research progress on informal care of the elderly living with multiple disease in a community home. Chin J Gen Pract. (2020) 18:471–5. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.001276
42. Liu, C, Chen, L, Xie, B, Chen, Y, Wang, J, and Xu, H. Prevalence and determinants of social isolation among community-living oldest-old adults. J Nurs Sci. (2022) 37:98–102. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2022.13.098
43. DiNapoli, EA, Wu, B, and Scogin, F. Social isolation and cognitive function in Appalachian older adults. Res Aging. (2014) 36:161–79. doi: 10.1177/0164027512470704
44. Wen, Z, Peng, S, Yang, L, Wang, H, Liao, X, Liang, Q, et al. Factors associated with social isolation in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2023) 24:322–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2022.11.008
45. Sebastian, MJ, Khan, SK, Pappachan, JM, and Jeeyavudeen, MS. Diabetes and cognitive function: an evidence-based current perspective. World J Diabetes. (2023) 14:92–109. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i2.92
46. Yang, ZF, Bai, JJ, Huang, R, Pan, X, and Lu, X. Analysis of status quo of daily exercise of elderly patients with diabetes mellitus and its influencing factors. Chin Nurs Res. (2015) 29:2972–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6493.2015.24.009
47. Mirahmadizadeh, A, Khorshidsavar, H, Seif, M, and Sharifi, MH. Adherence to medication, diet and physical activity and the associated factors amongst patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. (2020) 11:479–94. doi: 10.1007/s13300-019-00750-8
48. MacDonald, CS, Ried-Larsen, M, Soleimani, J, Alsawas, M, Lieberman, DE, Ismail, AS, et al. A systematic review of adherence to physical activity interventions in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2021) 37:e3444. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3444
49. Zhang, Y, Wang, J, Lai, K, Bian, H, Chen, H, and Gao, L. Socializing with smoker and social smoking behavior among Chinese male smokers with low nicotine dependence: the mediating roles of belief of smoking rationalization and smoker identity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:14765. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214765
50. Yang, L, Chu, TK, Lian, J, Lo, CW, Lau, PK, Nan, H, et al. Risk factors of chronic kidney diseases in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:14686. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32983-1
51. DiNardo, MM, Phares, AD, Jones, HE, Beyer, NM, Suss, SJ, McInnes, S, et al. Veterans’ experiences with diabetes: a qualitative analysis. Diabetes Educ. (2020) 46:607–16. doi: 10.1177/0145721720965498
52. Peng, X, Guo, X, Li, H, Wang, D, Liu, C, and Du, Y. A qualitative exploration of self-management behaviors and influencing factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:771293. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.771293
53. Maiorino, MI, Signoriello, S, Maio, A, Chiodini, P, Bellastella, G, Scappaticcio, L, et al. Effects of continuous glucose monitoring on metrics of glycemic control in diabetes: a systematic review with Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:1146–56. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1459
Keywords: type 2 diabetes, aged, social isolation, influencing factors, path analysis
Citation: Wang J, Bai X, Lin K, Sun C, Wu Q, Zhang R and Liu Y (2025) Social isolation in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus—a path analysis. Front. Public Health. 13:1562186. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1562186
Edited by:
Alejandro Gil-Salmerón, University of Valencia, SpainReviewed by:
Carlos Manuel Zapata-Martín del Campo, National Institute of Cardiology Ignacio Chavez, MexicoPedro Alexandre Duarte-Mendes, Polytechnic Institute of Castelo Branco, Portugal
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Bai, Lin, Sun, Wu, Zhang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yu Liu, bGl1eXUyMjJAaG90bWFpbC5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jing Wang
Jing Wang Xiaoyan Bai
Xiaoyan Bai Keke Lin
Keke Lin Chao Sun
Chao Sun Quanying Wu
Quanying Wu Ruiting Zhang
Ruiting Zhang Yu Liu
Yu Liu