- 1School of Physical Education, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 2Department of Physical Education, Dankook University, Yongin, Republic of Korea
Background: Internet Addiction Disorder (IAD) is a recurrent mental illness. It severely impacts both physical and mental health, leading to physiological symptoms such as neurological dysfunction and immunosuppression. This condition significantly affects adolescent development and has become a global public health concern. Scientific evidence supports the beneficial impact of integrative mind–body exercises for treating internet addiction disorders. Though these interventions show promise, their therapeutic efficacy exhibits considerable variation across different modalities. Currently, there exists a significant research gap, as no comprehensive clinical investigations have systematically evaluated the comparative therapeutic outcomes of distinct mind–body practices among individuals diagnosed with internet addiction.
Objective: To conduct a network meta-analytic investigation comparing the therapeutic efficacy of diverse mind–body exercise interventions for addressing symptoms associated with internet addiction disorder.
Methods: Data were retrieved from Web of Science, PubMed, CNKI, and VIP databases. After screening and data extraction, network meta-analysis was performed using STATA 18.0.
Results: Twenty-four studies were included in the analysis. Compared with the control group (Placebo), Mindfulness [SMD = 13.33, 95%CI (7.42,19.25), p < 0.05] and Taichi [SMD = −10.91, 95%CI (−18.71,−3.11), p < 0.05] significantly improved internet addiction symptoms. According to SUCRA values, the interventions were ranked in order of effectiveness: Mindfulness (SUCRA = 76.3%), DanceSport (SUCRA = 64.0%), Yoga (SUCRA = 63.1%), and Taichi (SUCRA = 62.6%).
Conclusion: Mindfulness and Tai Chi significantly reduce and alleviate internet addiction symptoms compared to Placebo. Based on SUCRA rankings, Mindfulness, Dance Sport, Yoga, and Tai Chi show the highest probability of effectiveness in descending order, providing promising options for managing internet addiction symptoms in young adults.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42025631096.
Introduction
As “digital natives,” young adults (aged 18–24 years) represent a distinctive developmental period characterized by continued neuroplasticity and incomplete prefrontal cortex maturation, making them particularly vulnerable to Internet addiction (1–3). Neurobiological research has demonstrated that the underdevelopment of the prefrontal cortex, which is critical for impulse control and executive decision-making, combined with heightened sensitivity to social and emotional stimuli, creates a neurological landscape that predisposes university students to addictive behaviors (4–6). This critical neurodevelopmental stage features heightened reward sensitivity and still-developing inhibitory control systems, coupled with increased independence and reduced external monitoring, creating unique susceptibility to problematic Internet use behaviors (2, 7). The convergence of neurological immaturity, digital immersion, and reduced self-regulatory mechanisms significantly elevates the risk of Internet addiction among this demographic, underscoring the urgent need for targeted interventional strategies (1, 8). Internet addiction refers to compulsive Internet use behavior, characterized by an individual’s inability to control their usage, resulting in negative physiological, psychological, and social consequences (9). IAD can not only lead to physiological symptoms such as neurological dysfunction and immunosuppression (10), but also lead to psychological problems such as cognitive decline, anxiety and depression (11, 12). Olson et al.’s (13) research shows that the incidence of Internet addiction disorder in young Adults is increasing year by year, and IAD has become a major public health problem affecting the development of young Adults (14).
Current IAD interventions span a wide range, including pharmacotherapy (15), acupuncture (16), and exercise behavior (17). Growing apprehension regarding pharmaceutical adverse reactions and contraindicated drug combinations has led to heightened interest in treatment approaches that do not rely on medication (18). Research has progressively demonstrated the significant impact of physical activity on psychological well-being (19, 20). Mind–body exercise (MBE) is classified by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health at the U.S. National Institutes of Health as a complementary and alternative therapeutic practice (21). Mind–body exercise represents a distinctive form of physical activity that synthesizes breathing techniques, physical movements, and meditative practices (22, 23). These exercises are characterized by their low to moderate-intensity aerobic nature, featuring gentle and precise movements that emphasize the synchronization between physical actions and respiratory patterns (24). These mind–body practices combine physiological and psychological therapeutic elements (25, 26). Compared to traditional aerobic and resistance training programs, these mindfulness-based exercise practices demonstrate extraordinary practicality and contribute to sustained health improvement (27, 28). Their unique value lies in their holistic philosophy, which prioritizes the complex connections between psychological states, physiological functions, and breathing patterns. Moreover, these mind–body exercises require no special equipment (29, 30), have low learning costs, high safety levels, and are suitable for large-scale promotion across diverse populations. For patients with Internet Addiction Disorder (IAD), these comprehensive exercises provide advantages beyond traditional exercise methods, as they not only enhance physical fitness but also effectively reduce anxiety levels and improve overall quality of life. Among various forms of mind–body exercise, this study selected four therapies based on the following considerations: Representativeness; Operability; Safety; Popularity; Preliminary research foundation.
Research has indicated that integrative movement practices like Tai Chi and Dance Sport demonstrate efficacy in alleviating internet dependency symptoms (3, 31, 32). The existing literature predominantly examines therapeutic approaches in isolation (33, 34), with limited comparative studies evaluating multiple mindfulness-based movement interventions for youth internet addiction (35, 36). As highlighted in the review of Pirwani et al. (37), contemporary investigations tend to concentrate on specific demographic segments, leaving broader age-range analyses underexplored (38, 39). Network meta-analysis offers advantages over traditional meta-analytic methods by enabling both direct and indirect effect comparisons, facilitating intervention rankings (40). This investigation examined randomized controlled trials evaluating seven distinct mind–body therapeutic approaches for internet addiction disorder. By implementing network meta-analytic methodology to synthesize both direct and indirect comparative data, this research assessed relative intervention effectiveness, established comparative efficacy metrics, and generated evidence-based rankings. The findings aim to inform clinical decision-making and provide empirical foundation for young adults internet addiction treatment protocols.
This study focused on young adults aged 18–24 years, a developmental period characterized by continued neuroplasticity and heightened vulnerability to internet addiction (41, 42). While this age range extends beyond traditional adolescence, it represents a critical transition period in cognitive and behavioral development.
Study design and methodology
Prior to initiating research, our systematic analysis protocol received formal registration through PROSPERO, an established global database for systematic review protocols (reference: CRD42025631096). This preregistration step ensured methodological transparency and adherence to standardized review practices (Table 1).

Table 1. PICOS-based eligibility criteria (participation, intervention comparison, outcomes, and study design).
Literature search
This study strictly followed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines (43) and established rigorous literature search, inclusion, screening, and exclusion criteria based on the PICOS (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Study design) principle of evidence-based medicine. Boolean logic searches were conducted in Elsevier ScienceDirect, Web of Science, PubMed, ProQuest, Scopus, The Cochrane Library, CNKI, WFSDP, and VIP databases. Literature retrieval encompassed publications in both English and Chinese, with Chinese-language sources limited to prominent academic periodicals. The temporal scope of the investigation spanned from the beginning of 2010 through April 1, 2024. Supplementary relevant publications were identified through reference list examination of pertinent studies and alternative search methods. The detailed search protocol employed for the PubMed database is presented in Box 1.
BOX 1. PubMed search strategy
#1 (“Mind”[Title/Abstract] OR “body exercise”[Title/Abstract] OR “Mind–body exercise”[Title/Abstract] OR “Taichi”[Title/Abstract] OR “Baduanjin”[Title/Abstract] OR “Mindfulness”[Title/Abstract] OR “Dance Sport”[Title/Abstract]) OR “Qigong”[Title/Abstract] OR “Yoga”[Title/Abstract] OR “Aerobicdance”[Title/Abstract] AND “Internet Addiction Disorder”[MeSH Terms]
#2 “Sports”[Title/Abstract] OR “Sport”[Title/Abstract] OR “Athletics”[Title/Abstract] OR “Athletic”[Title/Abstract]
#3 #1 OR #2
#4 “Internet Addiction Disorder”[Title/Abstract] OR “Addiction Disorder,Internet”[Title/Abstract] OR “Addiction Disorders,Internet”[Title/Abstract] OR “Disorder,Internet Addiction”[Title/Abstract] OR “Disorders,Internet Addiction”[Title/Abstract] OR “Internet Addiction Disorders”[Title/Abstract] OR “Internet Addiction”[Title/Abstract] OR “Addiction,Internet”[Title/Abstract] OR “Addictions,Internet”[Title/Abstract] OR “Internet Addictions”[Title/Abstract] OR “Internet Gaming Disorder”[Title/Abstract] OR “Disorder,Internet Gaming”[Title/Abstract] OR “Disorders,Internet Gaming”[Title/Abstract] OR “Gaming Disorder,Internet”[Title/Abstract] OR “Gaming Disorders,Internet”[Title/Abstract] OR “Internet Gaming Disorders[Title/Abstract] OR Smartphone Addiction[Title/Abstract] OR Addiction,Smartphone[Title/Abstract] OR Addictions,Smartphone[Title/Abstract] OR Smartphone Addictions[Title/Abstract] OR Social Media Addiction[Title/Abstract] OR Addiction,Social Media[Title/Abstract] OR Addictions,Social Media[Title/Abstract] OR Media Addiction,Social[Title/Abstract] OR Media Addictions,Social[Title/Abstract] OR Social Media Addictions[Title/Abstract]
#5 “randomized controlled trial”[Publication Type] OR “controlled clinical trial”[Publication Type]
#6 #3 AND #4 AND #5 AND #6
Inclusion criteria
The study only included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) examining mind–body exercise interventions for internet addiction. The intervention groups received one of four mind–body exercise forms (Tai Chi, Mindfulness, Baduanjin, or Dance Sport), while the control group engaged in unstructured physical activity. The outcome measure was IAD scale scores (intervention was considered effective if the difference between post-intervention and pre-intervention scores was less than 0 on any type of internet addiction scale used to assess participants’ psychological health).
Selection restrictions
The research team eliminated investigations that met any of the following conditions: experimental designs lacking randomized control trials; research conducted on non-human subjects; qualitative analyses, questionnaire-based investigations, literature syntheses, meta-analyses, symposium abstracts, or republished materials. Additionally, we removed papers that failed to report statistical measures using mean and standard deviation notation, incorporated supplementary treatments during the research period, or presented incomplete/incompatible datasets. Research papers whose metrics could not be properly extracted were also excluded from consideration.
Literature screening and data extraction
The evaluation process began with two independent reviewers utilizing NoteExpress V4.X to compile and manage references. After eliminating redundant entries, they assessed publication abstracts and headings. Following preliminary selection, comprehensive manuscript evaluation was conducted according to predetermined eligibility criteria. These criteria included: (1) only randomized controlled trials with human subjects; (2) studies reporting outcomes using mean and standard deviation; (3) research implementing a single intervention without supplementary treatments; (4) complete datasets with compatible metrics; and (5) studies published in peer-reviewed journals with full-text availability. When differences arose in selection outcomes, the reviewers consulted a third expert to reach consensus. Data extraction was performed independently by two team members using standardized documentation forms. The collected information encompassed: (1) Publication details (primary author identification, publication timeline, manuscript title); (2) Study population data (group sizes, demographic information including age distribution and sex ratio); (3) Methodological specifics (intervention protocols, treatment duration and intervals, Internet Addiction Disorder (IAD) measurements—specifically, baseline assessments conducted prior to intervention initiation (pre-intervention) using validated IAD diagnostic instruments such as Young’s Internet Addiction Test (IAT), Chen Internet Addiction Scale (CIAS), or other standardized tools, and follow-up assessments conducted after intervention completion (post-intervention) using identical instruments to evaluate changes in IAD severity, frequency, and associated symptoms); (4) literature quality assessment using the PEDro scale for RCTs; and (5) outcome indicators and main findings. Inter-coder reliability was 94%, with discrepancies resolved through re-checking and discussion.
Quality assessment protocol
Two autonomous evaluators employed RevMan 5.4’s evaluation framework to systematically analyze methodological integrity. The assessment encompassed multiple domains: randomization procedures, allocation masking techniques, participant-researcher blinding protocols, outcome evaluation objectivity, data completeness, reporting transparency, and additional potential sources of systematic error. The evaluation system utilized a three-tier classification: investigations fulfilling all methodological requirements received positive marks (+) indicating minimal bias risk; those failing to meet standards were designated with negative marks (−) signifying elevated bias risk; while instances of insufficient methodological documentation were marked with uncertainty indicators (?). When evaluators reached different conclusions, they engaged a third expert reviewer to establish consensus through collaborative deliberation.
Quantitative synthesis methods
The synthesis of data employed STATA 17.0’s networkMeta package to analyze continuous variables across studies. Given the diversity in measurement instruments, effect magnitudes were synthesized using standardized mean differences (SMD), with significance threshold established at α = 0.05. Statistical heterogeneity evaluation incorporated both Q and I2 statistics, while potential publication bias underwent examination through Egger’s regression approach. In cases involving closed-loop network configurations, inconsistency evaluation utilized node analysis techniques. When loop testing yielded p > 0.05, researchers proceeded with consistency model computations. Local inconsistency underwent evaluation via node-splitting methodology; instances where p < 0.05 prompted adherence to traditional meta-analytic direct comparison outcomes. Treatment effectiveness rankings were determined through surface under the cumulative ranking curves (SUCRA), yielding values between 0 and 1. To identify optimal therapeutic combinations, cluster analysis was performed based on these SUCRA metrics. The investigation of publication bias utilized adjusted comparison funnel plot visualization techniques.
Research outcomes
Document identification and selection process
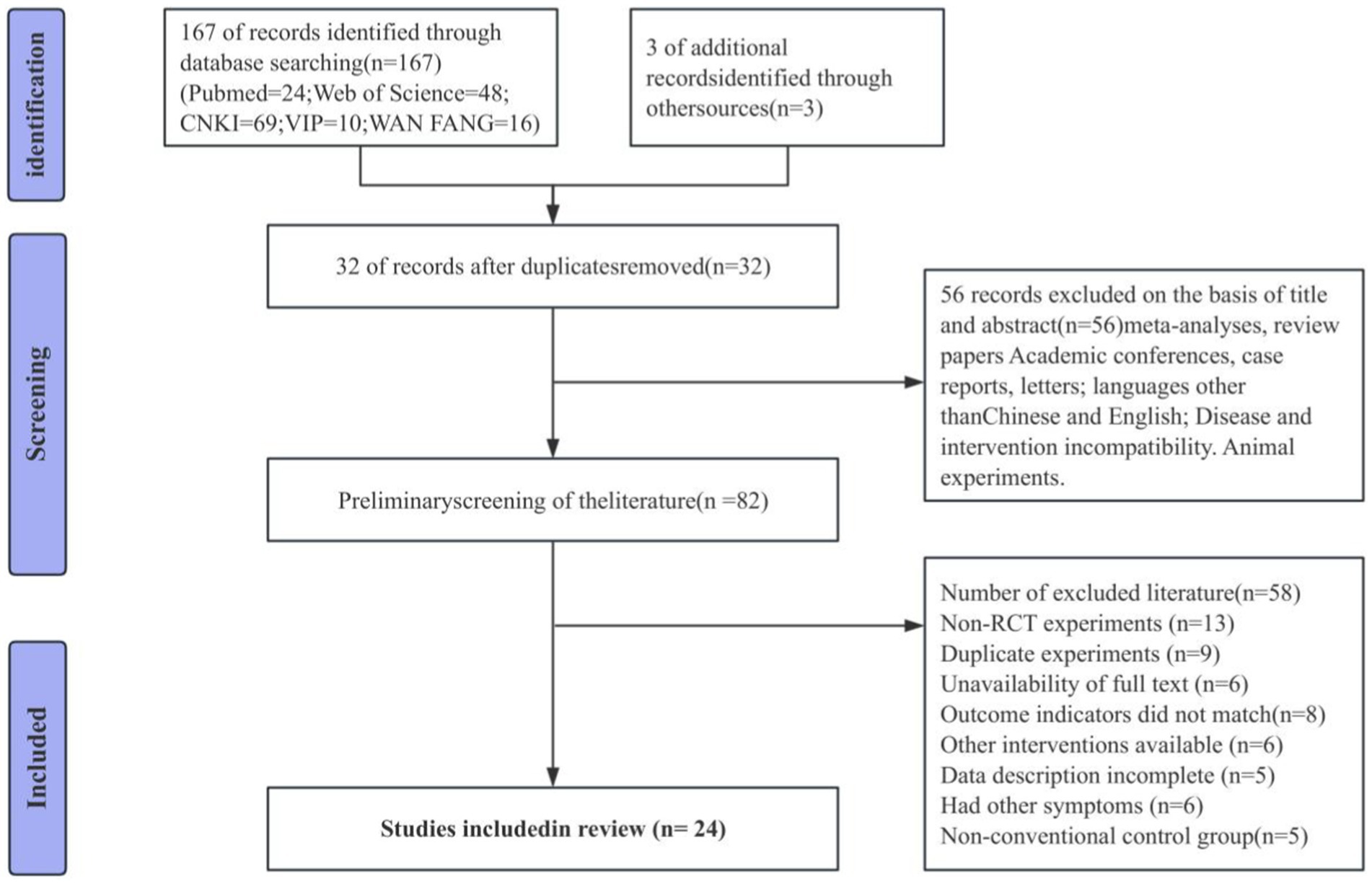
The systematic search protocol yielded 170 potentially relevant publications. Database management using EndNote software, combined with manual verification, identified 32 duplicate entries, leaving 138 unique manuscripts for evaluation. Comprehensive assessment, including examination of titles, abstracts, and complete manuscripts, resulted in the final selection of 24 publications that satisfied all inclusion parameters. The selected literature includes both English and Chinese publications. A detailed visualization of the selection methodology and outcomes appears in Figure 1.
Characteristics and quality evaluation of selected research
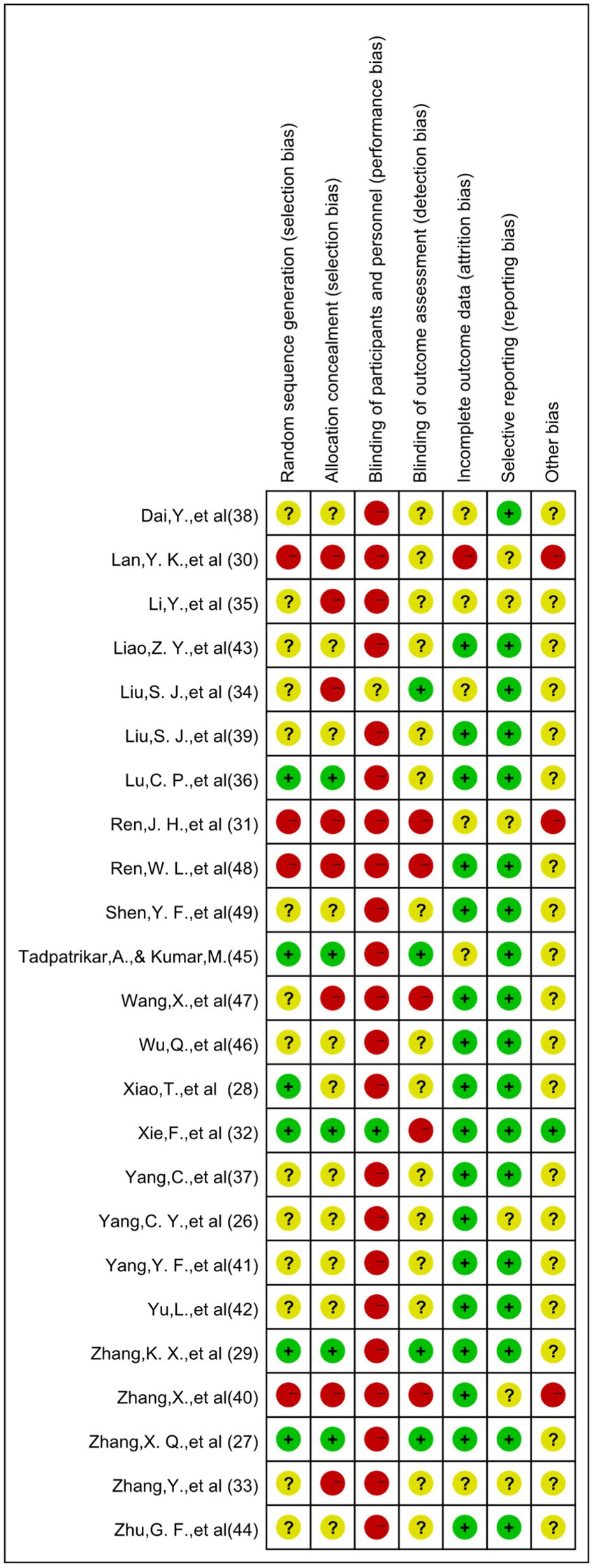
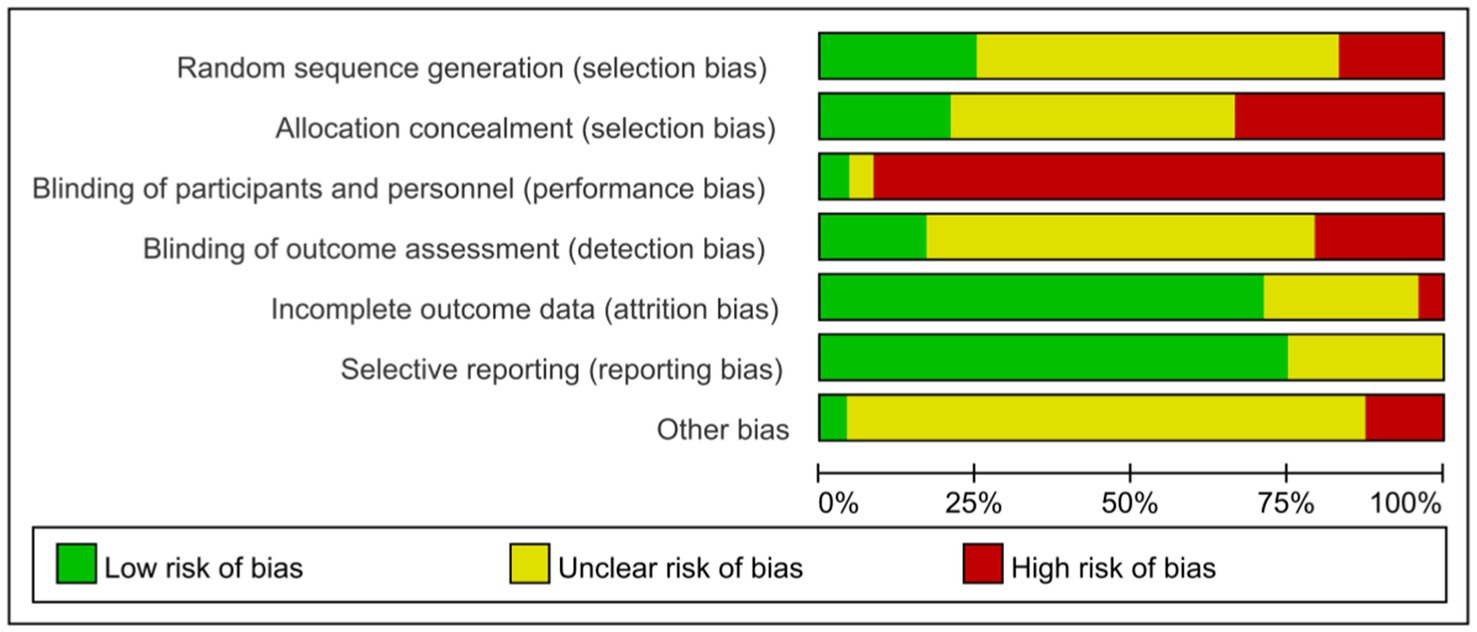
Our systematic review synthesized findings from 24 investigations meeting inclusion parameters. Comprehensive study details appear in Table 2, encompassing research conducted on 1,711 young adults (age range: 18–24). Intervention durations spanned 8–16 weeks for measuring outcomes. Given the exercise-based nature of interventions, implementing blinding presented methodological challenges—a single investigation achieved double-blind conditions, whereas remaining studies demonstrated various methodological constraints regarding blinding protocols. Quality evaluation outcomes for the literature are depicted through Figures 2, 3.
Network relationship diagram of included studies
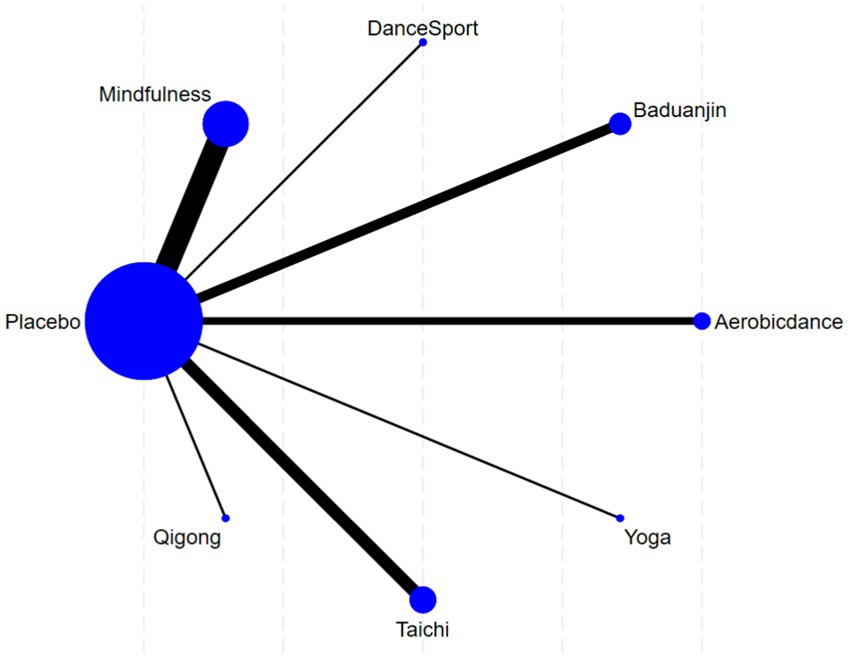
In Figure 4, the seven nodes represent seven intervention measures, with lines between nodes indicating direct comparisons. Within the network diagram, connecting lines vary in width to reflect frequency of direct analytical comparisons made between intervention pairs. The intervention groups include Tai Chi, Mindfulness, Baduanjin, Qigong, Aerobic dance, Yoga, and Dance Sport, while the control group (Placebo) consisted of unstructured physical activity.
Network meta-analysis
Global consistency test
Analysis of consistency revealed several interventions demonstrating superior efficacy in ameliorating IAD symptoms when compared to Placebo (p < 0.05). These interventions included: Mindfulness practices showing [SMD = −13.33, 95%CI(−7.42,19.25)]; Taichi demonstrating [SMD = −10.91, 95%CI(−18.71,−3.11)]; Yoga yielding [SMD = −11.60, 95%CI(−28.20,5.00)]; and Qigong with [SMD = −7.87, 95% CI(−24.61,8.87)].
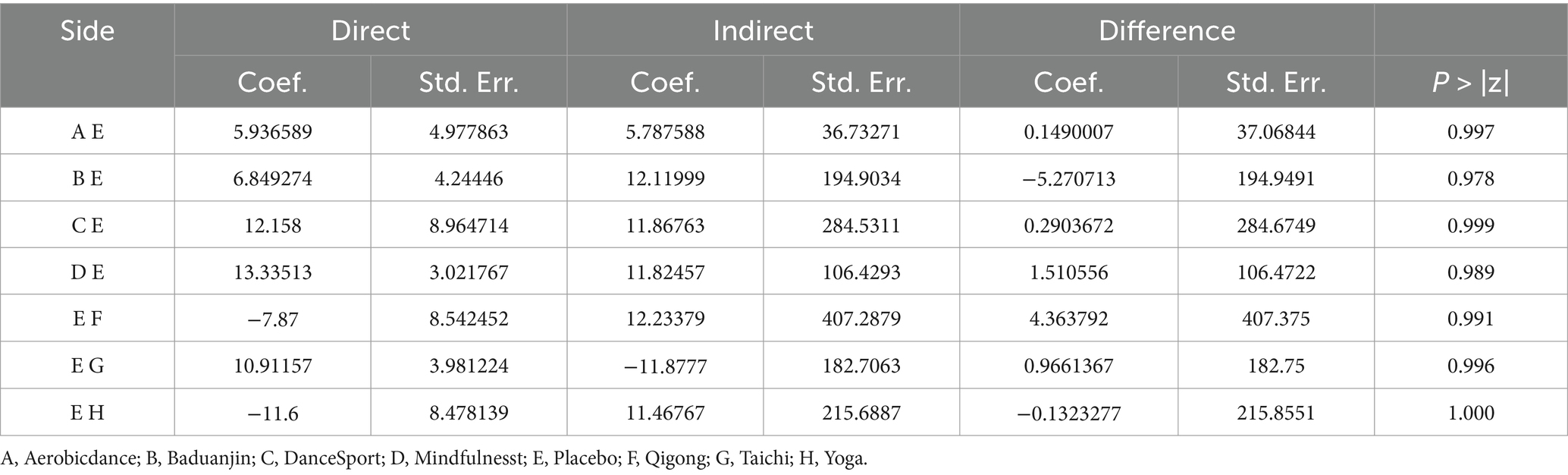
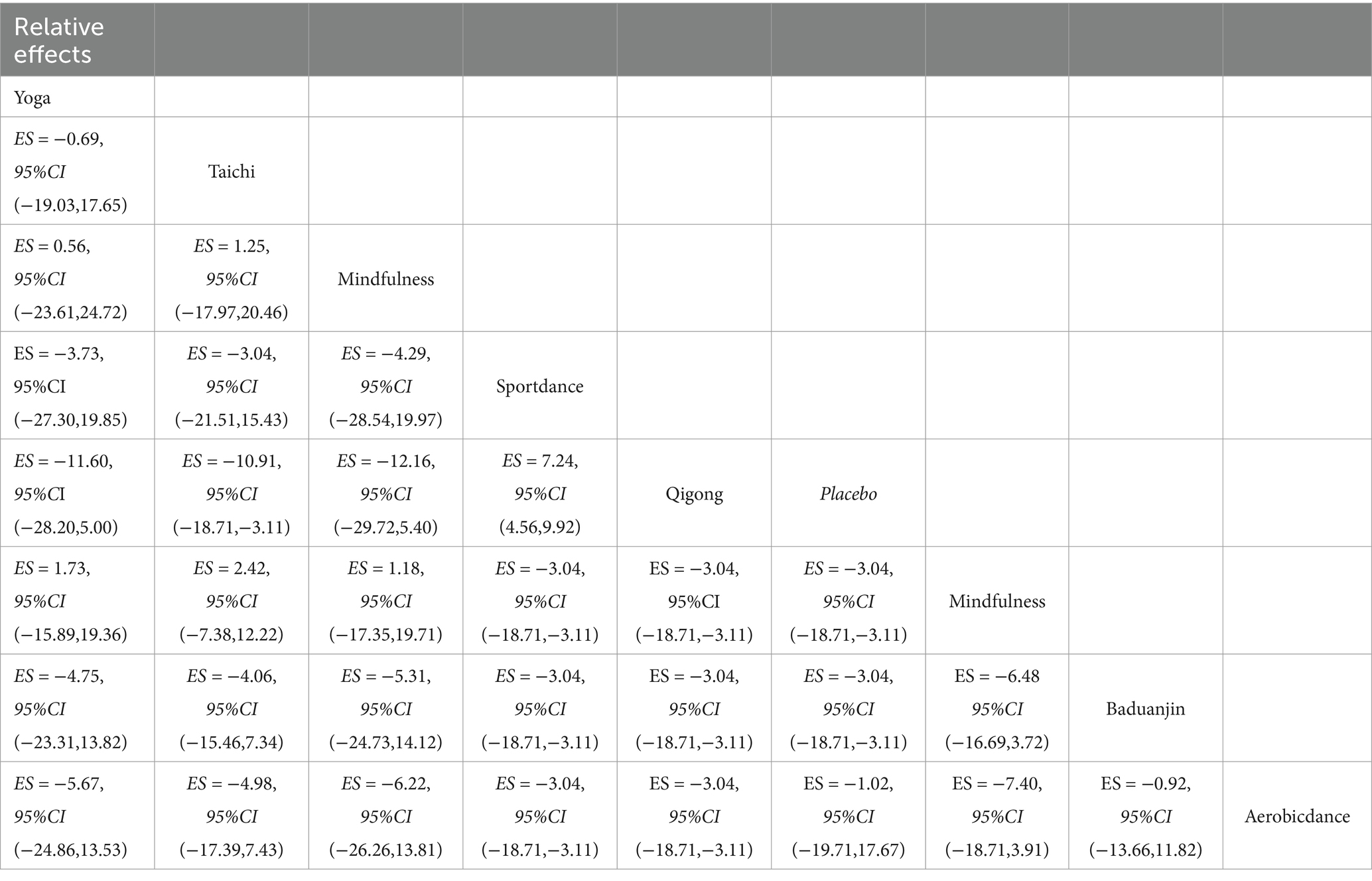
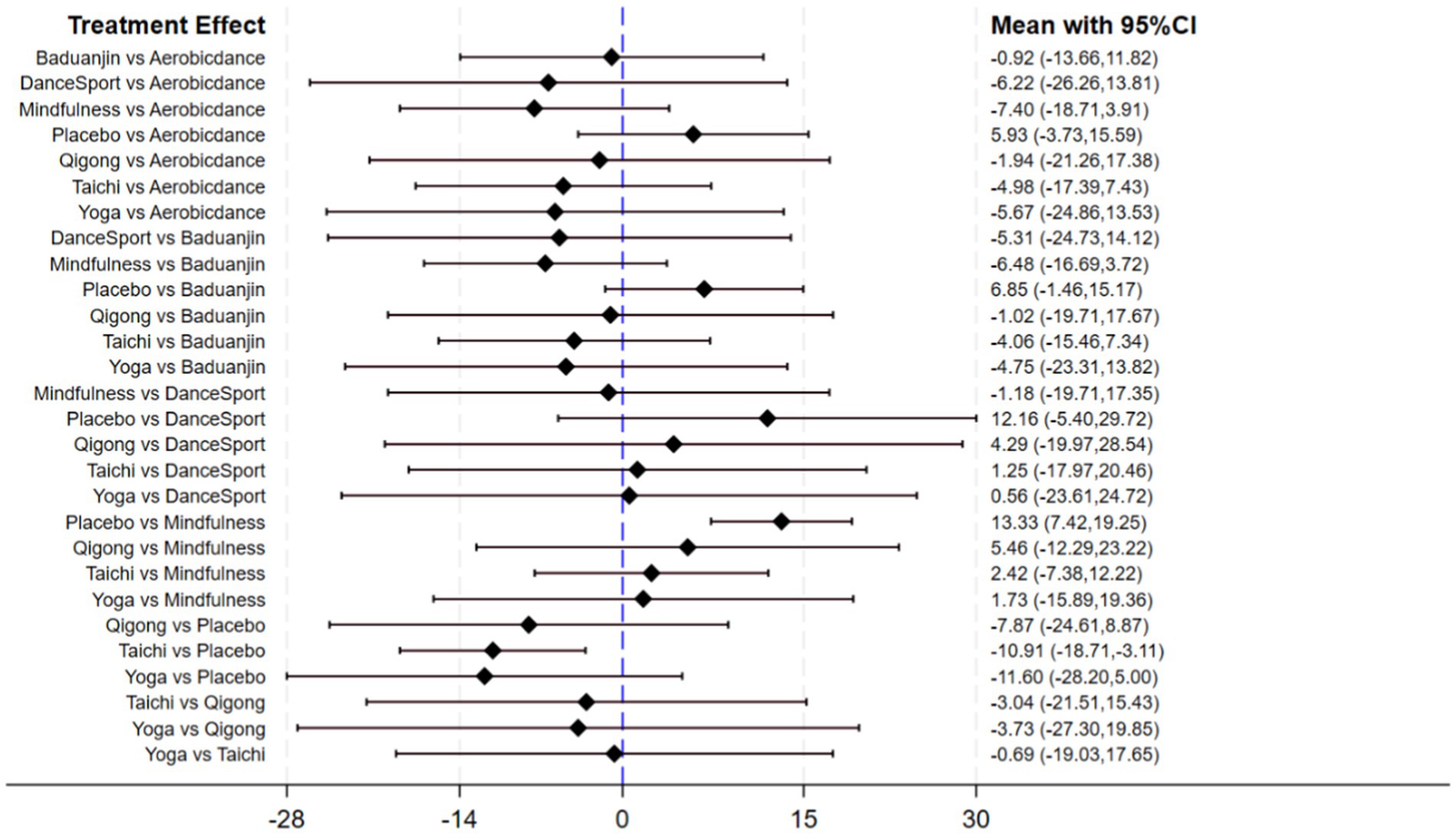
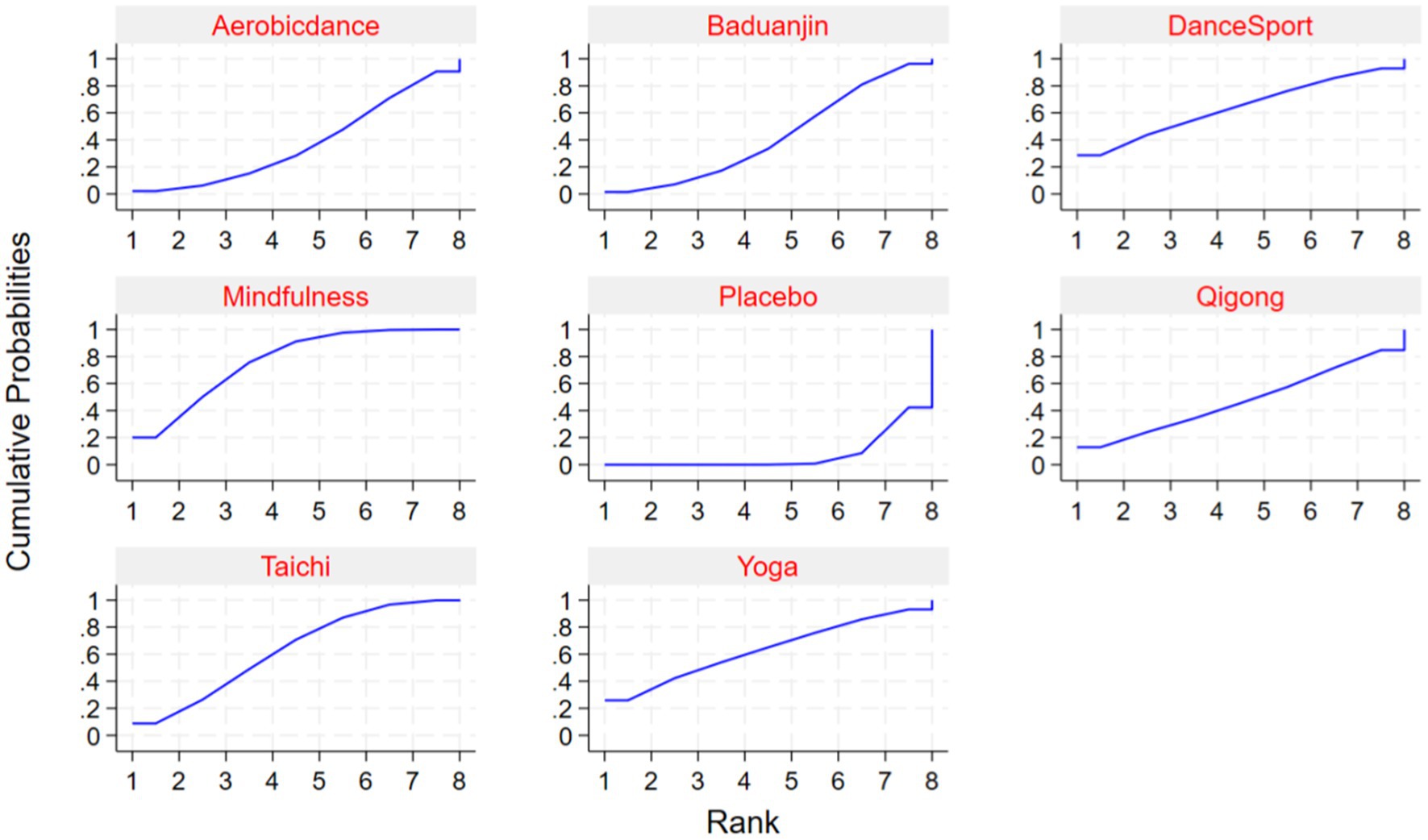
Comparative analyses between intervention pairs yielded no statistically meaningful differences among the therapeutic approaches. Specifically, Mindfulness showed comparable effectiveness when evaluated against Taichi, Qigong, and Yoga (p > 0.05). Similarly, DanceSport interventions demonstrated equivalent efficacy when compared with Baduanjin and Aerobicdance (p > 0.05). Furthermore, no significant variations in therapeutic outcomes emerged from pairwise comparisons across all mind–body exercise modalities, as evidenced by the high p-values (ranging from 0.978 to 1.000) shown in Table 3. The SUCRA analysis indicated that Mindfulness (76.3%), DanceSport (64%), and Yoga (63.1%) ranked highest in probability of being the most effective interventions for internet addiction symptom improvement, while Placebo ranked lowest (7.4%). Detailed comparative data and visual representations are available in Table 4 and Figure 5, respectively.
Local inconsistency test
Local inconsistency testing using the node-splitting method showed p > 0.05 for comparisons between all mind–body exercise therapies, indicating no statistically significant inconsistency and suggesting good consistency (Figure 6).
Rank of intervention effectiveness
Assessment of publication bias and study size impact
Analysis of potential reporting bias employed comparison-adjusted funnel plotting methodology. Examination revealed symmetrical distribution patterns relative to the null axis, suggesting minimal influence of study size variation and limited publication bias concerns. Detailed visual representation appears in Figure 7.
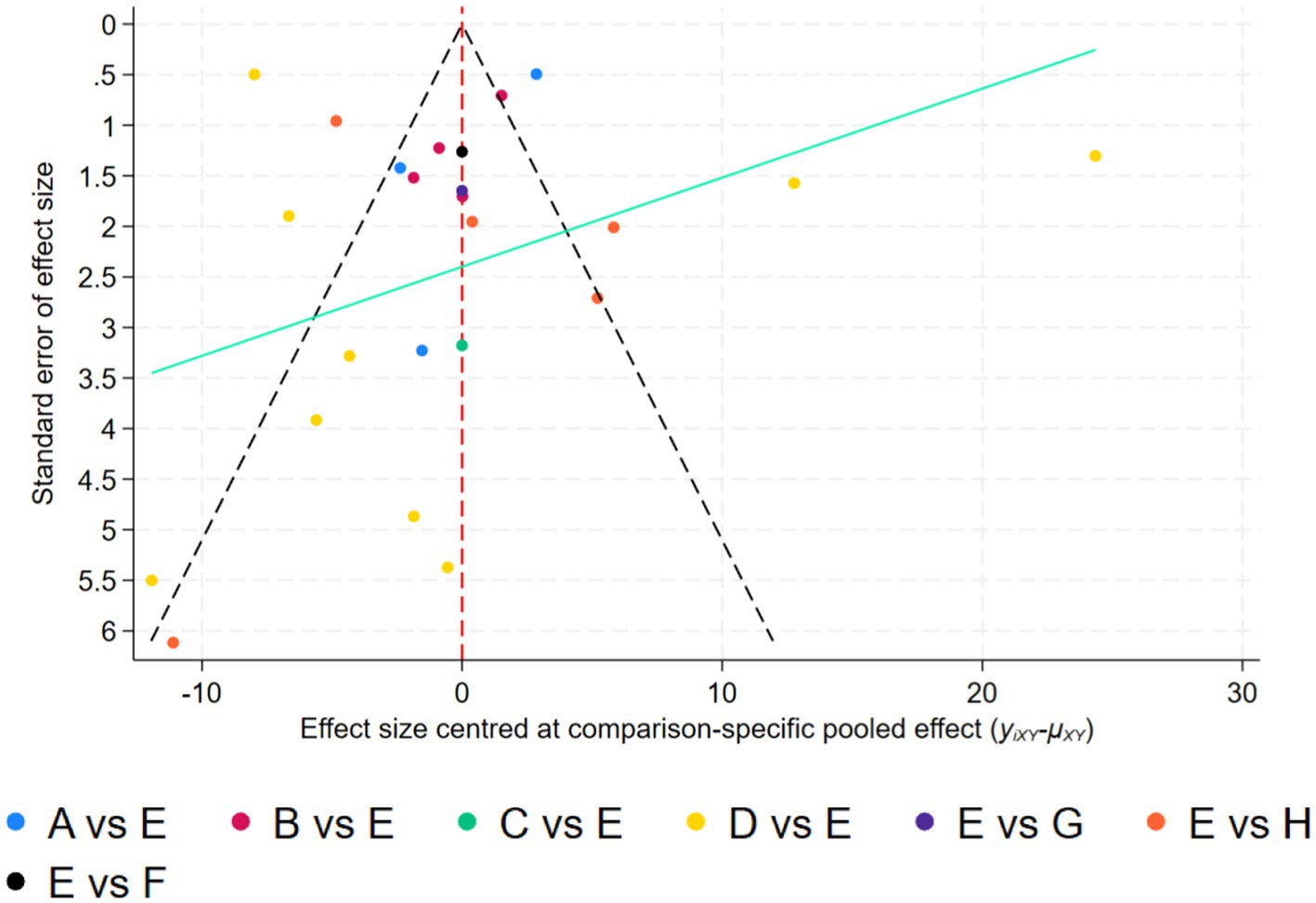
Figure 7. Adjusted comparison funnel plot. A, Aerobicdance; B, Baduanjin; C, DanceSport; D, Mindfulness; E, Placebo; F, Qigong; G, Taichi; H, Yoga.
Discussion
Based on our network meta-analysis of mind–body interventions for Internet Addiction Disorder (IAD), Mindfulness demonstrated superior efficacy among the evaluated approaches, with a SUCRA value of 76.3%. DanceSport (SUCRA = 64%), Yoga (SUCRA = 63.1%), and Taichi showed comparable therapeutic benefits. Qigong and Baduanjin exhibited moderate effectiveness, while Aerobicdance (SUCRA = 37.3%) displayed more modest outcomes compared to other mind–body practices. All interventions substantially outperformed placebo conditions, indicating the clinical value of these approaches for IAD management (Table 5).
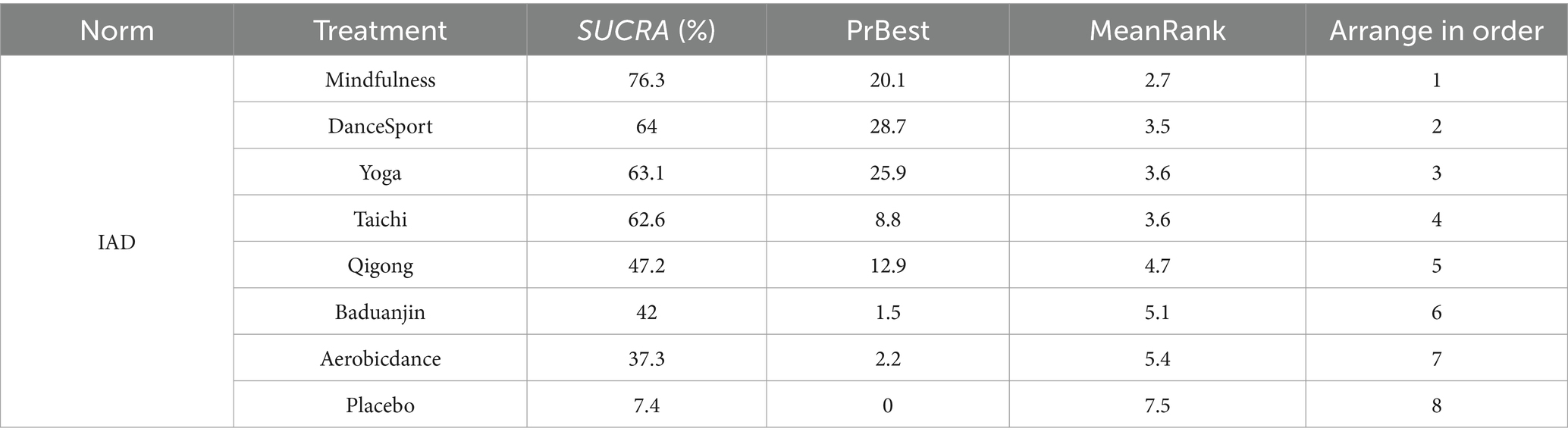
Table 5. Probability rankings and SUCRA values for internet addiction symptom improvement across therapeutic modalities.
The therapeutic effects of these mind–body interventions can be explained through several complementary neurobiological mechanisms:
Mindfulness’s superior efficacy can be attributed to its multifaceted neurobiological effects. At the neuroplasticity level, Tang et al. (8) found that mindfulness training significantly enhances connectivity between the default mode network and executive control network, optimizing attention regulation and self-awareness capabilities; Yang and Zeng (44) further discovered that 8 weeks of continuous mindfulness training significantly improves gray matter density in the prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex regions, and these structural changes directly enhance cognitive control ability, contributing to improved executive function in IAD patients. At the neurotransmitter regulation level, Zhang et al. (45) systematic review revealed several neurochemical regulatory pathways of Mindfulness: improving emotional state by stabilizing serotonin levels, alleviating anxiety symptoms by promoting GABA release, while reducing chronic stress response by inhibiting cortisol secretion. In terms of social cognition, Xiao et al. (46) research found that Mindfulness can significantly enhance participants’ self-awareness and interpersonal functioning by activating the insula and strengthening the functional connectivity between the anterior cingulate cortex and prefrontal regions.
However, despite these promising findings, several critical limitations of mindfulness interventions for IAD warrant careful consideration. Zhang et al. (47) comprehensive critical evaluation highlights significant methodological challenges in mindfulness research, including inconsistent operational definitions, inadequate control conditions, and limited measurement precision. These issues potentially confound the interpretation of mindfulness efficacy data in IAD treatment. Lan et al. (48) further argue that the neuroplasticity changes attributed to mindfulness practice often lack specificity and may be influenced by expectancy effects or general relaxation responses rather than mindfulness-specific mechanisms. Regarding clinical implementation, Ren et al. (49) identified substantial heterogeneity in individual responses to mindfulness interventions, with factors such as severity of addiction, comorbid conditions, and pre-existing attentional capacities significantly moderating treatment outcomes. This variability suggests that mindfulness may not be universally effective for all IAD patients. Furthermore, Xie (50) longitudinal study revealed significant attrition rates (averaging 25%–30%) in mindfulness programs for addiction disorders, indicating challenges in treatment adherence that may limit real-world effectiveness. Additionally, the cultural adaptability of traditional mindfulness protocols remains questionable when applied across diverse populations with varying cultural conceptualizations of attention training and mental health, as demonstrated by Kirmayer’s cross-cultural analysis (51). From a neurocognitive perspective, Britton’s research suggests that enhanced awareness through mindfulness might temporarily increase distress in some individuals with addiction disorders by heightening consciousness of withdrawal symptoms before therapeutic benefits emerge (52). These limitations underscore the importance of developing personalized approaches to mindfulness intervention for IAD, rather than adopting a one-size-fits-all approach.
Dance Sport, Yoga, and Aerobic Dance exert therapeutic effects on Internet Addiction Disorder (IAD) through distinct yet complementary neurobiological mechanisms. Dance Sport (SUCRA = 64%) enhances frontal-striatal circuit connectivity through complex sequential movements, with Li (53) demonstrating its ability to upregulate dopamine in reward pathways while simultaneously improving cognitive flexibility. This remodeling of reward circuitry provides IAD patients with alternative pleasure stimuli beyond digital engagement. Yoga (SUCRA = 63.1%), as investigated by Lu et al. (54), operates primarily through autonomic nervous system regulation, increasing parasympathetic activation and GABA levels, which directly counters the sympathetic hyperarousal common in excessive internet use. Its emphasis on breath-body integration strengthens interoceptive awareness, addressing the bodily disconnection often experienced during prolonged screen time. Meanwhile, Aerobic Dance (SUCRA = 37.3%), while showing lower efficacy, contributes through enhanced brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) production as demonstrated by Yang (55), supporting hippocampal neurogenesis and resilience against stress-induced relapse patterns. The rhythmic, synchronized movements across all three modalities also enhance social synchrony circuits, with Dai (56) finding increased mirror neuron system activation, potentially offering a neural substrate for rebuilding real-world social connections that may have atrophied during internet dependency.
Regarding traditional Chinese health-promoting exercises, our study found that Baduanjin, Tai Chi, and Qigong all showed significant effects in improving IAD. The mechanism of these effects can be elaborated from both modern neuroscience and traditional Chinese medicine perspectives. From a neuroscience perspective, Liu (57) found through systematic review and meta-analysis that mind–body exercises like Tai Chi and Qigong can significantly improve executive function, closely related to prefrontal cortex activation. Improved executive function directly affects individual self-control ability, crucial for IAD rehabilitation. Regarding neurotransmitter regulation, Zhang (58) research confirmed that traditional exercise interventions can significantly improve anxiety and depression symptoms, related to the regulation of neurotransmitters like serotonin. From a traditional Chinese medicine perspective, TCM emphasizes the unity of “form, qi, and spirit, “improving overall health by regulating physical form, breathing, and psychological state. As typical TCM exercise therapies, Tai Chi, Baduanjin, and Qigong emphasize training in breathing regulation, movement coordination, and mental focus (59). Yu et al. (60) systematic review and meta-analysis showed that exercises incorporating meditation elements (like Tai Chi and Qigong) have significant emotional regulation effects. Liao et al. (61) found that Qigong interventions specifically target the dysregulated attentional networks often observed in internet addiction, helping practitioners develop greater attentional flexibility and emotional regulation through its meditative movement practices and energy cultivation techniques.
Our findings both align with and differ from related domestic and international research. For instance, Zhu (62) meta-analysis found that Tai Chi’s effect size on improving mental health [SMD = −0.89, 95%CI (−1.40,−0.38)]was smaller than our results [SMD = −10.91, 95%CI (−18.71,−3.11)]. These differences may arise from several factors. First, Liu et al.’s study included both quasi-experimental designs and RCTs, while our study strictly focused on RCTs, which enhanced the methodological rigor of our findings. Second, Liu et al. used depression scale scores as the primary outcome measure, whereas our study directly assessed IAD symptom severity. Although depression and IAD demonstrate certain comorbidity and symptom overlap, they represent distinct psychopathological dimensions. Third, our study implemented more stringent quality evaluation criteria and utilized net change values for baseline adjustment, which contributed to more precise and reliable results. Similarly, Tadpatrikar et al. (63) systematic review confirmed the positive impact of mind–body exercise. However, the intervention effects in these studies were lower than the effect sizes observed in our research, possibly due to factors such as: (1) differences in intervention duration, with previous studies typically lasting 4–6 weeks while ours continued for 8–16 weeks, allowing more time for mind–body exercise effects to fully manifest; (2) differences in assessment tools, as our study employed a more comprehensive IAD evaluation system. Additionally, our study featured relatively higher intervention frequency and single-session duration, potentially enhancing intervention effects.
Meanwhile, Placebo’s significantly lower ranking stems from its lack of structured neural engagement, absence of specific therapeutic mechanisms, and failure to provide consistent activation of the prefrontal circuits necessary to counter IAD’s neurobiological effects. This pronounced difference between active interventions and placebo confirms the clinical value of structured mind–body approaches for IAD treatment.
This ranking aligns with the “Comprehensive Exercise Intervention Theory” proposed by Wu et al. (64), which suggests that intervention effectiveness positively correlates with the following factors: (1) moderate exercise intensity, (2) complexity of cognitive engagement, (3) richness of social interaction, and (4) diversity of emotional regulation. Dance Sport demonstrates clear advantages in all four dimensions, thus achieving the best results. While Tai Chi and Baduanjin also possess multi-dimensional intervention characteristics, they are relatively weaker in intensity and social aspects. Mindfulness training primarily targets a single dimension (attention and emotional regulation), resulting in lower overall effectiveness.
This study has certain limitations. First, although we strictly included RCT studies and none of the included studies involved clinical patients, dietary intake and daily activities were not strictly controlled between the exercise and control groups during the intervention, which may affect the results. Second, literature searches were limited to Chinese and English, not covering research in other languages, potentially affecting the comprehensiveness of the literature and external validity of the research results. Finally, due to the use of different IAD assessment tools across studies, there exists measurement tool heterogeneity. To address this, we used standardized mean difference to combine effect sizes, ensuring comparability of outcome variables and minimizing the impact of measurement tool differences.
Future research could explore the long-term effects of mind–body exercise therapy on IAD while controlling for diet and daily activities. It is also recommended to extend research to special occupational groups (such as military personnel, firefighters, medical staff, and other high-stress occupational groups) and special physical and mental condition groups (such as minors, disabled persons, chronic disease patients, etc.), exploring differentiated effects and intervention strategies of mind–body exercise therapy across different populations. Additionally, expanding literature search scope to include research in other languages would help improve research comprehensiveness and external validity. It is recommended to conduct higher quality multi-center, large-sample RCT studies focusing on: (1) adopting rigorous experimental designs such as stratified randomization and intention-to-treat analysis; (2) conducting dose–response relationship analysis; (3) setting long-term follow-up observation points, which will provide more reliable evidence support for developing evidence-based, personalized IAD intervention strategies.
Although the literature search of this study covers major international databases, a significant limitation is that all included studies are from Chinese population. This geographical distribution bias may reflect the special contributions of Chinese researchers in the field of mind body intervention research, but it also limits the cross-cultural dissemination of the results. Cultural specificity plays an important role in the study of addictive behavior, especially in Internet use patterns and acceptance of mental health interventions. It is worth noting that Tai Chi and Qigong, as traditional practices originating from China, may benefit from enhanced cultural identity and intrinsic motivation among local populations, resulting in greater intervention effects. These socio-cultural factors may partially explain the significant effect we observed. Future research should expand to populations with different cultural backgrounds, evaluate the applicability of these physical and mental interventions on a global scale, and may require appropriate adjustments for different cultural backgrounds to maximize intervention effectiveness.
Conclusion
Current evidence suggests that mind–body exercise therapy can effectively improve IAD symptoms in young adults. Among the interventions studied, Mindfulness demonstrated the strongest therapeutic effect (SUCRA = 76.3%), followed by DanceSport (SUCRA = 64%), Yoga (SUCRA = 63.1%), and Taichi (SUCRA = 62.6%). Given its superior effectiveness, Mindfulness should be prioritized in IAD intervention programs where feasible. However, all seven interventions showed significant improvements compared to controls, suggesting that selection of specific mind–body exercises can be tailored to individual preferences and practical constraints.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
SJ: Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DC: Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JY: Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft. HW: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. WC: Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZD: Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing. DZ: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds of the Central Universities (project name: empirical research on the empowerment of sports industry for common prosperity in the context of Chinese path to modernization; project number: 2024ESJSK12).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1565372/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Casey, BJ, and Caudle, K. The teenage brain: self control. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. (2013) 22:82–7. doi: 10.1177/0963721413480170
2. Prensky, M. H. sapiens digital: From digital immigrants and digital natives to digital wisdom [J]. Innovate. (2009) 5.
3. Kuss, DJ, and Griffiths, MD. Internet gaming addiction: a systematic review of empirical research. Int J Ment Heal Addict. (2012) 10:278–96. doi: 10.1007/s11469-011-9318-5
4. Crone, EA, and Dahl, RE. Understanding adolescence as a period of social–affective engagement and goal flexibility. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2012) 13:636–50. doi: 10.1038/nrn3313
5. Steinberg, L. A social neuroscience perspective on adolescent risk-taking In: Biosocial Theories of Crime : Routledge (2017). 435–63. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2007.08.002
6. Wang, Y, Yin, Y, Sun, Y, Zhou, Y, Chen, X, Ding, WN, et al. Decreased prefrontal lobe interhemispheric functional connectivity in adolescents with internet gaming disorder: a primary study using resting-state FMRI. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0118733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118733
7. Brand, M, Young, KS, Laier, C, Wölfling, K, and Potenza, MN. Integrating psychological and neurobiological considerations regarding the development and maintenance of specific internet-use disorders: an interaction of person-affect-cognition-execution (I-PACE) model. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2016) 71:252–66. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.033
8. Tang, YY, Hölzel, BK, and Posner, MI. The neuroscience of mindfulness meditation. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2015) 16:213–25. doi: 10.1038/nrn3916
9. Pezoa-Jares, RE, Espinoza-Luna, IL, and Vasquez-Medina, JA. Internet addiction: a review. J Addict Res Ther S. (2012) 6:4. doi: 10.4172/2155-6105.S6-004
10. Pontes, HM, Kuss, DJ, and Griffiths, MD. Clinical psychology of internet addiction: a review of its conceptualization, prevalence, neuronal processes, and implications for treatment. Neurosci Neuroecon. (2015) 4:11–23. doi: 10.2147/NAN.S60982
11. Jorgenson, AG, Hsiao, CJ, and Yen, CF. Internet addiction and other behavioral addictions. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. (2016) 25:509–20. doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2016.03.004
12. Zher, M, Khan, RB, Salim, M, Bilal, M, Hussain, A, and Haseeb, M. The relationship between internet addiction and anxiety among students of University of Sargodha. Int J Human Soc Sci. (2014) 4:288–93.
13. Olson, JA, Sandra, DA, Colucci, ES, Bikaii, AA, Nahas, J, Chmoulevitch, D, et al. Smartphone addiction is increasing across the world: a meta-analysis of 24 countries. Comput Human Behav. (2022) 129:107138. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2021.107138
14. Mishra, J, Behera, MR, Mitra, R, Samanta, P, Mahapatra, PK, and Kar, S. Prevalence and impact of internet addiction disorder among adolescents and young adults. Open Public Health J. (2024) 17:642. doi: 10.2174/0118749445345806241010081642
15. Wang, H, Li, X, Lok, GKI, Meng, C, Tan, Y, Lee, UM, et al. Family-based therapy for internet addiction among adolescents and young adults: a meta-analysis. J Behav Addict. (2024) 13:295–312. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00015
16. Chen, Y, Zhang, L, Liu, Y, Yang, Y, Qiu, M, Wang, Y, et al. Acupuncture for internet addiction: a protocol for systematic review. Medicine. (2021) 100:e24872. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024872
17. Ma, C, Yan, J, Hu, H, Shi, C, Li, F, and Zeng, X. Associations between 24-h movement behavior and internet addiction in adolescents: a cross-sectional study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:16873. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416873
18. Chen, H, Xiao, M, Lin, Y, Hämäläinen, J, Hagedon, A, and Yin, Y. Current development of a nonpharmacological intervention approach for mild cognitive impairment patients and a clinical trial in China. J Transl Intern Med. (2022) 10:5–8. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2022-0007
19. Chen, H, Dong, G, and Li, K. Overview on brain function enhancement of internet addicts through exercise intervention: based on reward-execution-decision cycle. Front Psych. (2023) 14:1094583. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1094583
20. Yang, H, Guo, H, Zhu, Z, Yuan, G, Zhang, X, Zhang, K, et al. Intervention of internet addiction and smartphone addiction: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses. Curr Addict Rep. (2024) 11:125–48. doi: 10.1007/s40429-023-00536-w
21. NCCIH. Complementary, alternative, or integrative health: What’s in a name? (2018). Available online at: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/complementary-alternative-or-integrative-health-whats-in-a-name (Accessed April, 2021).
22. Siu, PM, Angus, PY, Tam, BT, Chin, EC, Yu, DS, Chung, KF, et al. Effects of tai Chi or exercise on sleep in older adults with insomnia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4:e2037199. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37199
23. Guo, C, Xiang, G, Xie, L, Liu, Z, Zhang, X, Wu, Q, et al. Effects of tai Chi training on the physical and mental health status in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. (2020) 12:504–21. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2020.01.03
24. Li, Z, Liu, S, Wang, L, and Smith, L. Mind-body exercise for anxiety and depression in COPD patients: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:e422. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17010422
25. Zou, L, Yeung, A, Li, C, Chiou, SY, Zeng, N, Tzeng, HM, et al. Effects of mind-body movements on balance function in stroke survivors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2018) 15:1292. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15061292
26. Zou, L, Yeung, A, Zeng, N, Wang, C, Sun, L, Thomas, G, et al. Effects of mind-body exercises for mood and functional capabilities in patients with stroke: an analytical review of randomized controlled trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2018) 15:721. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15040721
27. Wang, K, Liu, S, Kong, Z, Zhang, Y, and Liu, J. Mind-body exercise (Wuqinxi) for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:72. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16010072
28. Zou, L, Loprinzi, PD, Yeung, AS, Zeng, N, and Huang, T. The beneficial effects of mind-body exercises for people with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2019) 100:1556–73. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2019.01.008
29. Zhou, S, Zhang, Y, Kong, Z, Loprinzi, PD, Hu, Y, Ye, J, et al. The effects of tai Chi on markers of atherosclerosis, lower-limb physical function, and cognitive ability in adults aged over 60: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:753. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16050753
30. Zou, L, Sasaki, JE, Wei, GX, Huang, T, Yeung, AS, Neto, OB, et al. Effects of mind−Body exercises (tai Chi/yoga) on heart rate variability parameters and perceived stress: a systematic review with Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Med. (2018) 7:404. doi: 10.3390/jcm7110404
31. Li, F, Harmer, P, Fisher, KJ, McAuley, E, Chaumeton, N, Eckstrom, E, et al. Tai Chi and fall reductions in older adults: a randomized controlled trial [J]. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Med Sci. (2005) 60:187–94. doi: 10.1093/gerona/60.2.187
32. Young, KS. Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder [J]. Cyberpsychol Behav. (1998) 1:237–44. doi: 10.1089/cpb.1998.1.237
33. Cash, HD, Rae, CH, Steel, A, and Winkler, A. Internet addiction: a brief summary of research and practice [J]. Curr Psychiatr Rev. (2012) 8:292–8. doi: 10.2174/157340012803520513
34. King, DL, Delfabbro, PH, Griffiths, MD, and Gradisar, M. Assessing clinical trials of internet addiction treatment: a systematic review and CONSORT evaluation [J]. Clin Psychol Rev. (2011) 31:1110–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.06.009
35. Mak, KK, Lai, CM, Watanabe, H, Kim, DI, Bahar, N, Ramos, M, et al. Epidemiology of internet behaviors and addiction among adolescents in six Asian countries [J]. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. (2014) 17:720–8. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2014.0139
36. Winkler, A, Dörsing, B, Rief, W, Shen, Y, and Glombiewski, JA. Treatment of internet addiction: a meta-analysis[J]. Clin Psychol Rev. (2013) 33:317–29. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2012.12.005
37. Pirwani, N, and Szabo, A. Could physical activity alleviate smartphone addiction in university students? A systematic literature review. Prev Med Rep. (2024) 42:102744. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2024.102744
38. Ko, CH, Yen, JY, Yen, CF, Chen, CS, and Chen, CC. The association between internet addiction and psychiatric disorder: a review of the literature [J]. Eur Psychiatry. (2012) 27:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2010.04.011
39. Lam, LT. Internet gaming addiction, problematic use of the internet, and sleep problems: a systematic review [J]. Curr Psychiatry Rep. (2014) 16:1–9. doi: 10.1007/s11920-014-0444-1
40. Shim, S, Yoon, BH, Shin, IS, and Bae, JM. Network meta-analysis: application and practice using Stata. Epidemiol Health. (2017) 39:e2017047. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2017047
41. Giedd, JN. The teen brain: insights from neuroimaging. J Adolesc Health. (2008) 42:335–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2008.01.007
42. Meshi, D, Tamir, DI, and Heekeren, HR. The emerging neuroscience of social media. Trends Cogn Sci. (2015) 19:771–82. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2015.09.004
43. Liberati, A, Altman, DG, Tetzlaff, J, Mulrow, C, Gøtzsche, PC, Ioannidis, JPA, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol. (2009) 62:e1–e34. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.006
44. Yang, CY, and Zeng, GF. Effects of tai Chi exercise on internet addiction among college students. Chin J Sch Health. (2017) 38:292–4. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2017.02.041
45. Zhang, X, Yang, H, Zhang, K, Zhang, J, Lu, X, Guo, H, et al. Effects of exercise or tai chi on internet addiction in college students and the potential role of gut microbiota: a randomized controlled trial. J Affect Disord. (2023) 327:404–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.12.060
46. Xiao, T, Jiao, C, Yao, J, Yang, L, Zhang, Y, Liu, S, et al. Effects of basketball and Baduan exercise interventions on problematic smartphone use and mental health among college students: a randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:8880716. doi: 10.1155/2021/8880716
47. Zhang, K, Guo, H, Zhang, X, Yang, H, Yuan, G, Zhu, Z, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise or tai Chi Chuan interventions on problematic mobile phone use and the potential role of intestinal flora: a multi-arm randomized controlled trial. J Psychiatr Res. (2024) 170:394–407. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.12.032
48. Lan, Y, Ding, JE, Li, W, Li, J, Zhang, Y, Liu, M, et al. A pilot study of a group mindfulness-based cognitive-behavioral intervention for smartphone addiction among university students. J Behav Addict. (2018) 7:1171–6. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.103
49. Ren, JH, Ao, ZH, He, CL, Bo, L, and Jiawei, W. Experimental research on physical exercise intervention for internet addiction among college students. Heilongjiang Med Sci. (2014) 37:93–4.
50. Xie, F. Status of mobile phone addiction among nursing students and intervention research using Baduanjin health education Shanxi Medical University (2019).
51. Zhang, Y. Research on the relationship between college students’ mobile phone dependence and physical health and exercise intervention Gannan Normal University (2018). doi: 10.16835/i.cnki.1000-9817.2022.06.007
52. Liu, SJ, Liu, YN, and Wang, L. An empirical study on exercise intervention and group cognitive therapy for college students’ mobile phone dependence. Chin J School Health. (2022) 43:825–9.
53. Li, Y. Effects of mindfulness training on response inhibition in college students with mobile phone addiction Guizhou Medical University (2022).
54. Lu, C, Zou, L, Becker, B, Griffiths, M, Yu, Q, Chen, ST, et al. Comparative effectiveness of mind-body exercise versus cognitive behavioral therapy for college students with problematic smartphone use: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Ment Health Promot. (2020) 22:271–82. doi: 10.32604/IJMHP.2020.014419
55. Yang, C. Experimental study on the effect of aerobic fitness and badminton on moderate cell phone addiction in vocational school students Yangzhou University (2022). doi: 10.27441/d.cnki.gyzdu.2022.000378
56. Dai, Y. A randomized controlled study of mindfulness training to reduce Mobile phone dependence level in Mobile phone dependents [D]. Zhejiang Normal University (2018).
57. Liu, SJ. Research on the intervention effect of different motor skills and group cognition on college Students’ Mobile phone dependence Wuhan University of Technology [D]. (2019). doi: 10.27381/d.cnki.gwlgu.2019.001621
58. Zhang, X. Study on the influence and intervention of junior middle school Students’ perceived social support and loneliness on Mobile phone dependence [D]. Hebei University (2021). doi: 10.27103/d.cnki.ghebu.2021.001962
59. Yang, YF. Research on the influence of college Students’ Mobile phone psychological craving on Mobile phone addiction and addiction intervention [D]. Jiangnan University (2021). doi: 10.27169/d.cnki.gwqgu.2021.001830
60. Yu, L, Xia, JM, and Lei, Y. Research on the comprehensive intervention of aerobic exercise on female college students’ mobile phone addiction [J]. Sichuan Sports Sci. (2023) 42:70–3. doi: 10.13932/j.cnki.sctykx.2023.06.15
61. Liao, ZY, Mai, ZZF, and Chen, ZJ. Effects of basketball and aerobic exercise intervention on improving smartphone addiction symptoms and mental health of college students [J]. Sports science and technology literature. Bulletin. (2022) 30:160–2. doi: 10.19379/j.cnki.issn.1005-0256.2022.06.043
62. Zhu, GF. Research on physical exercise intervention for college students’ mobile phone addiction tendency [J]. Zhejiang Sports Sci. (2017) 39:90–7.
63. Tadpatrikar, A, Sharma, MK, Bhargav, H, Anand, N, Sharma, P, Sharma, S, et al. Yoga as an adjuvant with multimodal psychological interventions for excessive use of technology: a randomized controlled trial from India [J]. Int J Yoga. (2024) 17:37–45. doi: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_187_23
64. Wu, Q, Shen, Y, Yuan, QQ, Jiming, Q, and Yang, L. Effect of mindfulness intervention on adolescents with internet gaming addiction [J]. Chin Med. (2023) 36:169–72. doi: 10.19296/j.cnki.1008-2409.2023-05-032
65. Wang, X, Cheng, ZH, Peng, Y, and Chunjuan, N. Intervention study of mindfulness cognitive therapy on improving anxiety and depression in college students with mobile phone addiction [J]. Psychol Monthly. (2024) 19:69–73. doi: 10.19738/j.cnki.psy.2024.19.019
66. Ren, WL. The intervention effect of mindfulness training on high school Students’ Mobile game addiction [D] Hebei North University (2020). doi: 10.27767/d.cnki.ghbbf.2020.000192
67. Shen, YF. The effect of mindfulness training on attentional Bias in college students with Mobile phone dependence [D]. North China University of Science and Technology (2022). doi: 10.27108/d.cnki.ghelu.2022.000031
68. Hölzel, BK, Carmody, J, Vangel, M, Congleton, C, Yerramsetti, SM, Gard, T, et al. Mindfulness practice leads to increases in regional brain gray matter density [J]. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. (2011) 191:36–43. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2010.08.006
69. Khoury, B, Sharma, M, Rush, SE, and Fournier, C. Mindfulness-based stress reduction for healthy individuals: a meta-analysis [J]. J Psychosom Res. (2015) 78:519–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2015.03.009
70. Vago, DR, and Silbersweig, DA. Self-awareness, self-regulation, and self-transcendence (S-ART): a framework for understanding the neurobiological mechanisms of mindfulness [J]. Front Hum Neurosci. (2012) 6:296. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00296
71. Van Dam, NT, Van Vugt, MK, Vago, DR, Schmalzl, L, Saron, CD, Olendzki, A, et al. Mind the hype: a critical evaluation and prescriptive agenda for research on mindfulness and meditation [J]. Perspect Psychol Sci. (2018) 13:36–61. doi: 10.1177/1745691617709589
72. Davidson, RJ, and Kaszniak, AW. Conceptual and methodological issues in research on mindfulness and meditation [J]. Am Psychol. (2015) 70:581–92. doi: 10.1037/a0039512
73. Baer, RA, Smith, GT, Hopkins, J, Krietemeyer, J, and Toney, L. Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness [J]. Assessment. (2006) 13:27–45. doi: 10.1177/1073191105283504
74. Wilson, AD, Roos, CR, Robinson, CS, Stein, ER, Manuel, JA, Enkema, MC, et al. Mindfulness-based interventions for addictive behaviors: implementation issues on the road ahead [J]. Psychol Addict Behav. (2017) 31:888–96. doi: 10.1037/adb0000319
75. Kirmayer, LJ. Mindfulness in cultural context. Transcult Psychiatry. (2015) 52:447–69. doi: 10.1177/1363461515598949
76. Britton, WB, Lindahl, JR, Cahn, BR, Davis, JH, and Goldman, RE. Awakening is not a metaphor: the effects of Buddhist meditation practices on basic wakefulness [J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2014) 1307:64–81. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12279
77. Koch, S, Kunz, T, Lykou, S, and Cruz, R. Effects of dance movement therapy and dance on health-related psychological outcomes: a meta-analysis [J]. Arts Psychother. (2014) 41:46–64. doi: 10.1016/j.aip.2013.10.004
78. Streeter, CC, Gerbarg, PL, Saper, RB, Ciraulo, DA, and Brown, RP. Effects of yoga on the autonomic nervous system, gamma-aminobutyric-acid, and allostasis in epilepsy, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder [J]. Med Hypotheses. (2012) 78:571–9. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2012.01.021
79. Heijnen, S, Hommel, B, Kibele, A, and Colzato, LS. Neuromodulation of aerobic exercise—a review [J]. Front Psychol. (1890) 6:6. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01890
80. Cross, ES, Kraemer, DJM, Hamilton, AFC, Kelley, WM, and Grafton, ST. Sensitivity of the action observation network to physical and observational learning [J]. Cereb Cortex. (2009) 19:315–26. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn083
81. Zhang, Y, Li, C, Zou, L, Liu, X, and Song, W. The effects of mind-body exercise on cognitive performance in elderly: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2018) 15:2791. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122791
82. Li, Y, Wang, R, Tang, J, Chen, C, Tan, L, Wu, Z, et al. Progressive muscle relaxation improves anxiety and depression of pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2015) 2015:792895. doi: 10.1155/2015/792895
83. Zhang, JW, Lv, SJ, and Wu, Y. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine exercise therapy intervention in stable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. J Basic Chin Med. (2020) 26:936–43.
84. Zou, L, Yeung, A, Li, C, Wei, GX, Chen, KW, Kinser, PA, et al. Effects of meditative movements on major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Med. (2018) 7:195. doi: 10.3390/jcm7080195
85. Liu, X, Clark, J, Siskind, D, Williams, GM, Byrne, G, Yang, JL, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of qigong and tai Chi for depressive symptoms. Complement Ther Med. (2015) 23:516–34. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2015.05.001
86. Wang, CC, Lo, J, Geraghty, S, and Yang, AWH. Effects of tai Chi on the quality of life, mental wellbeing, and physical function of adults with chronic diseases: protocol for a single-blind, two-armed, randomised controlled trial. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0270212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270212
87. Luo, S, Mei, Z, Fang, G, Mu, G, Zhang, X, and Luo, S. Effects of mind–body therapies on depression among adolescents: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1431062. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1431062
Keywords: mind–body exercise, young adults, internet addiction, intervention effectiveness, network meta-analysis
Citation: Jia S, Du Z, Chu D, Yao J, Wang H, Chen W, Zhang D and Zang X (2025) A network meta-analysis of mind–body exercise interventions for internet addiction symptoms in young adults. Front. Public Health. 13:1565372. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1565372
Edited by:
Francesca Latino, Pegaso University, ItalyReviewed by:
Sharon Jalene, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, United StatesFederica Marcolini, University of Bologna, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Jia, Du, Chu, Yao, Wang, Chen, Zhang and Zang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenjia Chen, Mjc3NDYzODI4QHFxLmNvbQ==; Dazhong Zhang, NTc4MTgxNjI5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Xin Zang, emFuZ3hpbl9tdEAxNjMuY29t
‡Present Address: Xin Zang, Graduate School Department of Physical Education, Dankook University, Yongin-si, Republic of Korea
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shiguan Jia
Shiguan Jia Zhihao Du1†
Zhihao Du1† Wenjia Chen
Wenjia Chen