- 1Department of Health Management Center, Sichuan Cancer Hospital & Institute, Sichuan Cancer Center, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan University/West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 3Institute of Disaster Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 4Nursing Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu, China
Background: Effort-reward imbalance (ERI) is a prevalent issue in the healthcare sector, particularly in the high-intensity, high-risk, and high-stress environment of the emergency department. This results in emergency department nurses bearing heavier workloads, responsibilities, and time commitments compared to their counterparts in other departments. ERI poses significant risks to their physical, psychological, and sleep quality. Therefore, it is essential to explore the mechanisms through which ERI influences the health of emergency department nurses.
Objective: The aim of this investigation is to analyze if work–family conflict moderates the mediating influence emotional exhaustion has on the association between ERI and somatic symptoms and sleep disorders.
Design: A cross-sectional study.
Settings: The emergency nurses (N = 1,540) were included from 30 tertiary hospitals in 20 provinces or autonomous regions (Northeast, North, East, Central, South, Southwest, and Northwest China) of mainland China between December 26, 2023, and January 18, 2024.
Methods: Participants were recruited using stratified cluster sampling, obtaining data through web-based questionnaires. The study investigated the mediating and moderating effects using the PROCESS macro for SPSS. The mediation effect is tested by the bias correction Bootstrap sample size was set to 5,000.
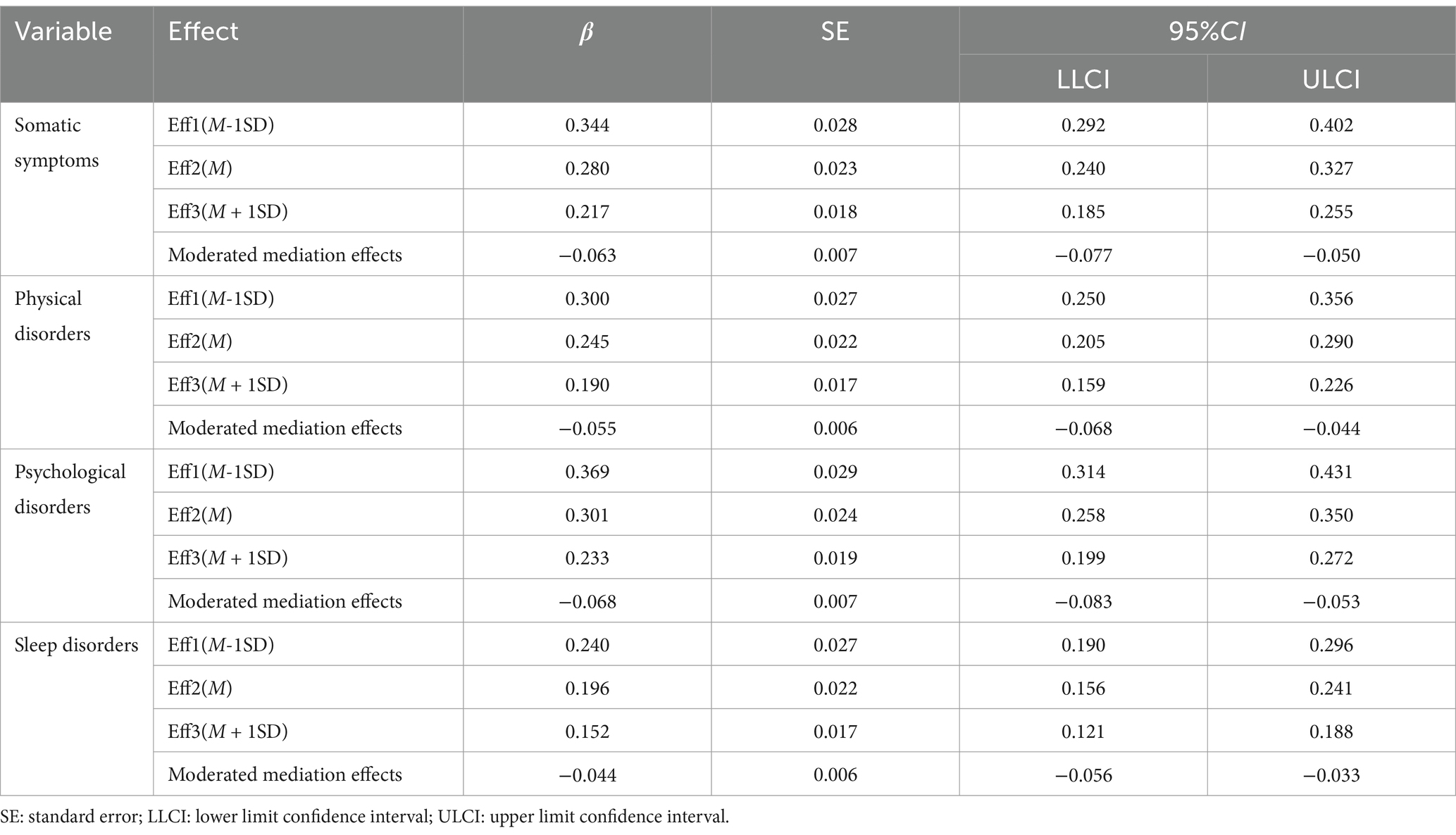
Result: Considering emotional exhaustion as a mediating variable, the direct predictive influence of ERI on somatic symptoms and sleep disorders continues to be statistically significant (β = 0.271, 0.137, p < 0.01). Compared to the high-level work–family conflict group, the positive moderating effect of low-level work–family conflict on the relationship between ERI and emotional exhaustion was more pronounced (simple slope = 0.479, 0.757, p < 0.01). The moderated mediation effects of emotional exhaustion on somatic symptoms and sleep disorders are −0.063 (95%CI: −0.077 ~ −0.050) and −0.044 (95%CI: −0.056 ~ −0.033) respectively.
Conclusion: The study findings indicate that ERI was correlated with heightened emotional exhaustion, somatic symptoms, and sleep disorders among emergency department nurses. As a result, interventions should be implemented to improve ERI, alleviate emotional exhaustion among nurses, monitor work–family conflict levels, and mitigate the effects of these factors on nurses’ overall well-being.
1 Introduction
Effort-reward imbalance (ERI) refers to an individual’s perception of the disparity between the efforts expended and the rewards received in the workplace (1). The balance between effort and reward will prompt employees to have a correct understanding of their work investment and increase their occupational well-being. It also holds great significance for enhancing organizational fairness and organizational production efficiency (63). Emergency department nurses are crucial in the emergency medical service system and are facing significant challenges (2–4). They frequently lack sufficient job compensation, respect, and professional recognition. Such circumstances can give rise to a high-effort, low-return scenario, which not only undermines their job satisfaction but also poses potential risks to the quality of emergency medical services (5–7). Studies from mainland China (8, 9) have shown a 59.66% incidence of ERI among emergency nurses, higher than nurses in general departments. Bardhan et al. found that the risk of ERI among emergency nurses in the United States was over 90% (10). Weyers et al. identified a link between nurses receiving both high effort-low return and experiencing cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal health issues (11). Deng et al.’s study further validated that elevated levels of ERI can significantly influence the sleep quality of community nurses (12). Yu et al. demonstrated that ERI is linked to the potential suboptimal health status for nurses, leading to the manifestation of symptoms across various domains, including fatigue, cardiovascular issues, digestive problems, compromised immune function, and mental well-being (13). These conclusions emphasize the urgent need to further explore the impact pathways of ERI on the health outcomes of emergency department nurses.
Research has found that the fundamental essence of emotional exhaustion serves as the most effective definition of burnout (14). The discrepancy between effort and reward at work leads to emotional distress, with ERI serving as a significant predictor of emotional exhaustion (15, 16). Emotional exhaustion, a key component of burnout, arises when an individual’s psychological and emotional resources are depleted due to workplace stressors (14, 17). Notably, the prevalence of emotional exhaustion among emergency department nurses was found to be 40.5%, significantly higher than in other departments (18, 19). Studies indicates a strong connection between emotional exhaustion and factors such as fatigue linked to stress, depression associated with work, psychosomatic issues, and anxiety (20). Alvarado et al. revealed that nurses’ effort directly correlates with emotional exhaustion, while reward indirectly affects emotional exhaustion through work experience (21). A systematic review indicates that reducing emotional exhaustion can enhance the health of healthcare workers (22).
Work–family conflict (WFC) is another significant potential moderating factor adversely affecting nurse health outcomes. Emergency department nurses not only contend with heavy workloads, prolonged stress, work interruptions, and responsibilities, but also require strong motivation and emotional involvement, which presents significant challenges in balancing family and work commitments (23). Kinman et al. identified that the effort, reward, ERI, and overcommitment influence employees’ experience of WFC (24). Ghorpade highlighted that role conflict and role ambiguity are key contributors to emotional exhaustion (25). Innstrand et al. discovered a delayed positive relationship between WFC and emotional exhaustion in a longitudinal study involving various occupational groups like teachers, doctors, and nurses (26). The study revealed that WFC depletes individuals’ physical and mental resources, exacerbating emotional exhaustion (27). WFC is fundamental aspect of life for individuals in any profession. Research by Wang et al. indicates that this conflict can result in significant emotional exhaustion among nurses (28). However, there is limited research on how WFC moderates the relationship between ERI and emotional exhaustion among emergency department nurses.
Siegrist et al. developed the ERI model to examine the impact of the non-reciprocal relationship between efforts and rewards on individual health and stress outcomes (29). The model posits that individuals invest time and energy at work with the expectation of receiving rewards such as money, respect, and status from the organization. This study aimed to fill this gap by exploring the interaction between ERI and occupational health among emergency nurses, with a particular focused on the mediating role of emotional exhaustion and the moderating effect of WFC. We hypothesized that: (I) ERI, emotional exhaustion, WFC, and occupational health are interrelated; (II) emotional exhaustion mediation affects the relationship between ERI and nurse health; and (III) Work-family balance can moderate the impact of ERI on occupational stress and nurse health.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design and participants
A cross-sectional survey was conducted from 30 tertiary hospitals in 20 provinces or autonomous regions of mainland China between December 26, 2023, and January 18, 2024. Participants were recruited using stratified cluster sampling. The stratification was based on the geographical regions of China (Northeast, North, East, Central, South, Southwest, and Northwest China). Two to three hospitals were selected in each city, which mainly include provincial capital cities, prefecture-level cities and municipalities. Inclusion criteria required participants to hold a nursing license, be actively working in the emergency department for over a year, and provide informed consent to participate voluntarily. Exclusion criteria encompassed emergency nurses undergoing standardized or further training, as well as those who were not on duty during the survey.
The research team has previously published the path mechanisms of the influences of different factors on the health of emergency nurses. Stratified cluster sampling was used to select public hospitals across China. Based on a test level of 0.05 and a test efficiency of 80%, the required sample size for the preliminary pre survey calculation was 1,330 cases (30, 31). A total of 1,555 emergency department nurses participated the survey. When the researchers discovered duplicate IP addresses, years of working inconsistencies in claimed age and all options yielded identical answers, the authors excluded such investigation data from the sample. Excluding 15 incomplete responses to the questionnaire, leaving an effective sample at 1540 participants.
2.2 Measuring tools
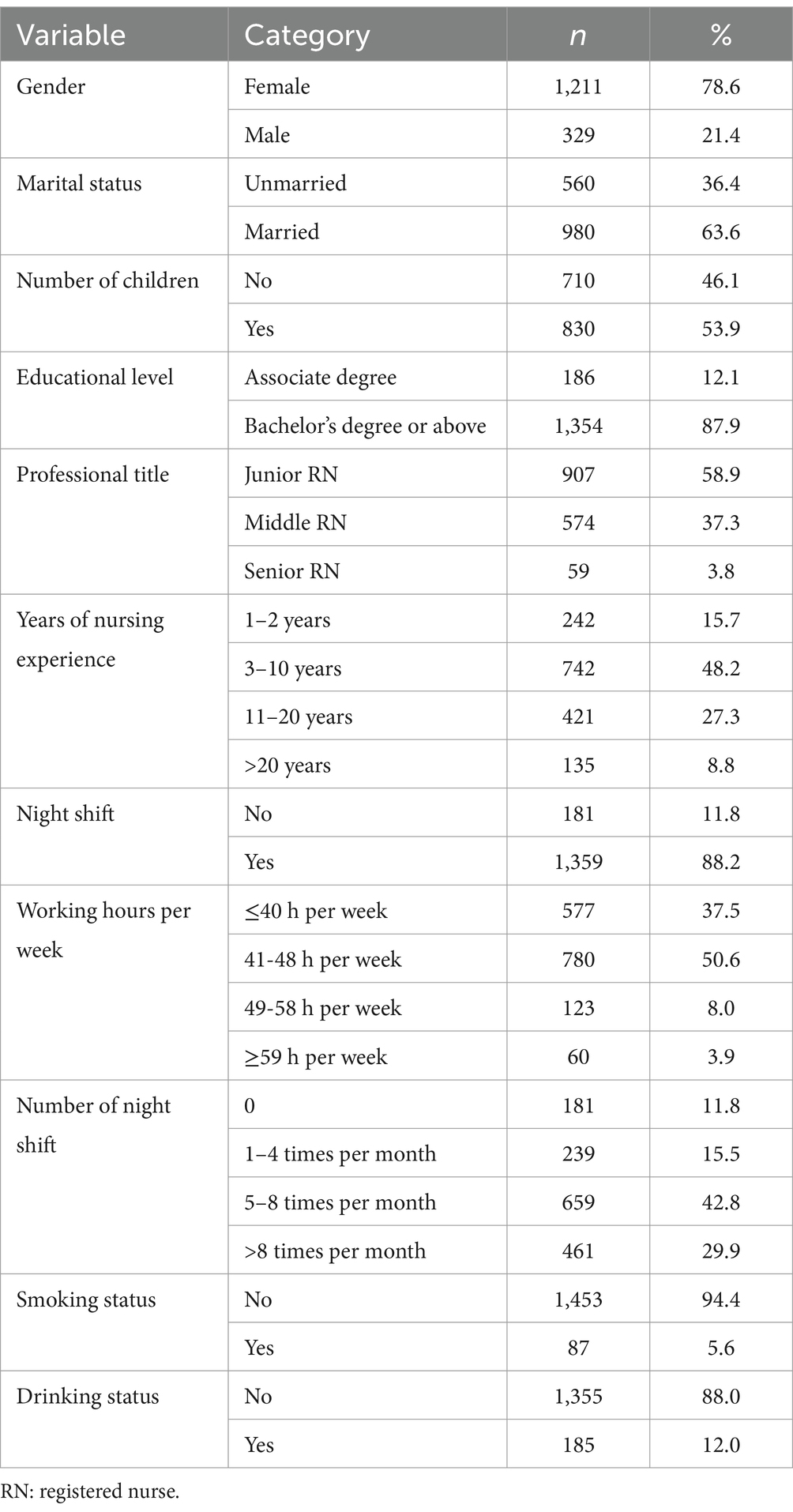
A self-designed basic information questionnaire was utilized to gather data on the demographic and sociological information (gender, marital status, number of children, educational level), work-related characteristics (professional title, years of nursing experience, night shift, working hours per week, number of night shift), and lifestyles (smoking status, drinking status) of emergency department nurses.
The ERI of emergency department nurses was evaluated using the ERI questionnaire developed by Siegrist, based on the ERI model (16). The Chinese version of the ERI scale was translated revised by Chinese scholar Junming Dai, demonstrating good reliability and validity (32). The results of the scale reliability analysis of the data in this study are as follows. The Cronbach’s α coefficient of the scale is 0.957, three dimensions are 0.894, 0.952, and 0.922, respectively. The scale consists of 6 items for effort, 11 items for reward, each rated on a Likert scale from 1 to 5. The ERI index is calculated by dividing the effort score by the product of the reward score and 6/11. Specifically, an ERI index exceeding 1.0 signifies an imbalanced condition characterized by high effort and low return.
The Maslach Burnout Inventory-General Survey (MBI-GS), developed by Maslach et al. (17), was utilized to evaluate the current level of emotional exhaustion among emergency department nurses. The Chinese version of the scale was translated and adapted by Chinese scholars Huang et al. (33). The emotional exhaustion dimension comprises 5 items, each rated on a 7-point Likert scale from 0 to 6, with higher scores indicating greater emotional exhaustion. The results of the scale reliability analysis of the data in this study are as follows. The Cronbach’s α coefficient of the scale is 0.904, and Cronbach’s α coefficient for emotional exhaustion dimension of 0.964.
The Self-administered Sleep Questionnaire (SSQ), developed by Japanese scholar Nakata, was utilized to assess sleep disorders among nurses in the emergency department (34). The questionnaire evaluated three categories of sleep symptoms—time to fall asleep, persistent sleep, and early morning awakening—through three items. Each item was scored on a scale from 1 to 5, with the total score being the sum of these scores. A higher total score indicated a more severe degree of sleep disorders. The results of the Cronbach’s α coefficient analysis of the data in this study is 0.809.
The health of emergency department nurses was evaluated using the Chinese version of the Somatization Symptom Self-Rating Scale-China (SSS-CN) developed by Jiang et al. (35). This scale comprises 20 items, with 10 items focusing on physical disorder and the other 10 items covering the psychological disorder aspects such as anxiety, depression, and anxiety-depression, enabling a thorough evaluation of the patient’s psychological, behavioral, and somatization symptoms. Each item was rated on a scale of 1 to 4 using the Likert 4-point scale. The results of the scale reliability analysis of the data in this study are as follows. The Cronbach’s α coefficient of the scale is 0.974, two dimensions are 0.951, and 0.954, respectively.
The Work-Family Behavioral Role Conflict Scale (WFBRC-S), developed by Clark et al., was utilized in this study. The Chinese version of the scale was translated and revised by Zhang, a respected Chinese scholar, demonstrating strong reliability and validity (36, 37). Consisting of 19 items, each rated on a 5-point Likert scale from 1 to 5, higher scores on the scale indicate greater levels of role conflicts. The results of the scale reliability analysis of the data in this study are as follows. The Cronbach’s coefficient for the Work-Family Behavioral Role Conflict Scale was calculated to be 0.969.
2.3 Data collection
Data collection was conducted through an online questionnaire distributed via the Wenjuanxing platform.1 Prior to the official release, a pilot survey was carried out in two tertiary hospitals in Chengdu to address any technical issues. The Emergency Nursing Specialty Committee of the Chinese Nursing Association supported the study, with nurse administrators in the emergency departments contacted to explain the study’s purpose and obtain consent. Eligible emergency nurses received the questionnaire link via WeChat, ensuring voluntary participation and anonymity. To prevent duplicate submissions, each IP address was limited to one response. Questionnaires with identical answers or inconsistent respondent information were excluded.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS 25.0 software and PROCESS macro. Continuous data that conforms to a normal distribution was described as ( ) and categorical data as n (%). Pearson correlation analysis was employed to investigate the initial relationships between dimensions and factors within the model. The mediation and moderated mediation model were examined for the effect of ERI on adverse health outcomes using the PROCESS macro for SPSS (38). When the bias correction Bootstrap sample size was set to 5,000 and the 95% confidence interval (CI) of the mediating effect did not contain 0, it was deemed statistically significant. A significance level of α = 0.05 (bilateral) was applied.
2.5 Ethical considerations
This study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of West China Hospital of Sichuan University (Approval No.:2024.309). All participants were informed and voluntarily participated in the study.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of participants
A total of 1,540 emergency department nurses from 30 tertiary general hospitals in 20 provinces or autonomous regions were surveyed. The nurses had a mean age of 32.23 ± 6.80 years, with ages ranging from 20 to 58 years. Among the participants, 78.6% were female, predominantly married with children. Of the surveyed nurses, 403 (26.2%) reported experiencing ERI. The socio-demographic information, work characteristics, and lifestyle of the participants are detailed in Table 1.
3.2 Correlation analysis of dimensions
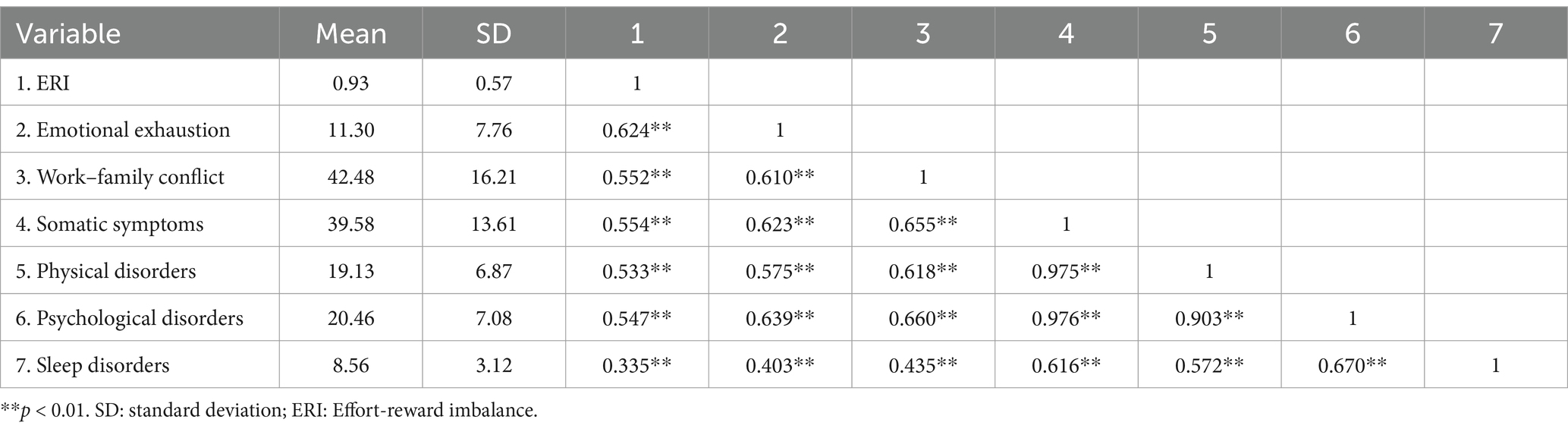
The score for ERI among emergency nurses was 0.93 ± 0.57, the emotional exhaustion score was 11.30 ± 7.76, the WFC score was 42.48 ± 16.21, the score for somatic symptoms was 39.58 ± 13.61, and the sleep disorder score was 8.56 ± 3.12. ERI was correlated significantly positively with emotional exhaustion, WFC, somatic symptoms and sleep disorders (r = 0.624, 0.552, 0.554, 0.335). The scores are detailed in Table 2.
3.3 The mediating effect of emotional exhaustion on ERI and adverse health
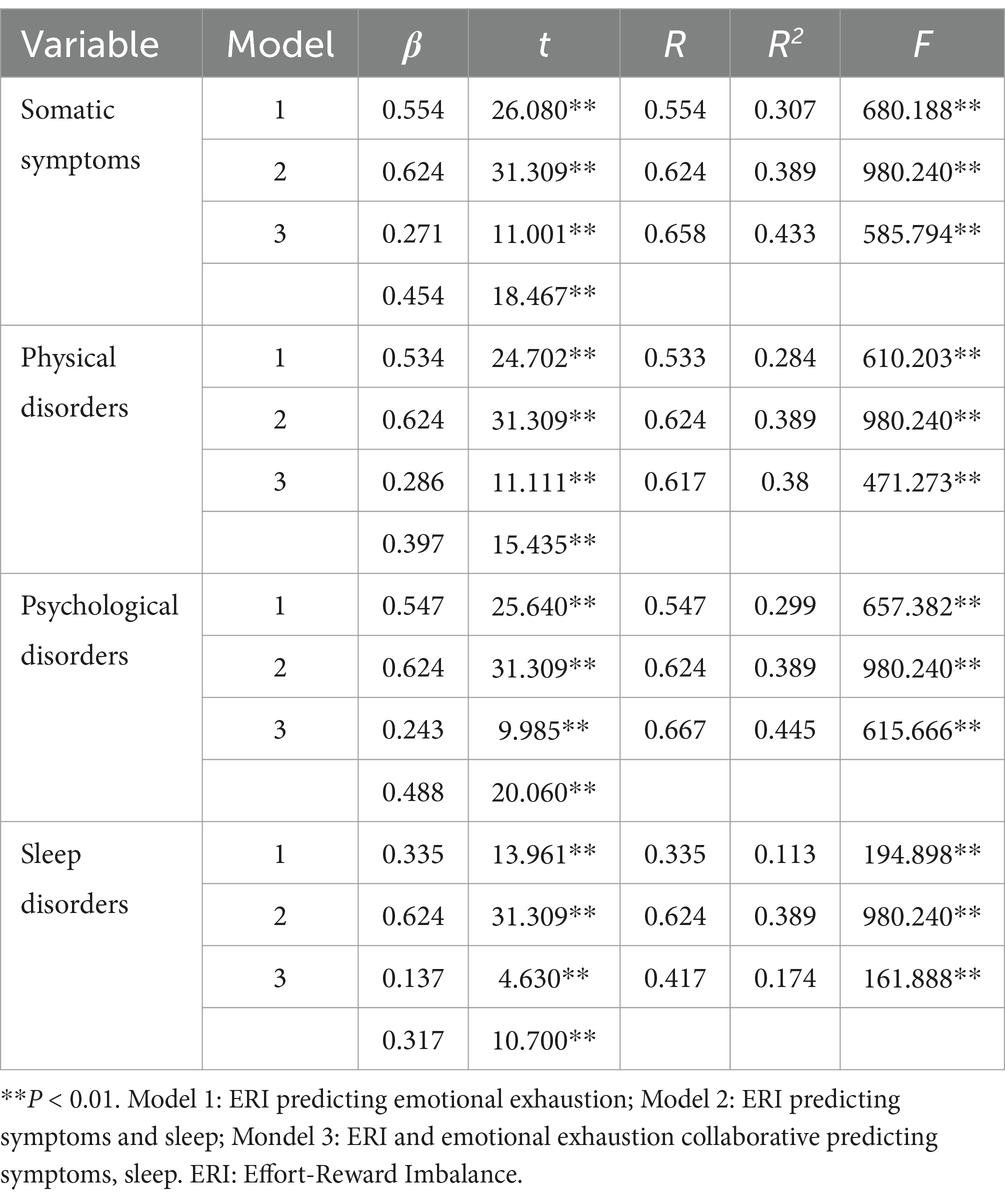
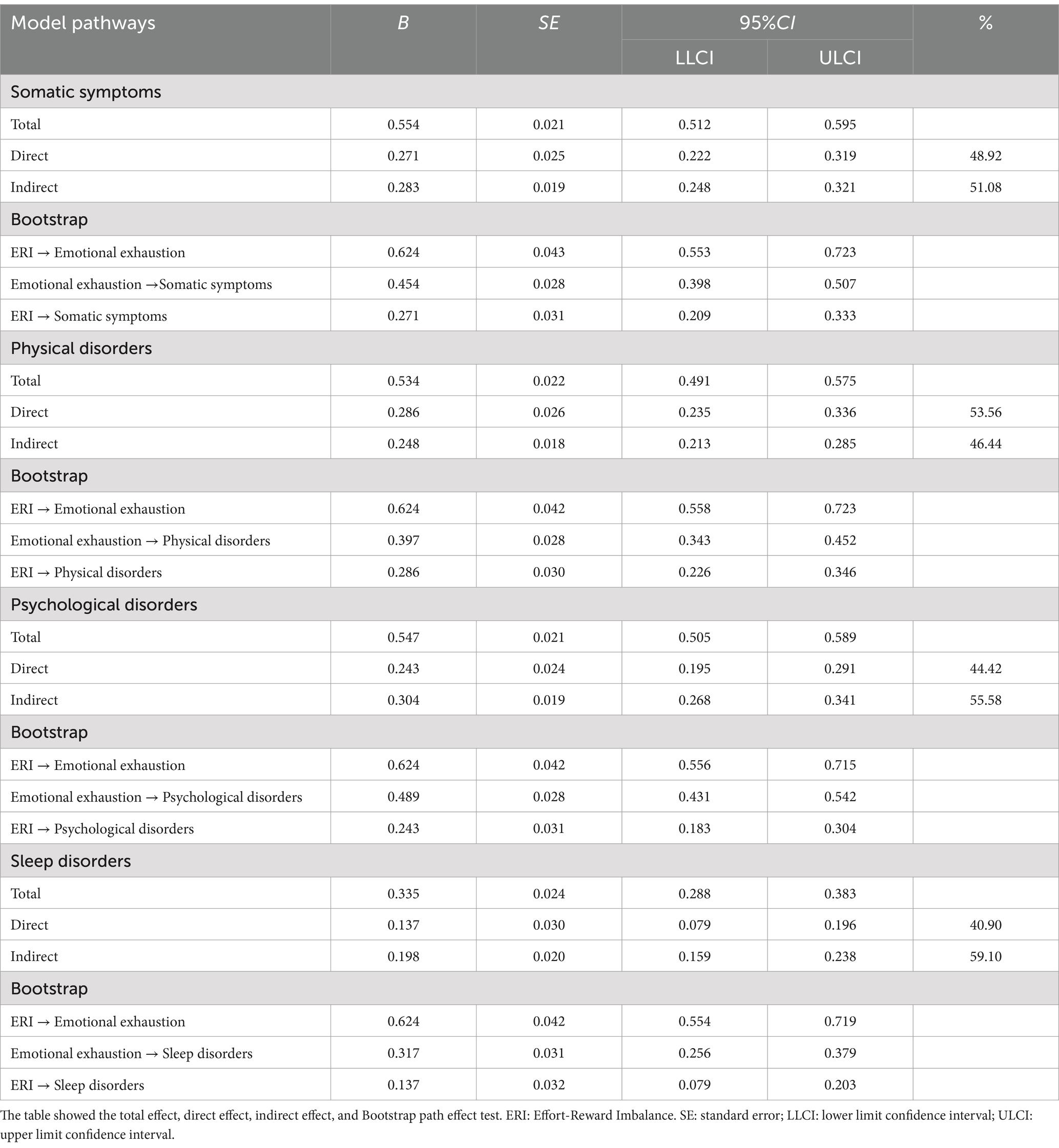
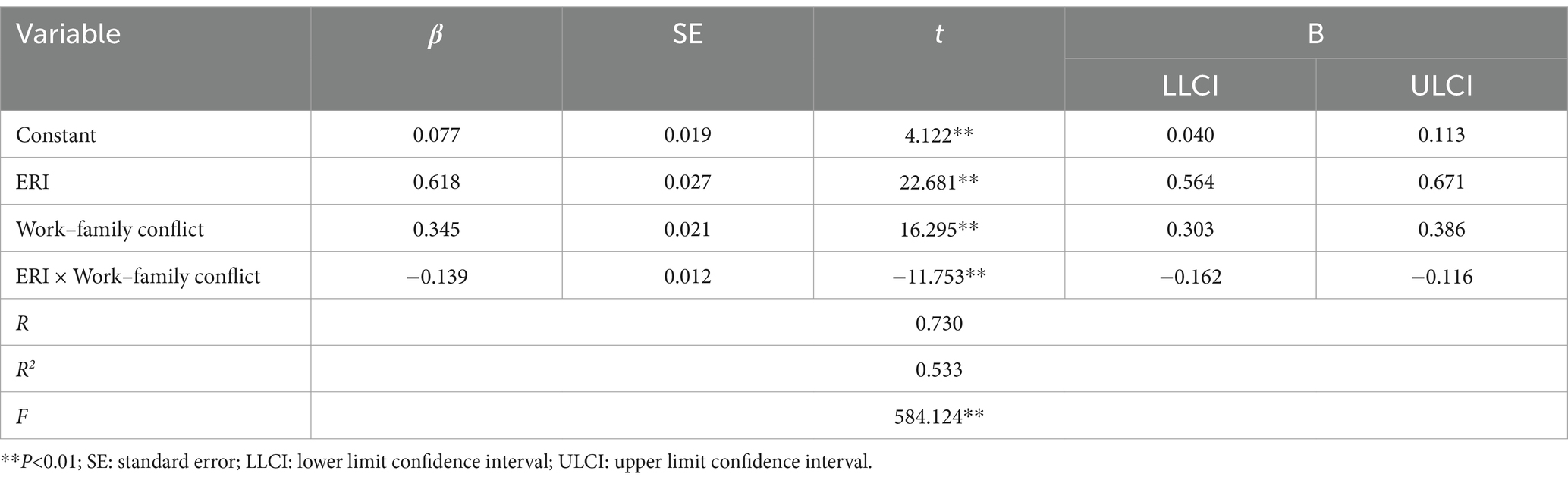
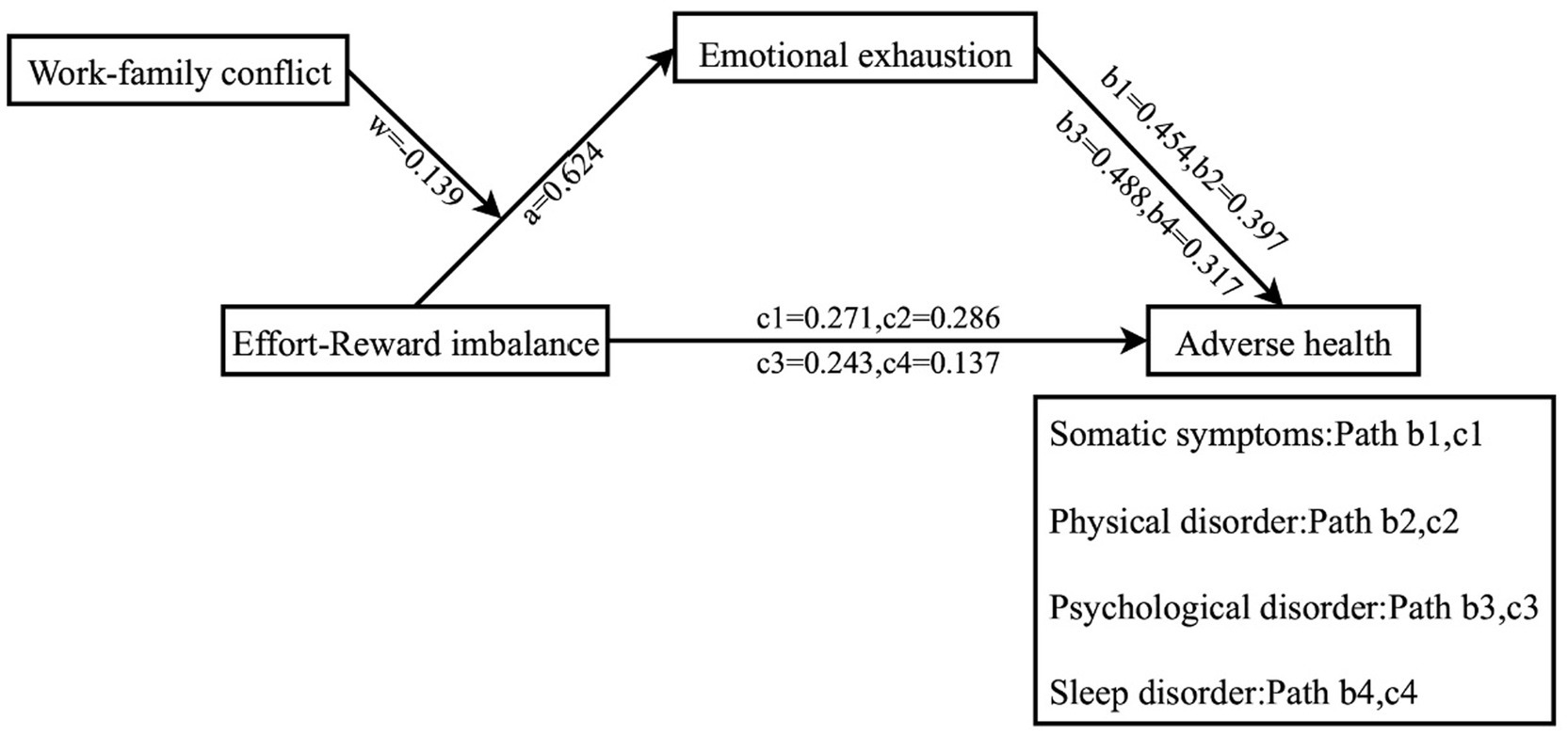
The standardized data underwent mediation tests using Model4 in the PROCESS macro for SPSS. The results presented in Table 3 demonstrate that the positive predictive influence of ERI on somatic symptoms (β = 0.554, t = 26.080, p < 0.01), physical disorder (β = 0.534, t = 24.702, p < 0.01), psychological disorder (β = 0.547, t = 25.640, p < 0.01), and sleep disorders was statistically significant (β = 0.335, t = 13.961, p < 0.01). Moreover, following emotional exhaustion being utilized as a mediator variable in Table 4, the positive predictive influence of ERI on somatic symptoms (β = 0.271, t = 11.001, p < 0.01), physical disorder (β = 0.286, t = 11.111, p < 0.01), psychological disorder (β = 0.243, t = 9.985, p < 0.01), and sleep disorders remained significant (β = 0.137, t = 4.603, p < 0.01). And the emotional exhaustion also had positive predictive effect on somatic symptoms (β = 0.454, t = 18.467, p < 0.01), physical disorder (β = 0.397, t = 15.435, p < 0.01), psychological disorder (β = 0.488, t = 20.060, p < 0.01), and sleep disorders remained significant (β = 0.317, t = 10.700, p < 0.01) in Table 4. Furthermore, the results in Table 4 reveal that the 95% CIs of the bootstrap test for the direct effect of ERI on somatic symptoms (β = 0.271), physical disorder (β = 0.286), psychological disorder (β = 0.243), and sleep disorders (β = 0.137), as well as for the mediating effect of emotional exhaustion, did not encompass 0. This suggests that ERI may influence the negative health outcomes of emergency department nurses by affecting emotional exhaustion in Table 4.
3.4 WFC moderated mediation model effect test
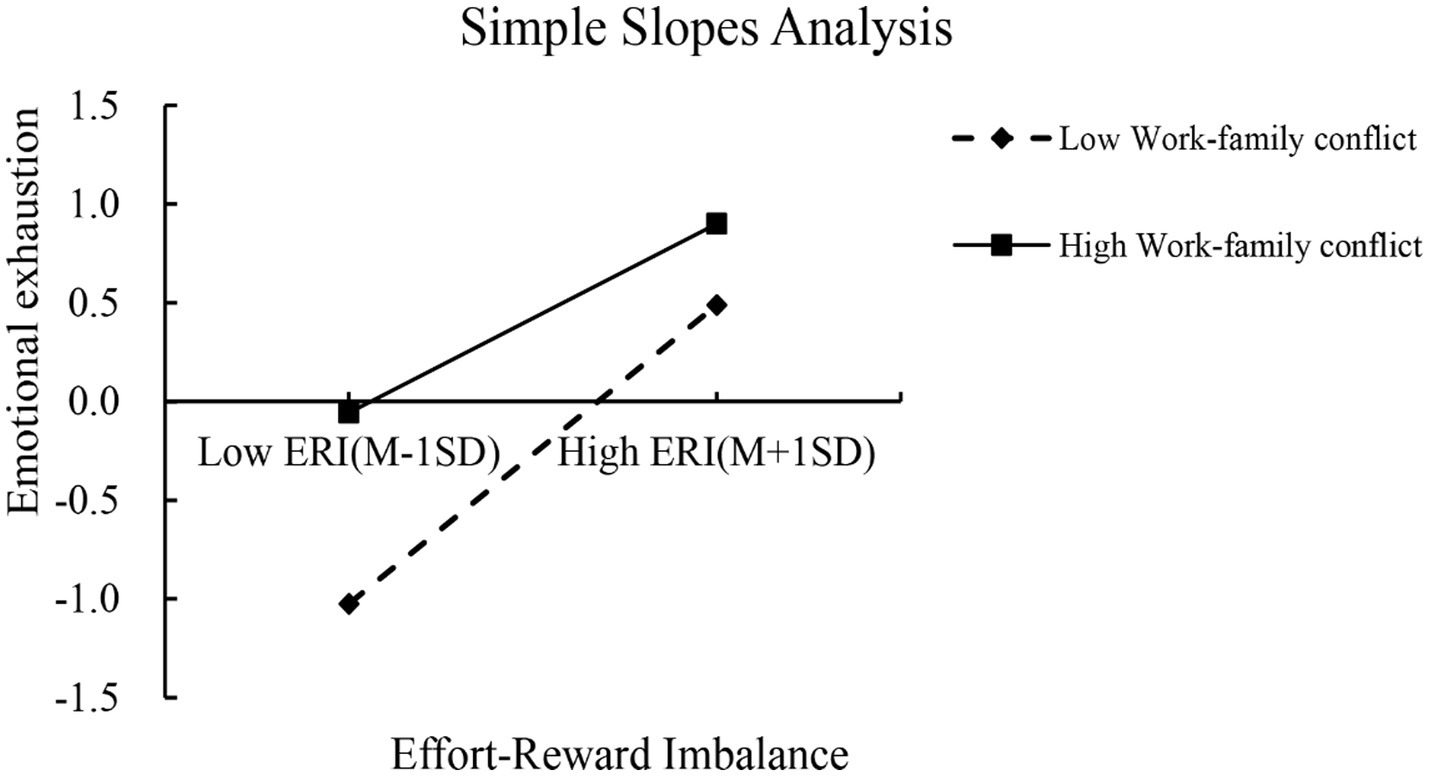
The mediated model with moderation was tested using Model7 in the PROCESS macro for SPSS assuming that the path X-M of the mediated model was moderated by WFC, in line with the theoretical model of the study. The results in Table 5 show that the interaction term between ERI and WFC significantly predicted emotional exhaustion (β = −0.139, t = −11.753, p < 0.01), indicating that work–family conflict moderates the influence of ERI on emotional exhaustion. Further simple slope analyses revealed that the relationship between ERI and emotional exhaustion was found to be significantly moderated by low levels of WFC (simple slope = 0.757, t = 21.035, p < 0.01) compared to high levels of WFC (simple slope = 0.479, t = 22.101, p < 0.01). Nurses with high levels of WFC showed a weaker moderated effect of ERI on emotional exhaustion than nurses with low levels of WFC. Additionally, the mediating effect of emotional exhaustion between ERI and somatic symptoms, physical disorder, psychological disorder, and sleep disorders also appeared to gradually decreases across three levels of WFC (M-1SD, M, and M + 1SD) in Table 6. This suggests that as WFC decreases among emergency department nurses, ERI is more likely to exacerbate emotional exhaustion, leading to somatic symptoms, physical disorder, psychological disorder, and sleep disorders in Figures 1, 2.
4 Discussion
The results revealed significant correlations between ERI, emotional exhaustion, and WFC with somatic symptoms and sleep disorders. Emotional exhaustion was found to mediate the link between ERI and somatic symptoms, as well as sleep disorders. Individuals should correctly view the relationship between effort and reward and avoid excessive investment. Meanwhile, organizations should increase the rewards given to employees in terms of salary, promotion prospects, and job security and reduce the workload.
In this study, the prevalence rate of ERI among emergency department nurses was 26.2%, which is lower than the overall prevalence rate of 68.7% among emergency department nurses reported in the most recent systematic review (39). Earlier studies indicated that the occurrence of ERI among general ward nurses in China ranged from 26.5 to 56.40% (8, 13). Previous studies have emphasized the prevalent challenges encountered by emergency department nurses, including unsustainable working conditions, shortages in human resources, and high workloads, which are consistent with the findings of Dong et al. (40). The demanding nature of their profession, especially during night shifts, leads to significant workloads for emergency department nurses. The necessity for 24/7 emergency medical care results in frequent shifts, which subsequently increases the occurrence of somatic symptoms and sleep disorders (41–43).
The study found a significant positive correlation between ERI by emergency department nurses and their somatic symptoms and sleep disorders. ERI is a key tool for assessing work-related stress, with research indicating that nurses facing high job stress have an 80% increased risk of major depressive episodes (44, 45). The study also revealed that ERI not only directly predicted anxiety symptoms but also correlated with burnout dimensions like emotional exhaustion and cynicism (46). This burnout, in turn, was linked to anxiety symptoms, highlighting a complex interplay between stress, burnout, and anxiety. Sleep disturbances among nurses in general hospitals were strongly linked to ERI, with sleep quality showing a negative correlation (47). Raju’s study further supported ERI as a predictor of poor sleep quality, underscoring the influence of occupational stress on nurses’ sleep health (48). The study’s findings stress the importance of physical and mental health and sleep quality interventions for emergency department nurses, given the strong connection between sleep disorders and work-related stress.
This study demonstrated that emotional exhaustion plays a mediating role between ERI and various health outcomes such as sleep disorders, somatic and psychiatric symptoms. ERI not only directly influenced these outcomes but also indirectly predicted them through emotional exhaustion, with a mediating effect of 59.10 and 51.08%, respectively. Consistent with previous research, emotional exhaustion was found to mediate the relationship between job stress and anxiety (49). Nurses, despite valuing their profession, reported stress as a significant factor contributing to feelings of frustration and exhaustion (50). As ERI increases, occupational stress rises, leading to burnout, depression, and lateral violence among nurses. Burnout, characterized by depersonalization, emotional exhaustion, and decreased personal fulfillment, is closely associated with perceived stress, particularly emotional exhaustion (51, 52). Previous studies have confirmed a strong correlation between ERI and emotional exhaustion (21, 53), a key component of burnout, within the nursing population. A systematic review of 67 articles on burnout and depression, as well as 34 articles on burnout and anxiety, demonstrated distinct and significant relationships between burnout and both anxiety and depression (54). Particularly, emotional depletion exhibited the highest effect sizes, reinforcing the mediating role of emotional depletion in the relationship between ERI and sleep disorders and somatic symptoms.
The moderated mediation analyses demonstrated that WFC moderated the strength of the relationship between ERI and somatic symptoms, sleep disorders mediated by emotional exhaustion. Nurses with high levels of somatic showed a weaker moderated effect of ERI on emotional exhaustion than nurses with low levels of somatic. More specifically, as somatic decreases among emergency department nurses, ERI is more likely to exacerbate emotional exhaustion, leading to somatic symptoms and sleep disorders, indicating a negative moderating influence. These results align with the study by Sugawara et al. on a cohort of Japanese nurses, where they observed that the relationships between emotional exhaustion, depression, and mental health became weaker with higher levels of somatic (55). According to Conservation of Resources theory, individuals aim to accumulate resources surplus as a precaution against potential future challenges. In reality, individuals juggle multiple roles within limitations of resource availability and distribution. To bolster their resource reserves, individuals focus on averting loss spirals and promoting gain spirals. Therefore, given the current medical and health conditions as well as working environment, nurses may prioritize career progression over family obligations to prevent depletion of valuable resources. Contrary to previous research, a survey of 964 nurses demonstrated a significant positive relationship between emotional exhaustion and WFC (56). Both work-to-family and family-to-work disruptions were positively correlated with emotional exhaustion (28). This indicates that women facing conflict between work and family are more likely to experience emotional exhaustion due to challenges in balancing work and family responsibilities (27). Longitudinal studies have consistently shown a significant positive influence of WFC on emotional exhaustion over time (57). Furthermore, high levels of WFC indirectly led to increased anxiety symptoms, with emotional exhaustion acting as a mediator (58). These findings suggest a link between WFC, emotional exhaustion, and anxiety symptoms. Galletta’s study with nurses supported these results by showing that emotional exhaustion levels rose with increased WFC (59). In contrast, Kida’s study revealed an intriguing trend: nurses with family roles experienced lower burnout levels compared to those without family responsibilities. This implies that family roles could serve as a protective factor against work-related emotional stress (60). The studies highlight the intricate relationship between WFC, emotional exhaustion, and occupational health. Discrepancies in findings may stem from variations in national contexts and study populations, underscoring the need for additional research in this area.
These results offered several important implications for nursing administration. Nursing managers should focus on improving the nursing work environment with good labor remuneration, and emotional support for emergency nurses (64). Developing a sound nursing career development system and providing a healthy work environment for emergency nurses. For example, nursing managers should proactively adjust the scheduling system for emergency nurses to reduce work stress and alleviate the work–family conflict (61, 62). These measures will not only help nurses maintain a healthy balance between their professional and personal lives but also improve the quality and safety of healthcare services, ultimately leading to better patient care.
4.1 Limitations
This study utilized a cross-sectional survey research design to conduct a one-time survey, rather than longitudinal sequential studies, which limited the ability to analyze how ERI influences nurse occupational health through emotional exhaustion over time. First, while the cross-sectional design provides valuable insights, it limits the ability to draw causal conclusions. Additionally, the reliance on self-reported data introduced potential bias. Although we fully respect the originality of the data, there might still be potential biases in statistical analysis. The focus on emergency nurses to investigate the mediation role of emotional exhaustion and the moderated effect of work–family conflict may not fully capture the variations in different clinical departments. Further validation of the research findings within nurse from different departments is recommended.
5 Conclusion
The findings of our study indicate that emotional exhaustion serves as a significant mediator in the relationship between ERI and negative health outcomes of emergency department nurses, while demonstrating a gradual decrease in the moderated influence of ERI on emotional exhaustion as WFC levels rose. Nursing administrators are encouraged to explore interventions such as individual counseling, reasonable shift system, adequate time off, and improving compensation for emergency department nurses to alleviate emotional exhaustion, ultimately enhancing their overall physical and mental health.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Review Committee of West China Hospital of Sichuan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XC: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. XY: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. LuZ: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. LiZ: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. YG: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (2023YFS0240, 2023YFS0074).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the participants of this project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ERI, Effort-reward imbalance; WFC, Work–family conflict.
Footnotes
References
1. Siegrist, J. Adverse health effects of high-effort/low-reward conditions. J Occup Health Psychol. (1996) 1:27–41. doi: 10.1037/1076-8998.1.1.27
2. Daniels, J, Robinson, E, Jenkinson, E, and Carlton, E. Perceived barriers and opportunities to improve working conditions and staff retention in emergency departments: a qualitative study. Emerg Med J. (2024) 41:257–65. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2023-213189
3. Staempfli, S, and Lamarche, K. Top ten: a model of dominating factors influencing job satisfaction of emergency nurses. Int Emerg Nurs. (2020) 49:100814. doi: 10.1016/j.ienj.2019.100814
4. Xu, D, Hou, L, and Zhou, H. Challenges faced by acute care surgeons in China. World J Emerg Surg. (2019) 14:16. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0236-3
5. Jiang, H, Ma, L, Gao, C, Li, T, Huang, L, and Huang, W. Satisfaction, burnout and intention to stay of emergency nurses in Shanghai. Emerg Med J. (2017) 34:448–53. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2016-205886
6. Lei, Z, Yan, S, Jiang, H, Feng, J, Han, S, Herath, C, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of workplace violence against emergency department nurses in China. Int J Public Health. (2022) 67:1604912. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2022.1604912
7. Nguyen, VH, Dinh Le, M, Nguyen Van, T, Nguyen Ngoc, D, Tran Thi Ngoc, A, and Nguyen The, PA. A systematic review of effort-reward imbalance among health workers. Int J Health Plann Manag. (2018) 33:e674–95. doi: 10.1002/hpm.2541
8. Kong, L, Li, W, Wang, H, Xu, N, Xu, Q, Sun, L, et al. The relationship between effort-reward imbalance and empathy among clinical nurses: a cross-sectional online survey. J Clin Nurs. (2020) 29:3363–72. doi: 10.1111/jocn.15367
9. Tian, M, Yang, H, Yin, X, Wu, Y, Zhang, G, Lv, C, et al. Evaluating effort-reward imbalance among nurses in emergency departments: a cross-sectional study in China. BMC Psychiatry. (2021) 21:353. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03344-6
10. Bardhan, R, Heaton, K, Davis, M, Chen, P, Dickinson, DA, and Lungu, CT. A cross-sectional study evaluating psychosocial job stress and health risk in emergency department nurses. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:3243. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16183243
11. Weyers, S, Peter, R, Boggild, H, Jeppesen, HJ, and Siegrist, J. Psychosocial work stress is associated with poor self-rated health in Danish nurses: a test of the effort-reward imbalance model. Scand J Caring Sci. (2006) 20:26–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-6712.2006.00376.x
12. Deng, X, Fang, R, and Cai, Y. Evaluation of the correlation between effort-reward imbalance and sleep quality among community health workers. BMC Health Serv Res. (2021) 21:490. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06526-w
13. Yu, L, Liu, W, Wang, J, Jin, Z, Meng, R, Wu, Z, et al. Evaluating the association between effort-reward imbalance and suboptimal health status among hospital nurses: a cross-sectional study. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. (2024) 37:165–75. doi: 10.13075/ijomeh.1896.02223
14. Maslach, C, and Jackson, SE. The measurement of experienced burnout. J Organ Behav. (1981) 2:99–113. doi: 10.1002/job.4030020205
15. Schulz, M, Damkröger, A, Heins, C, Wehlitz, L, Löhr, M, Driessen, M, et al. Effort-reward imbalance and burnout among German nurses in medical compared with psychiatric hospital settings. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. (2009) 16:225–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2850.2008.01355.x
16. Siegrist, J. Effort-reward imbalance at work and health. Res Occup Stress Well-being. (2002) 2:261–91. doi: 10.1016/S1479-3555(02)02007-3
17. Maslach, C, Schaufeli, WB, and Leiter, MP. Job burnout. Annual. Rev Psychol. (2001) 52:397–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.397
18. Li, H, Cheng, B, and Zhu, XP. Quantification of burnout in emergency nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Emerg Nurs. (2018) 39:46–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ienj.2017.12.005
19. Pradas, L, Ariza, T, Gómez, JL, Albendín, L, De, EI, and Cañadas, GA. Prevalence of burnout in paediatric nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0195039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195039
20. Demerouti, E, Bakker, AB, Nachreiner, F, and Schaufeli, WB. The job demands-resources model of burnout. J Appl Psychol. (2001) 86:499–512. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.86.3.499
21. Alvarado, LE, Bretones, FD, and Rodríguez, JA. The effort-reward model and its effect on burnout among nurses in Ecuador. Front Psychol. (2021) 12:760570. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.760570
22. West, CP, Dyrbye, LN, Erwin, PJ, and Shanafelt, TD. Interventions to prevent and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2272–81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31279-X
23. Wu, Y, Zhou, X, Gong, Y, Jiang, N, Tian, M, Zhang, J, et al. Work-family conflict of emergency nurses and its related factors: a National Cross-Sectional Survey in China. Front Public Health. (2021) 9:736625. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.736625
24. Kinman, G, and Jones, F. Effort-reward imbalance, over-commitment and work-life conflict: testing an expanded mode. J Manag Psychol. (2008) 23:236–51. doi: 10.1108/02683940810861365
25. Ghorpade, J, Lackritz, J, and Singh, G. Personality as a moderator of the relationship between role conflict, role ambiguity, and burnout. J Appl Soc Psychol. (2011) 41:1275–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2011.00763.x
26. Innstrand, ST, Langballe, EM, and Espnes, GA. Positive and negative work-family interaction and burnout: a longitudinal study of reciprocal relations. Work Stress. (2008) 22:1–15. doi: 10.1080/02678370801975842
27. Dukhayk, S. Exploring the relationship between work-family conflict, family-work conflict and job embeddedness: examining the mediating role of emotional exhaustion. Psychol Res Behav Manag. (2023) 16:4859–68. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S429283
28. Wang, Y, Chang, Y, Fu, J, and Wang, L. Work-family conflict and burnout among Chinese female nurses: the mediating effect of psychological capital. BMC Public Health. (2012) 12:915. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-915
29. Siegrist, J, and Li, J. Associations of extrinsic and intrinsic components of work stress with health: a systematic review of evidence on the effort-reward imbalance model. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2016) 13:432. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13040432
30. Diao, D, Chen, X, Zhong, L, Zhang, H, and Zhang, J. Sex differences in burnout and work-family conflict among Chinese emergency nurses: a cross-sectional study. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1492662. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1492662
31. Zhang, H, Zhou, J, Zhong, L, Zhu, L, and Chen, X. Relationship between workplace violence and occupational health in emergency nurses: the mediating role of dyssomnia. Nurs Crit Care. (2025) 30:e70008. doi: 10.1111/nicc.70008
32. Yang, WJ, and Li, J. Measurement of psychosocial factors in work environment:application of two models of occupational stress. China J Indust Hyg Occup Dis. (2004) 6:22–6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2004.06.008 (in Chinese).
33. Huang, L, Dai, JM, Zhang, H, Cheng, WH, and Fu, H. The association between burnout and impaired health productivity among medical professionals. Environ. Occup. Med. (2013) 30:321–7. doi: 10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2013.05.018 (in Chinese).
34. Nakata, A, Haratani, T, Takahashi, M, Kawakami, N, Arito, H, Kobayashi, F, et al. Job stress, social support, and prevalence of insomnia in a population of Japanese daytime workers. Soc Sci Med. (2004) 59:1719–30. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.02.002
35. Jiang, M, Zhang, W, Su, X, Gao, C, Chen, B, Feng, Z, et al. Identifying and measuring the severity of somatic symptom disorder using the self-reported somatic symptom scale-China (SSS-CN): a research protocol for a diagnostic study. BMJ Open. (2019) 9:e024290. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-024290
36. Clark, MA, Early, RJ, Baltes, BB, and Krenn, D. Work-family behavioral role conflict: scale development and validation. J Bus Psychol. (2019) 34:39–53. doi: 10.1007/s10869-017-9529-2
37. Sun, WL, Wu, Y, Gao, J, Wang, XX, Guo, CY, and Gao, J. Chinese version of the Work-Family Role Conflict Scale and its reliability and validity testing. Chinese Journal of Nursing. (2023) 58:1787–1793. doi: 10.16821/j.cnki.hsjx.2024.05.015
38. Hayes, AF, and Rockwood, NJ. Regression-based statistical mediation and moderation analysis in clinical research: Observations, recommendations, and implementation. Behav Res Ther. (2017) 98:39–57. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2016.11.001
39. Zhang, Y, Lei, S, and Yang, F. Incidence of effort-reward imbalance among nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychol. (2024) 15:1425445. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1425445
40. Dong, H, Zhang, Q, Zhu, C, and Lv, Q. Sleep quality of nurses in the emergency department of public hospitals in China and its influencing factors: a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2020) 18:116. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01374-4
41. Chaiard, J, Deeluea, J, Suksatit, B, Songkham, W, Inta, N, and Stone, TE. Sleep disturbances and related factors among nurses. Nurs Health Sci. (2019) 21:470–8. doi: 10.1111/nhs.12626
42. Chueh, KH, Chen, KR, and Lin, YH. Psychological distress and sleep disturbance among female nurses: anxiety or depression? J Transcult Nurs. (2021) 32:14–20. doi: 10.1177/1043659619881491
43. Ferkai, LA, Schiszler, B, Bánfai, B, Pandur, A, Gálos, G, Kívés, Z, et al. The occurrence of anxiety, depression, and distress among professionals working in emergency care. Healthcare (Basel). (2024) 12:579. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12050579
44. Fei, Y, Fu, W, Zhang, Z, Jiang, N, and Yin, X. The effects of effort-reward imbalance on emergency nurses’ turnover intention: The mediating role of depressive symptoms. J Clin Nurs. (2023) 32:4762–4770. doi: 10.1111/jocn.16518
45. Yuan, Z, Yu, D, Zhao, H, Wang, Y, Jiang, W, Chen, D, et al. Burnout of healthcare workers based on the effort-reward imbalance model: a cross-sectional study in China. Int J Public Health. (2021) 66:599831. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2021.599831
46. Ding, Y, Qu, J, Yu, X, and Wang, S. The mediating effects of burnout on the relationship between anxiety symptoms and occupational stress among community healthcare workers in China: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e107130. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107130
47. Hong, KJ, and Cho, SH. Effort-Reward Imbalance and Its Effects on Satisfaction With Working Conditions and Sleep-Related Problems: Comparison of Nurses and Other Occupations. J Nurs Scholarsh. (2021) 53:595–603. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12666
48. Raju, A, Nithiya, DR, and Tipandjan, A. Relationship between burnout, effort-reward imbalance, and insomnia among informational technology professionals. J Educ Health Promot. (2022) 11:296. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1809_21
49. Chen, J, Li, J, Cao, B, Wang, F, Luo, L, and Xu, J. Mediating effects of self-efficacy, coping, burnout, and social support between job stress and mental health among young Chinese nurses. J Adv Nurs. (2020) 76:163–73. doi: 10.1111/jan.14208
50. Zhang, Y, An, Y, Wang, L, Zhao, Q, Li, H, and Fan, X. Psychosocial factors associated with career success among nurses: A latent profile analysis. J Adv Nurs. (2023) 79:652–663. doi: 10.1111/jan.15524
51. Jachens, L, Houdmont, J, and Thomas, R. Effort-reward imbalance and burnout among humanitarian aid workers. Disasters. (2019) 43:67–87. doi: 10.1111/disa.12288
52. Spickard, A, Gabbe, S, and Christensen, J. Mid-careerburnout in generalist and specialist physicians. JAMA. (2002) 288:1447–50. doi: 10.1001/jama.288.12.1447
53. Padilla, FC, and Palmeiro-Silva, YK. Effort-reward imbalance and burnout among ICU nursing staff: a cross-sectional study. Nurs Res. (2017) 66:410–6. doi: 10.1097/NNR.0000000000000239
54. Koutsimani, P, Montgomery, A, and Georganta, K. The relationship between burnout, depression, and anxiety: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Front Psychol. (2019) 10:284. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00284
55. Sugawara, N, Danjo, K, Furukori, H, Sato, Y, Tomita, T, Fujii, A, et al. Work-family conflict as a mediator between occupational stress and psychological health among mental health nurses in Japan. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2017) 13:779–84. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S127053
56. Rhéaume, A. Job characteristics, emotional exhaustion, and work-family conflict in nurses. West J Nurs Res. (2022) 44:548–56. doi: 10.1177/01939459211005712
57. Jensen, MT. A two-wave cross-lagged study of work-role conflict, work-family conflict and emotional exhaustion. Scand J Psychol. (2016) 57:591–600. doi: 10.1111/sjop.12328
58. Zhang, H, Tang, L, Ye, Z, Zou, P, Shao, J, Wu, M, et al. The role of social support and emotional exhaustion in the association between work-family conflict and anxiety symptoms among female medical staff: a moderated mediation model. BMC Psychiatry. (2020) 20:266. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02673-2
59. Galletta, M, Portoghese, I, Melis, P, Gonzalez, CIA, Finco, G, D'Aloja, E, et al. The role of collective affective commitment in the relationship between work-family conflict and emotional exhaustion among nurses: a multilevel modeling approach. BMC Nurs. (2019) 18:5. doi: 10.1186/s12912-019-0329-z
60. Kida, R, Fujinami, K, Yumoto, Y, Togari, T, and Ogata, Y. The association between burnout and multiple roles at work and in the family among female Japanese nurses: a cross-sectional study. Ind Health. (2023) 61:195–202. doi: 10.2486/indhealth.2021-0280
61. Guille, C, and Sen, S. Burnout, depression, and diminished well-being among physicians. N Engl J Med. (2024) 391:1519–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2302878
62. Liang, HY, Tseng, TY, Dai, HD, Chuang, JY, and Yu, S. The relationships among overcommitment, effort-reward imbalance, safety climate, emotional labour and quality of working life for hospital nurses: a structural equation modeling. BMC Nurs. (2023) 22:204. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01355-0
63. Heming, M, Siegrist, J, Erschens, R, Genrich, M, Hander, NR, Junne, F, et al. Managers perception of hospital employees’ effort-reward imbalance. J Occup Med Toxicol. (2023) 18:8. doi: 10.1186/s12995-023-00376-4
Keywords: effort-reward imbalance, somatic symptoms, sleep disorders, emergency department nurses, mediation model
Citation: Tan Y, Zhou J, Zhang H, Lan L, Chen X, Yu X, Zhong L, Zhu L and Gao Y (2025) Effects of effort-reward imbalance on emergency nurses’ health: a mediating and moderating role of emotional exhaustion and work-family conflict. Front. Public Health. 13:1580501. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1580501
Edited by:
Feten Fekih-Romdhane, Tunis El Manar University, TunisiaReviewed by:
Oluwaseun Badru, The University of Iowa, United StatesYujie Zhang, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Tan, Zhou, Zhang, Lan, Chen, Yu, Zhong, Zhu and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongli Gao, Z3lsenh5MTk5M0AxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yuanyuan Tan
Yuanyuan Tan Jing Zhou2,3,4†
Jing Zhou2,3,4† Hao Zhang
Hao Zhang Xiaoli Chen
Xiaoli Chen Ling Zhu
Ling Zhu Yongli Gao
Yongli Gao