- 1State Key Laboratory of Cognitive Neuroscience and Learning and IDG/McGovern Institute for Brain Research, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
- 2Faculty of Psychology, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin, China
- 3Department of Psychology, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
A Commentary on
The mediating effect of resilience between physical activity and mental health: a meta-analytic structural equation modeling approach
by Lin, H., Zhu, Y., Liu, Q., and Li, S. (2024). Front. Public Health 12:1434624. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1434624
Introduction
The complex relationship between physical activity (PA) and mental health (MH) has received substantial attention in recent years. Numerous studies have confirmed the beneficial effects of PA on MH (1, 2), including reductions in depressive and anxiety symptoms. However, the bidirectional nature of this relationship remains insufficiently explored. Longitudinal studies, such as the Whitehall II cohort study (3, 4), indicate persistent bidirectional associations between PA and MH. These studies not only demonstrate that PA positively influences MH, but also show that individuals with better MH are more likely to engage in PA. These findings align with the growing recognition of the bidirectional relationship between PA and cognitive function, as highlighted in the 2024 Lancet Commission report on dementia prevention, intervention, and care (5).
Lin et al. (6) innovatively employed a meta-analytic structural equation modeling (MASEM) approach to investigate the relationship between PA, resilience, and MH. They confirmed the positive impact of PA on MH and identified the mediating role of resilience. However, their analysis primarily focused on the unidirectional path from PA to MH. To comprehensively understand the complex interactions between these factors, it is necessary to further explore the bidirectional associations between PA, resilience, and MH. Therefore, the purpose of this commentary is to conduct a secondary analysis based on Lin et al.'s meta-analytic data (6) using the MASEM approach, aiming to further validate and extend their conclusions and provide more evidence for the bidirectional relationship between PA and MH.
Methods
We utilized the coding data provided by Lin et al. (6) and performed statistical analyses using R software (version 4.4.2), employing the metaSEM (version 1.5.0) and lavaan (version 0.6-19) packages. First, we replicated the original analysis to verify the forward effect, whereby PA influences MH. Second, we examined the reverse effect, assessing the impact of MH on PA, with resilience as a mediating variable.
Results
Our forward analysis replicated the findings of Lin et al. (6) (Figures 1A, B), confirming the significant direct effect of PA on both positive (c = 0.162, 95% CI = [0.145, 0.179]) and negative indicators of MH (c = −0.184, 95% CI = [−0.205, −0.163]), as well as the mediating role of resilience (positive indicators: ab = 0.110, 95% CI = [0.101, 0.119]; negative indicators: ab = −0.074, 95% CI = [−0.082, −0.066]).
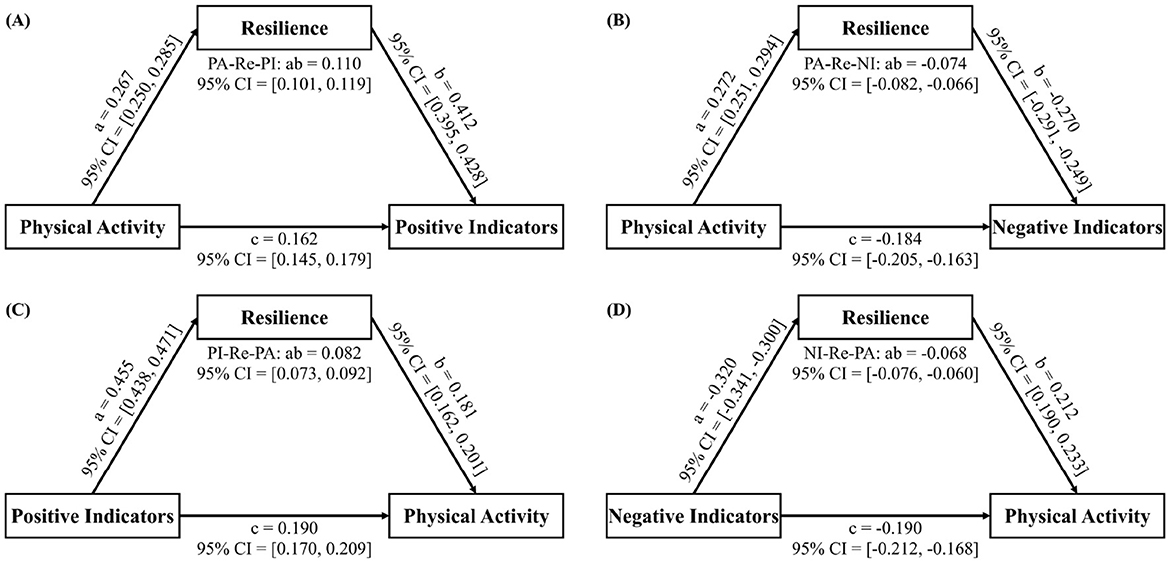
Figure 1. Bidirectional relationship between physical activity and mental health based on MASEM analysis. (A, B) Show the results of the forward analysis, where (A) illustrates the effect of PA on PI, and (B) illustrates the effect of PA on NI. (C, D) Show the results of the reverse analysis, where (C) illustrates the effect of PI on PA, and (D) illustrates the effect of NI on PA. PA, Physical Activity; Re, Resilience; PI, Positive Indicators; NI, Negative Indicators; MASEM, Meta-Analytic Structural Equation Model.
The reverse analysis revealed that MH also significantly predicted PA levels (Figures 1C, D), with resilience partially mediating this relationship (positive indicators: c = 0.190, 95% CI = [0.170, 0.209], ab = 0.082, 95% CI = [0.073, 0.092]; negative indicators: c = −0.190, 95% CI = [-0.212, −0.168], ab = −0.068, 95% CI = [−0.076, −0.060]). The full code, data, and results are available on OSF (https://osf.io/3cmj7/?view_only=e60278f4a2754a5285aff0809d2d376f).
Discussion
Our secondary analysis not only confirmed the reliability of Lin et al.'s conclusions (6) but also extended their findings by demonstrating the bidirectional relationship between PA and MH. The forward effect suggests that engaging in PA fosters resilience, which, in turn, enhances MH. Conversely, the reverse effect indicates that individuals with better MH are more likely to maintain regular PA, partially due to their stronger resilience. As shown in the Whitehall II study, depressive symptoms and anxiety can significantly reduce PA adherence, emphasizing the important role of MH in motivating PA engagement (3). These findings support a dynamic and reciprocal feedback loop between PA, resilience, and MH, offering new insights into the biopsychosocial model of health (7) and expanding it to incorporate resilience-specific frameworks such as the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (8).
The bidirectional relationship between PA and MH highlights the need for integrated intervention strategies that simultaneously target these factors and resilience. For sub-healthy populations, focusing on increasing PA levels and fostering resilience may synergistically enhance overall health. For individuals diagnosed with mental disorders, combining pharmacotherapy with appropriate exercise interventions and resilience training can optimize treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of relapse (9).
From a theoretical perspective, recognizing the bidirectional relationship between PA and MH advances our understanding of the intricate interplay between modifiable risk factors and psychological wellbeing. This knowledge can inform the development of targeted, multi-level interventions that acknowledge the reciprocal nature of these associations. Practically, our findings highlight the importance of incorporating PA and resilience-building strategies into MH promotion and treatment frameworks. Additionally, they provide a new perspective on exploring how MH, as a reverse driving factor, can further improve an individual's MH levels when promoting PA.
However, some limitations should be acknowledged, such as the relatively small number of included studies and the lack of heterogeneity tests across participant characteristics and measurement tools. Future research should aim to expand the sample size, explore potential moderators, and incorporate additional mediating factors to establish a more comprehensive, multi-level model of the PA-MH relationship.
Author contributions
JZ: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Software. YW: Validation, Writing – original draft, Methodology. CY: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. PG: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the original authors of the article, Hao Lin, Yuying Zhu, Qingzao Liu, and Shan Li, for their valuable contributions to this secondary analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Schuch FB, Vancampfort D, Firth J, Rosenbaum S, Ward PB, Silva ES, et al. Physical activity and incident depression: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Am J Psychiatry. (2018) 175:631–48. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17111194
2. Stubbs B, Vancampfort D, Rosenbaum S, Firth J, Cosco T, Veronese N, et al. An examination of the anxiolytic effects of exercise for people with anxiety and stress-related disorders: a meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. (2017) 249:102–8. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.12.020
3. Azevedo Da Silva M, Singh-Manoux A, Brunner EJ, Kaffashian S, Shipley MJ, Kivimäki M, et al. Bidirectional association between physical activity and symptoms of anxiety and depression: the Whitehall II study. Eur J Epidemiol. (2012) 27:537–46. doi: 10.1007/s10654-012-9692-8
4. Steinmo S, Hagger-Johnson G, Shahab L. Bidirectional association between mental health and physical activity in older adults: Whitehall II prospective cohort study. Prev Med. (2014) 66:74–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.06.005
5. Livingston G, Huntley J, Liu KY, Costafreda SG, Selbæk G, Alladi S, et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2024 report of the Lancet standing Commission. Lancet. (2024) 404:572–628. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01296-0
6. Lin H, Zhu Y, Liu Q, Li S. The mediating effect of resilience between physical activity and mental health: a meta-analytic structural equation modeling approach. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1434624. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1434624
7. Engel GL. The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science. (1977) 196:129–36. doi: 10.1126/science.847460
8. Connor KM, Davidson JR. Development of a new resilience scale: the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC). Depress Anxiety. (2003) 18:76–82. doi: 10.1002/da.10113
Keywords: physical activity, resilience, mental health, meta-analytic structural equation model, bidirectional relationship
Citation: Zhao J, Wang Y, Yang C and Guo P (2025) Commentary: The mediating effect of resilience between physical activity and mental health: a meta-analytic structural equation modeling approach. Front. Public Health 13:1599008. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1599008
Received: 24 March 2025; Accepted: 06 June 2025;
Published: 23 June 2025.
Edited by:
Wulf Rössler, Charité University Medicine Berlin, GermanyReviewed by:
Pan Liu, Beijing Institute of Petrochemical Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Zhao, Wang, Yang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peiyang Guo, Z3B5b3VuZ0B0anUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jiawei Zhao
Jiawei Zhao Yufeng Wang
Yufeng Wang Chao Yang
Chao Yang Peiyang Guo1*
Peiyang Guo1*