- 1School of Economics and Management, Southeast University, Nanjing, China
- 2School of Auditing, Nanjing Audit University Jinshen College, Nanjing, China
Introduction: Against the backdrop of deepening China’s medical and health system reform, public hospitals are responsible for improving modern hospital management systems. This article aimed to understand whether and how public hospital budget participation affects organizational performance in China.
Methods: Based on the novel insights of Latour’s Actor-Network Theory and self-efficiency theory, this article combines qualitative and quantitative research methods. In the qualitative research, this article used Grounded Theory and interviewed ten financial heads of public hospitals. In quantitative research, this article used an empirical research method and distributed 168 questionnaires, of which 164 valid responses were collected for analysis.
Result and discussion: This article reaches the following conclusions: (1) There is a positive correlation between budget participation and non-healthcare performance. (2) At the objective level, there was no significant correlation between budget participation and self-efficacy. From a subjective perspective, budget participation, planning self-efficacy, and interpersonal communication and coordination self-efficacy were significantly and positively correlated. (3) Budget participation could have an effect on NHP through planning self-efficacy, interpersonal communication and coordination self-efficacy The innovations of this article are: firstly, this article reasonably confirms the positive relationship between budget participation and organizational performance of public hospitals in China, providing useful references or subsequent research and other national and regional studies. Second, it analyzes the impact of budget participation on organizational performance based on a new perspective of Latour’s Actor-Network Theory. This article is among the first to apply ANT in the context of hospital budgeting, offering novel theoretical insights. Finally, it uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative research methods to analyze the data.
1 Introduction
Budget participation is defined as the practice of allowing subordinates to participate in and influence the budget-setting process (1). Over recent decades, the BP approach has drawn interest among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers (2). In terms of the impact of budgetary participation, existing studies have mainly explored its effects of budgetary participation on organizational performance (3), budgetary slack (4), job satisfaction (5), and self-efficacy (6). However, the existing research on the impact of budgetary participation on organizational performance is controversial (7). One view is that budget participation can promote organizational performance (8). Another view is that budget participation has a negative or no effect on organizational performance (9). This controversy may exist because traditional theories fail to explain the relationship between budgetary participation and organizational performance. In terms of research methodology, most existing studies have used a single quantitative research approach to explore the relationship between budgetary participation and organizational performance (3). Although there have been many studies on the impact of budgetary participation on organizational performance (52), there are fewer studies on the impact of budgetary participation on organizational performance in China, with only six articles (3).
In 2015, the Ministry of Finance’s National Health and Family Planning Commission’s National Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine’s Guidance on Strengthening Financial and Budgetary Management of Public Hospitals stated that all public hospitals should establish and implement a comprehensive budget management system by the end of 2016. Thus, the total budget management approach is also widely used in the health care sector (10). Public hospitals have responded to the requirements of the reform of the healthcare system and have implemented comprehensive budget management. The industry and theoretical community have achieved corresponding results in budget management in public hospitals. However, the focus of these results is on the more general issues of the construction of a comprehensive budget management system in public hospitals (10–12). Little research has been conducted on how to improve the overall performance of public hospitals by increasing staff motivation through budgetary participation in the overall budget (49, 51). Nevertheless, research on the impact of budgetary participation on organizational performance is important for improving both operational and budgetary management in public hospitals.
Based on the above analyses, this article attempts to fill the existing research gap. This article introduces Latour’s Actor-Network Theory and self-efficacy theory and uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative research methods. This article investigates the impact of budgetary participation on organizational performance in public hospitals in China and explores the mechanism of self-efficacy to promote the improvement of the level of operational management and budgeting in public hospitals. The innovations of this article are characterized by the following three main points: First, this article confirms the positive relationship between budget participation and organizational performance of public hospitals in China, providing useful references for subsequent research and other national and regional studies. Second, it analyzes the impact of budget participation on organizational performance based on a new perspective of Latour’s Actor-Network Theory. Finally, it uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative research methods to analyze the data.
2 Literature review
The main theoretical motivation for this article stems from the increasing number of recent studies that have begun to unify two disparate streams of literature: on one hand, the literature on public organizations and organizational performance and, on the other hand, the literature on budget behavior. Moreover, there is an increasing body of research on accounting practices using agency theory and other traditional theories that may lead to conflicting results. Therefore, a more appropriate and comprehensive method is required for in-depth analyses. In this section, this article offers in sub-sections 2.1, an insight into the positive correlation between the two variables and 2.2, an insight into the negative correlation between the two variables.
2.1 The positive correlation between the two variables
The contribution of budget participation to organizational performance can be systematically explained through multi-level theoretical mechanisms and differentiated practice scenarios. From an information integration perspective, the essence of budget participation is to break down information silos within the organization and optimize the quality of decision-making through a two-way flow of data (13). This effect is particularly pronounced in high-uncertainty environments (14). Behavioral science theories further reveal the deeper driving mechanisms of engagement in individuals and teams. The paths of action include the following three: The first is autonomy empowerment. Employees have a greater voice in equipment purchase budgets, and their commitment to production goals increases (15). Second, it enhances competence identity. The self-efficacy of junior managers increases through participation in setting phased budget goals, which directly reduces goal deviation behaviors (2). Third, there is a cross-sectoral synergy. The case of the Government’s Cross-Departmental Budget Working Group demonstrates that collaborative budgeting has led to a higher frequency of information sharing between departments and a reduction in the project delivery cycle (16). Quantitative studies of the effects of weights and measures reveal the law of fit for the budgetary participation model (8). In decentralized organizations, participatory budgeting leads to increased policy responsiveness by shortening the “decision-implementation” chain (17). However, in highly centralized firms, limited participation is more effective than full participation because it avoids decision-making stagnation (18). Digital transformation has amplified the effectiveness of budget participation. Local governments that have deployed blockchain budget tracking systems have seen a significant increase in the frequency of citizen engagement and higher rates of budget execution (19).
2.2 The negative correlation between the two variables
While some studies hold the view that budget participation may have a negative effect or no effect on organizational performance. This is mainly because the core stems from a mismatch between the institutional and organizational contexts. In a scenario where strong performance pressures coexist with weak monitoring, budgetary participation may be alienated as a strategic gaming tool (20). Local government department heads create budgetary slack by overestimating costs or underestimating revenues, which directly leads to less efficient resource allocation (21). The mechanism by which this distorted behavior occurs can be divided into three motivating factors. First, under an incentive system that strongly links compensation to budget achievement, managers tend to set aside “safety cushions” to reduce appraisal risk and increase the size of budgetary slack (22). Moreover, when participatory mechanisms lack social accountability, information rent-seeking behavior by management is systematically condoned by the board. Studies have shown that the size of budgetary slack is higher in the unsupervised group than in the supervised group (23). Thirdly, Lack of cultural appropriateness exacerbates formalized budget participation. Adoption of budget proposals by rank-and-file employees is grossly inadequate in countries with high power distances, resulting in participation being reduced to a symbolic process (24). A deeper contradiction is reflected in the disconnect between organizational capacity and the demand for participation (25). The contribution of budgetary engagement to performance plummets in firms where transformational leadership is absent. Managers are unable to translate employee suggestions into actionable programs (3). Weak technical support directly undermines the effectiveness of budget participation. Enterprises with paper-based budget processes experience delayed information integration and versioning confusion. This results in performance gains being offset by the increased time costs associated with budget participation (26).
In summary, existing studies have mainly used goal-setting, agency, and uncertainty theories and other traditional theories to analyze how budget participation influences organizational performance. However, these results are controversial. This may be because existing studies have considered factors within the organization and ignored those outside it. Therefore, this article introduces Latour’s Actor-Network Theory to explain the impact of budgetary participation on organizational performance. More importantly, most existing studies have been conducted using quantitative methods. A single quantitative method may have problems such as scale mismatch and time window mismatch. Therefore, this article attempts to address the shortcomings of previous studies by adopting a combination of directional and quantitative research methods.
3 Theoretical framework
3.1 The sociology of worth of Latour’s Actor-Network Theory for understanding the relationship between public hospital budget participation and organizational performance
Studies by Dunk and Nouri (27), Shields and Shields (28), and Derfuss (29) that focus on budget participation often only explain a small portion of budget efficiency and organizational performance. One possible reason for this problem is that research on budget participation often focuses on interactions within a binary system. However, budget goal setting spans the entire organization, with different actors involved in budget participation, such as the government, health agency management, healthcare personnel, and other human actors, thus exceeding the scope of the supervisor-subordinate binary (28, 30). Therefore, this article uses Latour’s Actor-Network Theory, which can comprehensively consider various actors and their interrelationships.
It is evident that past theories can no longer explain the relationship between budget participation and organizational performance. Latour’s Actor-Network Theory has attracted our attention. Latour emphasizes that science can only be understood through its practice; therefore, it is necessary to examine science in action, not just the results of science or simply facts (48). From this perspective, Latour developed an analytical method called “Actor Network Theory” (ANT). According to this method, science survives and develops in a network-like construction process, and this network needs to encompass all social resources and human strategies as much as possible. Latour’s basic orientation is that science is a domain in which neither human nor nonhuman factors are given special priority. This can be seen as a radical form of symmetry theory, which sets the symmetry between human and non-human actors, or rather, super symmetry. Latour’s Actor-Network Theory emphasizes the construction process of social networks and believes that social phenomena are formed by the interconnection of different actors. These connections are dynamic and can be changed through continuous interactions and exchanges. Therefore, the participation of each actor is crucial.
First, when this article applies Latour’s Actor-Network Theory to the field of budget accounting in public hospitals, it views accounting budgeting as a network composed of multiple actors, including human actors (such as management, financial departments, doctors, and nurses) and non-human actors (such as documents, reports, and technical equipment). By analyzing the interactions and impacts between these actors, it is possible to gain a deeper understanding of the relationships between the various actors involved in the budget formulation process.
Second, Latour’s Actor-Network Theory emphasizes the need for cooperation among actors in the budgeting process. Governments, health institutions, doctors, and nurses are all related.
Third, applying Latour’s Actor-Network Theory, there may be competition and conflict between different actors. Government departments may want to control the budget size, while health institution management may want to obtain more budget resources to meet the demand for medical services. Doctors and nurses may want to increase budget investment to improve medical facilities and provide better services. This type of competition and conflict must be weighed and negotiated in the actual budget formulation process.
Finally, Latour’s Actor-Network Theory emphasizes the interactions and influences between actors. During the budgeting process, government departments affect the behavior of health institution management and are also subject to feedback and adjustments from other participants. Through the analysis of Latour’s Actor-Network Theory, researchers can reveal the direct and indirect impact paths of institutions on participant behavior and understand how institutional settings shape participant budgeting behavior. The direct impact path is as follows: the system setter establishes norms and requirements for budget preparation. For example, government departments require the management of health institutions to provide specific financial information in budget reports, which directly affects the financial decision-making and reporting behavior of management in budget preparation. Institutions also influence participants’ behavior through other indirect channels. System setters may require transparency and accountability in the budgeting process, which motivates participants to handle budget-related matters more cautiously to avoid responsibility and punishment in the future.
Based on the above, this article innovatively introduces Latour’s Actor-Network Theory and believes that it is reasonable and necessary to study the relationship between budget participation and the organizational performance of public hospitals. Thus, this article formulates the following hypothesis:
H1: Budgetary participation promotes organizational performance.
3.2 Experience, theory, and mediating variables
Budget participation is an incentive mechanism that can improve organizational performance (50) and budget effectiveness. Personnel involved in the budget who hold a positive attitude and receive a high degree of motivation can produce improved budget effects (31). This is mainly because the cognitive ability and level of motivation of organization members are greatly improved when they participate in budget management. In addition, the impact of budget participation on organizational performance is influenced by cognitive mechanisms. Budgetary participation can have an informational effect. Under the cognitive mechanism, participating in budgeting is a process of sharing and understanding the information. Therefore, in the process of participating in budgeting, more information can be mastered, role ambiguity can be reduced, and a clearer understanding of the work environment and job responsibilities can be obtained. Organizational performance can be improved by fully utilizing and effectively allocating controllable economic resources (32). Macinati et al. (33) studied the relationship between budget participation and organizational performance in the context of professional hybrids in the healthcare industry. The results showed that the relationship between budget participation and organizational performance was not significant, suggesting the existence of potential mediating effects. As mentioned above, previous experience has taught us that research on the relationship between budget participation and public hospital performance often relies on the involvement of intermediary variables.
Based on theoretical foundations and empirical literature, Latour’s Actor-Network Theory emphasizes network construction and the equal importance of the roles of non-human and human actors. Therefore, when this article examines the relationship between budget participation and organizational performance in public hospitals, there should also be a network construction between the two. Combining the interactivity of theory, this article proposes self-efficacy as an intermediary variable to test the relationship between budget participation and public hospital performance.
Self-efficacy was first proposed by Bandura (34). Since its introduction, various fields have conducted numerous studies on this concept. Bandura (35) elaborated on self-efficacy as “an individual’s evaluation and perception of their ability to complete a task.” The so-called self-efficacy refers to the level of confidence an individual has in whether they can complete a task, which is not related to the skills themselves but to the level of confidence they have in whether they can use their skills to achieve the task. Current measurements of self-efficacy are generally in the form of Likert scales (36). The definition of self-efficacy in this article is based on Bandura’s definition and measures the confidence level of members of public hospital organizations in completing work. However, it not only refers to the self-efficacy of specific job responsibilities but also includes planning self-efficacy, interpersonal communication and coordination self-efficacy, information processing self-efficacy, decision-making, and problem-solving self-efficacy. Western scholars propose that self-efficacy comes from four types of experiences: (1) past successful experiences. (2) Imitation or substitution. There is a lot of knowledge and experience that is not obtained through personal practice but through observation and imitation of the behavior of others (37). If the indirect experiential information conveyed by peer behavior is successful, it can promote the improvement of one’s own self-efficacy. (3) Verbal or social persuasion: If others evaluate individuals as capable of performing a certain task, they will put in more effort, and correspondingly, their self-efficacy will improve. (4) The state of physiology and emotions. A stable, positive, and healthy emotional state can promote self-efficacy, whereas anxiety, tension, or fear can easily weaken it. Fatigue and pain can reduce task-related self-efficacy (38). Bandura’s summary of the sources of self-efficacy is overly broad. Therefore, Gist and Mitchell (51) conducted a more detailed analysis of the factors that affect self-efficacy from three levels: controllability, internal and external sources, and plasticity, and proposed a three-dimensional model of self-efficacy. The model proposed by Gist and Mitchell is more refined and specifies the dimensional characteristics of the influencing factors. Regarding self-efficacy and work effectiveness, Judge and Bono (39) examined the relationship between general self-efficacy and work attitudes and found that employees with higher self-efficacy believe that they can complete tasks well, resulting in higher job satisfaction.
Based on the above analysis, this article formulates the following hypothesis:
H2: Self-efficacy mediates between budgetary participation and organizational performance.
4 Methodology and results
This article combines directed and quantitative research methods. This is because purely quantitative studies may overlook the contextual factors and psychological mechanisms (e.g., dynamics of self-efficacy) of the participants. Qualitative studies have difficulty demonstrating statistical significance among variables. The mixed methods approach compensates for the shortcomings of a single approach through ‘triangulation’ and enhances the rigor of the article.
4.1 Qualitative research
4.1.1 Interview method
Qualitative research was conducted using Grounded Theory in interviews. Grounded Theory (GT) is a qualitative research approach that aims to establish theories based on empirical data (52). This article adopts Grounded Theory for the following reasons: First, the relationship between budgetary participation and organizational performance in public hospitals is multidimensional, dynamic, and context-dependent. Grounded Theory emphasizes the distillation of theory from raw data rather than relying on preconceived assumptions, which is suitable for exploring complex phenomena that are not yet fully understood. Second, budget management in public hospitals involves multiple stakeholders (e.g., government, management, healthcare workers, and patients), and their behavioral motivations and interaction logics need to be understood from the subjective perspectives of the participants. Through open coding and axial coding, Grounded Theory can systematically sort out the core concepts (e.g., ‘self-efficacy’ and ‘non-medical performance’) in the interview data and reveal how budgetary participation affects organizational performance through psychological mechanisms. Finally, previous studies are mostly based on traditional theories (e.g., agency theory), leading to conflicting conclusions or insufficient explanatory power. Grounded theory allows researchers to generate new theoretical frameworks from data (e.g., incorporating Latour’s Actor-Network Theory) to provide more contextualized explanations of the relationship between budgetary participation and performance.
The operational procedures of Grounded Theory generally include: (1) generating concepts from data and logging them step by step; (2) continuously comparing data and concepts and systematically asking generative theoretical questions related to concepts; (3) developing theoretical concepts and establishing connections between concepts; (4) theoretical sampling and systematic encoding of data; and (5) constructing theory, striving to obtain the density, variability, and high degree of integration of theoretical concepts. In the first level of coding (Open Coding), researchers require an open mindset, as much as possible, to “suspend” personal “biases” and research community “fixed opinions” and log all data in their own state. To address bias in data analysis, this article used the member check method. Initial analyses were fed back to the participants to confirm that their views were accurately understood and presented. The main task of secondary coding (also known as associative or axial coding) is to discover and establish various connections between conceptual categories to represent the organic relationships between various parts of the data. These connections can be causal, temporal order, or semantic relationships. Consider their language in the context of the time and the social and cultural context in which they are located, and from the following encoding points. To increase the credibility of the data, the results of the coding were further discussed using peer debriefing, in which no new ideas were generated.
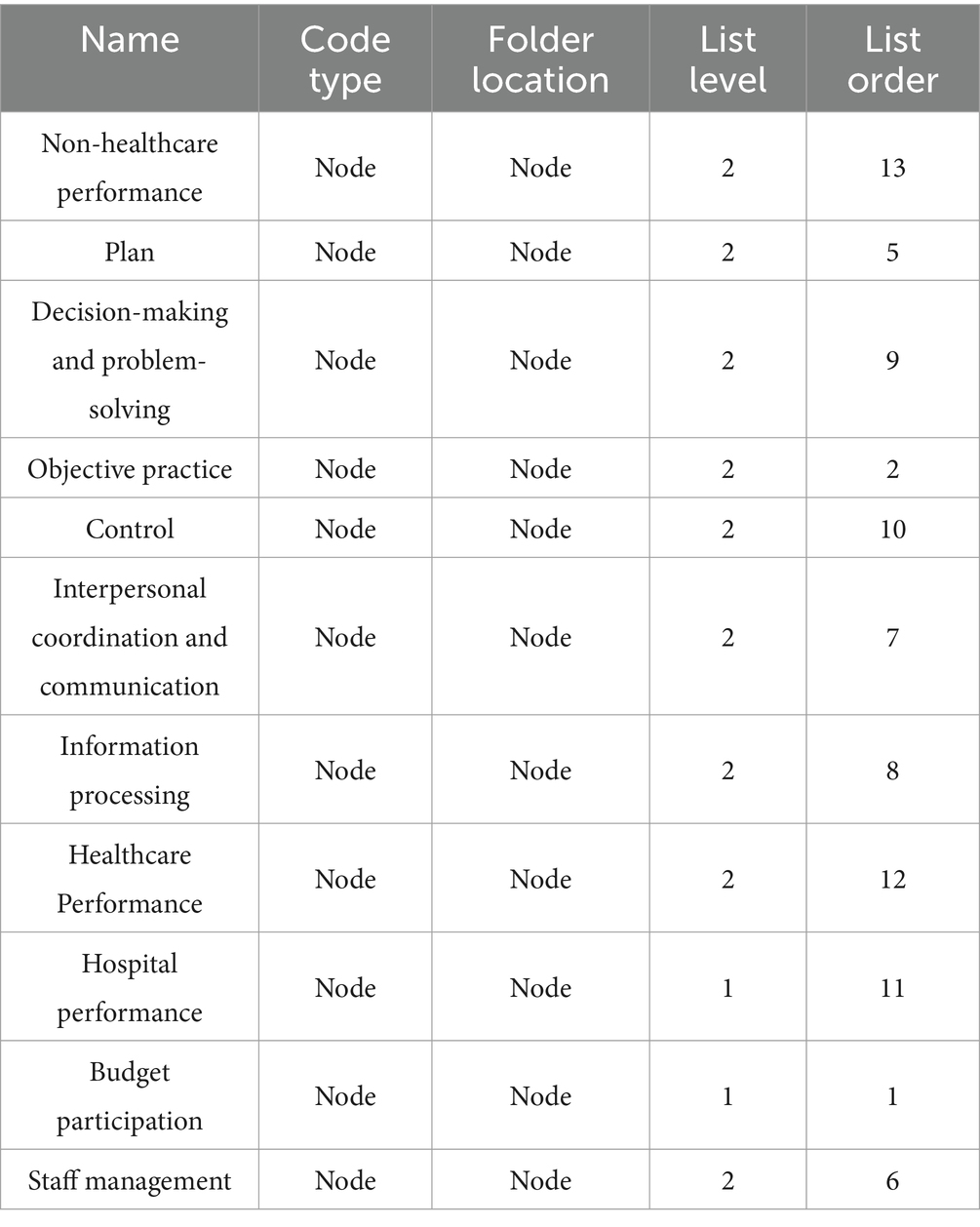
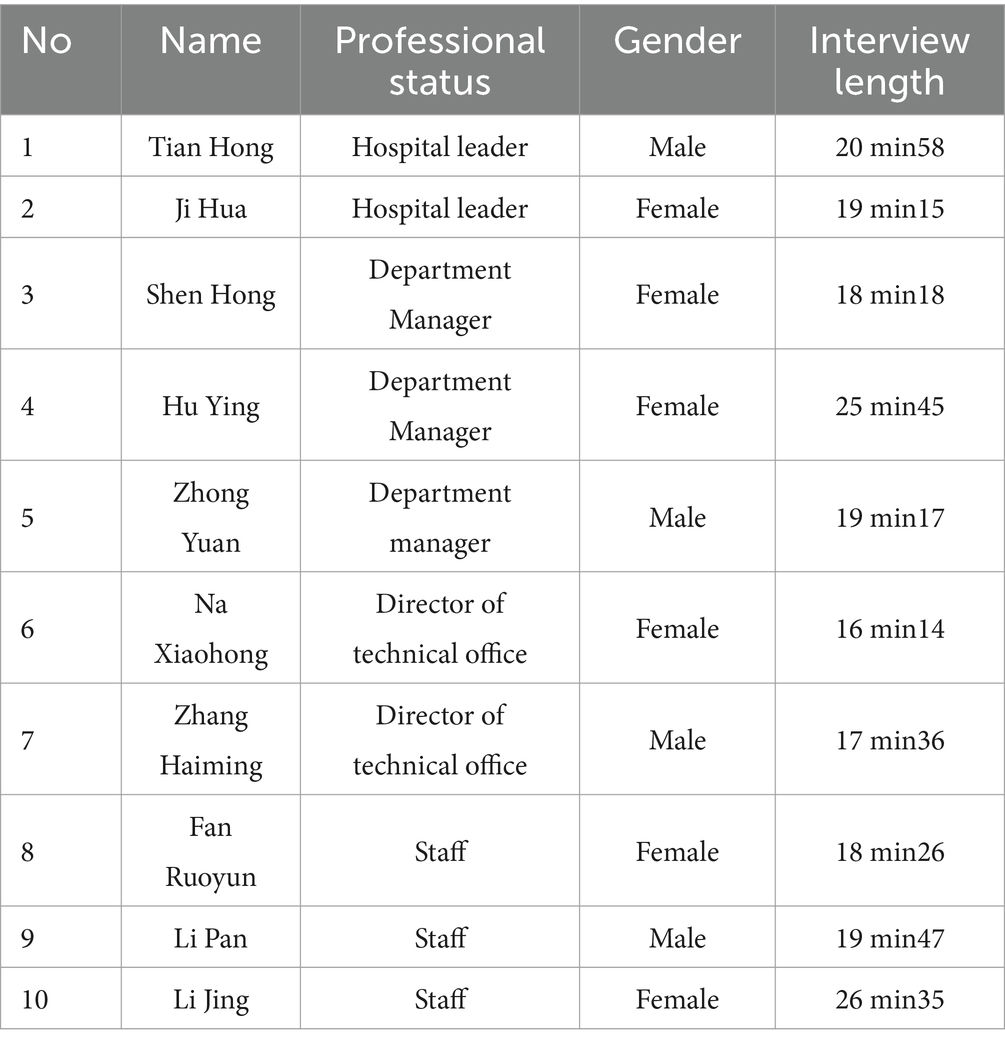
Based on the above, this article uses the GT interview method with ten public hospital-related personnel in China as interviewees to study the relationship between budget participation, self-efficacy, and hospital performance. These 10 people were chosen for this article because they were all directors or financial heads of public hospitals. They started from the grassroots and have a better understanding of the business situation, budgeting, and organizational performance of public hospitals. The sample size was established following the principle of theoretical saturation, whereby the information obtained was collated for each number of readers interviewed, and the interviews ended when the 10th personnel was interviewed and no new significant information was provided. Part of the qualitative analysis of the interview content used the Nvivo software. The details are presented in Table 1.
4.1.2 Data collection
As shown in Table 2, this article selected 10 respondents for in-depth interviews. The interviewees included two hospital-level leaders, three department managers, two business department managers, and three staff members from ten public hospitals. The article uses telephone interviews, and the average interview time is 20 min.
4.1.3 Interview topic
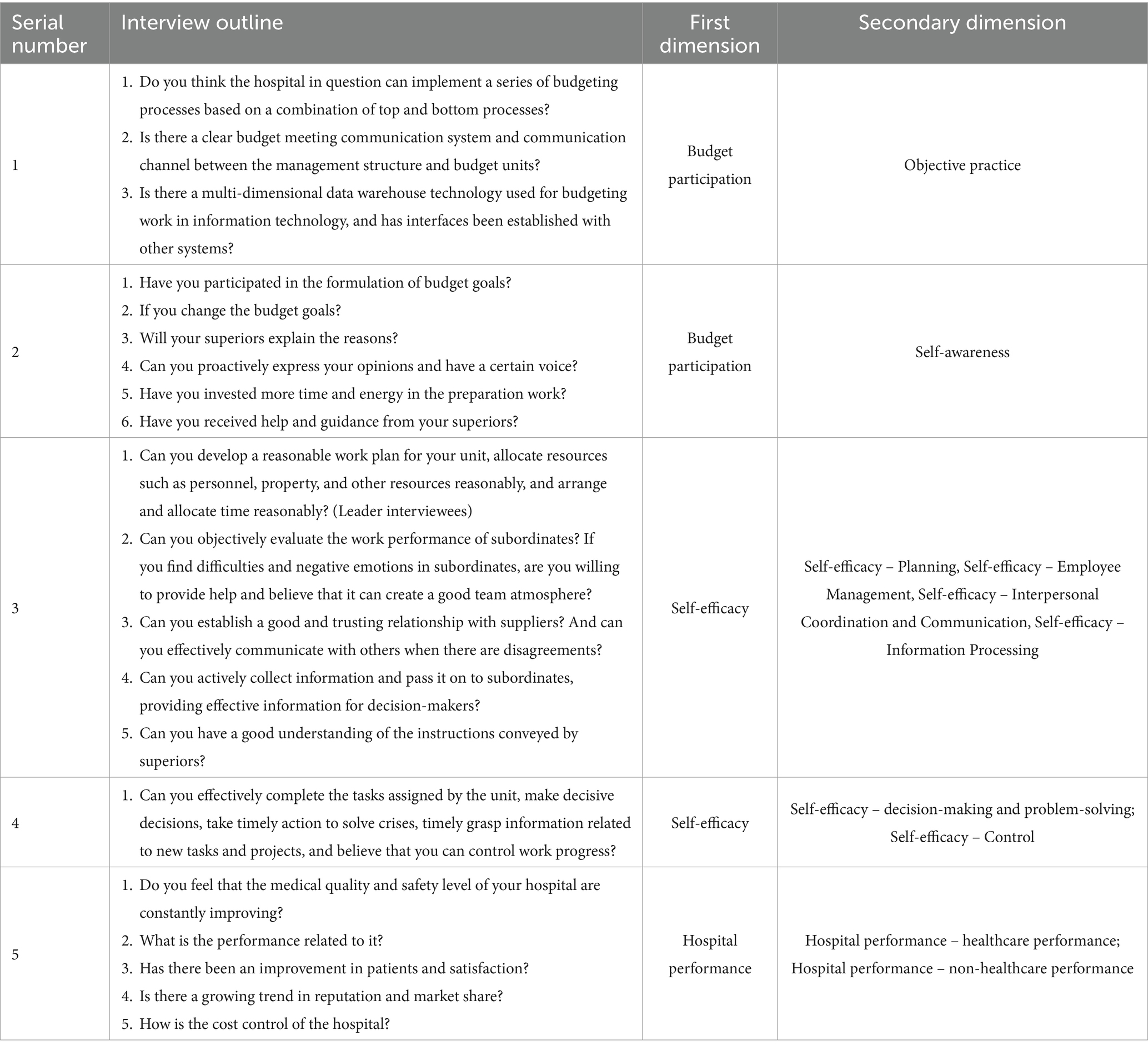
According to Latour’s Actor-Network Theory, using the interview method of GT, five interview outlines were designed in the interview outline. Table 3 presents the first-level dimension involved in the interview outline as budget participation, and the second-level dimension as objective practice. The first-level dimension involved in the second interview outline is budget participation, and the second-level dimension is the perspective of self-awareness. The first-level dimension involved in the third interview outline was self-efficacy, while the second-level dimension was self-efficacy planning, self-efficacy employee management, self-efficacy interpersonal coordination and communication, and self-efficacy information processing. The first-level dimension involved in the fourth interview outline was self-efficacy, and the second-level dimension was self-efficacy decision-making and problem-solving, and self-efficacy control. The first-level dimension involved in the fifth interview outline is hospital performance, and the second-level dimension is hospital performance – healthcare performance and hospital performance – non-healthcare performance.
4.1.4 Qualitative analysis findings
Through interviews with different subjects, this article obtained the relationship between budget participation and organizational performance in public hospitals and verified that the intermediary variable self-efficacy preliminarily determined under Latour’s Actor-Network Theory framework does indeed promote organizational performance under budget participation.
(1) Public hospitals can establish a comprehensive budget platform by designing comprehensive budget participation processes and systems, establishing clear budget meeting communication systems and channels, conducting appropriate and diverse budget communication, and improving employee and patient satisfaction and the public hospital’s reputation. From a subjective perspective, budget participation in non-healthcare performance is positively correlated. Therefore, public hospitals should strive to increase their staff’s perception of budget participation, thereby improving work efficiency, employee and patient satisfaction, and their reputation.
(2) Self-efficacy is more biased toward subjective perception of confidence in completing tasks, and there is a cognitive variable between it and budget participation from a practical perspective. From a subjective perspective, there is a significant positive correlation between budget participation and planning self-efficacy, and between interpersonal communication and coordination self-efficacy. Therefore, by promoting the participation of public hospital staff in budget preparation, improvement, and other processes, it is possible to encourage employees to reasonably and effectively allocate time, develop complete work task plans, carry out work according to plans, establish a frank and mutual trust relationship with other members, encounter disagreements in their work, and communicate effectively.
(3) Budget participation cognition influences non-healthcare performance through planning self-efficacy, interpersonal communication, and coordination self-efficacy.
4.2 Quantitative research
Researchers conducted an empirical research design to collect the information and data needed for the empirical study of this article by means of a questionnaire survey, and to refine and derive the corresponding scales with reference to domestic and international scholars’ measures of budget participation, self-efficacy, and organizational performance in public hospitals.
4.2.1 Data collection
The quantitative data of our public hospitals cannot be disclosed to the public, as in the case of enterprises, due to sensitivity issues. Moreover, Budgetary participation, self-efficacy, and organizational performance variables are mostly measured in national and international studies in the form of Likert scales. Thus, this article used questionnaires to collect data. The main steps taken in this article to ensure the validity of the data are as follows: (1) To ensure the validity of the structure and content of the questionnaire, this article first sorted out the measurement items of budgetary participation, self-efficacy, and organizational performance of public hospitals based on domestic and international studies, drew on widely used scales, and improved them. Subsequently, the researchers asked experts in public hospital management to assist in judging the reasonableness of the design of each measurement item. (2) Pre-testing of the questionnaire, inviting people to complete the questionnaire, improving some of the content based on their responses, and estimating the time required to complete the questionnaire. (3) In this article, we designed a web-based questionnaire with reasonable prompts to remind participants of the precautions for completing the questionnaire to reduce non-response bias. (4) Reliability and validity tests were conducted for each variable of the questionnaire.
With the help of the financial leaders of relevant public hospitals, the questionnaires were distributed through seminars on comprehensive asset and price management in public hospitals. The distribution of respondents was random. A total of 168 questionnaires were collected, and invalid questionnaires were excluded from the analysis. Four were answered incorrectly, and the remaining 164 were analyzed using the statistical analysis software SPSS 25.0.
4.2.2 Variables measurement
4.2.2.1 Budget participation
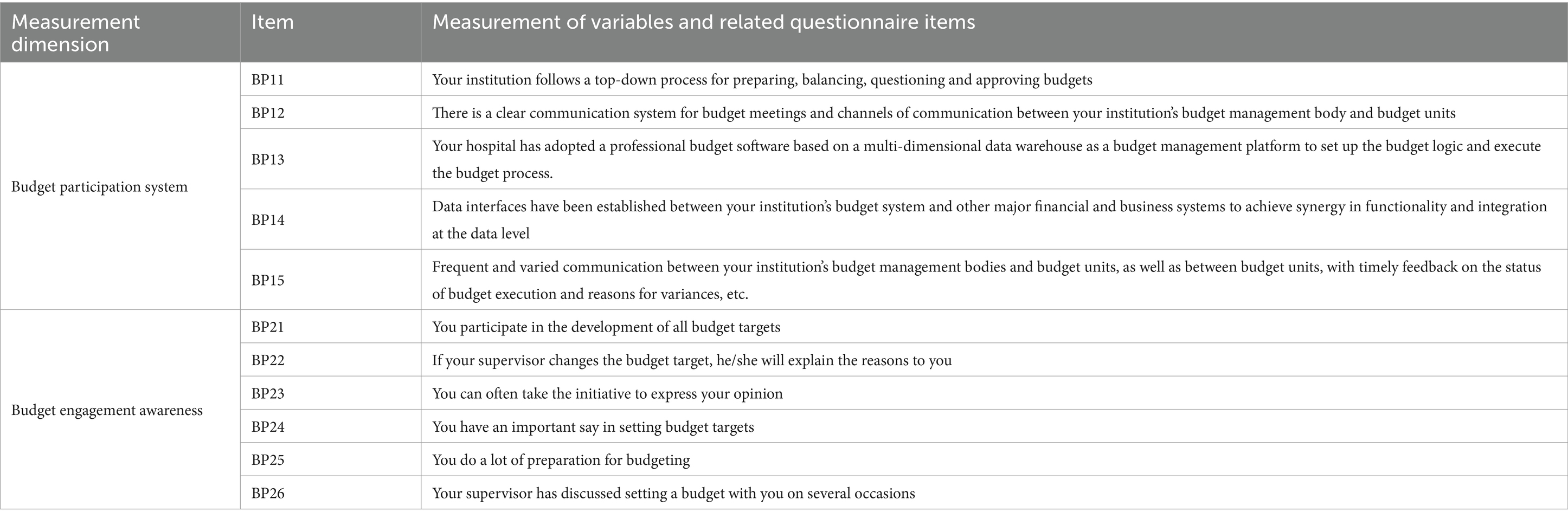
Milani (40) defined participation in budgeting as a continuous variable to measure the level of involvement of organizational members in the process of budgetary activities and measured it in several ways. The budget participation scale designed by Milani is widely used by management accounting scholars. However, its measure is a budget participant’s subjective perception of self-involvement and influence, which is likely to be subject to cognitive bias, leading to highly unstable results in testing the relationship between the two. Thus, this article adopts a methodology for measuring budgetary participation in terms of objectively occurring managerial practice activities that eliminate information asymmetry, combined with a scale designed by Milani to measure budgetary participation. See Table 4 for specific measurements.
4.2.2.2 Self-efficiency
The development of this part of the scale is based on the Self-Efficacy Scale for Managers in Chinese Enterprises constructed by Ling Wen wheel spokes and Fang Liluo (41), which is mainly used to measure managers’ performance in the four areas of ‘Planning’, ‘Interpersonal Coordination and Communication’, ‘Information Processing’, and ‘Decision-making and Problem-solving’. These dimensions were measured on a 7-point Likert scale of ‘completely disagree – completely agree’ (47), as shown in Table 5.
4.2.2.3 Organizational performance
This article focuses on Chinese public hospitals. China’s healthcare system is still in its infancy, and public financial information and data are not readily available. During the field research, it was evident that the interviewees were very cautious about disclosing specific financial data and information, which is understandable. In addition, public hospitals are non-profit organizations with a greater emphasis on social benefits. Therefore, this article focuses on the non-healthcare service performance of public hospitals. Non-healthcare performance (NHP) mainly includes internal and external customer satisfaction, organizational financial and market performance, as well as the image and reputation of public hospitals in the eyes of the public, and the specific measures are shown in Table 6.
4.2.2.4 Control variables
Considering that other factors also affect the organizational performance of public hospitals, they were included in the model as control variables. The level of public hospitals (Level), type of public hospitals (Status), and area where the public hospitals are located (Area) were selected.
The level of the public hospital can be divided into Level I, Level II, and Level III. Status indicates the category of public hospital, which can be divided into general public hospitals and specialized public hospitals. The area indicates the region where the public hospital is located; 0 indicates Northwest China (covering Shaanxi, Gansu, Ningxia, Qinghai, and Xinjiang), 1 indicates Northeast China (covering Liaoning, Jilin, and Heilongjiang), 2 indicates Southwest China (covering Sichuan, Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan, and Tibet), 3 indicates Central China (covering Hubei and Hunan), 4 indicates North China (covering Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shandong, Henan, Shanxi, and Nei Menggu), 5 indicates South China (covering Guangdong, Fujian, Guangxi, and Hainan), and 6 indicates East China (covering Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, and Jiangxi).
In addition, since budgetary participation and self-efficacy are related to the judgment of one’s own situation, based on the suggestions of previous studies (42–44), some control variables related to situational and individual factors that may affect the results were included in the model, including Tenure, Gender, Age, Background, and Education. Tenure was categorized as follows: Faculty Leaders, Functional Department Management, Operational Section Managers, and General Staff were denoted by 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively; Age (Age) was categorized into three levels: less than 40 years old, between 40 and 50 years old, and more than 50 years old; and educational attainment was categorized into three levels: college, bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, or doctoral degree.
4.2.3 Descriptive statistics
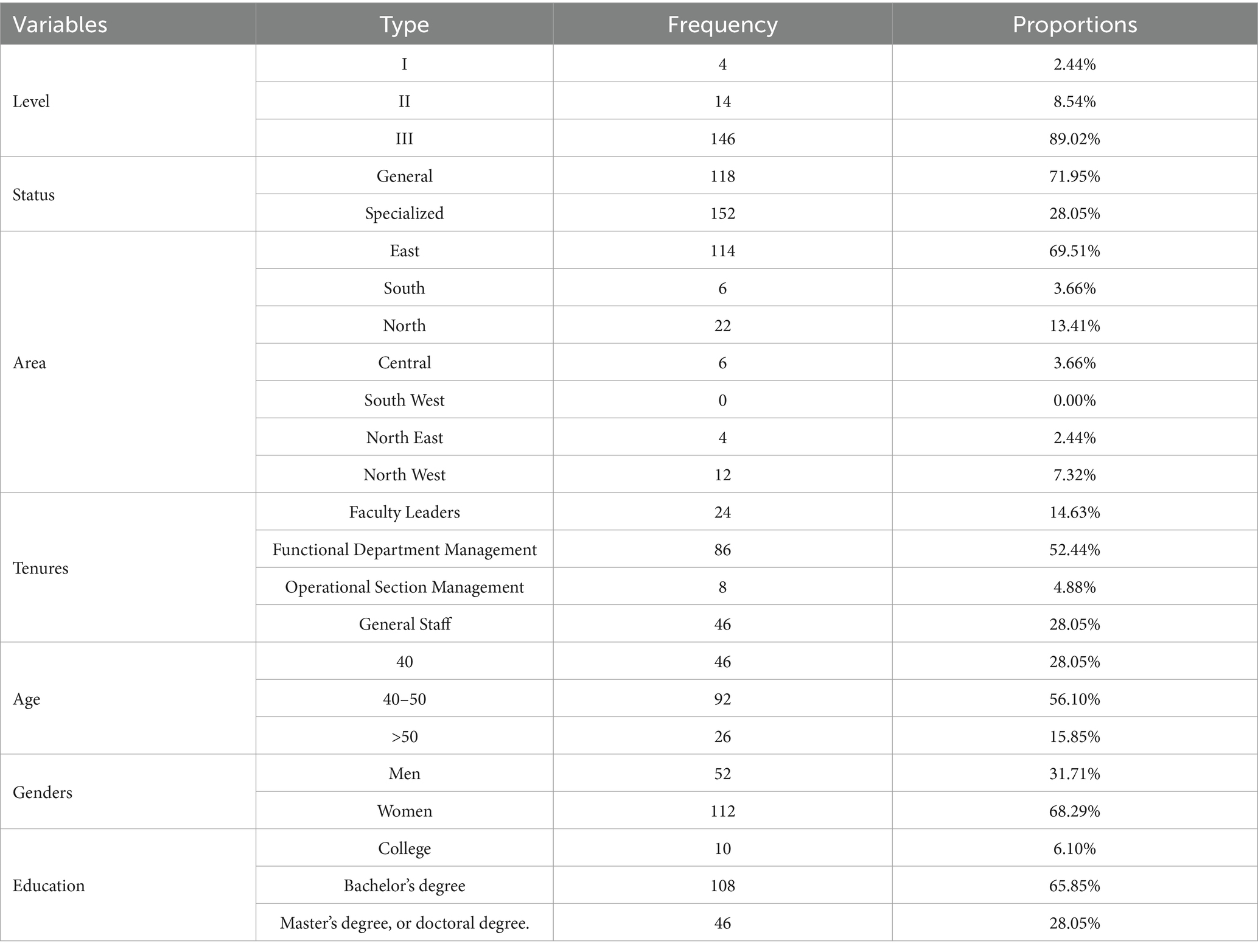
The distribution of the sample is shown in Table 7. The vast majority of public hospitals in the sample public hospitals studied in this paper are public hospitals of level I, accounting for 89.02 percent, while 8.54 percent of public hospitals are at level II, and 2.44 percent are at level III; 71.95 percent of them are general public hospitals, and 28.05 percent are specialist public hospitals; the location of the public hospitals is mainly concentrated in East China, accounting for 69.51 percent, while the distribution in other regions is more even. The age of the sample’s public hospital personnel was mainly concentrated between 40 and 50 years old, accounting for 56.10 per cent, followed by those under 40 years old, accounting for 28.05 per cent, and those over 50 years old, accounting for 15.85 per cent. The education level of the respondents was relatively high, with 65.85 per cent having a bachelor’s degree and 28.05 per cent having a master’s degree or PhD.
4.2.4 Correlation test
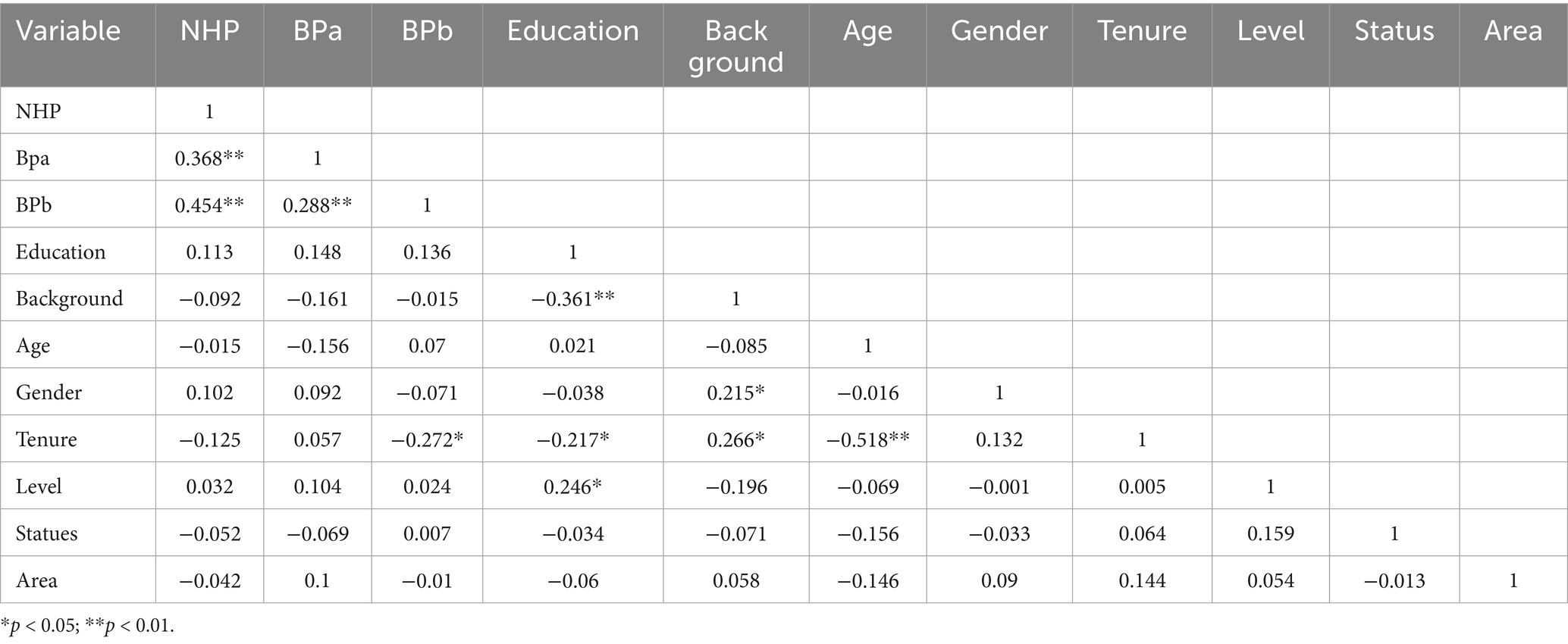
The results of the correlation analysis are shown in Table 8. From Table 8, the correlation coefficient between BPa and NHP is 0.368 which is significant at the 1% level. The correlation coefficient between BPb and NHP was 0.454 which was significant at the 1% level. This preliminarily verifies research hypothesis H1. The correlation coefficients between the variables are less than, and the VIF test is performed are less than 2, and the tolerance values are greater than 0.6. This indicates that there is no multicollinearity among the main variables of this article.
4.2.5 Reliability and validity analysis
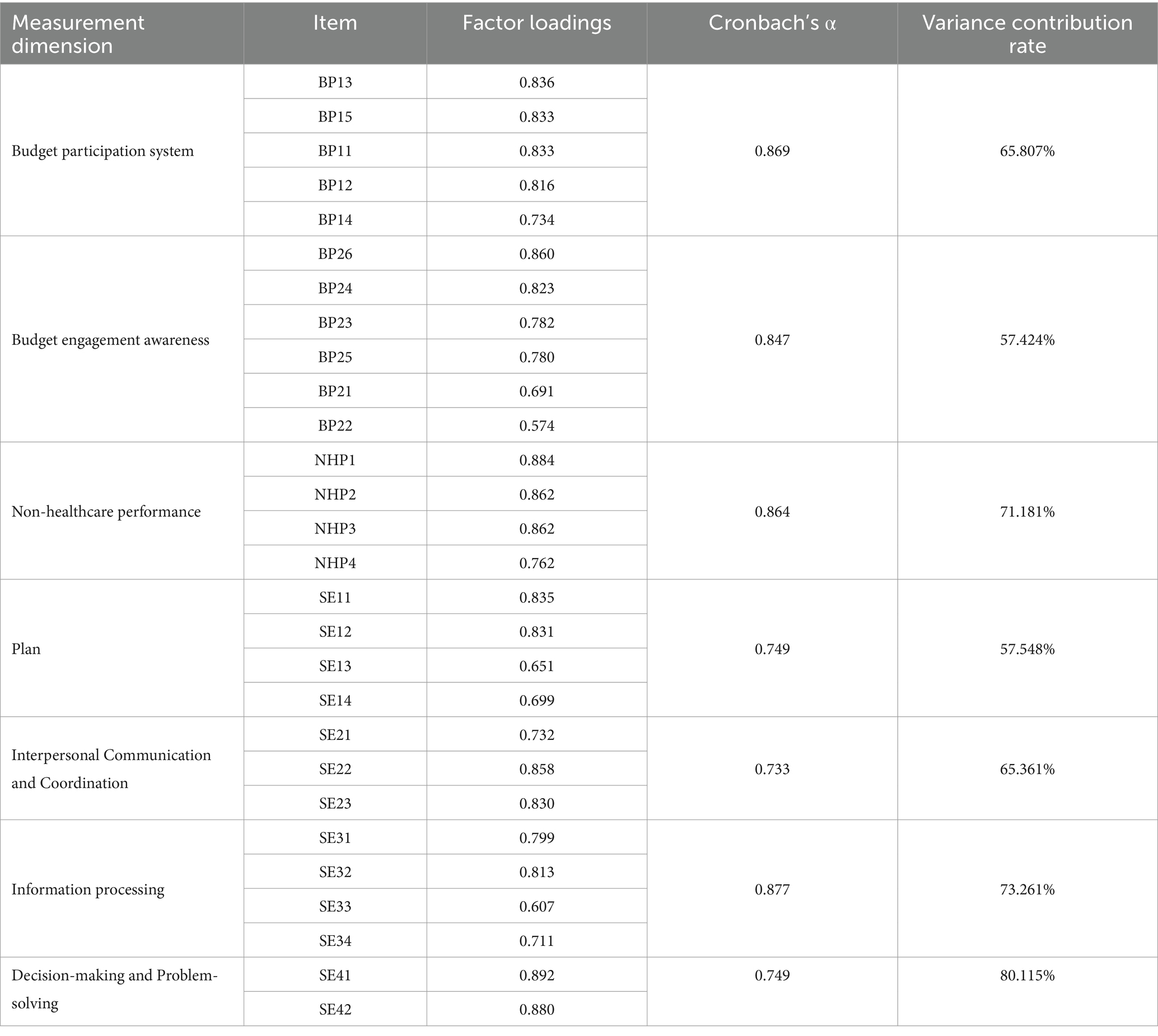
In this article, the internal consistency coefficient (Cronbach’s alpha value) was used to test the reliability of each variable in the questionnaire. The analysis results showed that the internal consistency coefficient of each variable exceeded 0.7, as shown in Table 9, indicating that the scale had good consistency and stability. Validity can be divided into content and construct validity. The measurement items used in this article were mature scales developed by scholars with good content validity. The standard factor loadings of each measurement index on their respective latent variables were all higher than 0.6, indicating that the scale could accurately measure each variable and had good convergent validity.
4.2.6 Regression analysis
4.2.6.1 Budget participation – organizational performance
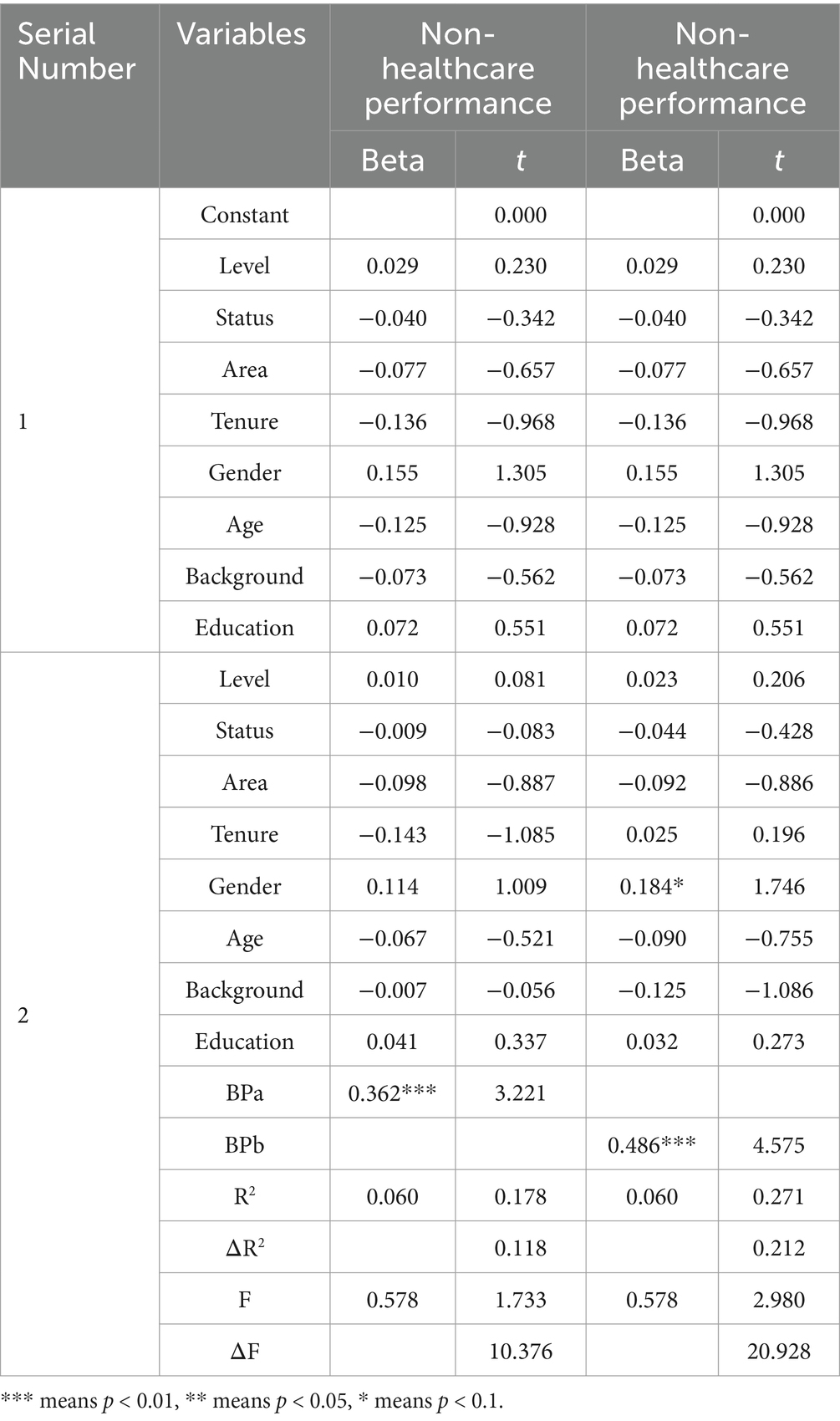
As shown in Table 10, the regression analysis found that the budget participation system was significantly and positively correlated with NHP, with a correlation coefficient of 0.362. In the regression model, excluding the explanation part (6%) of Model 1, the incremental explanation for the change in the NHP in Model 2 was (Change in R2) 11.8%. The above test results show that from an objective point of view, the higher the level of budget participation, the higher the NHP. The perception of budgetary participation was found to be significantly positively correlated with NHP, with a correlation coefficient of 0.486, excluding the explanation part of Model 1 (6%). The incremental interpretation of Model 2 for the changes in NHP was (Change in R2) of 21.2%. The above test results show that from the perspective of self-perception, the higher the level of budget participation, the higher the NHP.
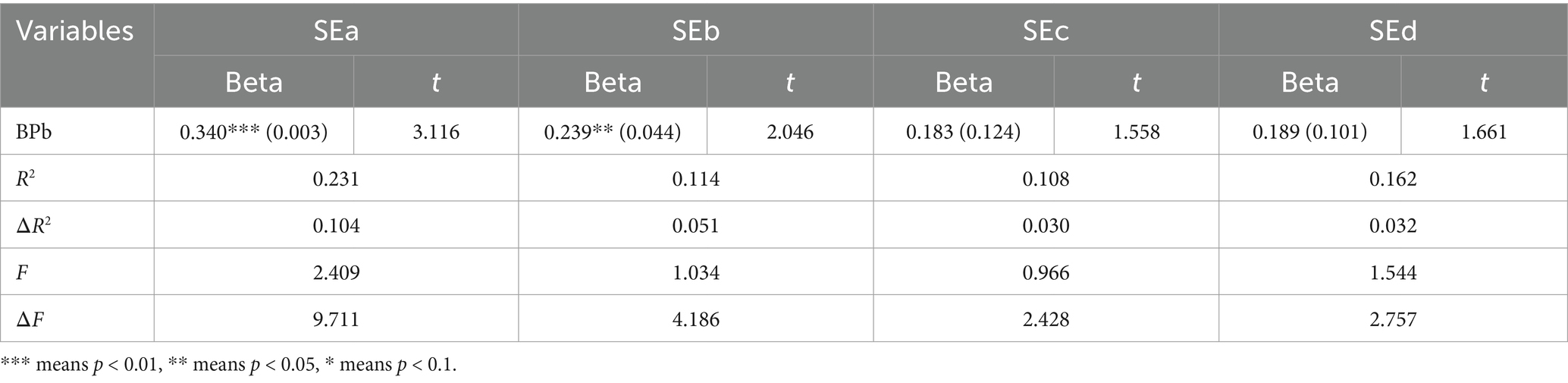
4.2.6.2 Budget participation – self-efficacy
After the regression analysis of self-efficacy in the budget participation system, it was found that there was no significant correlation between the two variables; therefore, the results are not shown here. After the regression analysis of budget participation cognition and self-efficacy, it was found that budget participation cognition and planning, and interpersonal communication and coordination self-efficacy were significantly positively correlated, with correlation coefficients of 0.340 and 0.239, respectively. In the regression model of budget participation self-perception and planning self-efficacy, excluding the explanation part of Model 1, the incremental interpretation of the self-efficacy change in Model 2 was (ΔR2) at 10.4%. In the regression model of budget participation, self-cognition and interpersonal communication and coordination self-efficacy, excluding the explanation part of Model 1, the incremental interpretation of the self-efficacy change in Model 2 was (Change in R2) 5.1%. The above test results showed that from the perspective of self-perception, the higher the level of budget participation, the higher the self-efficacy in terms of planning, and interpersonal communication and coordination. The details are presented in Table 11.
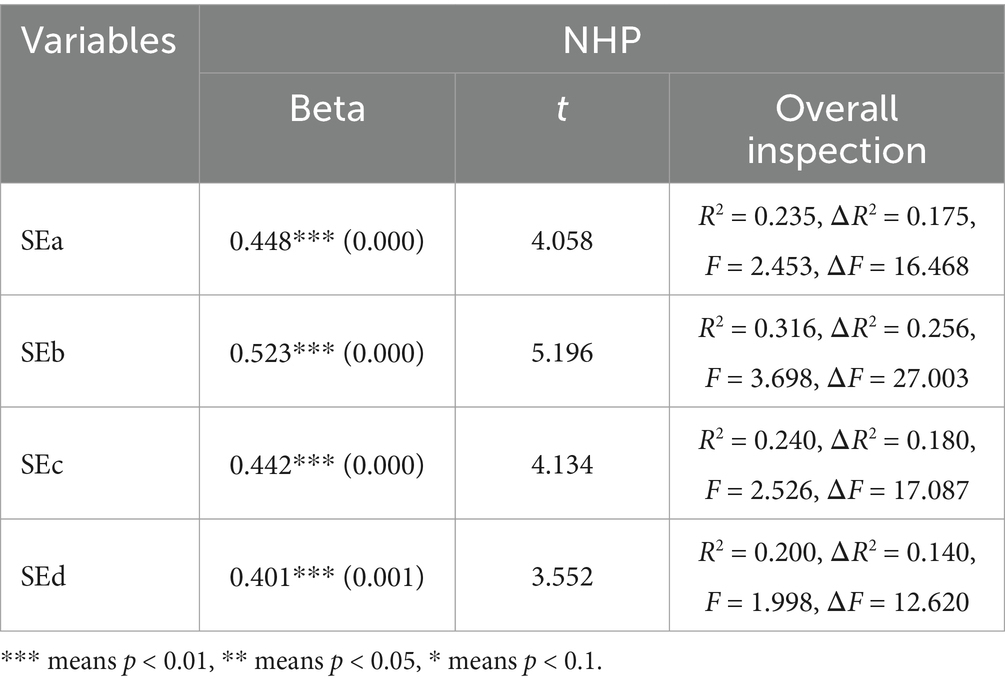
4.2.6.3 Budget participation, self-efficacy and organizational performance
Table 12 presents the results of the regression analysis, which found that planning, interpersonal communication and coordination, information processing, decision-making and problem-solving self-efficacy and NHP were significantly positively correlated, with correlation coefficients of 0.448, 0.523, 0.442, and 0.401, respectively. The results showed that the higher the self-efficacy of public hospital staff, the higher the NHP of public hospitals.
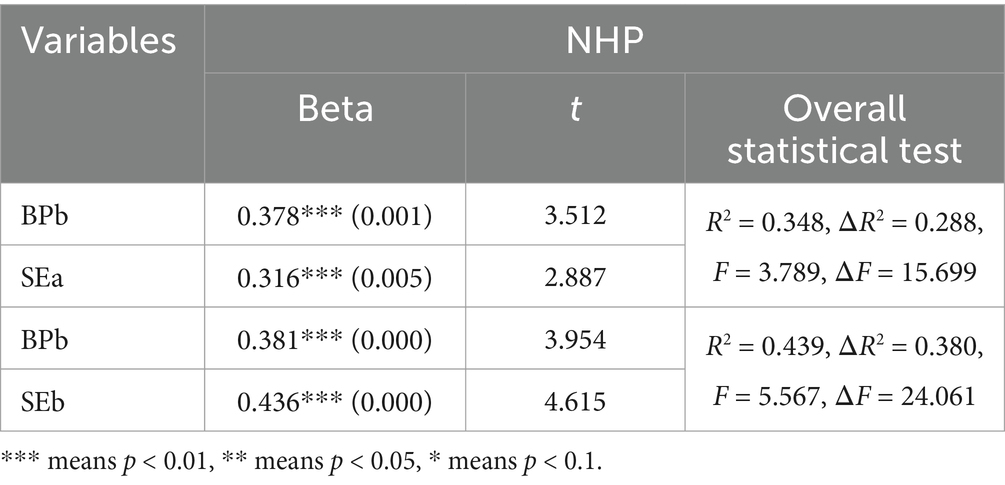
Planning, self-efficacy, and NHP were significantly correlated, with a correlation coefficient of 0.316. The perception of budget participation and NHP were significantly correlated, but the correlation coefficient (0.378) was smaller than the correlation coefficient without considering the mediation effect (0.486). Therefore, self-efficacy mediates the relationship between perceptions of budget participation and NHP. Interpersonal communication was significantly correlated with coordination self-efficacy and NHP, with a correlation coefficient of 0.436. The perception of budget participation and NHP were significantly correlated, but the correlation coefficient (0.381) was smaller than the correlation coefficient without mediating effects (0.486). Therefore, interpersonal communication and coordination self-efficacy mediate the relationship between the perception of budget participation and NHP. The details are presented in Table 13.
Figure 1 shows the factor-diameter analysis of the results. The ‘Diameter Diagram’ is essentially a summary of the regression analysis, showing the direct or indirect effects of budget participation (the independent variable) on the organizational performance (the dependent variable) of public hospitals (represented by the factor diameter coefficient, that is, the standard regression coefficients). Thus, this article aims to clarify the causal relationship between the three variables of public hospital budget participation, self-efficacy, and organizational performance.
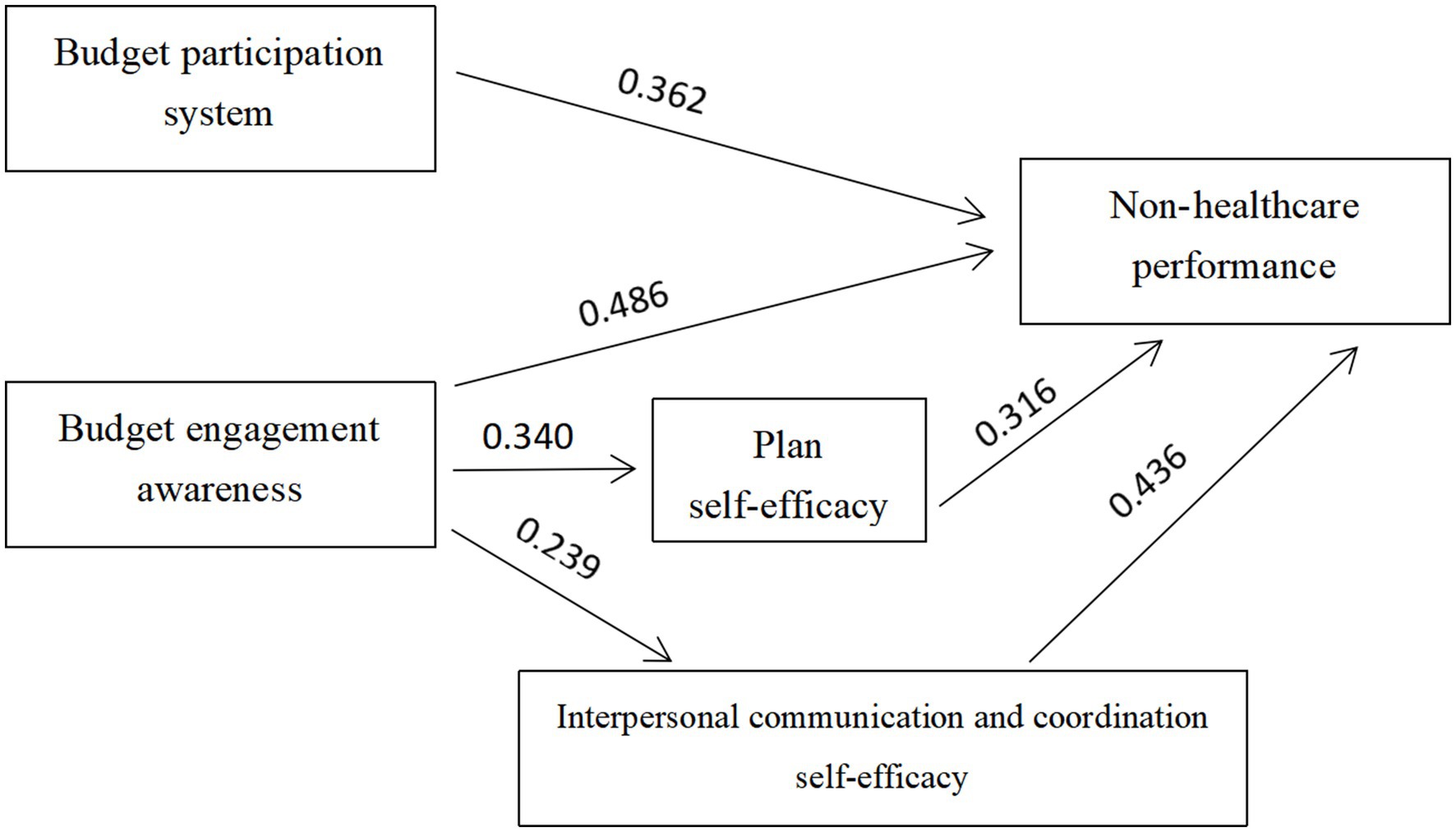
Figure 1. Path analysis of budget participation, self-efficacy and organizational performance in public hospitals.
5 Conclusion and discussion
5.1 Conclusion
This article obtained 164 valid questionnaires from public hospitals through a questionnaire survey, and the relationship between budget participation and organizational performance in public hospitals was analyzed using a combination of theoretical and empirical methods. Moreover, based on Latour’s Actor-Network Theory, self-efficacy was introduced to examine its role in this. This article found that in the context of public hospitals, budget participation has a significant positive effect on organizational performance, with self-efficacy having a mediating effect. The main conclusions of this article are as follows:
(1) On an objective and subjective level, budget participation is positively related to the NHP. This further supports existing research that argues that budgetary participation promotes organizational performance (8, 15). Nevertheless, this is contrary to research findings that suggest that budgetary participation has a negative or no effect on organizational performance (20, 22, 24). This may be because this article introduces the new theory of Latour’s actor network and an influx of quantitative research methods. Therefore, public hospitals should build a complete budget platform by designing a sound budget participation process and system, establishing clear communication channels to meet budgets, and conducting appropriate and diverse budget communication to improve employee and patient satisfaction, as well as the public hospital’s reputation. From a subjective analysis perspective, research demonstrates a significant positive correlation between budget participation and NHP outcomes. To leverage this connection, public hospitals should implement the following strategies: First, enhance staff engagement in budgetary processes through training and transparent communication; second, optimize operational efficiency by aligning resource allocation with frontline insights; and third, elevate stakeholder satisfaction through dual-focused improvements in both employee workplace experience and patient care quality. These synergistic enhancements can ultimately strengthen the reputation of institutions within the competitive healthcare landscape.
(2) At the objective level, there was no significant correlation between budget participation and self-efficacy. These results are inconsistent with those of previous studies (6). This may be because self-efficacy is more biased toward the subjective perception of a person’s degree of confidence in completing a task, and there is an intermediate cognitive variable with budget participation from a practical perspective. From a subjective perspective, budget participation, planning self-efficacy, and interpersonal communication and coordination self-efficacy were significantly and positively correlated. Therefore, by encouraging public hospital staff to participate in the process of budget preparation and improvement, it is possible to motivate staff to allocate their time reasonably and effectively, formulate a complete work task plan, and work according to the plan.
(3) Planning, interpersonal communication and coordination, information processing, decision-making, and problem-solving self-efficacy were significantly and positively related to NHP. Budget participation can affect NHP through planning self-efficacy, interpersonal communication, and coordination self-efficacy. Therefore, when using budget participation to improve organizational performance, this article suggests paying attention to the role of self-efficacy, especially in the formulation and implementation of plans, effective processing of information, and communication and coordination between employees.
5.2 Innovation
The main innovations of this article are as follows.
First, previous studies have conflicting conclusions on budget participation and organizational performance in public hospitals. Some studies suggest a positive relationship between budget participation and organizational performance in public hospitals, while others suggest a negative or no significant effect. In the face of such conflicting situations, this article summarizes and organizes past research viewpoints, and reasonably confirms the positive relationship between budget participation and organizational performance of public hospitals in China, providing useful references for subsequent research and other national and regional studies.
Second, the conflicting views in previous research were largely due to the use of traditional theories that lacked the characteristics of the times. This article innovatively uses Latour’s Actor-Network Theory to identify reasonable mediating variables of self-efficacy. Qualitative methods were used to verify the scientific and rational nature of the model. To explore the relationship between budget behavior and organizational performance accounting, a more effective and comprehensive theoretical path has been found that can be referenced and used by follow-up researchers.
Finally, this article combines qualitative and quantitative analyses to verify the relationship between budget participation, self-efficacy, and organizational performance in public hospitals. Through quantitative analysis of broader survey questionnaire data, this article further verifies that budget participation has a promoting effect on organizational performance.
5.3 Limitation
5.3.1 Limitations of the sample
Only 164 valid questionnaires were collected for the quantitative analysis. A total of 69.51 per cent of the hospitals in the sample were concentrated in East China, and the sample was unevenly distributed in other regions, which may have led to geographical bias. Future studies could expand the sample size and cover more regions (e.g., less developed regions in the central and western parts of the country) to enhance the generalizability of the findings.
5.3.2 Methodological limitations of the article
This article uses cross-sectional data and cannot verify the long-term causal relationship between budgetary participation and organizational performance. Self-reported data relying on questionnaires may lead to measurement errors due to social desirability bias or subjective cognitive differences.
Future research could use longitudinal tracking studies to observe the dynamic impact of budgetary participation on organizational performance over time. Without violating academic ethics and morals, future studies could combine objective data (e.g., hospital financial statements, patient visit records) with subjective data to reduce self-reporting bias.
5.3.3 Limitations of theoretical applications
Latour’s Actor-Network Theory emphasizes the reciprocal status of human and non-human actors. However, it was not possible to analyze the specific mechanisms of the role of non-human actors (e.g., budget software and policy documents) in budgetary participation in this article. Future research could further explore the impact of co-communication between human and non-human actors on budgetary participation in the public sector.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
QJ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Resources. JZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Data curation. XK: Writing – original draft, Software, Investigation. SC: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Committee Project Research on Budget Management of Public Hospital of the National Social Science Fund of China (grant number 21FGLB010).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Social Science Foundation for funding this research so that the project can be carried out smoothly. The authors also thank those who contributed to this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1601181/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Chong, VK, and Chong, KM. Budget goal commitment and informational effects of budget participation on performance: a structural equation modeling approach. Behav Res Acc. (2002) 14:65–86. doi: 10.2308/bria.2002.14.1.65
2. Nguyen, NP, Evangelista, F, and Kieu, TA. The contingent roles of perceived budget fairness, budget goal commitment and vertical information sharing in driving work performance. J Asian Bus Econ Stud. (2019) 26:98–116. doi: 10.1108/JABES-06-2018-0026
3. Alhasnawi, M, Said, RM, Daud, ZM, and Muhamad, H. Budget participation and managerial performance: bridging the gap through budget goal clarity. Adv Soc Sci Res J. (2023) 10:187–200. doi: 10.14738/assrj.109.15539
4. Kahar, SH, Ikbal, M, Jabid, AW, and Purbaya, A. Ethical optimism, participative budgeting, and managerial performance in regional government work unit in Indonesia: a contingency theory approach. CAL. (2019) 20:70–5.
5. Lau, CM, and Tan, SL. Budget targets as performance measures: the mediating role of participation and procedural fairness In:. Advances in management accounting. Epstein: Emerald Group Publishing Limited (2012). 151–85.
6. Yuliansyah, Y, and Khan, AA. A revisit of the participative budgeting and employees’ self-efficacy interrelationship–empirical evidence from Indonesia’s public sector. Int Rev Public Adm. (2017) 22:213–30. doi: 10.1080/12294659.2017.1325584
7. Silva, P, Mota, J, and Moreira, AC. Budget participation and employee performance in real estate companies: the mediating role of budget goal commitment, trust and job satisfaction. Balt J Manag. (2022) 18:226–41. doi: 10.1108/BJM-03-2022-0118
8. Fuadah, LL, Safitri, RH, Yuliani, Y, and Arisman, A. Determinant factors' impact on managerial performance through management accounting systems in Indonesia. J Asian Fin Econ Bus. (2020) 7:109–17. doi: 10.13106/jafeb.2020.vol7.no10.109
9. Astuti, NPW, and Yasa, INM. The effect of human resource quality and budgeting participation on organizational culture and organizational performance. Quant Econ Res. (2018) 1:39–46.
10. Jingyu, L, and Yongqin, Z. Research on optimization strategy of government procurement budget management in public hospitals. Health Econ Res. (2025) 42:53–5. doi: 10.14055/j.cnki.33-1056/f.2025.04.005
11. Yanxin, W, Lin, Y, and Wang, Z. Research on the optimization of comprehensive budget management path in hospitals under data middleware architecture. Health Econ Res. (2025) 42:68-70+75. doi: 10.14055/j.cnki.33-1056/f.2025.04.015
12. Jiapeng, D, Rui, L, and Yanyan, Z. Construction practice of hospital intelligent financial system based on comprehensive budget management. China Hosp Manag. (2024) 44:82–4.
13. Kanya, N. Budget participation and organizational commitment on managerial performance: the moderating role of locus of control. Atestasi J Ilmiah Akuntansi. (2021) 4:365–77. doi: 10.57178/atestasi.v4i2.659
14. Suwarto, FX, Subyantoro, A, and Tulasi, D. An analysis of the effect of budget participation on managerial performance with organizational commitment, motivation and decentralized structure as moderating variables in public sector organizations. Int J Manag Stud Soc Sci Res Conducted. (2022) 4:88–98.
15. Isgiyarta, J, Nugroho, DA, Ratmono, D, Helmina, MRA, and Pamungkas, ID. Budgetary participation on managerial performance: commitment organization, innovation perception, and job relevant information as mediating variable. CAL. (2019) 20:48–53.
16. Hermansson, H. Disaster response in Turkey: Conditions promoting cross-sectoral collaboration and implications for effectiveness. Admin Soc. (2019) 51:1051–78. doi: 10.1177/0095399716680058
17. Irawan, A. Budgeting participation, managerial roles and competence on financial management performance. Atestasi J Ilmiah Akuntansi. (2023) 6:587–601. doi: 10.57178/atestasi.v6i2.718
18. Subramaniam, N, McManus, L, and Mia, L. Enhancing hotel managers’ organisational commitment: an investigation of the impact of structure, need for achievement and participative budgeting. Int J Hosp Manag. (2002) 21:303–20. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4319(02)00010-5
19. Ebhota, OS, Hongxing, Y, and Sampene, AK. Investigating the influence of digital transformation, budgeting and budgetary control on the financial performance of SMEs. Sci African. (2024) 26:e02429. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2024.e02429
20. Gasana Herman, P. Assessment of budgetary influence on organizational performance of nonprofit entities in Rwanda a case study of Rwanda Pentecostal church association. Rwanda: Doctoral dissertation Kampala International University, College of Economics & management (2010).
21. Li, ZB. Participatory budgeting, budget slack and organizational performance. Bus Res. (2009) 11:63–5. doi: 10.13902/j.cnki.syyj.2009.11.027
22. Chong, KV, and Strauss, R. Participative budgeting: the effects of budget emphasis, information asymmetry and procedural justice on slack-additional evidence. Asia Pac Manag Acc J. (2017) 12:181–220.
23. Daumoser, C, Hirsch, B, and Sohn, M. Honesty in budgeting: a review of morality and control aspects in the budgetary slack literature. J Manag Control. (2018) 29:115–59. doi: 10.1007/s00187-018-0267-z
24. Choirunnisa, A. (2020). The moderation effect of power distance orientation and leadership personality on budget participation and relationship of university performance in Indonesia. In 3rd Asia Pacific international conference of management and business science (AICMBS 2019) (pp. 1–8). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Atlantis Press.
25. Huang, MJ, Cheng, KC, Chung, SH, Wang, HM, and Wang, KH. Budget participation capacity configuration (bpcc), budgeting participation requirement and product innovation performance. Sustain For. (2021) 13:5614. doi: 10.3390/su13105614
26. Derbeneva, V, and Starodubets, N. The impact of digitalization on the initiative budgeting processes In:. XV international conference "Russian regions in the focus of changes" (ICRRFC 2020). Ural Federal, Russia: Atlantis Press (2021). 14–20.
27. Dunk, AS, and Nouri, H. Antecedents of budgetary slack: a literature review and synthesis. J Account Lit. (1998) 17:72–96.
28. Shields, JF, and Shields, MD. Antecedents of participative budgeting. Acc Organ Soc. (1998) 23:49–76. doi: 10.1016/S0361-3682(97)00014-7
29. Derfuss, K. The relationship of budgetary participation and reliance on accounting performance measures with individual-level consequent variables: a meta-analysis. Eur Acc Rev. (2009) 18:203–39. doi: 10.1080/09638180802652371
30. Merchant, KA, and Van der Stede, WA. Management control systems: performance measurement, evaluation and incentives. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education (2007).
31. Mia, S, Shleifman, FM, and Tupchii, EP. Ways of improving working conditions in glasswork plants Gigiena Truda i Professional’nye Zabolevaniia. (1964) 8:8–12.
32. Chenhall, RH, and Brownell, P. The effect of participative budgeting on job satisfaction and performance: role ambiguity as an intervening variable. Acc Organ Soc. (1988) 13:225–33. doi: 10.1016/0361-3682(88)90001-3
33. Macinati, MS, Bozzi, S, and Rizzo, MG. Budgetary participation and performance: the mediating effects of medical managers’ job engagement and self-efficacy. Health Policy. (2016) 120:1017–28. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2016.08.005
34. Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: toward a unifying theory of behavioural change. Psychol Rev. (1977) 84:191–215. doi: 10.1016/0146-6402(78)90002-4
35. Bandura, A. A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: a social cognitive theory. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 6–417.
36. Maurer, TJ, Wrenn, KA, Pierce, HR, Tross, SA, and Collins, WC. Beliefs about ‘improvability’ of career-relevant skills: relevance to job/task analysis, competency modelling, and learning orientation. J Organ Behav. (2003) 24:107–31. doi: 10.1002/job.182
37. Wood, RE, and Bandura, A. Mechanisms governing organizational performance in complex decision making environments. New York: Prentice Hall (1990).
38. Wood, RE, and Bandura, A. Social cognitive theory of organizational management. Acad Manag Rev. (1989) 14:361–84. doi: 10.5465/amr.1989.4279067
39. Judge, TA, and Bono, JE. Relationship of core self-evaluations traits-self-esteem, generalized self-efficacy, locus of control, and emotional stability-with job satisfaction and job performance: a meta analysis. J Appl Psychol. (2001) 86:80–92. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.86.1.80
40. Milani, K. The relationship of participation in budget-setting to industrial supervisor performance and attitudes: a field stud. Account Rev. (1975) 50:274–84.
41. Wen, L, and Luo, FL. Psychological and behavioural measurement. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press (2003).
42. Abernethy, MA, Bouwens, J, and Van Lent, L. Leadership and control system design. Manag Account Res. (2010) 21:2–16. doi: 10.1016/j.mar.2009.10.002
43. Abernethy, MA, Bouwens, J, and Van Lent, L. The role of performance measures in the intertemporal decisions of business unit managers. Contemp Account Res. (2013) 30:925–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1911-3846.2012.01178.x
44. Bouwens, J, and Van Lent, L. Assessing the performance of business unit managers. J Account Res. (2007) 45:667–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-679X.2007.00251.x
45. Lindquist, TM. Fairness as an antecedent to participative budgeting: examing the effects of distributive justice, procedural justice and referent cognitions on satisfaction and performance. J Manag Account Res. (1995) 7:122–47.
46. Latour, B. On recalling ANT In: J Law and J Hassard, editors. Actor network and after. Lancaster, UK: Lancaster University Press (1999). 201–14.
47. Lei, J. Analysis and exploration on budget performance Management of Public Hospitals. Chinese Health Econ. (2019) 38:86–8.
48. Xie, H, and Dai, W. The practices of deepening budget management in public hospitals. Chinese Health Econ. (2018) 37:88–90.
49. Yousif Alhasnawi, M, Mohd Said, R, Raad Muhsen, Y, Alnoor, A, Mowafaq Alshdaifat, S, and Mohamed El Shlmani, Z. A systematic literature review of budget participation: foundations, trends, and ways forward. Int Rev Public Adm. (2024) 29:175–202. doi: 10.1080/12294659.2024.2377874
51. Gist, ME, and Mitchell, TR. Self-efficacy: A theoretical analysis of its determinants and malleability. Acad. Manag. Rev. (1992) 17:183–211.
Keywords: budget participation, organizational performance, public hospital, Latour’s Actor-Network Theory, self-efficacy
Citation: Jiang Q, Zhou J, Kuang X and Chen S (2025) Budgetary participation and organizational performance in Chinese public hospitals: facilitation or inhibition? Front. Public Health. 13:1601181. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1601181
Edited by:
Karolina Sobczyk, Medical University of Silesia, PolandReviewed by:
Ali Khudhair, Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, IraqJames Kizza, Kyambogo University, Uganda
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Zhou, Kuang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiwen Jiang, MTAxMDA1MzgyQHNldS5lZHUuY24=
 Qiwen Jiang
Qiwen Jiang Jing Zhou
Jing Zhou Xuemei Kuang
Xuemei Kuang Shuang Chen2
Shuang Chen2