- 1School of Health Care Management, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China
- 2School of Marxism, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China
- 3School of Management, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China
Background: The number of medical disputes in China has been increasing, highlighting the urgent need to improve doctor-patient relationships.
Objective: To improve doctor-patient relationships and enhance communication, a scale for measuring doctor-patient communication quality (DPCQ) was developed.
Methods: Based on existing relevant foreign scales, questionnaire items were designed to collect patients' perceptions of doctor-patient communication quality. Outpatients from a selected hospital were chosen as the study population, and 300 questionnaires were randomly sampled. SPSS 26 was used for preliminary item screening through dispersion trend analysis, t-tests, and Pearson correlation analysis. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) was conducted to assess the reliability of the questionnaire. Structural validity was examined using structural equation modeling (SEM) in R 4.4.3. Convergent and discriminant validity were evaluated using average variance extracted (AVE), composite reliability (CR), and maximum shared variance (MSV).
Results: The EFA identified two factors: Factor 1 (Interactive Communication and Emotional Support) and Factor 2 (Health Education and Behavioral Guidance), with a cumulative variance contribution rate of 63.81%. The results of the CFA indicated an acceptable model fit: χ2/df = 3.57, AGFI = 0.837, RMSEA = 0.093, CFI = 0.945, NFI = 0.926, PGFI = 0.609, and PNFI = 0.733. The final version of the questionnaire demonstrated excellent internal consistency, with a Cronbach's α coefficient of 0.950. In addition, AVE exceeded the threshold of 0.50, CR values were greater than 0.70, and MSV for each factor was lower than its corresponding AVE, supporting both convergent and discriminant validity of the scale.
Conclusion: The scale for measuring doctor-patient communication quality demonstrates good reliability and validity, making it a suitable measurement tool for research on doctor-patient communication.
1 Introduction
In recent years, the tension in doctor-patient relationships has become a widespread modern issue, not only in China but also globally (1, 2). In China, a series of factors, such as market-oriented healthcare reforms (3), have contributed to the frequent occurrence of medical violence and incidents of harm against doctors (4, 5). Patients are increasingly aware of their rights and have higher demands regarding the service attitude, quality, and efficiency of healthcare institutions. The doctor-patient relationship is commonly defined as “a form of communication expressed through interaction between doctors and patients” (6). The quality of the entire medical process, including accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of diseases, largely depends on the quality of the doctor-patient relationship (7). Today, patients have access to a vast amount of medical information through new media, leading them to take favorable treatment outcomes for granted. However, patients often lack a clear understanding of the uncertainties, risks, and individual variability involved in many medical technologies (8). Research has shown that good doctor-patient communication can improve patients' emotions and enhance treatment outcomes (9). Many studies have also emphasized the reciprocity of doctor-patient communication, gradually focusing on patients' perceptions of the communication (10). Therefore, this study conducts a measurement of doctor-patient communication quality from the patient's perspective, aiming to improve doctor-patient communication quality, strengthen the doctor-patient relationship, and promote better medical outcomes.
2 Literature review
The doctor-patient relationship is a matter of global concern. Studies from both domestic and international contexts have shown that doctor-patient trust, communication, quality of medical services, and patient satisfaction are key factors influencing the state of this relationship. Ha and Longnecker (11) conducted a comprehensive analysis of doctor-patient communication, highlighting five critical elements for improvement: the application of communication skills, updates in communication training, bidirectional information exchange between doctors and patients, appropriate management of doctor-patient conflict, and consideration of health-related beliefs and values. Numerous studies have explored how doctor-patient communication functions throughout the diagnostic and therapeutic process. As one of the fundamental driving forces in healthcare delivery, doctor-patient communication affects not only the treatment process but also the patient's adherence to medical advice (12). Street (13) suggested that certain communication strategies could directly or indirectly influence patient health outcomes. Wang et al. (14) found that trust in doctors is indirectly influenced by communication, particularly because patients often lack sufficient psychological preparation due to their relatively low risk perception in medical contexts (15). Therefore, doctor-patient trust may mediate the relationship between communication and patients' perception of medical risk. Other researchers have proposed that expected treatment outcomes and patient-centered care can positively affect communication satisfaction (16). When physicians actively attempt to understand the patient's perspective—including background, beliefs, and opinions—and are able to share that understanding, communication effectiveness is significantly enhanced (17, 18). In summary, doctor-patient communication plays a crucial role in the medical process, shaping patient trust, health perceptions, and therapeutic outcomes.
High-quality doctor-patient communication can significantly improve patient satisfaction and enhance the loyalty of patients and their families toward the hospital, bringing additional social and direct economic benefits to the hospital. Therefore, in recent years, scholars both domestically and internationally have conducted extensive research on how to reflect the quality of doctor-patient communication, accumulating a wealth of research findings. Matusitz and Spear (12) pointed out that doctor-patient communication is a powerful indicator of healthcare service quality and can be used to assess patients' self-management behaviors and health status. Scales measuring doctor-patient communication quality from the patient's perspective include scales for evaluating doctors' communication behaviors, such as the Interpersonal Relationship Process Scale (19, 20), the Empathy Scale for consultations (21), and the Patient Involvement in Decision-Making Evaluation Scale (22). Berkenstadt et al. developed the Personal Control Perception Scale (23), which is administered before and after the consultation. The differences between the two surveys are used to assess the impact of the consultation on the patient's sense of psychological control and the extent of that impact. If a patient actively participates in decision-making during doctor-patient communication, the Decision Conflict Scale (24) can quantify the patient's uncertainty in decision-making and identify the factors that cause uncertainty during the deliberation and subsequent choices, along with the Decision Satisfaction Scale (25). Research on patient satisfaction in China began later than in other countries, with scholars starting to explore this area only in the late 20th century. Representative domestic studies include: Zhang et al. (26), who developed a comprehensive hospital emergency patient satisfaction scale with 26 items across 8 factors, such as treatment outcomes and costs, doctor services, and the medical environment. Yan et al. (27), through follow-up visits to discharged patients, established a satisfaction evaluation system with 25 items across 8 aspects, including service attitude, medical costs, and medical ethics (28). In summary, although multiple tools have been developed to measure doctor-patient communication, several limitations remain. First, many existing scales focus on a single aspect of communication, such as physician empathy or patient involvement in decision-making, and therefore fail to capture the multidimensional nature of doctor-patient communication comprehensively. Second, many instruments are directly adapted from foreign contexts, lacking sufficient cultural and systemic alignment with the Chinese healthcare environment, which compromises their measurement accuracy and interpretability. Third, some scales were developed without adequately incorporating the patient's perspective, overlooking the subjective experiences of patients during the communication process.
Based on the above, this study aims to develop a doctor-patient communication quality scale suitable for the Chinese context, in order to address the limitations of existing tools. The DPCQ is designed to reflect patients' subjective experiences while ensuring high content validity and structural validity, thus providing a foundational instrument for future research and interventions in the field of doctor-patient communication quality.
3 Research methods
3.1 Item design
The purposes of a patient's visit can be summarized as: understanding health status, receiving information about diseases and related health education, making the best decisions, and gaining the doctor's support and assistance in coping with the disease. The communication outcomes include: alleviating psychological stress, increasing communication satisfaction, reducing the uncertainty of treatment plans, improving quality of life, and enhancing a sense of personal control. Achieving these visit purposes not only represents the outcome quality of doctor-patient communication but also indirectly reflects the quality of the communication process, as well as the communication behaviors of both parties, especially the doctor's communication behavior. The selection of items followed several criteria. First, priority was given to items directly related to the quality of doctor-patient communication, ensuring the inclusion of aspects such as information exchange, emotional support, and communication skills. Second, items were referenced from scales with established reliability and validity in both domestic and international studies, to guarantee scientific rigor and reliability. Additionally, cultural adaptability was fully considered to ensure that the content could be accurately understood and accepted by Chinese patient populations.
Based on this logic, relevant foreign scales were integrated and their content was refined and translated, resulting in a draft of a 30-item questionnaire. This includes the following scales:
The Interpersonal Process of Care Scale (IPC) (19, 20) is designed to assess the quality of interpersonal care across different patient groups. It presents and validates a conceptual framework for distinguishing specific components of the interpersonal process from the patient's perspective, aiming to identify specific aspects of the interpersonal relationship that may serve as targets for quality assessment and improvement. The Consultation and Relational Empathy Scale (CARE) (21) is generally used as a tool to measure patients' perceptions of relational empathy during medical consultations. The Observing Patient Involvement in Decision Making Scale (OPTIONG) (22) measures the behaviors of doctors in creating opportunities for patient involvement in decision-making during doctor-patient communication. It evaluates the extent to which clinicians involve patients in decisions under various circumstances (excluding emergencies or other adverse situations). The Personal Perceived Control Scale (PPC) (23) is used to assess the impact of the consultation on the patient's sense of psychological control and the degree of that impact. The Satisfaction with Decision Scale (SWD) (25) evaluates patients' satisfaction with the decision-making process in doctor-patient communication.
After conducting a pilot study with 150 patients, we performed preliminary item analysis and exploratory factor analysis (EFA) to assess the quality of the items. Based on the results, some items with inadequate performance were removed (see Table 1). Table 1 presents the survey items and their sources used in the pilot study, clearly indicating which items were retained (marked as T1–T16) and which were excluded. Following this screening process, a preliminary doctor-patient communication quality measurement scale consisting of 16 items was developed. Using a five-point Likert scale with positive wording, each item has five options: “Strongly Disagree,” “Disagree,” “Neutral,” “Agree,” and “Strongly Agree.” A score of 1–5 is assigned to each item, with higher scores indicating better doctor-patient communication quality.
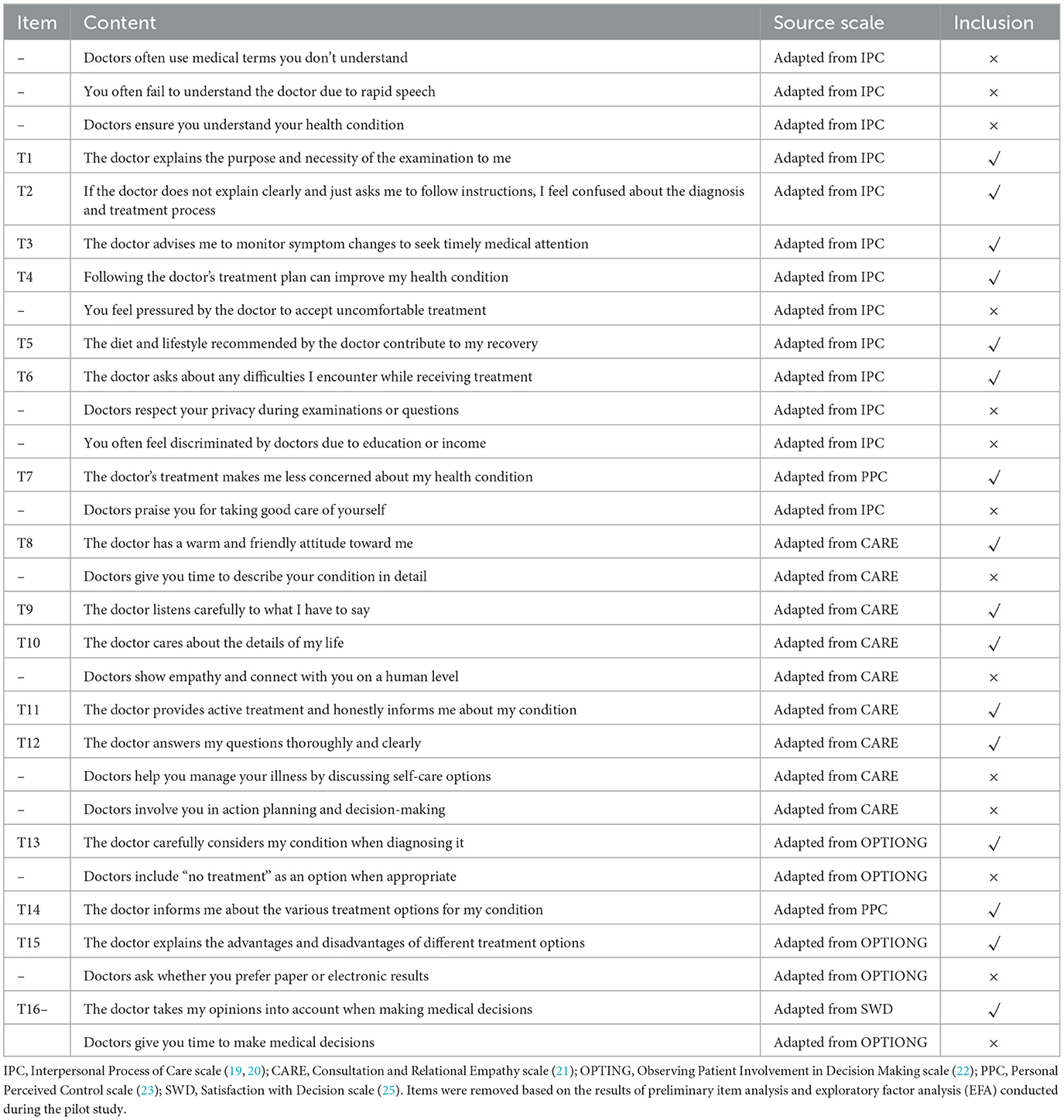
Table 1. Survey items tested in the pilot study and their selection status for the final instrument.
3.2 Data collection
In this study, a random sampling method was employed to distribute questionnaires to adult outpatients aged 18 years and above in the outpatient departments of three hospitals in Anhui Province. The inclusion criteria were outpatients with basic reading ability who provided informed consent and were willing to complete the questionnaire voluntarily. Patients with mental disorders or those with hearing or speech impairments were excluded. Participants were allowed to ask questions if they had any concerns, and the questionnaire took approximately five minutes to complete (29, 30). A database was established using EpiData 3.1 software to input and clean the data. A total of 150 valid questionnaires were collected for the pilot study. According to the requirement for an appropriate sample size, with 10–20 samples per item (31), 300 valid data sets were collected in the formal data collection phase.
3.3 Analysis tools
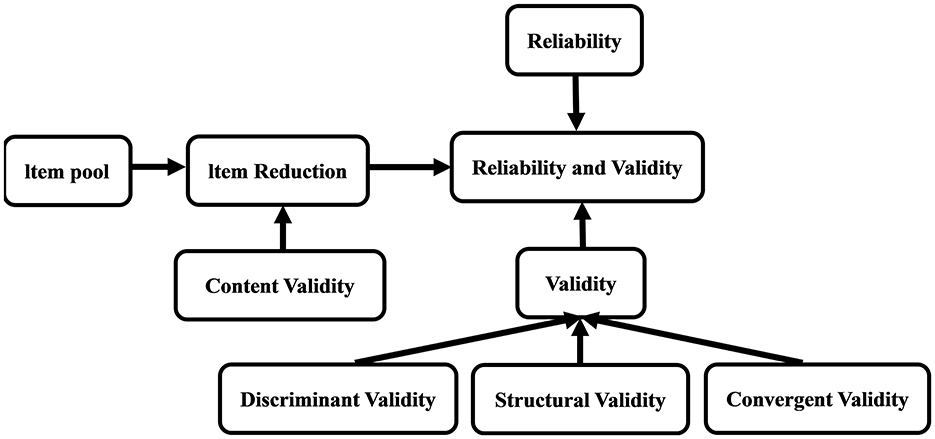
The data analysis for this study was conducted using SPSS 26 and R 4.4.3 software. SPSS 26 was used to assess the distribution characteristics of the data, inter-group differences, relationships between variables, scale reliability, and latent structures. R software was used to construct structural models to examine the structural validity of the DPCQ. Discriminant validity and convergent validity were evaluated using AVE, CR, and MSV to verify whether the DPCQ accurately measures predefined concepts and distinguishes different concepts. Through these analysis methods, the reliability and validity of the DPCQ were verified to ensure the reliability of the results. The specific research roadmap (32) is shown in Figure 1.
4 Results
4.1 Demographic characteristics
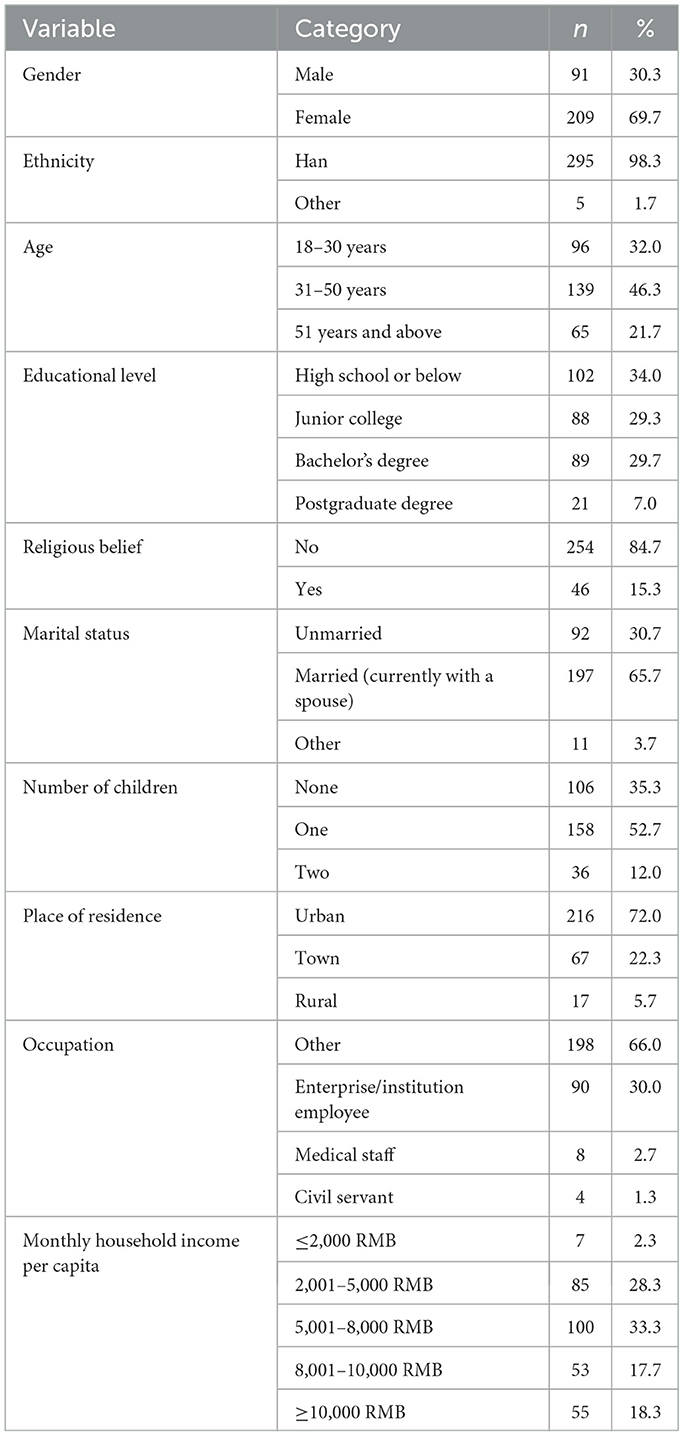
A total of 327 questionnaires were collected, among which 300 were valid, yielding a response rate of 91.7%. Among the respondents, 91 were male and 209 were female, with a mean age of 39.89 years (SD = 13.72). Other demographic characteristics are presented in Table 2.
4.2 Discrete trend analysis
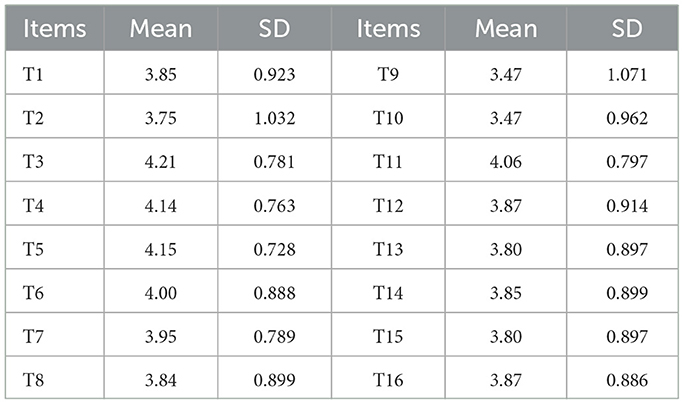
The standard deviation was used to reflect the dispersion trend of each item. Generally, when the standard deviation is less than 0.8, the discrimination is considered poor (33). Considering that discrete trend analysis is only the first step in item quality screening and that multiple subsequent rounds of quality assessments will be conducted, we appropriately lowered the screening threshold to 0.7 in this round to reduce the risk of mistakenly excluding items due to overly strict criteria at the preliminary stage. According to the subsequent analysis, the results in Table 3 generally meet the requirements, and no items were deleted.
4.3 T-test
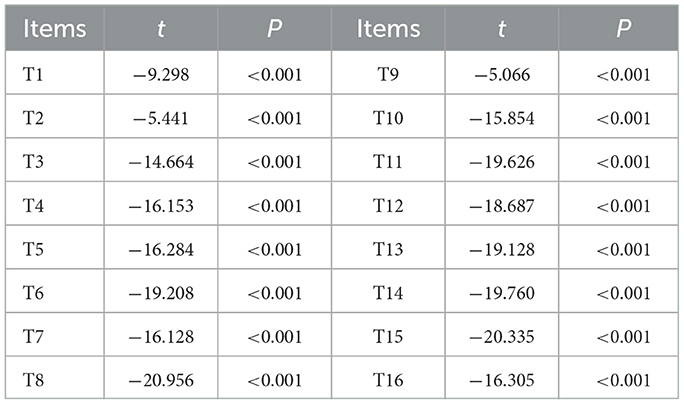
The total scores of doctor-patient communication quality were ranked from high to low. The top 27% of scores were classified as the high-score group, and the bottom 27% as the low-score group. In this study, the 81 participants with scores ≥68.73 were categorized as the high-score group, and the 81 participants with scores ≤ 57 were classified as the low-score group. The average score for each item in both groups was calculated, and a difference test was conducted between the means of the two groups. Items with a critical ratio (CR) <3.0 or no statistically significant difference (p > 0.05) were removed (34). According to the CR value of 9.643 and p < 0.05, no items were deleted. Details are shown in Table 4.
4.4 Pearson correlation coefficient method
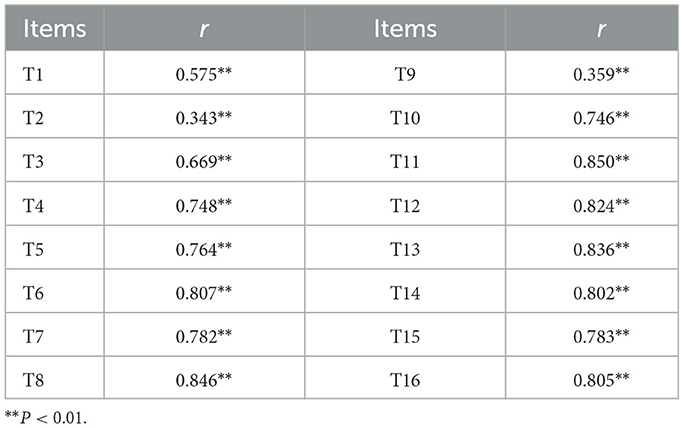
Pearson correlation analysis was used to examine the relationship between each item and the total score of the initial questionnaire. Items with r < 0.4 were removed (35). According to the results in Table 5, items 2 and 9 were deleted.
4.5 Cronbach's α coefficient method
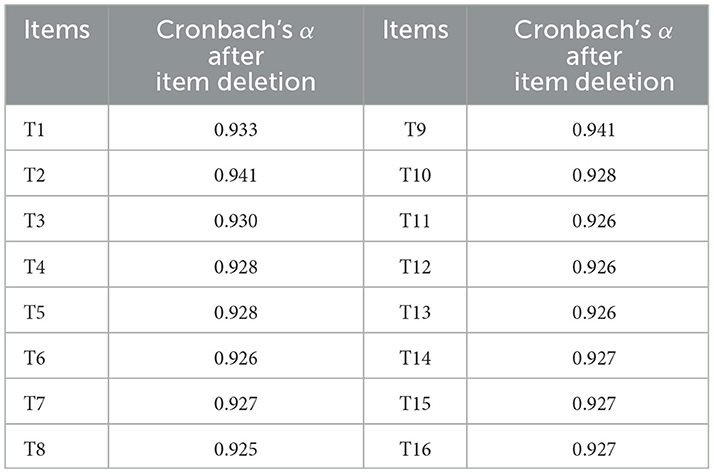
Cronbach's α coefficient was used to measure the degree of association among items, reflecting internal consistency. Generally, the Cronbach's α coefficient is positively correlated with the number of items in a questionnaire. If removing an item increases the overall Cronbach's α coefficient, it indicates that the item is not consistent with the intended content of the scale and should be deleted (36). As shown in Table 6, the Cronbach's α coefficient for the 16-item scale was 0.934. Therefore, items 2 and 9 were removed.
4.6 Exploratory factor analysis (EFA)
A Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) test and Bartlett's test of sphericity were conducted on the 16 items. The KMO value was 0.952, and Bartlett's test yielded a chi-square value that reached statistical significance (p < 0.001), indicating that the data were suitable for EFA. In this study, principal component analysis (PCA) was employed for item selection and extraction, using the orthogonal rotation method (Varimax). Factors with eigenvalues greater than 1 were extracted, and the retention or removal of items was determined based on the highest factor loading and professional judgment. The criteria for item retention and deletion were as follows (32):
1. Items with a maximum factor loading <0.4 were removed.
2. Items that loaded onto two or more factors, with a difference of <0.2 between the highest and second-highest factor loadings, were removed.
3. If a common factor contained fewer than three items, the factor and its corresponding items were removed.
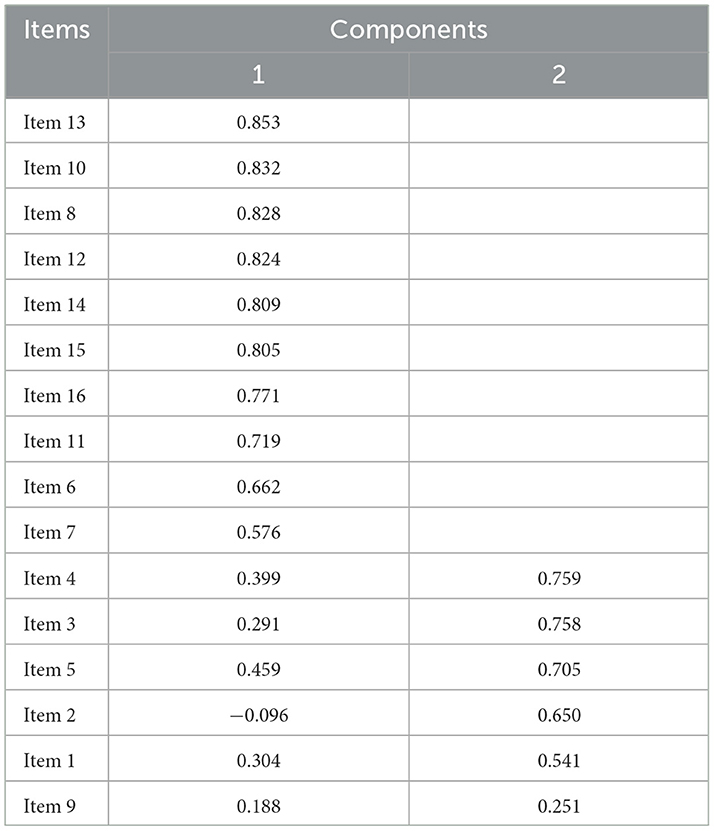
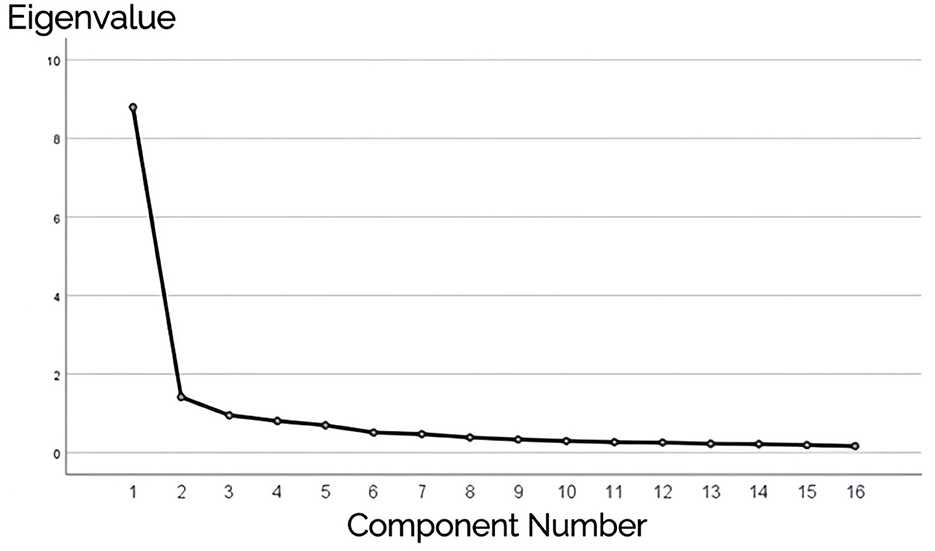
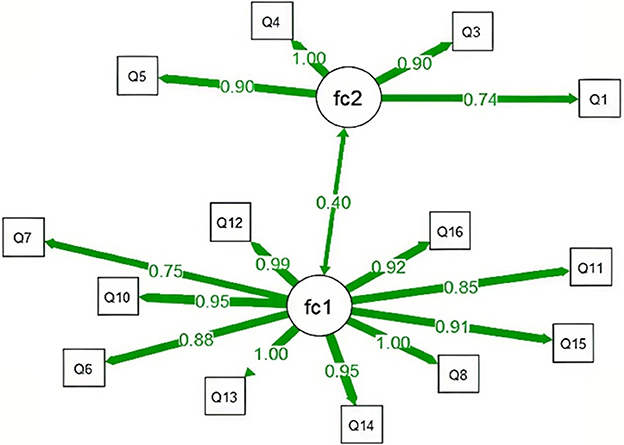
Further data analysis generated the rotated component matrix, identifying two common factors with eigenvalues >1 (Table 7 and Figure 2). The cumulative variance contribution rate was 63.810%, exceeding 60%. Based on these findings, Item 9 was removed.
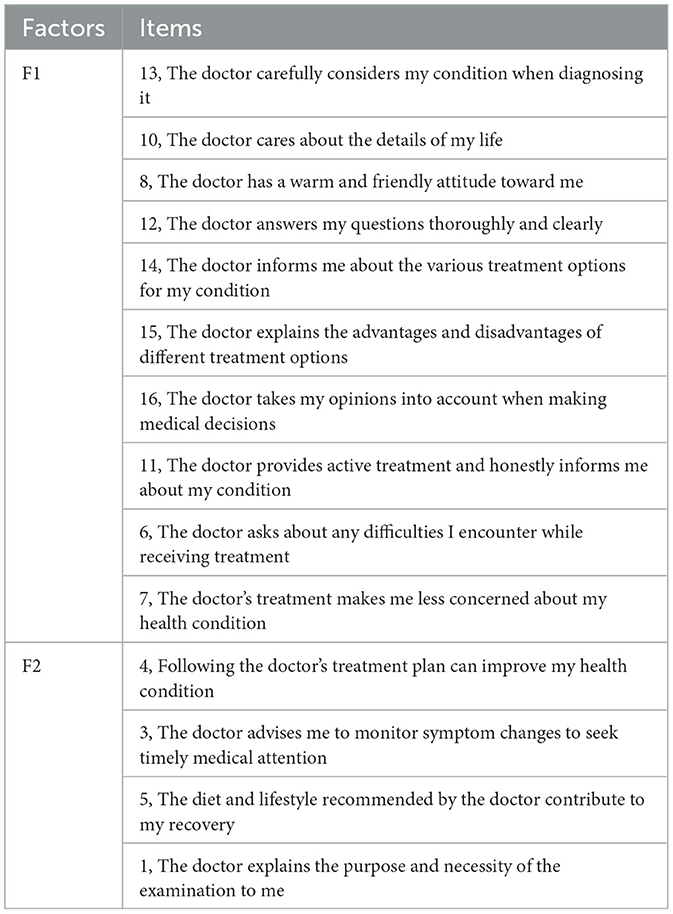
As can be seen in Figure 2, the eigenvalue of the first factor is significantly higher than those of the other factors, and the decline in eigenvalues after the second factor becomes very gradual. This suggests that the data structure is likely a two-factor model. Based on the above analysis, Item 2 and Item 9 were excluded, and the 14 items were divided into two factors: F1 (Doctor's Interactive Communication and Emotional Support) and F2 (Doctor's Health Education and Behavioral Guidance). F1 includes Items 13, 10, 8, 12, 14, 15, 16, 11, 6, and 7; F2 includes Items 4, 3, 5, and 1.
4.7 Construct validity
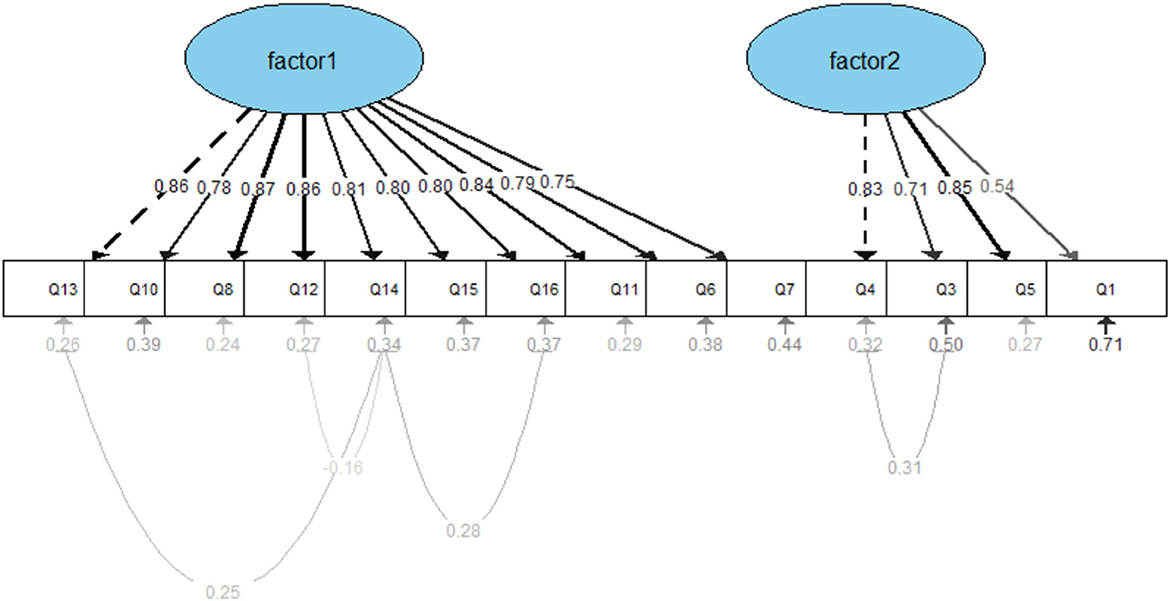
The SEM analysis assumes two latent factors, factor 1 and factor 2, with each factor composed of several measurement items (scale items), and there may be correlations between these two factors. Using the lavaan package, the relationships between latent variables and their observed indicators were specified. The initial results of the confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) showed: χ2/df = 4.274, AGFI = 0.809, GFI = 0.861, SRMR = 0.056, RMSEA = 0.104, TLI = 0.912, CFI = 0.927, IFI = 0.927, NFI = 0.907, PGFI = 0.624, and PNFI = 0.757. As the RMSEA exceeded 0.10, the model did not meet the ideal fit criteria (see Figure 3).
Therefore, based on the Modification Indices (MIs) and supported by theoretical justification, several covariance paths were added between measurement error terms. These modifications primarily involved correlating the residuals of items with similar content or expressions, such as Q4 and Q3, Q14 and Q16, among others. The modified model yielded improved fit indices: Absolute fit indices: χ2/df = 3.57, AGFI = 0.837, GFI = 0.888, SRMR = 0.049, RMSEA = 0.093; Incremental fit indices: TLI = 0.931, CFI = 0.945, IFI = 0.946, NFI = 0.926; Parsimony fit indices: PGFI = 0.609, PNFI = 0.733. All indices met the acceptable thresholds for model fit, indicating that the structural model of the questionnaire demonstrated a good overall fit (Figure 4).
4.8 Discriminant validity and convergent validity
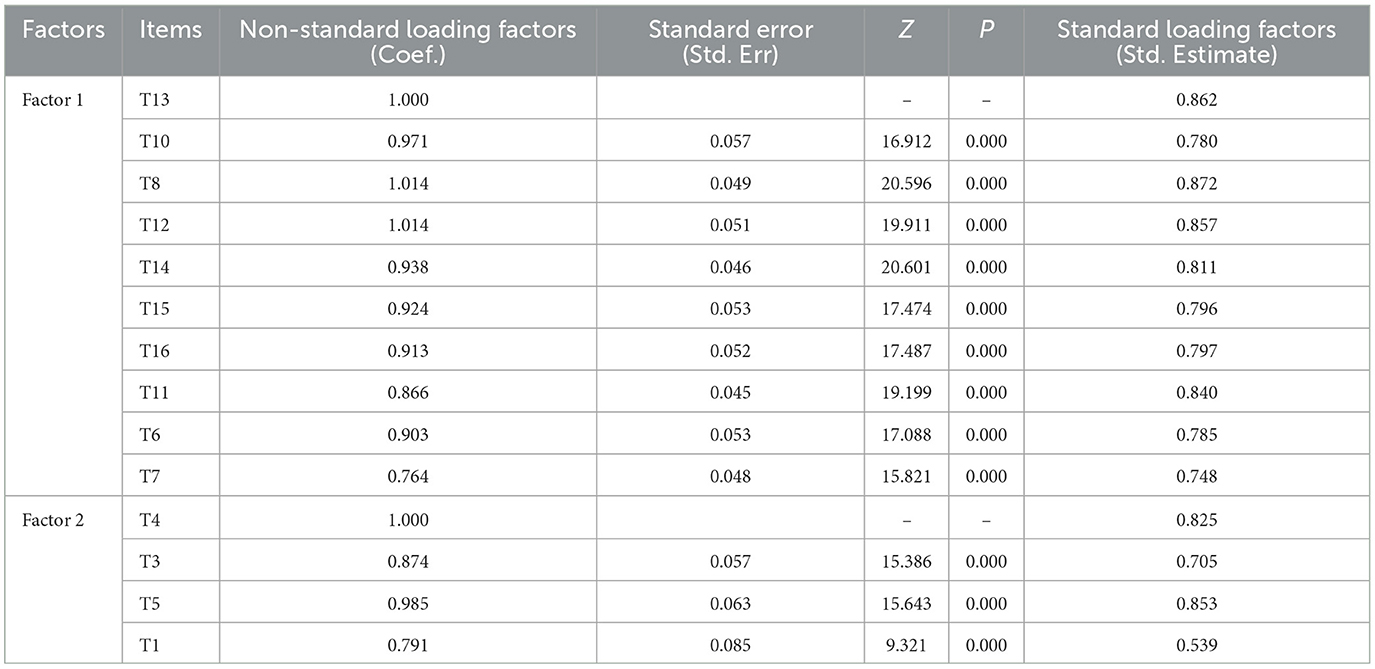
The standard factor loadings of each item were obtained through the CFA (Table 8), with the standard factor loadings being greater than or close to 0.6, indicating a reasonable relationship between each item and its respective factor.
To further analyze the convergent and discriminant validity of the questionnaire, the standardized coefficients were used to calculate MSV, which was found to be 0.661. AVE for Factor 1 and Factor 2 were 0.872 and 0.840, respectively. CR for Factor 1 was 0.949, and for Factor 2, it was 0.791. Since AVE is greater than 0.5 and CR exceeds 0.7, the questionnaire demonstrates good convergent validity. Additionally, as MSV is smaller than the corresponding AVE, this further indicates that the questionnaire exhibits good discriminant validity.
5 Discussion
The results of the dispersion trend analysis and t-test indicated that the initial items of the questionnaire were reasonable. Pearson correlation analysis further demonstrated that all 16 items were significantly correlated with the total score, indicating good item-total consistency. This method provides higher item precision and contributes to the optimization of the questionnaire item pool. The results of the EFA showed that Item 2 and Item 9 did not meet the requirements for the factor structure of the DPCQ, thus optimizing the initial scale from a statistical perspective and improving its quality. The overall Cronbach's α coefficient of the DPCQ was 0.950, which is >0.8. The Cronbach's α coefficients for the two factors were 0.95 and 0.82, both greater than 0.7. This indicates that the DPCQ has good reliability, and the internal consistency of each factor is acceptable (37), reflecting the rigor and scientific nature of the research process.
In the CFA, all fit indices of the modified model performed well, indicating that the model has high effectiveness in terms of fit and explanatory power. Both the Absolute Fit Indices and Incremental Fit Indices met the research requirements, suggesting that the model fits the data accurately. Additionally, the values of the Parsimony Fit Indices support the simplicity of the model, demonstrating a good balance between complexity and explanatory power. Further analysis of convergent and discriminant validity revealed that the AVE and CR values for Factor 1 and Factor 2 met the standards, indicating good convergent validity. The MSV value, calculated from the standardized coefficients, shows the associations between the factors, confirming good discriminant validity. In summary, the model excels in terms of fit, convergent validity, and discriminant validity, indicating that the measurement tool in this study has good reliability and validity and demonstrates strong adaptability within the theoretical framework (38). Due to research resource limitations, the same dataset was used for both EFA and CFA. Although best practices recommend conducting EFA and CFA on different samples to avoid result dependence, considering the moderate sample size in this study (N = 300) and the fact that only minor adjustments were made to a few items after EFA, the results of the CFA still hold certain reference value. In future research, further exploration of potential improvements to the model can be conducted, such as optimizing measurement variables, expanding the sample size, or adjusting model paths to enhance the fit. Additionally, the stability and applicability of the model should be validated, particularly in terms of its performance across different samples and contexts.
The dimensions and item contents of the questionnaire used in this study are presented below (Table 9).
F1 includes items primarily related to the doctor's communication effectiveness, information provision, decision-making involvement, and emotional support during the diagnosis and treatment process, reflecting the patient's perception of medical information transparency and humanistic care. Items 12, 14, and 15 directly reflect the doctor's communication effectiveness; items 8 and 10 reflect the emotional value provided by the doctor; items 16 and 6 indirectly reflect whether the doctor has decision-making consensus; and items 7, 13, and 11 reflect the doctor's treatment attitude. This dimension aligns with the “Patient-Centered Communication” (PCC) theory (39), which emphasizes that doctors should not only provide medical knowledge but also establish a strong trust relationship and interactive experience with patients during the medical process. F2 items focus more on the doctor's guidance of the patient's health behaviors and the promotion of medical adherence, specifically how the doctor encourages the patient to actively cooperate with treatment, monitor health changes, and practice health management. This dimension is related to the “Health Belief Model” (HBM) (40, 41), which posits that a patient's health behavior adherence is influenced by factors such as the perceived severity of the disease, health beliefs, and the doctor's advice. Studies have shown that doctors with better communication skills are more likely to inquire about patients' concerns, encourage exercise, and help set goals (42). These two dimensions jointly form a tripartite model of doctor-patient communication quality—emotional, cognitive, and behavioral—addressing the limitations of existing scales that tend to focus on a single aspect of communication behavior or attitude. The DPCQ developed in this study integrates concepts from PCC and HBM, balancing emotional support, information exchange, and behavioral guidance. It is designed to comprehensively assess the multidimensional communication experiences of patients within the context of the Chinese healthcare system.
In China, as healthcare reform continues to advance and public health awareness increases, patients are placing growing importance on the quality of doctor-patient communication. However, high-quality communication remains difficult to achieve in practice due to longstanding issues such as information asymmetry between doctors and patients, short consultation times, limited medical personnel, and the frequent occurrence of doctor-patient conflicts. Respect, empathy, and effective communication are the core elements of patient-centered care (43). Items 8 and 13 reflect patients' dual expectations of both professional competence and humanistic attitudes from physicians, indicating their need for both technical and emotional reassurance in an increasingly complex healthcare system. Items 12, 14, 15, and 16 address themes such as information transparency and shared decision-making, highlighting patients' urgent demand for informed consent and collaborative decision-making when facing multiple treatment options. These findings suggest that patients are no longer content with being passive recipients of care but prefer to engage in interactive relationships with their doctors. Furthermore, Items 4, 5, 6, and 7 reflect physicians' roles in guiding and promoting patients' long-term health behaviors, which align with China's current national policies on chronic disease management and the “Healthy China 2030” strategy (44, 45). As socioeconomic development leads to a transformation in public health perceptions, physicians play an increasingly vital role in maintaining patients' health and improving their health literacy (8). By incorporating dimensions such as “lifestyle guidance” and “symptom monitoring reminders,” the DPCQ emphasizes the value of doctor-patient communication from a health promotion perspective.
6 Conclusion
Through the study, a DPCQ (Doctor-Patient Communication Quality) measurement tool was developed, consisting of 14 items across two factors. The overall model's reliability, validity, and discriminant validity results suggest that the measurement model has good explanatory power and adaptability, although some items still need optimization. A higher total score on the DPCQ indicates better doctor-patient communication quality, which could lead to improved doctor-patient relationships and better medical outcomes. The application of the DPCQ can quantify the doctor-patient communication quality from the patient's perspective, providing data support and technical assistance for medical institutions to improve patient satisfaction, enhance doctor-patient relationships, and promote the development of the healthcare industry.
However, the generalizability of the DPCQ is limited. For example, there are significant differences in the social culture and healthcare systems across countries, and this DPCQ may only be applicable in the context of China.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (No.83230353). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants and participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
JSh: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Data curation, Methodology, Visualization, Validation, Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. MW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Software, Formal analysis, Validation, Methodology. YZ: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Visualization, Validation, Methodology. JSu: Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Resources, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72374005), the Natural Science Foundation for the Higher Education Institutions of Anhui Province of China (No. 2023AH050561), and Cultivation Programme for Young and Middle-aged Excellent Teachers in Anhui Province (No. YQZD2023021).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all of the patients who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1606403/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Data Sheet 1 | Doctor-Patient Communication Quality Questionnaire.
Supplementary Data Sheet 2 | Doctor-Patient Communication Quality Scale.
Supplementary Data Sheet 3 | Chinese Version of the Doctor-Patient Communication Quality Scale.
References
1. Freckelton IR. Internet disruptions in the doctor-patient relationship. Med Law Rev. (2020) 28:502–25. doi: 10.1093/medlaw/fwaa008
2. Li H, Zhang C, Li L, Liu T, Zhang L, Hao J, et al. Bibliometric and visualization analysis of risk management in the doctor-patient relationship: a systematic quantitative literature review. Medicine. (2024) 103:e37807. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037807
3. Tao S, Liu C, Wu Q, Zhao J, Xue Y, Song W, et al. Developing a scale measuring the doctor-patient relationship in China from the perspective of doctors. Fam Pract. (2022) 39:527–36. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmab142
4. He AJ, Qian J. Explaining medical disputes in Chinese public hospitals: the doctor-patient relationship and its implications for health policy reforms. Health Econ Policy Law. (2016) 11:359–78. doi: 10.1017/S1744133116000128
5. Sun JJ, Jiang XL, Hu WW, Zheng ZB, Liu J, Zhang LP, et al. Research on management of doctor-patient risk and status of the perceived behaviors of physician trust in the patient in China: new perspective of management of doctor-patient risk. In: Mathematical Problems in Engineering. Vol. 2020. London: Hindawi (2020). p. 1–8. doi: 10.1155/2020/2145029
6. Namazi H, Aramesh K, Larijani B. The doctor-patient relationship: toward a conceptual re-examination. J Med Ethics Hist Med. (2016) 9:10.
7. Hellin T. The physician-patient relationship: recent developments and changes. Haemophilia. (2002) 8:450–4. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2516.2002.00636.x
8. Liu C, Wang D, Liu C, Jiang J, Wang X, Chen H, et al. What is the meaning of health literacy? A systematic review and qualitative synthesis. Fam Med Community Health. (2020) 8:e000351. doi: 10.1136/fmch-2020-000351
9. Riedl D, Schüssler G. The influence of doctor-patient communication on health outcomes: a systematic review. Z Psychosom Med Psychother. (2017) 63:131–50. doi: 10.13109/zptm.2017.63.2.131
10. Verlinde E, De Laender N, De Maesschalck S, Deveugele M, Willems S. The social gradient in doctor-patient communication. Int J Equity Health. (2012) 11:12. doi: 10.1186/1475-9276-11-12
11. Ha JF, Longnecker N. Doctor-patient communication: a review. J Am Board Fam Med. (2022) 35:38–43.
12. Matusitz J, Spear J. Effective doctor-patient communication: an updated examination. Soc Work Public Health. (2014) 29:252–66. doi: 10.1080/19371918.2013.776416
13. Street RL Jr, Makoul G, Arora NK, Epstein RM. How does communication heal? Pathways linking clinician-patient communication to health outcomes. Patient Educ Couns. (2009) 74:295–301. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2008.11.015
14. Wang Y, Wu Q, Wang YJ, Wang P. The formation mechanism of trust in patient from healthcare professional's perspective: a conditional process model. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. (2022) 29:760–72. doi: 10.1007/s10880-021-09834-9
15. Wei D, Xu AQ, Wu X. The mediating effect of trust on the relationship between doctor-patient communication and patients' risk perception during treatment. Psych J. (2020) 9:383–91. doi: 10.1002/pchj.327
16. Paul-Bruno R. Doctor-Patient Communication: The Experiences of Black Caribbean Women Patients with Diabetes. Davie, FL: Nova Southeastern University (2020).
17. van Dalen J. Communication skills in context: trends and perspectives. Patient Educ Couns. (2013) 92:292–5. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2013.05.020
18. Van Dalen J, Bartholomeus P, Kerkhofs E, Lulofs R, Van Thiel J, Rethans JJ, et al. Teaching and assessing communication skills in Maastricht: the first twenty years. Med Teach. (2001) 23:245–51. doi: 10.1080/01421590120042991
19. Beach MC, Saha S, Korthuis PT, Sharp V, Cohn J, Wilson IB, et al. Patient-provider communication differs for black compared to white Hiv-infected patients. AIDS Behav. (2011) 15:805–11. doi: 10.1007/s10461-009-9664-5
20. Stewart AL, Napoles-Springer A, Perez-Stable EJ. Interpersonal processes of care in diverse populations. Milbank Q. (1999) 77:305–39, 274. doi: 10.1111/1468-0009.00138
21. Mercer SW, Maxwell M, Heaney D, Watt GCM. The consultation and relational empathy (care) measure: development and preliminary validation and reliability of an empathy-based consultation process measure. Fam Pract. (2004) 21:699–705. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmh621
22. Elwyn G, Edwards A, Wensing M, Hood K, Atwell C, Grol R. Shared decision making: developing the option scale for measuring patient involvement. Qual Saf Health Care. (2003) 12:93–9. doi: 10.1136/qhc.12.2.93
23. Berkenstadt M, Shiloh S, Barkai G, Katznelson MB, Goldman B. Perceived personal control (Ppc): a new concept in measuring outcome of genetic counseling. Am J Med Genet. (1999) 82:53–9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19990101)82:1<53::aid-ajmg11>3.0.co;2-#
24. O'Connor AM. Validation of a decisional conflict scale. Med Decis Making. (1995) 15:25–30. doi: 10.1177/0272989X9501500105
25. Holmes-Rovner M, Kroll J, Schmitt N, Rovner DR, Breer ML, Rothert ML, et al. Patient satisfaction with health care decisions: the satisfaction with decision scale. Med Decis Making. (1996) 16:58–64. doi: 10.1177/0272989X9601600114
26. Zhang, C, Yang, JM, Sang, XF, Zhang, LJ, Yang, HQ, Cai, ZY, et al. Discussion on the development of the satisfaction questionnaire for emergency patients in general hospitals. Chin J Hosp Admin. (2005):403–5.
27. Yan HP, Su XQ, Yan X, Teng YJ, Tao H. Development of hospital discharged patients'satisfaction assessment tool. Chin Hosp Manag. (2011) 31:72–3.
28. Qian Y Wang XH Zheng GG Wang H Fang WF and Feng W. Thinking of progress, problem and govenance of researches on doctor-patient satisfaction evaluation. Chin Hosp Manag. (2017) 37:11–3+7.
29. Sun J, Sun R, Jiang Y, Chen X, Li Z, Ma Z, et al. The relationship between psychological health and social support: evidence from physicians in China. Plos ONE. (2020) 15:e0228152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228152
30. Zhang L, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Sun J. Factors influencing parents' educational anxiety of primary and secondary school students: evidence from parents in China. BMC Public Health. (2025) 25:65. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-21197-y
31. Sun J, Zhang L, Sun R, Jiang Y, Chen X, He C, et al. Exploring the influence of resiliency on physician trust in patients: an empirical study of Chinese incidents. Plos ONE. (2018) 13:e0207394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207394
32. Sun J, Liu T, Gao Y, Li H, Chen Y, Diao H, et al. Questionnaire development on measuring parents' anxiety about their children's education: empirical evidence of parental perceived anxiety data for primary and secondary school students in China. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:1018313. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1018313
33. Sun J, Jiang X, Gao Y, He C, Wang M, Wang X, et al. Subhealth risk perception scale: development and validation of a new measure. Comput Math Methods Med. (2022) 2022:9950890. doi: 10.1155/2022/9950890
34. Tang Q, Zhang D, Chen J, Liu M, Xiang Y, Luo T, et al. Tests on a scale for measuring the core competencies of paediatric specialist nurses: an exploratory quantitative study. Nurs Open. (2023) 10:5098–107. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1745
35. Kim JS, Ko IS, Koh SJ. The development of a tool for assessment of spiritual distress in cancer patients. J Korean Acad Nurs. (2022) 52:52–65. doi: 10.4040/jkan.21120
36. Thom DH, Wong ST, Guzman D, Wu A, Penko J, Miaskowski C, et al. Physician trust in the patient: development and validation of a new measure. Ann Fam Med. (2011) 9:148–54. doi: 10.1370/afm.1224
37. Fletcher A, Gore S, Jones D, Fitzpatrick R, Spiegelhalter D, Cox D. Quality of life measures in health care. II: design, analysis, and interpretation. BMJ. (1992) 305:1145–8. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6862.1145
38. Fornell C, Larcker DF. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J Mark Res. (1981) 18:39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104
39. Epstein RM, Street RL Jr. Patient-Centered Communication in Cancer Care: Promoting Healing and Reducing Suffering. Publication 07-6225 ed. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute/National Institutes of Health (2007). doi: 10.1037/e481972008-001
40. Champion VL, Skinner CS. The health belief model. In:Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory Research and Practice. 4th, ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass (2008). p. 45–65.
41. Rosenstock IM. Why people use health services. Milbank Mem Fund Q. (1966) 44:94–127. doi: 10.2307/3348967
42. Cabana MD, Slish KK, Evans D, Mellins RB, Brown RW, Lin X, et al. Impact of physician asthma care education on patient outcomes. Pediatrics. (2006) 117:2149–57. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-1055
43. Buetow S, Fuehrer A, Macfarlane K, McConnell D, Moir F, Huggard P, et al. Development and validation of a patient measure of doctor-patient caring. Patient Educ Couns. (2012) 86:264–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2011.04.007
44. Fang EF, Xie C, Schenkel JA, Wu C, Long Q, Cui H, et al. A research agenda for ageing in China in the 21st century (2nd edition): focusing on basic and translational research, long-term care, policy and social networks. Ageing Res Rev. (2020) 64:101174. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101174
Keywords: doctor-patient communication, doctor-patient relationship, communication quality, measurement, scale
Citation: Shao J, Wen M, Zhang Y, Zhang L and Sun J (2025) Development of a measurement of doctor-patient communication quality scale. Front. Public Health 13:1606403. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1606403
Received: 08 April 2025; Accepted: 23 July 2025;
Published: 11 August 2025.
Edited by:
Yan Xiao, University of Texas at Arlington, United StatesReviewed by:
Xianqing Song, Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, ChinaFangmei Tang, Sichuan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Shao, Wen, Zhang, Zhang and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiangjie Sun, c3VuamlhbmdqaWVAYWhtdS5lZHUuY24=; Liping Zhang, emhhbmdsaXBpbmdAYWhtdS5lZHUuY24=
†ORCID: Liping Zhang orcid.org/0000-0002-3242-0822
Jiangjie Sun orcid.org/0000-0002-8185-0802
 Jiayi Shao1
Jiayi Shao1 Jiangjie Sun
Jiangjie Sun