- Department of Gastroenterology, Jiangyou People’s Hospital, Jiangyou, China
Background: Current approaches relying solely on work hours or sleep hours often fall short in comprehensively assessing health risks. To address this gap, this study introduces a novel metric: the Work-to-Sleep hours Ratio (WSR). The study aims to investigate the relationship between WSR and obesity.
Objective: To investigate the correlation between WSR and obesity.
Methods: We employing data from 7,847 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2017–2023. Data collected from all participants included demographic variables, health-related metrics and the presence of various health conditions. Logistic regression analysis, Restricted Cubic Spline (RCS) analysis, and interaction effects were employed to support the research objectives.
Results: In the final model of multivariate analysis showed positive relationship between WSR and obesity (OR = 1.54, 95% CI:1.33–1.77, p < 0.001). Additionally, multivariate smooth splines analysis indicated that WSR exhibited a significant inverted L-shaped nonlinear relationship with obesity (P for nonlinearity < 0.05).
Conclusion: The study observed a positive correlation between WSR and obesity, highlighting the importance of considering both work and sleep hours in assessing public health risks.
Introduction
Obesity has become a severe global health issue. As World Health Organization (WHO) criteria, individuals with body mass index (BMI) ≥ 30 kg/m2 are considered obesity (1). WHO data shows that the global obesity population reached 890 million in 2022 (1) with this number projected to grow to 1.12 billion by 2030 (2). By 2030, almost half of American adults will grapple with obesity. Nationwide, no state will have an obesity prevalence rate lower than 35% and the rate will exceed 50% in 29 states (3). Severe obesity will afflict nearly one - fourth of women, non - Hispanic Black adults, and low-income adults (3). Obesity is a high-risk factor for numerous diseases (4, 5). In terms of the cardiovascular system (5–8), a large number of studies have confirmed that obesity can significantly increase the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), myocardial infarction, and cerebral infarction. Obesity enhances insulin resistance (7, 9) and increases the likelihood of diabetes (6). In addition, obesity lead to obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (10), which affects the quality of sleep and causes damage to vital organs (10) such as the heart, brain, and kidneys. Moreover, obesity is closely related to the occurrence and development of diseases such as cancer (9) and osteoarthritis (11).
Factors contributing to obesity can be categorized into sociodemographic, behavioral, genetic, and living in obesogenic environment (12, 13). Researches hold that prolonged work hours (14–16) and short sleep duration (17–19) have become important factors contributing to obesity. Currently, the predominant work schedule is five workdays a week, with 8 h of work per workday. However, extended work hours are becoming increasingly common in many parts of the world. According to the information released by the International Labour Organization (ILO) (20), prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the average number of weekly work hours for paid employment globally was approximately 43.9 h. Notably, around one-third (35.4%) of the workforce worked more than 48 h per week (20). In Japan (21) approximately 25% of Japanese companies reported that their employees, on average, worked overtime for more than 80 h per month, and a significant amount of this overtime work was not recorded (22). In South Korea, the standard work hours per week are 52 h (20). Long work hours badly invade employees’ personal lives, restricting daily activities and disrupting sleep patterns.
Existing studies have examined the relationship between work hours (15, 23) or sleep hours (19, 24) and obesity. However, there is still a shortage of research that comprehensively takes into account both work and sleep hours. Therefore, we propose a brand-new indicator, the WSR, to make up for this deficiency. In this study, both work and sleep hours are measured on a weekly basis. This paper addresses this gap through a cross-sectional study, which included 7,847 participants with aged ≥ 18 years. The value of WSR is equal to the value of work hours divided by sleep hours (WSR = work hours/sleep hours).
Materials
Participants
Participants were recruited from the NHANES 2017–2023. The ethical review and informed consent procedures for the NHANES study have been approved by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Institutional Review Board.1 Therefore, this dataset does not require additional ethical review. This study adhered to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guidelines.
Inclusion and exclusion
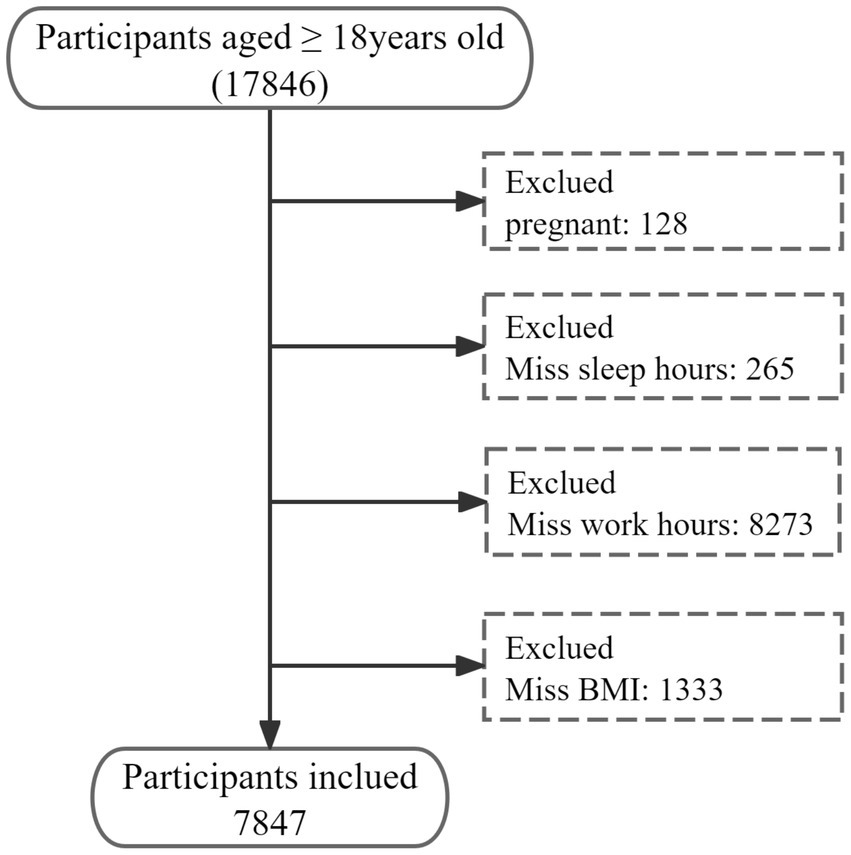
Data screening was conducted using R, version 4.4.4 (R Core Team, 2023). Missing BMI values were imputed using statistical software from the Free Software Foundation (version 2.1; Beijing Free Clinical Medical Technology Co., Ltd.) (25). The process of data inclusion and exclusion is illustrated in Figure 1. The data will be utilized to facilitate the implementation of various other research.
Covariates
In this study, covariates were selected based on a review of similar literature including age, gender, race, marital status, education level, BMI, poverty income ratio (PIR), alcohol consumption status, smoking status, time of vigorous and moderate leisure-time physical activity (VLTPA and MLTPA), sedentary activity, energy (kcal), heart failure (HF), CHD, diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, hyperlipidemia, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), thyroid problem, cancer, arthritis. The quantification of MLTPA, VLTPA and sedentary activity is based on daily minute counts.
Work hours, sleep hours, WSR and obesity
In this study, Work hours come from the response to the question “Number of hours worked in the last week.”Sleep hours were calculated by multiplying the response to the question “Sleep hours - weekdays or workdays” by 5 and the response to “Sleep hours - weekends” by 2, then summing the two products [Sleep hours = (weekday sleep × 5) + (weekend sleep × 2)]. WSR = work hours/sleep hours. BMI ≥ 30 was defined as obesity.
Other covariates
In this study, Individuals with age ≥60 year were classified as elder. PIR less than 1 were classified as poor. Values of MLTPA, VLTPA, sedentary activity, energy are derived from the answers to the questionnaire.
For race, the groups “Other Hispanic” and “Other Race - Including Multi-Racial” were combined into a single category labeled “Other Races,” while all other racial categories were retained as per the questionnaire. Participants who had completed more than the 11th grade were categorized as “High School or above.” Individuals who answered “Married/Living with partner” or “Widowed/Divorced/Separated” were classified as married. Alcohol consumption status was assessed based on responses to the questions “Ever had a drink of any kind of alcohol” and “Past 12 mos how often drink alc bev.” Individuals who answered “Yes” to the first question and reported more than zero days of alcohol consumption in the past 12 months were identified as drinkers. Individuals responses to the questions “Have you smoked at least 100 cigarettes in your lifetime?” and “Do you now smoke cigarettes?” Participants who answered “Yes” to both questions were classified as smokers.
The presence of HF, CHD, DM, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, stroke, COPD, thyroid problem, cancer, and arthritis was determined based on affirmative (“Yes”) responses to the corresponding questions in the questionnaire, such as “Have you/Has SP ever been told by a doctor or other health professional that you/s/he had cancer or a malignancy (ma-lig-nan-see) of any kind?”
Statistical analyses
Data analysis were performed using R, version4.4.1, along with Zstats v1.02 and Free Software Foundation statistics software (version 2.1; Beijing Free Clinical Medical Technology Co., Ltd.) (25). For skewed continuous data, they are presented as M (Q₁, Q₃), and the Mann–Whitney U test is used for comparison. For normally distributed continuous data, they are expressed as Mean ± SD, and the independent samples t-test is applied for comparison between two groups. Categorical data are presented as n (%), and the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test is used. A p-value < 0.05 is considered statistically significant for intergroup comparisons.
We employed a multivariate logistic regression model to examine the association between WSR and obesity. Four models were constructed for this analysis. The last model was adjusted for age, gender, race, marital status, education level, BMI, PIR, alcohol consumption status, smoking status, MLTPA, VLTPA, sedentary, energy, HF, CHD, DM, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, stroke, COPD, thyroid problem, cancer, arthritis.
Results
Baseline characteristics of the population
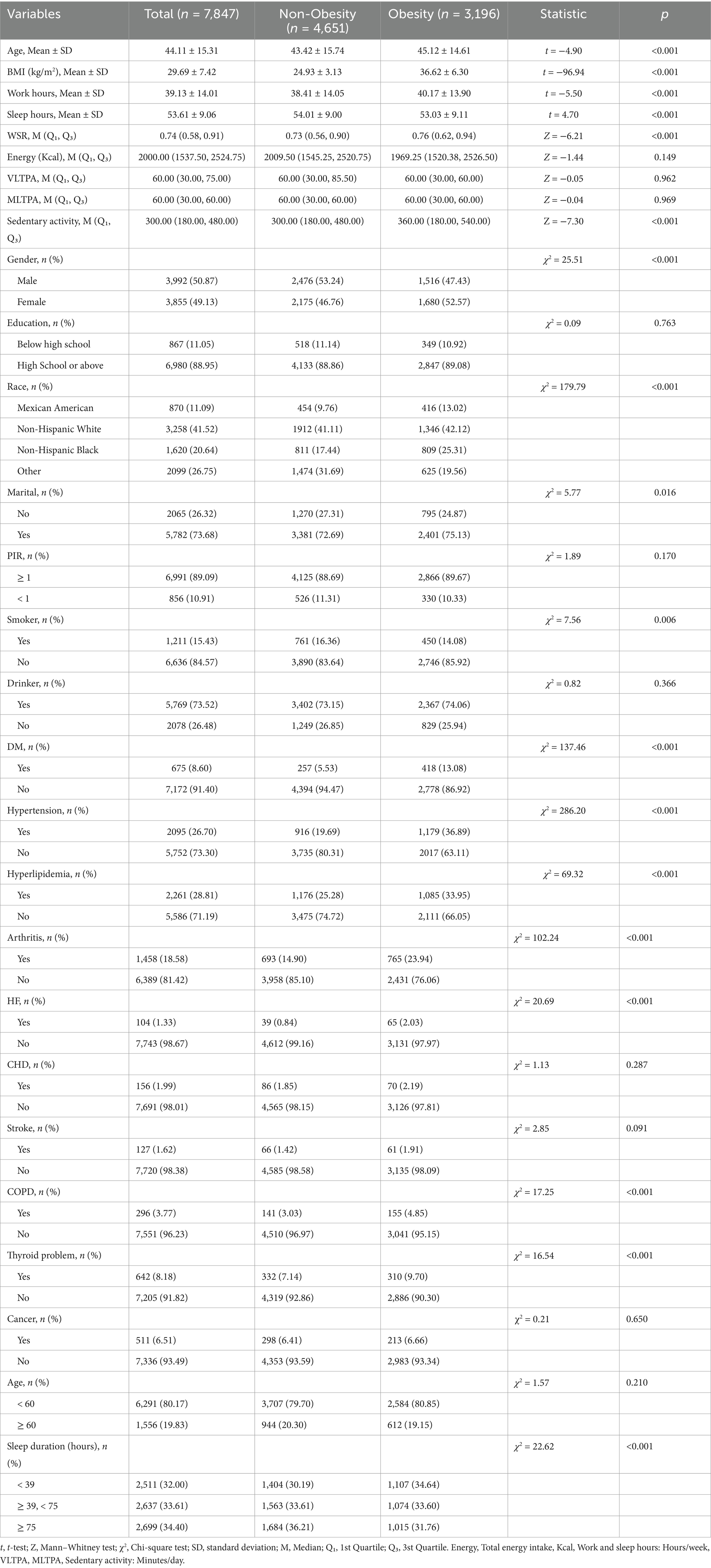
Table 1 presents the basic characteristics of 7,847 individuals drawn from the NHANES data rounds of 2017–2020 and 2021–2023. Among these participants, approximately 49.94% (3,196/7847) exhibited obesity. The mean age of the study population was 44.11 ± 15.31 years, with 3,855(49.13%) participants being female.
Table 1 reveals that 3,196 individuals with obesity have a higher proportion of females, married individuals, non-smokers, DM, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, angina, HF, thyroid problems, and COPD. Additionally, this group tends to be older, longer work hours, have shorter sleep duration, higher WSR and sedentary activity. In Table 1, individuals with obesity have a higher proportion of individuals with sleep hours < 39 h/week, and lower proportion of sleep hours ≥ 75 h/week (χ2 = 22.62, p < 0.001).
The correlation between WSR and obesity
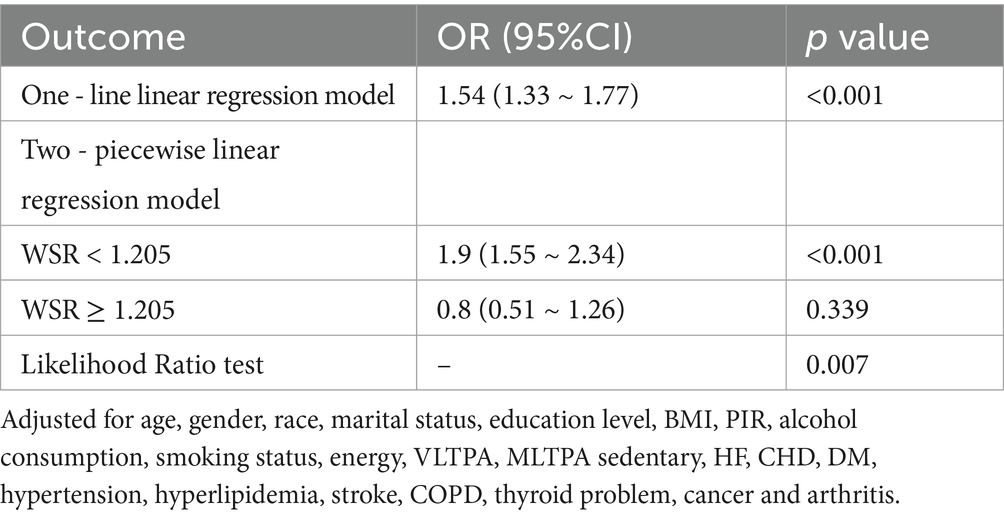
A significant association was observed between WSR and obesity in the univariate analyses (OR = 1.49, 95% CI = 1.31–1.70, p < 0.001, Supplementary Table 1). In the final model of multivariate analysis, WSR was identified as an independent risk factor for obesity. Specifically, compared with work hours (OR = 1.01, 95% CI = 1.01–1.01, p < 0.001) or sleep hours (OR = 0.99, 95% CI 0.98–0.99, p < 0.001) alone, WSR had a more pronounced effect on obesity (OR = 1.54, 95% CI = 1.33–1.77, p < 0.001) (Table 2). Subgroup analyses were conducted and no significant interactions was observed (P for interaction > 0.05) (Figure 2).
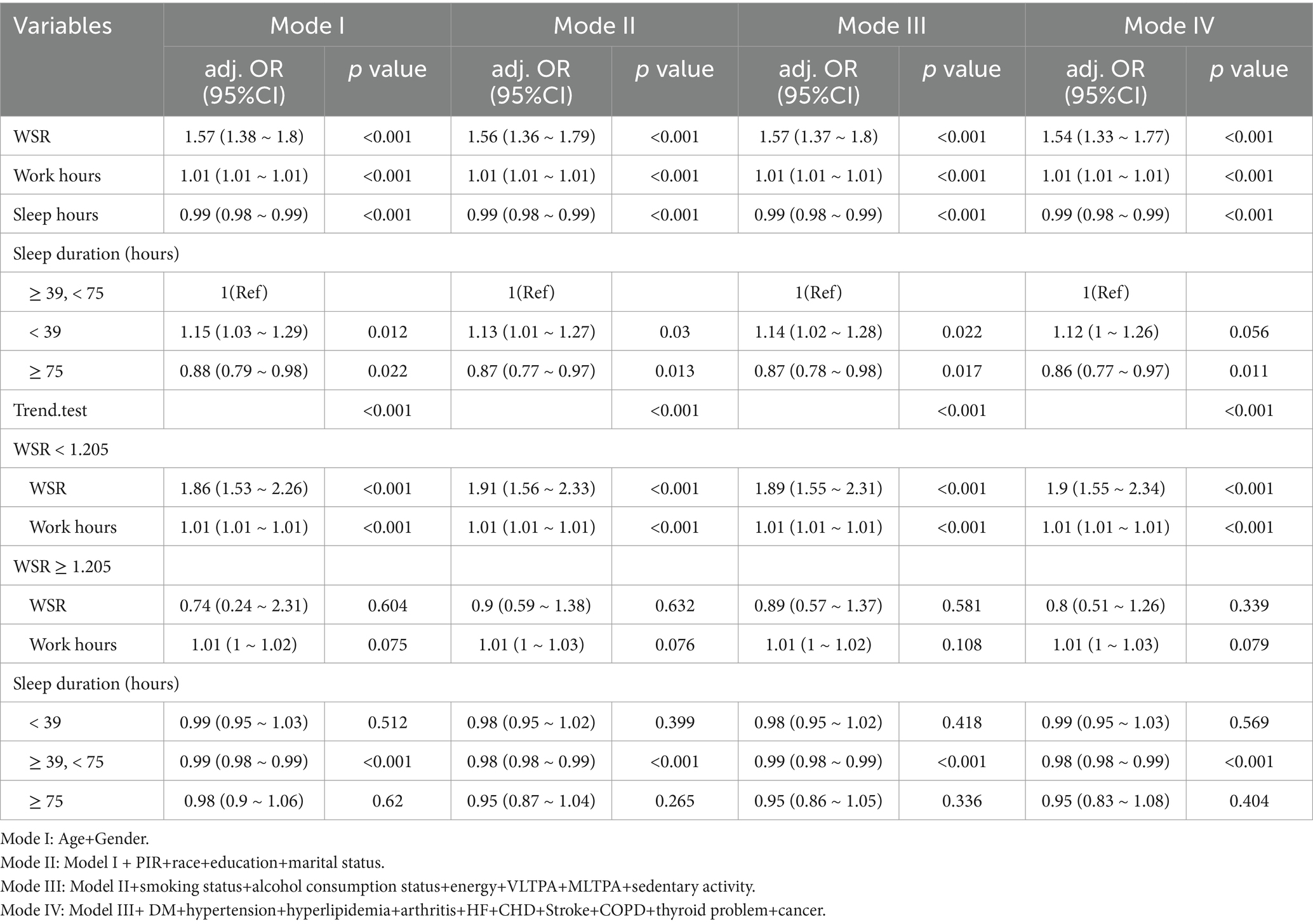
Table 2. Multivariate regression analysis of the association between WSR/work hours/sleep duration and obesity.
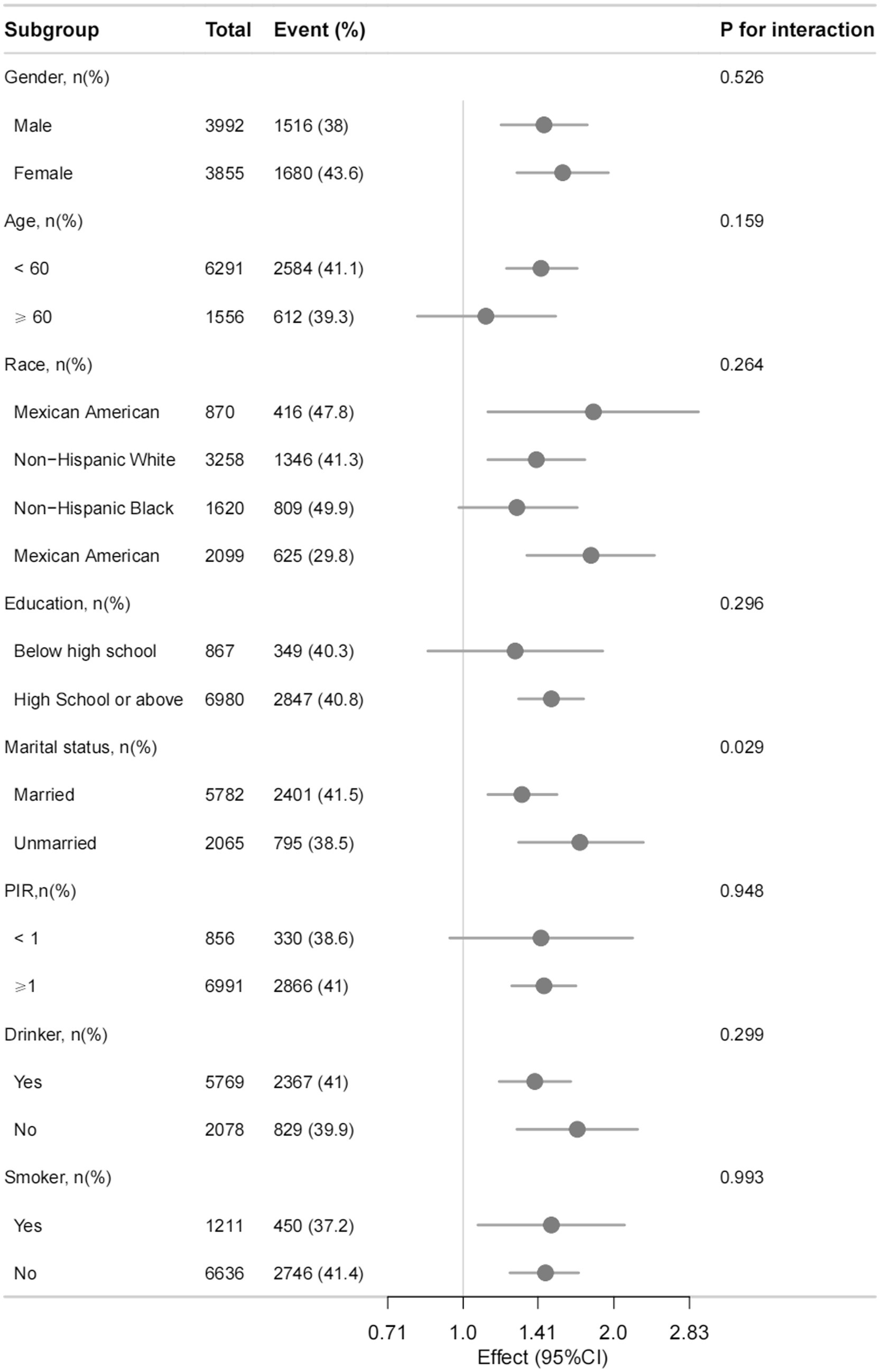
Figure 2. Association between WSR and obesity in different subgroups. Adjusted for othertime, age, gender, race, marital status, education level, BMI, PIR, alcohol consumption, smoking status, MLTPA, VLTPA, sedentary activity, HF, CHD, DM, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, stroke, COPD, thyroid problem, cancer and arthritis.
A non-linear relationship was observed between WSR and obesity (Figure 3) with RCS analysis. Table 3 and Figure 4 showed the cutpoint of WSR. The risk of developing obesity increased significantly with WSR < 1.205(OR = 1.9, 95% CI = 1.55–2.34, p < 0.001) and no association was observed with WSR ≥ 1.205(OR = 0.8, 95% CI = 0.51–1.26, p = 0.339) (Tables 2, 3).
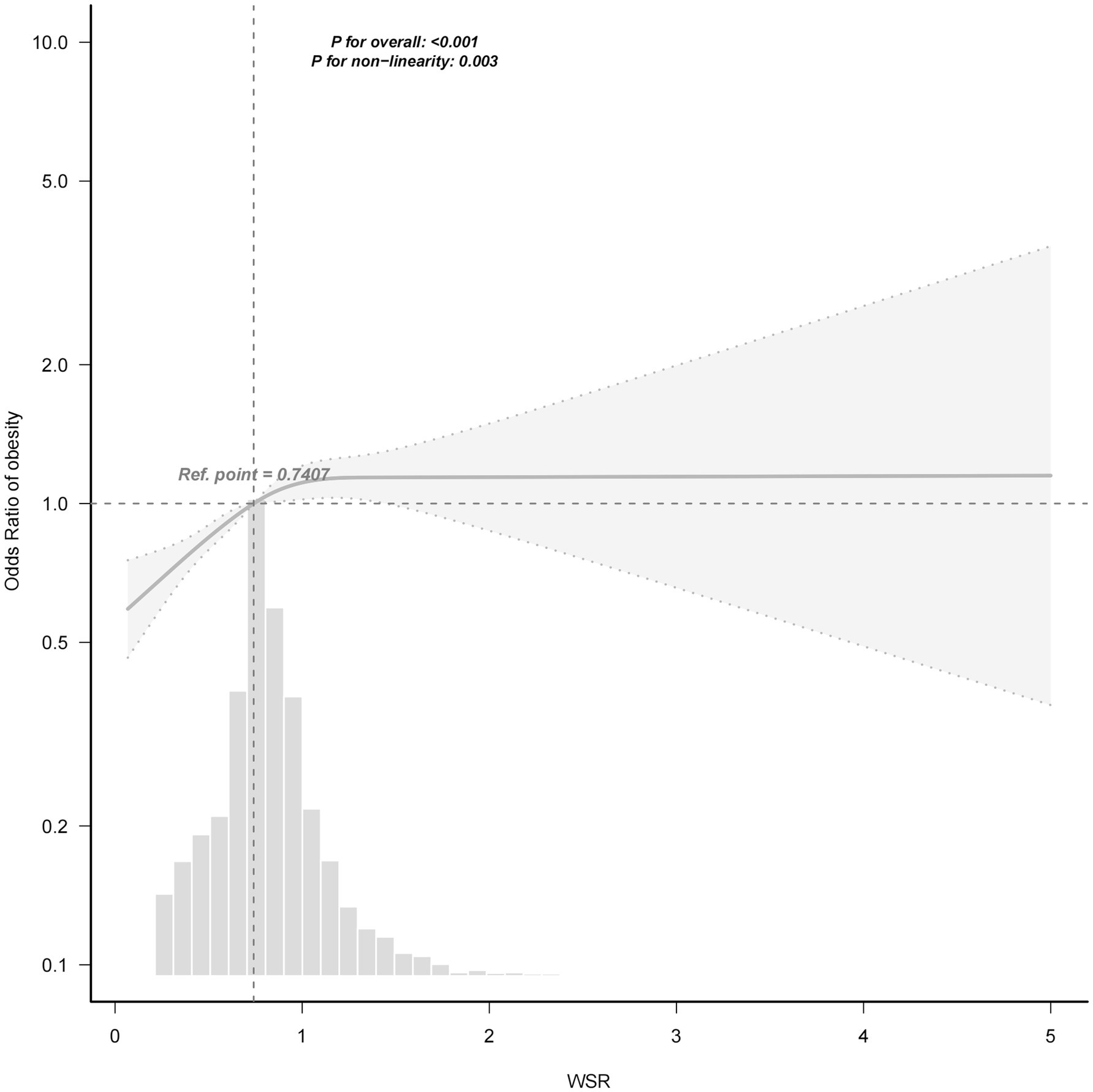
Figure 3. Association between WSR and obesity with RCS. Adjusted for othertime, age, gender, race, marital status, education level, BMI, PIR, alcohol consumption, smoking status, MLTPA, VLTPA, sedentary activity, HF, CHD, DM, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, stroke, COPD, thyroid problem, cancer and arthritis.
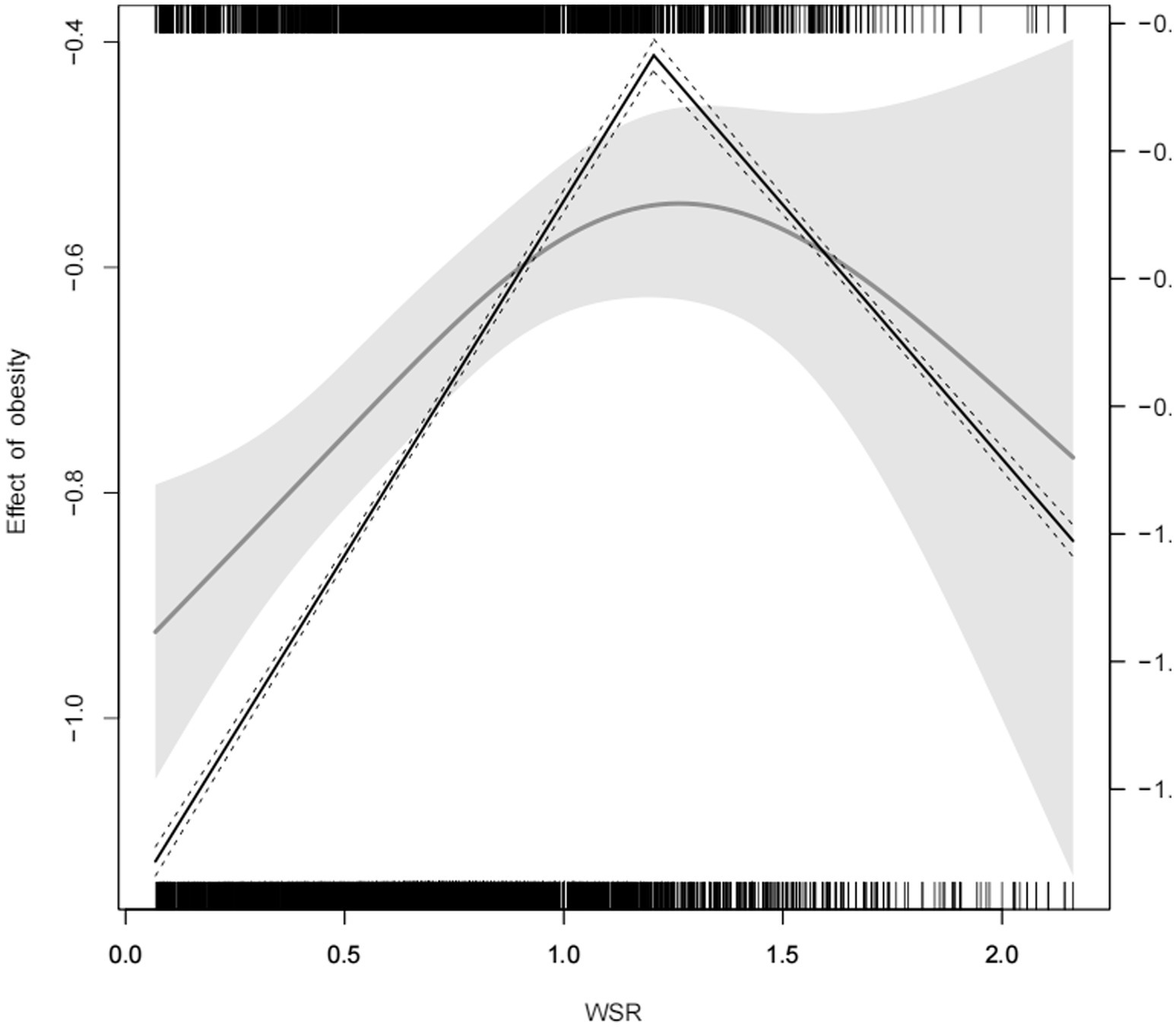
Figure 4. The cutpoint of WSR Adjusted for othertime, age, gender, race, marital status, education level, BMI, PIR, alcohol consumption, smoking status, MLTPA, VLTPA, sedentary activity, HF, CHD, DM, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, stroke, COPD, thyroid problem, cancer and arthritis.
The correlation between work hours and obesity
Multivariate analysis showed that work hours had positive effect on obesity (OR = 1.01, 95% CI = 1.01–1.01, p < 0.001) (Table 2). A linear relationship was identified between work hours and obesity (Supplementary Figure 1).
The correlation between sleep hours and obesity
Multivariate analysis showed that sleep hours was negative to obesity (OR = 0.99, 95% CI = 0.98–0.99, p < 0.001) (Table 2). A linear relationship was identified between sleep hours and obesity (P for non - linearity: 0.061, Supplementary Figure 2). The cutpoints of sleep hours were 39 and 75 (Supplementary Figure 3). When sleep hours are within the range of 39 to 75 h, the risk of developing obesity decreases significantly (Table 2). In the final model, compared with individuals who sleep 39 to 75 h per week, sleep duration < 39 was not significantly associated with obesity (OR = 1.12, 95% CI 1.00–1.26, p = 0.056, p for trend <0.001) (Table 2). In contrast, sleep duration ≥ 75 was significantly associated with a reduced incidence of obesity (OR = 0.86, 95% CI 0.77–0.97, p = 0.011, p for trend <0.001) (Table 2). When the sleep duration are less than 39 or more than 75 h, the incidence rate of obesity did not change with the variation of sleep duration in multivariate analysis (Table 2).
Discussion
In this context, our study represents a pioneering effort to explore the relationship between the WSR and obesity. This is the first article to evaluate the relationship between WSR and obesity. Our research has several key findings: (1) During the period when the value of WSR continues to rise, the incidence of obesity shows an upward trend accordingly. Nevertheless, once the WSR value exceeds the crucial cutoff of 1.205, a saturation effect emerges. (2) A linear correlation was observed between work hours and the incidence of obesity. 3. A “Z” shape was observed between sleep hours and the incidence of obesity. Furthermore, the influence of WSR on obesity was found to be significantly more pronounced than that of work hours or sleep hours considered in isolation. This innovative finding provides an additional dimension for comprehending the intricate associations among work, sleep, and obesity, thereby contributing novel insights to the existing body of literature on the topic.
The interaction between work and sleep has been elaborated in existing research (26, 27). WSR introduces a novel perspective by quantifying the synergistic effect of work and sleep hours in obesity. This approach addresses the limitation of traditional single-behavior analyses (work or sleep hours alone) and fills a long-standing research gap in their interactive effects. Specifically, by normalizing work hours against sleep hours, WSR captures daily time allocation strategies, strategically guiding interventions toward dynamic balance management rather than isolated adjustments to work or sleep. It is worth noting that the impact of WSR (OR = 1.54, 95% CI 1.33–1.77, p < 0.001) on obesity is far greater than that of work (OR = 1.01, 95% CI1.01–1.01, p < 0.001) or sleep hours (OR = 0.99, 95% CI0.98 ~ 0.99, p < 0.001) alone.
Lengthy work hours are generally acknowledged as a major factor contributing to obesity (15, 28) and sleep deprivation (27). Virtanen et al. (29) analyzed 19 cohort studies included 122,078 participants and observed that long work hours (≥ 55 h/week) were associated with the risk of weight gain from normal to overweight (RR = 1.16, 95% CI 1.07–1.26), but not from overweight to obesity (RR = 1.01, 95% CI 0.89–1.14) compared with standard weekly worktime (35–40 h). Another meta-analysis (30) stressed effect of long work hours on obesity with OR = 1.23 (95% CI 1.09–1.39). In our study, we identified a linear relationship between work hours and obesity. As worktime increased, the odds of obesity also rose. The OR was 1.01 (95% CI 1.01–1.01, p < 0.001). This result is consistent with existing research findings (14, 30).
Numerous studies have examined closely the relationship between sleep duration and obesity (17–19, 31, 32). A close link between short sleep duration and obesity has been established, but there’s no consensus yet on the connection between long sleep duration and obesity. In our study, there is a negative correlation between sleep hours and obesity (OR = 0.99, 95% CI 0.98–0.99, p < 0.001) and the time period of 39 to 75 h makes a major contribution to this relationship (OR = 0.98, 95%CI 0.98–0.99, p < 0.001) with the overall data. In the model adjustment, the positive impact of sleep hours < 39 h on obesity was progressively diluted with more variables were incorporated for adjustment compared to individuals with sleep hours 39 to 75 h. In the final model, individuals with sleep hours < 39 h did not show a significant association with obesity (OR = 1.12, 95% CI 1–1.26, p = 0.056). However, the proportion of obesity was relatively higher in the group (34.64%, χ2 = 22.62, p < 0.001) and p was less than 0.05 in model I/II/III. Conversely, individuals with sleep hours ≥ 75 h had a lower obesity rate (31.76%, χ2 = 22.62, p < 0.001), with a protective effect against obesity (OR = 0.86, 95% CI 0.77–0.97, p = 0.011). Therefore, in our results, the relationship between sleep hours and obesity presents a “Z” shape.
In schoolchildren aged 8 to 17 years, Tambalis et al. (31) observed that 40% of these children had insufficient sleep and insufficient sleep was associated with an increased risk of overweight or obesity (OR = 1.21, 95% CI 1.17–1.25), but the relationship between long sleep duration and obesity was not mentioned. Sa et al. (32) analyzed 1,578 students from U. S. and Korean colleges and observed that obesity was associated with both short (< 7 h/night) (OR = 1.67, 95% CI 1.16–2.41, p < 0.01) and long sleep duration (> 9 h/night) (OR = 1.79,95% CI 1.03–3.43, p < 0.05), and obesity was related to short sleep among blacks only (p < 0.05) in analyses stratified by race and nationality. Jike et al. (33) analyzed 95 articles found that long sleep was significantly associated with obesity (RR = 1.08, 95% CI 1.02–1.15, p = 0.010, I2 = 0%, N = 13). Maugeri et al. (34) analyzed a total of 1,482 participants aged 25 to 65 years and observed that individuals with short sleep duration (<7 h/night) have a 40% increased risk of obesity (OR = 1.40, 95%CI = 1.02–1.94, p = 0.047) and long sleep duration (>9 h/night) was associated with lower body weight (p = 0.001) and a higher proportion of underweight individuals (p = 0.002) compared to individuals with normal sleep duration. A meta-analysis of 6 articles (35) found that short sleep duration increased the risk of incident obesity in both men (OR = 1.26, 95% CI 1.13–1.40) and women (OR 1.36, 95% CI 1.16–1.59), with no significant gender differences. Another meta-analysis (36) analyzed a total of 5,172,710 participants from 153 studies suggests that short sleep not only increase the occurrence of obesity (RR = 1.38, 95%CI 1.25–1.53, p < 0.005, I2 = 60%, N = 16) but is also associated with other health outcomes, such as the mortality outcome, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, coronary heart diseases. Zheng et al. (37) found that each hour increase in average daily sleep duration was associated with decreased odds of receiving a new diagnosis for morbid obesity (OR = 0.62, 95% CI 0.53–0.73).
The potential mechanisms linking work, sleep, and obesity were elucidated. Dietary alteration is a keystone of weight control. In fact, the actual energy intake is usually 30 to 50% higher than the intake reported by individuals themselves (38). Moreover, the longer the individuals spend working (39), the less able they are to prepare healthy foods on their own. Instead, they frequent restaurants, visit fast-food joints, or rely on food delivery services to fulfill their daily dietary needs, and as a result, the foods they consume also contain less dietary fiber (13, 29, 39, 40). Low level of physical activity is another main factor contributing to obesity (13, 41). The changes in modern work patterns, along with the predominantly office - based work model, have restricted employees’ activity time. Meanwhile, long working hours have left employees mentally and physically exhausted, limiting their time for exercise after work. This is one of the possible mechanisms by which long work hours lead to obesity (13, 42). However, not all researchers think that long work has an effect on physical activity (42). The third possible factor is sleep abnormalities caused by long work hours, including sleep deprivation or sleep disorders (27, 43). Sleep alterations also contribute to the development of obesity to a certain extent (43, 44). The changes in the microecological environment are influenced by work (45) and sleep (46, 47), and the impact of the microecology on obesity is also gradually attracting more attention (48). At the molecular level, the possible mechanisms might be attributed to changes in metabolism-related hormones, such as leptin (43, 49).
In this study, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, the lack of weighted analyses, and the exclusion of individuals who do not work or have no need to work may restrict the generalizability of the results. Second, the cross-sectional nature of the study means that it only examined the potential association between the WSR and obesity, and thus cannot establish a causal relationship. Third, the limited number of covariates included in the analysis may have influenced the interpretation of the results and introduced potential biases. Fourth, this article does not count the staff who are currently looking for jobs. Fifth, the number of working days per week and the type of work have not been mentioned, that may limit the generalizability of results to specific occupational groups. Since the number of working days per week and the daily worktime of the participants were not available, there may be some bias in the analysis.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that the WSR, which combines the impact of work and sleep hours, exerts a more substantial impact on the occurrence of obesity compared to work or sleep hours alone. WSR can be used as a new reference indicator for relevant stakeholders to formulate strategies designed to promote employees’ occupational health and global health, thereby reducing the burden of obesity-related diseases.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about/erb.html. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)’ legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
JZ: Visualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The author grateful to thank all of the participants for their valuable contributions.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1616890/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Available online at: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (Accessed March 17, 2025).
2. Kelly, T, Yang, W, Chen, CS, Reynolds, K, and He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes. (2008) 32:1431–7. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.102
3. Ward, ZJ, Bleich, SN, Cradock, AL, Barrett, JL, Giles, CM, Flax, C, et al. Projected U.S. state-level prevalence of adult obesity and severe obesity. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:2440–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1909301
4. Ding, J, Chen, X, Shi, Z, Bai, K, and Shi, S. Association of Metabolically Healthy Obesity and Risk of cardiovascular disease among adults in China: a retrospective cohort study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2023) 16:151–9. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S397243
5. Wang, M, Xu, K, Yang, J, Bennett, DA, Du, H, and Liu, X. Normal-weight obesity subtypes and 10-year risks of major vascular diseases in 0.3 million adults. Clin Nutr. (2025) 45:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.12.027
6. Piché, ME, Tchernof, A, and Després, JP. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. (2020) 126:1477–500. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316101
7. Powell-Wiley, TM, Poirier, P, Burke, LE, Després, JP, Gordon-Larsen, P, Lavie, CJ, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2021) 143:e984–e1010. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000973
8. Ma, LZ, Sun, FR, Wang, ZT, Tan, L, Hou, XH, Ou, YN, et al. Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:197. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4387
9. Hopkins, BD, Goncalves, MD, and Cantley, LC. Obesity and Cancer mechanisms: Cancer metabolism. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:4277–83. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.9712
10. Lv, R, Liu, X, Zhang, Y, Dong, N, Wang, X, He, Y, et al. Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:218. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01496-3
11. Cao, Z, Wu, Y, Li, Q, Li, Y, and Wu, J. A causal relationship between childhood obesity and risk of osteoarthritis: results from a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Ann Med. (2022) 54:1636–45. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2085883
12. Endalifer, ML, and Diress, G. Epidemiology, predisposing factors, biomarkers, and prevention mechanism of obesity: a systematic review. J Obes. (2020) 2020:6134362. doi: 10.1155/2020/6134362
13. Pan, X, Wang, L, and Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2021) 9:373–92. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00045-0
14. Jang, TW, Kim, HR, Lee, HE, Myong, JP, and Koo, JW. Long work hours and obesity in Korean adult workers. J Occup Health. (2014) 55:359–66. doi: 10.1539/joh.13-0043-OA
15. Ervasti, J, Pentti, J, Nyberg, ST, Shipley, MJ, Leineweber, C, Sørensen, JK, et al. Long working hours and risk of 50 health conditions and mortality outcomes: a multicohort study in four European countries. Lancet Reg Health Eur. (2021) 11:100212. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100212
16. Le, AB, Balogun, AO, and Smith, TD. Long work hours, overtime, and worker health impairment: a cross-sectional study among stone, sand, and gravel mine workers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:7740. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19137740
17. Mitchell, JA, Williamson, A, and Fiks, AG. Targeting sleep duration and timing for prevention of adolescent obesity. JAMA Pediatr. (2019) 173:1018–20. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.3080
18. Antza, C, Kostopoulos, G, Mostafa, S, Nirantharakumar, K, and Tahrani, A. The links between sleep duration, obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Endocrinol. (2021) 252:125–41. doi: 10.1530/JOE-21-0155
19. Ogilvie, RP, and Patel, SR. The epidemiology of sleep and obesity. Sleep Health. (2017) 3:383–8. doi: 10.1016/j.sleh.2017.07.013
20. International Labour Organization. Working time and work-life balance around the world. Available online at: https://www.ilo.org/publications/working-time-and-work-life-balance-around-world (Accessed March 17, 2025).
21. Pilla, D, and Kuriansky, J. Mental health in Japan: intersecting risks in the workplace. J Stud Res. (2018) 7:38–41. doi: 10.47611/jsr.v7i2.509
22. Statista. Number of monthly workhours of hairdressers and beauticians in Japan 2015-2024. Available online at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1243025/japan-monthly-workhours-hairdressers-beauticians/ (Accessed April 17, 2025).
23. Solovieva, S, Lallukka, T, Virtanen, M, and Viikari-Juntura, E. Psychosocial factors at work, long work hours, and obesity: a systematic review. Scand J Work Environ Health. (2013) 39:241–58. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.3364
24. Ding, C, Lim, LL, Xu, L, and Kong, APS. Sleep and obesity. J Obes Metab Syndr. (2018) 27:4–24. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2018.27.1.4
25. Liu, H, Zhang, S, Gong, Z, Zhao, W, Lin, X, Liu, Y, et al. Association between migraine and cardiovascular disease mortality: a prospective population-based cohort study. Headache. (2023) 63:1109–18. doi: 10.1111/head.14616
26. Hakola, T, Niemelä, P, Rönnberg, S, and Ropponen, A. Longer work shifts, faster forward rotation-more sleep and more alert in aircraft inspection. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:8105. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18158105
27. Choi, H, Lee, S, Jeon, MJ, and Min, YS. Relationship between long work hours and self-reported sleep disorders of non-shift daytime wage workers in South Korea: data from the 5th Korean working conditions survey. Ann Occup Environ Med. (2020) 32:e35. doi: 10.35371/aoem.2020.32.e35
28. Kivimäki, M, Jokela, M, Nyberg, ST, Singh-Manoux, A, Fransson, EI, Alfredsson, L, et al. Long working hours and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished data for 603,838 individuals. Lancet. (2015) 386:1739–46. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60295-1
29. Virtanen, M, Jokela, M, Lallukka, T, Magnusson Hanson, L, Pentti, J, Nyberg, ST, et al. Long working hours and change in body weight: analysis of individual-participant data from 19 cohort studies. Int J Obes. (2020) 44:1368–75. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0480-3
30. Zhu, Y, Liu, J, Jiang, H, Brown, TJ, Tian, Q, Yang, Y, et al. Are long working hours associated with weight-related outcomes? A meta-analysis of observational studies. Obes Rev. (2019) 21:e12977. doi: 10.1111/obr.12977
31. Tambalis, KD, Panagiotakos, DB, Psarra, G, and Sidossis, LS. Insufficient sleep duration is associated with dietary habits, screen time, and obesity in children. J Clin Sleep Med. (2018) 14:1689–96. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.7374
32. Sa, J, Choe, S, Cho, BY, Chaput, JP, Kim, G, Park, CH, et al. Relationship between sleep and obesity among U.S. and south Korean college students. BMC Public Health. (2020) 20:96. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-8182-2
33. Jike, M, Itani, O, Watanabe, N, Buysse, DJ, and Kaneita, Y. Long sleep duration and health outcomes: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. Sleep Med Rev. (2018) 39:25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2017.06.011
34. Maugeri, A, Medina-Inojosa, JR, Kunzova, S, Agodi, A, Barchitta, M, Sochor, O, et al. Sleep duration and excessive daytime sleepiness are associated with obesity independent of diet and physical activity. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1219. doi: 10.3390/nu10091219
35. Lange, MG, Neophytou, C, Cappuccio, FP, Barber, TM, Johnson, S, and Chen, YF. Sex differences in the association between short sleep duration and obesity: a systematic-review and meta-analysis. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2024) 34:2227–39. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2024.06.008
36. Osamu, I, Maki, J, Norio, W, and Yoshitaka, K. Short sleep duration and health outcomes: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Sleep Med. (2016) 32:246–56. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2016.08.006
37. Zheng, NS, Annis, J, Master, H, Han, L, Gleichauf, K, Ching, JH, et al. Sleep patterns and risk of chronic disease as measured by long-term monitoring with commercial wearable devices in the all of us research program. Nat Med. (2024) 30:2648–56. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03155-8
38. Chao, AM, Quigley, KM, and Wadden, TA. Dietary interventions for obesity: clinical and mechanistic findings. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e140065. doi: 10.1172/JCI140065
39. Oostenbach, LH, Lamb, KE, Crawford, D, and Thornton, L. Influence of work hours and commute time on food practices: a longitudinal analysis of the household, income and labour dynamics in Australia survey. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e056212. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-056212
40. Min, J, Lee, DW, Kang, MY, Myong, JP, Kim, HR, and Lee, J. Working for Long hours is associated with dietary Fiber insufficiency. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:786569. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.786569
41. Hills, AP, Andersen, LB, and Byrne, NM. Physical activity and obesity in children. Br J Sports Med. (2011) 45:866–70. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2011-090199
42. Angrave, D, Charlwood, A, and Wooden, M. Long working hours and physical activity. J Epidemiol Community Health. (2015) 69:738–44. doi: 10.1136/jech-2014-205230
43. Chaput, JP, McHill, AW, Cox, RC, Broussard, JL, Dutil, C, da Costa, BGG, et al. The role of insufficient sleep and circadian misalignment in obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2023) 19:82–97. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00747-7
44. Chow, LS, Gerszten, RE, Taylor, JM, Pedersen, BK, van Praag, H, Trappe, S, et al. Exerkines in health, resilience and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2022) 18:273–89. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00641-2
45. Lopez-Santamarina, A, Mondragon, ADC, Cardelle-Cobas, A, Santos, EM, Porto-Arias, JJ, Cepeda, A, et al. Effects of unconventional work and shift work on the human gut microbiota and the potential of probiotics to restore dysbiosis. Nutrients. (2023) 15:3070. doi: 10.3390/nu15133070
46. Matenchuk, BA, Mandhane, PJ, and Kozyrskyj, AL. Sleep, circadian rhythm, and gut microbiota. Sleep Med Rev. (2020) 53:101340. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2020.101340
47. Li, W, Wang, Z, Cao, J, Dong, Y, and Chen, Y. Melatonin improves skin barrier damage caused by sleep restriction through gut microbiota. J Pineal Res. (2023) 75:e12874. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12874
48. Gomes, AC, Hoffmann, C, and Mota, JF. The human gut microbiota: metabolism and perspective in obesity. Gut Microbes. (2018) 9:308–25. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2018.1465157
Keywords: Work-to-Sleep hours Ratio, obesity, work hours, sleep hours, NHANES
Citation: Zhou J (2025) Positive relationship between Work-to-Sleep hours Ratio and obesity: a cross-sectional study, evidence from NHANES 2017–2023. Front. Public Health. 13:1616890. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1616890
Edited by:
Mohammad Hossein Ebrahimi, Shahroud University of Medical Sciences, IranReviewed by:
Catalina Ramírez-Contreras, University of the Bío Bío, ChileSatomi Okano, Asahikawa Medical University, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinggang Zhou, MjUxNTA3NjU2MEBxcS5jb20=
 Jinggang Zhou
Jinggang Zhou