- 1Medical Big Data and Bioinformatics Research Centre, First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 2School of Public Health and Health Management, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 3The First School of Clinical Medicine, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 4School of Basic Medicine, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 5Ganzhou Key Laboratory of Medical Big Data, Ganzhou, China
Digital technology and artificial intelligence have revolutionized predictive models based on clinical data, creating opportunities for proactive health management. This review systematically evaluates the role and effectiveness of biomarker-driven predictive models across disease detection, personalized intervention, and healthcare resource optimization. Critical challenges hindering their implementation include data heterogeneity, inconsistent standardization protocols, limited generalizability across populations, high implementation costs, and substantial barriers in clinical translation. To address these challenges, we propose an integrated framework prioritizing three pillars: multi-modal data fusion, standardized governance protocols, and interpretability enhancement, systematically addressing implementation barriers from data heterogeneity to clinical adoption. This systematic approach enhances early disease screening accuracy while supporting risk stratification and precision diagnosis, particularly for chronic conditions and oncology applications. By effectively connecting biomarker discovery with practical clinical utilization, our proposed framework offers actionable methodologies that address existing limitations while guiding multidisciplinary research teams. Moving forward, expanding these predictive models to rare diseases, incorporating dynamic health indicators, strengthening integrative multi-omics approaches, conducting longitudinal cohort studies, and leveraging edge computing solutions for low-resource settings emerge as critical areas requiring innovation and exploration.
1 Introduction
1.1 Research background and objectives
Digital technology and artificial intelligence are transforming healthcare research and practice paradigms. Improved computational capabilities now enable integration of clinical testing databases, electronic health records, and multi-omics data, creating a multidimensional health ecosystem across the human lifecycle (1, 2). This multimodal data integration captures disease progression trajectories (3) and elucidates mechanisms underlying individual drug response variations through integrated analysis of pharmacogenomics and proteomics (4), creating a robust foundation for developing prognosis assessment and health risk predictive models (5).
The evolution of Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies has introduced transformative tools for medical data analysis. Deep learning algorithms, specifically, with their advanced feature learning capabilities, have enhanced the efficiency of analyzing high-dimensional heterogeneous data (6). These computational approaches systematically identify complex biomarker-disease associations that traditional statistical methods often overlook, enabling more granular risk stratification. Research demonstrates that Transformer-based algorithms enable precise disease risk stratification (7), accurate diagnostic determinations (2), and personalized treatment regimen optimization (8) through systematic identification of complex non-linear associations. These technological advances are shifting medical practice from traditional population-based approaches toward precision medicine focused on individual characteristics, with clinical efficacy validated through multicenter randomized controlled trials (9, 10).
Despite technological advances, significant challenges persist in effectively integrating biomarker data, developing reliable predictive models, and implementing these in clinical practice (11). Key challenges requiring resolution include data standardization (12), model generalizability (9), and clinical implementation pathways (13). This review systematically analyzes the application value and technical approaches of biomarker-based disease predictive models in proactive health management, while examining key challenges and corresponding strategies. Through integration of multidisciplinary perspectives from epidemiology, clinical medicine, bioinformatics, and artificial intelligence, we propose a comprehensive framework encompassing biomarker discovery, data integration, model construction, and clinical translation, providing systematic guidance for the implementation of predictive models in precision medicine.
1.2 The new paradigm of proactive health management
Proactive health management represents a transformative shift in modern medicine, transitioning from traditional disease diagnosis and treatment models to health maintenance approaches based on prediction and prevention (14). This transformation is grounded in the biopsychosocial medical model, emphasizing early health risk identification and implementation of targeted interventions to prevent disease onset or delay progression (5). This paradigm specifically aims to extend healthspan through preemptive interventions targeting subclinical pathological processes. Unlike traditional episodic care models, proactive systems implement continuous physiological monitoring (15) integrated with dynamic risk assessment methodologies (16), thereby maintaining functional capacity through preventive intervention. Such paradigmatic transformation aligns with strategic health initiatives, including “Healthy China 2030,” and addresses demographic challenges posed by increasing chronic disease prevalence in aging populations (17).
The evolution of this new paradigm has advanced through significant breakthroughs in clinical testing technologies, initiating a new era of biomarker research. Contemporary detection platforms (e.g., single-cell sequencing, spatial transcriptomics, and high-throughput proteomics) generate comprehensive molecular profiles including metabolomic, proteomic, and epigenetic features, offering unprecedented insights into disease mechanisms (18). Integrated profiling across these platforms captures dynamic molecular interactions between biological layers, revealing pathogenic mechanisms otherwise undetectable via single-omics approaches. This technological advancement has transformed biomarker discovery from traditional experience-based approaches to data-driven precise identification processes. For instance, the integration of multi-omics data and advanced analytical methods has improved early Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis specificity by 32%, providing a crucial intervention window (19, 20).
These technological breakthroughs have been accompanied by continuous refinement in detection methodologies, enabling cost-effective biomarker discovery and longitudinal monitoring capabilities. Progressive refinement of detection methodologies coupled with reduction in implementation costs has expanded biomarker applications beyond traditional diagnostics toward prospective risk assessment and targeted intervention strategies (21). The evolution encompasses diversification of clinical applications, transition from univariate to multivariate biomarker panels, and development of longitudinal monitoring systems capturing temporal physiological variations (22). Nevertheless, expanded application domains introduce significant methodological challenges requiring systematic resolution to realize the full potential of biomarker-driven precision health management.
1.3 Research methodology and content framework
To address implementation challenges and evaluate current evidence supporting biomarker-driven predictive models, we conducted a systematic literature analysis using structured review methodology. Comprehensive database searches in PubMed encompassed peer-reviewed publications from January 2020 through April 2025, employing Boolean combinations of standardized medical subject headings and field-specific terminology including “biomarkers,” “predictive models,” “health risk assessment,” “proactive health management,” and “precision medicine.” The methodological approach specifically targeted research addressing critical challenges in data heterogeneity management, model interpretability, and clinical implementation within personalized medicine contexts.
Through systematic analysis of the selected studies, the research synthesized current findings and identified key deficiencies and unresolved issues. Based on these analyses, a theoretically grounded content framework was constructed to systematically elucidate the key elements, technical pathways, and application prospects of biomarker-driven predictive models. Specifically, this review initially clarifies biomarker concepts and their fundamental role in establishing disease relationships, establishing the theoretical foundation for subsequent discussions; then explores the core value of biomarker predictive models in proactive health applications, including early risk stratification, personalized health interventions, and public health optimization; the technical framework section details the complete methodological pathway from data acquisition, biomarker screening to model construction and optimization, providing specific guidance for practical applications; finally, it analyzes systematically key challenges in data quality, model generalizability, clinical translation, and proposes corresponding solution strategies, indicating directions for future research.
Through this structured research methodology and systematic content framework, this review aims to provide researchers, clinicians, and policy makers with comprehensive knowledge regarding biomarker predictive models in proactive health management, advancing related technologies and improvements in clinical practice improvements. Particularly, we focus on analyzing from multidisciplinary perspectives the translation of biomarker predictive models into clinical practice, supporting personalized health management systems in precision medicine and facilitating medical practice transformation from passive response to proactive prevention.
2 Biomarker concepts and disease relationship construction
2.1 Basic concept definition
Biomarkers, defined by the U. S. Institute of Medicine as “objectively measurable indicators of biological processes” (23), function as indicators of normal biological processes, pathological processes, or pharmacological responses to therapeutic interventions. This definition emphasizes biomarkers’ objectivity and measurability, establishing the foundation for their clinical application.
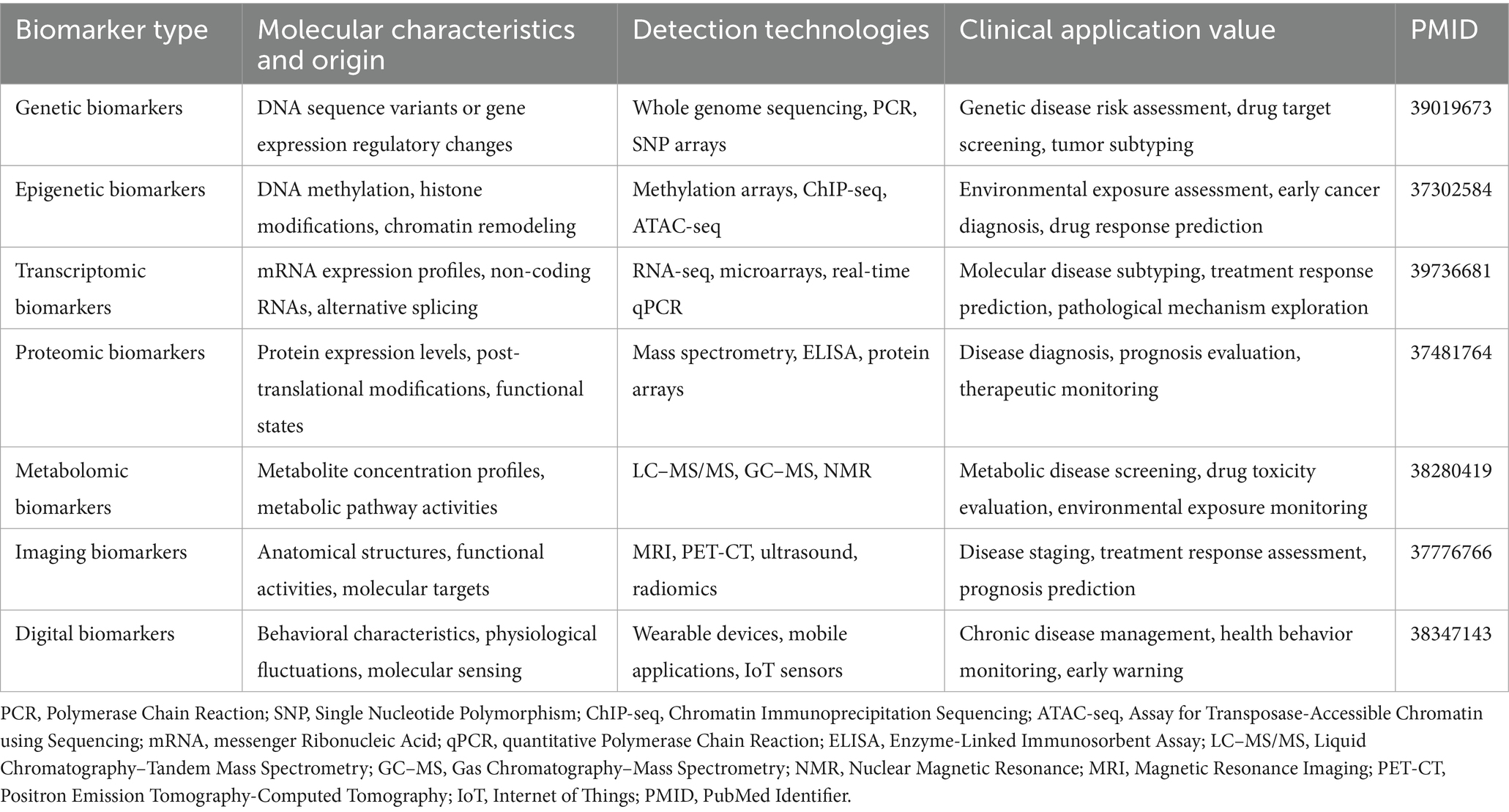
From a molecular classification perspective, biomarkers include genetic markers, epigenetic markers, transcriptomic markers, protein markers, and metabolic markers, reflecting multi-level biological information from genes to phenotypes (24). With technological advancement, biomarker research has evolved from single molecular indicators to multidimensional marker combinations, and from static measurements to dynamic monitoring, enabling more comprehensive capture of disease biological features and providing enhanced information for precision medicine (25). Table 1 summarizes the characteristics, detection technologies, and clinical applications of major biomarker types, demonstrating their distinct values and limitations in proactive health management.
2.2 Establishing associations between biomarkers and diseases
Establishing reliable associations between biomarkers and diseases requires integrating multidisciplinary approaches and multi-level validation. The advancement of big data and artificial intelligence technologies, has transformed biomarker research from hypothesis-driven to data-driven approaches, expanding potential marker identification (26). As illustrated in Figure 1, the relationship between biomarkers and diseases demonstrates multidimensional characteristics, including sensitivity, specificity, predictive value, dynamic changes, and technical limitations, which collectively determine their efficacy and constraints in clinical applications (27). These multidimensional characteristics collectively inform how biomarker data should be interpreted within specific clinical contexts, particularly when determining intervention thresholds that optimize the balance between diagnostic accuracy and early detection capabilities.
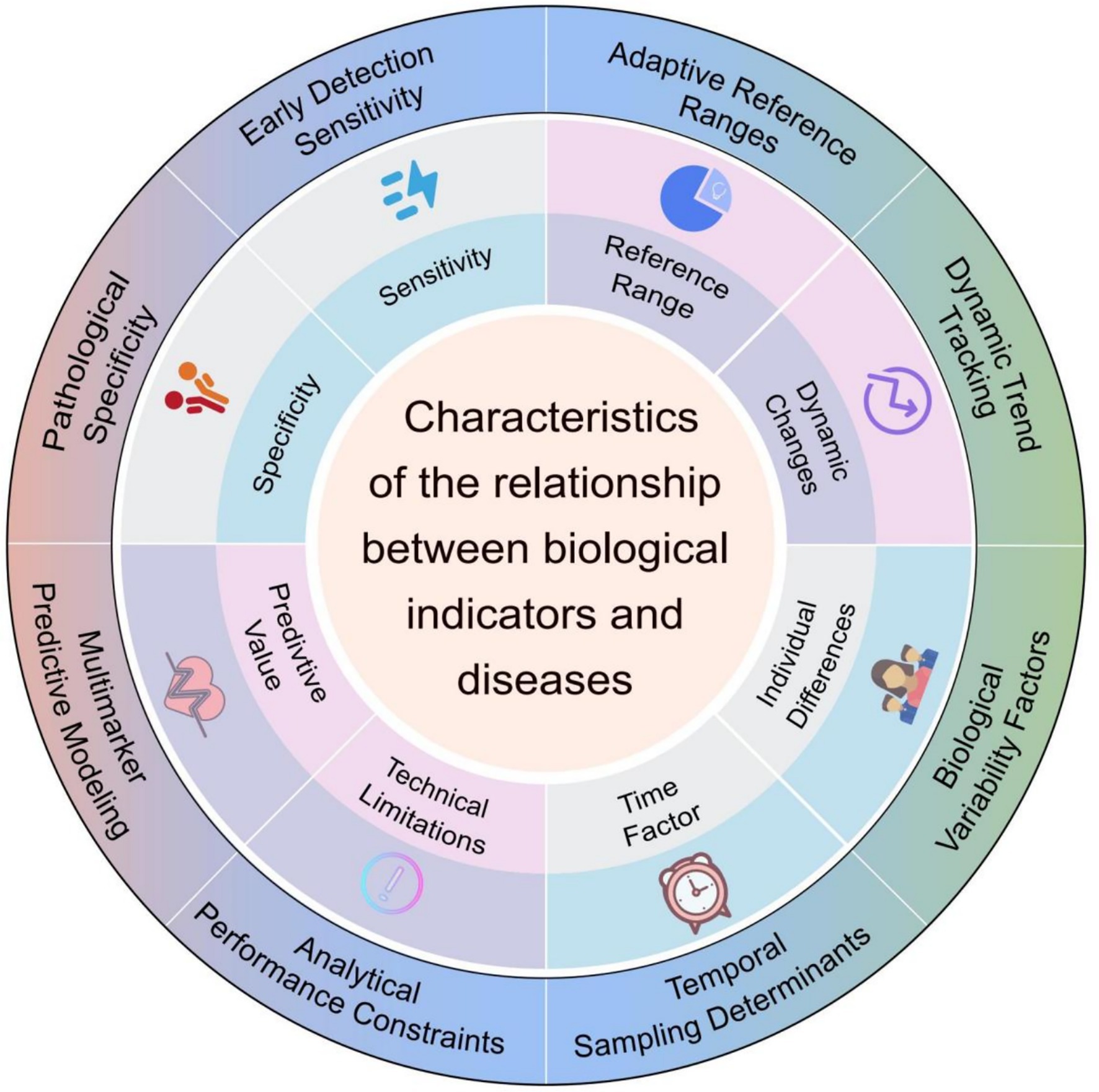
Figure 1. Characteristics influencing the relationship between biological indicators and diseases. The diagram outlines key factors such as sensitivity, specificity, adaptive reference ranges, dynamic changes, predictive value, technical limitations, and temporal or biological variability. These factors collectively shape the interpretive and diagnostic utility of biological indicators in disease contexts.
A systematic biomarker validation process encompasses discovery, validation, and clinical validation phases, ensuring research findings’ reliability and clinical applicability. Multi-omics integration methods serve a crucial role in this process, developing comprehensive molecular disease maps by combining genomics (5), transcriptomics (28), proteomics (29), and metabolomics data (30), thereby identifying complex marker combinations that traditional methods might overlook.
Temporal data holds distinct value in biomarker research. Through longitudinal cohort studies capturing markers’ dynamic changes over time, researchers obtain vital information about disease natural history. Studies demonstrate that marker trajectories generally provide more comprehensive predictive information than single time-point measurements (31).
2.3 Predictive model construction methods
Predictive model construction represents a crucial step in converting biomarker information into clinical decision-making tools. Model selection should consider data characteristics, prediction objectives, and application scenarios, aiming to a balance predictive accuracy, complexity, and interpretability (32).
Traditional statistical methods including logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models provide strong interpretability, quantifying each marker’s contribution and enhancing clinical understanding (33). However, these approaches show limitations in managing high-dimensional data and complex non-linear relationships.
Machine learning methods such as random forests, support vector machines, and gradient boosting trees effectively process high-dimensional data, identify non-linear relationships and variable interactions, particularly excelling in multi-omics data analysis (34). Studies indicate that gradient boosting tree-based models achieve superior accuracy in cardiovascular disease risk prediction compared to traditional risk scores (35).
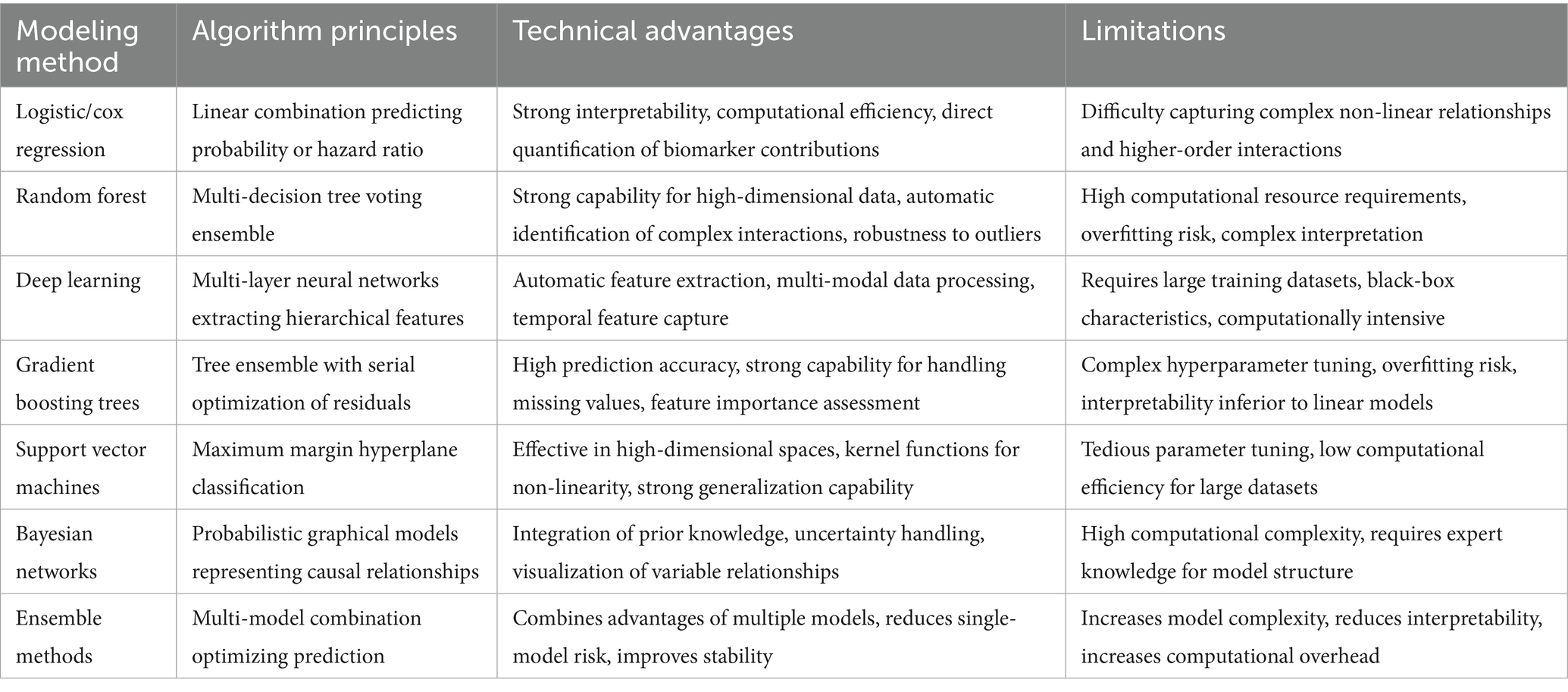
Deep learning shows significant potential in processing images, temporal data, and multimodal integration, though its “black box” nature restricts clinical interpretability (36). Model evaluation should thoroughly assess discriminatory power, calibration, and clinical utility, ensuring model generalizability through rigorous cross-validation and external validation. Table 2 presents a comparison of various predictive modeling methods’ advantages and limitations in processing biomarker data, offering guidance for selecting appropriate algorithms in specific health management contexts.
In summary, biomarker predictive models demonstrate substantial application value in early disease prevention, personalized diagnosis and treatment, and public health management, advancing medical practice from reactive response toward proactive prevention. The subsequent chapter explores these models’ specific value manifestations in proactive health applications. These methodological considerations necessitate the development of an integrated technical framework, as detailed in Section 4.
3 Prospects for proactive health applications
Biomarker-driven predictive models present extensive application prospects in proactive health management, with their core value manifesting in three key dimensions: early risk warning, personalized health management, and public health resource optimization. These applications are progressively evolving from theoretical possibilities to clinical practice, providing robust technical support for healthcare model transformation.
3.1 Early disease risk warning
Predictive models based on biomarkers can detect potential health risks before clinical symptoms manifest by identifying subtle changes at molecular and cellular levels. This early warning mechanism provides valuable intervention windows for chronic disease management and tumor intervention, altering the timing and effectiveness of disease interventions (37, 38).
Multiple prospective studies validate that biomarker warning systems effectively enhance disease management outcomes. For type 2 diabetes, predictive models incorporating glycemic control indicators (HbA1c), inflammatory markers (IL-6, TNF-α), and metabolomic features can identify high-risk individuals 5–7 years before clinical diagnosis (39, 40). This early identification enables implementation of lifestyle interventions before irreversible pancreatic β-cell damage occurs, effectively delaying or preventing disease progression. In the field of cardiovascular disease, genetic polymorphism analysis of TNF-α and IL-6 combined with assessment of inflammatory markers and metabolic variables can identify potential risk groups for cardiovascular events among patients with chronic heart failure (41, 42).
In neurodegenerative diseases, predictive models integrating blood biomarkers such as β-amyloid and tau proteins can identify high-risk populations for Alzheimer’s disease before significant cognitive decline (43, 44). This early identification provides critical opportunities for time-sensitive interventions, enhancing treatment success probability (45). Notably, this biomarker-based early warning system represents a paradigm shift from reactive to proactive medical practice.
3.2 Personalized health management
Personalized health management represents the core practice of the proactive health concept. Biomarker-based predictive models facilitate the transition from population-level averages to individual precision management by providing tailored risk assessments and intervention recommendations.
3.2.1 Precise prediction and intervention
Biomarker predictions based on individual genetic backgrounds and metabolic characteristics deliver more precise assessments of disease susceptibility. Machine learning methods enhance risk prediction accuracy by integrating multidimensional biomarkers with clinical data (46), particularly in specific subgroups such as diabetes patients and cancer survivors (47).
Digital twin technology facilitates the optimization of dynamic intervention strategies through real-time simulation of patient physiological data. Studies demonstrate that predictive models incorporating multiple dynamic biomarkers enable accurate patient risk stratification, establishing a more reliable foundation for clinical decision-making (48). The fundamental value of precision prediction lies in enabling targeted interventions, allowing medical resources to high-risk, patients while minimizing unnecessary medical interventions for low-risk populations (49).
3.2.2 Health risk stratification
Biomarker-driven risk stratification establishes the basis for implementing differentiated health management. In metabolic disease management, risk stratification systems utilizing multiple blood markers effectively identify subgroups with different complication risks, enabling targeted intervention strategies. These systems have demonstrated efficacy in identifying diabetes subtypes associated with elevated mortality risk, supporting evidence-based precision prevention and treatment (50, 51).
The combination of cardiac biomarkers (e.g., NT-proBNP, hs-cTnT) with polygenic risk scores enhances cardiovascular risk stratification (52). This enhanced risk stratification facilitates more efficient medical resource allocation while providing patients with clearer risk information, enabling their active participation in health decision-making processes (53, 54).
3.2.3 Dynamic monitoring and feedback
Periodic biomarker testing enables continuous health status monitoring. Regular assessment of marker trends facilitates early detection of abnormal changes and provides real-time feedback, supporting dynamic adjustment of intervention plans. Periodic biomarker testing enables continuous health status monitoring. Regular assessment of marker trends facilitates early detection of abnormal changes and provides real-time feedback, supporting dynamic adjustment of intervention plans. For example, wearable IoT biomarker sensors have been utilized for early disease diagnosis and continuous monitoring, significantly enhancing health management capabilities particularly in resource-limited regions (55). These devices achieve continuous sampling through microfluidic technology, providing technical support for individualized health tracking (55, 56).
Modern intelligent wearable devices incorporate continuous monitoring capabilities for multiple physiological parameters, establishing closed-loop health management systems (e.g., biofeedback-enabled wearables) when combined with specialized testing equipment. Research demonstrates that real-time heart rate monitoring through wearable devices has been implemented for stimulation decisions in closed-loop devices (57), while analysis of exercise-related electroencephalogram signals provides biomarker support for closed-loop neuroregulation (58). Such systems have significantly improved disease control outcomes, particularly in diabetes management, where closed-loop systems combining continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) with insulin pumps have achieved precise glycemic regulation (59, 60).
Dynamic monitoring enhances both disease management and long-term maintenance of healthy behaviors. Through real-time health data feedback, individuals can directly observe the immediate effects of lifestyle modifications on health indicators; for instance, biofeedback techniques in stress management can enhance positive behavioral reinforcement (61, 62). This “closed-loop” health management system embodies the fundamental concept of proactive health management-empowering individuals as active managers of their own health. The realization of personalized management ultimately depends on intelligent delivery systems that translate model outputs into actionable insights, as discussed in Section 4.4.
3.2.4 Public health resource optimization
At the population health level, biomarker-driven prediction systems enhance public health resource allocation efficiency. Analysis of population-level biomarker data enables disease trend prediction and high-risk community identification, facilitating precise resource allocation. As objective indicators for disease diagnosis, treatment response prediction, and personalized medicine, biomarkers reduce medical costs and improve population health outcomes through early detection (63). Their utility as early warning systems has been validated in medical practice, with notable increases disease risk assessment applications (64). In primary prevention contexts, biomarker-supported health monitoring systems effectively identify high-risk population distributions (65).
The cornerstone of public health resource optimization lies in achieving effective population-level risk stratification. Analysis of regional biomarker data, variations enable health decision-makers to identify area-specific health risk patterns and design targeted interventions. Studies confirm that adjusting resource allocation formulas based on biomarker variations enhances both equity and efficiency in health resource distribution (66). For instance, optimizing screening service distribution based on regional disease burden characteristics through small-area health data analysis has proven effective for resource allocation (67). In urological emergencies, rapid risk stratification of urosepsis in patients with urinary calculi through urinary biomarkers allows high-risk patients to receive priority access to intensive care resources while preventing overtreatment in medium and low-risk patients, thereby reducing emergency department length of stay and healthcare costs (68).
In public health emergencies, biomarker monitoring provides early warning indicators, supporting rapid response and resource deployment. During the COVID-19 pandemic, community wastewater SARS-CoV-2 monitoring emerged as an effective tool for predicting regional epidemic trends, assisting public health departments in optimizing testing and medical resource allocation (69). In dengue-endemic regions, early warning models constructed through mosquito-borne virus genomic surveillance combined with meteorological data enable the deployment of vector control resources and mobile medical units to high-risk communities before outbreak occurrence (70, 71).
Furthermore, correlation analysis between biomarkers and environmental factors provides scientific evidence for environmental health policy development. Environmental intervention effectiveness can be evaluated through monitoring environmental exposure markers in specific populations. This data-driven approach addresses health equity issues in resource allocation (72), particularly when exposure risks demonstrate significant geographical variations, biomarker data guides policymakers in prioritizing environmental governance (73).
The successful implementation of proactive health applications requires comprehensive technical support. The following chapter details the complete technical pathway from data acquisition, and biomarker screening to model construction and optimization, providing methodological guidance for practical application implementation.
4 Technical framework and methodological pathway
Realizing the application value of biomarker-driven predictive models in proactive health management requires a comprehensive technical framework and methodological pathway, encompassing data acquisition, analysis, processing, model construction, evaluation, and application. This chapter systematically examines each component of this technical framework and their interconnections, providing methodological guidance for practical applications.
4.1 Data acquisition and preprocessing
Data acquisition and preprocessing constitute fundamental elements of the technical framework, directly influencing the quality of subsequent analysis and model construction. The primary objective of this stage involves ensuring data completeness, consistency, and reliability, establishing a high-quality foundation for subsequent analyses.
4.1.1 Multi-source data integration
The integration of multi-source heterogeneous data is fundamental to developing comprehensive biomarker models. The establishment of unified data standards and interoperability frameworks facilitates seamless integration of clinical measurements, genomic information, and environmental factors (74). This integration process must address technical challenges including data format inconsistencies, terminology variations, and semantic compatibility issues (75).
Data source quality assessment and consistency verification are crucial in research practice to ensure integrated data reliability. This process involves implementing data quality scoring systems to evaluate different sources and adjust their analytical weights accordingly (76, 77). The integration process must maintain temporal consistency, ensuring proper alignment of data from various time points to support longitudinal analysis (78).
Ontology-based data integration methods serve as an effective approach, facilitating semantic mapping between diverse data sources by through shared conceptual frameworks (79). This methodology enables the creation of unified data views while maintaining original data characteristics, establishing structured foundations for subsequent analyses.
4.1.2 Data quality control and standardization
Rigorous data quality control serves as the cornerstone for ensuring model performance. Multi-level quality assurance mechanisms, incorporating automated anomaly detection and standardized preprocessing workflows, should be integrated into routine components of data processing (80). Quality control protocols must encompass anomaly identification and processing, missing value assessment and imputation, duplicate record detection, and additional measures to ensure data completeness and accuracy (81).
Standardization represents a critical step in processing multi-center and multi-source data. The variation in measurement units and reference ranges, across detection platforms and laboratories often renders direct data comparison impossible (82). Standardization techniques such as Z-score normalization or percentile transformation enable conversion of diverse data sources to a unified scale (83). For high-throughput omics data exhibiting significant, specialized batch effect correction methods such as ComBat are essential (84).
The implementation of standardized data governance frameworks enhances cross-institutional data comparability and consistency, thereby improving model stability. This encompasses the establishment of data dictionaries, standard operating procedures, and quality monitoring processes to maintain consistency in data collection and processing (84).
4.1.3 Privacy protection mechanisms
Clinical data processing requires adherence to strict privacy protection frameworks, that balance data utilization value with ethical requirements. Multi-level security architectures incorporate data source encryption and transmission endpoint encryption, providing continuous data protection throughout the process, exemplified by blockchain smart contract data integrity verification in multi-center medical alliances (85, 86). Attribute-based access control systems enable precise restrictions on user roles, identity characteristics, and specific operations, ensuring compliance and traceability through audit logs.
Contemporary security frameworks are designed to comply with the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requirements for sensitive medical information processing (87). Blockchain smart contracts enable regular data integrity verification, minimizing anomalies caused hardware failures, as validated on multi-center medical alliance platforms (84).
Balancing data usability with privacy protection a significant challenge. Advanced technologies including differential privacy and federated learning enable collaborative analysis and model training without raw data sharing (88, 89). These innovations create new opportunities for multi-center collaborative research while safeguarding patient privacy and data sovereignty.
The data acquisition and preprocessing phase establishes the foundation for subsequent biomarker screening and model development. High-quality, standardized, and secure data constitutes a prerequisite for achieving accurate predictions and effective clinical applications. The following section explores methods for screening and validating clinically valuable biomarkers from this data.
4.2 Biomarker screening and validation
Biomarker screening and validation is a key link connecting data and models, with the goal of identifying indicator combinations with clinical predictive value from massive data. This process requires combining statistical methods, machine learning techniques, and biological knowledge to ensure that the selected biomarkers have statistical significance, biological rationality, and clinical practicality.
4.2.1 Application of machine learning and statistical methods
The identification, of clinically valuable biomarkers from multi-omics data represents a central challenge in precision medicine. While traditional statistical methods offer robustness, they encounter limitations in processing high-dimensional data and non-linear relationships (90). Recent machine learning advances, particularly ensemble algorithms such as Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) and Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), have enhanced biomarker screening efficiency through automatic capture of non-linear interactions and hierarchical feature expressions (91, 92). Wrapper feature selection techniques utilizing genetic algorithms can evaluate multiple feature combinations to optimize model performance in supervised tasks such as cancer classification (93). These methodologies demonstrate superior capabilities in feature selection and pattern recognition compared to conventional approaches.
The integration of machine learning with statistical methods addresses the limitations of conventional approaches in identifying non-linear relationships. Evidence indicates that this combined approach enhances screening efficiency and accuracy while maintaining statistical rigor, generating novel insights for biomarker research (94). The practical implementation typically involves statistical methods for initial screening, followed by machine learning techniques for detailed analysis, and subsequent validation through biological knowledge assessment. Research demonstrates that these integrated approaches improve Area Under the Curve (AUC) values by 12–18% in survival prediction and disease classification compared to individual methods (95, 96).
Data preprocessing plays a vital role in ensuring reliable analysis and model performance. Box plots and interquartile range (IQR) methods effectively handle outliers, while missing data managed through Multiple Imputation by Chained Equations (MICE) maintains sample integrity (12, 90). For multi-center studies with batch effects, the ComBat normalization algorithm employs a Bayesian framework to address platform biases, enhancing cross-dataset biomarker comparability by over 30% (97).
The optimization of screening strategies necessitates a balance between statistical power and computational efficiency. For high-dimensional data analysis, two-stage screening approaches demonstrate superior effectiveness: initially employing rapid algorithms (e.g., LASSO regularization or random forest importance scoring) for preliminary screening (98), followed by comprehensive evaluations of candidate features, including statistical significance testing, stability analysis, and biological pathway enrichment analysis (99). This approach reduced model computation time by 58% in renal transplant cardiovascular risk prediction while maintaining 95% prediction accuracy (100). The integration of these computational approaches with biological context is particularly crucial in multi-omics research, where heterogeneous data layers demand unified analytical frameworks, as discussed below.
4.2.2 Multi-omics integration research design
Multi-omics research design facilitates comprehensive understanding of disease mechanisms. While single omics data (e.g., genomics) provides substantial information, it often fails to capture the complete complexity of diseases. The integration of multi-level biological information, including genotype, expression profiles, protein levels, and metabolites, enables the construction of more comprehensive molecular disease maps (101).
The combination of proteomics, metabolomics, and genomics data yields more comprehensive molecular characteristics. This integrated approach enables the identification of essential biomarkers and pathways that remain undetectable through single omics methods (102). Various integration strategies are applicable, including early integration (merging data at the feature level), intermediate integration (merging results at the model level), and late integration (merging predictions at the decision level).
Multi-omics integration presents technical challenges including data dimension imbalance, feature scale differences, and data completeness issues. Specialized integration algorithms, such as multi-view learning and tensor decomposition methods, effectively address these challenges by processing heterogeneous data sources and extract complementary information (103). During validation, careful consideration of the incremental value of integrated models compared to single omics models, ensures substantial improvements in predictive performance.
Multi-omics research design requires consideration of cost-effectiveness balance. Although comprehensive multi-omics analysis generates extensive information, clinical implementation remains costly and complex (104). Selecting optimal omics combinations with maximum incremental predictive value achieves optimal cost-effectiveness ratios for specific applications. For routine clinical applications, developing simplified models incorporating select high-value biomarkers based on previous research enhances clinical feasibility (105).
Systematic biomarker screening and validation enables the identification of clinically predictive indicator combinations, establishing a foundation for subsequent model construction. These validated biomarkers demonstrate both statistical predictive power and biological disease mechanisms, facilitating the translation from data to clinical insights.
4.3 Model development and optimization
Model development and optimization is the core component of the technical framework, transforming screened biomarkers into predictive tools for clinical decision-making. This stage requires selecting appropriate algorithms, optimizing model structure and parameters, validating model performance, and ensuring clinical applicability of the model.
4.3.1 Multifactor prediction model construction
In contemporary medical research, multifactor predictive models have largely superseded univariate analysis as primary tools for disease risk assessment. Biomarker screening provides fundamental support for model development (106), but comprehensive disease mechanism analysis requires integration of exogenous variables (e.g., environmental exposures and behavioral patterns). Model selection should align with data characteristics and research objectives: logistic regression offers high interpretability for quantifying biomarker-disease associations (107), while ensemble methods (e.g., random forests) provide robust performance in capturing complex nonlinear patterns (108).
Deep learning enhances high-dimensional heterogeneous data processing through multiple non-linear transformations to extract potential feature patterns (109). However, its inherent “black box” nature constrains clinical translation (110). The introduction of enhanced interpretability techniques (e.g., attention mechanisms and SHAP value frameworks) addresses this limitation, balancing predictive accuracy with model transparency (111). This technological integration establishes new pathways for clinical implementation of predictive models.
Hierarchical model building strategies demonstrate superior outcomes, by first assessing foundation models based on clinical and routine biochemical indicators, then evaluating the incremental predictive value of novel biomarkers (106). This methodology quantifies the contribution of new markers while ensuring models maintain clinical utility. For complex diseases, stratified modeling approaches, which develop specialized predictive models for distinct disease subtypes or risk levels, effectively enhance prediction accuracy.
4.3.2 Feature engineering
The predictive performance of multifactor models relies on the relevance and representativeness of selected features. As the foundation of model development, feature engineering significantly influences model accuracy and generalizability through the selection, transformation, and creation of variables to optimize attribute representation. Dimensionality reduction techniques (e.g., PCA, t-SNE) simplify complex biomarker data while preserving critical information (112).
In clinical applications, feature interpretability and stability are essential considerations, making feature combinations with clear biological significance preferable. Domain knowledge is instrumental in feature engineering, guiding the development of clinically meaningful derived features, such as establishing “intervention measures” and “orthotic device” related feature sets through medical expert knowledge (113), or developing dynamic indicators such as biomarker ratios and rates of change based on pathological progression mechanisms (114).
The synthesis of clinical experience and algorithmic feature selection optimally identifies variable combinations with biological significance. For instance, in cardiovascular risk prediction, combining 7 imaging features selected by LASSO regression with 4 clinical features achieved an AUC of 0.848 (115); while in sepsis prediction, incorporating hemodynamic fluctuation indicators with temporal trend features through random forest algorithms enhanced the model’s capacity to capture pathological dynamic changes (116). These dynamic features provide predictive information beyond traditional static indicators by reflecting longitudinal change patterns of biomarkers (e.g., cerebral blood volume fluctuations, metabolite time series fluctuations).
Feature engineering must address the feasibility of practical clinical applications. Optimal feature combinations should balance predictive performance, measurement cost, and operational complexity. Studies indicate that simplified models integrating routine examination indicators (e.g., prostate-specific antigen density) with radiomics features reduced feature dimensions from 107 to 8 while maintaining an AUC of 0.774 (117). In implementation, developing predictive models of varying complexity, from simplified versions with routine examination indicators to advanced versions incorporating multi-omics data, enables adaptation to different application scenarios and resource constraints.
4.3.3 Model validation and evaluation
Rigorous validation frameworks are essential for ensuring model reliability in real applications. Multi-level validation strategies, encompassing internal cross-validation, external independent cohort validation, and robustness testing for different populations, represent standard practices in modern model evaluation. Internal validation typically employs k-fold cross-validation (118) or bootstrapping to assess model stability on training data; external validation tests model generalizability in new populations or different clinical environments (119), a critical step in determining the model’s true value.
Comprehensive evaluation frameworks should incorporate multiple performance metrics to thoroughly assess the model’s predictive capability, stability, and clinical value. For classification tasks, beyond traditional AUC, sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value warrant examination; for prognosis prediction, calibration (consistency between predicted probabilities and actual event rates) and discriminative ability (e.g., C-index) require evaluation (120, 121). Decision Curve Analysis (DCA) has emerged as a vital tool for evaluating clinical value, quantifying net benefits at different decision thresholds (122).
Transparency and completeness in the validation process are crucial. In paper publications and clinical applications, validation methods, population characteristics, and all performance metrics require detailed reporting, enabling other researchers and clinical users to accurately assess the model’s applicable scope and limitations. Additionally, public sharing of model code and validation datasets promotes research transparency and reproducibility.
4.3.4 Clinical utility evaluation
The ultimate value of predictive models resides in their clinical utility. Tools such as decision curve analysis and clinical impact graphs quantify the net benefit of models at different decision thresholds. These methods evaluate the value of models in actual clinical scenarios, considering the relative costs of false positives and false negatives, providing a foundation for selecting decision thresholds (123).
Research demonstrates that integrating prediction results with existing clinical risk scores substantially increases physicians’ trust in model outputs (124). Developing decision support tools compatible with existing clinical workflows, enabling model predictions to integrate seamlessly into daily clinical practice, represents an effective strategy for improving clinical acceptance (125). Model outputs should be presented in intuitive and comprehensible forms, such as risk classifications, risk percentiles, or comparisons with reference populations, enabling informed decision-making by clinicians and patients.
Clinical utility evaluation should consider implementation costs and operational complexity. High-performance but complex and expensive models may face limitations in practical applications (126), necessitating balance between so performance and feasibility during model development. Early consideration of model clinical pathway integration strategies ensures effective translation of technological innovation into clinical value.
4.3.5 Iterative model optimization
Prediction model development is an iterative process necessitating continuous refinement based on evolving clinical needs, emerging data, and performance feedback from real-world deployment. Optimization cycles involve re-evaluating model architecture, retraining with updated datasets, adjusting hyperparameters, and incorporating novel biomarkers or features to enhance predictive accuracy, stability, and clinical utility over time (127, 128). Moreover, establishing mechanisms for regular model performance monitoring, feedback collection from end-users (clinicians, patients), and scheduled re-validation is critical, particularly as clinical practices evolve or population characteristics shift. This ongoing process ensures the model remains relevant, reliable, and effective in supporting clinical decision-making within the dynamic healthcare environment.
Following model development and optimization, the critical next phase involves effectively delivering prediction results to end users to realize their clinical value.
4.4 Model prediction results delivery
The effectiveness of model predictions ultimately depends on how results are communicated and used. Prediction results delivery is the key link in transforming model outputs into actionable information, requiring consideration of user needs, information presentation methods, and decision support functions.
4.4.1 Intelligent delivery system construction
Intelligent results delivery systems should adapt information display methods according to specific user roles and clinical contexts. For clinicians, the system provides comprehensive risk assessment results, including key risk factors, recommended interventions, and expected outcomes (129); for patients, it delivers accessible risk information and personalized health recommendations (130); for health management organizations, it generates population-level risk analysis reports to support resource allocation decisions (131).
Delivery mechanisms incorporating decision support functions and interpretability tools enhance clinical acceptance. These include providing evidence links, explaining primary predictive factors, comparing potential outcomes of different intervention strategies, and offering personalized recommendations based on historical decision patterns (132–134). Results delivery should integrate risk explanation with actionable intervention recommendations to maximize clinical utility.
From a technical perspective, delivery systems should facilitate multi-platform integration and real-time updates. Contemporary delivery architectures typically encompass web applications, mobile applications, and electronic health record system integration, ensuring accessibility across various environments (135). Moreover, systems should incorporate configurable alert mechanisms that automatically generate notifications based on predicted risk levels and time sensitivity, enabling timely intervention for high-risk cases (136).
Through a comprehensive technical framework and methodological pathway, biomarker-driven predictive models establish a closed loop from data acquisition and analysis to clinical application, achieving proactive health management objectives (Figure 2). This integrated framework illustrates how the systematic processing of biomarker data through standardized analytical pathways enables transition from reactive medical interventions to proactive health monitoring and personalized risk assessment, representing a paradigm shift in clinical practice methodology. Nevertheless, this process faces multiple challenges requiring systematic response strategies, which the next chapter examines in detail.
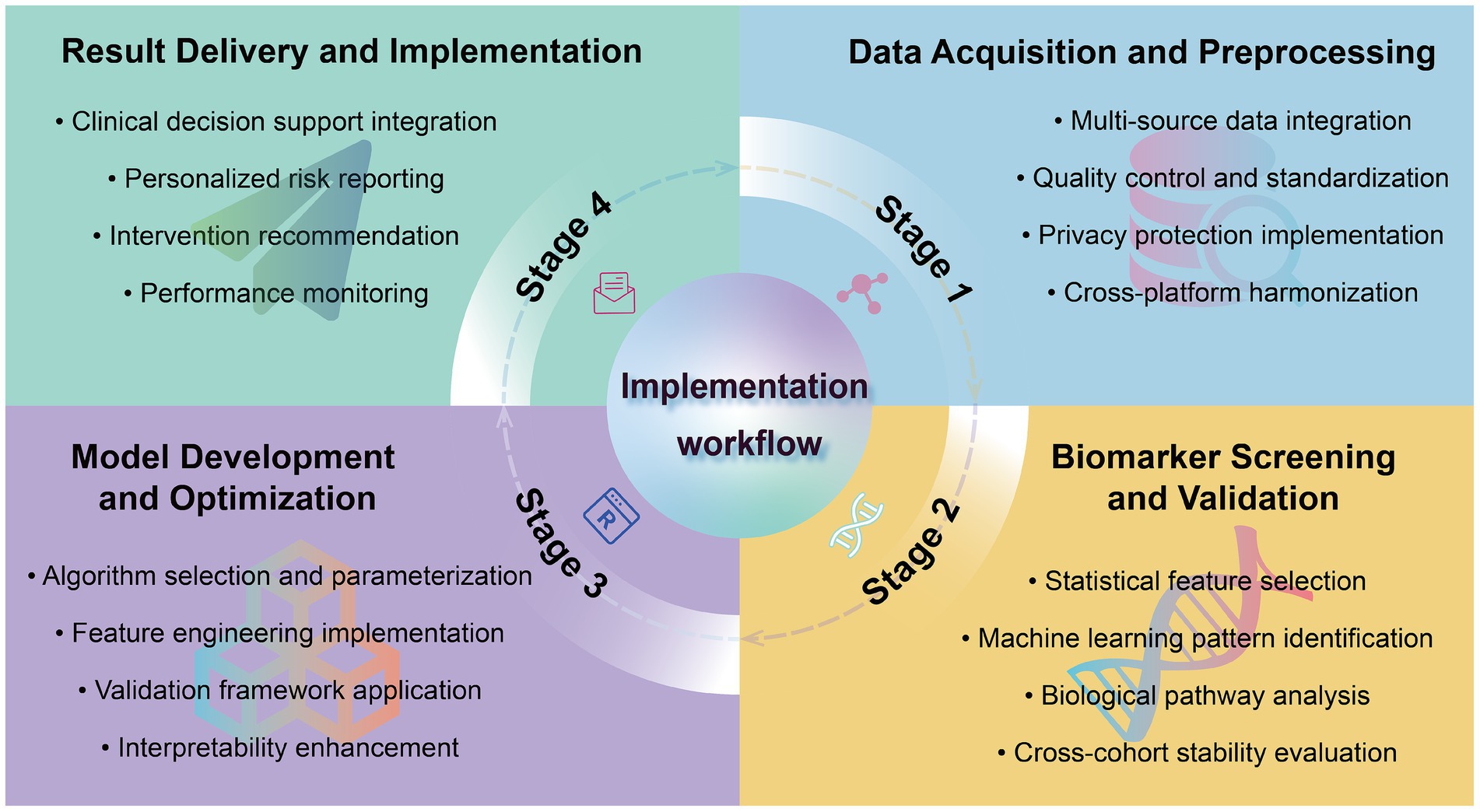
Figure 2. A data-driven framework for health management: from biomarker discovery to personalized health implementation. The diagram depicts the cyclical process of: (I) Data Acquisition and Preprocessing (show in blue); (II) Biomarker Screening and Validation(show in yellow); (III) Model Development and Optimization(show in purple); (IV) Result Delivery and Implementation(show in green). Each stage contains essential components for translating biomarker discovery into clinical application, with implementation workflow at the center.
5 Data quality and standardization challenges
The challenges facing biomarker-based predictive models span the entire pipeline from data to clinical implementation: data quality and standardization issues constitute fundamental barriers at the foundational level; limited model generalizability restricts the broad applicability of these technologies; difficulties in clinical translation of biomarkers impede the transformation of research findings into clinical practice; while public acceptance and resource constraints affect the ultimate implementation effectiveness. These challenges form a multi-layered problem system from technical to social dimensions, requiring systematic solutions.
5.1 Data quality and standardization
Challenges: Clinical test data originates from multiple sources, lacking standardized collection and storage protocols (137). Variations in testing equipment parameters and operational standards create systematic biases in cross-institutional indicators (138). Manual input errors and heterogeneous system compatibility issues may compromise data integrity, affecting the reliability and comparability of subsequent analyses (139). This data heterogeneity constrains predictive model optimization, creating structural barriers to multi-scenario applicability (140).
Solutions: Implement quality control systems and standardize data governance from the source, conducting regular equipment calibration and enhancing operator training. In data processing, establish traceable cleaning mechanisms and standardized outlier handling protocols (141). Systematically standardize the entire data lifecycle management process according to international clinical laboratory quality management systems (142). This includes establishing unified data collection and coding standards, implementing standardized medical terminology systems (e.g., SNOMED CT or LOINC) (140), and deploying automated data quality monitoring processes.
These measures will enhance data quality, establish a robust foundation for model construction, and strengthen prediction system reliability (143). Meanwhile, developing multi-center data collaboration networks and sharing standardized data collection and processing methods can accelerate high-quality health data accumulation (144), providing adequate training samples for accurate predictive models.
Additionally, we recommend developing intelligent data cleaning and standardization tools for automatic identification and processing of common data issues, including outlier detection, unit conversion, and missing value handling. These tools should be adaptable to accommodate the requirements of various medical environments and data types, while maintaining comprehensive records of the processing, to ensure transparency and traceability of data processing (145).
5.2 Model generalizability
Challenges: Current predictive models frequently experience performance degradation in “laboratory-to-clinical” scenarios, primarily due to limitations in training data regarding geographic, age, and racial diversity (146). This insufficient data representativeness impedes the model’s capacity to capture complex population differences, reducing its adaptability in clinical healthcare (147). Models demonstrate performance deterioration in real-world clinical practice implementation; this “laboratory-to-reality” performance gap represents a major obstacle to the implementation of precision medicine (128, 148).
Solutions: Enhancement of model generalizability necessitates constructing training datasets with greater ecological validity. Multi-center collaborative collection of health data encompassing geographic/demographic/environmental variations can strengthen model generalization capabilities through the integration of diverse feature sets (146). In model design, we recommend adopting domain adaptation and transfer learning techniques to enable models to better adapt to feature distributions in new populations. Incremental learning strategies facilitate model updates with new data without complete retraining (149), which is essential for dynamically adapting to changes in clinical environments.
In model validation, we recommend combining independent cohort validation with real-world data testing. Robustness testing that considers dynamic environmental factors and individual differences effectively identifies models with clinical utility (150, 151). This multidimensional validation system provides a scientific basis for model deployment, while identifying the model’s applicable scope and limitations, offering clear guidance for clinical use.
Furthermore, we advocate developing integrated and adaptive model architectures capable of automatically adjusting prediction strategies based on different population characteristics. For instance, utilizing meta-learning frameworks to build models that rapidly adapt to new populations, or adopting stratified model strategies to train specialized models for different population subgroups and then integrating results through ensemble methods. This approach better adapts to population heterogeneity while maintaining overall prediction accuracy (152).
5.3 Difficulty of clinical translation of biomarkers
Challenges: A substantial gap exists between basic biomarker research and clinical applications, with detection performance variability and disease heterogeneity serving as key bottlenecks (153). Although high-throughput detection enhances sensitivity, its high cost and complex operations restrict widespread use (154). Moreover, clinical validation requires large-scale, prospective longitudinal cohorts (155), further decelerating the translation process. Clinical application of novel biomarkers faces extended processes of regulatory approval (156) and inclusion in clinical guidelines (157), impeding the timely delivery of innovative results to patients.
Solutions: Addressing this challenge requires establishing “basic-clinical” feedback mechanisms. Systematic evaluation of marker predictive performance in various clinical scenarios through multi-center trials and establishment of automated testing platforms balances accuracy and cost. This evaluation should follow unified methodological standards and reporting guidelines (158), ensuring result comparability and reliability.
Formulating standardized clinical guidelines and dynamic evaluation systems is essential for biomarker standardization. We recommend establishing biomarker evaluation alliances (157), integrating resources from academic institutions, medical centers, and industry (158) accelerates the validation and translation of high-value markers. Meanwhile, developing simplified testing technologies and point-of-care devices reduces the cost and complexity of high-value biomarker detection, enhancing suitability for routine clinical applications.
We believe that constructing a complete translation pipeline from discovery to application, including early clinical validation, commercialization pathway planning, and regulatory strategy formulation (159), can expedite the clinical translation of biomarkers. This process, close collaboration between academia and industry for efficient transformation of scientific discoveries into clinical testing products. Establishing biomarker research and development sharing platforms promotes open sharing of data, methods, and resources helping avoid duplication and accelerate innovation.
5.4 Public acceptance of artificial intelligence and big data
Challenges: While technological safeguards (Section 4.1.3) address data security, public acceptance requires additional sociotechnical considerations, including algorithmic transparency and ethical governance. Advanced medical AI applications raise concerns regarding algorithmic interpretability and privacy security. Limited trust in prediction results among healthcare providers and patients stems from insufficient technological transparency and risk communication (160). Vulnerabilities in health data lifecycle management, particularly leakage risks, intensify public skepticism and concern (161). Inadequate consent mechanisms in data collection processes and concerns about health data usage impede public acceptance of AI-based health solutions (162).
Solutions: Establishing technological trust requires multidimensional public engagement. Creating open technology exchange platforms to explain AI decision logic and uncertainty enhances prediction result transparency for healthcare providers and patients. This includes developing visualization tools to display key predictive factors and uncertainties, and providing user-friendly explanation systems that translate complex model decisions into comprehensible language (163).
For data security, we recommend technologies such as differential privacy and federated learning, and implementing layered authorization and traceability mechanisms. These technologies enable model training and prediction while protecting data privacy, minimizing data sharing (164). Establishing robust data governance frameworks, including clear data usage policies, transparent consent processes, and comprehensive security measures, forms the foundation for building public trust.
We propose that comprehensive technological ethics governance frameworks can enhance public acceptance as a positive catalyst for implementation. This involves establishing multidisciplinary ethics committees to oversee the development and deployment of AI systems, ensuring technological innovation prioritizes patient welfare (160). Conducting systematic public education and engagement initiatives to explain the capabilities and limitations of AI in healthcare helps foster public understanding and acceptance of these emerging technologies.
Additionally, implementing clear responsibility and accountability mechanisms at the policy level clarifies the obligations of various stakeholders in data use and AI deployment. Well-defined regulatory frameworks protect patient rights while providing clear guidance for technological innovation, fostering sustainable industry development (165).
5.5 Resource and cost issues
Challenges: Developing high-performance predictive models requires integrating expertise from medicine, computer science, and biology, but the scarcity of interdisciplinary professionals presents a major constraint (166). Model development requires terabyte-scale data storage and high-performance computing, creating substantial hardware demands, while ongoing R&D investment strains small and medium-sized organizations (167, 168). In the large-scale clinical implementation, costs of iterative device upgrades and network infrastructure maintenance seriously impact resource allocation (169). These resource constraints affect both technological development and deployment in resource-limited settings (170).
Solutions: Developing comprehensive talent cultivation systems and industry-academia-research collaboration mechanisms is essential for addressing resource limitations. Higher education institutions can nurture multidisciplinary professionals with both clinical expertise and algorithm development capabilities through interdisciplinary laboratories (166). Meanwhile, implementing data science training programs for practicing healthcare professionals enhances the technical capabilities of existing medical teams effectively addressing immediate talent shortages (171).
Establishing data resource sharing and technology collaboration platforms between healthcare institutions, research institutes, and enterprises can minimize translation costs. Such partnerships can leverage the distinctive resources of different institutions, prevent redundant investments, and expedite the translation of innovations. For example, healthcare institutions provide clinical data and application scenarios, research institutions contribute algorithms and analytical methods, and enterprises deliver technological implementation and productization support, creating a synergistic research ecosystem (170, 172).
Developing intelligent medical technology training programs for practicing personnel can enhance the technological integration capabilities of existing teams, facilitating predictive model adoption. This includes developing modular and customizable learning resources, enabling healthcare professionals to learn according to their needs and schedules (173). Meanwhile, developing “technical assistant” systems to support clinicians using complex prediction tools effectively reduces technological usage barriers (174).
For resource optimization, we recommend implementing architectures that combine cloud computing and edge computing to balance performance and cost. Cloud computing offers flexible computational resources that adjust dynamically to demands, avoiding substantial fixed asset investments (175); edge computing processes certain data and computational tasks locally, reducing network bandwidth requirements and latency (167). For resource-constrained environments, developing efficient algorithms and model compression techniques enables prediction systems to operate effectively on standard hardware.
Through systematic approaches to these challenges, biomarker-based predictive models can overcome current development constraints and more effectively support proactive health management objectives. Table 3 summarizes the primary challenges facing biomarker predictive models and their solutions, highlighting the multifaceted efforts required to advance technology from laboratory to clinical application. This structured framework illustrates why successful implementation requires coordinated efforts across technical, clinical, and social domains to deliver the potential benefits of predictive models in real-world healthcare settings. The next chapter summarize the main findings and contributions of this research and look toward future development directions.
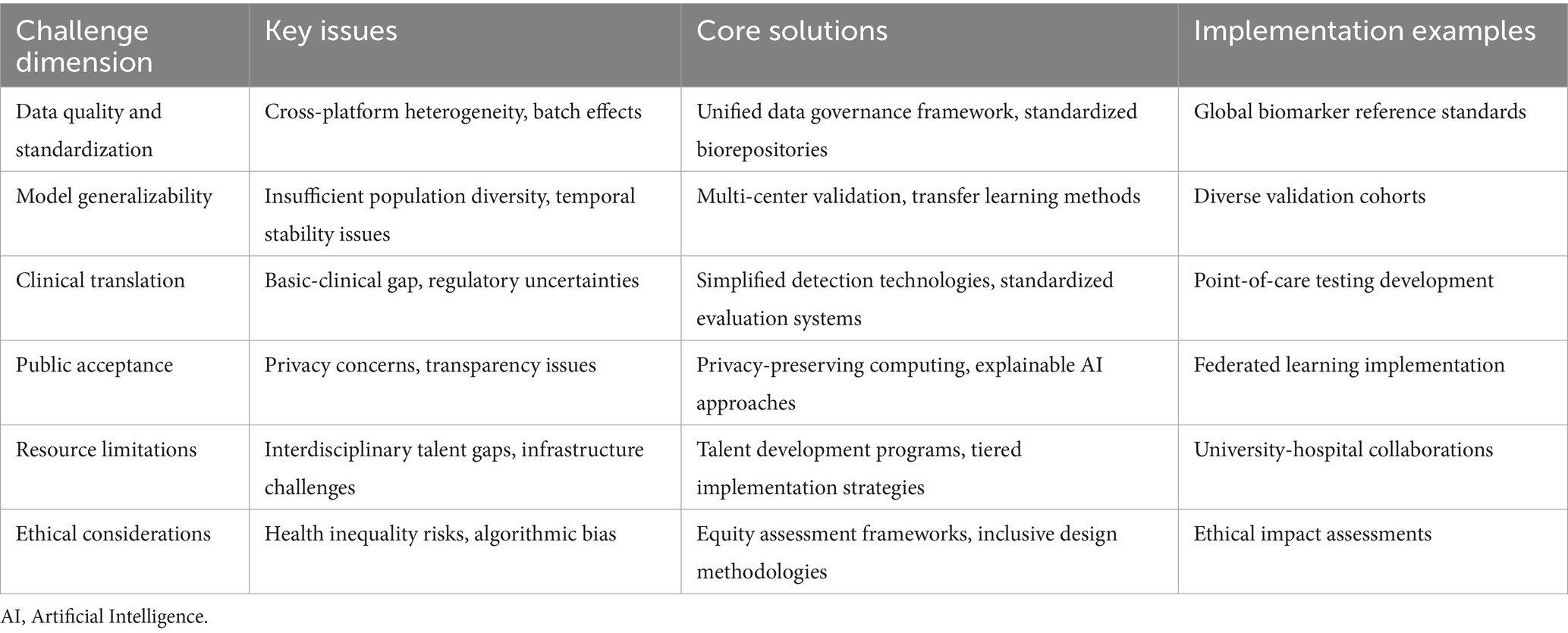
Table 3. Challenges and solution strategies for clinical translation of biomarker predictive models.
6 Conclusion and outlook
6.1 Application prospects and remaining challenges
Biomarker-based predictive models advance proactive health management by integrating biomarker data with computational technologies. These models demonstrate potential in: (1) Early disease detection at pre-clinical stages; (2) Dynamic health monitoring with real-time assessment; (3) Evidence-based healthcare resource optimization.
However, challenges persist: data heterogeneity, limited model generalizability, high costs, and public trust concerns. Technological advancements including federated learning, differential privacy techniques, simplified testing technologies, and improved model explanation tools will progressively address these barriers.
6.2 Research contributions and innovation value
This review’s contributions include: (1) Establishing a comprehensive framework connecting biomarker discovery with clinical application; (2) Presenting viable solutions for key implementation challenges through data governance frameworks and validation strategies; (3) Investigating the interplay between technological advancement and ethical considerations; (4) Expanding biomarker-driven frameworks to public health decision-making.
6.3 Future research directions
Future research should prioritize: expanding to rare disease markers and dynamic health indicators; deepening multi-omics integration through systematic analysis of genomic, epigenomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data; conducting longitudinal studies covering the entire life cycle; developing edge computing and lightweight algorithms for resource-constrained environments; and strengthening cross-collaboration between medicine, computer science, and social sciences.
6.4 Summary and vision
This review establishes a multidisciplinary framework for advancing biomarker-driven predictive models in proactive health management, addressing critical barriers in data standardization, model interpretability, and clinical implementation.
Biomarker-based predictive models represent a paradigm shift from reactive medicine to proactive prevention. Through integration of multidimensional biomarker data with advanced computational methodologies, these systems enable early disease detection, risk stratification, and personalized interventions—foundational elements for evidence-based health management. The technical framework proposed herein provides structured guidance for real-world healthcare applications.
This prevention-centered paradigm represents a viable approach for enhancing population health outcomes. As technological innovation advances and interdisciplinary collaboration strengthens, biomarker-driven predictive models will assume increasingly significant roles in health management, contributing substantially to disease prevention initiatives. This transition requires technological advancement alongside appropriate regulatory frameworks, ethical considerations, and societal engagement across medical, technological, and societal domains.
Author contributions
QZ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Writing – original draft. CZ: Writing – review & editing, Visualization. WZ: Writing – review & editing. SZ: Writing – review & editing. QL: Writing – review & editing. YG: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 82060618), the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province (20203BBGL73184), and Doctoral Fund of First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University.
Acknowledgments
The authors express gratitude to all participants who contributed to this review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AI, Artificial intelligence; AUC, Area under the curve; DNN, Deep neural network; GDPR, General data protection regulation; IQR, Interquartile range; LASSO, Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; MICE, Multiple imputation by chained equations; PCA, Principal component analysis; R&D, Research and development; SHAP, SHapley Additive exPlanations; t-SNE, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding; XGBoost, Extreme gradient boosting.
References
1. Strandberg, R, Jepsen, P, and Hagström, H. Developing and validating clinical prediction models in hepatology - an overview for clinicians. J Hepatol. (2024) 81:149–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.03.030
2. Carrasco-Zanini, J, Pietzner, M, Davitte, J, Surendran, P, Croteau-Chonka, DC, Robins, C, et al. Proteomic signatures improve risk prediction for common and rare diseases. Nat Med. (2024) 30:2489–98. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03142-z
3. Osipov, A, Nikolic, O, Gertych, A, Parker, S, Hendifar, A, Singh, P, et al. The molecular twin artificial-intelligence platform integrates multi-omic data to predict outcomes for pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients. Nat Cancer. (2024) 5:299–314. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00697-7
4. Rhodes, CJ, Sweatt, AJ, and Maron, BA. Harnessing big data to advance treatment and understanding of pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. (2022) 130:1423–44. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319969
5. Ioannou, A, Berkhout, MD, Geerlings, SY, and Belzer, C. Akkermansia muciniphila: biology, microbial ecology, host interactions and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2025) 23:162–77. doi: 10.1038/s41579-024-01106-1
6. Menendez-Gonzalez, M. Implementing a tridimensional diagnostic framework for personalized medicine in neurodegenerative diseases. Alzheimers Dement. (2025) 21:e14591. doi: 10.1002/alz.14591
7. Wu, H, Liu, Q, Li, J, Leng, X, He, Y, Liu, Y, et al. Tumor-resident microbiota-based risk model predicts Neoadjuvant therapy response of locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2024) 11:e2309742. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309742
8. Kong, J, Ha, D, Lee, J, Kim, I, Park, M, Im, S-H, et al. Network-based machine learning approach to predict immunotherapy response in cancer patients. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:3703. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31535-6
9. Ning, J, Spielvogel, CP, Haberl, D, Trachtova, K, Stoiber, S, Rasul, S, et al. A novel assessment of whole-Mount Gleason grading in prostate cancer to identify candidates for radical prostatectomy: a machine learning-based multiomics study. Theranostics. (2024) 14:4570–81. doi: 10.7150/thno.96921
10. Moingeon, P. Artificial intelligence-driven drug development against autoimmune diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2023) 44:411–24. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2023.04.005
11. Zheng, H, Petrella, JR, Doraiswamy, PM, Lin, G, and Hao, WAlzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Data-driven causal model discovery and personalized prediction in Alzheimer’s disease. NPJ Digit Med. (2022) 5:137. doi: 10.1038/s41746-022-00632-7
12. Hédou, J, Marić, I, Bellan, G, Einhaus, J, Gaudillière, DK, Ladant, F-X, et al. Discovery of sparse, reliable omic biomarkers with stabl. Nat Biotechnol. (2024) 42:1581–93. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-02033-x
13. Tayal, U, Verdonschot, JAJ, Hazebroek, MR, Howard, J, Gregson, J, Newsome, S, et al. Precision phenotyping of dilated cardiomyopathy using multidimensional data. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 79:2219–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.03.375
14. Zhou, Z, Jin, D, He, J, Zhou, S, Wu, J, Wang, S, et al. Digital health platform for improving the effect of the active health Management of Chronic Diseases in the community: mixed methods exploratory study. J Med Internet Res. (2024) 26:e50959. doi: 10.2196/50959
15. Steiger, C, Phan, NV, Huang, H-W, Sun, H, Chu, JN, Reker, D, et al. Dynamic monitoring of systemic biomarkers with gastric sensors. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2021) 8:e2102861. doi: 10.1002/advs.202102861
16. Walsh, CG, Johnson, KB, Ripperger, M, Sperry, S, Harris, J, Clark, N, et al. Prospective validation of an electronic health record-based, real-time suicide risk model. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4:e211428. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1428
17. Rozenblatt-Rosen, O, Regev, A, Oberdoerffer, P, Nawy, T, Hupalowska, A, Rood, JE, et al. The human tumor atlas network: charting tumor transitions across space and time at single-cell resolution. Cell. (2020) 181:236–49. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.053
18. Zhang, Y, Yang, H, Yu, Y, and Zhang, Y. Application of nanomaterials in proteomics-driven precision medicine. Theranostics. (2022) 12:2674–86. doi: 10.7150/thno.64325
19. Bai, B, Vanderwall, D, Li, Y, Wang, X, Poudel, S, Wang, H, et al. Proteomic landscape of Alzheimer’s disease: novel insights into pathogenesis and biomarker discovery. Mol Neurodegener. (2021) 16:55. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00474-z
20. Wang, H, Dey, KK, Chen, P-C, Li, Y, Niu, M, Cho, J-H, et al. Integrated analysis of ultra-deep proteomes in cortex, cerebrospinal fluid and serum reveals a mitochondrial signature in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. (2020) 15:43. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00384-6
21. Zhang, C, Li, T, Zhao, Q, Ma, R, Hong, Z, Huang, X, et al. Advances and prospects in liquid biopsy techniques for malignant tumor diagnosis and surveillance. Small. (2024) 20:e2404709. doi: 10.1002/smll.202404709
22. Daniore, P, Nittas, V, Haag, C, Bernard, J, Gonzenbach, R, and von Wyl, V. From wearable sensor data to digital biomarker development: ten lessons learned and a framework proposal. NPJ Digit Med. (2024) 7:161. doi: 10.1038/s41746-024-01151-3
23. Zhou, Y, Tao, L, Qiu, J, Xu, J, Yang, X, Zhang, Y, et al. Tumor biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:132. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01823-2
24. Zech, M, and Winkelmann, J. Next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics in rare movement disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. (2024) 20:114–26. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00909-9
25. Ozen, S, and Aksentijevich, I. The past 25 years in paediatric rheumatology: insights from monogenic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2024) 20:585–93. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01145-1
26. D’Alessandro, MCB, Kanaan, S, Geller, M, Praticò, D, and Daher, JPL. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev. (2025) 107:102713. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102713
27. Mataraso, SJ, Espinosa, CA, Seong, D, Reincke, SM, Berson, E, Reiss, JD, et al. A machine learning approach to leveraging electronic health records for enhanced omics analysis. Nat Mach Intell. (2025) 7:293–306. doi: 10.1038/s42256-024-00974-9
28. Macias, RIR, Cardinale, V, Kendall, TJ, Avila, MA, Guido, M, Coulouarn, C, et al. Clinical relevance of biomarkers in cholangiocarcinoma: critical revision and future directions. Gut. (2022) 71:gutjnl-2022-327099–1683. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327099
29. Yu, P, Bosholm, CC, Zhu, H, Duan, Z, Atala, A, and Zhang, Y. Beyond waste: understanding urine’s potential in precision medicine. Trends Biotechnol. (2024) 42:953–69. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2024.01.009
30. Simpson, KL, Rothwell, DG, Blackhall, F, and Dive, C. Challenges of small cell lung cancer heterogeneity and phenotypic plasticity. Nat Rev Cancer. (2025) 25:447–62. doi: 10.1038/s41568-025-00803-0
31. Baalbaki, N, Slob, EMA, Kazer, SW, Abdel-Aziz, I, Bogaard, HJ, Golebski, K, et al. The omics landscape of Long COVID-A comprehensive systematic review to advance biomarker, target and drug discovery. Allergy. (2025) 80:932–48. doi: 10.1111/all.16526
32. Saravi, B, Zink, A, Ülkümen, S, Couillard-Despres, S, Wollborn, J, Lang, G, et al. Clinical and radiomics feature-based outcome analysis in lumbar disc herniation surgery. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2023) 24:791. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06911-y
33. Zhang, X, Lin, Z, and Gu, S. A machine learning model the prediction of athlete engagement based on cohesion, passion and mental toughness. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:3220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87794-y
34. Lohmann, A, Groenwold, RHH, and van Smeden, M. Comparison of likelihood penalization and variance decomposition approaches for clinical prediction models: a simulation study. Biom J. (2024) 66:e2200108. doi: 10.1002/bimj.202200108
35. Liu, L, Lin, J, Liu, L, Gao, J, Xu, G, Yin, M, et al. Automated machine learning models for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease assessed by controlled attenuation parameter from the NHANES 2017-2020. Digit Health. (2024) 10:20552076241272535. doi: 10.1177/20552076241272535
36. Hauber, AL, Rosenblatt, M, and Timmer, J. Uncovering specific mechanisms across cell types in dynamical models. PLoS Comput Biol. (2023) 19:e1010867. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010867
37. Koyappayil, A, Yagati, AK, and Lee, M-H. Recent trends in metal nanoparticles decorated 2D materials for electrochemical biomarker detection. Biosensors (Basel). (2023) 13:91. doi: 10.3390/bios13010091
38. Caicedo, A, Benavides-Almeida, A, Haro-Vinueza, A, Peña-Cisneros, J, Pérez-Meza, ÁA, Michelson, J, et al. Decoding the nature and complexity of extracellular mtDNA: types and implications for health and disease. Mitochondrion. (2024) 75:101848. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2024.101848
39. Dhamija, R, Tewari, S, Gill, PS, Monga, N, Mittal, S, and Duhan, J. Association of Apical Periodontitis with glycated hemoglobin levels and systemic inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. J Endodont. (2025) 51:124–31. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2024.11.008
40. Kolte, RA, Kolte, AP, Bawankar, PV, and Bajaj, VA. Effect of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on metabolic control and systemic inflammatory markers in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus with stage III periodontitis. Contemp Clin Dent. (2023) 14:45–51. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_514_21
41. Sveklina, TS, Shustov, SB, Kolyubaeva, SN, Kuchmin, AN, Kozlov, VA, Oktysyuk, PD, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure with preserved ejection faction. Kardiologiia. (2024) 64:40–7. doi: 10.18087/cardio.2024.7.n2562
42. Molina-Flores, CA, Pinales-Rangel, JG, Santuario-Facio, SK, Urraza-Robledo, AI, Gutiérrez-Pérez, ME, Miranda-Pérez, AA, et al. Role of Proinflammatory cytokines and genetic factors related to metabolic alterations in people living with HIV/AIDS. J Interf Cytokine Res. (2024) 44:453–60. doi: 10.1089/jir.2024.0052
43. Sun, Q, Ni, J, Wei, M, Long, S, Li, T, Fan, D, et al. Plasma β-amyloid, tau, neurodegeneration biomarkers and inflammatory factors of probable Alzheimer’s disease dementia in Chinese individuals. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:963845. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.963845
44. Hansen, N, Juhl, AL, Grenzer, IM, Teegen, B, Wiltfang, J, and Fitzner, D. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in psychiatric autoimmune encephalitis: a retrospective cohort study. Front Psych. (2023) 14:1165153. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1165153
45. Faldu, KG, and Shah, JS. Ambroxol improves Amyloidogenic, NF-κB, and Nrf2 pathways in a scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Dev Res. (2024) 85:e70017. doi: 10.1002/ddr.70017
46. Chen, H, Zhang, J, Chen, X, Luo, L, Dong, W, Wang, Y, et al. Development and validation of machine learning models for MASLD: based on multiple potential screening indicators. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1449064. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1449064
47. Garg, M, Karpinski, M, Matelska, D, Middleton, L, Burren, OS, Hu, F, et al. Disease prediction with multi-omics and biomarkers empowers case-control genetic discoveries in the UK biobank. Nat Genet. (2024) 56:1821–31. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01898-1
48. Tunedal, K, Ebbers, T, and Cedersund, G. Uncertainty in cardiovascular digital twins despite non-normal errors in 4D flow MRI: identifying reliable biomarkers such as ventricular relaxation rate. Comput Biol Med. (2025) 188:109878. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.109878
49. Chowdhury, MA, Rizk, R, Chiu, C, Zhang, JJ, Scholl, JL, Bosch, TJ, et al. The heart of transformation: exploring artificial intelligence in cardiovascular disease. Biomedicine. (2025) 13:427. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020427
50. Chung, R-H, Chuang, S-Y, Zhuang, Y-S, Jhang, Y-S, Huang, T-H, Li, G-H, et al. Evaluating polygenic risk scores for predicting cardiometabolic traits and disease risks in the Taiwan biobank. HGG Adv. (2024) 5:100260. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2023.100260
51. Zeljkovic, A, Mihajlovic, M, Vujcic, S, Guzonjic, A, Munjas, J, Stefanovic, A, et al. The Prospect of genomic, transcriptomic, epigenetic and Metabolomic biomarkers for the personalized prevention of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. (2023) 21:185–96. doi: 10.2174/1570161121666230510141338
52. Schunkert, H, Di Angelantonio, E, Inouye, M, Patel, RS, Ripatti, S, Widen, E, et al. Clinical utility and implementation of polygenic risk scores for predicting cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. (2025) 46:ehae649. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae649
53. Wang, Y, Tsuo, K, Kanai, M, Neale, BM, and Martin, AR. Challenges and opportunities for developing more generalizable polygenic risk scores. Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. (2022) 5:293–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-111721-074830
54. Maamari, DJ, Abou-Karam, R, and Fahed, AC. Polygenic risk scores in human disease. Clin Chem. (2025) 71:69–76. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvae190
55. Faham, S, Salimi, A, and Ghavami, R. Electrochemical-based remote biomarker monitoring: toward internet of wearable things in telemedicine. Talanta. (2023) 253:123892. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123892
56. Ramachandran, B, and Liao, Y-C. Microfluidic wearable electrochemical sweat sensors for health monitoring. Biomicrofluidics. (2022) 16:051501. doi: 10.1063/5.0116648
57. Lee, S, Kim, H, Kim, JH, So, M, Kim, JB, and Kim, D-J. Heart rate variability as a preictal marker for determining the laterality of seizure onset zone in frontal lobe epilepsy. Front Neurosci. (2024) 18:1373837. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1373837
58. Sellers, KK, Cohen, JL, Khambhati, AN, Fan, JM, Lee, AM, Chang, EF, et al. Closed-loop neurostimulation for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2024) 49:163–78. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01631-2
59. Cruz, P, McKee, AM, Chiang, H-H, McGill, JB, Hirsch, IB, Ringenberg, K, et al. Perioperative care of patients using wearable diabetes devices. Anesth Analg. (2025) 140:2–12. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000007115
60. Bai, J, Liu, D, Tian, X, Wang, Y, Cui, B, Yang, Y, et al. Coin-sized, fully integrated, and minimally invasive continuous glucose monitoring system based on organic electrochemical transistors. Sci Adv. (2024) 10:eadl1856. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adl1856
61. Booth, GJ, Cole, J, Geiger, P, Adams, J, Barnhill, J, and Hughey, S. Pulse arrival time is associated with hemorrhagic volume in a porcine model: a pilot study. Mil Med. (2022) 187:e630–7. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usab069
62. Rabbani, S, and Khan, N. Contrastive self-supervised learning for stress detection from ECG data. Bioengineering (Basel). (2022) 9:374. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9080374
63. Das, S, Dey, MK, Devireddy, R, and Gartia, MR. Biomarkers in cancer detection, diagnosis, and prognosis. Sensors (Basel). (2023) 24:37. doi: 10.3390/s24010037
64. Bodaghi, A, Fattahi, N, and Ramazani, A. Biomarkers: promising and valuable tools towards diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of Covid-19 and other diseases. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e13323. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13323
65. Bocca, B, and Battistini, B. Biomarkers of exposure and effect in human biomonitoring of metal-based nanomaterials: their use in primary prevention and health surveillance. Nanotoxicology. (2024) 18:1–35. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2023.2301692
66. Binyaruka, P, Martinez-Alvarez, M, Pitt, C, and Borghi, J. Assessing equity and efficiency of health financing towards universal health coverage between regions in Tanzania. Soc Sci Med. (2024) 340:116457. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2023.116457
67. Stacy, SL, Chandra, H, Guha, S, Gurewitsch, R, Brink, LAL, Robertson, LB, et al. Re-scaling and small area estimation of behavioral risk survey guided by social vulnerability data. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:184. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14970-4
68. Villanueva-Congote, J, Hinojosa-Gonzalez, D, Segall, M, and Eisner, BH. The relationship between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, platelet/neutrophil ratio, and risk of urosepsis in patients who present with ureteral stones and suspected urinary tract infection. World J Urol. (2024) 42:596. doi: 10.1007/s00345-024-05229-1
69. Tomalty, E, Mercier, É, Pisharody, L, Nguyen, T, Tian, X, Kabir, MP, et al. Detection of measles virus genotype a in a non-endemic wastewater setting: insights from measles wastewater and environmental monitoring in Canada’s capital region. Environ Sci Technol Lett. (2025) 12:124–9. doi: 10.1021/acs.estlett.4c00945
70. Li, Z, Meng, F, Wu, B, Kong, D, Geng, M, Qiu, X, et al. Reviewing the progress of infectious disease early warning systems and planning for the future. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:3080. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20537-2
71. McClymont, H, Si, X, and Hu, W. Using weather factors and google data to predict COVID-19 transmission in Melbourne, Australia: a time-series predictive model. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e13782. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13782
72. Nobre, T, Fenner, ALD, Araújo, ELL, de Araújo, WN, Roux, E, Handschumacher, P, et al. Seroprevalence of dengue, Zika, and chikungunya in São Sebastião, Brazil (2020-2021): a population-based survey. BMC Infect Dis. (2025) 25:129. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10516-2
73. Rollings, KA, Noppert, GA, Griggs, JJ, Melendez, RA, and Clarke, PJ. Comparison of two area-level socioeconomic deprivation indices: implications for public health research, practice, and policy. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0292281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292281
74. Lim, S, and Johannesson, P. An ontology to bridge the clinical Management of Patients and Public Health Responses for strengthening infectious disease surveillance: design science study. JMIR Form Res. (2024) 8:e53711. doi: 10.2196/53711
75. De Filippis, GM, Amalfitano, D, Russo, C, Tommasino, C, and Rinaldi, AM. A systematic mapping study of semantic technologies in multi-omics data integration. J Biomed Inform. (2025) 165:104809. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2025.104809
76. Zhang, H, Zhang, R, Li, S, Du, L, Song, B, Ji, W, et al. Multi-source heterogeneous blockchain data quality assessment model for enterprise business activities. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0304835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304835
77. Zhang, Y, Wang, S, Lin, N, Fan, L, and Zong, C. A simple clustering approach to map the human brain’s cortical semantic network organization during task. NeuroImage. (2025) 309:121096. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2025.121096
78. Sundby, KK, Vaz, AP, Wittig, JH, Jackson, SN, Inati, SK, and Zaghloul, KA. Attention to memory content enhances single-unit spike sequence fidelity in the human anterior temporal lobe. Curr Biol (2025) 35:1085–1094.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2025.01.048
79. Ghorbani, A, Davoodi, F, and Zamanifar, K. Using type-2 fuzzy ontology to improve semantic interoperability for healthcare and diagnosis of depression. Artif Intell Med. (2023) 135:102452. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102452
80. Deady, M, Duncan, R, Jones, LD, Sang, A, Goodness, B, Pandey, A, et al. Data quality and timeliness analysis for post-vaccination adverse event cases reported through healthcare data exchange to FDA BEST pilot platform. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1379973. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1379973
81. Garza, MY, Williams, T, Myneni, S, Fenton, SH, Ounpraseuth, S, Hu, Z, et al. Measuring and controlling medical record abstraction (MRA) error rates in an observational study. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2022) 22:227. doi: 10.1186/s12874-022-01705-7
82. Kim, HJ, Chung, Y, Hwang, S-H, Oh, H-B, Kim, H, and Ko, D-H. ABO antibody titer testing harmonization in Korea: a 5-year analysis of external quality control data. Ann Lab Med. (2025) 45:334–8. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.0521
83. Bernardi, FA, Alves, D, Crepaldi, N, Yamada, DB, Lima, VC, and Rijo, R. Data quality in Health Research: integrative literature review. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e41446. doi: 10.2196/41446
84. Jeon, K, Park, WY, Kahn, CE, Nagy, P, You, SC, and Yoon, SH. Advancing medical imaging research through standardization: the path to rapid development, rigorous validation, and robust reproducibility. Investig Radiol. (2025) 60:1–10. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000001106
85. Liu, L, Liu, R, Lv, Z, Huang, D, and Liu, X. Dual blockchain-based data sharing mechanism with privacy protection for medical internet of things. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e23575. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23575
86. Bjerrum, A, and Lassen, U. Putting data to work for precision medicine. Cell Rep Med. (2023) 4:101090. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101090
87. Tewari, A. mHealth systems need a privacy-by-design approach: commentary on “federated machine learning, privacy-enhancing technologies, and data protection Laws in medical research: scoping review.”. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e46700. doi: 10.2196/46700
88. Chen, H, Pang, J, Zhao, Y, Giddens, S, Ficek, J, Valente, MJ, et al. A data-driven approach to choosing privacy parameters for clinical trial data sharing under differential privacy. J Am Med Inform Assoc. (2024) 31:1135–43. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocae038
89. Huang, J, Chen, Z, Liu, S-Z, Zhang, H, and Long, H-X. Improved intrusion detection based on hybrid deep learning models and federated learning. Sensors (Basel). (2024) 24:4002. doi: 10.3390/s24124002
90. Borah, K, Das, HS, Seth, S, Mallick, K, Rahaman, Z, and Mallik, S. A review on advancements in feature selection and feature extraction for high-dimensional NGS data analysis. Funct Integr Genomics. (2024) 24:139. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01415-x
91. Fu, X, Ma, W, Zuo, Q, Qi, Y, Zhang, S, and Zhao, Y. Application of machine learning for high-throughput tumor marker screening. Life Sci. (2024) 348:122634. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122634
92. Jiang, S, Wang, T, and Zhang, K-H. Data-driven decision-making for precision diagnosis of digestive diseases. Biomed Eng Online. (2023) 22:87. doi: 10.1186/s12938-023-01148-1
93. Cattelani, L, and Fortino, V. Dual-stage optimizer for systematic overestimation adjustment applied to multi-objective genetic algorithms for biomarker selection. Brief Bioinform. (2024) 26:bbae674. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae674
94. Wijaya, DR, Ibadurrohman, RIF, Hernawati, E, and Wikusna, W. Poverty prediction using E-commerce dataset and filter-based feature selection approach. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:3088. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52752-7
95. Yolchuyeva, S, Ebrahimpour, L, Tonneau, M, Lamaze, F, Orain, M, Coulombe, F, et al. Multi-institutional prognostic modeling of survival outcomes in NSCLC patients treated with first-line immunotherapy using radiomics. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:42. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04854-z
96. Ghazal, H, El-Absawy, E-SA, Ead, W, and Hasan, ME. Machine learning-guided differential gene expression analysis identifies a highly-connected seven-gene cluster in triple-negative breast cancer. Biomedicine (Taipei). (2024) 14:15–35. doi: 10.37796/2211-8039.1467
97. Thuy, NN, and Wongthanavasu, S. A novel feature selection method for high-dimensional mixed decision tables. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. (2022) 33:3024–37. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3048080
98. Henke, DM, Renwick, A, Zoeller, JR, Meena, JK, Neill, NJ, Bowling, EA, et al. Bio-primed machine learning to enhance discovery of relevant biomarkers. NPJ Precis Oncol. (2025) 9:39. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-00825-9
99. Syed Ahamed Kabeer, B, Subba, B, Rinchai, D, Toufiq, M, Khan, T, Yurieva, M, et al. From gene modules to gene markers: an integrated AI-human approach selects CD38 to represent plasma cell-associated transcriptional signatures. Front Med (Lausanne). (2025) 12:1510431. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1510431
100. Díez-Sanmartín, C, Sarasa Cabezuelo, A, and Andrés Belmonte, A. Ensemble of machine learning techniques to predict survival in kidney transplant recipients. Comput Biol Med. (2024) 180:108982. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108982
101. Li, M, Chen, Z, Deng, S, Wang, L, and Yu, X. MOSDNET: a multi-omics classification framework using simplified multi-view deep discriminant representation learning and dynamic edge GCN with multi-task learning. Comput Biol Med. (2024) 181:109040. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.109040
102. Jing, X, Ma, Y, Li, D, Zhang, T, Xiang, H, Xu, F, et al. Integration of bile proteomics and metabolomics analyses reveals novel insights into different types of gallstones in a high-altitude area. BMC Gastroenterol. (2024) 24:330. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03422-5
103. Liu, Z, and Park, T. DMOIT: denoised multi-omics integration approach based on transformer multi-head self-attention mechanism. Front Genet. (2024) 15:1488683. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1488683
104. Matsuoka, T, and Yashiro, M. Bioinformatics analysis and validation of potential markers associated with prediction and prognosis of gastric Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:5880. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115880
105. Chauhan, S, Bhandari, U, and Habib, A. Insights into the novel biomarkers expressed in diabetic nephropathy: potential clinical applications. Curr Pharm Des. (2025) 31:619–29. doi: 10.2174/0113816128333694240928161703
106. Wang, C-C, Liang, L-K, Luo, S-M, Wang, H-C, Wang, X-L, Cheng, Y-H, et al. Nomogram-based risk assessment model for left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with essential hypertension: incorporating clinical characteristics and biomarkers. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). (2024) 26:363–73. doi: 10.1111/jch.14786
107. Chen, J, Hu, T, Yang, J, Yang, X, Zhong, H, Zhang, Z, et al. A predictive model for secondary central nervous system infection after craniotomy based on machine learning. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:24942. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75122-9
108. Zhou, L, Wang, Y, Zhu, W, Zhao, Y, Yu, Y, Hu, Q, et al. A retrospective study differentiating nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease from pulmonary tuberculosis on computed tomography using radiomics and machine learning algorithms. Ann Med. (2024) 56:2401613. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2401613
109. Kokubo, T, Kodera, S, Sawano, S, Katsushika, S, Nakamoto, M, Takeuchi, H, et al. Automatic detection of left ventricular dilatation and hypertrophy from electrocardiograms using deep learning. Int Heart J. (2022) 63:939–47. doi: 10.1536/ihj.22-132
110. Mu, N, Rezaeitaleshmahalleh, M, Lyu, Z, Wang, M, Tang, J, Strother, CM, et al. Can we explain machine learning-based prediction for rupture status assessments of intracranial aneurysms? Biomed Phys Eng Exp. (2023) 9:037001. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/acb1b3
111. Ge, Y, Chang, W, Xie, L, Gao, Y, Xu, Y, and Zhu, H. A predictive model for secondary Posttonsillectomy hemorrhage in pediatric patients: an 8-year retrospective study. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. (2025) 10:e70080. doi: 10.1002/lio2.70080
112. Basthikodi, M, Chaithrashree, M, Ahamed Shafeeq, BM, and Gurpur, AP. Enhancing multiclass brain tumor diagnosis using SVM and innovative feature extraction techniques. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:26023. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77243-7
113. Vu-Han, T-L, Sunkara, V, Bermudez-Schettino, R, Schwechten, J, Runge, R, Perka, C, et al. Feature engineering for the prediction of scoliosis in 5q-spinal muscular atrophy. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2025) 16:e13599. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13599
114. Gao, Y, Yang, X, Li, H, and Ding, D-W. A knowledge-enhanced interpretable network for early recurrence prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma via multi-phase CT imaging. Int J Med Inform. (2024) 189:105509. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2024.105509
115. Wang, J, Xu, J, Mao, J, Fu, S, Gu, H, Wu, N, et al. A novel hybrid machine learning model for auxiliary diagnosing myocardial ischemia. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2024) 11:1327912. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1327912
116. Niu, Y, Chen, X, Fan, J, Liu, C, Fang, M, Liu, Z, et al. Explainable machine learning model based on EEG, ECG, and clinical features for predicting neurological outcomes in cardiac arrest patient. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:11498. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93579-0
117. Zhuang, Z, Zhang, Y, Yang, X, Deng, X, and Wang, Z. T2WI-based texture analysis predicts preoperative lymph node metastasis of rectal cancer. Abdom Radiol (NY). (2024) 49:2008–16. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04209-8
118. Yang, X, Wu, M, Li, T, Yu, J, Fu, T, Li, G, et al. Clinical features and a prediction model for early prediction of composite outcome in Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: a multi-Centre retrospective study in China. Infect Drug Resist. (2024) 17:3913–23. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S431543
119. Wang, Y, Zhang, Z, Zhang, Z, Chen, X, Liu, J, and Liu, M. Traditional and machine learning models for predicting haemorrhagic transformation in ischaemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. (2025) 14:46. doi: 10.1186/s13643-025-02771-w
120. Ding, N, Wang, P, Wang, X, and Wang, F. Constructing a logistic regression-based prediction model for subsequent early pregnancy loss in women with pregnancy loss. Eur J Med Res. (2025) 30:99. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02361-5
121. Hu, S, Chen, W, Tan, X, Zhang, Y, Wang, J, Huang, L, et al. Early identification of metabolic syndrome in adults of Jiaxing, China: utilizing a multifactor logistic regression model. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2024) 17:3087–102. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S468718
122. Pan, L, Wang, J, Deng, Y, Sun, Y, Nie, Z, Sun, X, et al. External validation of the kidney failure risk equation among Urban Community-based Chinese patients with CKD. Kidney Med. (2024) 6:100817. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2024.100817
123. Yang, S, Feng, L, Zhang, M, Zhang, M, Ma, Z, Zhang, H, et al. Development and validation of a clinical diagnostic model for myocardial ischaemia in borderline coronary lesions based on optical pumped magnetometer magnetocardiography: a prospective observational cohort study. BMJ Open. (2024) 14:e086433. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086433
124. Chen, C, and Guo, Y. Postoperative recurrence prediction model for atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis. Am J Transl Res. (2024) 16:6208–24. doi: 10.62347/IJEP7120
125. Hassan, N, Slight, R, Morgan, G, Bates, DW, Gallier, S, Sapey, E, et al. Road map for clinicians to develop and evaluate AI predictive models to inform clinical decision-making. BMJ Health Care Inform. (2023) 30:e100784. doi: 10.1136/bmjhci-2023-100784
126. Diniz, MA. Statistical methods for validation of predictive models. J Nucl Cardiol. (2022) 29:3248–55. doi: 10.1007/s12350-022-02994-7
127. Schubert, KM, Schmick, A, Stattmann, M, and Galovic, M. Prognostic models for seizures and epilepsy after stroke, tumors and traumatic brain injury. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. (2025) 10:116–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cnp.2025.02.008
128. Ende, HB. Risk assessment tools to predict postpartum hemorrhage. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. (2022) 36:341–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2022.08.003
129. Zhao, Y, Li, S, Yan, L, Yang, Z, Chai, N, Qiu, P, et al. Nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with invasive micropapillary carcinoma after breast-conserving surgery: a population-based analysis. Front Surg. (2022) 9:1009149. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1009149
130. Tiase, VL, Richards, G, Taft, T, Stevens, L, Balbin, C, Kaphingst, KA, et al. Patient perspectives on a patient-facing tool for lung Cancer screening. Health Expect. (2024) 27:e14143. doi: 10.1111/hex.14143
131. Allen, B, Neill, DB, Schell, RC, Ahern, J, Hallowell, BD, Krieger, M, et al. Translating predictive analytics for public health practice: a case study of overdose prevention in Rhode Island. Am J Epidemiol. (2023) 192:1659–68. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwad119
132. Tarnowska, KA, Ras, ZW, and Jastreboff, PJ. A data-driven approach to clinical decision support in tinnitus retraining therapy. Front Neuroinform. (2022) 16:934433. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2022.934433
133. Djulbegovic, B, Hozo, I, Kunnamo, I, and Guyatt, G. Improving guideline development processes: integrating evidence estimation and decision-analytical frameworks. J Eval Clin Pract. (2025) 31:e70051. doi: 10.1111/jep.70051
134. Ardito, V, Cappellaro, G, Compagni, A, Petracca, F, and Preti, LM. Implementation of machine learning applications in health care organizations: protocol for a systematic review of empirical studies. JMIR Res Protoc. (2023) 12:e47971. doi: 10.2196/47971
135. Adhyaru, BB, Hilburn, G, Oberg, M, Mann, K, and Wu, D. Push notifications for critical labs results: a pilot study in the intensive care unit (ICU). JAMIA Open. (2023) 6:ooad058. doi: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooad058
136. Awan, N, Kumar, RG, Juengst, SB, DiSanto, D, Harrison-Felix, C, Dams-O’Connor, K, et al. Development of individualized risk assessment models for predicting post-traumatic epilepsy 1 and 2 years after moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury: a traumatic brain injury model system study. Epilepsia. (2025) 66:482–98. doi: 10.1111/epi.18210
137. Shahbakhsh, F, Khajouei, R, Sabahi, A, Mehdipour, Y, and Ahmadian, L. Designing a minimum data set of laboratory data for the electronic summary sheet of pediatric ward in Iran: a cross-sectional study. Health Sci Rep. (2023) 6:e1315. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1315
138. Zaninotto, M, Graziani, MS, and Plebani, M. The harmonization issue in laboratory medicine: the commitment of CCLM. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2023) 61:721–31. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2022-1111
139. Coskun, A. Diagnosis based on population data versus personalized data: the evolving paradigm in laboratory medicine. Diagnostics (Basel). (2024) 14:2135. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14192135
140. Dighe, AS. Electronic health record optimization for artificial intelligence. Clin Lab Med. (2023) 43:17–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2022.09.003
141. Zayed, AM, Janssens, A, Mamouris, P, and Delvaux, N. lab2clean: a novel algorithm for automated cleaning of retrospective clinical laboratory results data for secondary uses. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. (2024) 24:245. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02652-7
142. Lu, S, Lu, H, Zheng, T, Yuan, H, Du, H, Gao, Y, et al. A multi-omics dataset of human transcriptome and proteome stable reference. Sci Data. (2023) 10:455. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02359-w
143. Dodig, S, Čepelak, I, and Dodig, M. Are we ready to integrate advanced artificial intelligence models in clinical laboratory? Biochem Med (Zagreb). (2025) 35:010501. doi: 10.11613/BM.2025.010501
144. Kim, S, Jeong, T-D, Lee, K, Chung, J-W, Cho, E-J, Lee, S, et al. Quantitative evaluation of the real-world harmonization status of laboratory test items using external quality assessment data. Ann Lab Med. (2024) 44:529–36. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.0082
145. Eloy, C, Fraggetta, F, van Diest, PJ, Polónia, A, Curado, M, Temprana-Salvador, J, et al. Digital transformation of pathology - the European Society of Pathology expert opinion paper. Virchows Arch. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s00428-025-04090-w
146. Naderalvojoud, B, Curtin, CM, Yanover, C, El-Hay, T, Choi, B, Park, RW, et al. Towards global model generalizability: independent cross-site feature evaluation for patient-level risk prediction models using the OHDSI network. J Am Med Inform Assoc. (2024) 31:1051–61. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocae028
147. Amaral, P, Silva, F, and Santos, V. Recognition of grasping patterns using deep learning for human-robot collaboration. Sensors (Basel). (2023) 23:8989. doi: 10.3390/s23218989
148. Chan, WX, and Wong, L. Accounting for treatment during the development or validation of prediction models. J Bioinforma Comput Biol. (2022) 20:2271001. doi: 10.1142/S0219720022710019
149. Camargo, E, Aguilar, J, Quintero, Y, Rivas, F, and Ardila, D. An incremental learning approach to prediction models of SEIRD variables in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Technol (Berl). (2022) 12:867–77. doi: 10.1007/s12553-022-00668-5
150. Minot, M, and Reddy, ST. Meta learning addresses noisy and under-labeled data in machine learning-guided antibody engineering. Cell Syst (2024) 15:4–18.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2023.12.003
151. Benyó, B, Paláncz, B, Szlávecz, Á, Szabó, B, Kovács, K, and Chase, JG. Classification-based deep neural network vs mixture density network models for insulin sensitivity prediction problem. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. (2023) 240:107633. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107633
152. Ran, H, Gao, X, Li, L, Li, W, Tian, S, Wang, G, et al. Brain-inspired fast-and slow-update prompt tuning for few-shot class-incremental learning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. (2025) 36:13417–13430. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3454237
153. Pai, MGJ, Biswas, D, Verma, A, and Srivastava, S. A proteome-level view of brain tumors for a better understanding of novel diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Expert Rev Proteomics. (2023) 20:381–95. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2023.2283498
154. Kennedy, JJ, Whiteaker, JR, Ivey, RG, Burian, A, Chowdhury, S, Tsai, C-F, et al. Internal standard triggered-parallel reaction monitoring mass spectrometry enables multiplexed quantification of candidate biomarkers in plasma. Anal Chem. (2022) 94:9540–7. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04382
155. Arif, T, Nazir, F, Aurangzeb, RF, Hussain, M, Aurangzeb, RI, Rehman, A, et al. The potential of fecal and urinary biomarkers for early detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review. Cureus. (2024) 16:e59248. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59248
156. Yule, MS, Thompson, J, Leesahatsawat, K, Sousa, MS, Anker, SD, Arends, J, et al. Biomarker endpoints in cancer cachexia clinical trials: systematic review 5 of the cachexia endpoint series. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2024) 15:853–67. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13491
157. Savva, K-V, Das, B, Antonowicz, S, Hanna, GB, and Peters, CJ. Progress with Metabolomic blood tests for gastrointestinal Cancer diagnosis-an assessment of biomarker translation. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2022) 31:2095–105. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-22-0307
158. Shaw, JR, Nopp, S, Stavik, B, Youkhana, K, Michels, AL, Kennes, S, et al. Thrombosis, translational medicine, and biomarker research: moving the needle. J Am Heart Assoc. (2025) 14:e038782. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.038782
159. Guillen, E, Barry, S, Jost, N, Ekman, N, Knippel, V, Kuhlmann-Gottke, J, et al. The tailored biosimilar approach: expectations and requirements. Drugs. (2025) 85:601–8. doi: 10.1007/s40265-025-02168-y
160. Badawy, W, Zinhom, H, and Shaban, M. Navigating ethical considerations in the use of artificial intelligence for patient care: a systematic review. Int Nurs Rev. (2024) 72:e13059. doi: 10.1111/inr.13059
161. Cascella, M, Shariff, MN, Viswanath, O, Leoni, MLG, and Varrassi, G. Ethical considerations in the use of artificial intelligence in pain medicine. Curr Pain Headache Rep. (2025) 29:10. doi: 10.1007/s11916-024-01330-7
162. Al-Ani, A, Rayyan, A, Maswadeh, A, Sultan, H, Alhammouri, A, Asfour, H, et al. Evaluating the understanding of the ethical and moral challenges of big data and AI among Jordanian medical students, physicians in training, and senior practitioners: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Ethics. (2024) 25:18. doi: 10.1186/s12910-024-01008-0
163. Giuste, F, Shi, W, Zhu, Y, Naren, T, Isgut, M, Sha, Y, et al. Explainable artificial intelligence methods in combating pandemics: a systematic review. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. (2023) 16:5–21. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2022.3185953
164. Lin, Y, Wang, H, Li, W, and Shen, J. Federated learning with hyper-network-a case study on whole slide image analysis. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:1724. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28974-6
165. Upadhyay, U, Gradisek, A, Iqbal, U, Dhar, E, Li, Y-C, and Syed-Abdul, S. Call for the responsible artificial intelligence in the healthcare. BMJ Health Care Inform. (2023) 30:e100920. doi: 10.1136/bmjhci-2023-100920
166. Zhu, T-T, Yang, F, and Zhang, Y-J. Evaluating the efficiency of online course resource allocation in universities of China. Eval Program Plann. (2024) 107:102481. doi: 10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2024.102481
167. Yang, L, He, Z, Cao, Y, and Fan, D. A progressive subnetwork searching framework for dynamic inference. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. (2024) 35:3809–20. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3199703
168. Qin, M, Liu, T, Hou, B, Gao, Y, Yao, Y, and Sun, H. A low-latency RDP-CORDIC algorithm for real-time signal processing of edge computing devices in smart grid cyber-physical systems. Sensors (Basel). (2022) 22:7489. doi: 10.3390/s22197489
169. Yang, J, Lee, T-Y, Lee, W-T, and Xu, L. A design and application of municipal service platform based on cloud-edge collaboration for smart cities. Sensors (Basel). (2022) 22:8784. doi: 10.3390/s22228784
170. Rafat, K, Islam, S, Mahfug, AA, Hossain, MI, Rahman, F, Momen, S, et al. Mitigating carbon footprint for knowledge distillation based deep learning model compression. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0285668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285668
171. Yang, HS, Rhoads, DD, Sepulveda, J, Zang, C, Chadburn, A, and Wang, F. Building the model. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2023) 147:826–36. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2021-0635-RA
172. Rosenberger, J, Selig, A, Ristic, M, Bühren, M, and Schramm, D. Virtual commissioning of distributed Systems in the Industrial Internet of things. Sensors (Basel). (2023) 23:3545. doi: 10.3390/s23073545
173. Atallah, L, Nabian, M, Brochini, L, and Amelung, PJ. Machine learning for benchmarking critical care outcomes. Healthc Inform Res. (2023) 29:301–14. doi: 10.4258/hir.2023.29.4.301
174. Zhang, W, Ji, L, Zhong, X, Zhu, S, Zhang, Y, Ge, M, et al. Two novel nomograms predicting the risk and prognosis of pancreatic Cancer patients with lung metastases: a population-based study. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:884349. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.884349
Keywords: proactive health management, biomarkers, predictive models, data heterogeneity, public health resources, multi-omics integration
Citation: Zhao Q, Zhang C, Zhang W, Zhang S, Liu Q and Guo Y (2025) Applications and challenges of biomarker-based predictive models in proactive health management. Front. Public Health. 13:1633487. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1633487
Edited by:
Wenlin Yang, University of Florida, United StatesReviewed by:
Shailesh Tripathi, Rajendra Institute of Medical Sciences, IndiaPanagiotis Theocharopoulos, Independent Researcher, Lamia, Greece
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Zhang, Zhang, Zhang, Liu and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: You Guo, Z3lAZ211LmVkdS5jbg==
 Qiming Zhao1,2
Qiming Zhao1,2 You Guo
You Guo