- 1School of Humanities and Social Science, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 2Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 3Guangxi Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 4Guangxi Hospital Association, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 5Nursing College, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 6School of Humanities and Social Science (School of Public Administration), Beihang University, Beijing, China
Background: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a malignant epithelial tumor most commonly in China. In 2013, NPC incidence and mortality in China were also at high levels worldwide, which poses a great health burden in China. This study analyzes the medical expenditure and influencing factors of inpatients with NPC and aims to provide reference suggestions for reducing medical expenditure for NPC.
Methods: Based on the data from one of the western China hospitals, we use the random forest model to identify the important factors in total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket costs, and the rates of out-of-pocket costs.
Results: Total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket costs, and the rates of out-of-pocket costs were decreased. According to the indicators of InNodePurti and %IncMSE, the top three influencing factors of total medical expenditure and out-of-pocket costs are Length of stay, Medical payment method, and Readmission status; the top three influencing factors of the rates of out-of-pocket costs are Medical payment method, Occupation, and Age.
Conclusion: Length of stay was an important factor in total medical expenditure and out-of-pocket costs, and the medical payment method was an important factor in the rates of out-of-pocket costs. To reduce the burden of NPC patients’ medical expenditure, (1) we can reduce the length of stay by improving the level of medical technology; (2) increasing government medical expenditures and improving the level of medical security; (3)promoting smoking bans, and strengthening screening in high-risk areas.
1 Introduction
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a malignant epithelial tumor most commonly arising from the Fossa of Rossenmueller (1). NPC has very distinct geographic areas of high risk, the highest rates are in populations in South-Eastern Asia (2), especially in China’s southern and eastern regions: Guangdong, Hainan, Guangxi, Hunan, and Fujian (3, 4). NPC is endemic to southern China, Southeast Asia, and Africa, with age-standardized incidence rates of 4–25 per 100,000 population in these regions, which are approximately 50–100 times higher than the incidence rates in the rest of the world (5). And an age-standardized rate (world) of 3.0 per 100,000 in China, which is about 7 times that the population mainly white (6). Over the last three decades, the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) and crude mortality rate (CMR) of NPC has decreased, but the ASIR and crude incidence rate (CIR) increased in China (7). In 2020, there were 62,000 new cases of NPC in China, accounting for about 80% of the world’s NPC cases (8).
NPC poses a significant public health burden in endemic regions (9). In 2013, NPC incidence and mortality in China were also at high levels worldwide (10), which poses a great health burden in China (7). NPC remains a significant public health issue in China’s southern provinces, southern provinces including Guangdong, Guangxi, and Hainan had the highest years of life lost (YLL) rate in 2020 (11). Since 2005, the Chinese Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Health have included rural cancer early diagnosis and treatment projects in the central subsidy for local special projects, and NPC has also been included in the scope of free screening (12). The NPC screening program can improve the long-term survival status of nasopharyngeal cancer patients (13). China has made great achievements in the prevention, control, diagnosis, and treatment of NPC in the past 30 years (14).
This study analyzes the medical expenditure and influencing factors of inpatients with NPC and aims to provide reference suggestions for reducing medical expenditure for NPC.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data source
The data used in this research was derived from one of the western area China hospitals. The data mainly includes the basic information and medical expenditure information of NPC inpatients, including age, gender, marital status, occupation, admission status, medical payment method, length of stay, surgical conditions, diagnosis and treatment of diseases, Surgical situation, blood transfusion conditions, treatment status, and readmission conditions, total medical expenditure, out-out-of-pocket costs, and the rate of out-out-of-pocket costs. According to Liao and Zhang (15), data for “total medical expenditure < 100 yuan,” “length of stay < 1 day,” and “length of stay > 90 days” were deleted. And we are removing the data on unreasonable medical expenditures. The sample includes inpatients from 2019 to 2023, with sample sizes of 2,489, 2,583, 3,058, 3,341, and 3,615.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Data description method
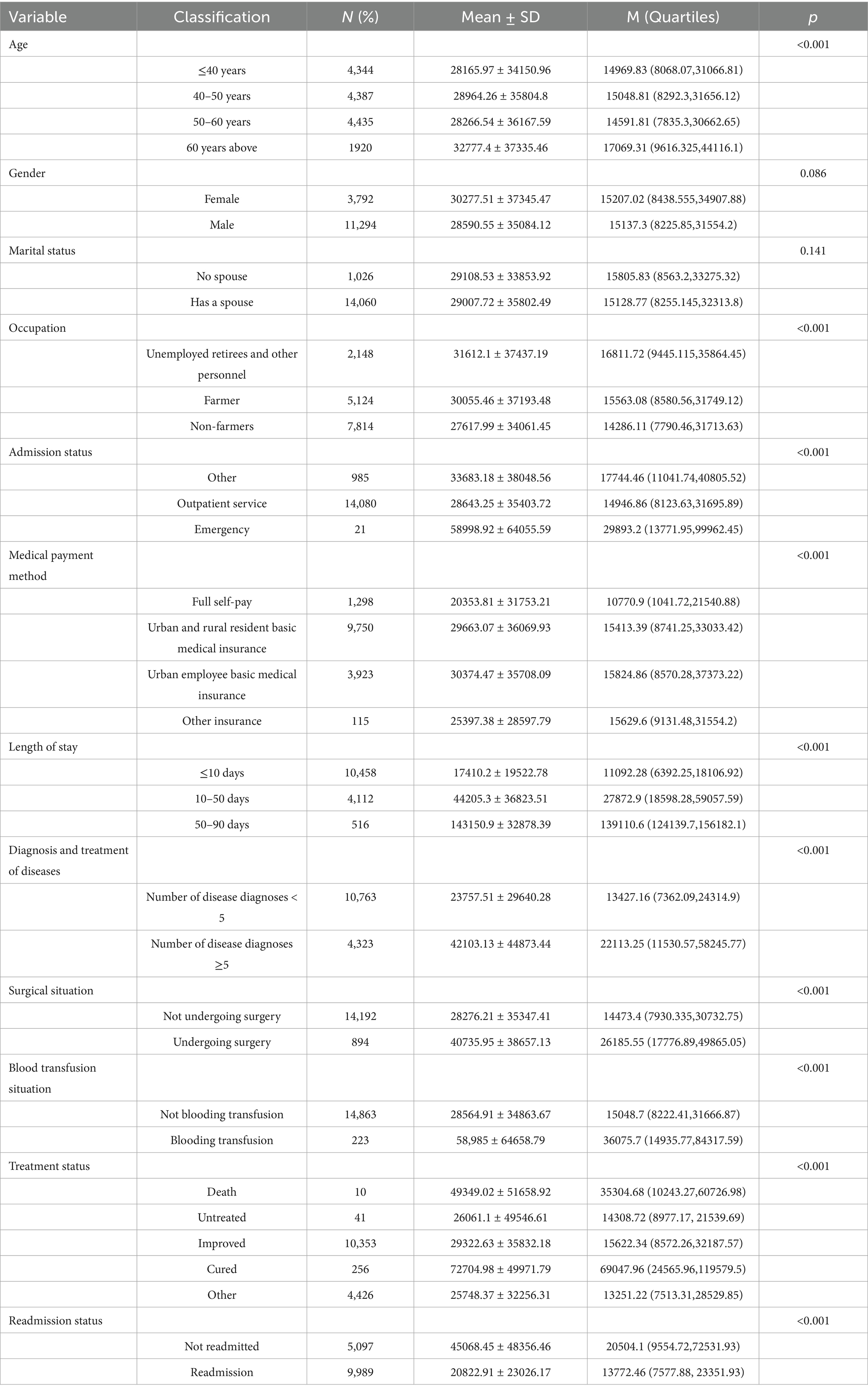
The data on medical expenditure followed a positively skewed distribution, so it was described with medians and quartiles. Additionally, mean and standard deviation were also provided. Rank-sum test was performed to analyze the correlation between the characteristics of inpatients and the expenditure. A p-value less than 0.05 indicates significance.
2.2.2 Random forest model
Random forest (RF) model is not very prone to overfitting (16), obtain predictions without obvious deviations (17), and provides a unique and essential feature for variable selection (18). Medical expenditure has a positively skewed distribution (19), therefore many researchers use the RF model to analyze the influence factors of medical expenditure.
Taloba et al. (20) use the d RF model to predict the medical expenditure. Wang and Shi (21) use the RF model to predict the medical expenditures of diagnosed diabetics and the assessment of its related factors. Kumagai and Jakovljević (22) use the RF model used to predict the medical out-of-pocket costs of hypertensive patients.
The sample is explained below into subsets: 80% of the data are used for training, and 20% of the data are used for testing. When an RF model randomly selects explanatory variables from among all the explanatory variables, the sample of the regression tree is split (22). At each internal node of the decision tree, entropy(E) is given by Equation (1).
Where c is the number of unique classes, and pi is the prior probability of each class (23).
The RF model’s analysis aim is to rank the important factors of the dependent variables. The RF model used the two measurements to rank all variables: increase in mean squared error (%IncMSE) and increase in node purity(IncNodePurity), with larger values indicating greater importance of the variable. %IncMSE by randomly assigning values to each predictor variable, if the predictor variable is more important, the model’s prediction error will increase after its value is randomly replaced. IncNodePurity is measured by the sum of squared residuals, representing the impact of each variable on the heterogeneity of observations at each node of the classification tree, to compare the importance of variables.
3 Results
3.1 General description
The change in total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket cost, and the rate of out-of-pocket costs in 2019–2023 are shown in Table 1.
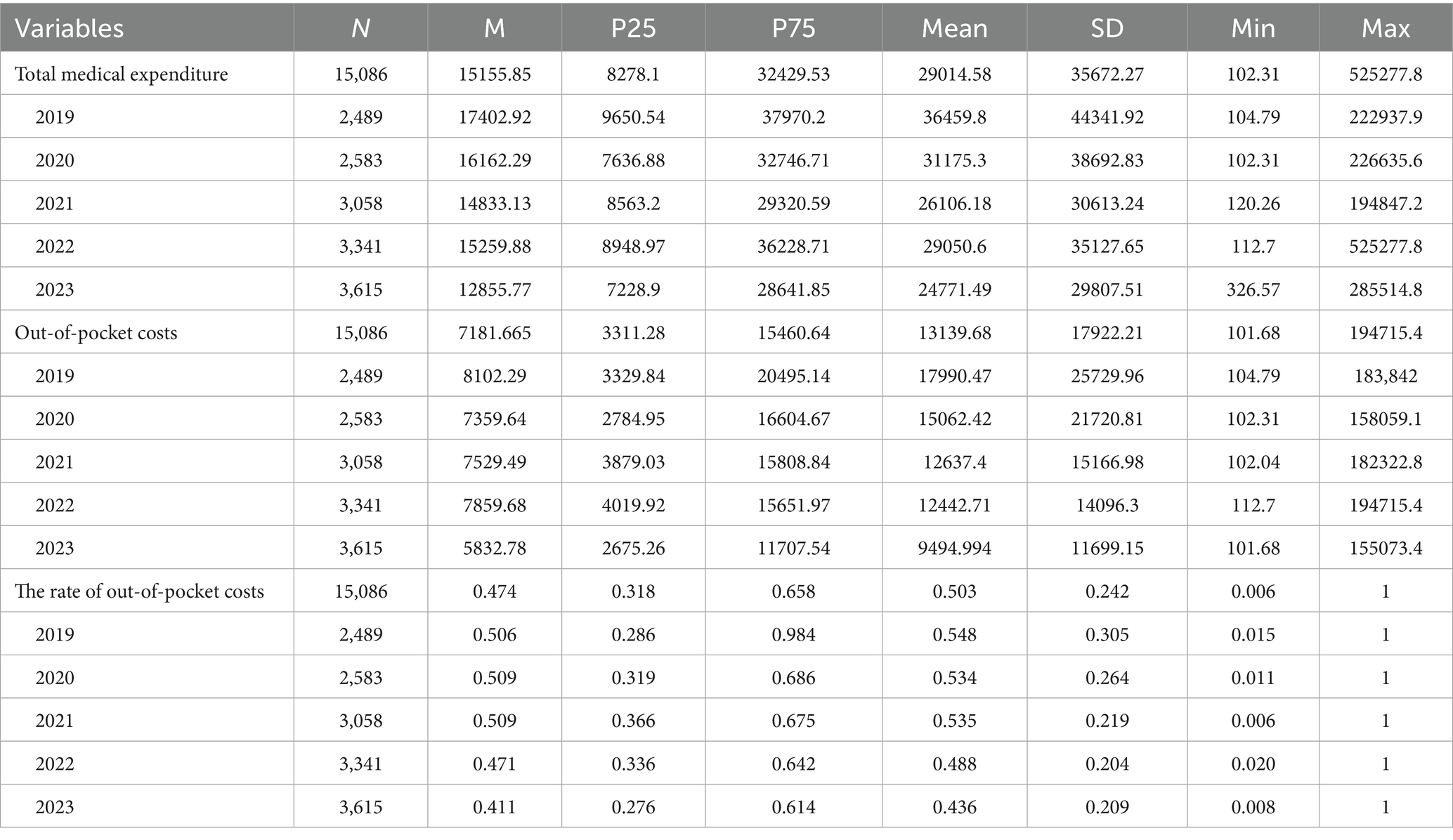
Table 1. Medical expenditure, out-of-pocket cost, and the rate of out-of-pocket cost of NPC inpatient 5 years.
Total medical expenditure decreased from 9650.54 yuan in 2019 to 7636.88 yuan in 2020, then continuously increased from 7636.88 yuan in 2020 to 15259.88 yuan in 2022, but it declined to 12855.77 in 2023. From 2019 to 2023, total medical expenditure decreased by 26.13%. Out-of-pocket cost decreased from 8102.29 yuan in 2019 to 7359.64 yuan in 2020, then continuously increased from 7359.64 yuan in 2020 to 7859.68 yuan in 2022, but it declined to 5832.78 in 2023. From 2019 to 2023, the out-of-pocket was decreased by 28.01%. Additionally, the rate of out-of-pocket costs was continuously increased from 0.506 in 2019 to 0.509 in 2021, then which continuously decreased from 0.509 in 2021 to 0.411 in 2023.
3.2 Univariate analyses between the total medical expenditure and potential variables
It was found that the total medical expenditure was different among age, occupation, admission status, medical payment method, length of stay, surgical conditions, diagnosis and treatment of diseases, Surgical situation, blood transfusion conditions, treatment status, and readmission conditions. Detail information was listed in Table 2.
3.3 The influence factors the medical expenditure of NPC inpatient with RF model
Total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket cost, and the rate of out-of-pocket costs were the output in the RF model, respectively. Total medical expenditures, out-of-pocket cost, and the rate of out-of-pocket payments (defined as Y, respectively), and the total medical expenditures, out-of-pocket cost were transformed into the new values (defined as Y′, respectively) with the transformation of Y′= ln(Y). Potential variables mentioned before were inputs in the RF model.
The data were randomly divided into the training dataset, which included 12,070 individuals, and the test dataset, which included 3,016 individuals, based on the proportion of eight-tenth and two-tenth, approximately.
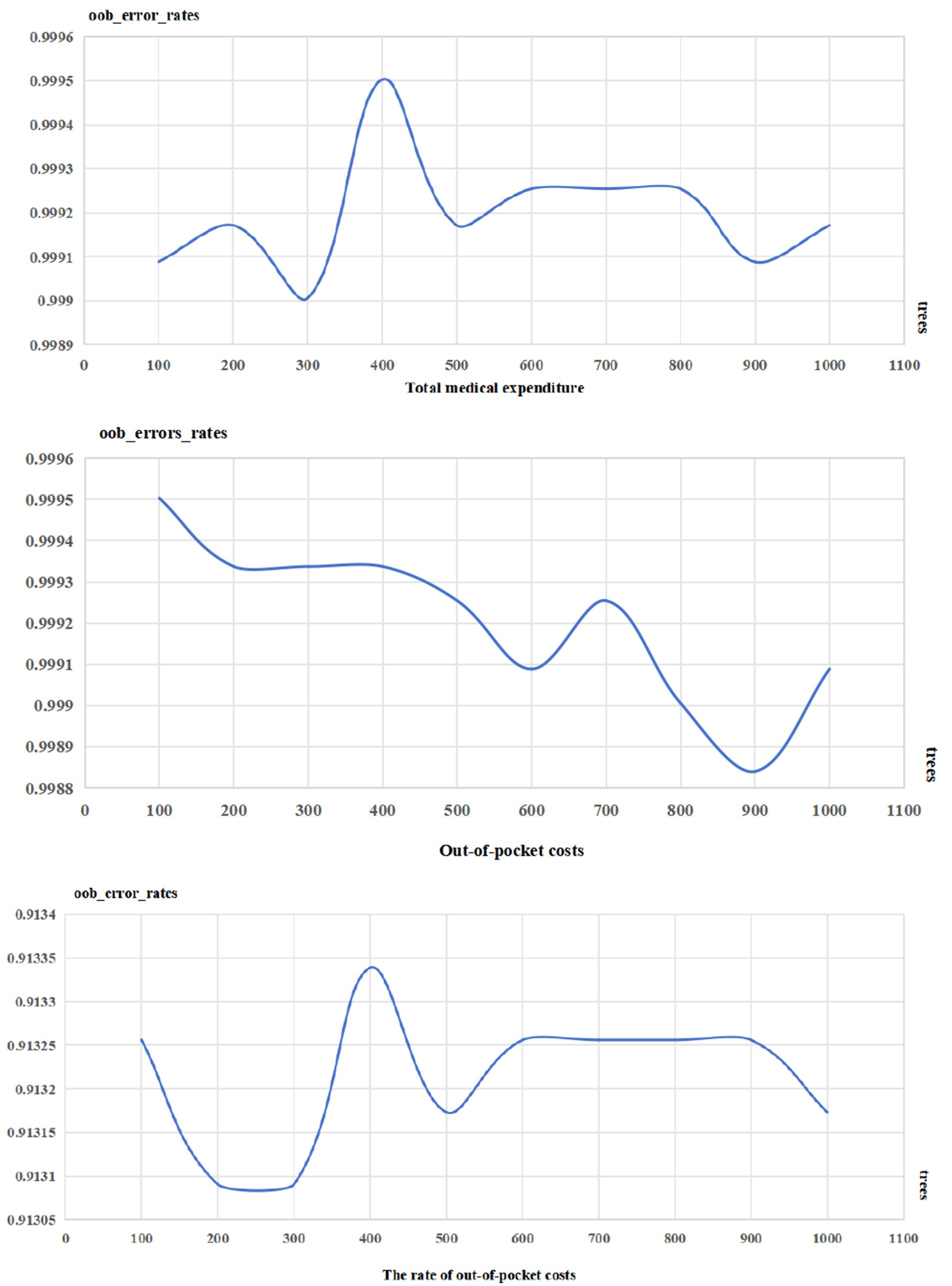
Finding the optimal mtry using grid search and 10-fold cross-validation method. Then using training dataset to build the RF model in which the number of trees was defined based on the trend of the values of out-of-bag error rates with different numbers of trees. Finally, according to the results build an RF model.
Next, the ln-transformed medical expenditures of NPC in the dataset were analyzed based on the RF model built.
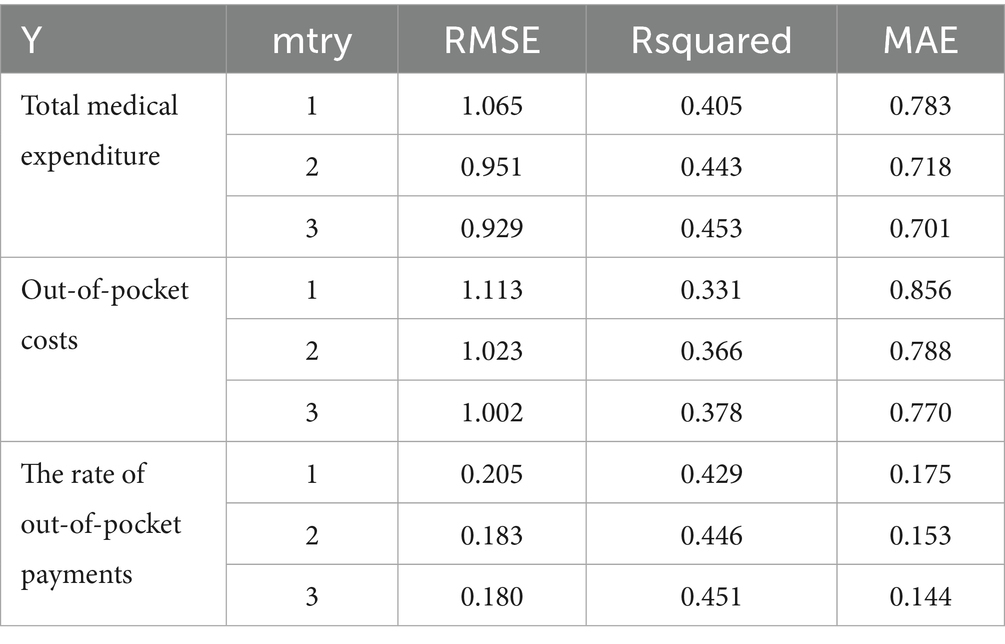
According the results, when the total medical expenditures was Y′, the optimal parameters for the model were 3 of mtry and 300 trees; when the out-of-pocket costs was Y′, the optimal parameters for the model were 3 of mtry and 900 trees; when the rate of out-of-costs was Y, the optimal parameters for the model were 3 of mtry and 200 trees. Detail information was listed in Table 3 and Figure 1.
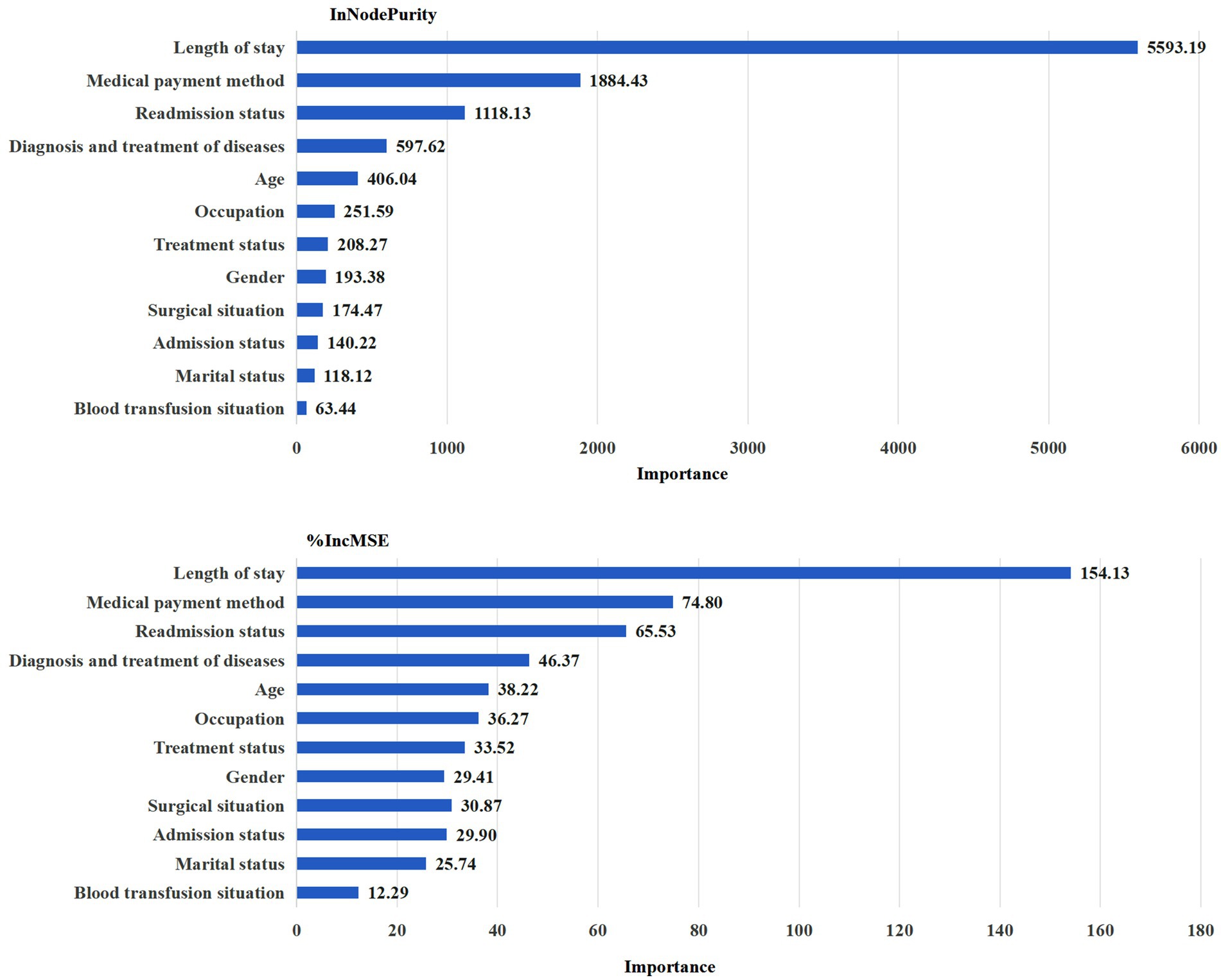
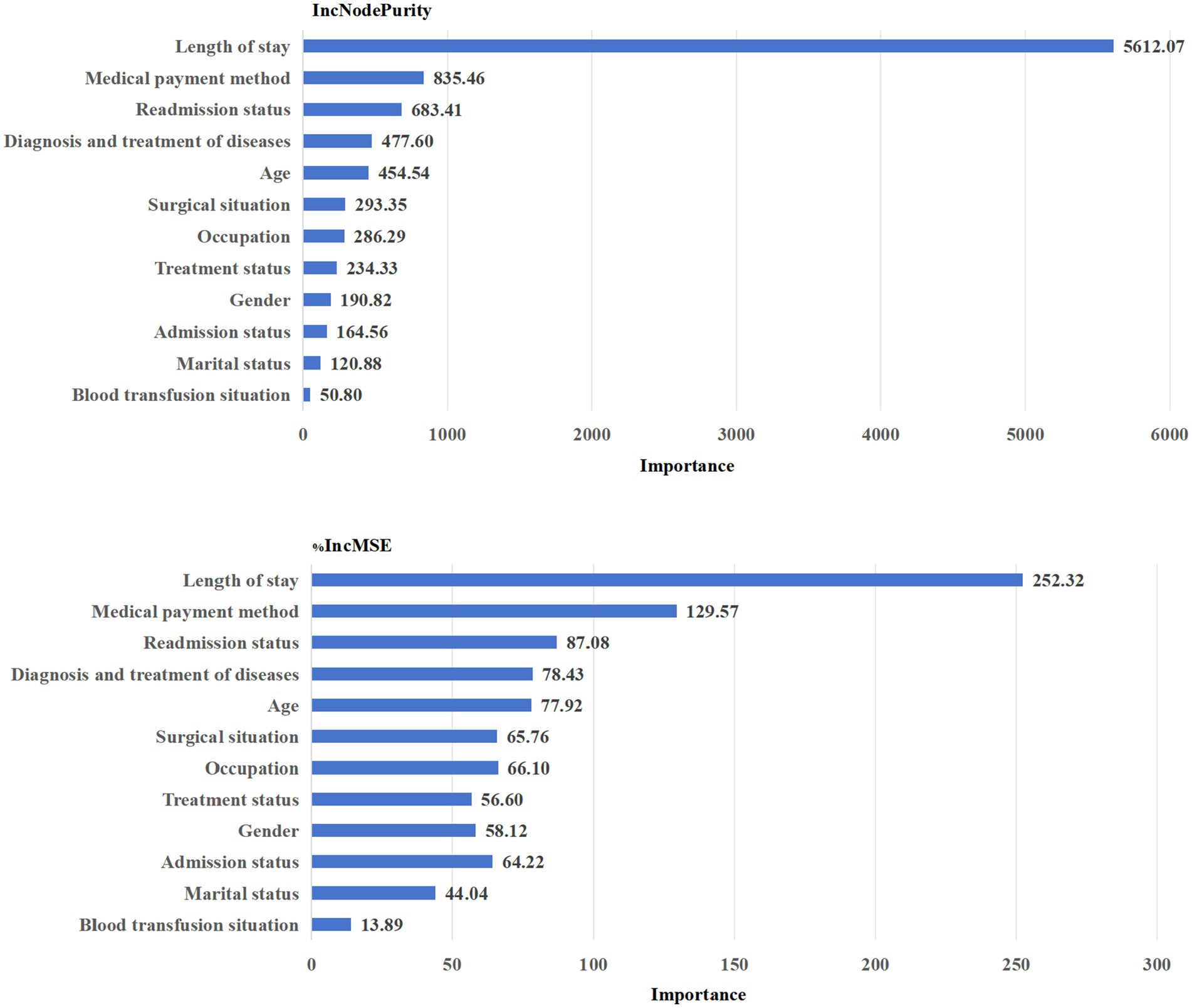
According to IncNodePurity and %IncMSE, the top five influence factors in total medical expenditure shown in Figure 2 that the top five influence factors were: Length of stay > Medical payment method > Readmission status > Diagnosis and treatment of diseases > Age.
According to IncNodePurity and %IncMSE, the top five influence factors in the out-of-pocket costs shown in Figure 3 that the top five influence factors were: Length of stay > Medical payment method > Readmission status > Diagnosis and treatment of diseases > Age.
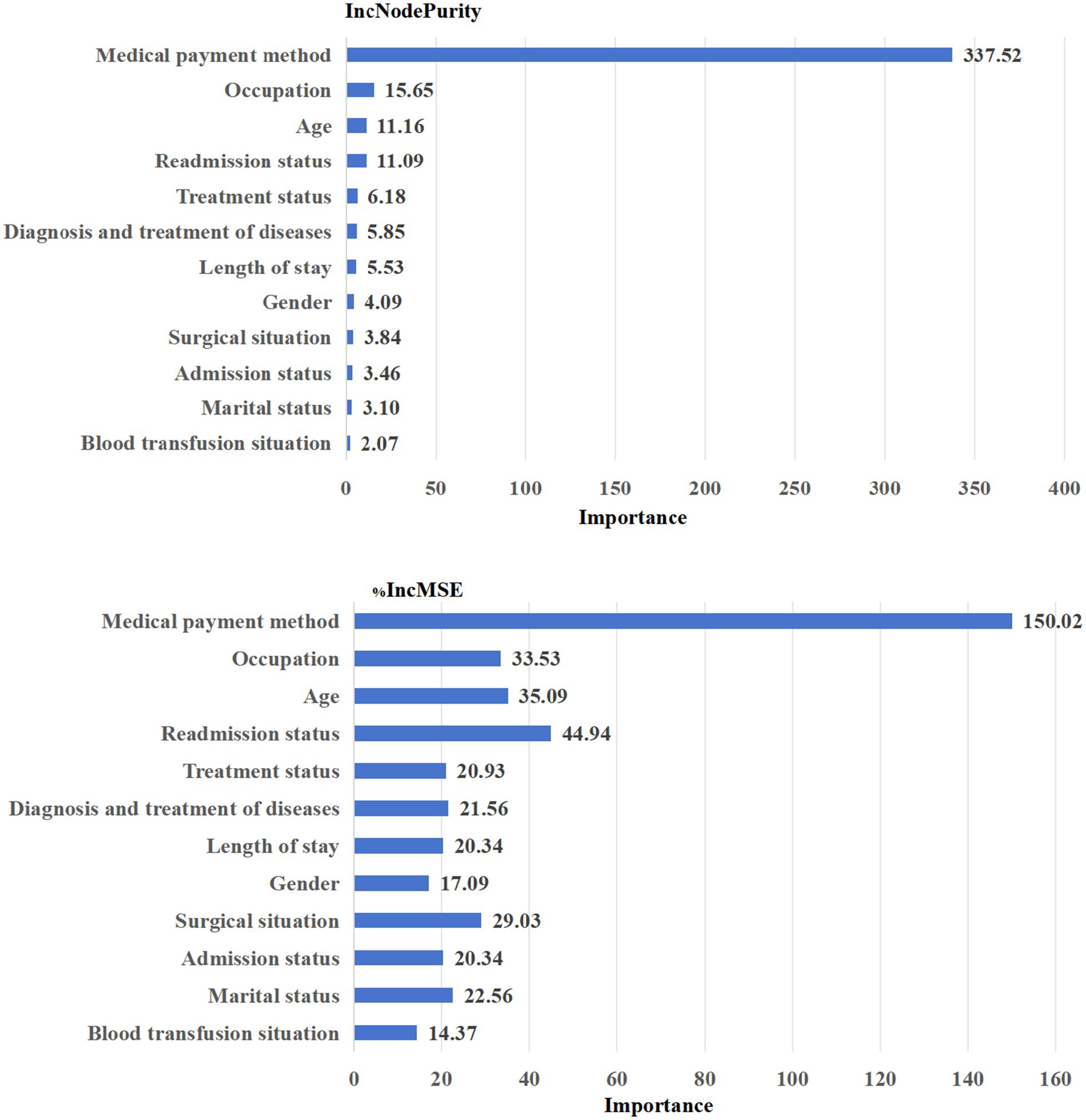
According to IncNodePurity and %IncMSE, the top five influence factors in the out-of-pocket costs shown in Figure 4 that the top five influence factors were: Medical payment method > Occupation > Age > Readmission status > Treatment status.
Detailed information on total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket costs the length of stay, and the rate of out-of-pocket costs are listed in Figure 5.
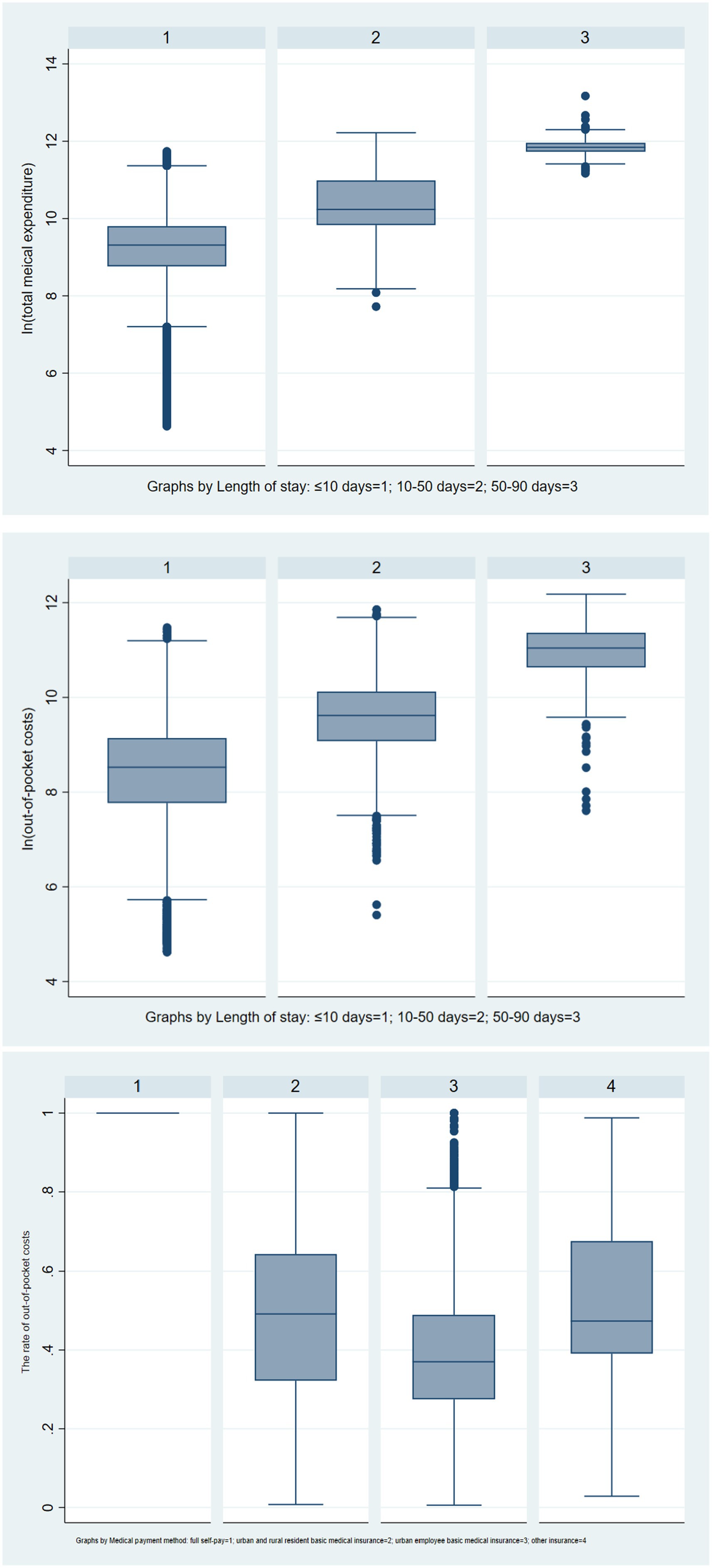
Figure 5. Boxplots of total medical expenditure and out-of-pocket costs varying with length of stay and the out-of-pocket costs varying with medical payment method.
About In(total medical expenditure), when the length of stay ≤ 10 days or between 50 and 90 days, the number of outliers is more than the length of stay between 10 and 50 days’ outliers. The median total medical expenditure varies among different groups, with the highest being between 50–90 days of the length of stay, the In(total medical expenditure) close to 12, followed by between 10–50 days of the length of stay, In(total medical expenditure) slightly higher at 10, and the lowest being ≤ 10 days of the length of stay, In(total medical expenditure) close to 10.
The median out-of-pocket costs vary among different groups, with the highest being between 50–90 days of the length of stay, the In(out-of-pocket costs) around 11, followed by between 10–50 days of the length of stay, In(out-of-pocket costs) slightly lower at 10, and the lowest being ≤ 10 days of the length of stay, In(out-of-pocket costs) slightly higher 9.
About the rates of out-of-pocket costs, when the medical payment method was urban employee basic medical insurance, there were some outliers. The median rates of out-of-pocket costs vary among different groups, with the highest being full self-pay, the rates of out-of-pocket costs were 1, followed by urban and rural resident basic medical insurance, the rates of out-of-pocket costs were close to 0.5, then other insurance, the rates of out-of-pocket costs was slighter higher 0.4, and the lowest was urban employee basic medical insurance, the rates of out-of-pocket costs was lower 0.4.
It is evident that the majority of NPC inpatients are aged between 40 and 60 years, and inpatients exhibiting a total medical expenditure ranging from 0 to 100,000 yuan demonstrate the highest density, and those with medical out-of-pocket costs between 0 and 50,000 yuan also exhibit the highest density. Detailed information is listed in Figure 6.
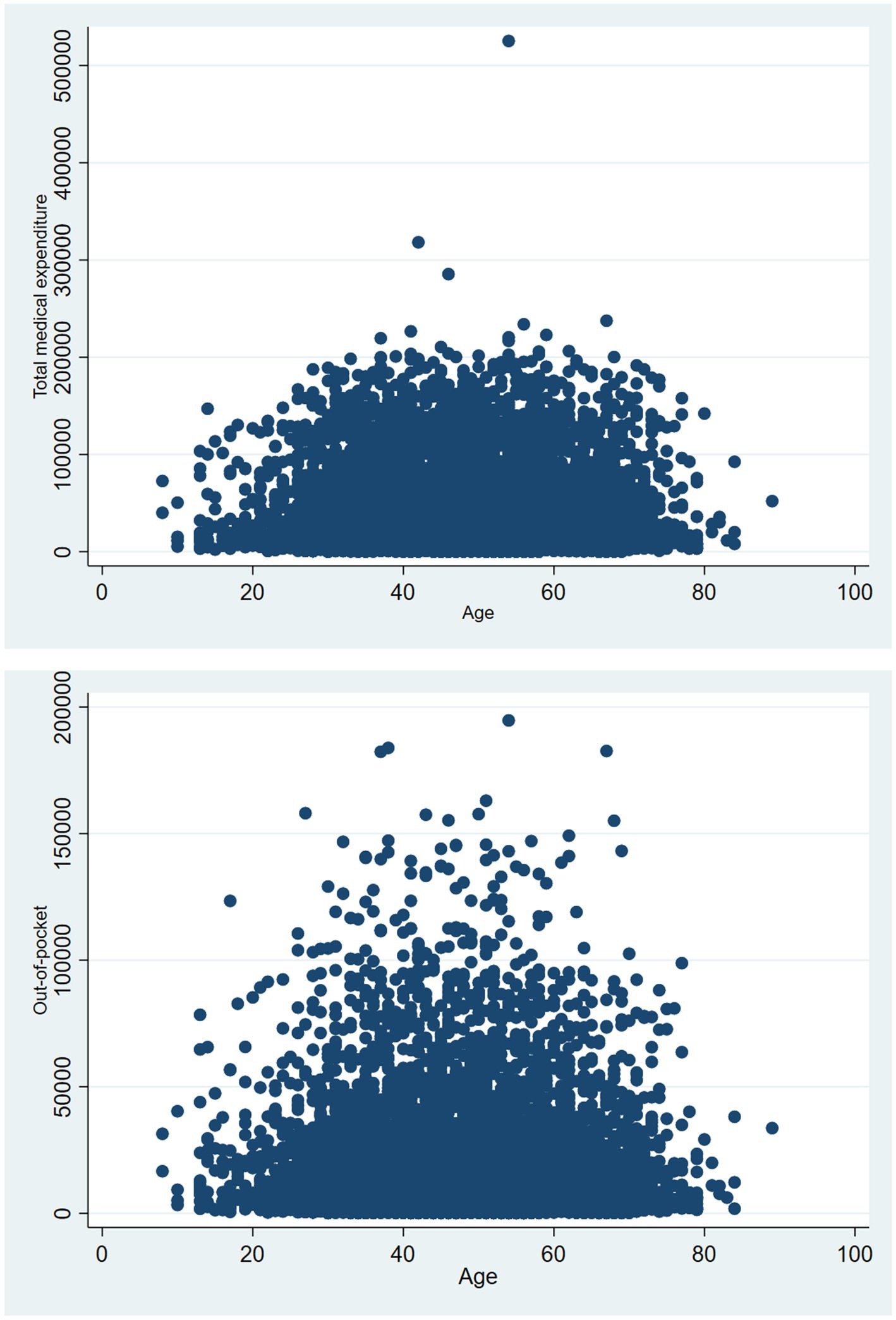
Figure 6. Density scatter plots of total medical expenditure varying with age and out-of-pocket costs varying with age.
4 Discussion
Total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket costs, and the rates of out-of-pocket costs from 2019 to 2023 among NPC inpatients in one of the western area China hospitals decreased and were consistent with each other. We further found the length of stay was an important factor in total medical expenditure and out-of-pocket costs, and the medical payment method was an important factor in the rates of out-of-pocket costs. Then, we found that with longer stays, the total medical expenditure and out-of-pocket costs were higher. Different insurance affects the rate of out-of-pocket costs differently, compared with other insurance, the urban employee basic medical insurance reduces the NPC inpatient’s medical expenditure burden the best. The majority of NPC inpatients are aged between 40 and 60 years, and inpatients exhibiting a total medical expenditure ranging from 0 to 100,000 yuan demonstrate the highest density, and those with medical out-of-pocket costs between 0 and 50,000 yuan also exhibit the highest density.
About NPC inpatients’ total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket costs, and the rates of out-of-pocket costs were decreased. We speculate that there are the following reasons: (1) the government increases health expenditure on NPC. Death and cancer mortality rates among rural residents were higher and increased faster than among urban residents (24). NPC patients with high socioeconomic status had better overall survival compared with those who had low and medium socioeconomic status (25). Women having financial concerns after diagnosis were more likely to reduce their non-medical expenses and even quit treatments (26). It can be seen that the economic level has a significant impact on health. In order to provide all citizens with equal access to basic healthcare with reasonable quality and financial risk protection, China launched a major healthcare reform in 2009 (27). From 2015 to 2022, the average annual growth rate of total health expenditure is 8.32% in China (28). The increase in government medical expenditure will help reduce personal medical expenditure. (2) Medical insurance develop. With the development of medical, the proportion of personal payments to total health expenditure has significantly decreased (29). The economic burden of diseases among the population with basic medical insurance for urban employees, public medical insurance, and commercial medical insurance has decreased by 5% or 4% (30). The cost of treating malignant tumors is a heavy personal burden (31). In 2017, the treatment of NPC with rituximab was on the medical insurance drug list, which significantly improved the level of medical insurance drug protection and greatly reduced the economic burden (32). (3) Medical technology improvement. In this case-matched study, we observed that endoscopic nasopharynx ectomy resulted in significant decreases in medical costs and length of hospital stay for recurrent NPC, as compared with intensity-modulated radiotherapy (33).
Our research findings are somewhat consistent with those of others. The length of stay was an important factor in total medical expenditure and out-of-pocket costs. Other research found that the length of stay is one of the main factors affecting the total hospitalization cost for malignant tumors (34).
We found that the medical payment method has the greatest impact on the rates of out-of-pocket costs. Urban employee basic medical insurance provides the best level of protection for NPC patients. Next are other medical insurance and rural resident basic medical insurance. The full self-pay medical payment method imposes a heavy burden on medical expenditure. Because the reimbursement ratio for urban employee basic medical insurance, the level of protection is also higher. Other medical insurance and rural resident basic medical insurance for residents can ensure the basic health of the people. Lack of insurance will increase the vulnerability to disease risks. In 2023, the current medical insurance coverage rate is over 95% in China. That is to say, there are still some people who do not have insurance, and attention should be paid to this group of people.
We found that the total medical expenditure of NPC inpatients shows no gender disparities. But NPC shows gender disparities, with higher rates in males (4, 35). In Asia, males below 50 years old are more prone to NPC and are often diagnosed at the late stage (36). That is, reducing the incidence rate of male NPC will help reduce the medical expenditure burden of NPC in China. Males’ biological factors and high-risk behaviors caused a higher NPC incidence rate. Cigarette smoking was associated with increased risk of NPC, especially for young smokers (37). Among the high-risk population for NPC, the EB virus infection rate in males is 9.50%, which is higher than that in females at 5.83%; in the population with a family history of inheritance, the EB virus infection rate in males is 24.75%, which is higher than the 18.08% rate in females (38). Therefore, to control the occurrence of NPC and reduce the medical expenditure of NPC, reduce smoking, and attention to oral hygiene to reduce the spread of EB virus.
We found the largest number of NPC in patients aged between 50 and 60 years. The result is the same as Chang et al.’ result, NPC incidence exhibits a single peak at approximate ages 45–59 years in high-risk populations (39). The effect of age on survival is marked in NPC, five-year survival rates were 72% in the youngest age group (15–45 years) and 36% in the oldest group of patients (65–74 years) (40). We further found that there is an age difference in the total medical expenditure for NPC inpatients. According to our research findings, the total medical expenditure and out-of-pocket costs of NPC inpatients are mainly between the ages of 40–60. NCP has a prognosis that is gloomy after metastases are diagnosed, with a fatality rate of 91% within a year of the first metastasis (41). NPC is a rare cancer in developed areas, which may be related to early prevention, screening, diagnosis, and later treatment in developed regions (42). NPC relatively common malignant tumor, screening in high-risk areas can significantly improve early diagnosis rates and reduce treatment costs (43). China has carried out several screening programs in high-incidence areas (4). In the future prevention and treatment of NPC, it is recommended to strengthen the screening of high-risk populations to detect early asymptomatic NPC patients and enhance the tertiary prevention of NPC.
5 Conclusion
Total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket costs, and the rates of out-of-pocket costs were decreased. Length of stay was an important factor in total medical expenditure and out-of-pocket costs, and the medical payment method was an important factor in the rates of out-of-pocket costs. There are suggestions to reduce the burden of NPC patients’ medical expenditure. First, we can reduce the length of stay by improving the level of medical technology. Second, increase government medical expenditures and improve the level of medical security. Third, promote smoking bans and strengthen screening in high-risk areas. This study has several limitations: (1) Existing data has limitations. The main treatment for NPC patients is Simultaneous chemoradiotherapy. The long radiotherapy cycle and the patients’ unwillingness to be hospitalized for a long period lead to the fact that some patients are not hospitalized at one time, and there are records of multiple hospitalizations. Radiotherapy costs are not charged according to the number of days. For patients who have been hospitalized numerous times, different parts of radiotherapy costs are charged in different hospitalization records. The above indicates that some data show patients have a higher out-of-pocket cost rate despite having medical insurance. In special circumstances where only out-of-pocket costs are collected, the out-of-pocket costs rate for medical insurance participants may be as high as 100%. This data situation may potentially lead to some bias in findings. (2) Due to the availability of data, we were unable to incorporate additional influential factors into the analysis. Then we could not explore additional factors and their mechanisms that affect the medical expenses of NPC. (3) The current data were collected from NPC patients across different periods rather than through longitudinal tracking of the same individuals, resulting in the loss of some influencing factors and limiting the exploration of their influencing mechanisms.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the dataset is private. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to emh1cGluZ2h1YUBneG11LmVkdS5jbg==.
Author contributions
PZh: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. LH: Writing – review & editing. BW: Writing – review & editing. XZ: Writing – review & editing. PZe: Writing – review & editing. JN: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by Study on the large hospitalization expenditure and influencing factors of common malignant tumor patients in a tumor hospital in Guangxi from 2015 to 2021 (2022RWB13).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Limkin, EJ, and Blanchard, P. Does east meet west? Towards a unified vision of the management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Radiol. (2019) 92:20190068. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20190068
2. Ferlay, J, Soerjomataram, I, Dikshit, R, Eser, S, Mathers, C, Rebelo, M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. (2015) 136:E359–86. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210
3. Xu, ZJ, Zheng, RS, Zhang, SW, Zou, XN, and Chen, WQ. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China in 2009. Chin J Cancer. (2013) 32:453–60. doi: 10.5732/cjc.013.10118
4. Guo, X, Cui, J, Yuan, X, Gao, Z, Yu, G, Wu, H, et al. Long-term trends of nasopharyngeal carcinoma mortality in China from 2006 to 2020 by region and sex: an age-period-cohort analysis. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:2057. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16892-1
5. Bray, F, Ferlay, J, Soerjomataram, I, Siegel, RL, Torre, LA, and Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2018) 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
6. Chen, YP, Chan, ATC, Le, QT, Blanchard, P, Sun, Y, and Ma, J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. (2019) 394:64–80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30956-0
7. Bai, R, Sun, J, Xu, Y, Sun, Z, and Zhao, X. Incidence and mortality trends of nasopharynx cancer from 1990 to 2019 in China: an age-period-cohort analysis. BMC Public Health. (2022) 22:1351. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13688-7
8. Sung, H, Ferlay, J, Siegel, RL, Laversanne, M, Soerjomataram, I, Jemal, A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
9. Zhang, Y, Cao, Y, Luo, L, Li, J, Wang, L, Lu, Y, et al. The global, regional, and national burden of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019. Acta Otolaryngol. (2022) 142:590–609. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2022.2111711
10. Wei, KR, Zheng, RS, Zhang, SW, Liang, ZH, Li, ZM, and Chen, WQ. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China, 2013. Chin J Cancer. (2017) 36:90. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0257-9
11. Long, Z, Wang, W, Liu, W, Wang, F, Meng, S, Liu, J, et al. Trend of nasopharyngeal carcinoma mortality and years of life lost in China and its provinces from 2005 to 2020. Int J Cancer. (2022) 151:684–91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33998
12. Cao, MM, and Chen, WQ. Persist in government led promotion of cancer screening development in China. Chin J Oncol. (2021) 30:803–5.
13. Lu, YQ, Hu, T, Lin, CY, Chen, GH, Xie, SH, Lin, W, et al. Long term effectiveness evaluation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma screening program in Sihui City, Guangdong Province. Chin J Oncol. (2018) 27:842–6.
14. Song, YX, Liu, XJ, Zhang, YQ, and Li, HQ. Analysis and prediction of nasopharyngeal carcinoma disease burden in China from 1990 to 2050 based on GBD database. J Central South Univ. (2025):1–9.
15. Liao, GQ, and Zhang, XY. Analysis of influencing factors on medical expenses of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients in a tertiary hospital in Guizhou Province. China Med Manage Sci. (2021) 11:73–9.
17. Ellis, K, Kerr, J, Godbole, S, Lanckriet, G, Wing, D, and Marshall, S. A random forest classifier for the prediction of energy expenditure and type of physical activity from wrist and hip accelerometers. Physiol Meas. (2014) 35:2191–203. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/35/11/2191
18. Hu, J, and Szymczak, S. A review on longitudinal data analysis with random forest. Brief Bioinform. (2023) 24:bbad002. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad002
19. Dai, P, Chang, W, Xin, Z, Cheng, H, Ouyang, W, and Luo, A. Retrospective study on the influencing factors and prediction of hospitalization expenses for chronic renal failure in China based on random Forest and LASSO regression. Front Public Health. (2021) 9:678276. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.678276
20. Taloba, AI, Abd El-Aziz, RM, Alshanbari, HM, and El-Bagoury, AH. Estimation and prediction of hospitalization and medical care costs using regression in machine learning. Healthc Eng. (2022) 2022:7969220–10. doi: 10.1155/2022/7969220
21. Wang, J, and Shi, L. Prediction of medical expenditures of diagnosed diabetics and the assessment of its related factors using a random forest model, MEPS 2000-2015. Int J Qual Health Care. (2020) 32:99–112. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzz135
22. Kumagai, N, and Jakovljević, M. Random forest model used to predict the medical out-of-pocket costs of hypertensive patients. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1382354. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1382354
23. Schonlau, M, and Zou, RY. The random forest algorithm for statistical learning. Stata J Promot Commun Stat Stata. (2020) 20:3–29. doi: 10.1177/1536867X20909688
24. Liu, L. Rural-urban inequities in deaths and cancer mortality amid rapid economic and environmental changes in China. Int J Public Health. (2019) 64:39–48. doi: 10.1007/s00038-018-1109-3
25. Meng, DF, Zhang, HB, Liu, GY, Peng, LX, Yang, Q, Liu, ZH, et al. Association of socioeconomic disparities with nasopharyngeal carcinoma survival in an endemic area, China. Cancer Control. (2023) 30:10732748231188261. doi: 10.1177/10732748231188261
26. Jing, J, Feng, R, Zhang, X, Li, M, and Gao, J. Financial toxicity and its associated patient and cancer factors among women with breast cancer: a single-center analysis of low-middle income region in China. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2020) 181:435–43. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05632-3
27. Yip, W, Fu, H, Chen, AT, Zhai, T, Jian, W, Xu, R, et al. 10 years of health-care reform in China: progress and gaps in universal health coverage. Lancet. (2019) 394:1192–204. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32136-1
28. Chai, PP, Li, Y, Zhai, TM, Guo, F, Fu, XG, Zhang, YH, et al. Results and analysis of China's total health expenditure accounting in 2022. Health Economics Research. (2024) 41:14–9. doi: 10.14055/j.cnki.33-1056/f.2024.01.020
29. Yu, BR, and Xu, Q. The impact of social medical security on residents' health and economic burden of diseases. China Health Serv Manage. (2016) 33:346–349+376.
30. Chen, Y, Xiong, XJ, Liu, GE, and Chen, G. Research on the impact of medical insurance on the economic burden of direct diseases for urban residents in China. China Health Econ. (2009) 28:13–6.
31. Li, Y, Wang, D, Xiang, GCH, Huang, YX, and Lv, SW. Analysis of the cost accounting results for malignant tumor treatment in Guangdong Province-based on “SHA2011”. Health Econ Res. (2019) 36:25–8. doi: 10.14055/j.cnki.33-1056/f.2019.09.007
32. Fang, WQ, Xu, XR, Dai, HZH, and Li, X. The impact of national medical insurance admission negotiation policies on the use of new anti-cancer drugs. Med News. (2020) 39:1665–72.
33. You, R, Zou, X, Hua, YJ, Han, F, Li, L, Zhao, C, et al. Salvage endoscopic nasopharyngectomy is superior to intensity-modulated radiation therapy for local recurrence of selected T1-T3 nasopharyngeal carcinoma – a case-matched comparison. Radiother Oncol. (2015) 115:399–406. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.04.024
34. Shi, XG, Wang, XX, Zhang, X, Chen, HP, Zhou, SC, Gong, X, et al. Analysis of factors influencing the economic burden of elderly malignant tumor patients in Macheng City. China Health Serv Manage. (2019) 36:751–752+776.
35. Chen, B, Zhan, Z, Xu, Y, Yu, S, Huang, J, Fang, Y, et al. Long-term trends in the burden of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China: a comprehensive analysis from 1990 to 2021 and projections to 2030 based on the global burden of disease study 2021. Radiother Oncol. (2024) 202:110613. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110613
36. Haji Noor Mohamed, NM, Mydin, S, Che Halim, H, and Musa, MY. A systematic review on Clinico-Aetiopathological trends of nasopharyngeal Cancer in Asia. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2023) 75:4151–7. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-03905-z
37. Long, M, Fu, Z, Li, P, and Nie, Z. Cigarette smoking and the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. BMJ Open. (2017) 7:e016582. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016582
38. Lv, WB, Liu, JH, Qu, HL, Luo, MH, Yu, XF, Huang, SP, et al. Analysis of the screening status of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the sample population of Shunde, Guangdong Province. Guangdong Med J. (2018) 39:86–8. doi: 10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.2018.s2.027
39. Chang, ET, Ye, W, Zeng, YX, and Adami, HO. The evolving epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2021) 30:1035–47. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-1702
40. Chua, MLK, Wee, JTS, Hui, EP, and Chan, ATC. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. (2016) 387:1012–24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00055-0
41. Khor, TH, Tan, BC, Chua, EJ, and Chia, KB. Distant metastases in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Radiol. (1978) 29:27–30. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(78)80160-3
42. Shen, Z, Cao, Y, Luo, L, Han, L, Li, J, Wang, L, et al. The global, regional, and national burden of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its attributable risk factors in 194 countries and territories, (2021) 2007–2017.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, total medical expenditure, out-of-pocket costs, the rates of out-of-pocket costs, random forest model
Citation: Zhu P, Zhang Y, Huang L, Wei B, Zhu X, Zeng P and Nong J (2025) Who determines nasopharyngeal carcinoma inpatients’ medical expenditure? Importance factor ranking using the random forest model. Front. Public Health. 13:1639687. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1639687
Edited by:
Chao Ma, Southeast University, ChinaReviewed by:
Gheorghe Gindrovel Dumitra, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, RomaniaRamkrishna Mondal, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (Patna), India
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Zhang, Huang, Wei, Zhu, Zeng and Nong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jingya Nong, amluZ3lhbm9uZ0AxNjMuY29t
 Pinghua Zhu
Pinghua Zhu Yu Zhang2
Yu Zhang2 Jingya Nong
Jingya Nong