- 1School of Management, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China
- 2College of Civil Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China
Background: With the aging of China’s population deepening, the development of age-friendly communities (AFCs) is playing an important role in alleviating the pressure of older adult care and enhancing the quality of life (QoL) of older adults. This paper aims to investigate the complicated impact of AFCs on the QoL of older adults through a questionnaire survey.
Methods: A questionnaire survey was designed to explore the intricate relationships between components of AFCs and QoL factors from older adults’ perspective. A total of 1,396 older adults completed the survey. Factor analysis was used to identify AFC components and QoL factors, and the relationships between AFC components and QoL factors were predicted using structural equation modeling (SEM).
Results: Four AFC components and three QoL factors for older adults were identified. The SEM results revealed that (1) physical health was mainly positively influenced by green spaces and negatively affected by public healthcare services; (2) apart from public transportation, most AFC components were indicative of psychological health; and (3) social networks were primarily influenced by green spaces and community support.
Conclusion: To provide a better living environment for older adults, it is suggested that communities renovate existing structures to expand green spaces, add accessible facilities, and increase greenery. Communities should also enhance social environments by improving healthcare services, ensuring accessible medical care, and organizing cultural and recreational activities to promote older adults’ social participation and improve their QoL.
1 Introduction
In the global context, the aging population phenomenon is gaining increasing significance. According to World Population Prospects 2024 published by the United Nations, it is projected that by the late 2070s, the global population of individuals aged 65 and above will reach 2.2 billion, surpassing the number of individuals under 18 years old (1). Developed countries, such as Japan and Germany, are already experiencing heavily aging societies, while developing countries also face challenges caused by accelerating aging rates. Since entering the aging society stage in 2000, China has witnessed a deepening level of population aging. At the end of 2023, there were 297 million people aged 60 or above in China, accounting for 21.1% of the country’s total population (2). Compared to developed countries, China has transitioned from an aging society to a deeply aging society at a faster pace. To effectively address the challenges posed by population aging, the Chinese government has initiated efforts to establish age-friendly communities (AFCs) since 2020.
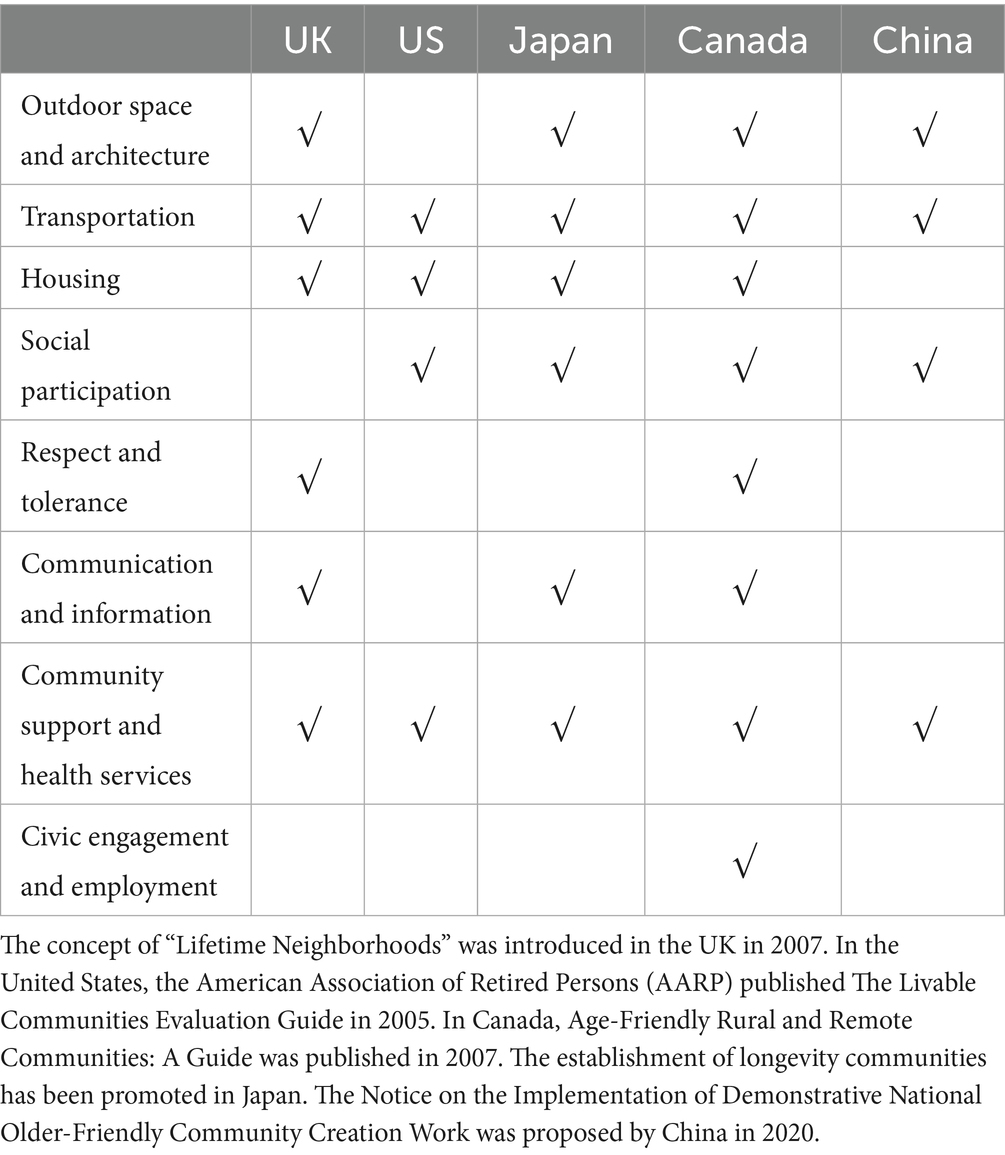
AFCs, which were first proposed and promoted by the World Health Organization (WHO), focus on meeting the needs of older people and improving their quality of life (QoL) and wellbeing (3). According to recent data, the WHO Global Network for Age-friendly Cities and Communities currently includes 1,606 cities and communities in 53 countries, covering over 330 million people worldwide (4); only 39 of these cities and communities are in China (including 18 in Hong Kong) (5). Different countries have formulated different frameworks and guidelines for AFCs (6). In the United States, the contents of AFC construction include housing planning, health and wellbeing, accessible services, and community participation (7). The United Kingdom promotes the concept of Lifetime Neighborhoods, which includes housing, free public transportation, a green environment, community safety, culture and learning opportunities, and care and support services (8). Canada was one of the first countries to propose the concept of healthy communities and start building age-friendly healthy communities (9); it primarily evaluates the degree of age-friendliness in terms of physical environment, social environment, and service in order to determine indicators suitable for rural and remote communities that meet older people’s needs while enhancing community support for their health and active living. The Japanese government actively advocates for aging-in-place by promoting home adaptations for older populations and constructing small-scale multifunctional nursing facilities in familiar neighborhoods, with the fundamental goal of providing support (10). Hence, it is evident that no universally applicable standard for the development of AFCs exists, necessitating the need for tailored solutions based on local contexts.
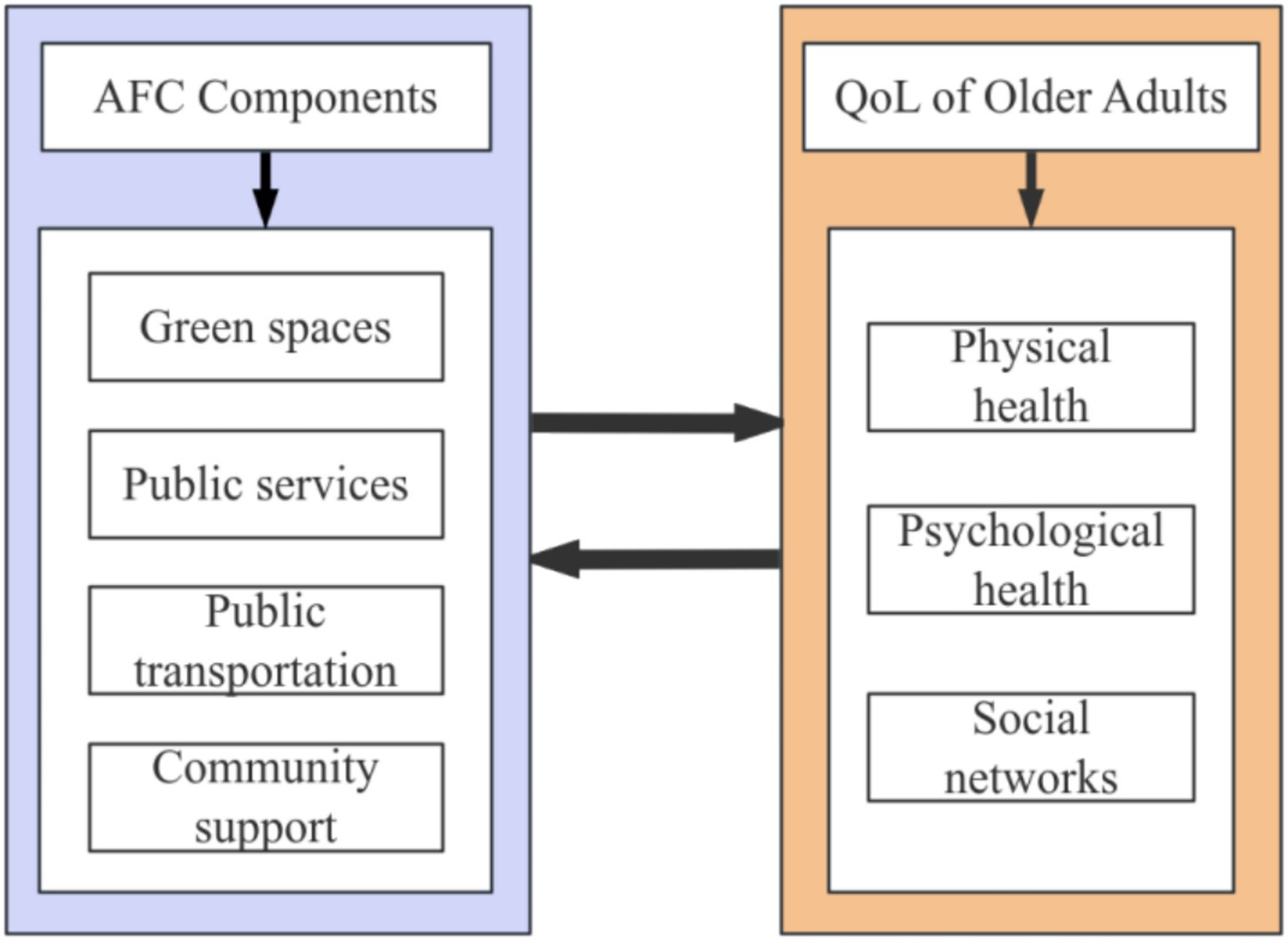
In recent years, the Chinese government has actively promoted the construction of AFCs. However, not every component of AFCs proposed by the WHO is suitable for the development of AFCs in China (11). In promoting the construction of AFCs, China primarily focuses on six aspects: living environment, transportation, community services, social participation, cultural life, and technological services (12). Taking into account the framework for AFCs proposed by the WHO and other countries, outdoor space and architecture, public transport, housing, social participation, community support, and health services are shared priorities in most countries. This article will discuss the impact of AFCs on the QoL of older adults, focusing on four aspects: green spaces, public health services, public transportation, and social support. The reason for not considering housing and social participation in this context is that this article takes a community-oriented approach, which focuses on the core public services and infrastructure of the community’s daily functions. This focus enables us to accurately examine the impact of these aspects managed by the community on the lives of the older adult. Therefore, the current study discusses the impact of different components of AFCs on older adults’ QoL across four dimensions. The objectives of this study are to (1) identify the components of AFCs, (2) ascertain the QoL factors of older adults, (3) examine the impact of AFC components on QoL factors for older adults, and (4) propose strategies to enhance the QoL of older adults and optimize the development of AFCs. The study aims to explore the development of AFCs in China, supplementing and enriching the existing literature on AFCs and the QoL of older adults. It investigates the impact of different components of AFCs on the QoL of older adults in China and provides empirical recommendations.
2 Literature review
With the acceleration of global aging, many countries and regions have begun practicing AFC construction, their efforts resulting in certain achievements. In the United Kingdom, London adopts an inclusive design strategy to ensure a friendly environment for older people, while Manchester, the first city in the UK to join the WHO Global Network of AFCs, encourages retrofitting housing and public places through policymaking and funding support (13). The United States provides policy and regulatory support for developing AFCs while encouraging research institutions and enterprises to develop specialized products that meet older people’s special needs (14). Japan focuses on using smart devices, such as smart home systems and wearable health monitoring devices, to protect older people’s safety while also establishing community safety networks to ensure their living security (15). Japan is the country in Asia that entered the aging society stage earliest. It has been promoting the construction of ‘longevity communities’ and advocating for the establishment of a comprehensive older adult care model that combines healthcare and nursing services within large community settings (16). Although different countries have different focuses with regard to AFCs, they all aim to improve older people’s QoL in various ways. Table 1 shows the emphasis of AFC construction in five countries.
QoL for older adults is generally considered to be a multidimensional concept. The WHO divides QoL into eight main dimensions: outdoor spaces, public transportation, housing, social participation, respect and social inclusion, communication and information, community, and health services (17). The main QoL factors for older adults have been identified as physical health, mental health, and social networks (18). Physical health refers to the physical fitness, pain management, and daily activity ability of older adults. Being in good physical condition is the foundation for maintaining a high QoL (19, 20) Psychological health reflects the satisfaction and happiness in older adults’ lives and effectively prevents and alleviates symptoms of depression (21, 22). Social networks provide emotional support and a sense of belonging for older adults, allowing them to enjoy richer life experiences through interactions with family, friends, and the community (23). Although existing research has explored the factors influencing QoL for older adults, further investigation is needed into the specific components of AFCs and their impact on older adults’ QoL. Therefore, it is important to further discuss the influence of each component of AFCs on the QoL of older adults in order to optimize AFC development and enhance their living environment.
The existing research has shown that the establishment of AFCs can effectively enhance the QoL of older adults from different dimensions (24–26). In recent years, the construction of AFCs has gradually attracted attention in various parts of China, enhancing older adults’ QoL by improving both their material and social environment. Local governments are also proposing policies to create suitable and livable environments for older adults in rural areas, thereby promoting their social participation (27).
Green spaces are important places for older adults to socialize and engage in outdoor activities, providing fitness equipment and entertainment facilities suitable for them, which promotes their physical health and enhances their life satisfaction (28, 29).
Public healthcare service institutions can provide basic medical services for older adults. The level of improvement in community public healthcare services has a significant promoting effect on older adults’ wellbeing. Providing psychological healthcare for older adults can effectively alleviate negative emotions (30, 31). With continuous technological advancements, intelligent older adult care services will become a future trend in older adult care (32).
Public transportation provides convenient travel options for older adults, and its accessible facilities reduce the difficulties of getting around, enabling them to participate in more social activities (33). Additionally, the fixed routes and schedules of public transportation also help older people to better plan their trips.
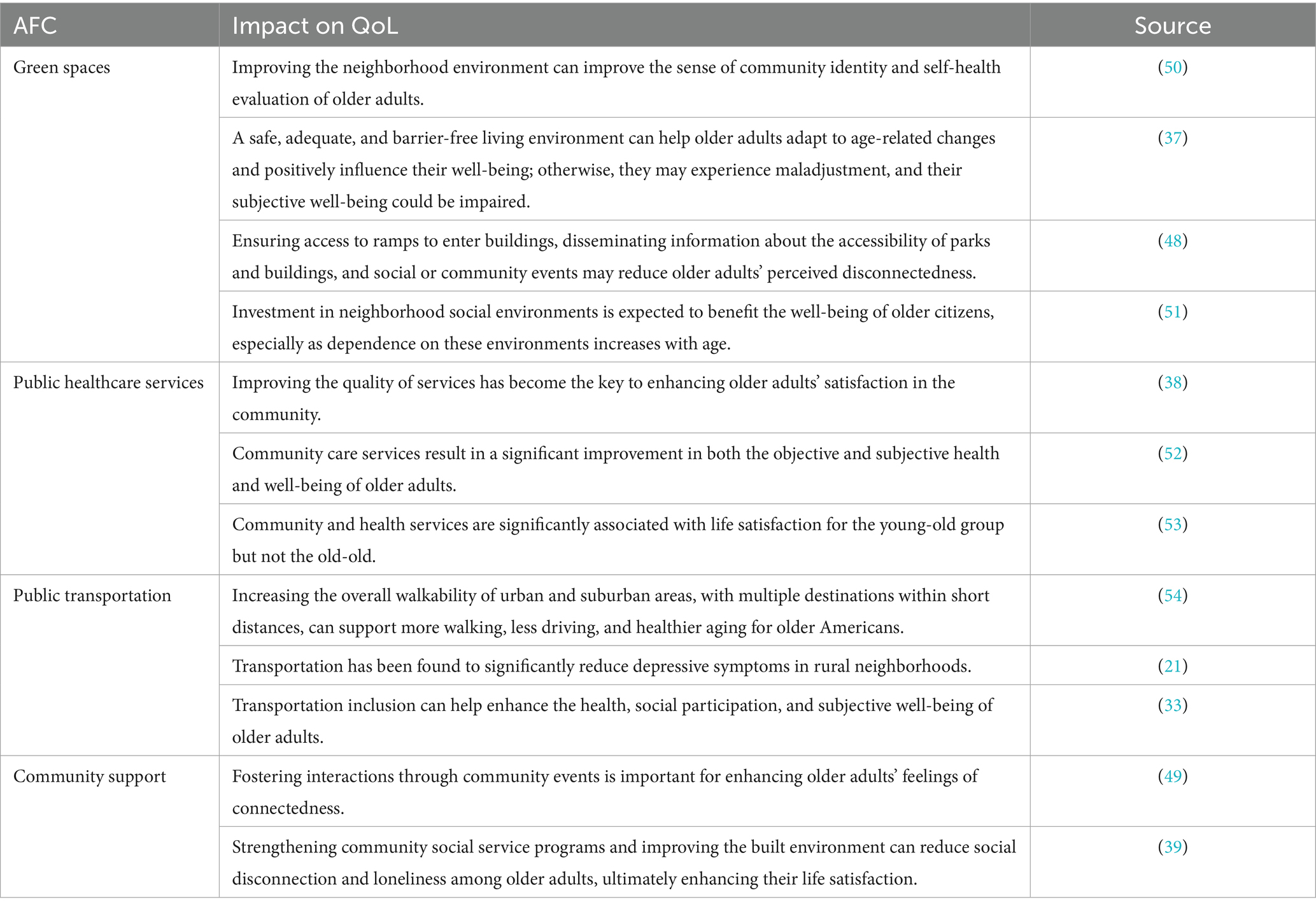
Community support is particularly important in enhancing the overall QoL of older adults (34). Moreover, such support can enhance older adults’ satisfaction with their lives (35). Dikken et al. (36) developed a specific questionnaire to gain a better understanding of older individuals’ experiences regarding the age-friendliness of cities. The composition of AFCs is therefore assumed to determine the QoL of older individuals. Previous studies on the impact of AFCs on QoL factors are summarized in Table 2.
Previous studies have examined the relationships between several AFC components and the QoL of older adults. Green spaces enhance the happiness and community identity of the older adult by optimizing the community environment (37). Public healthcare services directly affects community satisfaction (38). The accessibility of public transportation can alleviate depressive symptoms and contribute to improved social participation among the older adult (21). Community support effectively reduces feelings of loneliness and enhances life satisfaction by strengthening social activities and services (39). However, there is limited research on the comprehensive impact of AFC systems on various aspects of older adults’ QoL. In fact, AFCs are comprehensive systems with different elements, such as green spaces, community support, healthcare, and so on. Therefore, it is important to consider AFCs as a whole and to systematically evaluate the different components of AFCs to explore their multifaceted effects on older adults’ QoL. The conceptual model for this study is depicted in Figure 1.
3 Methodology
A questionnaire survey was conducted to investigate the impact of AFCs on the QoL of older adults. The questionnaire is shown in the appendix. The questionnaire was divided into three main sections: Appendix A, which covered the background information of the respondents (including age, gender, education level, living arrangements, and health status); Appendix B, which assessed the respondents’ satisfaction with current AFCs (green spaces, public healthcare services, public transportation, and community support); and Appendix C, which focused on their QoL (physical health, mental health, and social networks). The questionnaire incorporated items from the WHO Age-Friendly Cities Checklist and the WHOQOL-BREF scale to measure AFC components and QoL, respectively. The abbreviated version of the WHOQOL-BREF was chosen to mitigate respondent fatigue among the older adult (40). We conducted a questionnaire survey in Hefei, China, in 2022 to investigate the complicated relationships between the components of AFCs and the QoL of older adults. In 2022, the permanent population of Hefei was 9.634 million, and the older adult population aged 60 and above was 1.516 million, accounting for 15.74%. The study received support from the local community, including logistical support and assistance with participant recruitment.
The study employed a purposive sampling method in order to ensure data validity. Older respondents aged 60 or above who had resided in various communities for at least 6 months were selected to guarantee their sufficient understanding of AFCs. Furthermore, face-to-face interviews were conducted by trained research assistants, who provided support and explanations whenever necessary in order to ensure the accuracy and comprehensibility of the questionnaire responses. A total of 1,383 older adults completed the survey; 44% of the respondents were male and 56% were female. With regard to age there were 50.6% of participants in age group 60–67, 37% in age group 70–79, 11.4% in age group 80–89 and only 1% in age group over 90 years of age. Over 80% of the respondents were not well educated, and only 4.1% had attended college. Almost half of the respondents lived with their husband or wife, 13.7% lived alone, 42.1% lived with their children, and 5.0% lived with their relatives. Over 60% of the respondents were healthy; 12.2% were generally healthy and 0.9% were generally unhealthy.
The collected data underwent multiple statistical methods to construct a comprehensive structural model of the intricate relationship between different components of AFCs and the QoL of older adults. First, exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) were conducted to identify AFC factors and QoL factors for adults. The analysis was conducted using SPSS Statistics 27. EFA was utilized to preliminarily identify latent factors by examining the correlation matrix of the survey items and determining suitable data for factor extraction. Subsequently, CFA was employed to validate the initially identified factor structure by confirming the significant loadings of all items on their hypothesized latent factors, ensuring the validity and reliability of the model. To further establish internal consistency, a reliability analysis was performed on the identified factors using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient.
A structural equation model was adopted to incorporate the measurement items and latent factors. Structural equation modeling (SEM) allows the estimation of unobservable latent variables and the examination of complex causal relationships among these variables. The structural equation model was constructed to examine the relationships between the latent variables of AFC components and QoL factors. The SEM framework consists of two components: the measurement model and the structural model.
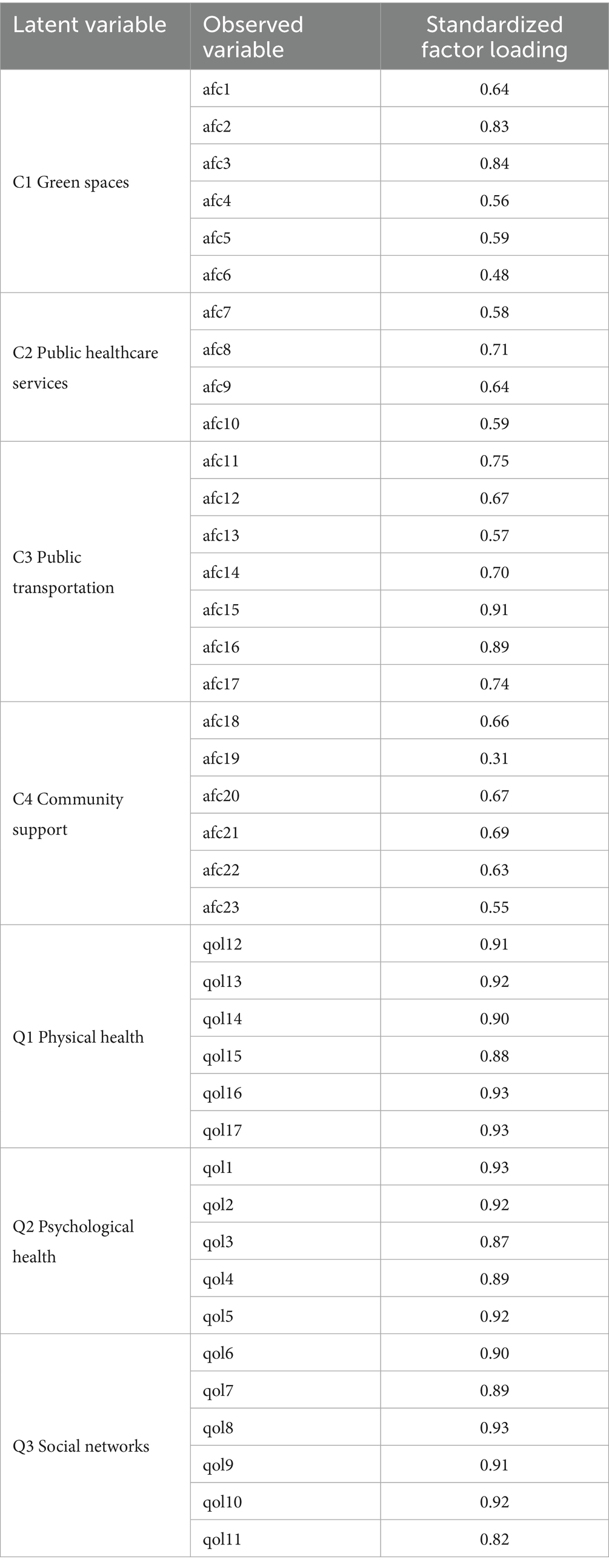
The measurement model was first established to link observed variables to their respective latent factors (C1-C4 and Q1-Q3) through confirmatory factor analysis, as shown in Equations 1, 2.
where and are vectors of observed indicators for AFC components and QoL factors, respectively; and denote the latent constructs; and are the matrices of standardized factor loadings; and represent measurement errors.
The structural model then specified the causal paths between AFC components and QoL domains, as shown in Equation 3.
Where represents the endogenous latent variables, denotes the exogenous latent variables, and are matrices of structural coefficients, and denotes the residual errors.
The fit indices used for evaluating model adequacy included root mean square error approximation, comparative fit index, normed fit index, incremental fit index, and non-normed fit index. The model with the optimal-fit indices was selected for interpretation. The analysis was conducted using AMOS 28, which facilitates the graphical representation of complex models and the handling of latent variables with multiple indicators.
4 Results
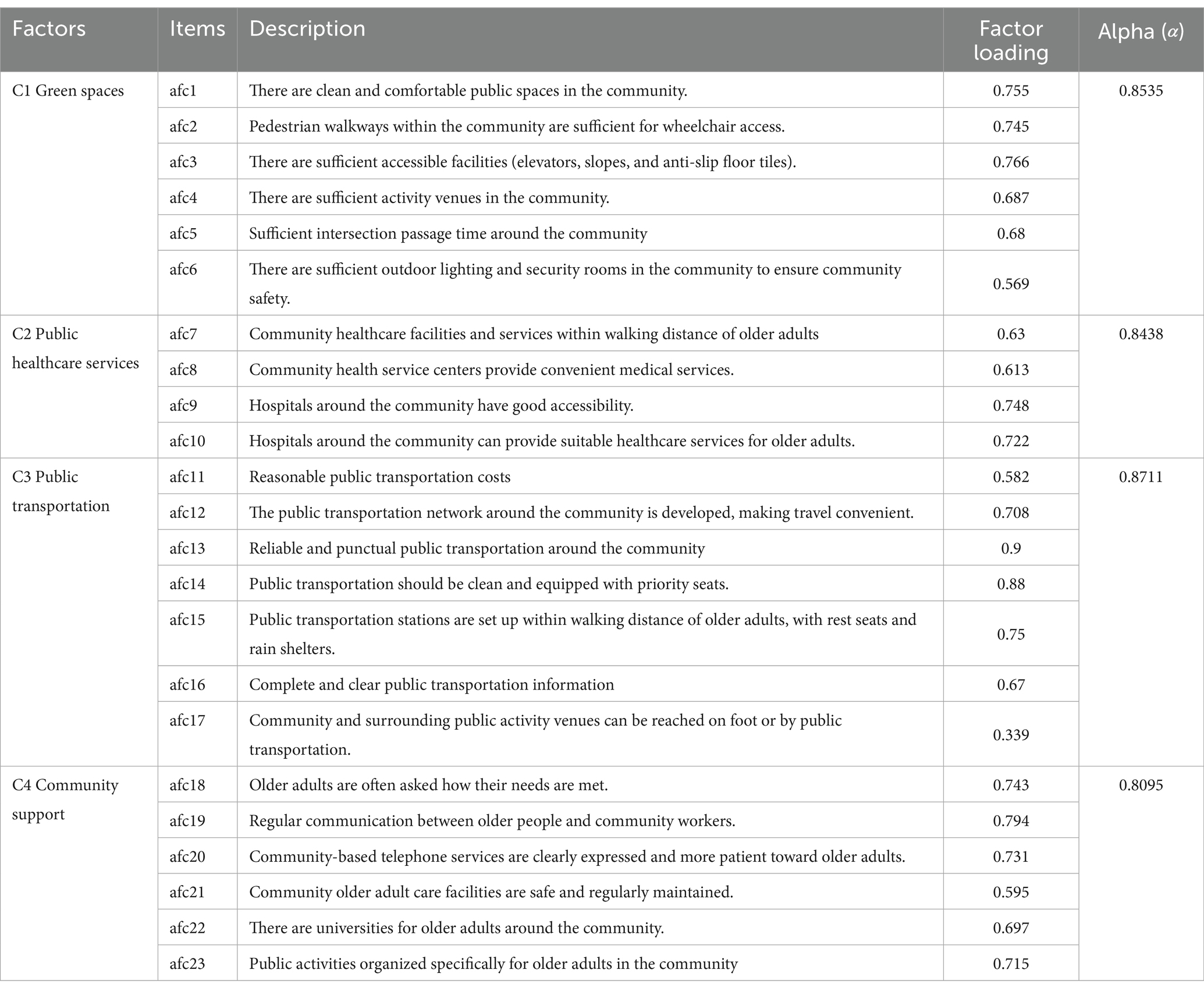
Factor analysis was adopted to reduce a large set of items to a smaller set of meaningful factors. To further validate the internal consistency, reliability analysis was conducted on the identified factors. The results of the EFA of AFCs and the QoL of older adults are presented in Tables 3, 4. The Kaiser–Meyer–Oklin (KMO) values for the components of AFCs and the factors of older adults’ QoL were 0.771 and 0.708, respectively, both of which exceeded the recommended value of 0.6. Bartlett’s Test reached statistical significance, thus supporting the factorability of the correlation matrix.
The four AFC components [i.e., green spaces (C1), public healthcare services (C2), public transportation (C3), and community support (C4)] had coefficient alphas ranging from 0.809 to 0.885. Apart from item afc17, all items were appropriately loaded into acceptable factors. Item afc17 was removed from public transportation (C3) due to its low factor loading of 0.339. Reliability testing showed a significant improvement in the Cronbach’s alpha value for public transportation (C3) after removing item afc17. As older adults in China age, their physical functions gradually decline and long walks or using public transportation may impose additional burdens on their bodies. Considering safety, older adults prefer to engage in daily activities near their homes or within the community. Additionally, the social circles of older adults are relatively small and mainly concentrated in the community and nearby areas, which also makes them more inclined to participate in activities in these familiar places.
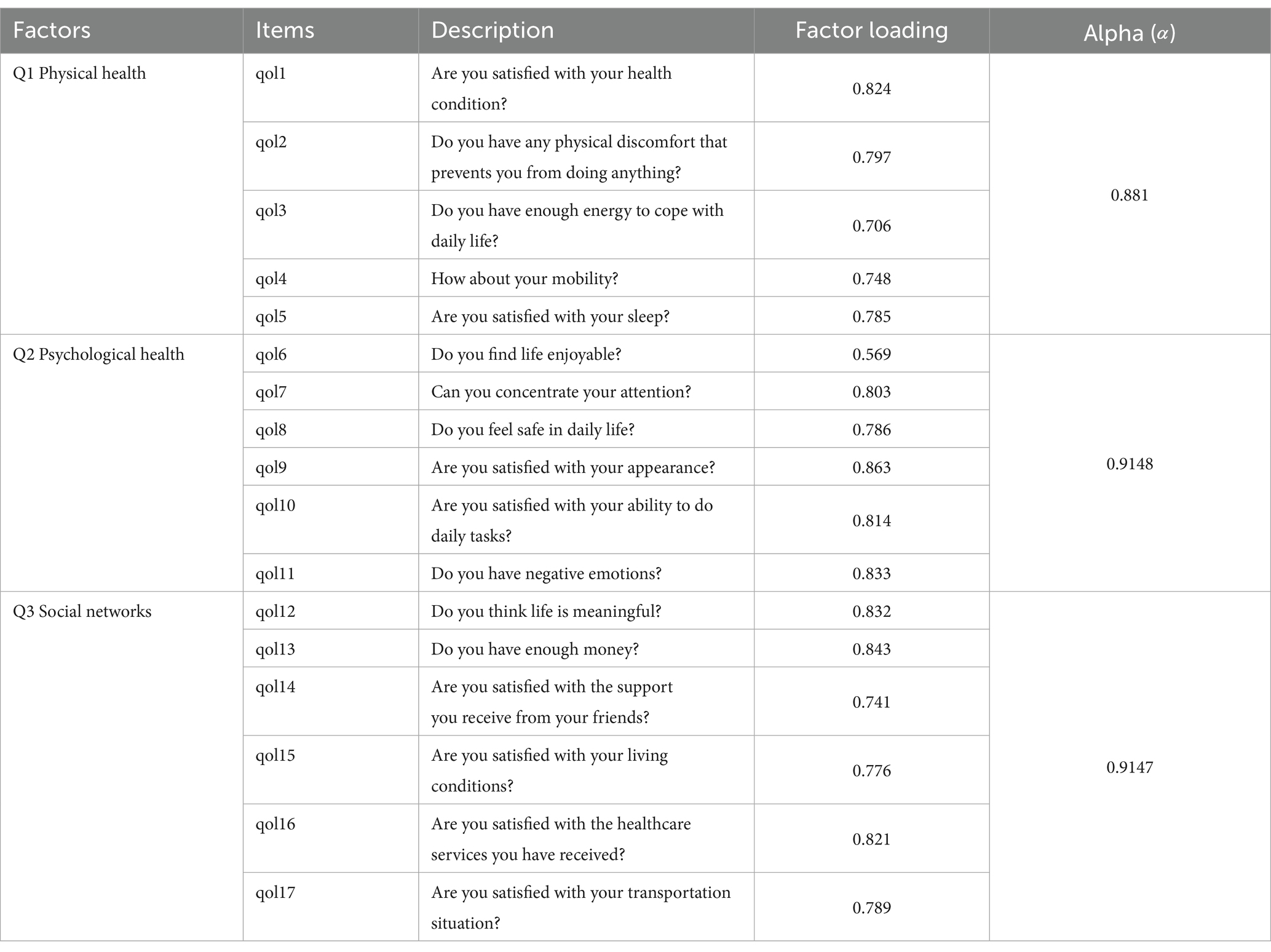
Three QoL factors were identified: physical health (Q1), psychological health (Q2), and social networks (Q3). Each of these QoL factors had a coefficient alpha >0.8, which meant that the factors were reliable, internally consistent, and valid for further analysis. Physical health includes health condition, absence of physical discomfort, energy levels for daily life, mobility, and satisfaction with sleep. Psychological health emphasizes enjoying life, ability to concentrate, feeling safe in daily life, and satisfaction with appearance and ability to perform daily tasks, as well as the absence of negative emotions. The social networks factor includes enjoying life, achieving financial sufficiency, and being satisfied with support from friends, living conditions, healthcare services received, and transportation situation.
To investigate the relationship between AFC components and the QoL of older adults, the SEM was further developed using AMOS. Through SEM, unobservable latent variables of the AFC factors and QoL factors were estimated from observed indicators by establishing the relationships (paths) among the latent variables (41). SEM can also be used to investigate complicated causal relationships using both quantitative data and qualitative assumptions (42).
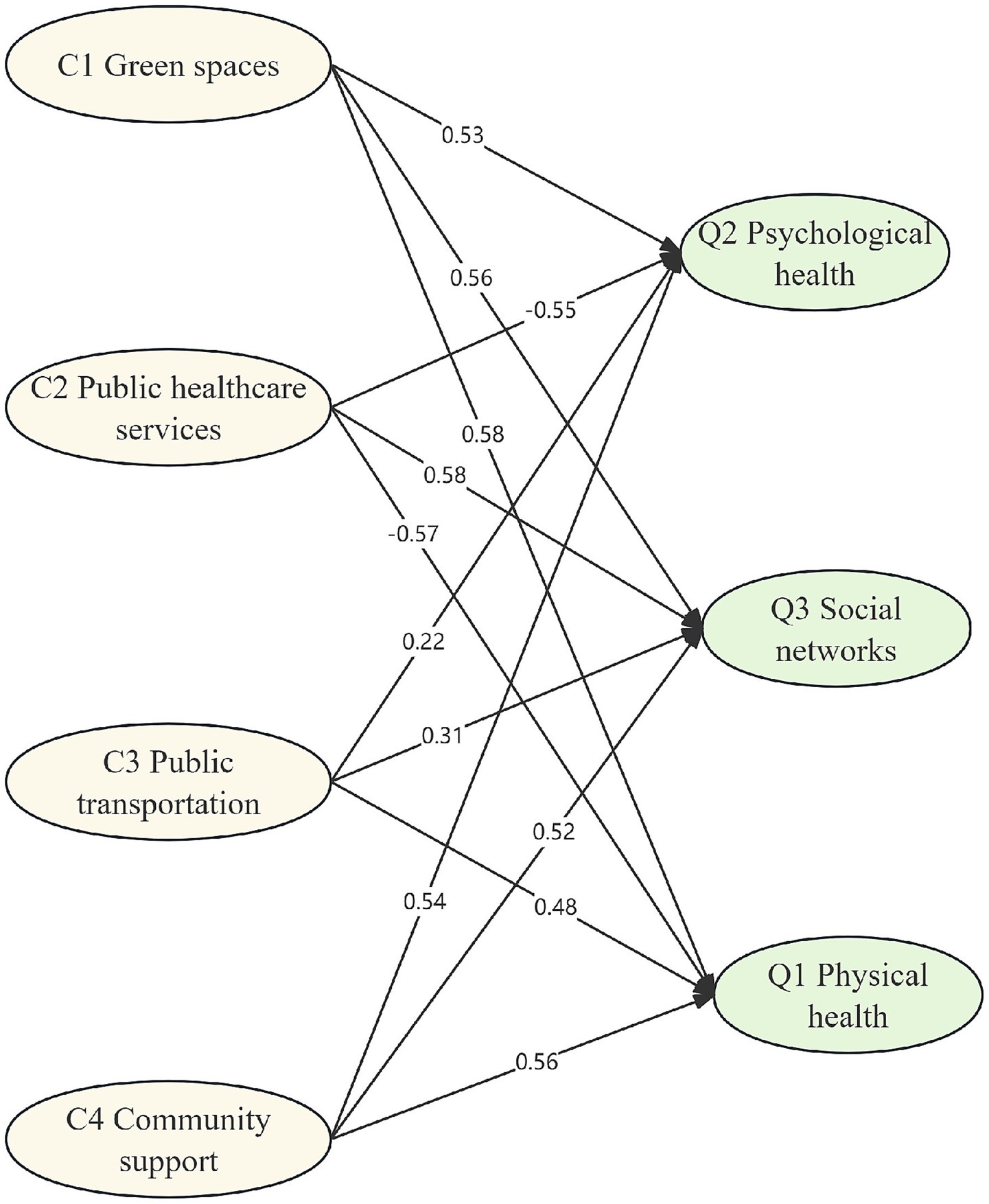
The measurement model was first evaluated using confirmatory factor analysis to verify the relationships between the latent constructs and their observed indicators. The standardized factor loadings of each indicator are presented in Table 5. The paths among the AFC and QoL factors in the structural model are shown in Figure 2. The hypothesized model was tested and subsequently refined to improve model fit. The results revealed that this final model had the lowest badness-of-fit indices (RMSEA: 0.073) and the highest overall fit indices (CFI: 0.883, NFI: 0.831, IFI: 0.894, NNFI: 0.819) (43). The paths of the SEM indicated the following: (1) green spaces (C1) positively influenced physical health (Q1), psychological health (Q2) and social networks (Q3); (2) public healthcare services (C2) negatively affected physical health (Q1) and psychological health (Q2); (3) the relationships between public transportation (C3) and the QoL factors were not significant; and (4) community support (C4) impacted psychological health (Q2) and social networks (Q3) positively.
5 Conclusion
The results support the argument that green spaces play a crucial role in significantly influencing the physical health, mental wellbeing, and social networks of older adults, which aligns with previous studies (44, 45). Green spaces, equipped with convenient facilities such as good lighting, spacious sidewalks, and comfortable resting areas, provide suitable venues for activities like daily walks, tai chi, and square dancing (40). These activities not only enhance physical fitness and prevent chronic diseases but also stimulate the vitality of older adults. Open spaces such as parks within the community can help improve the mood and reduce feelings of loneliness among older individuals, which is beneficial for their mental health. Moreover, green spaces and recreational areas in the community provide more social opportunities to meet with friends and neighbors, helping to strengthen the social network of older people and increase their emotional connection and sense of belonging in society. Therefore, communities can enhance older adults’ QoL by regularly maintaining and upgrading accessible facilities while improving environmental hygiene management to optimize green spaces further.
It is interesting to note that public healthcare services have a negative impact on the physical and psychological health of older individuals. Although community healthcare institutions may offer convenient and nearby medical services for older adults, the quality of their medical services often fails to meet older adults’ needs. Community healthcare facilities often lack advanced medical equipment and specialized medical personnel, making it difficult to provide complex or emergency medical services. Many older adults tend to go to tertiary hospitals with more comprehensive facilities and higher medical standards, especially in China (46). However, the long waiting times in tertiary hospitals affect their trust in and reliance on medical services, as well as causing inconvenience and psychological pressure when accessing necessary healthcare services. Thus, neither community hospitals nor top-tier hospitals provide adequate mental health treatment services for older adults, and this has a negative influence on their physical and psychological health.
The research findings indicate that not all components of AFCs have an impact on the QoL of older adults. In this study, public transportation did not have a significant impact on QoL factors, possibly because older adults prefer to engage in activities near their community and reduce their reliance on public transportation. Additionally, with the implementation of the “15-min living circle” concept in many cities in China, the daily needs of residents can be met within a 15-min walking or cycling distance. In this case, older adults may be more inclined to participate in activities within their community rather than relying solely on public transportation for travel, making the impact of public transportation on QoL negligible (47).
Community support has a significant positive impact on the mental health and social networks of older individuals. Regular communication between older adults and community workers, along with attention to their needs by the community, makes them feel cared for and supported, thus reducing feelings of loneliness and depression, which can improve their mental wellbeing (48). A supportive environment within the community, coupled with various social activities, provides more opportunities for social interaction among older adults. This helps to enhance emotional connections and foster a sense of belonging among them, ultimately improving their overall QoL (49). Therefore, communities should strengthen their focus on responding to the needs of older individuals by organizing regular community activities suitable for them while enhancing training for community workers to increase sensitivity toward these needs. Furthermore, improving the quality and safety of community older adult care facilities is crucial in ensuring comfortable living conditions that are secure.
6 Recommendations
6.1 Policy and practical implications
The results of the current study demonstrate the integrated relationships between AFC components and the QoL of older adults. Below are some suggestions for improving the construction of communities that are friendly to older individuals. Green space is crucial for the construction of AFCs. To enhance the physical environment of old neighborhoods, it is suggested that school facilities should be utilized and old buildings should be renovated to expand green spaces. Furthermore, accessible facilities, such as handrails and seating areas, should be installed; greenery and shade should be increased; and fitness equipment and recreational facilities suitable for older adults should be added in order to create aging-friendly transformations in outdoor areas. Encouraging active participation in outdoor activities among older adults helps meet their specific needs.
To enable public healthcare services to better fulfill their role in supporting older adults’ QoL, communities should enhance the coverage and quality of public facilities and services, improve the community healthcare service system, upgrade medical services in community health centers, and ensure timely access to medical care for older people. Therefore, it is necessary for us to enhance the quality of community health services and improve the accessibility of tertiary hospitals, particularly in terms of medical services and psychological health treatments. Communities can also utilize internet technology to establish smart older adult care service platforms that offer convenient services such as remote medical care, emergency rescue support, housekeeping appointments, and so on. Additionally, attention should be given to addressing mental health issues among older individuals by providing psychological counseling and support services. Simultaneously, establishing community canteens or meal assistance points to provide balanced meals and organizing various cultural and recreational activities, such as tai chi practice, square dancing, choir singing, and so on, can meet the basic living needs and spiritual-cultural pursuits of older people while enhancing their QoL.
6.2 Research implications
Although this study has explored the impact of AFCs on the QoL of older people in detail through SEM, there are still some limitations. First, the sample size of the questionnaire survey was limited, and although it included 1,396 older adults, the geographical and socioeconomic backgrounds of the sample may affect the universality of the results. Second, the study mainly used quantitative questionnaire methods, which provide broad data support but may overlook subjective experiences and individual differences among older people. Additionally, the study did not incorporate the potential role of digitalization, such as smart technologies and digital community platforms, which are increasingly relevant to modern age-friendly communities.
To address these limitations, future research should aim for more diverse samples from various geographic and socioeconomic backgrounds to enhance the generalizability and representativeness of the results. Combining quantitative and qualitative methods can allow the comprehensive exploration of AFCs’ impact on older people’s QoL to gain a more complete understanding. Longitudinal studies can track changes in older people’s QoL over different time periods to analyze the long-term effects resulting from the construction of AFCs. Future studies should also examine how digital tools, such as health monitoring wearables and smart home systems, could be integrated as components of AFCs or as moderating factors influencing older adults’ QoL. The implementation effect of related policies for AFCs can also be studied by analyzing their actual impact on older people’s QoL; specific community case studies could summarize successful experiences as well as practical lessons learned that provide actionable guidance for policymaking or community building programs.
7 Conclusion
Facing the challenge of rapid population aging in China, the Chinese government is actively promoting the construction of AFCs. However, there are currently only a limited number of AFCs in China that meet the requirements set by the WHO. Despite significant efforts from the government in terms of policies and resources, there is still a lack of systematic research on the effectiveness and specific impact mechanisms of these communities in practical operation. Therefore, this study sought to explore the impact of various components of AFCs on the QoL of older individuals through a large-scale questionnaire survey. The research findings identified four components of AFCs (green spaces, public healthcare services, public transportation, and community support) and three domains of older adults’ QoL (physical health, psychological health, and social networks). The results from the structural equation model revealed the comprehensive relationship between AFC components and older adults’ QoL. The SEM results predicted the comprehensive relationship between AFC components and older adults’ QoL. The study found that physical health QoL is mainly positively influenced by green spaces but negatively affected by public healthcare services. Except for public transportation, most components of AFCs can indicate psychological QoL. Social networks QoL is primarily influenced by green spaces and community support.
On the basis of the current research findings, suggestions have been proposed for improving AFCs by expanding green spaces, improving public healthcare services, enhancing healthcare services, and organizing various recreational and social activities. Strengthening community support is also recommended for promoting communication between older adults and community workers as well as improving the quality and safety of older adult care facilities in the community. Future research should consider increasing sample size and geographical diversity to enhance the generalizability of results. Additionally, employing digital methods, such as remote monitoring and analyzing engagement with smart community platforms, can provide objective, longitudinal data on older adults’ behaviors and needs, thereby validating and enriching the findings of this study.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YT: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Methodology. JX: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation. JY: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Resources, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 72274052).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Correction note
This article has been corrected with minor changes. These changes do not impact the scientific content of the article.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1646195/full#supplementary-material
References
1. World Population (2024). Prospects. Available online at: https://population.un.org/wpp/ (accessed September 25, 2024).
2. China Works to Provide Quality Elderly Care Services: Officials. Available online at: https://english.www.gov.cn/news/202409/25/content_WS66f35ba7c6d0868f4e8eb3ae.html (accessed October 14, 2024).
3. Lui, C-W, Everingham, J-A, Warburton, J, Cuthill, M, and Bartlett, H. What makes a community age-friendly: a review of international literature. Australas J Ageing. (2009) 28:116–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-6612.2009.00355.x
4. About the Global Network for Age-friendly Cities and Communities. Available online at: https://extranet.who.int/agefriendlyworld/who-network/ (accessed September 25, 2024).
5. Global Database of Age-friendly Practices. Available online at: https://extranet.who.int/agefriendlyworld/afp/ (accessed October 14, 2024).
6. Fitzgerald, KG, and Caro, FG. An overview of age-friendly cities and communities around the world. J Aging Soc Policy. (2014) 26:1–18. doi: 10.1080/08959420.2014.860786
7. Scharlach, A. Creating aging-friendly communities in the United States. Ageing Int. (2012) 37:25–38. doi: 10.1007/s12126-011-9140-1
8. Rooney, C, Hadjri, K, and Craig, C. Assessing lifetime homes standards and part M building regulations for housing design in the UK. Des J. (2013) 16:29–50. doi: 10.2752/175630613X13512595146871
9. Federal, Provincial and Territorial Ministers Responsible for Seniors Meet to Discuss Support for Canada’s Aging Population. (2024). Available online at: https://www.canada.ca/en/employment-social-development/news/2022/02/federal-provincial-territorial-ministers-responsible-for-seniors-meet-to-discuss-support-for-canadas-aging-population.html (accessed October 6, 2024).
10. Thang, LL, Yui, Y, Wakabayashi, Y, and Miyazawa, H. Promoting age-friendly Community of Support and Care in Japan’s aging neighborhood: the Nagayama model. Aging Health Res. (2022) 3:100111. doi: 10.1016/j.ahr.2022.100111
11. Wang, Y, Gonzales, E, and Morrow-Howell, N. Applying WHO’S age-friendly communities framework to a National Survey in China. J Gerontol Soc Work. (2017) 60:215–31. doi: 10.1080/01634372.2017.1292980
12. Notice on the Implementation of Exemplary National Elderly-friendly Community Creation Work. Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-12/14/content_5569385.htm (accessed September 25, 2024).
13. van Hoof, J, Marston, HR, Kazak, JK, and Buffel, T. Ten questions concerning age-friendly cities and communities and the built environment. Build Environ. (2021) 199:107922. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.107922
14. Buffel, T, Phillipson, C, and Rémillard-Boilard, S. Age-friendly cities and communities: new directions for research and policy In: D Gu and ME Dupre, editors. Encyclopedia of gerontology and population aging. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2019). 1–10.
15. Tanaka, M, Ishii, S, Matsuoka, A, Tanabe, S, Matsunaga, S, Rahmani, A, et al. Perspectives of Japanese elders and their healthcare providers on use of wearable technology to monitor their health at home: a qualitative exploration. Int J Nurs Stud. (2024) 152:104691. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2024.104691
16. Sudo, K, Kobayashi, J, Noda, S, Fukuda, Y, and Takahashi, K. Japan’s healthcare policy for the elderly through the concepts of self-help (ji-jo), mutual aid (go-jo), social solidarity care (Kyo-jo), and governmental care (ko-jo). Biosci Trends. (2018) 12:7–11. doi: 10.5582/bst.2017.01271
17. Plouffe, L, and Kalache, A. Towards global age-friendly cities: determining urban features that promote active aging. J Urban Health. (2010) 87:733–9. doi: 10.1007/s11524-010-9466-0
18. Bowling, A, Banister, D, Sutton, S, Evans, O, and Windsor, J. A multidimensional model of the quality of life in older age. Aging Ment Health. (2002) 6:355–71. doi: 10.1080/1360786021000006983
19. Warburton, DER, and Bredin, SSD. Health benefits of physical activity: a systematic review of current systematic reviews. Curr Opin Cardiol. (2017) 32:541–56. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000437
20. Yen, H-Y, and Lin, L-J. Quality of life in older adults: benefits from the productive engagement in physical activity. J Exerc Sci Fit. (2018) 16:49–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jesf.2018.06.001
21. Liu, Y, Pan, Z, Liu, Y, and Li, Z. Can living in an age-friendly neighbourhood protect older adults’ mental health against functional decline in China? Landsc Urban Plann. (2023) 240:104897. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2023.104897
22. Sivertsen, H, Bjørkløf, GH, Engedal, K, Selbæk, G, and Helvik, A-S. Depression and quality of life in older persons: a review. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. (2015) 40:311–39. doi: 10.1159/000437299
23. Qiu, Y, Liu, Y, Liu, Y, and Li, Z. Exploring the linkage between the Neighborhood environment and mental health in Guangzhou, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:3206. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16173206
24. Aung, MN, Koyanagi, Y, Ueno, S, Tiraphat, S, and Yuasa, M. A contemporary insight into an age-friendly environment contributing to the social network, active ageing and quality of life of community resident seniors in Japan. J Aging Environ. (2021) 35:145–60. doi: 10.1080/26892618.2020.1813232
25. Nieboer, AP, and Cramm, JM. Age-friendly communities matter for older people’s well-being. J Happiness Stud. (2018) 19:2405–20. doi: 10.1007/s10902-017-9923-5
26. Trombetti, A, Reid, KF, Hars, M, Herrmann, FR, Pasha, E, Phillips, EM, et al. Age-associated declines in muscle mass, strength, power, and physical performance: impact on fear of falling and quality of life. Osteoporos Int. (2016) 27:463–71. doi: 10.1007/s00198-015-3236-5
27. Chu, Y, and Zhang, H. Do age-friendly community policy efforts matter in China? An analysis based on five-year developmental plan for population aging. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:13551. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013551
28. Pan, Z, Liu, Y, Liu, Y, Huo, Z, and Han, W. Age-friendly neighbourhood environment, functional abilities and life satisfaction: a longitudinal analysis of older adults in urban China. Soc Sci Med. (2024) 340:116403. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2023.116403
29. Lei, X, and Bai, C. Cognitive function and mental health of elderly people in China: findings from 2018 CLHLS survey. China Popul Dev Stud. (2020) 3:343–51. doi: 10.1007/s42379-020-00054-6
30. Lyu, X, and Fan, Y. The impact of home- and community-based services on the health of older adults: a meta-analysis. SAGE Open. (2024) 14:21582440241285674. doi: 10.1177/21582440241285674
31. Sakr, S, and Elgammal, A. Towards a comprehensive data analytics framework for smart healthcare services. Big Data Res. (2016) 4:44–58. doi: 10.1016/j.bdr.2016.05.002
32. Hung, J. Smart elderly care services in China: challenges, progress, and policy development. Sustainability. (2023) 15:178. doi: 10.3390/su15010178
33. Zhang, N, and Yang, Q. Public transport inclusion and active aging: a systematic review on elderly mobility. JTTE. (2024) 11:312–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jtte.2024.04.001
34. Kim, K, Buckley, T, Burnette, D, Kim, S, and Cho, S. Measurement indicators of age-friendly communities: findings from the AARP age-friendly community survey. Gerontologist. (2022) 62:e17–27. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnab055
35. Au, A, Lai, DWL, Yip, H, Chan, S, Lai, S, Chaudhury, H, et al. Sense of community mediating between age-friendly characteristics and life satisfaction of community-dwelling older adults. Front Psychol. (2020) 11:86. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00086
36. Dikken, J, Van Den Hoven, RFM, Van Staalduinen, WH, Hulsebosch-Janssen, LMT, and Van Hoof, J. How older people experience the age-friendliness of their City: development of the age-friendly cities and communities questionnaire. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:6867. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186867
37. Flores, R, Caballer, A, and Alarcón, A. Evaluation of an age-Friendly City and its effect on life satisfaction: a two-stage study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:5073. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16245073
38. Pan, L, Sun, J, and Zhou, R. Research on the construction of age-friendly community based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model: evidence from community in Hefei of China. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. (2021) 14:3841–52. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S324109
39. Jiang, C, Chow, JC-C, Zhou, L, Song, H, and Shi, J. Community support, social isolation and older adults’ life satisfaction: evidence from a national survey in China. Aging Ment Health. (2024) 28:849–57. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2023.2277871
40. Yu, J, Ma, G, and Cai, S. Disparities in the provision of aging-friendly communities in old and new urban neighborhoods in China. Eng Constr Archit Manag. (2019) 26:1277–93. doi: 10.1108/ECAM-03-2018-0092
41. Tarka, P. An overview of structural equation modeling: its beginnings, historical development, usefulness and controversies in the social sciences. Qual Quant. (2018) 52:313–54. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0469-8
42. Fan, Y, Chen, J, Shirkey, G, John, R, Wu, SR, Park, H, et al. Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: an updated review. Ecol Process. (2016) 5:19. doi: 10.1186/s13717-016-0063-3
43. Browne, MW, and Cudeck, R. Alternative ways of assessing model fit. Sociol Methods Res. (1992) 21:230–58. doi: 10.1177/0049124192021002005
44. Kaczynski, AT, and Henderson, KA. Environmental correlates of physical activity: a review of evidence about parks and recreation. Leis Sci. (2007) 29:315–54. doi: 10.1080/01490400701394865
45. Kondo, M, Fluehr, J, McKeon, T, and Branas, C. Urban green space and its impact on human health. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2018) 15:445. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15030445
46. Jiang, S, Gu, Y, Yang, F, Wu, T, Wang, H, Cutler, H, et al. Tertiary hospitals or community clinics? An enquiry into the factors affecting patients’ choice for healthcare facilities in urban China. China Econ Rev. (2020) 63:101538. doi: 10.1016/j.chieco.2020.101538
47. Baobeid, A, Koç, M, and Al-Ghamdi, SG. Walkability and its relationships with health, sustainability, and livability: elements of physical environment and evaluation frameworks. Front Built Environ. (2021) 7:721218. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2021.721218
48. Cao, Q, Dabelko-Schoeny, HI, White, KM, and Choi, M-S. Age-friendly communities and perceived disconnectedness: the role of built environment and social engagement. J Aging Health. (2020) 32:937–48. doi: 10.1177/0898264319865421
49. Choi, MS, Dabelko-Schoeny, H, and White, K. Access to employment, volunteer activities, and community events and perceptions of age-friendliness: the role of social connectedness. J Appl Gerontol. (2020) 39:1016–24. doi: 10.1177/0733464819847588
50. Yu, R, Wong, M, and Woo, J. Perceptions of Neighborhood environment, sense of community, and self-rated health: an age-Friendly City project in Hong Kong. J Urban Health. (2019) 96:276–88. doi: 10.1007/s11524-018-00331-3
51. Cramm, JM, and Nieboer, AP. Social cohesion and belonging predict the well-being of community-dwelling older people. BMC Geriatr. (2015) 15:30. doi: 10.1186/s12877-015-0027-y
52. Ma, W, and Shen, Z. Impact of community care services on the health of older adults: evidence from China. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1160151. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1160151
53. Au, A, Chan, SCY, Yip, H, Kwok, J, Lai, K, Leung, K, et al. Age-friendliness and life satisfaction of young-old and old-old in Hong Kong. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. (2017) 2017:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2017/6215917
Keywords: age-friendly community, older adults, quality of life, structural equation modeling, healthcare
Citation: Tang Y, Xu J and Yu J (2025) The impact of age-friendly communities on the quality of life of older adults based on structural equation modeling. Front. Public Health. 13:1646195. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1646195
Edited by:
Bo-Wei Zhu, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
Sylvie Occelli, Institute of Social Economic Research of Piedmont, ItalyRenata Pecotić, University of Split, Croatia
Joao Fernandes Thomaz, University of Lisbon, Portugal
Copyright © 2025 Tang, Xu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Xu, eHVqaWVfMDEzMEAxNjMuY29t
 Ying Tang1
Ying Tang1 Jie Xu
Jie Xu Jingyu Yu
Jingyu Yu