- 1Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Mehmet Akif Ersoy University, Burdur, Türkiye
- 2Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Çankırı Karatekin University, Çankırı, Türkiye
Objective: Digital addiction, defined as spending excessive time on digital devices and online platforms, is a global problem that particularly affects young people. This form of addiction can lead individuals to a sedentary lifestyle while also increasing the risk of them turning to unhealthy and ready-made foods. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of digital addiction among Turkish adolescents. We also aimed to determine the relationships between digital addiction, adherence to the Mediterranean diet, and physical activity, and to determine the extent to which these variables mutually predict each other.
Method: The data of this cross-sectional study were collected from 400 high school students through a survey. The survey included general information, dietary habits, the Digital Addiction Scale (DAS), the Mediterranean Diet Quality Index (KIDMED), the Leisure Time Exercise Questionnaire (LTEQ), and the Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale (PACES). IBM SPSS 25.0 software was used for data analysis.
Results: Of the students, 23.8% had a digital addiction. Eating during social media use (Beta = 0.158) and night eating habits (Beta = 0.337) positively affected the DAS scores (p < 0.05). The KIDMED score (Beta = −0.233) and being physically active (Beta = −0.136) negatively affected the DAS scores (p < 0.05). Compliance with the Mediterranean diet was low in 26%, moderate in 46%, and high in 28% of the students. The number of main meals (Beta = 0.254) and father’s education level (Beta = 0.200) positively affected the KIDMED scores (p < 0.05). Of the students, 51.5% were active, 32% were moderately active, and 16.5% were sedentary. The PACES scores positively affected the LTEQ scores (Beta = 0.189, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Approximately a quarter of students had digital addiction symptoms. Digital addiction levels tended to decrease as Mediterranean diet adherence and physical activity levels increased. A holistic healthy lifestyle curriculum can be designed to promote healthy eating habits and physical activity among young people, reduce screen time, and increase media literacy. This curriculum, designed for implementation in schools, can support students in engaging in mindful behaviors.
Introduction
Technology is often beneficial to society, but problems can arise due to its overuse. Long-term and repetitive use of digital devices (such as computers and smartphones) and related activities (such as games and social media) can lead to digital addiction. The term digital addiction covers long-term problems of internet addiction, gaming addiction, and social media addiction (1). There is no consensus yet on the definition or diagnostic criteria of this concept. However, many studies highlight the psychological dependence on digital devices and online platforms (2, 3). It affects both the minds and bodies of children and adolescents. It can lead to visual loss, hearing impairment, and obesity. It can also affect young individuals’ sleeping and eating habits, causing significant damage to their health (4, 5).
Adolescence is a critical period for the acquisition of lifestyle habits that can continue through adulthood. A healthy lifestyle includes quality nutrition, regular physical activity, reduced screen time, avoidance of alcohol and tobacco use, adequate sleep, and positive social interactions (6, 7). It was reported that adolescents generally do not follow healthy lifestyles (7). The courage and curiosity to experiment with different and often unhealthy behaviors increase during this life stage (8). The Mediterranean diet represents a healthy lifestyle approach with nutritional, social, cultural, and environmental characteristics (9). However, compliance with this diet was observed to be low in children and adolescents, including in Mediterranean countries (10). The present study investigated compliance of adolescents to the Mediterranean diet and updated information was provided to the literature.
With the proliferation of the internet, advanced search engines, and social media, public access to information on nutrition and health has become easier (11). Media can stimulate many neural, physiological, and behavioral responses through images and videos of appetizing food (12). Viewing food images was associated with increased secretion of ghrelin, a hormone that increases appetite and calorie intake (13). In adolescents, digital media exposure was reported to increase the consumption of salty, sweet, and fatty foods by affecting their dietary preferences (14) Additionally, problematic use of technology was reported to be associated with meal skipping, appetite changes, irregular eating, snacking behaviors, and poor diet quality (15). Adolescents often exhibit low self-control due to their ongoing cognitive and emotional development (16). Digital addiction further weakens their self-control by overstimulating the reward system and poor self-control is associated with unhealthy food choices and obesity (17, 18). As such, this study examined the relationship between adherence to a Mediterranean diet and digital addiction in adolescents and determined the extent to which these two variables predict each other.
Adolescents’ social lives are increasingly shaped by digital environments, causing virtual interactions to replace physical activity (19). Globally, 8 in 10 adolescents do not engage in sufficient physical activity. Furthermore, a significant portion of adolescents spend more than 2 h a day in front of screens (20). Digital addiction leads to a sedentary lifestyle as it requires constant dependence on a screen (21). However, an optimal physical activity routine and a balanced and adequate diet play an important role in growth and development during adolescence (22). Digital exposure can lead to an unhealthy lifestyle, which, in turn, results in serious problems that negatively affect growth and development (20). Thus, this study also investigated the relationship between physical activity and digital addiction and analyzed the extent to which these two variables predict each other.
Today, since the use of digital devices starts at a younger age, digital addiction has become a global problem especially affecting young people (23). There are many studies in the literature in which a specific subtype of digital addiction, e.g., internet addiction and gaming addiction, has been addressed. However, digital technology is rapidly advancing and constantly changing. There are relatively few studies in which the overuse of digital devices, digital technologies, and digital platforms has been holistically evaluated. The assessment tool used in this study will help determine adolescents’ overexposure to technology in all its forms. We aimed to determine the relationship between digital addiction and diet quality, eating habits, exercise level, and enjoyment of exercise and expand the knowledge in this field.
Method
The study followed a cross-sectional research design and was conducted with 400 adolescent students studying in schools affiliated to the Ministry of National Education in Turkey. Participants were recruited used a convenience sampling method, which was based on accessibility and willingness to participate. Individuals aged between 11 and 19 years old who were using technological tools (computer, laptop, and phone) and who volunteered to participate in the study were included. Individuals with a physical or mental disability that prevented them from reading and understanding the survey questions were excluded from the study.
The research data were collected using a survey during face-to-face interviews at the schools. The individuals who agreed to participate in the study completed the survey, which included general information, eating habits, the Digital Addiction Scale (DAS), the Mediterranean Diet Quality Index (KIDMED), the Leisure Time Exercise Questionnaire (LTEQ), and the Physical Activity Enjoyment Scale (PACES). Before the survey was applied, the participants and their families were informed about the study and asked to complete the consent form.
Digital addiction scale for teenagers (DAS)
The DAS scale was developed by Seema et al. (24) to measure the digital addiction level of young individuals (24). The Turkish validity and reliability study was conducted by Çelik et al. in 2023 (25). The Turkish version of the DAS for Teenagers consists of 10 items. The scale has a 5-point Likert-type rating (never-always). This scale is a valid and reliable measurement tool for determining the digital addiction levels of young individuals aged between 11 and 19 years old or studying in middle and high school. The scale has no reverse items. The higher the scale score (between 10 and 50 points), the higher the risk of digital addiction (25).
Mediterranean diet quality index (KIDMED)
The KIDMED scale was developed by Serra Majem et al. in 2004 to determine the appropriateness of individuals’ eating habits to the Mediterranean diet (26). The Turkish validity and reliability study was conducted by Şahingöz et al. in 2019 (27). The scale consists of 16 items. Items 6, 12, 14, and 16 are scored −1 and the remaining 12 items are scored +1. A score of 3 or below indicates low diet quality, a score between 4 and 7 indicates moderate diet quality, and a score of 8 or more indicates high diet quality (27).
Leisure time exercise questionnaire (LTEQ)
The LTEQ was developed by Godin and Shephard (28) to measure the exercise activity of individuals during leisure time (28). The Turkish validity and reliability study for adolescents was conducted by Lapa et al. (29). The questionnaire includes questions about physical activity performed for at least 15 min during leisure time in the last week. Depending on the frequency of the activity, heavy activities are multiplied by a score of 9, moderate activities by 5, and mild activities by 3. The weekly leisure time activity score is calculated with the formula (9 x severe intensity) + (5 x moderate intensity) + (3 x mild intensity). Accordingly, an individual’s activity during leisure time in general is assessed. The score is classified at three levels: 24 and above as “active,” 14 to 23 as “moderately active,” and 13 or below as “not active enough” (29).
Physical activity enjoyment scale (PACES)
The PACES was developed by Mullen et al. (30) to assess expected and perceived positive emotions regarding physical activity (30). The Turkish validity and reliability study was conducted by Özkurt et al. (31). The scale consists of 8 items that are scored using a 7-point Likert-type scale. The scale is scored between 8 and 56 and a high score indicates a high level of physical activity enjoyment (31).
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was conducted with the IBM Statistical tool for Social Sciences (SPSS) 25.0 tool. Descriptive statistics included mean, standard deviation, number, and percentage values. The independent samples t-test and the Pearson chi-square test were used to compare continuous and categorical variables, respectively. The relationships between the scale scores were determined through correlation and regression analysis.
The discriminative power of the DAS scores, which is used to determine a participant’s digital addiction status, was evaluated with ROC analysis. As a result of the analysis, the area under the ROC curve (AUC value) was 0.921 (95% CI: 0.884–0.958). According to this value, the discriminative power of the scale was high in predicting digital addiction in the participants. The most appropriate cut-off point to discriminate between addicted and non-addicted individuals according to the DAS score was determined to be 28.5.
Results
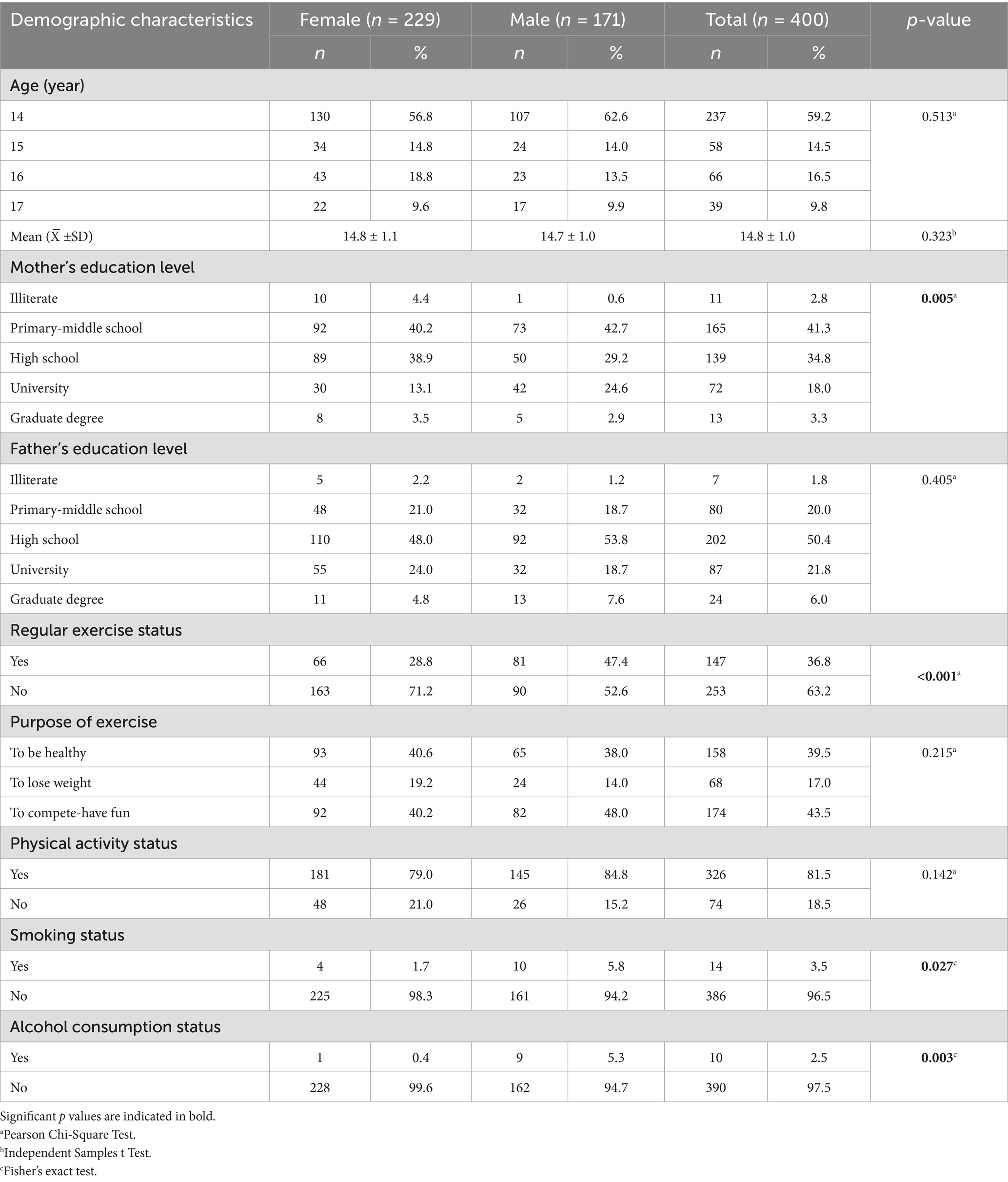
The distribution of the demographic characteristics of the participants according to gender is given in Table 1. A total of 400 students participated in the study. Of these students, 57.2% were female (n = 229) and 42.8% (n = 171) were male. The mean age of the participants was 14.8 ± 1.0 years. In terms of the educational status of the parents of the participants, the rate of primary or middle school graduates among the mothers (41.3%) and the rate of high school graduates among the fathers (50.4%) were higher. The rate of male students who regularly exercised (47.4%) was higher than female students who regularly exercised (28.8%; p < 0.001). The purpose of participation in exercise did not differ statistically according to gender, and the rate of those who exercised to compete and have fun (43.5%) was higher. Of the students, 39.5% exercised to be healthy and 17% exercised to lose weight. The rate of smoking (5.8%) and alcohol consumption (5.3%) was higher in male students than in female students (p = 0.027 and p = 0.003, respectively).
The distribution of the students’ eating habits and scale scores according to their digital addiction status is given in Table 2. The rate of skipping main meals was 40% in the students with a digital addiction and 21.6% in those without a digital addiction (p < 0.001). Breakfast was the most frequently skipped meal in both groups, and the rate of skipping breakfast was higher among the students with a digital addiction (82.1%; p = 0.017). Night eating habits (63.2%; p < 0.001), fast eating behavior (22.1%; p = 0.006), and eating during social media use (93.7%; p < 0.001) were also higher in the students with a digital addiction compared to those without a digital addiction. The rate of students with low diet quality was statistically significantly higher in the students with a digital addiction (48.4%) compared to the students without a digital addiction (19.3%; p < 0.001). According to digital addiction status, the mean total PACES and LTEQ scores were similar between the groups (p > 0.05). However, in the classification according to LTEQ scores, the rate of physically inactive students was higher among the students with a digital addiction (23.2%; p < 0.001). The mean body mass index (BMI) of the students was 20.7 ± 3.6 kg/m2 and did not differ statistically according to digital addiction status (p > 0.05).
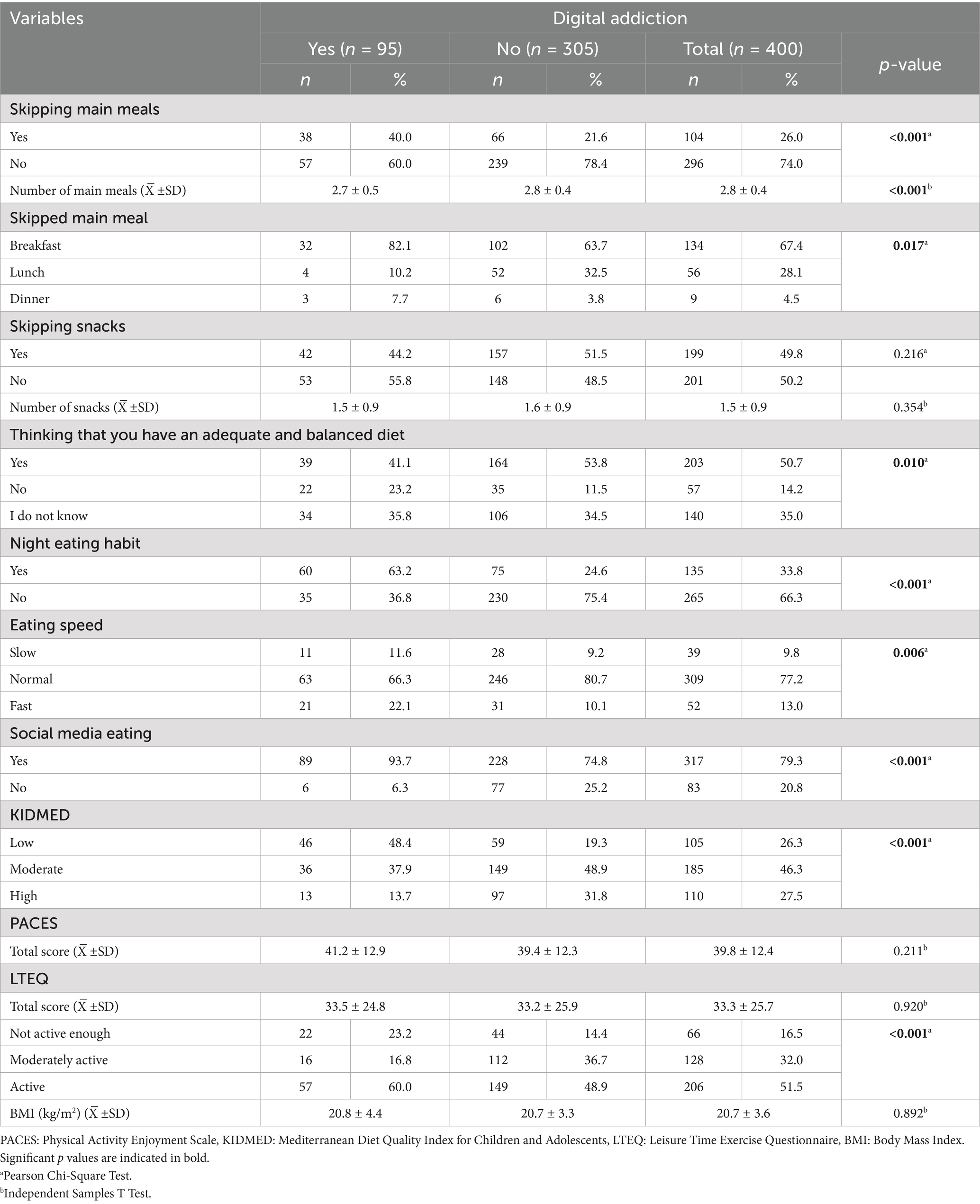
Table 2. Distribution of eating habits and scale scores of students according to their digital addiction status.
Figure 1 shows the factors affecting the KIDMED scores in a forest plot. There was a statistically significant negative correlation between the DAS scores and the KIDMED scores (Beta = −0.340, p < 0.001). The total KIDMED scores of the students increased as the education level of their fathers increased (Beta = 0.200, p < 0.001). The increase in BMI of the students positively affected their total KIDMED scores (Beta = 0.096, p = 0.028). An increase in the number of main meals positively affected the KIDMED scores (Beta = 0.254, p < 0.001). Gender and age had no effect on the KIDMED scores (p > 0.05).
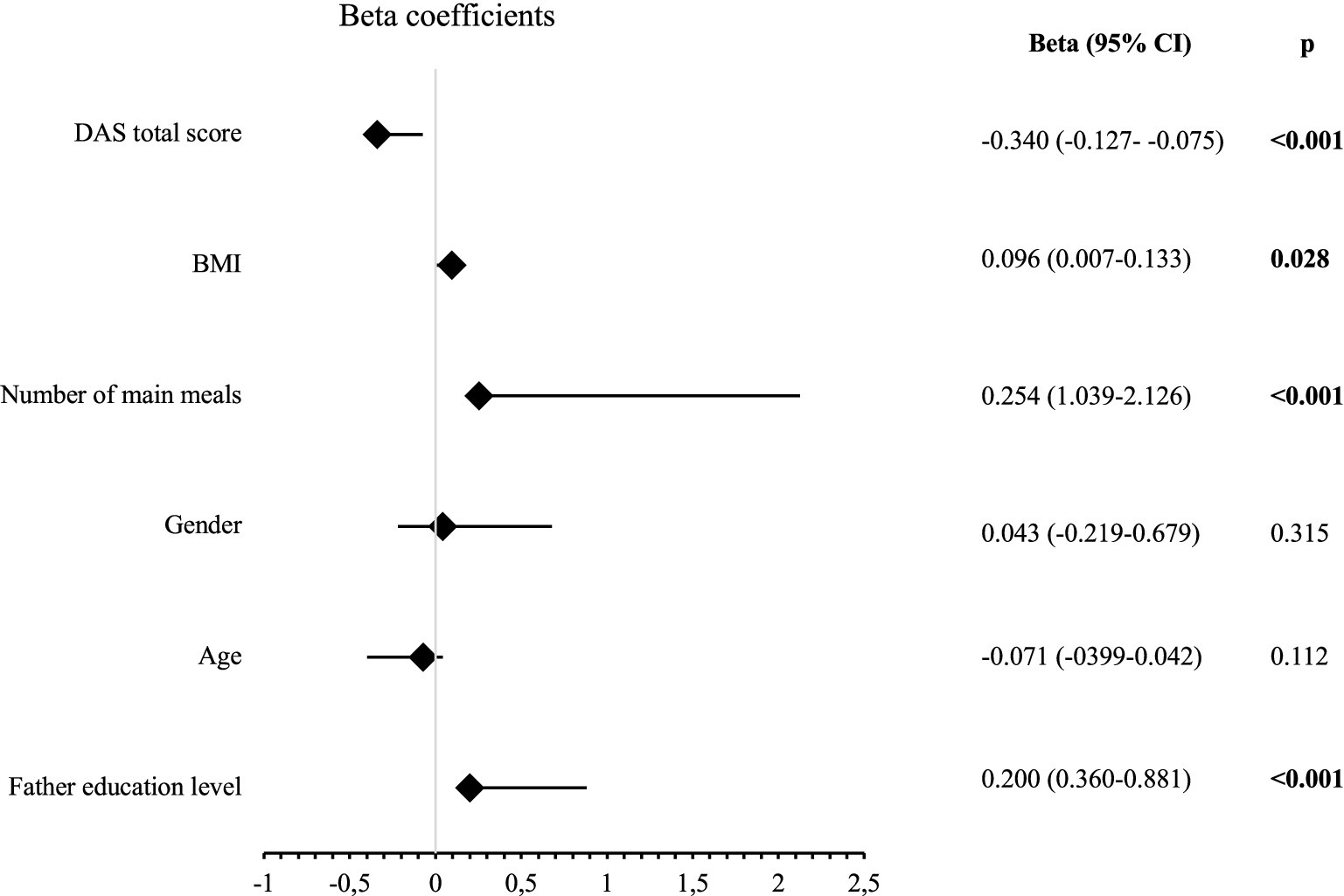
Figure 1. Forest Plot of linear regression analysis for KIDMED total score (DAS: digital addiction scale, BMI: body mass index, significant p values are indicated in bold). Gender (coded: 0 = Female, 1 = Male).
Figure 2 shows the factors that affected the DAS scores. Eating during social media use (Beta = 0.158, p < 0.001) and night eating habits (Beta = 0.337, p < 0.001) positively affected the DAS scores. The DAS scores decreased as the KIDMED scores increased (Beta = −0.233, p < 0.001). Being physically active negatively affected the DAS scores (Beta = −0.136, p = 0.001). Age, number of main meals, and number of snacks had no effect on the DAS scores (p > 0.05).
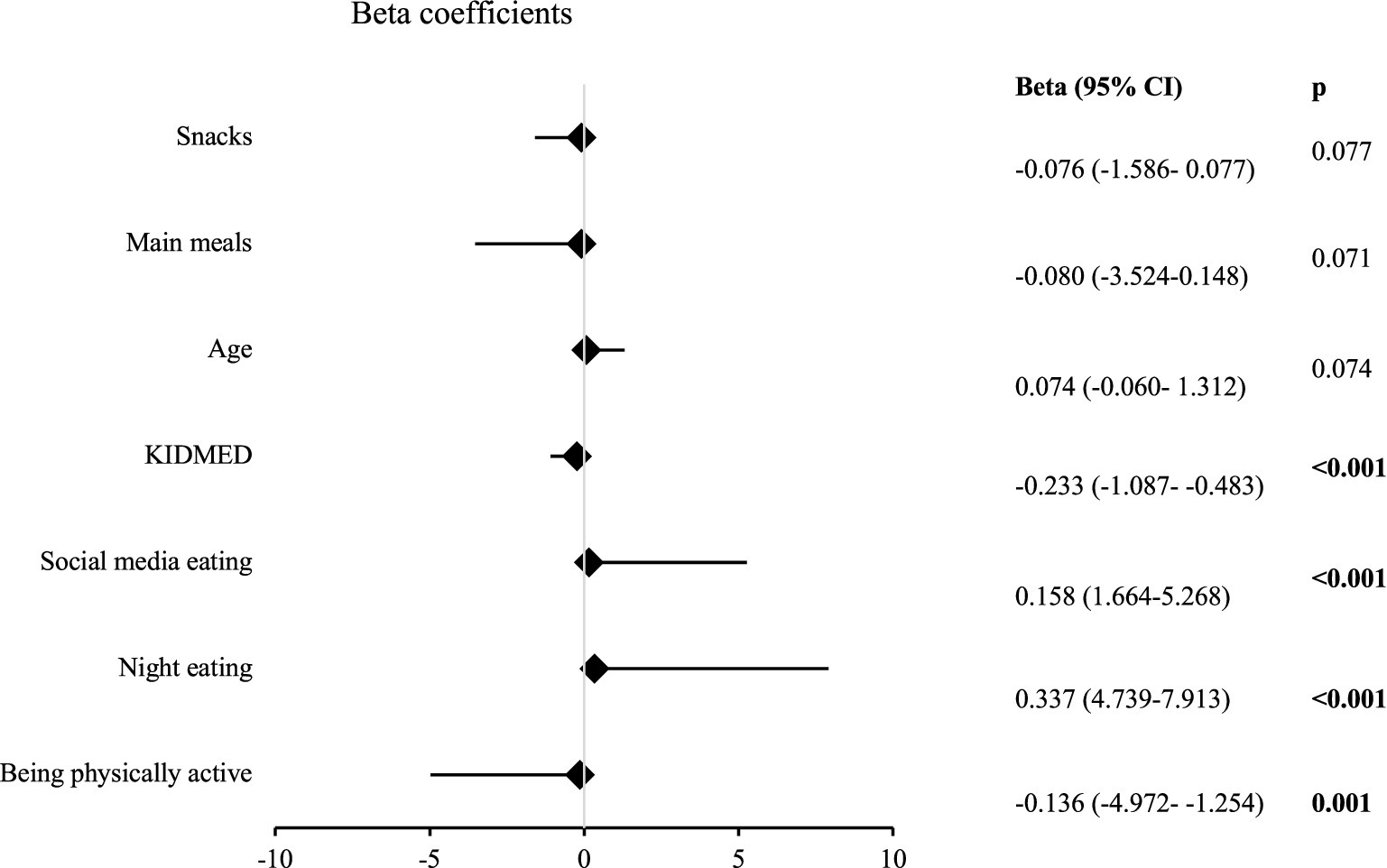
Figure 2. Results of linear regression analysis for the total DAS score [DAS: digital addiction scale, significant p values are indicated in bold. Social media eating (coded: 0 = No, 1 = Yes). Night eating (coded: 0 = No, 1 = Yes). Being physically active (coded: 0 = No, 1 = Yes)].
Figure 3 shows the factors that affected the PACES scores. Being physically active had a positive and significant effect (Beta = 0.122, p = 0.014). The LTEQ scores also positively affected physical activity enjoyment (Beta = 0.175, p < 0.001). Gender was not among the affecting factors (Beta = 0.025, p = 0.612).
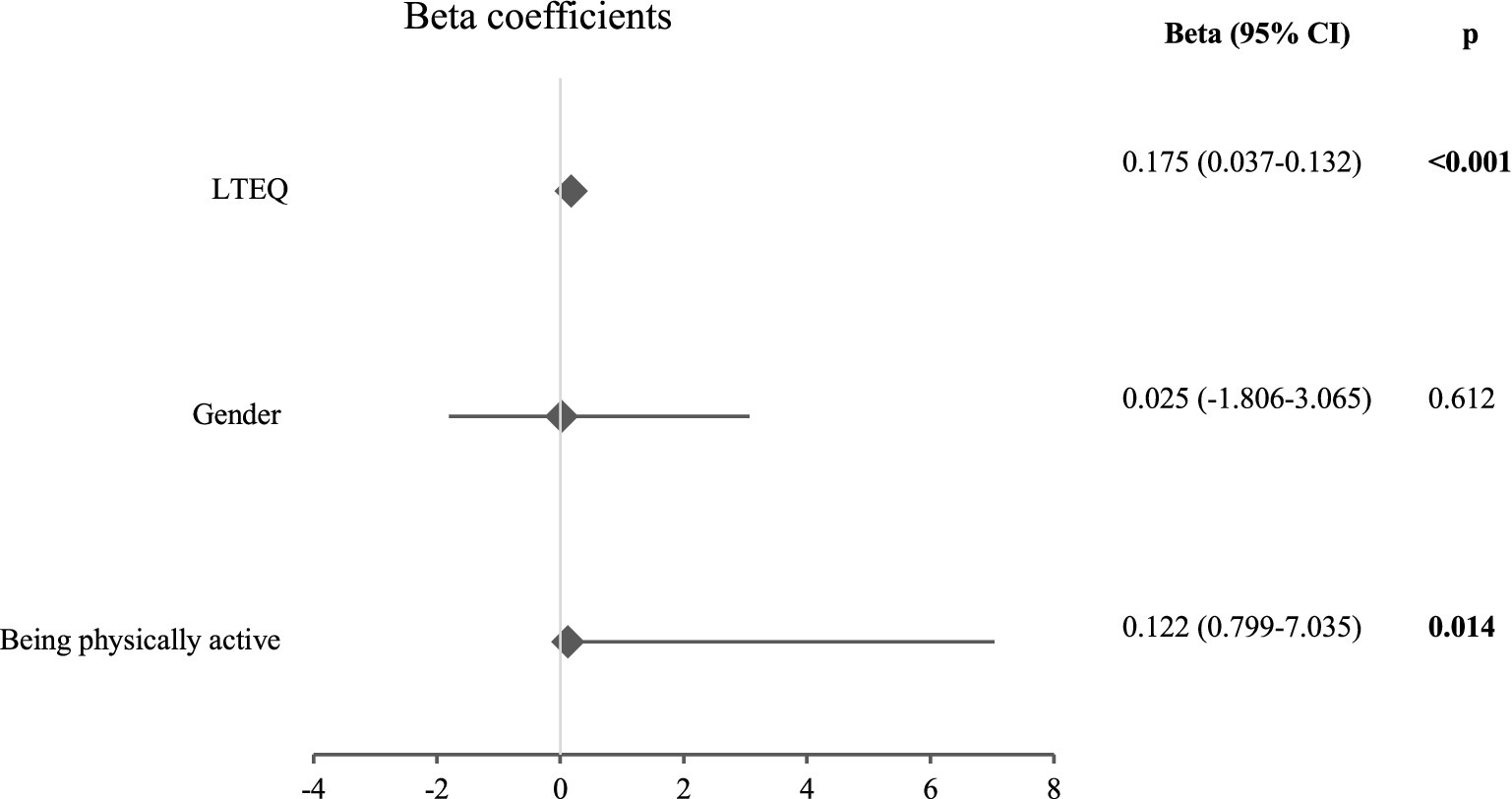
Figure 3. Results of linear regression analysis for the total PACES score [LTEQ: leisure time exercise questionnaire, significant p values are indicated in bold. Gender (coded: 0 = Female, 1 = Male). Being physically active (coded: 0 = No, 1 = Yes)].
When the factors affecting the level of leisure time exercise (LTEQ) were analyzed, physical activity enjoyment (Beta = 0.189, p < 0.001) had a positive effect. The effect of the DAS scores (Beta = 0.095, p = 0.053) on the LTEQ scores was statistically insignificant (p > 0.05; Figure 4).
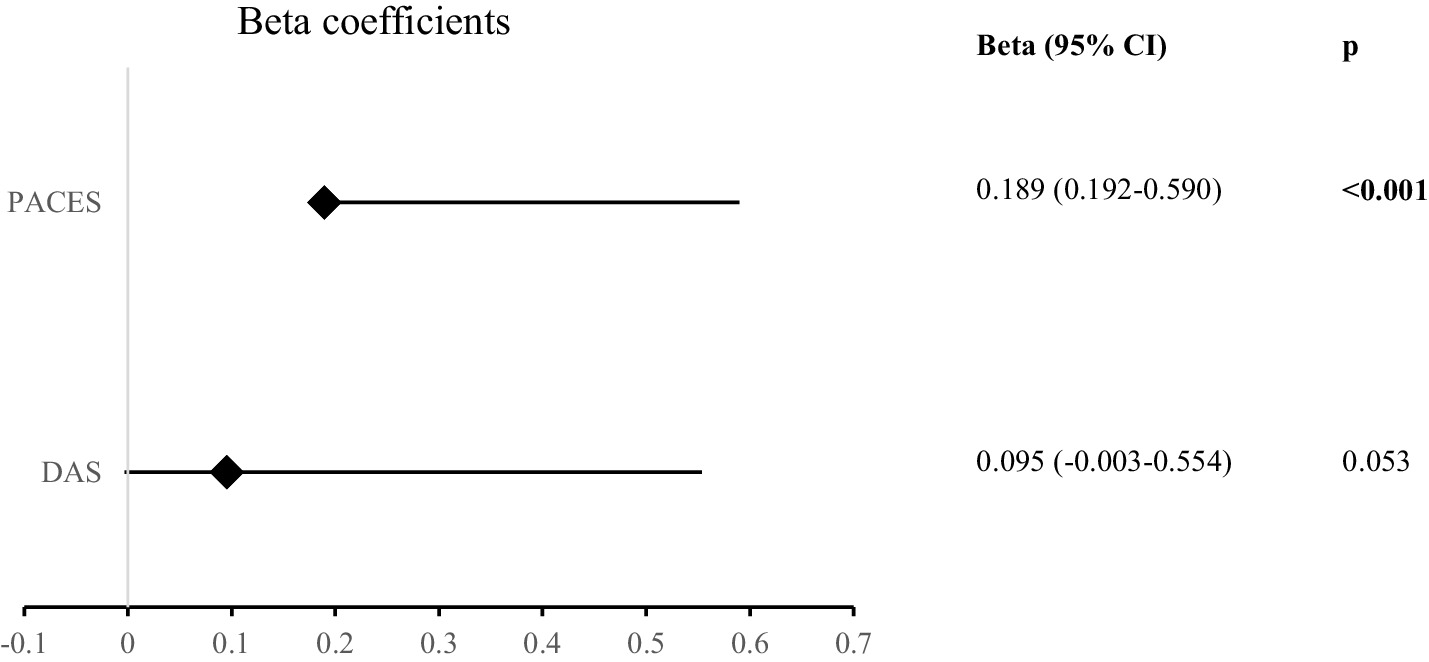
Figure 4. Results of linear regression analysis for the total LTEQ score (LTEQ: leisure time exercise questionnaire, DAS: digital addiction scale, PACES: physical activity enjoyment scale, significant p values are indicated in bold).
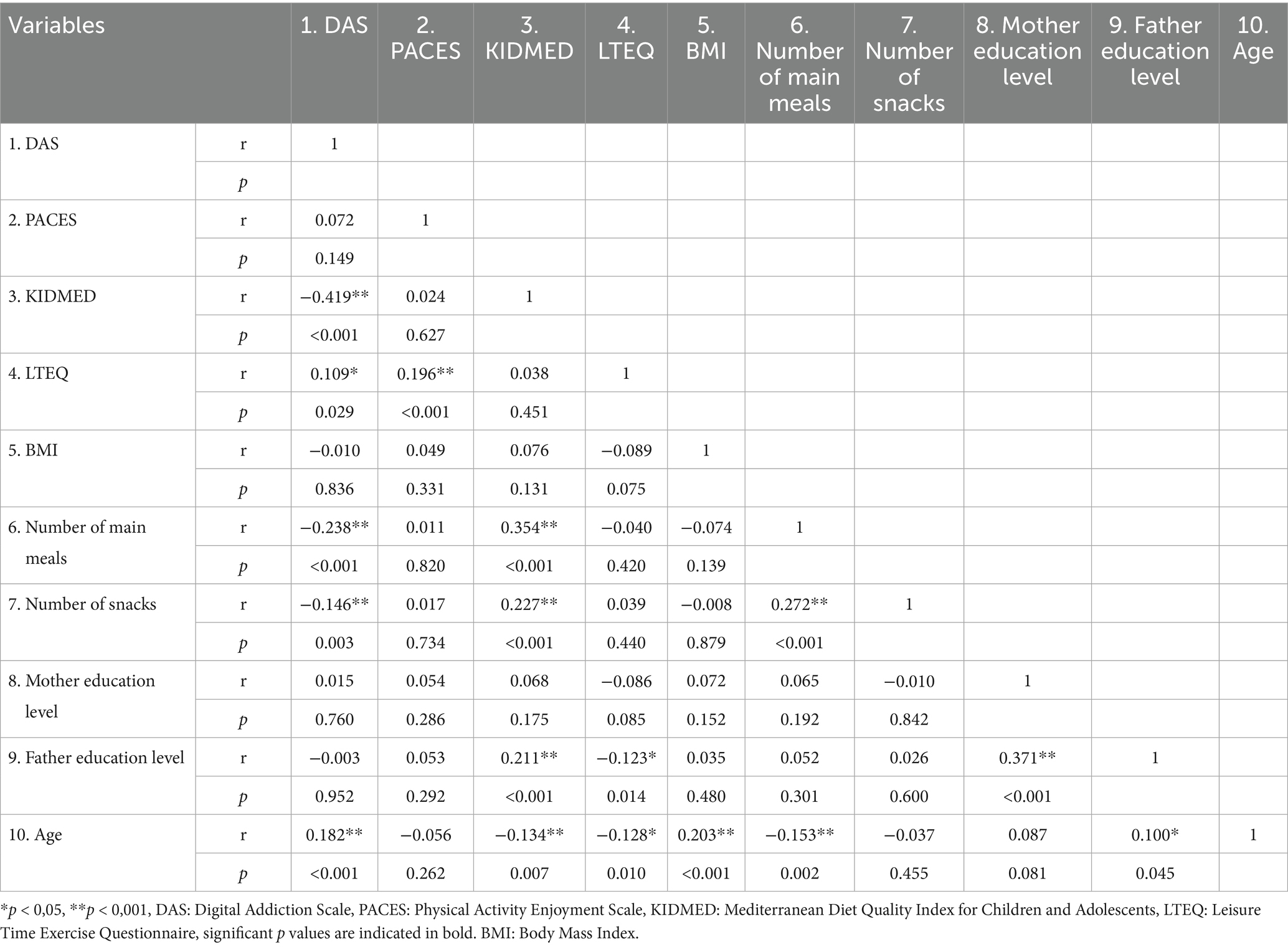
Table 3 shows the correlations between the scale scores and some variables. There was a negative correlation between the students’ DAS and KIDMED scores (r = −0.419, p < 0.001). There was a significant negative correlation between the DAS scores and the number of main meals consumed (r = −0.238, p < 0.001). The DAS scores of the students increased as their age increased (r = 0.182, p < 0.001). There was a positive correlation between the students’ compliance with the Mediterranean diet and their number of main meals (r = 0.354, p < 0.001). In addition, as compliance with the Mediterranean diet increased, the number of snacks increased (r = 0.227, p < 0.001). The students’ compliance with the Mediterranean diet increased as the educational level of their fathers increased (r = 0.211, p < 0.001). The students’ KIDMED scores, number of main meals, and LTEQ scores decreased as their age increased (p < 0.05).
Discussion
Digital addiction has emerged with the advancement of technology and has steadily spread globally. Moreover, the age of digital addicts has tended to decrease over time (32). Adolescents are more vulnerable to digital addiction due to various biological, psychological, and social factors (33, 34). In the present study, 23.8% of the high school students were found to have a digital addiction. In a meta-analysis study, a quarter of the general population was reported to suffer from at least one subtype of digital addiction (35). The prevalence reported for adolescents is wide and can reach higher levels than that of the general population (3–62%) (36–38). The evolving nature of digital engagement among young people and the methods used to determine their addiction status may explain the variability in reported prevalences.
Compliance with the Mediterranean diet, which is a health-promoting dietary pattern, tends to decline among adolescents (39). In our study, 26% of the students had low compliance with the Mediterranean diet, 46% had moderate compliance, and 28% had high compliance. In previous studies, the rate of moderate compliance constituted the majority, but the rate of ideal compliance was higher than or similar to the rate found in our study (40, 41). Despite living in a country on the Mediterranean coast, there is a need to improve Turkish adolescents’ commitment to a healthy dietary pattern. Several strategies for education and access to healthy foods should be developed and implemented to increase the rate of students with high levels of compliance with the Mediterranean diet.
In the present study, the main determinants of the students’ compliance with the Mediterranean diet were their fathers’ education level, number of main meals, BMI, and level of digital addiction. The children of fathers with higher education levels had better diet quality. Likewise, parental education level was reported to play an important role in shaping their children’s dietary behaviors (42). The students who consumed their main meals regularly were found to have high compliance with the Mediterranean diet. Similar results were obtained in the study conducted by Alim et al. (43), which showed that an increase in the frequency of meals was positively associated with dietary diversity and compliance with the Mediterranean diet (43). In our study, the students’ level of digital addiction was negatively correlated with their compliance with the Mediterranean diet. In previous research, it has been confirmed that the widespread use of technology and digital interaction among adolescents have a significant negative impact on food preferences and diet quality (44, 45).
Digital addiction is a new type of addiction that shares similar characteristics with other addictive behaviors (46). The World Health Organization emphasized the potential for digital devices to disrupt daily activities and well-being when used excessively and has recognized digital addiction as a mental health problem (47). Due to its prevalence and harmful effects, it is important to identify factors that predict digital addiction. In the present study, eating during social media use and night eating behaviors were among the determinants of digital addiction. Previously, eating in front of a screen was reported to be common among adolescents (48). This behavior can lead to increased screen time and time spent on social media, resulting in symptoms of digital addiction. Eating late at night can lead to delayed sleep and increased preoccupation with digital devices (49). According to the findings, other determinants of digital addiction were compliance with the Mediterranean diet and being physically active, which negatively affected digital addiction. The Mediterranean diet is known for its potential to promote a healthy lifestyle and social interactions (50). This characteristic may contribute to reducing the time spent using digital devices. It has been previously reported that in children, the types of digital activities (playing digital games, watching television, and watching streaming platforms) are associated with lower adherence to the Mediterranean diet (51). Other studies have reported that as social media addiction increases in young people, adherence to the Mediterranean diet decreases and the risk of eating disorders increases (52, 53). Another study reported that children’s use of television or gaming computers during off-school hours partially displaced the time they should have spent eating. Poor eating habits, including fast eating, skipping meals, snacking, and the disruption of family meal planning, may undermine adherence to the Mediterranean diet (54). Furthermore, consistent with our findings, many studies have reported that participation in regular physical activity protects against digital addiction in adolescents (55, 56). Physical activity can increase self-esteem, encourage socialization, and reduce the use of digital devices (57).
The current study found a bidirectional relationship between physical activity level and the enjoyment of physical activity. The fact that these variables mutually predict each other is a remarkable finding in terms of the continuity of physical activity behavior. Enjoyment from physical activity is important for the physical, psychological, and social development of adolescents. Consistent with our findings, it is reported to support participation in more physical activity (58–60). The results of this study demonstrated the importance of focusing on the emotional satisfaction that is derived from this behavior in interventions aimed at increasing physical activity. Additionally, exercise improves mood by modulating hormone and neurotransmitter levels (61). As individuals gain both physical and psychological benefits from exercise, they may be more likely to continue this behavior. Even if exercise participation is initially reluctant, feelings of enjoyment may develop over time. This positive cycle, reinforced by hormonal responses, may regulate voluntary participation in physical activity (62).
Strengths and limitations
This study’s strength is its holistic perspective, assessing the interrelationships between digital addiction, Mediterranean diet adherence, and exercise in adolescents. Additionally, using trusted and tested measurement tools (DAS, KIDMED, LTEQ, and PACES), which have been adjusted for Turkish teenagers, improves the quality and trustworthiness of the study’s results. However, the study also has several limitations. Firstly, due to its cross-sectional design, a causal relationship cannot be established between the variables that were examined. Longitudinal studies should be planned to explore the causality between digital addiction, healthy eating, and physical activity over time. Secondly, the use of convenience sampling may limit the representativeness of the sample, which could affect the generalizability of the findings. Selection bias is also a concern, as participants with similar characteristics may be overrepresented in this study. Thirdly, the study used a self-administered survey for the adolescents who participated, which may lead to recall and social desirability bias. Fourthly, although the sample represents the population, the sample size was relatively small. Further research on the subject, including larger and multicenter samples, is recommended. Finally, although the study utilized validated scales, the absence of qualitative data limits the depth of understanding regarding the psychosocial dimensions of digital addiction. Future research could be improved by using qualitative methods, including interviews, to better understand the complex experiences and situations that contribute to digital addiction. This approach would enhance the comprehensiveness of the findings.
Conclusion
Digital addiction symptoms were identified in about a quarter of the surveyed high school students. It is important to examine risk and protective factors to protect the young generation from the harms of the digital age. According to our results, eating during social media use and night eating habits are risk factors for digital addiction, while compliance with the Mediterranean diet and physical activity are preventive factors.
This study, which also provides information on diet and physical activity, gives an idea about the lifestyle of high school students living in Turkey. A large majority of the students had a moderate level of compliance with the Mediterranean diet. Parents and educators should encourage students to adopt the Mediterranean diet as a healthy lifestyle choice. Families can limit unhealthy snacks at home and involve children in healthy meal preparation. Educators can model healthy eating behaviors through school activities. Policymakers can support adherence to the Mediterranean diet by facilitating access to healthy foods and allocating resources to school-based nutrition programs. In this study, approximately half of the students were physically active. Physical activity enjoyment positively affected the activity level of the students. Providing opportunities for students to identify which type of physical activity they enjoy and education that emphasizes the importance of physical activity may be some ways to promote sustainable physical activity habits.
Additionally, families, educators, and policymakers can take measures to combat digital addiction. Technology-free areas and time periods can be created to increase face-to-face communication in schools and homes. Additionally, establishing rules to limit device use may prove effective. Policymakers can impose stricter regulations on games and applications that target young people. A holistic healthy lifestyle curriculum can be designed to promote healthy eating habits and physical activity among young people, to reduce screen time, and to increase media literacy. This curriculum, which is designed for implementation in schools, could support students in engaging in mindful behaviors. To guide families, educators and policy makers, further studies are required to explore all lifestyle habits in more detail and to identify the effects of digital addiction.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines specified in the Helsinki Declaration. Ethical permission was obtained from the Çankırı Karatekin University Health Sciences Ethics Committee to conduct the research (meeting number: 14/25.06.2024). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
GH: Methodology, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Resources, Validation. FT: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Formal analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the students who participated in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Christakis, DA. The challenges of defining and studying “digital addiction” in children. JAMA. (2019) 321:2277–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.4690
2. Cemiloglu, D, Almourad, MB, McAlaney, J, and Ali, R. Combatting digital addiction: current approaches and future directions. Technol Soc. (2022) 68:101832. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101832
3. Lam, H, and Harcourt, M. Digital addiction in organizations: challenges and policy implications. Empl Responsib Rights J. (2024) 36:519–33. doi: 10.1007/s10672-024-09493-6
4. Strasburger, VCCouncil on Communications and Media. Children, adolescents, obesity, and the media. Pediatrics. (2011) 128:201–8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-1066
5. Muntz, A, Turnbull, PR, Kim, AD, Gokul, A, Wong, D, Tsay, TSW, et al. Extended screen time and dry eye in youth. Contact Lens Anterior Eye. (2022) 45:101541. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2021.101541
6. Manasova, IS, and Mansurova, MX. Youth's look for a healthy lifestyle. Central Asian J Med Nat Sci. (2021) 2:149–53.
7. Marques, A, Loureiro, N, Avelar-Rosa, B, Naia, A, and de Matos, MG. Adolescents’ healthy lifestyle. J Pediatria. (2020) 96:217–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedp.2018.09.001
8. Miles, DR, van den Bree, MB, Gupman, AE, Newlin, DB, Glantz, MD, and Pickens, RW. A twin study on sensation seeking, risk taking behavior and marijuana use. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2001) 62:57–68. doi: 10.1016/S0376-8716(00)00165-4
9. Guasch-Ferré, M, and Willett, WC. The Mediterranean diet and health: a comprehensive overview. J Intern Med. (2021) 290:549–66. doi: 10.1111/joim.13333
10. Idelson, PI, Scalfi, L, and Valerio, G. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2017) 27:283–99. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2017.01.002
11. Nath, S, Bhattacharya, S, Golla, VB, and Kumar, R. Effect of social media on diet, lifestyle, and performance of athletes: a review of current evidence. Curr Nutr Rep. (2024) 13:240–50. doi: 10.1007/s13668-024-00526-y
12. Spence, C, Okajima, K, Cheok, AD, Petit, O, and Michel, C. Eating with our eyes: from visual hunger to digital satiation. Brain Cogn. (2016) 110:53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2015.08.006
13. Schüssler, P, Kluge, M, Yassouridis, A, Dresler, M, Uhr, M, and Steiger, A. Ghrelin levels increase after pictures showing food. Obesity. (2012) 20:1212–7. doi: 10.1038/oby.2011.385
14. Sina, E, Buck, C, Ahrens, W, De Henauw, S, Jilani, H, Lissner, L, et al. Digital media use in association with sensory taste preferences in European children and adolescents—results from the I. Family study. Foods. (2021) 10:377. doi: 10.3390/foods10020377
15. Kim, Y, Park, JY, Kim, SB, Jung, IK, Lim, YS, and Kim, JH. The effects of internet addiction on the lifestyle and dietary behavior of Korean adolescents. Nutr Res Pract. (2010) 4:51–7. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2010.4.1.51
16. Meldrum, RC, Young, JT, and Weerman, FM. Changes in self-control during adolescence: investigating the influence of the adolescent peer network. J Crim Just. (2012) 40:452–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrimjus.2012.07.002
17. Koike, S, Hardy, R, and Richards, M. Adolescent self-control behavior predicts body weight through the life course: a prospective birth cohort study. Int J Obes. (2016) 40:71–6. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2015.213
18. Burnell, K, Andrade, FC, and Hoyle, RH. Longitudinal and daily associations between adolescent self-control and digital technology use. Dev Psychol. (2023) 59:720–32. doi: 10.1037/dev0001444
19. Kennedy, J, and Lynch, H. A shift from offline to online: adolescence, the internet and social participation. J Occup Sci. (2016) 23:156–67. doi: 10.1080/14427591.2015.1117523
20. van Sluijs, EM, Ekelund, U, Crochemore-Silva, I, Guthold, R, Ha, A, Lubans, D, et al. Physical activity behaviours in adolescence: current evidence and opportunities for intervention. Lancet. (2021) 398:429–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01259-9
21. Aziz, N, Nordin, MJ, Abdulkadir, SJ, and Salih, MMM. Digital addiction: systematic review of computer game addiction impact on adolescent physical health. Electronics. (2021) 10:996. doi: 10.3390/electronics10090996
22. Rogol, AD, Clark, PA, and Roemmich, JN. Growth and pubertal development in children and adolescents: effects of diet and physical activity. Am J Clin Nutr. (2000) 72:521S–8S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/72.2.521S
23. Ding, K, and Li, H. Digital addiction intervention for children and adolescents: a scoping review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2023) 20:4777. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20064777
24. Seema, R, Heidmets, M, Konstabel, K, and Varik-Maasik, E. Development and validation of the digital addiction scale for teenagers (DAST). J Psychoeduc Assess. (2022) 40:293–304. doi: 10.1177/07342829211056394
25. Çelik, OT, Tunç, Y, Candemir, B, Kapkın İçen, B, and Acar, D. Validity and reliability study of the Turkish adaptation of the digital addiction scale for teenager (DAST). J Inonu Univ Health Ser Vocat Sch. (2023) 11:1715–28. doi: 10.33715/inonusaglik.1288302
26. Serra-Majem, L, Ribas, L, Ngo, J, Ortega, RM, García, A, Pérez-Rodrigo, C, et al. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean diet quality index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. (2004) 7:931–5. doi: 10.1079/PHN2004556
27. Şahingöz, S.A., Özgen, L., and Yalçın, E. (2019). “Validity and reliability of the Mediterranean Diet Quality Scale (KIDMED).” In Proceedings Book of 5th International Eurasian Congress on Natural Nutrition, Healthy Life & Sport. pp. 1078–1088.
28. Godin, G, and Shephard, RJ. Godin leisure-time exercise questionnaire. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (1997) 29:S36–8.
29. Lapa, TY, Certel, Z, Kaplan, K, and Yağar, G. The validity and reliability study of leisure time exercise questionnaire for adolescents. J Res Educ Teach. (2016) 5:1–9.
30. Mullen, SP, Olson, EA, Phillips, SM, Szabo, AN, Wójcicki, TR, Mailey, EL, et al. Measuring enjoyment of physical activity in older adults: invariance of the physical activity enjoyment scale (PACES) across groups and time. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. (2011) 8:103. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-8-103
31. Özkurt, B, Küçükibiş, HF, and Eskiler, E. Physical activity enjoyment scale (PACES): adaptation to Turkish culture, validity and reliability study. J Soc Sci Mus Alparslan Univ. (2022) 10:21–37. doi: 10.18506/anemon.976300
32. Ding, K, Shen, Y, Liu, Q, and Li, H. The effects of digital addiction on brain function and structure of children and adolescents: a scoping review. Healthcare. (2024) 12:15. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12010015
33. Peris, M, de la Barrera, U, Schoeps, K, and Montoya-Castilla, I. Psychological risk factors that predict social networking and internet addiction in adolescents. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:4598. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17124598
34. Reddy, RS. Newer addictions in children and adolescents. Telangana J Psychiatry. (2021) 7:79–86. doi: 10.4103/tjp.tjp_45_21
35. Meng, SQ, Cheng, JL, Li, YY, Yang, XQ, Zheng, JW, Chang, XW, et al. Global prevalence of digital addiction in general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. (2022) 92:102128. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2022.102128
36. Chung, TW, Sum, SM, and Chan, MW. Adolescent internet addiction in Hong Kong: prevalence, psychosocial correlates, and prevention. J Adolesc Health. (2019) 64:S34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.12.016
37. Mutimmatul, F., Wibawa, S.C., and Ekawati, R.. (2018). “Digital addiction in Indonesian adolescents.” in Mathematics, Informatics, Science, and Education International Conference (MISEIC 2018). pp. 274–277. Atlantis Press.
38. Ngamo, MSA, Aipipidely, D, Junias, MS, and Benu, JMY. The relationship between social media addiction and emotional stability in adolescents in Kupang City. J Health Behav Sci. (2023) 5:240–8. doi: 10.35508/jhbs.v5i2.9703
39. Grosso, G, and Galvano, F. Mediterranean diet adherence in children and adolescents in southern European countries. NFS J. (2016) 3:13–9. doi: 10.1016/j.nfs.2016.02.004
40. Santomauro, F, Lorini, C, Tanini, T, Indiani, L, Lastrucci, V, Comodo, N, et al. Adherence to Mediterranean diet in a sample of Tuscan adolescents. Nutrition. (2014) 30:1379–83. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.04.008
41. Rosi, A, Giopp, F, Milioli, G, Melegari, G, Goldoni, M, Parrino, L, et al. Weight status, adherence to the Mediterranean diet, physical activity level, and sleep behavior of Italian junior high school adolescents. Nutrients. (2020) 12:478. doi: 10.3390/nu12020478
42. Wärnberg, J, Pérez-Farinós, N, Benavente-Marín, JC, Gómez, SF, Labayen, I, Zapico, AG, et al. Screen time and parents’ education level are associated with poor adherence to the Mediterranean diet in Spanish children and adolescents: the PASOS study. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:795. doi: 10.3390/jcm10040795
43. Alim, NE, Çalışkan, G, and Beşler, ZN. Assessment of adherence to the Mediterranean diet and behaviors of fruit and vegetable consumption in adolescents. Value Health Sci. (2022) 12:152–9. doi: 10.33631/sabd.1055497
44. Myszkowska-Ryciak, J, Harton, A, Lange, E, Laskowski, W, Wawrzyniak, A, Hamulka, J, et al. Reduced screen time is associated with healthy dietary behaviors but not body weight status among polish adolescents. Report from the WISE nutrition—healthy generation project. Nutrients. (2020) 12:1323. doi: 10.3390/nu12051323
45. Mumena, WA, Alnezari, AI, Safar, HI, Alharbi, NS, Alahmadi, RB, Qadhi, RI, et al. Media use, dietary intake, and diet quality of adolescents in Saudi Arabia. Pediatr Res. (2023) 94:789–95. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02505-5
46. Almourad, MB, McAlaney, J, Skinner, T, Pleya, M, and Ali, R. Defining digital addiction: key features from the literature. Psihologija. (2020) 53:237–53. doi: 10.2298/PSI191029017A
47. Anas, N, Aziz, N, Ahmat, AC, and Alwi, EAZE. Digital addiction and mental-physical health: a scenario in Asia. Int J Acad Res Bus Soc Sci. (2023) 13:1682–890. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v13-i1/15900
48. Alves, RL, Toral, N, and Gonçalves, VSS. Individual and socioeconomic contextual factors associated with obesity in Brazilian adolescents: vigiNUTRI Brasil. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 20:430. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010430
49. Jang, E, Ko, E, Sim, J, Jeong, M, and Park, S. Mukbang media: correlations with the dietary behavior of children and adolescents in Korea. Nutr Res Pract. (2024) 18:674–86. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2024.18.5.674
50. Diolintzi, A, Panagiotakos, DB, and Sidossis, LS. From Mediterranean diet to Mediterranean lifestyle: a narrative review. Public Health Nutr. (2019) 22:2703–13. doi: 10.1017/S1368980019000612
51. Buja, A, Miatton, A, Zanovello, A, Brocadello, F, Baldovin, T, Muhiddin, MN, et al. Media usage and adherence to the Mediterranean diet in children. Nutrients. (2024) 16:3481. doi: 10.3390/nu16203481
52. Imperatori, C, Panno, A, Carbone, GA, Corazza, O, Taddei, I, Bernabei, L, et al. The association between social media addiction and eating disturbances is mediated by muscle dysmorphia-related symptoms: a cross-sectional study in a sample of young adults. Eat Weight Disord-Stud Anorex Bulim Obes. (2022) 27:1131–40. doi: 10.1007/s40519-021-01232-2
53. Bilim, ZŞT, and Yurttagül, SM. Social media addiction among university students and its impact on adherence to the Mediterranean diet. İzmir Katip Çelebi Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Fakültesi Dergisi. (2025) 10:187–93. doi: 10.61399/ikcusbfd.1542263
54. Van den Bulck, J, and Eggermont, S. Media use as a reason for meal skipping and fast eating in secondary school children. J Hum Nutr Diet. (2006) 19:91–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-277X.2006.00683.x
55. Gülü, M, Yagin, FH, Gocer, I, Yapici, H, Ayyildiz, E, Clemente, FM, et al. Exploring obesity, physical activity, and digital game addiction levels among adolescents: a study on machine learning-based prediction of digital game addiction. Front Psychol. (2023) 14:1097145. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1097145
56. Xiao, W, Wu, J, Yip, J, Shi, Q, Peng, L, Lei, QE, et al. The relationship between physical activity and mobile phone addiction among adolescents and young adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. JMIR Public Health Surveill. (2022) 8:e41606. doi: 10.2196/41606
57. Zhihao, D, Tao, W, Yingjie, S, and Feng, Z. The influence of physical activity on internet addiction among Chinese college students: the mediating role of self-esteem and the moderating role of gender. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:935. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18474-1
58. Bajamal, E, Abou Hashish, EA, and Robbins, LB. Enjoyment of physical activity among children and adolescents: a concept analysis. J Sch Nurs. (2024) 40:97–107. doi: 10.1177/10598405221137718
59. Hagberg, LA, Lindahl, B, Nyberg, L, and Hellénius, ML. Importance of enjoyment when promoting physical exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2009) 19:740–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2008.00844.x
60. Salmon, J, Brown, H, and Hume, C. Effects of strategies to promote children's physical activity on potential mediators. Int J Obes. (2009) 33:S66–73. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2009.21
61. Heijnen, S, Hommel, B, Kibele, A, and Colzato, LS. Neuromodulation of aerobic exercise—a review. Front Psychol. (2016) 6:1890. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01890
Keywords: digital addiction, Mediterranean diet, physical activity, adolescent, healthy lifestyle
Citation: Helvacı G and Tayhan F (2025) Determinants and relationships of digital addiction, diet quality, and physical activity in adolescents. Front. Public Health. 13:1654322. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1654322
Edited by:
Jaime Camacho Ruiz, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México, MexicoReviewed by:
Tuğba Türkkan, Gumushane University, Türkiyeİbrahim Hakkı Çağiran, Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Helvacı and Tayhan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gizem Helvacı, Z2hlbHZhY2lAbWVobWV0YWtpZi5lZHUudHI=
†ORCID: Gizem Helvaci, http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8654-9245
Fatma Tayhan, http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8524-9048
 Gizem Helvacı
Gizem Helvacı Fatma Tayhan
Fatma Tayhan