- 1Department of Nursing, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University/West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Birth Defects and Related Diseases of Women and Children (Sichuan University), Ministry of Education, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3The Second People’s Hospital, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 4Chengdu University of TCM, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Objective: This cross-sectional study investigates the demand for CB-IHSC among older adults in Chengdu and identifies the factors influencing this demand, thereby providing a reference for developing and optimizing such services.
Methods: From August to December 2023, 511 eligible older adults residing in the central districts of Chengdu were selected through convenience sampling. Guided by the Andersen Health Service Utilization Behavior Model, the study categorized influencing factors into three dimensions: predisposing factors, enabling factors and need factors. Chi-square tests were first used to identify statistically significant variables within each dimension. These variables were then included in a binary logistic regression model to assess their association with service demand. Model calibration was assessed using the Hosmer–Lemeshow test.
Results: Demand for CB-IHSC was high (87.08%). Independent predictors included number of children (OR = 2.12), living with spouse (vs alone, Ref; OR = 0.48), lower income (OR = 0.40), convenient community medical access (OR = 1.75), children’s support (OR = 3.71), lower self-care ability (OR = 0.18), poorer self-rated health, and higher awareness. Policies should improve accessibility, financing, and public awareness to increase uptake.
Conclusion: To support the sustainable development of CB-IHSC, Chengdu should continue strengthening capacity building in this sector. Efforts should be directed toward establishing diversified financing and support mechanisms, improving the accessibility and convenience of service delivery, and enhancing public awareness and education regarding CB-IHSC.
1 Introduction
With the global trend of an aging population, China is facing increasingly severe demographic and healthcare challenges. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, by the end of 2024, over 310 million people in China will be aged 60 and above, representing 22% of the total population. Among them, approximately 78% suffer from at least one chronic disease (1). Despite the growing demand for care services for older adults, the availability remains inadequate, with only 406,000 care institutions and 7.99 million beds nationwide (1). This imbalance between demand and supply underscores the urgent need to develop efficient long-term care system in China.
In response, the Chinese government has implemented policies to develop long-term care services and foster a supportive environment for older adults. Since the release of the Opinions on Accelerating the Development of the Care-for-older-adults in 2013, various models have emerged, including integrated health and care institutions for older adults, community-based integrated health and social care (CB-IHSC), and home-based integrated care. However, while these models have proliferated, gaps remain in their accessibility, quality, and integration.
The developed countries have already established comprehensive care system for older adults, such as the U.S. Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elder Adults (PACE), the UK’s community-based older adults care framework, and Japan’s Kaigo Hoken (Long-Term Care Insurance) system. However, China’s care-for-older-adults industry is still in its early stages, with limited empirical research on CB-IHSC. Existing studies are primarily theoretical, focusing on framework development and public awareness, particularly in large cities. For instance, a study by Liu Xiaochu et al. reported a 66.3% demand for CB-IHSC in Luzhou (2), whereas a survey in Guangzhou indicated a higher demand of 86.26% (3). In Chengdu, older residents mainly require health management, smart care, medical consultations, psychological care, and rehabilitation nursing (4).
Further research across other megacities in China, such as Nanchang, Changsha, and Guangzhou, has identified multiple factors influencing demand for CB-IHSC, including health status, family support, and community environment (5, 6). For example, a survey in Guangzhou found a strong correlation between demand and factors such as health conditions, number of children, and self-rated health (3). Similarly, studies in Changsha highlighted the importance of family support, income levels, and the availability of medical resources in determining the use of community-based integrated care services (6). These findings underscore the need to understand how similar mechanisms operate in Chengdu.
The Andersen Health Service Utilization Behavior Model, proposed by Ronald M. Anderson in 1968, provides a robust theoretical framework for analyzing healthcare-seeking behavior. It posits that service utilization is jointly influenced by three categories of factors: Predisposing Characteristics (e.g., age, education), Enabling Resources (e.g., accessibility, family support), and Need (e.g., self-rated health, disease burden). This model’s relevance for understanding the demand for CB-IHSC is well-supported, as existing studies indicate that such demand arises from a complex interaction of individual health conditions, socio-economic factors, and service availability (7–9). Furthermore, the model’s applicability in the Chinese context has been extensively demonstrated in long-term care research conducted in settings such as Shaanxi, Suzhou, and Beijing (10–14). While alternative frameworks exist (e.g., the WHO’s ICOPE model), the Andersen model’s comprehensive and behavioral-focused structure makes it the most appropriate choice for systematically investigating the factors influencing demand for integrated care in this study.
1.1 The case of Chengdu
Chengdu, located in the southwest of China and as a national pilot for CB-IHSC, faces rapid population aging. Despite establishing 28 CB-IHSC complexes, challenges such as limited service scope and low public awareness persists (15, 16). Most studies on Chengdu focus on demand descriptions but lack a unified theoretical framework to explain the underlying drivers.
This study aims to fill this gap by applying the Andersen Health Service Utilization Behavior Model to identify key factors driving CB-IHSC demand in Chengdu. The following hypotheses are proposed, based on the model and prior literature:
H1 (Need): Poorer self-rated health and lower self-care ability are associated with higher demand for CB-IHSC.
H2 (Enabling—Access): Greater convenience of community medical care would be associated with higher odds of demand.
H3 (Enabling—Resources): Higher income is positively associated with demand for CB-IHSC.
H4 (Enabling—Family): Support from children positively influences demand. The more children an individual has, the lower the demand for services.
H5 (Predisposing—Co-residence): Compared with living alone, co-residence with a spouse/children would be associated with lower odds due to informal care.
H6 (Awareness): Higher awareness of CB-IHSC would be associated with higher odds of demand.
These hypotheses guide the model specification and analysis in the following sections.
Terminology: We use the term Community-Based Integrated Health and Social Care (CB-IHSC) throughout. Terms such as “integrated medical and social care” are treated as synonyms and, after first mention, replaced by CB-IHSC.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and participants
A cross-sectional survey was conducted among older residents aged 60 years and above in the main urban areas of Chengdu. The inclusion criteria were as follows: individuals who had resided for at least 6 months in one of the following districts—Jinjiang, Qingyang, Wuhou, Chenghua, Jinniu, Gaoxin, or Tianfu New District; individuals who regularly visited a designated community health service center for medical care; those aged 60 or older; and individuals capable of clear and logical communication. Exclusion criteria included: individuals with communication or expression impairments; individuals who refused to participate in the survey; respondents who completed the questionnaire in less than 3 minutes; those who selected the same response option throughout the questionnaire; individuals whose answers were internally inconsistent or logically contradictory. A total of 530 questionnaires were distributed, with 511 valid responses retained (effective response rate: 96.41%).
2.2 Data collection
Data were collected from August to December 2023 using electronic questionnaires administered at various community health service centers and nearby residential areas. Trained research assistants approached potential participants in waiting areas or common spaces of these centers, as well as in public areas of residential communities. They introduced themselves and the study purpose, explaining that the survey aimed to understand the needs and preferences of the CB-IHSC. Participation was voluntary, anonymous, and could be withdrawn at any time. Upon obtaining informed consent from the older participants or their accompanying family members, data were completed either by self-administration or with interviewer assistance as needed. Each survey session lasted approximately 5–10 min.
2.3 Questionnaire and measures
The questionnaire was designed based on the Andersen Health Service Utilization Behavior Model, which categorizes influencing factors into three dimensions: predisposing characteristics, enabling resources, and need factors. The following key factors were assessed:
Predisposing characteristics: Demographic characteristics: Age, gender, marital status, education level; Social structure variables: Occupation, living arrangements and number of children; Health beliefs: Factors such as attitudes toward health care and health-seeking behaviors.
Enabling resources: Financial resources: Monthly income, pension, monthly medical expenses and insurance coverage; Social support: Support from children, caregivers, or other family members (life care and financial support); Access to services: The proximity of healthcare facilities and the availability of medical resources in the community (ease of accessing medical services).
Need factors: Self-care ability: the ability to perform activities of daily living independently; Chronic conditions: Number of chronic illnesses the individual is managing; Health status: Self-reported health condition (e.g., good, fair, or poor); Awareness of services: awareness of CB-IHSC and actual demand for such services.
Outcome variable: Demand for CB-IHSC.
Demand, as a key concept in this study, is defined as the actual need or desire for CB-IHSC. It was operationalized in the questionnaire by asking participants the following question: “Do you currently have a need for community-based integrated health and social care services?” The response options were “Yes” or “No.” This was captured as a binary variable: “1” for respondents expressing a need (demand) for the services, and “0” for those indicating no demand.
2.4 Statistical methods
Data were processed and analyzed using SPSS 22.0 software. After assigning values to variables, both univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted. Univariate analysis was conducted using chi-square tests to identify significant variables associated with service demand. Multivariate analysis was performed using binary logistic regression. The model fit was evaluated by the Hosmer–Lemeshow test. The dependent variable was demand for CB-IHSC, coded as a binary variable: “0” representing no demand and “1” representing demand. In the binary logistic regression model, the relationship between the independent variables and the log-odds of demand is modeled. Let P represent the model-estimated probability that an individual has a demand for the services (i.e., Prob(Y = 1)). The odds of demand is then defined as P / (1 − P). The odds ratio (OR) for each independent variable, as reported in the results, represents the factor by which the odds of demand multiply for a one-unit change in the predictor variable, while holding other variables constant. An OR greater than 1 indicates that the predictor variable is associated with an increased likelihood of demand for the services, while an OR less than 1 suggests a decreased likelihood. Ordered categorical variables (e.g., income, satisfaction, self-rated health, convenience) were treated as ordinal predictors in the regression; dichotomous variables were binary-coded; nominal multi-level variables used the reference categories specified in Table 1 and Appendix Table A1.
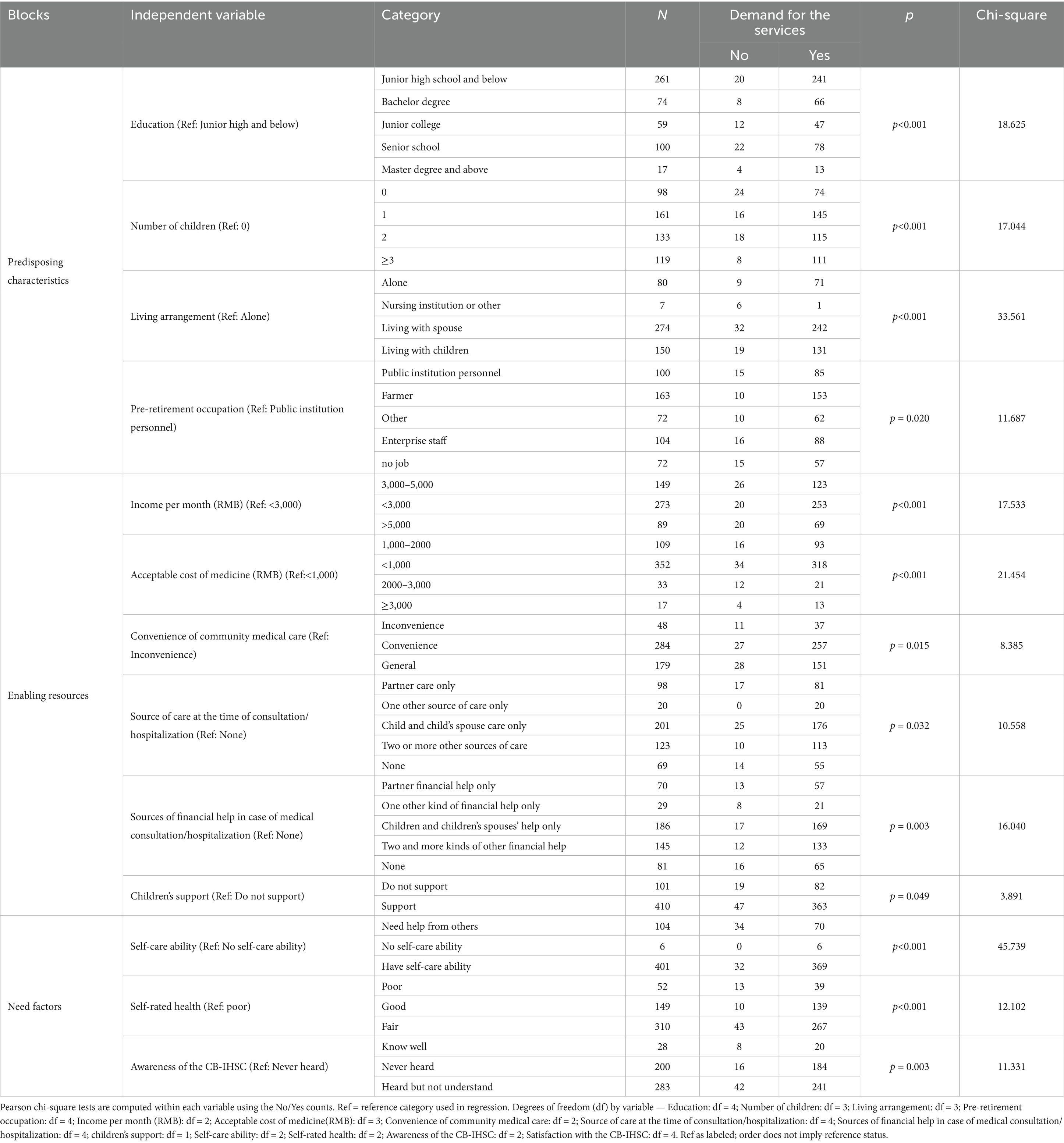
Table 1. Analysis of factors influencing the demand for CB-IHSC among older participants with different characteristics.
The hierarchical modeling approach was applied to assess how much additional variance in demand was explained by adding successive sets of factors. Three logistic regression models were constructed accordingly: Model 1 included statistically significant variables from the predisposing characteristics. Model 2 included significant variables from both predisposing and enabling factors. Model 3 included significant variables from all three dimensions: predisposing, enabling, and needs. Each model followed the general form. Changes in Cox & Snell R2 and Nagelkerke R2 were used to evaluate improvements in model fit, indicating how each block of variables contributed to explaining demand.
Where α is the intercept, β denotes the partial regression coefficients, X represents the independent variables, and ε is the residual error term not explained by the model.
2.5 Quality control
Before the formal survey, all research personnel underwent standardized training to ensure familiarity with the questionnaire content and mastery of appropriate survey techniques. A pilot study was conducted to test the survey procedures, identify potential issues, and refine the questionnaire and the overall research plan. Based on feedback, adjustments were made to ensure the reliability and validity of the survey instrument and methodology.
3 Results
3.1 Basic characteristics of the respondents
3.1.1 Predisposing factors
A total of 511 older participants participated in the survey, comprising 154 males (30.14%) and 357 females (69.86%). The respondents ranged in age from 60 to 100 years, with the majority aged between 60 and 70 years(68.49%), followed by those aged 71–80 (18.20%), 81–90 (9.39%) and above 90 (3.91%). Regarding educational attainment, 261 respondents (51.08%) had completed junior high school or below, while 250 (48.92%) had received a high school education or higher, including college, university, and postgraduate degrees. In terms of marital status, 78.67% of the respondents were married or living with a spouse. Concerning the number of children, 98 individuals (19.18%) were childless; 161 (31.51%) had one child; 133 (26.03%) had two children; and 119 (23.29%) had three or more children. Regarding living arrangements, 80 respondents (15.66%) lived alone, 274 (53.62%) lived with a spouse, 150 (29.35%) lived with their children, and 7 individuals (1.37%) resided in nursing homes or other care facilities. As for occupational background prior to retirement, 100 respondents (19.57%) were public sector employees, 104 (20.35%) worked in enterprises, and 163 (31.90%) were farmers. In addition, 72 individuals (14.09%) were unemployed, while another 72 (14.09%) were engaged in various other occupations (see Table 2).
3.1.2 Enabling factors
Regarding monthly income, 29.16% of respondents reported earning between 3,000 and 5,000 RMB, 53.42% earning less than 3,000 RMB, and 17.42% earning more than 5,000 RMB. The primary source of income was retirement pensions (56.56%), followed by financial support from children (19.57%). Pension insurance coverage was high, with 95.50% of the respondents indicating they had it, and 71.62% of them also possessing medical insurance. Monthly medical expenses varied: 352 individuals (68.88%) spent less than 1,000 RMB, 109 (21.33%) spent between 1,000 and 2,000 RMB, 33 (6.46%) spent between 2,000 and 3,000 RMB, and 17 (3.33%) reported spending over 3,000 RMB. While the majority of respondents reported relatively easy access to medical care, 9.39% experienced difficulties in accessing treatment. In terms of care-giving support during outpatient visits or hospitalization, 201 individuals (39.33%) relied solely on their children or spouses; 123 (24.07%) had two or more sources of care; 98 (19.18%) were cared for only by a spouse; 20 (3.91%) relied on a single other caregiver, and 69 (13.50%) reported having no care-giving support. Regarding financial support for medical expenses, 186 respondents (36.40%) received assistance exclusively from their children or spouse; 145 (28.38%) had multiple financial support sources; 70 (13.70%) relied solely on their spouse; 29 (5.68%) relied on one other person, and 81 (15.85%) had no support from others in any form. When asked whether their children supported their participation in CB-IHSC, 410 individuals (80.23%) responded affirmatively, while 101 (19.77%) indicated a lack of support (see Table 2).
3.1.3 Need factors
About the Self-care ability, 401 respondents (78.47%) were entirely self-sufficient, 104 (20.35%) partially dependent, and 6 (1.17%) entirely dependent. Concerning chronic disease status, most respondents reported having at least one chronic condition, while only 26.03% of them reported having no chronic illnesses. In terms of self-rated health status, 310 respondents (60.67%) considered their health to be good, 149 (29.16%) rated it as fair, and 52 (10.18%) assessed their health as poor. s of CB-IHSC was generally low: 283 individuals (55.38%) had heard of the model but lacked a clear understanding; 200 (39.14%) had never heard of it; and only 28 (5.48%) reported being very familiar with it. When asked about their need for CB-IHSC, 445 respondents (87.08%) expressed a clear demand, while 66 (12.92%) indicated no current need.
3.2 Analysis of factors influencing the demand for CB-IHSC with different characteristics
To identify variables significantly associated with the demand for CB-IHSC, bivariate analyses were performed using Chi-square tests for all predisposing, enabling, and need factors. As an example, Appendix Table A2 presents the cross-tabulation and Chi-square analysis between the convenience of community medical care and service demand. The analysis revealed a statistically significant association between these two variables (χ2 = 8.385, p = 0.015). The demand for CB-IHSC was highest (90.5%) among older adults who reported “Convenience” in accessing community medical care, followed by those reporting “General” convenience (87.3%). In contrast, the group reporting “Inconvenience” showed a comparatively lower demand rate (77.1%). This gradient suggests that better accessibility to local medical care is positively associated with a higher demand for integrated health and social care services. Following this approach, significant variables (p < 0.05) identified from the comprehensive bivariate screening are summarized in Table 1 below.
Among the predisposing factors, significant variables such as education, number of children, living arrangements, and occupation were found to have a statistically significant impact on the demand for CB-IHSC (p < 0.05). In terms of enabling factors, variables including income per month, acceptable cost of medicine, convenience of community care, sources of daily care and financial assistance during outpatient visits or hospitalization, as well as children’s support for CB-IHSC, were identified as significant factors (p < 0.05). For need factors, self-care ability, self-rated health, awareness of CB-IHSC were all statistically significant (p < 0.05), as seen in Table 1.
3.3 Logistic regression analysis
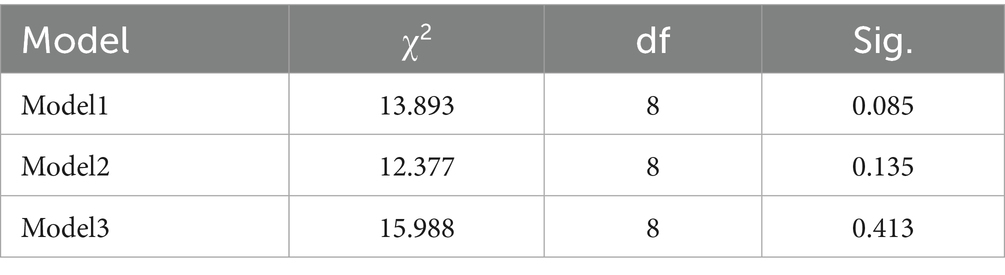
As demonstrated in Table 3, Model 3 (269.736) exhibited the lowest −2 log-likelihood value compared to Models 1 (348.491) and 2 (323.742). The smaller the −2 Log Likelihood, the better the model fit, indicating lower model error and better overall performance. The Cox & Snell R2 value for Model 3 was 0.215, which was higher than the values for Model 1 (0.084) and Model 2 (0.138). The Nagelkerke R2 value for Model 3 was 0.400, also surpassing that of Model 1 (0.156) and Model 2 (0.257). The Nagelkerke R2 increased from 0.156 (Model 1) to 0.257 (Model 2) and 0.400 (Model 3), indicating a progressive improvement in explanatory power as additional factors were included. The larger the Cox & Snell R2 and Nagelkerke R2 values, the better, as they represent a higher proportion of variance explained by the model. Model 3 has the lowest −2 Log Likelihood, and both the Cox & Snell R2 and Nagelkerke R2 are the highest, indicating the best fit. Additionally, from Model 1 to Model 2, the Nagelkerke R2increased by 0.101. From Model 2 to Model 3, the Nagelkerke R2 increased by 0.143, which is the largest improvement, confirming the most significant contribution of need-related variables and suggesting that these factors have the strongest influence in explaining the dependent variable. Therefore, Model 3 is the optimal model.
As shown in Table 4, the p-values for Model 1 (p = 0.085), Model 2 (p = 0.135), and Model 3 (p = 0.413) were all greater than 0.05. Furthermore, the Hosmer-Lemeshow test also yielded p-values above 0.05, suggesting that the data extraction process was sufficient and that the model specification was appropriate. Among the models, Model 3 demonstrated the highest level of significance and the best overall fit. Therefore, Model 3 was selected for binary logistic regression analysis to examine how much each factor influences the demand for CB-IHSC among older participants.
Based on the results from Model 3, variables including the number of children, living arrangements, income per month, convenience of community care, support’s children, self-care ability, self-rated health, and awareness of the CB-IHSC were all found to be statistically significant (p < 0.05). These factors were identified as significantly impacting older participants’ demand for CB-IHSC. Detailed results are presented in Table 5.
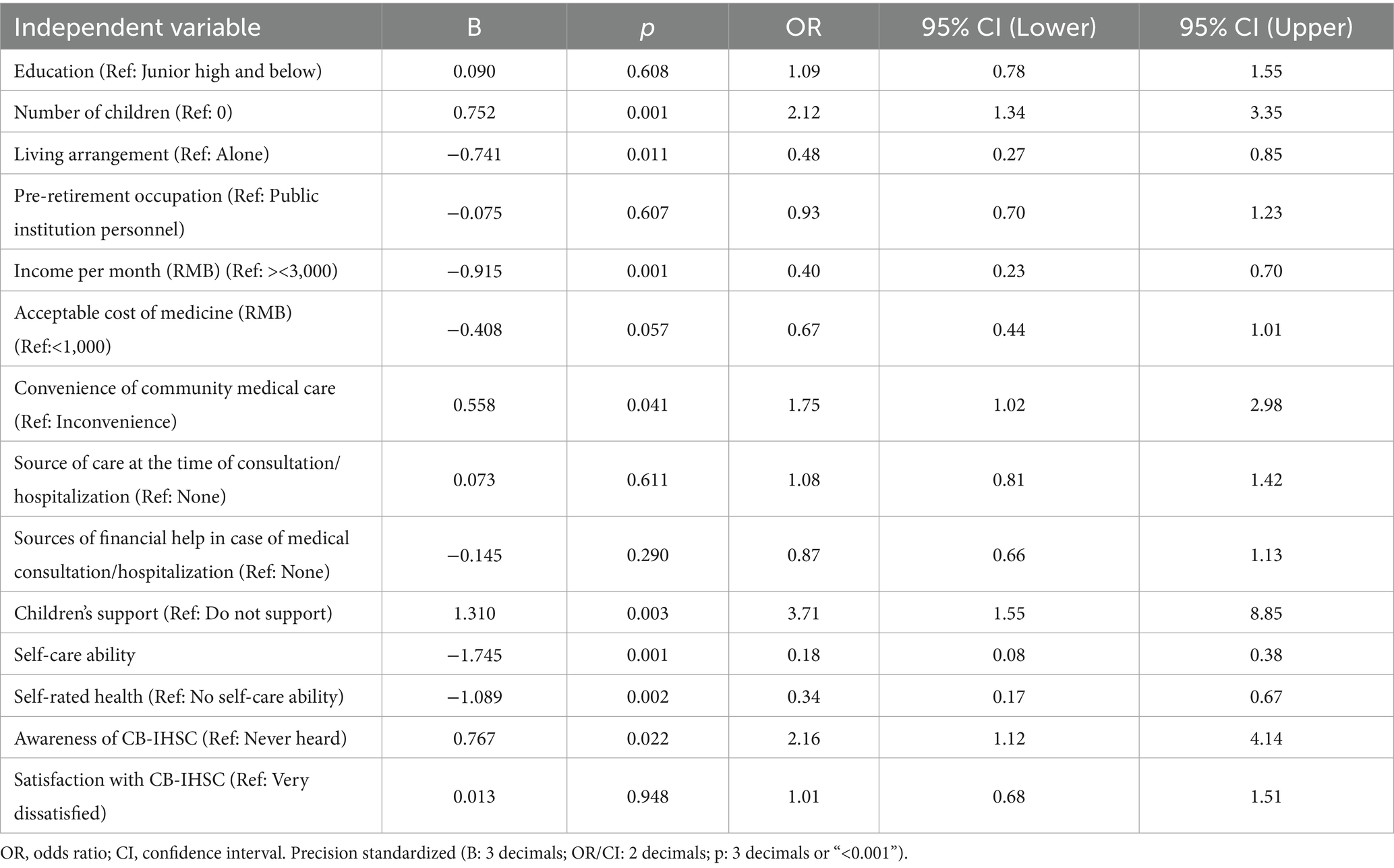
Table 5. Logistic regression analysis including variables associated with CB-IHSC demand for the old adults.
4 Discussion
4.1 The demand for the CB-IHSC
The results of this study indicate a strong demand for CB-IHSC among older adults in Chengdu. Specifically, 87.08% of the respondents reported a need for such services, which is comparable to the demand level in Guangzhou (86.2%) (3) and slightly higher than that in Luzhou (66.3%) (2).
This elevated demand in Chengdu can be effectively interpreted through the Andersen Health Service Utilization Behavior Model. The city’s proactive policy support and investment in CB-IHSC complexes and creating a “15-min convenient living circle” have directly enhanced Enabling Resources by improving the accessibility and availability. Our findings confirm that convenient of community medical is a significant positive predictor of demand (OR = 1.747). Simultaneously, these government-led initiatives have shaped Predisposing Characteristics, particularly health beliefs, by raising public awareness and fostering a more positive attitude toward integrated care models. This is corroborated by our regression results, which identified awareness of CB-IHSC as a key driver of demand (OR = 2.155). Therefore, the high demand in Chengdu is not merely an external phenomenon but is likely mediated by the model’s core components: policy efforts improve enabling resources and shape predisposing characteristics, which in turn, as our model demonstrates, significantly influence the expressed demand for CB-IHSC.
4.2 Factors influencing demand
A key strength of this study is the hierarchical regression grounded in the Andersen Health Service Utilization Behavior Model, which allowed us to assess pre-specified hypotheses about the relative importance of factor domains. The results largely supported our hypotheses, yet several findings provided new insights. The data suggest that multiple factors—predisposing, enabling, and need factors—affect the demand for CB-IHSC among older adults in Chengdu. Specifically, the number of children and living arrangements were identified as significant predisposing factors; income, convenience of community medical care, and children’s support as enabling factors; and self-care ability, self-rated health, and awareness of CB-IHSC as key need factors. Each of these is discussed below.
4.2.1 The composite role of children: quantity and support
Among the predisposing characteristics, the association between the number of children and higher demand for CB-IHSC (OR = 2.12) is one of our most surprising yet insightful findings. This is contrary to our H4 regarding the number of children. This positive relationship contrasts with the initial intuition that more children would substitute for formal services, as well as with the results of Xu Haijiao, who reported an inverse relationship between the number of children and demand for CB-IHSC suggesting that fewer children correlate with higher demand (17). Similarly, Li Qiang found that an increased number of children was associated with lower life satisfaction and higher levels of depression among their parents, indicating that more children do not necessarily bring more happiness (18). In families with multiple children, care responsibilities may be neglected or deferred, leaving older adults’ care needs unmet and prompting them to seek alternative models such as CB-IHSC.
As hypothesized in H4, regarding the support from children, it appears to be a significant positive factor influencing demand (OR = 3.71), aligning with the findings of Tan Mei and colleagues (19). When children express understanding and support for CB-IHSC, older adults’ confidence and demand for these services increase. Material and emotional support from children not only eases financial burdens but also reinforces the psychological readiness of older adults to adopt new care models.
This divergence finding underscores that the decision to utilize CB-IHSC is not solely determined by the structural aspect of family size (number of children), but is more significantly influenced by the functional aspect—the quality and nature of the support those children provide. A plausible explanation is that structural family size (quantity) does not translate into functional support unless accompanied by children’s active support (an enabling resource). Our analysis suggests the enabling dimension—children’s support for participation—shows a strong positive association with demand, indicating that who helps and how may matter more than how many children one has.
4.2.2 Living arrangements
Living arrangements may influence the demand for the CB-IHSC with solitary living potentially linked to higher demand. Studies have shown that empty-nest older adults exhibit a hierarchical needs structure, prioritizing medical care, emotional support, and basic life assistance (20). Due to declining physical functions, older adults often require greater medical support and daily care. The CB-IHSC provide continuous support, such as health check-ups, rehabilitation, in-home care, and life assistance, which help meet these needs. Additionally, older adults living alone are more likely to experience loneliness and insecurity, increasing their reliance on CB-IHSC for social interaction and emotional support. Thus, as the number of cohabitants decreases, the demand for CB-IHSC tends to increase. This finding partially supports H5, which hypothesized that co-residence with family reduces demand due to informal care. However, the quality of family support is crucial; older individuals with limited or no caregiving capacity from family may still require formal care. Therefore, while co-residence often reduces demand, the need for CB-IHSC remains higher among those living alone, where informal care is insufficient.
4.2.3 Monthly income
Contrary to hypothesis H3, monthly income was negatively associated with the demand for integrated care services. As income increases, the likelihood of choosing CB-IHSC decreases. This contradicts the findings of Nie Jie, who suggested that individuals with higher socioeconomic status were more likely to choose such services (21). However, the current results align with Zhi Mengjia and Xue Yuan, who found that higher-income individuals were more inclined to choose institutional care, while those with lower incomes preferred community or home-based care models (22, 23). This may be because traditional institutional care facilities have undergone years of development and offer better amenities and more comprehensive services, attracting wealthier older adults. In contrast, community-based care, which is more affordable, tends to appeal to those with lower incomes. The CB-IHSC is still relatively new and under development, so high-income individuals may remain cautious or hesitant to adopt it.
4.2.4 Convenience of community medical care
As predicted by H2, the ease of accessing medical services within the community may influence demand, with more convenient access potentially linked to greater demand. This finding is consistent with the results of Lü Xinrui (24). When nearby medical institutions are available, frequent needs such as medication, follow-up visits, and basic nursing care can be addressed locally, thereby reducing travel time, financial costs, and physical risks (such as falls) associated with hospital visits. The convenient of community medical care enhances older adults’ trust in and reliance on CB-IHSC, thus increasing their willingness to use these services.
4.2.5 Self-care ability and self-rated health
Self-care ability and health condition were strongly associated with demand for CB-IHSC. Poorer self-rated health may be associated with an increase in demand, consistent with H1. Physical function typically declines as people age, resulting in reduced self-care ability. Older adults with poorer health and lower levels of independence—particularly those who are semi-dependent or disabled—tend to have a higher demand for integrated care services compared to those who are self-sufficient. These findings are consistent with the study by Lin Qin (25). The CB-IHSC offers personalized care plans according to varying levels of dependency, covering both basic daily needs and professional medical care. This model remains applicable even as the health status of older adult’s changes, ensuring that their evolving care needs are effectively met.
4.2.6 Awareness of the CB-IHSC
As expected and in support of H6, a positive correlation was observed between the level of awareness of the CB-IHSC and the demand for the services. Higher awareness may be linked to a greater intent to participate (26), aligning with the research of Zhang Yujie (27). In this study, only 28 respondents reported a comprehensive understanding of CB-IHSC; 283 had heard of it but did not understand it, and 200 reported never having heard of it. These findings indicate limited dissemination and awareness of CB-IHSC.
4.3 Limitations
This study has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. First, the use of convenience sampling in main urban areas, while practical, means that our sample may not be fully representative of all older adults in Chengdu, particularly those in suburban or rural districts, or those who are completely home-bound and do not access community health services. Consequently, the applicability of our findings to the entire older population of Chengdu or other regions of China may be limited. Second, the cross-sectional design captures a snapshot in time and cannot establish causal relationships between the factors and service demand.
5 Conclusion and policy recommendations
This study identifies the factors influencing the demand for CB-IHSC among older adults in Chengdu. With the aging population and rising demand for CB-IHSC, it is critical to bridge gaps in service availability, accessibility, and awareness. Based on these findings, the following policy recommendations are proposed.
5.1 Improve service accessibility and quality
Efforts could be directed toward enhancing the accessibility and quality of CB-IHSC. Expanding and upgrading community-based facilities may contribute to equitable distribution and comprehensive coverage. CB-IHSC might be further developed by strengthening cooperation between community health centers and care institutions for older adults. Standardized protocols for service delivery, health management, and emergency response should be established to ensure continuity, safety, and effectiveness of care. Professional staff training could also be prioritized to improve service capacity.
5.2 Tailor services to individual needs
Given the varying health conditions, economic statuses, and family support structures of older adults, it is crucial to provide personalized and differentiated services. For instance, semi-dependent or disabled older adults may require more intensive medical and nursing support. At the same time, independent individuals may benefit more from health education, regular check-ups, and social activities. By implementing needs-based stratification and care planning, service efficiency and user satisfaction can be significantly improved.
5.3 Enhance family and social support systems
Family support remains a key enabling factor in older adults’ decisions to utilize integrated care services. Therefore, it is essential to strengthen the role of families in eldercare through policy incentives such as tax benefits, subsidies, or caregiver training programs. At the same time, community-based support networks could be developed to provide supplemental care and companionship, particularly for solitary or empty-nest older adults. Volunteer programs, inter-generational activities, and mutual-aid models may effectively complement formal care services.
5.4 Promote policy innovation and support
Local governments may continue to play a leading role by formulating long-term strategic plans and introducing targeted policies to support the development of CB-IHSC. It is crucial to increase financial investment, expand pilot programs, and disseminate best practices across communities. Furthermore, enhancing cross-sectoral coordination among departments such as health, civil affairs, and housing could support the sustainable development of these services. Additionally, promotional efforts should be enhanced using community bulletin boards, cultural events, and digital platforms (such as official WeChat accounts) to raise awareness and provide detailed information on available services. Increasing public understanding is essential to improving participation and ensuring that more older adults benefit from integrated care.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SL: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. PL: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Medical Research Project of Health Commission of Chengdu, Sichuan Province (grant number: 2025030).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the older participants in Chengdu who generously shared their time and experiences. We extend our appreciation to the community health centers of Jinjiang, Qingyang, Wuhou, Chenghua, Jinniu, Gaoxin, and Tianfu New District for their invaluable assistance in data collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1684187/full#supplementary-material
References
1. China MOCA. (2024) National Bulletin on the development of aging affairs. Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/bumen/202507/content\_7033724.htm (Accessed October 2, 2025).
2. Liu, X, Yang, L, Luo, Y, Luo, J, and Ju, M. An analysis of the demand for integrated medical and social care among community-dwelling older adults based on the Andersen behavioral model. Chin General Pract. (2019) 22:180–7. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2018.00.272
3. Yang, Y, Wu, W, Chen, Y, Wang, X, and Wu, T. A study on the demand for community-based home care services and influencing factors among older adults in Guangzhou. China Market. (2020) 12:34–6. doi: 10.13939/j.cnki.zgsc.2020.12.034
4. Wan, L, Wei, H, Yang, G, Liang, X, Dong, H, and He, Y. Analysis of the demand for integrated medical and social care among community-dwelling older adults based on the EQ-5D scale. J Zhengzhou Univ. (2022) 57:810–5. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6825.2022.01.015
5. Wang, X, and Cheng, J. Analysis of the demand differences for integrated medical and social care among community-dwelling older adults in Nanchang City and its multidimensional influencing factors. China: China Health Care Management (2025).
6. Wang, Z, Wei, H, and Liu, Z. Older adults' demand for community-based adult services (CBAS) integrated with medical care and its influencing factors: a pilot qualitative study in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:869. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214869
7. Wen, F, Liu, Z, Zhang, B, Zhang, Y, Zhang, Z, and Zhang, Y. A machine learning-based study on the demand for community care services in Central Urban Areas of major Chinese cities. Appl Sci. (2025) 15:141. doi: 10.3390/app15084141
8. Shi, Y, Lu, P, Mi, Y, Zhang, P, Gong, H, and Liu, Z. A study on the utilization and influencing factors of integrated medical and social care among community-dwelling elderly based on the Andersen model. Guizhou Med J. (2024) 48:1027–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2024.07.004
9. Dong, H, Jia, S, Wan, L, Yang, G, Liang, X, and He, Y. Analysis of the utilization and influencing factors of community-based integrated medical and social care using the chi-squared automatic interaction detector model. Modern Prev Med. (2023) 50:3742–8. doi: 10.20043/j.cnki.MPM.202304218
10. Lu, S, and Li, Y. The Andersen health service utilization behavior model: interpretation and operationalization of the Indicator system. China Health Econ. (2018) 37:5–10. doi: 10.7664/CHE20180901
11. Tan, M, Zhang, Y, Zhang, Y, Bai, S, Zhang, M, and Chen, Y. Analysis of the demand for and influencing factors of integrated medical and care services for older adults in the community based on the Andersen model. Chin J Gen Pract. (2023) 21:1179–83. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003079
12. Song, Y, Song, Y, Liu, J, Yan, S, Ma, M, Tarimo, CS, et al. Factors influencing health service utilization among 19,869 China’s migrant population: an empirical study based on the Andersen behavioral model. Front Public Health. (2025) 13:1456839. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1456839
13. Liu, G, Xue, Y, Qian, Z, Yang, L, Yang, Y, Geng, Q, et al. Healthcare-seeking behavior among pregnant women in the Chinese hierarchical medical system: a cross-sectional study. Int J Equity Health. (2019) 18:129. doi: 10.1186/s12939-019-1037-8
14. Zeng, Y, Que, S, Lin, C, and Fang, Y. The expected demand for long-term care services and anticipated living arrangements among the oldest old in China based on the Andersen model. Front Public Health. (2021) 9:715586. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.715586
15. Qu, Z. High-quality integration: the direction of Urban Community-based integrated medical and elderly care. Health Econ Res. (2022) 39:27–30. doi: 10.14055/j.cnki.33-1056/f.2022.01.009
16. Tang, J, and He, T. From "fragmented supply" to "collaborative governance": the logic rebuilding of the stakeholder-based community "integrated medical and elderly care" supply subject. J Yunnan Minzu Univ. (2022) 39:52–9. doi: 10.13727/j.cnki.53-1191/c.20220905.015
17. Xu, H. The impact of children’s factors on the demand for integrated medical and Care Services for Empty-Nest Older Adults in urban areas: a case study of Ma'anshan City. J Luoyang Inst Technol. (2018) 33:28–33,38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5035.2018.05.005
18. Li, Q, Dong, J, and Zhang, X. The impact of the number and quality of children on parents’ self-rated happiness. J East China Normal Univ. (2021) 53:150–65. doi: 10.16382/j.cnki.1000-5579.2021.04.014
19. Tan, M, Zhang, Y, Zhang, Y, Zhang, M, Li, Y, and Chen, Y. Analysis of the demand for and influencing factors of integrated medical and care services for older adults in Chengdu based on the Andersen model. Chin J Soc Med. (2024) 41:475–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5625.2024.04.022
20. Wang, X, Li, D, Mai, C, Hao, Y, and Hu, J. Research on the demand for and influencing factors of integrated medical and Care Services for Empty-Nest older adults in the community. Health Soft Sci. (2024) 38:38–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2800.2024.04.009
21. Nie, J, Pan, H, Rong, Y, Wang, Y, and Jiang, H. Analysis of the influencing factors of the demand for integrated medical and care services for older adults based on the Andersen health behavior model. Chin J Clin Healthcare. (2023) 26:307–12. doi: 10.3969/J.issn.1672-6790.2023.03.005
22. Zhi, M, Ji, J, and Hu, L. Analysis of the willingness and influencing factors of 1389 older adults to choose community-based integrated medical and care services. J Nurs. (2021) 28:50–6. doi: 10.16460/j.issn1008-9969.2021.04.050
23. Xue, Y, and Gao, J. Analysis of the willingness to choose elderly care models and influencing factors among middle-aged people in Jiangsu Province based on the Andersen model. Modern Prev Med. (2021) 48:3660–6. doi: 10.20043/j.cnki.mpm.2021.20.004
24. Lu, X, Wang, Z, Qin, W, Zhang, W, Chen, X, Peng, J, et al. A qualitative study on the current situation and problems of provider-based integrated medical and care services for older adults. Chin Gen Pract. (2021) 24:2459–64. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.189
25. Lin, Q, Zhang, W, Sun, K, Wang, H, Qiu, L, Fu, N, et al. The demand and influencing factors of integrated medical and Care Services for Community-Dwelling older adults in Chengdu. Med Soc. (2020) 33:74. doi: 10.13723/j.yxysh.2020.10.013
26. Fu, Y, Cheng, X, Liu, J, and Lin, L. The current situation and influencing factors of integrated medical and Care Services for Urban Older adults in the community. Chin Gen Pract. (2023) 21:1903–6. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003254
Keywords: Andersen Health Service Utilization Behavior Model, CB-IHSC, long-term care, older adults, demand
Citation: Zheng H, Yang M, Zeng Q, Liao S and Li P (2025) An analysis of factors influencing the demand for community-based integrated health and social care in Southwestern China. Front. Public Health. 13:1684187. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1684187
Edited by:
Matthew Lee Smith, Texas A&M University, United StatesReviewed by:
Theo Van Der Voordt, Delft University of Technology, NetherlandsAndriej Szpakow, Lomza State University of Applied Sciences, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Zheng, Yang, Zeng, Liao and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ping Li, NTEwNDUzNDQxQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Hanzhi Zheng
Hanzhi Zheng Min Yang1,2
Min Yang1,2 Qin Zeng
Qin Zeng Shujuan Liao
Shujuan Liao