- 1Department for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Yunnan Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Kunming, China
- 2Department for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Xishuangbanna, China
- 3School of Public Health, Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
Background: Based on data from the seventh China Chronic Diseases and Risk Factors Surveillance (CCDRFS) conducted in Yunnan Province in 2023, this study aimed to provide province-wide estimates of the prevalence, awareness, and treatment of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and to describe their distribution.
Methods: This provincial-level representative cross-sectional study included 6,231 adults sampled from 10 county- or district-level surveillance sites in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. All participants were subject to questionnaires, physical examinations, and laboratory tests. CKD-EPI equation was used to estimate glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) based on serum creatinine.
Results: A total of 6,231 adults with measurements of eGFR and urine albumin were included in this study. The weighted prevalence of CKD was 13.1% (95% CI: 10.9–15.6%) overall, 12.7% (95% CI: 10.1–15.8%) among males, and 13.5% (95% CI: 10.2–17.6%) among females. Higher prevalence of CKD was observed in subgroups characterized by older age, lower education levels, being divorced/widowed/separated, and the presence of comorbidities (hypertension, diabetes, and hyperuricemia). Among participants with CKD, 61.5, 34.2, 3.2, 0.7, 0.2, and 0.1% were classified into stage G1, G2, G3a, G3b, G4, and G5, respectively. Overall CKD awareness and treatment rates were 3.0% (95% CI: 1.5–5.8%) and 1.0% (95% CI: 0.4–2.2%). Among individuals aware of their CKD status, 11.5% (95%CI: 6.5–19.9%) were receiving treatment. Participants with stage G4 or G5 demonstrated higher awareness and treatment. CKD patients with comorbid hypertension had higher awareness, while underweight CKD patients had higher treatment rates.
Conclusion: The estimated CKD prevalence among adults in Yunnan Province in 2023 exceeded the national average (8.2%). CKD awareness and treatment rates were critically low. Targeted early screening programs or community-based interventions should be prioritized as urgent public health initiatives to improve disease recognition and treatment adherence for CKD prevention and management in China’s less developed regions.
1 Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as abnormalities in kidney structure or function persisting for over 3 months (1). Its primary manifestations include kidney damage and reduced kidney function. Characterized by high prevalence, substantial healthcare costs, and significant comorbidity risks—including severe cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases—CKD can lead to serious outcomes such as death and disability (2).
According to research led by the Global Kidney Health Atlas of the International Society of Nephrology (ISN-GKHA), the median prevalence of CKD across 167 countries worldwide is 9.5% (3). CKD was associated with 41.5 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). It is estimated that there are approximately 697 million CKD patients globally, and the prevalence of CKD has increased by 40% over the past 30 years (4).
The disease burden of CKD in China is also substantial. In 2018, the prevalence among Chinese residents was 8.2% (5). The age-standardized incidence of CKD in China was 163.74 per 100,000 population, with an age-standardized mortality of 10.84 per 100,000. Notably, the standardized incidence exhibited an upward trend between 1990 and 2021 (6).
Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) require renal replacement therapy for survival, imposing substantial economic costs on families and society. Consequently, the prevention and treatment of CKD crucially depend on early detection, diagnosis, and intervention to reduce progression to ESRD.
Despite its high prevalence, CKD awareness remains relatively low compared to common chronic non-communicable diseases such as hypertension and diabetes (7, 8). This low awareness contributes to suboptimal treatment rate, thereby elevating the risk of ESRD progression.
Currently, published data on the prevalence, awareness, and treatment of CKD in Yunnan Province and across China remain scarce. Utilizing data from the seventh round of the China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance (CCDRFS) conducted in Yunnan Province in 2023, this study provides more recent estimates of the prevalence, awareness, and treatment of CKD within the region. Pioneering in its scope, this study is the first to disclose the prevalence and distribution patterns of chronic kidney disease across underdeveloped provinces in Western China, based on a robust, provincially representative sample. The findings aim to inform future strategies for the prevention and management of CKD in less-developed areas.
2 Methods
2.1 Survey design and participants
This study is based on primary research conducted as part of the seventh CCDRFS in Yunnan. The CCDRFS is a cross-sectional, provincial representative survey, in 2023. Ten counties/districts were selected as monitoring sites from the 129 counties and districts in Yunnan Province. Site selection considered socio-economic development, demographic structure, while also adhering to principles of cost-effectiveness and sampling feasibility. This approach ensured provincial-level representativeness in terms of population composition, urbanization, education level, and birth and mortality rates (9).
Study participants comprised residents from the CCDRFS surveillance sites in Yunnan. Inclusion criteria were: ① age ≥ 18 years and ② permanent residency (residing in the county/district for ≥6 months within the past year). Pregnant women and individuals with cognitive or mental disorders, severe illnesses, or disabilities potentially affecting survey participation were excluded.
2.2 Data collection
Sampling was conducted by a multi-stage cluster random design across all Surveillance site. In the first two stages, three townships or streets and six administrative villages or neighborhood committees were systematically selected based on population size ranking. n the subsequent third and fourth stages, a total of 270 households were randomly selected from six residential clusters for survey inclusion. All residents within the selected households who met the inclusion criteria were enrolled as survey respondents. All investigators received standardized training and collected data using an electronic questionnaire system.
The CCDRFS collected data through three primary methods: standardized questionnaires, physical measurements, and laboratory tests. The face-to-face questionnaire was used to collect demographic characteristics, individual and family disease histories, behavior and lifestyle habits, as well as mental health indicators, etc. The physical measurements encompassed height, weight, waist circumference, blood pressure, and grip strength. Anthropometric measurements were obtained following a standardized protocol (10). Laboratory testing procedures were as follows: a 10-mL sample of fasting venous blood was collected from all participants for the quantification of hemoglobin, fasting blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, uric acid, creatinine, potassium, albumin, and total protein. Participants without a history of diabetes underwent an oral glucose tolerance test using 75 g of anhydrous glucose; a 2-mL venous blood sample was obtained 2 h after glucose administration to measure postprandial blood glucose levels. Additionally, a 5-mL morning urine sample was collected from all participants for the analysis of urinary creatinine, microalbuminuria, sodium, and potassium. All examinations, except for the questionnaire, were performed in the morning after an overnight fast.
Blood glucose and hemoglobin were analyzed at certified monitoring laboratories that had passed standardized performance verification. All other biochemical indicators were measured at a central laboratory accredited by the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and holding all relevant certifications. The following analytical methods were applied: plasma glucose was measured on-site either by the hexokinase method or glucose oxidase method; hemoglobin was determined on-site using the HemoCue® system; glycated hemoglobin was quantified via high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); total cholesterol was assessed with the cholesterol oxidase-aminoantipyrine phenol (CHOD-PAP) method; triglycerides were analyzed using the phosphoglyceric oxidase method; high-density and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were both measured via homogeneous enzyme colorimetric assays; uric acid was determined by the uricase-peroxidase method; both blood and urinary creatinine were analyzed using an enzyme-coupled sarcosine oxidase assay; total serum protein was measured with the biuret method; serum albumin was quantified via the bromocresol green method; urinary microalbumin was determined by immunoturbidimetry; and blood potassium, urinary potassium, and urinary sodium were analyzed using ion-selective electrode methods.
2.3 Assessment criteria
The diagnosis and staging of chronic kidney disease (CKD) adhered to the 2024 Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDIGO) Clinical Practice Guideline for Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. CKD was defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) ≥ 30 mg/g. For patients meeting these diagnostic criteria, stages Grade 1 to Grade 5 are defined based on eGFR [ml/min/1.73 m2] as follows: (1) G1: ≥90, G2: 60–89, G3a: 45–59, G3b: 30–44, G4: 15–29, G5: <15. The eGFR was calculated using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) 2021 creatinine equation based on serum creatinine (Scr) values for males and females, respectively (11): Due to the limitations inherent in the cross-sectional study design, serum creatinine and urinary albumin measurements were performed at a single time point without repeated assessment after 3 months. As a result, it was not possible to exclude some cases of reversible renal impairment or transient proteinuria, which may have led to an overestimation of the prevalence rates.
The prevalence of chronic kidney disease was defined as the proportion of individuals meeting diagnostic criteria within the surveyed population.
The CKD awareness was defined as the proportion of individuals meeting CKD diagnostic criteria and self-report a prior diagnosis of CKD by a medical institution.
The CKD treatment was defined as the proportion of individuals meeting CKD diagnostic criteria who self-report receiving any form of treatment for the disease, including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), glucocorticoid, immunosuppressant, or dialysis.
The treatment-awareness rate was defined as the proportion of individuals receiving kidney disease treatment among those aware of their CKD diagnosis.
Hypertension (12) was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mmHg and/or a diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 90 mmHg, and/or self-reported prior diagnosis of hypertension by a hospitals at township (community) level or higher.
Diabetes was defined as fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 7.0 mmol/L and/or a 2 h oral glucose tolerance test plasma glucose (OGTT-2 h) ≥ 11.1 mmol/L and/or self-reported prior diagnosis of diabetes by a hospitals at township (community) level or higher (13).
Weight status categories (underweight, normal weight, overweight, obesity) were determined based on body mass index (BMI) (14): BMI < 18.5 considered as underweight, BMI between 18.5 and 23.9 considered as normal weight, BMI between 24.0 and 27.9 considered as overweight, and BMI ≥ 28.0 considered as obesity.
Hyperuricemia was defined as a serum uric acid level >420 μmol/L measured under fasting conditions.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by SPSS 20.0’s complex samples module. Prevalence estimates were calculated using sample weights that incorporated the multistage sampling weight, the non-response weight, and the post-stratification weight is equivalent to direct standardization based on the 2010 China’s Sixth National Census population. The 95% CIs of the prevalence estimates were calculated using Taylor series linearization with finite population correction implemented. The χ2 test was used to compare rate distributions across populations.
2.5 Ethics statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the National Center for Chronic and Noncommunicable Diseases Control and Prevention (NCNCD), Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (Approval No. 202305). The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
3 Results
3.1 Study population
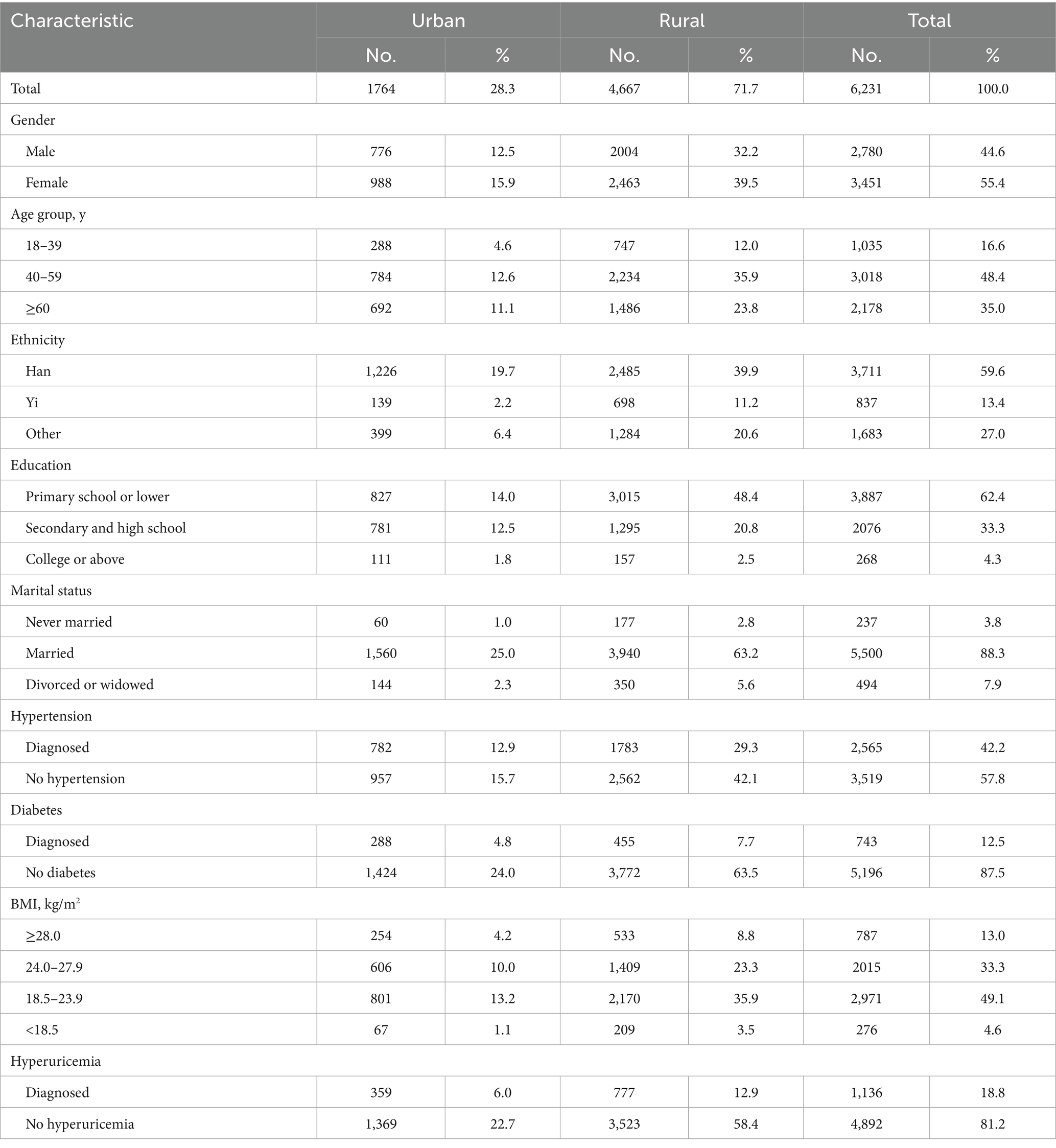
A total of 6,231 participants were included. The sample distribution was as follows: 44.6% male and 55.4% female; 28.3% urban residents and 71.7% rural residents; and 16.6% aged 18–39 years, 48.4% aged 40–59 years, and 35.0% aged ≥60 years, as shown in Table 1.
3.2 Prevalence of CKD
The overall prevalence of CKD among participants was 13.1% (95% CI: 10.9–15.6%). No statistically significant difference was observed between males (12.7%; 95% CI: 10.1–15.8%) and females (13.5%; 95% CI: 10.2–17.6%) (χ2 = 0.114, p > 0.05). Prevalence increased significantly with age (χ2 = 15.556, p < 0.001). Significant prevalence variations were also found across education levels (χ2 = 10.495, p < 0.001) and marital statuses (χ2 = 19.988, p < 0.001). Participants with chronic conditions (hypertension, diabetes, hyperuricemia) exhibited significantly higher CKD prevalence than those without (p < 0.05) (Table 2).
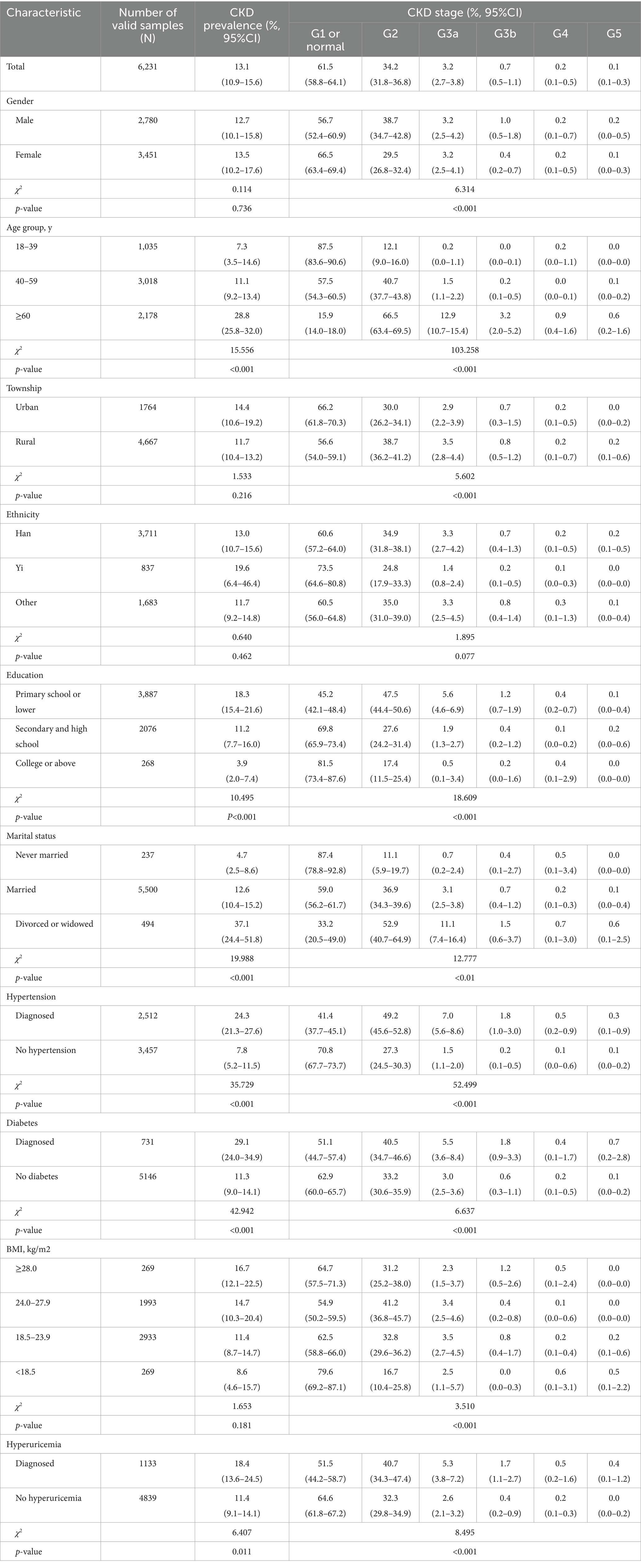
Table 2. Weighted prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) by stage and ethnic group among adults in Yunnan Province, 2023.
Among CKD patients, 95.7% were classified as G1/G2 renal function, while G3a, G3b, G4, and G5 stages accounted for 3.2, 0.7, 0.2, and 0.1%, respectively. Stage distribution varied significantly by gender (χ2 = 6.314, p < 0.01) and exhibited strong age-dependency (χ2 = 103.258, p < 0.001): the proportion of G1/G2 stages decreased with advancing age, whereas G3a + stages increased progressively. Significant variations were also observed across township (χ2 = 5.602, p < 0.001), educational levels (χ2 = 18.609, p < 0.001), marital statuses (χ2 = 12.777, p < 0.001). Patients with hypertension, diabetes, overweight/obesity, or hyperuricemia showed significantly higher proportions of CKD G2 + stages compared to those without these comorbidities (p < 0.001; Table 2).
3.3 Awareness and treatment of CKD
Among CKD patients, the awareness was 3.0% (95% CI: 1.5–5.8%). Awareness varied significantly by renal function stage, with G4+ patients demonstrating higher awareness than G3- patients (χ2 = 6.977, p < 0.001). Hypertensive CKD patients also showed elevated awareness versus non-hypertensive patients (χ2 = 3.913, p = 0.048) (Table 3).
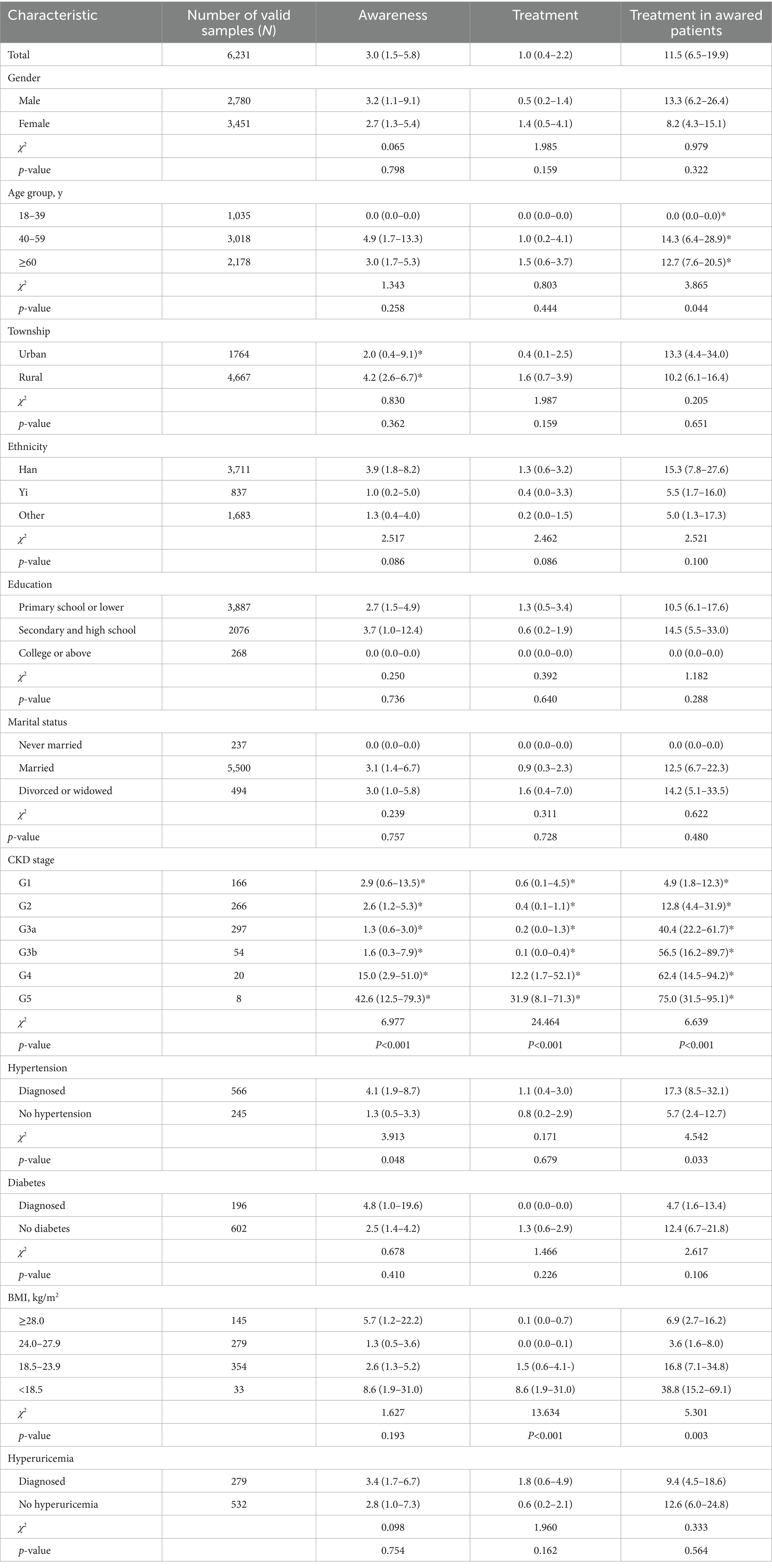
Table 3. Weighted prevalence, awareness, treatment, and treatment in awared patients among population with CKD, 2023 (%, 95%CI)
Among CKD patients, the self-reported treatment was 1.0% (95% CI: 0.4–2.2%). Treatment rates significantly differed by renal function stage, with G4 + patients demonstrating higher rates than G3- patients (χ2 = 24.464, p < 0.001). Underweight CKD patients showed higher treatment rates than normal/overweight-obese patients (χ2 = 13.634, p < 0.001) (Table 3).
Among CKD patients aware of their diagnosis, 11.5% (95% CI: 6.5–19.9%) reported current treatment. Treatment rates varied significantly by age (χ2 = 3.865, p = 0.044), renal function stage (χ2 = 6.639, p < 0.001). Hypertensive patients showed higher rates than non-hypertensive counterparts (χ2 = 4.542, p = 0.033), with underweight patients demonstrating higher rates than normal/overweight-obese patients (χ2 = 5.301, p = 0.003) (Table 3).
4 Discussion
The prevalence of CKD in Yunnan Province is higher than the national average and is on an upward trend. This study analyzed CKD prevalence, renal function staging, awareness, treatment, and epidemiological characteristics among Yunnan residents using surveillance data from over 6,000 adults in 10 surveillance sites in 2023. Results revealed a 13.1% CKD prevalence. Based on Yunnan’s Seventh National Census data (age ≥ 15 years), this corresponds to approximately 4.9 million affected individuals. According to the same diagnostic criteria for CKD, the prevalence in Yunnan Province is significantly exceeds China’s 2018 national prevalence (8.2%) (15). Yunnan’s CKD prevalence exceeds published rates for Henan Province (10.5%) (16), Guangzhou (12.1%) (17), and Zhejiang Province (9.9%) (18). However, it remains lower than the 25.8% prevalence reported for Pudong New Area in Shanghai (age 20–79 cohort) (19).
The global prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) varies significantly across different regions. In high-income countries, including the United States (20), Australia (21), Netherlands, and Norway (22, 23), the estimated prevalence of CKD ranges between 10 and 13%. In contrast, low- and middle-income countries exhibit considerable disparities. For instance, Bolivia and Iran report relatively lower rates, between 5.5 and 6.3%, whereas China, Mongolia, India, Nepal, and Nigeria show markedly higher prevalence, ranging from 16 to 29.9% (24). Furthermore, the primary etiologies of CKD differ across regions with varying development levels and are not limited to hypertension and diabetes. In certain developing countries, up to 40% of CKD cases are attributable to non-traditional risk factors, such as infectious diseases (e.g., HIV and tuberculosis) (25), environmental toxin exposure (26), or unknown causes (27), rather than diabetes or cardiovascular conditions.
Compared to the other common chronic diseases in Yunnan Province, the prevalence of CKD is lower than that of hypertension (24.1% in 2018), but higher than that of diabetes (7.1% in 2018) 28. The CKD prevalence in 2023 has increased by 5.4% compared to in 2018 (7.7%) While the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes in Yunnan are both below the national average (5), the CKD prevalence exceeds it. This disparity may stem from two factors: First, hypertension and diabetes are key drivers in the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and have been major contributors to the growing burden of CKD over the past several decades (28–30). Although effective management of blood pressure and blood glucose levels plays a critical role in controlling the prevalence and progression of CKD, the control rates for both hypertension and diabetes in the province remain below the national average (31). This suboptimal management leading to inadequate control of blood pressure and blood glucose levels, and subsequent progression to CKD. Second, smoking, high-salt diet, and physical inactivity are well-established risk factors for chronic kidney disease (CKD) (32). These risk behaviors are highly prevalent in Yunnan Province (24), which likely contributes to the region’s high burden of CKD. However, most residents currently lack corresponding CKD intervention measures, highlighting an urgent need to strengthen CKD related health promotion efforts (15).
Previous studies have indicated that gender is a risk factor for CKD, with women generally exhibiting a higher prevalence than men (33). However, in our survey, no statistically significant difference was observed between males (12.7%; 95% CI: 10.1–15.8%) and females (13.5%; 95% CI: 10.2–17.6%). This finding may be attributed to the higher prevalence of hypertension and diabetes among males in Yunnan, potentially increasing their risk of developing CKD.
Advancing age is associated with an increased prevalence of CKD, consistent with findings from previous studies. This trend stems from two primary factors: Firstly, age-related physiological decline involves sclerosis of renal arteries and micro-vessels. Consequently, urinary protein excretion rises while the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreases. According to the current diagnostic criteria for CKD, this manifests as a higher prevalence rate among the older adult. Secondly, the older adult exhibit higher prevalence rates of comorbidities like hypertension and diabetes, which are significant pathological contributors to CKD development. However, the current CKD diagnostic criteria (1) are not age-adjusted. Consequently, establishing age-specific diagnostic criteria holds practical significance for distinguishing between physiological age-related renal decline and pathological renal impairment in the older adult population (34).
Additionally, this study found that educational level and marital status are associated with CKD prevalence. This association is largely attributable to the older age profile observed among individuals with lower education and those who are divorced, widowed, or separated, leading to a relatively higher CKD prevalence in these groups. Among patients with hypertension, diabetes, or hyperuricemia, CKD prevalence is significantly higher than in those without these conditions, aligning with findings from national surveys (35, 36). Hypertension, diabetes, and hyperuricemia are all established risk factors for CKD development and progression. Hypertension is present in up to 90% of CKD cases (37), while over 40% of diabetic patients develop chronic kidney disease (38). Hyperuricemia may trigger chronic kidney inflammation, resulting in renal function decline (39).
Previous studies indicate that 67% of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients present with blood creatinine levels exceeding 177 μmol/L at diagnosis. Therefore, improving awareness and treatment is crucial to slowing down progression of CKD to end-stage renal disease. However, this study reveals alarmingly low rates in Yunnan Province: the CKD awareness is only 3.0%, and the treatment rate is 1.0%. This awareness is significantly lower than the national average (10.0%) (8) and findings from Shijingshan District, Beijing (7.3%) (7). Previous studies have found that among patients diagnosed with chronic kidney disease (CKD), approximately 75% of cases are attributed to infections, exposure to toxins (such as from animal bites, herbal remedies, or medications), or complications during pregnancy, which are often the circumstances leading to diagnosis (40). The low awareness and treatment rates are partly attributable to CKD’s insidious onset and lack of obvious early symptoms. However, the primary reason lies in insufficient societal understanding of CKD. While government, societal sectors, and individuals have increasingly focused on chronic diseases in recent years, the emphasis has predominantly been on four major conditions: cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, cancer, and diabetes (41). Consequently, investment and publicity efforts for CKD prevention and control remain relatively weaker compared to these priority diseases.
Media coverage of CKD is also limited especially in economically underdeveloped areas. In some remote mountainous regions of western China, residents often have relatively low health literacy, live in scattered communities, and have limited access to healthcare services. When confronted with illnesses that present subtle symptoms—such as chronic kidney disease, many lack sufficient health awareness or face financial constraints, which can prevent them to recognizing the severity of the condition.
Furthermore, in the management of patients with hypertension and diabetes though China national essential public health services, routine physical examinations do not include renal function or urine protein tests. This omission represents a key barrier to the timely identification of CKD complications among these patients. Compounding this issue is the insufficient attention some primary care providers pay to potential complications in their managed patients. In China, a vast number of patients are managed for hypertension and diabetes within the national essential public health services system. Leveraging these follow-up visits to integrate CKD interventions, such as screening, patient education, lifestyle guidance, and rational medication use, would help control relevant behavioral risk factors. In addition, cost-effective CKD risk prediction models should be incorporated into opportunistic screening strategies for various populations.
5 Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, CKD was defined solely by eGFR and urinary protein levels, without incorporating supplementary indicators such as serum cystatin C. This approach may have led to an underestimation of the true population prevalence. Second, the use of the CKD-EPI equation for eGFR estimation, while widely adopted, may overestimate CKD prevalence in Chinese populations due to ethnic-specific calibration limitations (42). Third, constrained by research design limitations, renal function parameters were assessed at a single time point, lacking confirmatory retesting after 3 months as recommended by clinical guidelines. Due to the incorporation of reversible conditions, such as acute kidney injury (AKI) and transient proteinuria, may compromise diagnostic accuracy and inflate the estimated prevalence rate. Fourth, due to the small sample size in certain subgroups-such as the Yi ethnic group, the precision of rate estimates is limited, as reflected in wider 95% confidence intervals. Fifth, as a cross-sectional study, it establishes associations between risk factors and CKD but cannot infer causality. The complex interplay of CKD determinants, including potential mediating effects and factor interactions requires prospective cohort studies for deeper exploration.
6 Conclusion
The findings of this study revealed that the estimated prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) exceeds the national average (8.2%), among adults in Yunnan Province. Critically, CKD awareness and treatment remain alarmingly low. Therefore, implementing targeted early screening programs or community-based interventions be prioritized as urgent public health initiatives to improve disease recognition and treatment adherence for CKD prevention and management in China’s less developed regions.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Review Committee of the National Center for Chronic and Noncommunicable Diseases Control and Prevention in China Center for Diseases Control and Prevention. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YS: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Formal analysis. YF: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Investigation. JG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HM: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Investigation. MW: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. QS: Supervision, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Resources. YC: Resources, Project administration, Supervision, Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Yunnan Provincial High-level Health and Technical Personnel Training Program (H-2024002). The Chinese central government (Key Project of Public Health Program) funded the China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance (CCDRFS) program.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all participants for their contributions, and acknowledge fieldwork support from municipal and county-level Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) staff.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
CCDRFS, China Chronic Diseases and Risk Factors Surveillance; CKD, Chronic kidney disease; CKD-EPI, Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration; GFR, Glomerular filtration rate; DALYs, Disability-adjusted life years; ESRD, End-stage renal disease; Scr, Serum creatinine; SBP, Systolic blood pressure; DBP, Diastolic blood pressure; FPG, Fasting plasma glucose; OGTT-2 h, Two-hour oral glucose tolerance test; BMI, Body mass index; CI, Confidence interval.
References
1. Stevens, PE, and Levin, AKidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Chronic Kidney Disease Guideline Development Work Group Members. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. (2013) 158:825–30. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-11-201306040-00007
2. Stevens, LA, and Levey, AS. Chronic kidney disease in the elderly--how to assess risk. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:2122–4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe058035
3. Bello, AK, Okpechi, IG, Levin, A, Ye, F, Damster, S, Arruebo, S, et al. An update on the global disparities in kidney disease burden and care across world countries and regions. Lancet Glob Health. (2024) 12:e382–95. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(23)00570-3
4. Wei, H, Ren, J, Li, R, Qi, X, Yang, F, and Li, Q. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease attributable to high fasting plasma glucose from 1990 to 2019: a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1379634. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1379634
5. Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. China chronic disease and risk factor surveillance report [M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House (2021).
6. Lihong, QIN, Jing, CHEN, Yadie, XIANG, Binghui, LI, Lisha, LUO, and Ling, CHEN. An analysis of disease burden and risk factors of chronic kidney disease in China from 1990 to 2021. New Med. (2024) 34:957–69. doi: 10.12173/j.issn.1004-5511.202408076
7. Lu-xia, ZHANG, Li, ZUO, Guo-bin, XU, Fang, WANG, Shu-yu, WANG, Mei, WANG, et al. Community-based screening for chronic kidney disease among population older than 40 years in Beijing. Chin J Nephrol. (2006) 22:67–71. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1001-7097.2006.02.003
8. Zhang, L, Wang, F, Wang, L, Wang, W, Liu, B, Liu, J, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet. (2012) 379:815–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60033-6
9. Mairgeng, ZHOU, Yong, JIANG, Zheng-jing, HUANG, and Fan, WU. Adjustment and representativeness evaluation of national disease surveillance points system. Dis Surveillance. (2010) 25:239–44. doi: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2010.03.023
10. Zhang, M, Wang, LH, Wu, J, Huang, Z, Zhao, Z, Zhang, X, et al. Data resource profile: China chronic disease and risk factor surveillance (CCDRFS). Int J Epidemiol. (2022) 51:e1–8. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyab255
11. Inker, LA, Eneanya, ND, Coresh, J, Tighiouart, H, Wang, D, Sang, Y, et al. New creatinine- and cystatin C-based equations to estimate GFR without race. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:1737–49. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2102953
12. Writing Group of 2018 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension, Chinese Hypertension League, Chinese Society of Cardiology, Hypertension Professional Committee of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Hypertension Branch of China International Exchange and Promotive Association for Medical and Health Care, Hypertension Branch of Chinese Geriatric Society. Chin J Cardiovasc Med. (2019) 24:24–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2019.01.002
13. Chinese diabetes society. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020). Chin J Endocrinol Metab (2021). 37: 311–398. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20210304-00142
14. Chen, CM, and Kong, LZ. Guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House (2006).
15. Wang, L, Xu, X, Zhang, M, Hu, C, Zhang, X, Li, C, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: results from the sixth China chronic disease and risk factor surveillance. JAMA Intern Med. (2023) 183:298–310. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.6817
16. Gu, DF, Shi, YL, Chen, YM, Liu, HM, Ding, YN, Liu, XY, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and prediabetes and associated risk factors: a community-based screening in Zhuhai, Southern China. Chin Med J. (2013) 126:1213–9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.20123504
17. Chen, W, Chen, W, Wang, H, Dong, X, Liu, Q, Mao, H, et al. Prevalence and risk factors associated with chronic kidney disease in an adult population from southern China. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2009) 24:1205–12. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn604
18. Duan, JY, Wang, CJ, Liu, DW, Qiao, Y, Pan, S, Jiang, D, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease and diabetic kidney disease in Chinese rural residents: a cross-sectional survey. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:10408. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46857-7
19. Shan, Y, Zhang, Q, Liu, ZS, Liu, Z, Hu, X, and Liu, D. Prevalence and risk factors associated with chronic kidney disease in adults over 40 years: a population study from Central China. Nephrology. (2010) 15:354–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2009.01249.x
20. Coresh, J, Astor, BC, Greene, T, Eknoyan, G, and Levey, AS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: third National Health and nutrition examination survey. Am J Kidney Dis. (2003) 41:1–12. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2003.50007
21. Chadban, SJ, Briganti, EM, Kerr, PG, Dunstan, DW, Welborn, TA, Zimmet, PZ, et al. Prevalence of kidney damage in Australian adults: the AusDiab kidney study. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2003) 14:S131–8.
22. Hallan, SI, Coresh, J, Astor, BC, Asberg, A, Powe, NR, Romundstad, S, et al. International comparison of the relationship of chronic kidney disease prevalence and ESRD risk. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2006) 17:2275–84. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005121273
23. Hillege, HL, Janssen, WM, Bak, AA, Diercks, GF, Grobbee, DE, Crijns, HJ, et al. Microalbuminuria is common, also in a nondiabetic, nonhypertensive population, and an independent indicator of cardiovascular risk factors and cardiovascular morbidity. J Intern Med. (2001) 249:519–26. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.2001.00833.x
24. Ene-Iordache, B, Perico, N, Bikbov, B, Carminati, S, Remuzzi, A, Perna, A, et al. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk in six regions of the world (ISN-KDDC): a cross-sectional study. Lancet Glob Health. (2016) 4:e307–19. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(16)00071-1
25. Rosenberg, AZ, Naicker, S, Winkler, CA, and Kopp, JB. HIV-associated nephropathies: epidemiology, pathology, mechanisms and treatment. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2015) 11:150–60. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.9
26. Jha, V, Garcia-Garcia, G, Iseki, K, Li, Z, Naicker, S, Plattner, B, et al. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. (2013) 382:260–72. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60687-X
27. Correa-Rotter, R, Wesseling, C, and Johnson, RJ. CKD of unknown origin in Central America: the case for a Mesoamerican nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. (2014) 63:506–20. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.10.062
28. Li, HX, Lu, WH, Wang, AN, Jiang, H, and Lyu, J. Changing epidemiology of chronic kidney disease as a result of type 2 diabetes mellitus from 1990 to 2017: estimates from global burden of disease 2017. J Diabetes Investig. (2021) 12:346–56. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13355
29. Ren, Y, Wang, ZW, and Wang, QJ. The trend of hypertension-related chronic kidney disease from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions over 25 years: an analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019. Int Urol Nephrol. (2024) 56:707–18. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03707-w
30. Ke, CR, Liang, JJ, Liu, M, Liu, S, and Wang, C. Burden of chronic kidney disease and its risk-attributable burden in 137 low-and middle-income countries, 1990-2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMC Nephrol. (2022) 23:17. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02597-3
31. Chen, Yang, Shao, Ying, and Shi, Qingping. Report on China chronic disease risk factor surveillance in Yunnan Province (2013 and 2018). Kunming: Yunnan University Press (2023).
32. Kelly, JT, Su, G, Zhang, L, Qin, X, Marshall, S, González-Ortiz, A, et al. Modifiable lifestyle factors for primary prevention of CKD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2021) 32:239–53. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020030384
33. Carrero, JJ, Hecking, M, Chesnaye, NC, and Jager, KJ. Sex and gender disparities in the epidemiology and outcomes of chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2018) 14:151–64. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.181
34. Delanaye, P, Jager, KJ, Bökenkamp, A, Christensson, A, Dubourg, L, Eriksen, BO, et al. CKD: A call for an age-adapted definition. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2019) 30:1785–805. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019030238
35. Chen, YM, Zhao, ZP, Zhang, M, Zhang, X, Li, C, Yu, MT, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and risk factors in adults with hypertension in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. (2025) 46:33–42. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20240423-00212
36. Chen, TK, Knicely, DH, and Grams, ME. Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: a review. JAMA. (2019) 322:1294–304. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.14745
37. Habas, E, Habas, E, Khan, FY, Rayani, A, Habas, A, Errayes, M, et al. Blood pressure and chronic kidney disease progression: an updated review. Cureus. (2022) 14:e24244. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24244
38. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2022 clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. (2022) 102:S1–S127. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.06.008
39. Sharaf El Din, UAA, Salem, MM, and Abdulazim, DO. Uric acid in the pathogenesis of metabolic, renal, and cardiovascular diseases: a review. J Adv Res. (2017) 8:537–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2016.11.004
40. Francis, A, Harhay, MN, Ong, ACM, Tummalapalli, SL, Ortiz, A, Fogo, AB, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: an international consensus. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2024) 20:473–85. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00820-6
41. Health China action promotion committee. Healthy China Initiative. (In Chinese). Available online at: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-07/15/content_5409694.htm
Keywords: chronic kidney disease, prevalence, awareness, treatment, distribution
Citation: Shao Y, Fan Y, Gao J, Meng H, Wang M, Shi Q and Chen Y (2025) Prevalence, awareness, and treatment of chronic kidney disease among adults in Yunnan Province, China: findings from the 2023 chronic disease and risk factors surveillance. Front. Public Health. 13:1685691. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1685691
Edited by:
Munkhtuya Tumurkhuu, Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Jeremiah Laktabai, Moi University, KenyaSatyaveni Malasala, University of South Carolina, United States
Yanjinlkham Munkhsaikhan, The University of Tokyo, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Shao, Fan, Gao, Meng, Wang, Shi and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Chen, eW5jZGNjeUAxMjYuY29t; Qingping Shi, eW5jZGNzcXA0NUAxMjYuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Ying Shao
Ying Shao Yunyuan Fan2†
Yunyuan Fan2†